I was asked if I had heard of the “Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis”?
The aquatic apes theory/hypothesis (AAH) to me is more like the stuff of unsupported myth like: humans come from or were created by aliens, intelligent design, creationism, and not proven evolution. Standard evolutionary models suggest and supporting evidence shows the different features that make humans different appeared at separate times and for many different reasons. The AAH argues they all occurred because our ancestors decided to live in or near water.
There are several problems with this bad idea…
Here Are objections to the ridiculous hypothesis listed on RationalWiki:
The first is that convergent evolution predicts adaptations serving similar function, not necessarily similar structure. A platypus bill looks like a duck bill because it solves the precise same problem (sucking bugs out of mud); but the wings of a bat, a bird, and a bumblebee are products of convergent evolution in solving the problem of flight, but are structurally very different. Morgan’s convergent evolution adaptations focus on structure.
The second problem is that evidence provided for the AAH is equally well accounted for by savannah-based adaptations without needing to posit an aquatic phase of human development. Loss of body hair: lower parasite load (early hominids appear to have been disgusting skanks) and maintenance through sexual selection. Furthermore, many aquatic mammals have actually kept their body hair. Several other savannah species have also lost much of their hair including elephants, rhinoceroses, and naked mole rats. Although it is interesting to note that both elephants and rhinoceroses are theorized to have evolved from aquatic ancestors so they may not be the best counter-examples, though the only modern rhinoceros that spends much of its time in the water is the hairy rhinoceros. Diet: the fatty acids for the brain were present in sufficient quantities on the savannah. Diving reflex: terrestrial mammals show this too; there has been insufficient study of other apes to use this as evidence that humans are special in this regard. Body fat: distribution is similar to that of other primates. The quantities seen in present-day humans accord with those seen in domesticated mammals, i.e. we’re quite well fed compared with wild dumb beasts. Humans have relatively more fat below the waist which serves as insulation when wading. Bipedalism: the AAH compares humans to quadrupeds, but we went from quadrupedal locomotion to brachiation; bipedalism follows quite readily from that. Descended larynx: again, speech. The human larynx is not shaped like that of aquatic mammals, and descended larynxes are also seen in dogs, pigs, goats, monkeys and young chimps. Nose shape: again, speech. Speech was rather important in human development, oddly enough. Sebaceous glands: not actually found in aquatic mammals. Appear to be sexually dimorphic (highly active in adolescent human males, scent receptors highly active in adolescent human females). Swimming: humans really aren’t that good at swimming. Dogs and cats do about as well.
A third major problem is there are actual characteristics indicative of aquatic mammals which humans notably lack. Aquatic mammals are testicond and have internal testes to insulate the gonads; humans are not testicond. Aquatic mammals also store large amounts of oxygen in the blood rather than the lungs; a trait lacked by humans. The aquatic ape theory cannot easily explain why these features were maintained after our ancestors supposedly left the water and moved to savannahs. Further, there’s good evidence that many of the traits claimed to fall under the umbrella of the aquatic ape hypothesis evolved at radically different points in human evolutionary history. Fossils from 4.4 million years ago display bipedalism, while still possessing small brains long after, and not evolving sparse body hair until later still. One of the largest problem with the theory is that since the 1960s rather than improving and gathering evidence, the theory has become more nebulous and vague. Rather than some specific aquatic phase modern Aquatic Ape theorists cite anything from fresh water millions of years ago, salt water habitation more recently, several different aquatic phases or a general proximity to water to a greater degree than other apes. Incidentally other apes and even some monkeys sometimes gather food from water and may stand bipedally to do this. There are also anti-science objections lodged against the creation of the hypothesis because Morgan had the idea first and then simply found differences between humans and other apes and composed ad hoc reasons associated with water. One could cherry pick data for many such pet theories without any merit behind them, while making them sound good on paper. http://rationalwiki.org/wiki/Aquatic_ape_hypothesis
Debunking Aquatic Ape Theory
Aquatic Ape Theory (AAT): Sink or Swim?
How the Aquatic Ape Theory Keeps Floating On | Motherboard
Why anthropologists don’t accept the Aquatic Ape Theory · john hawks
Aquatic Ape ‘theory’… again. | Richard Dawkins Foundation
Sorry David Attenborough, we didn’t evolve from ‘aquatic apes
Aquatic ape Hypothesis
“The aquatic ape hypothesis (AAH), also referred to as aquatic ape theory (AAT) or the waterside hypothesis of human evolution, is highly controversial, and has been criticized as pseudoscience. The hypothesis is thought to be more popular with the lay public than with scientists; in the scientific literature, it is generally ignored by anthropologists, as it postulates that the ancestors of modern humans took a divergent evolutionary pathway from the other great apes by becoming adapted to a more aquatic habitat.” ref
“The hypothesis was initially proposed by the marine biologist Alister Hardy in 1960, who argued that a branch of apes was forced by competition over terrestrial habitats to hunt for food such as shellfish on the seashore and sea bed, leading to adaptations that explained distinctive characteristics of modern humans such as functional hairlessness and bipedalism. Elaine Morgan‘s 1990 book on the hypothesis, Scars of Evolution, received some favorable reviews but was subject to criticism from the anthropologist John Langdon in 1997, who characterized it as an “umbrella hypothesis” with inconsistencies that were unresolved and a claim to parsimony that was false.” ref
“In 1942 the German pathologist Max Westenhöfer (1871–1957) discussed various human characteristics (hairlessness, subcutaneous fat, the regression of the olfactory organ, webbed fingers, direction of the body hair etc.) that could have derived from an aquatic past, quoting several other authors who had made similar speculations. As he did not believe human beings were apes, he believed this might have been during the Cretaceous, contrary to what is possible given the geologic and evolutionary biology evidence available at the time. He stated: “The postulation of an aquatic mode of life during an early stage of human evolution is a tenable hypothesis, for which further inquiry may produce additional supporting evidence.” He later abandoned the concept.” ref
“Independently of Westenhöfer’s writings, the marine biologist Alister Hardy had since 1930 also hypothesized that humans may have had ancestors more aquatic than previously imagined, although his work, unlike Westenhöfer’s, was rooted in the Darwinian consensus. On the advice of his colleagues, Hardy delayed presenting the hypothesis for approximately thirty years. After he had become a respected academic and knighted for contributions to marine biology, Hardy finally voiced his thoughts in a speech to the British Sub-Aqua Club in Brighton on 5 March 1960. Several national newspapers reported sensational presentations of Hardy’s ideas, which he countered by explaining them more fully in an article in New Scientist on 17 March 1960: “My thesis is that a branch of this primitive ape-stock was forced by competition from life in the trees to feed on the sea-shores and to hunt for food, shellfish, sea-urchins etc., in the shallow waters off the coast.” ref
“The idea was generally ignored by the scientific community after the article was published. Some interest was received, notably from the geographer Carl Sauer whose views on the role of the seashore in human evolution “stimulated tremendous progress in the study of coastal and aquatic adaptations” inside marine archaeology. In 1967, the hypothesis was mentioned in The Naked Ape, a popular book by the zoologist Desmond Morris, who reduced Hardy’s phrase “more aquatic ape-like ancestors” to the bare “aquatic ape”, commenting that “despite its most appealing indirect evidence, the aquatic theory lacks solid support”. While traditional descriptions of ‘savage’ existence identified three common sources of sustenance: gathering of fruit and nuts, fishing, and hunting, in the 1950s, the anthropologist Raymond Dart focused on hunting and gathering as the likely organizing concept of human society in prehistory, and hunting was the focus of the screenwriter Robert Ardrey‘s 1961 best-seller African Genesis.” ref
“Another screenwriter, Elaine Morgan, responded to this focus in her 1972 Descent of Woman, which parodied the conventional picture of “the Tarzanlike figure of the prehominid who came down from the trees, saw a grassland teeming with game, picked up a weapon and became a Mighty Hunter,” and pictured a more peaceful scene of humans by the seashore. She took her lead from a section in Morris’s 1967 book which referred to the possibility of an Aquatic Ape period in evolution, his name for the speculation by the biologist Alister Hardy in 1960. When it aroused no reaction in the academic community, she dropped the feminist criticism and wrote a series of books–The Aquatic Ape (1982), The Scars of Evolution (1990), The Descent of the Child (1994), The Aquatic Ape Hypothesis (1997) and The Naked Darwinist (2008)–which explored the issues in more detail. Books published on the topic since then have avoided the contentious term aquatic and used waterside instead.” ref
“Hardy’s hypothesis as outlined in the New Scientist was: “My thesis is that a branch of this primitive ape-stock was forced by competition from life in the trees to feed on the sea-shores and to hunt for food, shell fish, sea-urchins etc., in the shallow waters off the coast. I suppose that they were forced into the water just as we have seen happen in so many other groups of terrestrial animals. I am imagining this happening in the warmer parts of the world, in the tropical seas where Man could stand being in the water for relatively long periods, that is, several hours at a stretch.” ref
“Hardy argued a number of features of modern humans are characteristic of aquatic adaptations. He pointed to humans’ lack of body hair as being analogous to the same lack seen in whales and hippopotamuses, and noted the layer of subcutaneous fat humans have that Hardy believed other apes lacked, although it has been shown that captive apes with ample access to food have levels of subcutaneous fat similar to humans. Additional features cited by Hardy include the location of the trachea in the throat rather than the nasal cavity, the human propensity for front-facing copulation, tears, and eccrine sweating, though these claimed pieces of evidence have alternative evolutionary adaptationist explanations that do not invoke an aquatic context.” ref
“Hardy additionally posited that bipedalism evolved first as an aid to wading before becoming the usual means of human locomotion, and tool use evolved out of the use of rocks to crack open shellfish. These last arguments were cited by later proponents of AAH as an inspiration for their research programs. Morgan summed up her take on the hypothesis in 2011: “Waterside hypotheses of human evolution assert that selection from wading, swimming and diving and procurement of food from aquatic habitats have significantly affected the evolution of the lineage leading to Homo sapiens as distinct from that leading to Pan.” ref
“The AAH is generally ignored by anthropologists, although it has a following outside academia and has received celebrity endorsement, for example from David Attenborough. Academics who have commented on the aquatic ape hypothesis include categorical opponents (generally members of the community of academic anthropology) who reject almost all of the claims related to the hypothesis. Other academics have argued that the rejection of Hardy and Morgan is partially unfair given that other explanations which suffer from similar problems are not so strongly opposed. A conference devoted to the subject was held at Valkenburg, Netherlands, in 1987.” ref
“Its 22 participants included academic proponents and opponents of the hypothesis and several neutral observers headed by the anthropologist Vernon Reynolds of the University of Oxford. His summary at the end was: “Overall, it will be clear that I do not think it would be correct to designate our early hominid ancestors as ‘aquatic’. But at the same time there does seem to be evidence that not only did they take to water from time to time but that the water (and by this I mean inland lakes and rivers) was a habitat that provided enough extra food to count as an agency for selection.” ref
“The AAH is not accepted as empirically supported by the scholarly community, and has been met with significant skepticism. The Nature editor and paleontologist Henry Gee has argued that the hypothesis has equivalent merit to creationism, and should be similarly dismissed. In a 1997 critique, anthropologist John Langdon considered the AAH under the heading of an “umbrella hypothesis” and argued that the difficulty of ever disproving such a thing meant that although the idea has the appearance of being a parsimonious explanation, it actually was no more powerful an explanation than the null hypothesis that human evolution is not particularly guided by interaction with bodies of water. Langdon argued that however popular the idea was with the public, the “umbrella” nature of the idea means that it cannot serve as a proper scientific hypothesis.” ref
“Langdon also objected to Morgan’s blanket opposition to the “savannah hypothesis” which he took to be the “collective discipline of paleoanthropology”. He observed that some anthropologists had regarded the idea as not worth the trouble of a rebuttal. In addition, the evidence cited by AAH proponents mostly concerned developments in soft tissue anatomy and physiology, whilst paleoanthropologists rarely speculated on evolutionary development of anatomy beyond the musculoskeletal system and brain size as revealed in fossils. After a brief description of the issues under 26 different headings, he produced a summary critique of these with mainly negative judgments. His main conclusion was that the AAH was unlikely ever to be disproved on the basis of comparative anatomy, and that the one body of data that could potentially disprove it was the fossil record.” ref
“Anthropologist John D. Hawks wrote that it is fair to categorize the AAH as pseudoscience because of the social factors that inform it, particularly the personality-led nature of the hypothesis and the unscientific approach of its adherents. Physical anthropologist Eugenie Scott has described the aquatic ape hypothesis as an instance of “crank anthropology” akin to other pseudoscientific ideas in anthropology such as alien-human interbreeding and Bigfoot.” ref
In The Accidental Species: Misunderstandings of Human Evolution (2013), Henry Gee remarked on how a seafood diet can aid in the development of the human brain. He nevertheless criticized the AAH because “it’s always a problem identifying features [such as body fat and hairlessness] that humans have now and inferring that they must have had some adaptive value in the past.” Also “it’s notoriously hard to infer habits [such as swimming] from anatomical structures”.
“Popular support for the AAH has become an embarrassment to some anthropologists, who want to explore the effects of water on human evolution without engaging with the AAH, which they consider “emphasizes adaptations to deep water (or at least underwater) conditions”. Foley and Lahr suggest that “to flirt with anything watery in paleoanthropology can be misinterpreted”, but argue “there is little doubt that throughout our evolution we have made extensive use of terrestrial habitats adjacent to fresh water, since we are, like many other terrestrial mammals, a heavily water-dependent species.” But they allege that “under pressure from the mainstream, AAH supporters tended to flee from the core arguments of Hardy and Morgan towards a more generalized emphasis on fishy things.” ref
“In “The Waterside Ape”, a pair of 2016 BBC Radio documentaries, David Attenborough discussed what he thought was a “move towards mainstream acceptance” for the AAH in the light of new research findings. He interviewed scientists supportive of the idea, including Kathlyn Stewart and Michael Crawford who had published papers in a special issue of the Journal of Human Evolution on “The Role of Freshwater and Marine Resources in the Evolution of the Human Diet, Brain and Behavior”. Responding to the documentaries in a newspaper article, paleoanthropologist Alice Roberts criticized Attenborough’s promotion of AAH and dismissed the idea as a distraction “from the emerging story of human evolution that is more interesting and complex”. She argued that AAH had become “a theory of everything” that is simultaneously “too extravagant and too simple.” ref
“Philosopher Daniel Dennett, in his discussion of evolutionary philosophy, commented “During the last few years, when I have found myself in the company of distinguished biologists, evolutionary theorists, paleoanthropologists and other experts, I have often asked them to tell me, please, exactly why Elaine Morgan must be wrong about the aquatic theory. I haven’t yet had a reply worth mentioning, aside from those who admit, with a twinkle in their eyes, that they have also wondered the same thing.” He challenged both Elaine Morgan and the scientific establishment in that “Both sides are indulging in adapt[at]ionist Just So stories“. Along the same lines, historian Erika Lorraine Milam noted that independent of Morgan’s work, certain standard explanations of human development in paleoanthropology have been roundly criticized for lacking evidence, while being based on sexist assumptions. Anatomy lecturer Bruce Charlton gave Morgan’s book Scars of Evolution an enthusiastic review in the British Medical Journal in 1991, calling it “exceptionally well written” and “a good piece of science.” ref
“In 1995, paleoanthropologist Phillip Tobias declared that the savannah hypothesis was dead, because the open conditions did not exist when humanity’s precursors stood upright and that therefore the conclusions of the Valkenberg conference were no longer valid. Tobias praised Morgan’s book Scars of Evolution as a “remarkable book”, though he said that he did not agree with all of it. Tobias and his student further criticized the orthodox hypothesis by arguing that the coming out of the forest of man’s precursors had been an unexamined assumption of evolution since the days of Lamarck, and followed by Darwin, Wallace, and Haeckel, well before Raymond Dart used it.” ref
“Alister Hardy was astonished and mortified in 1960 when the national Sunday papers carried banner headlines “Oxford professor says man a sea ape”, causing problems with his Oxford colleagues. As he later said to his ex-pupil Desmond Morris, “Of course I then had to write an article to refute this saying no this is just a guess, a rough hypothesis, this isn’t a proven fact. And of course, we’re not related to dolphins.” Elaine Morgan’s 1972 book Descent of Woman became an international best-seller, a Book of the Month selection in the United States, and was translated into ten languages. The book was praised for its feminism but paleoanthropologists were disappointed with its promotions of the AAH. Morgan removed the feminist critique and left her AAH ideas intact, publishing the book as The Aquatic Ape 10 years later, but it did not garner any more positive reaction from scientists.” ref
“Although the general reaction to Hardy and Morgan’s proposals was silence by the relevant academic community, there have been over the last decades some academics who were inspired by AAH proposals, even to the point of pursuing particular lines of research on its basis. Some of the academics and professional scientists who have supported the AAH include Michael Crawford, Professor and Director of the Institute of Brain Chemistry and Human Nutrition at Imperial College London, his former postdoctoral researcher, Stephen Cunnane, now professor of medicine at Université de Sherbrooke, Erika Schagatay, professor of Environmental Physiology at Mid Sweden University, Kathlyn M. Stewart, Section Head of Palaeobiology at the Canadian Museum of Nature, and Tom Brenna, Professor of Paediatrics and Chemistry at University of Texas.” ref
“AAH proponent Algis Kuliukas, performed experiments to measure the comparative energy used when lacking orthograde posture with using fully upright posture. Although it is harder to walk upright with bent knees on land, this difference gradually diminishes as the depth of water increases and is still practical in thigh-high water. In a critique of the AAH, Henry Gee questioned any link between bipedalism and diet. Gee writes that early humans have been bipedal for 5 million years, but our ancestors’ “fondness for seafood” emerged a mere 200,000 years ago.” ref
“Evidence supports aquatic food consumption in Homo as early as the Pliocene, but its linkage to brain evolution remains controversial. Further, there is no evidence that humans ate fish in significant amounts earlier than tens to hundreds of thousands of years ago. Supporters argue that the avoidance of taphonomic bias is the problem, as most hominin fossils occur in lake-side environments, and the presence of fish remains is therefore not proof of fish consumption. They also claim that the archaeological record of human fishing and coastal settlement is fundamentally deficient due to postglacial sea level rise.” ref
“In their 1989 book The Driving Force: Food, Evolution and The Future, Michael Crawford and David Marsh claimed that omega-3 fatty acids were vital for the development of the brain: “A branch of the line of primitive ancestral apes was forced by competition to leave the trees and feed on the seashore. Searching for oysters, mussels, crabs, crayfish and so on they would have spent much of their time in the water and an upright position would have come naturally.” ref
“Crawford and Marsh opined that the brain size in aquatic mammals is similar to humans, and that other primates and carnivores lost relative brain capacity. Cunnane, Stewart, Crawford, and colleagues published works arguing a correlation between aquatic diet and human brain evolution in their “shore-based diet scenario”, acknowledging the Hardy/Morgan’s thesis as a foundation work of their model. As evidence, they describe health problems in landlocked communities, such as cretinism in the Alps and goitre in parts of Africa due to salt-derived iodine deficiency, and state that inland habitats cannot naturally meet human iodide requirements.” ref
“Biologists Caroline Pond and Dick Colby were highly critical, saying that the work provided “no significant new information that would be of interest to biologists” and that its style was “speculative, theoretical and in many places so imprecise as to be misleading.” British palaeontologist Henry Gee, who remarked on how a seafood diet can aid in the development of the human brain, nevertheless criticized AAH because inferring aquatic behavior from body fat and hairlessness patterns is an unjustifiable leap.” ref
“Aside from working as a professor, Erika Schagatay is also an experienced scuba and freediver whose research centers around human diving abilities. She suggests that such abilities are consistent with selective pressure for underwater foraging during human evolution, and discussed other anatomical traits speculated as diving adaptations by Hardy/Morgan. John Langdon suggested that such traits could be enabled by a human developmental plasticity.” ref
“Tom Brenna, professor of pediatrics whose primary research focuses on fats, oils, and fatty acids, listened to the 2005 radio documentary Scars of Evolution where David Attenborough reported an observation that harbor seals were born with something that resembled human vernix caseosa. Intrigued, Brenna led a team that collaborated with Judy St Leger at San Diego Seaworld to compare the chemistry of human vernix and samples from California sea lion pups. They established that the molecular composition of both is similar, being rich in branched chain fatty acids and squalene.” ref
Actual Human Evolution
“Human evolution is the evolutionary process within the history of primates that led to the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species of the hominid family, which includes the great apes. This process involved the gradual development of traits such as human bipedalism and language, as well as interbreeding with other hominins, which indicate that human evolution was not linear but a web.” ref
“The study of human evolution involves several scientific disciplines, including physical anthropology, primatology, archaeology, paleontology, neurobiology, ethology, linguistics, evolutionary psychology, embryology, and genetics. Genetic studies show that primates diverged from other mammals about 85 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period, and the earliest fossils appear in the Paleocene, around 55 million years ago.” ref
“Within the superfamily Hominoidea, the family Hominidae diverged from the family Hylobatidae some 15–20 million years ago; subfamily Homininae (African apes) diverged from Ponginae (orangutans[a]) about 14 million years ago; the tribe Hominini (including humans, Australopithecus, and chimpanzees) parted from the tribe Gorillini (gorillas) between 8–9 million years ago; and, in turn, the subtribes Hominina (humans and extinct biped ancestors) and Panina (chimpanzees) separated 4–7 million years ago.” ref
“Human evolution from its first separation from the last common ancestor of humans and chimpanzees is characterized by a number of morphological, developmental, physiological, and behavioral changes. The most significant of these adaptations are bipedalism, increased brain size, lengthened ontogeny (gestation and infancy), and decreased sexual dimorphism. The relationship between these changes is the subject of ongoing debate. Other significant morphological changes included the evolution of a power and precision grip, a change first occurring in H. erectus.” ref
“Bipedalism is the basic adaptation of the hominid and is considered the main cause behind a suite of skeletal changes shared by all bipedal hominids. The earliest hominin, of presumably primitive bipedalism, is considered to be either Sahelanthropus[11] or Orrorin, both of which arose some 6 to 7 million years ago. The non-bipedal knuckle-walkers, the gorillas and chimpanzees, diverged from the hominin line over a period covering the same time, so either Sahelanthropus or Orrorin may be our last shared ancestor. Ardipithecus, a full biped, arose approximately 5.6 million years ago.” ref
“The early bipeds eventually evolved into the australopithecines and still later into the genus Homo. There are several theories of the adaptation value of bipedalism. It is possible that bipedalism was favored because it freed the hands for reaching and carrying food, saved energy during locomotion, enabled long-distance running and hunting, provided an enhanced field of vision, and helped avoid hyperthermia by reducing the surface area exposed to direct sun; features all advantageous for thriving in the new savanna and woodland environment created as a result of the East African Rift Valley uplift versus the previous closed forest habitat.” ref
“A 2007 study provides support for the hypothesis that walking on two legs, or bipedalism, evolved because it used less energy than quadrupedal knuckle-walking. However, recent studies suggest that bipedality without the ability to use fire would not have allowed global dispersal. This change in gait saw a lengthening of the legs proportionately when compared to the length of the arms, which were shortened through the removal of the need for brachiation. Another change is the shape of the big toe. Recent studies suggest that australopithecines still lived part of the time in trees as a result of maintaining a grasping big toe. This was progressively lost in habilines.” ref
“Anatomically, the evolution of bipedalism has been accompanied by a large number of skeletal changes, not just to the legs and pelvis, but also to the vertebral column, feet and ankles, and skull. The femur evolved into a slightly more angular position to move the center of gravity toward the geometric center of the body. The knee and ankle joints became increasingly robust to better support increased weight. To support the increased weight on each vertebra in the upright position, the human vertebral column became S-shaped and the lumbar vertebrae became shorter and wider. In the feet the big toe moved into alignment with the other toes to help in forward locomotion. The arms and forearms shortened relative to the legs making it easier to run. The foramen magnum migrated under the skull and more anterior.” ref
“The most significant changes occurred in the pelvic region, where the long downward facing iliac blade was shortened and widened as a requirement for keeping the center of gravity stable while walking; bipedal hominids have a shorter but broader, bowl-like pelvis due to this. A drawback is that the birth canal of bipedal apes is smaller than in knuckle-walking apes, though there has been a widening of it in comparison to that of australopithecine and modern humans, permitting the passage of newborns due to the increase in cranial size but this is limited to the upper portion, since further increase can hinder normal bipedal movement.” ref
“The shortening of the pelvis and smaller birth canal evolved as a requirement for bipedalism and had significant effects on the process of human birth which is much more difficult in modern humans than in other primates. During human birth, because of the variation in size of the pelvic region, the fetal head must be in a transverse position (compared to the mother) during entry into the birth canal and rotate about 90 degrees upon exit. The smaller birth canal became a limiting factor to brain size increases in early humans and prompted a shorter gestation period leading to the relative immaturity of human offspring, who are unable to walk much before 12 months and have greater neoteny, compared to other primates, who are mobile at a much earlier age. The increased brain growth after birth and the increased dependency of children on mothers had a major effect upon the female reproductive cycle, and the more frequent appearance of alloparenting in humans when compared with other hominids. Delayed human sexual maturity also led to the evolution of menopause with one explanation providing that elderly women could better pass on their genes by taking care of their daughter’s offspring, as compared to having more children of their own.” ref
“The human species eventually developed a much larger brain than that of other primates—typically 1,330 cm3 (81 cu in) in modern humans, nearly three times the size of a chimpanzee or gorilla brain. After a period of stasis with Australopithecus anamensis and Ardipithecus, species which had smaller brains as a result of their bipedal locomotion, the pattern of encephalization started with Homo habilis, whose 600 cm3 (37 cu in) brain was slightly larger than that of chimpanzees. This evolution continued in Homo erectus with 800–1,100 cm3 (49–67 cu in), and reached a maximum in Neanderthals with 1,200–1,900 cm3 (73–116 cu in), larger even than modern Homo sapiens. This brain increase manifested during postnatal brain growth, far exceeding that of other apes (heterochrony). It also allowed for extended periods of social learning and language acquisition in juvenile humans, beginning as much as 2 million years ago.” ref
“Furthermore, the changes in the structure of human brains may be even more significant than the increase in size. The temporal lobes, which contain centers for language processing, have increased disproportionately, as has the prefrontal cortex, which has been related to complex decision-making and moderating social behavior. Encephalization has been tied to increased meat and starches in the diet, and the development of cooking, and it has been proposed that intelligence increased as a response to an increased necessity for solving social problems as human society became more complex. Changes in skull morphology, such as smaller mandibles and mandible muscle attachments, allowed more room for the brain to grow.” ref
“The increase in volume of the neocortex also included a rapid increase in size of the cerebellum. Its function has traditionally been associated with balance and fine motor control, but more recently with speech and cognition. The great apes, including hominids, had a more pronounced cerebellum relative to the neocortex than other primates. It has been suggested that because of its function of sensory-motor control and learning complex muscular actions, the cerebellum may have underpinned human technological adaptations, including the preconditions of speech.” ref
“The immediate survival advantage of encephalization is difficult to discern, as the major brain changes from Homo erectus to Homo heidelbergensis were not accompanied by major changes in technology. It has been suggested that the changes were mainly social and behavioral, including increased empathic abilities, increases in size of social groups, and increased behavioral plasticity. Encephalization may be due to a dependency on calorie-dense, difficult-to-acquire food.” ref

Herpes Infected Humans Before They Were Human
“The viral family tree showed that HSV-2 was far more genetically similar to the herpes virus found in chimpanzees. This level of divergence indicated that humans must have acquired HSV-2 from an ancestor of modern chimpanzees about 1.6 million years ago, prior to the rise of modern humans roughly 200,000 years ago.” ref

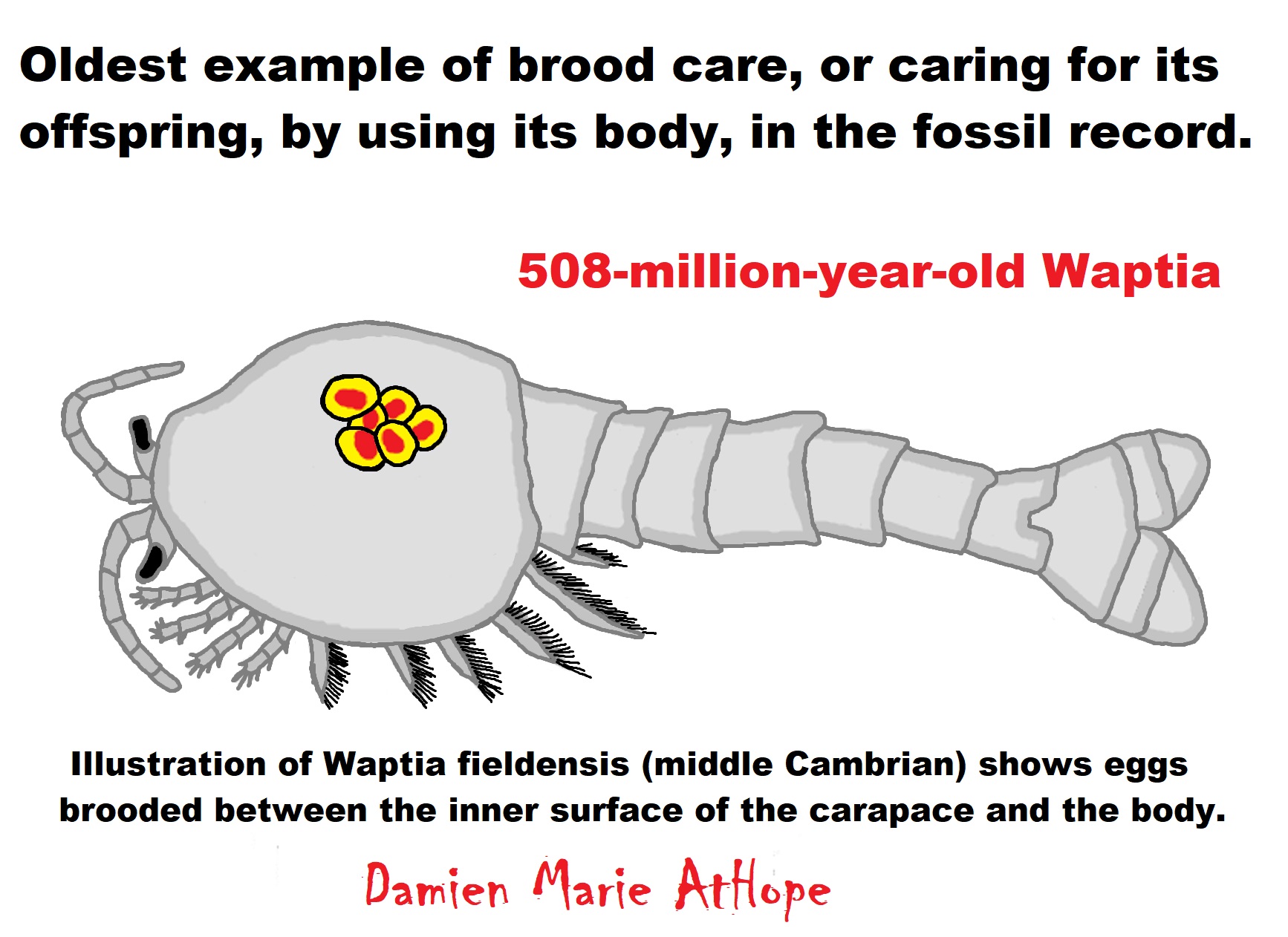
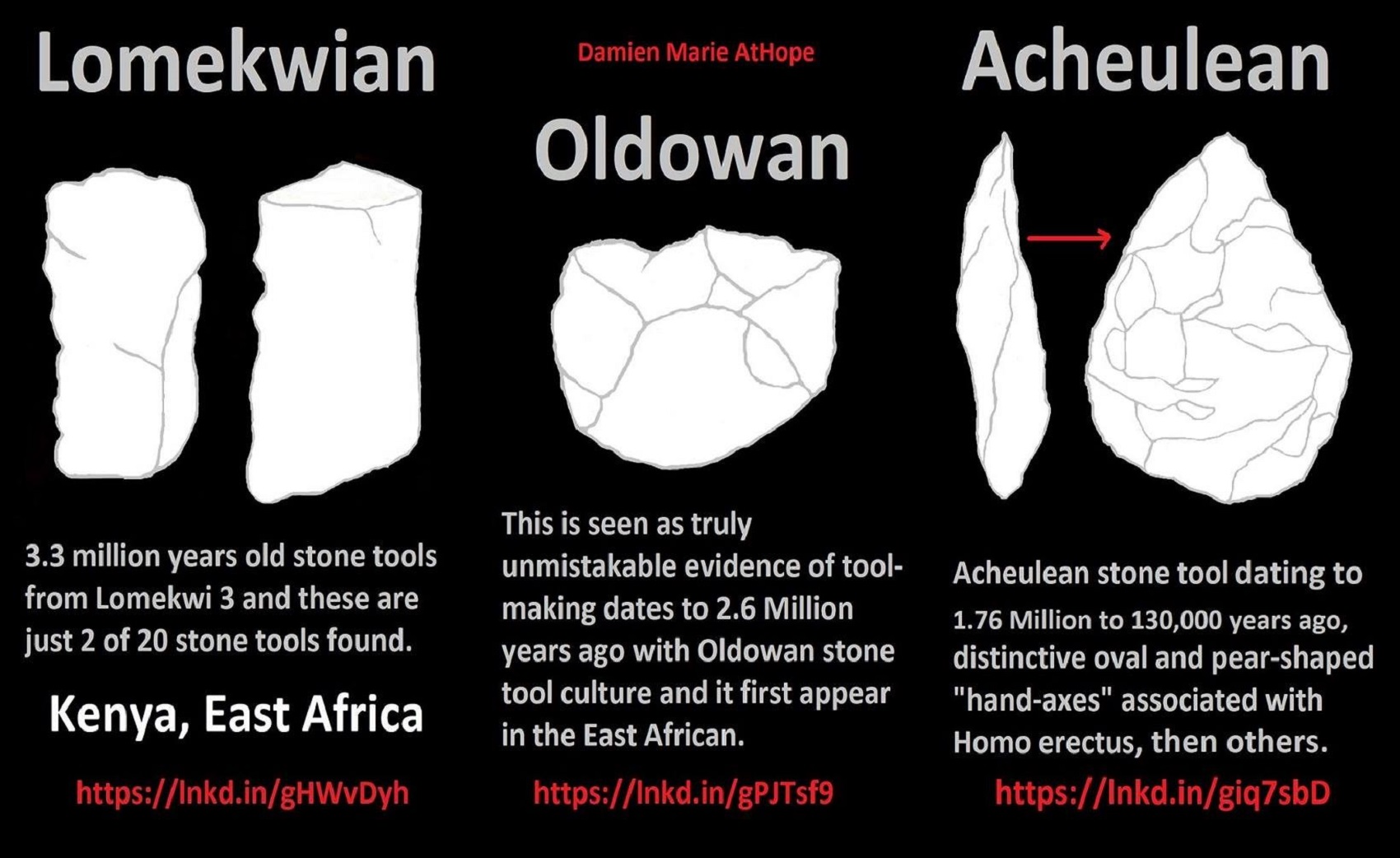
“Two parallel marks that look like cut marks on a 3.4-million-year-old bone from a buffalo-sized creature from Ethiopia in East Africa. Along with scores of crude stone tools discovered at Lomekwi 3 in Kenya are East Africa that date back 3.3 million years. And more interesting is Kenyanthropus a hominin genus identified from the Lomekwi site by Lake Turkana, Kenya, dated to 3.3 to 3.2 million years ago.” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
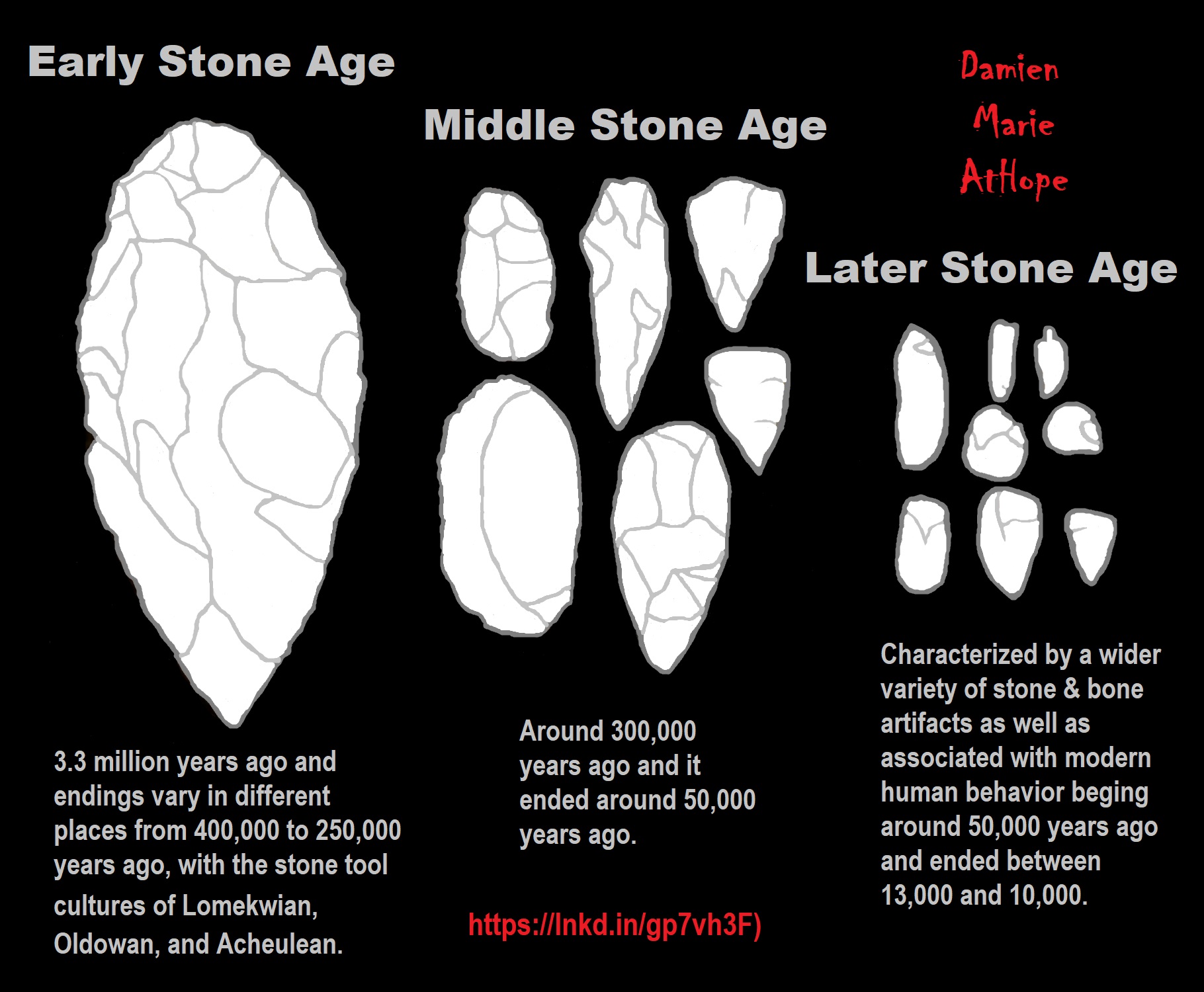
Early Stone Age (Lower Paleolithic): “The Lower Paleolithic is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in the current archaeological record, until around 300,000 years ago, spanning the Oldowan (“mode 1”) and Acheulean (“mode 2”) lithics industries. In African archaeology, the time period roughly corresponds to the Early Stone Age, the earliest finds dating back to 3.3 million years ago, with Lomekwian stone tool technology, spanning Mode 1 stone tool technology, which begins roughly 2.6 million years ago and ends between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago, with Mode 2 technology.” ref
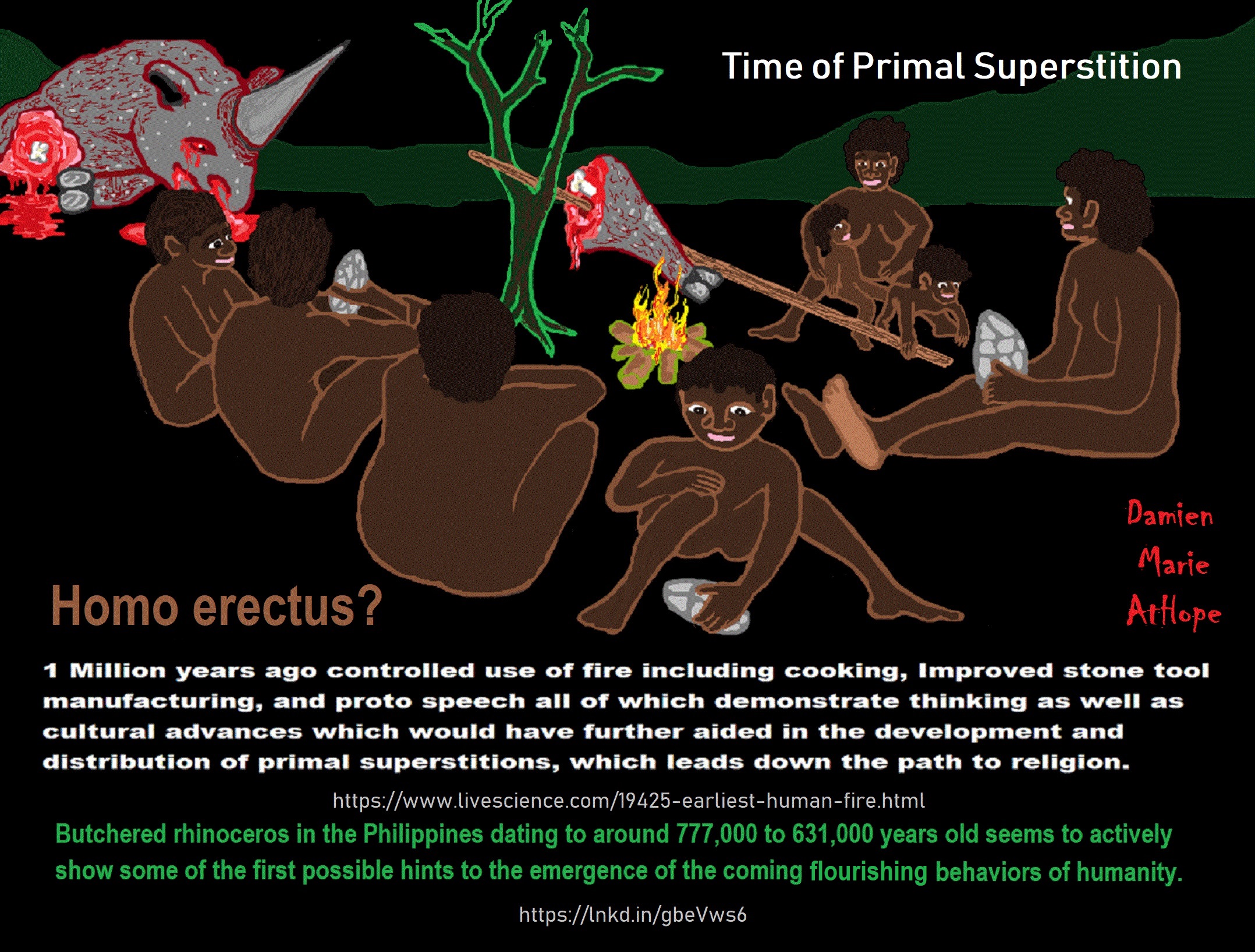
Middle Stone Age (Middle Paleolithic): “The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa, and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to replace earlier pre-existent Homo species such as the Neanderthals and Homo erectus.” ref
“Middle Paleolithic burials at sites such as Krapina in Croatia (dated to c. 130,000 BP) and the Qafzeh and Es Skhul caves in Israel (c. 100,000 BP) have led some anthropologists and archeologists (such as Philip Lieberman) to believe that Middle Paleolithic cultures may have possessed a developing religious ideology which included concepts such as an afterlife; other scholars suggest the bodies were buried for secular reasons. According to recent archeological findings from Homo heidelbergensis sites in the Atapuerca Mountains, the practice of intentional burial may have begun much earlier during the late Lower Paleolithic, but this theory is widely questioned in the scientific community.” ref
“The earliest undisputed evidence of artistic expression during the Paleolithic period comes from Middle Paleolithic/Middle Stone Age sites such as Blombos Cave in the form of bracelets, beads, art rock, ochre used as body paint and perhaps in ritual, though earlier examples of artistic expression such as the Venus of Tan-Tan and the patterns found on elephant bones from Bilzingsleben in Thuringia may have been produced by Acheulean tool-users such as Homo erectus prior to the start of the Middle Paleolithic period. Activities such as catching large fish and hunting large game animals with specialized tools indicate increased group-wide cooperation and more elaborate social organization. In addition to developing advanced cultural traits, humans also first began to take part in long-distance trade between groups for rare commodities (such as ochre (which was often used for religious purposes such as ritual) and raw materials during the Middle Paleolithic as early as 120,000 years ago. Inter-group trade may have appeared during the Middle Paleolithic because trade between bands would have helped ensure their survival by allowing them to exchange resources and commodities such as raw materials during times of relative scarcity (i.e., famine or drought).” ref
Later Stone Age (Upper Paleolithic): “The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. Homo sapiens) are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago, it has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of artifacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to an expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which contributed to the extinction of the Neanderthals. The Upper Paleolithic has the earliest known evidence of organized settlements, in the form of campsites, some with storage pits. Artistic work blossomed, with cave paintings, petroglyphs, carvings, and engravings on bone or ivory.” ref
“The first evidence of human fishing is also found, from artifacts in places such as Blombos cave in South Africa. More complex social groupings emerged, supported by more varied and reliable food sources and specialized tool types. This probably contributed to increasing group identification or ethnicity. The peopling of Australia most likely took place before c. 60,000 years ago. Europe was peopled after c. 45,000 years ago. Anatomically modern humans are known to have expanded northward into Siberia as far as the 58th parallel by about 45 ka (Ust’-Ishim man). The Upper Paleolithic is divided by the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), from about 25,000 to 15,000 years ago. The peopling of the Americas occurred during this time, with East and Central Asia populations reaching the Bering land bridge after about 35 ka, and expanding into the Americas by about 15,000 years ago. In Western Eurasia, the Paleolithic eases into the so-called Epipaleolithic or Mesolithic from the end of the LGM, beginning 15 ka. The Holocene glacial retreat begins 11.7,00 years ago (10th millennium BCE), falling well into the Old World Epipaleolithic, and marking the beginning of the earliest forms of farming in the Fertile Crescent.” ref

430,000 years ago, Sima de los Huesos, “Pit of Bones”, Atapuerca, Spain, seeming evidence of intentional storing of 28 individuals in a cave chamber pit (a symbolic pseudo-womb?) and a reddish quartzite tool found with the bodies, seems like a kind of ritual funeral offering in this possibly early cemetery. Fossil remains of 430,000-400,000-years-old 28 individuals, 6,500 bone fragments and 500 teeth, in one of several important sections of the Cueva Mayor-Cueva del Silo cave system in north-central Spain. The bone pit is at the bottom of the cave, beneath an abrupt vertical shaft measuring between 6.5-13 feet in diameter, and located about .1/3 of a mile in down a 42.5 ft shaft and it is possibly an expression of mortuary practices. ref
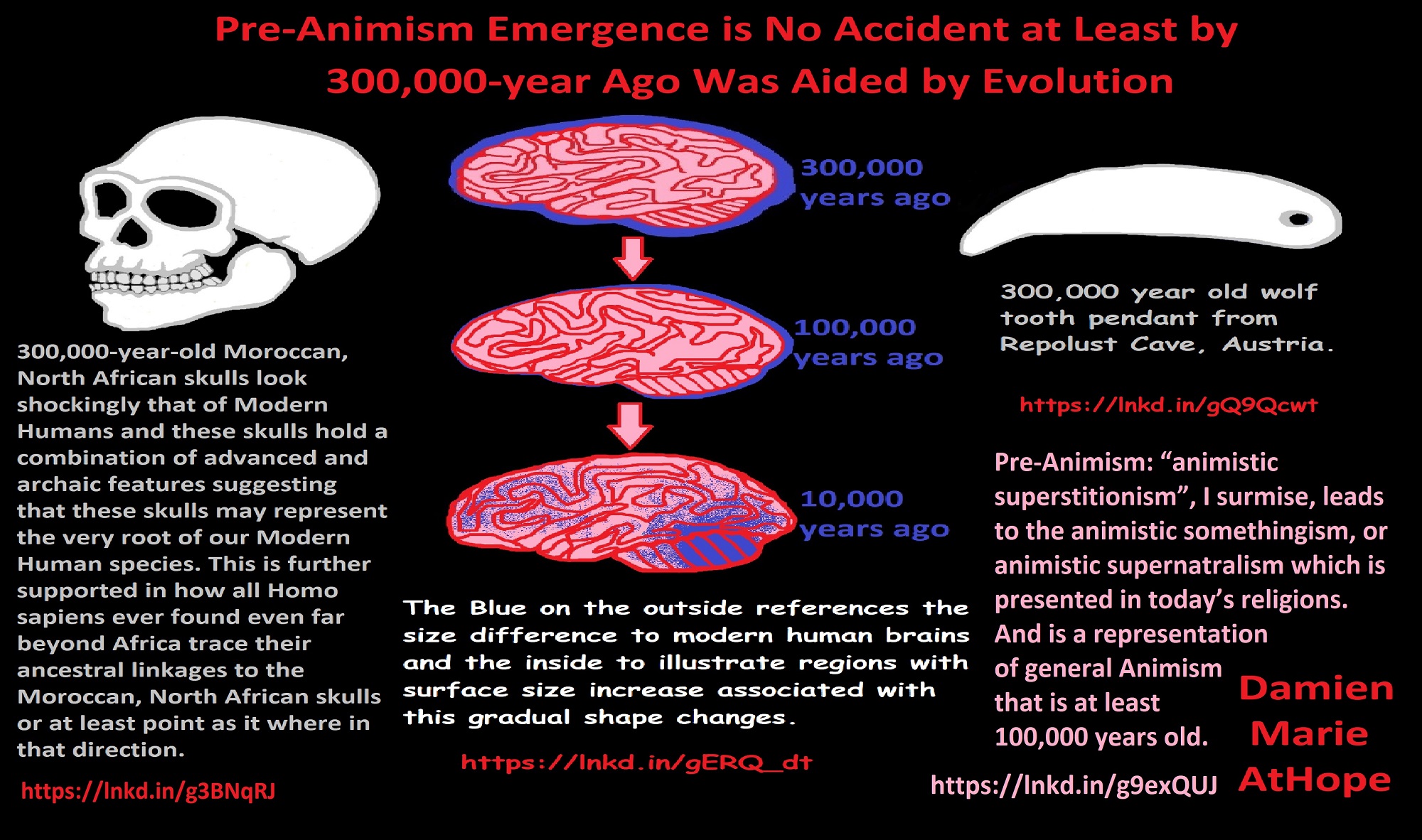
Pre-Animism Emergence is No Accident at Least by 300,000-year Ago Was Aided by Evolution
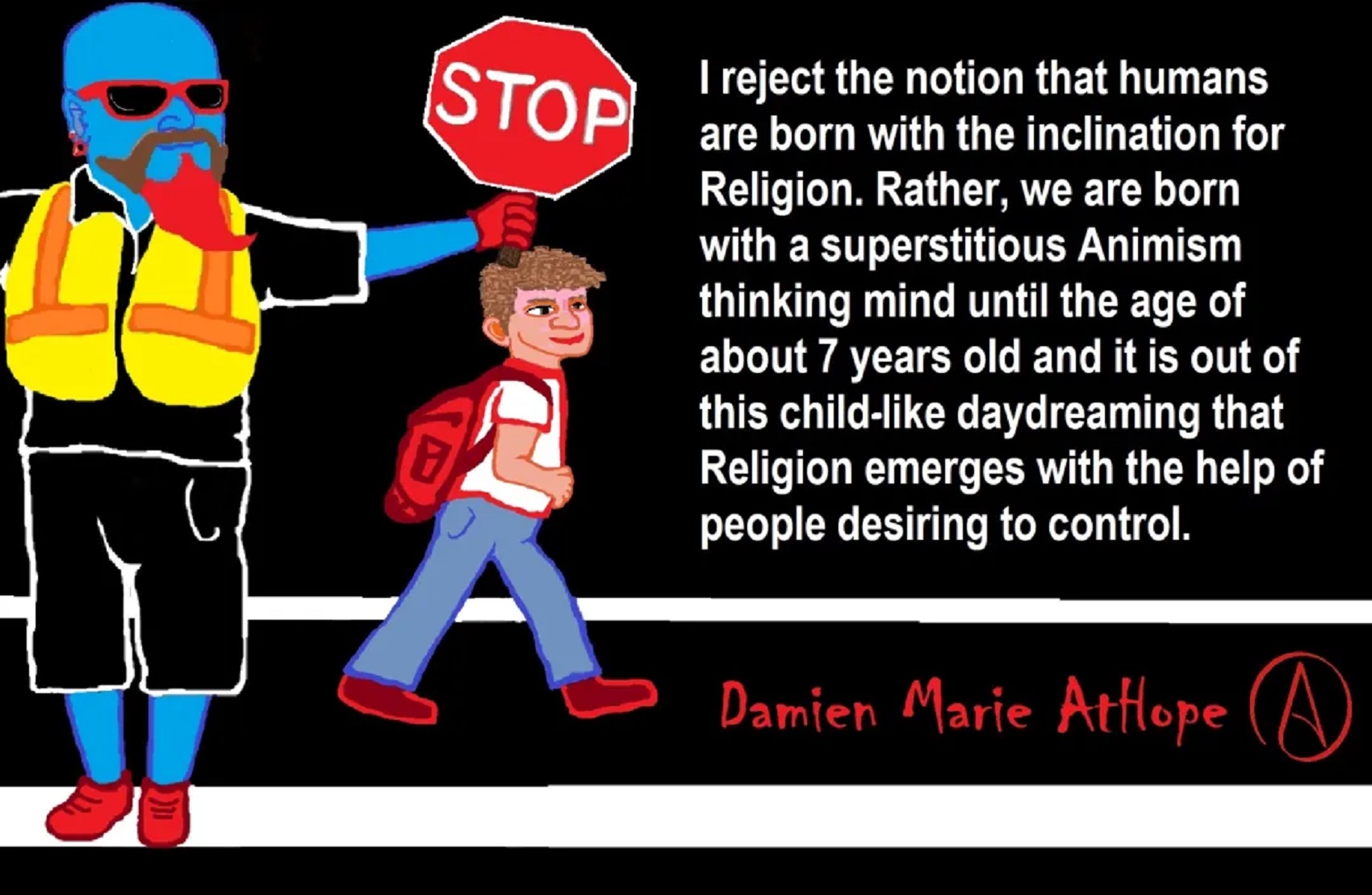
Pre-Animism: “animistic superstitionism”, I surmise, leads to the animistic somethingism, or animistic supernatralism is presented in today’s religions and is a representation of general Animism that is at least 100,000 years old. ref
The Blue on the outside references the size difference to modern human brains and the inside to illustrate regions with surface size increase associated with this gradual shape changes. ref
300,000-year-old Moroccan, North African skulls look shockingly that of Modern Humans and these skulls hold a combination of advanced and archaic features suggesting that these skulls may represent the very root of our Modern Human species. This is further supported in how all Homo sapiens ever found even far beyond Africa trace their ancestral linkages to the Moroccan, North African skulls or at least point as it where in that direction. And seemingly Homo sapiens could have been living across Africa and sem9ingly engaging in extensive movement, which could have involved exchange both in ideas, technology as well as even genetics. ref
300,000-year-old wolf tooth pendant from Repolust Cave, Austria. ref

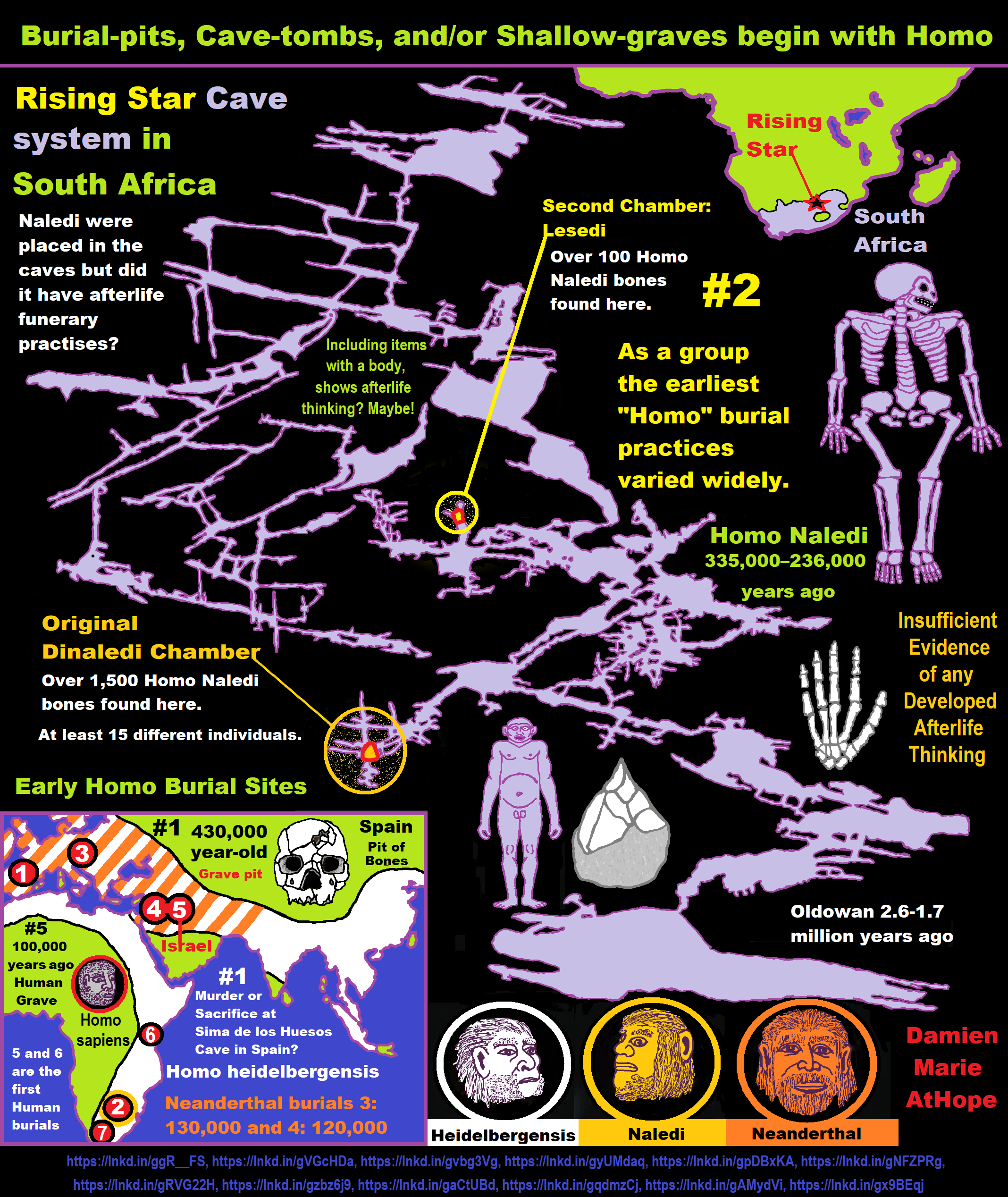
Homo Naledi and an Intentional Cemetery “Pre-Animism” dating to around 250,000 years ago?
To me, it seems likely Homo Naledi did have an intentional cemetery as seen at Dinaledi Chamber, in South Africa, thus “Pre-Animism” dating to around 250,000 years ago. The odd cache of bones from several Homo Naledi were recovered from a deep chamber in a South African cave, seeming to express a cemetery far from the cave entrance, accessible only through a narrow, difficult passage impossible place to live, and not by accident this purposeful cave chamber was most likely kind of graveyard. ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref ,ref ,ref ,ref ,ref, ref, ref
Homo Naledi
“Homo Naledi is a species of archaic human discovered in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago. The initial discovery comprises 1,550 specimens, representing 737 different elements, and at least 15 different individuals. Despite this exceptionally high number of specimens, their classification with other Homo remains unclear.” ref
“Along with similarities to contemporary Homo, they share several characteristics with the ancestral Australopithecus and early Homo as well (mosaic anatomy), most notably a small cranial capacity of 465–610 cm3 (28.4–37.2 cu in), compared to 1,270–1,330 cm3 (78–81 cu in) in modern humans. They are estimated to have averaged 143.6 cm (4 ft 9 in) in height and 39.7 kg (88 lb) in weight, yielding a small encephalization quotient of 4.5. Nonetheless, Homo Naledi’s brain anatomy seems to have been similar to contemporary Homo, which could indicate equatable cognitive complexity. The persistence of small-brained humans for so long in the midst of bigger-brained contemporaries revises the previous conception that a larger brain would necessarily lead to an evolutionary advantage, and their mosaic anatomy greatly expands the known range of variation for the genus.” ref
“Homo Naledi anatomy indicates that, though they were capable of long-distance travel with a humanlike stride and gait, they were more arboreal than other Homo, better adapted to climbing and suspensory behavior in trees than endurance running. Tooth anatomy suggests consumption of gritty foods covered in particulates such as dust or dirt. Though they have not been associated with stone tools or any indication of material culture, they appear to have been dextrous enough to produce and handle tools, and likely manufactured Early or Middle Stone Age industries. It has also been controversially postulated that these individuals were given funerary rites, and were carried into and placed in the chamber.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Animism: a belief among some indigenous people, young children, or all religious people!
Over 100,000 years ago or so, Southern Africa, in the Land before and the beginning Time of Animism: LINK
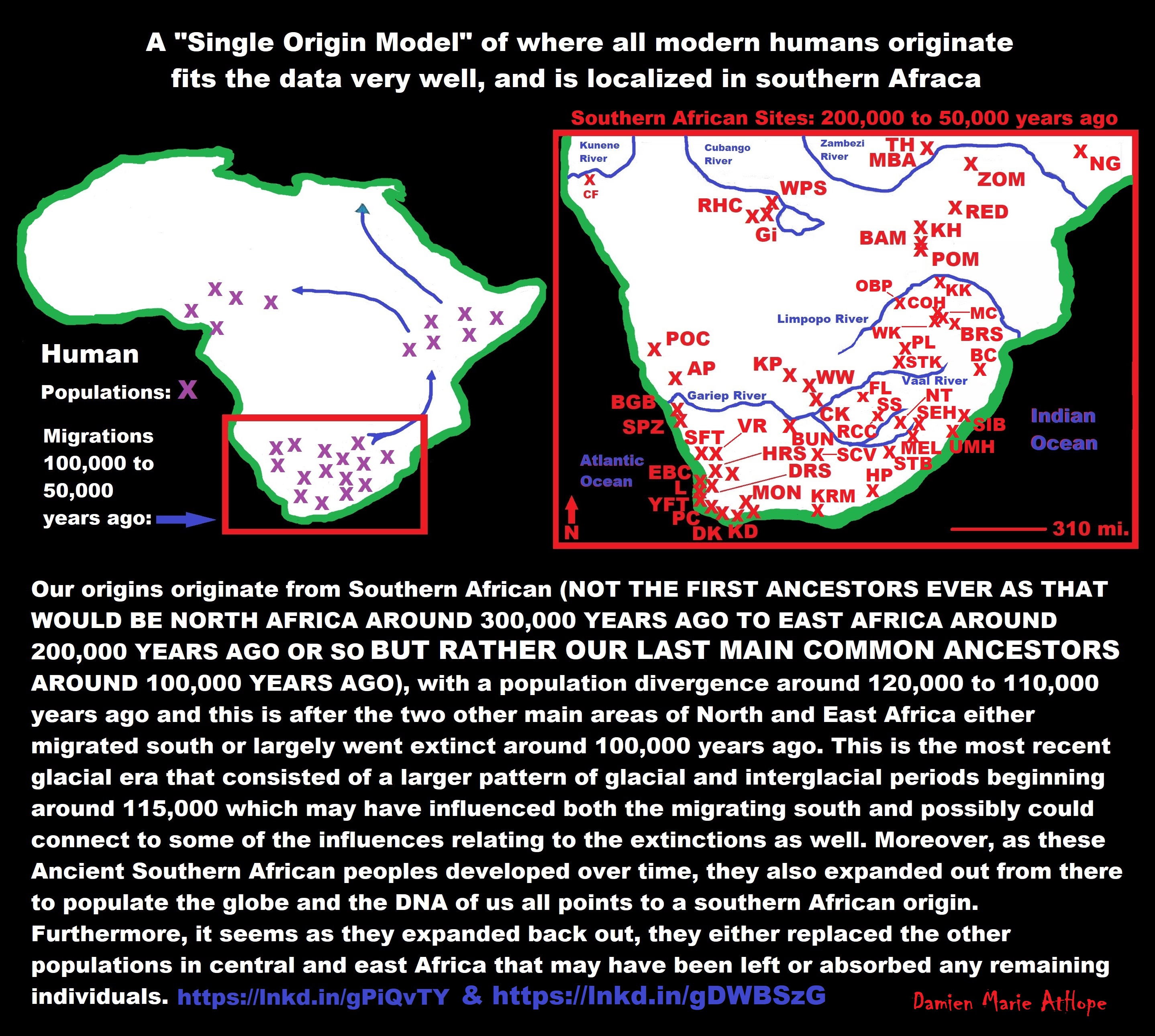
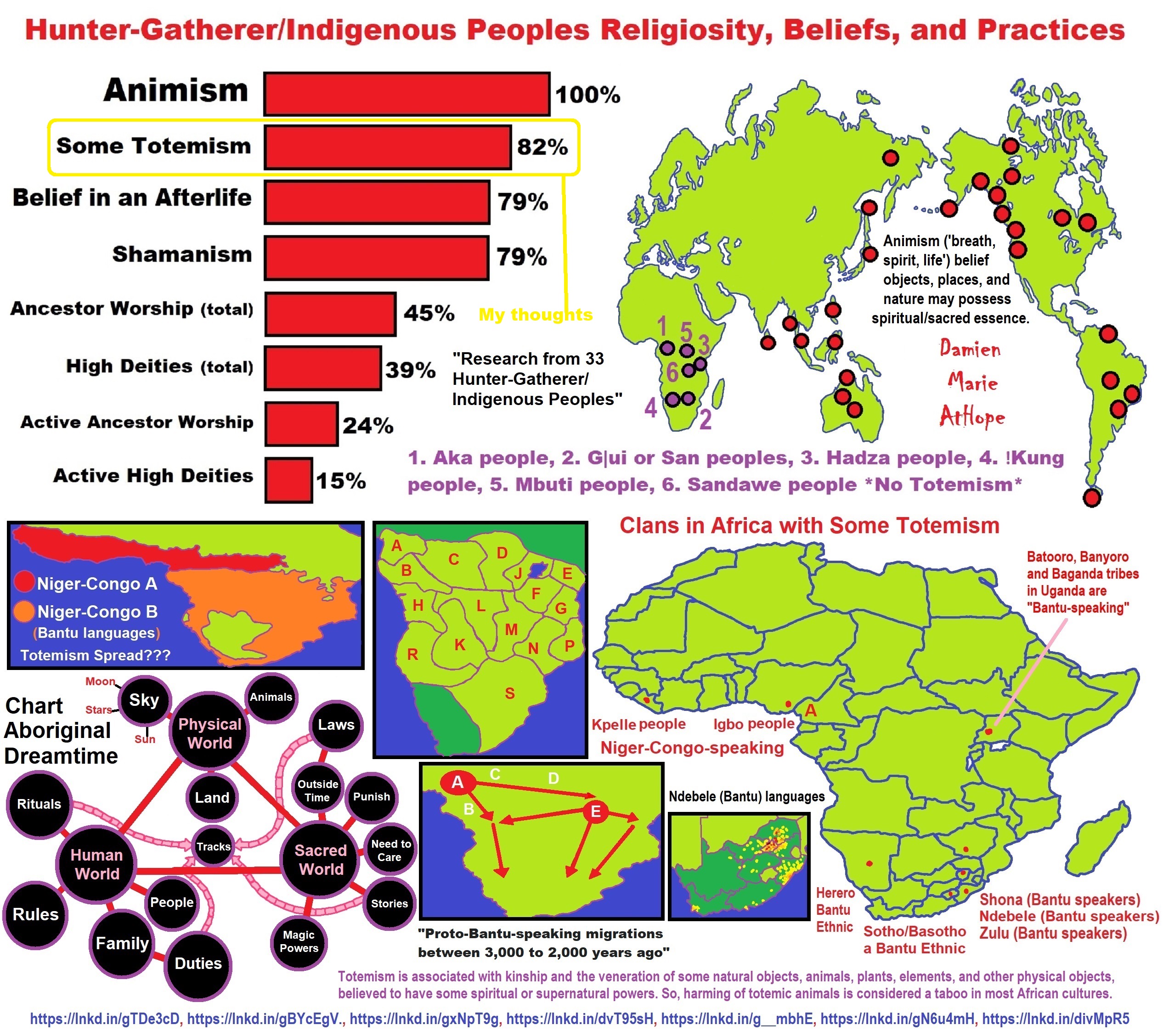
Our origins originate from Southern African (NOT THE FIRST ANCESTORS EVER AS THAT WOULD BE NORTH AFRICA AROUND 300,000 YEARS AGO TO EAST AFRICA AROUND 200,000 YEARS AGO OR SO BUT RATHER OUR LAST MAIN COMMON ANCESTORS AROUND 100,000 YEARS AGO), with a population divergence around 120,000 to 110,000 years ago and this is after the two other main areas of North and East Africa either migrated south or largely went extinct around 100,000 years ago. This is the most recent glacial era that consisted of a larger pattern of glacial and interglacial periods beginning around 115,000 which may have influenced both the migrating south and possibly could connect to some of the influences relating to the extinctions as well. Moreover, as these Ancient Southern African peoples developed over time, they also expanded out from there to populate the globe, and the DNA of us all points to a southern African origin. Furthermore, it seems as they expanded back out, they either replaced the other populations in central and east Africa that may have been left or absorbed any remaining individuals. ref
Southern African Middle Stone Age sites:
(Ap) Apollo 11; (BAM) Bambata; (BBC) Blombos Cave; (BC) Border Cave; (BGB)Boegoeberg; (BPA) Boomplaas; (BRS) Bushman Rock Shelter; (BUN) Bundu Farm; (CF)Cufema Reach; (CK) Canteen Kopje; (COH) Cave of Hearths; (CSB) Cape St Blaize; (DK)Die Kelders Cave 1; (DRS) Diepkloof Rock Shelter; (EBC) Elands Bay Cave; (FL) Florisbad; (≠GI) ≠Gi; (HP) Howiesons Poort; (HRS) Hollow Rock Shelter; (KD) Klipdrift; (KKH) Klein Kliphuis; (KH) Khami; (KK) Kudu Koppie; (KP) Kathu Pan; (KRM) Klasies River Main Site; (L) Langebaan; (MBA) Mumbwa Caves; (MC) Mwulu’s Cave; (MEL)Melikane; (MON) Montagu Cave; (NBC) Nelson Bay Cave; (NG) Ngalue; (NT) Ntloana Tšoana; (OBP) Olieboomspoort; (PC) Peers Cave; (POC) Pockenbank; (PL) Plover’s Lake; (POM) Pomongwe; (PP) Pinnacle Point; (RCC) Rose Cottage Cave; (RED) Redcliff; (RHC) Rhino Cave; (SCV) Seacow Valley; (SFT) Soutfontein; (SEH) Sehonghong; (SIB)Sibudu Cave; (SPZ) Spitzkloof Rock Shelter; (SS) Sunnyside 1; (STB) Strathalan Cave B; (STK) Sterkfontein; (TR) Twin Rivers; (UMH) Umhlatuzana; (VR) Varsche Rivier 003; (WPS) White Paintings Shelter; (WK) Wonderkrater; (WW) Wonderwerk; (YFT)Ysterfontein 1; (ZOM) Zombepata Cave. ref

“When researchers completed the final analysis of the Human Genome Project in April 2003, they confirmed that the 3 billion base pairs of genetic letters in humans were 99.9 percent identical in every person. It also meant that individuals are, on average, 0.1 percent different genetically from every other person on the planet. And in that 0.1 percent lies the mystery of why some people are more susceptible to a particular illness or more likely to be healthy than their neighbor – or even another family member.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref,
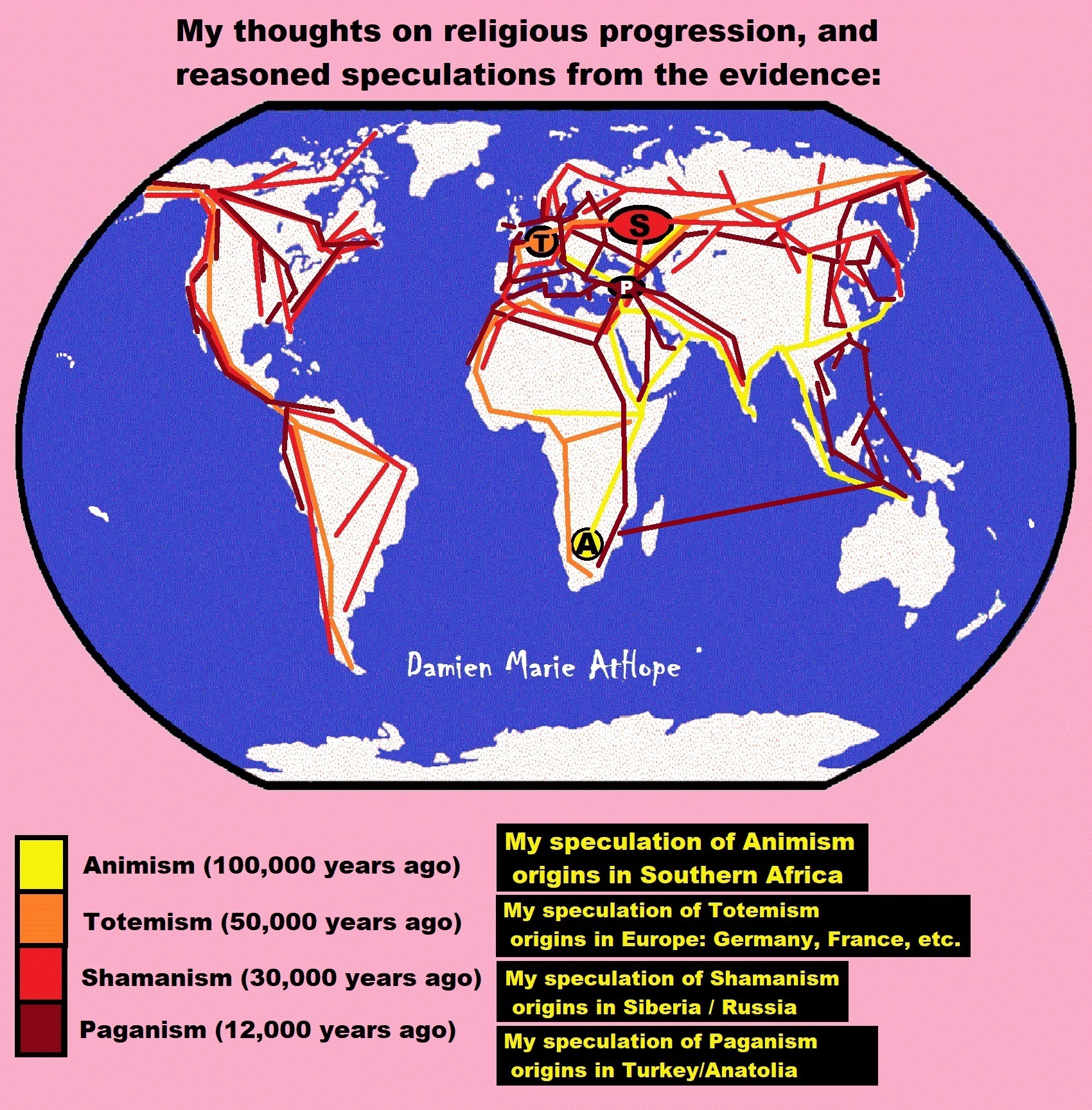
Explaining the Earliest Religious Expression, that of Animism (beginning 100,000 to 70,000 years ago?) to Totemism (beginning 30,000 to 3,000 years ago?) in Southern Africa: LINK

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref


My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
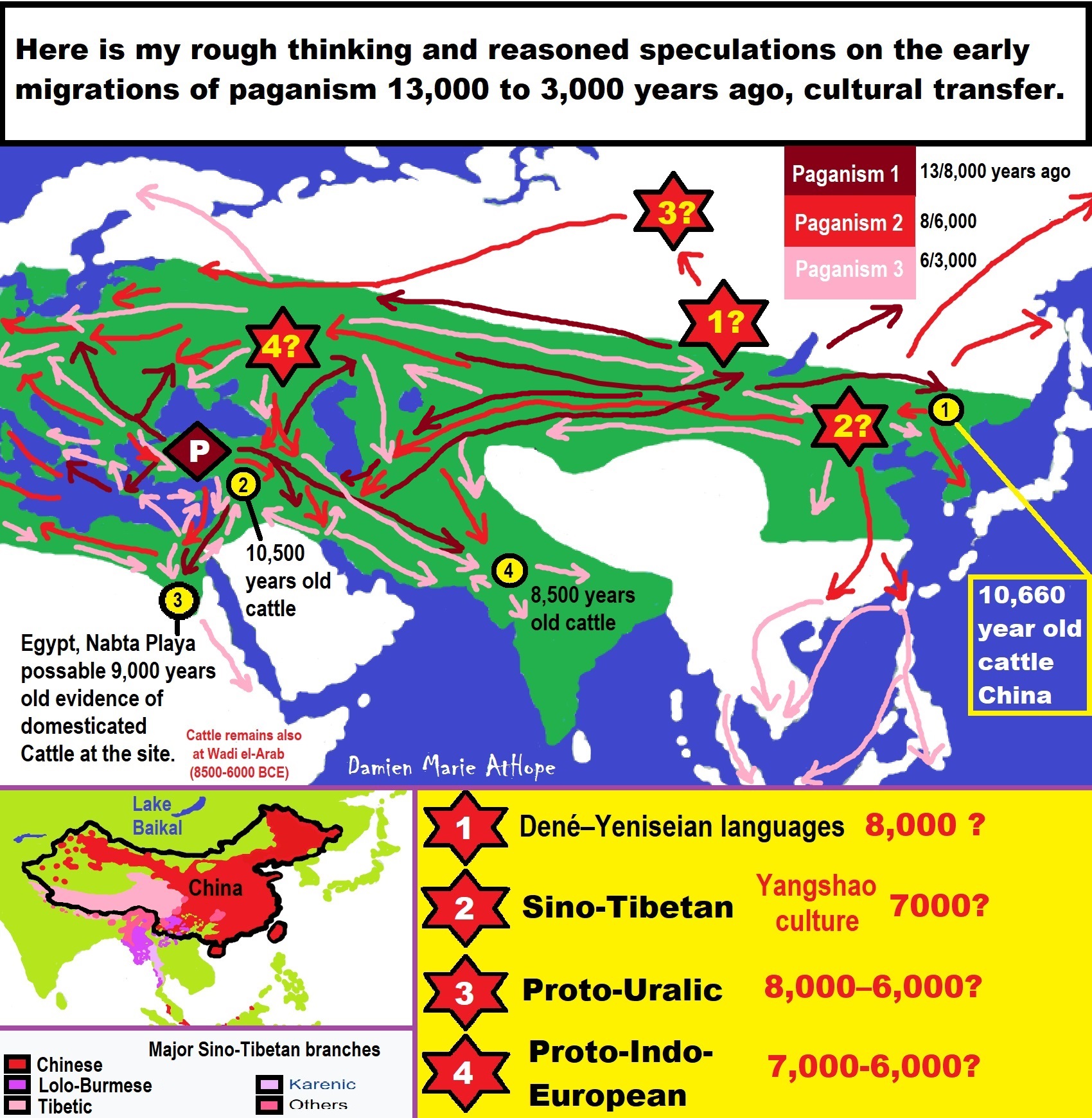
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.







ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com