Understanding Religion Evolution per Damien’s speculations from the evidence:
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) possibly Africa, Middle East, and Eurasia
Animism (at least 100,000 years ago) possibly Southern Africa or maybe Central Africa
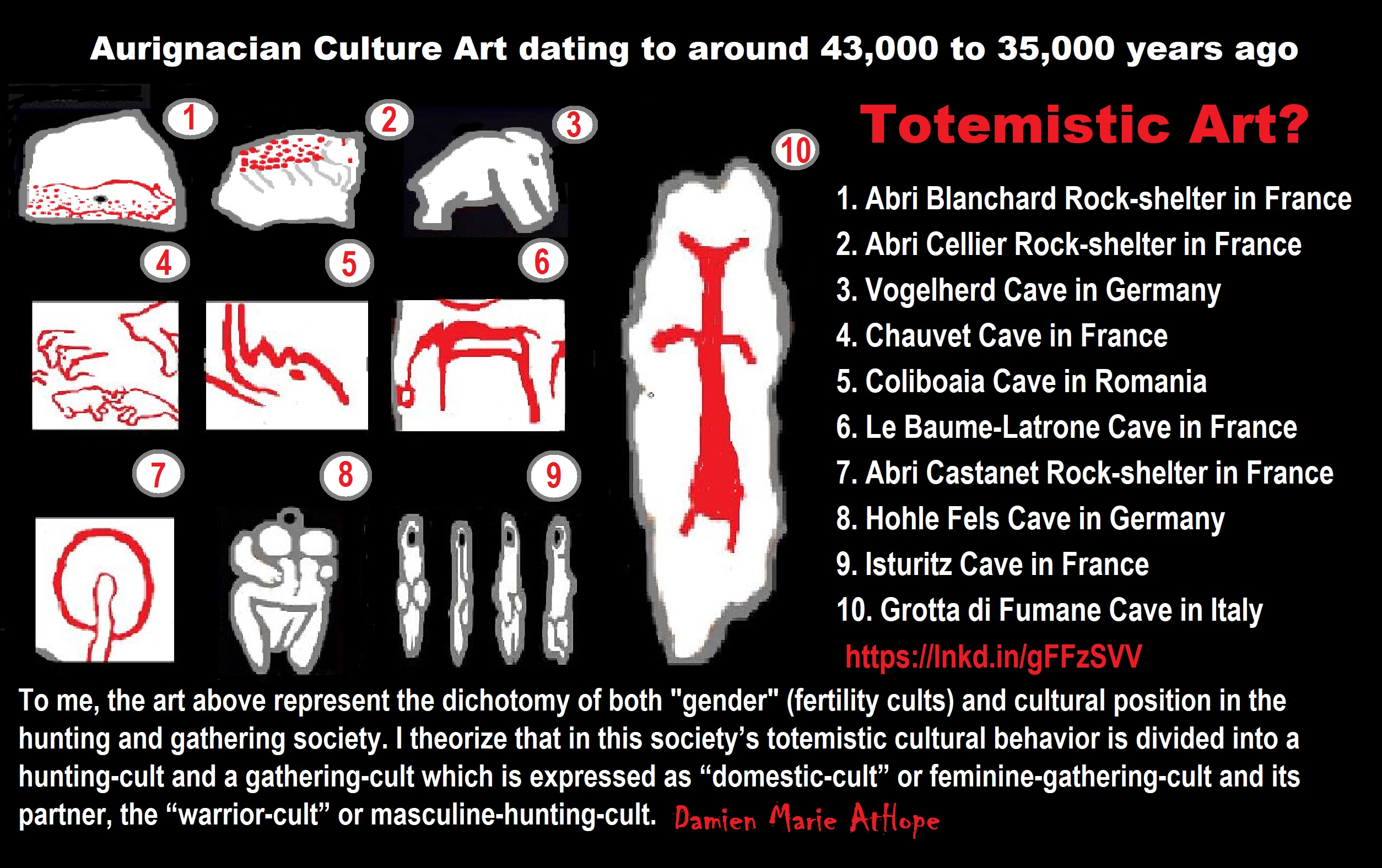
Totemism (at least 50,000/45,000 years ago) possibly around Germany, France, or somewhere in West Europe
Shamanism (at least 30,000/35,000 years ago) possibly West Siberia or East Russia
Paganism (at least 12,000/13,000 years ago) Turkey And/or Levant: “Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Syria”
Progressed organized religion (at least 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
I think animism started 100,000 years ago, totemism 50,000-45,000 years ago, and shamanism 30,000-35,000 years ago.
Animism (simplified to me as a belief in a perceived spirit world) passably by at least 100,000 years ago “the primal stage of early religion” To me, Animistic Somethingism: You just feel/think there has to be something supernatural/spirit-world or feel/think things are supernatural/spirit-filled.
Totemism (simplified to me, as a belief that these perceived spirits could be managed or related with by created physical expressions) passably by at least 50,000 years ago “progressed stage of early religion” A totem is a representational spirit being, a sacred object, or symbol of a group of people, clan, or tribe.
Shamanism (simplified to me as a belief that some special person can commune with these perceived spirits on the behalf of others by way of rituals) passably by at least 30,000 years ago Shamanism is an otherworld connection belief thought to heal the sick, communicate with spirits/deities, and escort souls of the dead.
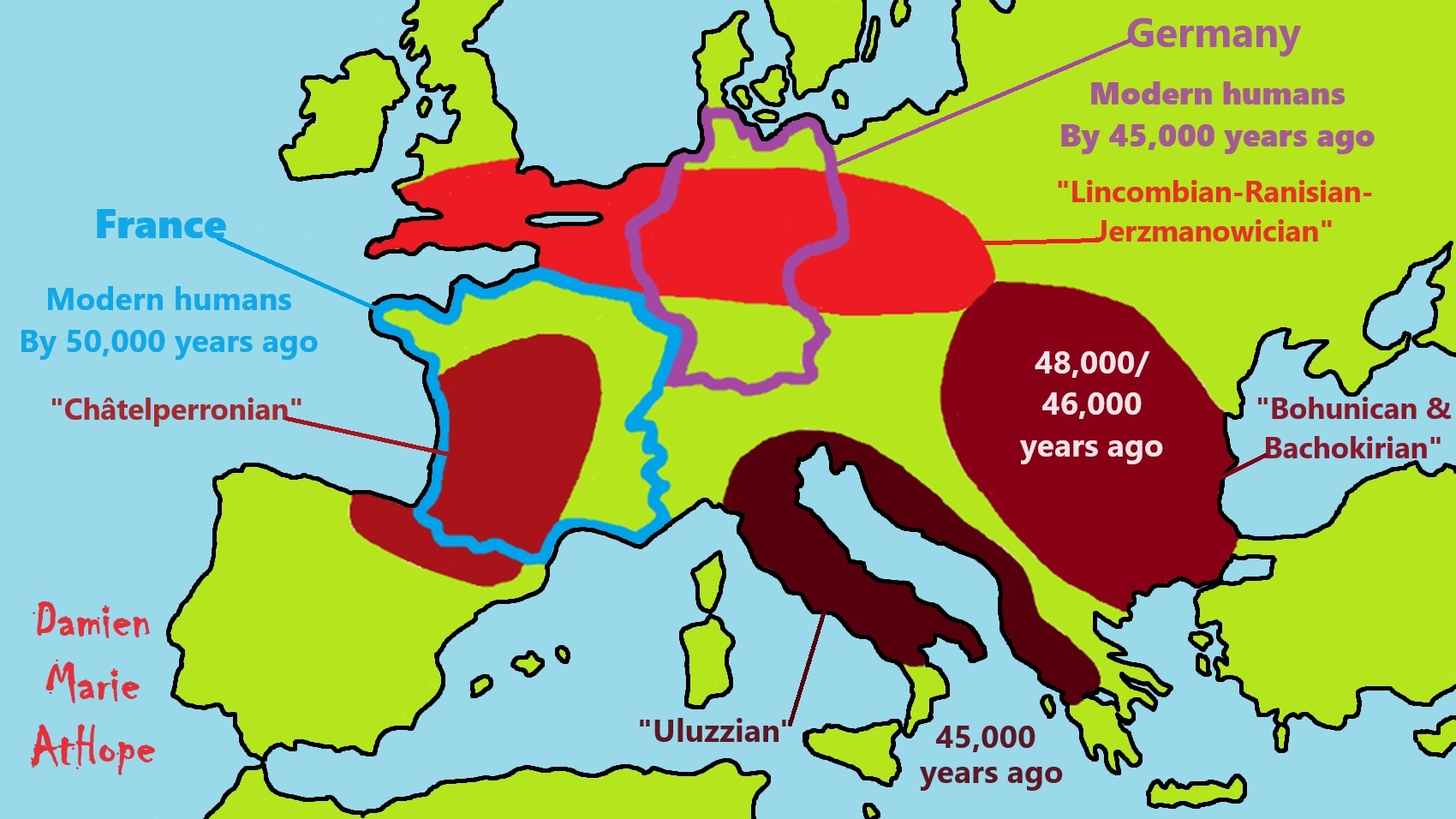
Evidence shows earliest modern humans lived 50,000 years ago in the South of France.
“Archaeologists found a 54,000-year-old tooth belonging to a homo sapiens buried at Grotte Mandrin in the Rhone Valley. They also found small, sharp projectiles carved out of stone and which might have been used as spearheads or arrowheads. It was thought that the first humans arrived in what is modern-day Europe around 40,000 years ago. But the latest finds suggest we were here much earlier and mingling with Neanderthals for much longer than had been believed. Prof Chris Stringer, of London’s Natural History Museum, said: “This new find shows there were modern humans there about 54,000 years ago, much earlier than we thought. “And what’s interesting is they seem to come and go.” He added the world was in the grip of an Ice Age at the time, so temperatures would be extremely cold.” ref
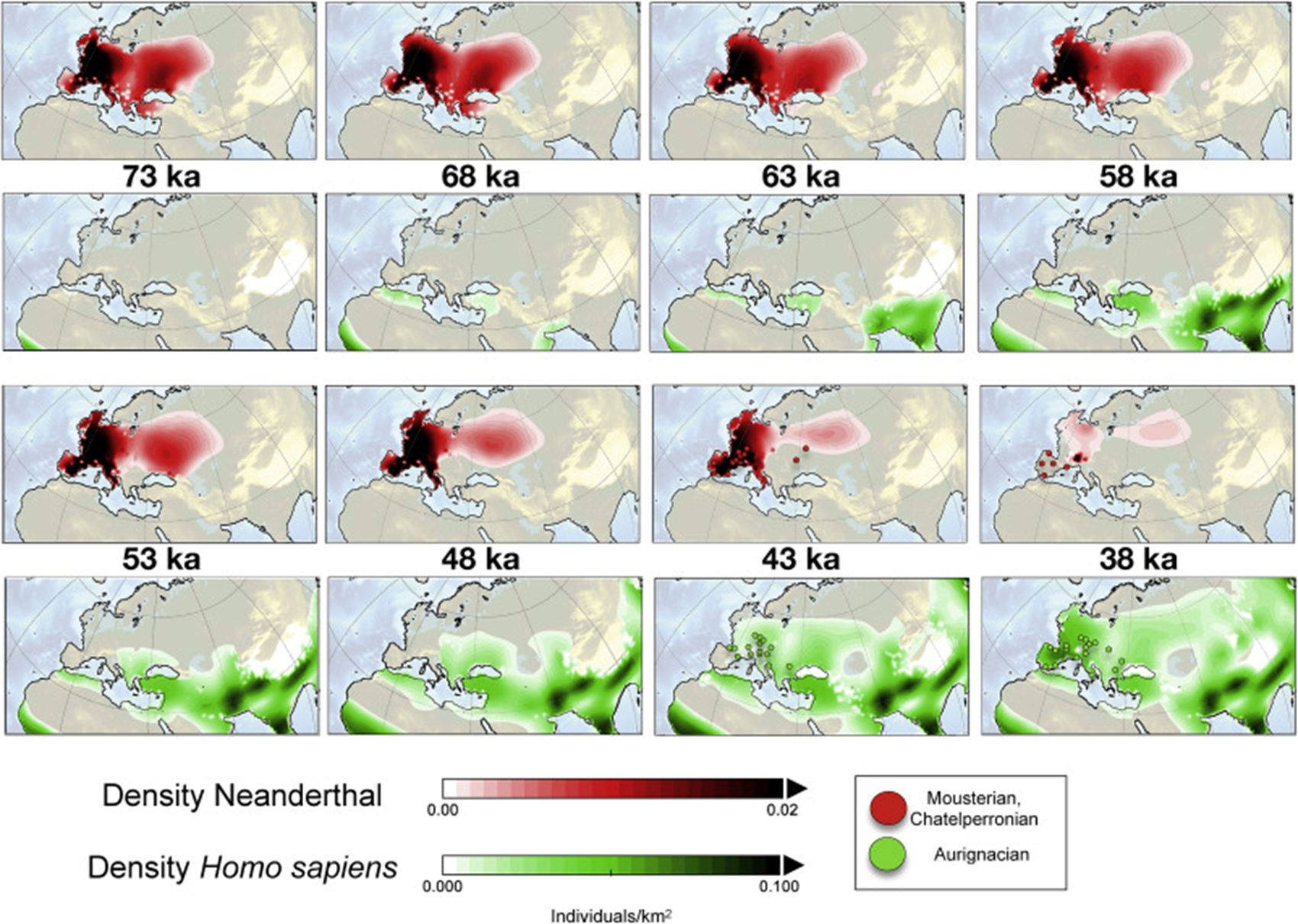
“Quantifying the potential causes of Neanderthal extinction: Abrupt climate change versus competition and interbreeding. Neanderthals experienced rapid population decline due to competitive exclusion. Interbreeding is only a minor contributor to Neanderthal extinction. Abrupt Climate Change was not a major cause for the demise of Neanderthals.” ref
“Anatomically Modern Humans are the sole survivor of a group of hominins that inhabited our planet during the last ice age and that included, among others, Homo neanderthalensis, Homo denisova, and Homo erectus. Whether previous hominin extinctions were triggered by external factors, such as abrupt climate change, volcanic eruptions or whether competition and interbreeding played major roles in their demise still remains unresolved. Here I present a spatially resolved numerical hominin dispersal model (HDM) with empirically constrained key parameters that simulates the migration and interaction of Anatomically Modern Humans and Neanderthals in the rapidly varying climatic environment of the last ice age. The model simulations document that rapid temperature and vegetation changes associated with Dansgaard-Oeschger events were not major drivers of global Neanderthal extinction between 50,000 and 35,000 years ago, but played important roles regionally, in particular over northern Europe. According to a series of parameter sensitivity experiments conducted with the HDM, a realistic extinction of the Neanderthal population can only be simulated when Homo sapiens is chosen to be considerably more effective in exploiting scarce glacial food resources as compared to Neanderthals.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
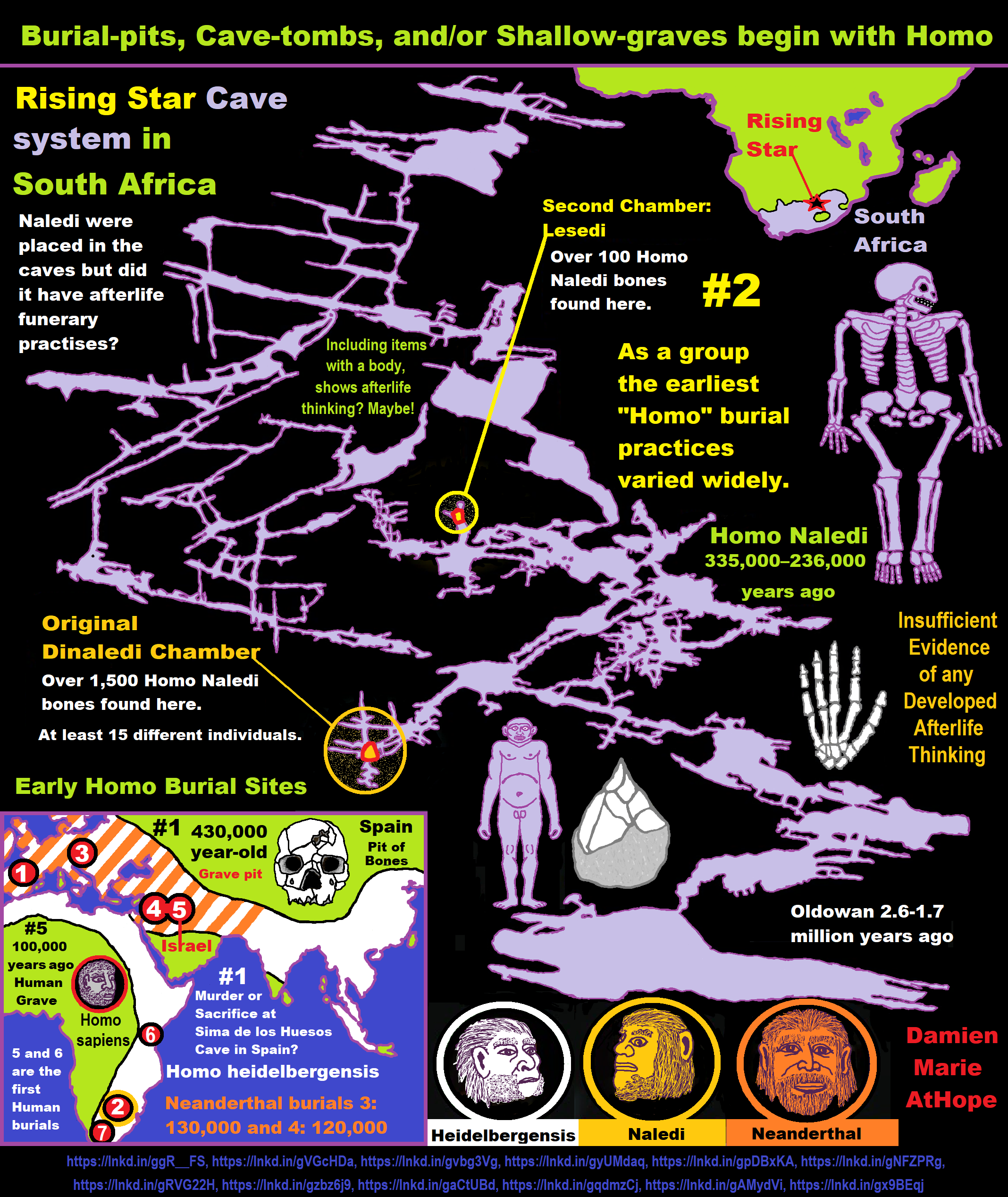
Homo Naledi
“Homo Naledi is a species of archaic human discovered in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago. The initial discovery comprises 1,550 specimens, representing 737 different elements, and at least 15 different individuals. Despite this exceptionally high number of specimens, their classification with other Homo remains unclear.” ref
“Along with similarities to contemporary Homo, they share several characteristics with the ancestral Australopithecus and early Homo as well (mosaic anatomy), most notably a small cranial capacity of 465–610 cm3 (28.4–37.2 cu in), compared to 1,270–1,330 cm3 (78–81 cu in) in modern humans. They are estimated to have averaged 143.6 cm (4 ft 9 in) in height and 39.7 kg (88 lb) in weight, yielding a small encephalization quotient of 4.5. Nonetheless, Homo Naledi’s brain anatomy seems to have been similar to contemporary Homo, which could indicate equatable cognitive complexity. The persistence of small-brained humans for so long in the midst of bigger-brained contemporaries revises the previous conception that a larger brain would necessarily lead to an evolutionary advantage, and their mosaic anatomy greatly expands the known range of variation for the genus.” ref
“Homo Naledi anatomy indicates that, though they were capable of long-distance travel with a humanlike stride and gait, they were more arboreal than other Homo, better adapted to climbing and suspensory behavior in trees than endurance running. Tooth anatomy suggests consumption of gritty foods covered in particulates such as dust or dirt. Though they have not been associated with stone tools or any indication of material culture, they appear to have been dextrous enough to produce and handle tools, and likely manufactured Early or Middle Stone Age industries. It has also been controversially postulated that these individuals were given funerary rites, and were carried into and placed in the chamber.” ref
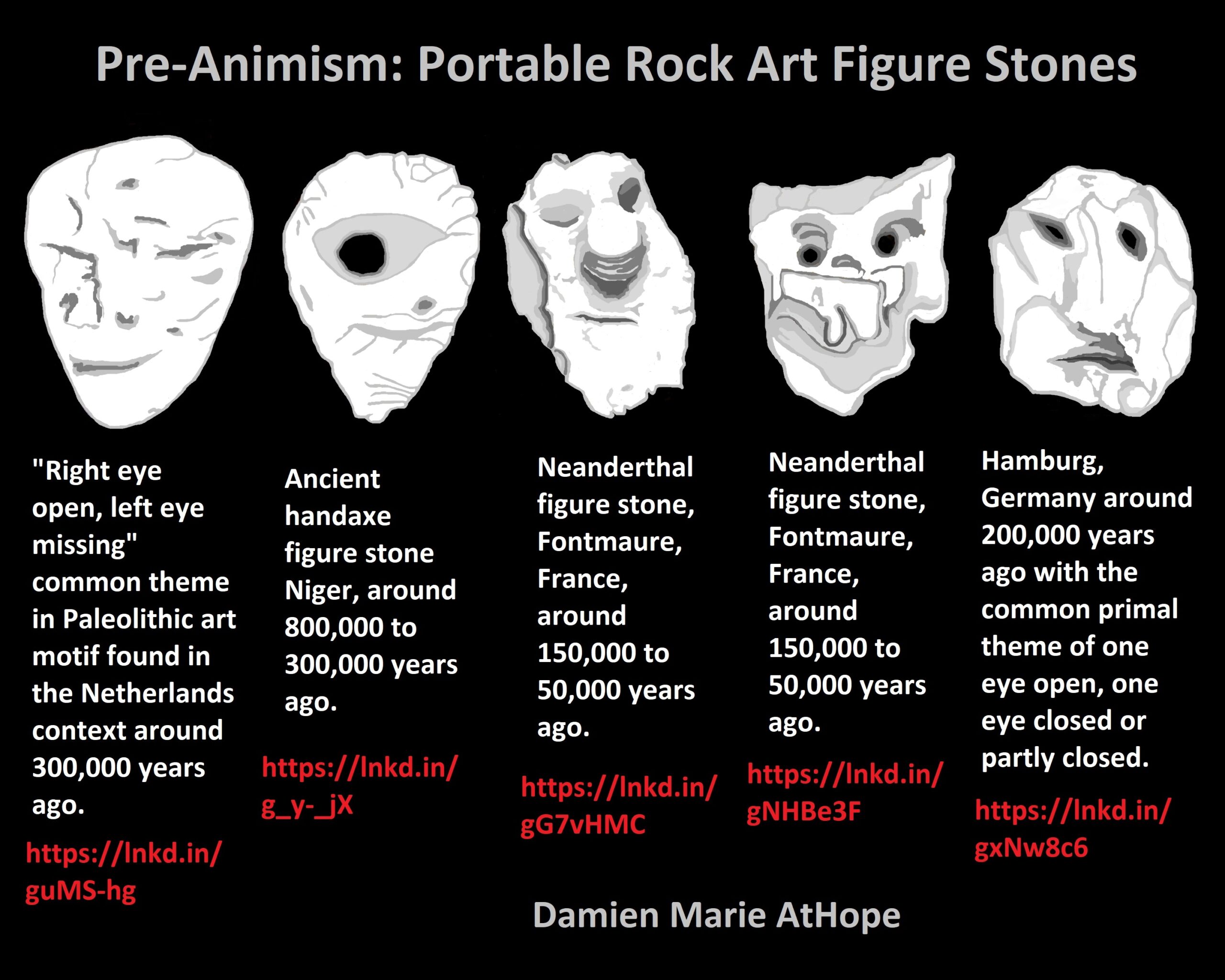
Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art Figure Stones
Neanderthal figure stone, Fontmaure, France, around 150,000 to 50,000 years ago. ref, ref
Hamburg, Germany around 200,000 years ago with the common primal theme of one eye open, one eye closed, or partly closed. ref
Ancient handaxe figure stone Niger, around 800,000 to 300,000 years ago. ref
“Right eye open, left eye missing” a common theme in Paleolithic art motif found in the Netherlands context around 300,000 years ago. ref

Neanderthals “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)”, Mystery Cave Rings 175,000 Years Ago, possibly a chapel or sacred space? Well, we do know it had meaning in some symbolic way, and they easily predate the arrival of modern humans in Europe. Thus, likely, they were built by Neanderthals, the only hominins in the region. The stalagmite structures are 50 centimeters high in places, says Jaubert. They are built from around 400 individual stalagmites with a combined weight of about 2 tons which must take time [to shift] and thus some time and effort to arrange the structures. ref

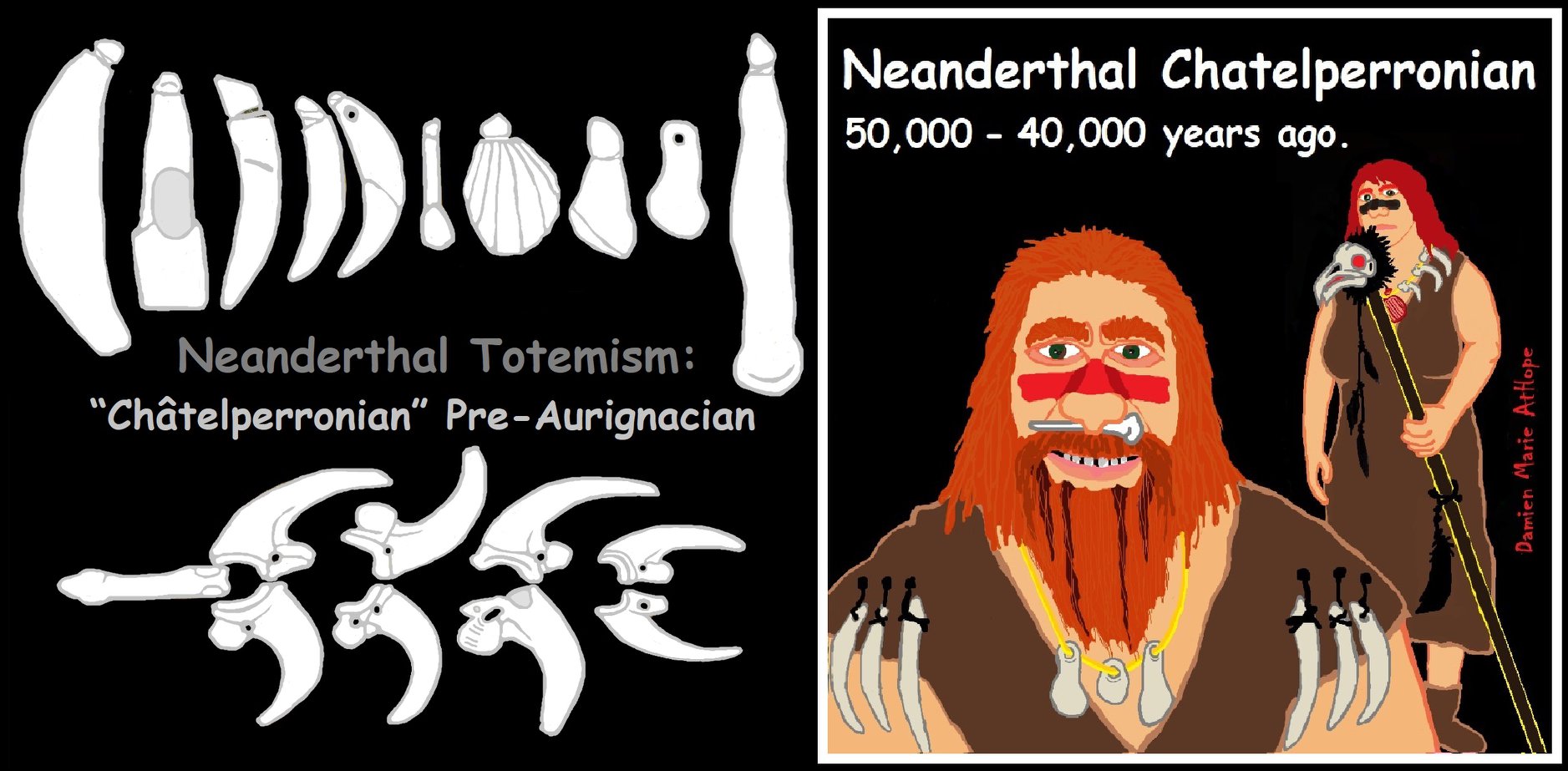
Neanderthal Mousterian: Animism/Totemism?
The Mousterian (stone-tool culture/industry) of flint lithic tools associated primarily with the earliest anatomically modern humans in North Africa and West Asia, as well as with the Neanderthals in Europe from 160,000 to 40,000 years ago. If its predecessor, known as Levallois or “Levallois-Mousterian” is included, the range is extended to as early as c. 300,000–200,000 years ago. Moreover, Mousterian continued alongside the new Neandertal Châtelperronian industry during the 45,000-40,000 ref

130,000 years ago – Earliest undisputed evidence for intentional burial and it is Neanderthals…
Evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead and possibly doing cannibalism which could be evidence of a death ritual, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. 130,000 years ago – Earliest undisputed evidence for intentional burial. Neanderthals bury their dead at sites such as Krapina in Croatia. There was a total of 876 single Neanderthal fossil remnants found at the Hušnjak hill. The Bones belonged to several dozen different individuals, of different sex, from 2 to 40 years of age. Over a thousand pieces of various stone tools and weapons from the Paleolithic era were found, all witnessing to the material culture of the Krapina proto-human. This rich locality is approximately 130.000 years old.
Numerous fossil remnants of the cave bear, wolf, moose, large deer, warm climate rhinoceros, wild cattle, and many other animals were also found. Moreover, there is bird skeletons, with some of the parts modified, are found in association with the Neanderthal bones. Here are some talons and foot bones from the white-tailed eagle. There appears to be cut marks in the talons and foot bones to which they were attached, suggesting that Neanderthals were using the talons and bones as jewelry. This is supported by recent findings of gut “fiber” tied around part of a talon. Here are a foot bone and a talon that have been modified by having grooves cut in them. Neanderthals were largely carnivores, though we know they also used medicinal plants. ref, ref, ref

Neanderthal jewels fashioned out of the talons of white-tailed eagles.
Evidence seems to imply that Neanderthals wore jewels and possibly body-paint, which would point to higher levels of consciousness: jewels have communicative functions, for which abstract thought is necessary. The conscious transformation of an object which does not have an obvious use as a tool points to symbolic or aesthetic thought. That the Neandertals nursed the sick and gave burials to the dead, even to stillborns leads to a better picture of these early people. The recent discovery of their genes in the modern European genome, leaving no doubt about interbreeding with homo sapiens, gave rise to speculations that they had acquired this culture through contact with the latter, but had not developed it independently. This time-span matches many of the supposedly artistic artifacts attributed to the Neanderthals possibly transferring some ideas to us and receiving some transfer from us as well. Neanderthal eagle tlons jewelry is dated to an age of 130,000 years in Croatia at that time there were no modern humans there yet not for tens of thousands of years. This set of eight white-tailed eagles’ talons is described as a jewel because of the consciously and purposefully added groovings and the very significant traces of wear. Four of the claws display signs of cutmarks, three of them have grooves cut in exactly the same places. And all eight show abrasion traces, and seem almost polished – such that would occur if they had been worn for a long time in the same position over the same surface. This surface could then have been a chest, or an upper-arm, the scientists surmise – they think that the talons were part of a chain, or of a bracelet. The cuts and grooves indicate the spots where they would have been tied together. ref
White-tailed eagle talons and an associated phalanx had numerous cut marks made from by the extinct people in what is modern-day Croatia. The Krapina site, around 31 miles north of Zagreb, has yielded the world’s richest collection of Neanderthal fossils. The site containing the remains of some 80 individuals, and including the talons which may have been jewelry and therefore used for a symbolic purpose as a necklace or bracelet assemblages from at least three individual birds. Up until this many thought that early jewelry was mainly linked to anatomically modern humans—estimated to be up to 110,000 years old—and consisting of shell beads found at prehistoric sites in Israel. ref
The amazingly rich Neanderthal Krapina site?
Only evidence of Neandertals is found at Krapina, confirmed by the appearance of Mousterian tools and human remains. Gorjanović-Kramberger and his assistant Osterman collected hundreds of Neandertal bones and teeth, more than 800 stone tools and almost 2800 animal remains. Everything at Krapina derived from excavations in stratified levels and has been curated in the Croatian Natural History Museum (Zagreb) for more than a century. Animal bones as represented by minimum number of individuals (MNI), consist primarily of large mammals, especially rhinos (21.7%), bears (17.0%), and bison/bos (7.5%), while other species like pigs, deer, and small carnivores make up a lesser extent of the fauna. Beavers (Castor fiber) are the exception, mostly coming from the fluvial base of the shelter and constitute 17.9% of the bones from the site. A full listing of mammalian fauna includes 25 taxa and of these 13.6% of show evidence of burning and another 4.1% preserve stone tool cut marks. In addition, to the mammals, Gorjanović-Kramberger recorded a turtle (Testudo) humerus, freshwater mussel shells of at least three taxa, several taxa of different land snail species and a few bird remains. Except for some of the bird bones, none of the non-mammalian bones or shells shows signs of human manipulation. ref

I added the feathers hanging, in the art above, so they can swing back and forth to simulate a bird in flight. Thus, my thinking, is that it could relate to shape-shifting beliefs, embodying a totem animal (bird/sky spirit), or soul-travel/pseudo-out-of-body experience.
“This is the oldest stone bracelet in the world, believed to have been made by the extinct Denisovan species of early humans, dated as being between 40,000 – 50,000 to be 65,000 – 70,000 years old, long before ancient people were believed to capable of making such remarkable objects. The bracelet is thought to have adorned a very important woman or child on only special occasions. And it is unlikely it was used as an everyday jewelry piece. I believe this beautiful and very fragile bracelet was worn only for some exceptional moments.” ref
A stone bracelet is the oldest ever found in the world
Dating back 40,000 years to the Denisovan species of early humans, new pictures show beauty and craftsmanship of prehistoric jewelry. Made of chlorite, the bracelet was found in the same layer as the remains of some of the prehistoric people and believe to fragile to have been worn often, thus must have only been for a ritual purpose. The bracelet was found inside the famous Denisova Cave, in the Altai Mountains. What made the discovery especially striking was that the manufacturing technology is more common to a much later period, such as the Neolithic era. Indeed, it is not clear yet how the Denisovans, if it was them, could have made the bracelet with such skill. Chlorite was not found in the vicinity of the cave and is thought to have come from a distance of at least 125 miles away, showing how valued the material was at the time. Dr Derevyanko said the bracelet had suffered damage, including visible scratches and bumps although it looked as if some of the scratches had been sanded down. Experts also believe that the piece of jewelry had other adornments to make it more beautiful. ref
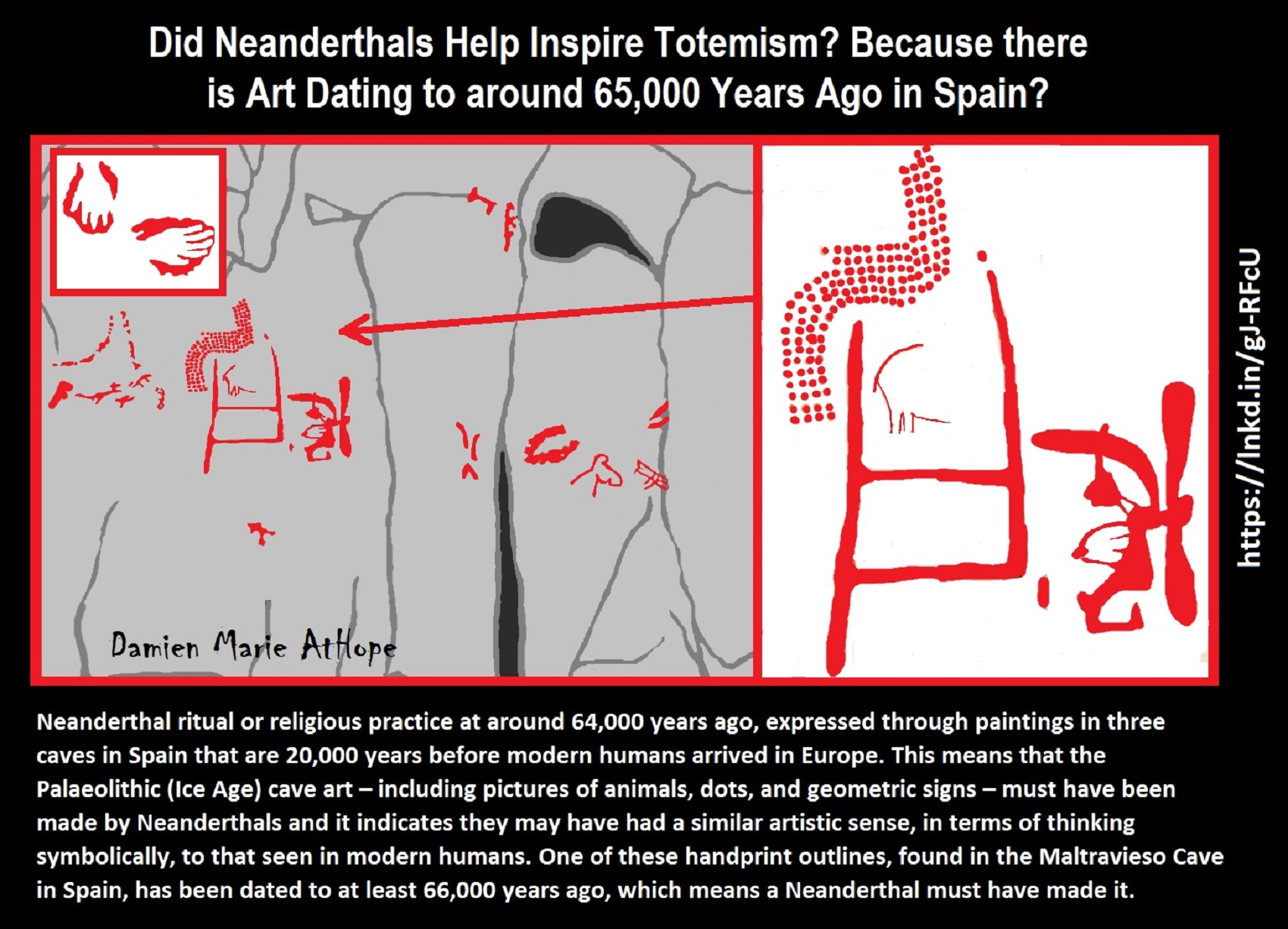
“Prehistoric cave paintings in Spain show Neanderthals were artists. Red ochre pigment discovered on stalagmites in the Caves of Ardales, near Malaga in southern Spain, were created by Neanderthals about 65,000 years ago, making them possibly the first artists on earth, according to the study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal. Modern humans were not inhabiting Europe at the time the cave images were made.” ref

Denisovan Totemism 50,000 years ago?
Suspicion is that this male tiara or diadem (mammoth ivory) was made by Denisovans and hints at the depth of Denisovan technology 50,000 to 45,000 years ago. Expression for family, clan, or tribe, So maybe early Totemistic behaviors. ref
Denisovan technology is at least by 50,000 years ago, such as their making elegant needles out of ivory and a sophisticated and beautiful stone bracelet. It appears to have had a practical use: to keep hair out of the eyes; its size indicates it was for male, not female, use. Interestingly tiaras were made 20,000 to 28,000 years later by people living in the Russian Far East, around the Yana River in Yakutia and they could have denoted the family, clan, or tribe, So maybe early Totemistic behaviors. ref
Neanderthals Decorated Their Caves With Giant Skulls Around 42,000 years ago?
“The cave in this study, called the Cueva Des-Cubierta, is located to the north of the Madrid Region in Spain, and is believed to have been sporadically used by Neanderthals as a place for ritual activities, perhaps as a burial ground. The cave held an array of tools and bone fragments have been recovered from the site. In the main gallery of the cave, the researchers found the remains of a human-like child, who is without a doubt, a Neanderthal. The third level of the site is scattered with animal bones, with a high concentration of skull fragments from large herbivores. Moreover, there have been discoveries up to 35 crania of large herbivores, which were arranged in an area where the cave enlarges,” Baquedano said. “The dates of the level three, where the remains have been found, are around 42,000 years old. The majority of these skulls belonged to bison and aurochs—the extinct relatives of the modern-day cow. The assemblage also includes five male deer skulls and two rhinoceroses. To see so many large animal skulls in a cave like this is fairly unusual. Modern-day hunter-gatherer groups tend to discard the heavy heads of large animals outside of their camp as they are less useful as a source of food. The fact that the Des-Cubierta cave contains a disproportionate number of these large skulls suggests that they have been brought there deliberately, and not purely for their nutritional value.” ref
So, I wonder, did Neanderthal Totemism, maybe inspire Denisovan Totemism???
Denisova 11: Hybrid of Denisovan and Neanderthal
DNA in a 50,000-year-old finger bone, from Denisova Cave, where the 40,000-year-old remains were found. that belonged to a 13-year-old girl whose mother was a Neanderthal — one of the ancient people who inhabited Europe and Asia between 450,000 and 40,000 years ago. But the girl’s father was a Denisovan, a distinct lineage of protohuman that split off from Neanderthals about 400,000 years ago. Both groups shared a common ancestor who migrated out of Africa a few hundred thousand years before that. Denisovans have been found only in that single cave. But Neanderthal fossils show they flourished in Eurasia, ranging in location from the British Isles to the mountains of Siberia. Hybrids may not have been all that uncommon. Such as, a modern human who lived in what is now Romania 40,000 years ago had a great-great-grandparent who was Neanderthal. This finger bone’s DNA, from Denisova Cave, didn’t resemble the genes of the “Altai Neanderthal” who had lived in Denisova Cave thousands of years before with other bone fragments dating as far back as 120,000 years ago. Instead, she seemed more closely related to a Neanderthal woman who lived in Croatia around the same time. This seems to imply that Neanderthals undertook multiple migrations across Eurasia. And from the girl’s father’s DNA contributions there also was Denisovan yet traces of a distant Neanderthal ancestor. ref, ref

Neanderthal ritual or religious practice at around 50,000 years old burial in Sima de las Palomas in Murcia, Southeast Spain of a female covered with rocks interred with a cut-off panther paw, suggesting that Neanderthals—much like today’s bear hunters—ceremoniously cut off panther paws and kept them as totemistic trophies. This 50,000-year-old Neanderthal burial ground actually includes the remains of at least three individuals intentionally buried, with each Neanderthal’s arms folded such that the hands were close to the head. Remains of other Neanderthals have been found in this position, suggesting that it held meaning. The remains of six to seven other Neanderthals, including one baby and two juveniles, have also been excavated at the site. The tallest individual appears to have been an adult who stood around 5 feet 1 inch tall. ref, ref

Cave Bear Hunting by Neanderthals 50,000 years ago
50,000 years ago, at least, Neanderthals were hunting the “now-extinct” and ferocious cave bears (weighing 1,300 lbs, twice that of grizzlies), seen in Neanderthals’ bite marks spotted on cave bear bones. Furthermore, the remains belonged to a total of 50 cave bears that lived 50,000 to 43,000 years ago. Bands of Neanderthals would regularly ambush sleeping bears (belonging to male and female adults, cubs, and fetuses) as they awoke from their annual targets for their pelts, meat, and living quarters. Among the fossil, remains are penis bones, showing that Neanderthals did hunt the seeming hardest to kill, the adult male cave bear. Cave bears may have spent more time in caves than the brown bear, which uses caves only for hibernation. ref, ref, ref
800 specimens were collected throughout western Eurasia and dated between 80,000 and 20,000 years ago. The team documented incidents of skull trauma, perceived sex and age at death, degree of skeleton preservation, and geographical location of each sample. Based on 836 cranial elements analyzed from 204 individuals, researchers found no differences in injury rates between Neanderthals and contemporaneous humans, Gizmodo reported. ref, ref

“Fossil bone evidence of the Denisovans uncovered in Denisova Cave in the Russian Altai Mountains which are a sister group to Neanderthals showed that Denisovans lived in the cave from at least 200,000 to less than 50,000 years ago. And that Denisovans are closer in terms of shared ancestry to Neanderthals than they are to modern humans at one time lived alongside Neanderthals in the same cave, the evidence showed. Moreover, that Neanderthals were present at Denisova Cave from at least 190,000 years ago until at least 90,000 years ago. Evidence shows that the two groups certainly interbred first giving rise a daughter of mixed ancestry about 100,000 years ago.” ref
“A 50,000-year-old bone fragment of a 13-year-old female was discovered in the Denisova Cave who had a Neanderthal mother and a Denisovan father.” ref
The so-called “transitional industries” are a key for understanding the replacement process of Neanderthals by modern humans in western Eurasia at the beginning of the Upper Paleolithic between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. While in Europe the older Mousterian industry of the Middle Paleolithic can be clearly attributed to Neanderthals and the later Upper Paleolithic assemblages to modern humans, the nature of the makers of the transitional Châtelperronian (CP) industry has long been disputed. ref, ref, ref
Neandertals Seem to collect Feathers, preferably Black?
Researchers found in a Neanderthal abri in Fumane, Italy 44,000-year-old bones of eagles, falcons, and vultures. Besides their belonging to the species of raptors, they share one characteristic: they are unedible. But the Neanderthaler found something about them which was to their taste, most likely their large pinion feathers which they plucked or cut out in order to wear them as ornaments – and/in order to symbolize rank and power? Neanderthals plucked the feathers from falcons and vultures, perhaps for symbolic value, scientists find. This new discovery adds to evidence that our closest known extinct relatives were capable of creating art. Scientists investigated the Grotta di Fumane — “the Grotto of Smoke” — in northern Italy, a site loaded with Neanderthal bones. After digging down to layers that existed at the surface 44,000 years ago, the researchers discovered 660 bones belonging to 22 species of birds, with evidence of cut, peeling and scrape marks from stone tools on the wing bones of birds that had no clear practical or culinary value. There are taces on the bones of large raptors. These birds included red-footed falcons (Falco vespertinus); bearded lammergeiers (Gypaetus barbatus), a type of vulture; Alpine choughs (Pyrrhocorax graculus), a relative of crows; and common wood pigeons (Columba palumbus). The birds’ plumages come in a variety of colors — the gray of the red-footed falcon, the orange-shaded slate gray of the bearded lammergeier, the black of the Alpine chough, and the blue-gray of the common wood pigeon. Such evidence along with others seems to express that the use of bird feathers was very widespread. ref
These discoveries and others show this practice was not confined to the small site but wide-spread in space and time all across the Neanderthal world, assorted with an undisputable bias towards black and dark-colored feathers. They examined 1,699 sites across Eurasia containing either the remains of paleontological birds alone, or birds side-by-side with paleolithic Neanderthal remains. There was a clear association between Neanderthal occupation and the remains of raptor and corvid species. 604 bird bones from three different Neanderthal sites in Gibraltar (Gorham’s Cave, Vanguard Cave and Ibex Cave). Several of the bones showed clear cut-marks made by Neanderthal stone tools, and more than half (337) were wing bones — a finding that the researchers say isn’t random. Wing bones are low in meat compared with other parts of the birds, which suggests the Neanderthals weren’t collecting these animals for food, but rather intentionally harvesting them for their feathers. ref
Dyed Shells?
In the cave of Aviones, close to the Spanish Mediterranean coast, many heart- and other sea shells, four to nine centimeters in size, and pierced. On these, they found traces of reddish and yellow pigments which were taken from a deposit located 4.5 miles away. One scallop, dyed orange with a mineral dye, was found in the cave of Cueva Antòn, 60 kilometers inland. The respective layers of the finds can be attributed securely an age of 50.000 years, Zilhao‘s team writes in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. The Spanish Neanderthalers evidently produced the dyes out of red and yellow pigments, which they must have collected intentionally. One especially aesthetic container used a colored spondylus gaederopus shell, of a kind which, much later, during the late Stone Age, would have a widespread use as a means of payment. Already Neanderthals seem to have been attracted to their many colors and ribbed surfaces. Scientists surmise that dye which they contained were used for possibly large body paintings. Two sites of the Neandertal-associated Middle Paleolithic of Iberia, dated to as early as approximately 50,000 years ago, yielded perforated and pigment-stained marine shells. At Cueva de los Aviones, three umbo-perforated valves of Acanthocardia and Glycymeris were found alongside lumps of yellow and red colorants, and residues preserved inside a Spondylus shell consist of a red lepidocrocite base mixed with ground, dark red-to-black fragments of hematite and pyrite. A perforated Pecten shell, painted on its external, white side with an orange mix of goethite and hematite, was abandoned after breakage at Cueva Antón, 60 km inland. Comparable early modern human-associated material from Africa and the Near East is widely accepted as evidence for body ornamentation, implying behavioral modernity. The Iberian finds show that European Neandertals were no different from coeval Africans in this regard, countering genetic/cognitive explanations for the emergence of symbolism and strengthening demographic/social ones. ref
A little Fossil Pendant?
47,600 – 45,000 years ago in Italy a Neandertal craftsperson utilized a snail shell which was colored red and probably hung with animal sinew. There was clearly nothing useful about using it other than abstract expressions, I presume, also some ritual religious expression or symbolism. The shell of the tiny Aspa marginata was a fossil from the Miocene or the Pliocene: it could be anywhere between 2.5 and 23 million years old not found anywhere near to the cave and the closest resources for this would have been over 62 miles away. Modern humans had not yet reached Northern Italy. Red paint still adhered in tiny pores and rilles of the shell. But it was not evenly distributed. Some spots on the surface seemed to be lightly polished. Less dye was found there. And there was none at all inside the shell. Someone evidently rubbed the pigment with force into the surface of the snail shell. The pigments were made of iron oxyde, hematite. ref
The location of the micrographs (a–c) taken on the Fumane Aspa marginata; two Aspa marginata from Pliocene deposits close to Asti, Piemonte region. Notice in b the palimpsest of striations present on the inner lip of the archaeological specimen. ref
Ancient human burials, By Sally McBrearty
Whereas with modern people, anatomically modern Homo sapiens from somewhat later in time, you find artifacts that are definitely grave offerings. You find quantities of red ochre, which have been sprinkled over the skeleton, beads, and other kinds of objects, bone tools and things like that, which appear to have been placed in the grave with the person when they were interred. And there’s really no doubt that they’re deliberate burials. The evidence for the burial of the dead in Africa is very very spotty. There’s one site in South Africa that’s called Border Cave, where there are a number of burials, including the burial of an infant, with a little shell ornament, it’s a pierced sea shell ornament, and the argument has been about whether that is in good stratographic context or whether it is an intrusive burial into earlier deposits. And so the age of that is not particularly well established. If it is in good context, then it’s about 100,000 years old, and it is the earliest in Africa. There are early burials of anatomically modern Homo sapiens in Israel, from the site of Qafzeh. There is a modern human that probably dates to about the same time, about maybe 90,000 to 100,000 years ago. ref
Neandertal burials, By Sally McBrearty
The Neandertals have always been thought to bury their dead, because there’s so many complete skeletons of Neandertals which have been found. And I think from the number of skeletons that have been found, it’s probably a good guess that they were deliberately burying the dead. However, there are a lot of skeletons of other cave-dwelling animals that are found in caves: cave bears or hyenas, that because they live in caves they often die in caves. And there, people have argued about whether rock falls, or simply accidental death, or natural death, occurring in a cave could preserve whole skeletons better than in the open air. But the argument has also been about the objects that you find associated with the Neandertal burials, because what you find together with Neandertal skeletons are really mundane objects, like stone tools, or animal bones that would be food remains. ref
Neanderthals may have transmitted:
“Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife may have been transferred from Neanderthals to arcane humans when they bread with them.
“Proto Religion (Totemism)” or at least thoughts of cave art and body ornamentation, totemistic type rituals/behaviors may have been transferred from Neanderthals to Modern humans when they bread/interacted with them.
Modern Humans may have also transmitted religious and cultural ideas as much as they may have learned or had transferred from Neanderthals. I think both shared ideas and culture with each other.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
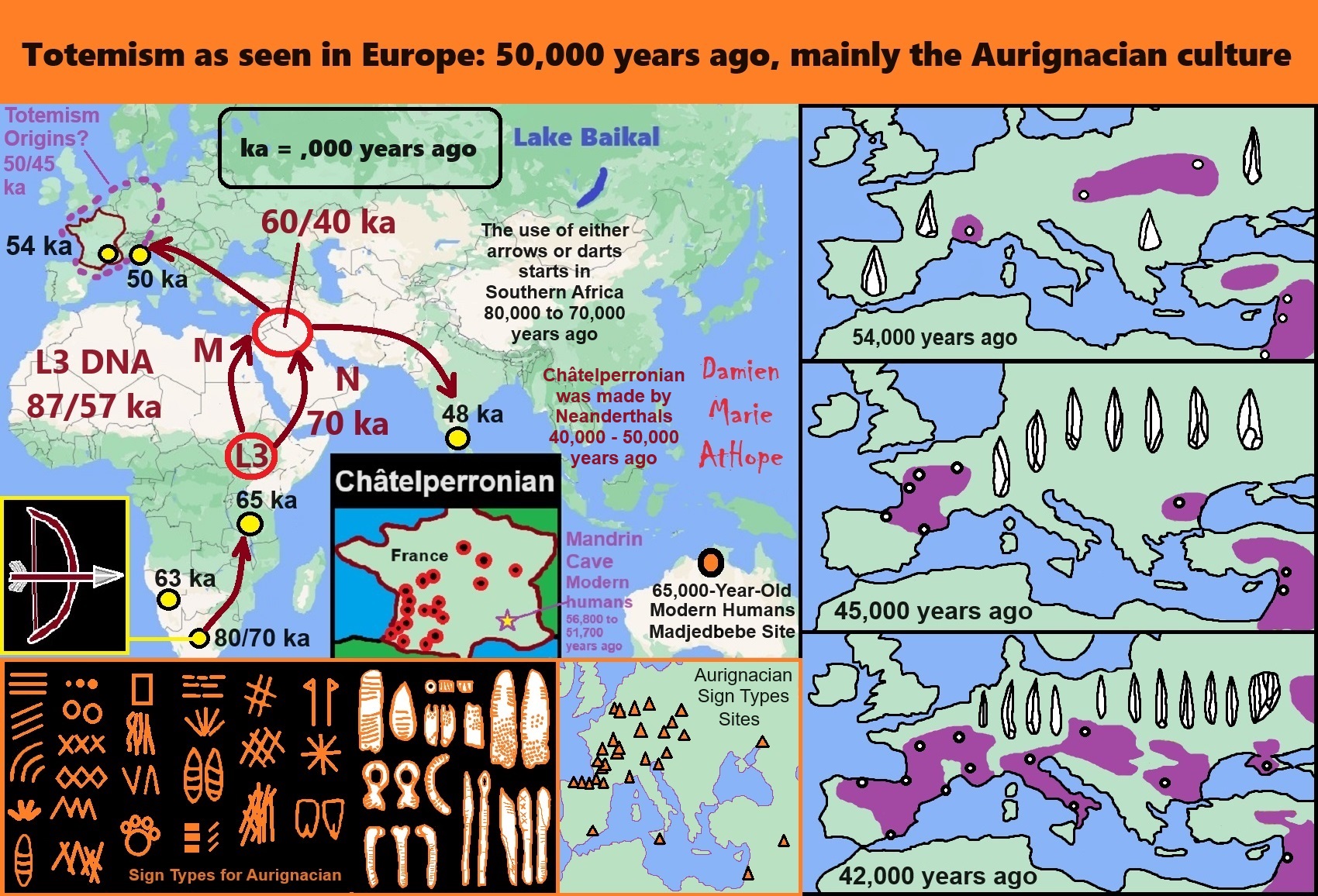
This is my thoughts/speculations on the origins of Totemism
Totemism as seen in Europe: 50,000 years ago, mainly the Aurignacian culture
- Pre-Aurignacian “Châtelperronian” (Western Europe, mainly Spain and France, possible transitional/cultural diffusion between Neanderthals and humans around 50,000-40,000 years ago)
- Archaic–Aurignacian/Proto-Aurignacian (Europe around 46,000-35,000)
- Aurignacian “classical/early to late” (Europe and other areas around 38,000 – 26,000 years ago)
“In the realm of culture, the archeological evidence also supports a Neandertal contribution to Europe’s earliest modern human societies, which feature personal ornaments completely unknown before immigration and are characteristic of such Neandertal-associated archeological entities as the Chatelperronian and the Uluzzian.” – (PDF) Neandertals and Moderns Mixed, and It Matters: Link
Totemism as seen in Europe: 50,000 years ago, mainly the Aurignacian culture


Châtelperronian Culture
“The Châtelperronian is a proposed industry of the Upper Palaeolithic, the existence of which is debated. It represents both the only Upper Palaeolithic industry made by Neanderthals and the earliest Upper Palaeolithic industry in Central and Southwestern France, as well as in Northern Spain. It derives its name from Châtelperron, Allier, France (the closest commune to the type site, the cave La Grotte des Fées). It is preceded by the Mousterian industry, and lasted from c. 45,000 to c. 40,000 years ago. The industry produced denticulate stone tools, and a distinctive flint knife with a single cutting edge and a blunt, curved back. The use of ivory at Châtelperronian sites appears to be more frequent than that of the later Aurignacian, while antler tools have not been found. It is followed by the Aurignacian industry. Scholars who question its existence claim that it is an archaeological mix of Mousterian and Aurignacian layers. The Châtelperronian industry may relate to the origins of the very similar Gravettian culture. French archaeologists have traditionally classified both cultures together under the name Périgordian, Early Perigordian being equivalent to the Châtelperronian and all the other phases corresponding to the Gravettian, though this scheme is not often used by Anglophone authors.” ref
Aurignacian Culture
“Key Issues/Current Debates: Variants of the Aurignacian Across Time and Space… Today, the Aurignacian is separated into many variants that are thought to be temporally or spatially meaningful. The first is the Protoaurignacian (i.e., Proto-Aurignacian, Fumanian) characterized by the production of large (c. 30–45 mm), straight bladelets (subtype
Dufour) from prismatic and pyramidal cores seen by some as the oldest phase of the Aurignacian. In southwest France, northern Italy, and Spain, when found together, the ProtoAurignacian is always superimposed by the Classic (Early)
Aurignacian where bladelets are generally produced from carinated cores. This production method resulted in smaller bladelets (c. 15–20 mm) with characteristic “twisted” profiles that were often retouched into Dufour bladelets (subtype Roc du Combe). However further east, where the ProtoAurignacian is less known, Classic Aurignacian assemblages often
directly follow the Middle Paleolithic and so-called transitional industries and are associated with radiocarbon dates as old as the first occurrence of the ProtoAurignacian in the Mediterranean thus making it difficult to simply consider the two assemblages as successive stages of the same cultural unit. It is also thought by some that the Classic Aurignacian later grew into the Late (Evolved) Aurignacian that is defined as having a larger, more varied tool kit including (backed) micro-
blades. However, such assemblages often share many cultural traits associated with the Gravettian, possibly relating to mechanical admixture, or suggesting that they represent a distinct cultural phenomenon.” ref
“The Aurignacian is an archaeological industry of the Upper Paleolithic associated with European early modern humans (EEMH) lasting from 43,000 to 26,000 years ago. The Upper Paleolithic developed in Europe some time after the Levant, where the Emiran period and the Ahmarian period form the first periods of the Upper Paleolithic, corresponding to the first stages of the expansion of Homo sapiens out of Africa. They then migrated to Europe and created the first European culture of modern humans, the Aurignacian. An Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian stage is dated between about 43,000 and 37,000 years ago. The Aurignacian proper lasts from about 37,000 to 33,000 years ago. A Late Aurignacian phase transitional with the Gravettian dates to about 33,000 to 26,000 years ago. The type site is the Cave of Aurignac, Haute-Garonne, south-west France. The main preceding period is the Mousterian of the Neanderthals.” ref
“One of the oldest examples of figurative art, the Venus of Hohle Fels, comes from the Aurignacian or Proto-Gravettian and is dated to between 40,000 and 35,000 years ago (though now earlier figurative art may be known, see Lubang Jeriji Saléh). It was discovered in September 2008 in a cave at Schelklingen in Baden-Württemberg in western Germany. The German Lion-man figure is given a similar date range. The Bacho Kiro site in Bulgaria is one of the earliest known Aurignacian burials. A “Levantine Aurignacian” culture is known from the Levant, with a type of blade technology very similar to the European Aurignacian, following chronologically the Emiran and Early Ahmarian in the same area of the Near East, and also closely related to them. The Levantine Aurignacian may have preceded European Aurignacian, but there is a possibility that the Levantine Aurignacian was rather the result of reverse influence from the European Aurignacian: this remains unsettled.” ref

40,000 to 50,000 years ago, the Emergence of Norm Violations
Around 50,000 to 40,000 years ago there seems to be the emergence of norm violations relating to what I think is totemistic cultural influenced behavior, on what research suggests is moral disgust. This early moralistic totemism or “taboo” beliefs, which, to me, relates to genetic evidence of possible moral disgust with genetics showing that after 40,000 years ago there is an extreme lowering of incest behaviors also coinciding with the emergence of more complex cave art, figurines, and personal adornments around 50,000 to 40,000 years ago. All this and more offers some confirming evidence of my thoughts on totemism’s emergence around 50,000 years ago in western Europe, seen in the Pre-Aurignacian Neanderthal “Châtelperronian” and/or by the Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian times.
In the video “Robert Sapolsky: The Biology of Humans at Our Best and Worst” (17 or so minutes in) states the emergence of norm violations of moral disgust occurred around 40,000 to 50,000 years ago which is about the time that genetics shows after 40,000 years ago there was an extreme lowering of insect behaviors coinciding with the emergence of more complex cave art, figurines, and personal adornments all confirming my thoughts on totemism emerging after 50,000 years ago in Europe by the Early Aurignacian or Proto-Aurignacian stage. And in the video “DNA Mammoths, Neanderthals, and Your Ancestors,” it also quickly including the evidence for early people following incest taboos, are clearly evident after 40,000 years ago by genetics. Which, to me, likely connects to the motivations adopted by societies believing in Totemism. ref, ref
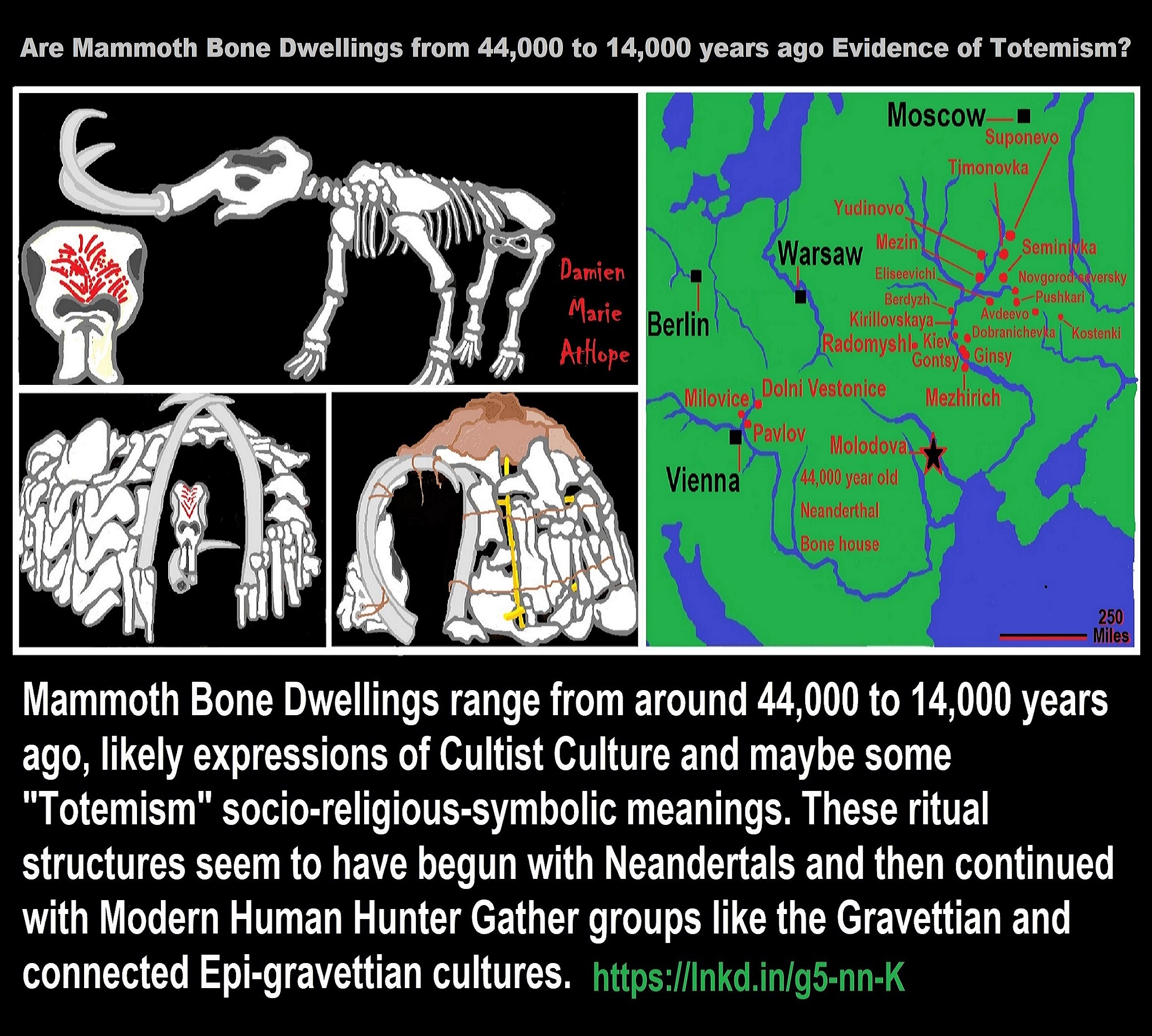
“Mammoth bone dwellings are a very an early type of housing constructed by Upper Paleolithic hunter-gatherers mainly in central Europe.” ref
“Mammoth Bone Dwellings range from around 44,000 to 14,000 years ago, likely expressions of Cultist Culture and maybe some “Totemism” socio-religious-symbolic meanings. These ritual structures seem to have begun with Neandertals (who lived in Eurasia until about 40,000 years ago) and then continued with Modern Human Hunter Gather groups like the Gravettian (around 33,000 to 21,000 years ago) and connected Epi-gravettian (around 21,000 to 10,000 years ago) cultures.” ref, ref
“A number of examples of symbolic thought and Palaeolithic art have been inconclusively attributed to Neanderthals, namely possible ornaments made from bird claws and feathers or shells, collections of unusual objects including crystals and fossils, engravings, music production (possibly indicated by the Divje Babe flute), and Spanish cave paintings contentiously dated to before 65,000 years ago. Some claims of religious beliefs have been made. Neanderthals were likely capable of speech, possibly articulate, although the complexity of their language is not known.” ref
“Gravettian and Epigravettian mammoth bone dwellings range from: Pavlovian (Early Gravettian of Moravia), Gagarino and Pouchkari (Gravettian of Eastern Europe), Kostienki 11/1a (Zamiatnine culture), and Mezinian.” ref
“Gravettian culture thrived on their ability to hunt animals. They utilized a variety of tools and hunting strategies. Compared to the theorized hunting techniques of Neanderthals and earlier human groups, Gravettian hunting culture appears much more mobile and complex. They lived in caves or semi-subterranean or rounded dwellings which were typically arranged in small “villages”. Gravettians are thought to have been innovative in the development of tools such as blunted-back knives, tanged arrowheads, and boomerangs. Other innovations include the use of woven nets and oil lamps made of stone. Blades and bladelets were used to make decorations and bone tools from animal remains. Gravettian culture extends across a large geographic region, as far as Estremadura in Portugal. but is relatively homogeneous until about 27,000 years ago. They developed burial rites, which included simple, purpose-built offerings and/or personal ornaments owned by the deceased, placed within the grave or tomb. Surviving Gravettian art includes numerous cave paintings and small, portable Venus figurines made from clay or ivory, as well as jewelry objects. The fertility deities mostly date from the early period; there are over 100 known surviving examples. They conform to a very specific physical type, with large breasts, broad hips, and prominent posteriors. The statuettes tend to lack facial details, and their limbs are often broken off. During the post-glacial period, evidence of the culture began to disappear from northern Europe but was continued in areas around the Mediterranean.” ref
“The 44,000-year-old site from Molodova in eastern Ukraine was a Neanderthal “Mousterian Culture” Mammoth Bone Dwelling with possible “Totemism” connections due to how some of the bones used to build the ritual structure home had decorative carvings and added pigments. It was an incredible 26 foot wide circular building believed to be earliest bone built cultural structure and where they lived for extended periods of time.” ref, ref
“The 44,000-year-old Neanderthal bone structure near Molodova was constructed with 116 large deliberately selected mammoth bones including skulls, jaws, tusks and leg. Inside there was at least 25 fire pits and from the artifacts found Neanderthals made many decorated carvings in addition to the symbolic adding of ochre pigments to the bones.” ref, ref
“The painting in red on the front of the mammoth skull may represent the flames and sparks of a fire and as bones were found burned in fire pits, so there could be a ritualistic representation connection, which I think it is. It could be a prehistoric “drum” consisting of a mammoth skull, which may relate to a change from totemism to shamanism and was set at the entrance as well as contained a painted pattern of red ocher dots and lines. The top of this skull bears depressions where it seems to have been beaten by “drumsticks,” the animal’s long bones that were found to bear corresponding damage on their ends. It is possible that the building may have served some ritual or communal function at which the mammoth bone rhythms were beaten out, although many Ukrainian huts of similar size seem to have been ordinary living places.” ref, ref, ref
“Even more telling of its ritualistic relevance is that it was found at the entrance to one of the mammoth hunter’s huts, which could also hold a vaginal/womb reference, and as there was also an oddly placed signal tusk pointing in and hugging the head sticking upright out of the ground almost as if it represents a phallus entering the vaginal/womb thus fertility hunting cult suggestions as well as maybe fire worship.” ref, ref
“Inside the Mezherich building, there were some remarkable finds: amber ornaments and fossil shells, transported an estimated 218 to 310 miles from their source, and the remains of one of the earliest percussion instruments ever found. The middle Dnepr basin is the origin of amber is well known near Kiev where it was collected throughout the Upper Palaeolithic. Amber objects have been used as pieces of small adornment in the Upper Palaeolithic sites of the Dnepr basin: Gontsy, Dobra-nichivka, Mejiriche, Semenivka 2, Ioudinovo, Chulatovo 2, Mezine, Osokorivka (level 2), and Kaistrova balka 2.” ref, ref
“A spectacular prehistoric art is visible in the dwellings of the Mezinian, in the grouping in the outer wall of jaws and long bones showing a geometric pattern of lines, chevrons, and zigzags, which are also figured in the painted bones of the dwellings and in the mobile art of the statuettes, tools and various artifacts, confirming they are the manifestation of a socio-symbolic system of the Mezinian culture.” ref
“A mammoth bone dwelling holds a common form of a circular or oval structure with walls made of stacked large mammoth bones often modified to allow them to be lashed together or implanted into the soil. Within the interior is typically found a central fire pits or several scattered fire pits. External fire pits, butchering areas, and flint workshops are often found in association with the hut: scholars call these combinations Mammoth Bone Settlements (MBS).” ref
“The mammoth bone dwellings are not random. They seem to express a pattern, thus this may demonstrate cultural/religious transfer inclinations and consistency in tradition over thousands of years. Similarly, they are composed of several hundred bones and tusks arranged in rough circles with a diameter of 20 to 33 feet. Even more interesting is that the first Neanderthal mammoth bone dwelling at 44,000-year-old was also in the range at 26 feet, thus it too is consistent with all the rest seeming to hit that they share some deep possible connection.” ref
“A Mysterious 25,000-Year-Old Structure Built of the Bones of 60 Mammoths. The purpose of such an elaborate structure remains a big open question. “Clearly a lot of time and effort went into building this structure so it was obviously important to the people that made it for some reason,” says Alexander Pryor, an archaeologist at the University of Exeter (U.K.). He is the lead author of a new study published this week in the journal Antiquity describing the find at Kostenki, a place where many important Paleolithic sites lie clustered around the Don River. The ancient builders did leave some clues. Fires once burned within the structure and food scraps, including vegetables, remain. Several pits containing mammoth bones lie just outside of the bone circle and may suggest food storage. “You obviously get a lot of meat from a mammoth,” Pryor said, “so the idea that there were food processing and food storage activities going on at the site is something that we want to investigate more.” However the mammoths got here, their presence was crucial to the humans living in the area. Lioudmila Lakovleva of the French National Centre for Scientific Research notes that “the complete settlement shows several mammoth bone dwellings, walls, enclosure, pits, working areas, hearths, dumping areas and butchering areas,” she says.” ref
“To some, though, the grandeur of the structure suggests more than practical significance. “People have also speculated a lot about a likely ritual element to this and it’s really hard to say what that might have been,” Pryor adds. “Ritual is embedded in human lives in all sorts of ways. The fact they might have designed a structure of this type as part of both their ritual and their sustenance activities is very reasonable.” The site stands out most obviously for its scale. “The size of the structure makes it exceptional among its kind, and building it would have been time-consuming,” says Marjolein Bosch, a zooarchaeologist at the University of Cambridge. “This implies that it was meant to last, perhaps as a landmark, a meeting place, a place of ceremonial importance, or a place to return to when the conditions grew so harsh that shelter was needed,” Bosch was not involved with the new research on this “ truly exceptional find” but has personally visited the site. Indeed, the structure’s sheer size makes it an unlikely everyday home. “I cannot possibly imagine how they would have roofed over this structure,” Pryor said. The smaller mammoth houses feature more definite cooking hearths, and they contain the remains of reindeer, horse and fox, which suggests the people in them were living on whatever they could find in the area. The new mammoth bone structure lacks evidence of other animal remains. “It’s almost exclusively woolly mammoth remains and that is one of the interesting things about it,” Pryor said. “With no other animal bones, this doesn’t look much like a dwelling where people lived for a while,” Shipman added.” ref
“Intriguingly, the new structure is the first of its kind to yield evidence that its occupants burnt wood inside and not just bone. “It’s the first time anyone’s found large pieces of charcoal inside one of these structures. So it does show that trees were in the environment,” Pryor said. Tree ring widths in the charcoal are narrow, suggesting the trees probably struggled to survive in that landscape. Previous studies suggested that even on the Ice Age’s arid steppes, coniferous trees would have endured in forests stretching along riversides like those close to Kostenki—a draw for people looking to survive. Still, if people weren’t living in the structure, then why did they make fires? “Fire in the past can be seen as a tool much the same as chipped stone implements and worked bones are,” Bosch says. Fires provided heat and light, barbecued and roasted food, dried meat for storage, and processed glues for stone-tipped tools. “Here, the fires were lit inside a structure and its use as a light source seems intuitive,” she says. “If the authors are correct in their assumption of its use as a place for food storage, it may also have been used to dry meat.” There may be ways to test these ideas. Finding drops of fat on the floor, for example, could show that meat was dried over the flames.” ref
“There must be something about the topography of the site that makes it a place where, over and over, herds of mammoths are coming through and can be killed or will be killed naturally, like at a river crossing,” says Penn State’s Pat Shipman. “I can imagine no way [these] people could possibly kill 60 mammoths at a time, because proboscideans (the order of mammals to which both mammoths and living elephants belong) are smart and catch on if members of their herd are being killed, even with modern automatic weapons.” Further studies of the mammoth bones will yield more clues about their source. Some were arranged in the same order and position as they were in the skeleton. “This means that the bones were brought to the site as body part which some soft tissue (skin, muscle, and tendons) still attached,” Bosch said. “Therefore, they must have been transported before carnivores had the chance to eat and clean the bones. This implies that the builders had early access to the mammoth remains.” Shipman adds: “I want to know if the bones have been processed or transported or if we are looking at whole skeletons or carcasses piled up for future use. Moving a dead mammoth cannot have been easy even if it was largely de-fleshed.” ref
“Such bone houses have been found in considerable numbers, often clustered together in little “villages” of four or five houses in the fertile valleys of the Ukraine and the same method of construction has appeared as far west as Kracow, in Poland, with three rings of mammoth bones exactly similar to those in Russia and dating to about 20 000 years ago.” ref
“Relatively all of the mammoth bone-dwelling sites date to the Upper Paleolithic period (Gravettian or Epi-Gravettian), with the sole exception of Molodova 1, which dates to the Middle Stone Age and is associated with Neanderthals.” ref


Images of wild cattle that scientists have dated to at least 40,000 years old in Borneo cave Above and between the three beasts are hand stencils. The animal is one of a trio of large creatures that adorn a wall in the Lubang Jeriji Saléh cave in the East Kalimantan province of Indonesian Borneo. If the measurement is accurate the Borneo paintings may be 4,500 years older than depictions of animals that adorn cave walls on the neighboring island of Sulawesi. But there is room for doubt. Writing in the journal Nature, the researchers concede that the crusts they analyzed had formed on top of a heavily weathered part of the animal painting and that pigment analyses could not distinguish the underlying paint from that of a nearby mulberry-colored hand stencil. Cave art in East Kalimantan can be grouped into three distinct phases. The oldest includes the reddish-orange hand stencils and animal paintings that mostly appear to depict Bornean banteng, the wild cattle still found on the island. The next phase consists of younger hand stencils, intricate motifs and symbols, and depictions of elegant, thread-like people, some wearing elaborate headdresses, some apparently dancing, painted in dark purple or mulberry on the cave walls. ref
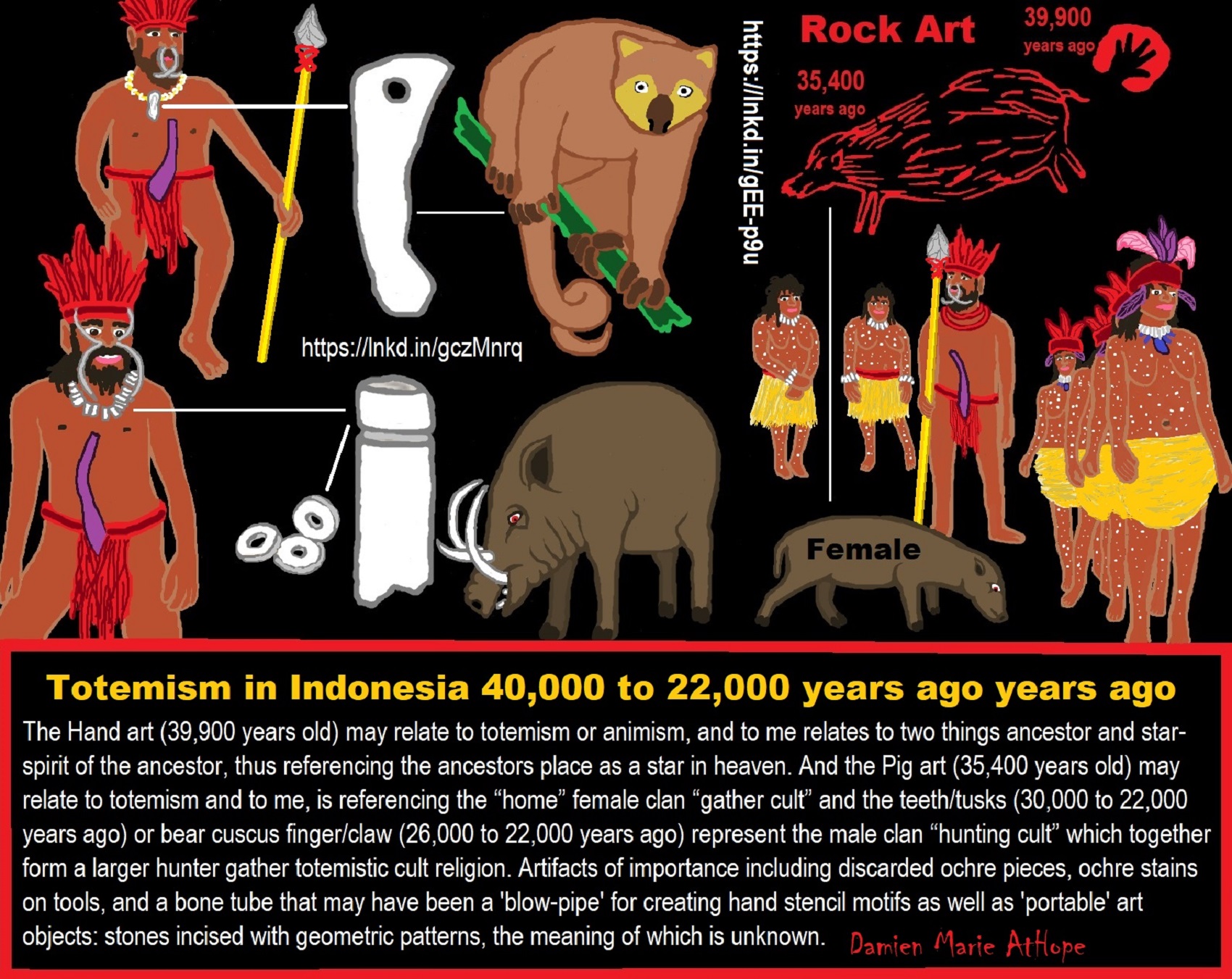
While humans seem to first settle in East Timor 42,000 years ago and a 39,900 years old hand stencil that is from the Leang Timpuseng Cave on the Island of Sulawesi in Indonesia also includes some of the most ancient animal paintings, all made by Aborigine migrants who were probably heading for Australia. and the image of the “pig-deer” at the Sulawesi Cave, Indonesia, dating to as old as 35,400 years ago. ref, ref, ref
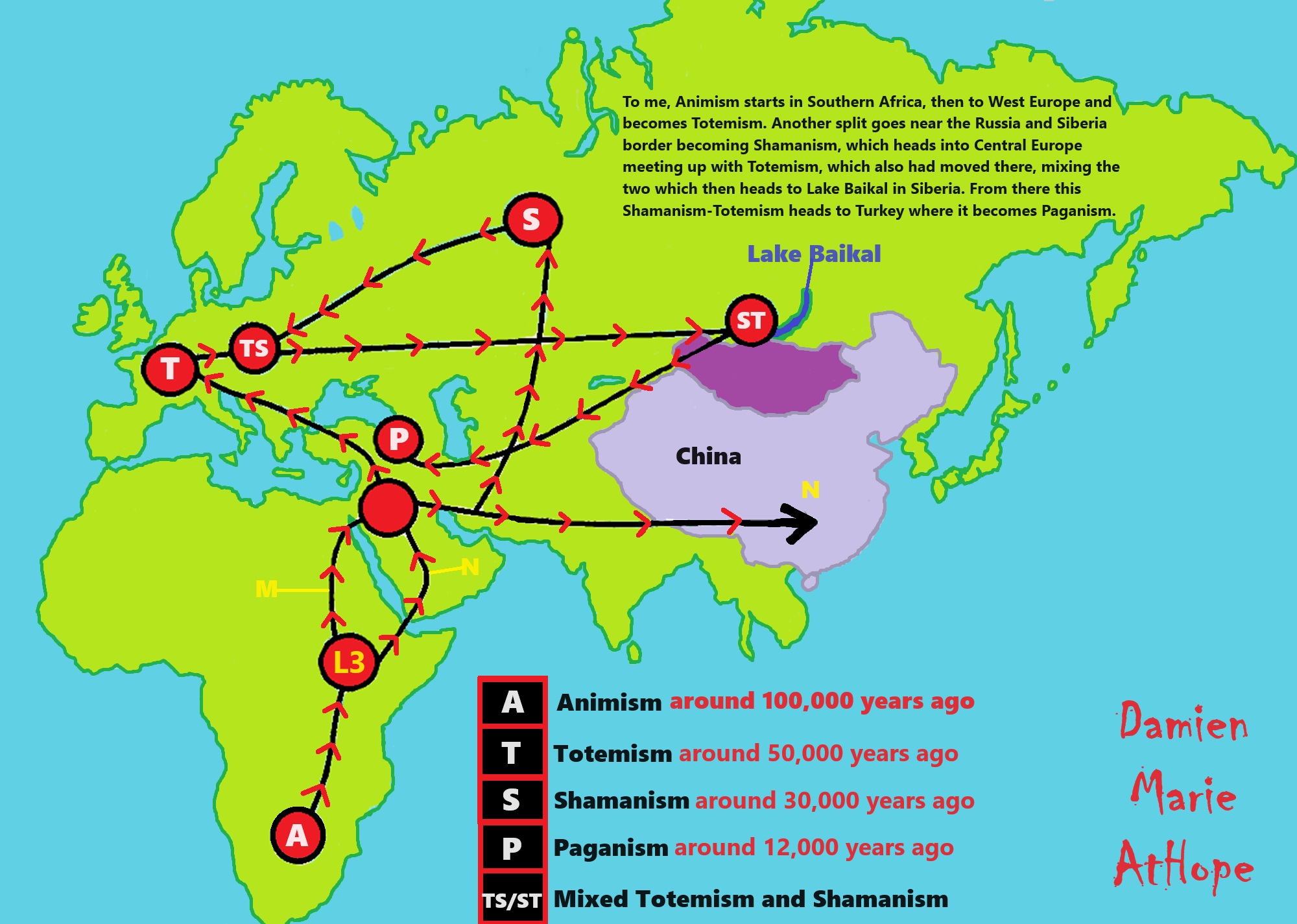
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Animism: a belief among some indigenous people, young children, or all religious people!
Over 100,000 years ago or so, Southern Africa, in the Land before and the beginning Time of Animism: LINK

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref,
Explaining the Earliest Religious Expression, that of Animism (beginning 100,000 to 70,000 years ago?) to Totemism (beginning 30,000 to 3,000 years ago?) in Southern Africa: LINK
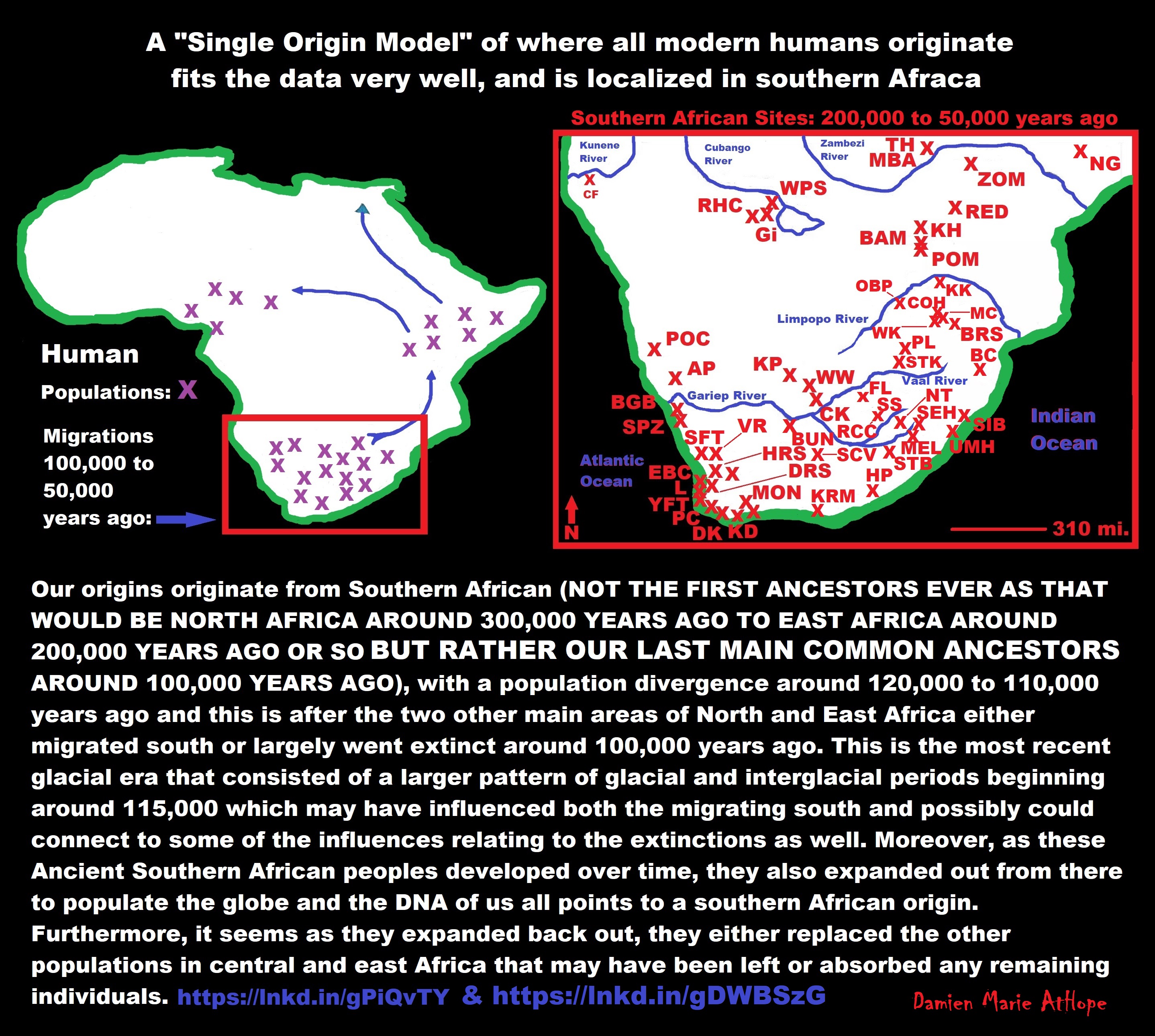
Our origins originate from Southern African (NOT THE FIRST ANCESTORS EVER AS THAT WOULD BE NORTH AFRICA AROUND 300,000 YEARS AGO TO EAST AFRICA AROUND 200,000 YEARS AGO OR SO BUT RATHER OUR LAST MAIN COMMON ANCESTORS AROUND 100,000 YEARS AGO), with a population divergence around 120,000 to 110,000 years ago and this is after the two other main areas of North and East Africa either migrated south or largely went extinct around 100,000 years ago. This is the most recent glacial era that consisted of a larger pattern of glacial and interglacial periods beginning around 115,000 which may have influenced both the migrating south and possibly could connect to some of the influences relating to the extinctions as well. Moreover, as these Ancient Southern African peoples developed over time, they also expanded out from there to populate the globe, and the DNA of us all points to a southern African origin. Furthermore, it seems as they expanded back out, they either replaced the other populations in central and east Africa that may have been left or absorbed any remaining individuals. ref
Southern African Middle Stone Age sites:
(Ap) Apollo 11; (BAM) Bambata; (BBC) Blombos Cave; (BC) Border Cave; (BGB)Boegoeberg; (BPA) Boomplaas; (BRS) Bushman Rock Shelter; (BUN) Bundu Farm; (CF)Cufema Reach; (CK) Canteen Kopje; (COH) Cave of Hearths; (CSB) Cape St Blaize; (DK)Die Kelders Cave 1; (DRS) Diepkloof Rock Shelter; (EBC) Elands Bay Cave; (FL) Florisbad; (≠GI) ≠Gi; (HP) Howiesons Poort; (HRS) Hollow Rock Shelter; (KD) Klipdrift; (KKH) Klein Kliphuis; (KH) Khami; (KK) Kudu Koppie; (KP) Kathu Pan; (KRM) Klasies River Main Site; (L) Langebaan; (MBA) Mumbwa Caves; (MC) Mwulu’s Cave; (MEL)Melikane; (MON) Montagu Cave; (NBC) Nelson Bay Cave; (NG) Ngalue; (NT) Ntloana Tšoana; (OBP) Olieboomspoort; (PC) Peers Cave; (POC) Pockenbank; (PL) Plover’s Lake; (POM) Pomongwe; (PP) Pinnacle Point; (RCC) Rose Cottage Cave; (RED) Redcliff; (RHC) Rhino Cave; (SCV) Seacow Valley; (SFT) Soutfontein; (SEH) Sehonghong; (SIB)Sibudu Cave; (SPZ) Spitzkloof Rock Shelter; (SS) Sunnyside 1; (STB) Strathalan Cave B; (STK) Sterkfontein; (TR) Twin Rivers; (UMH) Umhlatuzana; (VR) Varsche Rivier 003; (WPS) White Paintings Shelter; (WK) Wonderkrater; (WW) Wonderwerk; (YFT)Ysterfontein 1; (ZOM) Zombepata Cave. ref
Adapted from: ref
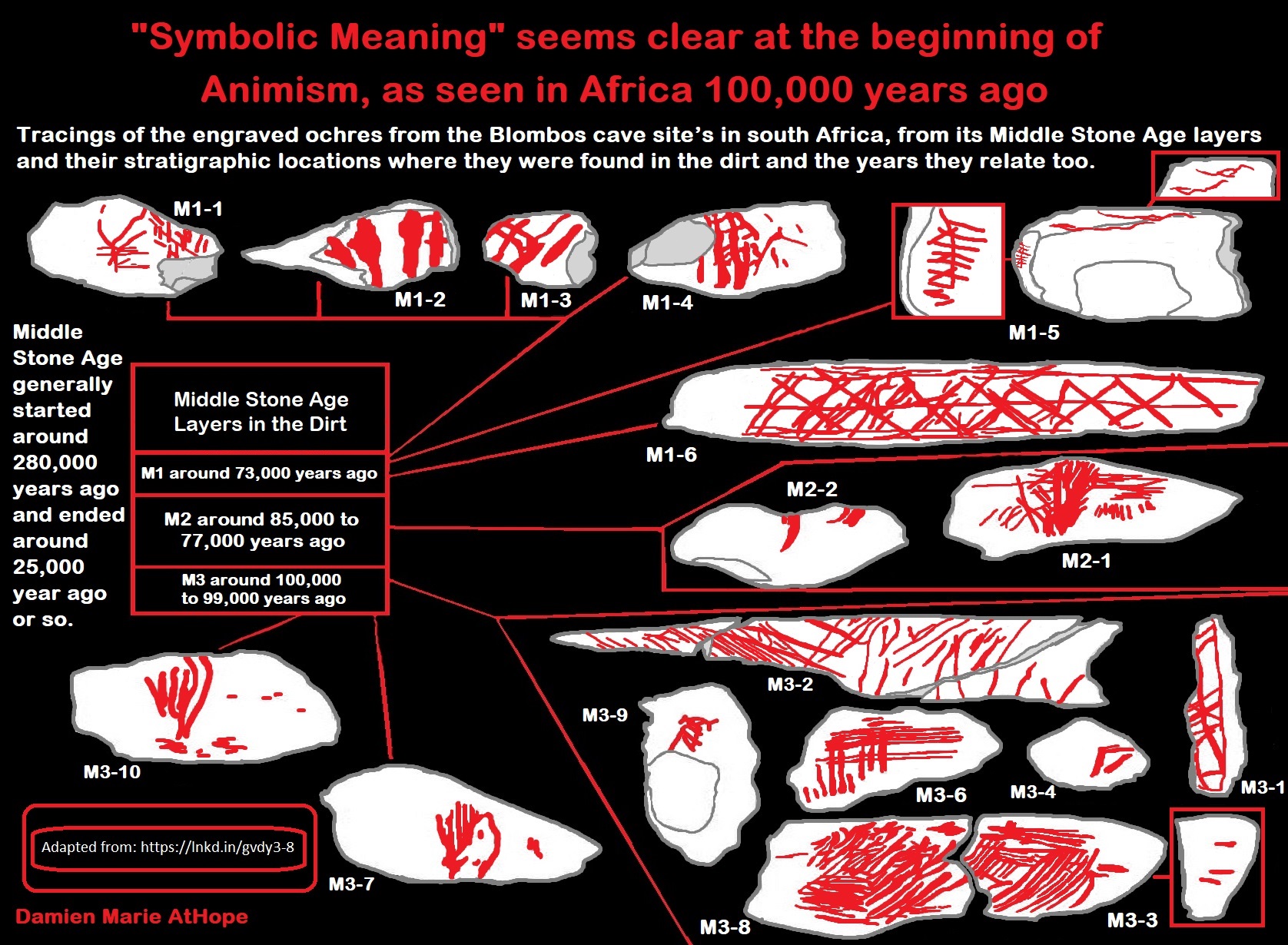
Here we see the tracings of the engraved ochres from the Blombos cave site’s in South Africa, from its Middle Stone Age layers and their stratigraphic locations where they were found in the dirt and the years they relate to. M1 dates to around 73,000 years ago, M2 around 85,000 to 77,000 years ago, and M3 dates to around 100,000 to 99,000 years ago. Middle Stone Age generally started around 280,000 years ago and ended around 25,000 years ago or so. Therefore, amazing as it is, here we have proof that “Symbolic Meaning,” seems to be clear at the beginning of Animism, as seen in Africa 100,000 years ago. In a landmark study, it was demonstrated, for the first time, that there are seeming tradition in the production of geometric engraved representations, includes the production of a number of different patterns and this set of evolving traditions have roots that go back in time to at least 100,000 years ago (around a time I say Animism begins in Africa). The fact that they were created, that most of them are deliberate and were made with representational intent, strongly suggests they functioned as artifacts within a society by symbols with meaning. ref
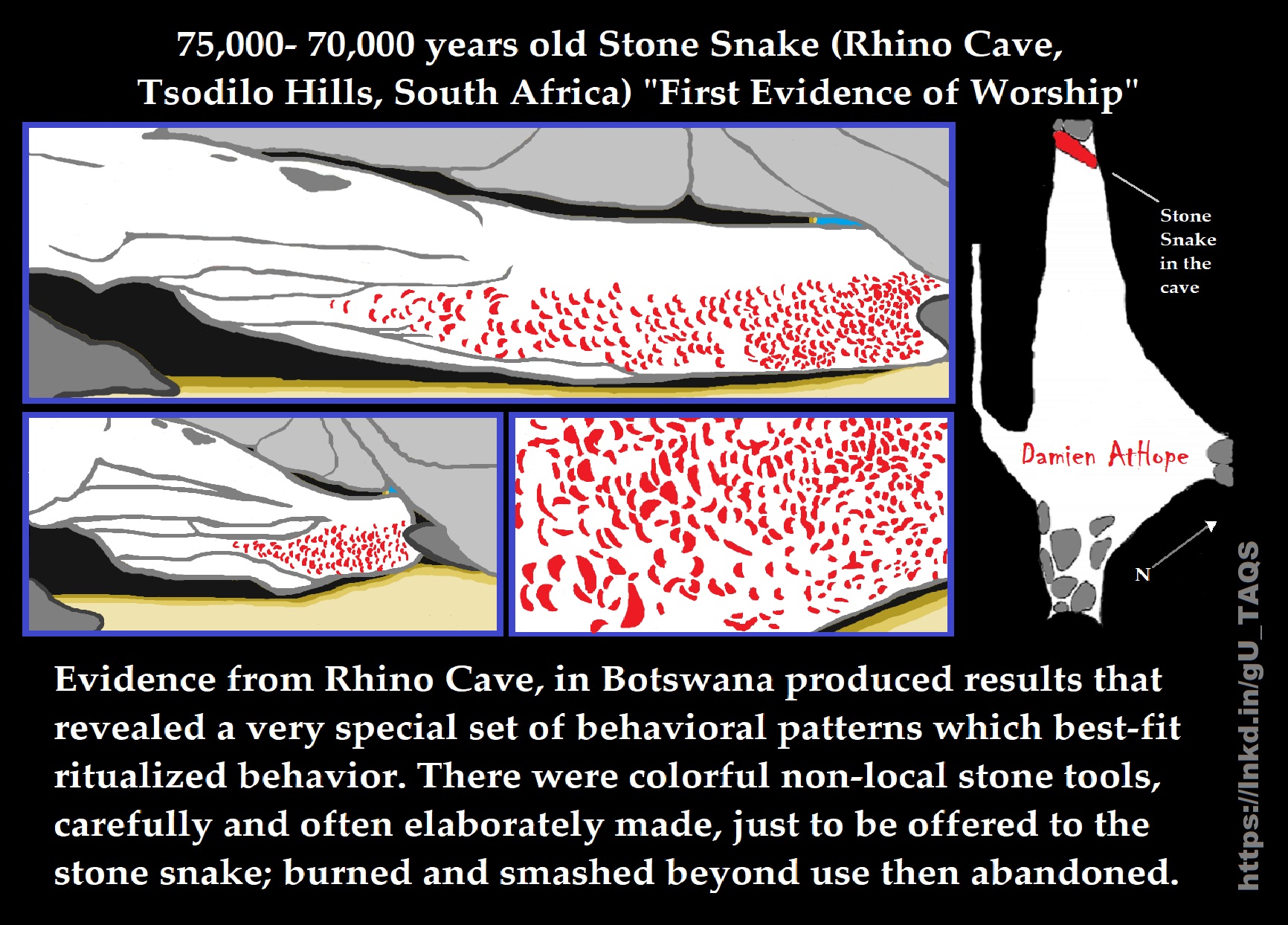
Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago
Evidence from Rhino Cave, in Botswana produced results that revealed a very special set of behavioral patterns which best-fit ritualized behavior. There were colorful non-local stone tools carefully and often elaborately made just to be offered to the stone snake; burned and smashed beyond use then abandoned. ref

60,000 years old fragments of engraved ostrich eggshells from the Diepkloof Rock Shelter, Western Cape, South Africa.
Symbolic meaning expressed in art or designs and patterns, starting with animism at 100,000 years ago and more so around 50,000 years ago with the emergence of totemism and shamanism 30,000 years ago which I think all connect in a general way to religious thinking or mindsets that create the art or patterns and are not only a much older phenomenon than previously thought and has its roots in the African continent. Such early symbolic expression is seen in things like personal ornamentation and engraved designs, traditions that go far back into African prehistory. The patterns are symbolic and could have been used to express religious clan connections, group relations or personal expression. The patterns may indeed have a meaning and while abstract in representation they are unequivocal evidence for symbolic thought and one step closer to language. Ref
Modern human incursion into Neanderthal territories
54,000 years ago at Mandrin, France
“Abstract: Determining the extent of overlap between modern humans and other hominins in Eurasia, such as Neanderthals and Denisovans, is fundamental to understanding the nature of their interactions and what led to the disappearance of archaic hominins. Apart from a possible sporadic pulse recorded in Greece during the Middle Pleistocene, the first settlements of modern humans in Europe have been constrained to ~45,000 to 43,000 years ago. Here, we report hominin fossils from Grotte Mandrin in France that reveal the earliest known presence of modern humans in Europe between 56,800 and 51,700 years ago. This early modern human incursion in the Rhône Valley is associated with technologies unknown in any industry of that age outside Africa or the Levant. Mandrin documents the first alternating occupation of Neanderthals and modern humans, with a modern human fossil and associated Neronian lithic industry found stratigraphically between layers containing Neanderthal remains associated with Mousterian industries.” ref

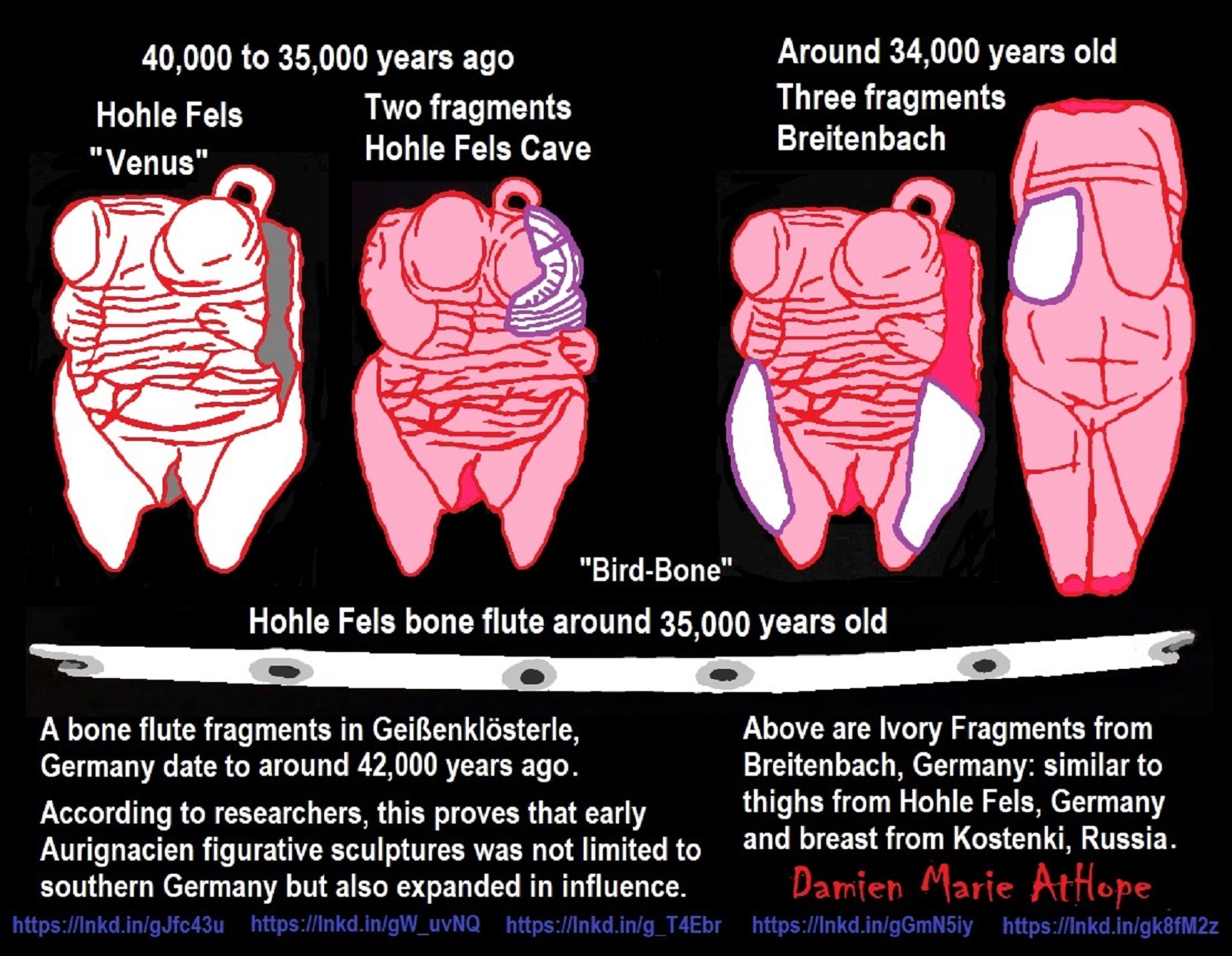
“The Adorant from the Geißenklösterle cave is a 35,000-to-40,000-year-old section of mammoth ivory with a depiction of a human figure, found in the Geißenklösterle cave in the Swabian Jura near Blaubeuren, Germany. The front face has a human figure of uncertain sex in relief, with raised arms and outstretched legs, but no hands. The posture is usually interpreted as an expression of worship, which is why in German the figure is called an “adorant”, a word meaning “worshipper”. It has been claimed that a belt and sword can be seen, although these are probably natural features of the ivory. On the plate’s reverse are rows of small notches. The piece is 38 mm (1.50 in) tall, 14 mm (0.55 in) wide, and 4.5 mm (0.18 in) thick. Traces of manganese and ochre can be found on it by microscope analysis. It is somewhat like the Lion-Human of Hohlenstein-Stadel ivory statue also found in Germany.” ref
“The Löwenmensch figurine, also called the Lion-Human of Hohlenstein-Stadel, is a prehistoric ivory sculpture discovered in Hohlenstein-Stadel, a German cave. The German name, Löwenmensch, meaning “lion-person” or “lion-human”, is used most frequently because it was discovered and is exhibited in Germany. Determined by carbon dating of the layer in which it was found to be between 35,000 and 40,000 years old, it is one of the oldest-known examples of an artistic representation and the oldest confirmed statue ever discovered. Its age associates it with the archaeological Aurignacian culture of the Upper Paleolithic. An example of zoomorphic art, the Lion-Human was carved out of mammoth ivory, using a flint stone knife. Seven parallel, transverse, carved gouges are on the left arm.” ref


In Kostënki 17, Russia, there were numerous pendants recovered and at least one, seen above, was dated to 43,000 years ago, which was made from fossil belemite rostrum. The artifacts include a group of more than 40 pendants made from fox canines teeth. In addition, there were pendants made from stone and fossils as well. Along with shell beads from the lower layers of Kostënki 14 and the Kostënki 17 pendants are the earliest good evidence for personal adornment anywhere in Eastern Europe. The occupations at Kostenki include several Late Early Upper Paleolithic levels, dated between 42,000 to 30,000 calibrated years ago (cal BP). Kostenki, the Aurignacian sequence was considered the oldest component associated with modern humans at archaeological sites in Europe, underlain by Mousterian-like deposits representing Neanderthals. Kostenki 14, also known as Markina Gora, is the main site at Kostenki, and it has been found to contain genetic evidence concerning the migration of early modern humans from Africa into Eurasia. ref, ref

To me, the importance of talon ornaments, like the one in Üçagızlı Cave, “Sky burial”
Ornament from Üçağızlı I Cave, Turkey (41,000–43,000 years ago). ref
The early Upper Paleolithic occupations at Uçagızlı Cave (Hatay, Turkey)
Ornaments at Üçağızlı I Cave, Turkey
Ornaments are abundant in the Initial Upper Paleolithic and Ahmarian layers of Üçağızlı I cave, and they are also present in the small Epipaleolithic as well. With the exception of one notched raptor talon (probably vulture, Gyps or Gypaetus) from layer B, all of the ornaments were made from small marine and freshwater mollusk shells. ref
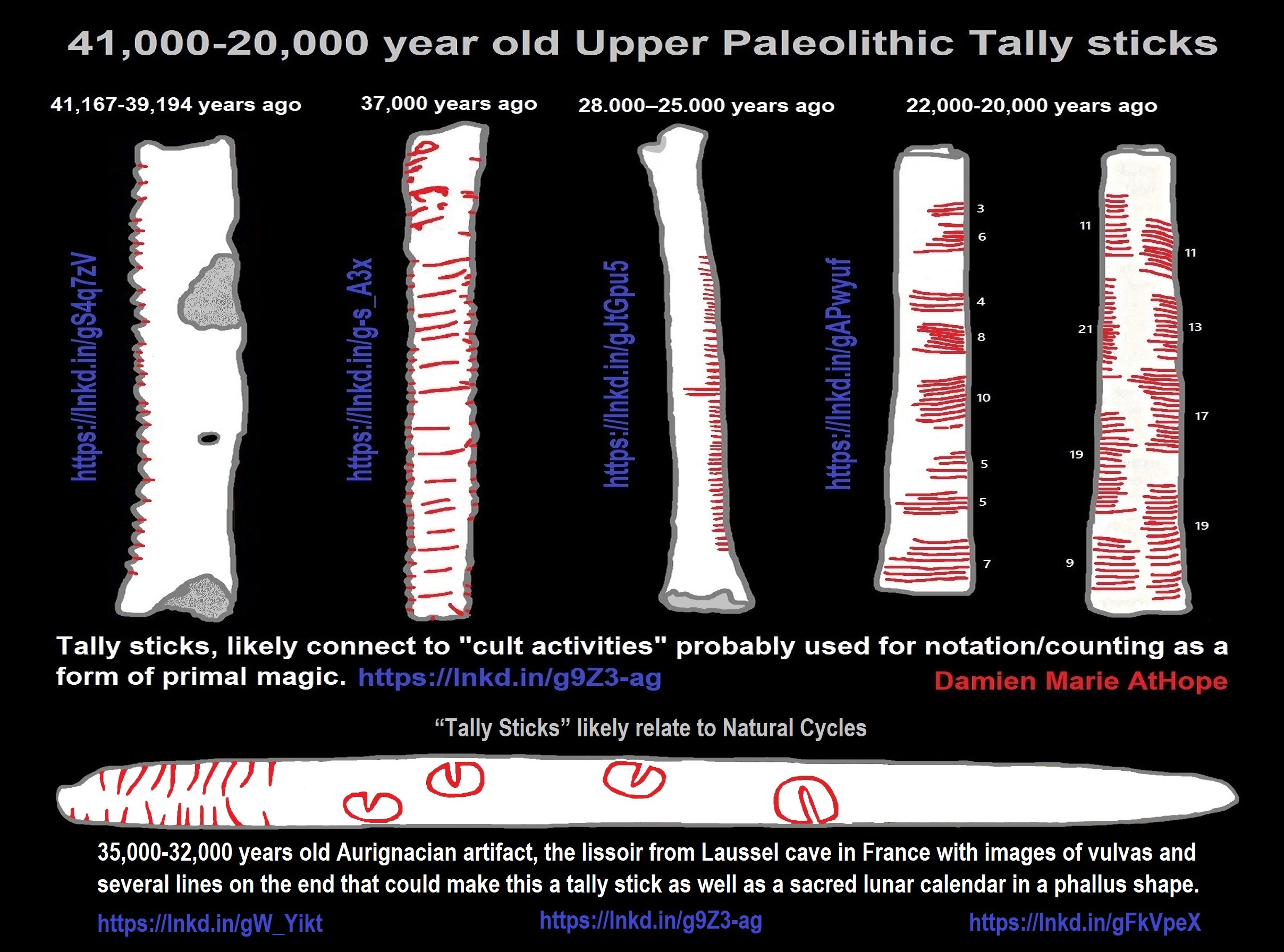
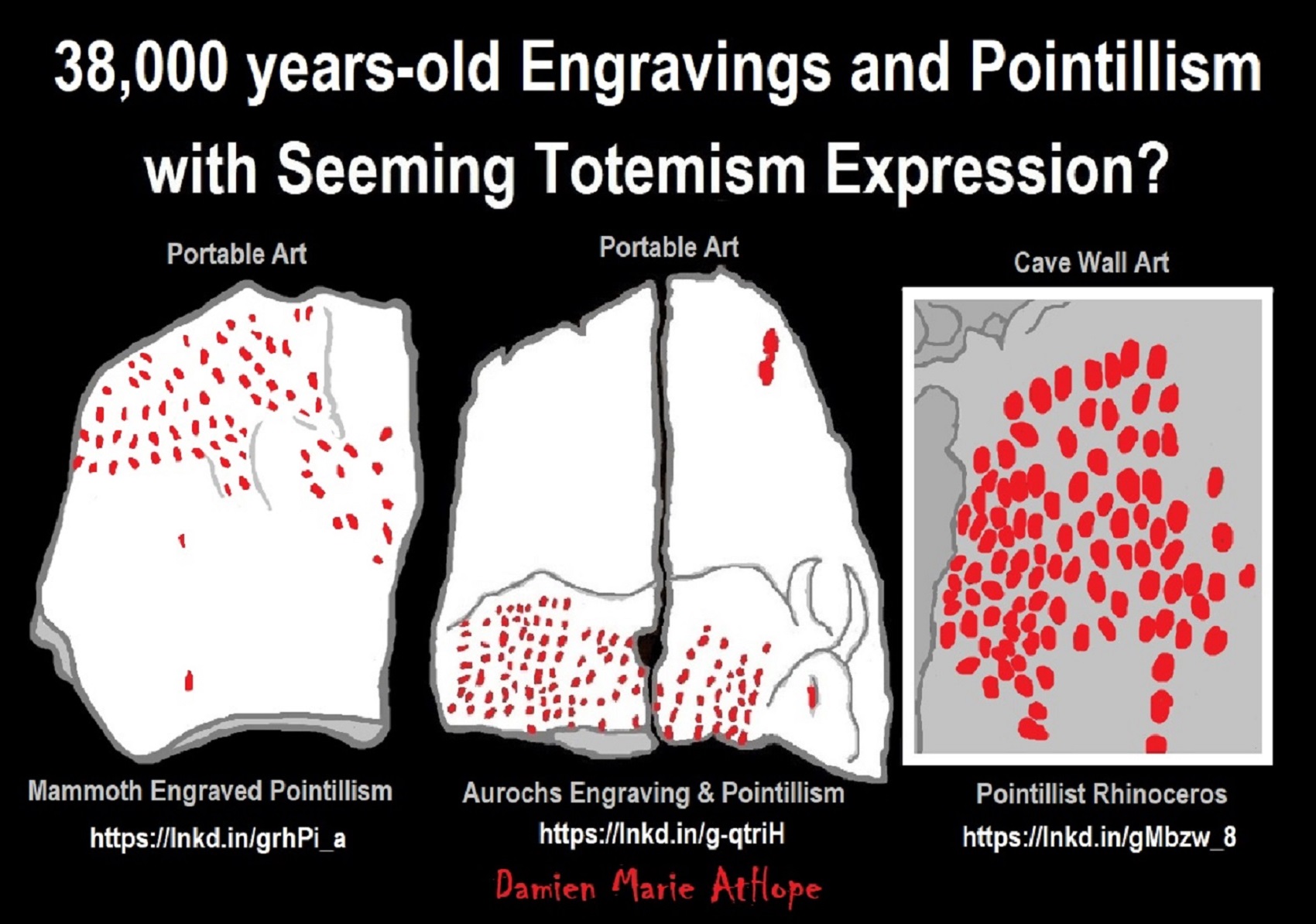
Ritual Pointillism, to me, references stars/ancestor worship in Aurignacian culture totemism, which I think relates to the Neanderthal Châtelperronian culture totemism. There was 16 engraved and otherwise modified limestone blocks, created 38,000 years ago, pointillist techniques: small dots to create the illusion of a larger image. ref

Around 37,500 to 32,500 years old Aurignacian bison skull from Régismont-le-Haut (Hérault). Possibility symbolic or ritualized item and certainly a major animal for them, as shown by the ornamentation of certain caves (for example, the Aurignacian of Chauvet Cave in France. The trophy-head belongs to a male individual. The many depictions of bison in Palaeolithic art back up, the symbolic interpretation as possible. ref
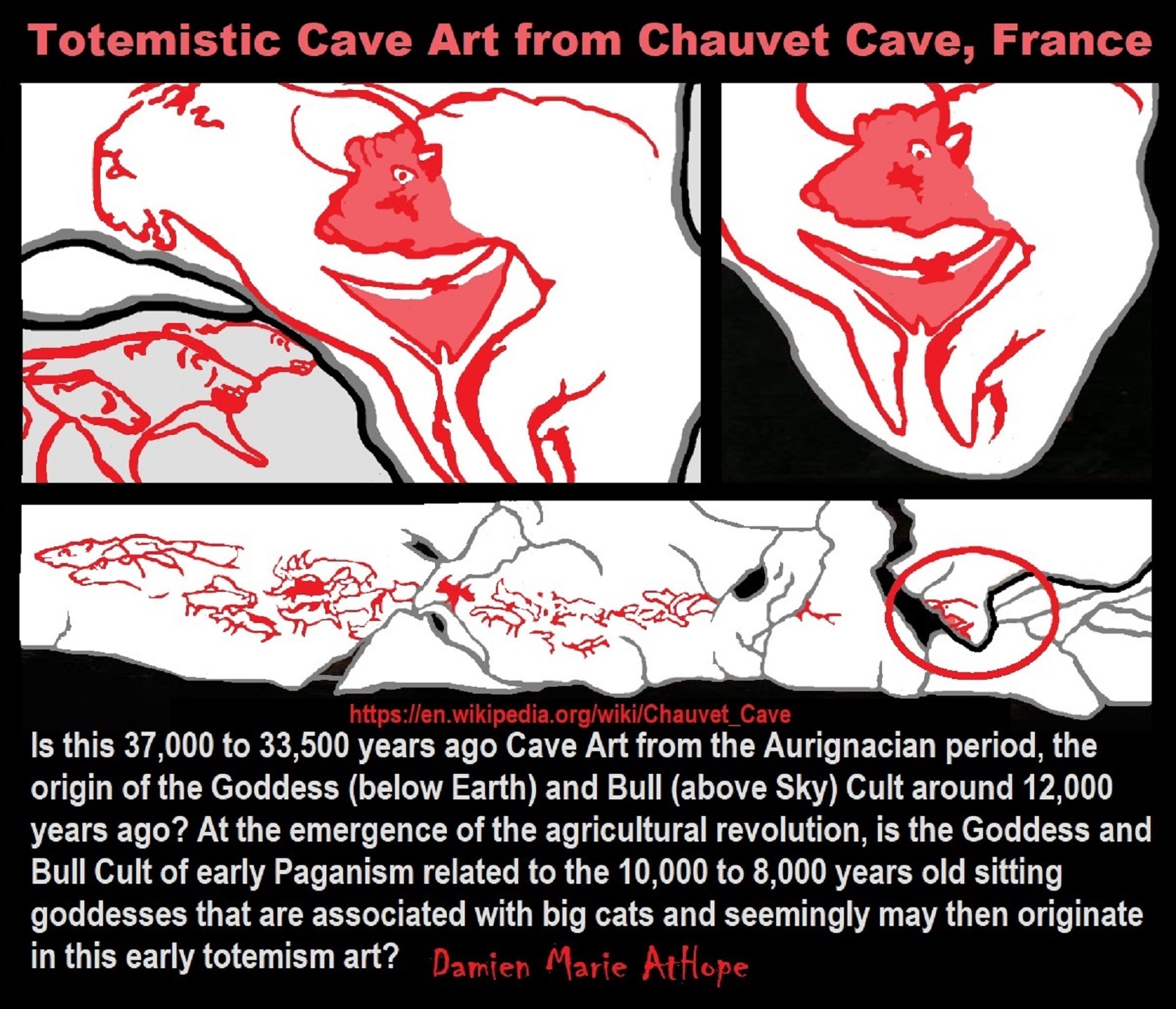
Chauvet cave
“The Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc Cave in the Ardèche department of southeastern France is a cave that contains some of the best-preserved figurative cave paintings in the world, as well as other evidence of Upper Paleolithic life. It is located near the commune of Vallon-Pont-d’Arc on a limestone cliff above the former bed of the river Ardèche, in the Gorges de l’Ardèche. The dates have been a matter of dispute but a study published in 2012 supports placing the art in the Aurignacian period, approximately 32,000–30,000 years ago. A study published in 2016 using additional 88 radiocarbon dates showed two periods of habitation, one from 37,000 to 33,500 years ago and the second from 31,000 to 28,000 years ago, with most of the black drawings dating to the earlier period.” ref
“Hundreds of animal paintings have been cataloged, depicting at least 13 different species, including some rarely or never found in other ice age paintings. Rather than depicting only the familiar herbivores that predominate in Paleolithic cave art, i.e. horses, aurochs, mammoths, etc., the walls of the Chauvet Cave feature many predatory animals, e.g., cave lions, leopards, bears, and cave hyenas. There are also paintings of rhinoceroses. Typical of most cave art, there are no paintings of complete human figures, although there is one partial “Venus” figure composed of what appears to be a vulva attached to an incomplete pair of legs. Above the Venus, and in contact with it, is a bison head, which has led some to describe the composite drawing as a Minotaur. There are a few panels of red ochre hand prints and hand stencils made by blowing pigment over hands pressed against the cave surface. Abstract markings—lines and dots—are found throughout the cave. There are also two unidentifiable images that have a vaguely butterfly or avian shape to them. This combination of subjects has led some students of prehistoric art and cultures to believe that there was a ritual, shamanic, or magical aspect to these paintings.” ref
“One drawing, later overlaid with a sketch of a deer, is reminiscent of a volcano spewing lava, similar to the regional volcanoes that were active at the time. If confirmed, this would represent the earliest known drawing of a volcanic eruption. The artists who produced these paintings used techniques rarely found in other cave art. Many of the paintings appear to have been made only after the walls were scraped clear of debris and concretions, leaving a smoother and noticeably lighter area upon which the artists worked. Similarly, a three-dimensional quality and the suggestion of movement are achieved by incising or etching around the outlines of certain figures. The art is also exceptional for its time for including “scenes”, e.g., animals interacting with each other; a pair of woolly rhinoceroses, for example, are seen butting horns in an apparent contest for territory or mating rights.” ref
Aurignacian burials (around 37,000-30,000 years ago) belong to the early phase of this period in Europe. Examples have been excavated at Cave of Cavillon, Liguria – a burial wearing a cap of netted whelk shells with a border of deer’s teeth, red ochre around the face, and a bone awl at the side. ref
Aurignacian in the Zagros region dates back to about 35,500 years ago at Yafteh Cave, Lorestan, Iran. ref
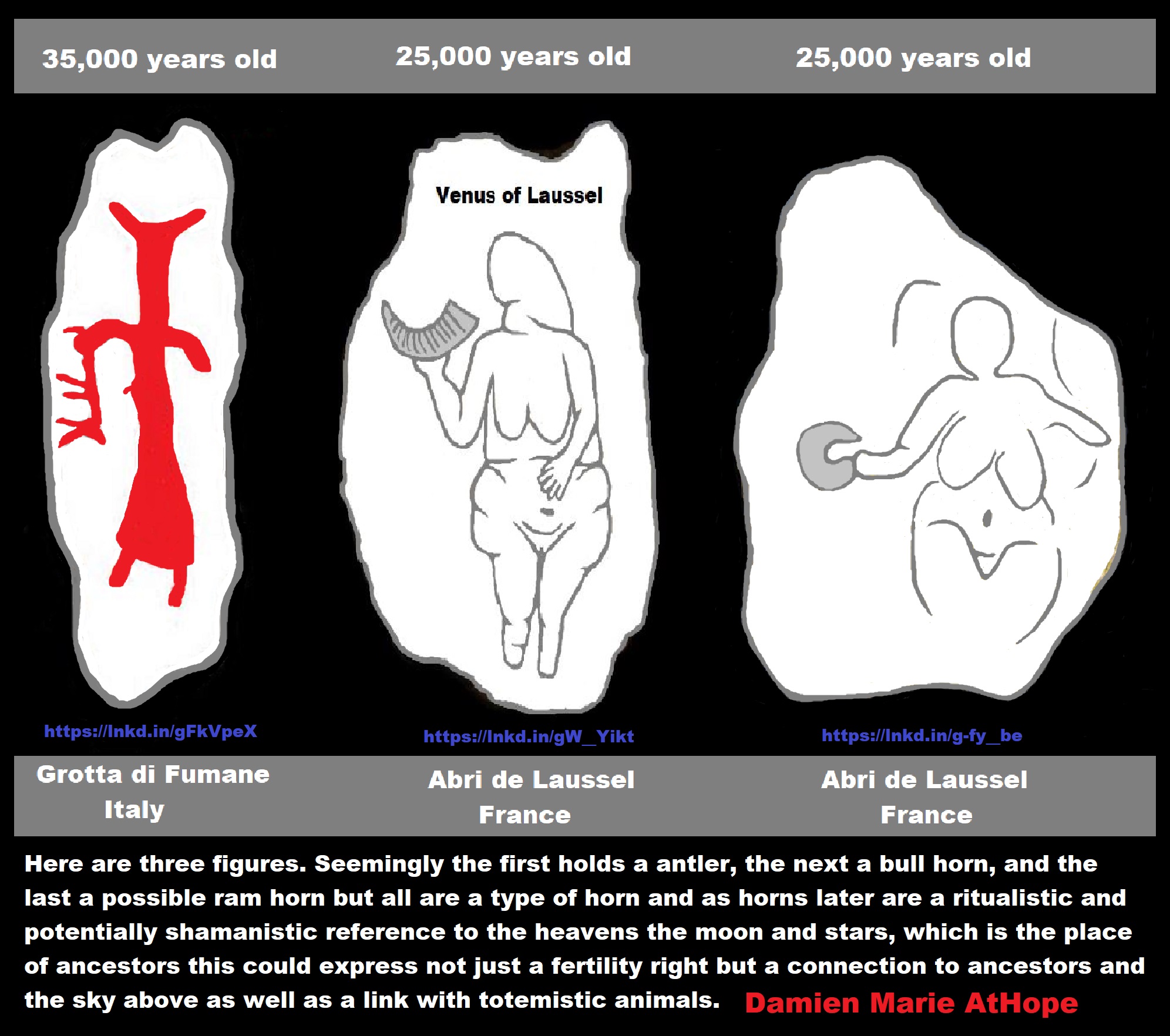

34,000 years ago Lunar Calendar Cave art around the Time Shift From Totemism to Early Shamanism?
“The Oldest Lunar Calendars and Earliest Constellations have been identified in cave art found in France and Germany. The astronomer-priests of these late Upper Paleolithic Cultures understood mathematical sets, and the interplay between the moon annual cycle, ecliptic, solstice and seasonal changes on earth. The archaeological record’s earliest data that speaks to human awareness of the stars and ‘heavens’ dates to the Aurignacian Culture of Europe, around 34,000 years ago. Between 1964 and the early 1990s, Alexander Marshack published breakthrough research that documented the mathematical and astronomical knowledge in the Late Upper Paleolithic Cultures of Europe. Marshack deciphered sets of marks carved into animal bones, and occasionally on the walls of caves, as records of the lunar cycle. These marks are sets of crescents or lines. Artisans carefully controlled line thickness so that a correlation with lunar phases would be as easy as possible to perceive. Sets of marks were often laid out in a serpentine pattern that suggests a snake deity or streams and rivers. Many of these lunar calendars were made on small pieces of stone, bone or antler so that they could be easily carried. These small, portable, lightweight lunar calendars were easily carried on extended journeys such as long hunting trips and seasonal migrations.” ref
“Hunting the largest animals was arduous, and might require hunters to follow herds of horses, bison, mammoth or ibex for many weeks. (Other big animals such as the auroch, cave bear and cave lion were well known but rarely hunted for food because they had a special status in the mythic realm. The Auroch is very important to the search for earliest constellations.) The phases of the moon depicted in these sets of marks are inexact. Precision was impossible unless all nights were perfectly clear which is an unrealistic expectation. The arithmetic counting skill implied by these small lunar calendars is obvious. The recognition that there are phases of the moon and seasons of the year that can be counted – that should be counted because they are important – is profound. “All animal activities are time factored, simply because time passes, the future is forever arriving. The reality of time factoring is objective physics and does not depend upon human awareness or consciousness. Until Marshack’s work, many archeologists believed the sets of marks he chose to study were nothing but the aimless doodles of bored toolmakers. What Marshack uncovered is the intuitive discovery of mathematical sets and the application of those sets to the construction of a calendar.” Bone is the preferred medium because it allows for easy transport and a long calendar lifetime. Mankind’s earliest astronomy brought the clan into the multi-dimensional universe of the gods. Objects used in the most potent rituals had the highest contextual, cultural value and were treated with great reverence.” ref
“Regarding the Aurignacian, between 43,000 and 35,000 years ago, the archaeological record from habitations is relatively poor in the Ardèche (Abri des Pécheurs, Grotte du Figuier) while appearing more abundant in the Languedoc (La Salpétrière, La Balauzière, Esquicho-Grapaou, La Laouza etc.). The same applies to the sites of the early phases of the Gravettian. During climatic fluctuations, and unlike the deep caves such as Chauvet, the porch and shelter fills seem to have better recorded the cold episodes than the humid phases. To date, 20 decorated caves are indexed in the gorges of the Ardèche and nearby; in other words as far as the valley of the Gardon (Baume-Latrone). This group includes several important caves (Ebbou, Oulen, Émilie etc.) which are not precisely dated and were judged to be of secondary importance until the discovery of the Chauvet Cave.” ref
“A 10,000-year-old engraved stone could be a lunar calendar. The rare pebble — found high up in the mountains near Rome, Italy, the hammer-stone was found on top of Monte Alta in the Alban Hills. It’s believed that our early ancestors would’ve used the stone to keep track of the moon’s cycles. Notches were engraved “as if they were being used to count, calculate or store the record of some kind of information. And these notches — which total either 27 or 28 — suggest the stone’s engraver used the pebble to track lunar cycles.” ref
“Archaeologists excavating in Scotland found a series of huge pits were dug by Mesolithic people to track the cycle of the Moon. They found a series of twelve huge, specially shaped pits designed to mimic the various phases of the Moon. The holes aligned perfectly on the midwinter solstice to help the hunter-gathers of Mesolithic Britain keep precise track of the passage of the seasons and the lunar cycle. The holes were dug in the shapes of various phases of the moon. “Waxing, waning, crescents, and gibbous, they’re all there and arranged in a 50-meter-long (164-foot) arc. The one representing the full moon is large and circular, approximately two meters (roughly seven feet) across, and placed right in the center. And this arc is arranged perfectly with a notch in the landscape where the sun would have risen on the day of the midwinter solstice about 10,000 years ago. Placing their calendar in the landscape the way they did would have let the people who built it to recalibrate the lunar months every winter to bring their lunar calendar in line with the solar year. This means that any effort to keep track of the seasons using the moon alone will slowly drift ever further from true. An observer needs to know when to add or subtract an extra month to make good the time or hit the reset button and start counting again.” ref
“A moon-shaped calendar was found in Smederevska Palanka, Serbia that dates back 8,000 years, and is made from a wild boar’s tusk engraved with markings to denote a lunar cycle. Farmers may have used the device to plan when to plant crops. It is made from the tusk of a wild boar and is marked with engravings thought to denote a lunar cycle of 28 days, as well as the four phases of the moon.” ref
“A lunisolar calendar was found at Warren Field in Scotland and has been dated to c. 8000 BCE, during the Mesolithic period. Some scholars argue for lunar calendars still earlier—Rappenglück in the marks on a c. 17,000-year-old cave painting at Lascaux and Marshack in the marks on a c. 27,000-year-old bone baton—but their findings remain controversial. Scholars have argued that ancient hunters conducted regular astronomical observations of the Moon back in the Upper Palaeolithic. Samuel L. Macey dates the earliest uses of the Moon as a time-measuring device back to 28,000–30,000 years ago.” ref
“A lunar calendar is a calendar based on the monthly cycles of the Moon‘s phases (synodic months, lunations), in contrast to solar calendars, whose annual cycles are based only directly on the solar year. The most commonly used calendar, the Gregorian calendar, is a solar calendar system that originally evolved out of a lunar calendar system. A purely lunar calendar is also distinguished from a lunisolar calendar, whose lunar months are brought into alignment with the solar year through some process of intercalation. The details of when months begin varies from calendar to calendar, with some using new, full, or crescent moons and others employing detailed calculations.” ref
“Since each lunation is approximately 29+1⁄2 days, it is common for the months of a lunar calendar to alternate between 29 and 30 days. Since the period of 12 such lunations, a lunar year, is 354 days, 8 hours, 48 minutes, 34 seconds (354.36707 days), purely lunar calendars are 11 to 12 days shorter than the solar year. In purely lunar calendars, which do not make use of intercalation, like the Islamic calendar, the lunar months cycle through all the seasons of a solar year over the course of a 33–34 lunar-year cycle.” ref
“Although the Gregorian calendar is in common and legal use in most countries, traditional lunar and lunisolar calendars continue to be used throughout the world to determine religious festivals and national holidays. Such holidays include Rosh Hashanah (Hebrew calendar); Easter (the Computus); the Chinese, Korean, Vietnamese, and Mongolian New Year (Chinese, Korean, Vietnamese, and Mongolian calendars, respectively); the Nepali New Year (Nepali calendar); the Mid-Autumn Festival and Chuseok (Chinese and Korean calendars); Loi Krathong (Thai calendar); Sunuwar calendar; Vesak/Buddha’s Birthday (Buddhist calendar); Diwali (Hindu calendars); Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr and Eid al-Adha (Islamic calendar).” ref
“The Japanese Calendar formerly used both the lunar and lunisolar calendar before it was replaced by the Gregorian Calendar during the Meiji government in 1872. Holidays such as the Japanese New Year were simply transposed on top as opposed to being calculated like other countries that use the lunisolar and Gregorian calendars together, for example, the Japanese New Year now falls on January 1, creating a month delay as opposed to other East Asian Countries. See customary issues in modern Japan.” ref
“Most calendars referred to as “lunar” calendars are in fact lunisolar calendars. Their months are based on observations of the lunar cycle, with intercalation being used to bring them into general agreement with the solar year. The solar “civic calendar” that was used in ancient Egypt showed traces of its origin in the earlier lunar calendar, which continued to be used alongside it for religious and agricultural purposes. Present-day lunisolar calendars include the Chinese, Vietnamese, Hindu, and Thai calendars.” ref
“Synodic months are 29 or 30 days in length, making a lunar year of 12 months about 11 to 12 days shorter than a solar year. Some lunar calendars do not use intercalation, for example, the lunar Hijri calendar used by most Muslims. For those that do, such as the Hebrew calendar, and Buddhist Calendars in Myanmar, the most common form of intercalation is to add an additional month every second or third year. Some lunisolar calendars are also calibrated by annual natural events which are affected by lunar cycles as well as the solar cycle. An example of this is the lunar calendar of the Banks Islands, which includes three months in which the edible palolo worms mass on the beaches. These events occur at the last quarter of the lunar month, as the reproductive cycle of the palolos is synchronized with the moon.” ref
“Lunar and lunisolar calendars differ as to which day is the first day of the month. In some lunisolar calendars, such as the Chinese calendar, the first day of a month is the day when an astronomical new moon occurs in a particular time zone. In others, such as some Hindu calendars, each month begins on the day after the full moon. Others are based on the first sighting of the lunar crescent, such as the lunar Hijri calendar (and, historically, the Hebrew calendar).” ref
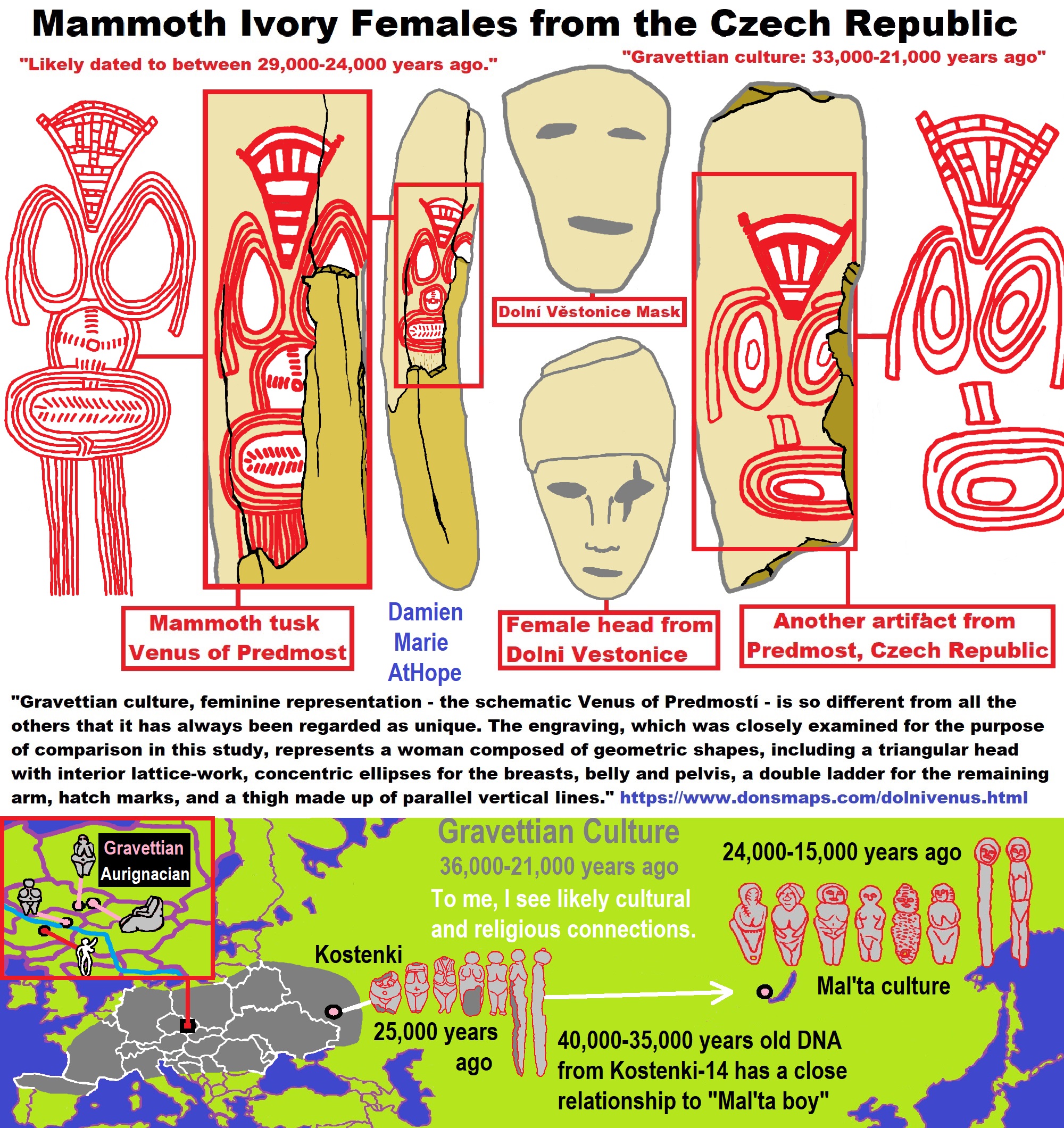
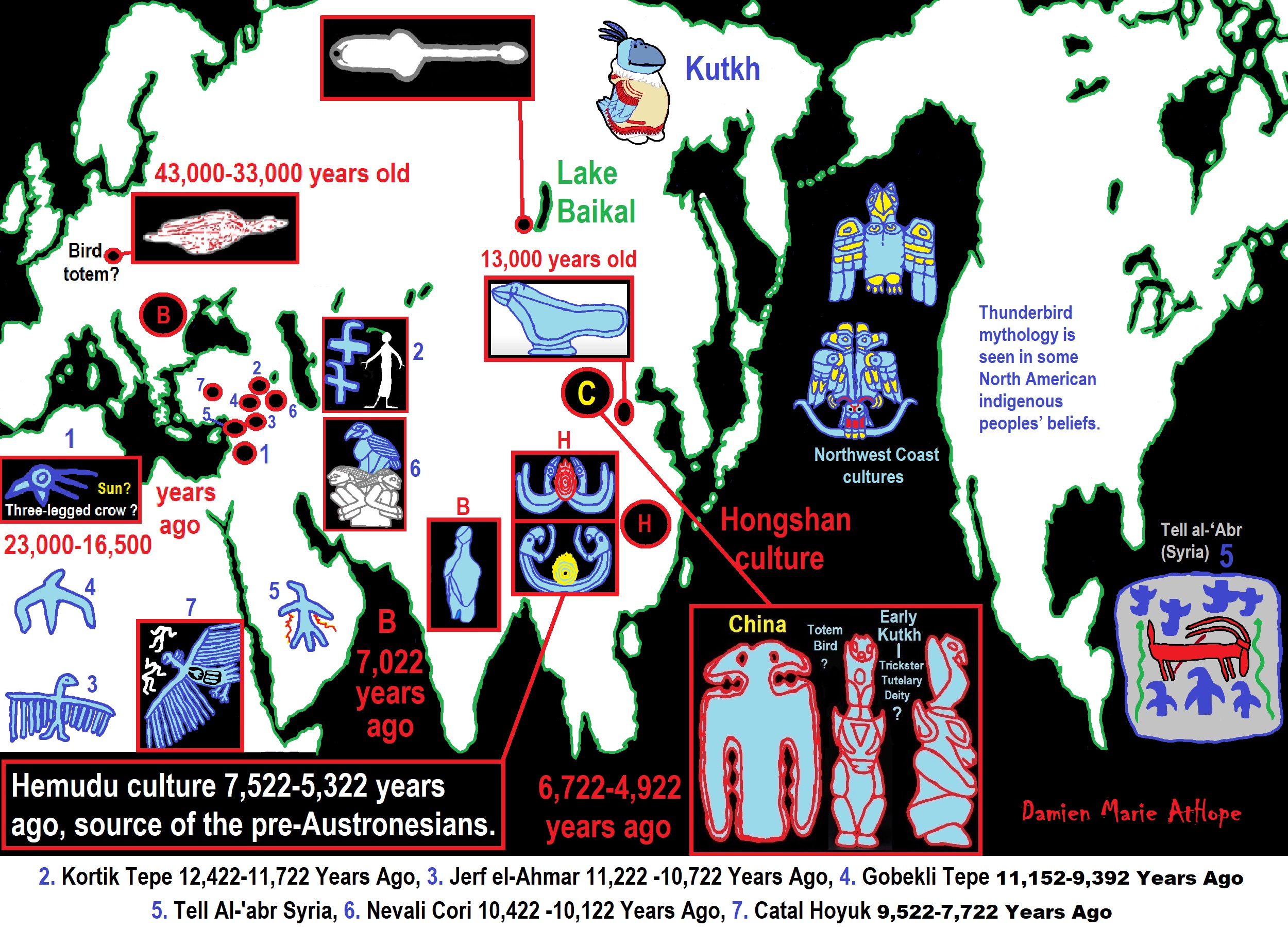

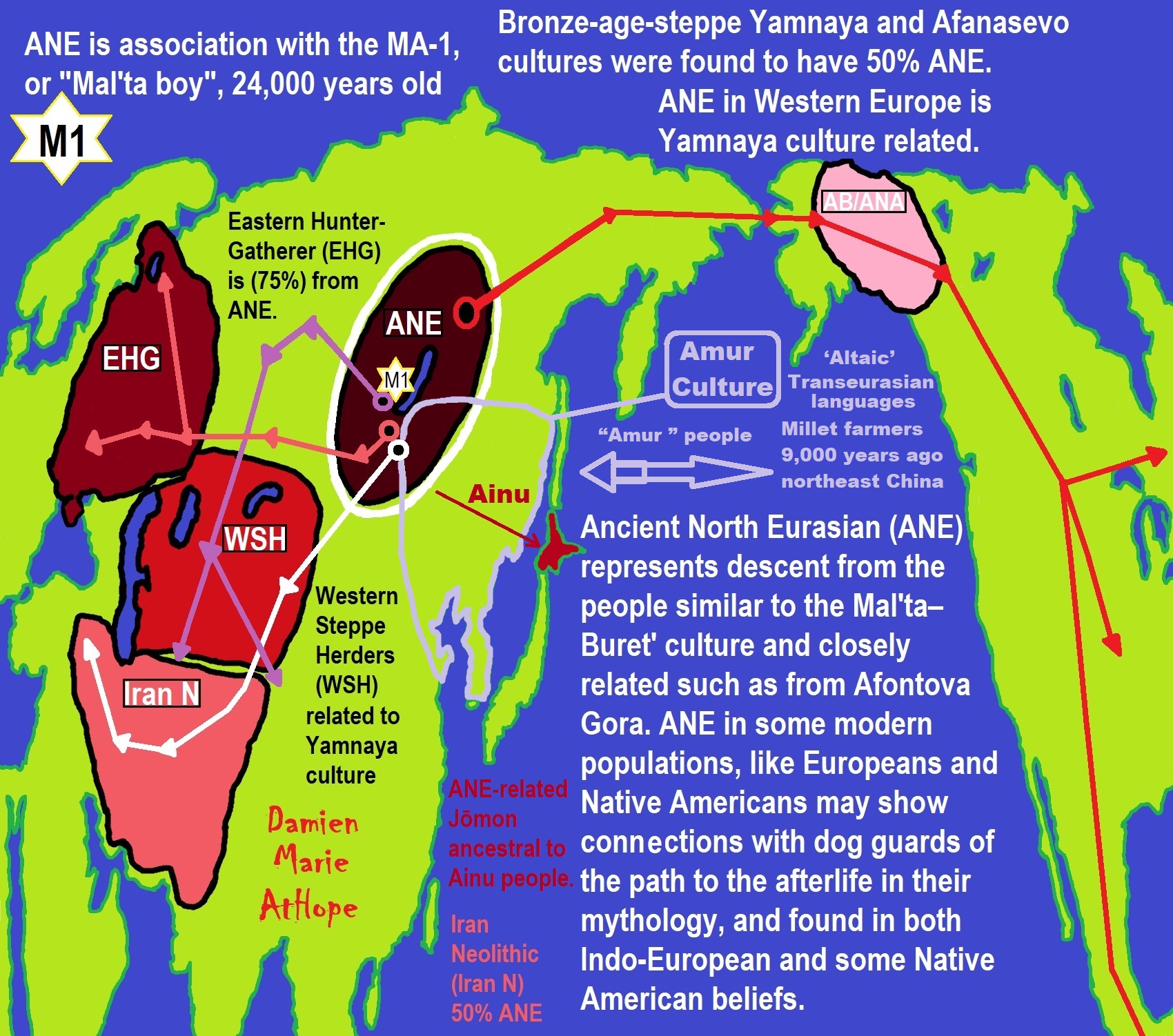

Young Mother goddess, Pregnant Mother goddess, Grandmother goddess:
Young Mother: dawn or new crescent moon
Pregnant Mother: noon, full sun, or full moon
Grandmother: setting sun or dying crescent moon
Bible god arrangement: “Father, Son, Holy Ghost”
Father: dawn or new crescent moon
Son: noon, full sun, or full moon
Holy Ghost: setting sun or dying crescent moon
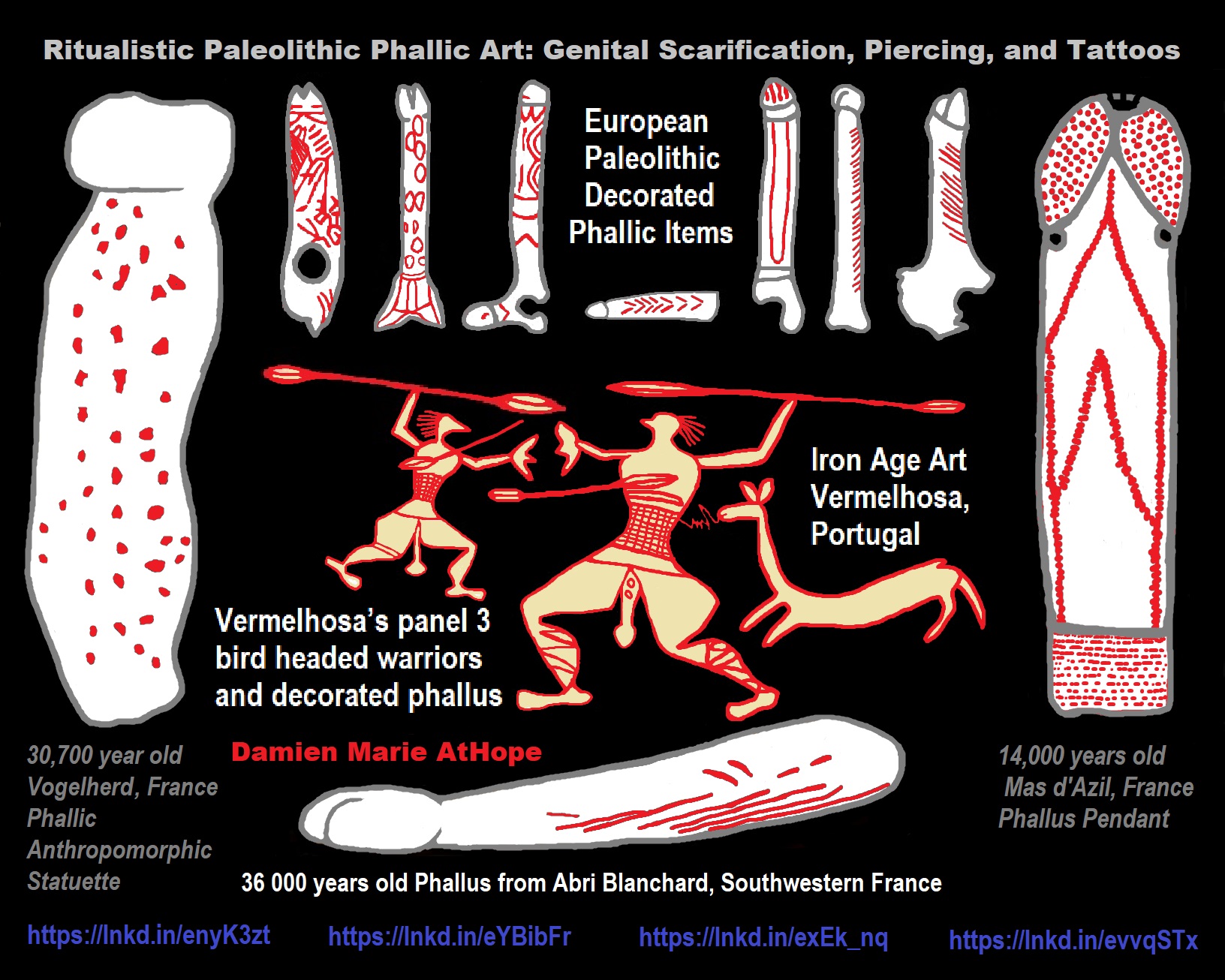
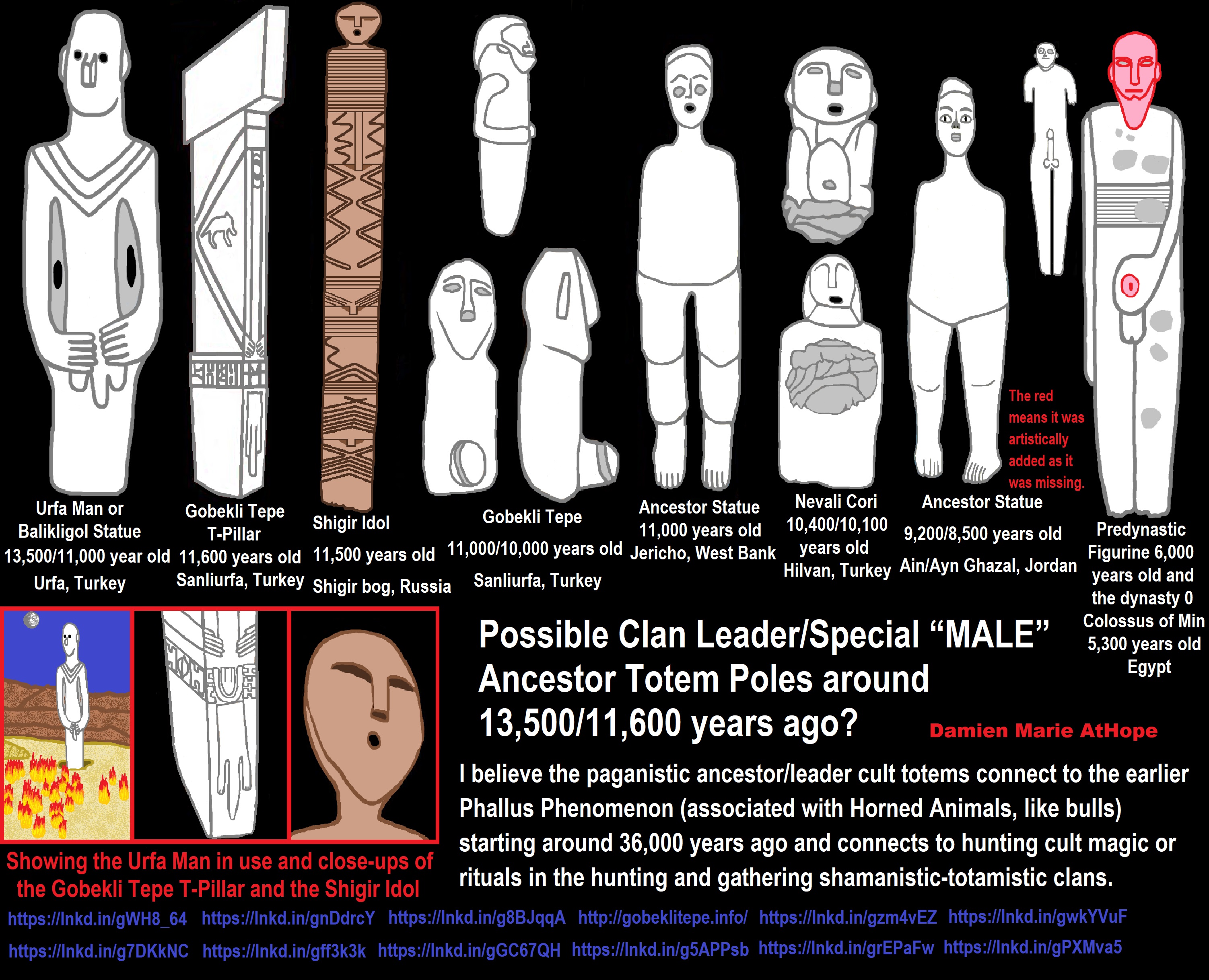
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
I believe the paganistic ancestor/leader cult totems connect to the earlier Phallus Phenomenon (associated with Horned Animals, like bulls) starting around 36,000 years ago and connects to hunting cult magic or rituals in the hunting and gathering shamanistic-totamistic clans.
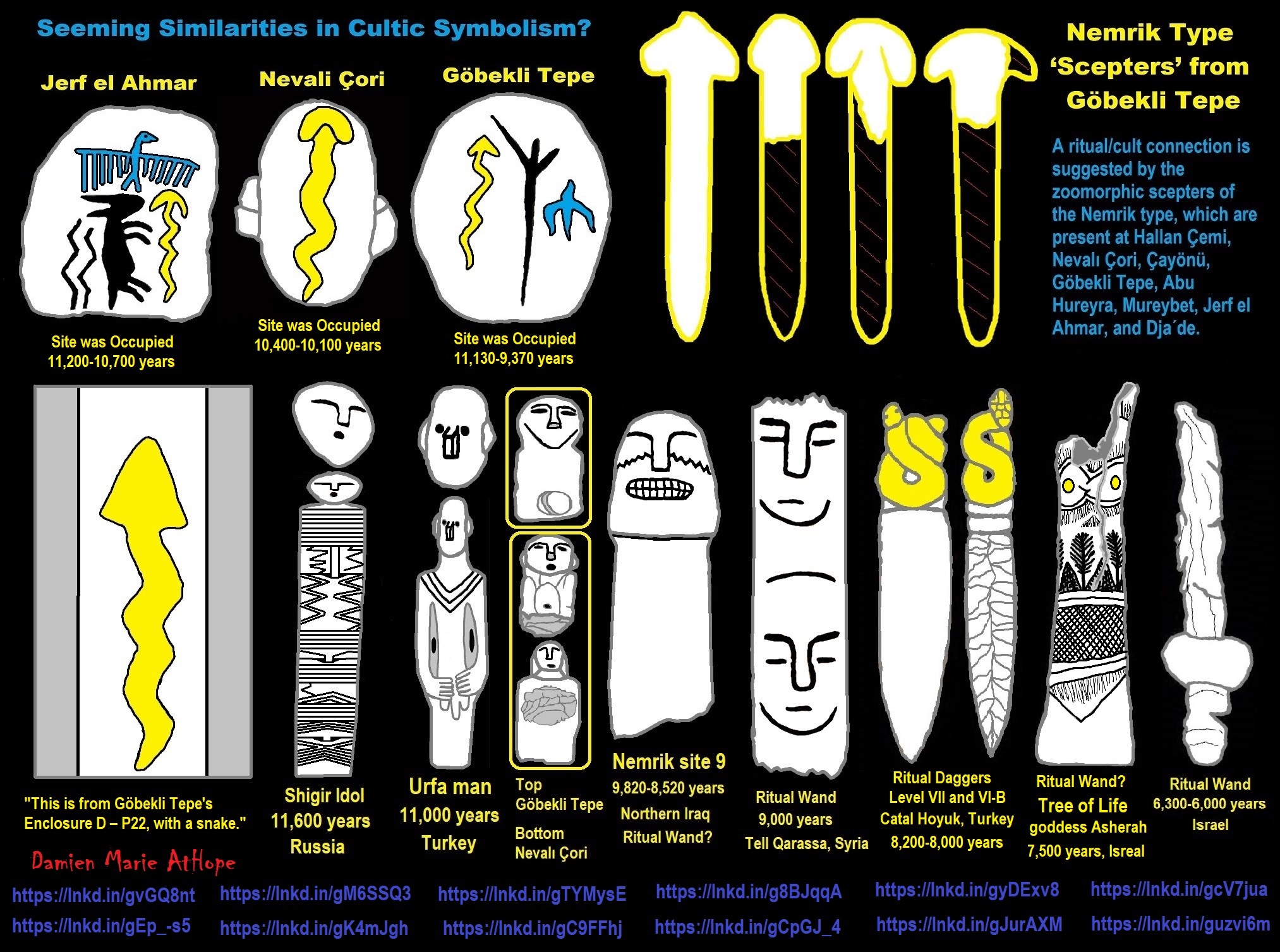


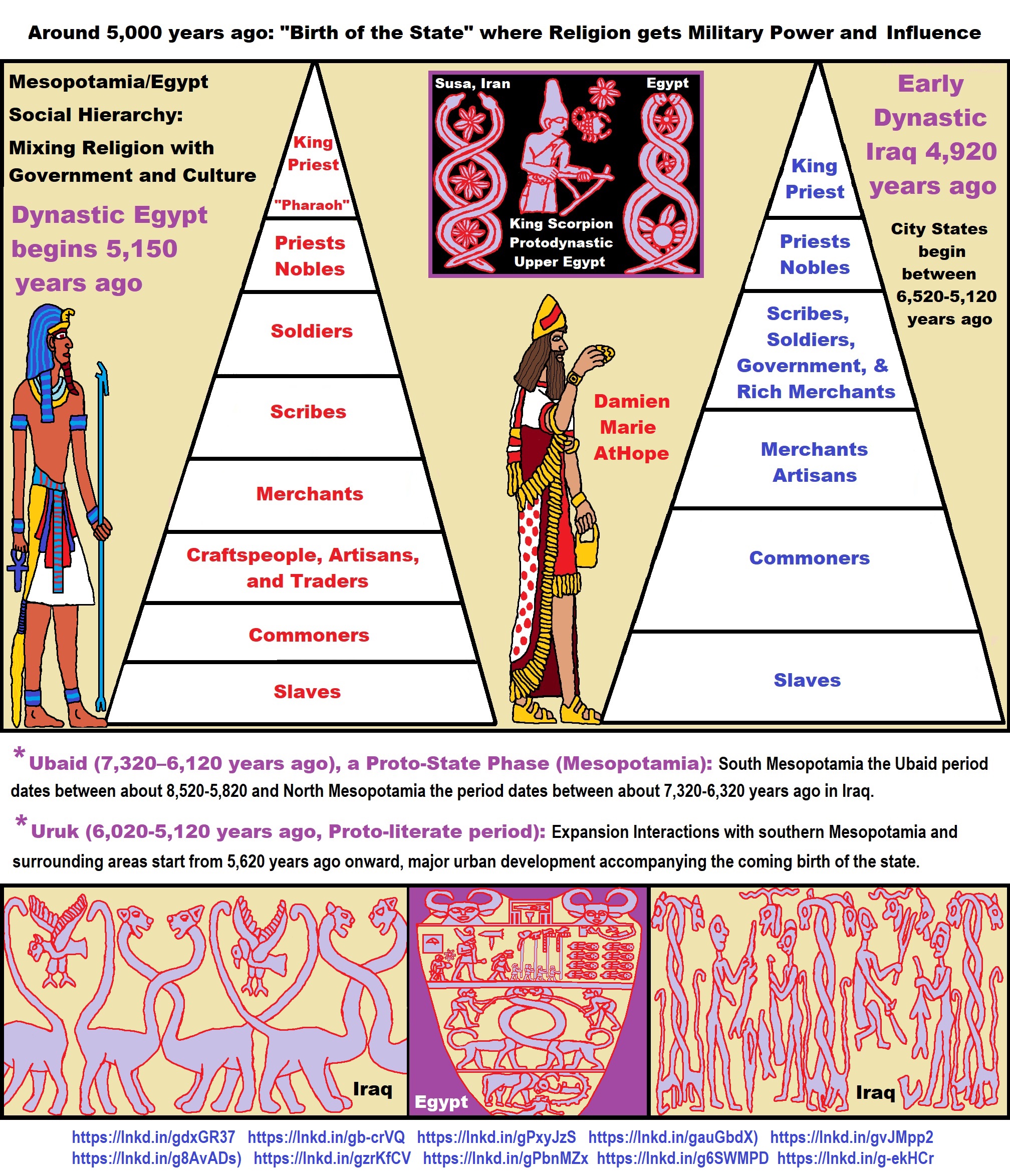
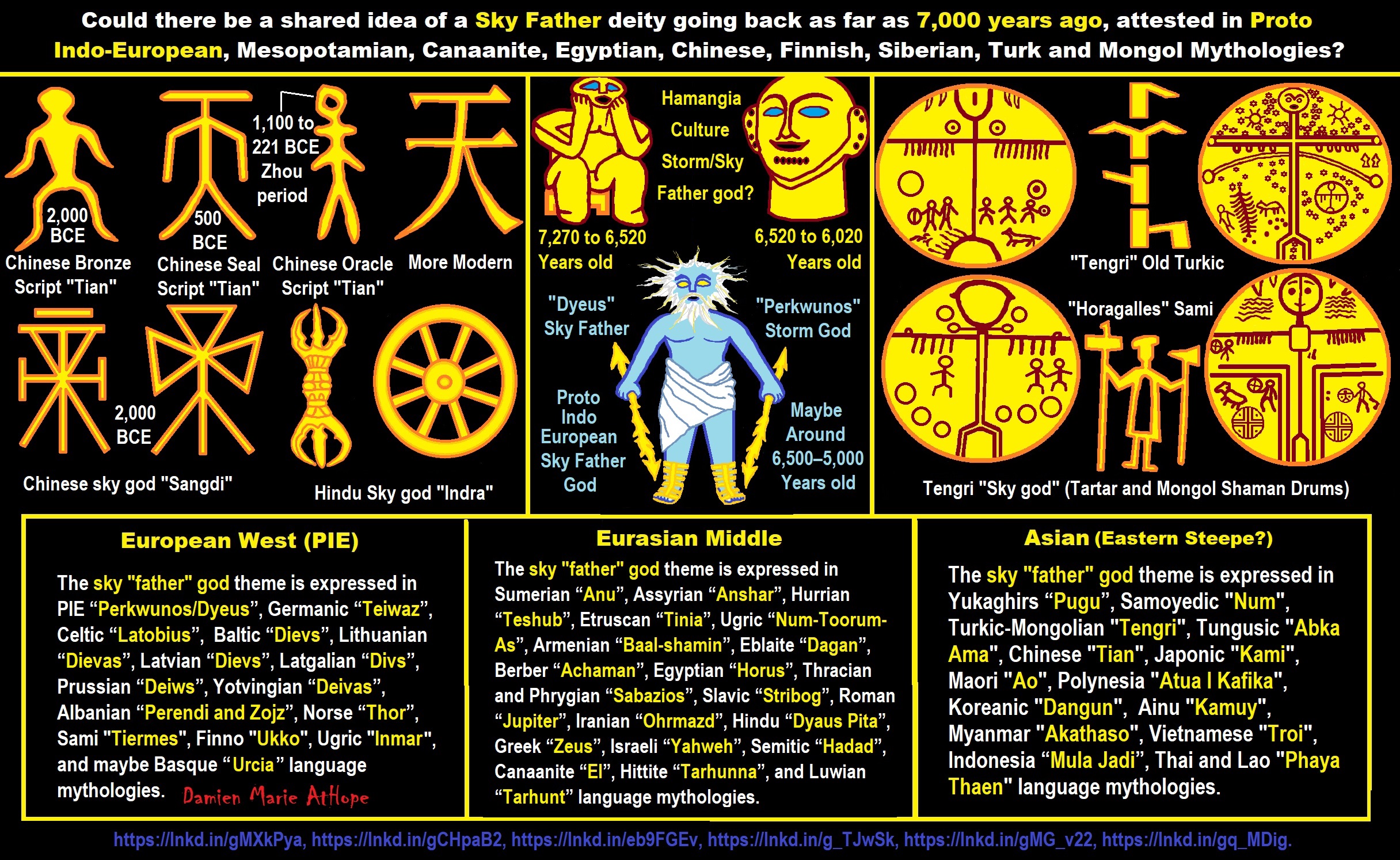
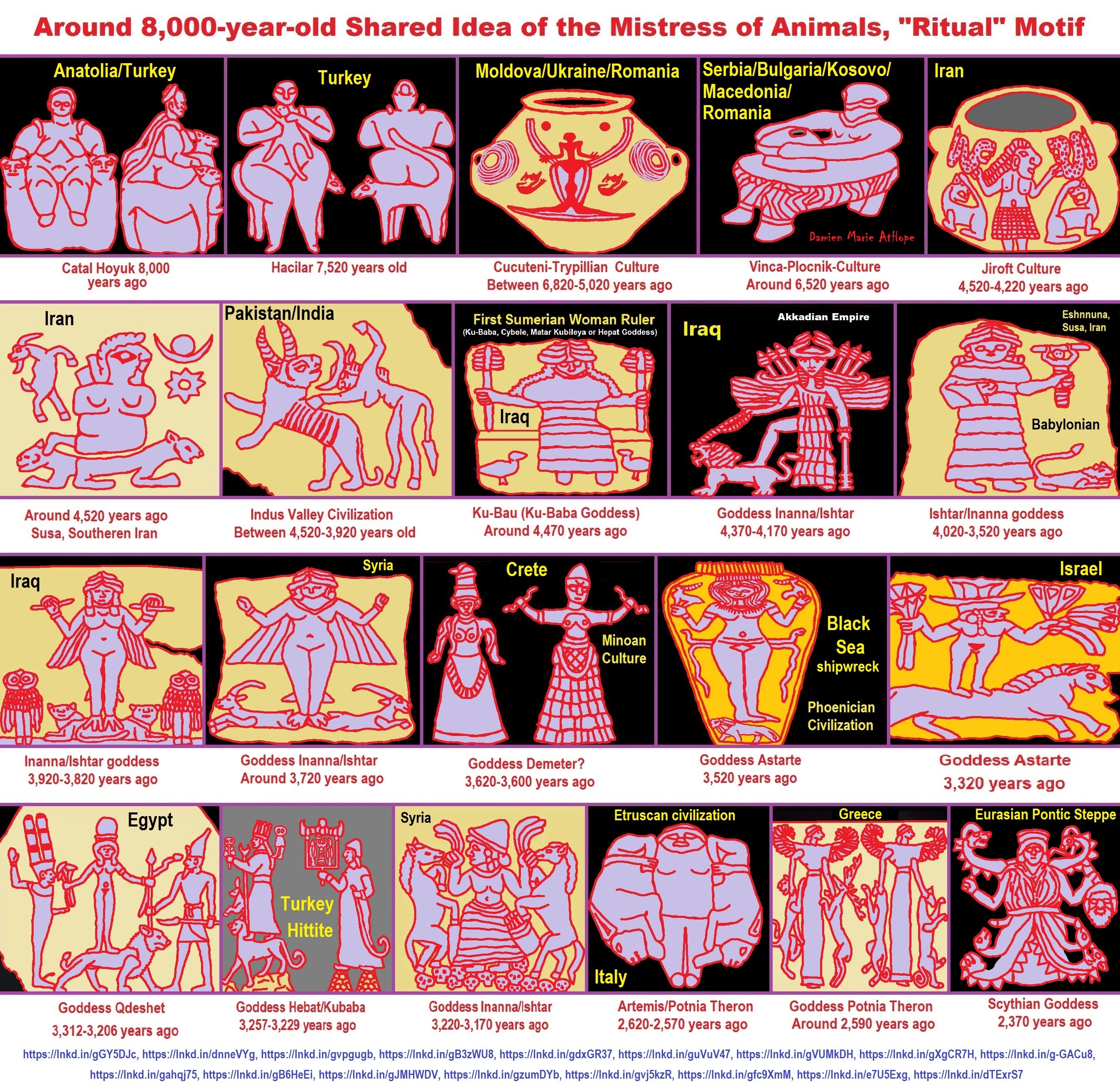
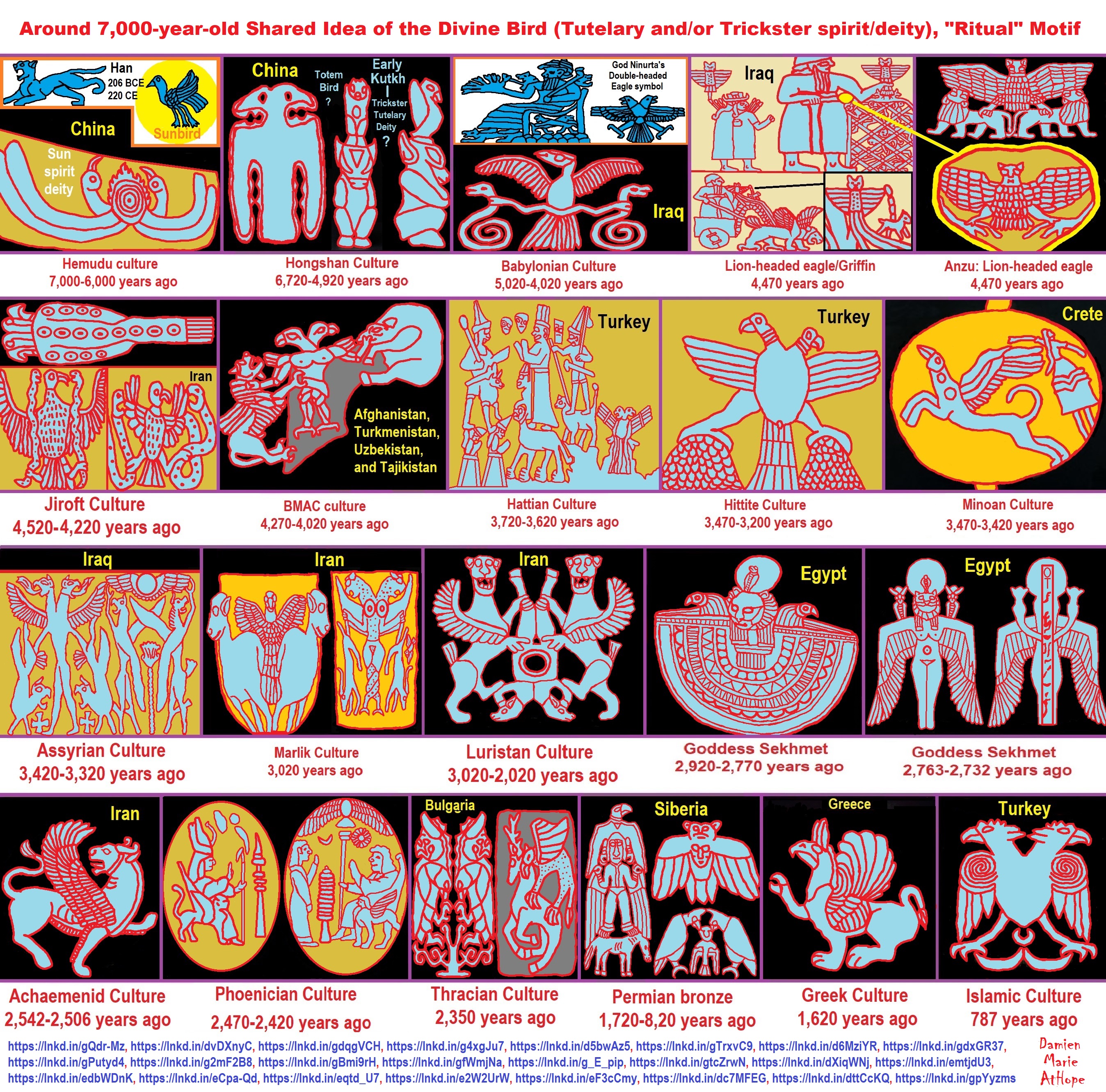
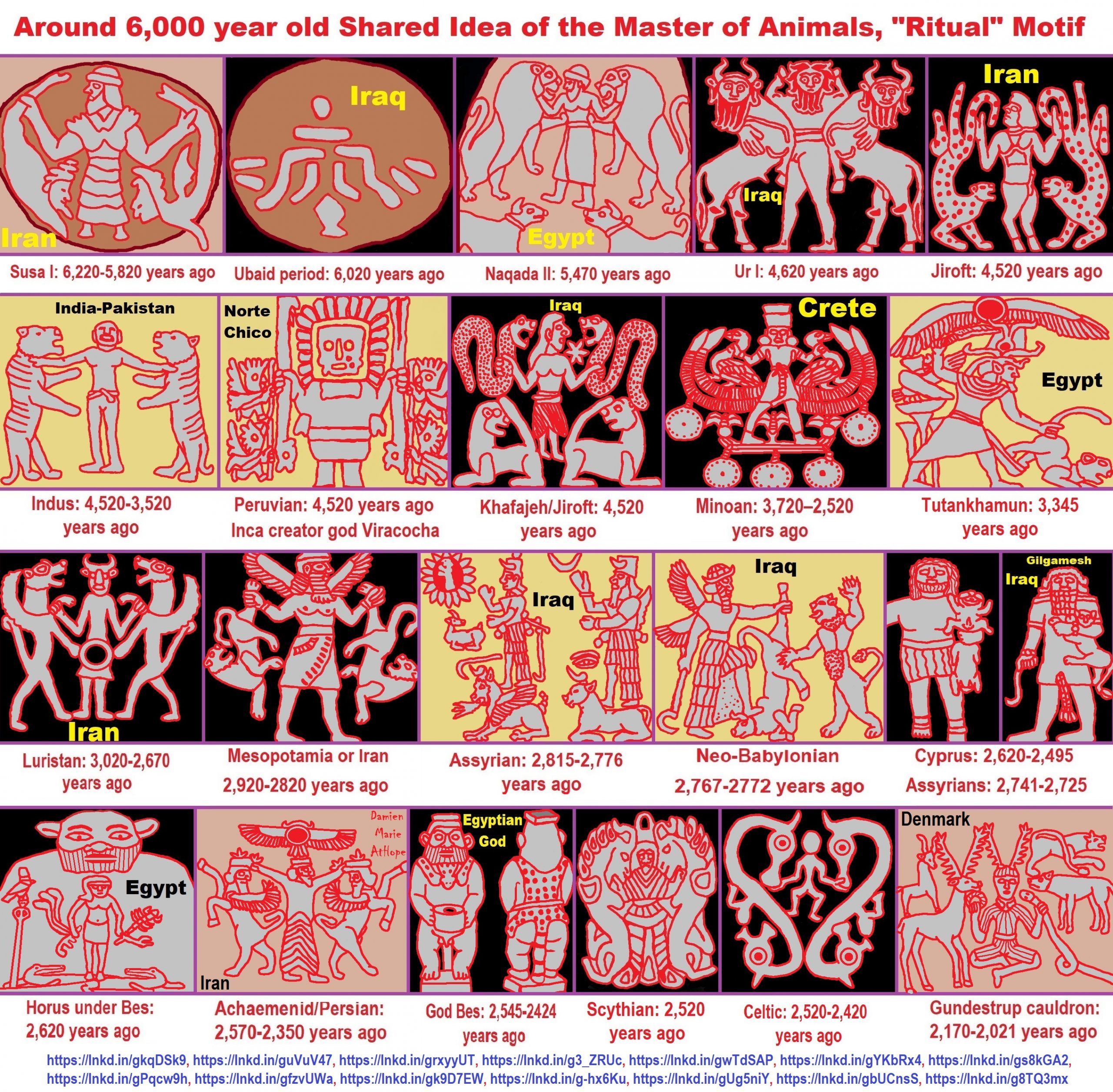
Next are a few to get the context of art and animals to stars or other “sky” bodies/elements.





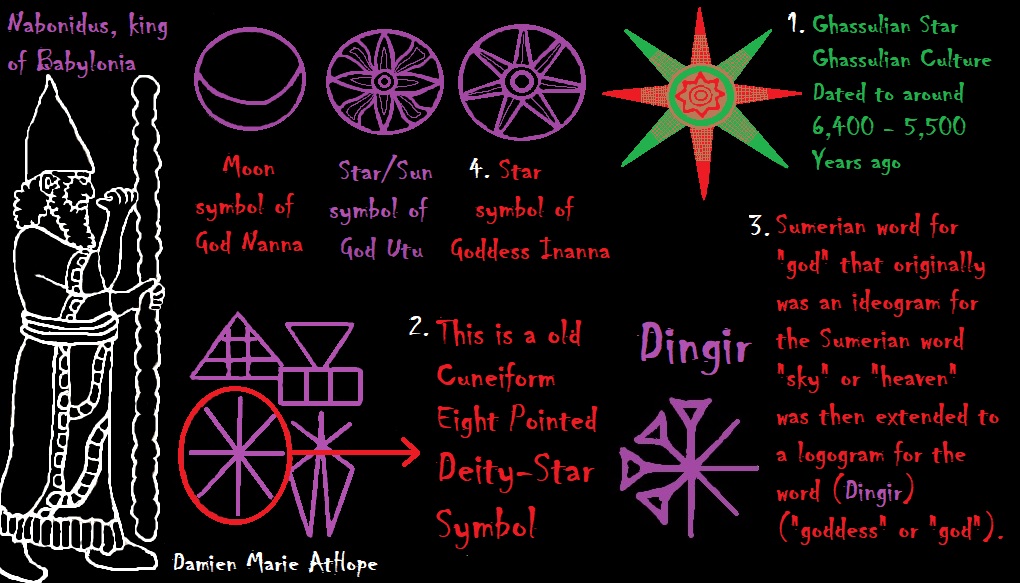


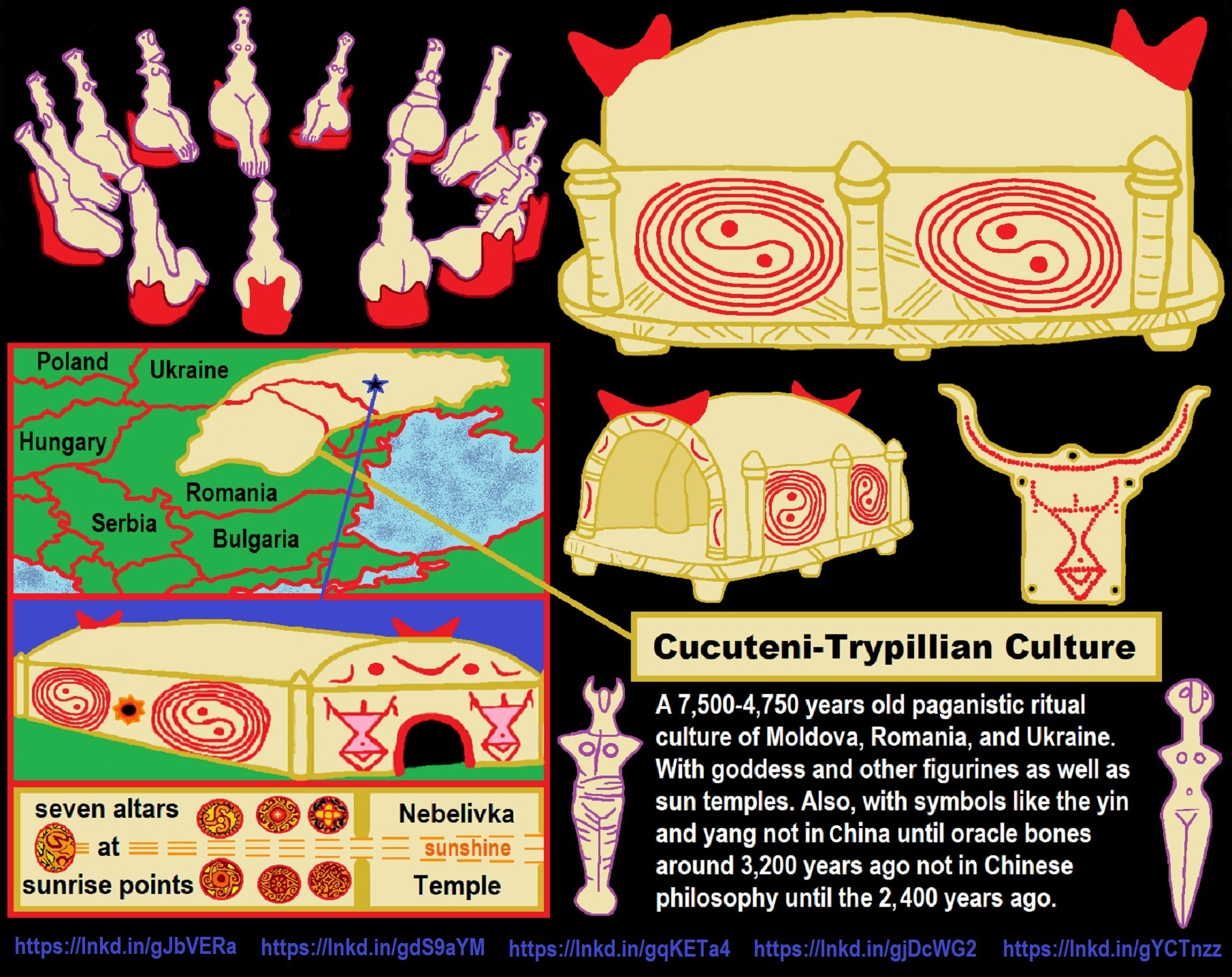
Totemism: an approximately
50,000-year-old belief system?
In a general way, Totemism is sacralizing relationships expressed
by metaphorical connection imparted items or behavior with people.
Seen most commonly in current religious food taboos and sacrifice as well as sacred art
(whether real or metaphorical and be it a behavior, thing, or person being sacrificed).
“A totem is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage, or tribe.” – Wikipedia
Totemism | religion | Britannica.com
“Totemism, system of belief in which humans are said to have kinship or a mystical relationship with a spirit-being, such as an animal or plant. The entity, or totem, is thought to interact with a given kin group or an individual and to serve as their emblem or symbol. The term totemism has been used to characterize a cluster of traits in the religion and in the social organization of many peoples.
Totemism is manifested in various forms and types in different contexts and is most often found among populations whose traditional economies relied on hunting and gathering, mixed farming with hunting and gathering, or emphasized the raising of cattle. The term totem is derived from the Ojibwa word ototeman, meaning “one’s brother-sister kin.” The grammatical root, ote, signifies a blood relationship between brothers and sisters who have the same mother and who may not marry each other. In English, the word totem was introduced in 1791 by a British merchant and translator who gave it a false meaning in the belief that it designated the guardian spirit of an individual, who appeared in the form of an animal—an idea that the Ojibwa clans did indeed portray by their wearing of animal skins. It was reported at the end of the 18th century that the Ojibwa named their clans after those animals that live in the area in which they live and appear to be either friendly or fearful. The first accurate report about totemism in North America was written by a Methodist missionary, Peter Jones, himself an Ojibwa, who died in 1856 and whose report was published posthumously. According to Jones, the Great Spirit had given toodaims(“totems”) to the Ojibwa clans, and because of this act, it should never be forgotten that members of the group are related to one another and on this account may not marry among themselves. ref, ref
Totemism is a complex of varied ideas and ways of behavior based on a worldview drawn from nature. There are ideological, mystical, emotional, reverential, and genealogical relationships of social groups or specific persons with animals or natural objects, the so-called totems. It is necessary to differentiate between group and individual totemism. These forms share some basic characteristics, but they occur with different emphases and in different specific forms. For instance, people generally view the totem as a companion, relative, protector, progenitor, or helper, ascribe to it superhuman powers and abilities, and offer it some combination of respect, veneration, awe, and fear. Most cultures use special names and emblems to refer to the totem, and those it sponsors engage in partial identification with the totem or symbolic assimilation to it. There is usually a prohibition or taboo against killing, eating, or touching the totem. Although totems are often the focus of ritual behavior, it is generally agreed that totemism is not a religion. ref, ref
Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
Did Neanderthals Help Inspire Totemism? Because there is Art Dating to Around 65,000 Years Ago in Spain? Totemism as seen in Europe: 50,000 years ago, mainly the Aurignacian culture. Pre-Aurignacian “Châtelperronian” (Western Europe, mainly Spain and France, possible transitional/cultural diffusion between Neanderthals and Humans around 50,000-40,000 years ago). Archaic–Aurignacian/Proto-Aurignacian Humans (Europe around 46,000-35,000). And Aurignacian “classical/early to late” Humans (Europe and other areas around 38,000 – 26,000 years ago).
Totemism is approximately a 50,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden totemist.
Toetmism may be older as there is evidence of what looks like a Stone Snake in South Africa, which may be the “first human worship” dating to around 70,000 years ago. Many archaeologists propose that societies from 70,000 to 50,000 years ago such as that of the Neanderthals may also have practiced the earliest form of totemism or animal worship in addition to their presumably religious burial of the dead. Did Neanderthals help inspire Totemism? There is Neanderthals art dating to around 65,000 years ago in Spain. ref, ref
Totemism can certainly include religious elements in varying degrees, just as it can appear conjoined with magic. Totemism is frequently mixed with different kinds of other beliefs, such as ancestor worship, ideas of the soul, or animism. Such mixtures have historically made the understanding of particular totemistic forms difficult. Social or collective totemism is the most widely disseminated form of this belief system. It typically includes one or more of several features, such as the mystic association of animal and plant species, natural phenomena, or created objects with unilineally related groups (lineages, clans, tribes, moieties, phratries) or with local groups and families; the hereditary transmission of the totems (patrilineal or matrilineal); group and personal names that are based either directly or indirectly on the totem; the use of totemistic emblems and symbols; taboos and prohibitions that may apply to the species itself or can be limited to parts of animals and plants (partial taboos instead of partial totems); and a connection with a large number of animals and natural objects (multiplex totems) within which a distinction can be made between principal totems and subsidiary ones (linked totems). ref, ref
Group totems are generally associated or coordinated on the basis of analogies or on the basis of myth or ritual. Just why particular animals or natural things—which sometimes possess no economic worth for the communities concerned—were originally selected as totems is often based on eventful and decisive moments in a people’s past. Folk traditions regarding the nature of totems and the origin of the societies in question are informative, especially with regard to the group’s cultural presuppositions. For example, a group that holds that it is derived directly or indirectly from a given totem may have a tradition in which its progenitor was an animal or plant that could also appear as a human being. In such belief systems, groups of people and species of animals and plants can thus have progenitors in common. In other cases, there are traditions that the human progenitor of a kin group had certain favorable or unfavorable experiences with an animal or natural object and then ordered that his descendants respect the whole species of that animal. Group totemism was traditionally common among peoples in Africa, India, Oceania (especially in Melanesia), North America, and parts of South America. These peoples include, among others, the Australian Aborigines, the African Pygmies, and various Native American peoples—most notably the Northwest Coast Indians (predominantly fishermen), California Indians, and Northeast Indians. Moreover, group totemism is represented in a distinctive form among the Ugrians and west Siberians (hunters and fishermen who also breed reindeer) as well as among tribes of herdsmen in north and Central Asia. ref, ref
Individual totemism is expressed in an intimate relationship of friendship and protection between a person and a particular animal or a natural object (sometimes between a person and a species of animal); the natural object can grant special power to its owner. Frequently connected with individual totemism are definite ideas about the human soul (or souls) and conceptions derived from them, such as the idea of an alter ego and nagualism—from the Spanish form of the Aztec word naualli, “something hidden or veiled”—which means that a kind of simultaneous existence is assumed between an animal or a natural object and a person; i.e., a mutual, close bond of life and fate exists in such a way that in case of the injury, sickness, or death of one partner, the same fate would befall the other member of the relationship. Consequently, such totems became most strongly tabooed; above all, they were connected with family or group leaders, chiefs, medicine men, shamans, and other socially significant persons. Studies of shamanism indicate that individual totemism may have predated group totemism, as a group’s protective spirits were sometimes derived from the totems of specific individuals. To some extent, there also exists a tendency to pass on an individual totem as hereditary or to make taboo the entire species of animal to which the individual totem belongs. Individual totemism is widely disseminated. It is found not only among tribes of hunters and harvesters but also among farmers and herdsmen. Individual totemism is especially emphasized among the Australian Aborigines and the American Indians. Among the Wiradjuri, an Aboriginal people who traditionally lived in New South Wales (Australia), totem clans are divided among two subgroups and corresponding matrilineal moieties. ref, ref
The group totem, named “flesh,” is transmitted from the mother. In contrast to this, individual totems belong only to the medicine men and are passed on patrilineally. Such an individual totem is named bala, “spirit companion,” or jarawaijewa, “the meat (totem) that is within him.” There is a strict prohibition against eating the totem. Breach of the taboo carries with it sickness or death. It is said: “To eat your jarawaijewa is the same as if you were to eat your very own flesh or that of your father.” The medicine man identifies himself with his personal totem. Every offense or injury against the totem has its automatic effect upon the man who commits it. It is a duty of the totem to guard the ritualist and the medicine man while he is asleep. In the case of danger or the arrival of strangers, the animal goes back into the body of the medicine man and informs him. After the death of the medicine man, the animal stands watch as a bright flickering light near the grave. The individual totem is also a helper of the medicine man. The medicine man emits the totem in his sleep or in a trance so that it can collect information for him. In this tradition, sorcery may also be practiced by the medicine man. ref, ref
By singing, for instance, the medicine man can send out his totem to kill an enemy; the totem enters the chest of the enemy and devours his viscera. The transmission of the individual totem to novices is done through the father or the grandfather, who, of course, himself is also a medicine man. While the candidate lies on his back, the totem is “sung into” him. The blood relative who is transmitting the totem takes a small animal and places it on the chest of the youngster. During the singing, the animal supposedly sinks slowly into his body and finally disappears into it. The candidate is then instructed on how he has to treat the animal that is his comrade, and he is further instructed in song and the ritual concentration that is necessary to dispatch the totem from his body. Among the Nor-Papua of New Guinea, patrilineal, exogamous groups (consanguineous sibs) are spread over several villages and are associated with animals, especially fish. They believe that they are born from totems, and they make them taboo. Children are given an opportunity to decide during their initiation whether they will respect the paternal or maternal totem. ref, ref
Each group of relatives has a holy place to which the totem animal brings the souls of the dead and from which the souls of children are also believed to come. Totem animals are represented in various manifestations: as spirit creatures in sacred flutes, in disguises, and in figures preserved in each man’s house. At the end of initiation ceremonies, the totems are mimicked by the members of the group. Among the Iban of Sarawak (Malaysia), individual totemism has been the tradition. Particular persons dream of a spirit of an ancestor or a dead relative; this spirit appears in a human form, presents himself as a helper and protector, and names an animal (or sometimes an object) in which he is manifested. The Iban then observe the mannerisms of animals and recognize in the behavior of the animals the embodiment of their protector spirit (ngarong). Sometimes, members of the tribe also carry with them a part of such an animal. Not only this particular animal, but the whole species, is given due respect. Meals and blood offerings are also presented to the spirit animal. Young men who wish to obtain such a protector spirit for themselves sleep on the graves of prominent persons or seek out solitude and fast so that they may dream of a helper spirit. ref, ref
Actually, only a few persons can name such animals as their very own. Individuals with protector spirits have also attempted to require from their descendants the respect and the taboo given the animal representing the spirit. As a rule, such descendants do not expect special help from the protector spirit, but they observe the totemistic regulations anyway. The Birhor, a people that were traditionally residents of the jungle of Chotanagpur Plateau in the northeast Deccan (India), are organized into patrilineal, exogamous totem groups. According to one imperfect list of 37 clans, 12 are based on animals, 10 on plants, 8 on Hindu castes and localities, and the rest on objects. The totems are passed on within the group, and tales about the tribe’s origins suggest that each totem had a fortuitous connection with the birth of the ancestor of the clan. The Birhor think that there is a temperamental or physical similarity between the members of the clan and their totems. Prohibitions or taboos are sometimes cultivated to an extreme degree. ref, ref
In regard to eating, killing, or destroying them, the clan totems are regarded as if they were human members of the group. Moreover, it is believed that an offense against the totems through a breach of taboo will produce a corresponding decrease in the size of the clan. If a person comes upon a dead totem animal, he must smear his forehead with oil or a red dye, but he must not actually mourn over the animal; he also does not bury it. The close and vital relationship between the totem and the clan is shown in a definite ceremony: the yearly offering to the chief spirit of the ancestral hill. Each Birhor community has a tradition of an old settlement that is thought to be located on a hill in the area. Once a year, the men of each clan come together at an open place. ref, ref
The elder of the clan functions as the priest who gives the offering. A diagram with four sections is drawn on the ground with rice flour. In one of these, the elder sits while gazing in the direction of the ancestral hill. The emblem of the particular totem is placed in one of the other sections of the diagram; depending on the circumstances, this emblem could be a flower, a piece of horn or skin, a wing, or a twig. This emblem represents the clan as a whole. If an animal is needed for such a ceremony, it is provided by the members of another clan who do not hold it as a totem. The Birhor show great fear of the spirits of the ancestral hill and avoid these places as far as possible. Among the Kpelle people of Liberia there is not only group totemism but also individual totemism. ref, ref
Both kinds of totems are referred to variously as “thing of possession,” “thing of birth,” or “thing of the back of men.” These phrases express the idea that the totem always accompanies, belongs to, and stands behind one as a guide and warner of dangers. The totem also punishes the breach of any taboo. Kpelle totems include animals, plants, and natural phenomena. The kin groups that live in several villages were matrilineal at an earlier time, but during the 20th century they began to exhibit patrilineal tendencies. The group totems, especially the animal totems, are considered as the residence of the ancestors; they are respected and are given offerings. ref, ref
Moreover, a great role is played by individual totems that, in addition to being taboo, are also given offerings. Personal totems that are animals can be transmitted from father to son or from mother to daughter; on the other hand, individual plant totems are assigned at birth or later. The totem also communicates magical powers. It is even believed possible to alter one’s own totem animal; further, it is considered an alter ego. Persons with the same individual totem prefer to be united in communities. The well-known leopard confederation, a secret association, seems to have grown out of such desires. Entirely different groups produce patrilineal taboo communities that are supposedly related by blood; they comprise persons of several tribes. The animals, plants, and actions made taboo by these groups are not considered as totems. In a certain respect, the individual totems in this community seem to be the basis of group totemism.” ref
50,000 – 40,000 Years Ago – (Africa), found evidence of a marked increase in the diversity of artifacts including art appear along with diversity of food accusation with evidence of human fishing. The artifacts of Africa that can be classified as less than 50,000 years become more differentiated and technologically advanced such as projectile points, engraving tools, knife blades, and drilling and piercing tools. Likewise, by this time humans had evolved the traits associated with modern human behavior and findings suggests that cave art became somewhat common by around 40,000 years ago and after. Modern human behavior includes abilities such as modern language, abstract thought, symbolism, and some form of early religion. Like most behaviors that are found in societies throughout the world, some form of religion must have been present in the ancestral human population before the dispersal from Africa. ref, ref, ref, ref
50,000 – 40,000 Years Ago – Le Moustier (France), found evidence of Neanderthal cave burials covered in red ochre, with many stone tools and two young Neanderthal children fossils. In Europe some 50,000 years ago can be seen as the beginning of large bodied animal extinction, so too did their predators shortly after which seems to also include Neanderthals. This extinction of large bodied animal contributing in some party to the eventual extinction which includes Neanderthals is because of their almost total dependence on large bodied animals for fat and protein needs. One of the reasons this is hypothesized beyond just associated animal bones it is inferred in their body structure which had been triggered by an Ice-Age diet.
This Ice-Age diet of fat and high-protein intake from large animals by Neanderthals had caused physical changes specifically wider pelvises and rib-cages compared to modern human. While one of the main causes hypothesized for large bodied animal extinction is natural climate change one of the other is overkill by humans, who appeared as early as 48,000 years ago evidenced in modern human artifact found in South-Central and possibly Eastern Europe similar to artifact probably made by modern humans in the Levant at an earlier date and apparently represent a population movement traveling through Turkey into then the Balkans during a warm climate interval. The earliest known human remains in Europe date to around 42,000 years ago.
And 40,000 years ago a second population movement may be represented by a diverse set of artifact termed Proto-Aurignacian culture found in the Balkans, parts of Southwest Europe, and probably in Eastern Europe are also similar to those made by modern humans in the Levant. After 40,000 years ago is the beginning of Aurignacian culture artifacts which seems to have developed in Europe, spreading throughout the continent. Lastly this modern human migration did not just likely assisting in animal extinction but also started a ”creative explosion” associated with the wonderful cave paintings in Chauvet Cave in France 36,000 years ago. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
50,000 – 35,000 Years Ago – (southeast Asia), found evidence humans who arrived over 50,000 years ago brought with them an artistic skill, produced paintings of naturalistic animals in rock shelters in southwest China, Indonesia, Thailand, Cambodia, and Malaysia. Moreover, early Indonesian rock art seems to show the artistic practice that was brought to Asia and Europe comes from Africa, because the oldest rock art of Southeast Asia is more often found in rock shelters rather than deep caves like in Europe. This significantly supports ideas that the origins of art making are a fundamental human behavior which began with our most ancient ancestors in Africa rather than Europe. If the considerations of the evidence is right it has implications not only for Southeast Asian and European rock art but Australian rock art as well. This is because Australia’s oldest surviving rock art also consists of naturalistic animals, which could show it to was brought from Africa as well.
Putting this seeming global connectedness in rock art is then to consider the origins and functions of the art in terms of two very broad categories: art intended to portray visionary or altered states of consciousness imagery (shamanic); and motifs made to illustrate other subjects and/or created for other reasons (non-shamanic). This distinction roughly, but imperfectly, parallels the difference between shamanic and non-shamanic religions. Shamanistic rock art commonly portrays visionary imagery; symbolizing, in a general sense, a supernatural experience or event. Despite this commonality and depending upon cultural context, the shamanistic rock art was made for a variety of purposes by a full range of social and gender groups beyond the shaman alone. Shamanism is part of a broader trend in early prehistory and is still found in contemporary peoples as well.
The common aspects of many shamanic belief systems are: 1) the concept of the three-tiered world with an upper world (world of spirits), middle world (world of living), and underworld (world of the dead) often linked by some natural aspect as a representation such as a tree, pillar, mountain, lake, or river; 2) the world is perceived as inhabited by supernatural beings; 3) nature is perceived as a ‘giving environment’, lacking the dichotomization of nature and culture of modern worldviews; 4) ideas of reciprocal relations with animals and the animals need to be treated with respect in order that they continue to give themselves up to the hunter; 5) the concept of the soul as possessed by both humans and animals; 6) the shaman or shamaness (female shaman) is preceded as a religious specialist and mediator between the worlds; and 7) the importance of animals. ref, ref
45,000 Years Ago – Ust’-Ishim (western Siberia), found evidence of an early modern human male, who’s DNA shows he belonged to the same group of early humans as the Mal’ta boy, who lived 24,000 years ago, part of the Mal’ta-Buret’ culture (24,000 to 15,000). The Mal’ta people belonged to a population which may have made a substantial contribution to the genetic ancestry of the American Indians.
The Ust’-Ishim man’s DNA is more closely related to the East Asians of today than to today’s Europeans and the evidence shows that his ancestors mixed with Neanderthals close to the time of the major expansion of modern humans out of Africa and the Middle East. They found that between one and two mutations per year have accumulated in the genomes of populations in Europe and Asia since the Ust’-Ishim man lived. This is similar to recent estimates from counting genetic differences between parents and children but lower than more traditional, indirect estimates based on fossil divergences between species. (108) ref
43,500 – 42,300 Years Ago – Malaga (Spain), found evidence of Neanderthal red looking cave paintings as well as charcoal remains found beside six of the paintings. Modern humans are believed to have also been in the area at the time, arriving about 41,500 years ago and although this does add credence to the case for Neanderthal art it does not prove that it was made by Neanderthals. ref, ref
43,000 Years Ago – “Lion Cave” Swaziland (southern Africa), found evidence of one of the oldest known mines and in contrast to the majority of prehistoric mines, was a red ochre mine not mined for materials for standard utilitarian items for tool making but can and where used in ritualistic concepts. This is leads us to ponder the motivation of such a mine red ochre which although it had widespread use in prehistoric it was often in what could lend some support to a religious connotation when used in burial rituals and shamanistic cave art. There are similar age flint mines in Hungary and chert (lower quality flint) mine in Bulgaria believed to be connected to our cousins the Neanderthals who shared about 99.84 % of their DNA with us and seemed to have mined for weapons and tools.
Many Neanderthal sites show them to be more masteries then we typically think such as how such Neanderthal archeological sites include red ochre sometimes worn down in a way that could have been used in an artistic or ritualistic way but we may never know. For too long the term Neanderthal has been conceived as a label of slow thinking brutish nonhuman creatures with human looking features. However, quite the opposite Homo sapiens Neanderthalensis, although still largely unknown, mysterious, or unidentified do show themselves to be more like fellow humans should no longer be seen as mentally inferior to modern humans. The support for this rational involves evidence seeming to show advanced thinking beyond just the craftsmanship of tools belong to utilitarian evidence they had or seem to demonstrates abstract thinking with ritualistic graves, made body ornaments (fathers, animal-tooths or claws and shells pendants), engraved symbols or spots and hand stencils like those in El Castillo cave, Spain as well as others.
Although it must be understood that there is in general only limited evidence relating to Neanderthal culture. There are good circumstantial reasons for thinking that Neanderthals not only had advanced thinking they possibly had some form of language, as some of their advanced technology, rituals and hunting tactics would have been difficult to learn and execute without some form of language, though this is not some full proof it is interesting. Moreover, Neanderthal do also have relatively advanced brains with such things as a well-developed Broca’s area, and in their DNA we find the FOXP2 gene involved in speech production and by the way is carried by modern humans and in us too is required for proper development of speech and language. The FOXP2 gene is more active in females than in males, and mutations of FOXP2 in humans causes a severe speech and language disorder. Versions of FOXP2 exist in similar forms in animals such as in songbirds.
Unfortunately, none of this reveals anything specific about Neanderthal language, socio-cultural, or religious for that matter. And although the full extent of socio-cultural-driven gene-culture coevolution (interaction between genes and culture) is unknown some evidence suggest that such effects were and likely are profound. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
42,000 – 35,000 Years Ago – Hohle Fels (Germany), found a mammoth ivory female figurine called “The Venus of Hohle Fels” may have had some fertility connection and was discovered among flint chips and burnt animal bones. This figurine is about two and a half inches and has a polished nob with a hole like a hoop in place of a head. This top hoop could demonstrate that it may have worn some kind of amulet or pendant. Also a 35,000 years old flute was found made of vulture bone and is thought to be one of the oldest crafted musical instrument in the world. ref, ref, ref
42,000 – 17,000 Years Ago – Ucagizli Cave (southern Turkey), found evidence includes the production and use of large numbers of ornamental shells showing evidence of extended use and appearing to be selected for quality rather that as just as food. There are hundreds shell ornaments alongside well-defined stone, bone tools, and one incised talon probably frim a vulture. A focus on basket-shaped shells changed little over thousands of years, despite significant changes in other technology which almost certainly reflecting the influence of cultural norms suggesting elements of design traditions or symbol systems reflective expression of human communication. ref, ref
40,800 Years Ago – El Castillo Cave (Spain), found evidence of cave paintings that could have been made by Neanderthals. Red colored cave art consisting of hand stencils and disks made by blowing paint onto the wall of the cave, possibly showing more evidence that Neanderthals were possibly some of the first cave painters. ref
40,000 Years Ago – Hohlenstein-Stadel cave (Germany), found evidence of a figurine labeled the Lion man, which is a lion-headed figurine made of mammoth ivory one of the oldest known zoomorphic (animal-shaped) and anthropomorphic (human-traits) sculpture in the world, and is associated with the archaeological titled Aurignacian culture. Also identified was a similar, but smaller, and cruder or warn lion-headed human sculpture dated to around 32,000 to 30,000 years ago, along with other animal figurines found in another cave in the same region of Germany. This leads to the possibility that such figurines may in some way have played an important role in the symbolism or mythology of early humans or may have been seen as a spirit helper or amulet that gave power or safety or the like.
I think the belief in spirits came long before the idea of goddesses or gods. Following these discoveries, female figurines from approximately the same prehistoric period, such as the Venus of Hohle Fels, where discovered in the same mountainous area of Germany. ref
40,000 – 30,000 Years Ago – Laura, Queensland (Australia), found evidence at Sandy Creek Shelter cupules “cut cup-holes” and cut marks thought to represent vulva-forms are found through the world on every continent and some of the oldest rock art is linear grooves and cupules, often ignored as utilitarian rock markings. Engraved or incised cups or pits may hold different, similar, or connected meaning and within the limits of Native California alone there seems to have been three ritual origins and known purposes.
In Northern California, cupules were called ‘rain-rocks’ and they were made by shamans to bring either rain or the wind ceremony conducted by shamans making non-visionary rock art. In Central California (in the San Francisco Bay region), so-called ‘pit-and-groove’ rocks known as ‘baby rocks’ were created during a private fertility rite. This shamanistic ritual was done mainly by women having a difficulty conceiving who would rub the rocks collect the dust as there was a belief supernatural power existed within rocks, which was placed in the woman’s vagina and sometimes on other parts of both people prior to intercourse. In south-central California and the Great Basin girls also made cupules during puberty initiations by grinding briefly in all of the cups on a given rock, the girls were said to reconnect with all of the earlier and older women of the tribe.
All of this represents non-visionary art created by shamans and non-shamans within the context of shamanistic cultures and thus means hypothetically we can conceive that other cupules may be more than just art and may have some connections too religion. Moving further we can look to Hawaiian women perform a ritual following childbirth for the baby’s health by preserving the umbilical cord and creating cupule symbolic of the bellybutton and thus the child’s connection to its mother. Again we can see cupules and similar kinds of rock art worldwide many also have ritual origins or functions. The vulva-form motifs are mostly seen as engravings on stone, bone, or ivory as well as paintings and though found worldwide are almost invariably interpreted as evidence of fertility rituals of some kind. To support this reasoning we can look to Polynesian girls’ puberty ceremonies involved a ‘clitoris stretching’ ceremony, for example, after which an engraved ‘portrait’ of the girl’s genitalia was created. ref, ref, & ref
40,000 – 10,000 Years Ago – (Europe), found evidence of several figurines mostly female, although a few are known which are no gendered or (fewer still) definitely male thus the title of ‘venus’ is often attached to the figurines found, implying female sexuality and believed goddess status though this is more speculative then confirmed. Although some proclaimed, the first god was a goddess which I believe is a likely possibility the socio-cultural-religious meaning or use of these figures may never be known.
So even if they were believed to be goddess this did not mean that there was full equality of women, any more then Barack Obama being president means there is no more racism. For the most part even where this could be so that meaning or use of these figures was as goddess and that a first theme in religion was woman as the first god believed indicated by the figurines, it still could possibly be presumed to serve male purposes, and more rightly be related to fertility and sexuality than a valuing of female status as some think such things would confirm. ref
39,000 Years Ago – Gorham’s Cave (Spain) found markings considered Neanderthal “abstract art” in a natural sea cave located in the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. This art was presumably done not just by Neanderthals but buy some of the last known Neanderthals habitations in Europe and where they left some strange markings that while unrepresentative of direct representation but as it took effort must of been some meaning; possibly art, ritual or some reflective design. There are three levels of design: visceral (what nature does), behavioral (all about use), and reflective (all about the message). That said what the markings may mean, however, is anyone’s guess.
It can be certain it was not Humans as they did not show up for more than 10,000 years later which is long after Neanderthals were gone. We cannot get into the minds of these people but it looks geometric with a crisscross patterning and perhaps it represents some kind of art, map or ritual. However, what is clear is that it is abstract, deliberate, and speaks to their cognition identifying a symbolic behavior on the part of Neanderthals. There are three other caves are the nearby one of which is Vanguard Cave supplied evidence that Neanderthals diet included fish such as Bluefin tuna and marine animals like monk seal, dolphin, mollusks, and sea urchins.
Neanderthals were driven into extinction because of modern humans who might have competed with or simply assimilated Neanderthals into their populations when they appeared in southern Europe about 42,000 years ago. It is either modern humans caused, directly or indirectly, led to the end of Neanderthals. It is also possible that Neanderthals may have been near extinction before modern humans arrived (decline in genetic diversity) even if they assisted in Neanderthal extinction after they arrived. Moreover, modern humans having a greater technological and cultural development along with group size is also thought to have a factor in Neanderthal extinction not that Neanderthals didn’t have some culture but also tended to have much smaller clans. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
39,900 – 35,400 Years Ago – Sulawesi (Indonesia), found cave art including stencils of hands one of which is 39,900 years old and a painting of a babirusa, or pig-deer which is 35,400 years old. Also found crude stone tools are thought to date to perhaps 50,000 years old. A modern human settlement dated to 30,000 years old is the main proof of occupation but the island almost certainly formed part of the land bridge used for the settlement of Australia and New Guinea by at least 40,000 years ago. Cave art and harpoon tips seem to point to likely African roots and that as well as other cave painting suggests that art may have been universal among early modern people, including those who left Africa and traveled across southern Arabia to Indonesia and Australia within the past 50,000 years. ref, ref, ref
I found this quote about totemism funny and it shows the redicoulessness of religion in general, “The dream-totem may be revealed to the future mother when she feels the first symptoms of pregnancy, sometimes after eating some meat which because of its unusual fattiness is taken to have a supernatural character.” – Totemism: Claude Levi-Strauss
Yes, you need to know about Animism to understand Religion

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.



To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
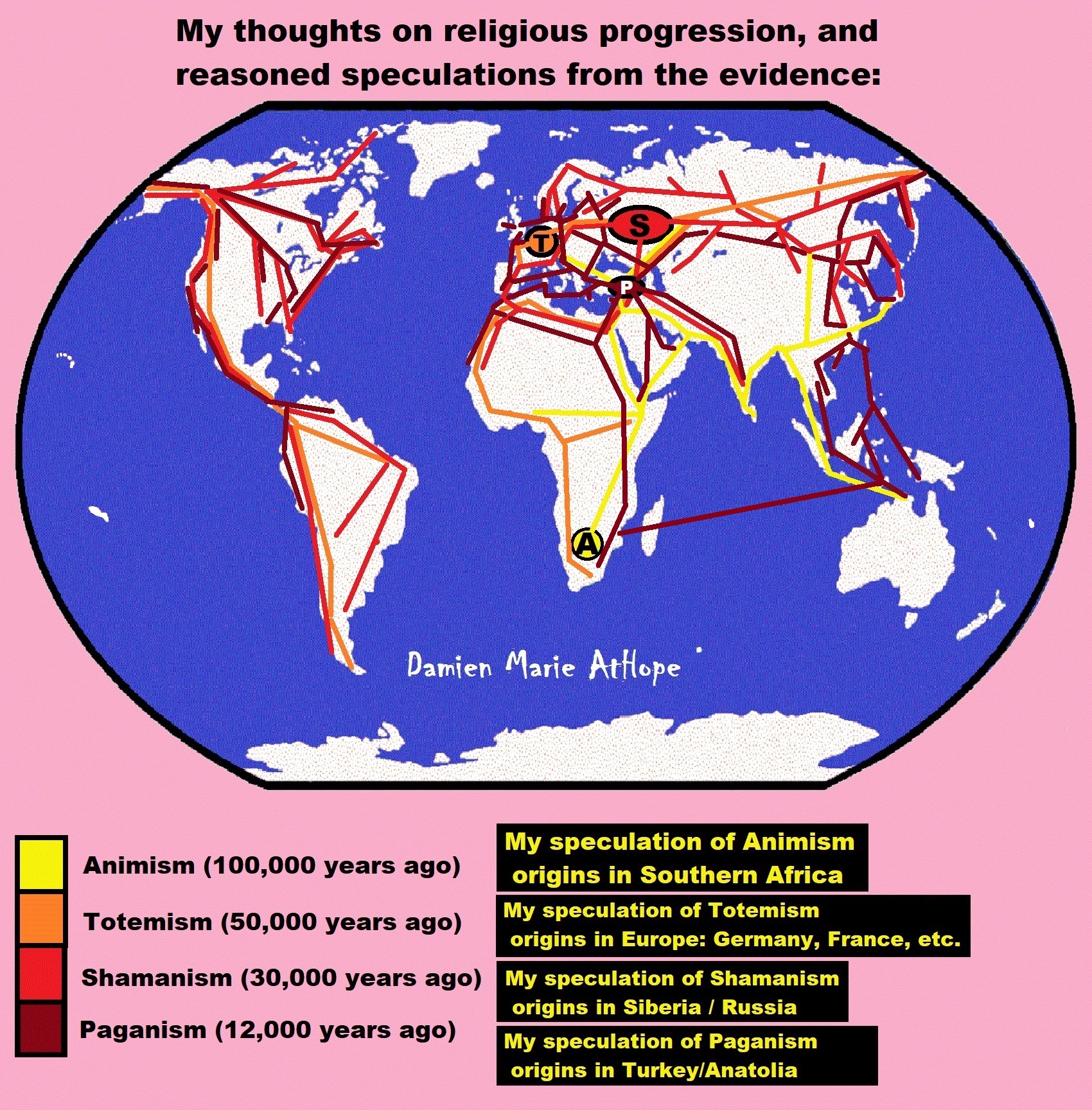

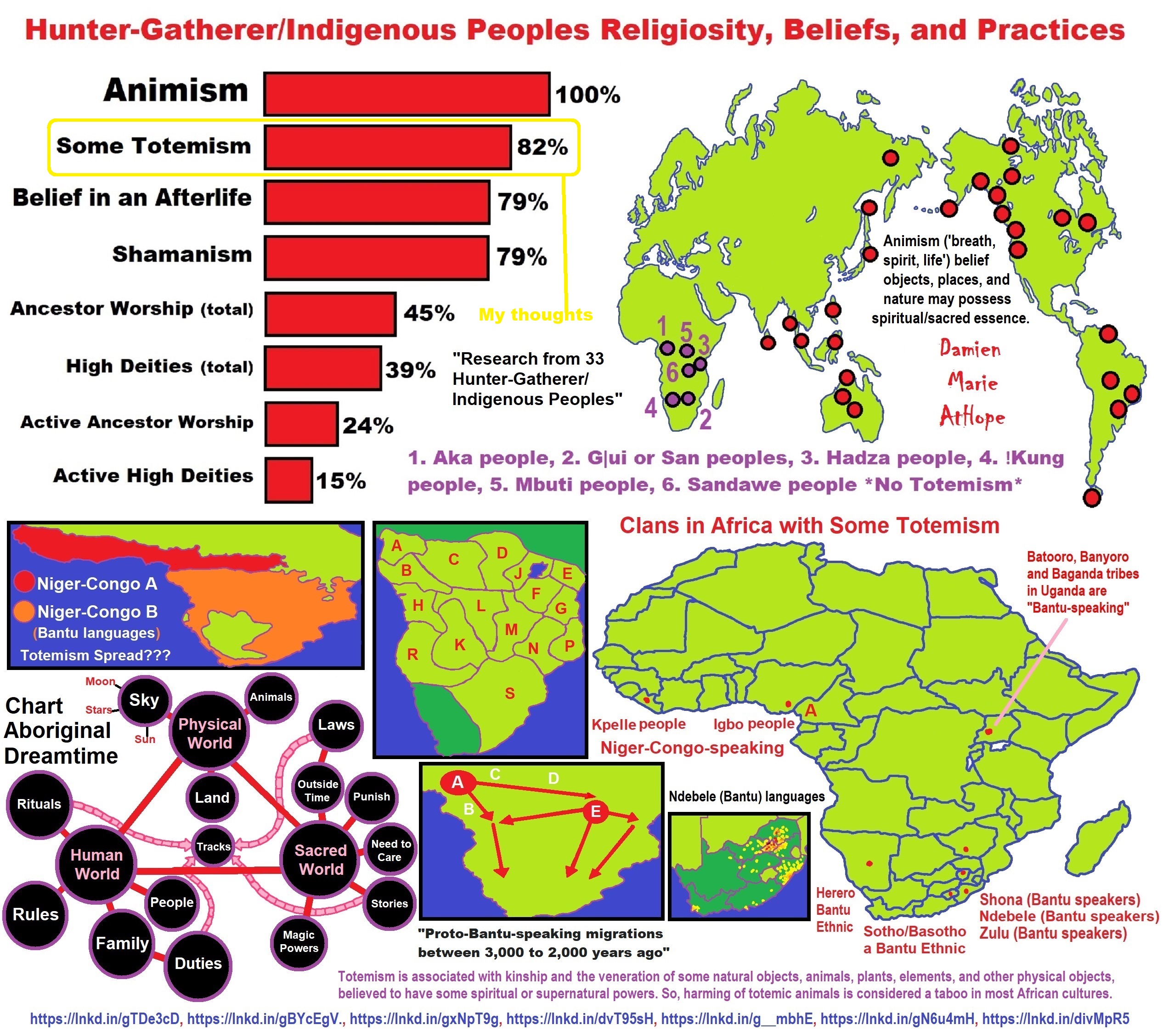
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
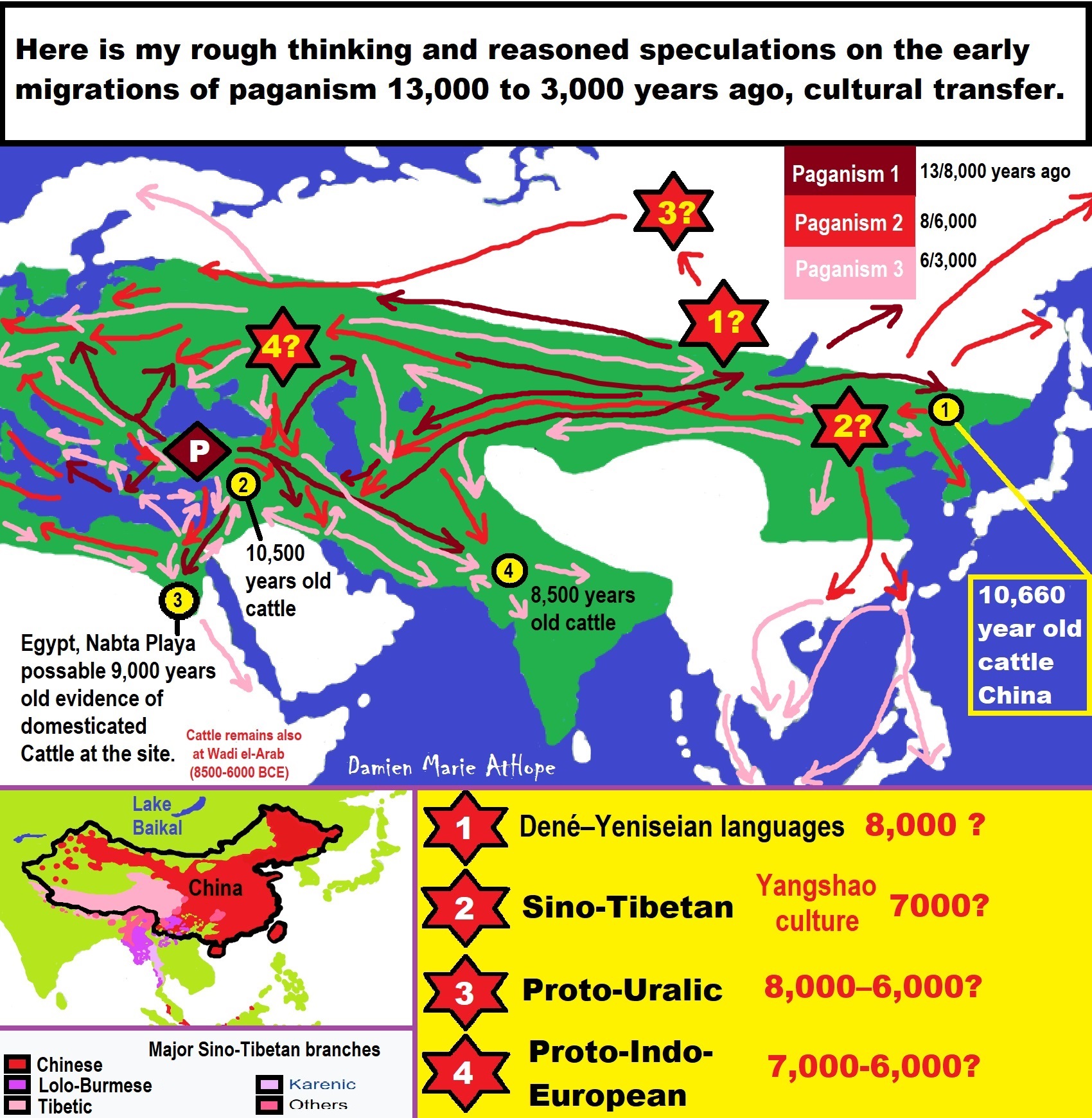
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
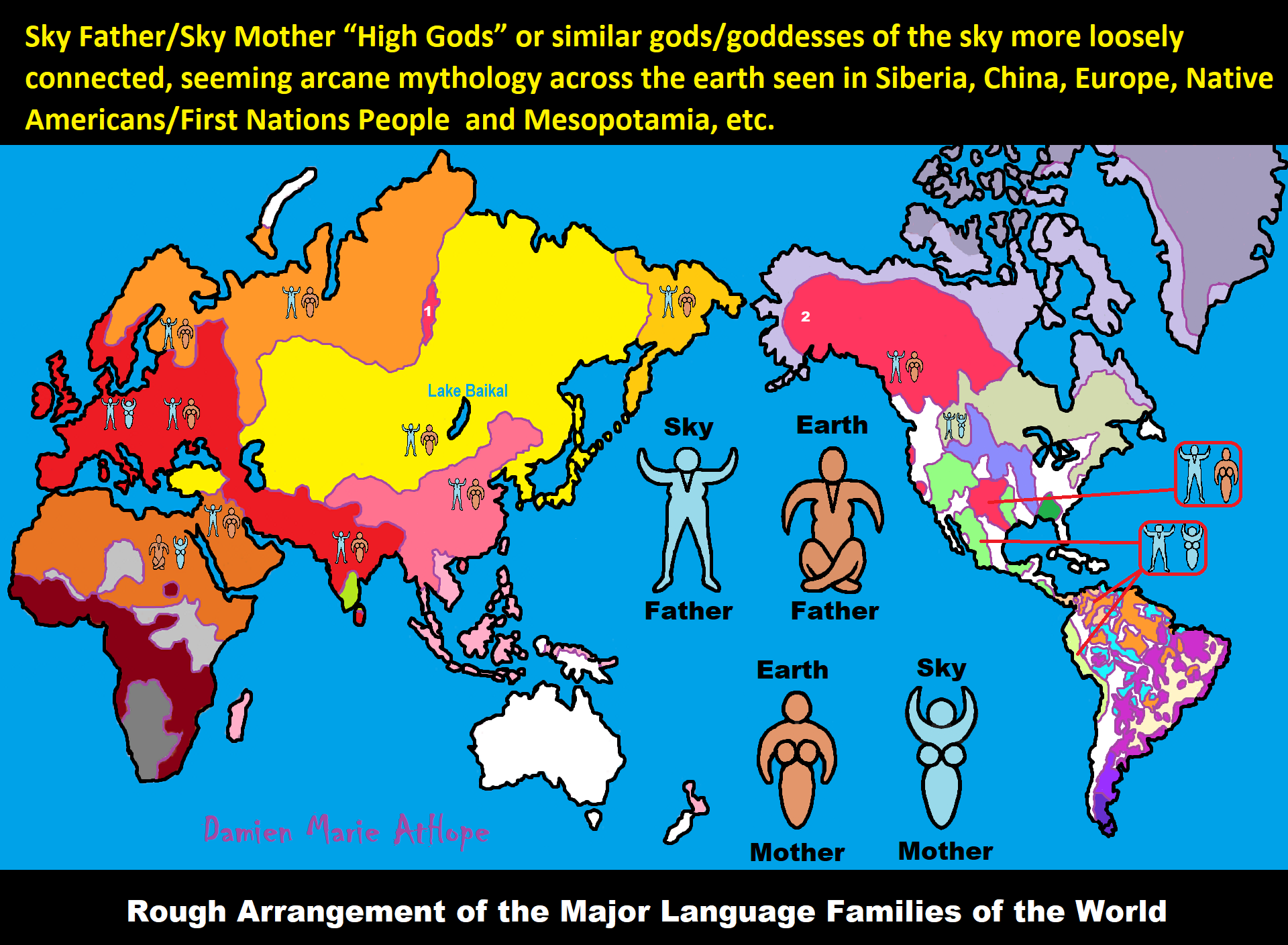
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com


