
If axiology is a value-based ethics system, how are the ethical values established?
Using Axiological Awareness to Assist in Argumentation.
I hear some saying that the universe does not care and thus no one matters. However, the universe is not aware to make any thought or judgment of any kind. Just as a tree or rock, not understanding love does nothing to devalue love. Therefore, the universe not caring about humans is an invalid argument because it cannot be said to assess humans’ value. Because of this fact, it is disqualified to provide any valid rebuke of value or what matters. Let me make this clearer, the universe can make no assessment at all and this means nothing to the truth status of anything, such as I could say the universe does not know I exist but that expresses nothing about my existing or not.
Damien, I understand that axiology is a value-based ethics system, but I don’t understand why the values are what they are?
Why is life > nonlife?
Why are humans > nonhumans?
Why are family members > strangers?
If it is a logical system, the reasons for the values must be logically validated, not just presumed.
The logico-deductive method whereby conclusions (new knowledge) follow from premises (old knowledge) through the application of sound arguments (syllogisms, rules of inference), was developed by the ancient Greeks, and has become the core principle of modern mathematics.
“A logical system or, for short, logic, is a formal system together with a form of semantics, usually in the form of model-theoretic interpretation, which assigns truth values to sentences of the formal language, that is, formulae that contain no free variables. A formal system or logical calculus is any well-defined system of abstract thought based on the model of mathematics. A formal system need not be mathematical as such; for example, Spinoza’s Ethics imitates the form of Euclid’s Elements. Spinoza employed Euclidiean elements such as “axioms” or “primitive truths“, rules of inferences, etc., so that a calculus can be built using these. An axiom or postulate is a statement that is taken to be true, to serve as a premise or starting point for further reasoning and arguments. The term has subtle differences in definition when used in the context of different fields of study. As defined in classic philosophy, an axiom is a statement that is so evident or well-established, that it is accepted without controversy or question. As used in modern logic, an axiom is simply a premise or starting point for reasoning. As used in mathematics, the term axiom is used in two related but distinguishable senses: “logical axioms” and “non-logical axioms”. Logical axioms are usually statements that are taken to be true within the system of logic they define. To axiomatize a system of knowledge is to show that its claims can be derived from a small, well-understood set of sentences (the axioms). The word axiom comes from the Greek word ἀξίωμα (axíōma), a verbal noun from the verb ἀξιόειν (axioein), meaning “to deem worthy”, but also “to require”, which in turn comes from ἄξιος (áxios), meaning “being in balance”, and hence “having (the same) value (as)”, “worthy”, “proper”. Among the ancient Greek philosophers an axiom was a claim which could be seen to be true without any need for proof. A logic is sound if all sentences that can be derived are true in the interpretation, and complete if, conversely, all true sentences can be derived. Deductive inference: A deductive system, also called a deductive apparatus, consists of the axioms (or axiom schemata) and rules of inference that can be used to derive theorems of the system. Such deductive systems preserve deductive qualities in the formulas that are expressed in the system. Usually, the quality we are concerned with is truth as opposed to falsehood. However, other modalities, such as justification or belief may be preserved instead. In order to sustain its deductive integrity, a deductive apparatus must be definable without reference to any intended interpretation of the language. The aim is to ensure that each line of a derivation is merely a syntactic consequence of the lines that precede it. There should be no element of any interpretation of the language that gets involved with the deductive nature of the system.” ref, ref
“Distinctions between theories of moral reasoning can be accounted for by evaluating inferences (which tend to be either deductive or inductive) based on a given set of premises. Deductive inference reaches a conclusion that is true based on whether a given set of premises preceding the conclusion are also true, whereas, inductive inference goes beyond the information given in a set of premises to base the conclusion on provoked reflection. This branch of psychology is concerned with how these issues are perceived by ordinary people, and so is the foundation of descriptive ethics. There are many different moral reasonings. Moral reasoning is culturally defined, and thus is difficult to apply, yet human relationships define our existence and thus defy cultural boundaries.” ref
My response, there are several approaches to addressing this set of questions, and will be approached or addressed differently from different axiology styles and there are several but two main philosophies with value theory (philosophic axiology) or with formal axiology (scientific axiology). I am a philosophical axiologist, not a formal axiologist just so you know. Also, I do not speak for other philosophical axiologists only myself.
“The term “Value Theory” is used in at least three different ways in philosophy. In its broadest sense, “Value Theory” is a catch-all label used to encompass all branches of moral philosophy, social and political philosophy, aesthetics, and sometimes feminist philosophy and the philosophy of religion — whatever areas of philosophy are deemed to encompass some “evaluative” aspect. In its narrowest sense, “value theory” is used for a relatively narrow area of normative ethical theory particularly, but not exclusively, of concern to consequentialists. In this narrow sense, “value theory” is roughly synonymous with “axiology”. Axiology can be thought of as primarily concerned with classifying what things are good, and how good they are. For instance, a traditional question of axiology concerns whether the objects of value are subjective psychological states, or objective states of the world.” ref
Real Morality, to me, is referring to “ethics (our interactions with others, not morals that one holds them self too)” morality motivation, and ethical behavior, with our moral/ethical reasoning, and moral judgment, we use in judging the behaviors in a social dynamic behavioral event or interaction and can only accrue in a social dynamic (social behavioral realm) as such all morality propositions removed from a social dynamic and which accrue only in a personal dynamic lack attachment to “Real Morality” referring to the social nature of “ethics.” A moral choice can involve some ethical code, or regulated by ethical relationships with others, this can be stem from many morality motivations or sensitivities. In other words, if you are by yourself and do something only to yourself, it is neither ethical nor immorality; thus, doing a behavior that is only personal (a believed moral or otherwise) by yourself and only something to yourself, is amorality to everyone but that chosen person doing a behavior that is only personal. I hold the assumptions that to understand morality more fully we need to understand its synthesis and properties by emphasizing its relations to conceptual tools for understanding motivation and behavior such as Biopsychosocial model, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, Bronfenbrenner’s Ecological Systems Theory, Lawrence Kohlberg’s moral development theory and Formal Axiology interactions across multiple levels. Real Morality is an emergent aspect limited to a sphere of social dynamics (social) resulting in human progress and social evolution understood in mental processes of highly cognitively developed beings (biological) with developed psychological quality of awareness (psychological) and the so-called moral facts and the values that support or motivate them is limited to the realm of possible harm psychological or physical (actual external world or experiential internal world).
My Axiological Dignity Being Theory: An “Axiological assessment of human beings” shows with an axiological awareness a logic of values is clear which takes as its basic premise that “all persons always deserve positive regard.” – Progressive Logicby William J. Kelleher, Ph.D. And the reason why we should care is that we are Dignity Beings. “Dignity is an internal state of peace that comes with the recognition and acceptance of the value and vulnerability of all living things.” – Donna Hicks (2011). Dignity: Its Essential Role in Resolving Conflict
*Why is life > nonlife? Well, awareness contains a dignity value over nonlife that does not contain a moral weight value do to the lack of ability to access awareness, to me. The term “value theory” is used in at least three different ways in philosophy. In its broadest sense, “value theory” is a catch-all label used to encompass all branches of moral philosophy, social and political philosophy, aesthetics, and sometimes feminist philosophy and the philosophy of religion — whatever areas of philosophy are deemed to encompass some “evaluative” aspect. In its narrowest sense, “value theory” is used for a relatively narrow area of normative ethical theory particularly, but not exclusively, of concern to consequentialists. In this narrow sense, “value theory” is roughly synonymous with “axiology”. Axiology can be thought of as primarily concerned with classifying what things are good, and how good they are. For instance, a traditional question of axiology concerns whether the objects of value are subjective psychological states, or objective states of the world.
*Why are humans > nonhumans? We are “moral beings” and can be expected to both understand the moral weight of behavior nonhumans don’t and thus only humans can be held to moral standards as well as this puts humans in a different category with rights as well as responsibilities, to me. The level of intelligence as a general rule has a relation to its value as it’s connected to moral awareness or right ethical action.
*Why are family members > strangers? “In order to conceptualize value, you need to understand the environmental contexts, with five ecological systems.” We are limited beings can only do so much as in for almost all people in the world if they gave everything to the world could not support the world’s population as we are limited this means that too there is a survival requirement of ration/rationing by connected value, starting with one’s self then radiating out in general to the level of connection, here is just a rough outline: your child/spouse/partner(possibly friends seen as close family), then parents/siblings(possibly friends seen as family), then extended family(possibly friends seen as extended family), then remote extended family(possibly friends seen as remote extended family), then friends, then acquaintances/lesser friends, then people you work with or for, then people you know in your immediate area, then your city, then nearby cities then your state, then your region, then you country, then countries favorable to your country, then the then the world but for hostile countries, then the rest of the world regardless of if even if they are hostile countries. When a person accepts a certain position such as one that involves the welfare of others. Here is my Axiological Valuation approach to moral decision making would likely use an Ecological Systems Theory modal:
Individual: usually the highest value, though for some family(possibly a friend) members may have the same or higher value.
Microsystem: the next highest value is closest relationships, those connected to the individual, and encompasses interpersonal relationships and direct interactions with immediate surroundings for example family or friends.
Mesosystem: the next high value includes close to semi-close relationships, for example, family friends or friends of friends.
Exosystem: the next value includes only semi or non-directly involved individuals/groups, for example, people at one’s job, places you frequent, then moving out and lessening in value as it goes city, then state, then region, then country, etc.
Macrosystem: the next lesser value includes all others outside with no connections, including other parts of the world, not one’s country.
I appreciate that, Damien.
But it seems all you’ve done toward answering my questions is to label the >< relationships as axiomatic. That doesn’t make them axiomatic. I don’t value close relationships as having any higher value than strangers, and I see nothing in your blog to explain why I should other than that it’s easier, and more convenient, to have more influence over family than strangers. I don’t see any reason that my convenience in having an effect on them as a reason to value them higher.
My response, pioneering new research by archaeologists at the University of York suggests that Neanderthals belied their primitive reputation and had a deep-seated sense of compassion. We are social beings with a general evolutionary persuasion that motivates familial bonds over non-familial bonds? To me, is connected to our ability to express and understand caregiver compassion. The evolutionary roots of caregiver compassion are where organisms within a species adopt different strategies of parental investment and what would later involve a reliance on caregiver compassion. Moreover, we may never completely know when and why caregiver compassion in general or familial compassion specifically. However, the fossil record can, in principle, provide a glimpse, and what we see is altruism and even levels of compassion are seen in a variety of species and Kin Selection (genetic), Familial (upbringing) or Familiars (chance) Compassion are the primary evolutionary mechanism. The fossil record shows the arthropod “Kunmingella douvillei” 515 million years ago, arthropod “Waptia fieldensis” 508 million years ago, and arthropod “Ostracods” 450 million years ago to exhibit changes that played a key role in the early evolution of parental care. 1.9 million years ago Homo habilis, the first of our genus Homo who appeared, with modest expansion of a language part of the brain and 1.8 million years ago Homo erectus appeared and had a larger expansion of brain beginning to be regulated as an emotion integrated with rational thought and seem to demonstrate forms of compassion such as caring of sick which represents an extensive compassionate investment. By 500,000 years ago Homo heidelbergensis developed language skills and intelligence and what seems to have been an upward march in the commitments to the welfare of others. And evidence from 120,000 years ago demonstrates modern humans were involved in compassion which was extended to strangers, animals, objects, and abstract concepts. Thus, we cannot think of survival of the fittest without realizing that the aspects of altruism, compassion, empathy, and kindness are part of what assists in that survival. In general, all social animals (which includes humans and their evolutionary ancestors) have had to modify or restrain their behaviors for group living which involves interacting highly with other animals, usually of their own species. Social animals are cooperative animals adding to their evolutionary fitness in this solidarity and can roughly be said to exhibit one of more of these behaviors: cooperative sustenance, cooperative upbringing, cooperative generational living, cooperative defense, and cooperative learning. To me, caregiver compassion is similar to what in general motivates family bonds with a closer connection and this is largely psychologically hardwired, though I do think there’s a big nurture factor as well. Such preference bonds added us in the fitness to survive. There are reasons to acknowledge that there can be psychological consequences in the weakening of familial bonds. There are reasons to acknowledge that strong relationships with other family members can help raise self-esteem and reduce anxiety. Are you asking me why you should care or that in any general rule it will not incapacitate every unique person’s persuasion? A long-running study published in September 2016 in Psychological Science found that men who grew up in warmer, more nurturing family environments had stronger relationships as older adults. It is argued that family psychology is relationship specific: the relationship between mother and daughter is different from that between father and daughter or that between brother and sister or sister and sister. In other words, humans have evolved specialized mechanisms for processing information and motivating behavior that deals with the distinct demands of being a mate, father, mother, sibling, child, or grandparent. Such an evolutionary perspective on family dynamics provides a unique insight into human behavior. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Kindness is in our genes: How desire to do good deeds is hard-wired into us by evolution: link
The Evolutionary Biology of Altruism, Compassion, cooperation, and community are key to our survival: link
What Price Kindness: Exposing the life and work of a visionary and troubled scientist opens a window onto the evolution of altruism: link
“The Evolution of Empathy by Frans de Waal We tend to think of empathy as a uniquely human trait. But it’s something apes and other animals demonstrate as well, says primatologist Frans de Waal. He shows how our evolutionary history suggests a deep-rooted propensity for feeling the emotions of others.” link
“Compassion: An Evolutionary Analysis: What is compassion? And how did it evolve? In this review, we integrate three evolutionary arguments that converge on the hypothesis that compassion evolved as a distinct affective experience whose primary function is to facilitate cooperation and protection of the weak and those who suffer. Our empirical review reveals compassion to have distinct appraisal processes attuned to undeserved suffering, distinct signaling behavior related to caregiving patterns of touch, posture, and vocalization, and a phenomenological experience and physiological response that orients the individual to a social approach. This response profile of compassion differs from those of distress, sadness, and love, suggesting that compassion is indeed a distinct emotion. We conclude by considering how compassion shapes moral judgment and action, how it varies across different cultures, and how it may engage specific patterns of neural activation, as well as emerging directions of research.” link
“Human inclinations are not primarily selfish: kindness and altruism have been evolutionarily valued in mates, and even the youngest children often try to be helpful.” link
“Endangered Bonobos Reveal Evolution of Human Kindness: Experiments show the great apes share with strangers and empathize.” link
The Homeless Scientist Who Tried to Prove Selflessness Doesn’t Exist: link
Does evolution explain human nature: link
But, Why Ought We Even Care?
Because kindness is like chicken soup to the essence of who we are, by validating the safety needs of our dignity. When the valuing of dignity is followed, a deep respect for one’s self and others as dignity beings has become one’s path. When we can see with the eyes of love and kindness, how well we finally see and understand what a demonstrates of a mature being of dignity when we value the human rights of others, as we now see others in the world as fellow beings of dignity. We need to understand what should be honored in others as fellow dignity beings and the realization of the value involved in that. As well as strive to understand how an attack to/on a person’s “human rights” is an attack to/on the value and worth of a dignity being. Yes, I want to see “you” that previous being of dignity worthy of high value and an honored moral weight to any violation of their self-ownership. And this dignity being with self-ownership rights is here before you seeking connection. what will you do, here you are in the question ever present even if never said aloud, do you see me now or are you stuck in trying to evaluate my value and assess worth as a fellow being of dignity. A violation of one’s dignity (Which it the emotional, awareness or the emotional detection of the world) as a dignity being can be quite harmful, simply we must see how it can create some physiological disturbance in the dignity being its done to. I am a mutualistic thinker and to me, we all are in this life together as fellow dignity beings. Therefore, I want my life to be of a benefit to others in the world. We are natural evolutionary derived dignity beings not supernatural magic derived soul/spirit beings. Stopping lying about who we are, as your made-up magic about reality which is forced causing a problem event (misunderstanding of axiological valuations) to the natural wonder of reality. What equals a dignity worth being, it is the being whose species has cognitive awareness and the expense of pain. To make another dignity being, feel pain is to do an attack to their dignity as well as your own. What equals a dignity worth being, it is the being whose species has cognitive awareness and the expense of pain. When I was younger I felt proud when I harmed those I did not like now I find it deserving even if doing it was seen as the only choice as I now see us for who we are valuable beings of dignity. I am not as worried about how I break the box you believe I need to fit as I am worried about the possibility of your confining hopes of hindering me with your limits, these life traps you have decided about and for me are as owning character attacks to my dignity’s needs which can be generalized as acceptance, understanding, and support. As I see it now, how odd I find it to have prejudice or bigotry against other humans who are intact previous fellow beings of dignity, we too often get blinded by the external packaging that holds a being of dignity internally. What I am saying don’t judge by the outside see the worth and human value they have as a dignity being. Why is it easier to see what is wrong then what is right? Why do I struggle in speaking what my heart loves as thorough and as passionate as what I dislike or hate? When you say “an act of mercy” the thing that is being appealed to or for is the proposal of or for the human quality of dignity. May my lips be sweetened with words of encouragement and compassion. May my Heart stay warm in the arms kindness. May my life be an expression of love to the world. Dignity arises in our emotional awareness depending on cognition. Our dignity is involved when you feel connected feelings with people, animals, plants, places, things, and ideas. Our dignity is involved when we feel an emotional bond “my family”, “my pet”, “my religion”, “my sport’s team” etc. Because of the core sensitivity of our dignity, we feel that when we connect, then we are also acknowledging, understanding, and supporting a perceived sense of dignity. Even if it’s not actually a dignity being in the case of plants, places, things, and ideas; and is rightly interacting with a dignity being in people and animals. We are trying to project “dignity developing motivation” towards them somewhere near equally even though human and animals don’t have the same morality weight to them. I am anthropocentric (from Greek means “human being center”) as an Axiological Atheist. I see humans value as above all other life’s value. Some say well, we are animals so they disagree with my destination. But how do the facts play out? So, you don’t have any difference in value of life? Therefore, a bug is the same as a mouse, a mouse is the same as a dolphin, a dolphin is the same as a human, all to you have exactly the same value? Do you fight to protect the rights of each of them equally? And all killing of any of them is the same crime murder? I know I am an animal but you also know that we do have the term humans which no other animal is classified. And we don’t take other animals to court as only humans and not any other animals are like us. We are also genetically connected to plants and stars and that still doesn’t remove the special class humans removed from all other animals. A society where you can kill a human as easily as a mosquito would simply just not work ethically to me and it should not to any reasonable person either. If you think humans and animals are of equal value, are you obviously for stronger punishment for all animals to the level of humans? If so we need tougher laws against all animals including divorce and spousal or child support and we will jail any animal parent (deadbeat animal) who does not adequately as we have been avoiding this for too long and thankfully now that in the future the ideas about animals being equal we had to create a new animal police force and animal court system, not to mention are new animal jails as we will not accept such open child abuse and disregard for responsibilities? As we don’t want to treat animals as that would be unjust to some humans, but how does this even make sense? To me it doesn’t make sense as humans a different from all other animals even though some are similar in some ways. To further discuss my idea of *dignity developing motivation” can be seen in expressions like, I love you and I appreciate you. Or the behavior of living and appreciating. However, this is only true between higher cognitive aware beings as dignity and awareness of selfness is directly related to dignity awareness. The higher the dignity awareness the higher the moral weight of the dignity in the being’s dignity. What do you think are the best ways to cultivate dignity? Well, to me dignity is not a fixed thing and it feels honored or honoring others as well as help self-helping and other helping; like ones we love or those in need, just as our dignity is affected by the interactions with others. We can value our own dignity and we can and do grow this way, but as I see it because we are a social animals we can usually we cannot fully flourish with our dignity. Thus, dignity is emotionally needy for other dignity beings that is why I surmise at least a partially why we feel empathy and compassion or emotional bonds even with animals is a dignity awareness and response. Like when we say “my pet” cat one is acknowledging our increased personal and emotional connecting. So, when we exchange in experience with a pet animal what we have done is we raze their dignity. Our dignity flourishes with acceptance, understanding and support. Our dignity withers with rejection, misunderstanding, and opposition. Dignity: is the emotional sensitivity of our sense of self or the emotional understanding about our sense of self. When you say, they have a right to what they believe, what I hear is you think I don’t have a right to comment on it. Dignity is the emotional sensitivity of our sense of self or the emotional understanding about our sense of self. To me when we say it’s wrong to kill a human, that person is appealing to our need to value the dignity of the person.’ The person with whom may possibly be killed has a life essence with an attached value and moral weight valuations. And moral weight,’ which is different depending on the value of the dignity being you are addressing understanding moral weight as a kind of liability, responsibility, or rights is actualized. So, it’s the dignity to which we are saying validates the right to life. But I believe all living things with cognitively aware have a dignity. As to me dignity is the name I home to the emotional experience, emotional expression, emotional intelligence or sensitivity at the very core of our sense of self the more aware the hire that dignity value and thus worth. Dignity is often shredded similar to my thinking: “Moral, ethical, legal, and political discussions use the concept of dignity to express the idea that a being has an innate right to be valued, respected, and to receive ethical treatment. In the modern context dignity, can function as an extension of the Enlightenment-era concepts of inherent, inalienable rights. English-speakers often use the word “dignity” in prescriptive and cautionary ways: for example, in politics it can be used to critique the treatment of oppressed and vulnerable groups and peoples, but it has also been applied to cultures and sub-cultures, to religious beliefs and ideals, to animals used for food or research, and to plants. “Dignity” also has descriptive meanings pertaining to human worth. In general, the term has various functions and meanings depending on how the term is used and on the context.” Dignity, authenticity and integrity are of the highest value to our experience, yet ones that we must define for ourselves. People of hurt and harm, you are not as free to attack other beings of dignity without any effect on you as you may think. So, I am sorry not sorry that there is no such thing in general, as hurting or harming other beings of dignity without psychological destruction to the dignity being in us. This is an understanding that once done hunts and harm of other beings of dignity emotionally/psychologically hurts and harms your life as an acceptance needy dignity being, as we commonly experience moral discuss involuntary as on our deepest level as dignity beings. Disgust is deeply related to our sense of morality.
We honor the dignity in ourselves when we respect the dignity of others.
Babies & Morality?
“They believe babies are in fact born with an innate sense of morality, and while parents and society can help develop a belief system in babies, they don’t create one. A team of researchers at Yale University’s Infant Cognition Center, known as The Baby Lab, showed us just how they came to that conclusion.” Ref
Animals and Morality?
5 Animals With a Moral Compass Moreover, Animals can tell right from wrong: Scientists studying animal behavior believe they have growing evidence that species ranging from mice to primates are governed by moral codes of conduct in the same way as humans. Likewise, in the book: Wild Justice: The Moral Lives of Animals: Scientists have long counseled against interpreting animal behavior in terms of human emotions, warning that such anthropomorphizing limits our ability to understand animals as they really are. Yet what are we to make of a female gorilla in a German zoo who spent days mourning the death of her baby? Or a wild female elephant who cared for a younger one after she was injured by a rambunctious teenage male? Or a rat who refused to push a lever for food when he saw that doing so caused another rat to be shocked? Aren’t these clear signs that animals have recognizable emotions and moral intelligence? With Wild Justice Marc Bekoff and Jessica Pierce unequivocally answer yes. Marrying years of behavioral and cognitive research with compelling and moving anecdotes, Bekoff and Pierce reveal that animals exhibit a broad repertoire of moral behaviors, including fairness, empathy, trust, and reciprocity. Underlying these behaviors is a complex and nuanced range of emotions, backed by a high degree of intelligence and surprising behavioral flexibility. Animals, in short, are incredibly adept social beings, relying on rules of conduct to navigate intricate social networks that are essential to their survival. Ultimately, Bekoff and Pierce draw the astonishing conclusion that there is no moral gap between humans and other species: morality is an evolved trait that we unquestionably share with other social mammals.
Moral Naturalism (James Lenman):
While “moral naturalism” is sometimes used to refer to any approach to metaethics intended to cohere with naturalism in metaphysics more generally, the label is more usually reserved for naturalistic forms of moral realism according to which there are objective moral facts and properties and these moral facts and properties are natural facts and properties. Views of this kind appeal to many as combining the advantages of naturalism and realism. Ref
Here are my further thoughts on Real Morality vs. Pseudo Morality:
+Morals (Personal Morality relating to a “self” morality): are not held by all in the same way since all are not held to Orthodox faith and though most start with good and bad or right and wrong values, which usually are personally, familially, socially or religiously give or in some way otherworldly defined, thus not universal.
+Ethics (Social Morality relating to a “others” morality): Ethics are not constrained by a given religion’s value systems to motivate its ideas of right and wrong instead it relies on universal truths found in universal principles of just human action. Ethics is set standers uses to personally engage with others and universal truths assist goals of universal ethical standards. Thus, ethics are general prosocial prescription we as morality aware beings in a rather universal way tend to have some awareness of and it is not just an awareness as in one who holds to ethics often get it applies to all peoples. Some may wish to devalue people but to do so is not really unethical, though often it can lead to unethical behavior. So what I am trying to highlight is how in the behaviour that the ethics violation could occur as the internal attitude of devaluing others would only be a possible morals violation such as one who valued virtue and not getting it but failing by the persuasion of devaluing the life of other humans. This simple internal devaluing of humans, that they may be doing is vile. But ethics would not be involved until public behaviors with others, as such ethics is not so much a persuasion as an adherence to a standard(s) that should cover all thus it is highly applicable to utilize in environmental decision making.
Axiology, Naturalism, Realism and Moral Theory Ideas
Real (true/valid/reasoned) Morality is referrs to “ethics” (Social Morality relating to a “others” morality) as opposed to +Morals (Personal Morality relating to a “self” morality) because we use Real Morality or need to to assist in judging the behaviors in a social dynamic behavioral event or interaction and can only accrue in a social dynamic (social behavioral realm) as such all morality propositions removed from a social dynamic and which accrue only in a personal dynamic lack attachment to “Real Morality” referring to the social nature of “ethics.” In other words, if you are by yourself and do something only to yourself, it is neither ethical nor immorality; thus, doing a behavior that is only personal (a believed moral or otherwise) by yourself and only something to yourself, is amorality to everyone but that chosen person doing a behavior that is only personal. Pseudo Morality is seen when holy books or people “cognitively reconstruct” an inhumane idea or behaviour to make it into something different from than it is, to something more moral than what it actually is. Or turn something highly immoral into something highly moral. One way to do that is to cloak the behaviour “in moral wrappings” or “in divine authority” such as god hates gays, gays are evil, thus killing gays is doing good by destroying evil. This thinking is obviously pseudo morality as gays are not evil but killing them is an evil and inhumane idea or behaviour thus very immoral. The god justified immorality into what is then called moral is some of the most common pseudo-morality, though political leaders and others in power tend to employ it as well. They all are using “pseudo-moral justifications” to describe something immoral as moral. True morality is not as simple as the golden rule…
Did you know the Golden Rule is found in some variation in almost all faiths?
Baha’i Faith: “Lay not on any soul a load that you would not want to be laid upon you, and desire not for anyone the things you would not desire for yourself” –Bahu’u’llah
Buddhism: “Treat not others in ways that you yourself would find hurtful” –Udana-Varga 5:18
Christianity: “In everything do to others as you would have them do to you; for this is the law of the prophets” –Jesus in Matthew 7:12
Confucianism: “One word which sums up the basis of all good conduct…loving kindness. Do not do to others what you do not want done to yourself” –Confucius, Analects 15:23
Hinduism: ” This is the sum of duty: do not do to others what would cause pain if done to you” –Mahabharata 5:15-17
Humanism: “Try to embrace the moral principle known as the ‘Golden Rule’, otherwise known as the ethic of reciprocity, which means we believe that people should aim to treat each other as they would like to be treated themselves – with tolerance, consideration and compassion.” – Maria MacLachlan, Think Humanism
Islam: “Not one of you truly believes until you wish for others what you wish for yourself” –The Prophet Mohammad, Hadith
Jainism: “One should treat all creatures in the world as one would like to be treated” –Mahavira, Sutrakritanga
Judaism: “What is hateful to you, do not do to your neighbor. This is the whole Torah: all the rest is commentary” –Hillel, Talmud, Shabbat 31a
Native American: “We are as much alive as we keep the earth alive” –Chief Dan George
Satanism: “Do unto others as they do unto you”; because if you “Do unto others as you would have them do unto you,” and they, in turn, treat you badly, it goes against human nature to continue to treat them with consideration. You should do unto others as you would have them do unto you, but if your courtesy is not returned, they should be treated with the wrath they deserve.” ― Anton Szandor LaVey, The Satanic Bible
Sikhism: “I am a stranger to no one; and no one is a stranger to me. Indeed, I am a friend to all” –Guru Granth Sahib, pg. 1299
Taoism: “Regard your neighbor’s gain as your own gain, and your neighbor’s loss as your own loss” –T’ai Shang Kan Yin P’ien 213-218
Unitarianism: “We affirm and promote respect for the interdependent web of all existence of which we are a part” –Unitarian Principle
Wicca: “An’ it harm none, do as thou wilt” –The Wiccan Reed
Zoroastrianism: “Do not do unto others whatever is injurious to yourself. –Shayast-na-Shayast 13:29
True (real) morality is a valued behaviour we do that interacts with others; it is not really related to what we do to ourselves. Which is why I do not agree with the so-called golden rule as it is what you don’t want do to others but this fails in that its focused on ourselves which is us focused and true morality needs to be other focused on what valued behaviour we do that interacts with others. I say treat others the way they should be treated. People have self-ownership, self-rights, right to dignity, freedom, and equality. True morality is a valued behaviour we do that interacts with others starting with the conception that people matter, they have worth and value, It is in this way they should be treated.
Pseudo Morality is seen when holy books or people “cognitively reconstruct” an inhumane idea or behaviour to make it into something different from than it is, to something more moral than what it actually is. Or turn something highly immoral into something highly moral. One way to do that is to cloak the behaviour “in moral wrappings” or “in divine authority” such as god hates gays, gays are evil, thus killing gays is doing good by destroying evil. This thinking is obviously pseudo morality as gays are not evil but killing them is an evil and inhumane idea or behaviour thus very immoral. The god justified immoral into moral is some of the most common pseudo morality though political and others in power tend to employ it as well. They all are using “pseudo-moral justifications” to describe something immoral as moral. To me, true morality is not starting with an us or me focused morality, as morality is a social interaction exchange thus it must be other focused. “treating others as they should be treated” To me, I see everyone as owning themselves all equal in this right as humans. Moreover, to me morality is behavioural and a social property, there is no immoral thing one can do to themselves as one cannot violate themselves or their own consent as they choose their own actions. Thus, to me, all morality is about others and our interactions with them and them with us. So, morality arises in a social context with all things not that all things have the same moral weight. Therefore, moral relationships with life outside humans have a different moral weight or value. Such as, killing 100 humans is not the same as killing 100 dogs, killing 100 fish, killing 100 flies, etc. Of course, the method of killing used should inflict the least amount of suffering to the animal or plant. And to not do that could make it immoral. Such as torturing them to death is immoral even if the killing was not.
So, the golden rule? No thanks, I want real morality not reverse-selfishness driven morality.
Harm is often a violation of trust and a violation of expected trust makes bad things even worse like if I told you a child was killed, you would feel it was terrible but if I further told you it was the child’s doctor that murdered the child out of anger. You would be more angered as doctors are expected to care for people not harm them. And if you think that is bad what if I further told you the doctor who killed the child was her mother would you hold her even mone in contempt as mothers also are expected to care and not kill children, so a violation of trust is terrible and even makes things worse. Therefore, we can see why people that hold places of trust should never abuse them, and that we should hold them accountable if they do violate such trust by harming others. Morality first, that is morality should be at the forefront in all I do. I hope I am always strong enough to put my morality at the forefront in all I do, so much so, that it is obvious in the ways I think and behave. To better grasp, a naturalistic morality one should see the perspective of how there is a self-regulatory effect on the self-evaluative moral emotions, such as shame and guilt. Broadly conceived, self-regulation distinguishes between two types of motivation: approach/activation and avoidance/inhibition. one should conceptually understand the socialization dimensions (parental restrictiveness versus nurturance), associated emotions (anxiety versus empathy), and forms of morality (proscriptive versus prescriptive) that serve as precursors to each self-evaluative moral emotion.
Real Morality vs. Pseudo Morality
Religions Promote Pseudo-Morality
Think there is no objective morality?
True Morality Not the Golden Rule…
Axiological Atheism Morality Critique: of the bible god
Moral fear and Moral love (which together motivate my axiological ethics)?
“Sometimes justice has to outweigh care and sometimes care has to outweigh justice.”
And one may ask or question how do you discern the appropriate morality course of action between what is ethically right? To me, it takes Axiology (i.e. value consciousness: value judgment analysis of ethical appropriateness do to assess value involved).
MORAL FEAR (fight or flight “justice perspective”):
To feel a kind of morality “anxiety” (ethical apprehension to potentially cause harm) about behaviors and their outcomes empathy (I feel you) or sympathy (I feel for you) about something moral that may be done, is being done, or that has been done, thus feeling of distress, apprehension or alarm caused by value driven emotional intelligence concern; moral/ethical anxiety to the possibility; chance (to do something as a moral thinker and an ethical actor) or dread; respect (to take the sensitivity of a personal moral choice that leads one to choose an ethical behavior(s) and grasping the moral weight of the actions involved and potential outcomes this engagement can or will likely create (using data from learning whether theoretical or practical to lessen the effect of an unpleasant choice as much as posable (morality development/awareness/goals/persuasion). “Moral Anxiety, improves us, while Social Anxiety kills. Some anxieties are indicators of healthy curiosity and strong moral fiber, while others are a source of severe stress. Knowing which is which can help you to navigate your personal, professional, and intellectual life more effectively.” Ref Moral fear thus is a kind of morality “anxiety” that motivates a fascinating aspect of humanity, which is that we hold ourselves to high moral standards. With our values and emotional intelligence and moral development, we gain a developed prosocial persuasion thus “tend to self-impose rules on ourselves to protect society from the short-term temptations that might cause us to do things that would have a negative impact in the long-run. For example, we might be tempted to harm a person who bothers us, but a society in which everyone gave in to the temptation to hurt those who made us angry would quickly devolve into chaos. And once we accept that emotion plays some role in complex decisions, it is important to figure out which emotions are influencing different kinds of choices. Therefore, when we make these moral judgments to an extent we are somewhat driven by our ability to reason about the consequences of the actions or are influenced by their emotions to or about the outcomes of the consequences of the actions.” https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/ulterior-motives/201308/anxiety-and-moral-judgment
*ps. MORAL FEAR (fight or flight “consequentialist ethics/utilitarian ethics”) is roughly referring to the fight-or-flight response, also known as the acute stress response, refers to a physiological reaction that occurs in the presence of something that is terrifying, either mentally or physically. The fight-or-flight response (also called hyperarousal, or the acute stress response) is a physiological reaction that occurs in response to a perceived harmful event, attack, or threat to survival. An evolutionary psychology explanation is that early animals had to react to threatening stimuli quickly and did not have time to psychologically and physically prepare themselves. The fight or flight response provided them with the mechanisms to rapidly respond to threats against survival. This response is recognized as the first stage of the general adaptation syndrome that regulates stress responses among vertebrates and other organisms. The reaction begins in the amygdala, which triggers a neural response in the hypothalamus. The initial reaction is followed by activation of the pituitary gland and secretion of the hormone ACTH. The adrenal gland is activated almost simultaneously and releases the hormone epinephrine. The release of chemical messengers results in the production of the hormone cortisol, which increases blood pressure, blood sugar, and suppresses the immune system. The initial response and subsequent reactions are triggered in an effort to create a boost of energy. This boost of energy is activated by epinephrine binding to liver cells and the subsequent production of glucose. Additionally, the circulation of cortisol functions to turn fatty acids into available energy, which prepares muscles throughout the body for response. Catecholamine hormones, such as adrenaline (epinephrine) or noradrenaline (norepinephrine), facilitate immediate physical reactions associated with a preparation for violent muscular action and :
- Acceleration of heart and lung action
- Paling or flushing, or alternating between both
- Inhibition of stomach and upper-intestinal action to the point where digestion slows down or stops
- General effect on the sphincters of the body
- Constriction of blood vessels in many parts of the body
- Liberation of metabolic energy sources (particularly fat and glycogen) for muscular action
- Dilation of blood vessels for muscles
- Inhibition of the lacrimal gland (responsible for tear production) and salivation
- Dilation of pupil (mydriasis)
- Relaxation of bladder
- Inhibition of erection
- Auditory exclusion (loss of hearing)
- Tunnel vision (loss of peripheral vision)
- Disinhibition of spinal reflexes
- Shaking
The physiological changes that occur during the fight or flight response are activated in order to give the body increased strength and speed in anticipation of fighting or running. Some of the specific physiological changes and their functions include:
- Increased blood flow to the muscles activated by diverting blood flow from other parts of the body.
- Increased blood pressure, heart rate, blood sugars, and fats in order to supply the body with extra energy.
- The blood clotting function of the body speeds up in order to prevent excessive blood loss in the event of an injury sustained during the response.
- Increased muscle tension in order to provide the body with extra speed and strength. Ref, Ref
Here is a little on Consequentialist ethics and Utilitarian ethics
*Consequentialist ethics: involves a class of normative ethical theories holding that the consequences of one’s conduct are the ultimate basis for any judgment about the rightness or wrongness of that conduct. Thus, from a consequentialist standpoint, a morally right act (or omission from acting) is one that will produce a good outcome, or consequence. In an extreme form, the idea of consequentialism is commonly encapsulated in the saying, “the end justifies the means“, meaning that if a goal is morally important enough, any method of achieving it is acceptable. Consequentialism is usually contrasted with deontological ethics (or deontology), in that deontology, in which rules and moral duty are central, derives the rightness or wrongness of one’s conduct from the character of the behaviour itself rather than the outcomes of the conduct. It is also contrasted with virtue ethics, which focuses on the character of the agent rather than on the nature or consequences of the act (or omission) itself, and pragmatic ethics which treats morality like science: advancing socially over the course of many lifetimes, such that any moral criterion is subject to revision. Consequentialist theories differ in how they define moral goods. Some argue that consequentialist and deontological theories are not necessarily mutually exclusive. For example, T. M. Scanlon advances the idea that human rights, which are commonly considered a “deontological” concept, can only be justified with reference to the consequences of having those rights. Similarly, Robert Nozick argues for a theory that is mostly consequentialist, but incorporates inviolable “side-constraints” which restrict the sort of actions agents are permitted to do. Ref
*Utilitarian ethics: involve an ethical theory which states that the best action is the one that maximizes utility. “Utility” is defined in various ways, usually in terms of the well-being of sentient entities. Jeremy Bentham, the founder of utilitarianism, described utility as the sum of all pleasure that results from an action, minus the suffering of anyone involved in the action. Utilitarianism is a version of consequentialism, which states that the consequences of any action are the only standard of right and wrong. Unlike other forms of consequentialism, such as egoism, utilitarianism considers the interests of all beings equally. Proponents of utilitarianism have disagreed on a number of points, such as whether actions should be chosen based on their likely results (act utilitarianism) or whether agents should conform to rules that maximize utility (rule utilitarianism). There is also disagreement as to whether total (total utilitarianism) or average (average utilitarianism) utility should be maximized. Though the seeds of the theory can be found in the hedonists Aristippus and Epicurus, who viewed happiness as the only good, the tradition of utilitarianism properly began with Bentham, and has included John Stuart Mill, Henry Sidgwick, R. M. Hare, David Braybrooke, and Peter Singer. It has been applied to social welfare economics, the crisis of global poverty, the ethics of raising animals for food and the importance of avoiding existential risks to humanity. Because utilitarianism is not a single theory but a cluster of related theories that have been developed over two hundred years, criticisms can be made for different reasons and have different targets. Karl Marx, in Das Kapital, criticises Bentham’s utilitarianism on the grounds that it does not appear to recognize that different people have different joys:
Not even excepting our philosopher, Christian Wolff, in no time and in no country has the most homespun commonplace ever strutted about in so self-satisfied a way. The principle of utility was no discovery of Bentham. He simply reproduced in his dull way what Helvétius and other Frenchmen had said with esprit in the 18th century. To know what is useful for a dog, one must study dog-nature. This nature itself is not to be deduced from the principle of utility. Applying this to man, he who would criticize all human acts, movements, relations, etc., by the principle of utility, must first deal with human nature in general, and then with human nature as modified in each historical epoch. Bentham makes short work of it. With the driest naivete he takes the modern shopkeeper, especially the English shopkeeper, as the normal man. Whatever is useful to this queer normal man, and to his world, is absolutely useful. This yard-measure, then, he applies to past, present, and future. The Christian religion, e.g., is “useful,” “because it forbids in the name of religion the same faults that the penal code condemns in the name of the law.” Artistic criticism is “harmful,” because it disturbs worthy people in their enjoyment of Martin Tupper, etc. With such rubbish has the brave fellow, with his motto, “nulla dies sine linea [no day without a line]”, piled up mountains of books.
An article in the American Journal for Economics has addressed the issue of Utilitarian ethics within redistribution of wealth. The journal stated that taxation of the wealthy is the best way to make use of the disposable income they receive. This says that the money creates utility for the most people by funding government services. Many utilitarian philosophers, including Peter Singer and Toby Ord, argue that inhabitants of developed countries, in particular, have an obligation to help to end extreme poverty across the world, for example by regularly donating some of their income to charity. Peter Singer, for example, argues that donating some of one’s income to charity could help to save a life or cure somebody from a poverty-related illness, which is a much better use of the money as it brings someone in extreme poverty far more happiness than it would bring to oneself if one lived in relative comfort. However, Singer not only argues that one ought to donate a significant proportion of one’s income to charity, but also that this money should be directed to the most cost-effective charities, in order to bring about the greatest good for the greatest number, consistent with utilitarian thinking. Singer’s ideas have formed the basis of the modern effective altruist movement. ref
MORAL LOVE (tend and befriend “voice of care perspective”):
To me, this relates to care/caring ethics, which affirms the importance of caring motivation, emotion and the body in moral deliberation, as well as reasoning from particulars.This moral theory is known as “ the ethics of care” implies that there is moral significance in the fundamental elements of relationships and dependencies in human life. Normatively, care ethics seeks to maintain relationships by contextualizing and promoting the well-being of care-givers and care-receivers in a network of social relations. Most often defined as a practice or virtue rather than a theory as such, “care” involves maintaining the world of, and meeting the needs of, ourself and others. It builds on the motivation to care for those who are dependent and vulnerable, and it is inspired by both memories of being cared for and the idealizations of self. Following in the sentimentalist tradition of moral theory, care ethics affirms the importance of caring motivation, emotion and the body in moral deliberation, as well as reasoning from particulars. One of the original works of care ethics was Milton Mayeroff’s short book, On Caring, but the emergence of care ethics as a distinct moral theory is most often attributed to the works of psychologist Carol Gilligan and philosopher Nel Noddings in the mid-1980s. Though there are notable thinkers who express early strains of care ethics such as those that can be detected in the writings of feminist philosophers such as Mary Wollstonecraft, Catherine and Harriet Beecher, and Charlotte Perkins. Offering a general charged that traditional moral approaches contain a kinda of male bias, and asserted the “voice of care” as a legitimate alternative to the “justice perspective” of liberal human rights theory. Annette Baier, Virginia Held, Eva Feder Kittay, Sara Ruddick, and Joan Tronto are some of the most influential among many subsequent contributors to care ethics. Typically contrasted with deontological/Kantian and consequentialist/utilitarian ethics, is that of care ethics.
*ps. MORAL LOVE (tend and befriend “care ethics (ethics of care)/reciprocity (reciprocal altruism) ethics”) is similar to the fight or flight which is also only part of a bigger picture, according to Shelley Taylor, Ph.D., a psychology professor at the University of California, Los Angeles, and her colleagues. In the Psychological Review, as in evolutionary psychology, researchers describe how stress can elicit another behavioral pattern they call “tend and befriend”–especially in females. Tend-and-befriend is a behavior exhibited by some animals, including humans, in response to threat. It refers to protection of offspring (tending) and seeking out the social group for mutual defense (befriending), tend-and-befriend is theorized as having evolved as the typical female response to stress, just as the primary male response was fight-or-flight. This kind of gender determinism within the field is the subject of some controversy but I see it as to limited as well because we tend to use multiple sstrategiesto further sucuresafty depending of avalable resorces and if one regardless of gender persuasion is not able to either adequately defend themselves/or others (the fight part of fight or flight ) or is not able to either adequately flee a given threat (the flight part of fight or flight ) then other options such as The tend-and-befriend theoretical model was originally developed by Dr. Shelley E. Taylor and her research team at the University of California, Los Angeles and first described in a Psychological Review article published in the year 2000.
Here is a little on Care ethics and Reciprocal altruism
*Care ethics: is a normativeethical theory that holds interpersonal relationships and care or benevolence as a virtue as central to moral action. It is one of a cluster of normative ethical theories that were developed by feminists in the second half of the twentieth century. Here is a link to Feminist ethics. While consequentialist and deontological ethical theories emphasize universal standards and impartiality, ethics of care emphasize the importance of response. The shift in moral perspective is manifested by a change in the moral question from “what is just?” to “how to respond?”. Ethics of care criticize application of universal standards as “morally problematic since it breeds moral blindness or indifference.”
Some beliefs of the theory are basic:
- Persons are understood to have varying degrees of dependence and interdependence on one another. This is in contrast to deontological and consequentialist theories that tend to view persons as having independent interests and interactions.
- Those particularly vulnerable to one’s choices and their outcomes deserve extra consideration to be measured according to their vulnerability to one’s choices.
- It is necessary to attend to contextual details of situations in order to safeguard and promote the actual specific interests of those involved.
Care ethics contrasts with more well-known ethical models, such as consequentialist theories (e.g. utilitarianism) and deontological theories (e.g. Kantian ethics) in that it seeks to incorporate traditionally feminized virtues and values which, proponents of care ethics contend, are absent in such traditional models of ethics. While some feminists have criticized care-based ethics for reinforcing traditional stereotypes of a “good woman” others have embraced parts of this paradigm under the theoretical concept of care-focused feminism. Care-focused feminism is a branch of feminist thought, informed primarily by ethics of care as developed by Carol Gilligan and Nel Noddings. This body of theory is critical of how caring is socially engendered to women and consequently devalued. “Care-focused feminists regard women’s capacity for care as a human strength” which can and should be taught to and expected of men as well as women. Noddings proposes that ethical caring has the potential to be a more concrete evaluative model of moral dilemma, than an ethic of justice. Noddings’ care-focused feminism requires practical application of relational ethics, predicated on an ethic of care. Ethics of care is also a basis for care-focused feminist theorizing on maternal ethics. Critical of how society engenders caring labor, theorists Sara Ruddick, Virginia Held, and Eva Feder Kittay suggest caring should be performed and caregivers valued in both public and private spheres. Their theories recognize caring as an ethically relevant issue. This proposed paradigm shift in ethics encourages that an ethic of caring be the social responsibility of both men and women. Joan Tronto argues that the definition of the term “ethic of care” is ambiguous due in part to the lack of a central role it plays in moral theory. She argues that considering moral philosophy is engaged with human goodness, then care would appear to assume a significant role in this type of philosophy. However, this is not the case and Tronto further stresses the association between care and “naturalness”. The latter term refers to the socially and culturally constructed gender roles where care is mainly assumed to be the role of the woman. As such, care loses the power to take a central role in moral theory. Tronto states there are four ethical elements of care:
- Attentiveness
Attentiveness is crucial to the ethics of care because care requires a recognition of others’ needs in order to respond to them. The question which arises is the distinction between ignorance and inattentiveness. Tronto poses this question as such, “But when is ignorance simply ignorance, and when is it inattentiveness”? - Responsibility
In order to care, we must take it upon ourselves, thus responsibility. The problem associated with this second ethical element of responsibility is the question of obligation. Obligation is often, if not already, tied to pre-established societal and cultural norms and roles. Tronto makes the effort to differentiate the terms “responsibility” and “obligation” with regards to the ethic of care. Responsibility is ambiguous, whereas obligation refers to situations where action or reaction is due, such as the case of a legal contract. This ambiguity allows for ebb and flow in and between class structures and gender roles, and to other socially constructed roles that would bind responsibility to those only befitting of those roles. - Competence
To provide care also means competency. One cannot simply acknowledge the need to care, accept the responsibility, but not follow through with enough adequacy – as such action would result in the need of care not being met. - Responsiveness
This refers to the “responsiveness of the care receiver to the care”. Tronto states, “Responsiveness signals an important moral problem within care: by its nature, care is concerned with conditions of vulnerability and inequality”. She further argues responsiveness does not equal reciprocity. Rather, it is another method to understand vulnerability and inequality by understanding what has been expressed by those in the vulnerable position, as opposed to re-imagining oneself in a similar situation. Ref
Reciprocal altruism: (the evolution of cooperation)is a social interaction phenomenon where an individual makes sacrifices for another individual in expectation of similar treatment in the future. Originally introduced as a concept by biologist Robert Trivers, reciprocal altruism explains how altruistic behavior and morality can arise from evolutionary causes, as evolution selects for the best possible game theory results. If the benefit is higher than the initial cost, then multiple reciprocal interactions can actually out-compete more “greedy” forms of relationships, thus providing an evolutionary incentive for altruistic behavior. At the same time (and in opposition to unlimited altruism), reciprocity ensures that cheaters are also harmed when they choose to do so and are gradually made less fit as a result of their own behavior. Modern ethnology seems to support at least part of this hypothesis, as many societies on all continents have developed highly complex forms of gift economy where gifts are given with no immediately obvious material return, but the implicit societal expectation of “repayment” in gift form at some later point in time. Amazingly, those societies work. The custom of giving gifts for birthdays in the West may be seen as a remnant of this. It’s not uncommon for someone to engage in this behavior with the object of their affection, i.e. being nice to them with the expectation of a sexual relationship. Since a lot of these situations tend to involve lonely, single straightmen, the common term for this is “Nice Guy” — in other words, the suitor’s claim “but I’m a nice guy…” translates to “I went through all the motions and she still won’t sleep with me.” As a general rule, this is not an effective strategy, and often even drifts into stalking behavior. Women who engage in the same behavior do not get as much attention but are still known (naturally) as Nice Girls. Either way, such people are seldom actually nice, and frequently come off as manipulative and bitter without realizing it. The fallacy lies in their equating sexual relationship with being nice – if their expectation of tit for tat was actually equal, aka being nice for being nice and being honest for being honest (which they, coming into relationship with entirely different expectations than they communicate, fail at), they wouldn’t face such a problem. Ref
I see my Axiological driven morality to involve an enmeshed union of both: fight or flight “justice perspective” and a tend and befriend “voice of care perspective”
Helping is Helpful: Valuing, Motivating, Supporting
How to Grow in Our Positive Outcomes: Gratitude, Empathy, and Kindness
We can become a more quality person by actively being aware and developing a gratitude for life, which supports as well as grows our feelings of empathy, that then motivates the behavior of kindness.
Universal Ethical Standards?
There are several ethical standards that are considered to be self-evident and seem to apply to all people throughout all of history, regardless of cultural, political, social, or economic context. The non-aggression principle, which prohibits aggression, or the initiation of force or violence against another person, is a universal ethical principle. My Examples of aggression include murder, rape, kidnapping, assault, robbery, theft, and vandalism. On the other hand, the commission of any of such acts in response to aggression does not necessarily violate universal ethics. There are obvious reasons why universal ethics are beneficial to society. For example, if people were allowed to kill or steal, this would lead to widespread chaos and violence and would be detrimental to the well-being of society. Most people agree that it’s better to prohibit aggression than to allow everyone to commit it. Therefore, aggression is intrinsically immoral. Although nearly all societies have laws prohibiting aggression, this does not mean that universal ethics are necessarily reflected by that society’s government or its dominant ideology. Universal ethics does not mean the imposition of one set of morals by one group on another. It means a shared way or means of reaching a consensus on norms and values that also accepts diversity. A shared understanding of what is right and what is wrong. In any circumstance or situation, we can start by examining the present state of affairs. This should be done with the aim of gaining an understanding of other cultural differences, history, and tradition, remembering that an explanation is not necessarily a justification. Next, what is the minimum that is acceptable? There has to be an acceptance that some disagreements cannot be resolved at that time. The aim is to change the present situation for the better. Once an acceptable minimum is reached, it is possible to work towards an eventual ideal state. We are all one community and we are all responsible for upholding human rights for each other. More than ever there is a need for agreement on the existence of universally held values and the content of those values. It may prove to be impossible to find one set of universal ethical principles that apply to all cultures, philosophies, faiths and professions but the destination is only part of the journey. The value lies in the search for principles that can be shared by all and can underpin the framework for global dialogue on ethical issues. A universal moral code might be a set of underlying dispositions we are all born with. Or it might be a set of explicit norms and values humans might one day universally accept. But a more important sense of ‘universal moral code’ is of a set of moral values that is universally valid, whether or not it is inscribed in our brains, or accepted by people. Of course, that is a very controversial idea. If there is such a universal moral code, then we have an imperative to try to discover it, and to make it universally accepted (to make it a moral code in the descriptive sense). But this requires thinking hard about ethics, not looking for some code that might or might not be written into our brains. RefRefRef
1.Values (morality motivations): are a amalgam of personal, family, local or extended group environmental, religious and/or cultural content etc. we are what we eat we are the knowledge we consume and the ideas we are sounded by. Values to me thus are self driven ideals others influenced. I like to think myself out of the matrix though if I would have grown up in china would I not be a different me. Born rich and loved as a child be different or adopted be Angelina Jolie be forever changed. Or the love child of Jeffry Dahmer or Mahatma Gondi would I still be the same me with the same values? I think not. Values are not fixed they change throughout one’s lifetime they can be absolute or relative, the assumption of which can be the basis for any sort of chosen action. Thus, a value system is a set of consistent values and measures one chooses because of their connectedness to chosen ideals. Values to me can be a foundation upon which other thinking streams and measures of ideal integrity are based. Those values which are not physiologically determined and normally considered objective, such as a desire to avoid physical pain, seek pleasure, etc., are considered subjective, vary across individuals and cultures and are in many ways aligned with belief and belief systems only truth to a set of people.
2.Morals (personal morality): are not held by all in the same way since all are not held to Orthodox faith and though most start with good and bad or right and wrong values, which usually are personally, familially, socially or religiously give or in some way otherworldly defined, thus not universal.
3.Ethics (public morality): Ethics are not constrained by a given religion’s value systems to motivate its ideas of right and wrong instead it relies on universal truths found in universal principles of just human action. Ethics is set standers uses to personally engage with others and universal truths assist goals of universal ethics standards. Thus, ethics are general prosocial prescription we as morality aware beings in a rather universal way tend to have some awareness of and it is not just an awareness as in one who holds to ethics often get it applies to all peoples. Some may wish to devalue people but to do so is not really unethical, though often it can lead to unethical behavior. So what I am trying to highlight is how in the behaviour that the ethics violation could occur as the internal attitude of devaluing others would only be a possible morals violation such as one who valued virtue and not getting it but failing by the persuasion of devaluing the life of other humans. This simple internal devaluing of humans, that they may be doing is vile. But ethics would not be involved until public behaviors with others, as such ethics is not so much a persuasion as an adherence to a standard(s) that should cover all thus it is highly applicable to utilize in environmental decision making.
In general, I am a Universal Ethicist?
But What Good is a Set of Principles?
There are many tools for decision making, but few (secular) guides to indicate when situations might have an ethical implication. Yet this awareness is a crucial first step before decisions are made. Recognizing the moral context of a situation must precede any attempt to resolve it. Otherwise, what’s to resolve? Ethical dilemmas rarely present themselves as such. They usually pass us by before we know it or develop so gradually that we can only recognize them in hindsight – a little like noticing the snake after you’ve been bitten. But what are the signs that a snake might be present? An ethical framework is like a ‘snake detector’. I offer the following principles as landmarks – generic indicators to be used as compelling guides for an active conscience. They are NOT absolute rules or values. They are more like a rough measurement where an exact one is not possible. They often conflict with each other in practice, and some will trump others under certain circumstances. But as principles that need to be considered, they appear constant. These principles are compatible with the argument that we should simply follow our intuition and rely on the ‘inner voice’. However, that voice is not always audible, and today’s society presents a wide range of complex circumstances that require more guidance than simply ‘concern for others’ or ‘does it feel right?’ And so these principles are offered effectively as a more detailed reference. In a sense, the principles are outcomes of the mother of all principles – unconditional love and compassion – which appears in virtually all faiths, and is expressed here as ‘concern for the well-being of others’. (This principle is at the heart of the stakeholder model of ethics, i.e. what is my impact on others?) At first glance, they will appear obvious and perhaps trite or simplistic. Keep in mind that they are meant to be practical rather than groundbreaking, and that many people have found them useful in the absence of other guides.
“Universal ethics: there are several ethical standards that are considered to be self-evident, and seem to apply to all people throughout all of history, regardless of cultural, political, social, or economic context. The non-aggression principle, which prohibits aggression, or the initiation of force or violence against another person, is a universal ethical principle. Examples of aggression include murder, rape, kidnapping, assault, robbery, theft, and vandalism. On the other hand, the commission of any of such acts in response to aggression does not necessarily violate universal ethics. There are obvious reasons why universal ethics are beneficial to society. For example, if people were allowed to kill or steal, this would lead to widespread chaos and violence, and would be detrimental to the well-being of society. Most people agree that it’s better to prohibit aggression than to allow everyone to commit it. Therefore, aggression is intrinsically immoral. Although nearly all societies have laws prohibiting aggression, this does not mean that universal ethics are necessarily reflected by that society’s government or its dominant ideology. In ethics, a ‘universal code of ethics’ is a system of ethics that can apply to every sentient being.” Ref
It seems, in general, the less education and higher poverty have a higher correlation to being religious.
I am an Axiological Atheist, with a Rationalist Persuasion, who Supports Anarcho-Humanism
Anarcho-Humanism, to me, is atheistic humanism with an unconditional social awareness:
Anarcho (anarchism): “No Gods – No Masters”
Humanism: “No Harm – Do Good”
Rationalism, Freethinker, Humanism & Secular humanism?
My core definition of humanism is that humans can solve human problems by human means. I am not saying other things can’t or shouldn’t be added to it but to me a definition of humanism must always contain something coherent to such a thinking or not contradict such as I have offered. Thus, why it is appropriate to say “good without god” when one is a humanist.
Confusions in Atheism and Humanism
Categories and Versions of Humanism
Believe in Good, Humanist Morality?
If one states they are a humanist and they believe in good, are they for or against a form of axiology or formal axiology? Axiology is the philosophical study of goodness, or value, in the widest sense of these terms. It may be used as the collective term for ethics and aesthetics—philosophical fields that depend crucially on notions of value—or the foundation for these fields, and thus similar to value theory and meta-ethics. The word “axiology” (Greek: axios = good, worth, or value; logos = “science”) means “study of good”, “study of worth ” or “study of value.” The axiologists sought to characterize the notion of value in general, of which moral value is only one species. They argue (with notable differences between them), that goodness does not exclusively derive from the will, but exists in objective hierarchies. Formal axiology, the attempt to lay out principles regarding value with mathematical rigor, is exemplified by Robert S. Hartman’s Science of Value. The fundamental principle of Hartman’s Science of Value, functions as an axiom, and can be stated in symbolic logic, is that a thing is good insofar as it exemplifies its concept. To put it another way, “a thing is good if it has all its descriptive properties.” This means, according to Hartman, that the good thing has a name, that the name has a meaning defined by a set of properties, and that the thing possesses all of the properties in the set. A thing is bad if it does not fulfill its description. If it doesn’t fulfill its definition it is terrible (awful, miserable.) A car, by definition, has brakes. A car which accelerates when the brakes are applied is an awful car, since a car by definition must have brakes. A horse, if we called it a car, would be an even worse car, with fewer of the properties of a car. The name we put on things is very important: it sets the norm for how we judge them. If one states they are a humanist, are they for or against a form of universal or realism morality? The 1948 Universal Declaration of Human Rights of the United Nations can be seen as an example of global efforts to bring a universalist, equal and common moral justice to all people, and Moral Universalism is, at least in part, the basis for modern human rights, and an integral part of any Humanist philosophy. Human rights which are commonly considered a “deontological” concept, sometimes described as “duty-” or “obligation-” or “rule-” based ethics, because rules “bind you to your duty.” Which T. M. Scanlon advances the idea that human rights, can only be justified with reference to the consequences of having those rights. Secular morality is the aspect of philosophy that deals with morality outside of religious traditions. Modern examples include humanism, freethinking, and most versions of consequentialism. Consequentialism is the class of normative ethical theories holding that the consequences of one’s conduct are the ultimate basis for any judgment about the rightness or wrongness of that conduct. Thus, from a consequentialist standpoint, a morally right act (or omission from acting) is one that will produce a good outcome, or consequence. Consequentialist theories differ in how they define moral goods. Some argue that consequentialist theories are not necessarily mutually exclusive. For example, Robert Nozick argues for a theory that is mostly consequentialist, but incorporates inviolable “side-constraints” which restrict the sort of actions agents are permitted to do. Consequentialists can and do differ widely in terms of specifying the Good. Some consequentialists are monists about the Good. Utilitarians, for example, identify the Good with pleasure, happiness, desire satisfaction, or “welfare” in some other sense. Other consequentialists are pluralists regarding the Good. Some of such pluralists believe that how the Good is distributed among persons (or all sentient beings) is itself partly constitutive of the Good, whereas conventional utilitarians merely add or average each person’s share of the Good to achieve the Good’s maximization. Moreover, there are some consequentialists who hold that the doing or refraining from doing, of certain kinds of acts are themselves intrinsically valuable states of affairs constitutive of the Good. An example of this is the positing of rights not being violated, or duties being kept, as part of the Good to be maximized—the so-called “utilitarianism of rights”. None of these pluralist positions erase the difference between consequentialism and deontology. For the essence of consequentialism is still present in such positions: an action would be right only insofar as it maximizes these Good-making states of affairs being caused to exist. However much consequentialists differ about what the Good consists in, they all agree that the morally right choices are those that increase (either directly or indirectly) the Good. Moreover, consequentialists generally agree that the Good is “agent-neutral”. That is, valuable states of affairs are states of affairs that all agents have reason to achieve without regard to whether such states of affairs are achieved through the exercise of one’s own agency or not. “Consequentialism”, as described by Peter Singer, “start not with moral rules, but with goals. They assess actions by the extent to which they further those goals.” Consequentialism contains in itself no explanation for why pleasure or utility are morally good, or why consequences should matter to morality at all. Nor does consequentialism/deontology make any claims about how we know moral facts (if there are any). That is a meta-ethical question, so the question ‘how do we know that it is wrong to kill?’ is not a normative but a meta-ethical question. Some consequentialists and deontologists are also moral realists. Some are not. Moral Realism a similar position to universal morality, that certain acts are objectively right or wrong, independent of human opinion. that there exist such things as moral facts and moral values, and that these are objective and independent of our perception of them or our beliefs, feelings or other attitudes towards them. Therefore, moral judgments describe moral facts, which are as certain in their own way as mathematical facts. It is a cognitivist view in that it holds that ethical sentences express valid propositions (and are therefore “truth-apt” i.e. they are able to be true or false), and that they describe the state of the real world. Moral Realism has the advantage of purportedly allowing the ordinary rules of logic to be applied straightforwardly to moral statements, (so that we can say, for example, that a moral belief is false or unjustified or contradictory in the same way we would about a factual belief). It also allows for the resolution of moral disagreements, because if two moral beliefs contradict one another, Moral Realism (unlike some other meta-ethical systems) says that they cannot both be right and so there should be some way of resolving the situation. Two main variants of moral realism are: Ethical Naturalism and Ethical Non-Naturalism.
Ethical Naturalism: holds that there are objective moral properties of which we have empirical knowledge, but that these properties are reducible to entirely non-ethical properties. It assumes cognitivism (the view that ethical sentences express propositions and can therefore be true or false), and that the meanings of these ethical sentences can be expressed as natural properties without the use of ethical terms.
Ethical Non-Naturalism: holds that ethical statements express propositions (in that sense it is also cognitivist) that cannot be reduced to non-ethical statements (e.g. “goodness” is indefinable in that it cannot be defined in any other terms). G. E. Moore claimed that a naturalistic fallacy is committed by any attempt to prove a claim about ethics by appealing to a definition in terms of one or more natural properties (e.g. “good” cannot be defined in terms of “pleasant”, “more evolved”, “desired”, etc). Ethical Intuitionism is a variant of Ethical Non-Naturalism which claims that we sometimes have intuitive awareness of moral properties or of moral truths.
Critics have argued that, while Moral Realism may be able to explain how to resolve moral conflicts, it cannot explain how these conflicts arose in the first place. Others have argued Moral Realism posits a kind of “moral fact” which is non-material and unobservable (in the way as objective material facts are observable), and therefore not accessible to the scientific method. Some philosophers who only believe in the physical world and don’t believe in anything immaterial say that they are also moral realists, but when they describes the type of morality that they believe in, often what they are talking about is the moral beliefs that people have acquired through evolution, which is called evolutionary moral realism. This includes the human instinct to care for the well being of others in one’s own group and the instinct to hold others accountable for transgressions against members of the group. A physicalist/materialist understanding of morality is therefore purely descriptive of human nature within a deterministic system. The physicalist/materialist conception of morality differs from normative moral realism, in which one believes that things ought be a certain way or that people should act in a certain way because such states of affairs or actions would be better, not purely as a function of anything physical such as the instincts people have evolved to have, but at least partially for reasons that ultimately transcend the physical world. For example, if someone believes that oppressing others is always wrong even though humans have an instinctual predisposition to favor their own group over others, and this person does not otherwise explain how this belief is descriptive of something in the physical world, then this implies that this person believes in normative morality. A similar concept to normative ethics is prescriptive ethics, which are those that are supposed to logically commit someone to act a certain way. For example, the normative statement “Murder is wrong” can be restated as “Do not murder”, which is prescriptive. This is similar to how doctors can prescribe medications for one to use. Essentially, prescriptive moral statements are prescribed to people in order for them to act morally. Normative statements simply state the relation a certain state of affairs has to rightness or wrongness without telling anyone how to act. The distinction between descriptive and normative/prescriptive morality is important to understand. One study found that 56% of professional philosophers accept or lean towards moral realism and 28%: anti-realism. Cognitive psychologist Steven Pinker has argued that the game theoretic advantages of ethical behavior support the idea that morality is “out there” in a certain sense (as part of the evolutionary fitness landscape). Journalist Robert Wright has similarly argued that natural selection moves sentient species closer to moral truth as time goes on. Writer Sam Harris has also argued that ethics could be objectively grounded in an understanding of neuroscience. He has admitted to being committed to some form of moral realism (viz. moral claims can really be true or false) and some form of consequentialism (viz. the rightness of an act depends on how it affects the well-being of conscious creatures). Being a moral anti-realist is compatible with having, and following, a moral theory: you just think you have reasons to be moral which are not based on mind-independent facts. For example, you might think convention gives you reason to be moral, where conventionalism is traditionally described as a form of non-realism. see: link A delineation of moral realism into a minimal form, a moderate form, and robust form has been put forward in the literature. The robust model of moral realism commits moral realists to three theses:
The semantic thesis: The primary semantic role of moral predicates (such as “right” and “wrong”) is to refer to moral properties (such as rightness and wrongness), so that moral statements (such as “honesty is good” and “slavery is unjust”) purport to represent moral facts, and express propositions that are true or false (or approximately true, largely false, and so on).
The alethic thesis: Some moral propositions are in fact true.
The metaphysical thesis: Moral propositions are true when actions and other objects of moral assessment have the relevant moral properties (so that the relevant moral facts obtain), where these facts and properties are robust: their metaphysical status, whatever it is, is not relevantly different from that of (certain types of) ordinary non-moral facts and properties.
The minimal model, i.e. moral universalism, leaves off the metaphysical thesis, treating it as matter of contention among moral realists (as opposed to between moral realists and moral anti-realists). This dispute is not insignificant, as acceptance or rejection of the metaphysical thesis is taken by those employing the robust model as the key difference between moral realism and moral anti-realism. Moral universalism (also called moral objectivism or universal morality) is the meta-ethical position that some system of ethics, or a universal ethic, applies universally, that is, for “all similarly situated individuals”, regardless of culture, race, sex, religion, nationality, sexual orientation, or any other distinguishing feature. Not all forms of moral universalism are absolutist, nor are they necessarily value monist; many forms of universalism, such as utilitarianism, are non-absolutist, and some forms may be value pluralist. A moral theory must be able to solve and thus to be on solid philosophical grounds:
The ontological problem: an adequate theory must account for ethics without assuming the existence of anything that does not actually exist.
The epistemological problem: if we have knowledge of right and wrong, an adequate theory must explain how we acquire such knowledge.
The experience problem: An adequate theory about ethics must account for the phenomenology of moral experience.
The supervenience problem: An adequate theory must be consistent with the supervenient character of evaluative concepts.
The motivation problem: an adequate theory must account for the internal connection between moral belief and motivation (or if there is no such connection, it must offer an alternative account of how morality guides action).
The reason problem: An adequate theory must account for the place of reason in ethics.
The disagreement problem: An adequate theory must explain the nature of ethical disagreement.
Atheism is the reality position.
Theism is the anti-reality position!
I don’t need religion or its fake gods.
I am will to power!
- Deconstructing Pseudo-Morality with Axiology Understanding?
- Pragmatic Ethical/Axiology Driven Assumptions, Overcome the Weight of Solipsism Doubt
- Methodological Rationalism (Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) and Skepticism
- Axiology, Morality and the Dignity Being: “Human Entity”
- On the Nature of Value (axiology)
- If axiology is a value-based ethics system, how are the ethical values established?
- Axiology is both a philosophy and a science of value.
- My Methodological Rationalism: investigate (ontology), expose (epistemology) and judge (axiology)
- Hammer of Truth: Yes, you too, have lots of beliefs…
- Axiological/axiology (value theory/value science) Atheism?
- My quick definition of Axiology and Axiological Atheism?
- Here is a Little on how I got into Axiology
- Axiology and Value Consciousness
- “The Hammer of Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
- Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology argument/challenge protocol
- Axiology vs. Nihilism
- Axiology, Naturalism, Realism and Moral Theory Ideas
- I am a caring firebrand axiological atheist, wishing to be hard on ideas but kind to people.
- Caring Firebrand Axiological Atheist, Antitheist, and Antireligionist as a Valuized Ethical Duty.
- Axiological Atheism Starts in Apatheism?





People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.





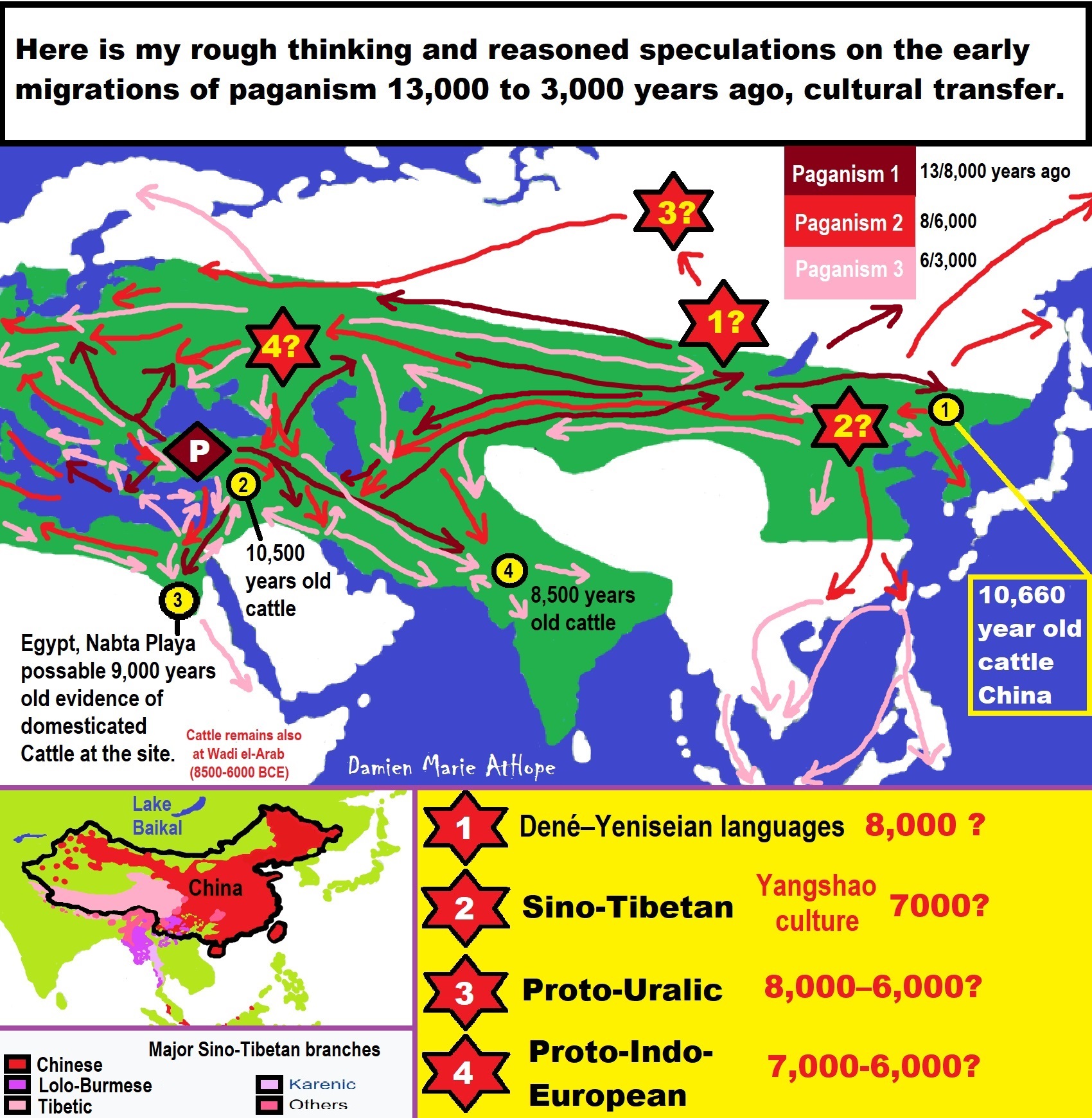

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
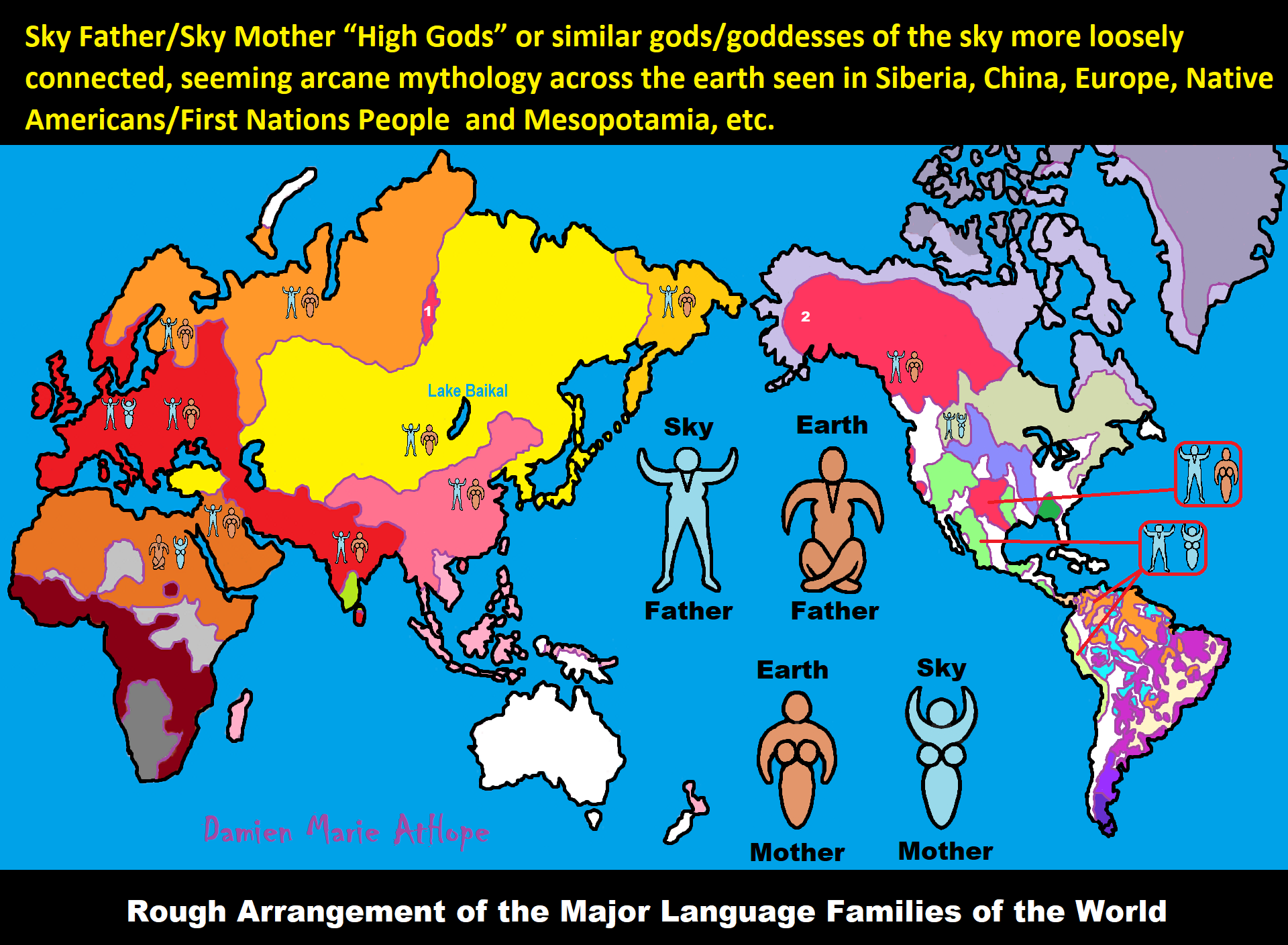
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com


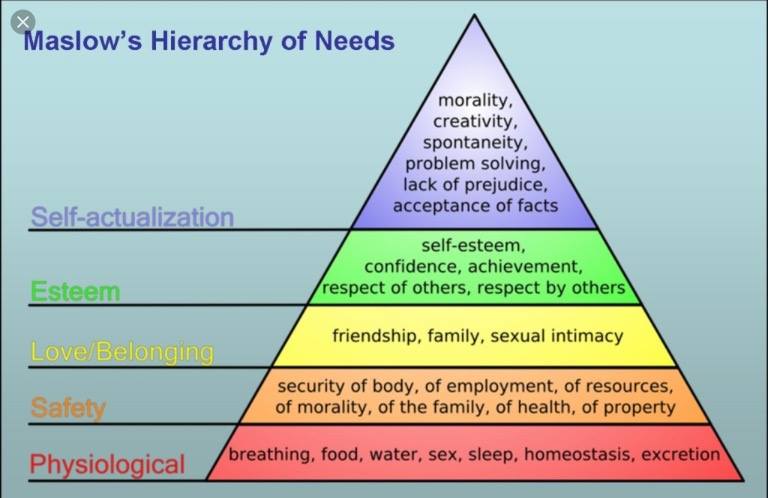
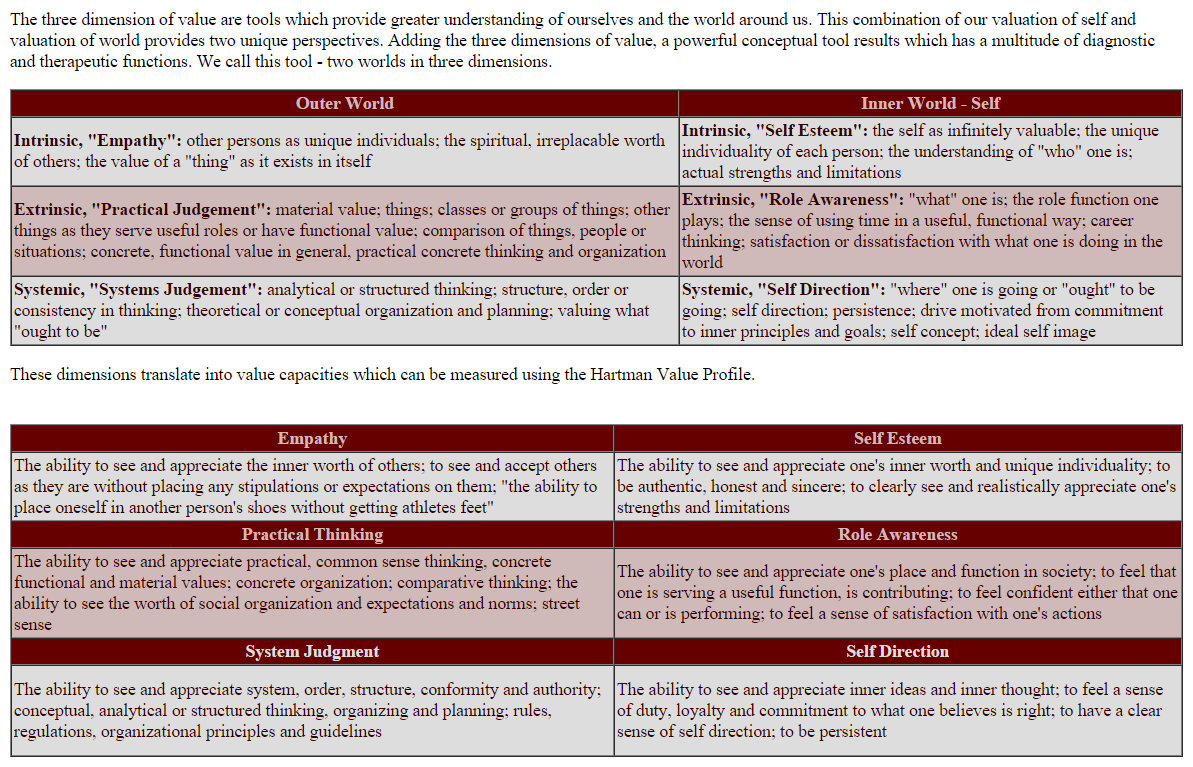





My thinking is strong like a bomb,
deep like the ocean,
and creatively imaginative as if a star shining brightly.
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolves all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred. So, it all starts in a general way with Animism (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). I try with everything I have, to show you can be a caring firebrand atheist. Having a good belief standard and a good education religion, gods, ghosts, or goblins are but fantasy lacking all justification that demands strong atheism. But strong atheism, is hard on beliefs it needs not be anything but caring to the believer as we get they are a victim of indoctrination. I feel for them and wish to free the word, breaking the chains of ignorance and dogmatic religious propaganda hurting all humanity.
firebrand atheist. Having a good belief standard and a good education religion, gods, ghosts, or goblins are but fantasy lacking all justification that demands strong atheism. But strong atheism, is hard on beliefs it needs not be anything but caring to the believer as we get they are a victim of indoctrination. I feel for them and wish to free the word, breaking the chains of ignorance and dogmatic religious propaganda hurting all humanity.
Caring Firebrand Atheist Activism Event: Indianapolis, In. May 5
Threatened, for my Caring Firebrand Atheist Activism Event: Indianapolis, In. May 5