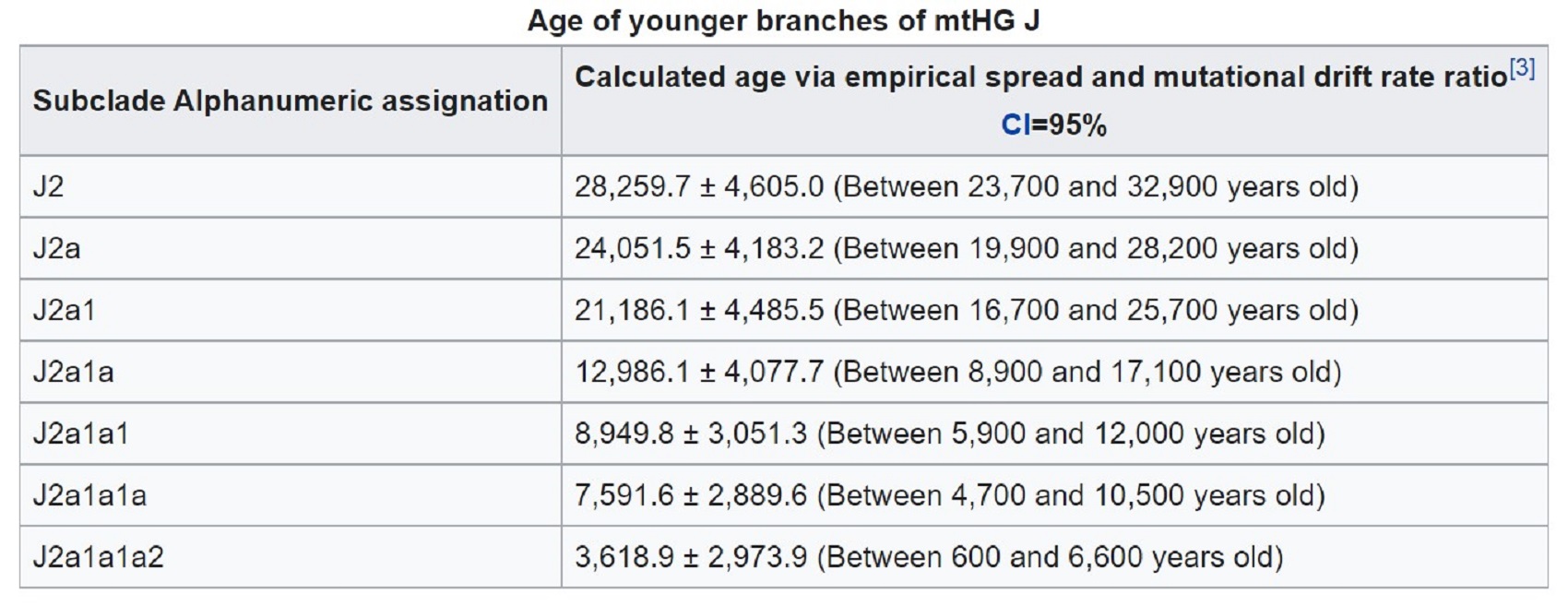
“Around 45,000 years before present, a mutation took place in the DNA of a woman who lived in the Near East or the Caucasus. Further mutations occurred in the J line, which can be identified as the subclades J1a1, J1c1 (27,000 yrs ago), J2a (19,000 yrs ago), J2b2 (16,000 years ago), and J2b3 (5,800 yrs ago). Haplogroup J bearers along with persons carrying the T mtDNA clade settled in Europe from the Near East during the late Paleolithic and Mesolithic.” ref
Neolithic diffusion of agriculture
“Samples have been identified from various Neolithic sites, including Linear Pottery culture (LBK) in Central Europe, the Cardium Pottery culture in southern France, Megalithic cultures in northern Spain, and the Funnelbeaker culture in Germany and Sweden. All Neolithic samples tested to date belonged to J1*, J1c or J2b1a. J1c is by far the most common form of mtDNA J in Europe today, making up over three-quarters of all J lineages.” ref
One question that follows is: did J1c and J2b1a lineages actually come from the Near East during the Neolithic, or whether they were already in the Balkans and just expanded from there? Both being rare in the Near East today, the second hypothesis might seem more convincing at first. However, the age of J2b1a has been estimated at 11,000 years before present, while the Neolithic started over 12,000 years ago in the Near East. In other words, it could have arrived from the Near East as J2b1* and developed into J2b1a only after reaching Europe, which would explain why this particular subclade is almost exclusively European while all other subclades of J2b1 are mostly Middle Eastern or the eastern Mediterranean. J2b1a would therefore have come as a maternal lineage of early agriculturalists alongside the paternal lineage G2a (and perhaps also E1b1b and T1a). J1c, however, is too old (15,000 years) for that scenario.” ref
“If it had been part of the Neolithic expansion from the Fertile Crescent, many J1c subclades it would be assumed would be primarily West Asian today, which isn’t the case. The only J1c individuals outside Europe belong to deep clades that clearly originated in Europe or in Anatolia. Mathieson et al. (2015) tested the DNA of Early Neolithic farmers from western Anatolia and from the Starcevo culture in Hungary and Croatia, and found that J1c was present in both cultures, alongside other typical European Neolithic lineages like H5, K1a, N1a, T2 and X2. Lazaridis et al. (2016) tested 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, and well as Chalcolithic and Bronze Age samples from Armenia and the Levant, but did not find any J1c, apart from a single sample in Neolithic Iran. This suggests that J1c lineages were probably not found among the very first farmers of the Fertile Crescent, but was rather assimilated in neighboring populations further north, notably in Anatolia and Iran, but probably also in the Balkans, which were connected to Anatolia by a land bridge during the glacial and immediate post-glacial periods.” ref
Neolithic Cattle Herders
“It has been hypothesized that R1b people (perhaps alongside neighboring J2 tribes) were the first to domesticate cattle in northern Mesopotamia some 10,500 years ago. R1b tribes descended from mammoth hunters, and when mammoths went extinct, they started hunting other large game such as bisons and aurochs. With the increase of the human population in the Fertile Crescent from the beginning of the Neolithic (starting 12,000 years ago), selective hunting and culling of herds started replacing indiscriminate killing of wild animals. The increased involvement of humans in the life of aurochs, wild boars, and goats led to their progressive taming. Cattle herders probably maintained a nomadic or semi-nomadic existence, while other people in the Fertile Crescent (presumably represented by haplogroups E1b1b, G, and T) settled down to cultivate the land or keep smaller domesticates. The analysis of bovine DNA has revealed that all the taurine cattle (Bos taurus) alive today descend from a population of only 80 aurochs. The earliest evidence of cattle domestication dates from circa 8,500 BCE in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic cultures in the Taurus Mountains. The two oldest archaeological sites showing signs of cattle domestication are the villages of Çayönü Tepesi in southeastern Turkey and Dja’de el-Mughara in northern Iraq, two sites only 250 km away from each others. This is presumably the area from which R1b lineages started expanding – or in other words the “original homeland” of R1b.” ref
“The early R1b cattle herders would have split in at least three groups. One branch (M335) remained in Anatolia, but judging from its extreme rarity today wasn’t very successful, perhaps due to the heavy competition with other Neolithic populations in Anatolia, or to the scarcity of pastures in this mountainous environment. A second branch migrated south to the Levant, where it became the V88 branch. Some of them searched for new lands south in Africa, first in Egypt, then colonizing most of northern Africa, from the Mediterranean coast to the Sahel. The third branch (P297), crossed the Caucasus into the vast Pontic-Caspian Steppe, which provided ideal grazing grounds for cattle. They split into two factions: R1b1a1 (M73), which went east along the Caspian Sea to Central Asia, and R1b1a2 (M269), which at first remained in the North Caucasus and the Pontic Steppe between the Dnieper and the Volga. It is not yet clear whether M73 actually migrated across the Caucasus and reached Central Asia via Kazakhstan, or if it went south through Iran and Turkmenistan. In any case, M73 would be a pre-Indo-European branch of R1b, just like V88 and M335.” ref
“R1b-M269 (the most common form in Europe) is closely associated with the diffusion of Indo-European languages, as attested by its presence in all regions of the world where Indo-European languages were spoken in ancient times, from the Atlantic coast of Europe to the Indian subcontinent, which comprised almost all Europe (except Finland, Sardinia, and Bosnia-Herzegovina), Anatolia, Armenia, European Russia, southern Siberia, many pockets around Central Asia (notably in Xinjiang, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Afghanistan), without forgetting Iran, Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal. The history of R1b and R1a are intricately connected to each others.” ref
“The first J1 men lived in the Late Upper Paleolithic, shortly before the end of the last Ice Age. The oldest identified J1 sample to date comes from Satsurblia cave (c. 13200 BCE) in Georgia (Jones et al. (2015)), placing the origins of haplogroup J1 in all likelihood in the region around the Caucasus, Zagros, Taurus, and eastern Anatolia during the Upper Paleolithic. Like many other successful lineages from the Middle East, J1 is thought to have undergone a major population expansion during the Neolithic period. Chiaroni et al. (2010) found that the greatest genetic diversity of J1 haplotypes was found in eastern Anatolia, near Lake Van in central Kurdistan. Eastern Anatolia and the Zagros mountains are the region where goats and sheep were first domesticated, some 11,000 years ago. Chiaroni et al. estimated that J1-P58 started expanding 9,000 to 10,000 years ago as pastoralists from the Fertile Crescent. Although they did not analyze the other branches, it is likely that all surviving J1a1b (L136) lineages share the same origin as goat and sheep herders from the Taurus and Zagros mountains.” ref
“The mountainous terrain of the Caucasus, Anatolia, and modern Iran, which wasn’t suitable for early cereal farming, was an ideal ground for goat and sheep herding and catalyzed the propagation of J1 pastoralists. Having colonized most of Anatolia, J1 herders would have settled the mountainous regions of Europe, including the southern Balkans, the Carpathians, and central as well as southern Italy (Apennines, Sicily, Sardinia), southern France (especially Auvergne), and most of the Iberian peninsula. Hotspots of J1 in northern Spain (Cantabria, Asturias) appear to be essentially lineages descended from these Southwest Asian Neolithic herders.” ref
“Most J1 Europeans belong to the J1-Z1828 branch, which is also found in Anatolia and the Caucasus, but not in Arabic countries. The Z1842 subclade of Z1828 is the most common variety of J1 in Armenia and Georgia. There are also two other minor European branches: J1-Z2223, which has been found in Anatolia and Western Europe, and J1-M365.1, also found a bit everywhere across Western Europe. Their very upstream position in the phylogenetic tree and their scarcity in the Middle East suggests that these were among the earliest J1 lineages to leave the Middle East, perhaps as Late Paleolithic or Mesolithic hunter-gatherers that wandered outside Anatolia and, pushed by successive waves of migrations from the Neolithic to the Bronze Age, ended up in Western Europe.” ref
“Within the Middle East, SNP analysis shows that the J1-L136 branch migrated south from eastern Anatolia and split in four directions: Anatolia/Europe (PF7263), the Levant, the southern Zagros (and southern Mesopotamia ?), and the mountainous south-western corner of the Arabian peninsula (mostly in Yemen), bypassing the Arabian Desert. That latter group, consisting essentially of J1-P56 lineages, crossed the Red Sea to settle Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, and northern Somalia. The climate would have been considerably less arid than today during the Neolithic period, allowing for a relatively easy transmigration across the Middle East with herds of goats.” ref
“Neolithic J1 goat herders were almost certainly not homogenous tribes consisting exclusively of J1 lineages, but in all likelihood a blend of J1 and T1 lineages. So much is evident from the presence of both J1 and T1 in north-east Africa, Yemen, Saudi Arabia, but also in the Fertile Crescent, the Caucasus, and the mountainous parts of southern Europe. Maternal lineages also correlate. Wherever J1 and T1 are found in high frequency, mtDNA haplogroups HV, N1, and U3 are also present, as well as J, K, and T to a lower extent (=>see Correlating the mtDNA haplogroups of the original Y-haplogroup J1 and T1 herders). It is unclear whether goats were domesticated by a tribe that already comprised both J1 and T1 lineages, or if the merger between the two groups happened during the Neolithic expansion, when two separate tribes would have bumped into each others, intermixed, and thereafter propagated together.” ref
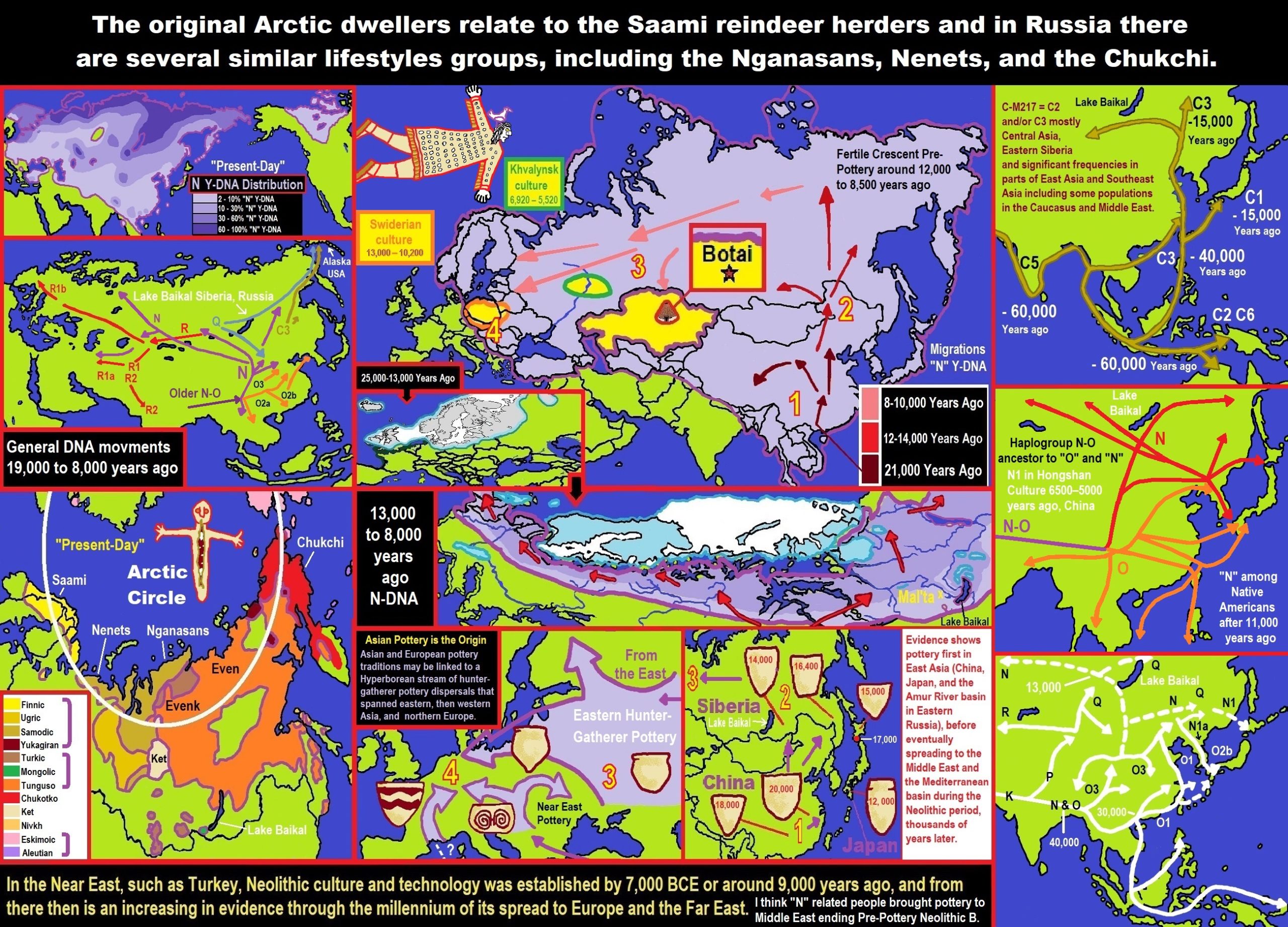
“Haplogroup N’s founding father may have lived as long as 20,000 to 30,000 years ago. This common father may have lived in today’s South-East-Asia. The Y-DNA haplogroup N has a wide distribution primarily in Northern Eurasia often associated (but not necessarily) with current and earlier Uralic speakers in Europe. It is a myth that haplogroup N in Europe is from the Huns and the Mongols. To quote Rootsi at the University of Tartu, Estonia who is leading the research on hg N. The age of hg N3 in the Finnic-Ugric speaking population in eastern Europe suggests a much earlier arrival from the east. “From the archaeological point of view, hg N3 is spread in Europe in the area of comb-ceramic culture. It is not, however, obvious that the spread of the two can be temporarily connected, because STR diversity-based calculations of the time depth of hg N3 among the Finn-speaking European population suggest expansion time before-around the end of Pleistocene – that is long before the rise of the comb-ceramic culture in the 4th millennium BCE or around 6,000 years ago.” ref
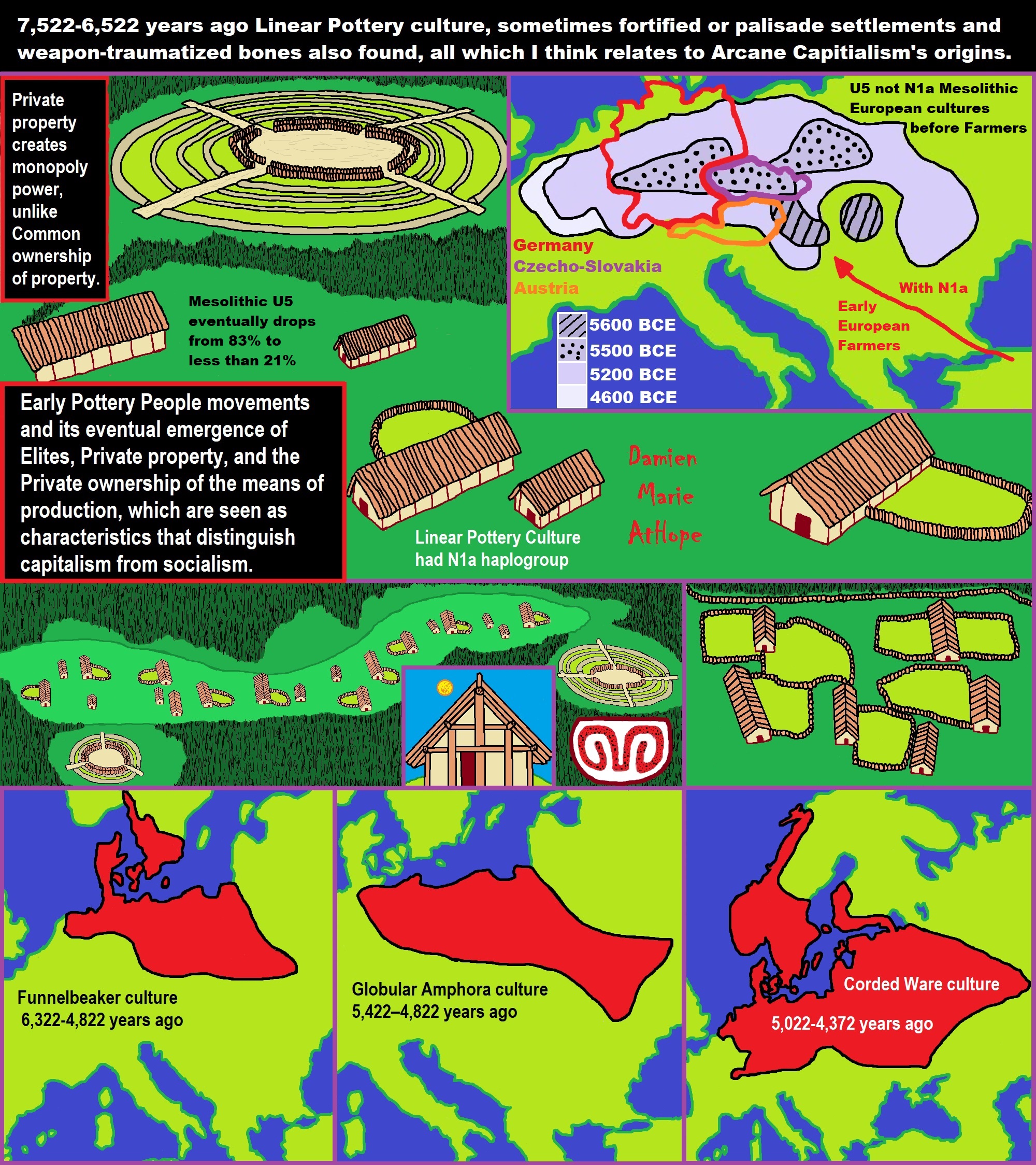
“N1a became particularly prominent in this debate when a team led by Wolfgang Haak analyzed skeletons from Linear Pottery Culture sites. The Linear Pottery Culture is credited with the first farming communities in Central Europe, marking the beginning of Neolithic Europe in the region some 7500 years ago. As of 2010, mitochondrial DNA analysis has been conducted on 42 specimens from five locations. Seven of these ancient individuals were found to belong to haplogroup N1a. A separate study analyzed 22 skeletons from European hunter-gatherer sites dated 13,400-2,300 BCE. Most of these fossils carried the mtDNA haplogroup U, which was not found in any of the Linear Pottery Culture sites. Conversely, N1a was not identified in any of the hunter-gatherer fossils, indicating a genetic distinction between Early European Farmers and late European hunter-gatherers.” ref
“Haak’s team concludes that “the transition to farming in central Europe was accompanied by a substantial influx of people from outside the region.” However, they note that haplogroup frequencies in modern Europeans are substantially different from early farming and late hunter-gatherer populations. This indicates that “the diversity observed today cannot be explained by admixture between hunter-gatherers and early farmers alone” and that “major demographic events continued to take place in Europe after the early Neolithic. The N1 subclade has also been found in various other fossils that were analyzed for ancient DNA, including specimens associated with the Starčevo (N1a1a1, Alsónyék-Bátaszék, Mérnöki telep, 1/3 or 33%), Linearbandkeramik/Linear Pottery Culture (N1a1a1a3, Szemely-Hegyes, 1/1 or 100%; N1a1b/N1a1a3/N1a1a1a2/N1a1a1/N1a1a1a, Halberstadt-Sonntagsfeld, 6/22 or ~27%), Alföld Linear Pottery (N1a1a1, Hejőkürt-Lidl, 1/2 or 50%), Transdanubian Late Neolithic (N1a1a1a, Apc-Berekalja, 1/1 or 100%), Protoboleráz (N1a1a1a3, Abony, Turjányos-dűlő, 1/4 or 25%), Iberia Early Neolithic cultures (N1a1a1, Els Trocs, 1/4 or 25%), Rinaldone–Gaudo Eneolithic cultures (N1a1a1a3, Monte San Biagio, 1/1 or 100%).” ref
“In 2010, researchers led by Palanichamy conducted a genetic and phylogeographic analysis of N1a. Based on the results, they conclude that some of the LBK samples were indigenous to Europe while others may have resulted from ‘leapfrog’ colonization. Deguilloux’s team agreed with Haak’s conclusion on a genetic discontinuity between ancient and modern Europeans. However, they consider demic diffusion, cultural diffusion, and long-distance matrimonial exchanges all equally plausible explanations for the current genetic findings. Seven of 42 skeletons from Linear Pottery Culture (Linearbandkeramik) sites were found to be members of the N1a haplogroup (see Neolithic European). N1a was also identified in skeletal remains within a 6200-year-old megalithic long mound near Prissé-la-Charrière, France. A 2500-year-old fossil of a Scytho-Siberian in the Altai Republic, the easternmost representative of the Scythians, was found to be a member of N1a1. A study of a 10th and 11th century Hungarians found that N1a1a1 was present in high-status individuals but absent from commoners. One of thirteen skeletons analyzed from a medieval cemetery dated 1250-1450 AD in Denmark was found to be a member of subclade N1a1a.” ref
“Haplogroup N1a – Arabian Peninsula and Northeast Africa. Found also in Central Asia and Southern Siberia. This branch is well attested in ancient people from various cultures of Neolithic Europe, from Hungary to Spain, and among the earliest farmers of Anatolia.” ref
“The Comb Ceramic culture or Pit-Comb Ware culture, was a northeast European culture characterized by its Pit–Comb Ware. It existed from around 4200 BCE to around 2000 BCE. The bearers of the Comb Ceramic culture are thought to have still mostly followed the Mesolithic hunter-gatherer lifestyle, with traces of early agriculture. The distribution of the artifacts found includes Finnmark (Norway) in the north, the Kalix River (Sweden) and the Gulf of Bothnia (Finland) in the west and the Vistula River (Poland) in the south. It would include the Narva culture of Estonia and the Sperrings culture in Finland, among others. They are thought to have been essentially hunter-gatherers, though e.g. the Narva culture in Estonia shows some evidence of agriculture. Some of this region was absorbed by the later Corded Ware horizon.” ref
“The Pit–Comb Ware culture is one of the few exceptions to the rule that pottery and farming coexist in Europe. In the Near East farming appeared before pottery, then when farming spread into Europe from the Near East, pottery-making came with it. However, in Asia, where the oldest pottery has been found, pottery was made long before farming. It appears that the Comb Ceramic Culture reflects influences from Siberia and distant China. The ceramics consist of large pots that are rounded or pointed below, with a capacity from 40 to 60 litres. The forms of the vessels remained unchanged but the decoration varied. By dating according to the elevation of land, the ceramics have traditionally (Äyräpää 1930) been divided into the following periods: early (Ka I, c. 4200 – 3300 BCE), typical (Ka II, c. 3300 – 2700 BCE), and late Comb Ceramic (Ka III, c. 2800 – 2000 BCE). However, calibrated radiocarbon dates for the comb-ware fragments found (e.g., in the Karelian isthmus), give a total interval of 5600 – 2300 BCE (Geochronometria Vol. 23, pp 93–99, 2004).” ref
“The settlements were located at sea shores or beside lakes and the economy was based on hunting, fishing, and the gathering of plants. In Finland, it was a maritime culture that became more and more specialized in hunting seals. The dominant dwelling was probably a teepee of about 30 square meters where some 15 people could live. Also, rectangular houses made of timber become popular in Finland from 4000 BCE cal. Graves were dug at the settlements and the dead were covered with red ochre. The typical Comb Ceramic age shows an extensive use of objects made of flint and amber as grave offerings. The stone tools changed very little over time. They were made of local materials such as slate and quartz. Finds suggest a fairly extensive exchange network: red slate originating from northern Scandinavia, asbestos from Lake Saimaa, green slate from Lake Onega, amber from the southern shores of the Baltic Sea, and flint from the Valdai area in northwestern Russia.” ref
“The culture was characterized by small figurines of burnt clay and animal heads made of stone. The animal heads usually depict moose and bears and were derived from the art of the Mesolithic. There were also many rock paintings. There are sources noting that the typical comb ceramic pottery had a sense of luxury and that its makers knew how to wear precious amber pendants. Saag et al. (2017) analyzed three CCC individuals buried at Kudruküla as belonging to Y-hg R1a5-YP1272 (R1a1b~ after ISOGG 2020), along with three mtDNA samples of mt-hg U5b1d1, U4a, and U2e1. Mittnik (2018) analyzed two CCC individuals. The male carried R1 (2021: R1b-M343) and U4d2, while the female carried U5a1d2b. Generally, the CCC individuals were mostly of Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) descent, with even more EHG than people of the Narva culture. Lamnidis et al. (2018) confirmed and specified this to 65% Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), 20% Western Steppe Herder (WSH), and 15% Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) ancestry. This amount of EHG ancestry was higher than among earlier cultures of the eastern Baltic, while WSH ancestry had previously not even been attested among such an early culture in the region.” ref
“In earlier times, it was often suggested that the spread of the Comb Ware people was correlated with the diffusion of the Uralic languages, and thus an early Uralic language would have been spoken throughout this culture. It was also suggested that bearers of this culture likely spoke Finno-Ugric languages. Another view is that the Comb Ware people may have spoken Palaeo-European languages, as some toponyms and hydronyms also indicate a non-Uralic, non-Indo-European language at work in some areas. In addition, modern scholars have located the Proto-Uralic homeland east of the Volga, if not even beyond the Urals. The great westward dispersal of the Uralic languages is suggested to have happened long after the demise of the Comb Ceramic culture, perhaps in the 1st millennium BCE.” ref
“Genetic studies suggest that the Pitted Ware peoples, unlike their Neolithic neighbors, were descended from earlier Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHGs). At the time of the emergence of the Pitted Ware culture, these hunter-gatherers persisted to the north of the agricultural Funnelbeaker culture. Their ceramic traditions are related to those of the Comb Ceramic culture. The Pitted Ware culture arose around 3,500 BCE. Its earliest sites are found in east-central Sweden, where it appears to have replaced the Funnelbeaker culture. Its subsequent expansion is accompanied by the disappearance of settlements of the Funnelbeaker culture throughout large parts of southern Scandinavia. It came to occupy the coasts of Denmark, southern Sweden, southern Norway, and various islands of the Baltic Sea, such as Öland, Gotland, and Åland.” ref
“There were lively contacts with hunter-gatherer communities of Finland and the eastern Baltic. During its initial years, the Pitted Ware culture co-existed with the Funnelbeaker culture. Although the two cultures exchanged goods with each other, their peoples appear to have had widely different identities, and they did not mix with each other to any notable extent. During the period of Pitted Ware expansion, the Funnelbeakers constructed a number of defensive palisades, which may mean that the two peoples were in conflict with each other. Throughout its existence of more than 1,000 years, the Pitted Ware culture remained virtually unchanged.” ref
“From around 2,800 BCE, the Pitted Ware culture co-existed for some time with the Battle Axe culture and the Single Grave culture, which succeeded the Funnelbeaker culture in southern Scandinvia. Both were variants of the Corded Ware culture. Like the Funnelbeakers, the Corded Ware constructed a series of defensive palisades during this period, which may be a sign of violent conflict between them and the Pitted Ware. Though cultural influences of the Battle Axe culture are detectable in Pitted Ware burials, its peoples do not appear to have mixed with each other. By ca. 2,300 BCE, the Pitted Ware culture had merged with the Battle Axe culture. The subsequent Nordic Bronze Age represents a fusion of elements from the Pitted Ware culture and the Battle Axe culture.” ref
“The A10398G mutation defining haplogroup J (a back mutation from macrohaplogroup N) has been associated with increased longevity Dato et al. (2005), Shlush et al. (2008) and Nijiati et al. (2013) and protection against PD (Ghezzi et al. (2005) and Clark et al. (2011)). It is found in all members of haplogroup J except J1c8. The common C150T mutation has been found at strikingly higher frequency among Chinese and Italian centenarians and may be advantageous for longevity and resistance to stress according to Chen et al. (2012). C150T defines haplogroups J1b7, J1c1c, and J2, but may also be found among other subclades.” ref
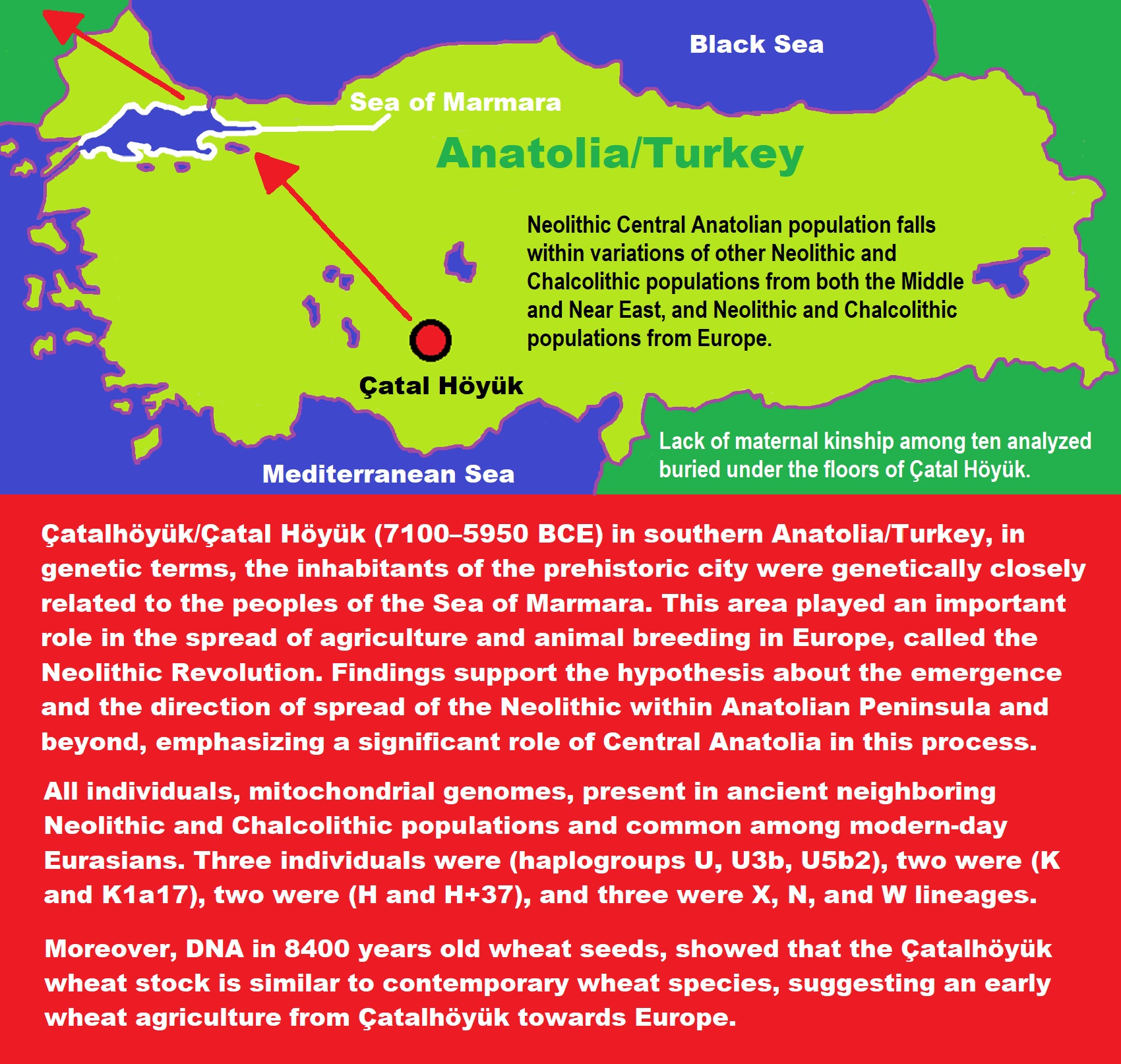
“There is a distinct association of ancient J2 civilizations with bull worship. The oldest evidence of a cult of the bull can be traced back to Neolithic central Anatolia, notably at the sites of Çatalhöyük and Alaca Höyük. Bull depictions are omnipresent in Minoan frescos and ceramics in Crete. Bull-masked terracotta figurines and bull-horned stone altars have been found in Cyprus (dating back as far as the Neolithic, the first presumed expansion of J2 from West Asia). The Hattians, Sumerians, Babylonians, Canaanites, and Carthaginians all had bull deities (in contrast with Indo-European or East Asian religions). The sacred bull of Hinduism, Nandi, present in all temples dedicated to Shiva or Parvati, does not have an Indo-European origin, but can be traced back to Indus Valley civilisation. Minoan Crete, Hittite Anatolia, the Levant, Bactria, and the Indus Valley also shared a tradition of bull leaping, the ritual of dodging the charge of a bull. It survives today in the traditional bullfighting of Andalusia in Spain and Provence in France, two regions with a high percentage of J2 lineages.” ref
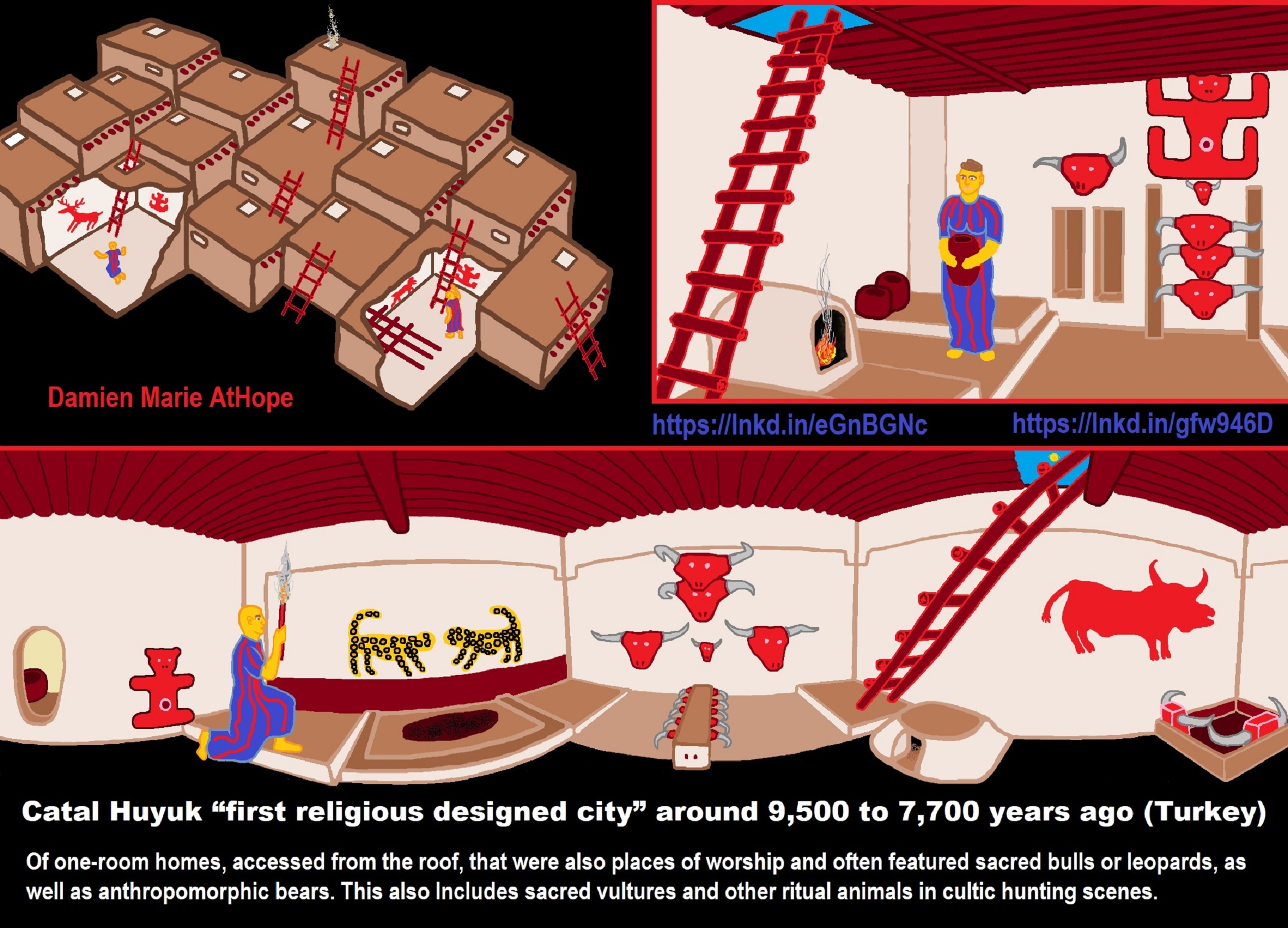
“Çatalhöyük was composed entirely of domestic buildings, with no obvious public buildings. While some of the larger ones have rather ornate murals some involve bull-heads or pseudo-bull-heads made from the horns. Vivid murals and figurines are found throughout the settlement, on interior and exterior walls. Although no identifiable temples have been found, the graves, murals, and figurines suggest that the people of Çatalhöyük had a religion rich in symbols. Rooms with concentrations of these items may have been shrines or public meeting areas. Predominant images include men with erect phalluses, hunting scenes, red images of the now extinct aurochs (wild cattle/bulls) and stags, and vultures swooping down on headless figures. Relief figures are carved on walls, such as Neolithic hunters attacking an aurochs (Bull) as well as lionesses facing one another. Heads of animals, especially of cattle (commonly bull-heads or horns in pseudo-modeled constructed bull-head shapes), were mounted on walls.” ref
“The aurochs was one of the largest herbivores in Holocene Europe. The aurochs exhibited considerable sexual dimorphism in the size of males and females. The proportions and body shape of the aurochs were strikingly different from many modern cattle breeds. For example, the horns were massive, and the skull, carrying the large horns, was substantially larger and more elongated than in most cattle breeds. Some cattle breeds still show horn shapes similar to that of the aurochs, such as the Spanish fighting bull, and occasionally also individuals of derived breeds.” ref

12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
“Haplogroup J-M304, also known as J*, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is believed to have evolved in Western Asia. A possible time of origin is around 48,000 years ago and the main current subgroups J-M267 and J-M172, which now comprise between them almost all of the haplogroup’s descendant lineages, are both believed to have arisen very early, at least 10,000 years ago. Y-DNA haplogroup J1, defined by the SNP mutation M267, is estimated to be approximately 20 thousand years old and is thought to have originated somewhere between Anatolia and Mesopotamia. ref Haplogroup J-M304 is found in its greatest concentration in the Arabian peninsula. Outside of this region, haplogroup J-M304 has a significant presence in North Africa and the Horn of Africa. It also has a moderate occurrence in Southern Europe, especially in central and southern Italy, Malta, Greece, and Albania. The J-M410 subclade is mostly distributed in Anatolia, Greece, and southern Italy. Additionally, J-M304 is observed in Central Asia and South Asia, particularly in the form of its subclade J-M172. J-12f2 and J-P19 are also found among the Herero (8%). The basal haplogroup J*(xJ1, J2) is found at its highest frequencies among the Soqotri (71.4%).” ref
“Haplogroup J-M267 defined by the M267 SNP is in modern times most frequent in the Arabian Peninsula: Yemen (up to 76%), Saudi (up to 64%) (Alshamali 2009), Qatar (58%), and Dagestan (up to 56%). J-M267 is generally frequent among Arab Bedouins(62%), Ashkenazi Jews (20%) (Semino 2004), Algeria (up to 35%) (Semino 2004), Iraq (up to 33%) (Semino 2004), Tunisia (up to 31%), Syria (up to 30%), Egypt (up to 20%) (Luis 2004), and the Sinai Peninsula. To some extent, the frequency of Haplogroup J-M267 collapses at the borders of Arabic/Semitic-speaking territories with mainly non-Arabic/Semitic speaking territories, such as Turkey (9%), Iran(5%), Sunni Iraqi Biradari of North India (38%) and Northern Indian Shia (11%) (Eaaswarkhanth 2009). However, it should be noted that some figures above tend to be the larger ones obtained in some studies, while the smaller figures obtained in other studies are omitted. It is also highly frequent among Jews, especially the Kohanim line (46%) (Hammer 2009). ISOGG states that J-M267 originated in the Middle East. It is found in parts of the Near East, Anatolia, and North Africa, with a much sparser distribution in the southern Mediterranean flank of Europe, and in Ethiopia. But not all studies agree on the point of origin. The Levant has been proposed but a 2010 study concluded that the haplogroup had a more northern origin, possibly Anatolia. The origin of the J-P58 subclade is likely in the more northerly populations and then spreads southward into the Arabian Peninsula. The high Y-STR variance of J-P58 in ethnic groups in Turkey, as well as northern regions in Syria and Iraq, supports the inference of an origin of J-P58 in nearby eastern Anatolia. Moreover, the network analysis of J-P58 haplotypes shows that some of the populations with low diversity, such as Bedouins from Israel, Qatar, Sudan, and the United Arab Emirates, are tightly clustered near high-frequency haplotypes. This suggests that founder effects with star burst expansion into the Arabian Desert (Chiaroni 2010).” ref
J-M172
“Haplogroup J-M172 is found in the highest concentrations in the Caucasus and the Fertile Crescent/Iraq and is found throughout the Mediterranean(including the Italian, Balkan, Anatolian, and Iberian peninsulas and North Africa) (Giacomo 2003). The highest ever reported concentration of J-M172 was 72% in Northeastern Georgia (Nasidze 2004). Other high reports include Ingush 32% (Nasidze 2004), Cypriots30-37% (Capelli 2005), Lebanese 30% (Wells et al. 2001), Assyrian, Mandean, and Arab Iraqis 29.7% (Sanchez et al. 2005), Syrians and Syriacs 22.5%, Kurds24%-28%, Iranians 23% (Aburto 2006), Ashkenazi Jews 24%, Palestinian Arabs 16.8%-25%, Sephardic Jews 29% and North Indian Shia Muslim 18%, Chechens 26%, Balkars 24%, Yaghnobis 32%, Armenians 21-24%, and Azerbaijanis 24%-48%. Some J-M172 haplotypes (as well as some J-M267 ones) belong to the “Cohen Modal Haplotype“. In South Asia, J2-M172 was found to be significantly higher among Dravidian castes at 19% than among Indo-European castes at 11%. J2-M172 and J-M410 is found 21% among Dravidian middle castes, followed by upper castes, 18.6%, and lower castes 14%. (Sengupta 2006) Subclades of M172 such as M67 and M92 were not found in either Indian or Pakistani samples which also might hint at a partial common origin.(Sengupta 2006) According to a genetic study in China by Shou et al., J2-M172 is found with high frequency among Uygurs (17/50 = 34%) and Uzbeks (7/23 = 30.4%), moderate frequency among Pamiris (5/31 = 16.1%), and low frequency among Yugurs (2/32 = 6.3%) and Monguors (1/50 = 2.0%). The authors also found J-M304(xJ2-M172) with low frequency among the Russians (1/19 = 5.3%), Uzbeks (1/23 = 4.3%), Sibe people (1/32 = 3.1%), Dongxiangs (1/35 = 2.9%), and Kazakhs (1/41 = 2.4%) in Northwest China.” ref
http://www.kerchner.com/images/dna/ydna_migrationmap_(FTDNA2006).jpg
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
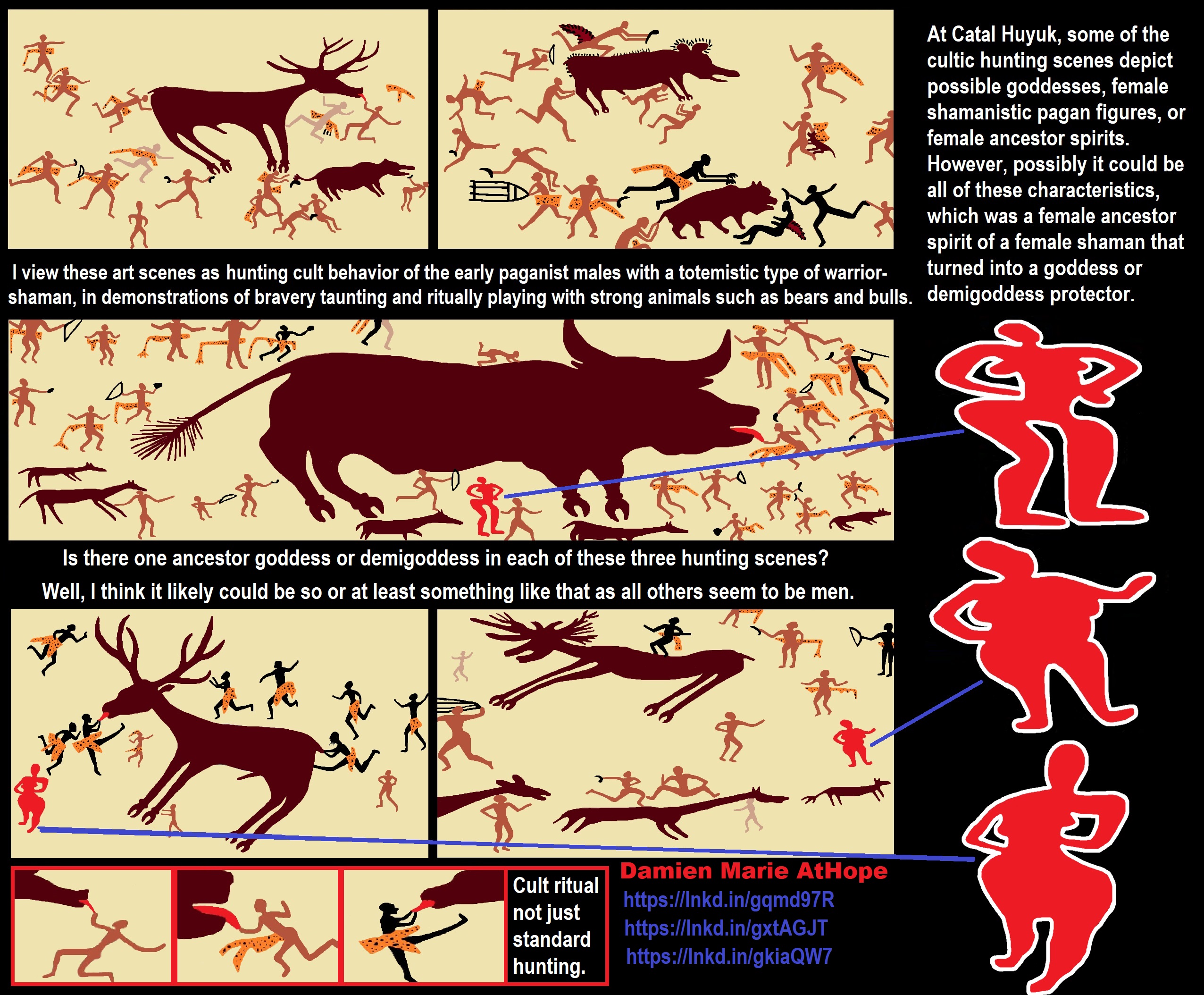
“The shaman is, above all, a connecting figure, bridging several worlds for his people, traveling between this world, the underworld, and the heavens. He transforms himself into an animal and talks with ghosts, the dead, the deities, and the ancestors. He dies and revives. He brings back knowledge from the shadow realm, thus linking his people to the spirits and places which were once mythically accessible to all.–anthropologist Barbara Meyerhoff” ref
Haplogroup J2 (Y-DNA) – Eupedia
Author: Maciamo Hay
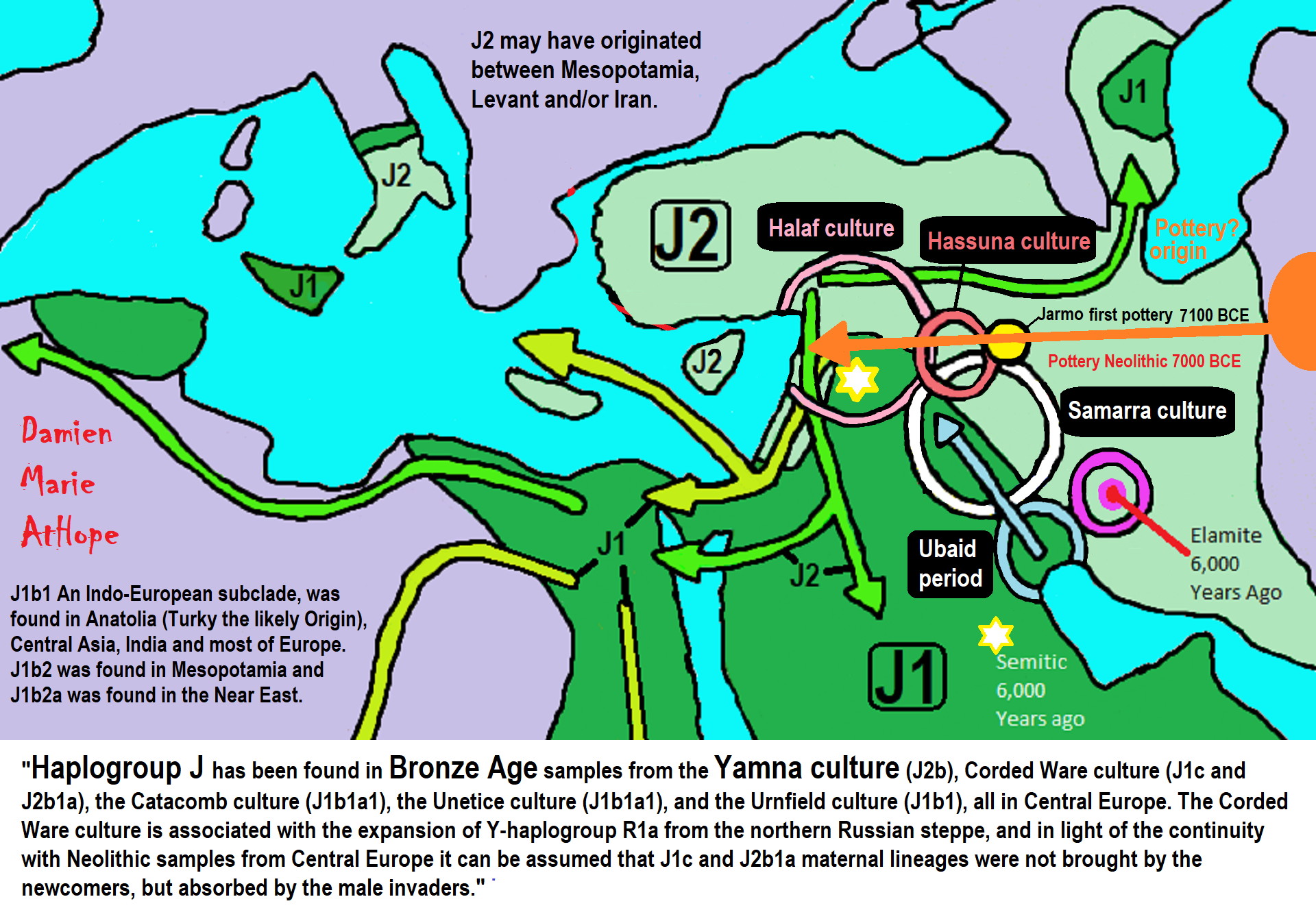
“Haplogroup J2 is thought to have appeared somewhere in the Middle East towards the end of the last glaciation, between 15,000 and 22,000 years ago. The oldest known J2a samples at present were identified in remains from the Hotu Cave in northern Iran, dating from 9100-8600 BCE (Lazaridis et al. 2016), and from Kotias Klde in Georgia, dating from 7940-7600 BCE (Jones et al. (2015)). This confirms that haplogroup J2 was already found around the Caucasus and the southern Caspian region during the Mesolithic period. The first appearance of J2 during the Neolithic came in the form of a 10,000-year-old J2b sample from Tepe Abdul Hosein in north-western Iran in what was then the Pre-Pottery Neolithic (Broushaki et al. 2016).” ref
Notwithstanding its strong presence in West Asia today, haplogroup J2 does not seem to have been one of the principal lineages associated with the rise and diffusion of cereal farming from the Fertile Crescent and Anatolia to Europe. It is likely that J2 men had settled over most of Anatolia, the South Caucasus, and Iran by the end of the Last Glaciation 12,000 years ago. It is possible that J2 hunter-gatherers then goat/sheep herders also lived in the Fertile Crescent during the Neolithic period, although the development of early cereal agriculture is thought to have been conducted by men belonging primarily to haplogroups G2a (northern branch, from Anatolia to Europe), as well as E1b1b and T1a (southern branch, from the Levant to the Arabian peninsula and North Africa).” ref
“Mathieson et al. (2015) tested the Y-DNA of 13 Early Neolithic farmers from the Barcın site (6500-6200 BCE) in north-western Anatolia, and only one of them belonged to haplogroup J2a. Lazaridis et al. (2016) tested 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, but only the above-mentioned sample from Mesolithic Iran belonged to J2. Likewise, over 100 Y-DNA samples have been tested from Neolithic Europe, covering most of the important cultures, and only two J2 samples were found, in the Sopot and Proto-Lengyel cultures in Hungary, dating from 7,000 years ago. J2 was also absent from all Chalcolithic and Bronze Age Indo-European cultures, apart from one J2a1b sample in Hungary dating from the end of the Bronze Age (c. 1150 BCE, see Gamba et al. 2014), in the minor Kyjatice culture, an offshoot of the Urnfield culture, which differs from typical Indo-European cultures by its use of cremation instead of single-grave burials.” ref
“No Neolithic sample from Central or South Asia has been tested to date, but the present geographic distribution of haplogroup J2 suggests that it could initially have dispersed during the Neolithic from the Zagros mountains and northern Mesopotamia across the Iranian plateau to South Asia and Central Asia, and across the Caucasus to Russia (Volga-Ural). The first expansion probably correlated with the diffusion of domesticated of cattle and goats (starting c. 8000-9000 BCE), rather than with the development of cereal agriculture in the Levant.” ref
“A second expansion would have occurred with the advent of metallurgy. J2 could have been the main paternal lineage of the Kura-Araxes culture (Late Copper to Early Bronze Age), which expanded from the southern Caucasus toward northern Mesopotamia and the Levant. After that J2 could have propagated through Anatolia and the Eastern Mediterranean with the rise of early civilizations during the Late Bronze Age and the Early Iron Age.” ref
“Quite a few ancient Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations flourished in territories where J2 lineages were preponderant. This is the case of the Hattians, the Hurrians, the Etruscans, the Minoans, the Greeks, the Phoenicians (and their Carthaginian offshoot), the Israelites, and to a lower extent also the Romans, the Assyrians, and the Persians. All the great seafaring civilizations from the Middle Bronze Age to the Iron Age were dominated by J2 men.” ref
“There is a distinct association of ancient J2 civilizations with bull worship. The oldest evidence of a cult of the bull can be traced back to Neolithic central Anatolia, notably at the sites of Çatalhöyük and Alaca Höyük. Bull depictions are omnipresent in Minoan frescos and ceramics in Crete. Bull-masked terracotta figurines and bull-horned stone altars have been found in Cyprus (dating back as far as the Neolithic, the first presumed expansion of J2 from West Asia). The Hattians, Sumerians, Babylonians, Canaanites, and Carthaginians all had bull deities (in contrast with Indo-European or East Asian religions). The sacred bull of Hinduism, Nandi, present in all temples dedicated to Shiva or Parvati, does not have an Indo-European origin, but can be traced back to the Indus Valley civilization. Minoan Crete, Hittite Anatolia, the Levant, Bactria, and the Indus Valley also shared a tradition of bull leaping, the ritual of dodging the charge of a bull. It survives today in the traditional bullfighting of Andalusia in Spain and Provence in France, two regions with a high percentage of J2 lineages.” ref
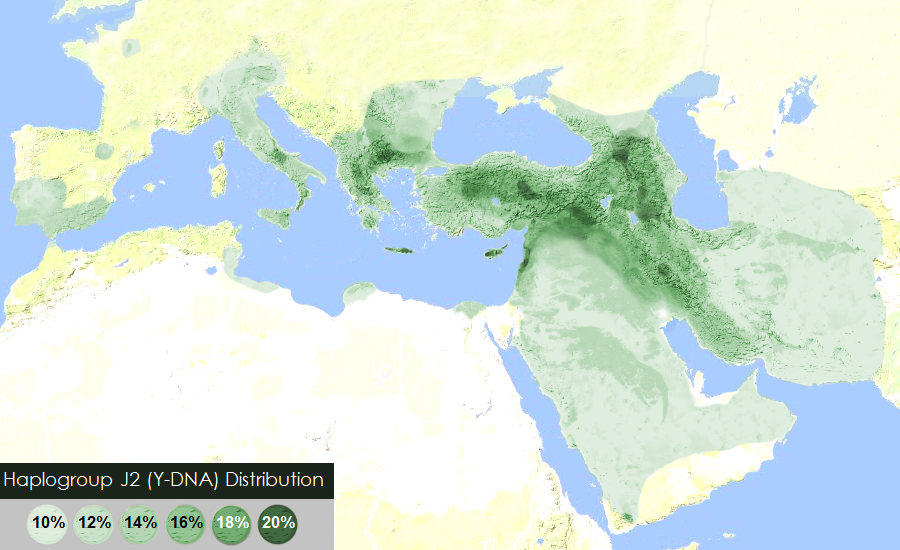
“The world’s highest frequency of J2 is found among the Ingush (88% of the male lineages) and Chechen (56%) people in the Northeast Caucasus. Both belong to the Nakh ethnic group, who have inhabited that territory since at least 3000 BCE. Their language is distantly related to Dagestanian languages, but not to any other linguistic group. However, Dagestani peoples (Dargins, Lezgins, Avars) belong predominantly to haplogroup J1 (84% among the Dargins) and almost completely lack J2 lineages. Other high incidences of haplogroup J2 are found in many other Caucasian populations, including the Azeri (30%), the Georgians (27%), the Kumyks (25%), and the Armenians (22%). Nevertheless, it is very unlikely that haplogroups J2 originated in the Caucasus because of the low genetic diversity in the region. Most Caucasian people belong to the same CTS6804subclade and share a common patrilineal ancestor who lived some 7,500 years ago, at the time of the Neolithic expansion to the Caucasus.” ref
“The Chechens and Ingushs belong almost exclusively to the Y7800 clade, which formed only 2,000 years ago and has a TMRCA of approximately 1,500 years. The high local frequencies observed would rather be the result of founder effects, for instance, the proliferation of chieftains and kings’s lineages through a long tradition of polygamy, a practice that the Russians have tried to suppress since their conquest of the Caucasus in the 19th century.” ref
“Outside the Caucasus, the highest frequencies of J2 are observed in Cyprus (37%), Crete (34%), northern Iraq (28%), Lebanon (26%), Turkey (24%, with peaks of 30% in the Marmara region and in central Anatolia), Greece (23%), Central Italy (23%), Sicily (23%), South Italy (21.5%), and Albania (19.5%), as well as among Jewish people (19 to 25%).” ref
“One-fourth of the Vlach people (isolated communities of Romance language speakers in the Balkans) belong to J2, considerably more than the average of Macedonia and northern Greece where they live. This, combined to the fact that they speak a language descended from Latin, suggests that they could have a greater part of Roman (or at least Italian) ancestry than other ethnic groups in the Balkans.” ref
“It is very likely that J2a, J1-Z1828, L1b, T1a-P77, and G2a-L293 were the dominant male lineages the Early Bronze Age Kura-Araxes culture (3,400-2,000 BCE), which expanded from the South Caucasus to eastern Anatolia, northern Mesopotamia, and the western Iran. From then on, J2 men would have definitely have represented a sizeable portion of the population of Bronze and Iron Age civilizations such as the Hurrians, the Assyrians or the Hittites. It is very possible that bronze technology spread from the South Caucasus across the Iranian plateau until the Indus Valley, giving rise to the Harappan Civilisation (see below).” ref
“The Minoan civilization emerged from 2,700 BCE and could have been founded by colonists from the Kura-Araxes culture who would have brought bronze working with them. Modern Cretans have the highest percentage of G2a (11%), J1 (8.5%), J2a (32%), and L + T (2.5% together) in Greece (and the highest percentage of J1 and J2a in all Europe for that matter), the three haplogroups associated with the Kura-Araxes culture. Although little data is available at present about deep clades in Crete or Aegean Greece, the parts of Italy that were colonized by Ionic and Doric Greeks, notably Sicily, Calabria, and Basilicata, possess substantial percentages of typically Caucasian haplogroups, such as G2a-L297, J1-Z1828, and J2a-L581, as well as considerable levels of Middle Eastern and Caucasian autosomal admixture by European standards. In fact, it seems that many branches of J2a (e.g. M319, Z7671, F3133, Z6046, L581) may have expanded from the South Caucasus from the Chalcolithic onwards. The presence of these haplogroups and admixtures in southern Italy almost certainly represents Kura-Araxes ancestry inherited from Minoan Greeks from the Aegean islands.” ref
“The Phoenicians, Jews, Greeks, and Romans all contributed to the presence of J2a in Iberia. The particularly strong frequency of J2a and other Near Eastern haplogroups (J1, E1b1b, T) in the south of the Iberian peninsula, suggests that the Phoenicians and the Carthaginians played a more decisive role than other peoples. This makes sense considering that they were the first to arrive, founded the greatest number of cities (including Gadir/Cadiz, Iberia’s oldest city), and their settlements match almost exactly the zone where J2 is found at a higher frequency in southern Andalusia.” ref
“The high incidence of J2a in Italy is owed in great part to the migration of the Etruscans from western Anatolia to central and northern Italy, and to the Greek colonization of southern Italy. However, both the Etruscans and Greeks would have carried many other Y-DNA lineages, including G2a, J1, R1b-Z2103, T1a, and probably also E-M34. J2a levels would have been higher among the Greeks than the Etruscans, and particularly among the insular Greeks that colonized Magna Graecia. Immigration from the eastern Mediterranean to Rome during the Roman Empire, then from Anatolia, Thrace, and Greece during the Byzantine period (particularly in north-eastern Italy) further increased the incidence of J2 in the peninsula.” ref
“Several common Italian J2a subclades are found mainly in the south of Italy (M319, M92, Z467, Z7671, all under L558) and are likely to be of Greek origin. The highest concentrations of J2a in Europe are found in Crete (32% of the population) and Calabria (26%). M319, one of the principal J2a1 subclades in Greece, Italy, and Western Europe, reaches is maximum frequency in Crete (6-9%).” ref
Roman J2a1-Z435
“The Romans probably helped spread haplogroup J2 within their borders, judging from the distribution of J2 within Europe (frequency over 5%), which bears an uncanny resemblance to the borders of the Roman Empire (once concessions are made for the Germanic invasions that appear to have lowered the frequency of J2 between Belgium and Switzerland). There is a high diversity of J2a in Italy, but the most common branch found all over the peninsula and therefore most likely linked with a Roman diffusion is L70, and particularly its subclade Z435. All L70 carriers today descend from a single patrilineal ancestor who lived about 5,000 years ago. This corresponds to the time when the Proto-Indo-Europeans started invading Central Europe from the Pontic Steppe. It is not yet clear where J2-L70 was located at the time. It could have been present in the Steppe and tagged along the predominantly R1b branch of the Proto-Indo-Europeans that moved to the Balkans and Central Europe. Or it could have been one of the lineages of Chalcolithic Southeast and Central Europe. A third alternative is that L70 originated in Anatolia or Greece and moved to Italy with the migration that gave rise to the Etruscan civilization.” ref
“Z435 was formed about 3,600 years ago and has a TMRCA of only 3,100 years (± 300 years). The latter corresponds roughly to the timing of the invasion of the Italian peninsula by Italic tribes from the Alps. Z435 has numerous subclades of its own, and most have been identified in central Italy. This could either mean that Z435 was one of the founding Italic lineages, or that it was already in Italy and was assimilated by the Italic tribes. The PF5456 subclade is barely 2500 years old, and would have emerged and propagated after the founding of Rome. Outside Italy, it is now found in such varied places as Portugal, Spain, France, Britain, Belgium, southern Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, Tunisia or Lebanon, all regions colonized by the Romans. Z2177, another subclade of Z435, is a bit under 3,000 years old. It has various subclades of its own which are scattered today around Italy (northern Italy, Tuscany, Latium, Sicily, Sardinia) and in places like Switzerland, south-west Germany, Britain, Spain, Romania, Greece, Turkey, and Syria – also all these regions were part of the Roman Empire. Italy has by far the highest concentration of Z2177 of any country.” ref
J2a in Central & South Asia: the Harappan and Oxus Civilizations
“Within the Indian subcontinent, J2a peaks at frequencies of 15-25% around the Indo-Pakistani border, from Punjab to Gujarat and Sindh. This region matches exactly the confines of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilization, also known as the Harappan Civilisation, that existed from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE and which practiced bull worship like other J2a civilizations. Bronze started being used by the Harappan Civilization circa 3000 BCE, a few centuries after its earliest known regular use around the Caucasus by the Maykop culture (from 3700 BCE) and the Kura–Araxes culture (from 3500 BCE). While the Maykop culture was closely linked to the Yamnaya culture in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe and is thought to be associated with Proto-Indo-European speakers and Y-haplogroups R1a and R1b, the Kura-Araxes culture would have allowed the diffusion of Y-haplogroup J1 and J2a around the Middle East, taking over the Neolithic societies primarily associated with Y-haplogroup G2a and G2b.” ref
“Archeological evidence of a massive migration from the southern Caucasus to the Indus Valley is elusive at present, but it cannot be excluded as it has been proven now that large-scale Indo-European migrations took place during the same period from the Pontic-Caspian Steppe to Europe and Central Asia. There is no reason to believe that J2a people from the Kura-Araxes culture couldn’t have expanded in the same way westward toward Anatolia, Greece, and Italy and eastward to Iran, southern central Asia, Pakistan, and India.” ref
“There is another cluster of J2a with a frequency approximating 15% in Bactria, in southern-central Asia, in what is now northern Afghanistan, eastern Turkmenistan, southern Uzbekistan, and western Tajikistan. This region corresponds to the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex(BMAC), also known as the Oxus civilization, which flourished between 2300 and 1700 BCE. Oxen were used to draw wheeled carts and camels were domesticated in this region c. 2500 BCE, just before the start of this civilization. The BMAC was eventually overrun by the Indo-Iranian migrations from the Andronovo culture and the Sintashta culture further north, and became Indo-Europeanized. The Indo-Aryans pursued their southward expansion, invading northern Pakistan and northwest India from 1800 BCE to 1500 BCE, and eventually bringing about the demise of the Indus Valley Civilisation around 1300 BCE.” ref
“There is a wide variety of J2a branches found in South Asia. Some are over 10,000 years old (CTS6002, F3133, M68, M319, PF5174, Z6065) and could have migrated from West to South Asia during the Neolithic, Chalcolithic or Early Bronze Age. Based on their phylogeographies, F3133 and M319 could be associated with the Kura-Araxes expansion. Y21500 has a TMRCA of 3700 years and is also found in Russia, which suggests an Indo-Aryan origin – perhaps one of the J2a1 subclades assimilated by R1a invaders in Central Asia before conquering the Indian subcontinent. A few much younger clades are also found in western India and Pakistan, such as L534 (TMRCA 2,800 years before present) and YSC246 (TMRCA 1,750 years before present), and would have come to India in historical times, for example with the Mughals.” ref
J2b1: West Asian Copper & Bronze Age
“Today J2b1 is most common in the Western Balkans (Serbia, Bosnia, Croatia) and Cyprus. It is also found in above 1% of the population in parts of southern Italy (Calabria, Apulia), the Peloponnese in Greece, Lebanon, Jordan, eastern Turkey, Armenia, and Iran. The oldest samples recovered so far were from Early Bronze Age Jordan (c. 2400 BCE, Lazaridis et al. (2016)) and Late Bronze Age Lebanon (Canaanite burial from Sidon, Haber et al. (2017). It was also found in an Egyptian mummy (c. 660 BCE, Schuenemann et al. (2017).” ref
“J2b1’s origins remain unclear, but it probably originated in the South Caucasus and/or Iran and might have spread to the Levant, Cyprus, and Greece with the Kura-Araxes culture during the Bronze Age. The branch found in the western Balkans (Y22069) is distinct from the East Mediterranean and Caucasian branch. It seems to have formed 6,000 years ago, but its TMRCA is very young at 900 years before present, suggesting a medieval founder effect.” ref
J2b2-L283: from Neolithic Iran to the Indo-Europeans
“J2b has a quite different distribution from J2a. At first sight, the modern distribution of J2b seems to have a stronger association with the Neolithic and Chalcolithic cultures of Southeast Europe. Yet, at present, J2b has never been found in Neolithic, Chalcolithic, or even Bronze Age Europe, nor in the Fertile Crescent during the Neolithic or Chalcolithic. J2b is also absent from western and central Anatolia, but is present in eastern Anatolia and western Iran, as well as in the Volga-Ural region, notably among the Mordvins, Chuvashs, and Tatars. The oldest known J2b sample comes from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic site of Tepe Abdul Hosein in western Iran, dating from approximately 10,000 years ago. This is the strongest evidence that J2b actually originated in the mountains of the Zagros or the Caucasus, rather than in the plains of the Fertile Crescent.” ref
“The vast majority of J2b lineages belong to J2b2 and its subclades. While J2b* and J2b1 lineages are mostly restricted to the Caucasus, eastern Anatolia, and the Balkans, J2b2 is found throughout Europe, in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe, in Central Asia, and in South Asia, particularly in India. Although J2b2 itself was formed 14,000 years ago, almost all European J2b2 members belong to the L283 branch and share a common patrilineal ancestor who lived 6,000 years ago. What’s more, 99% of them fall under the Z628 (aka Z597) clade, with a shared common ancestor who lived only 4,500 years ago. This Z628 clade is also found in India, Armenia, and the Levant, among others.” ref
“The most likely hypothesis is that J2b2a1 (L283) penetrated into the Pontic Steppe region during the Neolithic or Chalcolithic period, by crossing the Caucasus from western Iran, then migrated to the Volga-Ural region, where it was absorbed by the R1a-Z93 tribes in the Early Bronze Age. As a minor lineage within the R1a-Z93 dominant populations, it would have expanded from the Volga-Ural region to Central and South Asia with the Indo-Aryan invasions approximately from 4,300 to 3,500 years ago. Other J2b lineages could have ended up in the Balkans during a number of Steppe invasions from the Bronze Age until the Middle Ages.” ref
“Another conceivable possibility is that a minority of J2b2-L283 accompanied R1b-M269 from the Caucasus region and migrated to the Volga-Ural region in the early Bronze Age, propagating with them the Proto-Indo-European language and bronze technology to the Caspian steppe before the expansion of this new culture to Central and South Asia. The drawback of this hypothesis is that it doesn’t explain why R1b lineages strongly outnumber J2b2 in Europe but not in South Asia.” ref
“The oldest J2b2-L283 sample recovered among ancient DNA samples is a Late Bronze Age (1700-1500 BCE) individual from southern Croatia (Mathieson et al. 2017). His genome possessed about 30% of Steppe admixture and 15% of Eastern Hunter-Gatherer, which suggest a recent arrival from the Steppe. He was accompanied by a woman with similar admixtures, and both possessed typical Pontic-Caspian Steppe mtDNA (I1a1 and W3a). The timing, location, and admixtures of these samples fit with the Illyrian colonization of the Dinaric Alps, which is thought to have taken place between 1600 and 1100 BCE. The Illyrians may have been late Steppe migrants from the Volga region that were forced out of the Steppe by the invasion of the northern R1a tribes who established the Srubna culture (from 2000 BCE). Through a founding effect, J2b2-L283 lineages might have considerably increased their original frequency after reaching Illyria.” ref
“Both J2b1 and J2b2-L283 are also found at high frequency in Greece and in regions that used to be part of the ancient Greek world (Ionia, Magna Graecia). However, they are almost absent from Crete (where J2a1 lineages are dominant). J2b was also not found among Neolithic Anatolian or European farmers, and is absent from central Anatolia. This suggests that J2b was not associated with the Neolithic Greeks nor with the Minoan civilization, but may well have come to Greece with the Mycenaeans, who also appear to have been pushed out of the Steppe by the advance of the Srubna culture. As a result, both the Illyrians and the Mycenaeans (and possibly the Albanians) would be descended from Middle to Late Bronze Age Steppe migrants to the Southeast Europe, in a migration that was particularly rich in J2b lineages from the Middle Volga region. That would explain why it has been so hard to identify R1a or R1b lineages that could be of Illyrian or Mycenaean origin. The only variety of R1b that is found at reasonably high frequencies in Southeast Europe, and particularly in Greece, is R1b-Z2103, the branch found in the eastern Yamna culture, including the Volga-Ural region. J2b2-Z2432: West Asian Neolithic expansion to South Asia.” ref
“The other main J2b2 subclade is Z2432, which split from L283 some 10,000 years ago, during the Early Neolithic. This branch is found almost exclusively in South Asia today, apart from a few reported samples from the Middle East (Syria, Iraq, Arabian peninsula, Egypt). In all likelihood, it represents the descendants of Iranian Neolithic farmers toward the Indian subcontinent, although it can’t be ruled out at present that some clades migrated later from Iran, during the Chalcolithic period or the Bronze Age.” ref
Haplogroup J2 (Y-DNA) – Eupedia
Haplogroup J (mtDNA) – Wikipedia
Haplogroup J (Y-DNA) – Wikipedia
Early origins J DNA and the spread of Haplogroup J
by familytreedna.com
“In Human Genetics, J2 haplogroup (AKA J-M172) is among the most frequent Y DNA haplogroups in the Middle East and in the Arab World. The geographic origin is believed to be in the crescent fertile (Iraq, Turkey, and Syria) The age is estimated to be 18,500 +/- 3,500 thousand years ago See more details about J2 haplogroup in this page: Haplogroup_J2_(Y-DNA)” ref
“The origin of Y-DNA Haplogroup J maps to the Middle East around the Fertile Crescent, an area also known as the ‘Cradle of Civilization’ since this area saw the birth of many technological advancements that helped humans move from nomadic hunter-gatherers to an agriculture-based society living in one place. The sprouting of some of the first cities and empires in human history were contingent on these developments and featured the proliferation of Haplogroup J. Y-DNA Haplogroup J is a descendent of supra-haplogroup F, which encompasses a large group Y-DNA lineages (haplogroups F-T). Suprahaplogroup F is believed to have migrated from Africa at approximately 50,000 years ago.” ref
“Haplogroup J arose approximately 30,000 years ago and has been defined by a number of unique Y-chromosome polymorphisms; the 12f2a deletion and the M304 and P209 SNPs. The precise location for the origin of Haplogroup J is not known, but its prominence in the Near East/West Asia and the Middle East/Central Asia indicates that it likely arose in one of these regions. It is closely associated with the Fertile Crescent; an area spanning the Nile and Tigris/Euphrates River systems, with the Levant (present-day Lebanon) in between. This region has encompassed many early cultures and empires from the Stone Age (Neolithic) to the Iron Age and has also been dubbed the ‘Cradle of Civilization’. Societies, dynasties, and empires in this broad region include the Sumerian, Assyrian, Babylonian, Egyptian, Phoenician and Persian. Haplogroup J is also particularly abundant in Anatolia (present-day Turkey) and the Y-chromosome diversity observed here suggests that this area is a possible source of this clade.” ref
“Owing to these strategic locations, Y-DNA Haplogroup J is common on three continents: Asia, Europe, and Africa. Middle East populations belonging to Y-DNA Haplogroup J migrated during or after the Neolithic era to Mediterranean regions and back to Africa; although this did not reach sub-Saharan regions. This spread contributes significantly to populations in European and African countries around the Mediterranean Sea. Moreover, this migration, also termed a “demic diffusion”, is believed to be the source of new agriculture practices, which included domestication of animals or pastoralism. It is also associated with sedentism or the custom of living in one place as opposed to the more mobile hunter-gatherer and nomadic lifestyle. Thus, the movement is tied to the rise of cities and city-states. While Y-DNA Haplogroup J is linked with this important Neolithic demic diffusion, additional migrations subsequent to this provided other diasporic episodes of this haplogroup and its subclades.” ref
J2. M172.
“The J2 subclade is similar in distribution to J1, but it is typically present at a higher frequency. J2 is distinguished from J1 by a lower frequency in Arab populations and the near absence in Africa. The J2 subclade is highest in Anatolia and prominent in Mesopotamia and the Levant – all areas that served as centers of the agricultural revolution. J2 is common among Turkish, Kurdish, and Jewish populations, and significant frequencies are found in the Caucasus, Iran, and Southcentral Asia. TMRCA estimates for this haplogroup range from 4,000-15,000 years ago. J2 may be an important Y-chromosome lineage that was part of the demic diffusion and introduction of new agricultural practices into Europe from the Middle East and Anatolia during the Neolithic period. Anatolia could represent a Mesolithic pocket of the J2 subclade, which spread later to Europe in the Neolithic-Holocene periods (10,000 years ago) and subsequently featured in the emergence and progress of the Bronze Age (5,000 years ago).” ref
“Prominent European areas of J2 abundance include the Iberian Peninsula, Italy, the Balkans, and Greece. An interesting general feature is that J2 frequencies drop off considerably in the Northward direction. From the Balkan Peninsula, there is a drop in abundance moving into and beyond the Carpathian Mountain countries of Ukraine, Romania, and Hungary. A similar sharp drop-off between Nepal and Tibet is attributed to the geographic barrier of the Himalayan Mountains. In Russia, the J2 subclade is more frequent than J1, but because it is much lower than the neighboring Caucasus region (e.g. Georgia, Azerbaijan) to the South, there appears to be infrequent patrilineal gene flow from the Caucasus to Russia. The Caucasus Mountain Range may have been an effective barrier separating Russia to the North and the Caucasus to the South. The diffusion of the J2 subclade into Europe may have been by mediated by the Mediterranean Sea.” ref
“The J2 subclade is abundant on several Mediterranean Islands: Crete, Cyprus, Malta, Sicily, Sardinia, and Korčula (Croatia). The frequency of J haplogroups can distinguish Mediterranean groups (North Africa) (Near East/Arabs) (Central/East/Lebanon) (West). Similarly, using STR data, three groups can be revealed (North African)(Arab/Palestinians)(and Mediterranean/Italy/Sardinia). The J2 chromosomes in Crete are more similar to those found in Anatolia than those found in Greece when the DYS413 and other STR data are taken into account. This shows that there are sufficient genetic differences to differentiate the populations and it may represent multiple episodes of J subclade expansion and dispersal. The J2 subclade is abundant in Iran (30%), known throughout much of history as Persia. Studies support the introduction of this subclade here from Anatolia, with less contribution from the East in the direction of Pakistan. The barriers presented by the Hindu Kush mountains in Pakistan and deserts in Iran, may have limited gene flow from the East. The attraction of the fertile Mesopotamian valley may have favored the migration from Anatolia in the West, thus producing a general West to East migration pattern and spread of J2 into Iran.” ref
“A genetic separation between the North and South of Iran may have also been aided by the deserts separating these regions. Furthermore, cultural alliances between Anatolia and Persia have been strong as exemplified by the Babylonian, Assyrian, Persian and Ottoman Empires, lending support to the idea that there was a strong connection from Turkey, through Iraq to South Iran. It is quite possible that these empires aided the dissemination of Haplogroup J. The J2 subclade is abundant in India (2-20%), and its frequency peaks in the Northwest region. Anatolia is most likely the source of this subclade in India, again consistent with the West to East flow of J2. The date of this invasion points to a period during or after the Neolithic era. J2 lineage is also found in SW India with an interesting frequency trend: a higher fraction of J2 in the higher castes and decreasing amounts in lower castes. The J2a subclade is present in the Middle East and Southcentral Asia (~4%), the latter of which includes India and Nepal. In India, there is a general trend for increased J2a frequency in higher castes. It has also been found in Crete (1-2%).” ref
J2a4h(10).L24 L25
“This subgroup has a wide distribution in the world. It is found in the Middle East, North Africa, Europe, India, and the Americas.” ref
J2a4a. M47
“The J2a4a subclade is found at low levels in Anatolia (1-4%) and Georgia (2%). In the Middle East, it has been detected at similar levels in Iran, Iraq, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. This appears to be a relatively low-frequency J subclade.” ref
J2a4b. M67
“The estimated TMRCA is 9kya for the J2a4b subclade. This subclade is abundant in the Caucasus (Georgia 13%, Azerbaijan 4%) and is an ancient group – TMRCA estimated at 12kya. It has also been found at appreciable levels (1-8%) in Anatolia, with preponderance in the Northwest as well as in Italy (~5%) and the Iberian Peninsula (2-3%). This has led to proposals for migration over land from Anatolia via the Bosphorus Isthmus or over the Mediterranean Sea. Notably, 10% of the Y-chromosomes on Crete are of this variety. J2a4b is also found in the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Lebanon, Pakistan, and India. Significant frequencies (10-20%) are also found in Jewish populations.” ref
J2a4b1. M92
“Its distribution has been recorded in Italy (5%), Anatolia (~4%), and the Balkan Peninsula (~3%). Notable levels have also been located in southern Iran, Iraq, Pakistan, and Northwest India. Its presence in Europe, may indicate that the Bosphorus Isthmus was a migratory route. Alternatively, the Mediterranean Sea could have been used for the spread of this subclade. It has been found in Ashkenazi Jews, but not Sephardic Jews.” ref
J2a4b1a. M327
“Little information is currently known for the J2a4b1a subclade, but it appears to be a minor and infrequent subclade. It has been found in Konya in Turkey (<1%).” ref
J2a4b2. M163
“A minor J subclade, currently it has only been found at very low levels (0.2%) in Spain (non-Basques).” ref
J2a4c. M68
“J2a4c appears to be a minor subclade with low levels (1%) detected in Iraq and India.” ref
J2a4h2. M158
“Modest levels (1-2%) of the J2a4h2 subclade have been uncovered in Anatolia, Pakistan, and India.” ref
J2a4h1a1b. M289
“J2a4h1a1b appears to be a minor subclade. Currently, it has only been detected in the Druze in Israel (5%).” ref
J2a4h3. M318
“J2a4h3 appears to be a minor subclade. Currently, it has been detected in Israel for those of Libyan Jewish ancestry (5%) and among the Jewish population of Jerba island in Tunisia.” ref
J2a4d. M319
“The J2a4d subclade, defined by SNP M319, has been found in Crete (6-9%), which may be a source of M319 subclade, as this subclade is infrequent and not found in many other areas. Presently, Israel is the only other location where this subclade has been found.” ref
J2a4e. M339
“The J2a4e subclade has not been studied extensively. It appears with a very low frequency in parts of Anatolia (1%).” ref
J2a2. M340
The J2a2 subclade has not been studied extensively. It appears with a very low frequency in parts of Anatolia (1%).
J2a4f. M419
“The M419 defines the J2a4f subclade. It has not been widely studied, and has been found at <1% in Northern Iran. Likely to be a minor subclade.” ref
J2b. M12, M102, M221, M314
“The J2b subclade has a similar European distribution to Y-chromosome subclade E-V13 and TMRCA estimate (~4.4kya), which is consistent with a common route of dispersal. It is most prominent in Balkans, Greece, and Italy (North and Central regions), reaching frequencies around 5-10%. Present-day countries with the highest frequencies include Albania, Hungary, Greece, and Macedonia. This haplogroup population may have moved through the Balkans and north into Europe via rivers, such as the Danube. It is present in Crete and the Iberian Peninsula, which could also indicate a spread by sea-faring routes in the Mediterranean. The J2b subclade is also present in Pakistan, India, and Iran (3-4%). It displays a modest frequency in Egypt, Oman, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates (1-4%), and Africa.” ref
“These trends in Arab populations and Africa are reminiscent of the distribution of the J1 subclade and provides evidence that the several of the J subclades share some history in dispersal and expansion. Currently, no information is available for the distribution and frequency of this haplogroup J subclade. The J2b2 subclade is present in India, where it appears to have the highest frequency among the middle castes (Dravidian and Indo-European). Its overall level in India is ~5% and this frequency drops in half in neighboring Pakistan. J2b2 is also found in Nepal, but no J2b2 has been found in Tibet, providing strong evidence that the Northern spread of this subclade was prevented by the Himalaya Mountains. The J2b2 subclade is also present in Anatolia, specifically in the southern and eastern regions, which have been proposed as a source of J haplogroups for many regions. An interesting peak of the J2b2 subclade has been detected in Kosovar Albanians (~17%), whereas the J2b2 levels range from 1 to 4% in the Balkans overall. Within the J2b2 subclade defined by SNP241, there is a DYS455 deletion allele (8 repeats or DYS455=8) that is not found in the J2b1 (SNP M205) subclade.” ref
J2b2b. M280
“The J2b2b subclade has so far only been detected in Greece (2%). It appears to be absent from surrounding areas and it is likely to represent a minor J subclade.” ref
J2b2c. M321
“Limited information is available for the J2b2c subclade and the information available so far has only shown it to be present in Libyan Jewish population in Israel (5%).” ref
J2b2d. P84
“Currently, no information is available for the distribution and frequency of this haplogroup J subclade.” ref
External Links
The Levantine & African branch of R1b (V88)
“Like its northern counterpart (R1b-M269), R1b-V88 is associated with the domestication of cattle in northern Mesopotamia. Both branches of R1b probably split soon after cattle were domesticated, approximately 10,500 years ago (8,500 BCE). R1b-V88 migrated south towards the Levant and Egypt. The migration of R1b people can be followed archeologically through the presence of domesticated cattle, which appear in central Syria around 8,000-7,500 BCE (late Mureybet period), then in the Southern Levant and Egypt around 7,000-6,500 BCE (e.g. at Nabta Playa and Bir Kiseiba). Cattle herders subsequently spread across most of northern and eastern Africa. The Sahara desert would have been more humid during the Neolithic Subpluvial period (c. 7250-3250 BCE), and would have been a vast savannah full of grass, an ideal environment for cattle herding.” ref
“Evidence of cow herding during the Neolithic has shown up at Uan Muhuggiag in central Libya around 5500 BCE, at the Capeletti Cave in northern Algeria around 4500 BCE. But the most compelling evidence that R1b people related to modern Europeans once roamed the Sahara is to be found at Tassili n’Ajjer in southern Algeria, a site famous pyroglyphs (rock art) dating from the Neolithic era. Some painting dating from around 3000 BCE depict fair-skinned and blond or auburn haired women riding on cows. The oldest known R1b-V88 sample in Europe is a 6,200 year-old farmer/herder from Catalonia tested by Haak et al. (2015). Autosomally this individual was a typical Near Eastern farmer, possessing just a little bit of Mesolithic West European admixture. After reaching the Maghreb, R1b-V88 cattle herders could have crossed the Strait of Gibraltar to Iberia, probably accompanied by G2 farmers, J1 and T1a goat herders. These North African Neolithic farmers/herders could have been the ones who established the Almagra Pottery culture in Andalusia in the 6th millennium BCE.” ref
“Nowadays small percentages (1 to 4%) of R1b-V88 are found in the Levant, among the Lebanese, the Druze, and the Jews, and almost in every country in Africa north of the equator. Higher frequency in Egypt (5%), among Berbers from the Egypt-Libya border (23%), among the Sudanese Copts (15%), the Hausa people of Sudan (40%), the Fulani people of the Sahel (54% in Niger and Cameroon), and Chadic tribes of northern Nigeria and northern Cameroon (especially among the Kirdi), where it is observed at a frequency ranging from 30% to 95% of men. According to Cruciani et al. (2010) R1b-V88 would have crossed the Sahara between 9,200 and 5,600 years ago, and is most probably associated with the diffusion of Chadic languages, a branch of the Afroasiatic languages. V88 would have migrated from Egypt to Sudan, then expanded along the Sahel until northern Cameroon and Nigeria. However, R1b-V88 is not only present among Chadic speakers, but also among Senegambian speakers (Fula-Hausa) and Semitic speakers (Berbers, Arabs).” ref
“R1b-V88 is found among the native populations of Rwanda, South Africa, Namibia, Angola, Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, Ivory Coast, Guinea-Bissau. The wide distribution of V88 in all parts of Africa, its incidence among herding tribes, and the coalescence age of the haplogroup all support a Neolithic dispersal. In any case, a later migration out of Egypt would be improbable since it would have brought haplogroups that came to Egypt during the Bronze Age, such as J1, J2, R1a, or R1b-L23. The maternal lineages associated with the spread of R1b-V88 in Africa are mtDNA haplogroups J1b, U5, and V, and perhaps also U3 and some H subclades (=> see Retracing the mtDNA haplogroups of the original R1b people).” ref
The North Caucasus and the Pontic-Caspian steppe : the Indo-European link
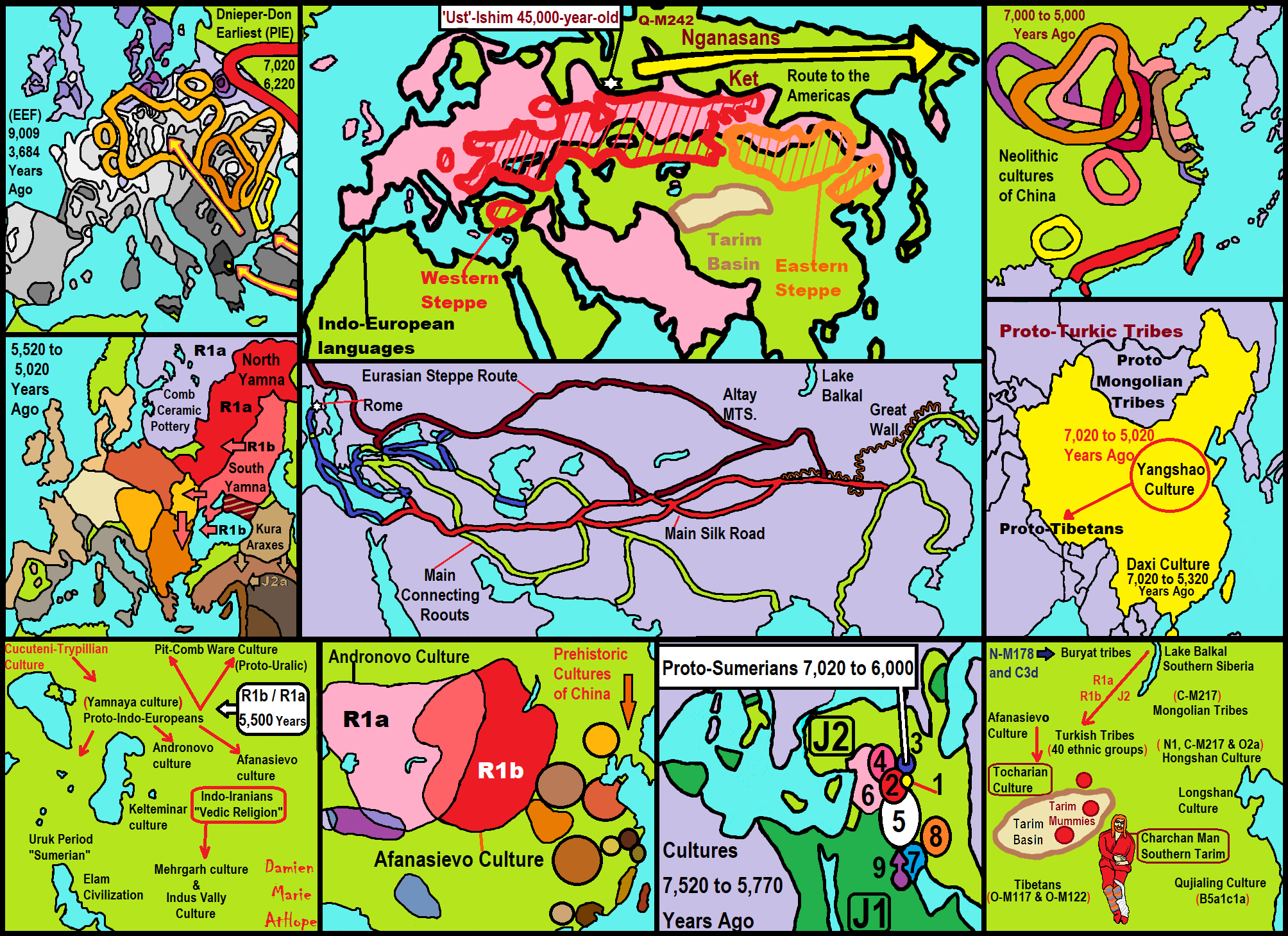
“Modern linguists have placed the Proto-Indo-European homeland in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe, a distinct geographic and archeological region extending from the Danube estuary to the Ural mountains to the east and North Caucasus to the south. The Neolithic, Eneolithic, and early Bronze Age cultures in Pontic-Caspian steppe has been called the Kurgan culture (4200-2200 BCE) by Marija Gimbutas, due to the lasting practice of burying the deads under mounds (“kurgan”) among the succession of cultures in that region. It is now known that kurgan-type burials only date from the 4th millenium BCE and almost certainly originated south of the Caucasus. The genetic diversity of R1b being greater around eastern Anatolia, it is hard to deny that R1b evolved there before entering the steppe world.” ref
“Horses were first domesticated around 4600 BCE in the Caspian Steppe, perhaps somewhere around the Don or the lower Volga, and soon became a defining element of steppe culture. Nevertheless, it is unlikely that R1b was already present in the eastern steppes at the time, so the domestication of the horse should be attributed to the indigenous R1a people, or tribes belonging to the older R1b-P297 branch, which settled in eastern Europe during the Late Paleolithic or Mesolithic period. Samples from Mesolithic Samara (Haak 2015) and Latvia (Jones 2017) all belonged to R1b-P297. Autosomally these Mesolithic R1a and R1b individuals were nearly pure Mesolithic East European, sometimes with a bit of Siberian admixture, but lacked the additional Caucasian admixture found in the Chalcolithic Afanasevo, Yamna, and Corded Ware samples.” ref
“It is not yet entirely clear when R1b-M269 crossed over from the South Caucasus to the Pontic-Caspian steppe. This might have happened with the appearance of the Dnieper-Donets culture (c. 5100-4300 BCE). This was the first truly Neolithic society in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe. Domesticated animals (cattle, sheep, and goats) were herded throughout the steppes and funeral rituals were elaborate. Sheep wool would play an important role in Indo-European society, notably in the Celtic and Germanic (R1b branches of the Indo-Europeans) clothing traditions up to this day. However, many elements indicate a continuity in the Dnieper-Donets culture with the previous Mesolithic hunter-gatherers, and at the same time an influence from the Balkans and Carpathians, with regular imports of pottery and copper objects. It is therefore more likely that Dnieper-Donets marked the transition of indigenous R1a and/or I2a1b people to early agriculture, perhaps with an influx of Near Eastern farmers from ‘Old Europe’. Over 30 DNA samples from Neolithic Ukraine (5500-4800 BCE) were tested by Mathieson et al. (2017). They belonged to Y-haplogroups I, I2a2, R1a, R1b1a (L754), and one R1b1a2 (L388). None of them belonged to R1b-M269 or R1b-L23 clades, which dominated during the Yamna/Yamnaya period.” ref
“Mitochondrial lineages were also exclusively of Mesolithic European origin (U4a, U4b, U4d, U5a1, U5a2, U5b2, as well as one J2b1 and one U2e1). None of those maternal lineages include typical Indo-European haplogroups, like H2a1, H6, H8, H15, I1a1, J1b1a, W3, W4 or W5 that would later show up in the Yamna, Corded Ware, and Unetice cultures. Indeed, autosomally genomes from Neolithic Ukraine were purely Mesolithic European (about 90% EHG and 10% WHG) and completely lacked the Caucasian (CHG) admixture later found in Yamna and subsequent Indo-European cultures during the Bronze Age. The first clearly Proto-Indo-European cultures were the Khvalynsk (5200-4500 BCE) and Sredny Stog (4600-3900 BCE) cultures in the Pontic-Caspian Steppe. This is when small kurgan burials begin to appear, with the distinctive posturing of the dead on the back with knees raised and oriented toward the northeast, which would be found in later steppe cultures as well. There is evidence of population blending from the variety of skull shapes. Towards the end of the 5th millennium, an elite starts to develop with cattle, horses, and copper used as status symbols.” ref
“It is at the turn of the Khvalynsk and Sredny Stog periods that R1b-M269’s main subclade, L23, is thought to have appeared, around 4,500 BCE. 99% of Indo-European R1b descends from this L23 clade. The other branch descended from M269 is PF7562, which is found mostly in the Balkans, Turkey, and Armenia today, and may represent an early Steppe migration to the Balkans dating from the Sredny Stog period. Another migration across the Caucasus happened shortly before 3700 BCE, when the Maykop culture, the world’s first Bronze Age society, suddenly materialized in the north-west Caucasus, apparently out of nowhere. The origins of Maykop are still uncertain, but archeologists have linked it to contemporary Chalcolithic cultures in Assyria and western Iran. Archeology also shows a clear diffusion of bronze working and kurgan-type burials from the Maykop culture to the Pontic Steppe, where the Yamna culture developed soon afterwards (from 3500 BCE). Kurgan (a.k.a. tumulus) burials would become a dominant feature of ancient Indo-European societies and were widely used by the Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, and Scythians, among others.” ref
“The Yamna/Yamnaya period (3500-2500 BCE) is the most important one in the creation of Indo-European culture and society. Middle Eastern R1b-M269 people had been living and blending to some extent with the local R1a foragers and herders for over a millennium, perhaps even two or three. The close cultural contact and interactions between R1a and R1b people all over the Pontic-Caspian Steppe resulted in the creation of a common vernacular, a new lingua franca, which linguists have called Proto-Indo-European (PIE). It is pointless to try to assign another region of origin to the PIE language. Linguistic similarities exist between PIE and Caucasian and Hurrian languages in the Middle East on the one hand, and Uralic languages in the Volga-Ural region on the other hand, which makes the Pontic Steppe the perfect intermediary region.” ref
Yamnaya culture
“The Yamnaya culture, also known as the Yamnaya Horizon, Yamna culture, Pit Grave culture, or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: Я́мная (romanization: yamnaya) is a Russian adjective that means ‘related to pits (yama)’, and these people used to bury their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG) and people related to hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus (CHG), an ancestral component which is often named “Steppe ancestry”, with an additional admixture of up to 18% from Early European Farmers. Their material culture was very similar to the Afanasevo culture, and the populations of both cultures are genetically indistinguishable. They lived primarily as nomads, with a chiefdom system and wheeled carts and wagons that allowed them to manage large herds.” ref
“The people of the Yamnaya culture are also closely connected to Final Neolithic cultures, which later spread throughout Europe and Central Asia, especially the Corded Ware people and the Bell Beaker culture, as well as the peoples of the Sintashta, Andronovo, and Srubnaya cultures. Back migration from Corded Ware also contributed to Sintashta and Andronovo. In these groups, several aspects of the Yamnaya culture are present. Genetic studies have also indicated that these populations derived large parts of their ancestry from the steppes. The Yamnaya culture is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans, and the Pontic-Caspian steppe is the strongest candidate for the Urheimat (original homeland) of the Proto-Indo-European language. According to Pavel Dolukhanov (1996) the emergence of the Pit-Grave culture represents a social development of various local Bronze Age cultures, representing “an expression of social stratification and the emergence of chiefdom-type nomadic social structures”, which in turn intensified inter-group contacts between essentially heterogeneous social groups.” ref
“According to Mallory (1999), “The origin of the Yamnaya culture is still a topic of debate,” with proposals for its origins pointing to both Khvalynsk and Sredny Stog. The Khvalynsk culture (4700–3800 BCE) (middle Volga) and the Don-based Repin culture (ca.3950–3300 BCE) in the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe, and the closely related Sredny Stog culture (c. 4500–3500 BCE) in the western Pontic-Caspian steppe, preceded the Yamnaya culture (3300–2500 BCE). According to Anthony (2007), the Yamnaya culture (3300–2600 BCE) originated in the Don–Volga area at ca. 3400 BCE, preceded by the middle Volga-based Khvalynsk culture and the Don-based Repin culture (c. 3950–3300 BCE), arguing that late pottery from these two cultures can barely be distinguished from early Yamnaya pottery. Earlier continuity from Eneolithic/Copper Age but largely hunter-gatherer Samara culture and influences from the more agricultural Dnieper–Donets II are apparent. In the Baltic, Jones et al. (2017) found that the Neolithic transition – the passage from a hunter-gatherer economy to a farming-based economy – coincided with the arrival en masse of individuals with Yamnaya-like ancestry. This is different from what happened in Western and Southern Europe, where the Neolithic transition was caused by a population that came from Anatolia, with Pontic steppe ancestry being detected from only the late Neolithic onward. Per Haak et al. (2015), the Yamnaya contribution in the modern populations of Eastern Europe ranges from 46.8% among Russians to 42.8% in Ukrainians. Finland has one of the highest Yamnaya contributions in all of Europe (50.4%).” ref
“Alternatively, Parpola (2015) relates both the Corded ware culture and the Yamnaya culture to the late Tripolye culture. (Cucuteni–Trypillia culture, also known as the Tripolye culture, is a Neolithic–Eneolithic archaeological culture (c. 5500 to 2750 BCE) of Eastern Europe). He hypothesizes that “the Tripolye culture was taken over by PIE speakers by c. 4000 BCE,” and that in its final phase the Tripolye culture expanded to the steppes, morphing into various regional cultures which fused with the late Sredny Stog pastoralist cultures, which, he suggests, gave rise to the Yamnaya culture. During its middle phase (c. 4000 to 3500 BCE), populations belonging to the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture built the largest settlements in Neolithic Europe, some of which contained as many as three thousand structures and were possibly inhabited by 20,000 to 46,000 people.” ref, ref
“According to Jones et al. (2015) and Haak et al. (2015), autosomal tests indicate that the Yamnaya people were the result of a genetic admixture between two different hunter-gatherer populations: distinctive “Eastern Hunter-Gatherers” (EHG), from Eastern Europe, with high affinity to the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture or other, closely related people from Siberia and a population of “Caucasus hunter-gatherers” (CHG) who probably arrived from the Caucasus or Iran. Each of those two populations contributed about half the Yamnaya DNA. This admixture is referred to in archaeogenetics as Western Steppe Herder (WSH) ancestry. Autosomal tests also indicate that the Yamnaya are the most likely vector for “Ancient North Eurasian” admixture into Europe. “Ancient North Eurasian” is the name given in literature to a genetic component that represents descent from the people of the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture or a population closely related to them. That genetic component is visible in tests of the Yamnaya people as well as modern-day Europeans, but not of Europeans predating the Bronze Age.” ref
“Admixture between EHGs and CHGs is believed to have occurred on the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe starting around 5,000 BCE, while admixture with Early European Farmers (EEF) happened in the southern parts of the Pontic-Caspian steppe sometime later. As Yamnaya Y-DNA is exclusively of the EHG and WHG type, displaying genetic continuity from the paternal lineages of the Dnieper-Donets culture, the admixture appears to have occurred predominantly between EHG males, and CHG and EEF females. Haplogroup R1b, especially subclades of R1b-M269, is the most common Y-DNA haplogroup found among both the Yamnaya and modern-day Western Europeans. Additionally, a minority are found to belong to haplogroup I2. They are found to belong to a wider variety of mtDNA haplogroups, including U, T, and haplogroups associated with Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers and Early European Farmers. It has been hypothesized that an allele associated with lactase persistence (conferring lactose tolerance into adulthood) was brought to Europe from the steppe by Yamnaya-related migrations.” ref
“People of the Yamnaya culture are believed to have had mostly brown eye color, light to intermediate skin, and brown hair color, with some variation. Some individuals are believed to have carried a mutation to the KITLG gene associated with blond hair, as several individuals with Steppe ancestry are later found to carry this mutation. The Ancient North Eurasian population, who contributed significant ancestry to Western Steppe Herders, are believed to be the source of this mutation. A study in 2015 found that Yamnaya had the highest ever calculated genetic selection for height of any of the ancient populations tested. The geneticist David Reich has argued that the genetic data supports the likelihood that the people of the Yamnaya culture were a “single, genetically coherent group” who were responsible for spreading many Indo-European languages. Reich also argues that the genetic evidence shows that Yamnaya society was an oligarchy dominated by a small number of elite males. The genetic evidence for the extent of the role of the Yamnaya culture in the spread of Indo-European languages has however been questioned by Russian archaeologist Leo Klejn and Balanovsky et al., who note a lack of male haplogroup continuity between the people of the Yamnaya culture and the contemporary populations of Europe.” ref
The number of settlements contemporaneous with Gobekli Tepe Layer II (assigned to Pre-Pottery Neolithic B: 10,800 – 8,500 years ago) increased amongst the Neolithic settlements in the Urfa region and become widespread all around the region.
- Gobekli Tepe, 2. Nevali Cori, 3. Tasli Tepe, 4. Kurt Tepesi, 5. Sefer Tepe, 6. Karahan Tepe, 7. Harbetsuvan Tepesi, 8. Hamzan Tepe, 9. Urfa, 10. Ayanlar Hoyuk/Gaziantep, 11. Kilisik, 12. Tell Abr 3, 13. Boncuklu Tarla, 14. Gusir Hoyuk, 15. Nemrik 9, 16. Qermez Dere, 17. Hasankeyf, 18. Cayonu, 19. Hallan Cemi, 20. Demirci, 21. Kortik Tepe, 22. Mureybet, 23. Cheik Hassan, 24. Jerf el Ahmar, 25. Dja’de, 26. Tell Abr, 27. Akarcay, and 28. Tell Qarmel
Göbekli Tepe is not alone, in fact, it is part of a religious/cultural connected ritual culture in the general region. There are several other similar sites with similar T-pillars to Göbekli Tepe or other types of stone pillar providing a seeming connected cult belief or religious culture of pillars seen in the PPNA-PPNB in the northern portion of the Near East.
“The locations of the sites that contain “T” shaped pillars are the main topic that needs more understanding to grasp the larger sociocultural-religious cultural complex in the same general region. Another matter under discussion is to comprehend the differences between the small-scale settlements that contain cult centers and “T” shaped pillars and the larger ones found at Gobekli Tepe layer III. The fact that settlements with “T” shaped pillars contain both the remains of circular domestic buildings and the pillars such as seen at Cayonu and Nevali Cori, which are also known to contain cult and domestic buildings. It is contemplated that such settlements are contemporary with Gobekli Tepe layer II and the cult building known from Nevali Cori based on the similarities and differences of the “T” shaped pillars. In the light of the finds unearthed from the settlements in Şanliurfa region that contain “T” shaped pillars, such settlements should be dated to the end of Late Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (LPPNA) and the Early Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (EPPNB).” ref
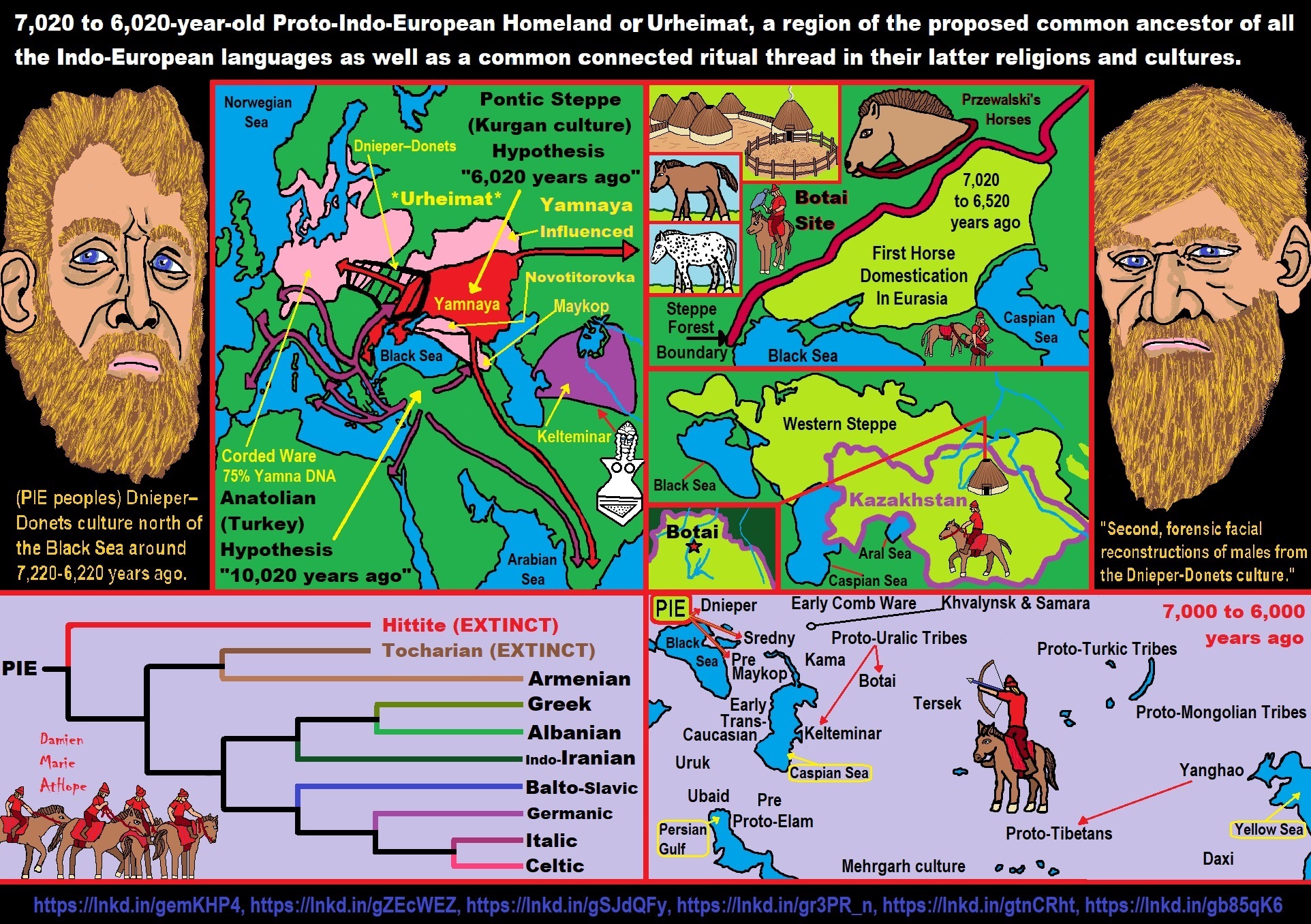
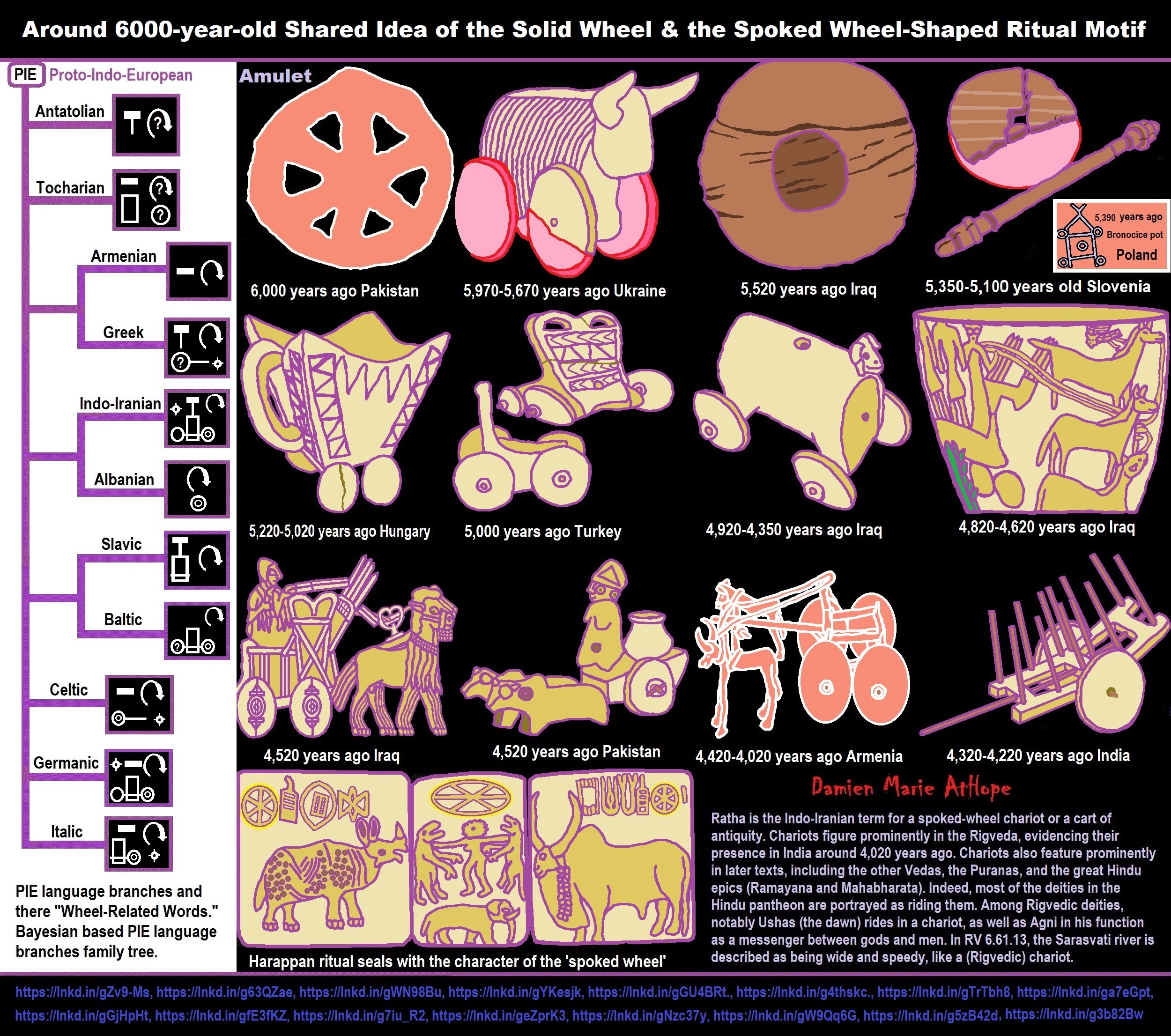
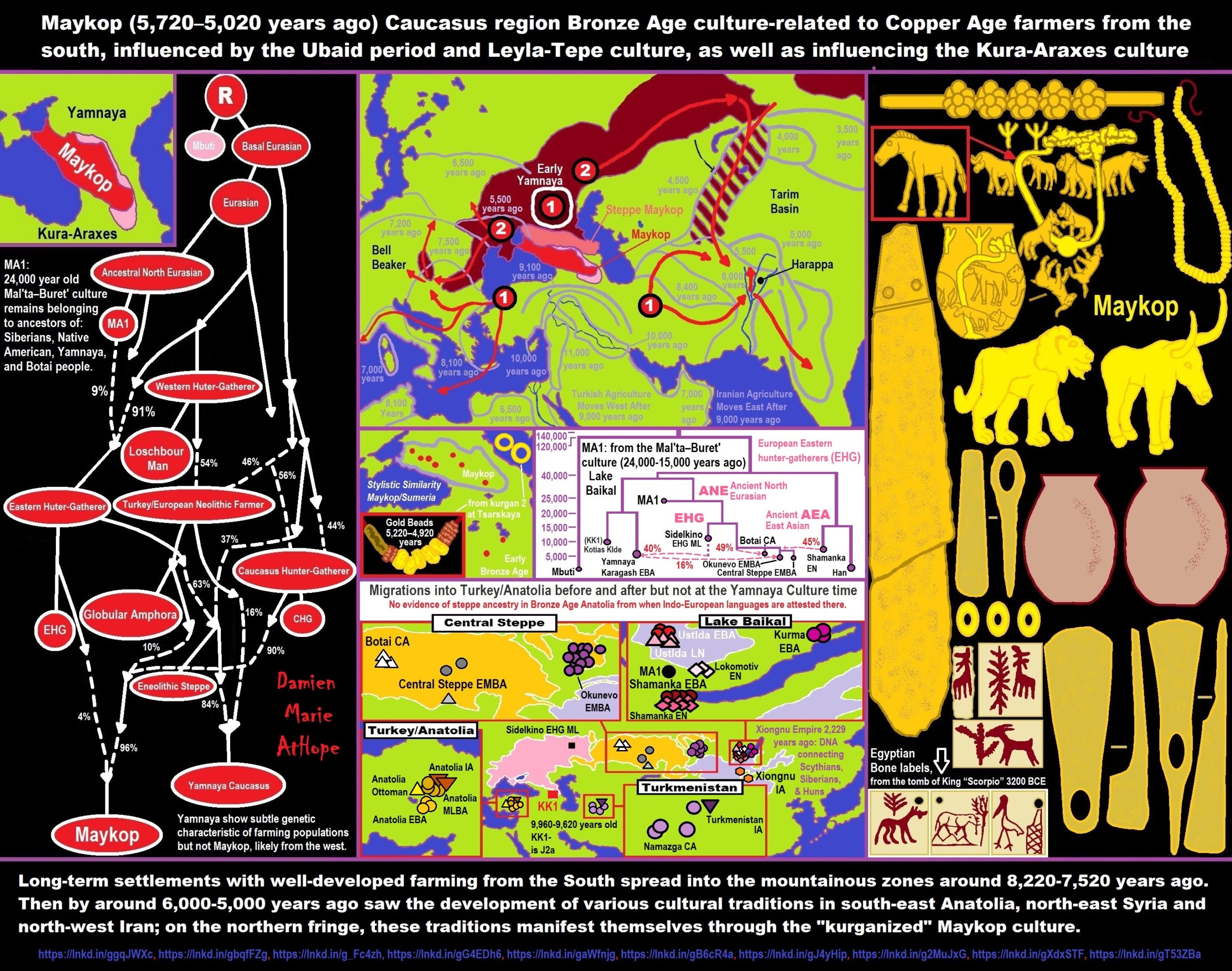
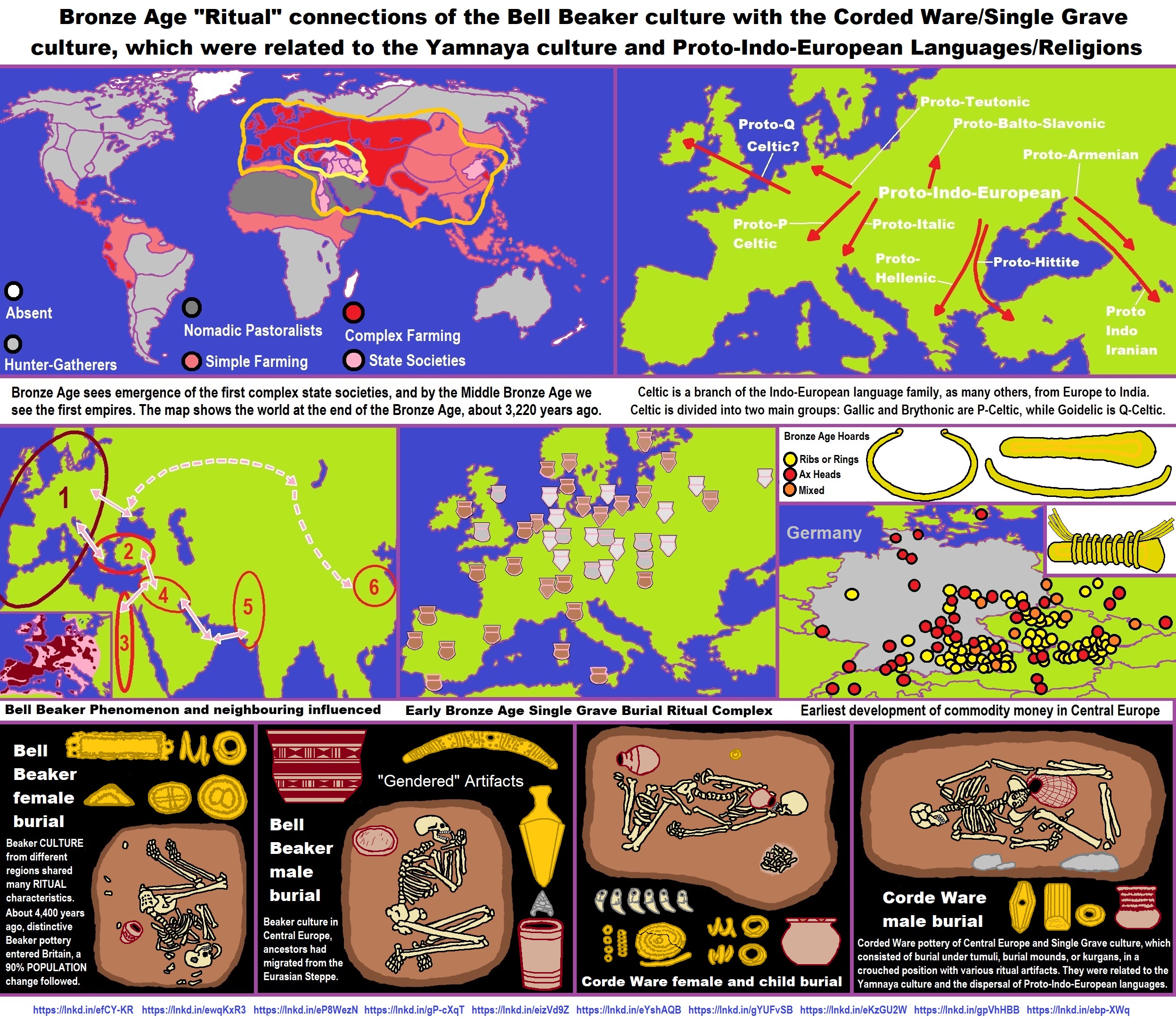
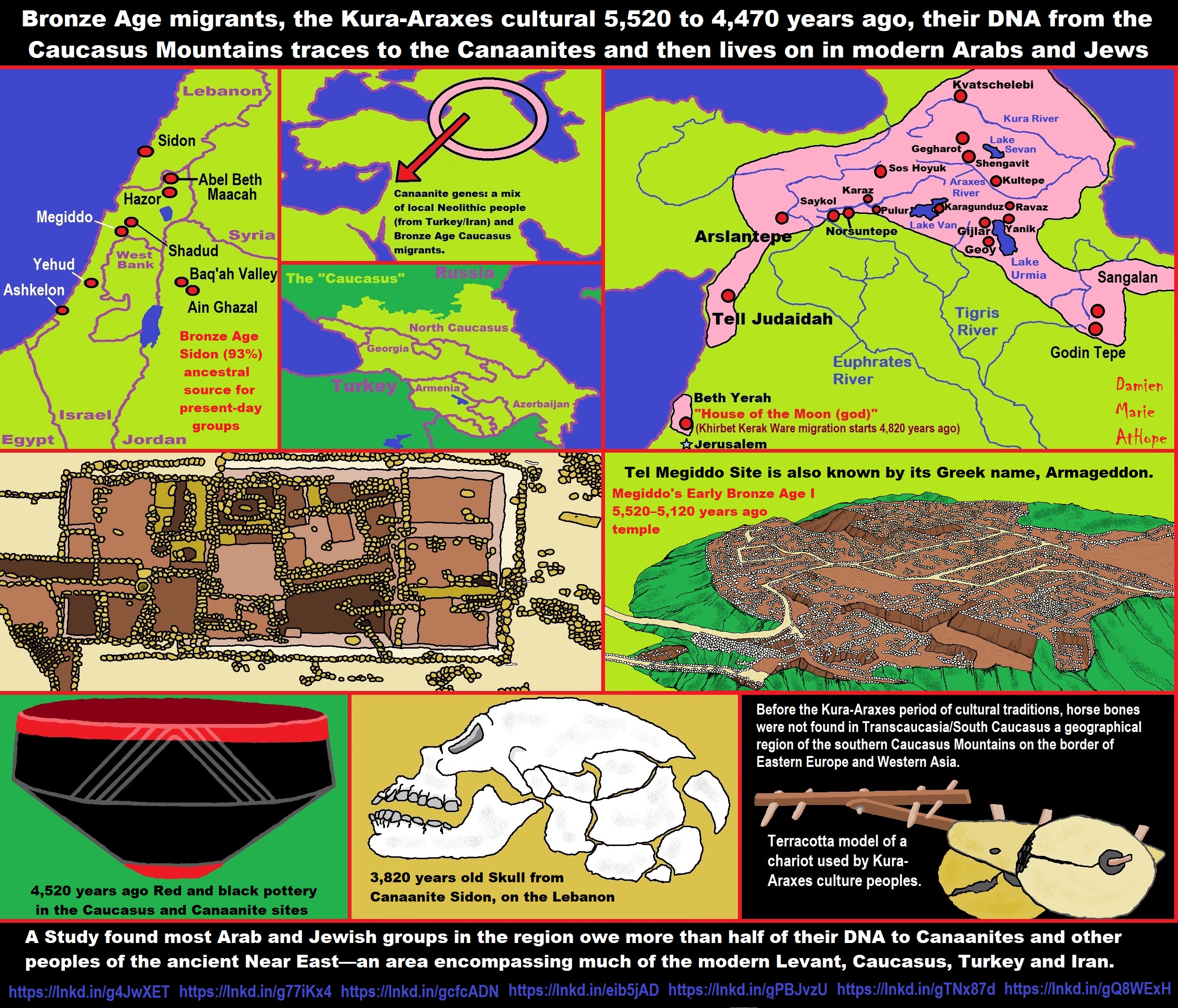
Bronze Age expansion of J1-P58
“Kitchen et al. (2009) estimated through a Bayesian phylogenetic analysis that Semitic languages originated in the Levant around 3,750 BCE, during the Early Bronze Age. It evolved into three groups: East Semitic (an extinct branch that comprised Akkadian), Central Semitic (which gave rise to Aramaic, Ugaritic, Phoenician, Hebrew, and Arabic), and South Semitic (South Arabian and Ethiopian).” ref
“J1-P58, the Central Semitic branch of J1, appears to have expanded from the southern Levant (Israel, Palestine, Jordan) across the Arabian peninsula during the Bronze Age, from approximately 3,500 to 2,500 BCE. Camels were domesticated in Somalia and southern Arabia c. 3,000 BCE, but did not become widely used in the southern Levant before approximately 1,100 BCE. Camels played an important role in the further diffusion of J1-P58 lineages, notably with the Bedouins in the desertic parts of the Middle East and North Africa. Bedouins now make up a substantial percentage of the population of Sudan (33%), Libya (15%), the United Arab Emirates (8%), and Saudi Arabia (5%).” ref
“The two most common Jewish subclades of J1 downstream of P58 are Z18297 and ZS227. The latter includes the Cohanim haplotype. Most of the other branches under P58 could be described as Semitic, although only FGC12 seems to be genuinely linked to the medieval Arabic expansion from Saudi Arabia.” ref
“Based on very limited data, the main Lebanese subclades of J1 appear to be J1-Z640 and J1-YSC76. Both subclades have also been found in Sicily, Andalusia, and Portugal, which suggests that they were already found among the Phoenicians. However, since the Arabs conquered the same regions as those colonized by the Phoenicians, it is too early to reach such a conclusion. Subclades found in Sardinia are very useful as practically all J1-P58 on the island were supposedly brought by the Phoenicians. They include Z18297 (could also be Jewish), Z2324>YP4763, YSC76>FGC15940>ZS1690, and YSC76>FGC8223>FGC8216>FGC8196.” ref
“Frequencies of haplogroup J1 in Europe and West Asia tend to vary considerably from one regional community to the next. The highest local percentages in Europe are found in Greece, Italy, France, Spain, and Portugal and hardly ever exceed 5% of the population. However, Italy, France, and Spain also have areas where J1 appears completely absent. Even in northern Europe, where the nation-wide frequencies are below 0.5%, very localized pockets of J1 have been observed in Scotland, England, Belgium, Germany, and Poland. Larger sample sizes are needed to get a clearer picture of the distribution of J1 in Europe.” ref
“Surprisingly, even in the Caucasus and in Anatolia, the region where this haplogroup is thought to have originated, there are wide discrepancies between regions. For example, the Kubachi and Dargins from Dagestan in the Northeast Caucasus have over 80% of J1 lineages, while in their Ingush neighbors, 200 km to the north, it barely reaches 3%. East Anatolia around Lake Van sees over 30% of J1, whereas south-west Anatolia has only 2%. Even within Kurdistan frequencies vary greatly. The small sample sizes for each region is surely to blame.” ref
“In Arabic countries, J1 climaxes among the Marsh Arabs of South Iraq (81%), the Sudanese Arabs (73%), the Yemeni (72%), the Bedouins (63%), the Qatari (58%), the Saudi (40%), the Omani (38%) and the Palestinian Arabs (38%). High percentages are also observed in the United Arab Emirates (35%), coastal Algeria (35%), Jordan (31%), Syria (30%), Tunisia (30%), Egypt (21%), and Lebanon (20%). Most of the Arabic J1 belongs to the J1-P858 variety.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
By day the LORD went ahead of them in a pillar of cloud to guide them on their way and by night in a pillar of fire to give them light, so that they could travel by day or night.
- By day the “Bible God” was in a cloud pillar.
- By night the “Bible God” was in a fire pillar.
When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF RELIGIONS
Damien, is it possible, there’s a God you haven’t considered?
Paganism?
Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, and Paganism
Damien, I was wondering what your thoughts are on Paganism?
Paganism, Folk religion, & Ethnic/indigenous religion
Sky Burials: Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, and Paganism
Yes, you need to know about Animism to understand Religion
Religions once worshipped women as gods, now religions tears women down
The interconnectedness of religious thinking
Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, and Paganism and Beyond……….
So, it all starts in a general way with Animism (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employing of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from).
My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Religion started rather female-centric but generally egalitarianist and was so at least tell like after 7,000 and definitely by 5,000 and the birth of statism women fall in status but to me it’s 13,000 to 12,000-year-old proto-paganism goddess and animal gods that seem to come first I presume likely was driven from lesser earlier spirit beings/mythic ancestors, like a greater symbol of clan protectors in totemism which seems to go back like 50,000 to possibly 70,000 years ago which they already believed in from both proto-animism which seems to go back like 100,000 to ? years ago (possibly pre-human maybe as far back as 300,000? years ago) and further developed in shamanism which seems to go back like 30,000.
Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
[Antireligionist] My blogs that address Religion: Archaeology, Anthropology, Philosophy and History
Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses as well as gods
Main deity or religious belief systems
Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
Damien, What’s Worse Christians or Spiritual Non-religious?
First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status
Gobekli Tepe: “first human made temple”
Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
Black women of Courage: Elizabeth Jennings, Claudette Colvin, Rosa Parks, and Coretta Scott King.
Horned female shamans and Pre-satanism Devil/horned-god Worship?

Paganism (beginning around 12,000 years ago)
Paganism (such as that seen in Turkey: 12,000 years ago). Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” around 12,000 years ago. Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago. Pagan-Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and 12,000 – 10,000 years old Paganistic-Shamanistic Art in a Remote Cave in Egypt. Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago and Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 10,000 years ago.
Paganism is approximately a 12,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife and who are guided/supported by a goddess/god, goddesses/gods, magical beings, or supreme spirits. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden paganist.
Around 12,000 years ago, in Turkey, the first evidence of paganism is Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” and around 9,500 years ago, in Turkey, the second evidence of paganism is Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”. In addition, early paganism is connected to Proto-Indo-European language and religion. Proto-Indo-European religion can be reconstructed with confidence that the gods and goddesses, myths, festivals, and form of rituals with invocations, prayers, and songs of praise make up the spoken element of religion. Much of this activity is connected to the natural and agricultural year or at least those are the easiest elements to reconstruct because nature does not change and because farmers are the most conservative members of society and are best able to keep the old ways.
The reconstruction of goddesses/gods characteristics may be different than what we think of and only evolved later to the characteristics we know of today. One such characteristic is how a deity’s gender may not be fixed, since they are often deified forces of nature, which tend to not have genders. There are at least 40 deities and the Goddesses that have been reconstructed are: *Pria, *Pleto, *Devi, *Perkunos, *Aeusos, and *Yama.
The reconstruction of myths can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and by additional research, many of these myths have since been confirmed including some areas that were not accessible to the early writers such as Latvian folk songs and Hittite hieroglyphic tablets. There are at least 28 myths and one of the most widely recognized myths of the Indo-Europeans is the myth, “Yama is killed by his brother Manu” and “the world is made from his body”. Some of the forms of this myth in various Indo-European languages are about the Creation Myth of the Indo-Europeans.
The reconstruction of rituals can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and is estimated to have been spoken as a single language from around 6,500 years ago. One of the earliest ritual is the construction of kurgans or mound graves as a part of a death ritual. kurgans were inspired by common ritual-mythological ideas. Kurgans are complex structures with internal chambers. Within the burial chamber at the heart of the kurgan, elite individuals were buried with grave goods and sacrificial offerings, sometimes including horses and chariots.
The speakers of Pre-Proto-Indo-European lived in Turkey and it associates the distribution of historical Indo-European languages with the expansion around 9,000 years ago, with a proposed homeland of Proto-Indo-European proper in the Balkans around 7,000 years ago. The Proto-Indo-European Religion seemingly stretches at least back around 6,000 years ago or likely much further back and I believe Paganism is possibly an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system.
The earliest kurgans date to 6,000 years ago and are connected to the Proto-Indo-European in the Caucasus. In fact, around 7,000 years ago, there appears to be pre-kurgan in Siberia. Around 7,000 to 2,500 years ago and beyond, kurgans were built with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia, which display the continuity of the archaic forming methods. Kurgan cultures are divided archaeologically into different sub-cultures such as Timber Grave, Pit Grave, Scythian, Sarmatian, Hunnish, and Kuman–Kipchak. Kurgans have been found from the Altay Mountains to the Caucasus, Ukraine, Romania, and Bulgaria. Around 5,000 years ago, kurgans were used in the Ukrainian and Russian flat unforested grasslands, and their use spread with migration into eastern, central, and northern Europe, Turkey, and beyond. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref


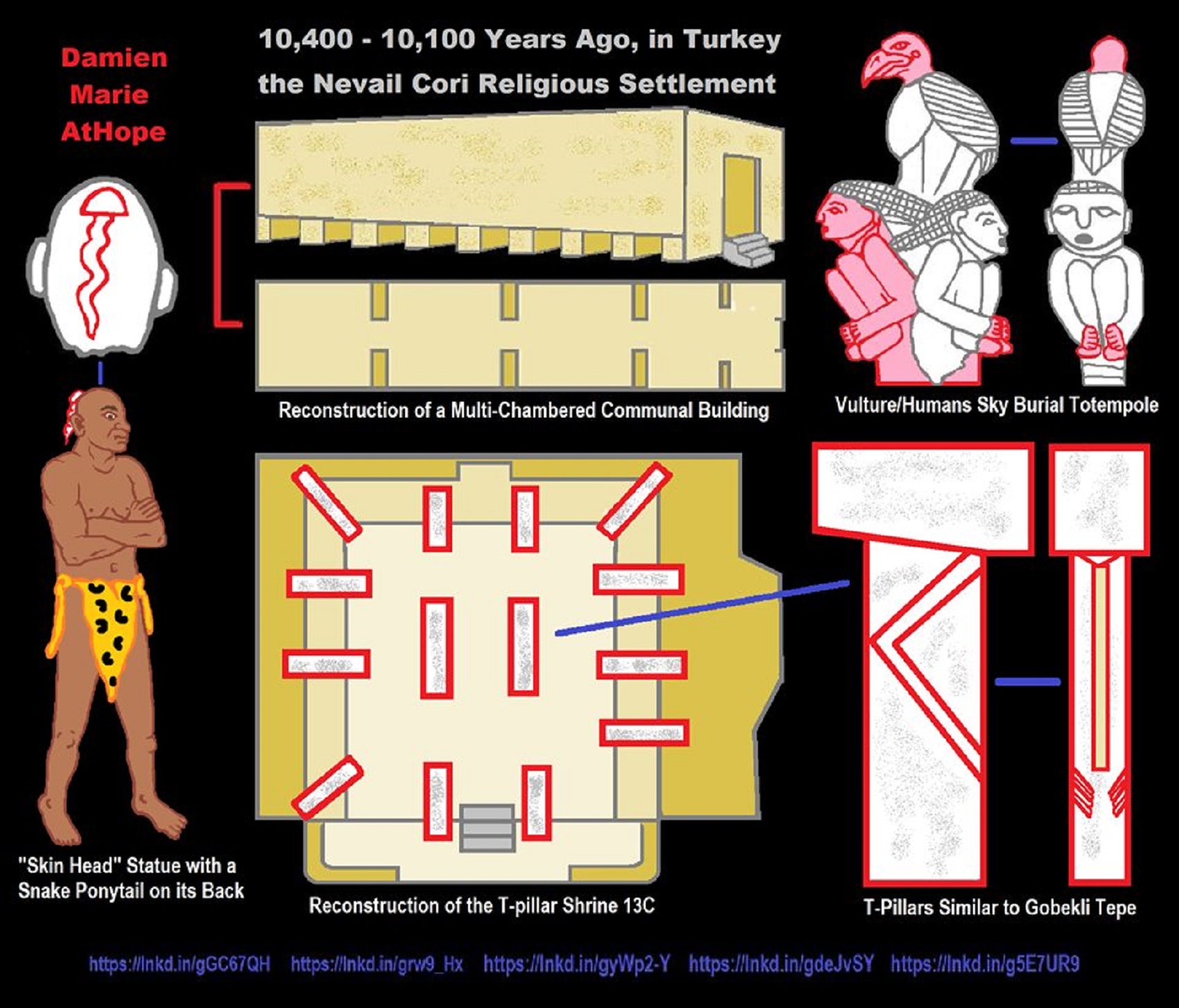

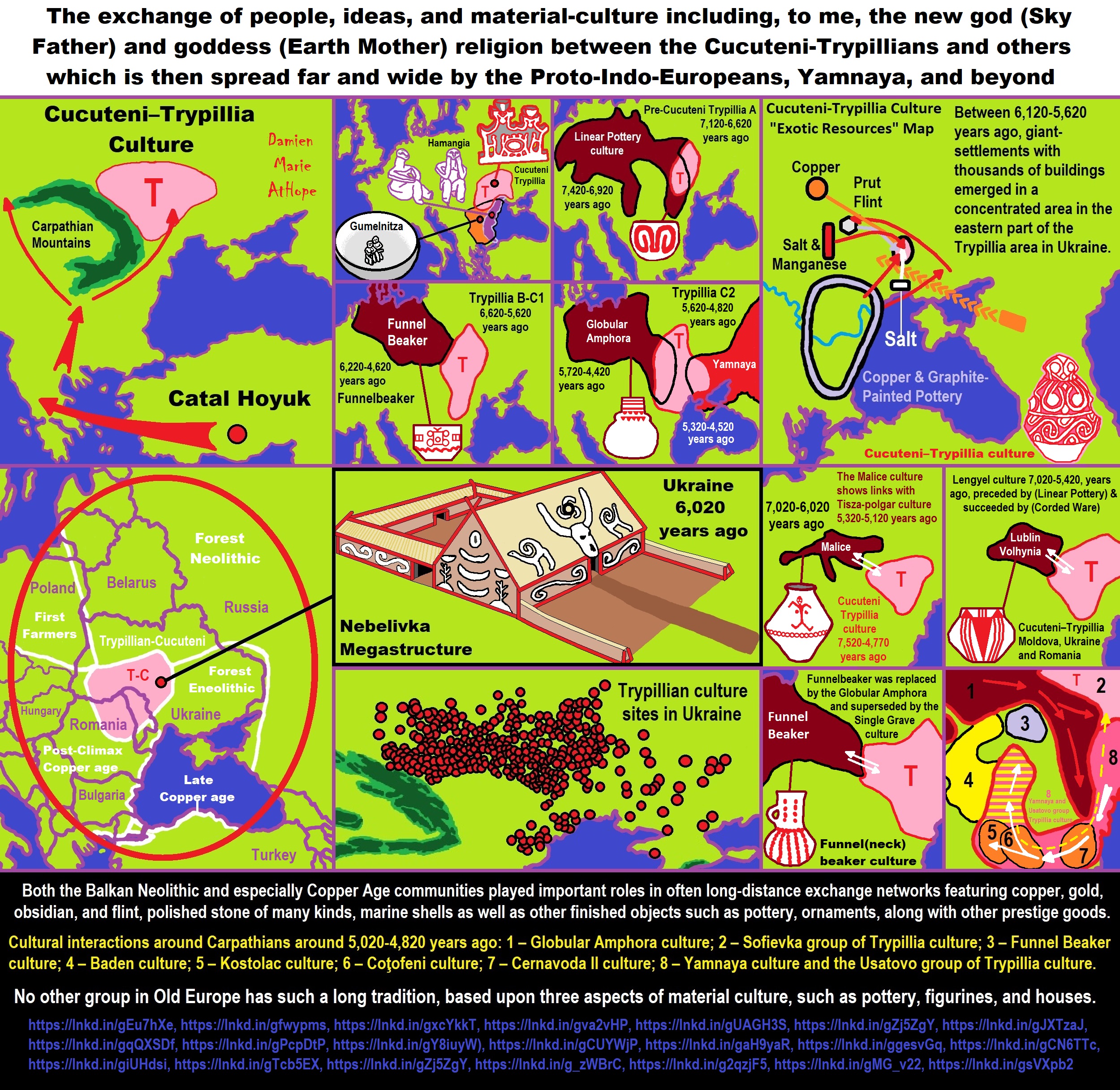
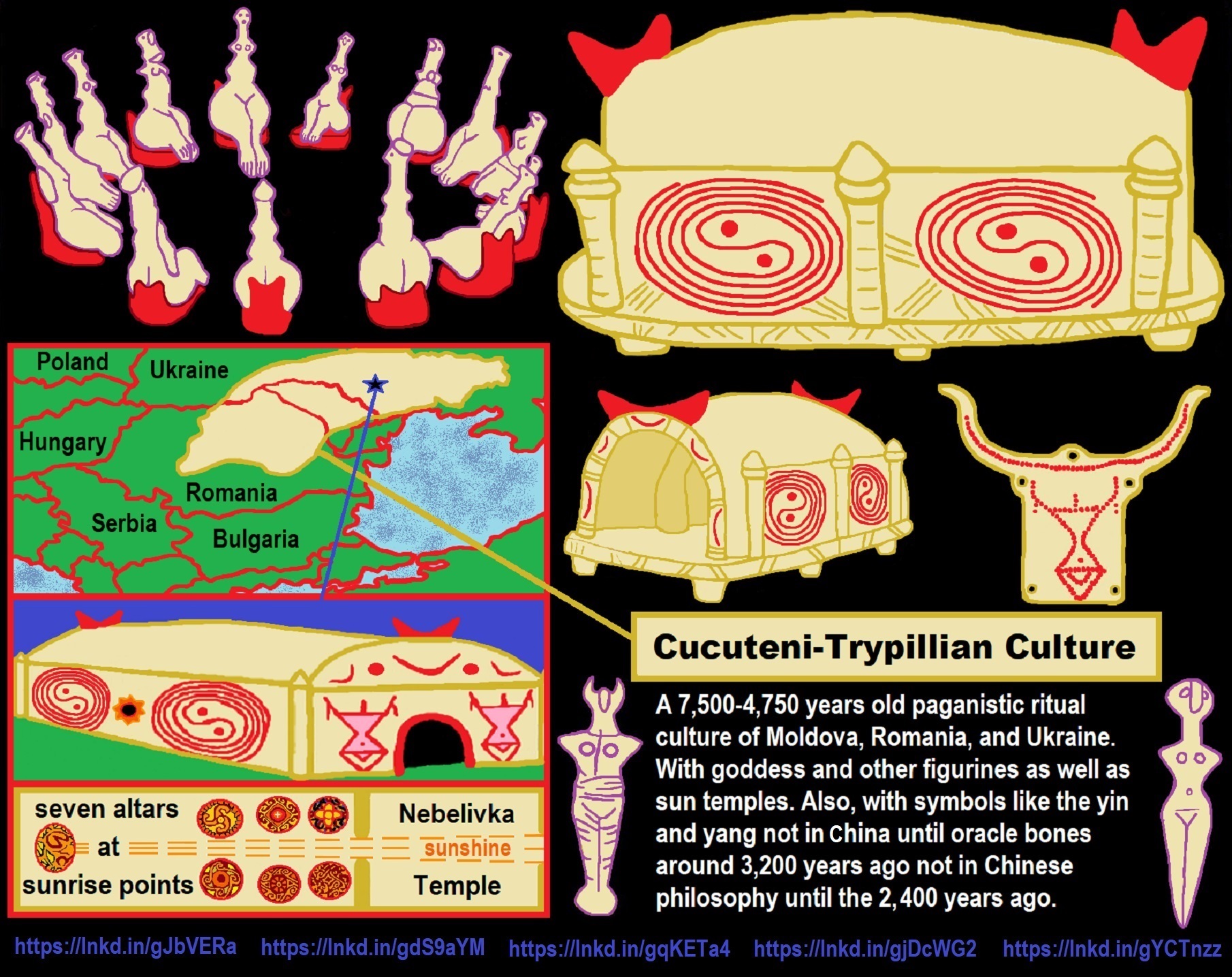



- From a Gerzeh/Naqada II Late Predynastic Egyptian palette with a goddess “Bat/Hathor” cow-head sun/stars motif.
- From a Hierakonpolis late Gerzeh/Naqada II Predynastic or early Naqada III Proto-Dynastic Egyptian porphyry fluted bowl with two reliefs on the rim, one of which was a goddess “Hathor/Bat” cow-head sun/stars motif.
- From an Abydos tomb, u-210 which held a small seal with a goddess “Bat/Hathor” sun/stars motif from the Gerzeh/Naqada II Late Predynastic Egyptian period.
- A Mongolian Copper Age bull sun/star shamanism petroglyph
- A Mongolian Bronze Age deer sun/star shamanism petroglyph symbol.
- A Kyrgyzstan Saimaly-Tash possibly Bronze Age shamanism cow-sun person symbol petroglyph.
- Similar X-ray style images among different peoples of the North from Siberia to Central Asia with shamanism petroglyphs of horned animals with sun symbols from possibly as old as the Neolithic to the Bronze Age. ref, ref, ref
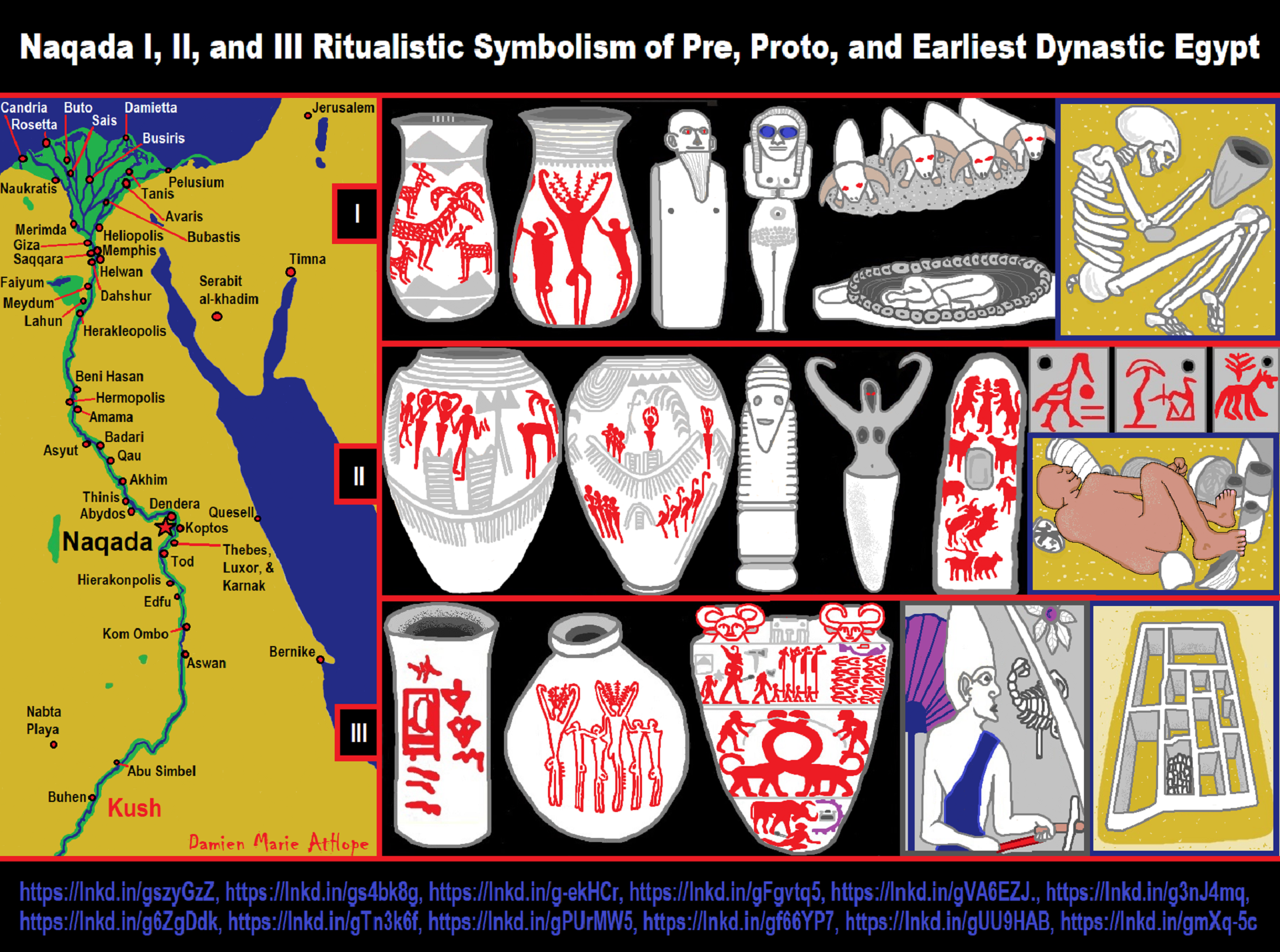


If you are a religious believer, may I remind you that faith in the acquisition of knowledge is not a valid method worth believing in. Because, what proof is “faith”, of anything religion claims by faith, as many people have different faith even in the same religion?
Religious Sexism
- Speech on the Evolution of Religion & Religious Sexism
- Sexism in the Major World Religions
- Sexism in the BIBLE: chapter and verse!
- Sexism in Christianity (New Testament)
- Sexism in Judaism (old Testament)
- Sexism in Islam? Face Covering: Religious Freedom or Religious Oppression
- Sexism in Islam
- Sexism in Protestantism
- Sexism in Catholicism
- Sexism in Mormonism
- Sexism in Jehovah Witness
- Sexism in Bahaism
- Sexism in Sikhism
- Sexism in Confucianism
- Sexism in Taoism
- Sexism in Jainism
- Sexism in Shintoism
- Sexism in Buddhism
- Sexist Buddha
- Sexism in Hinduism
- Taoism yang and yin is very sexist


Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref



My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.



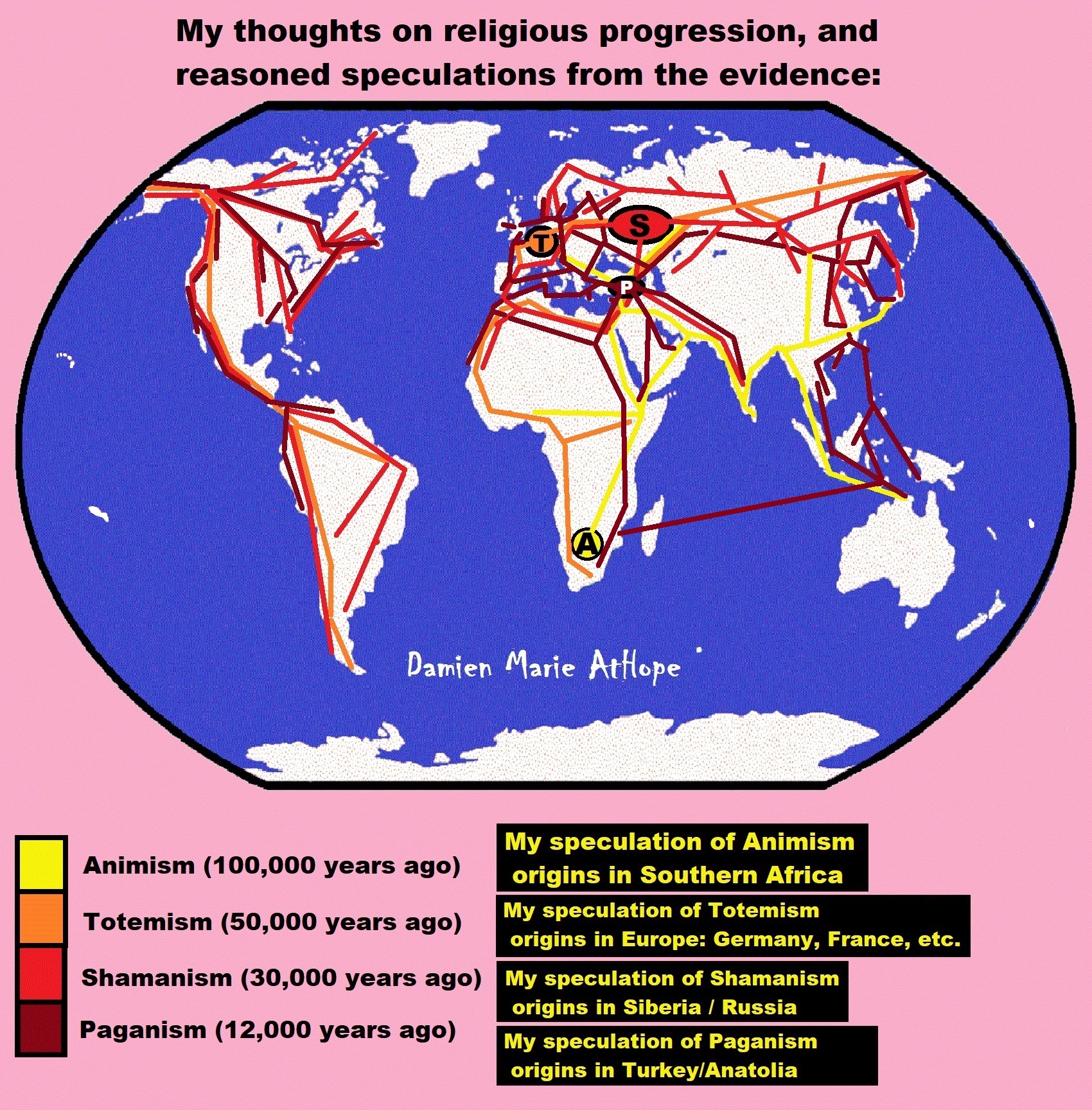

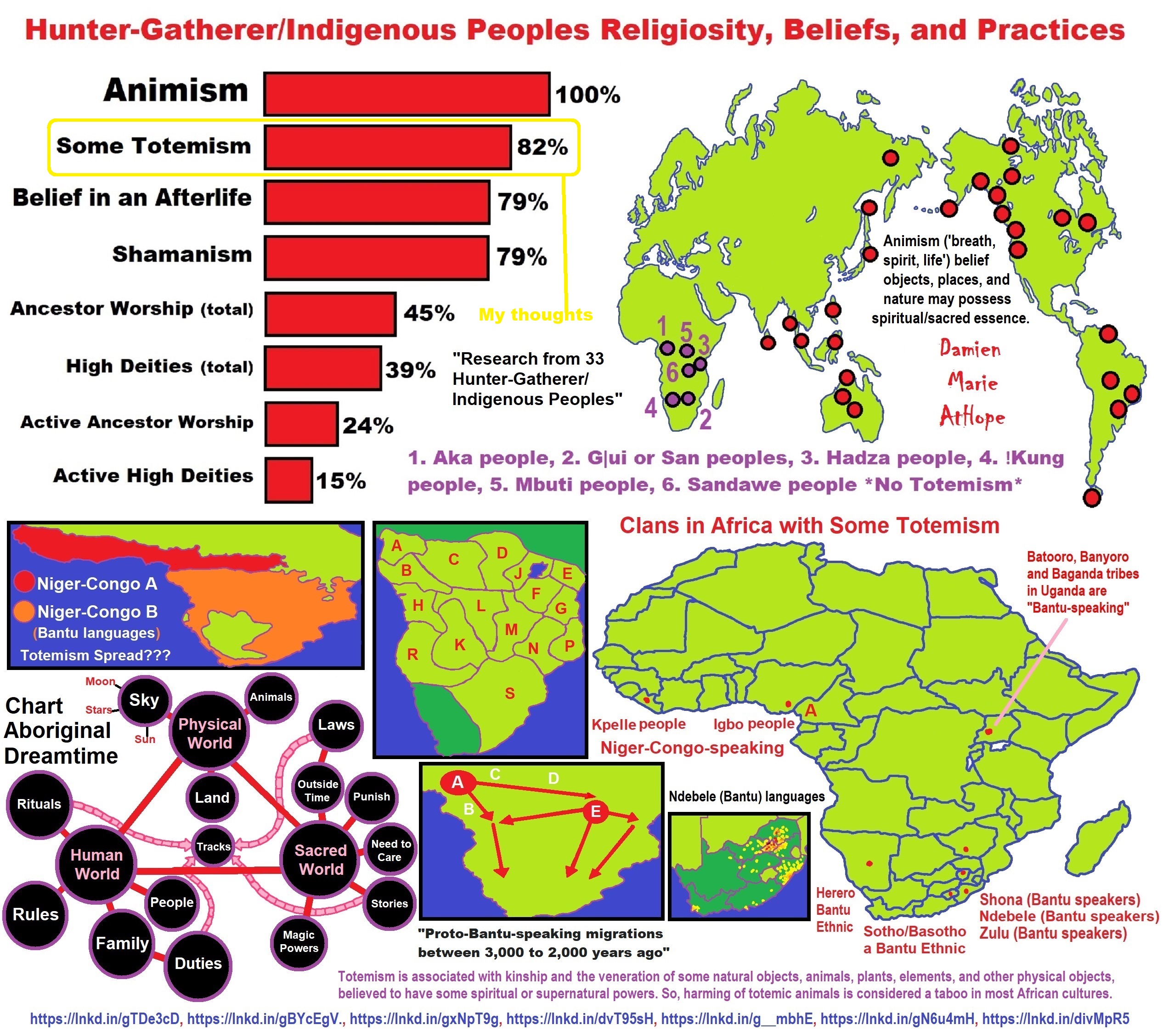
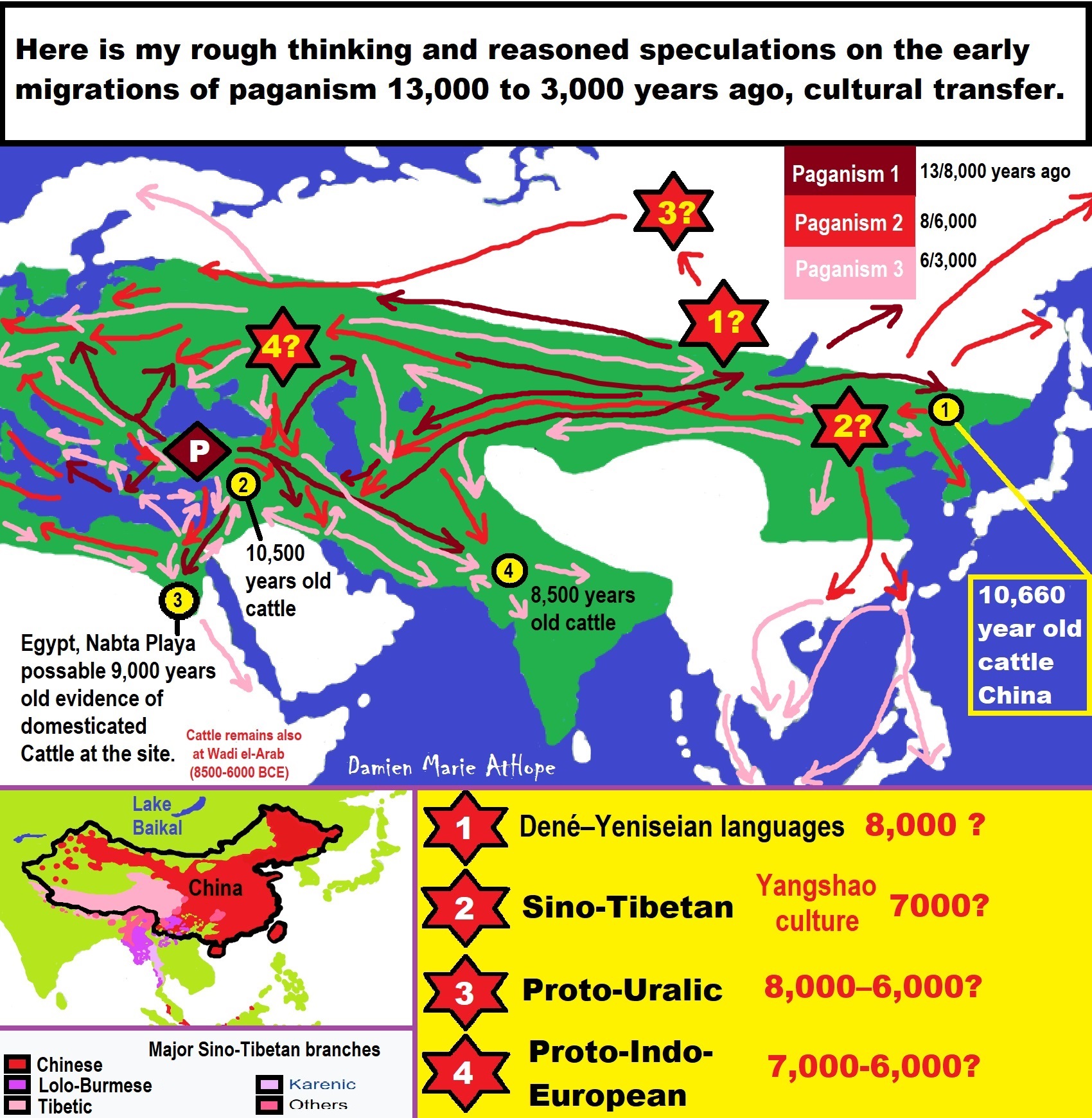

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.



While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com