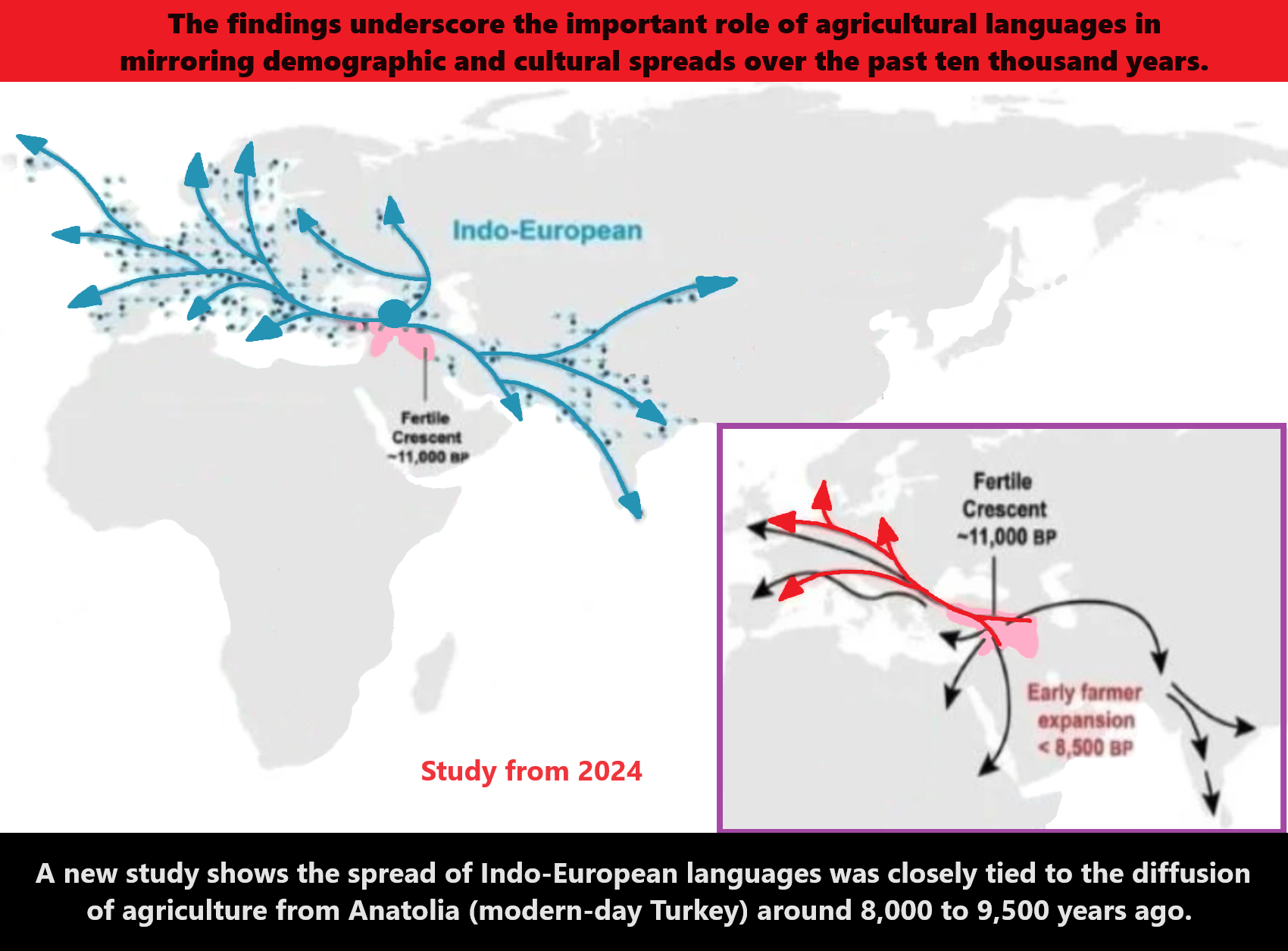
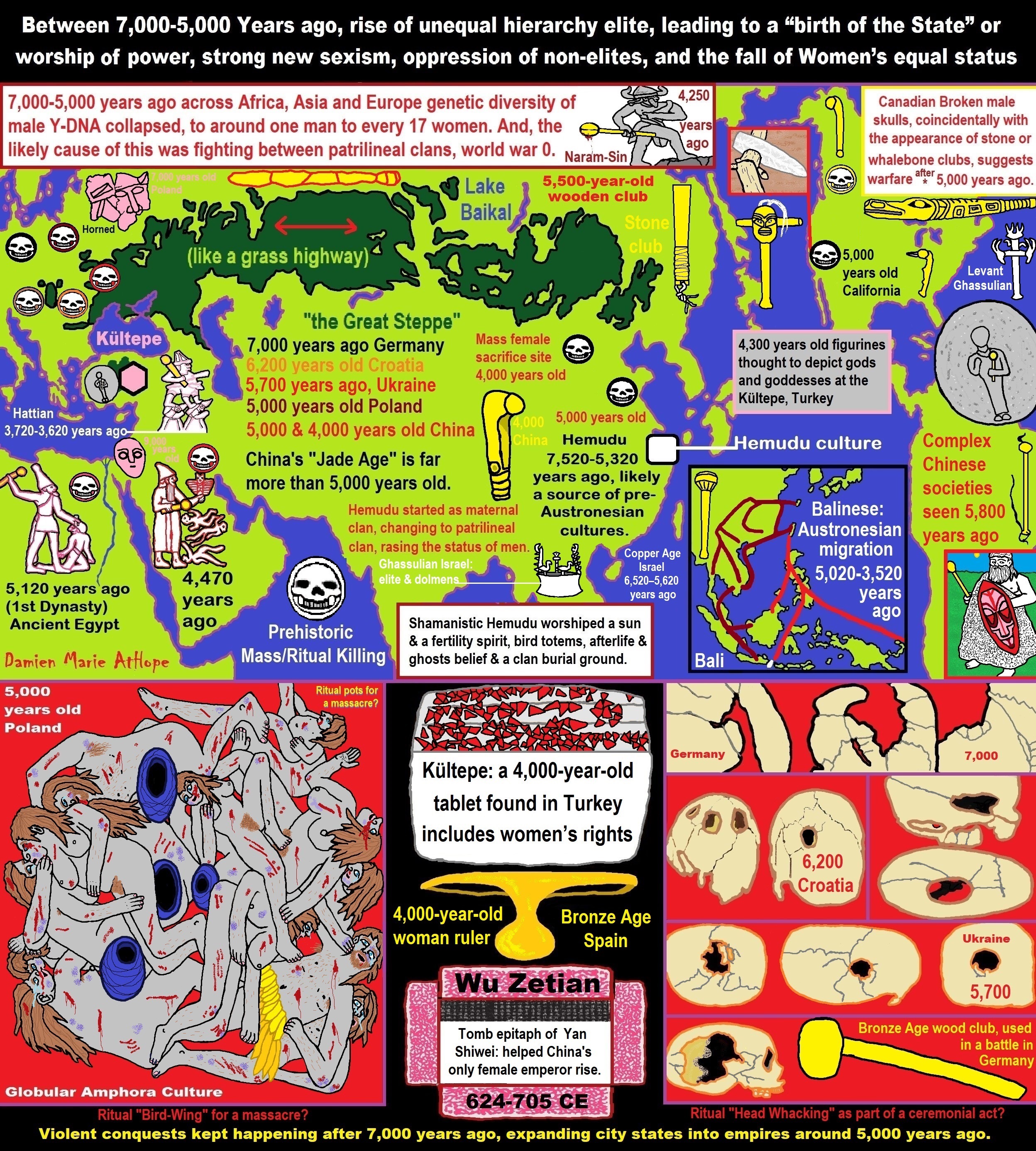
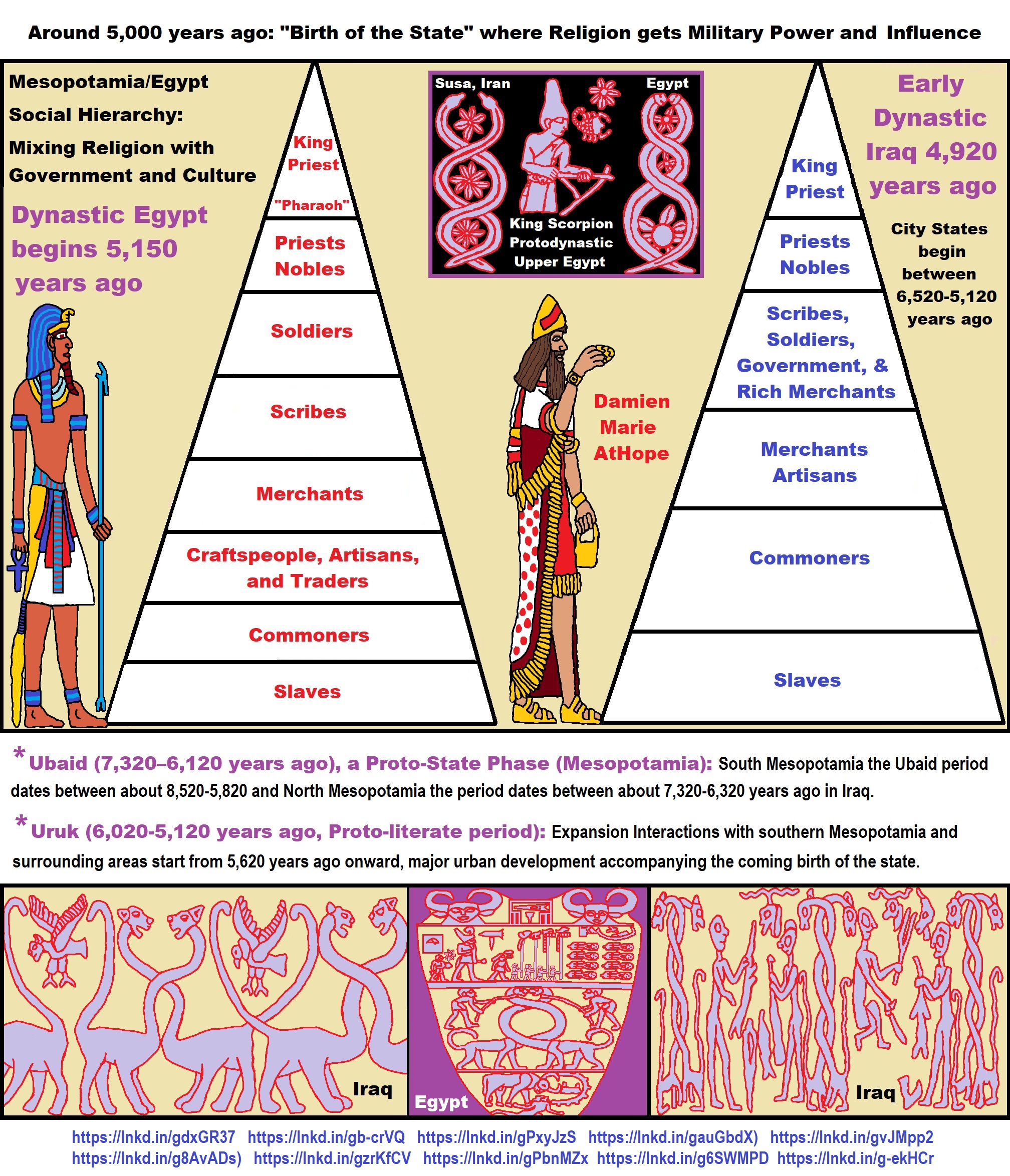
Progressed organized religion (around 5,000 years ago)
Progressed organized religion (such as that seen in Egypt: 5,000 years ago “The First Dynasty dates to 5,150 years ago”). This was a time of astonishing religion development and organization with a new state power to control. Around the time of 5,000 to 4,000 years ago, saw the growth of these riches, both intellectually and physically, became a source of contention on a political stage, and rulers sought the accumulation of more wealth and more power.
*The First Dynasty* Date: 3,150 B.C.E. (5,150 years ago) and the Beginning Rise of the Unequal State Government Hierarchies, Religions and Cultures Merger
The Pharaoh in ancient Egypt was the political and religious leader holding the titles ‘Lord of the Two Lands’ Upper and Lower Egypt and ‘High Priest of Every Temple’. In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt and this reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later.
Around 4,890 years ago during the Second Dynasty, the King was linked with the divine and reign with the will of the gods. Following this, rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due to those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth, the intermediary between the gods and the people, and when he died, he was thought to become Osiris, the god of the dead. As such, in his role of ‘High Priest of Every Temple’, it was the pharaoh’s duty to build great temples and monuments celebrating his own achievements and paying homage to the gods of the land. Among the earliest civilizations that exhibit the phenomenon of divinized kings are early Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt.
In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by the king Menes (now believed to be Narmer). Menes/Narmer is depicted on inscriptions wearing the two crowns of Egypt, signifying unification, and his reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later. During the Second Dynasty of Egypt 4,890-4,670 years ago King Raneb (also known as Nebra) linked his name with the divine and his reign with the will of the gods. Following Raneb, the rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due to those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth. The honorific title of `pharaoh’ for a ruler did not appear until the period known as the New Kingdom 3,570-3,069 years ago. Monarchs of the dynasties before the title of `pharaoh’ from the New Kingdom were addressed as `your majesty’ by foreign dignitaries and members of the court and as `brother’ by foreign rulers; both practices would continue after the king of Egypt came to be known as a pharaoh.
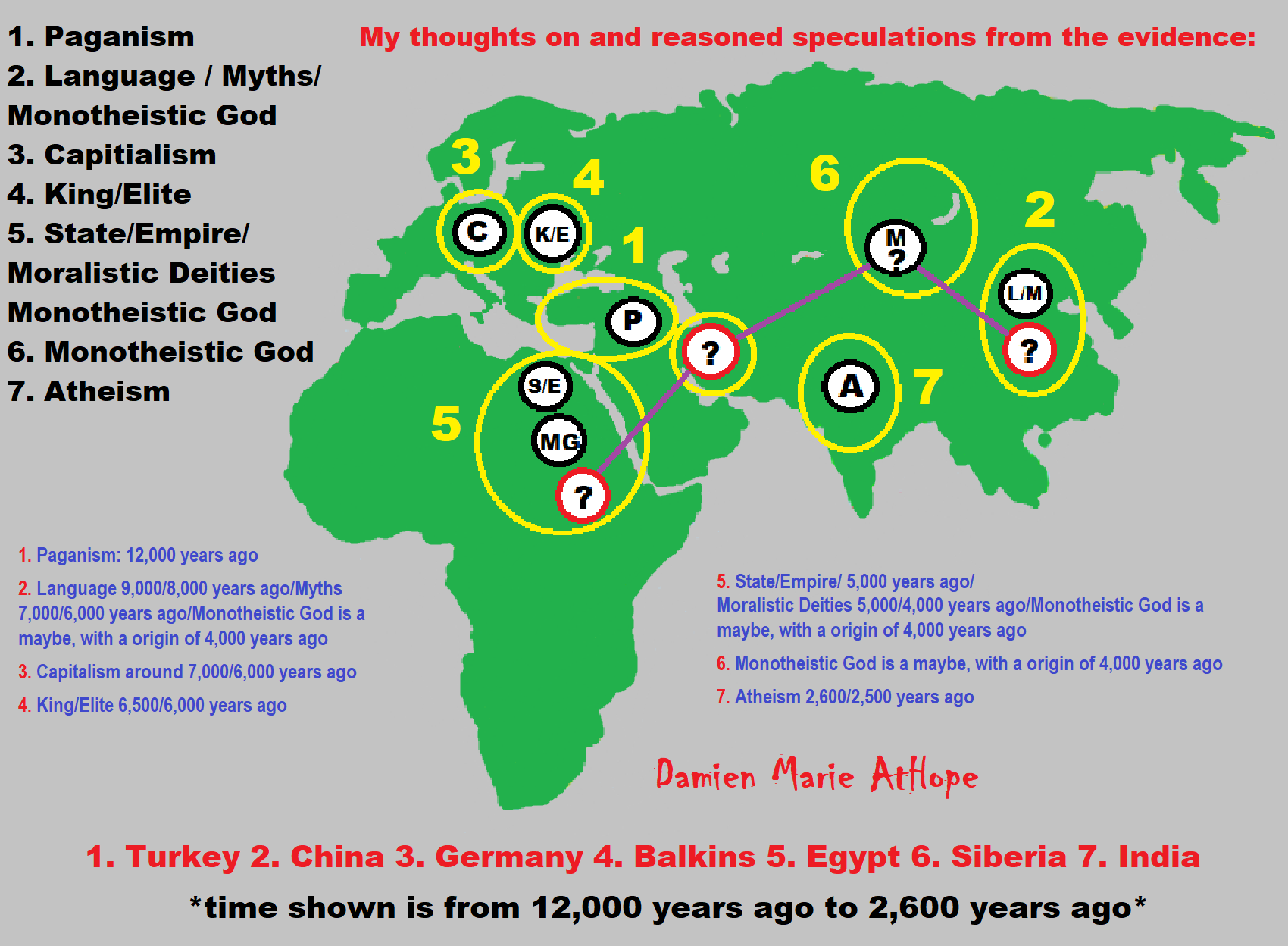
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism): LINK
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves: LINK
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State): LINK
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): LINK
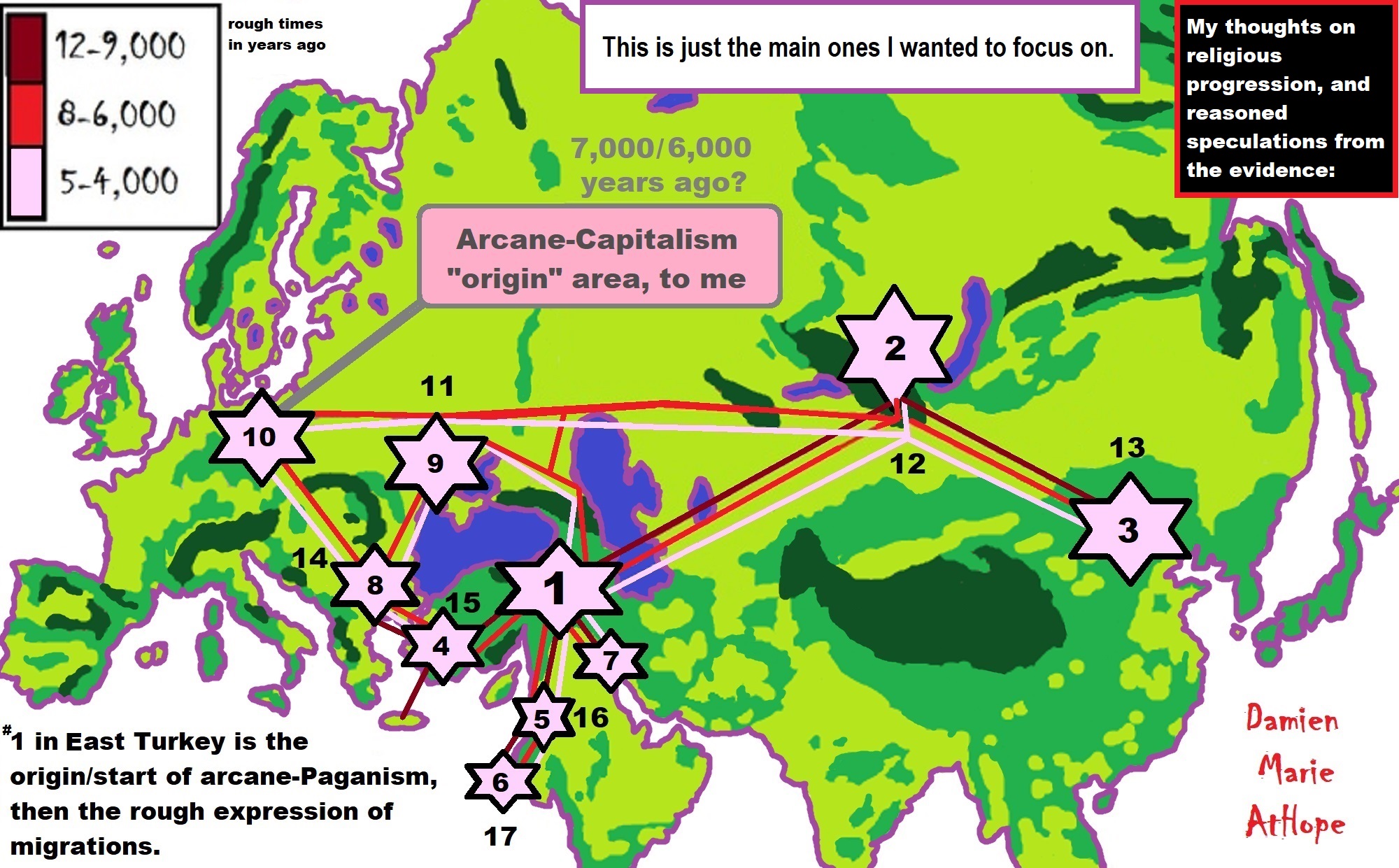
Arcane = complicated and therefore understood or known by only a few people
To me, societies start with primitive anarchism and socialism at least 100,000 years ago and are seen in animist-only thinking that is now largely limited to southern Africa today. Then they lose systematic anarchism possibly by 50,000 to 40,000 years ago but keeps socialism/primitive communism with the emergence of totemism largely limited to Europe and then spreading out from there. And to me, arcane/primitive capitalism emerges at or around 7,000 to 5,000 years ago in central Europe especially southern Germany or surrounding areas (Czecho-Slovakia and Austria), and then spread out from there.
7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
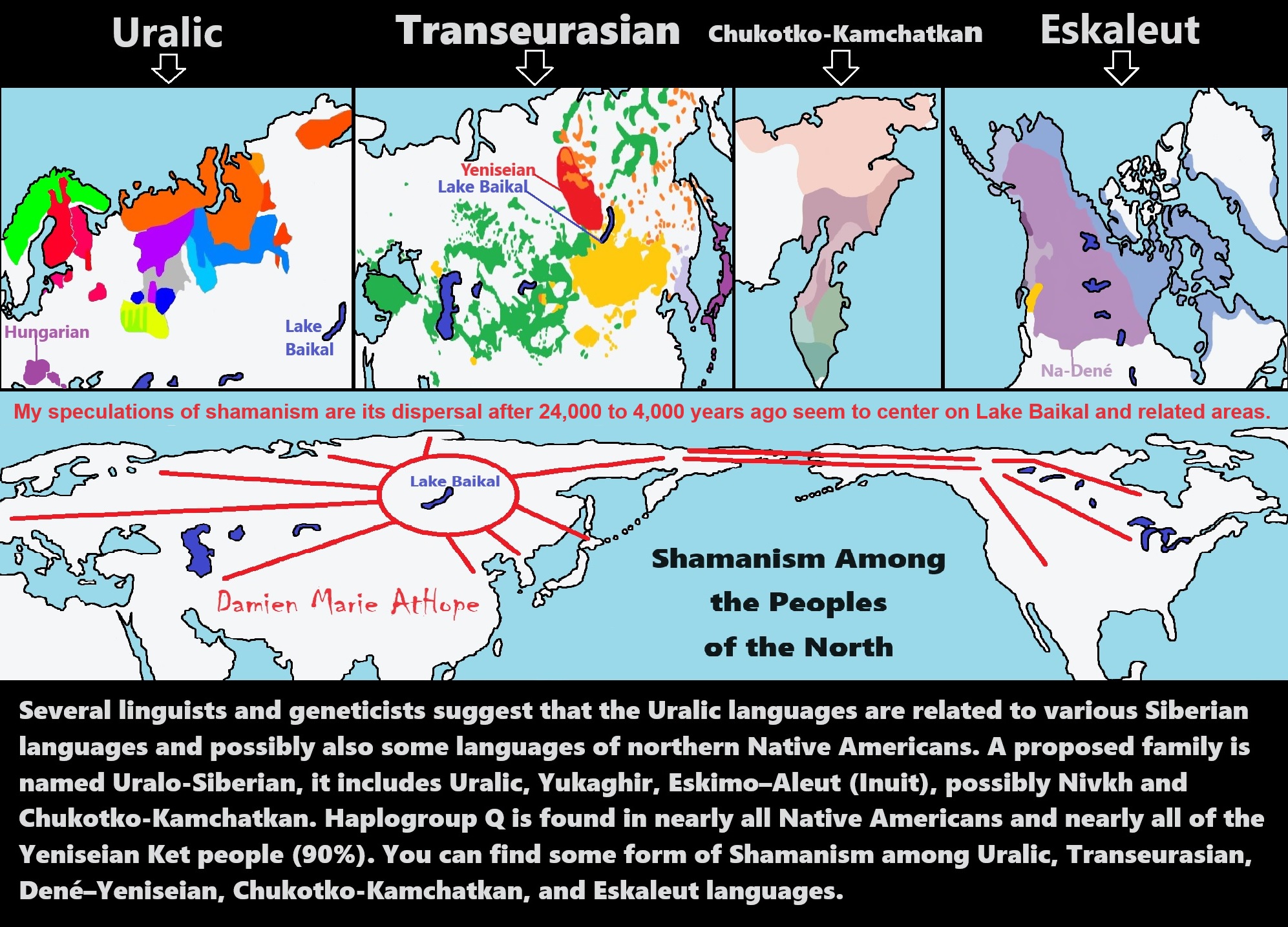
“Several linguists and geneticists suggest that the Uralic languages are related to various Siberian languages and possibly also some languages of northern Native Americans. A proposed family is named Uralo-Siberian, it includes Uralic, Yukaghir, Eskimo–Aleut (Inuit), possibly Nivkh, and Chukotko-Kamchatkan. Haplogroup Q is found in nearly all Native Americans and nearly all of the Yeniseian Ket people (90%).” ref, ref
You can find some form of Shamanism, among Uralic, Transeurasian, Dené–Yeniseian, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskaleut languages.
My speculations of shamanism are its dispersals, after 24,000 to 4,000 years ago, seem to center on Lake Baikal and related areas. To me, the hotspot of Shamanism goes from west of Lake Baikal in the “Altai Mountains” also encompassing “Lake Baikal” and includes the “Amur Region/Watershed” east of Lake Baikal as the main location Shamanism seems to have radiated out from.
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Postglacial genomes from foragers across Northern Eurasia reveal prehistoric
mobility associated with the spread of the Uralic and Yeniseian languages
Abstract
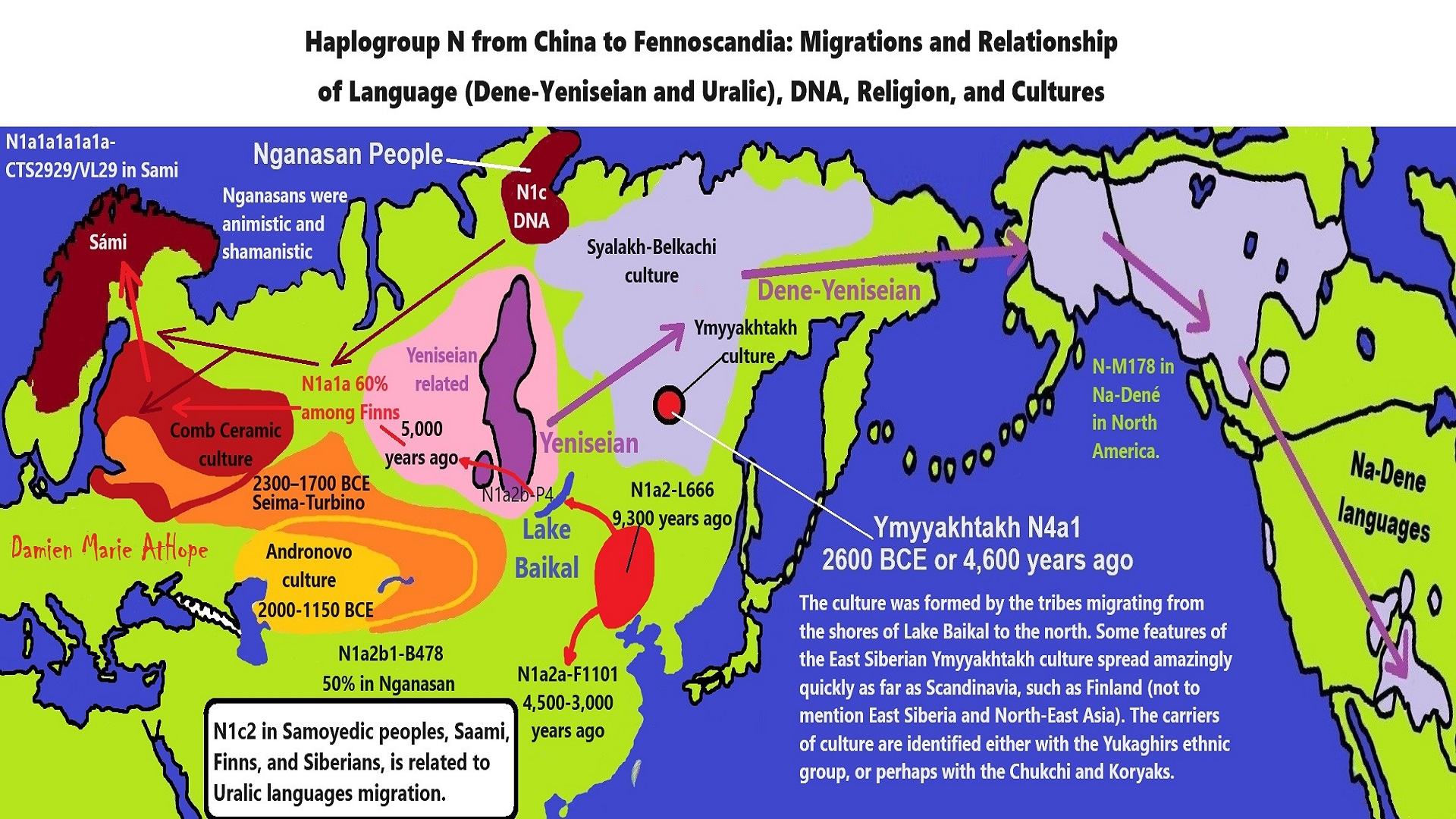
“The North Eurasian forest and forest-steppe zones have sustained millennia of sociocultural connections among northern peoples. We present genome-wide ancient DNA data for 181 individuals from this region spanning the Mesolithic, Neolithic, and Bronze Age. We find that Early to Mid-Holocene hunter-gatherer populations from across the southern forest and forest-steppes of Northern Eurasia can be characterized by a continuous gradient of ancestry that remained stable for millennia, ranging from fully West Eurasian in the Baltic region to fully East Asian in the Transbaikal region. In contrast, cotemporaneous groups in far Northeast Siberia were genetically distinct, retaining high levels of continuity from a population that was the primary source of ancestry for Native Americans. By the mid-Holocene, admixture between this early Northeastern Siberian population and groups from Inland East Asia and the Amur River Basin produced two distinctive populations in eastern Siberia that played an important role in the genetic formation of later people. Ancestry from the first population, Cis-Baikal Late Neolithic-Bronze Age (Cisbaikal_LNBA), is found substantially only among Yeniseian-speaking groups and those known to have admixed with them. Ancestry from the second, Yakutian Late Neolithic-Bronze Age (Yakutia_LNBA), is strongly associated with present-day Uralic speakers. We show how Yakutia_LNBA ancestry spread from an east Siberian origin ~4.5kya, along with subclades of Y-chromosome haplogroup N occurring at high frequencies among present-day Uralic speakers, into Western and Central Siberia in communities associated with Seima-Turbino metallurgy: a suite of advanced bronze casting techniques that spread explosively across an enormous region of Northern Eurasia ~4.0kya. However, the ancestry of the 16 Seima-Turbino-period individuals–the first reported from sites with this metallurgy–was otherwise extraordinarily diverse, with partial descent from Indo-Iranian-speaking pastoralists and multiple hunter-gatherer populations from widely separated regions of Eurasia. Our results provide support for theories suggesting that early Uralic speakers at the beginning of their westward dispersal where involved in the expansion of Seima-Turbino metallurgical traditions, and suggests that both cultural transmission and migration were important in the spread of Seima-Turbino material culture.” ref
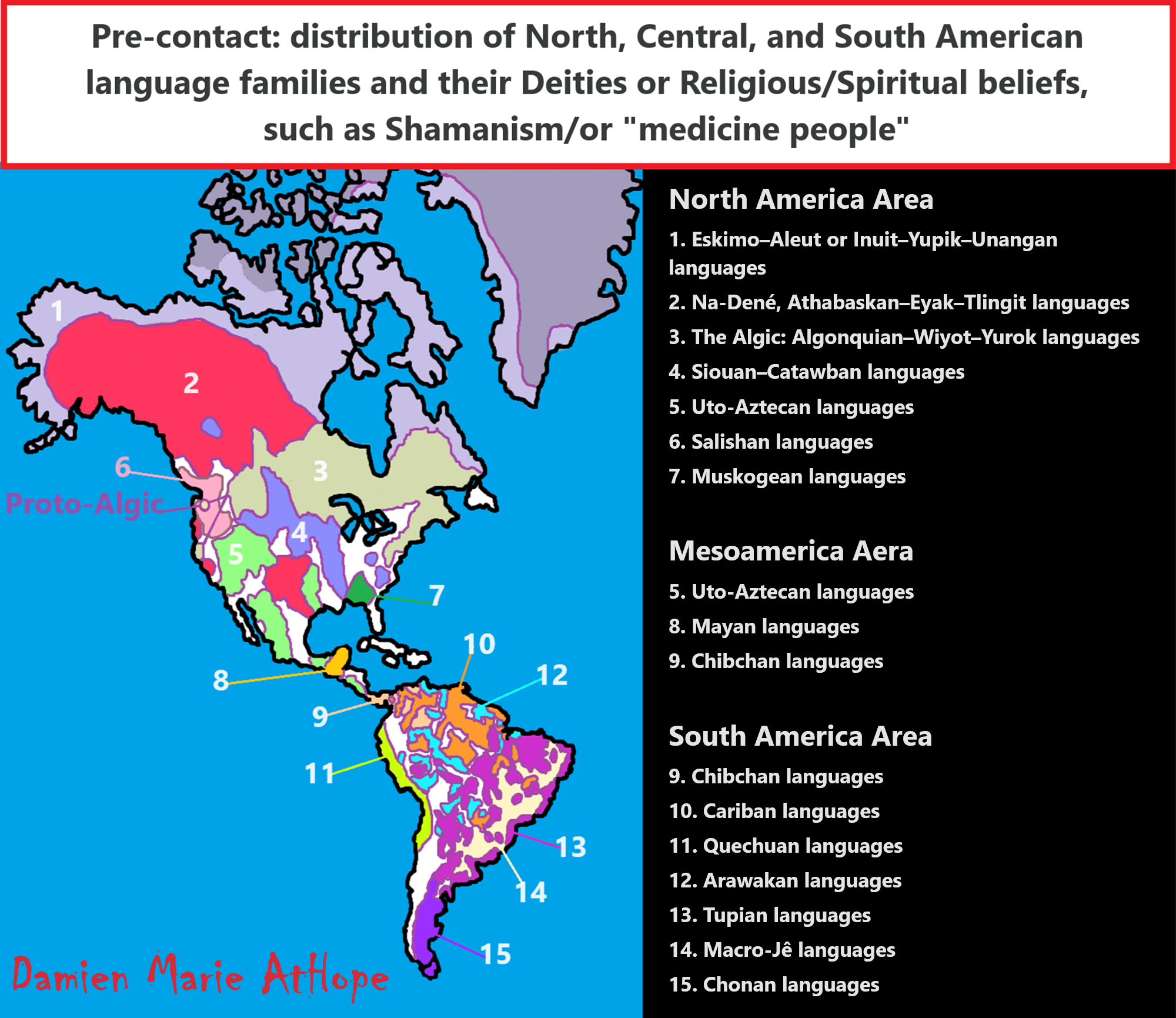
North America Area (with Deities/paganism and Shamanism/or “medicine people”)
- Eskimo–Aleut or Inuit–Yupik–Unangan languages
- Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit languages
- The Algic: Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok languages
- Siouan–Catawban languages
- Uto-Aztecan languages
- Salishan languages
- Muskogean languages
Mesoamerica Aera (with Deities/paganism and Shamanism/or “medicine people”)
South America Area (with Deities/paganism and Shamanism/or “medicine people”)
- Chibchan languages
- Cariban languages
- Quechuan languages
- Arawakan languages
- Tupian languages
- Macro-Jê languages
- Chonan languages
Shamanism (simplified to me as a belief that some special person can commune with these perceived spirits on the behalf of others by way of rituals) possibly by at least 30,000 years ago Shamanism is an otherworld connection belief thought to heal the sick, communicate with spirits/deities, and escort souls of the dead.
I think shaman beliefs came into the Americas from North Asia from 24,000 to 1,000 years ago. I think these peoples brought into the Americas a kind/several kinds of Shamanism-totemism with heavy animism. You can find some form of Shamanism, among Uralic, Transeurasian, Dené–Yeniseian, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskaleut languages.
Dené–Yeniseian languages? (I think similar to the Sami or Ainu peoples, Dené–Yeniseian peoples who migrated related to beliefs that were likely “paganistic” Shamanism, with heavy totemism and Animism themes). Human Migration from Asia into Alaska (North America) (11,000 to 6,000 years ago) “likely relates to the Na-Dene languages described as C-M217/C2/C3/C-M130 DNA lineage”
I think god beliefs (great spirit/shy father god) came into the Americas from North Asia from 7,000 to 5,000 years ago. I think it likely relates to the Na-Dene languages migrations as all of the Na-Dene languages have “great spirit” beliefs and some have shy father god/creator beliefs as well.
I think Na-Dene speakers brought into the Americas a kind/several kinds of Shamanism-Paganism with Totemism and Animism. Especially a daytime blue sky-god/sun-god but also an earth/moon goddess and bird mythology beliefs. Similar to the Hemudu culture (5500 – 3300 BCE or around 7,500 to 5,300 years ago) from China.
“Hemudu’s inhabitants worshiped a sun spirit as well as a fertility spirit. They also enacted shamanistic rituals to the sun and believed in bird totems. A belief in an afterlife and ghosts is thought to have been widespread as well. People were buried with their heads facing east or northeast and most had no burial objects. Infants were buried in urn-casket style burials, while children and adults received earth level burials. They did not have a definite communal burial ground, for the most part, but a clan communal burial ground has been found from the later period. Two groups in separate parts of this burial ground are thought to be two intermarrying clans. There were noticeably more burial goods in this communal burial ground.” ref
“The Great Spirit has at times been conceptualized as an “anthropomorphic celestial deity,” a god of creation, history, and eternity, who also takes a personal interest in world affairs and might regularly intervene in the lives of human beings. Numerous individuals are held to have been “speakers” for the Great Spirit; persons believed to serve as an earthly mediator responsible for facilitating communication between humans and the supernatural more generally. Such a speaker is generally considered to have an obligation to preserve the spiritual traditions of their respective lineage. The Great Spirit is looked to by spiritual leaders for guidance by individuals as well as communities at large.” ref
“While belief in an entity or entities known as the Great Spirit exists across numerous indigenous American peoples, individual tribes often demonstrate varying degrees of cultural divergence. As such, a variety of stories, parables, fables, and messages exhibiting different, sometimes contradictory themes and plot elements have been attributed to the same figure by otherwise disparate cultures. Wakan Tanka (Wakȟáŋ Tȟáŋka) can be interpreted as the power or the sacredness that resides in everything, resembling some animistic and pantheistic beliefs. This term describes every creature and object as wakan (“holy”) or having aspects that are wakan; tanka corresponds to “great” or “large.” ref
“The Lakota used Wakan Tanka to refer to an organization or group of sacred entities whose ways were considered mysterious and beyond human understanding. It was the elaboration on these beliefs that prompted scholarly debate suggesting that the term “Great Mystery” could be a more accurate translation of such a concept than “Great Spirit”. Activist Russell Means also promoted the translation “Great Mystery” and the view that Lakota spirituality is not originally monotheistic.” ref
(Native American mythology)
“HAYICANAKO is a Tlingit (Na-dene Language) Earth Goddess. An elderly Goddess who has the world on a stick. ’The Old Woman Beneath Us’. She holds the pole supporting the Earth and gives it a shake now and then if she is not happy about something. In case of earthquakes it is best to placate her by pouring some melting fat on the fire — it will drip down until it reaches her.” ref
“HAYICANAKO is the Tlingit Goddess of natural order. She is a giantess who lives in a mountain, where she holds up a column that supports the earth. When she gets hungry, she loses her concentration and the column starts to quiver, causing earthquakes. Her hunger can be fed by her worshippers throwing fat into their fires. Another version says that earthquakes happen when Raven jostles her arm and tries to make her lose her grip. Hayicanako’s name, which means “Old Woman Underneath Us,” is also seen as HAYICANAK.” ref
Raven made a woman under the earth to have charge of the rise and fall of the tides.
“Raven made a woman under the earth to have charge of the rise and fall of the tides. One time he wanted to learn about everything under the ocean and had this woman raise the water so that he could go there. He had it rise very slowly so that the people had time to load their canoes and get into them. When the tide had lifted them up between the mountains they could see bears and other wild animals walking around on the still unsubmerged tops. Many of the bears swam out to them, and at that time those who had their dogs had good protection. Some people walled the tops of the mountains about and tied their canoes inside. They could not take much wood up with them. Sometimes hunters see the rocks they piled up there, and at such times it begins to grow foggy. That was a very dangerous time. The people who survived could see trees swept up roots and all by the rush of waters and large devilfish and other creatures were carried up by it.” ref
Click for more on the myth of Raven and the Tides: Tlingit myth about the origin of the tides.
Tlingit Raven Mythology
“In the lore of Tlingit, Haida and other northern Native Americans a raven was both a trickster spirit and the creator of the world. The most interesting story about the raven in Tlingit folklore is the one concerning his responsibility for placement of the Sun in the sky.” ref
“There are countless Raven stories in the Tlingit community, and there are many versions of how Raven came to bring the light to the world. The stories are not necessarily contradictory, but they do emphasize different points and have different details, depending on whom the caretaker of that story was and how he or she was taught to tell the story. Smarch described how angry Raven’s grandfather was when Raven released all of his treasures into the sky. In her telling, he gathered the pitch from all around the house, placed it into a bentwood box and threw it in the fire. Raven could not find the smoke hole and flew around in the black smoke, becoming the black bird we know today. Raven sacrificed his supernatural state of being in order to bring light to the world.” ref
“In many versions of “Raven and the Box of Daylight” — including both ethnographic accounts and popular English versions of the story — at the beginning of his journey, Raven is white, one marker of his supernatural status. Tlingit scholar and professor Maria Williams wrote in her children’s book “How Raven Stole the Sun (Tales of the People)” that Raven was “pure white from the tips of his claws to the ends of his wings.” Hammond described Raven as a white or translucent being early on in his telling of the story. Depending on whom is telling the story, the details of how Raven became black differ, but the results are always the same. The story of “Raven and the Box of Daylight” contains messages and symbolism of hope, forgiveness, tolerance, love and sacrifice — messages and symbolism that encourage humans to be kinder toward each other.” ref
“Early records suggest that the Tlingit believed in a creator, Kah-shu-goon-yah, whose name was sacred and never mentioned above a whisper. This primordial grandfather, or “divisible-rich-man,” controlled the sun, moon, stars, and daylight in addition to creating all living things. Little more is known of him. The sacred past centers upon Raven (cultural hero, benefactor, trickster, and rascal) who was credited with organizing the world in its present form and in initiating many Tlingit customs. Raven was never represented, symbolized, or made equal with the supreme being who transcended Tlingit legends. The Tlingit inhabited a world filled with spirits, or jek. These spirits could manifest their power through individuals, animals, or things.”
“Since every material object or physical force could be inhabited by a spirit, Tlingit were taught to respect everything in the universe. The penalty for disrespect was the loss of ability to obtain food. Properly purified persons could acquire spirit power for curing illnesses, for protection in warfare, for success in obtaining wealth, and for ceremonial prerogatives. Each Tlingit had a mortal and an immortal spirit. Spirits of the dead traveled to the appropriate level of heaven commensurate with their moral conduct in this life. Morally respectable people went to the highest heaven, Kiwa-a, a realm of happiness; moral delinquents went to a second level, or Dog Heaven, Ketl-kiwa, a place of torment. Individuals remained in the afterworld for a period of time and then returned to this world as a reincarnation of some deceased maternal relative.” ref
“Tlingit legends have one great word in our culture: haa shageinyaa. This was a Great Spirit above us, and today we have translated that reverence to God.” ref
“Wisakedjak (Wìsakedjàk in Algonquin, Wīsahkēcāhk(w) in Cree and Wiisagejaak in Oji-cree) is the Crane Manitou found in northern Algonquian and Dene storytelling, similar to the trickster Nanabozho in Ojibwa aadizookaanan (sacred stories), Inktonme in Assiniboine lore, and Coyote or Raven from many different tribes. His name is found in a number of different forms in the related languages and cultures he appears in, including Weesack-kachack, Wisagatcak, Wis-kay-tchach, Wissaketchak, Woesack-ootchacht, Vasaagihdzak, and Weesageechak. As with most mythological characters, Wisakedjak is used to explain the creation of animals or geographical locations. He is generally portrayed as being responsible for a great flood which destroyed the world. In other stories he is also one of the beings who created the current world, either on his own, or with magic given to him by the Creator for that specific purpose.” ref
Blackfoot (Algonquian language) Native American Legends: Komorkis (Ko’komiki’somm)
“Komorkis is the Moon Goddesses, second eldest of the sacred Sky People. Komorkis is the wife of the sun god Natos and mother of the stars, of which the most important is Morning-Star. Komorkis is said to be the grandmother of several heroes of Blackfoot legend, such as Star-Boy.” ref
Manchu Shamanism Sky Deities?
“The ethnic religion practiced by most of the Manchu people, the major Tungusic group in China. this religion is an animistic and polytheistic religion, believing in several gods and spirits, led by a universal sky god called Abka Enduri (“Sky God” or “God of Heaven”), also referred to as Abka Han (“Sky Khan” or “Khan of Heaven”) and Abka Ama (“Sky Father”), originally Abka Hehe (“Sky Woman”, by extension “Sky Mother”) who is the source of all life and creation. Deities (enduri) enliven every aspect of nature, and the worship of these gods is believed to bring favor, health, and prosperity. Many of the deities were originally Manchu ancestors, and people with the same surname are generated by the same god.” ref
(Taevaisa: Taevas = sky, isa = father) – On Etymology of Finnic Term for ‘Sky’
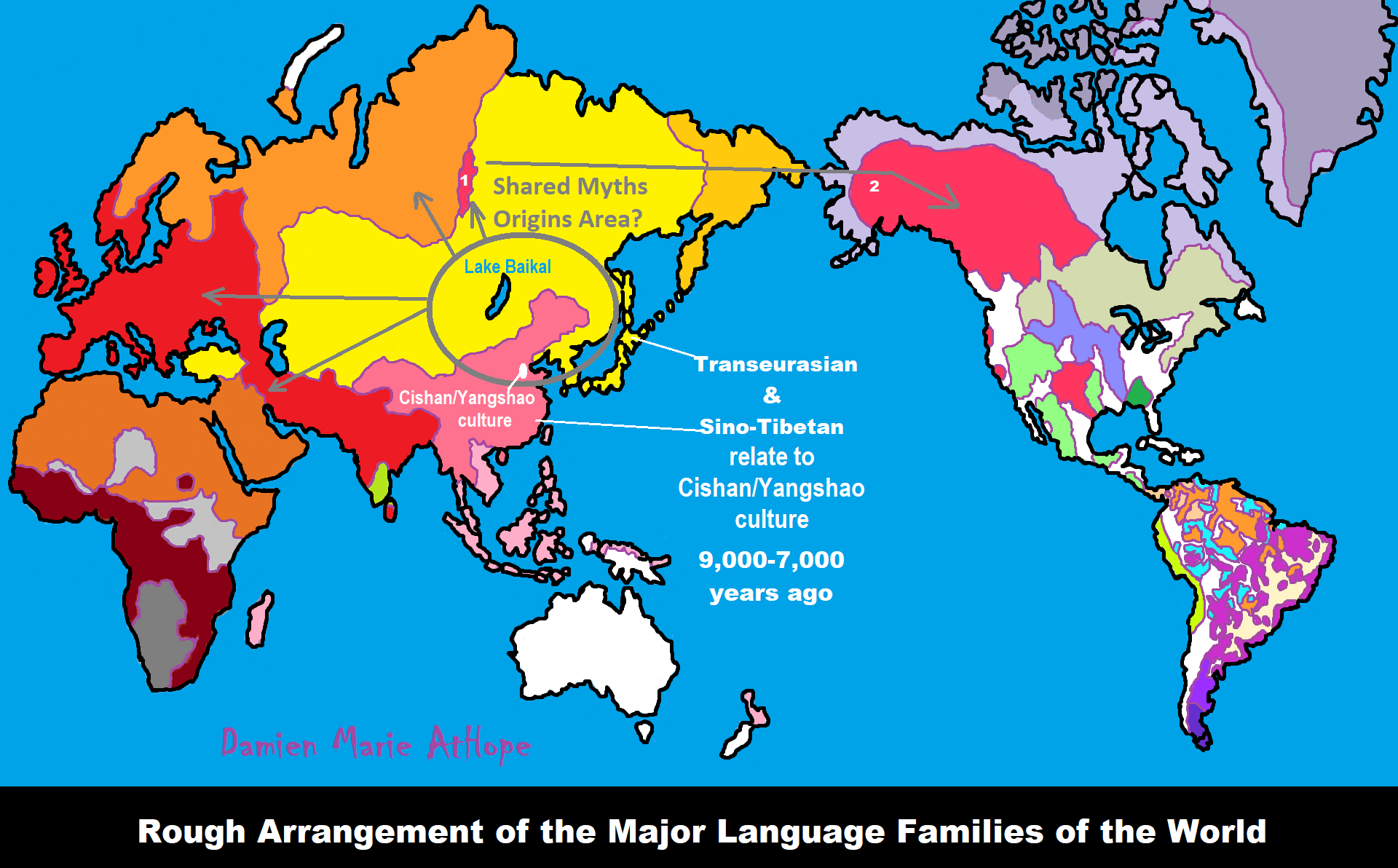
“The Finnic term for ‘sky’ (Estonian taevas; Finnish taivas; Livonian tōvaz; Veps taivaz; Votic taivas) has no cognate in other Uralic languages. The present study finds that this Finnic word has cognates in Sinitic languages supported by a deep rhyme correspondence consisting of five etymologies; therefore, this word root must be aboriginal in Sino-Uralic languages. Using etymological methods, the present study has identified five Sinitic and Uralic shared etymologies. These five etymologies form a rhyme correspondence. This regular sound change validates the etymological connection between Sinitic and Uralic. The Finnic term for ‘sky’ is among these five etymologies. It is demonstrated that this word root should be aboriginal in Sino-Uralic languages.” ref, ref
Sino-Uralic or Sino-Finnic is a proposed language family consisting of the Sinitic languages (Chinese) and the Uralic languages.
“Gao suggested the proto-population could have been lived in Neolithic China and carried the Haplogroup N, claiming that a common proto-language could have been spoken around 5.000-10.000 years ago. Gao argued that Chinese has three major layers, he saw the root of Chinese as coming from a common Sino-Uralic source, the second layer coming from Indo-European during the Chalcolithic age or later and the third layer coming from Yeniseian during the Bronze Age.” ref
“Buga” Siberian Evenki Supreme God of Everything?
“One significant feature of the Evenki is that the supreme deities can be both male gods and female goddesses. According to traditional Evenk ideas, the Universe consists of three worlds: the upper (Ugu Buga), the middle (Doolin Buga), the lower (Hergu Buga). The upper world was located at sunrise, the lower at sunset. The upper and lower worlds are inaccessible to ordinary people and are inhabited by spirit gods. One of the main deities is Seveki spirit, whose function is the creator of all living things. The spirit of Enekan Buga monitors the life of people and animals, periodically visiting the earth. His assistant, Enekan Togo, is a spirit of fire living in a home. Through fire, the Evenki address spirits.” ref, ref
Nanabozho great spirit-being?
“Nanabozo is a supernatural being of various Indigenous oral traditions. He is the embodiment of life, with the power to create life in others. In some Anishinaabe and Cree stories, Nanabozo is a main player in the creation of Turtle Island. Nanabozho is a shapeshifter who is both zoomorphic as well as anthropomorphic, meaning that Nanabozho can take the shape of animals or humans in storytelling. Thus Nanabush takes many different forms in storytelling, often changing depending on the tribe. The majority of storytelling depicts Nanabozho through a zoomorphic lens. In the Arctic and sub-Arctic, the trickster is usually called Raven. Coyote is present in the area of California, Oregon, the inland plateau, the Great Basin, and the Southst and Southern Plains. Rabbit or Hare is the trickster figure in the Southeast, and Spider is in the northern plains. Meanwhile, Wolverine and Jay are the trickster in parts of Canada. Often, Nanabozho takes the shape of these animals because of their frequent presence among tribes. The animals listed above have similar behavioral patterns. The gender identity of Nanabozho changes depending on the storytelling. Because Nanabozho is a shapeshifter, they are androgynous. While the majority of stories told about the trickster figure are written with he/him pronouns, the gender identity changes depending on the story and many are written with feminine pronouns.” ref, ref
Puebloan Sky Father and Earth Mother?
Puebloan–Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
“The mist clouds formed into the Great Waters, where Earth Mother, Áwitelin Tsíta, and Sky Father, Ápoyan Ta’chu, formed, the two of whom conceived all men and creatures in the four-fold womb of the world. The Sun Father and Earth Mother then brought forth the Twin Children of the Sun, the twin brothers Ko’wituma and Wats’usi. These twins were endowed with sacred knowledge, caps, bows, arrows, and shields to have dominion over all men and creatures as Twin War Gods.” ref
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti) Earth Mother
“Tawa (the sun god) and Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman (Spider Grandmother) who is identified with the Earth Goddess. They separate themselves to create other lesser gods, then create the earth and its creatures.(close to the Zuni creation myth)” ref
Puebloan-Navajo: (TSOHANOAI) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother
“Estsanatlehi a Fertility goddess probably regarded as the most powerful deity in the Navaho pantheon is the consort of the Sun god TSOHANOAI and the mother of the war god NAYENEZGANI.” ref, ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
- Medicine Wheel
- Serpent Mound
- Mesa Verde
- Chaco Canyon
- Casas Grandes/Paquime
- Ciudad Perdida“lost city”; Teyuna
- Ingapirca“Inca”
- Chavín de Huántar“pre-Inca”
- Sacred City of Caral-Supe*Caral culture developed between 3000 – 1800 BCE*
- Machu Picchu
- Nazca Lines
- Sacsayhuamán
- Tiwanaku/Tiahuanaco
- Atacama Giant/Lines
- Pucará de Tilcara“pre-Inca”
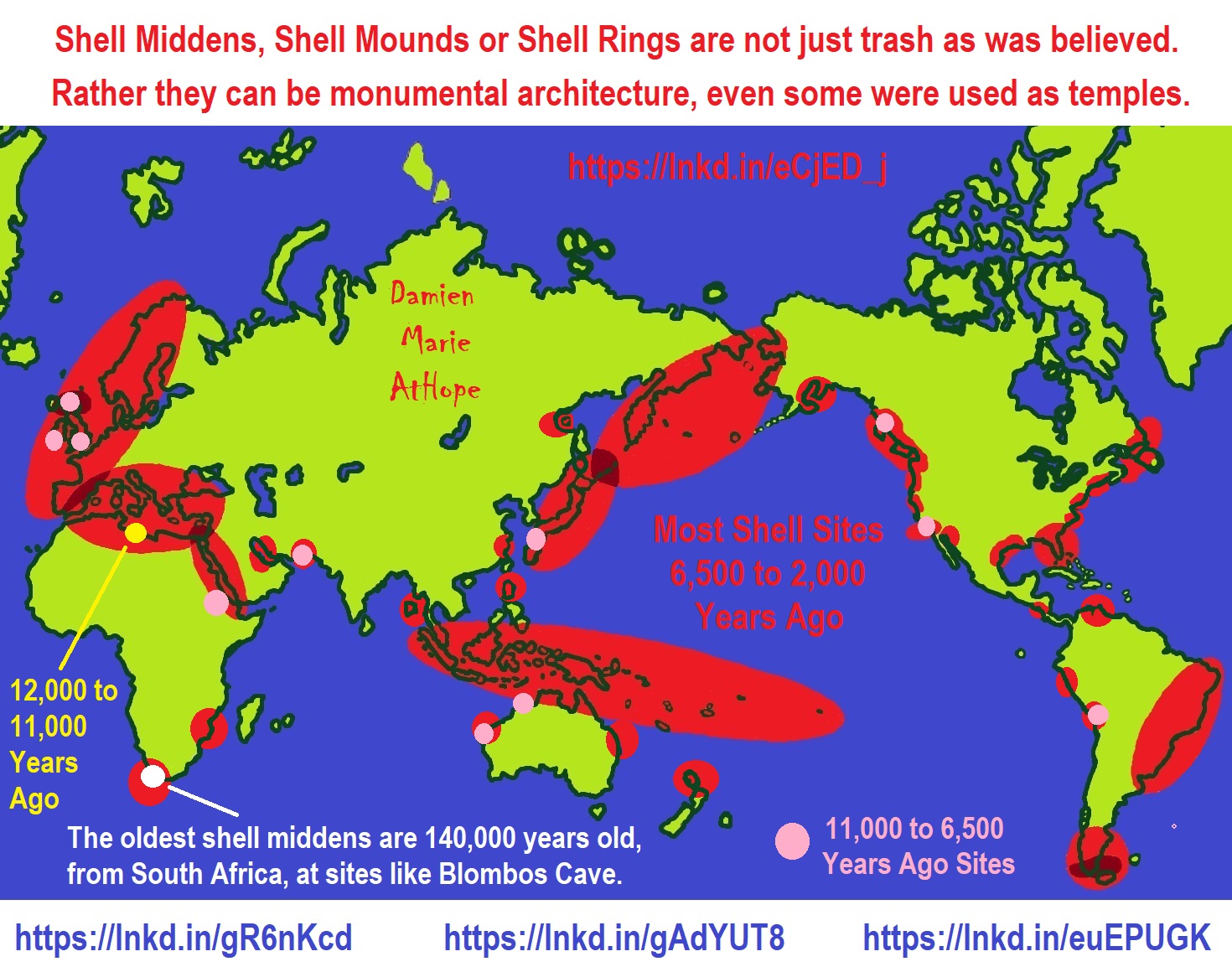
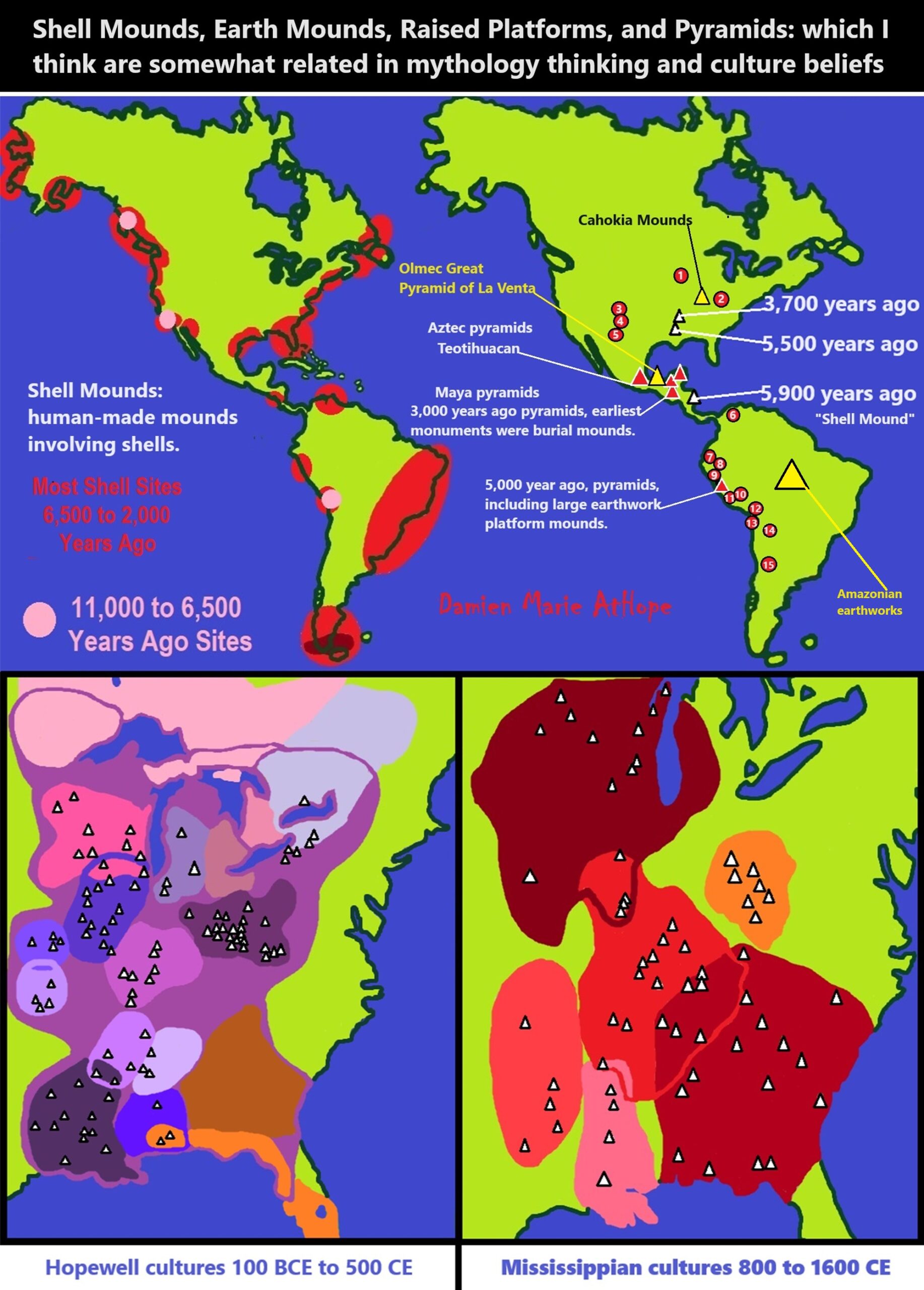
Eighth Millennium Pottery from a Prehistoric Shell Midden in the Brazilian Amazon
“The top layer was left by the Tupinamba people, who inhabited the region when European colonizers founded Sao Luis in 1612. Then comes a layer of artifacts typical of Amazon rainforest peoples, followed by a “sambaqui”: a mound of pottery, shells and bones used by some Indigenous groups to build their homes or bury their dead. Beneath that, about 6.5 feet below the surface, lies another layer, left by a group that made rudimentary ceramics and lived around 8,000 to 9,000 years ago, based on the depth of the find. Far older than the oldest documented “pre-sambaqui” settlement found so far in the region, which dates to 6,600 years ago.” ref
Sambaqui (Shell Mound) Societies of Coastal Brazil
“Sambaquis (the Brazilian term for shell mounds, derived from the Tupi language) are widely distributed along the shoreline of Brazil and were noted in European accounts as early as the sixteenth century. They typically occur in highly productive bay and lagoon ecotones where the mingling of salt and fresh waters supports mangrove vegetation and abundant shellfish, fish, and aquatic birds. More than one thousand sambaqui locations are recorded in Brazil’s national register of archaeological sites, but represent a fraction of the original number because colonial through modern settlements coincide with these favorable environments. Although sambaquis are of variable scale overall, massive shell mounds are characteristic of Brazil’s southern coast.” ref
“The term “sambaqui” is applied to cultural deposits of varying size and stratigraphy in which shell is a major constituent, undoubtedly encompassing accumulations with a range of functions and origins. Proportions of soil, sand, shell, and the kinds of cultural inclusions and features in sambaquis also are variable. Small sambaquis often consist of shell layers over sandy substrates or sequences of shell and sand layers, with or without signs of burning or significant numbers of artifacts. Larger shell mounds typically have horizontally and vertically complex stratigraphy, including alternating sequences of shell deposits, narrower and darker layers of charcoal and burned bone that mark occupation surfaces, and clusters of burials, hearths, and postholes descending from these surfaces.” ref
Mound cultures are some of the most amazing things in North America and so-called “Americans” don’t care, think it’s Aliens, or believe some mythical white people from the minds of bigots. All Americans should have to learn about Indigenous American history.
“Many pre-Columbian cultures in North America were collectively termed “Mound Builders” ref
Bleera Kaanu-Shell Mound Nicaragua 5,900 years ago human-made shell mound
Watson Brake Louisiana 5,500 years ago human-made mounds
Caral culture 5,000 years ago pyramids, large earthwork platform mounds, and sunken circular plazas
“Archaeological evidence suggests use of textile technology and, possibly, the worship of common deity symbols, both of which recur in pre-Columbian Andean cultures. A sophisticated government is presumed to have been required to manage the ancient Caral.” ref, ref
“The alternative name, Caral–Supe, is derived from the city of Caral in the Supe Valley, a large and well-studied Caral–Supe civilization site. Complex society in the Caral–Supe arose a millennium after Sumer in Mesopotamia, was contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids, and predated the Mesoamerican Olmec by nearly two millennia. In archaeological nomenclature, Caral–Supe is a pre-ceramic culture of the pre-Columbian Late Archaic; it completely lacked ceramics and no evidence of visual art has survived. The most impressive achievement of the civilization was its monumental architecture, including large earthwork platform mounds and sunken circular plazas.” ref
Poverty Point Louisiana 3,700 years ago human-made mounds
Olmec La Venta Great pyramid 2,394 years ago human-made earth and clay mound
“Olmecs can be divided into the Early Formative (1800-900 BCE), Middle Formative (900-400 BCE), and Late Formative (400 BCE-200 CE). Olmecs are known as the “mother culture” of Mesoamerica, meaning that the Olmec civilization was the first culture that spread and influenced Mesoamerica. The spread of Olmec culture eventually led to cultural features found throughout all Mesoamerican societies. Rising from the sedentary agriculturalists of the Gulf Lowlands as early as 1600 BCE in the Early Formative period, the Olmecs held sway in the Olmec heartland, an area on the southern Gulf of Mexico coastal plain, in Veracruz and Tabasco. Prior to the site of La Venta, the first Olmec site of San Lorenzo dominated the modern day state of Veracruz (1200-900 BCE).” ref
“Unlike later Maya or Aztec cities, La Venta was built from earth and clay—there was little locally abundant stone for the construction. Large basalt stones were brought in from the Tuxtla Mountains, but these were used nearly exclusively for monuments including the colossal heads, the “altars” (actually thrones), and various stelae. For example, the basalt columns that surround Complex A were quarried from Punta Roca Partida, on the Gulf coast north of the San Andres Tuxtla volcano. “Little more than half of the ancient city survived modern disturbances enough to map accurately.” Today, the entire southern end of the site is covered by a petroleum refinery and has been largely demolished, making excavations difficult or impossible. Many of the site’s monuments are now on display in the archaeological museum and park in the city of Villahermosa, Tabasco.” ref
“Complex C, “The Great Pyramid,” is the central building in the city layout, is constructed almost entirely out of clay, and is visible from a distance. The structure is built on top of a closed-in platform—this is where Blom and La Farge discovered Altars 2 and 3, thereby discovering La Venta and the Olmec civilization. A carbon sample from a burned area of the Structure C-1’s surface resulted in the date of 394 ± 30 BCE.” ref
“One of the earliest pyramids known in Mesoamerica, the Great Pyramid is 110 ft (34 m) high and contains an estimated 100,000 cubic meters of earth fill. The current conical shape of the pyramid was once thought to represent nearby volcanoes or mountains, but recent work by Rebecca Gonzalez Lauck has shown that the pyramid was in fact a rectangular pyramid with stepped sides and inset corners, and the current shape is most likely due to 2,500 years of erosion. The pyramid itself has never been excavated, but a magnetometer survey in 1967 found an anomaly high on the south side of the pyramid. Speculation ranges from a section of burned clay to a cache of buried offerings to a tomb.” ref
“Complex A is a mound and plaza group located just to the north of the Great Pyramid (Complex C). The centerline of Complex A originally oriented to Polaris (true north) which indicates the Olmec had some knowledge of astronomy. Surrounded by a series of basalt columns, which likely restricted access to the elite, it was erected in a period of four construction phases that span over four centuries (1000 – 600 BCE). Beneath the mounds and plazas were found a vast array of offerings and other buried objects, more than 50 separate caches by one count, including buried jade, polished mirrors made of iron-ores, and five large “Massive Offerings” of serpentine blocks. It is estimated that Massive Offering 3 contains 50 tons of carefully finished serpentine blocks, covered by 4,000 tons of clay fill.” ref
“Also unearthed in Complex A were three rectangular mosaics (also known as “Pavements”) each roughly 4.5 by 6 metres (15 by 20 feet) and each consisting of up to 485 blocks of serpentine. These blocks were arranged horizontally to form what has been variously interpreted as an ornate Olmec bar-and-four-dots motif, the Olmec Dragon, a very abstract jaguar mask, a cosmogram, or a symbolic map of La Venta and environs. Not intended for display, soon after completion these pavements were covered over with colored clay and then many feet of earth.” ref
“Five formal tombs were discovered within Complex A, one with a sandstone sarcophagus carved with what seemed to be an crocodilian earth monster. Diehl states that these tombs “are so elaborate and so integrated to the architecture that it seems clear that Complex A really was a mortuary complex dedicated to the spirits of deceased rulers.” ref
Maya 3,000 years ago mounds, raised platforms, pyramids
“The Maya are a people of southern Mexico and northern Central America (Guatemala, Belize, western Honduras, and El Salvador) (1000 BCE, approximately 3,000 years ago) they were building pyramidal-plaza ceremonial architecture. The earliest monuments consisted of simple burial mounds, the precursors to the spectacular stepped pyramids from the Terminal Pre-classic period and beyond. These pyramids relied on intricate carved stone in order to create a stair-stepped design. Many of these structures featured a top platform upon which a smaller dedicatory building was constructed, associated with a particular Maya deity. Maya pyramid-like structures were also erected to serve as a place of interment for powerful rulers. Maya pyramidal structures occur in a great variety of forms and functions, bounded by regional and periodical differences.” ref
“Hopewell mtDNA, showed clear links between Adena culture, and earlier Glacial Kame culture, confirming Hopewell culture as the descendants of Adena culture (circa 800 BCE to CE 1) who were, in turn, descended from Archaic cultures (circa 3000-500 BCE).” ref
“The Glacial Kame culture was a culture of Archaic people in North America that occupied southern Ontario, Michigan, Ohio, and Indiana from around 8000 to 1000 BCE. The name of this culture derives from its members’ practice of burying their dead atop glacier-deposited gravel hills. Among the most common types of artifacts found at Glacial Kame sites are shells of marine animals and goods manufactured from a copper ore, known as float copper. Other regional cultures include the Maple Creek Culture of southwestern Ohio, Red Ocher Culture and Old Copper Culture of Wisconsin.” ref
“Glacial Kame culture produced ceramics, as seen in the discovery of basic pottery at the Zimmerman site near Roundhead, Ohio. Excavation of Glacial Kame sites frequently yields few projectile points — some of the most important sites have yielded no projectile points at all — and their few points that have been found are of diverse styles. For this reason, it appears that different groups of Glacial Kame peoples independently developed different methods of manufacturing their projectile points. This diversity appears even in the culture’s heartland in Champaign, Hardin, and Logan counties in western Ohio; one large Logan County site yielded just three points, each of which was significantly different from the other two.” ref
“Glacial Kame Culture, Late Archaic cultural grouping found around Michigan, Ohio, Indiana, and southern Ontario in the period c.1500–1000 BCE. Characterized by mortuary rituals which involved interring the dead in natural hills of glacial gravel. Grave goods of copper ornaments and marine shells were sometimes included and attested to long‐distance trade links.” ref
“The Adena “mound-building” culture was a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that existed from 500 BCE to 100 CE, in a time known as the Early Woodland period. The Adena culture refers to what were probably a number of related Native American societies sharing a burial complex and ceremonial system. The Adena culture was centered on the location of the modern state of Ohio, but also extended into contiguous areas of northern Kentucky, eastern Indiana, West Virginia, and parts of extreme western Pennsylvania. The culture is the most prominently known of a number of similar cultures in eastern North America that began mound building ceremonialism at the end of the Archaic period.” ref
Amazonian Earthworks
“More than 1,100 ancient Amazonian earthworks, with over 1,050 geoglyphs and zanjas plus over 50 mound villages documented in both the Excel file and the KML placemarks file linked above. Almost all earthworks are outlined, along with highlighting of 1,000 lines, visible ancient roads and embankments. Hundreds of Geoglyphs Discovered in the Amazon.” ref
“Cahokia Mounds were involved in the largest and most influential urban settlement of the Mississippian culture, which developed advanced societies across much of what is now the Central and the Southeastern United States, beginning more than 1,000 years before European contact.” ref
“In the Americas, middens are represented by radiocarbon dates of 5000–2000 BCE from Panama and eastern North America. Middens of South America and California probably antedate 2000 BCE.” ref
“The oldest pottery of northern Europe, eastern North America, and Central America occurs in shell mounds.” ref
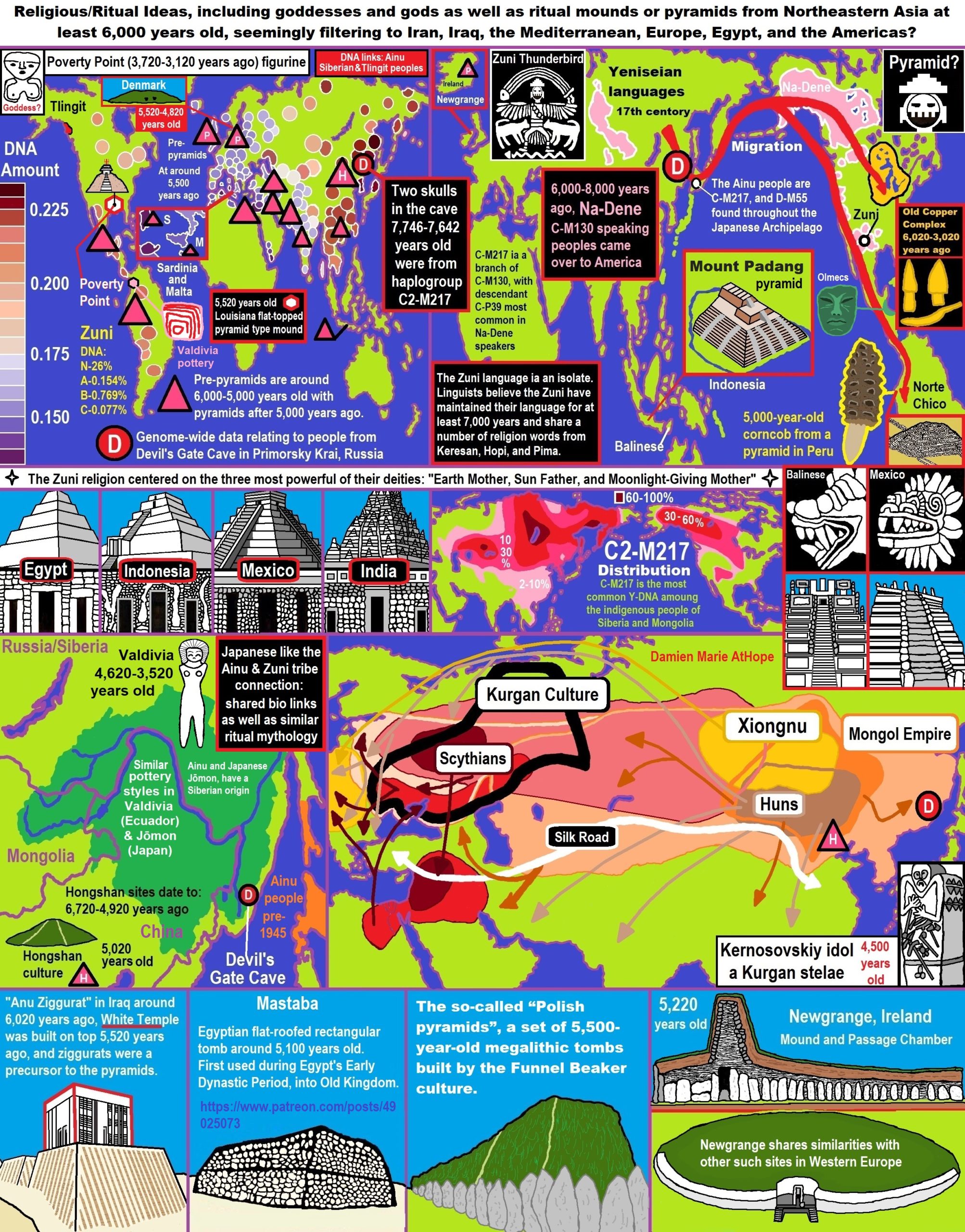
A 5,000-year-old Earth Pyramid a human-made earth mound is found in North China as well. I actually think the thinking that leads to pyramid/Step Platform mounds is all related to North Asia, Southern Siberia/North China area. To me there are shared ideas related to the people’s movements that spread ideas including mounds/pyramids/step platform mounds. Platform Mounds/Pyramids, to me, relate to several kinds of mythology, creation myths, deity beliefs, heaven/spirits/afterlife/stars/moon/sun, etc. Along with power/elites/inequality/hierarchy.
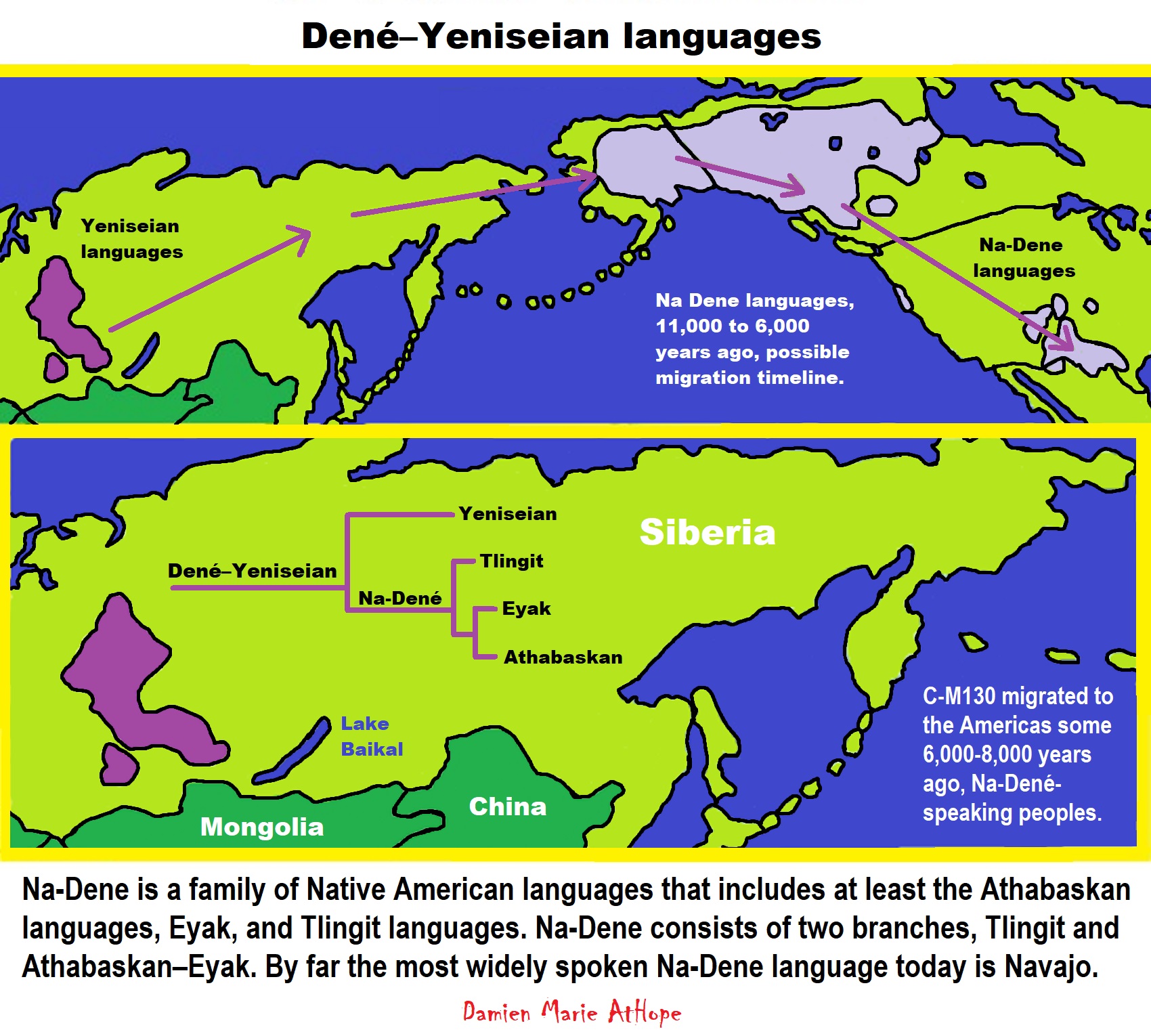
My art and when as well as who may have brought in the new elitism and compulsory authority to the Americas.
“For the Tlingit (branch of the Na-Dené language family), hereditary slavery was practiced extensively until it was outlawed by the United States. Wealth and economic power are important indicators of rank. Scientists suggest that the main ancestor of the Ainu and of the Tlingit can be traced back to Paleolithic groups in Southern Siberia.” ref
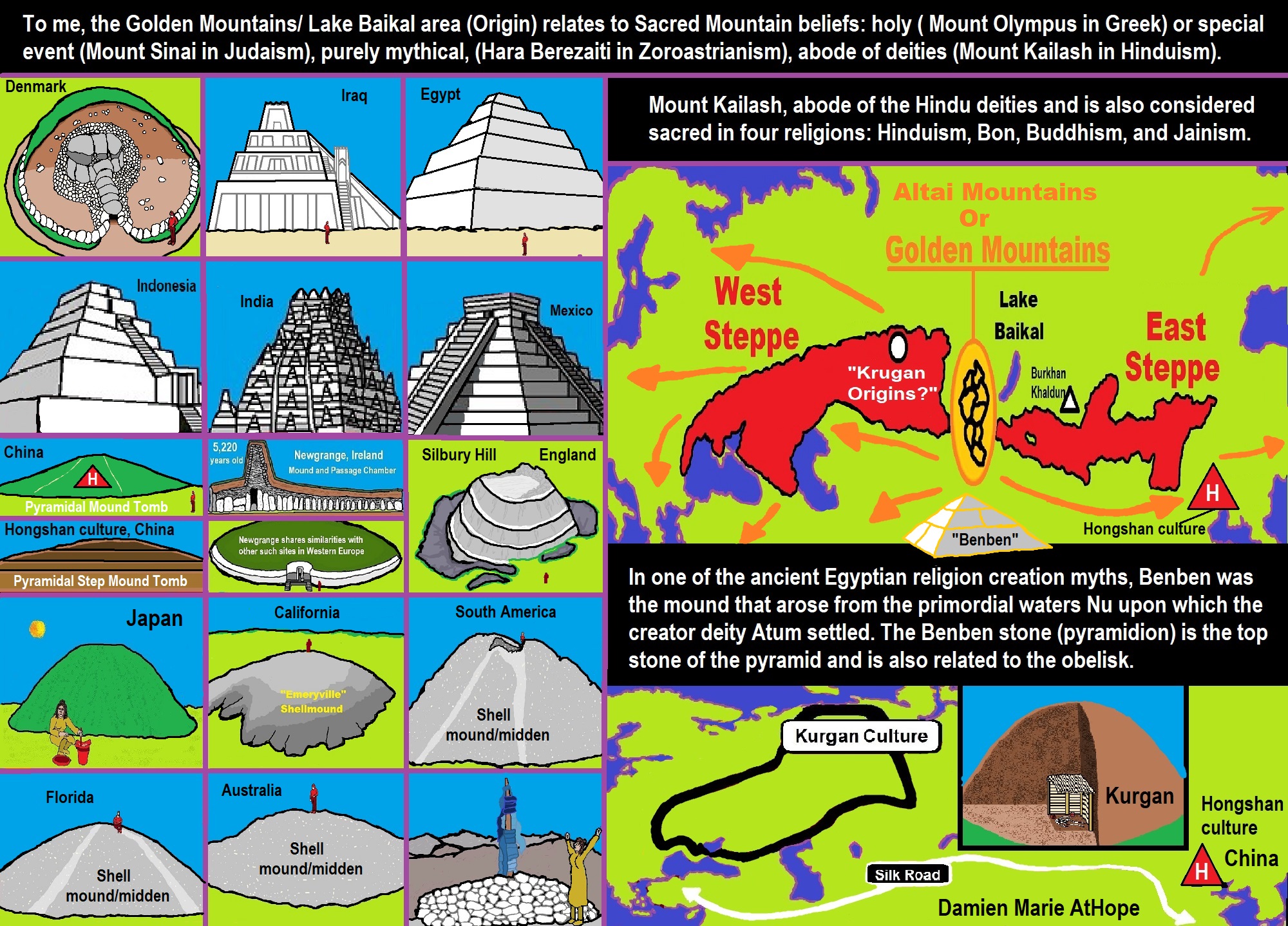
My Speculations are in Comparative Mythologies?
For instance, the mytheme of an ancient belief that is seemingly shared though changed and adapted, a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure seems to be shared a common relation with mountains/ancestors/gods or sacred animals with Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids.
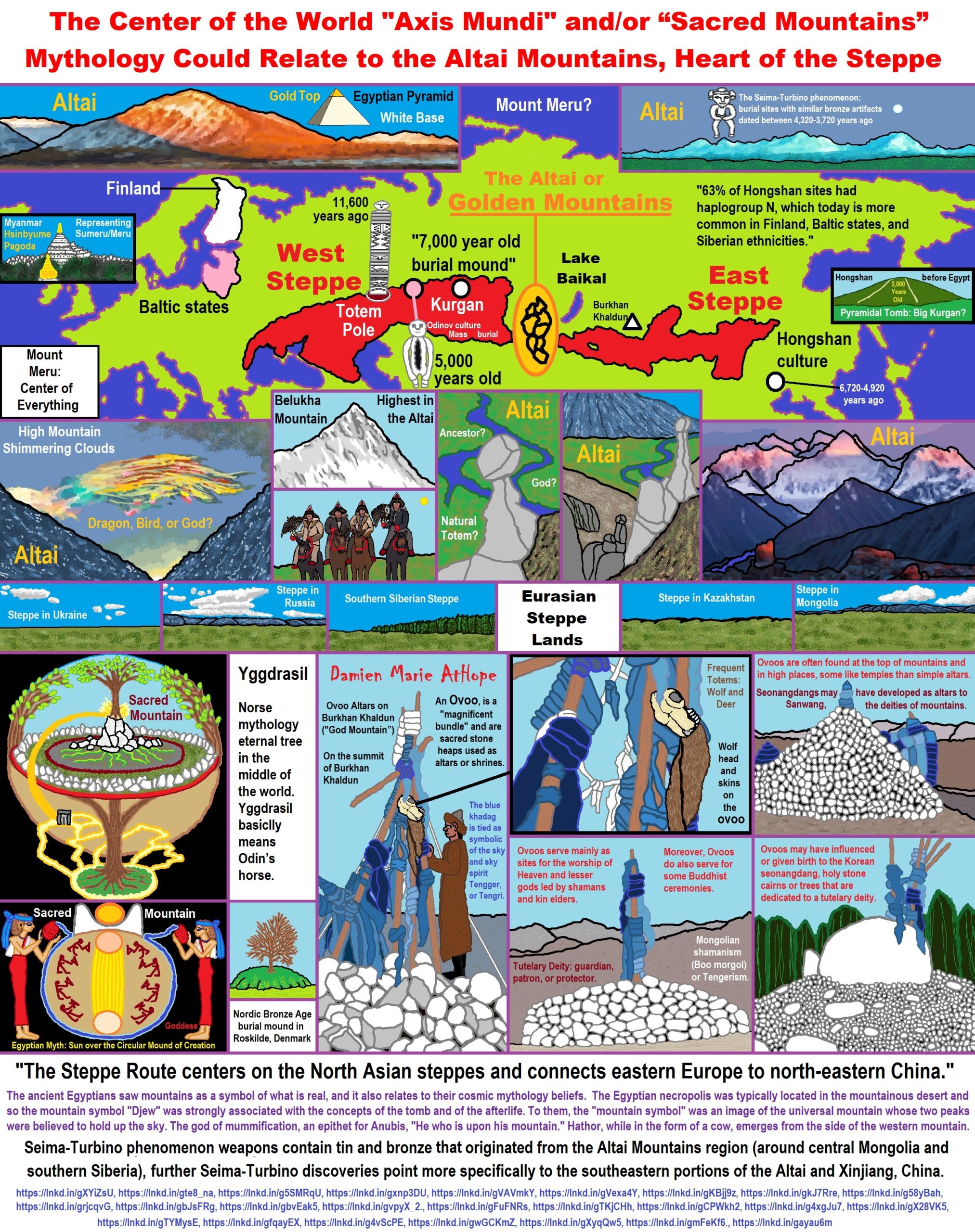
“My speculation is that Sacred Mountain Mythology all may relate to beliefs relating to the Altai Mountains.”
“The Altai Mountains, also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge. The Altai Mountains have been identified as being the point of origin of a cultural enigma termed the Seima-Turbino Phenomenon which arose during the Bronze Age around the start of the 2nd millennium BCE and led to a rapid and massive migration of peoples from the region into distant parts of Europe and Asia. The Altaic language family takes its name from this mountain range. Altaic (also called Transeurasian) may include Turkic languages, Mongolic languages, Tungusic languages, Koreanic languages, Japonic languages, and Ainu languages. The research on their supposedly common linguistics origin has inspired various comparative studies on the folklore and mythology among the Turks, Proto-Mongols and Tungus people.” ref, ref
High mobility of ancient hunter-gatherers 7,500 years ago,
Indicated by genetic data from the Altai
“Research has identified a previously unknown hunter-gatherer population in the Altai some 7,500 years ago which illustrates the high mobility between populations in Siberia and elsewhere in North Asia. Furthermore, the Altai hunter-gatherer group contributed genetically to many contemporaneous and subsequent populations across North Asia, showing how great the mobility of those foraging communities was. The Altai region (Altai Mountains) is widely known as the place where an archaic hominin group, the Denisovans, was first discovered. Yet this region is also highly important for the demographic history of our own species, says Cosimo Posth. “Its geographic location makes the Altai an important crossroads for population movements between northern Siberia, Central Asia, and East Asia over millennia.” ref
“The genetic data from the Altai show that East Eurasia harbor highly connected gene pools since at least the Early Holocene, some 10,000 years ago. “Such connection across long geographic distances is remarkable. This suggests that human migrations and admixtures were the norm and not the exception also for ancient hunter-gatherer societies. Moreover, a burial in the region in the same period as the other Altai hunter-gatherers had a completely different genetic profile, carrying genetic affinities to populations located in the Russian Far East. This man, known as the Nizhnetytkesken individual, was found in a cave containing rich burial goods and with a costume and objects interpreted as a possible representation of shamanism.” ref
“These 6,500-year-old remains discovered in Nizhnetytkesken Cave in the Altai Mountains had genetic ties to a group living about 900 miles away. “This implies that individuals with very different [genetic] profiles were living in the same region, and with belongings indicate that this person may have been a shaman. His ancestral group may have inhabited a larger area than previously thought, or he may have been a traveling healer. Therefore, it seems that mixing between ancient hunter-gatherer groups probably occurred more frequently than previously believed.” ref
“This shows that people with very different genetic profiles were living in the area. It is not clear if the Nizhnetytkesken individual came from far away or the population from which he originated was living close by. “However, his grave goods appear different from other archeological sites, implying movements of both culturally and genetically diverse individuals into the Altai region,” says Wang. This study also reports data from a 7,000-year-old individual from the Russian Far East which show genetic links with hunter-gatherer groups from the Japanese Archipelago.” ref
Furthermore, newly generated ancient genomes from the Kamchatka Peninsula reveal multiple phases of North America-related gene flow to northeastern Asia over the last multiple millennia. These results raise the question to what extend genetic profiles and archaeological cultures were correlated in Siberian forager groups. There are still large temporal gaps across this huge geographic region to fill with more interdisciplinary archeological and ancient DNA research, according to Posth. “We need more archaeogenetic studies focusing on North Asia to find out which demographic processes were involved in the formation of distinct hunter-gatherer gene-pools, and how these were possibly linked with different cultural practices,” he says.” ref
“And the study of 10 sets of human remains in North Asia dating back as many as 7,500 years ago suggests that hunter-gatherers traveled far and wide, including back and forth across the Bering Land Bridge, according to a Live Science report. Genes from groups in North America were also detected in remains in central Siberia and on Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula. The researchers suggest that genes flowed back and forth between North America and Asia for about 5,000 years.” ref
“Volcanos and Mountains in the Mesoamerican Highlands’ Mythology” by Juan Carlos Barrientos-García
“The Mesoamericans are the hombres delmaíz, the “Men of corn” (Christenson, 2003). Mountains were also regarded as the depositaries of water, therefore becoming sanctuaries of water worship. Evidence of the mountains being considered as natural temple structures where the water gods were venerated remains in the name of several locations throughout modern Honduras, Nicaragua, El Salvador, and Guatemala. Many mountain places bear the name Azacualpa, which literally means the “water-worshipping place”, from the Nahuatl atl-“water”, -zacualli “temple pyramid” and – pa “place” (Incer, 1985). It is interesting to mention that Nahuatl (the language of the Mexica) had become before the arrival of the Spanish, the lingua franca spoken by the Mesoamericans due to the sway of powerful polities in Mexico which culturally and economically influenced the greater Mesoamerican area. Several place names in the region have their origins in this language (Carmack, 1981).In essence, volcanoes and mountains represented for ancient Mesoamericans portal to the spiritual world. The imposition of their massive presence in the scenery made them into natural temples enclosing riches and the vital waters people needed for sustenance. Volcanoes were producers of life and holders of the primordial fire of life, home to powerful spirits, and were also high altars for worshipping the heavens. They were unequivocally the backdrop for the myths and the materialization of the powers of the spirits that inhabited within their midst.” ref
Mountains in the ancient Mesoamerican Mythology
Animism in Altai Mountain Area?
“Worship of nature, the three worlds in Altai mythology, Altai shamanism, Altai epic myths, Altai annual communal ceremonies marking the season cycles, sacred fire mythology, Prayers/Blessings, Altai magic (tarmalga), afterlife/soul belief, and Shamanistic Healing.”
“The Republic of Altai, (the mountainous Altai), is a republic of Russia located in southern Siberia, and is part of the Russian Federation. The Republic is located about 500km South of Novosibirsk, bordering China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan. The Altai people, in total, number 76,000, and are made of 6 different groups; Telengit, Altai Kizhi, Tubular, Kumandin, Shor, and Chalkan. This research paper will focus on the 65,000 Altai (Telengit and Altai Kizhi) people who speak Southern Altai fluently. The language is used in arts, media, in education and in everyday life. The majority of the Altai are also fairly fluent in Russian, with the exception of those living in remote villages. I am interested in researching their animistic and shamanistic worldview and practices more thoroughly in order to have increased insight into their culture.” ref
Axis Mundi?
“In astronomy, axis mundi is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles. In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere. Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the axis mundi is the axis of rotation of the planetary spheres within the classical geocentric model of the cosmos. In 20th-century comparative mythology, the term axis mundi — also called the cosmic axis, world axis, world pillar, center of the world, or world tree — has been greatly extended to refer to any mythological concept representing “the connection between Heaven and Earth” or the “higher and lower realms.” Mircea Eliade introduced the concept in the 1950s. Axis mundi closely relates to the mythological concept of the omphalos (navel) of the world or cosmos. Items adduced as examples of the axis mundi by comparative mythologists include plants (notably a tree but also other types of plants such as a vine or stalk), a mountain, a column of smoke or fire, or a product of human manufacture (such as a staff, a tower, a ladder, a staircase, a maypole, a cross, a steeple, a rope, a totem pole, a pillar, a spire). Its proximity to heaven may carry implications that are chiefly religious (pagoda, temple mount, minaret, church) or secular (obelisk, lighthouse, rocket, skyscraper). The image appears in religious and secular contexts. The axis mundi symbol may be found in cultures utilizing shamanic practices or animist belief systems, in major world religions, and in technologically advanced “urban centers.” In Mircea Eliade‘s opinion: “Every Microcosm, every inhabited region, has a Centre; that is to say, a place that is sacred above all.” ref
“There are multiple interpretations about the origin of the concept of the axis mundi. One psychological and sociological interpretation suggests that the symbol originates in a natural and universal psychological perception — i.e., that the particular spot that one occupies stands at “the center of the world.” This space serves as a microcosm of order because it is known and settled. Outside the boundaries of the microcosm lie foreign realms that — because they are unfamiliar or not ordered — represent chaos, death, or night. From the center, one may still venture in any of the four cardinal directions, make discoveries, and establish new centers as new realms become known and settled. The name of China — meaning “Middle Nation” (中国 pinyin: Zhōngguó) — is often interpreted as an expression of an ancient perception that the Chinese polity (or group of polities) occupied the center of the world, with other lands lying in various directions relative to it.” ref
“A second interpretation suggests that ancient symbols such as the axis mundi lie in a particular philosophical or metaphysical representation of a common and culturally shared philosophical concept, which is that of a natural reflection of the macrocosm (or existence at grand scale) in the microcosm (which consists of either an individual, community, or local environment that shares the same principles and structures as the macrocosm). In this metaphysical representation of the universe, mankind is placed into an existence that serves as a microcosm of the universe or the entire cosmic existence, and who — in order to achieve higher states of existence or liberation into the macrocosm — must gain necessary insights into universal principles that can be represented by his life or environment in the microcosm.” ref
“In many religious and philosophical traditions around the world, mankind is seen as a sort of bridge between either: two worlds, the earthly and the heavenly (as in Hindu, and Taoist philosophical and theological systems); or three worlds, namely the earthly, heavenly, and the “sub-earthly” or “infra-earthly” (e.g., the underworld, as in the Ancient Greek, Incan, Mayan, and Ancient Egyptian religious systems). Spanning these philosophical systems is the belief that man traverses a sort of axis, or path, which can lead from man’s current central position in the intermediate realms into heavenly or sub-earthly realms. Thus, in this view, symbolic representations of a vertical axis represent a path of “ascent” or “descent” into other spiritual or material realms, and often capture a philosophy that considers human life to be a quest in which one develops insights or perfections in order to move beyond this current microcosmic realm and to engage with the grand macrocosmic order.” ref
“In other interpretations, an axis mundi is more broadly defined as a place of connection between heavenly and the earthly realms — often a mountain or other elevated site. Tall mountains are often regarded as sacred and some have shrines erected at the summit or base. Mount Kunlun fills a similar role in China. Mount Kailash is holy to Hinduism and several religions in Tibet. The Pitjantjatjara people in central Australia consider Uluru to be central to both their world and culture. The Teide volcano was for the Canarian aborigines (Guanches) a kind of axis mundi. In ancient Mesopotamia, the cultures of ancient Sumer and Babylon built tall platforms, or ziggurats, to elevate temples on the flat river plain. Hindu temples in India are often situated on high mountains — e.g., Amarnath, Tirupati, Vaishno Devi, etc. The pre-Columbian residents of Teotihuacán in Mexico erected huge pyramids, featuring staircases leading to heaven. These Amerindian temples were often placed on top of caves or subterranean springs, which were thought to be openings to the underworld. Jacob’s Ladder is an axis mundi image, as is the Temple Mount. For Christians, the Cross on Mount Calvary expresses this symbol. The Middle Kingdom, China, had a central mountain, Kunlun, known in Taoist literature as “the mountain at the middle of the world.” To “go into the mountains” meant to dedicate oneself to a spiritual life.” ref
“As the abstract concept of axis mundi is present in many cultural traditions and religious beliefs, it can be thought to exist in any number of locales at once. Mount Hermon was regarded as the axis mundi in Canaanite tradition, from where the sons of God are introduced descending in 1 Enoch (1En6:6). The ancient Armenians had a number of holy sites, the most important of which was Mount Ararat, which was thought to be the home of the gods as well as the center of the universe. Likewise, the ancient Greeks regarded several sites as places of Earth’s omphalos (navel) stone, notably the oracle at Delphi, while still maintaining a belief in a cosmic world tree and in Mount Olympus as the abode of the gods. Judaism has the Temple Mount; Christianity has the Mount of Olives and Calvary; and Islam has the Ka’aba (said to be the first building on Earth), as well as the Temple Mount (Dome of the Rock). In Hinduism, Mount Kailash is identified with the mythical Mount Meru and regarded as the home of Shiva; in Vajrayana Buddhism, Mount Kailash is recognized as the most sacred place where all the dragon currents converge and is regarded as the gateway to Shambhala. In Shinto, the Ise Shrine is the omphalos.” ref
“Sacred places can constitute world centers (omphalos), with an altar or place of prayer as the axis. Altars, incense sticks, candles, and torches form the axis by sending a column of smoke, and prayer, toward heaven. It has been suggested by Romanian religious historian Mircea Eliade that architecture of sacred places often reflects this role:”Every temple or palace — and by extension, every sacred city or royal residence — is a Sacred Mountain, thus becoming a Centre.” Pagoda structures in Asian temples take the form of a stairway linking earth and heaven. A steeple in a church or a minaret in a mosque also serve as connections of earth and heaven. Structures such as the maypole, derived from the Saxons‘ Irminsul, and the totem pole among indigenous peoples of the Americas also represent world axes. The calumet, or sacred pipe, represents a column of smoke (the soul) rising from a world center. A mandala creates a world center within the boundaries of its two-dimensional space analogous to that created in three-dimensional space by a shrine.” ref
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
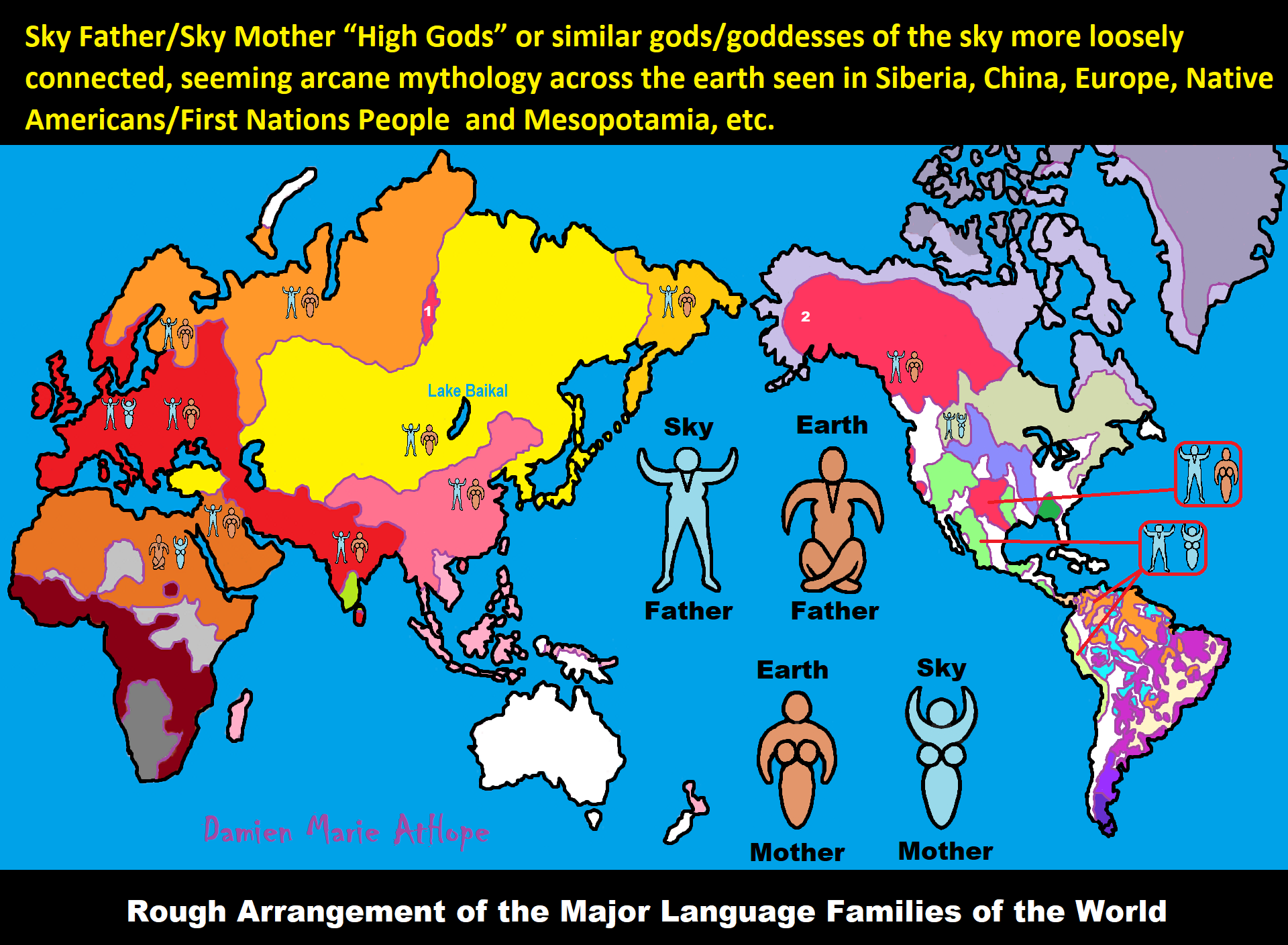
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“1 central Eurasian Neolithic individual from Tajikistan (around 8,000 years ago) and approximately 8,200 years ago Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov group from Karelia in western Russia formed by 19 genomes affinity to Villabruna ancestry than all the other Eastern Hunter-Gatherer groups” https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-05726-0
Eastern Hunter-Gatherer?
“In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers of Eastern Europe. The Eastern Hunter Gatherer genetic profile can be modeled as an admixture between a Siberian Paleolithic population called Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) with European Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), although the relationship between the ANE and EHG ancestral components is not yet well understood due to lack of samples that could bridge the spatiotemporal gap. During the Mesolithic, the EHGs inhabited an area stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Urals and downwards to the Pontic–Caspian steppe.” ref
“Along with Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHG) and Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), the EHGs constituted one of the three main genetic groups in the postglacial period of early Holocene Europe. The border between WHGs and EHGs ran roughly from the lower Danube, northward along the western forests of the Dnieper towards the western Baltic Sea. During the Neolithic and early Eneolithic, likely during the 4th millennium BC EHGs on the Pontic–Caspian steppe mixed with Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHGs) with the resulting population, almost half-EHG and half-CHG, forming the genetic cluster known as Western Steppe Herder (WSH). WSH populations closely related to the people of the Yamnaya culture are supposed to have embarked on a massive migration leading to the spread of Indo-European languages throughout large parts of Eurasia.” ref
“Haak et al. (2015) identified the Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHG) as a distinct genetic cluster in two males only. The EHG male of Samara (dated to ca. 5650-5550 BCE) carried Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a* and mt-haplogroup U5a1d. The other EHG male, buried in Karelia (dated to ca. 5500-5000 BCE) carried Y-haplogroup R1a1 and mt-haplogoup C1g. The authors of the study also identified a Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) cluster and a Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG) cluster, intermediate between WHG and EHG. Also, Lazaridis et al. (2016) confirmed SHGs to be a mix of EHGs and WHGs. They suggested that EHGs harbored mixed ancestry from Ancient North Eurasians (ANEs) and WHGs. The people of the Yamnaya culture were found to be a mix of EHG and a “Near Eastern related population”. During the 3rd millennium BC, the Yamnaya people embarked on a massive expansion throughout Europe, which significantly altered the genetic landscape of the continent. The expansion gave rise to cultures such as Corded Ware, and was possibly the source of the distribution of Indo-European languages in Europe.” ref
“EHGs may have mixed with “an Armenian-like Near Eastern source”, which formed the Yamnaya culture, as early as the Eneolithic (5200-4000 BCE). Researchers have found that EHGs may have derived different amounts of their ancestry from WHGs and ANEs. Their relationship to the WHG and ANE is not well clarified. The people of the Mesolithic Kunda culture and the Narva culture of the eastern Baltic were a mix of WHG and EHG, showing the closest affinity with WHG. Samples from the Ukrainian Mesolithic and Neolithic were found to cluster tightly together between WHG and EHG, suggesting genetic continuity in the Dnieper Rapids for a period of 4,000 years. The Ukrainian samples belonged exclusively to the maternal haplogroup U, which is found in around 80% of all European hunter-gatherer samples.” ref
“The people of the Pit–Comb Ware culture (PCW/CCC) of the eastern Baltic bear 65% EHG ancestry. This is in contrast to earlier hunter-gatherers in the area, who were more closely related to WHG. This was demonstrated using a sample of Y-DNA extracted from a Pit–Comb Ware individual. This belonged to R1a15-YP172. The four samples of mtDNA extracted constituted two samples of U5b1d1, one sample of U5a2d, and one sample of U4a. Günther et al. (2018) analyzed 13 SHGs and found all of them to be of EHG ancestry. Generally, SHGs from western and northern Scandinavia had more EHG ancestry (ca 49%) than individuals from eastern Scandinavia (ca. 38%). The authors suggested that the SHGs were a mix of WHGs who had migrated into Scandinavia from the south, and EHGs who had later migrated into Scandinavia from the northeast along the Norwegian coast. SHGs displayed higher frequencies of genetic variants that cause light skin (SLC45A2 and SLC24A5), and light eyes (OCA/Herc2), than WHGs and EHGs.” ref
“Members of the Kunda culture and Narva culture were also found to be more closely related with WHG, while the Pit–Comb Ware culture was more closely related to EHG. Northern and eastern areas of the eastern Baltic were found to be more closely related to EHG than southern areas. The study noted that EHGs, like SHGs and Baltic hunter-gatherers, carried high frequencies of the derived alleles for SLC24A5 and SLC45A2, which are codings for light skin. Mathieson et al. (2018) analyzed the genetics of a large number of skeletons of prehistoric Eastern Europe. Thirty-seven samples were from Mesolithic and Neolithic Ukraine (9500-6000 BC). These were classified as intermediate between EHG and SHG. The males belonged exclusively to R haplotypes (particularly subclades of R1b1 and R1a) and I haplotypes (particularly subclades of I2). Mitochondrial DNA belonged almost exclusively to U (particularly subclades of U5 and U4).” ref
“A large number of individuals from the Zvejnieki burial ground, which mostly belonged to the Kunda culture and Narva culture in the eastern Baltic, were analyzed. These individuals were mostly of WHG descent in the earlier phases, but over time EHG ancestry became predominant. The Y-DNA of this site belonged almost exclusively to haplotypes of haplogroup R1b1a1a and I2a1. The mtDNA belonged exclusively to haplogroup U (particularly subclades of U2, U4 and U5). Forty individuals from three sites of the Iron Gates Mesolithic in the Balkans were estimated to be of 85% WHG and 15% EHG descent. The males at these sites carried exclusively R1b1a and I (mostly subclades of I2a) haplotypes. mtDNA belonged mostly to U (particularly subclades of U5 and U4).” ref
“People of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture were found to harbor about 20% hunter-gatherer ancestry, which was intermediate between EHG and WHG. Narasimshan et al. (2019) coined a new ancestral component, West Siberian Hunter-Gatherer (WSHG). WSHGs contained about 30% EHG ancestry, 50% ANE ancestry, and 20% East Asian ancestry. Unlike the Yamnaya culture, in the Dnieper–Donets culture no Caucasian Hunter-Gatherer (CHG) or Early European Farmer (EEF) ancestry has been detected. Dnieper-Donets males and Yamnaya males carry the same paternal haplogroups (R1b and I2a), suggesting that the CHG and EEF admixture among the Yamnaya came through EHG males mixing with EEF and CHG females. According to David W. Anthony, this suggests that the Indo-European languages were initially spoken by EHGs living in Eastern Europe.” ref
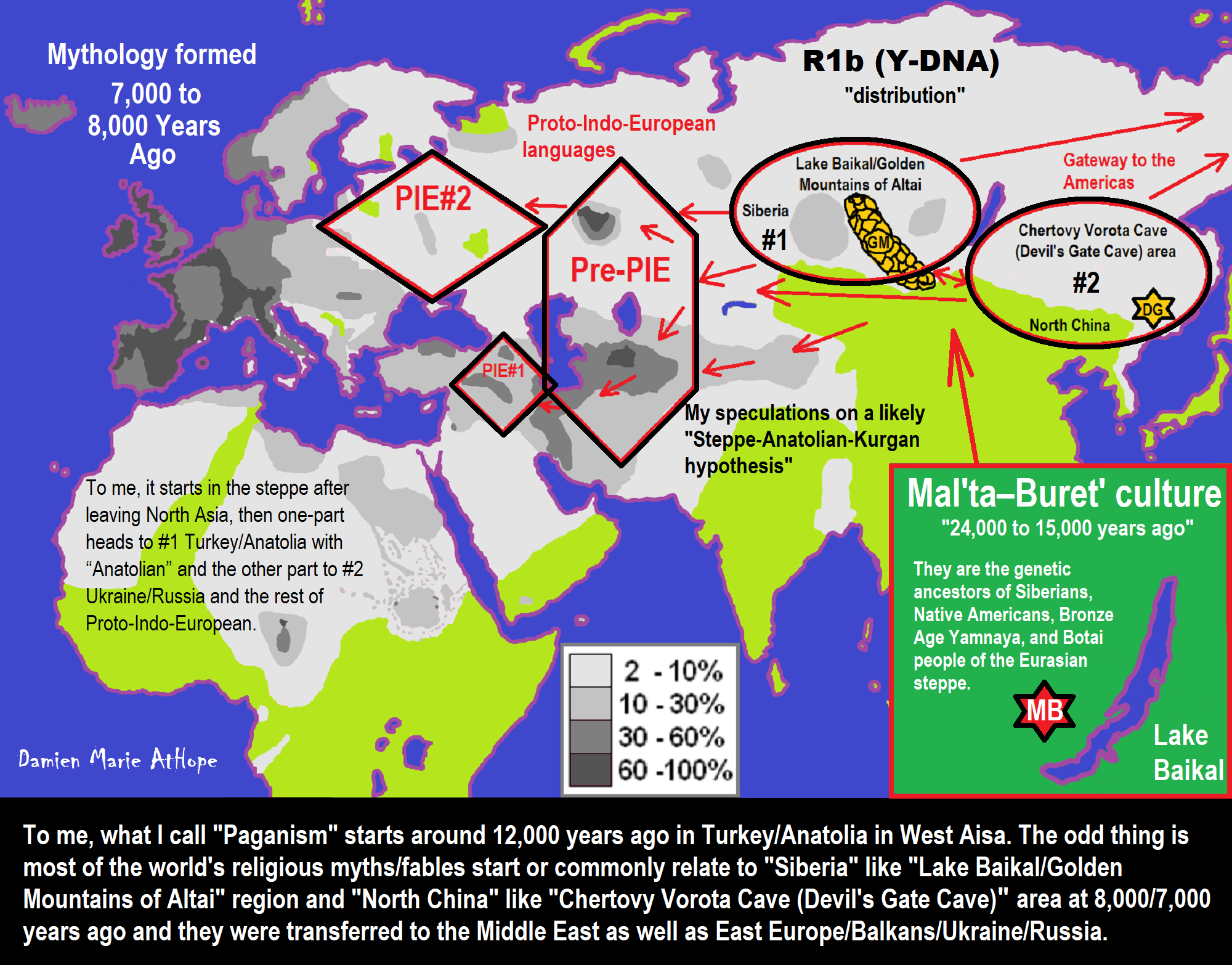
Yamnaya Western Steppe Herders
“According to Jones et al. (2015) and Haak et al. (2015), autosomal tests indicate that the Yamnaya people were the result of a genetic admixture between two different hunter-gatherer populations: distinctive “Eastern Hunter-Gatherers” (EHG), from Eastern Europe, with high affinity to the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture or other, closely related people from Siberia and a population of “Caucasus hunter-gatherers” (CHG) who probably arrived from the Caucasus or Iran. Each of those two populations contributed about half the Yamnaya DNA. This admixture is referred to in archaeogenetics as Western Steppe Herder (WSH) ancestry. Admixture between EHGs and CHGs is believed to have occurred on the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe starting around 5,000 BCE, while admixture with Early European Farmers (EEF) happened in the southern parts of the Pontic-Caspian steppe sometime later. More recent genetic studies have found that the Yamnaya were a mixture of EHGs, CHGs, and to a lesser degree Anatolian farmers and Levantine farmers, but not EEFs from Europe due to lack of WHG DNA in the Yamnaya. This occurred in two distinct admixture events from West Asia into the Pontic-Caspian steppe.” ref
“Haplogroup R1b, especially subclades of R1b-M269, is the most common Y-DNA haplogroup found among both the Yamnaya and modern-day Western Europeans. Additionally, a minority are found to belong to haplogroup I2. They are found to belong to a wider variety of mtDNA haplogroups, including U, T, and haplogroups associated with Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers and Early European Farmers. People of the Yamnaya culture are believed to have had mostly brown eye colour, light to intermediate skin, and brown hair colour, with some variation. A 022 study by Lazaridis et al. found that the typical phenotype among the Yamnaya population was brown eyes, brown hair, and intermediate skin color. None of the Yamnaya samples were predicted to have either blue eyes or blonde hair. Some individuals are believed to have carried a mutation to the KITLG gene associated with blond hair, as several individuals with Steppe ancestry are later found to carry this mutation. The Ancient North Eurasian population, who contributed significant ancestry to Western Steppe Herders, are believed to be the source of this mutation. A study in 2015 found that Yamnaya had the highest ever calculated genetic selection for height of any of the ancient populations tested. It has been hypothesized that an allele associated with lactase persistence (conferring lactose tolerance into adulthood) was brought to Europe from the steppe by Yamnaya-related migrations.” ref
“The geneticist David Reich has argued that the genetic data supports the likelihood that the people of the Yamnaya culture were a “single, genetically coherent group” who were responsible for spreading many Indo-European languages. Reich’s group recently suggested that the source of Anatolian and Indo-European subfamilies of the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language was in west Asia and the Yamna were responsible for the dissemination of the latter. Reich also argues that the genetic evidence shows that Yamnaya society was an oligarchy dominated by a small number of elite males. The genetic evidence for the extent of the role of the Yamnaya culture in the spread of Indo-European languages has however been questioned by Russian archaeologist Leo Klejn and Balanovsky et al., who note a lack of male haplogroup continuity between the people of the Yamnaya culture and the contemporary populations of Europe. Klejn has also suggested that the autosomal evidence does not support a Yamnaya migration, arguing that Western Steppe Herder ancestry in both contemporary and Bronze Age samples is lowest around the Danube in Hungary, near the western limits of the Yamnaya culture, and highest in Northern Europe, which Klejn argues is the opposite of what would be expected if the geneticists’ hypothesis is correct.” ref
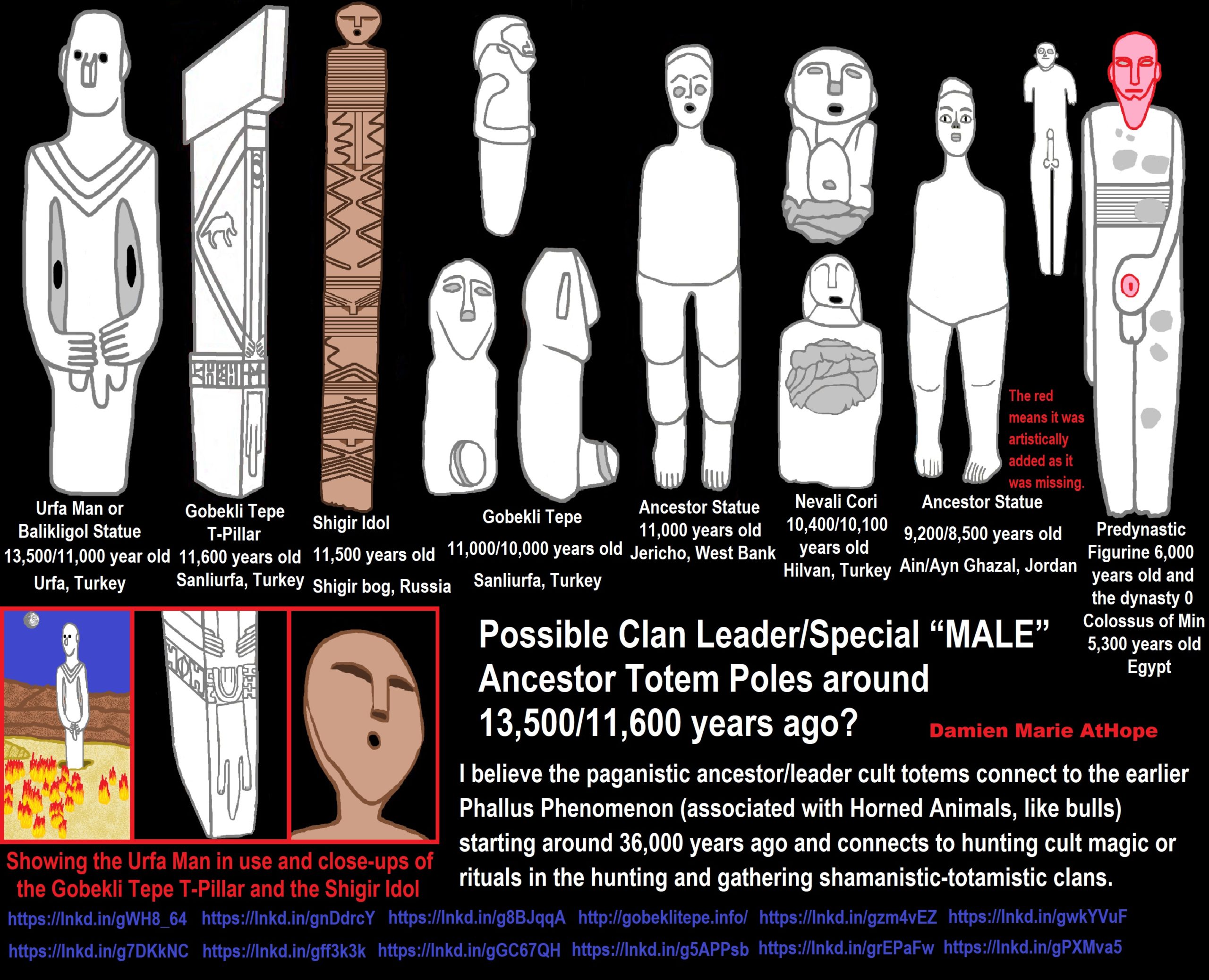
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
I believe the paganistic ancestor/leader cult totems connect to the earlier Phallus Phenomenon (associated with Horned Animals, like bulls) starting around 36,000 years ago and connects to hunting cult magic or rituals in the hunting and gathering shamanistic-totamistic clans.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref


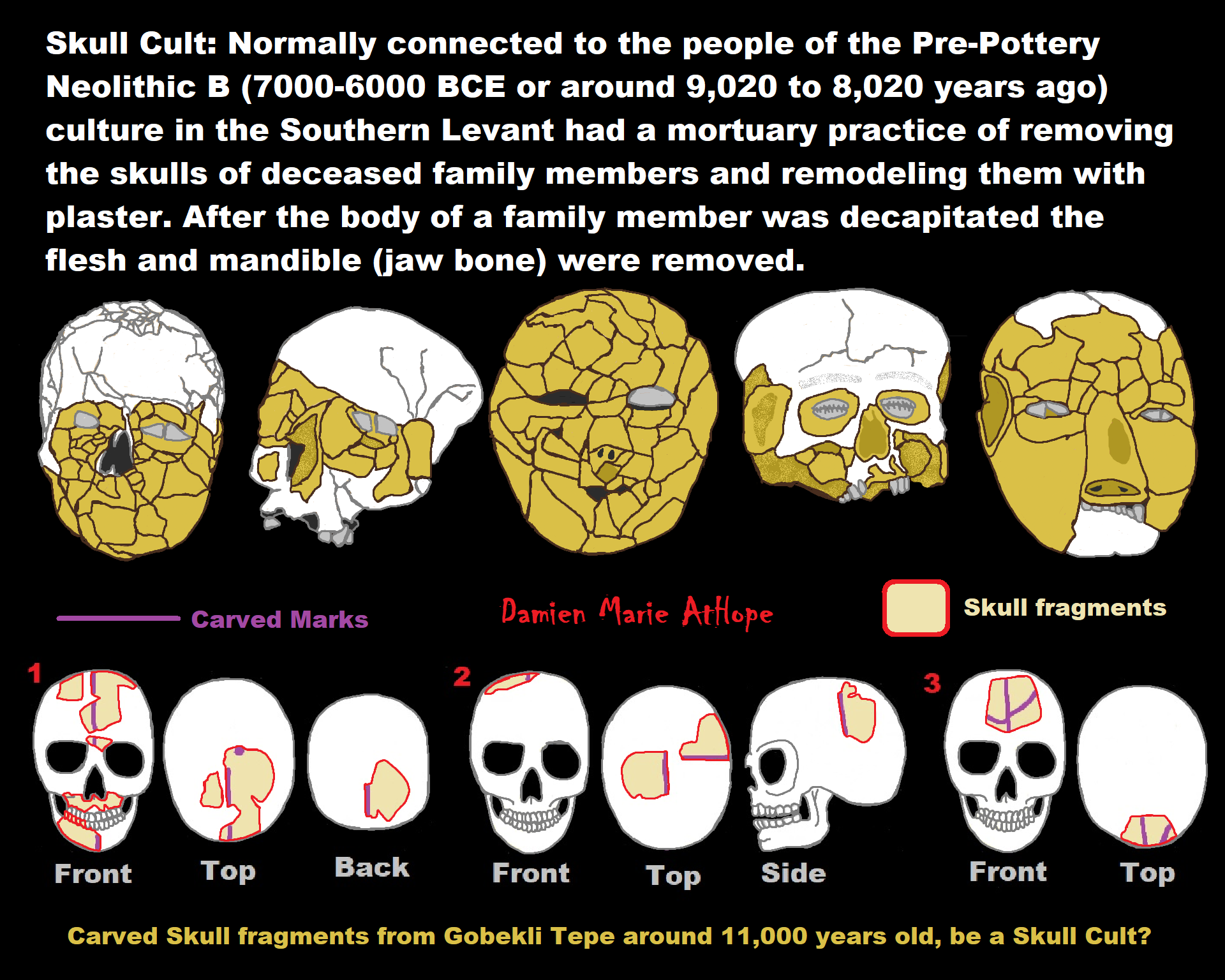
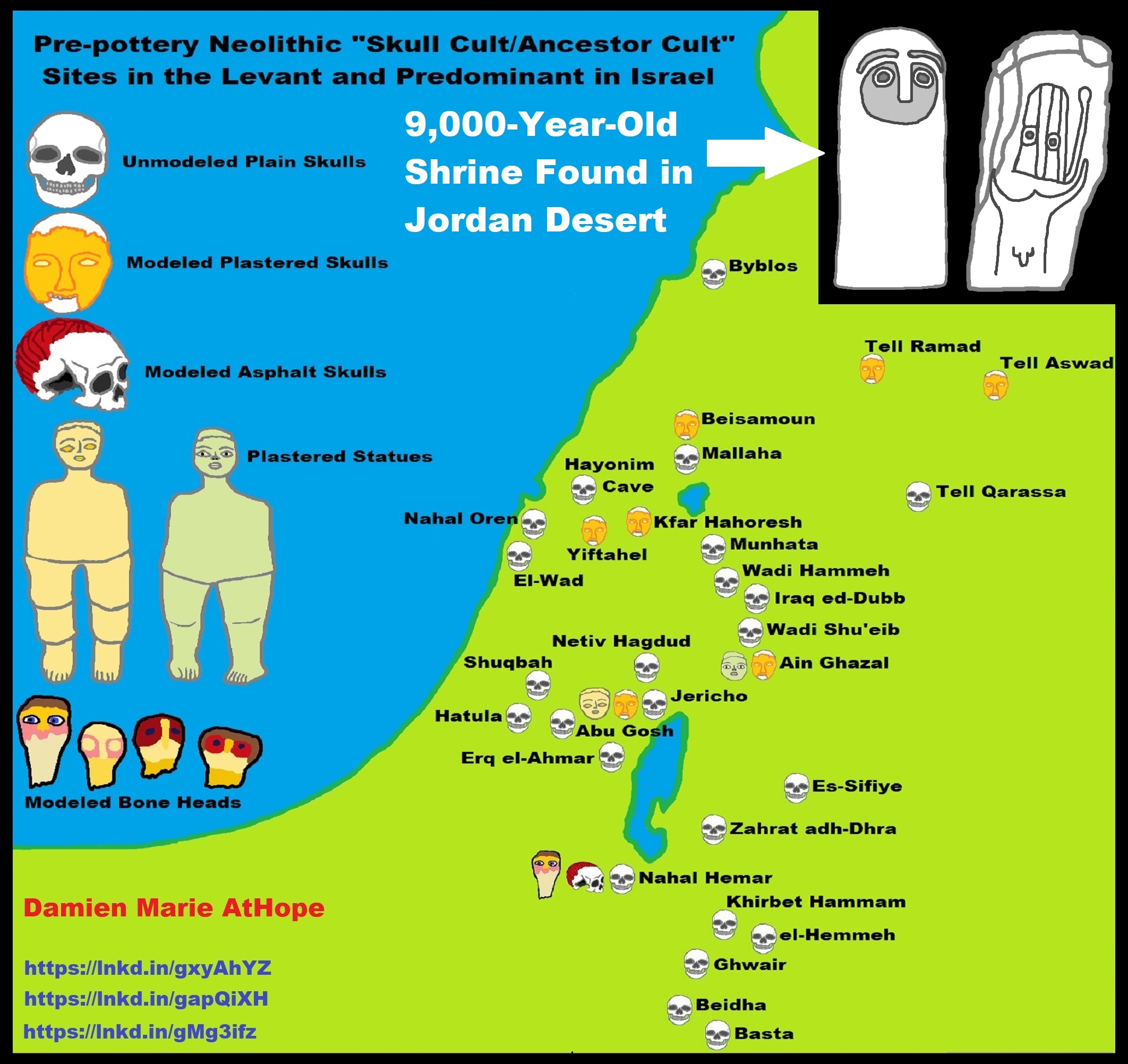
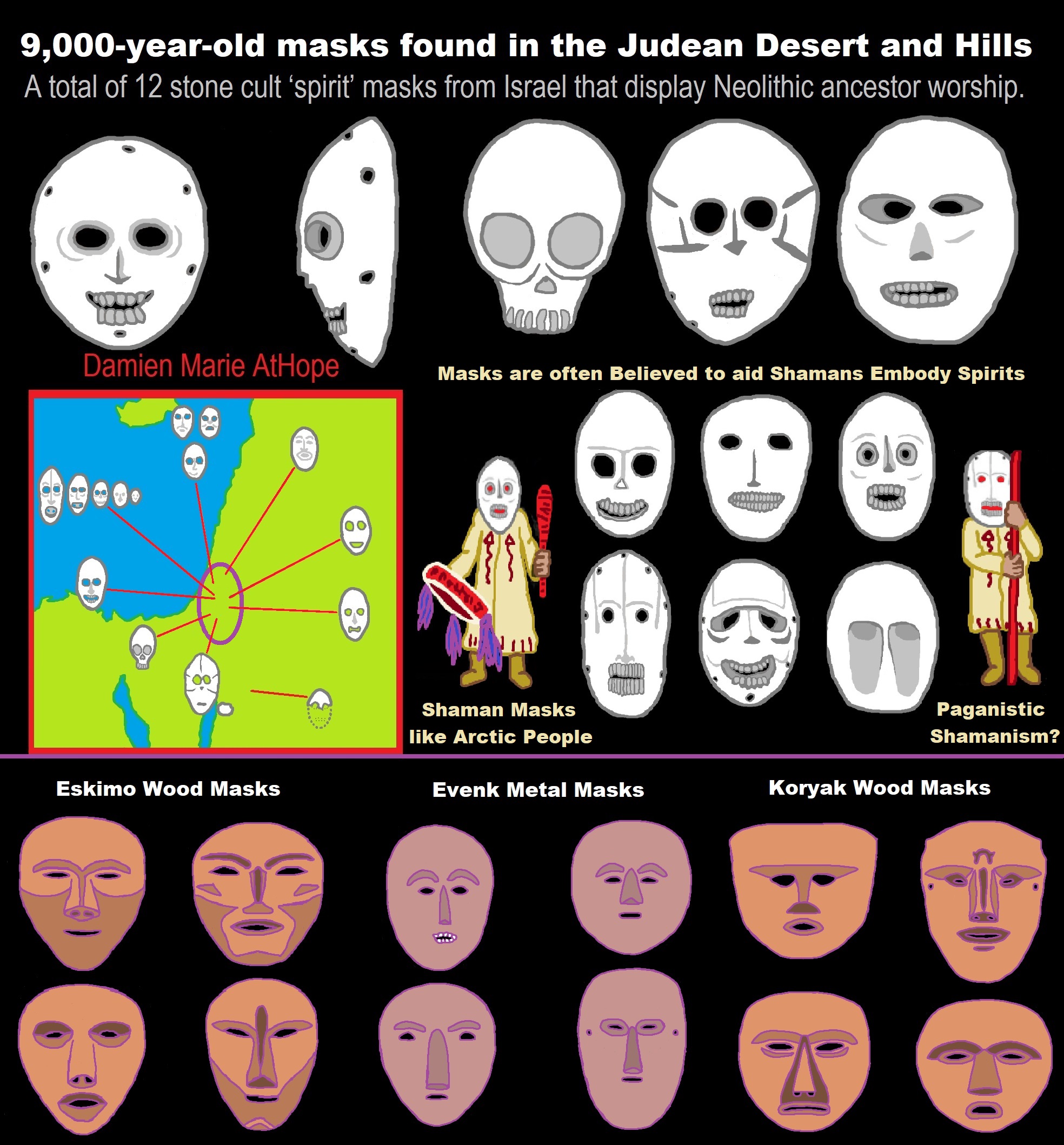
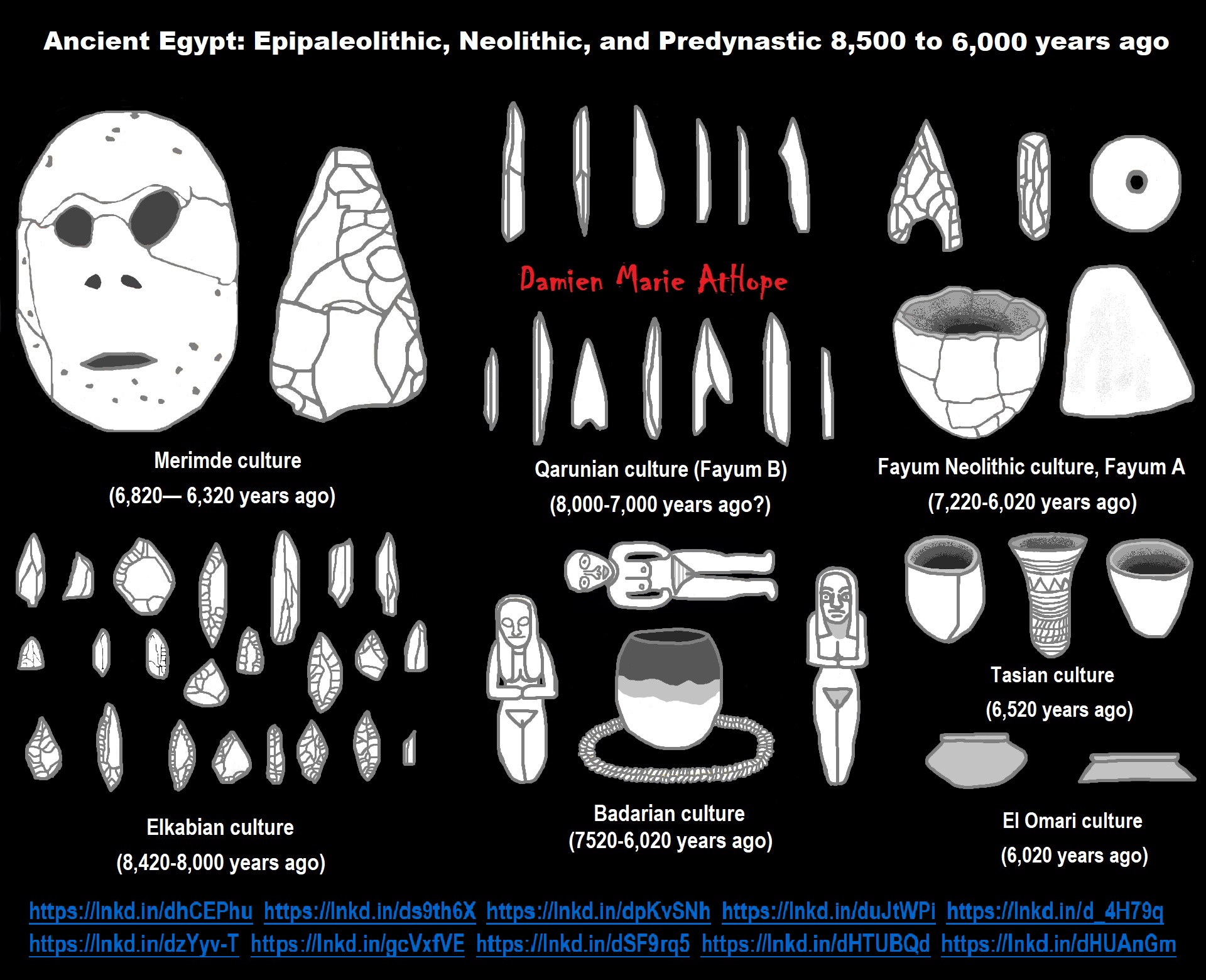
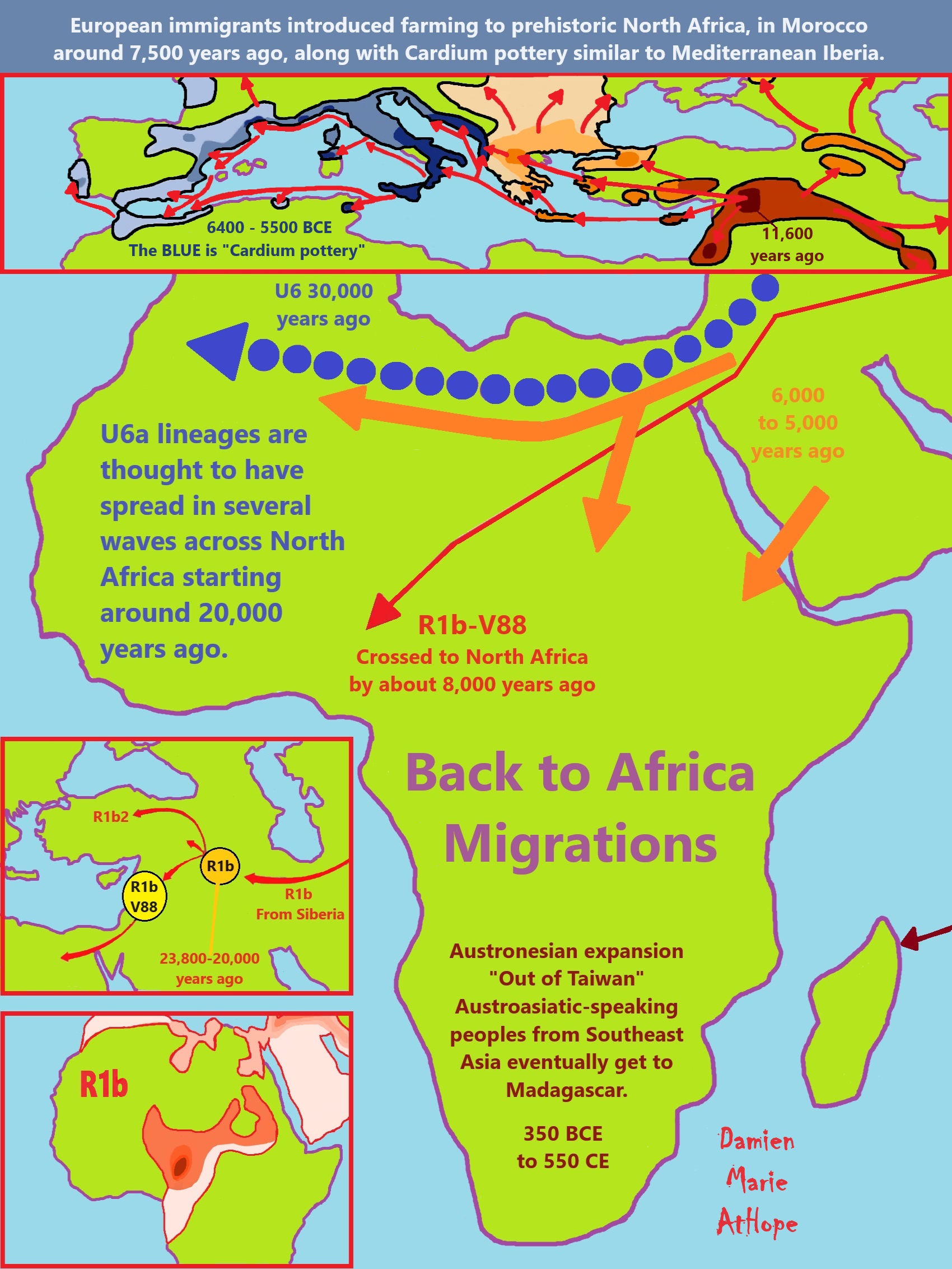
African Back Migrations and the Status of Shamanism Origins as well as its Spreading
“Various DNA studies have found Christian-era and modern Nubians along with modern Afro-Asiatic speaking populations in the Horn of Africa to be descended from a mix of West Eurasian and East African populations.” ref
“The results showed that King Tut belonged to a genetic profile group, known as haplogroup R1b1a2, to which more than 50 percent of all men in Western Europe belong, indicating that they share a common ancestor. Among modern-day Egyptians this haplogroup contingent is below 1 percent, according to iGENEA. Up to 70 percent of British men and half of all Western European men are related to the Egyptian Pharaoh Tutankhamun, geneticists in Switzerland said.” ref
“A 2020 study by Gad, Hawass, et al. analysed mitochondrial and Y-chromosomal haplogroups from Tutankhamun‘s family members of the 18th Dynasty, using comprehensive control procedures to ensure quality results. The study found that the Y-chromosome haplogroup of the family was R1b. Haplogroup R1b is carried by modern Egyptians. Modern Egypt is also the only African country that is known to harbor all three R1 subtypes, including R1b-M269. The Y-chromosome profiles for Tutankhamun and Amenhotep III were incomplete and the analysis produced differing probability figures despite having concordant allele results. Because the relationships of these two mummies with the KV55 mummy (identified as Akhenaten) had previously been confirmed in an earlier study, the haplogroup prediction of both mummies could be derived from the full profile of the KV55 data.” ref
“Genetic analysis indicated the following haplogroups for the 18th Dynasty:
- Amenhotep III: YDNA R1b& mtDNA H2b.
- Tutankhamun: YDNA R1b & mtDNA K.
- Akhenaten: YDNA R1b & mtDNA K.
- Tiye: mtDNA K.
- Yuya: YDNA G2a& mtDNA K.
- Thuya: mtDNA K.
Both Y-DNA haplogroups R1b and G2a, as well as both mtDNA haplogroups H and K, are carried by modern Egyptians.” ref
“In 2020, three mummies, dating from the 1st millennium BCE, from the Pushkin Museum of Arts collection were tested at the Kurchatov Institute of Moscow for their mitochondrial and Y-chromosomal haplogroups. Two of the mummies were found to belong to the Y-chromosomal haplogroup R1b1a1b (R1b-M269), which originated either in Eastern Europe or in the Near East, and to the Y-chromosome haplogroup E1b1b1a1b2a4b5a, which originated in North Africa. They also belonged to mtDNA haplogroups L3h1 and N5, common in Africans and Middle Easterners, respectively. The third mummy was found to belong to mtDNA haplogroup N, which is widely distributed across Eurasia as well as eastern and northeastern Africa.” ref
(Haplogroup N5 – found in India)
“In Southern Asia, N5 haplogroup, arose; N5 is extremely rare and has also been recently described in Iran, raising the possibility that this lineage could also have arisen in Southwest Asia. A greater number of N(xR) branches exist in Eastern Asia, Southeast Asia, and Australasia, showing that N(xR) certainly crossed into this region, along with lineages within R haplogroups.” ref
“”The Predynastic of Upper Egypt and the Late Dynastic of Lower Egypt are more closely related to each other than to any other population” and most similar to modern Egyptians among modern populations, stating that “the Egyptians have been in place since back in the Pleistocene and have been largely unaffected by either invasions or migrations.” The craniometric analysis of predynastic Naqada human remains found that they were closely related to other Afroasiatic-speaking populations inhabiting North Africa, parts of the Horn of Africa and the Maghreb, as well as to Bronze Age and medieval period Nubians and to specimens from ancient Jericho.” ref
“Kaiser’s chronology began c. 4000 BCE or around 6,000 years ago, but the modern version has been adjusted slightly, as follows:
- Naqada I(about 3900–3650 BCE or 5,900-5,650 years ago)
- black-topped and painted pottery
- trade with Nubia, Western Desertoases, and Eastern Mediterranean
- obsidianfrom Ethiopia
- Naqada II(about 3650–3300 BCE or 5,650-5,300 years ago)
- represented throughout Egypt
- first marlpottery, and metalworking
- Naqada III(about 3300–2900 BCE or 5,300-4,900 years ago)
- more elaborate grave goods, first Pharaohs
- cylindrical jars
- writing” ref
“The Naqada skeletons were also morphologically proximate to modern osteological series from Europe and the Indian subcontinent. However, the Naqada skeletons and these ancient and recent skeletons were phenotypically distinct from skeletons belonging to modern Niger-Congo-speaking populations inhabiting Sub-Saharan Africa and Tropical Africa, as well as from Mesolithic skeletons excavated at Wadi Halfa in the Nile Valley. ” ref
“The ancient Egyptian individuals in their own dataset possessed highly similar mtDNA haplogroup profiles, and cluster together, supporting genetic continuity across the 1,300-year transect. Modern Egyptians shared this mtDNA haplogroup profile, but also carried 8% more African component. A wide range of mtDNA haplogroups were found including clades of J, U, H, HV, M, R0, R2, K, T, L, I, N, X, and W. In addition, three ancient Egyptian individuals were analyzed for Y-DNA, two were assigned to Middle Eastern haplogroup J and one to haplogroup E1b1b1a1b2. Both of these haplogroups are carried by modern Egyptians, and are also common among Afroasiatic speakers in Northern Africa, Eastern Africa, and the Middle East. The researchers cautioned that the examined ancient Egyptian specimens may not be representative of those of all ancient Egyptians since they were from a single archaeological site from the northern part of Egypt.” ref
“The analyses revealed that Ancient Egyptians had higher affinities with Near Eastern and European populations than do modern Egyptians, likely due to the 8% increase in the African component found in modern Egyptians. The absolute estimates of sub-Saharan African ancestry in these three ancient Egyptian individuals ranged from 6 to 15%, and the absolute estimates of sub-Saharan African ancestry in the 135 modern Egyptian samples ranged from 14 to 21%, which show an 8% increase in African component.” ref
“The age of the ancient Egyptian samples suggests that this 8% increase in African component occurred predominantly within the last 2000 years. Verena Schuenemann and the authors of this study suggest a high level of genetic interaction with the Near East since ancient times, probably going back to Prehistoric Egypt although the oldest mummies at the site were from the New Kingdom: “Our data seem to indicate close admixture and affinity at a much earlier date, which is unsurprising given the long and complex connections between Egypt and the Middle East. These connections date back to Prehistory and occurred at a variety of scales, including overland and maritime commerce, diplomacy, immigration, invasion and deportation. According to the results of an analysis published by FTDNA in 2023, Nakht Ankh’s most likely Y-DNA haplogroup was H-Z19008, a subclade of H2.” ref
“The primary branch H2 (P96) seems to have been found in sparse levels primarily in Europe and West Asia since prehistory. It has been found in remains of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB), which is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to c. 10,800 – c. 8,500 years ago, and also the later Linear Pottery culture and Neolithic Iberia. H2 likely entered Europe during the Neolithic with the spread of agriculture. The earliest sample of H2 is found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B culture of the Levant 10,000 years ago. From ancient samples, it is clear that H2 also has a strong association with the spread of agriculture from Anatolia into Europe, and is commonly found with haplogroup G2a. H2 was found in Neolithic Anatolia, as well as in multiple later Neolithic cultures of Europe, such as the Vinča culture in Serbia, and the Megalith culture of Western Europe. While being found in numerous ancient samples, H2 has only been found scarcely in modern populations across West Eurasia.” ref
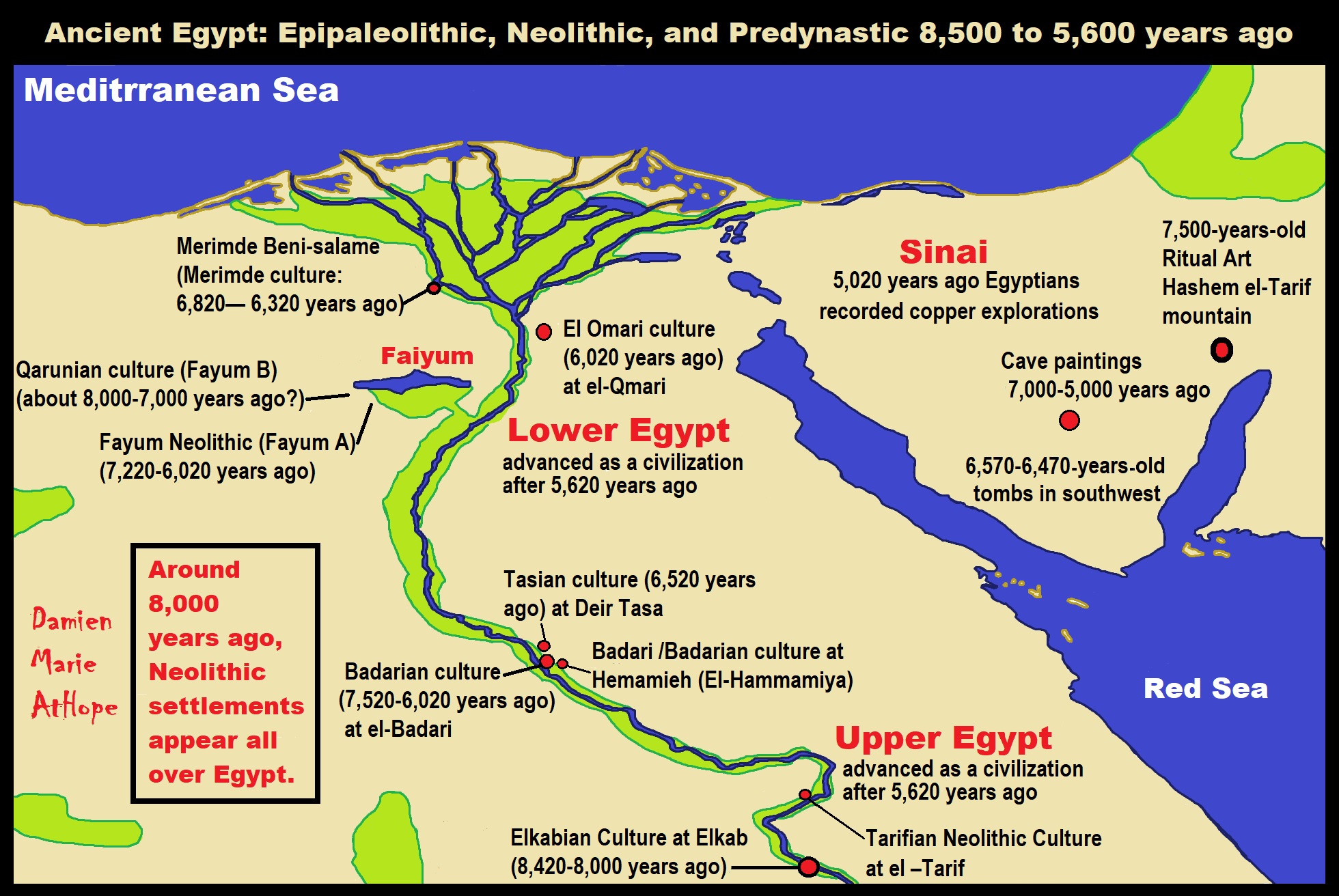
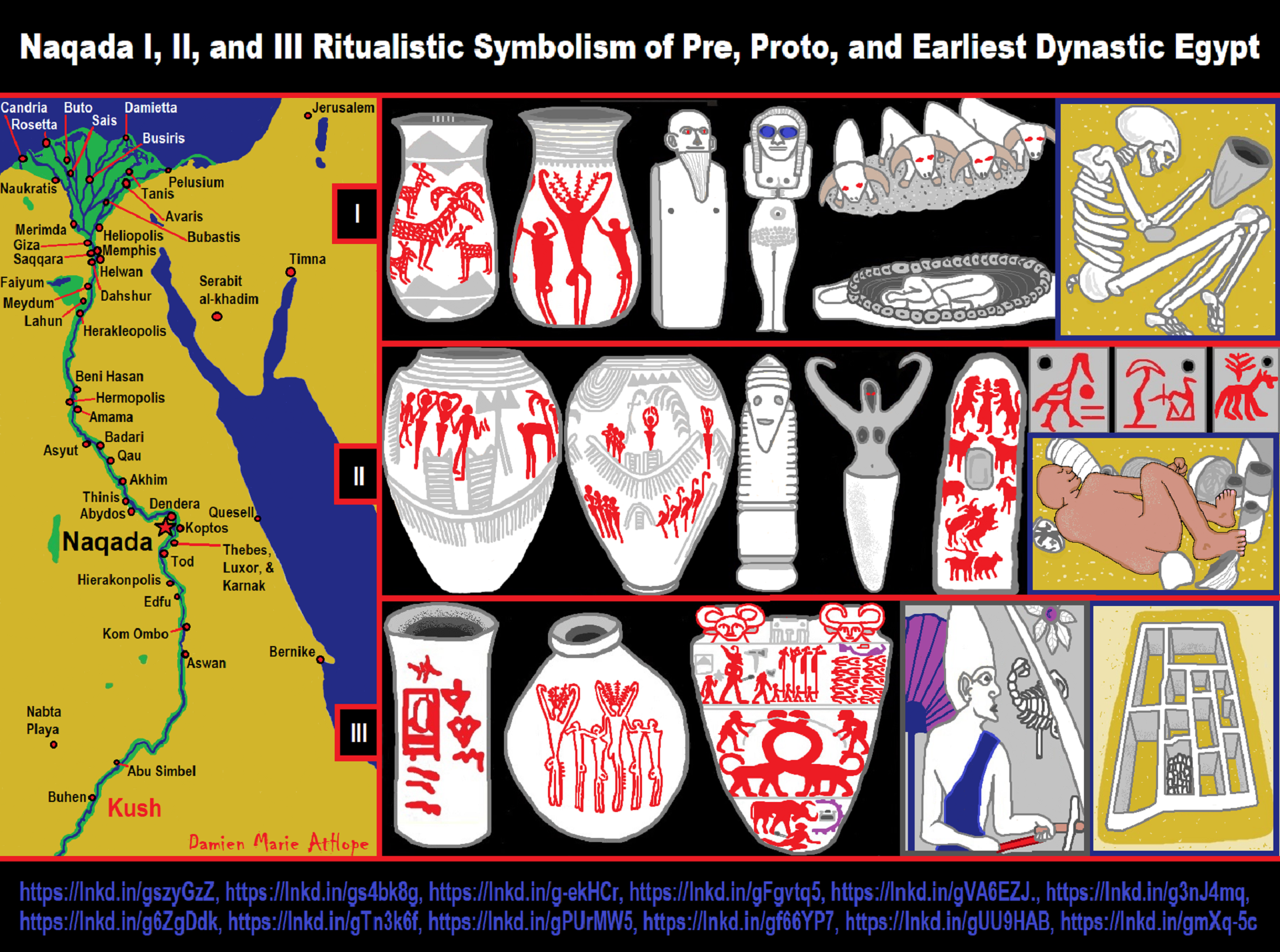
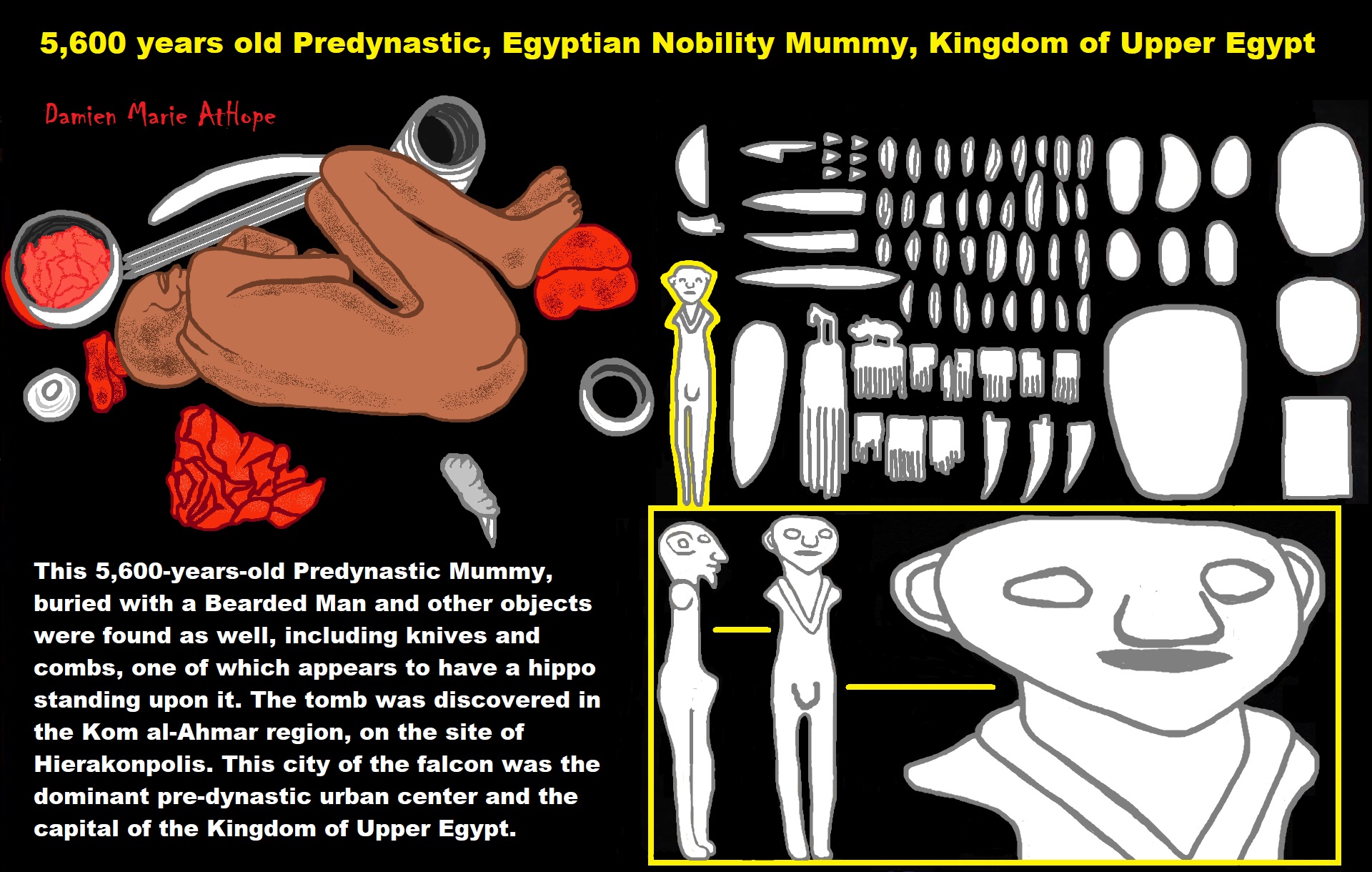
Progressed organized religion starts and is approximately a 5,000-year-old belief system)
Modern Europe was formed by milk-drinking Russians:
Mass migration brought new genetic make-up to continent 5,000 years ago.
Megalithic Mass Grave From 5,000 Years Ago Discovered in Kenya
“Researchers studied the DNA of skeletons from the Bronze Age period. They found white Europeans only arrived on the continent 5,000 years ago Came after a mass period of migration by the Yamnaya in southern Russia. They brought new technology and a genetic mutation allowing them to drink cow’s milk.” Ref
5,000-year-old tomb in southeast Turkey gives the earliest evidence of child sacrifice
Paganism (beginning around 12,000 years ago)
Paganism (such as that seen in Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
Haplogroup G2a (Y-chromosomal DNA) and the Seeming Development of Early Agriculture – “Haplogroup G descends from macro-haplogroup F, which is thought to represent the second major migration of Homo sapiens out of Africa, at least 60,000 years ago. Haplogroup G has 303 mutations confirming a severe bottleneck before splitting into haplogroups G1 and G2. G1might have originated around modern Iran around 26,000 years ago. G2 would have developed around the same time in West Asia and haplogroup G2 appear to have been closely linked to the development of early agriculture in the Fertile Crescent part, around 11,500 years before present. G2a branch expanded to Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Europe, while G2b diffused from Iran across the Fertile Crescent and east to Pakistan. There has so far been ancient Y-DNA analysis from Early Neolithic Anatolia, Iran, Israel, Jordan as well as most Neolithic cultures in Europe (Thessalian Neolithic in Greece, Starčevo culture in Hungary/Croatia, LBK culture in Germany, Remedello in Italy, and Cardium Pottery in south-west France and Spain) and all sites yielded a majority of G2a individuals, except those from the Levant. This strongly suggests that farming was disseminated by members of haplogroup G at least from Anatolia/Iran then moved to Europe. 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, and found one G2b sample dating from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic (9,250 years ago) and a G2a1 from the Early Pottery Neolithic (7,700 years ago), both from Iran. The highest genetic diversity within haplogroup G is found in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent, between the Levant and the Caucasus, which is a good indicator of its region of origin. Çatalhöyük in south-central Anatolia/Turkey was founded by farmers who also brought domesticated goats and sheep. Also around 8,500 years ago, G2a Neolithic farmers arrived in northwest Anatolia and Thessaly in central Greece, as attested by the ancient genomes around the time that it seems cattle domestication was introduced to Çatalhöyük and other sites in Central Anatolia, presumably by trading with their eastern neighbors. Ancient skeletons from the Starčevo–Kőrös–Criș culture (8,000-6,500 years ago) in Hungary and Croatia, and the Linear Pottery culture (7,500-6,500 years ago) in Hungary and Germany, all confirmed that G2a (both G2a2a and G2a2b) remained the principal paternal lineage even after farmers intermingled with indigenous populations as they advanced. G2a farmers from the Thessalian Neolithic quickly expanded across the Balkans and the Danubian basin, reaching Serbia, Hungary, and Romania by 7,800 years ago, Germany by 7,500 years ago, and Belgium and northern France by 7,200 years ago. By 7,800 years ago, farmers making cardial pottery arrived at the Marmara coast in northwest Anatolia with ovicaprids and pigs. These people crossed the Aegean by boat and colonized the Italian peninsula, the Illyrian coast, southern France and Iberia, where they established the Cardium Pottery culture (5000-1500 BCE). Once again, ancient DNA yielded a majority of G2a samples in the Cardium Pottery culture, with G2a frequencies above 80% (against 50% in Central and Southeast Europe). Nevertheless, substantial minorities of other haplogroups have been found on different Neolithic sites next to a G2a majority, including C1a2, H2, I*, I2a1, I2c, and J2a in Anatolia, C1a2, E-M78, H2, I*, I1, I2a, I2a1, J2 and T1a in Southeast and Central Europe (Starčevo, Sopot, LBK), as well as E-V13, H2, I2a1, I2a2a1 and R1b-V88 in western Europe (Cardium Pottery, Megalithic). H2 and T1a were found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levant and are undeniably linked to the early development of agriculture alongside G2a. That being said, C1a2 was also found in Mesolithic Spain and, as it is an extremely old lineage associated with the first Paleolithic Europeans, it could have been found all over Europe and Anatolia before the Neolithic. E1b1b was also found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levant, but the subclades may not be E-M78 or E-V13 (more likely E1b1b1* or E-M123). R1b-V88 surely spread from the Near East too, although through a different route, with cattle herders via North Africa, then crossing over to Iberia. The rest probably represent assimilated hunter-gatherers descended from Mesolithic western Anatolian (I*, I2c, J2) and Europeans (E-V13, I*, I1, I2a, I2a1, I2a2). It is interesting to note that many of these lineages, such as C1a2, H2 and I* are virtually extinct anywhere nowadays, and several others are now very rare in Europe (I2c, R1b-V88).” ref
Haplogroup J (mtDNA) and the Seeming Spread of Early Agriculture – “Samples have been identified from various Neolithic sites, including Linear Pottery culture (LBK) in Central Europe, the Cardium Pottery culture in southern France, Megalithic cultures in northern Spain, and the Funnelbeaker culture in Germany and Sweden. All Neolithic samples tested to date belonged to J1*, J1c or J2b1a. One question that follows is: did J1c and J2b1a lineages actually come from the Near East during the Neolithic, or whether they were already in the Balkans and just expanded from there? Both being rare in the Near East today, the second hypothesis might seem more convincing at first. However, the age of J2b1a has been estimated at 11,000 years before present, while the Neolithic started over 12,000 years ago in the Near East. In other words, it could have arrived from the Near East as J2b1* and developed into J2b1a only after reaching Europe, which would explain why this particular subclade is almost exclusively European while all other subclades of J2b1 are mostly Middle Eastern or the eastern Mediterranean. J2b1a would, therefore, have come as a maternal lineage of early agriculturalists alongside the paternal lineage G2a (and perhaps also E1b1b and T1a). J1c, however, is too old (15,000 years) for that scenario. If it had been part of the Neolithic expansion from the Fertile Crescent, many J1c subclades would be primarily West Asian today, which isn’t the case. The only J1c individuals outside Europe belong to deep clades that clearly originated in Europe or in Anatolia. DNA of Early Neolithic farmers from western Anatolia and from the Starcevo culture in Hungary and Croatia, and found that J1c was present in both cultures, alongside other typical European Neolithic lineages like H5, K1a, N1a, T2, and X2. Of 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, and well as Chalcolithic and Bronze Age samples from Armenia and the Levant, but did not find any J1c, apart from a single sample in Neolithic Iran. This suggests that J1c lineages were probably not found among the very first farmers of the Fertile Crescent but were rather assimilated in neighboring populations further north, notably in Anatolia and Iran, but probably also in the Balkans, which were connected to Anatolia by a land bridge during the glacial and immediate post-glacial periods. Haplogroup J has been found in Bronze Age samples from the Yamna culture (J2b), Corded Ware culture (J1c and J2b1a), the Catacomb culture (J1b1a1), the Unetice culture (J1b1a1), and the Urnfield culture (J1b1), all in Central Europe. The Corded Ware culture is associated with the expansion of Y-haplogroup R1a from the northern Russian steppe, and in light of the continuity with Neolithic samples from Central Europe it can be assumed that J1c and J2b1a maternal lineages were not brought by the newcomers, but absorbed by the male invaders. On the other hand, J1b has never been found in Europe before the Bronze Age and was very probably brought by the Indo-Europeans carrying R1b paternal lineages. Both the Unetice and the Urnfield cultures are thought to have been founded mainly by R1b men.” ref
* “paganist” Believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife who are guided/supported by a goddess/god or goddesses/gods (you are a hidden paganist/Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system) And Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” as well as Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” are both evidence of some kind of early paganism. early paganism is connected to Proto-Indo-European language and religion. Proto-Indo-European religion can be reconstructed with confidence such as the Gods and Goddesses, the myths, the festivals, and the form of rituals with invocations, prayers, and songs of praise that make up the spoken element of religion. Much of this activity is connected to the natural and agricultural year, or at least those are the easiest elements to reconstruct because nature doesn’t change and because farmers are the most conservative members of society and are best able to keep the old ways. Goddesses: There are at least 40 deities although the gods may be different than we think of and only evolved later to the ways we know. Such as, how a deity’s gender may not be a fixed characteristic since they are often deified forces of nature which tended to not have genders. Among the Goddesses reconstructed so far are: *Pria, *Pleto, *Devi, *Perkunos, *Aeusos and *Yama. Myths: There are at least 28 myths that can be reconstructed to Proto-Indo-European. Many of these myths have since been confirmed by additional research, including some in areas which were not accessible to the early writers, such as Latvian folk songs and Hittite hieroglyphic tablets. One of the most widely recognized myths of the Indo-Europeans is the myth in which *Yama is killed by his brother *Manu and the world is made from his body. Some of the forms of this myth in various Indo-European languages are given in this article about the Creation Myth of the Indo-Europeans. The Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is estimated to have been spoken as a single language from at around 6,500 years ago, the Kurgan hypothesis relating to the construction of kurgans (mound graves). The earliest kurgans date to the 6,000 years ago in the Caucasus and are associated with the Indo-Europeans. Kurgans were built in the Eneolithic, Bronze, Iron, Antiquity and Middle Ages, with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia. Kurgan cultures are divided archeologically into different sub-cultures, such as Timber Grave, Pit Grave, Scythian, Sarmatian, Hunnish, and Kuman–Kipchak. Kurgan barrows were characteristic of Bronze Age peoples, and have been found from the Altay Mountains to the Caucasus, Ukraine, Romania, and Bulgaria. Kurgans were used in the Ukrainian and Russian steppes, their use spreading with migration into eastern, central, and northern Europe in the around 5,000 yea5rs ago. Burial mounds are complex structures with internal chambers. Within the burial chamber at the heart of the Kurgan, elite individuals were buried with grave goods and sacrificial offerings, sometimes including horses and chariots. The structures of the earlier Neolithic period from the 4th to the 3rd millenniums BC, and Bronze Age until the 1st millennium BC, display continuity of the archaic forming methods. They were inspired by common ritual-mythological ideas.Whereas, the Anatolian hypothesis suggests that the speakers of Pre-Proto-Indo-European to the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) lived in Anatolia during the Neolithic era, and it associates the distribution of historical Indo-European languages with the expansion during the Neolithic revolution around 9,000 years ago, with a proposed homeland of Proto-Indo-European proper in the Balkans around 7,000 years ago, which he explicitly identified as the “Old European culture“. This hypothesis states that Indo-European languages began to spread peacefully, by demic diffusion, into Europe from Asia Minor or Turkey, the Neolithic advance of farming (wave of advance). Accordingly, most inhabitants of Neolithic Europe would have spoken Indo-European languages, and later migrations would have replaced the Indo-European varieties with other Indo-European varieties. The expansion of agriculture from the Middle East would have diffused three language families: Indo-European toward Europe, Dravidian toward Pakistan and India, and Afro Asiatic toward Arabia and North Africa. Reconstructions of a Bronze Age PIE society, based on vocabulary items like “the wheel”, do not necessarily hold for the Anatolian branch, which appears to have separated at an early stage, prior to the invention of wheeled vehicles. The Proto-Indo-European Religion seemingly stretches at least back around 6000 years ago or likely much further back I believe possibly an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
- “12,000 years ago: Jericho has evidence of settlement dating back to 10,000 BC. Jericho was a popular camping ground for Natufian hunter-gatherer groups, who left a scattering of crescent microlith tools behind them.
- 12,000 years ago: Earliest dates suggested for the domestication of the goat.
- 11,600 years ago: Start of the current Holocene epoch.
- 11,000 -12,00/13,000 years ago (9,000 BC): Earliest date recorded for construction of temenoi ceremonial structures at Göbekli Tepe in southern Turkey, as possibly the oldest surviving proto-religious site on Earth.
- 11,000 years ago: Emergence of Jericho, which is now one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Giant short-faced bears and giant ground sloths go extinct. Equidae goes extinct in North America.
- 10,500 years ago: Earliest supposed date for the domestication of cattle.
- 10,000 years ago: The Quaternary extinction event, which has been ongoing since the mid-Pleistocene, concludes. Many of the ice age megafauna go extinct, including the megatherium, woolly rhinoceros, Irish elk, cave bear, cave lion, and the last of the sabre-toothed cats. The mammoth goes extinct in Eurasia and North America, but is preserved in small island populations until ~1650 BC.
- 11,000 – 9,000 years ago: Byblos appears to have been settled during the PPNB period, approximately 8800 to 7000 BC. Neolithic remains of some buildings can be observed at the site.
- 10,000 – 8,000 years ago: The post-glacial sea level rise decelerates, slowing the submersion of landmasses that had taken place over the previous 10,000 years.
- 10,000 – 9,000 years ago: In northern Mesopotamia, now northern Iraq, cultivation of barley and wheat begins. At first they are used for beer, gruel, and soup, eventually for bread. In early agriculture at this time, the planting stick is used, but it is replaced by a primitive plow in subsequent centuries. Around this time, a round stone tower, now preserved to about 8.5 meters high and 8.5 meters in diameter is built in Jericho.
- 9,500–5,900 years ago: Neolithic Subpluvial in North Africa. The Sahara desert region supports a savanna-like environment. Lake Chad is larger than the current Caspian Sea. An African culture develops across the current Sahel region.
- 9,500 years ago: Çatalhöyük urban settlement founded in Anatolia. Earliest supposed date for the domestication of the cat.
- 9,200 years ago: First human settlement in Amman, Jordan; ‘Ain Ghazal Neolithic settlement was built spanning over an area of 15 hectares.
- 9,000 years ago: Jiahu culture began in China.
- 9,000 years ago: large first fish fermentation in southern Sweden.
- 8,200–8,000 years ago: 8.2 kiloyear event: a sudden decrease of global temperatures, likely caused by the final collapse of the Laurentide Ice Sheet, which leads to drier conditions in East Africa and Mesopotamia.
- 8,000-5,000 years ago: development of proto-writing in China, Southeast Europe (Vinca symbols) and West Asia (proto-literate cuneiform).
- 8,000 years ago: Evidence of habitation at the current site of Aleppo dates to about c. 8,000 years ago, although excavations at Tell Qaramel, 25 kilometers north of the city show the area was inhabited about 13,000 years ago, Carbon-14 dating at Tell Ramad, on the outskirts of Damascus, suggests that the site may have been occupied since the second half of the seventh millennium BC, possibly around 6300 BC. However, evidence of settlement in the wider Barada basin dating back to 9000 BC exists.
- 7,500 years ago: Copper smelting in evidence in Pločnik and other locations.
- 7,200–6,000 years ago: 5200–4000 BC:Għar Dalam phase on Malta. First farming settlements on the island.
- 6,100–5,800 years ago: Żebbuġ phase. Malta.
- 6,070–6,000 years ago: Trypillian build in Nebelivka (Ukraine) settlement which reached 15,000—18,000 inhabitants.
- 6,500 years ago: The oldest known gold hoard deposited at Varna Necropolis, Bulgaria.
- 6,000 years ago: Civilizations develop in the Mesopotamia/Fertile Crescent region (around the location of modern-day Iraq). Earliest supposed dates for the domestication of the horse and for the domestication of the chicken, invention of the potter’s wheel.
- 5,900 years ago: 5.9 kiloyear event: a rapid and intense aridification event, which likely started the current Sahara Desert dry phase and a population increase in the Nile Valley due to migrations from nearby regions. It is also believed this event contributed to the end of the Ubaid period in Mesopotamia.
- 5,800 years ago: The Post Track and Sweet Track causeways are constructed in the Somerset Levels.
- 5,800 years ago: Trypillian build in Talianki (Ukraine) settlement which reached 15,600—21,000 inhabitants.
- 5,800–5,600 years ago: Mġarr phase A short transitional period in Malta’s prehistory. It is characterized by pottery consisting of mainly curved lines.
- 5,700 years ago: starts mass graves at Tell Brak in Syria.
- 5,700 years ago: Trypillian build in Maidanets (Ukraine) settlement which reached 12,000—46,000 inhabitants and built 3-story building.
- 5,700 years ago: Minoan culture begins on Crete.
- 5,600–5,200 years ago: Ġgantija phase on Malta. Characterized by a change in the way the prehistoric inhabitants of Malta lived.
- 5,500 years ago: Uruk period in Sumer. The first evidence of mummification in Egypt.
- 5,500 years ago: the oldest known depiction of a wheeled vehicle (Bronocice pot, Funnelbeaker culture)
- 5,300 years ago: Bronze Age begins in the Near East, Newgrange is built in Ireland. Hakra Phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins in the Indian subcontinent.
- 5,300–5,000 years ago: Saflieni phase in Maltese prehistory.” ref
Invasion vs. diffusion scenarios?
Genetic analyses shows that 7,000-8,000 years ago, a closely related group of early farmers moved into Europe from the Near East, confirming the findings of previous studies. According to the “Anatolian hypothesis“, Indo-European languages were spread by the first farmers from the Near East 7,000-8,000 years ago. the “Steppe/Kurgan hypothesis“, which proposes that early Indo-European speakers were farmers on the grasslands north of the Black and Caspian Seas. Anthony’s “Revised Steppe Theory”, which David Anthony‘s The Horse, the Wheel and Language describes his “Revised Steppe Theory”. David Anthony considers the term “Kurgan culture” so lacking in precision as to be useless, instead of using the core Yamna culture and its relationship with other cultures as a point of reference. He points out that the Kurgan culture | prehistoric culture was so broadly defined that almost any culture with burial mounds, or even (like the Baden culture) without them could be included. He does not include the Maykop culture among those that he considers being IE-speaking, presuming instead that they spoke a Caucasian language.
Kurgans 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory or Kurgan model) or steppe theory is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian kurgan, meaning tumulus or burial mound.
Researchers have identified a massive migration of Kurgan populations (Yamna culture) which went from the Russian steppes to the center of Europe some 4,500 years ago, favoring the expansion of Indo-European languages throughout the continent.
This was a time of astonishing creativity as city-states and empires emerged in a vast area stretching from the Mediterranean to the Indus Valley. The previous millennium had seen the emergence of advanced, urbanized civilizations, new bronze metallurgy extending the productivity of agricultural work, and highly developed ways of communication in the form of writing. In the 3rd millennium BC, the growth of these riches, both intellectually and physically, became a source of contention on a political stage, and rulers sought the accumulation of more wealth and more power. Along with this came the first appearances of mega-architecture, imperialism, organized absolutism and internal revolution. The civilizations of Sumer and Akkad in Mesopotamia became a collection of volatile city-states in which warfare was common. Uninterrupted conflicts drained all available resources, energies and populations. In this millennium, larger empires succeeded the last, and conquerors grew in stature until the great Sargon of Akkad pushed his empire to the whole of Mesopotamia and beyond. It would not be surpassed in size until Assyrian times 1,500 years later. In the Old Kingdom of Egypt, the Egyptian pyramids were constructed and would remain the tallest and largest human constructions for thousands of years. Also in Egypt, pharaohs began to posture themselves as living gods made of an essence different from that of other human beings. Even in Europe, which was still largely neolithic during the same period, the builders of megaliths were constructing giant monuments of their own. In the Near East and the Occident around 5,000 years ago and religion developed and advanced to roughly the ways we are somewhat familiar to a large amount, limits were being pushed by architects and rulers. Towards the close of the millennium, Egypt became the stage of the first popular revolution recorded in history. After lengthy wars, the Sumerians recognized the benefits of unification into a stable form of national government and became a relatively peaceful, well-organized, complex technocratic state called the 3rd dynasty of Ur. This dynasty was later to become involved with a wave of nomadic invaders known as the Amorites, who were to play a major role in the region during the following centuries. In the Near East and the Occident during the around 5,000 years ago and religion developed and advanced to roughly the ways we are somewhat familiar to a large amount, limits were being pushed by architects and rulers. Towards the close of the millennium, Egypt became the stage of the first popular revolution recorded in history. After lengthy wars, the Sumerians recognized the benefits of unification into a stable form of national government and became a relatively peaceful, well-organized, complex technocratic state called the 3rd dynasty of Ur. This dynasty was later to become involved with a wave of nomadic invaders known as the Amorites, who were to play a major role in the region during the following centuries. ref
Stars: Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities (at least back to around 6,000 years ago)
- 5,750 years ago: The Proto-Semitic people emerged from a generally accepted urheimat in the Levant. The Proto-Semitic people would migrate throughout the Near East into Mesopotamia, Egypt, Ethiopia and the eastern shore of the Mediterranean.
- 5,700 years ago: Lothal: Indus Valley trade-port city in India.
- 5,650 years ago: Minoan culture appeared on Crete.
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- 5,300 years ago: The Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilization (3300–1300 BCE; mature period 2600–1900 BCE) in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, noted for its cities built of brick, roadside drainage system and multi-storeyed houses, as well as for creating artifacts which could be linked to pre-vedic religions.
- 5,200 years ago: Helladic culture and Cycladic culture both emerge in Greece.
- 5,102 years ago: This was the beginning of Kaliyuga, a new age among the followers of Indian religions.
- 5,100 years ago: The initial form of Stonehenge was completed. The circular bank and ditch enclosure, about 110 metres (360 ft) across, may have been completed with a timber circle.
- 5,100 years ago: Newgrange, the 250,000 ton (226,796.2 tonne) passage tomb aligned to the winter solstice in Ireland, was built.
- 5,000 years ago: Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt.
- 5,000 years ago: First evidence of gold being used in the Middle East.
- 5,000 years ago: Vessels from Denmark
- 5,000 years ago: Sumerian Cuneiform emerged from the proto-literate Uruk period, allowing the codification of beliefs and creation of detailed historical religious records.
- 5,000 years ago: The second phase of Stonehenge was completed and appeared to function as the first enclosed cremation cemetery in the British Isles.
- 4,900 years ago: Beginning of the Early Dynastic Period I in Sumer.
- 4,900 years ago: Sumerianpictographs evolve into phonograms.
- 4,900 years ago: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period.
- 4,900 years ago: Votive statues from the Square Temple of Eshnunna (modern Tell Ashmar, Iraq) were made.
- 4,900 years ago: Syria: Foundation of the city of Mari.
- 4,900 years ago: Semitic tribes occupy Assyria in northern part of the plain of Shinar and Akkad.
- 4,900 years ago: Phoenicians settle on Syrian coast, with centers at Tyre and Sidon.
- 4,900 years ago: Beginning of the period of the Sage Kings in China, also known as the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors.
- 4,900 years ago: Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- 4,879 years ago: Rise of the Văn Lang Kingdom and the Hồng Bàng Dynasty in northern Viet Nam.
- 4,874 years ago: The 365-day calendar year was installed in ancient Egypt
- 4,852 years ago: The beginning of the period of the Three August Ones and Five Emperors in China.
- 4,832 years ago: Estimated germination of the Methuselah Tree, the oldest known living organism
- 4,807 years ago: Suggested date for an asteroid or comet impact occurring between Africa and Antarctica, around the time of a solar eclipse on May 10, based on an analysis of flood stories. Possibly causing the Burckle crater and Fenambosy Chevron.
- 4,800 years ago: Ur becomes one of the richest cities in Sumer
- 4,800 years ago: Harp Player, from Keros, Cyclades, was made. It is now at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
- 4,800 years ago: Iran: Creation of the Kingdom of Elam.
- 4,800 years ago: Seated Harp Player, from Keros, Cyclades, is made.
- 4,775 years ago: Second Dynasty wars in Ancient Egypt.
- 4,773 years ago: the 365-day calendar is introduced in Egypt.
- 4,750 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic I Period, and the beginning of the Early Dynastic II Period in Mesopotamia.
- 4,750 years ago: Estimated ending of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture in the region of modern-day Romania, Moldova, and southwestern Ukraine
- 4,700 years ago: Germination of the Bristlecone pine tree “Methuselah“, one of the oldest known trees still living now.
- 4,700 years ago: Merit-Ptah is world’s first female physician mentioned by name.
- 4,700 years ago: Old Kingdom of Egypt begins. 3rd–6th Dynasties.
- 4,700 years ago: Mesoamericans begin to plant and domesticate maize.
- 4,697 years ago: The Yellow Emperor starts to reign in China.
- 4,685 years ago: Bull lyre from the tomb of Queen Puabi, Ur (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) was made.
- 4,640 years ago: The cultivation and weaving of silk starts to be a closely guarded secret in China.
- 4,630 years ago: Imhotep, Vizier of Egypt, constructs the Pyramid of Djoser The Djoser pyramid is a step pyramid (or proto-pyramid) is considered to be the earliest large-scale cut stone construction and was thought to function in both life and the afterlife, which was sealed with a 3.5 ton block after the burial. The symbolism of the step pyramid form, which did not survive the 3rd Dynasty, is unknown, but it has been suggested that it may be a monumental symbol of the crown, especially the royal mortuary cult, since seven small step pyramids (not tombs) were built in the provinces.
- 4,627 years ago: Construction of the Caral metropolis in Peru
- 4,600 years ago: Mature Harappan phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins. The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro become large metropolises and the civilization expands to over 2,500 cities and settlements across the whole of Pakistan, much of northern India, and parts of Afghanistan and Iran, covering a region of around one million square miles, which was larger than the land area of its contemporaries Egypt and Mesopotamia combined, and also had superior urban planning and sewage systems. The civilization began using the mature Indus script for its writing system.
- 4,600 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic II Period and the beginning of the Early Dynastic IIIa Period in Mesopotamia.
- 4,600 years ago: Founding of the Chalcolithic Iberian civilizations of Los Millares and Zambujal.
- 4,600 years ago: the Indus Valley Civilisation rises to become a powerful civilization.
- 4,600 years ago: Pre-Palace Period, phase I, in Crete
- 4,600 years ago: Wild horses still provide hunting feasts in Denmark. (Clutton-Brock)
- 4,600 years ago: Large water tank, possibly a public or ritual bathing area, Mohenjo-daro, Indus Valley Civilisation, is made.
- 4,600 years ago: Butmir culture existed in Butmir, near Ilidža, Bosnia and Herzegovina, dating from the Neolithic. It is characterized by its unique pottery, and is one of the best researched European cultures from 2600-2400 BC.
- 4,600 years ago: Unified Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 4,550 years ago: Estimated date of completion of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
- 4,550 years ago: Mesannepada is king of Ur (followed by his son, A-annepadda) who founds the First Dynasty of Ur and overthrows the last king of Uruk, as well as Mesilim of Kish.
- 4,550 years ago:: Great Lyre with bull’s head, from the tomb of King Meskalamdug, Ur (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) is made.
- 4,500 years ago: Excavation and development of the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni at Paola, Malta, a subterranean temple complex subsequently used as a necropolis.
- 4,500 years ago: The legendary line of Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors of China is founded by the Yellow Emperor.
- 4,500 years ago: the construction of the stone circle at Stonehenge begins and continues for the next five hundred years.
- 4,500 years ago: Rice was first introduced to Malaysia
- 4,500 years ago: Scribal schools flourish throughout Sumer.
- 4,500 years ago: Assyria is established.
- 4,500 years ago: Cylinder seal from Sumer and its impression are made. It is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
- 4,500 years ago: Excavation and development of the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni at Paola, Malta, a subterranean temple complex subsequently used as a necropolis.
- 4,500 years ago: Valley Temple of Khafra, Giza, is built.
- 4,500 years ago: Khafra from Giza Valley, Temple of Khafra is made. Fourth Dynasty of Egypt. Discovered by Auguste Mariette. It is now kept in Egyptian Museum, Cairo.
- 4,500 years ago: Mohenjo-daro is about 7 square miles (18 km2) in size and has a population of c. 20,000 to 50,000.
- 4, 500 years ago: Incised panel “Frying pan”, from Syros, Cyclades is made.
- 4,500 years ago: Two figures of women, from the Cyclades, are made.
- 4,494 years ago: End of Fourth Dynasty, start of Fifth Dynasty in Egypt. Construction of the Pyramids begins.
- 4,494 years ago: “Sculptors at work”, relief from Saqqara, Fifth Dynasty. It is now at Egyptian Museum, Cairo, Egypt.
- 4,494 years ago: The Seated Scribe, a sculpture found at Saqqara, Fifth Dynasty of Egypt is made.
- 4,494 years ago: The first of the oldest surviving religious texts, the Pyramid Texts, was composed in Ancient Egypt.
- 4,492 years ago: Traditional date for the legendary foundation of Armenia by Hayk.
- 4,492 years ago: The Armenian patriarch Hayk defeats the Babylonian king Bel (legendary account) and Hayk founds Armenia.
- 4,474 years ago: Golden age of Ur in Mesopotamia.
- 4,450 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic IIIa Period and beginning of the Early Dynastic IIIb Period in Sumer.
- 4,450 years ago: Kish is lost to Hamazi tribesmen of the Kurdistan mountains; Elam under the Awan dynasty occupies parts of Sumer.
- 4,419 years ago: Neferefre is pharaoh
- 4,410 years ago: By this time, kings in Sumer have ceased to be automatically high priests of the city deity. Infiltration and conquest of Mesopotamia by ancient Semitic-speaking peoplesbegins.
- 4,400 years ago: Construction of Stonehenge
- 4,400 years ago: Megalithic culture begins to spread through Europe and the western Mediterranean.
- 4,400 years ago: Earliest signs of Corded Ware culture from the Caucasus.
- 4,400 years ago: Southeastern Spain is settled from the Mediterranean, by people using Prehistoric Egyptian-style pottery.
- 4,400 years ago: Amorites and Canaanites occupy Syria and Lebanon.
- 4,334 years ago: Sargon of Akkad conquers Mesopotamia, establishing the Akkadian Empire.
- 4,334 years ago: City of Lothal founded under the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 4,333 years ago: According to the Korean creation story, Dangun Wanggeom established the first Korean Empire, Gojoseon
- 4,300 years ago: C-Group pastoralists arrive in Nubia.
- 4,300 years ago: Megalithic, Corded Ware culture and the Beaker flourish in Europe.
- 4,300 years ago: Sumerian poetry, lamenting the death of Tammuz, the shepherd god.
- 4,300 years ago: Sumerian cuneiform writing reduces pictographs still in use to about 550 BC.
- 4,300 years ago: Major religious festival in Sumeria celebrates the victory of god of spring over goddess of chaos.
- 4,300 years ago: Earliest Trojan culture.
- 4,300 years ago: Beginning of the Pengtoushan culture in China.
- 4,300 years ago: Indus Valley Civilization (Harappan) flourishing in modern day eastern Pakistan – western India.
- 4,300 years ago: Metals start to be used in Northern Europe.
- 4,300 years ago: Unetice culture emerges in the modern day Czech Republic.
- 4,300 years ago: Disk of Enheduanna, from Ur, (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) is made.
- 4,300 years ago: “Head of a man from Nineveh” (modern Kuyunjik, Iraq) is made.
- 4,285 years ago: Enheduanna, high priestess of the moon god Nanna in Ur, was born.
- 4,254 years ago: Stela of Naram-Sin, probably from Sippar, discovered in Susa (modern Shush, Iran), is made.
- 4,250 years ago: Earliest evidence of maize cultivation in Central America.
- 4,240 years ago: Akkad, capital of the Akkadian Empire, becomes the largest city in the world, surpassing Memphis, capital of Egypt.
- 4,220 years ago: Scord of Brouster farmstead established in Shetland, Scotland
- 4.2 kiloyear event– a severe aridification event that probably lasted the entire 22nd century BC and caused the collapse of several Old World civilizations.
- 4,217 years ago: Nomadic invasions of Akkad.
- 4,200 years ago: The Minoan Civilization developed in Crete. Citizens worshipped a variety of goddesses.
- 4,150 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh—originally titled He who Saw the Deep (Sha naqba īmuru) or Surpassing All Other Kings (Shūtur eli sharrī)—were written.
- 4,104 years ago: Approximate date of the Biblical flood according to the Hebrew Calendar.
- 4,070 years ago: Xia Dynasty, first Chinese dynasty and government system established.
- 4,000 years ago: Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- 3,700 years ago: The oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,600 years ago: The ancient development of Stonehenge came to an end.
- 3,500 years ago: The Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 3,450 years ago: This is the traditionally accepted period in which, according to legend, the Israelite lawgiver Moses gave the Ten Commandments.
- 3,351 years ago: The reign of Akhenaten, sometimes credited with starting the earliest known recorded monotheistic religion, in Ancient Egypt
- 3,300 years ago: The “standard” Akkadian version of the Epic of Gilgamesh was edited by Sin-liqe-unninni.
- 3,250 years ago: The Upanishads (Vedic texts) were composed, containing the earliest emergence of some of the central religious concepts of Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“Religion is an Evolved Product”
Religions continuing in our modern world, full of science and facts, should be seen as little more than a set of irrational conspiracy theories of reality. Nothing more than a confused reality made up of unscientific echoes from man’s ancient past. Rational thinkers must ask themselves, why continue to believe in religions’ stories? Religion myths which are nothing more than childlike stories and obsolete tales once used to explain how the world works, acting like magic was needed when it was always only nature. These childlike religious stories should not even be taken seriously, but sadly too often they are. Often without realizing it, we accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives. In order to bring about awareness, we need to be willing to alter skewed beliefs. Rational thinkers must examine the facts instead of blindly following beliefs or faith.
Below is a collection of researched information such as archaeology, history, linguistics, genetics, art, science, sociology, geography, psychology, philosophy, theology, biology, and zoology. It will make you question your beliefs with information, inquiries, and ideas to ponder and expand on. The two main goals are to expose the evolution of religion starting 100,000 years ago and to offer challenges to remove the rationale of faith. It is like an intervention for belief in myths that have plagued humankind for way too long. We often think we know what truth is nevertheless this can be but a vantage point away from losing credibility if we are not willing to follow valid and reliable reason and evidence. The door of reason opens not once but many times. Come on a journey to free thought where the war is against ignorance and the victor is a rational mind.
If you are a religious believer, may I remind you that faith in the acquisition of knowledge is not a valid method worth believing in. Because, what proof is “faith”, of anything religion claims by faith, as many people have different faith even in the same religion?
Religious Sexism
- Speech on the Evolution of Religion & Religious Sexism
- Sexism in the Major World Religions
- Sexism in the BIBLE: chapter and verse!
- Sexism in Christianity (New Testament)
- Sexism in Judaism (old Testament)
- Sexism in Islam? Face Covering: Religious Freedom or Religious Oppression
- Sexism in Islam
- Sexism in Protestantism
- Sexism in Catholicism
- Sexism in Mormonism
- Sexism in Jehovah Witness
- Sexism in Bahaism
- Sexism in Sikhism
- Sexism in Confucianism
- Sexism in Taoism
- Sexism in Jainism
- Sexism in Shintoism
- Sexism in Buddhism
- Sexist Buddha
- Sexism in Hinduism
- Taoism yang and yin is very sexist
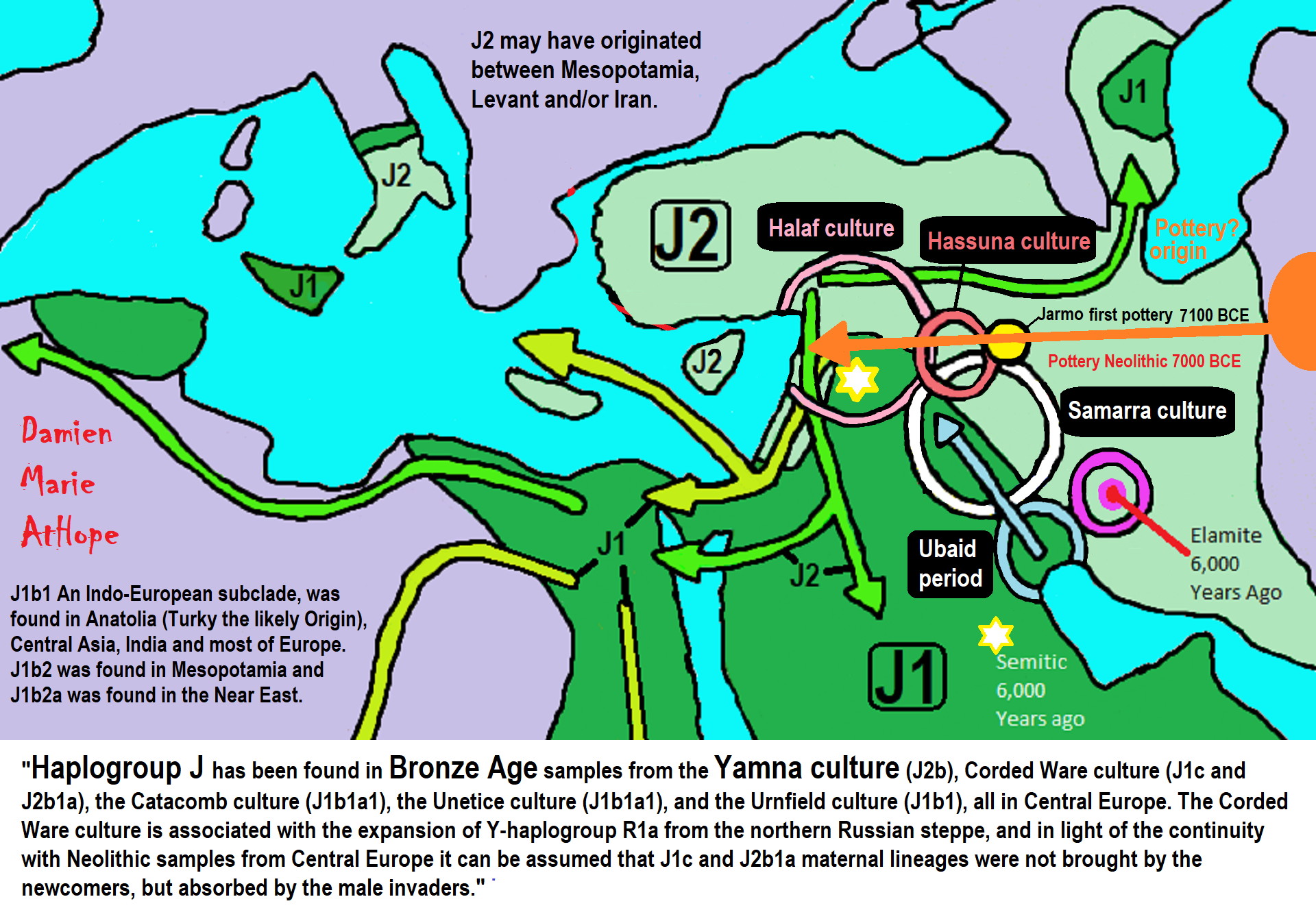

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
12 Powerful Women that Held the Position of Rulers/Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt
Here are the names and possible dates for these women who may have been rulers. 1. Queen Meryt-Neith ruled 5,020 years ago. 2. Queen Nimaathap (Third Dynasty, 4,706–4,633 years ago). 3. Queen Khentkaus (Fourth Dynasty, 4,633–4,514 years ago). 4. Queen Ankhesenpepi II (Sixth Dynasty, 4,385–4,201 years ago). 5. Princess Neithhikret (Died 4,201 years ago). 6. Princess-Queen Sobeknefru (Died 3,822 years ago). 7. Queen Ashotep (3,580–3,550 years ago). 8. Princess-Queen Ahmose-Nefertari (3,582–3,515 years ago). 9. Queen Hatshepsut (3,527–3,478 years ago). 10. Queen Nefertiti (3,390–3,350 years ago). 11. Queen Tausret (Died 3,209 years ago). 12. Queen Cleopatra I (2,224–2,196 years ago).

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
I think most represent a Goddess as well as it is possible, a some could relate to a Demi-goddesses/Grandmother-Mother Ancestor Spirits
“ A demigoddess or demi-goddess is a minor deity, or a mortal or immortal who is the offspring of a god and a human, or a figure who has attained divine status after death.” ref
Many figures were found in, under or in the walls or foundations of houses.
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in pagan religions as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, with examples including the Greek Hestia and Norse Frigg. The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism.” ref
“These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownieand Slavic Domovoy. Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“Sumerian religion was the religion practiced and adhered to by the people of Sumer, the first literate civilization of ancient Mesopotamia. The Sumerians regarded their divinities as responsible for all matters pertaining to the natural and social orders. Before the beginning of kingship in Sumer, the city-states were effectively ruled by theocratic priests and religious officials. Later, this role was supplanted by kings, but priests continued to exert great influence on Sumerian society. In early times, Sumerian temples were simple, one-room structures, sometimes built on elevated platforms.” ref
“The Sumerians believed that the universe had come into being through a series of cosmic births. First, Mother Goddess Nammu, the primeval waters, gave birth to An (the sky) and Ki (the earth), who mated together and produced a son named Enlil. Enlil separated heaven from earth and claimed the earth as his domain. Humans were believed to have been created by Enki, the son of An and Nammu. Heaven was reserved exclusively for deities and, upon their deaths, all mortals’ spirits, regardless of their behavior while alive, were believed to go to Kur, a cold, dark cavern deep beneath the earth, which was ruled by the goddess Ereshkigal and were the only food available was dry dust. In later times, Ereshkigal was believed to rule alongside her husband Nergal, the god of death.” ref
“Deities in ancient Mesopotamia were almost exclusively anthropomorphic, ( attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions). The Anunnaki were believed to be the offspring of An and his consort, the earth goddess Ki, has been identified with the Sumerian mother goddess Ninhursag, stating that they were originally the same figure. The oldest of the Anunnaki was Enlil, the god of air and chief god of the Sumerian pantheon. The deities typically wore melam, an ambiguous substance which “covered them in terrifying splendor”. Melamcould also is worn by heroes, kings, giants, and even demons. The effect that seeing a deity’s melam has on a human is described as ni, a word for the physical tingling of the flesh. Deities were almost always depicted wearing horned caps, consisting of up to seven superimposed pairs of ox-horns.” ref
“The ancient Mesopotamians believed that their deities lived in Heaven, but that a god’s statue was a physical embodiment of the god himself. As such, cult statues were given constant care and attention and a set of priests were assigned to tend to them. These priests would clothe the statues and place feasts before them so they could “eat”. A deity’s temple was believed to be that deity’s literal place of residence. The gods had boats, full-sized barges which were normally stored inside their temples and were used to transport their cult statues along waterways during various religious festivals. Virtually every major deity in the Sumerian pantheon was regarded as the patron of a specific city and was expected to protect that city’s interests. The deity was believed to permanently reside within that city’s temple.” ref
“One text mentions as many as fifty Anunnaki associated with the city of Eridu. In Inanna’s Descent into the Netherworld, there are only seven Anunnaki, who reside within the Underworld and serve as judges. Inannastands trial before them for her attempt to take over the Underworld; they deem her guilty of hubris and condemn her to death. Major deities in Sumerian mythology were associated with specific celestial bodies. Inanna was believed to be the planet Venus. In the mythologies of the Hurrians and Hittites (which flourished in the mid to late second millennium BC in Turkey not that far from Catal Huyuk), the oldest generation of gods was believed to have been banished by the younger gods to the Underworld, where they were ruled by the goddess Lelwani. Hittite scribes identified these deities with the Anunnaki. In ancient Hurrian, the Anunnaki are referred to as karuileš šiuneš, which means “former ancient gods”, or kattereš šiuneš, which means “gods of the earth. The old gods had no identifiable cult in the Hurrio-Hittite religion; instead, the Hurrians and Hittites sought to communicate with the old gods through the ritual sacrifice of a piglet in a pit dug in the ground. The old gods were often invoked to perform ritual purifications. ” ref
Grandmother-Mother Ancestor Spirits
“Ancestor worship is perhaps the world’s oldest religion. Some anthropologists theorize that it grew out of belief in some societies that dead people still exist in some form because they appear in dreams. Ancestor worship involves the belief that the dead live on as spirits and that it is the responsibility of their family members and descendants to make sure that they are well taken care of. If they are not they may come back and cause trouble to the family members and descendants that have ignored or disrespected them. Unhappy dead ancestors are greatly feared and every effort is made to make sure they are comfortable in the afterlife. Accidents and illnesses are often attributed to deeds performed by the dead and cures are often attempts to placate them.” ref
“In some societies, people go out of their way to be nice to one another, especially older people, out of fear of the nasty things they might do when they die. Ancestor worship is found in many forms in cultures throughout the world, Veneration of ancestors is regarded as a means through which an individual can assure his or her own immortality. Children are valued because they could provide for the spirits of their parents after death. Family members who remained together and venerated their forebears with strict adherence to prescribed ritual find comfort in the belief that the souls of their ancestors are receiving proper spiritual nourishment and that they are insuring their own soul’s nourishment after death.” ref
Goddesses/Demigoddesses/Grandmother-Mother Ancestor Spirits from Catal Huyuk?

Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük
“The Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük (also Çatal Höyük) is a baked-clay, nude female form, seated between feline-headed arm-rests. It is generally thought to depict a corpulent and fertile Mother goddess in the process of giving birth while seated on her throne, which has two hand rests in the form of feline (lioness, leopard, or panther) heads in a Mistress of Animals motif. The statuette, one of several iconographically similar ones found at the site, is associated to other corpulent prehistoric goddess figures, of which the most famous is the Venus of Willendorf. It is a neolithic sculpture shaped by an unknown artist, and was completed in approximately 6000 BCE.” ref
Kubaba
“Kubaba is the only queen on the Sumerian King List, which states she reigned for 100 years – roughly in the Early Dynastic III period (ca. 2500–2330 BCE) of Sumerian history. A connection between her and a goddess known from Hurro–Hittite and later Luwian sources cannot be established on the account of spatial and temporal differences. Kubaba is one of very few women to have ever ruled in their own right in Mesopotamian history. Most versions of the king list place her alone in her own dynasty, the 3rd Dynasty of Kish, following the defeat of Sharrumiter of Mari, but other versions combine her with the 4th dynasty, that followed the primacy of the king of Akshak. Before becoming monarch, the king list says she was an alewife, brewess or brewster, terms for a woman who brewed alcohol.” ref
“Kubaba was a Syrian goddess associated particularly closely with Alalakh and Carchemish. She was adopted into the Hurrian and Hittite pantheons as well. After the fall of the Hittite empire, she continued to be venerated by Luwians. A connection between her and the similarly named legendary Sumerian queen Kubaba of Kish, while commonly proposed, cannot be established due to spatial and temporal differences. Emmanuel Laroche proposed in 1960 that Kubaba and Cybele were one and the same. This view is supported by Mark Munn, who argues that the Phrygian name Kybele developed from Lydian adjective kuvavli, first changed into kubabli and then simplified into kuballi, and finally kubelli. However, such an adjective is a purely speculative construction.” ref
Cybele
“Cybele (Phrygian: “Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother”, perhaps “Mountain Mother”) is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forerunner in the earliest neolithic at Çatalhöyük, where statues of plump women, sometimes sitting, have been found in excavations. Phrygia‘s only known goddess, she was probably its national deity. Greek colonists in Asia Minor adopted and adapted her Phrygian cult and spread it to mainland Greece and to the more distant western Greek colonies around the 6th century BCE. In Greece, Cybele met with a mixed reception. She became partially assimilated to aspects of the Earth-goddess Gaia, of her possibly Minoan equivalent Rhea, and of the harvest–mother goddess Demeter. Some city-states, notably Athens, evoked her as a protector, but her most celebrated Greek rites and processions show her as an essentially foreign, exotic mystery-goddess who arrives in a lion-drawn chariot to the accompaniment of wild music, wine, and a disorderly, ecstatic following.” ref
“Uniquely in Greek religion, she had a eunuch mendicant priesthood. Many of her Greek cults included rites to a divine Phrygian castrate shepherd-consort Attis, who was probably a Greek invention. In Greece, Cybele became associated with mountains, town and city walls, fertile nature, and wild animals, especially lions. In Rome, Cybele became known as Magna Mater (“Great Mother”). The Roman State adopted and developed a particular form of her cult after the Sibylline oracle in 205 BCE recommended her conscription as a key religious ally in Rome’s second war against Carthage (218 to 201 BCE). Roman mythographers reinvented her as a Trojan goddess, and thus an ancestral goddess of the Roman people by way of the Trojan prince Aeneas. As Rome eventually established hegemony over the Mediterranean world, Romanized forms of Cybele’s cults spread throughout Rome’s empire. Greek and Roman writers debated and disputed the meaning and morality of her cults and priesthoods, which remain controversial subjects in modern scholarship.” ref
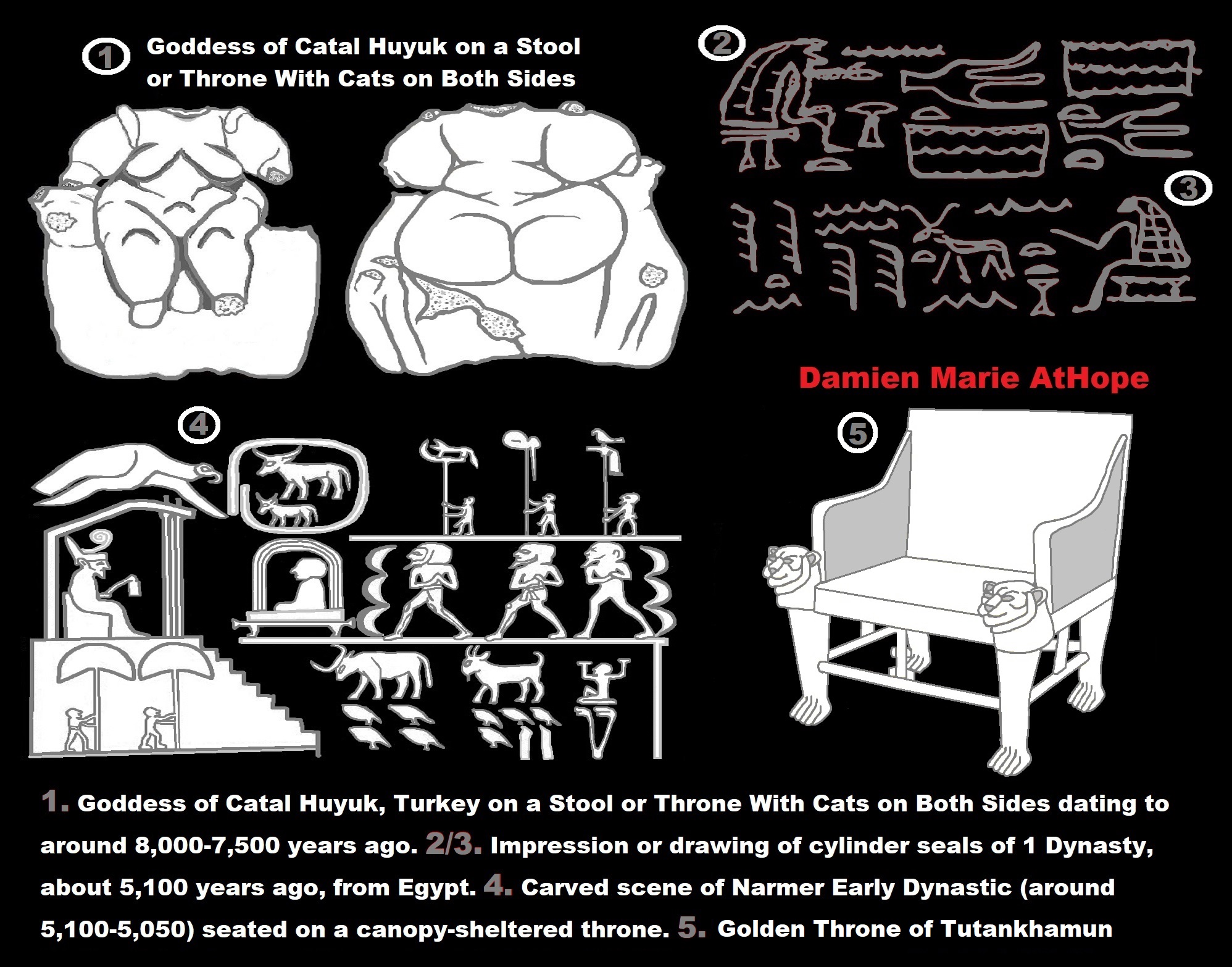
- Goddess of Catal Huyuk, Turkey on a Stool or Throne With Cats on Both Sides around 8,000-7,500 years ago.
- Impression or drawing of cylinder seals of 1 Dynasty, about 5,100 years ago, from Egypt.
- Impression or drawing of cylinder seals of 1 Dynasty, about 5,100 years ago, from Egypt.
- This carved scene pictures Narmer Early Dynastic (around 5,100-5,050) seated on a canopy-sheltered throne mounted on a high stepped dais, the successor to the Proto-dynastic king Ka, or possibly Scorpion.
- Throne for Tutankhamun
“The first piece of domestic furniture seen in use is the stool with a rectangular frame. It is found over and over again on early Egyptian cylinder seals. These seals, short and fat, usually of black steatite (soapstone), are peculiar to the earliest dynastic period 5,100 years ago. The inscriptions they bear – among the first exam-pies of writing – often give the name and title of some priest or official, followed by a group of signs that represent the deceased seated on a stool behind a pile of offerings (Figures 2, 3). For the stool, or the chair, has always been the mark of an important personage: it raises him above the level of his inferiors. (Most people in Egypt and other parts of the Near East seem to still sit/squatting on the ground) This sign, scarcely changing, remained the determinative for a person of rank in Egyptian hieroglyphic writing.” ref
“The stools on the seals are seen either from the side (Figure 2), or from the top (Figure 3) in what was to become a characteristic Egyptian mode of illustration: the representation of each separate part of the whole in its most recognizable aspect. Many of these early seals show a feature retained in pictures of stools throughout the dynastic period and much exaggerated in late times: the frames end in projections shaped like papyrus umbels, suggesting that the first Egyptian furniture was of wickerwork and that the frames were made of bundles of reeds bound together. Sometimes the legs of the stools shown on the seals were carved in the form of bulls’ legs.” ref
“And when the legs of lions began to replace those of bulls, about the end of the III Dynasty, the idea was similar: the sitter was to share the characteristic qualities of the King of Beasts; spool-like supports under the animal hooves or paws. Known as casters, even though rigid, they were always present with animal feet. Although, as one might expect, stools were made before chairs, there is a picture of a royal throne of about the same period as the cylinder seals. Narmer, the first king of Egypt, dedicated a giant mace head – symbolizing the weapon with which he had conquered his enemies and united Upper and Lower Egypt – in the temple at Hierakonpolis.” ref
‘One of the scenes carved on its surface pictures Narmer seated on a canopy-sheltered throne mounted on a high stepped dais (Figure 4). The throne seems to be a rectangular block scooped out to fit the king’s posterior and offer support for his back. But possibly he is really shown suspended, as it were, above curving arms, and this, accordingly, would be one of the first examples of the Egyptian artist’s reluctance to conceal any part of an object by another closer to the spectator. There is no indication of the material of the throne, but the dais, to judge by its Egyptian name, was of wood. A couch of the I Dynasty was actually more a commodious stool and several beds. The couch also has the familiar bull legs.” ref
“The stool, no matter how it is embellished, remains a raised seat without back or arms. But as early as the II Dynasty, officials, as well as kings, seemed to feel the need of support behind them, and the world’s first chairs were born. A hieroglyph in the pyramid of Pepi I of the 6th Dynasty (4,323-4,150 years ago) implies that his “shining throne” had lions’ heads and constitute the Old Kingdom of Dynastic Egypt with a pyramid built at Saqqara. (Figure 5) Arm panel of the throne of Tuthmosis iv, from his tomb, Thebes, xviii Dynasty, about 3,420 years ago, Cedar, height 94 inches.” ref
What is Isis’ Connection with the Throne?
“The symbol of the throne has an intimate connection with Isis because “Throne” is the meaning of Her name. The Great Goddess Isis is the Great Goddess Throne. Many Egyptologists explain this by saying that Isis was originally the personification of the royal throne.” ref
“It is certainly true that Isis was associated with the kingship—as were all the major Deities and most of the minor ones. The living king, seen as the embodiment of the God Horus, was considered the son of Isis (and of many other Goddesses). After death, the king became an Osiris so naturally Isis became his mourning widow. As the personification of the royal throne, Isis is the institution of the kingship itself. If we seek a feminist interpretation, we could rightly say that no king could take his place on the throne unless he had a close relationship with the Goddess Throne. To rule, the king must sit in the lap of the Goddess as Her child and husband.” ref
“Yet for me, this explanation of the origin of the Goddess Who is the greatest Goddess of Egypt—and arguably the greatest Goddess of all time—is bloodless and boring. And it is a vast understatement of the true meaning of the Throne.” ref
“As many readers know, Isis is the Greek version of the Goddess’ name. In Egyptian, She is Iset (Eset; Aset; Auset). One of the meanings of iset is throne. More generally, it means seat. The ancient Egyptians seemed to have had a flexible, idiomatic use for the word similar to its use in English. For example, when we say “he is in the seat of power,” we are not often referring to an actual seat, but mean that he is in charge. Similarly, iset smeter means judgment seat and the term referred to a tribunal of judges. Just as we say we have our heart set (a word that comes from seat) on something, the Egyptian wished for her iset ib—literally the seat of the heart—but meaning her heart’s desire.” ref
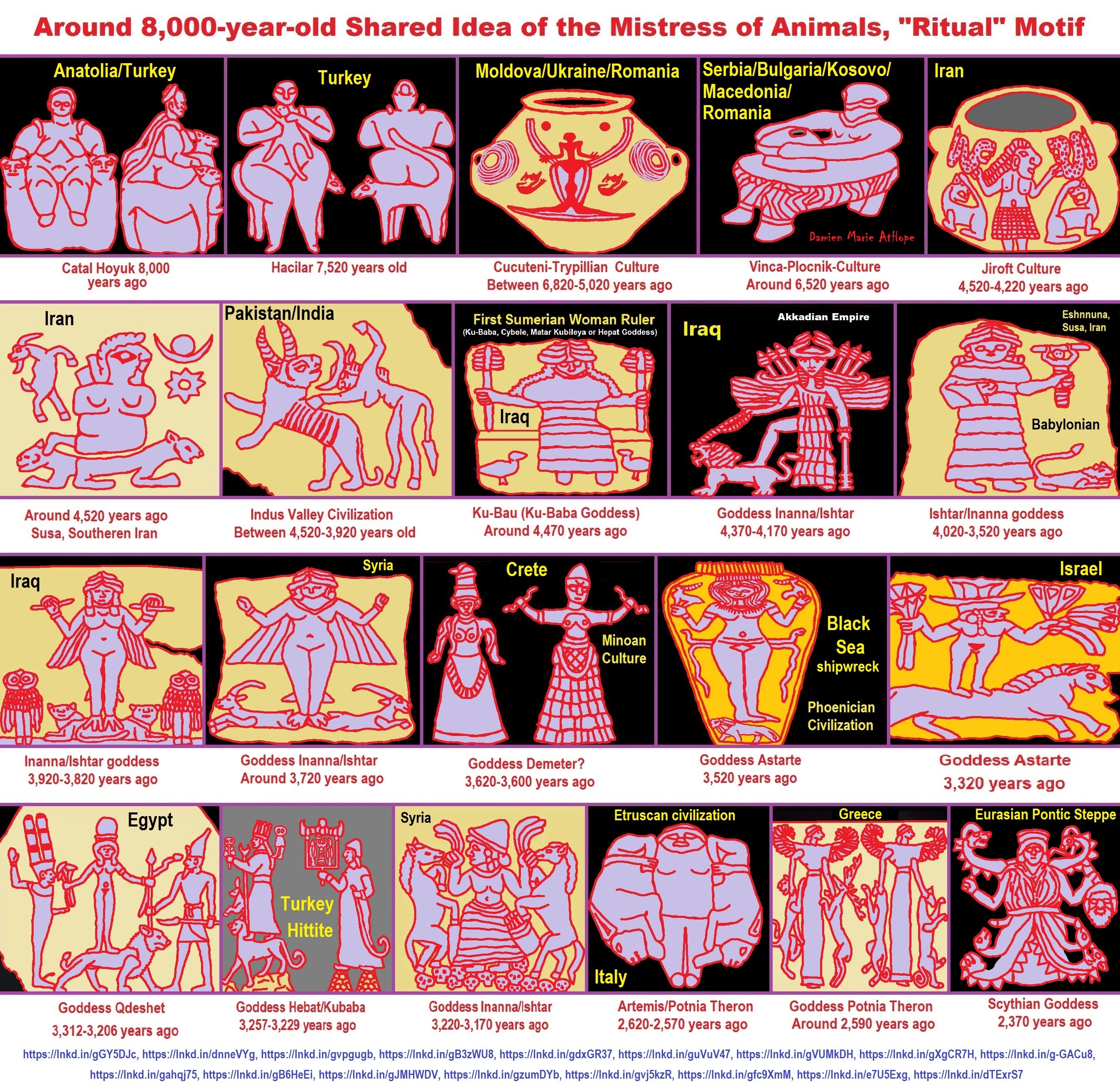
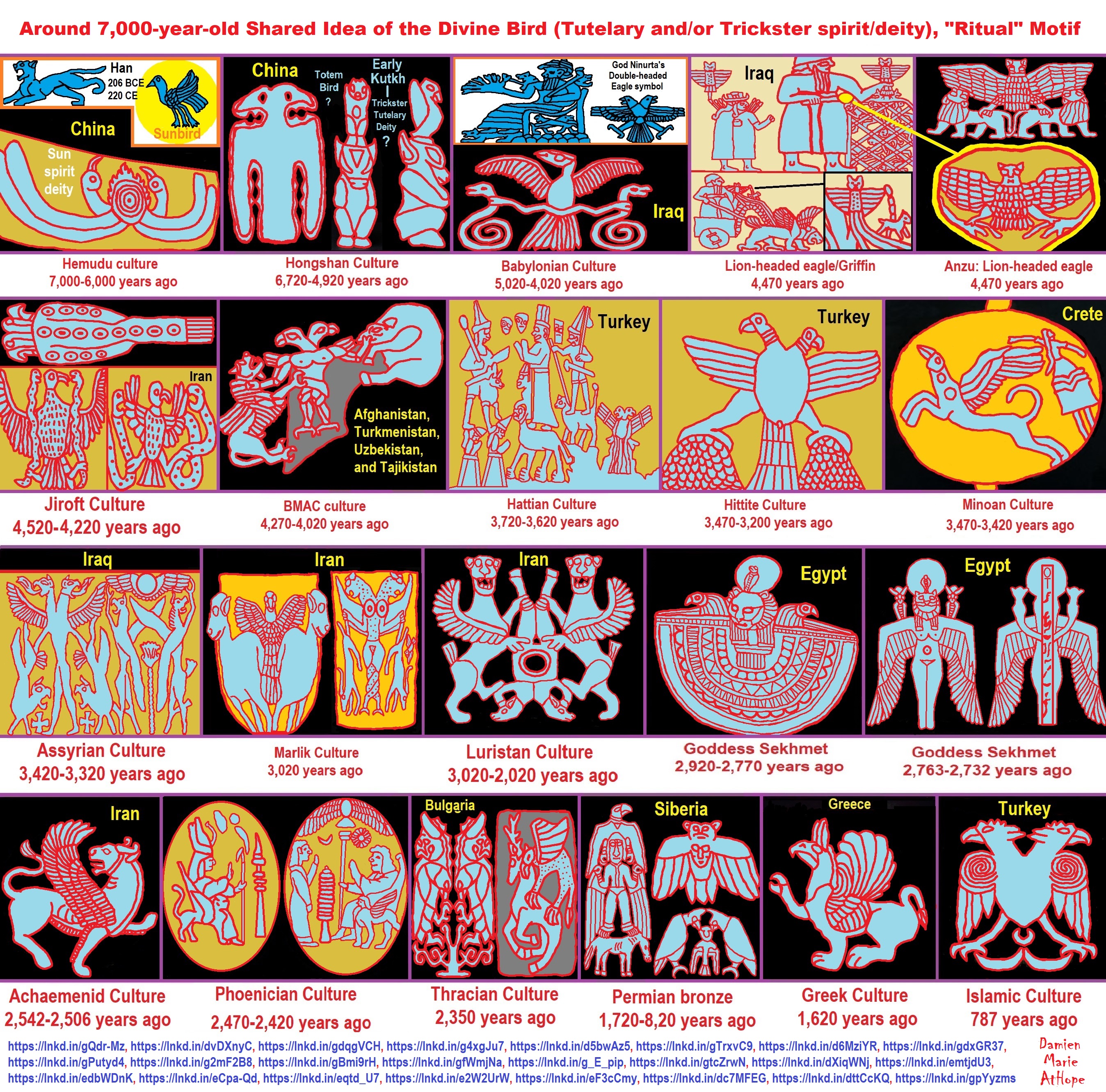
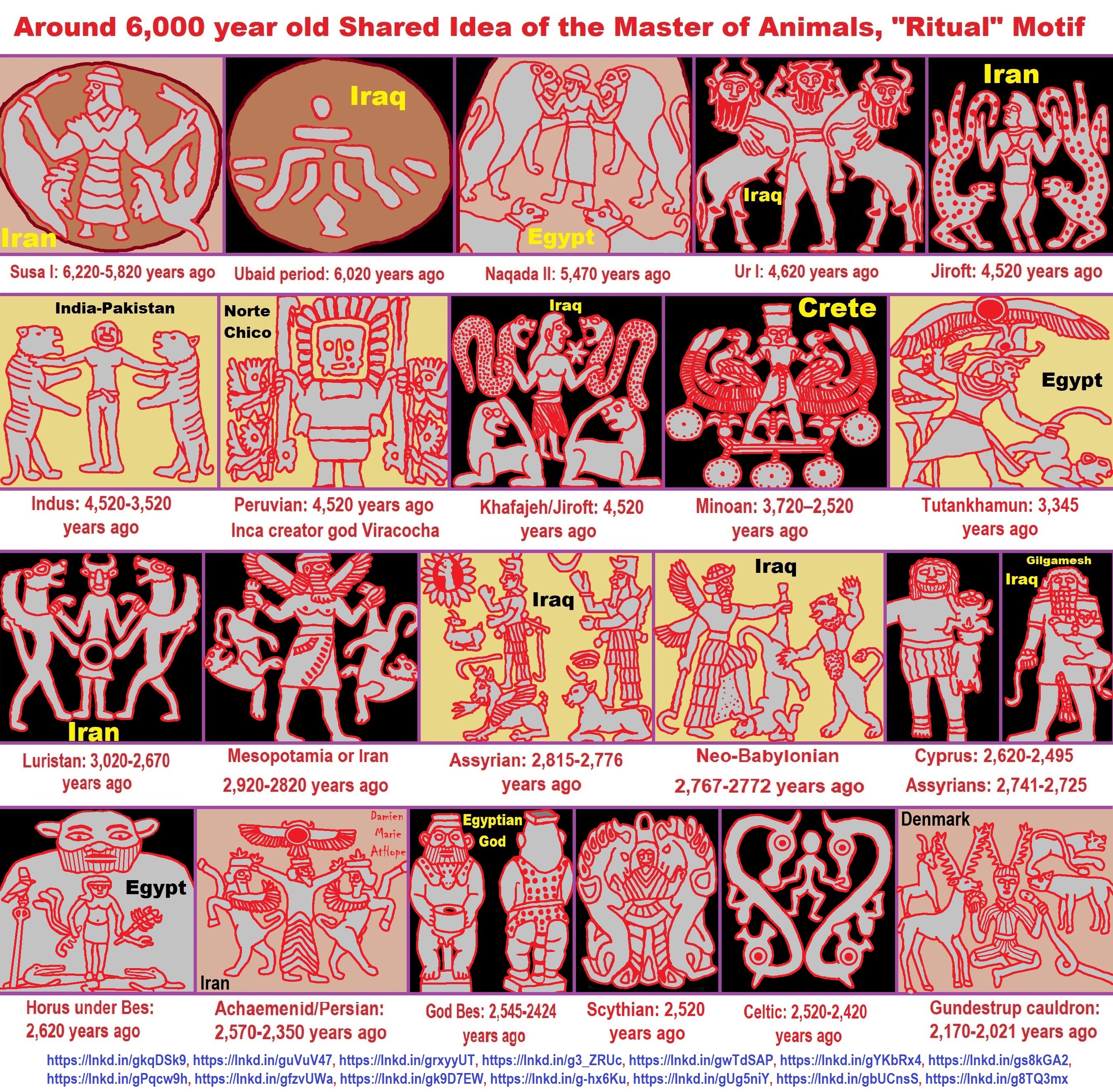
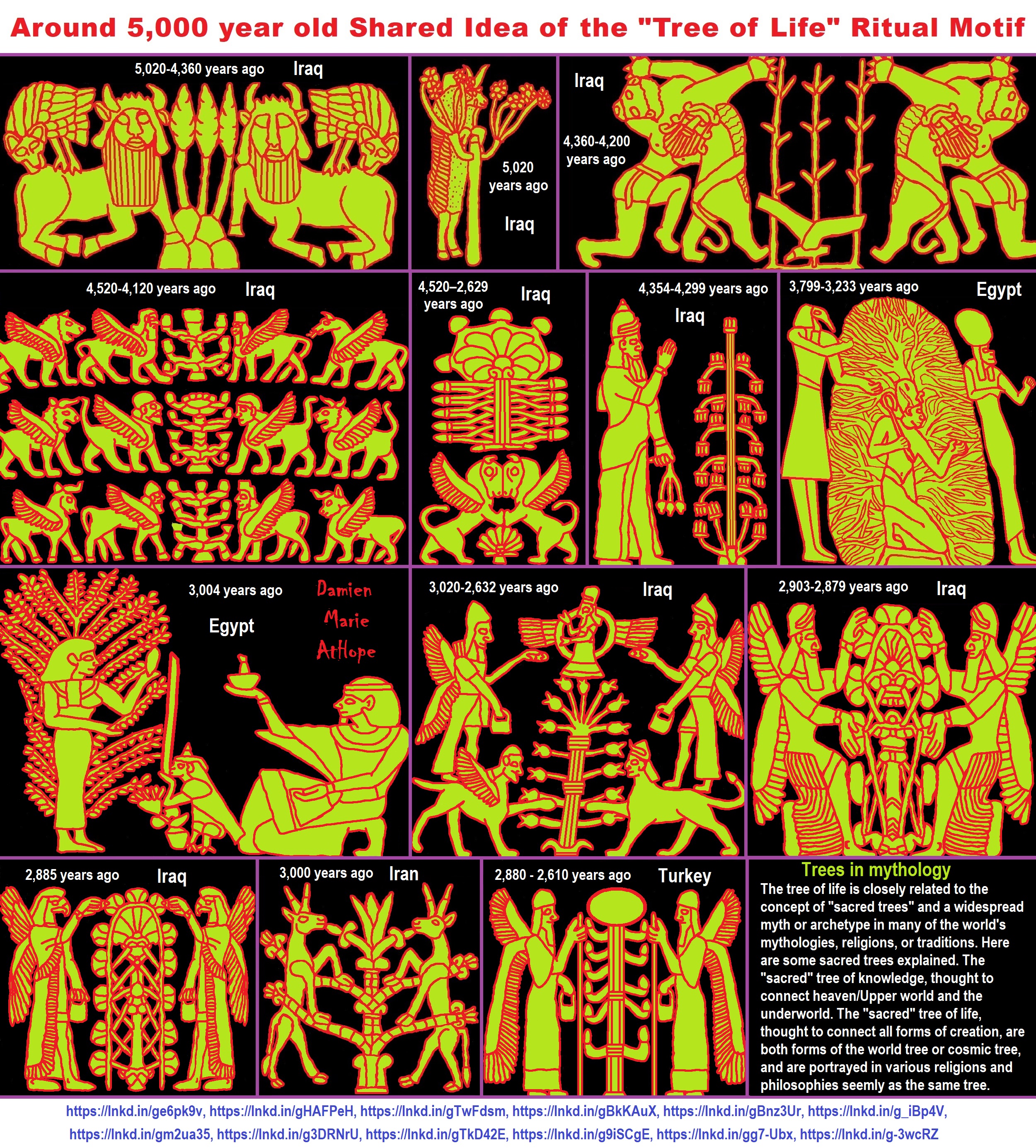


- From a Gerzeh/Naqada II Late Predynastic Egyptian palette with a goddess “Bat/Hathor” cow-head sun/stars motif.
- From a Hierakonpolis late Gerzeh/Naqada II Predynastic or early Naqada III Proto-Dynastic Egyptian porphyry fluted bowl with two reliefs on the rim, one of which was a goddess “Hathor/Bat” cow-head sun/stars motif.
- From an Abydos tomb, u-210 which held a small seal with a goddess “Bat/Hathor” sun/stars motif from the Gerzeh/Naqada II Late Predynastic Egyptian period.
- A Mongolian Copper Age bull sun/star shamanism petroglyph
- A Mongolian Bronze Age deer sun/star shamanism petroglyph symbol.
- A Kyrgyzstan Saimaly-Tash possibly Bronze Age shamanism cow-sun person symbol petroglyph.
- Similar X-ray style images among different peoples of the North from Siberia to Central Asia with shamanism petroglyphs of horned animals with sun symbols from possibly as old as the Neolithic to the Bronze Age. ref, ref, ref
REPRESENTATIONS OF BOVINES
“Representations of bovines in Predynastic art are frequently attested from Nagada I times onwards. We will first turn our attention to the more realistic images, although a clear distinction between ‘realistic’ and ‘stylized’ is not always possible. As will be discussed further, stylized elements may be combined with overall realistic representations. The earliest examples, probably all of them bulls, occur on White Cross-lined pottery, typical of Nagada IA-IIA times. Because of the rarity of White Cross-lined pottery with figurative decoration, it is not surprising that the corpus of examples is limited (Appendix A, nos. 1-5).” ref
“Modeled figurines of bulls were also attached to the rims of White Cross-lined pots (Appendix A, nos. 6-8). Although one could still claim that the fundamental reason for the depiction of bovines is to be found in the economic importance of the animals, these are evidently not merely representations illustrating economic wealth. Indeed, animals such as the hippopotamus and the crocodile figure more frequently on White Cross-lined pottery than bovines, and exceptionally even in combination with them. Although crocodile and hippopotamus could have been hunted for their meat, they are not of economic importance to farmers, but on the contrary extremely harmful for their crops.” ref
“Therefore, a more symbolic, probably religious and/or sociological interpretation for the bovines must be taken into consideration. Contemporaneous with the White Cross-lined pottery, a number of clay figurines of bovines is also known. The examples found at el-Amra (plates V, IX) are from a funerary context and date mainly to the Nagada I and early Nagada II period. Many of these figurines represent cows and calves and are probably not of great relevance for the present study, which will place the emphasis on bulls. A clay statuette of a bull has recently been found in the elite tomb U-235 at Abydos.” ref
In the shift from hunter-gather culture or in the emerging neolithic women may be hypothesized to typically relate the the concept of protectors. This is because, they do not just care/protect children but also can be said to stay and protect the crops from birds or care for or protect domesticated animals while the men hunt. So such thinking may be behind the goddess watching/protecting the hinters/hunting art from which seems to hold possible correlations in Egypt.
“The Red Crown frequently is mentioned in texts and depicted in reliefs and statues. An early example is the depiction of the victorious pharaoh wearing the deshret on the Narmer Palette. A label from the reign of Djer records a royal visit to the shrine of the Deshret which may have been located at Buto in the Nile delta. The fact that no crown has ever been found buried with any of the pharaohs, even in relatively intact tombs, might suggest that it was passed from one regent to the next, much as in present day monarchies. In mythology, the earth deity Geb, original ruler of Egypt, invested Horus with the rule over Lower Egypt. The Egyptian pharaohs, who saw themselves as successors of Horus, wore the deshret to symbolize their authority over Lower Egypt. Other deities wore the deshret too, or were identified with it, such as the protective serpent goddess Wadjet and the creator-goddess of Sais, Neith, who often is shown wearing the Red Crown.” ref
“The white crown, Hedjet (Ancient Egyptian: “White One”) is the formal name for the white crown of pharaonic Upper Egypt. After the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, it was combined with the deshret, the red crown of Lower Egypt, to form the pschent, the double crown of Egypt. The symbol sometimes used for the white crown was the vulture goddess Nekhbet shown next to the head of the cobra goddess Wadjet, the uraeus on the pschent. Nekhbet, the tutelary goddess of Nekhebet (modern el Kab) near Hierakonpolis, was depicted as a woman, sometimes with the head of a vulture, wearing the white crown. The falcon god Horus of Hierakonpolis (Egyptian: Nekhen) was generally shown wearing a white crown.” ref
“A famous depiction of the white crown is on the Narmer palette found at Hierakonpolis in which the king of the South wearing the hedjet is shown triumphing over his northern enemies. The kings of the united Egypt saw themselves as successors of Horus. Vases from the reign of Khasekhemwy show the king as Horus wearing the white crown. Evidence from Abydos, however, particularly the excavation of Cemetery U and the tome U-j, dating to Naqada IIIA has shown that this iconography appears earlier in Egypt. The white crown, along with the red crown, has a long history with each of their respective representations going back into the Predynastic Period, indicating that kingship had been the base of Egyptian society for some time. Where as before it had been thought that the earliest image of the hedjet was thought to have been in the Qustul in Nubia.” ref
“The cobra goddess Wadjet, was said to be the patron and protector of Lower Egypt, and upon unification with Upper Egypt, the joint protector and patron of all of Egypt “goddess” of Upper Egypt. The image of Wadjet with the sun disk is called the uraeus, and it was the emblem on the crown of the rulers of Lower Egypt. She was also the protector of kings and of women in childbirth. Wadjet was said to be the nurse of the infant god Horus. With the help of his mother Isis, they protected Horus from his treacherous uncle, Set, when they took refuge in the swamps of the Nile Delta. Wadjet was closely associated in ancient Egyptian religion with the Eye of Ra, a powerful protective deity. The hieroglyph for her eye is shown below; sometimes two are shown in the sky of religious images. Per-Wadjet also contained a sanctuary of Horus, the child of the sun deity who would be interpreted to represent the pharaoh. Much later, Wadjet became associated with Isis as well as with many other deities.” ref
“Wadjet relates to the Egyptian word wꜣḏ signifies blue and green. It is also the name for the well-known “Eye of the Moon”. Indeed, in later times, she was often depicted simply as a woman with a snake’s head, or as a woman wearing the uraeus. The uraeus originally had been her body alone, which wrapped around or was coiled upon the head of the pharaoh or another deity. Wadjet was depicted as a cobra. As patron and protector, later Wadjet often was shown coiled upon the head of Ra; in order to act as his protection, this image of her became the uraeus symbol used on the royal crowns as well. Another early depiction of Wadjet is as a cobra entwined around a papyrus stem, beginning in the Predynastic era (prior to 5,100 years ago) and it is thought to be the first image that shows a snake entwined around a staff symbol. This is a sacred image that appeared repeatedly in the later images and myths of cultures surrounding the Mediterranean Sea, called the caduceus, which may have had separate origins.” ref
Eye of Horus / Eye of Ra
“The Wadjet (or Ujat, meaning “Whole One”) is a powerful symbol of protection in ancient Egypt also known as the “Eye of Horus” and the “all seeing eye”. The symbol was frequently used in jewelry made of gold, silver, lapis, wood, porcelain, and carnelian, to ensure the safety and health of the bearer and provide wisdom and prosperity. However, it was also known as the “Eye of Ra”, a powerful destructive force linked with the fierce heat of the sun which was described as the “Daughter of Ra“. The “eye” was personified as the goddess Wadjet and associated with a number of other gods and goddesses (notably Hathor, Bast, Sekhmet, Tefnut, Nekhbet and Mut).” ref
“Horus was an ancient a sky god whose eyes were said to be the sun and the moon. However, he soon became strongly associated with the sun (and the sun god Ra as Ra-Horakhty (“Ra, who is Horus of the two horizons”) while Thoth was associated with the moon. An ancient myth describes a battle between Horus and Set in which Horus´ right eye was torn out and Set lost his testicles! Thoth magically restored Horus’ eye, at which point it was given the name “Wadjet” (“whole” or “healthy”). In this myth it is specifically stated that it is Horus´ left eye which has been torn out, so the myth relates to the waxing and waning of the moon during which the moon appears to have been torn out of the sky before being restored once every lunar month.” ref
“There are a number of depictions of the restoration of the eye in Greco-Roman temples. Thoth is assisted by fourteen gods including the gods of the Ennead of Hermopolis or thirty male deities (in Ismant el-Kharab, the Dakhla Oasis). Each god represented one of the fifteen days leading up to the full moon, and to the waning moon. The restored eye became emblematic of the re-establishment of order from chaos, thus closely associating it with the idea of Ma´at. In one myth Horus made a gift of the eye to Osiris to help him rule the netherworld. Osiris ate the eye and was restored to life. As a result, it became a symbol of life and resurrection. Offerings are sometimes called “the Eye of Horus” because it was thought that the goods offered became divine when presented to a god. The Eye of Horus was believed to have healing and protective power, and it was used as a protective amulet. It was also used as a notation of measurement, particularly for measuring the ingredients in medicines and pigments. The symbol was divided into six parts, representing the shattering of Horus’ eye into six pieces. Each piece was associated with one of the six senses and a specific fraction.” ref


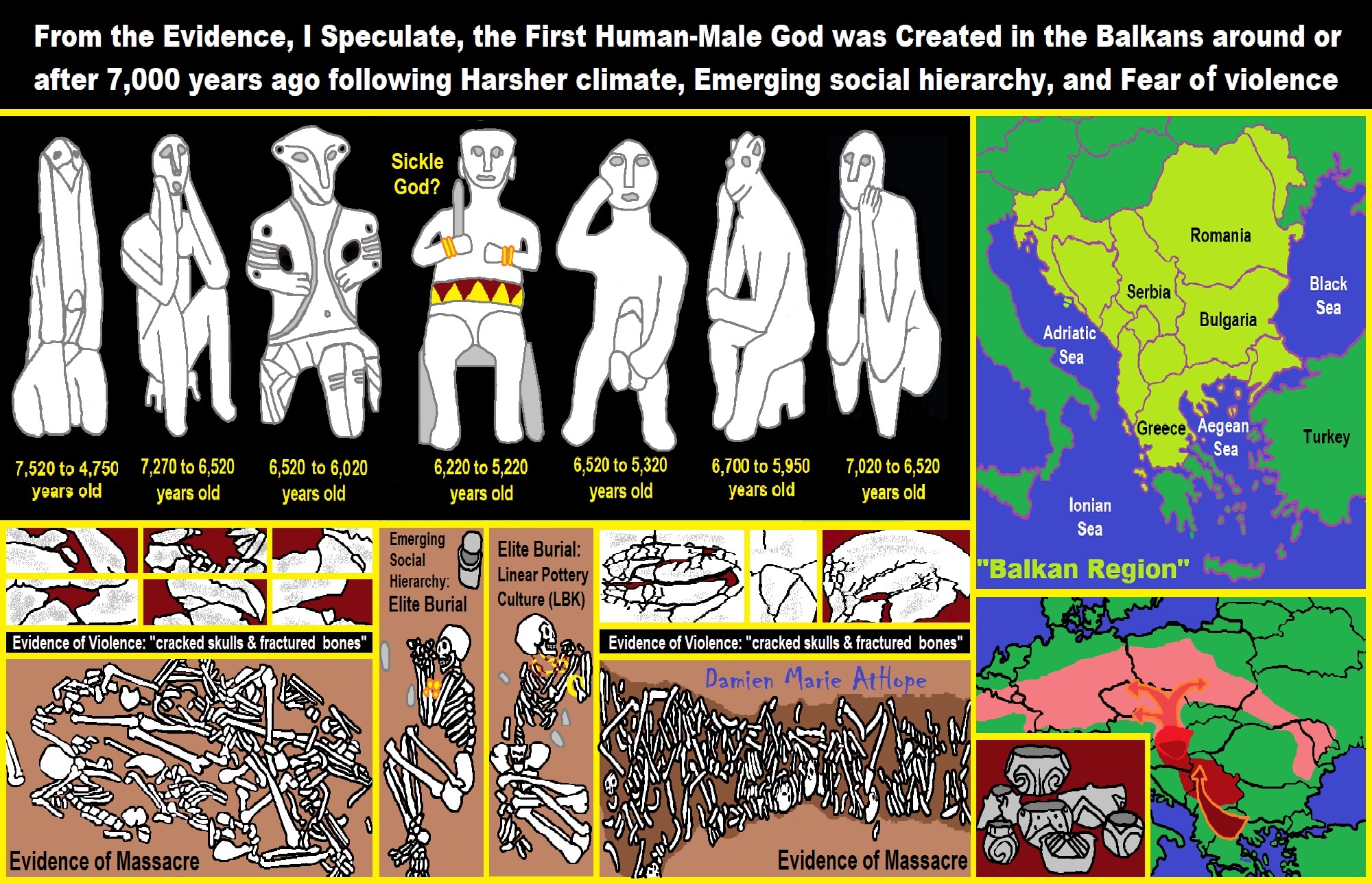
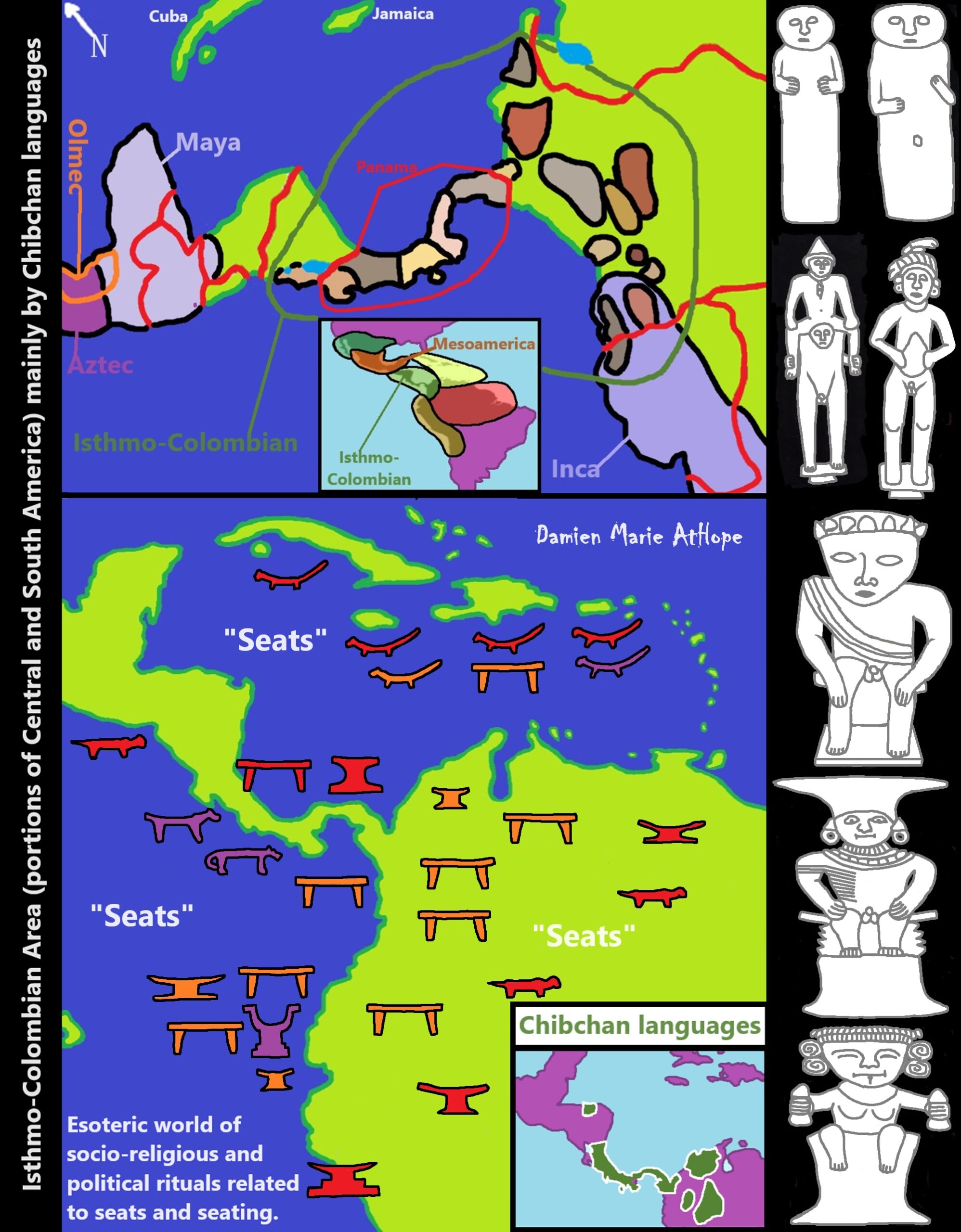
“We recognize that communities and constellations of practice entail activities that overlap, transcend, and defy categorization within conventional geographic or cultural boundaries. Indigenous peoples of the Americas include more than half a million speakers of indigenous languages. And while identity can sometimes to linked to indigenous languages, indigenous identities are further complicated for indigenous groups whose identities are not strictly tied to language.” – Info from: Pre-Columbian Central America, Colombia, and Ecuador: Toward an Integrated Approach (Dumbarton Oaks Other Titles in Pre-Columbian Studies) by Colin McEwan (Editor), John W. Hoopes (Editor)
“Shellfish was a major source of protein, and shells also became tools and artifacts. In Pre-Colombia art and oral traditions, many animals that were not utilized for food, still feature prominently: birds (Vultures and Eagles), felids (Jaguars, Ocelots, Margays, and others), crocodiles (Crocodiles and Caymans), saurian (Iguanas and basilisks), anurans (Frogs and Toads), rodents (Agoutis and Rabbits), snakes (Pit vipers and Rattlesnakes), and simians (Spider, Howler, Capuchin, and Squirrel monkeys) .” – Info from: Pre-Columbian Central America, Colombia, and Ecuador: Toward an Integrated Approach (Dumbarton Oaks Other Titles in Pre-Columbian Studies) by Colin McEwan (Editor), John W. Hoopes (Editor)
“The early Holocene period (“The Holocene: began approximately 9,700 BCE or 11,650 cal years ago, and corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth, and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present.” ref), saw the first documented use of wild food plants.” – Info from: Pre-Columbian Central America, Colombia, and Ecuador: Toward an Integrated Approach (Dumbarton Oaks Other Titles in Pre-Columbian Studies) by Colin McEwan (Editor), John W. Hoopes (Editor)
“Genetic diversity may have begun in the Late Pleistocene (“between 129,000 to 11,700 years ago” ref) as populations crossing the Isthmus (“Isthmus and land bridge are related terms, with isthmus having a broader meaning. A land bridge is an isthmus connecting Earth’s major land masses.” ref) dispersing both eastward and south. According to the linguistic and genetic evidence, the Chibchan-speaking populations separated into distinct groups in the Early Holocene and maintained a significant level of identity and cohesion thought the archaeological record.” – Info from: Pre-Columbian Central America, Colombia, and Ecuador: Toward an Integrated Approach (Dumbarton Oaks Other Titles in Pre-Columbian Studies) by Colin McEwan (Editor), John W. Hoopes (Editor)
“People spoke Chibchan languages throughout the Isthmo-Colombian Area, from eastern Honduras to southern Colombia. There is no reason to characterize Chibchan languages as “South American” than there is to label them “Central American.” Furthermore, what some authors called “Mesoamerican influence” in Colombia may have come from southern Central America instead. New evidence confirms chthonous expansion beginning in the Late Pleistocene of populations, technologies, sociopolitical strategies, interregional interactions, and ideological systems.” – Info from: Pre-Columbian Central America, Colombia, and Ecuador: Toward an Integrated Approach (Dumbarton Oaks Other Titles in Pre-Columbian Studies) by Colin McEwan (Editor), John W. Hoopes (Editor)
“Shaman Seats”
Photo credits for the first Pic is John Hoopes. The objects are in the Real Alto site museum.
Seats of Power
“It was common for ancient furniture to have religious or symbolic purposes. The Incans had chacmools which were dedicated to sacrifice. Similarly, in Dilmun they had sacrificial altars. In many civilizations, the furniture depended on wealth. Sometimes certain types of furniture could only be used by the upper class citizens. For example, in Egypt, thrones could only be used by the rich. Sometimes the way the furniture was decorated depended on wealth. For example, in Mesopotamia tables would be decorated with expensive metals, chairs would be padded with felt, rushes, and upholstery. Some chairs had metal inlays.” ref
“As some of the earliest forms of seat, stools are sometimes called backless chairs despite how some modern stools have backrests. The origins of stools are obscure, but they are known to be one of the earliest forms of wooden furniture. Several kingdoms and chiefdoms in Africa had and still have traditions of using stools in the place of chairs as thrones. One of the most famous of them, the Golden Stool of the Asantehene in Ghana, was the cause of one of the most famous events in the history of colonized Africa, the so-called War of the Golden Stool between the British and the Ashanti.” ref
“Some of the first people that Christopher Columbus met in the American continent were the Taino people. Duhos are carved seats found in the houses of Taino caciques or chiefs throughout the Caribbean region. Duhos “figured prominently in the maintenance of Taino political and ideological systems . . . [and were] . . . literally seats of power, prestige, and ritual.” The Taíno ritual seat is a Pre-Columbian wooden seat made in the form of a man on all fours. It was made by the Taino people and found in a cave near the city of Santo Domingo in the Dominican Republic. The seat was made before Christopher Columbus landed in the Caribbean and is an important remnant of the Taino culture and civilisation that existed before the arrival of Europeans.” ref
“In Akkad, Chairs would also have brightly colored wooden and ivory finials depicting arms and bull’s heads. Oftentimes the chairs would have bronze panels that had images of griffins and winged deities carved into them. The Royal Standard of Ur showcases the king of Ur on a low-back chair with animal legs. The seats depicted on the Royal Standard were likely made of Rush and Cane. During this period of Sumerian history chairs were not used by the majority of people. Most people simply sat on the floor. Low-backed chairs with curved or flat seats and turned legs were incredibly common in the Akkadian Empire.” ref
“From the Assyrian records we learn that Mesopotamian furniture was similar to Egyptian furniture. There was a wide variety of Assyrian chairs. Some chairs had backs and arms, some resembled a footstool. Tombs dating back to the First Dynasty have wooden furniture. The chair developed from the stool in the second dynasty. A stele found in a tomb from this time period depicts Prince Nisuheqet sitting on a chair. The chair has a high back made of plain sawn boards. Suggesting that the earliest chairs were used by the wealthy. Egyptian chairs likely continued to be status symbols. In another tomb, this time from the third dynasty, more depictions of chairs are found.” ref
“Animal legs were usually supported on a small cone-shaped pedestal. In the Middle Kingdom of Egypt chairs were still straight legged with cushioned backs and upholstered vertical backs. During this period, chairs became more stylized. The legs of these chairs were animal shaped, however instead of bovine shaped, they were slender and gazelle shaped or lion shaped. Much of the old Egyptian furniture which still survives to this day has only survived due to the ancient Egyptians beliefs about the afterlife. Furniture would be placed in tombs, and a result would survive to the modern day.” ref
“The chairs from Tutankhamen’s tomb were highly decorated with imported ebony and ivory inlay. They were also made for ceremonial purposes. Funerary paraphernalia was common amongst these chairs. Stools did not come into being in Egypt until the 18th Dynasty. Still, the majority of people did not have chairs, so stools were most people’s only option for comfortable seating. Ceremonial stools would be blocks of stone or wood. If the stool was made out of wood it would have a flint seat. Footstools were made of wood. The Royal Footstool had enemies of Egypt painted on the footstool, so that way the pharaoh could symbolically crush them. Stools used by the upper-class would have upward sweeping corners and woven leather seats, with a padded cushion on top.” ref
“The modern word “throne” is derived from the ancient Greek thronos (Greek singular: θρόνος), which was a seat designated for deities or individuals of high status or honor. The colossal chryselephantine statue of Zeus at Olympia, constructed by Phidias and lost in antiquity, featured the god Zeus seated on an elaborate throne, which was decorated with gold, precious stones, ebony, and ivory, according to Pausanias. Less extravagant though more influential in later periods is the klismos (Greek singular: κλισμός), an elegant Greek chair with a curved backrest and legs whose form was copied by the Romans and is now part of the vocabulary of furniture design. A fine example is shown on the grave stele of Hegeso, dating to the late fifth century BCE. As with earlier furniture from the east, the klismos and thronos could be accompanied by footstools.” ref
“The most common form of Greek seat was the backless stool. These were known as diphroi (Greek singular: δίφρος) and they were easily portable. The Parthenon frieze displays numerous examples, upon which the gods are seated. Several fragments of a stool were discovered in the forth-century BCE. tomb in Thessaloniki, including two of the legs and four transverse stretchers. The Greek folding stool survives in numerous depictions, indicating its popularity in the Archaic and Classical periods; the type may have been derived from earlier Minoan and Mycenaean examples, which in turn were likely based on Egyptian models. Greek folding stools might have plain straight legs or curved legs that typically ended in animal feet. The sella curulis, or folding stool, was an important indicator of power in the Roman period.” ref
“In one Mayan ceramic, a god who is possibly the God L is shown seated on a throne-like stool covered in cloth placed on a raised platform. Most likely, the only big furniture in a home would be wooden stools or benches. A quantity of furniture in an Aztec home would have been uncommon sight. Usually instead of beds or chairs, mats made of reeds or dirt platforms were used to sit or sleep on.” ref
“Chair comes from the early 13th-century English word chaere, from Old French chaiere (“chair, seat, throne”), from Latin cathedra (“seat”). Chairs were in existence since at least the Early Dynastic Period of Egypt (c. 3100 BCE or around 5,100 years ago). In ancient Egypt, chairs appear to have been of great richness and splendor. Generally speaking, the higher ranked an individual was, the taller and more sumptuous was the chair he sat on and the greater the honor. On state occasions, the pharaoh sat on a throne, often with a little footstool in front of it. The average Egyptian family seldom had chairs, and if they did, it was usually only the master of the household who sat on a chair.” ref
“According to the Hebrew Bible, the kaporet (Hebrew: כַּפֹּרֶת kapōreṯ) or mercy seat was the gold lid placed on the Ark of the Covenant, with two cherubim beaten out of the ends to cover and create the space in which Yahweh appeared and dwelled. This was connected with the rituals of the Day of Atonement. The term also appears in later Jewish sources, and twice in the New Testament, from where it has significance in Christian theology. Two golden cherubim were placed at each end of the cover facing one another and the mercy seat, with their wings spread to enclose the mercy seat (Exodus 25:18–21). The cherubim formed a seat for Yahweh (1 Samuel 4:4). The Holy of Holies could be entered only by the high priest on the Day of Atonement. The high priest sprinkled the blood of a sacrificial bull onto the mercy seat as an atonement for the sins of the people of Israel.” ref
“Although the Holy See is sometimes metonymically referred to as the “Vatican“, the Vatican City State was distinctively established with the Lateran Treaty of 1929, the word “see” comes from the Latin word sedes, meaning ‘seat’, which refers to the episcopal throne (cathedra). The Holy See is one of the last remaining seven absolute monarchies in the world, along with Saudi Arabia, Eswatini, United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Brunei and Oman.” ref
“A sacrificial tripod, whose name comes from the Greek meaning “three-footed”, is a three-legged piece of religious furniture used in offerings and other ritual procedures. Tripods had two types and several functions. Firstly, some oracles sat on large tripods to pronounce. Far more common were the tripods and bowls in which smaller sacrifices were burnt. These are particularly associated with Apollo and the Delphic oracle in ancient Greece. These were also given to temples as votive offerings, awarded as prizes in contests associated with religious festivals, and just given as gifts between individuals. The most famous tripod of ancient Greece was the Delphic Tripod on which the Pythian priestess took her seat to deliver the oracles of the deity.” ref
“Sacrificial tripods also were used as dedicatory offerings to the deities, and in the dramatic contests at the Dionysia the victorious choregus (a wealthy citizen who bore the expense of equipping and training the chorus) received a crown and a tripod. He would either dedicate the tripod to some deity or set it upon the top of a marble structure erected in the form of a small circular temple in a street in Athens, called the street of tripods, from the large number of memorials of this kind. According to Herodotus (The Histories, I.144), the victory tripods were not to be taken from the temple sanctuary precinct, but left there as dedications.” ref
Thrones: Seating of Power
Isaiah 40:22: 22 “God sits on his throne above the circle of the earth, and compared to him, people are like grasshoppers.”
Matthew 23:22: “And whoever swears by heaven, swears both by the throne of God and by Him who sits upon it.”
Revelation 4:9: “When the living creatures give glory and honor to Him who sits on the throne, to Him who lives forever and ever.”
“A throne is the seat of state of a potentate or dignitary, especially the seat occupied by a sovereign (or viceroy) on state occasions; or the seat occupied by a pope or bishop on ceremonial occasions. “Throne” in an abstract sense can also refer to the monarchy or the Crown itself, an instance of metonymy, and is also used in many expressions such as “the power behind the throne“. A throne is a symbol of divine and secular rule and the establishment of a throne as a defining sign of the claim to power and authority. It can be with a high backrest and feature heraldic animals or other decorations as adornment and as a sign of power and strength.” ref
“The throne of God is the reigning centre of God in the Abrahamic religions: primarily Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. The throne is said by various holy books to reside beyond the Seventh Heaven which is called Araboth (Hebrew: עֲרָבוֹת ‘ărāḇōṯ) in Judaism. The heavenly throne room or throne room of God is a more detailed presentation of the throne, into the representation of throne room or divine court. Micaiah‘s extended prophecy (1 Kings 22:19) is the first detailed depiction of a heavenly throne room in Judaism. Zechariah 3 depicts a vision of the heavenly throne room where Satan and the Angel of the Lord contend over Joshua the High Priest in the time of his grandson Eliashib the High Priest. “The concept of a heavenly throne occurs in three Dead Sea Scroll texts.” ref
“Abu Mansur al-Baghdadi (d. 429/1037) in his al-Farq bayn al-Firaq (The Difference between the Sects) reports that ‘Ali ibn Abi Talib, said: “God created the Throne as an indication of His power, not for taking it as a place for Himself.” The vast majority of Islamic scholars, including Sunnis (Ash’aris, Maturidis and Sufis), Mu’tazilis, and Shi’is (Twelvers and Isma’ilis) believe the Throne (Arabic: العرش al-‘Arsh) as a symbol of God’s power and authority and not as a dwelling place for Himself, while some Islamic sects, such as the Karramis and the Salafis/Wahhabis believe that God has created it as a place of dwelling. The Quran depicts the angels as carrying the throne of God and praising his glory, similar to Old Testament images. Prophetic hadith also establish that The Throne is above the roof of Al-Firdaus Al-‘Ala, the highest level of Paradise where God’s closest and most beloved servants in the hereafter shall dwell.” ref
“The Quran mentions the throne some 25 times (33 times as Al-‘Arsh), such as in verse Q10:3 and Q23:116:
Indeed, your Lord is Allah, who created the heavens and the earth in six days and then established Himself above the Throne (Arsh), arranging the matter [of His creation]. There is no intercessor except after His permission. That is Allah, your Lord, so worship Him. Then will you not remember? – Yunus 10:3
And it is He who created the heavens and the earth in six days – and His Throne had been upon water – that He might test you as to which of you is best in deed. But if you say, “Indeed, you are resurrected after death,” those who disbelieve will surely say, “This is not but obvious magic.” – Hud 11:7
So Exalted be Allah, the True King – None has the right to be worshipped but He – Lord of the Supreme Throne! – al-Mu’minoon 23:116” ref
“A throne can be placed underneath a canopy or baldachin. The throne can stand on steps or a dais and is thus always elevated. The expression “ascend (mount) the throne” takes its meaning from the steps leading up to the dais or platform, on which the throne is placed, being formerly comprised in the word’s significance. Coats of arms or insignia can feature on throne or canopy and represent the dynasty. Even in the physical absence of the ruler an empty throne can symbolise the everlasting presence of the monarchical authority.” ref
“When used in a political or governmental sense, a throne typically exists in a civilization, nation, tribe, or other politically designated group that is organized or governed under a monarchical system. Throughout much of human history societies have been governed under monarchical systems, in the beginning as autocratic systems and later evolved in most cases as constitutional monarchies within liberal democratic systems, resulting in a wide variety of thrones that have been used by given heads of state. These have ranged from stools in places such as in Africa to ornate chairs and bench-like designs in Europe and Asia, respectively.” ref
“Often, but not always, a throne is tied to a philosophical or religious ideology held by the nation or people in question, which serves a dual role in unifying the people under the reigning monarch and connecting the monarch upon the throne to his or her predecessors, who sat upon the throne previously. Accordingly, many thrones are typically held to have been constructed or fabricated out of rare or hard to find materials that may be valuable or important to the land in question. Depending on the size of the throne in question it may be large and ornately designed as an emplaced instrument of a nation’s power, or it may be a symbolic chair with little or no precious materials incorporated into the design. When used in a religious sense, throne can refer to one of two distinct uses. Many of these thrones—such as China’s Dragon Throne—survive today as historic examples of nation’s previous government.” ref
“The first use derives from the practice in churches of having a bishop or higher-ranking religious official (archbishop, pope, etc.) sit on a special chair which in church referred to by written sources as a “throne”, or “cathedra” (Latin for ‘chair’) and is intended to allow such high-ranking religious officials a place to sit in their place of worship. The other use for throne refers to a belief among many of the world’s monotheistic and polytheistic religions that the deity or deities that they worship are seated on a throne. Such beliefs go back to ancient times, and can be seen in surviving artwork and texts which discuss the idea of ancient gods (such as the Twelve Olympians) seated on thrones. In the major Abrahamic religions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, the Throne of God is attested to in religious scriptures and teachings, although the origin, nature, and idea of the Throne of God in these religions differs according to the given religious ideology practiced.” ref
“Thrones were found throughout the canon of ancient furniture. The depiction of monarchs and deities as seated on chairs is a common topos in the iconography of the Ancient Near East. The word throne itself is from Greek θρόνος (thronos), “seat, chair”, in origin a derivation from the PIE root *dher- “to support” (also in dharma “post, sacrificial pole”). Early Greek Διὸς θρόνους (Dios thronous) was a term for the “support of the heavens”, i.e. the axis mundi, which term when Zeus became an anthropomorphic god was imagined as the “seat of Zeus”. In Ancient Greek, a “thronos” was a specific but ordinary type of chair with a footstool, a high status object but not necessarily with any connotations of power. The Achaeans (according to Homer) were known to place additional, empty thrones in the royal palaces and temples so that the gods could be seated when they wished to be. The most famous of these thrones was the throne of Apollo in Amyclae.” ref
“The word “throne” in English translations of the Bible renders Hebrew כסא kissē’. The pharaoh of the Exodus is described as sitting on a throne (Exodus 11:5, 12:29), but mostly the term refers to the throne of the kingdom of Israel, often called the “throne of David” or “throne of Solomon“. The literal throne of Solomon is described in 1 Kings 10:18–20: “Moreover the king made a great throne of ivory, and overlaid it with the best gold.. The throne had six steps, and the top of the throne was round behind: and there were stays on either side on the place of the seat, and two lions stood beside the stays. And twelve lions stood there on the one side and on the other upon the six steps: there was not the like made in any kingdom.” In the Book of Esther (5:3), the same word refers to the throne of the king of Persia.” ref
“The God of Israel himself is frequently described as sitting on a throne, referred to outside of the Bible as the Throne of God, in the Psalms, and in a vision Isaiah (6:1), and notably in Isaiah 66:1, YHWH says of himself “The heaven is my throne, and the earth is my footstool” (this verse is alluded to by Matthew 5:34-35). In the Old Testament, Book of Kings I explicits the throne of Solomon: “Then the king made a great throne covered with ivory and overlaid with fine gold. The throne had six steps, and its back had a rounded top. On both sides of the seat were armrests, with a lion standing beside each of them. Twelve lions stood on the six steps, one at either end of each step” in Chapter 10 18-20. Jesus promised his apostles that they would sit upon “twelve thrones”, judging the twelve tribes of Israel (Matthew 19:28). John‘s Revelation states: “And I saw a great white throne, and him that sat on it, from whose face the earth and the heaven fled away” (Revelation 20:11).” ref
“In the Indian subcontinent, the traditional Sanskrit name for the throne was siṃhāsana (lit., seat of a lion). In the Mughal times the throne was called Shāhī takht ([ˈʃaːhiː ˈtəxt]). The term gadi or gaddi (Hindustani pronunciation: [ˈɡəd̪ːi], also called rājgaddī) referred to a seat with a cushion used as a throne by Indian princes. That term was usually used for the throne of a Hindu princely state‘s ruler, while among Muslim princes or Nawabs, save exceptions such as the Travancore State royal family, the term musnad ([ˈməsnəd]), also spelt as musnud, was more common, even though both seats were similar.” ref
“The Dragon Throne is the term used to identify the throne of the emperor of China. As the dragon was the emblem of divine imperial power, the throne of the emperor, who was considered a living god, was known as the Dragon Throne. The throne of the emperors of Vietnam are often referred to as ngai vàng (“golden throne”) or ngôi báu (大寳/寶座) literally “great precious” (seat/position). The throne is always adorned with the pattern and motif of the Vietnamese dragon, which is the exclusive and privileged symbol of the Vietnamese emperors. In Vietnamese folk religion, the gods, deities and ancestral spirits are believed to seat figuratively on thrones at places of worship. Therefore, on Vietnamese altars, there are various types of liturgical “throne” often decorated with red paint and golden gilding.” ref
Chatting with John Hoopes
“The oldest known “shaman seats” are small ceramic models from the Valdivia culture in Ecuador that date to about 2500 BCE. Seats and their relations are such a rich source of information. I could do a whole book on just seats, stools, duhos, and thrones. Donald Lathrap thought this modeled spout was an early representation (ca. 2500 BCE) of a shaman wearing a jaguar pelt. You’ll be interested to know that I’m returning to more scholarship on shamanism.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
My response, Wonderful, I look forward to learning more from you. I support you and all you do. I want to understand what is actually true. And I think it is an interesting topic as what seems like the emergence of male god/elite: socio-political or religious all are sitting around 7,000 years ago in the Balkins.
“Archaeology is all about getting as close as we can to the best possible approximation of the truth without actually declaring that we know it. We are always tinkering and fine-tuning as well as trying to answer more questions. As technical as those books from Dumbarton Oaks are, they do have art as the central focus. I’ve always felt that art is a more successful path to truth than science. It’s nice to combine the two. On the jadeite and gold objects: for the people who made and used them, they were tools for creating both magic and power. And together, the books help tell the story of peoples who have been largely forgotten but deserve to be remembered.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
“The Isthmo-Colombian Area was the first part of the mainland to be colonized by the Spanish. As a consequence, its peoples were the first—after the Taíno of the Antilles—to suffer genocide and see their ancient cultures destroyed. However, because they did not build pyramids, they tend to be overlooked, even by archaeologists. The first Spanish colony on the mainland was in Panama in 1500. Cortes didn’t arrive in Mexico until 1519 and Pizarro didn’t reach Peru until 1532. The first place Columbus’s men set foot on the mainland was in southern Costa Rica.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
“Conquest, Imagination, and the Dawn of the Modern Age: The Gold of Panama In Its Historical Context, this article helps put things in context. A lot of what shapes our world right now has roots in what happened back then. The anticipation of vast quantities of stolen gold from the Americas is the story that Charles V took to his bankers in order to get massive loans to underwrite the Spanish conquest. Ultimately, much less loot was found than was expected. Charles V ultimately stepped down because of his massive debts.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
“However, in the meantime, these loans allowed Charles V to equip armies that successfully prevented Muslim armies from invading Central Europe. Ironically, the promise of gold from the Americas is what kept Europe Christian. And, of course, allowed the spread of Christianity in the Americas. It was the beginning of massive international debt and its consequences. The engine of capitalism. The beginning of the Modern Age. The notion of progress is highly overrated. For me, progress is discovering, recovering, and learning from what was destroyed long ago.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
“The intimate relationship between European conquests of the Americas and the Protestant Reformation is worth exploring. Martin Luther was doing his thing as Cortes and his men were dismantling the Aztec empire. Jean Cauvin (John Calvin) was doing his thing as the Pizarros and their thugs were destroying the Inca empire. These big events of long ago shaped the world we have now.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
My response, You have a lot to teach. I think you are great.
“Yes, and teachers gonna teach. Thanks. I do what I can but without getting all commercial about it. I get zero royalties from those books and don’t have anything to sell. In our capitalist society, that confuses people about the issue of value.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
My response, I like how open you are to teaching for free. I do the same. I do plan on finishing writing my book, “The Tree of Lies and its Hidden Roots: exposing the evolution of religion and removing the rationale of faith.” I have been working on it for years. I will make something on it but will not try that hard to push it all the time. Rather, I will do a little promoting, and then I plan on transitioning to making my own Jewelry and doing that commercially. But still will do most things for free as I want to make my stuff available for anyone and money is not stopping them.
“The compensation that academic archaeologists get comes in the form of our salaries. In my case, that’s from a state university. So, public funds pay for my labor. I’m grateful for that and try to give back what I can.” – John Hoopes @KUHoopes (Anthropologist with broad training in the archaeology of pre-Hispanic indigenous cultures in Latin America)
My response, I am happy John, that public funds, pay for your labor as you are working on understanding humanity, from the past.
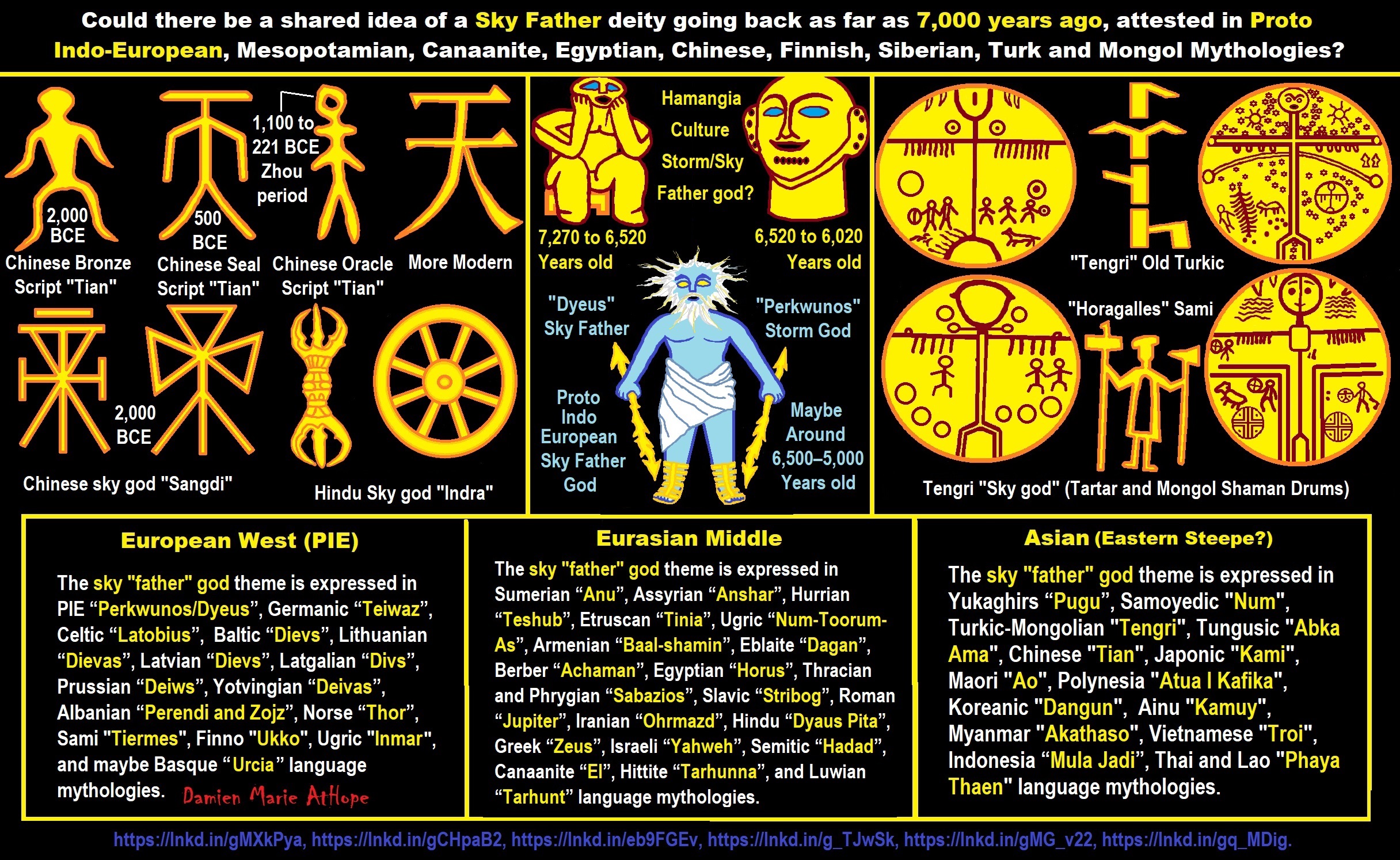

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
List of Lunar Deities
“In mythology, a lunar deity is a god or goddess of the Moon, sometimes as a personification. These deities can have a variety of functions and traditions depending upon the culture, but they are often related. Some forms of moon worship can be found in most ancient religions. The Moon features prominently in art and literature, often with a purported influence in human affairs. Many cultures are oriented chronologically by the Moon, as opposed to the Sun. The Hindu calendar maintains the integrity of the lunar month and the moon god Chandra has religious significance during many Hindu festivals (e.g. Karwa Chauth, Sankashti Chaturthi, and during eclipses). The ancient Germanic tribes were also known to have a lunar calendar.” ref
“Many cultures have implicitly linked the 29.5-day lunar cycle to women’s menstrual cycles, as evident in the shared linguistic roots of “menstruation” and “moon” words in multiple language families. This identification was not universal, as demonstrated by the fact that not all moon deities are female. Still, many well-known mythologies feature moon goddesses, including the Greek goddess Selene, the Roman goddess Luna, and the Chinese goddess Chang’e. Several goddesses including Artemis, Hecate, and Isis did not originally have lunar aspects, and only acquired them late in antiquity due to syncretism with the de facto Greco-Roman lunar deity Selene/Luna. In traditions with male gods, there is little evidence of such syncretism, though the Greek Hermes has been equated with the male Egyptian lunar god Thoth.” ref
“Male lunar gods are also common, such as Sin of the Mesopotamians, Mani of the Germanic tribes, Tsukuyomi of the Japanese, Igaluk/Alignak of the Inuit, and the Hindu god Chandra. The original Proto-Indo-European lunar deity appears to have been male, with many possible derivatives including the Homeric figure of Menelaus. Cultures with male moon gods often feature sun goddesses. An exception is Hinduism, featuring both male and female aspects of the solar divine. The ancient Egyptians had several moon gods including Khonsu and Thoth, although Thoth is a considerably more complex deity. Set represented the moon in the Egyptian Calendar of Lucky and Unlucky Days.” ref
List of Solar Deities
“A solar deity is a god or goddess who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it, usually by its perceived power and strength. Solar deities and Sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The following is a list of solar deities. A dawn god or goddess is a deity in a polytheistic religious tradition who is in some sense associated with the dawn. These deities show some relation with the morning, the beginning of the day, and, in some cases, become syncretized with similar solar deities.” ref, ref



Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref


My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


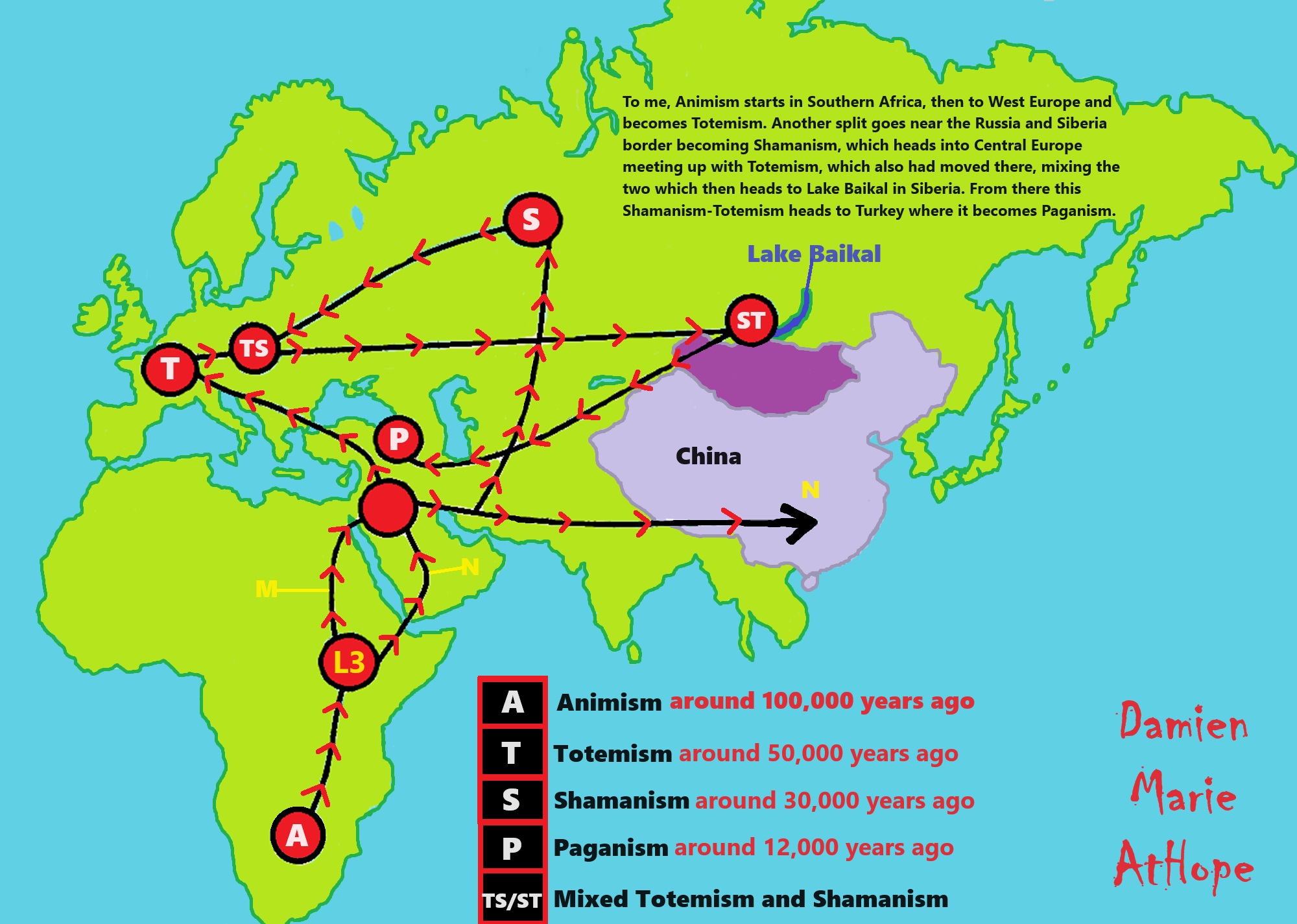
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
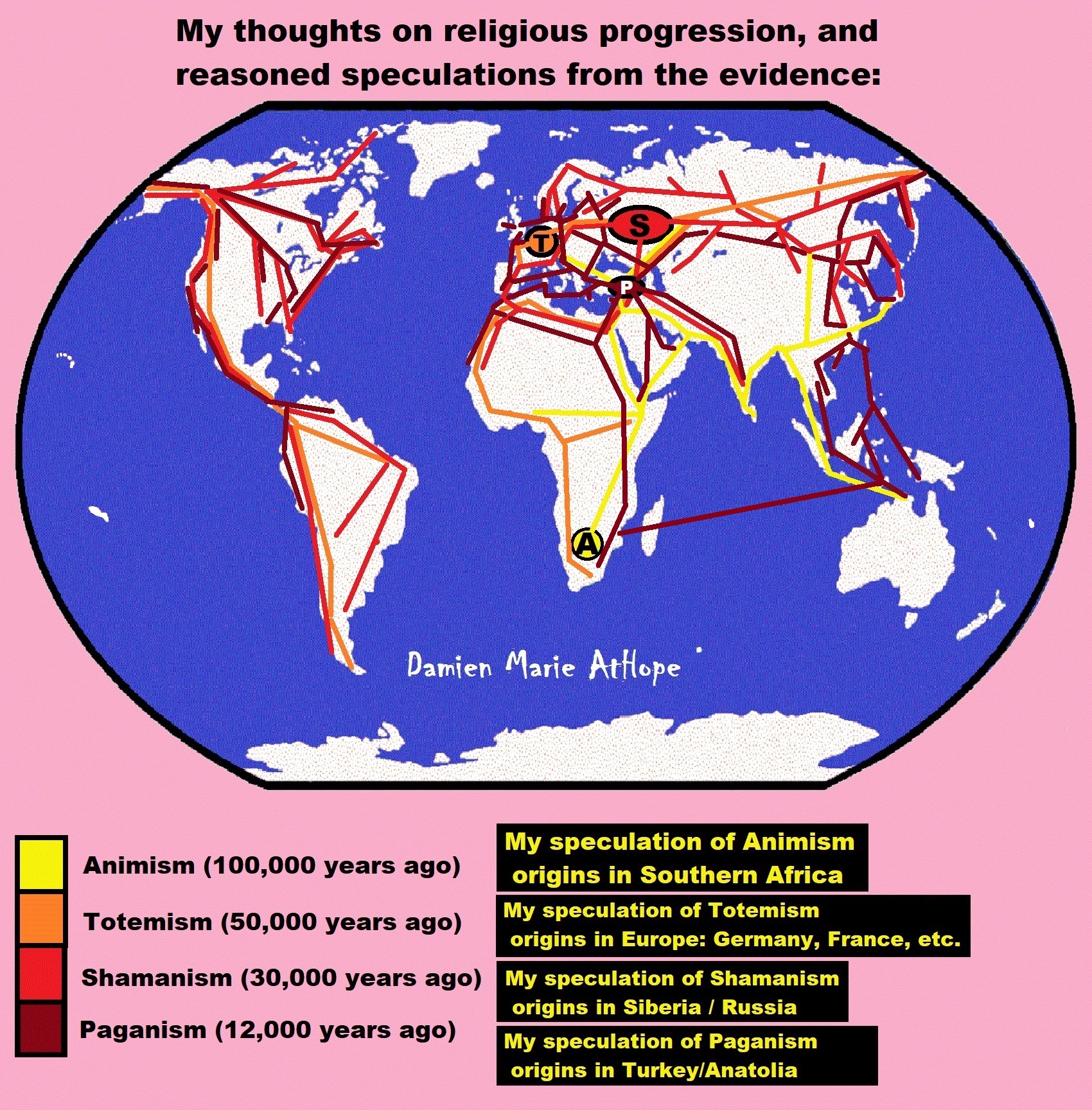

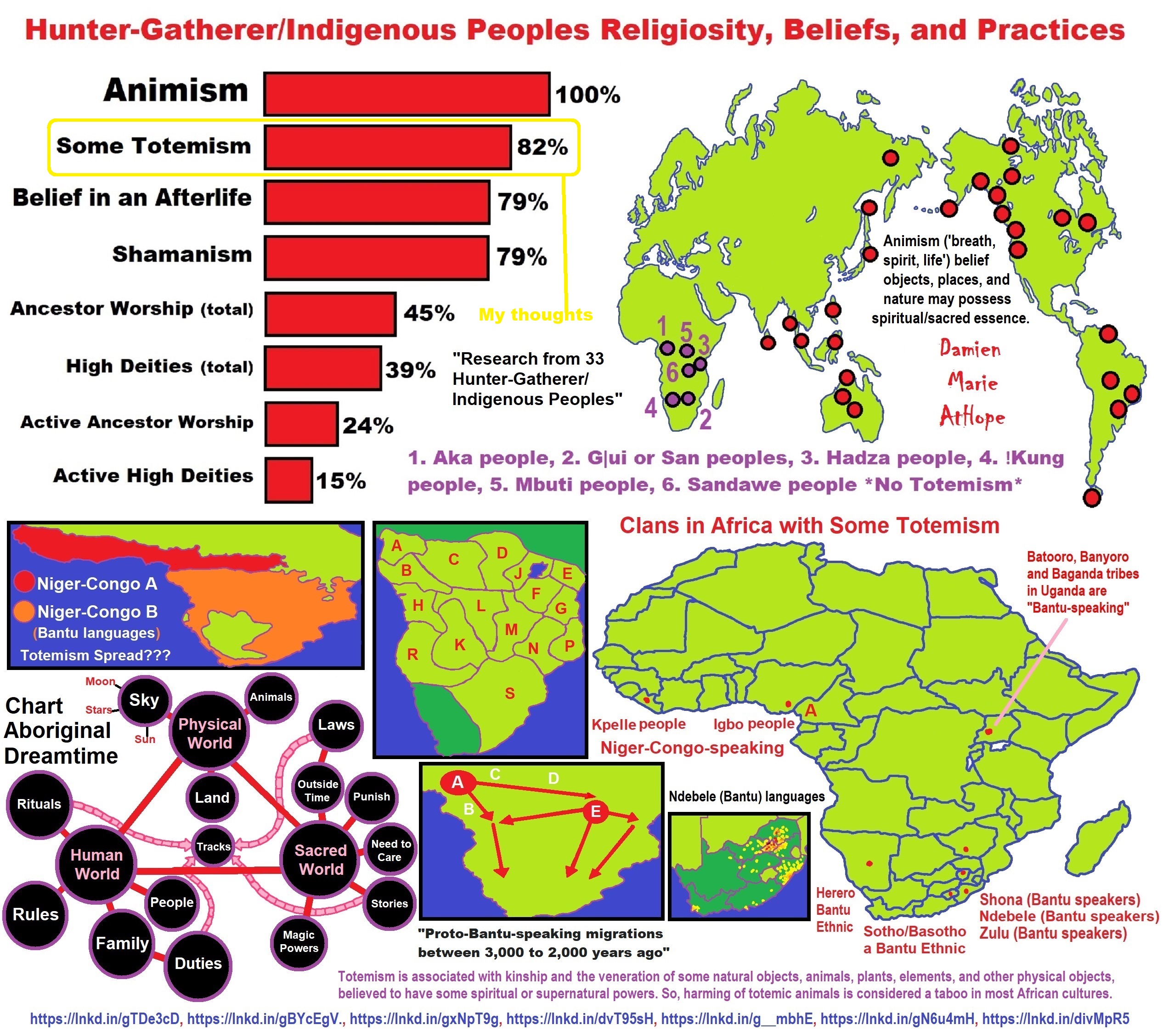
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
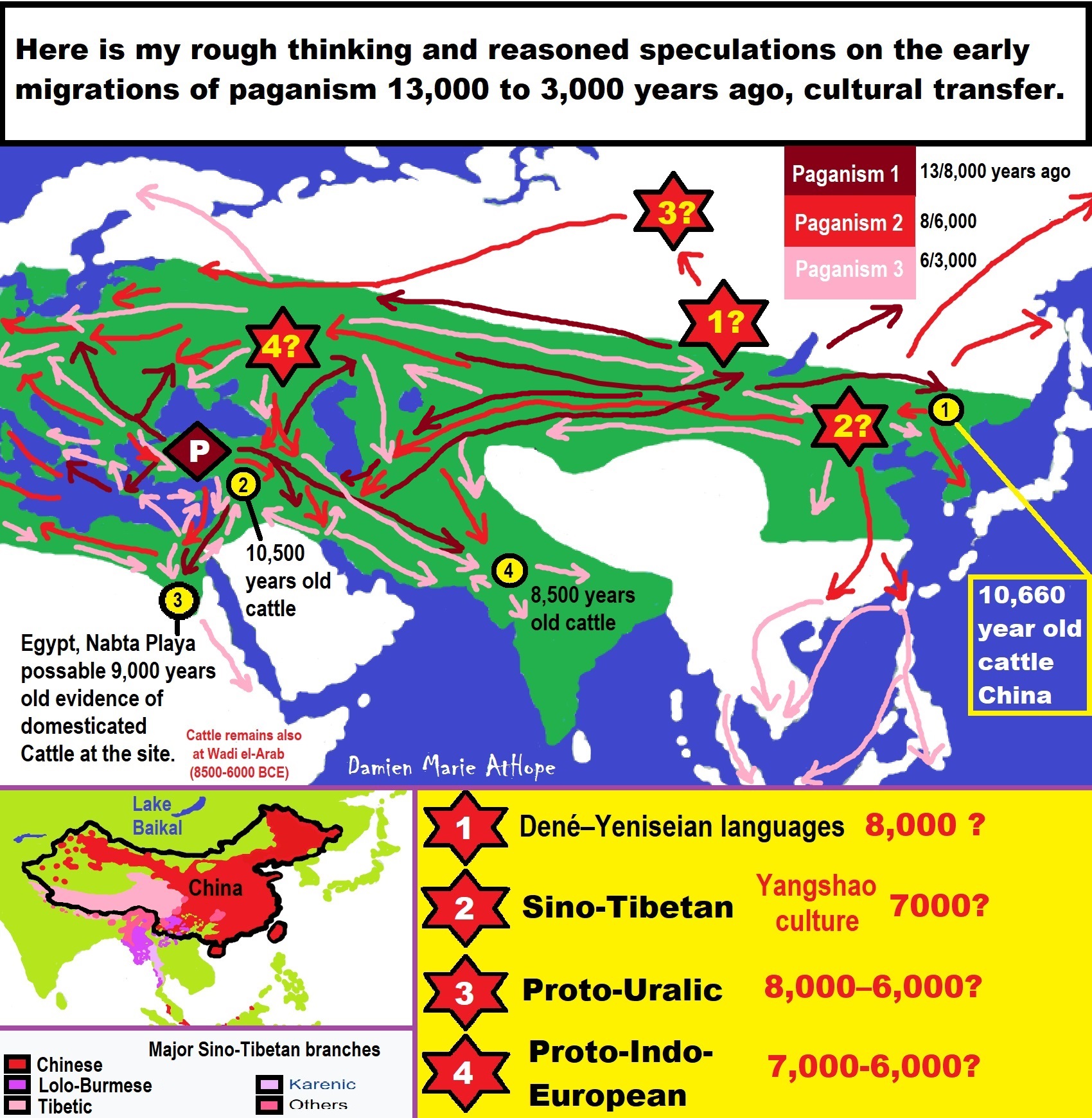
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com