The Sami are one of Europe’s oldest ethnic groups.
“Long before the concept of national borders existed, the Sami people of arctic Europe inhabited the regions now known as Norway, Sweden, Finland, and the Russian Kola Peninsula. They led a nomadic life—hunting, fishing, and following the seasonal migration of wild reindeer—and their culture and spirituality developed around their relationship with the land and its resources. The Sami culture survives today, despite centuries of repression from the region’s four modern nations.” ref
“However, an astonishing array of factors, from mining to military installations to tourism development, threaten lands whose ecology and biodiversity have been preserved for millennia under the Sami’s care. These lands are some of Europe’s last remaining wilderness areas. At the same time, the Sami themselves are seeking to preserve their traditional livelihoods, reassert their culture and claim their right to self-determination. Because of the Sami’s relationship with the land, cultural survival and land rights are inextricably tied—and they depend on protecting nature. One Sami man explains, “Nature is the most important thing. Reindeer herders lived here long before anyone else arrived. The Samis did not disturb nature, and we have lived here for thousands of years.” ref
The making of a sacred mountain. Meanings of nature and sacredness in Sápmi and northern Norway
“A case study of sacred landscapes in the contemporary era, the article deals with a particular mountain and its rise to sacredness. Fuelled by plans of ski‐slope development, the fate of Tromsdalstind caused a lively debate in local newspapers, as well as a report issued by the Sami Parliament. The report connected sacredness to Sami traditions in the past and to current laws on the protection of Sami cultural memories.” ref
“This, then, was a case of sacredness constructed outside the context of organized religions and ongoing religious traditions, as well as a case of using secular laws as the primary basis for definitions of sacredness. Through this process, love for the mountain appears to have grown deeper and more religious, both for the Sami as well as for other northern Norwegians. Neither more nor less authentic than those of the past, these concepts of sacredness belong to the late modern world of law culture, nature romanticism, and to pan‐indigenous spirituality as a ‘‘religion’’ in the making.” ref
Atoklimpen – Sami sacred hill
“Atoklimpen is a large hill rising high above the surrounding landscapes. It is part of the Sami cultural environment and provides an insight into how the nomadic Sami reindeer herding practice has affected the landscape over the centuries. It reflects the cultural heritage of the Sami and the conditions for survival in a mountain environment.” ref
“The curiously formed Atoklimpen hill (Aatoklimpoe in Sami) used to be regarded by the Sami as a very holy mountain. The mountain has many geological and botanical features that are worth seeing. The word “Ato”, in “Aatoklimpoe”, means “that there” in Sami. The mountain was deemed so holy by the Sami that it could not be referred to directly by name. There have been numerous places of sacrifice here.” ref
Áhkká (Sami Holy Mountain)
“Áhkká (Lule Sami: “old woman”), is a massif in the southwestern corner of Stora Sjöfallet National Park in northern Sweden. The massif has twelve individual peaks and ten glaciers, of which Stortoppen is the highest at 2,015 meters (6,611 feet). This peak is the eighth-highest in Sweden. Most notable is that the mountain has a vertical drop of 1,563 m (5,128 ft), from the top of the highest summit down to the lake Akkajaure in the valley below, which is located at 453 m (1,486 ft). This is the highest vertical drop found in Sweden. Since the lake below the mountain is regulated by a hydroelectric power station, its surface can drop down to 423 m (1,388 ft), which makes the mountain’s vertical drop rise to a maximum of 1,593 m (5,226 ft). Due to the large level differences and the massif being well held together and rather isolated, it looks impressive, earning it the nickname Queen of Lapland. In the Sámi tradition, it is a holy mountain, and some hikers regard it with a sense of awe and mystique.” ref
“Sami Mythology, Jousáhkká, a combination of “Juoksa” and Sami “áhkká”, meaning “wife, woman, mother”. Jousáhkká is a goddess in Sami mythology, who decides whether an unborn baby will be a boy or girl… Her sisters are Uksáhkká and Sáráhkká. Combination of the male name “Sárra” and the word áhkká “wife, woman, mother”. Sáráhkká is the goddess of childbirth. Uksáhkká, means “door goddess”, from Sami uksa “door” and áhkká “wife, woman, mother”. In Sami mythology, Uksáhkká lived under the door sill and protected the home against all evil. She watched over children during their first year, especially when they learned to walk.” ref
Parallelism in Sioux and Sami Spiritual Traditions
By Ben Baird
“There are two explanations for cross-cultural mythological or spiritual similarities. One explanation for this phenomenon is diffusion, where one idea or image is physically brought from one culture and adopted by another as a result of mixing and contact. The problem with this theory is that it cannot account for correspondence between cultures with no contact. There has been no historical contact or communication between the distant Scandinavian Sami and the North American Sioux, and yet their spiritual mythologies share varied and rich symbols which correspond to a degree of detail that cannot be mistaken for coincidence or chance. One theory that explains the ubiquity of spiritual symbols, introduced by Carl Jung in the first half of the twentieth century, states that the human psyche is essentially the same all over the world. Out of this common ground or collective unconscious come the various archetypes which can be observed in cultures all over the world regardless of time and place. For the Sami and the Sioux, this incredible parallelism of mythic themes can be observed through the three main features of their spiritual worldview: animism, polytheism, and shamanism.” ref
“For the indigenous groups of North Eastern American plains, the Sioux, or Dakota as they are sometimes referred to, and the indigenous Scandinavian people, the Sami, nature was recognized as sacred. The sacred places were not man-made temples or churches, but particularly spectacular or prominent features of the natural landscape. For the Sami, these sacred places tended to be large rocks (called sieidi), the sides of lakes, rocky crevasses or caverns, or mountaintops. These sacred mountains were somewhat isolated and had a jutting tall peak. A sacred mountain named Haldi, which rests among a group of mountains near Alta, and an 814 meter-tall conical sacred hill named Tunnsjøguden in central Norway are examples. In general, the word saivu is applied to sacred mountains in the South while the terms bassi, ailigas, and haldi are used for sacred mountains by Northern Sami. Similarly, mountaintops were also of spiritual importance to Sioux groups who lived in their regions, for instance, the sacred mountain Harney Peak in modern-day South Dakota.” ref
“While natural surroundings create special sacred places, for the Sami and the Sioux the whole world is animated with the divine source of life. This idea finds expression in the Lakota Sioux Black Elk’s beautiful and profound vision of standing on the central mountain of the world” ref:
“Then I was standing on the highest mountain of them all, and round about beneath me was the whole hoop of the world…And I saw that the sacred hoop of my people was one of many hoops that made one circle, wide as daylight and starlight, and in the center grew one mighty flowering tree to shelter all the children of one mother and one father. And I saw that it was holy.” ref
“And then he added, “But anywhere is the center of the world” (Neihardt+ 33). On one level this vision is about cooperation between tribes. On a more subtle level, Black Elk’s vision is important because it illustrates the larger connotation and meaning of the spiritual imagery of his culture. The image of the central mountain comes to be understood as the central point of existence for all things which is manifesting everywhere and through all ephemeral reality. For the Sami, this is the eternal source or “soul” which is imbued in all-natural phenomena: lakes, boulders, mountains, animals, plants, etc. The Sioux commonly characterized this all-pervasive consciousness or spirit as Wonka Tonka. This term referred to a fluid category that held numerous connotations including, incomprehensibility, transcendence, or, more generally, Great Spirit. The physical world was viewed as the manifestation of this animating force and therefore the Sioux, like the Sami, viewed all natural objects as indistinguishable from this sacred spirit. Both the Sami and the Sioux also express this existential truth through the symbol of the world pillar or world tree.” ref
“This image, common among many circumpolar peoples, connotes the central point around which all else revolves, which is neither up nor down, right nor left. The axis mundi, that which is beyond the world of duality yet holds the world up, is found in the spiritual imagery of the Sami as the “world tree.” In the northern regions of Sami territory, this world tree is said to be both a source of life and knowledge and to hold up the sky. For the Sioux, this central tree is beautifully described in Black Elk’s vision as the “one mighty flowering tree to shelter all the children of one mother and one father.” Phenomenally, both cultures use the same exact mythological symbol to express the same truth.” ref
“In contrast to monotheistic religions, practitioners of polytheism believe in and worship more than one god. In these nature-based religions, divine power is attributed to natural phenomenon and the gods are the personifications of elemental or natural forces. An important deity in the Sami pantheon is Horagallis, the god of thunder who is depicted as a person carrying a hammer or an ax. Horagallis was revered for the life-giving rain of his storms which cleansed the air, nurtured the lichen and grass, and drove away evil spirits, but he was feared for the forest fires and injuries to people and animals caused by his storms. As a result of this fear of thunder, Horagallis was regularly worshipped and sacrificed to.” ref
“For the Sioux, thunder is personified loosely as the “thunder beings” who were active participants in the everyday events of the tribe. Black Elk describes how the tribe “could hear low thunder rumbling all over the village outside, and we knew the thunder beings were glad and had come to help us.” (Neihardt 125) The thunder beings could additionally act as aids by darkening the sky if needed for hiding from enemies. The Sioux also personify thunder as Haokah, the god of thunder who is also god of the hunt. Haokah, a double-horned figure, laughs when he is sad, and cries when he is happy, thus creating the rain. The sun, known as Wi-Dakota to the Sioux and beaivi to the Sami, was of primary importance to both mythologies.” ref
“In the center of the Sami shaman or noaidi’s drum is the sun (beaivi) drawn as a rhomboid with four rays which spread to the sides. Along the rays spreading outward and surrounding the sun are the various gods which are the personified forces of nature. In this sense, the sun symbolizes the same central, animating source of the world as personified by the world tree or pillar, and all the gods are shown as subsidiary representations of this one central source of existence. A traditional Sioux mythological tale states that the White Buffalo Woman gave the Sioux people a pipe through which they could communicate with the divine reality or spirit world.” ref
“When a Sioux Indian would smoke from this pipe, also called a calumet, a specific ritualistic act was always performed. The possessor of the pipe would always hold it up to the sky to allow the sun to take the first draw from it and then he would address the four directions. This is the exact spiritual expression found on the face of the Sami shaman’s drum with the central sun with four rays, symbolizing the four directions, spreading from it. So it is clear that ultimately the Sami did not worship the natural phenomena themselves, nor did they idolize the personifications or gods, which represent those phenomena in and of themselves. Rather, they revered the mysterious power that manifested itself through them. This is the central spiritual idea of the ancient nature religions of man.” ref
“The Sioux had many different names for this omnipresent Great Spirit, including skan, wakonda, wagi tonka and wonka tonka. Black Elk explains this understanding: “But these four spirits are only one Spirit after all, and this eagle feather here is for that one, which is like a father…” (Neihardt 2) The Sun as the father of all creatures is an important symbol in the ancient mythology of the Sami as well. One of the two main Sami creation epics “The Son of the Sun’s Courting in the Land of the Giants” describes the Son making love to his bride and begetting the Gállábártnit, the ancestors of the Sámi. A passage from the poem describes the Son as father of the people: “On skin of bear and young reindeer doe / Bride is transformed to a Sámi / Becomes a human in size. / And with an ax from her own chest /Her doors become wider / The room made larger. / To the Sun’s sons she gave birth” (Gaski 101)” ref
“The ancient spiritualities of both cultures contain the same fundamental ideas and use virtually identical symbols to convey those ideas. Both spiritual traditions metaphorically describe the Sun as the father of all and the Earth as the mother of all. In both spiritual traditions, the symbolically masculine Sun represents the father-like central source point which is transcendent of the transitory physical world of the four directions. In both traditions, this eternal consciousness or source pours into the field of time through the symbolically feminine mother Earth and is characterized through a vast array of gods which are all ultimately part of this one mysterious thing represented by the Sun.” ref
“For the Sioux and the Sami, all of nature is viewed as being “alive”; they both possess an animistic perception of the universe. Their worldview is thus radically different from a modern perspective, emphasizing a sacred connection and interdependence of all things— including their prey and their enemies. Sioux society was primarily based on the buffalo, from which they derived everything they needed to survive. The itinerant patterns of the buffalo forced the Sioux to live nomadically in impermanent settlements, and their existence as a tribal unit was based on the movement of the buffalo herds.” ref
“The Sami were herders of another animal, the reindeer, whom they developed an almost symbiotic relationship with over many centuries. As the Sioux did with the buffalo, the Sami always made maximum use of the reindeer as food and commodities were often scarce in the harsh winter environment. It is as impossible to separate the Sami from their reindeer as it is to separate the Sioux from their buffalo and a deep bond of dependence and spiritual connection existed between each pair. Rather than a context of prey and predator, this relationship was one of coexistence within a sacred and interconnected universe. This worldview based on interconnection is further emboldened by their unwavering adherence and insistence upon it in times of discord, and their humble attitude in the face of great suffering imposed by others.” ref
“Both the Sami and the Sioux have faced historical conflicts with encroaching outside groups which resulted in violent confrontations. In the 18th and 19th century, the Sioux were forced from their land and had to continuously evade the superior forces of the U.S. Cavalry. As their lands shrank it became increasingly difficult to find a safe place to live in peace. When the Sioux and forces of the U.S. military did meet, the mass devastation was not surprisingly shouldered by the indigenous peoples unprepared for war, outnumbered, and lacking modern technology and weapons. At the Battle of Wounded Knee in 1890, four hundred Sioux men, women, and children were massacred. Yet on that terrifying day, the men ran into battle knowing they would be killed with the war cry “It’s a great day to die!” This deep knowledge of the interconnectedness and sacredness of all life had totally freed them from a materialistic conception of self and the fear of death.” ref
“For many hundreds of years, the Sami have faced encroachments by the Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish and Russian governments which have attempted to assimilate the Sami, levy taxes on them, divide the land they once freely roamed, and impose restrictions on movement between borders. The Sami also faced more violent and overt forms of oppression, especially in Norway and Sweden, where in the early part of the twentieth century the Norwegian government implemented efforts to wipe out Sami culture.” ref
“Additionally, the Sami faced confrontation by roaming groups of armed warriors known as the Tsjudes. This conflict is the focus of Nils Gaup’s 1987 film Pathfinder. Though based partially on legend, as a work of art the film contains many scenes which capture the heart of the Sami spiritual philosophy and its resilience in the face of adversity. In one of these scenes Aigin, a boy who has recently witnessed the slaughter of his entire family by the Tsjudes, is consulted by Raste, the shaman. Raste, instead of consoling Aigin, tells him to do away with his feelings of revenge because he is connected by invisible bonds to the Tsjudes and all other things through an infinite brotherhood. Raste explains that the Tsjudes have simply forgotten this fundamental truth and warns Aigin that to forget it would make him a Tsjude. For both groups, this deeply held conviction in the underlying unity of all life not only places their relationship to enemies and prey into a radically different framework than conventional or modern perspective, but it is a crucial component of their cultural identity.” ref
“The shaman, the Sami noaidi, was an important feature of Sami culture and spiritual tradition. The shaman was able to fulfill many practical purposes with his special talent and function as a leader in the community. Although the shaman had no formal authority, he traditionally held a dignified position and was well respected. By listening closely to the drum (called a meavrresgarri) to its “speech” or watching the particular pointers (arpa) while drumming with his hammer, it is said that a shaman could predict future events. The drumming of the shaman also served practical purposes for reindeer herding, finding lost objects, and hunting. Most important, however, the shaman served as a spiritual guide or priest, a mediator between this world and the spiritual realm, and a healer of illnesses.” ref
“According to the Sami, illness was caused by a person’s soul becoming lost or the invasion of a hostile object into the person’s body. The shaman would either retrieve the lost soul while in trance or expel the foreign object by invoking the aid of spirits or powers. Although the Sioux do not specify a specific cause for all illness, the shaman or medicine man employs a generally similar technique of entering into a trance-like state and calling for the assistance of natural powers. Black Elk recalls how he was “drumming as I cried to the Spirit of the World, and while I was doing this I could feel the power coming through me from my feet up, and I knew that I could help the sick boy” (Neihardt 154).” ref
“One important distinction between Sioux shamanism and that of the Sami is how one becomes a shaman. An old chieftain of the Oglalla Sioux, Chief Piece of Flat Iron, describes how shamans are chosen by a higher power:
To the Holy Man comes in youth the knowledge that he will be holy. The Great Mystery makes him know this. Sometimes it is the spirits who tell him…he goes into the hills in solitude. When he returns to men he teaches them and tells them what the Great Mystery has bidden him to tell. He counsels, he heals, and he makes holy charms to protect the people from all evil. (Campbell 243)” ref
“While these shamans are selected by their nature, Sami shamanism is most often passed down through family lineage. The noaidi is trained within the family by an elder and the training is initiated after the pupil reaches adolescence. After a period of time, the aspiring shaman must demonstrate to other noaidi control over his powers and practice. Despite this distinction, however, the shamanism of the Sioux contains basic thematic elements that also exist in the shamanism of the Sami.” ref
“One of these themes is a cyclical conception of time. Rather than being linear, time operates in the same manner as the natural world. Just as the day, the month, the year, and the seasons all move in a perpetual cycle, so time is viewed with an understanding of the movements of celestial bodies—the earth, the moon and the sun. This cyclical movement of time also applies to the lives of humans and other living beings as all things come into being, live, and then come to an inevitable end. However, there is also the notion that the cycle of time does not ultimately exist, and that the flux of the temporal world rests on the eternal source of being which is infinite and always “now.” ref
“This concept is expressed beautifully in the words of Nils-Aslak Valkeapää, a contemporary Sami poet:
and time does not exist, no end, none…and time is, eternal, always, is…rises, falls…is born, dies…thus,…days, years are rounded…snow melts…buds push…the river of life…into deep pools…in motion…the trek in the heart…land…rounded off…life’s circle…infinite…without…beginning…or end…fulfills…changes…colors…life (Valkeapää #566).” ref
“Additionally, shamans’ accounts of experiences while in trance are astonishingly similar in Sioux and Sami culture. The spiritual realm is described as existing in three levels: the upper world of the gods, the physical level of the world and living things, and the lower world where people and things go after death (known as Saivo to the Sami). Although these realms have slightly different meanings for each culture, the detail to which the imagery is in agreement suggests a common experience among shamans, which is transcendent of cultural and geographical boundaries.” ref
“References to Sami and Sioux spirituality in this work are directed at pre-Christian heritage and culture. Today the subtle, intricate, and sublime mythologies, rituals, and spiritual practices of these indigenous peoples are all but lost. Their relevance has been marginalized if not lost completely. The Sioux battled for centuries for their land and the maintenance of their cultural and spiritual practices. This battle was lost, however, as Western civilization forced the cultural extinction of one of the most spiritually enhanced peoples in world history. In Scandinavia in the 17th century, Christian missionaries murdered shamans in the name of spirituality and burned the sacred drums. Today only seventy-three of these drums remain preserved in museums.” ref
“For centuries, Christian missionaries have used violence and intimidation to attempt to convert the Sami. However, hundreds of years of subjugation under the boot of Christian hegemony have not totally crushed the ancient Sami spiritual worldview. Some remain critical of the form of spirituality brought by Christian missionaries and skeptical of missionaries’ ability even to understand their own spiritual symbols: “ you speak of eternal life…without knowing…what eternal is…what life is…and even you contain…infinity…the universe…strength, power…undiscovered…unused” (Valkeapää #432).” ref
“Today, some facets of the ancient spirituality of the Sami live. In the post-World War II era, some elements of Sami culture have been revived and there is an emerging self-identification with Sami ethnicity accompanied by a sense of cultural pride. Today, the spiritual experience of the Sami continues to manifest through the sacred interaction between the Sami and their environment and will remain until modernity and Western religion squeeze their anorexic physical and spiritual space to total annihilation—as occurred with the tragic death of the Sioux people and their sacred world.” ref
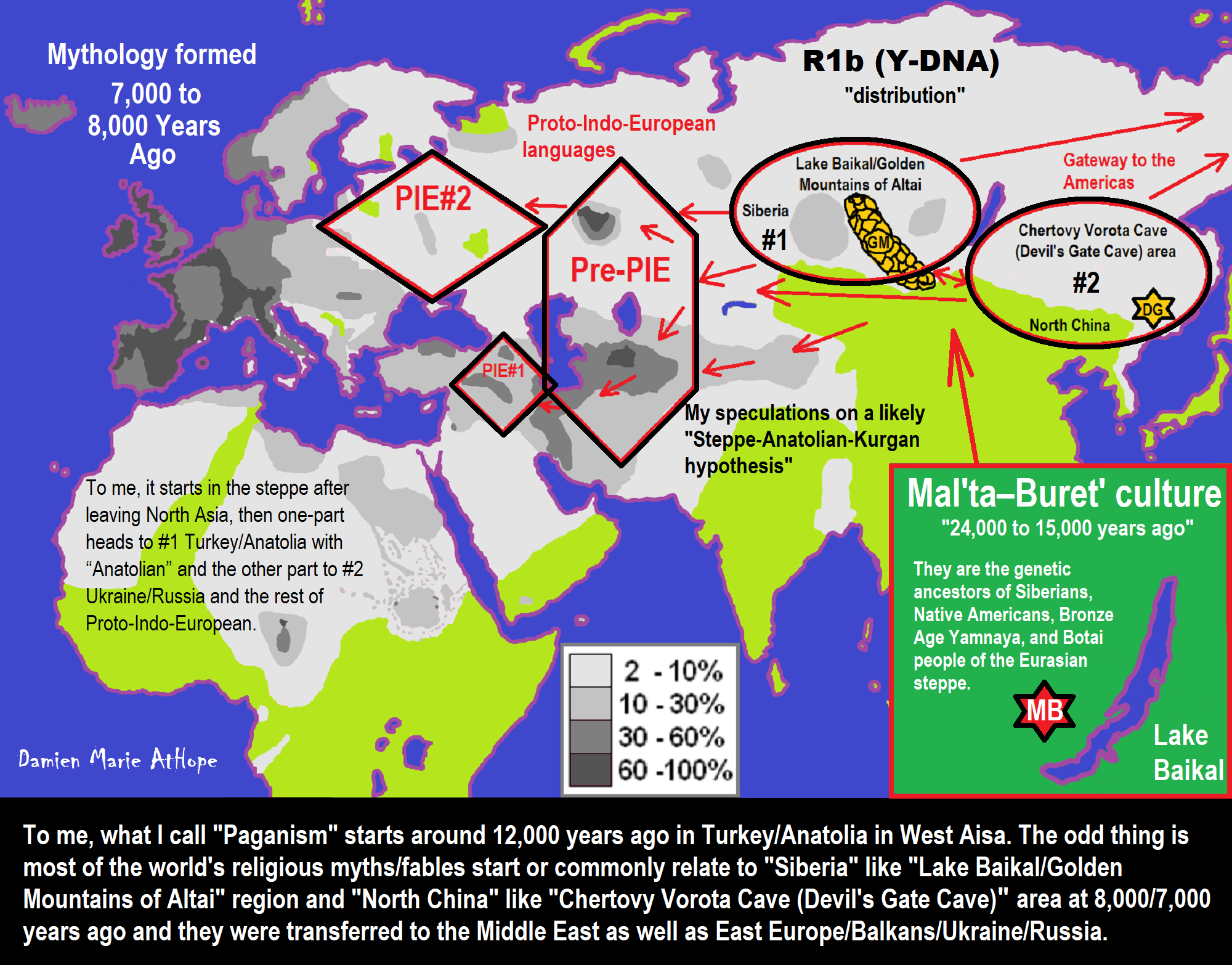
Haplogroup R possible time of origin about 27,000 years in Central Asia, South Asia, or Siberia:
- Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (24,000-15,000 years ago)
- Afontova Gora culture (21,000-12,000 years ago)
- Trialetian culture (16,000–8000 years ago)
- Samara culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Khvalynsk culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Afanasievo culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Yamna/Yamnaya Culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Andronovo culture (4,000–2,900 years ago) ref
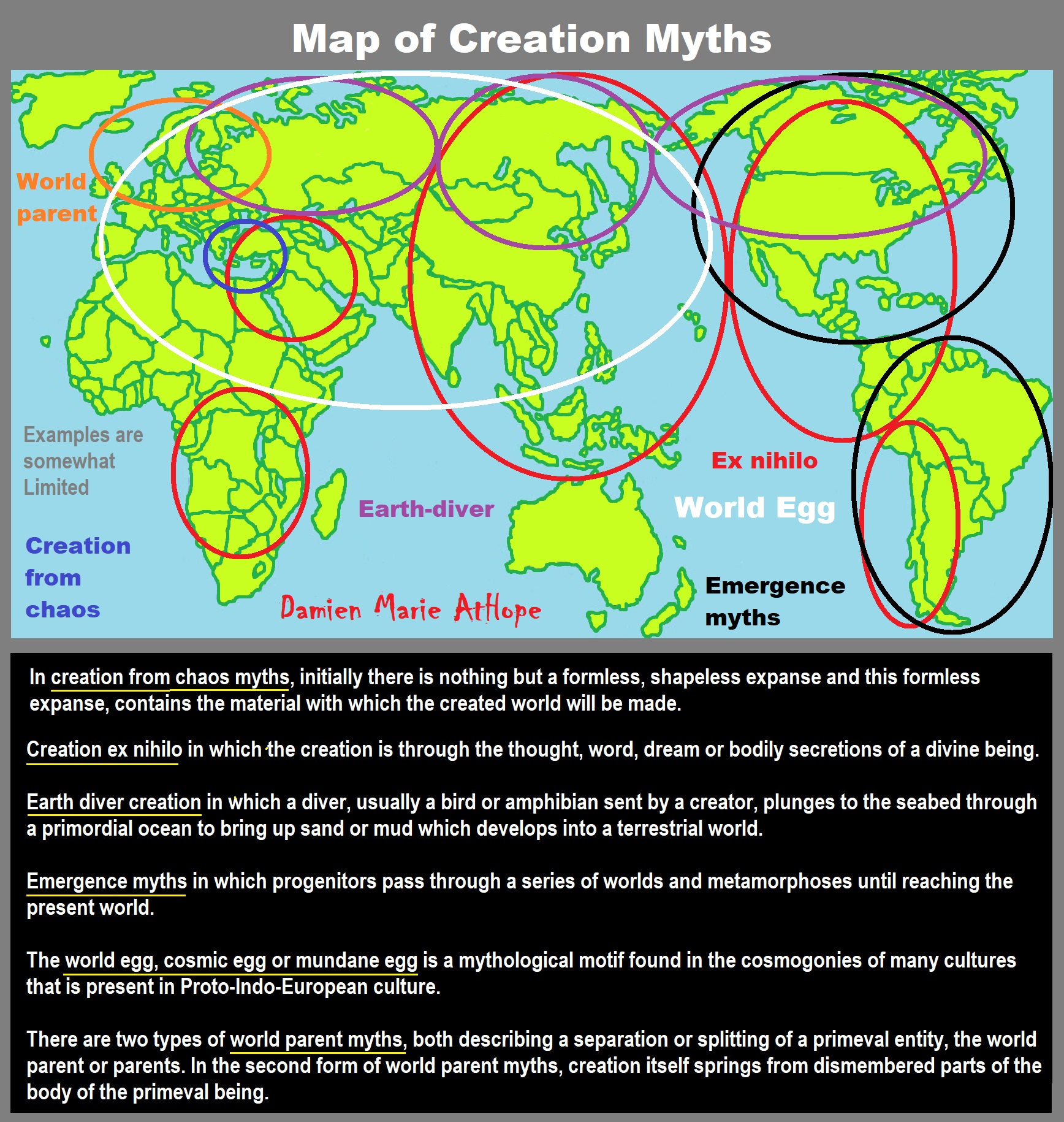
Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
“A creation myth (or cosmogonic myth) is a symbolic narrative of how the world began and how people first came to inhabit it. While in popular usage the term myth often refers to false or fanciful stories, members of cultures often ascribe varying degrees of truth to their creation myths. In the society in which it is told, a creation myth is usually regarded as conveying profound truths – metaphorically, symbolically, historically, or literally. They are commonly, although not always, considered cosmogonical myths – that is, they describe the ordering of the cosmos from a state of chaos or amorphousness.” ref
“Creation myths often share a number of features. They often are considered sacred accounts and can be found in nearly all known religious traditions. They are all stories with a plot and characters who are either deities, human-like figures, or animals, who often speak and transform easily. They are often set in a dim and nonspecific past that historian of religion Mircea Eliade termed in illo tempore (‘at that time’). Creation myths address questions deeply meaningful to the society that shares them, revealing their central worldview and the framework for the self-identity of the culture and individual in a universal context. Creation myths develop in oral traditions and therefore typically have multiple versions; found throughout human culture, they are the most common form of myth.” ref
Creation myth definitions from modern references:
- “A “symbolic narrative of the beginning of the world as understood in a particular tradition and community. Creation myths are of central importance for the valuation of the world, for the orientation of humans in the universe, and for the basic patterns of life and culture.”
- “Creation myths tell us how things began. All cultures have creation myths; they are our primary myths, the first stage in what might be called the psychic life of the species. As cultures, we identify ourselves through the collective dreams we call creation myths, or cosmogonies. … Creation myths explain in metaphorical terms our sense of who we are in the context of the world, and in so doing they reveal our real priorities, as well as our real prejudices. Our images of creation say a great deal about who we are.”
- A “philosophical and theological elaboration of the primal myth of creation within a religious community. The term myth here refers to the imaginative expression in narrative form of what is experienced or apprehended as basic reality … The term creation refers to the beginning of things, whether by the will and act of a transcendent being, by emanation from some ultimate source, or in any other way.” ref
Religion professor Mircea Eliade defined the word myth in terms of creation:
“Myth narrates a sacred history; it relates an event that took place in primordial Time, the fabled time of the “beginnings.” In other words, myth tells how, through the deeds of Supernatural Beings, a reality came into existence, be it the whole of reality, the Cosmos, or only a fragment of reality – an island, a species of plant, a particular kind of human behavior, an institution.” ref
“All creation myths are in one sense etiological because they attempt to explain how the world formed and where humanity came from. Myths attempt to explain the unknown and sometimes teach a lesson.” ref
“Some Ethnologists and anthropologists who study origin myths say that in the modern context theologians try to discern humanity’s meaning from revealed truths and scientists investigate cosmology with the tools of empiricism and rationality, but creation myths define human reality in very different terms. In the past, historians of religion and other students of myth thought of such stories as forms of primitive or early-stage science or religion and analyzed them in a literal or logical sense. Today, however, they are seen as symbolic narratives which must be understood in terms of their own cultural context. Charles Long writes: “The beings referred to in the myth – gods, animals, plants – are forms of power grasped existentially. The myths should not be understood as attempts to work out a rational explanation of deity.” ref
“While creation myths are not literal explications, they do serve to define an orientation of humanity in the world in terms of a birth story. They provide the basis of a worldview that reaffirms and guides how people relate to the natural world, to any assumed spiritual world, and to each other. A creation myth acts as a cornerstone for distinguishing primary reality from relative reality, the origin and nature of being from non-being. In this sense, cosmogonic myths serve as a philosophy of life – but one expressed and conveyed through symbol rather than through systematic reason. And in this sense, they go beyond etiological myths (which explain specific features in religious rites, natural phenomena, or cultural life). Creation myths also help to orient human beings in the world, giving them a sense of their place in the world and the regard that they must have for humans and nature.” ref
Historian David Christian has summarised issues common to multiple creation myths:
“Each beginning seems to presuppose an earlier beginning. … Instead of meeting a single starting point, we encounter an infinity of them, each of which poses the same problem. … There are no entirely satisfactory solutions to this dilemma. What we have to find is not a solution but some way of dealing with the mystery …. And we have to do so using words. The words we reach for, from God to gravity, are inadequate to the task. So we have to use language poetically or symbolically; and such language, whether used by a scientist, a poet, or a shaman, can easily be misunderstood.” ref
“Mythologists have applied various schemes to classify creation myths found throughout human cultures. Eliade and his colleague Charles Long developed a classification based on some common motifs that reappear in stories the world over. The classification identifies five basic types: Brahmā, the Hindu deva of creation, emerges from a lotus risen from the navel of Viṣņu, who lies with Lakshmi on the serpent Ananta Shesha.” ref
- “Creation ex nihilo in which the creation is through the thought, word, dream, or bodily secretions of a divine being.
- Earth diver creation in which a diver, usually a bird or amphibian sent by a creator, plunges to the seabed through a primordial ocean to bring up sand or mud which develops into a terrestrial world.
- Emergence myths in which progenitors pass through a series of worlds and metamorphoses until reaching the present world.
- Creation by the dismemberment of a primordial being.
- Creation by the splitting or ordering of a primordial unity such as the cracking of a cosmic egg or a bringing order from chaos.” ref
“Marta Weigle further developed and refined this typology to highlight nine themes, adding elements such as deus faber, a creation crafted by a deity, creation from the work of two creators working together or against each other, creation from sacrifice, and creation from division/conjugation, accretion/conjunction, or secretion.” ref
An alternative system based on six recurring narrative themes was designed by Raymond Van Over:
- “Primeval abyss, an infinite expanse of waters or space.
- Originator deity which is awakened or an eternal entity within the abyss.
- Originator deity poised above the abyss.
- Cosmic egg or embryo.
- Originator deity creating life through sound or word.
- Life generating from the corpse or dismembered parts of an originator deity.” ref

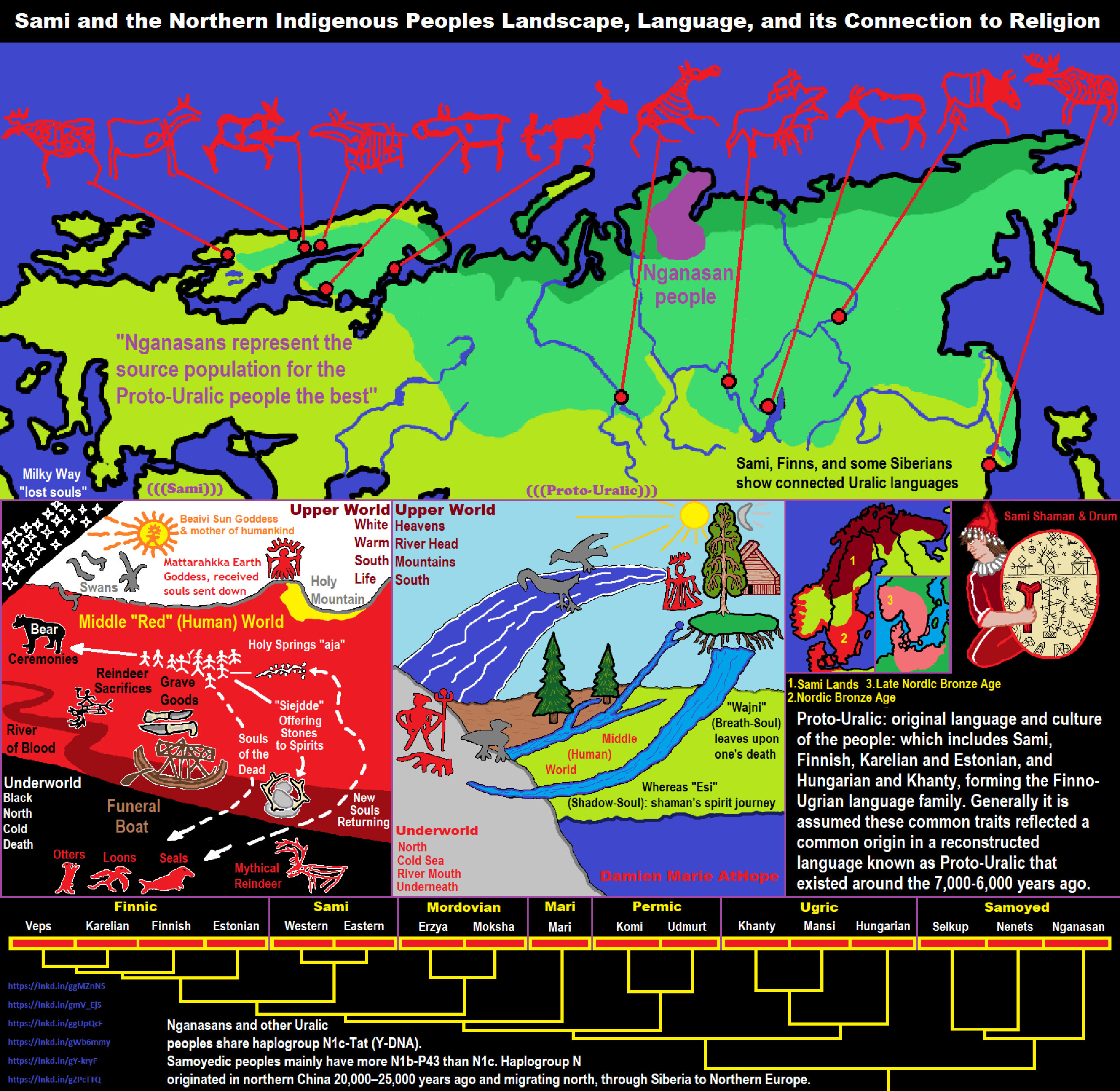
Proto-Uralic religion
“Elements of a Proto-Uralic religion can be recovered from reconstructions of the Proto-Uralic language. According to linguist Ante Aikio, although “evidence of immaterial culture is very limited” in the Proto-Uralic language, “a couple of lexical items can be seen as pointing to a shamanistic system of beliefs and practices.” The concept of soul dualism, which is widely attested among Uralic-speaking peoples, probably dates back to the Proto-Uralic period: the word *wajŋi (‘breath-soul’) designated the soul bound to the living body, which only left it at the moment of death, whereas *eśi (or *iśi, *ićći) referred to the ‘shadow-soul’, believed to be able to leave the body during lifetime, as when dreaming, in a state of unconsciousness or in a shaman’s spirit journey.” ref
“The Indo-Iranian loanword *pi̮ŋka designated a ‘psychedelic mushroom’, perhaps the one used by the shaman to enter altered states of consciousness. The verb *kixi– meant both ‘to court [of birds]’ and ‘to sing a shamanistic song’, suggesting that it referred to states of both sexual and spiritual excitement. If the etymology remains uncertain, the word ‘shaman’ itself may be rendered as *nojta, and the shamanic practice as *jada-, although semantic variations in the daughter languages make the reconstruction debatable (cf. Erzya Mordvin jɑdɑ– ‘to conjure, do magic, bewitch’, East Khanty jɔːl– ‘to tell fortunes, shamanize’, Ket Selkup tjɑːrә– ‘to curse; quarrel’). Several Finno-Ugric languages have a theonym that can be derived from the Proto-Finno-Ugric word *ilma meaning sky or weather. These include Udmurt Inmar, Komi-Zyrjan Jen, Khanty Num-Ilәm, and Finnish Ilmarinen. These theonyms suggest an early central Proto-Finno-Ugric sky-god.” ref
Indigenous Sámi religion
“Indigenous Sámi religion is a type of polytheism. (See Sámi deities.) There is some diversity due to the wide area that is Sápmi, allowing for the evolution of variations in beliefs and practices between tribes. The beliefs are closely connected to the land, animism, and the supernatural. Sámi spirituality is often characterized by pantheism, a strong emphasis on the importance of personal spirituality and its interconnectivity with one’s own daily life, and a deep connection between the natural and spiritual “worlds”. Among other roles, the Noaidi, or Sámi shaman, enables ritual communication with the supernatural through the use of tools such as drums, Joik, Fadno, chants, sacred objects, and fly agaric. Some practices within the Sámi religion include natural sacred sites such as mountains, springs, land formations, Sieidi, as well as man-made ones such as petroglyphs and labyrinths.” ref
“Sámi cosmology divides the universe into three worlds. The upper world is related to the South, warmth, life, and the color white. It is also the dwelling of the gods. The middle world is like the Norse Midgard, it is the dwelling of humans and it is associated with the color red. The third world is the underworld and it is associated with the color black, it represents the north, the cold and it is inhabited by otters, loons, seals, and mythical animals. Sámi religion shares some elements with Norse mythology, possibly from early contacts with trading Vikings (or vice versa). They were the last worshippers of Thor, as late as the 18th century according to contemporary ethnographers.” ref
“Through a mainly French initiative from Joseph Paul Gaimard as part of his La Recherche Expedition, Lars Levi Læstadius began research on Sámi mythology. His work resulted in Fragments of Lappish Mythology, since by his own admission, they contained only a small percentage of what had existed. The fragments were termed Theory of Gods, Theory of Sacrifice, Theory of Prophecy, or short reports about rumorous Sami magic and Sami sagas. Generally, he claims to have filtered out the Norse influence and derived common elements between the South, North, and Eastern Sámi groups. The mythology has common elements with other indigenous religions as well—such as those of indigenous peoples in Siberia and North America.” ref
“Anthropologists have been studying the Sámi people for hundreds of years for their assumed physical and cultural differences from the rest of the Europeans. Recent genetic studies have indicated that the two most frequent maternal lineages of the Sámi people are the haplogroups V (Neolithic in Europe and not found in Finland 1500 years ago) and U5b (ancient in Europe). Y-chromosome haplogroup N-VL29 makes up 20%, came from Siberia 3500 years ago. Y-chromosome N-Z1936 makes up similarly about 20%, and likely came from Siberia with the Sámi language, but slightly later than N-VL29. This tallies with archeological evidence suggesting that several different cultural groups made their way to the core area of Sámi from 8000 to 6000 BCE, presumably including some of the ancestors of present-day Sámi. The Sámi have been found to be genetically unrelated to people of the Pitted Ware culture. The Pitted Ware culture are in turn genetically continuous with the original Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers.” ref
Norse mythology
“Norse or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths of the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Norse paganism and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Scandinavian folklore of the modern period. The northernmost extension of Germanic mythology and stemming from Proto-Germanic folklore, Norse mythology consists of tales of various deities, beings, and heroes derived from numerous sources from both before and after the pagan period, including medieval manuscripts, archaeological representations, and folk tradition. Norse mythology has been the subject of scholarly discourse since the 17th century, when key texts attracted the attention of the intellectual circles of Europe. By way of comparative mythology and historical linguistics, scholars have identified elements of Germanic mythology reaching as far back as Proto-Indo-European mythology.” ref
“The source texts mention numerous gods, such as the hammer-wielding, humanity-protecting thunder-god Thor, who relentlessly fights his foes; the one-eyed, raven-flanked god Odin, who craftily pursues knowledge throughout the worlds and bestowed among humanity the runic alphabet; the beautiful, seiðr-working, feathered cloak-clad goddess Freyja who rides to battle to choose among the slain; the vengeful, skiing goddess Skaði, who prefers the wolf howls of the winter mountains to the seashore; the powerful god Njörðr, who may calm both sea and fire and grant wealth and land; the god Freyr, whose weather and farming associations bring peace and pleasure to humanity; the goddess Iðunn, who keeps apples that grant eternal youthfulness; the mysterious god Heimdallr, who is born of nine mothers, can hear grass grow, has gold teeth, and possesses a resounding horn; the jötunn‘s son, the god Loki, who brings tragedy to the gods by engineering the death of the goddess Frigg‘s beautiful son Baldr; and numerous other deities.” ref
“Most of the surviving mythology centers on the plights of the gods and their interaction with several other beings, such as humanity and the jötnar, beings who may be friends, lovers, foes, or family members of the gods. The cosmos in Norse mythology consists of Nine Worlds that flank a central sacred tree, Yggdrasil. Units of time and elements of cosmology are personified as deities or beings. Various forms of a creation myth are recounted, where the world is created from the flesh of the primordial being Ymir, and the first two humans are Ask and Embla. These worlds are foretold to be reborn after the events of Ragnarök when an immense battle occurs between the gods and their enemies, and the world is enveloped in flames, only to be reborn anew. There the surviving gods will meet, and the land will be fertile and green, and two humans will repopulate the world.” ref
Proto-Indo-European mythology
“Proto-Indo-European mythology is the body of myths and deities associated with the Proto-Indo-Europeans, the hypothetical speakers of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language. Although the mythological motifs are not directly attested – since Proto-Indo-European speakers lived in preliterate societies – scholars of comparative mythology have reconstructed details from inherited similarities found among Indo-European languages, based on the assumption that parts of the Proto-Indo-Europeans’ original belief systems survived in the daughter traditions.” ref
The Proto-Indo-European pantheon includes a number of securely reconstructed deities, since they are both cognates – linguistic siblings from a common origin –, and associated with similar attributes and body of myths: such as *Dyḗws Ph₂tḗr, the daylight-sky god; his consort *Dʰéǵʰōm, the earth mother; his daughter *H₂éwsōs, the dawn goddess; his sons the Divine Twins; and *Seh₂ul, a solar goddess. Some deities, like the weather god *Perkʷunos or the herding-god *Péh₂usōn, are only attested in a limited number of traditions – Western (European) and Graeco-Aryan, respectively – and could therefore represent late additions that did not spread throughout the various Indo-European dialects.” ref
“Some myths are also securely dated to Proto-Indo-European times, since they feature both linguistic and thematic evidence of an inherited motif: a story portraying a mythical figure associated with thunder and slaying a multi-headed serpent to release torrents of water that had previously been pent up; a creation myth involving two brothers, one of whom sacrifices the other in order to create the world; and probably the belief that the Otherworld was guarded by a watchdog and could only be reached by crossing a river. Various schools of thought exist regarding possible interpretations of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European mythology. The main mythologies used in comparative reconstruction are Indo-Iranian, Baltic, Roman, and Norse, often supported with evidence from the Celtic, Greek, Slavic, Hittite, Armenian, Illyrian, and Albanian traditions as well.” ref
“Rare unclassified haplogroup N* has been found among fossils belonging to the Cardial and Epicardial culture (Cardium pottery) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B. Haplogroup N1a – Arabian Peninsula and Northeast Africa. Found also in Central Asia and Southern Siberia. This branch is well attested in ancient people from various cultures of Neolithic Europe, from Hungary to Spain, and among the earliest farmers of Anatolia.” ref
Cardium pottery
“Cardium pottery or Cardial ware is a Neolithic decorative style that gets its name from the imprinting of the clay with the heart-shaped shell of the Corculum cardissa , a member of the cockle family Cardiidae. These forms of pottery are in turn used to define the Neolithic culture which produced and spread them, commonly called the “Cardial culture”. The alternative name, impressed ware, is given by some archaeologists to define this culture, because impressions can be made with sharp objects other than cockle shells, such as a nail or comb.” ref
“Impressed pottery is much more widespread than the Cardial. Impressed ware is found in the zone “covering Italy to the Ligurian coast” as distinct from the more western Cardial extending from Provence to western Portugal. The sequence in prehistoric Europe has traditionally been supposed to start with widespread Cardial ware, and then to develop other methods of impression locally, termed “epi-Cardial”. However the widespread Cardial and Impressed pattern types overlap and are now considered more likely to be contemporary.” ref
“This pottery style gives its name to the main culture of the Mediterranean Neolithic: Cardium pottery culture or Cardial culture, or impressed ware culture, which eventually extended from the Adriatic sea to the Atlantic coasts of Portugal and south to Morocco. The earliest impressed ware sites, dating to 6400–6200 BCE, are in Epirus and Corfu. Settlements then appear in Albania and Dalmatia on the eastern Adriatic coast dating to between 6100 and 5900 BCE. The earliest date in Italy comes from Coppa Nevigata on the Adriatic coast of southern Italy, perhaps as early as 6000 cal BCE.” ref
“Also during Su Carroppu culture in Sardinia, already in its early stages (low strata into Su Coloru cave, c. 6000 BCE) early examples of cardial pottery appear. Northward and westward all secure radiocarbon dates are identical to those for Iberia c. 5500 cal BCE, which indicates a rapid spread of Cardial and related cultures: 2,000 km from the gulf of Genoa to the estuary of the Mondego in probably no more than 100–200 years. This suggests a seafaring expansion by planting colonies along the coast. Older Neolithic cultures existed already at this time in eastern Greece and Crete, apparently having arrived from the Levant, but they appear distinct from the Cardial or impressed ware culture.” ref
“The ceramic tradition in the central Balkans also remained distinct from that along the Adriatic coastline in both style and manufacturing techniques for almost 1,000 years from the 6th millennium BCE. Early Neolithic impressed pottery is found in the Levant, and certain parts of Anatolia, including Mezraa-Teleilat, and in North Africa at Tunus-Redeyef, Tunisia. So the first Cardial settlers in the Adriatic may have come directly from the Levant.” ref
“Of course, it might equally well have come directly from North Africa, and impressed pottery also appears in Egypt. Along the East Mediterranean coast impressed ware has been found in North Syria, Palestine, and Lebanon. Cardial and Epicardial fossils that were analyzed for ancient DNA were found to carry the rare mtDNA (maternal) basal haplogroup N*, supporting an early Neolithic maritime colonization of Mainland Europe through Cyprus and the Aegean Islands by Near-Eastern farmers.” ref
“Fernández et al. 2014 found traces of maternal genetic affinity between people of the Linear Pottery Culture and Cardium pottery with earlier peoples of the Near Eastern Pre-Pottery Neolithic B, and suggested that Neolithic period was initiated by seafaring colonists from the Near East. Olalde et al. 2015 examined the remains of 6 Cardials buried in Spain c. 5470-5220 BCE. The 6 samples of mtDNA extracted belonged to the maternal haplogroups K1a2a, X2c, H4a1a (2 samples), H3, and K1a4a1.” ref
“The authors of the study suggested that the Cardials and peoples of the Linear Pottery Culture were descended from a common farming population in the Balkans, which had subsequently migrated further westwards into Europe along the Mediterranean coast and Danube river respectively. Among modern populations, the Cardials were found to be most closely related to Sardinians and Basque people. The Iberian Cardials carried a noticeable amount of hunter-gatherer ancestry. This hunter-gatherer ancestry was more similar to that of Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHGs) than Iberian hunter-gatherers, and appeared to have been acquired before the Cardial expansion into Iberia.” ref
“Mathieson et al. 2018 examined three Cardials buried at the Zemunica Cave in modern-day Croatia c. 5800 BCE. The two samples of Y-DNA extracted belonged to the paternal haplogroups C1a2 and E1b1b1a1b1, while the three samples of mtDNA extracted belonged to the maternal haplogroups H1, K1b1a, and N1a1. The team further examined two Cardials buried at Kargadur in modern-day Croatia c. 5600 BCE. The one male carried the paternal haplogroup G2a2a1, and the maternal haplogroup H7c, and the female carried H5a.” ref
“All three belonged to the Early European Farmer (EEF) cluster, thus being closely related to earlier Neolithic populations of north-west Anatolia, of the Balkan Neolithic, contemporary peoples of the Central European Linear Pottery culture, and later peoples of the Cardial Ware culture in Iberia. This would suggest that the Cardial Ware people and the Linear Pottery people were derived from a single migration from Anatolia into the Balkans, which then split into two and expanded northward and westward further into Europe.” ref
Haplogroup N1c (Y-DNA)
“Haplogroup N1c is found chiefly in north-eastern Europe, particularly in Finland (61%), Lapland (53%), Estonia (34%), Latvia (38%), Lithuania (42%), and northern Russia (30%), and to a lower extent also in central Russia (15%), Belarus (10%), eastern Ukraine (9%), Sweden (7%), Poland (4%) and Turkey (4%). N1c is also prominent among the Uralic-speaking ethnicities of the Volga-Ural region, including the Udmurts (67%), Komi (51%), Mari (50%), and Mordvins (20%), but also among their Turkic neighbors like the Chuvashs (28%), Volga Tatars (21%) and Bashkirs (17%), as well as the Nogais (9%) of southern Russia.” ref
“N1c represents the western extent of haplogroup N, which is found all over the Far East (China, Korea, Japan), Mongolia, and Siberia, especially among Uralic speakers of northern Siberia. Haplogroup N1 reaches a maximum frequency of approximately 95% in the Nenets (40% N1c and 57% N1b) and Nganassans (all N1b), two Uralic tribes of central-northern Siberia, and 90% among the Yakuts (all N1c), a Turkic people who live mainly in the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic in central-eastern Siberia.” ref
“Haplogroup N is a descendant of East Asian macro-haplogroup NO. It is believed to have originated in Indochina or southern China approximately 15,000 to 20,000 years ago. Haplogroup N1* and N1c were both found at high frequency (26 out of 70 samples, or 37%) in Neolithic and Bronze Age remains (4500-700 BCE) from the West Liao River valley in Northeast China (Manchuria) by Yinqiu Cui et al. (2013). Among the Neolithic samples, haplogroup N1 made up two thirds of the samples from the Hongshan culture (4700-2900 BCE) and all the samples from the Xiaoheyan culture (3000-2200 BCE), hinting that N1 people played a major role in the diffusion of the Neolithic lifestyle around Northeast China, and probably also to Mongolia and Siberia.” ref
“Ye Zhang et al. 2016 found 100% of Y-DNA N out of 17 samples from the Xueshan culture (Jiangjialiang site) dating from 3600–2900 BCE, and among those 41% belonged to N1c1-Tat. It is therefore extremely likely that the N1c1 subclade found in Europe today has its roots in the Chinese Neolithic. It would have progressively spread across Siberia until north-eastern Europe, possibly reaching the Volga-Ural region around 5500 to 4500 BCE with the Kama culture (5300-3300 BCE), and the eastern Baltic with the Comb Ceramic culture (4200-2000 BCE), the presumed ancestral culture of Proto-Finnic and pre-Baltic people. There is little evidence of agriculture or domesticated animals in Siberia during the Neolithic, but pottery was widely used. In that regard it was the opposite development from the Near East, which first developed agriculture then only pottery from circa 5500 BCE, perhaps through contact with East Asians via Siberia or Central Asia.” ref
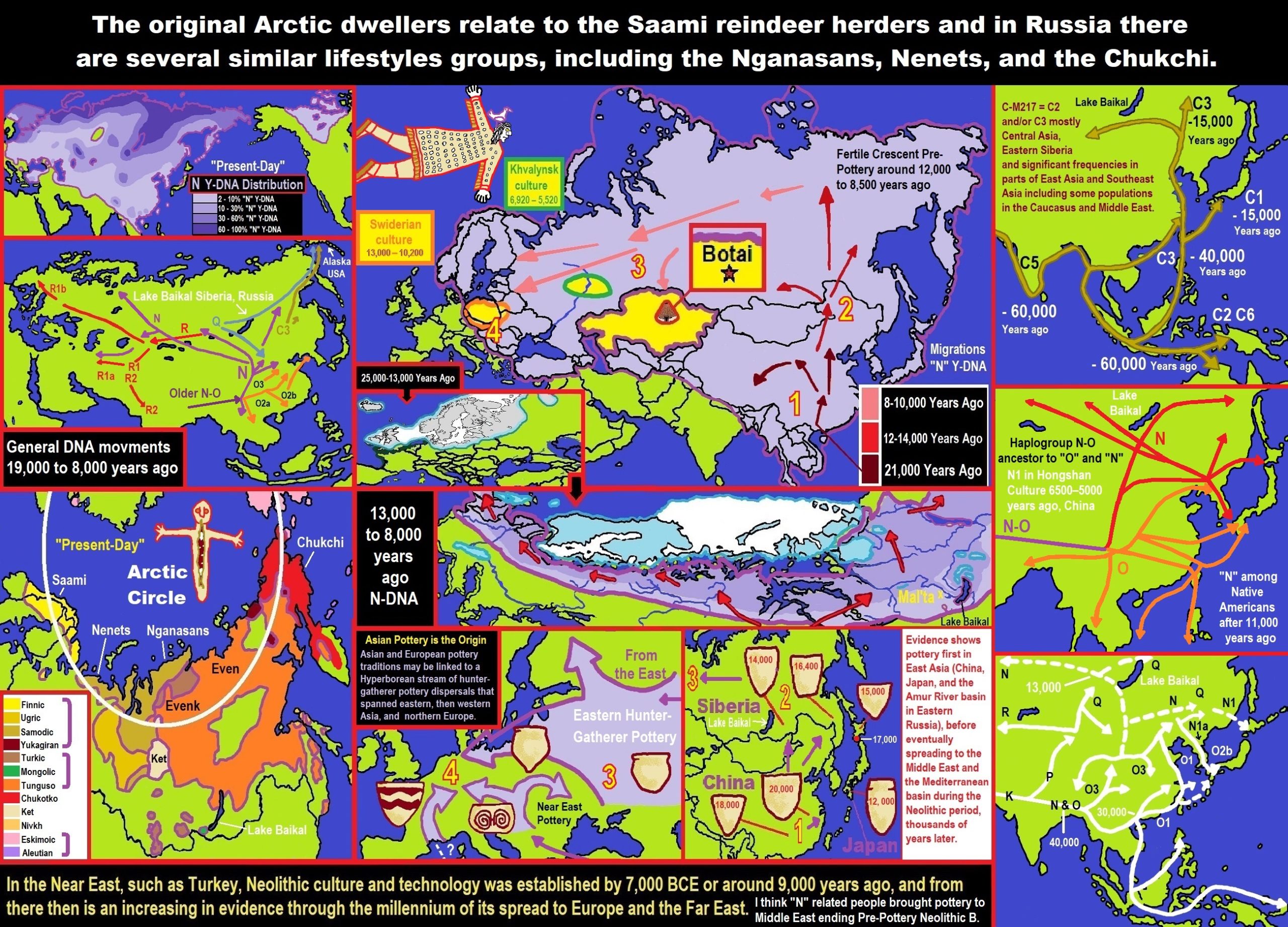
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“The shaman is, above all, a connecting figure, bridging several worlds for his people, traveling between this world, the underworld, and the heavens. He transforms himself into an animal and talks with ghosts, the dead, the deities, and the ancestors. He dies and revives. He brings back knowledge from the shadow realm, thus linking his people to the spirits and places which were once mythically accessible to all.–anthropologist Barbara Meyerhoff” ref
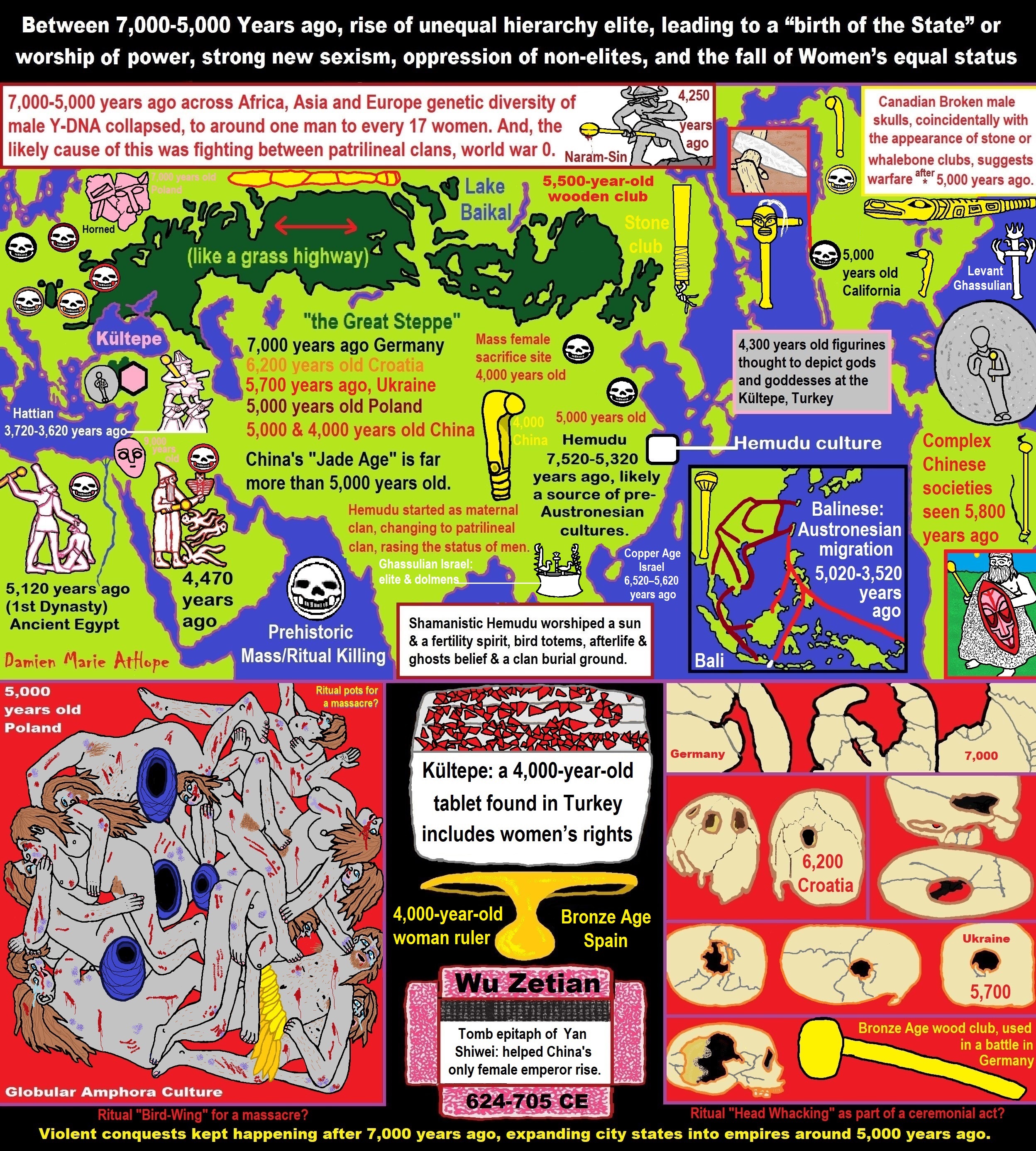
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref


Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref


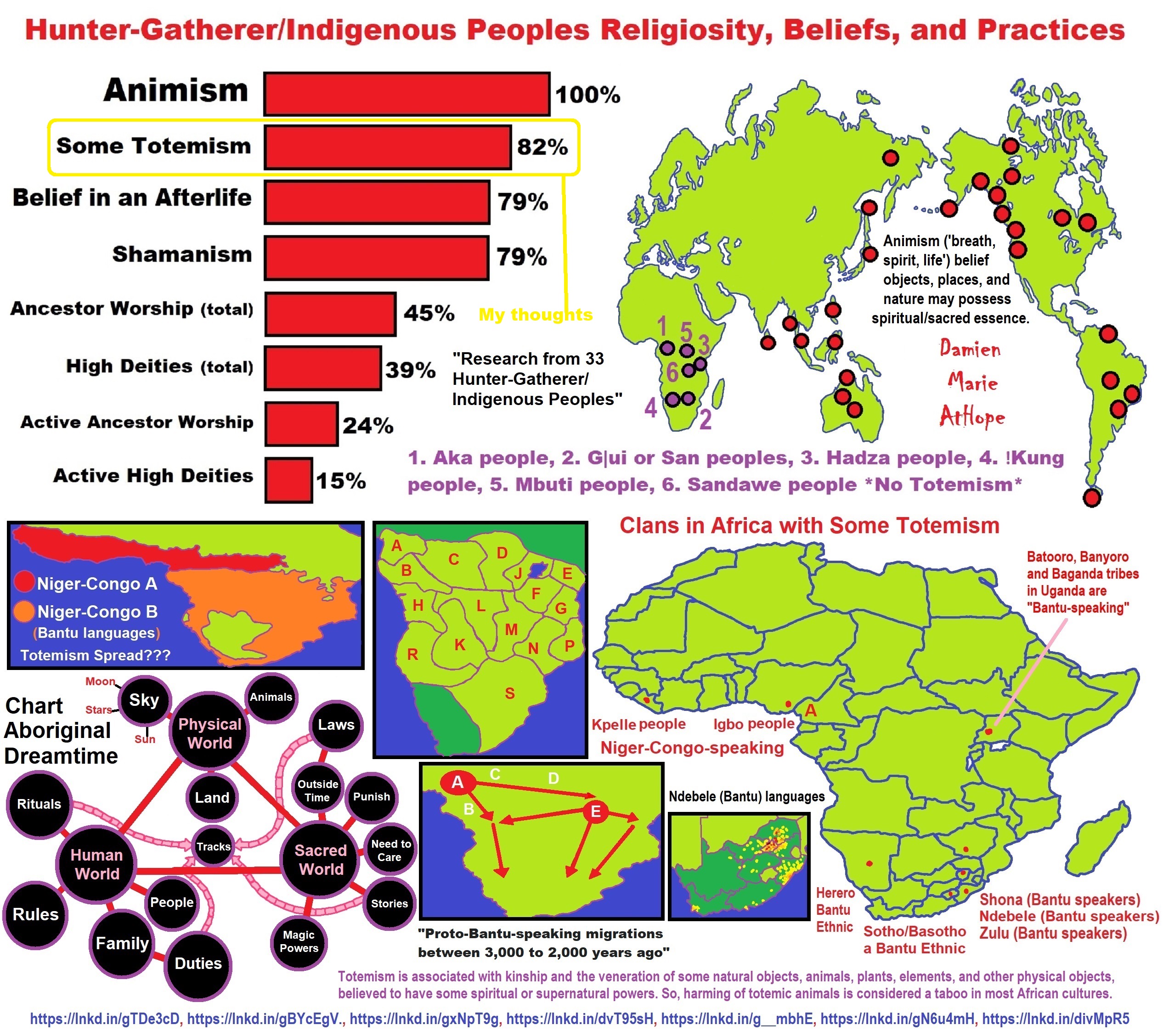
My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
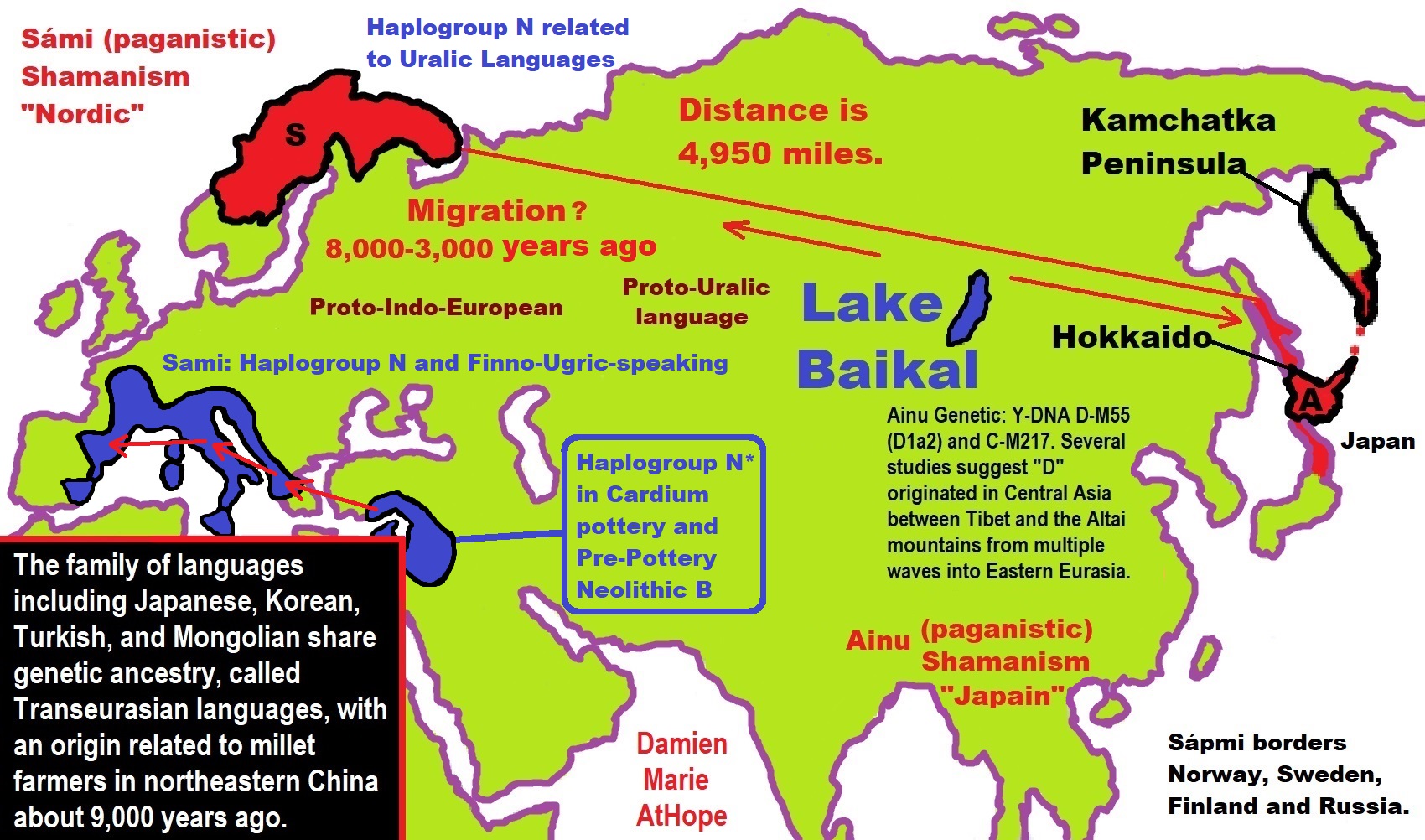
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
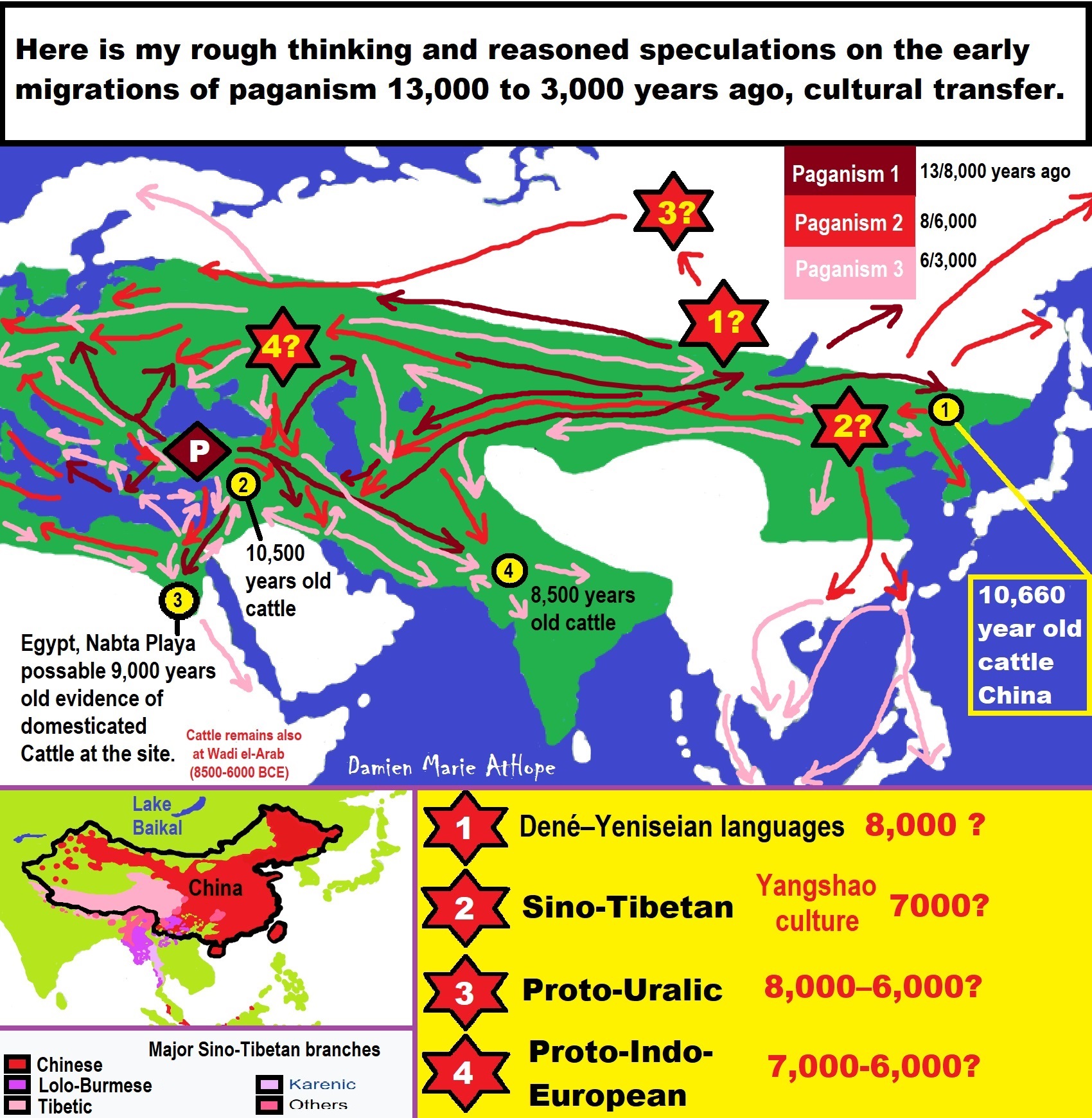
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
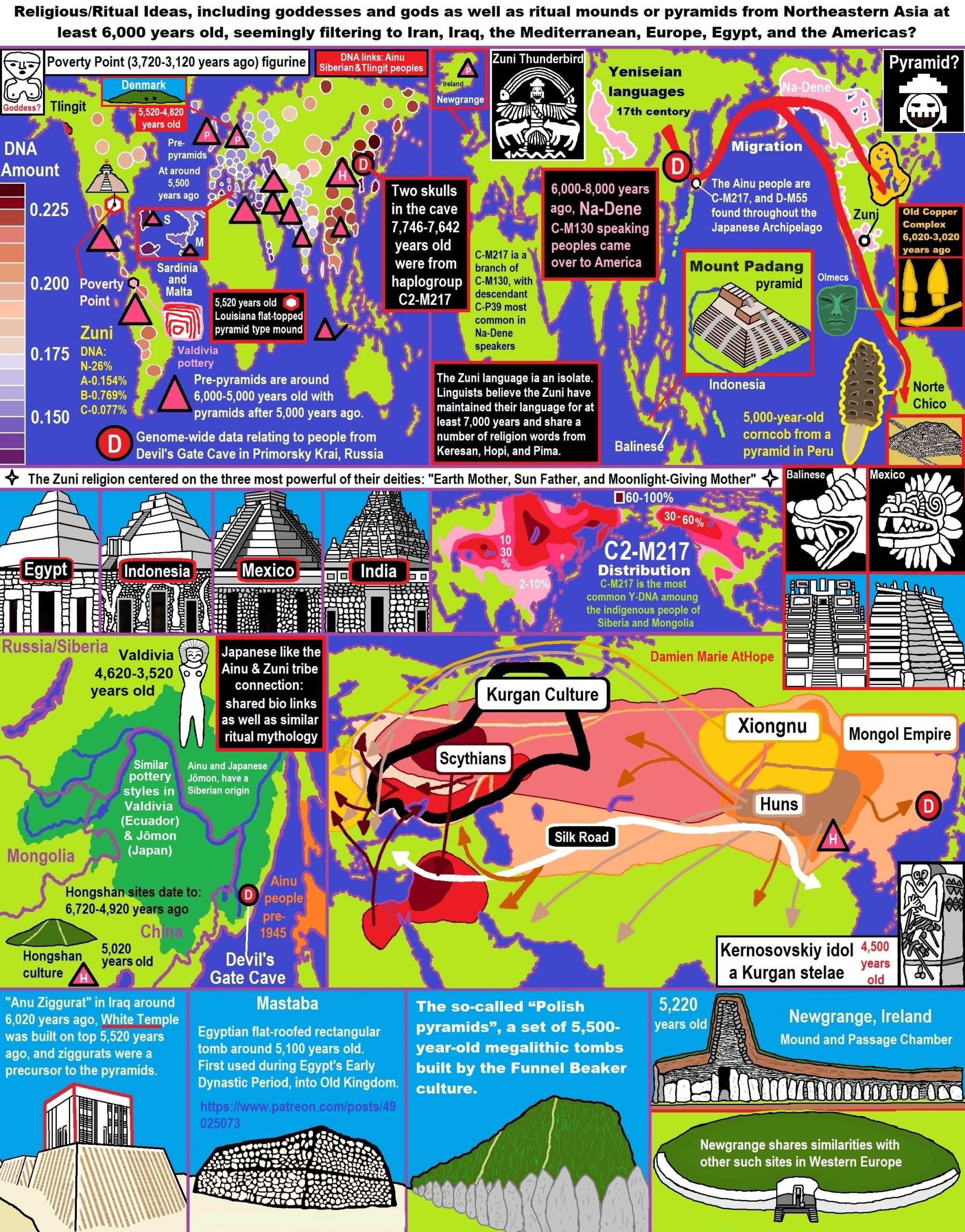
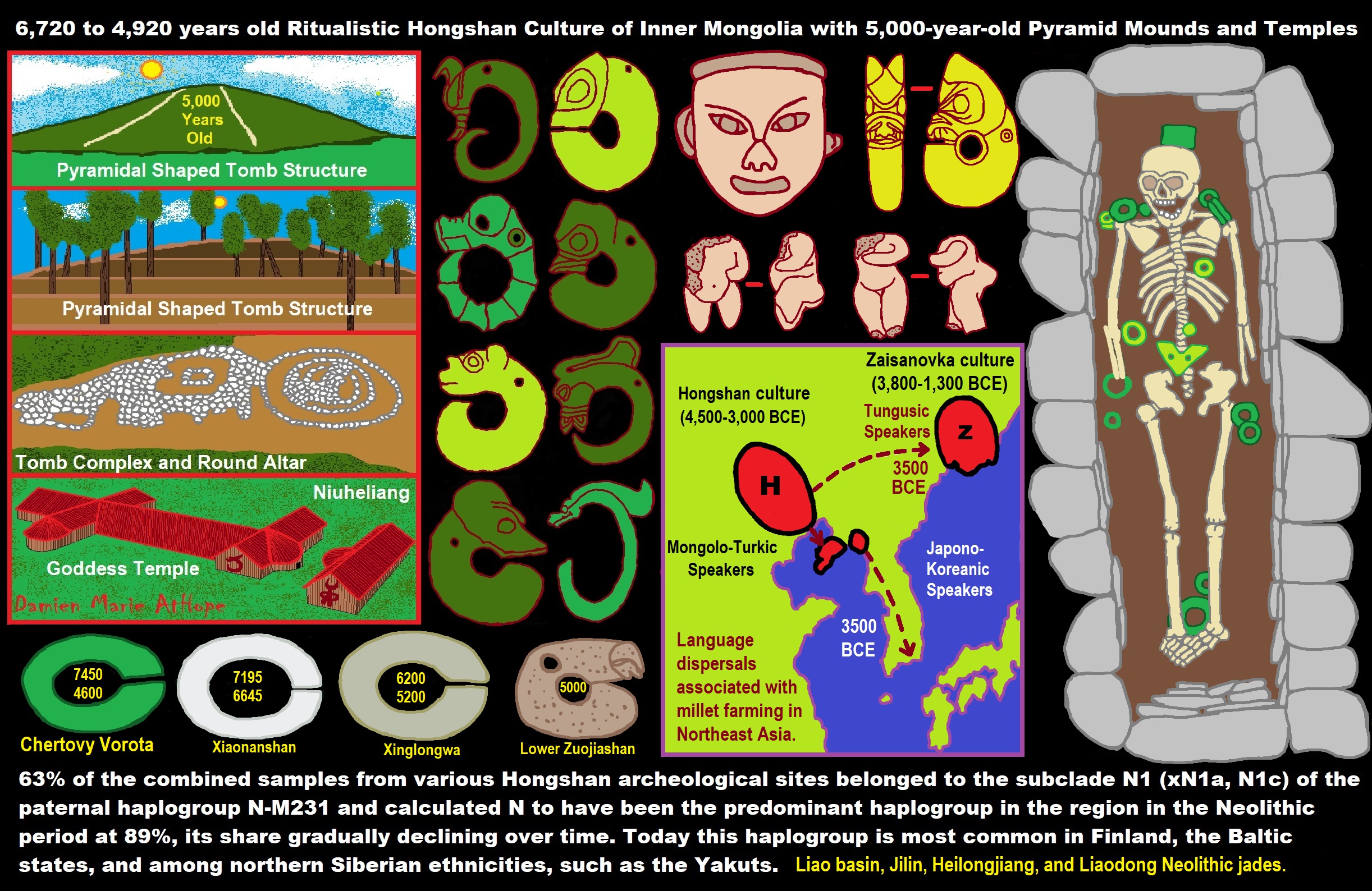
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
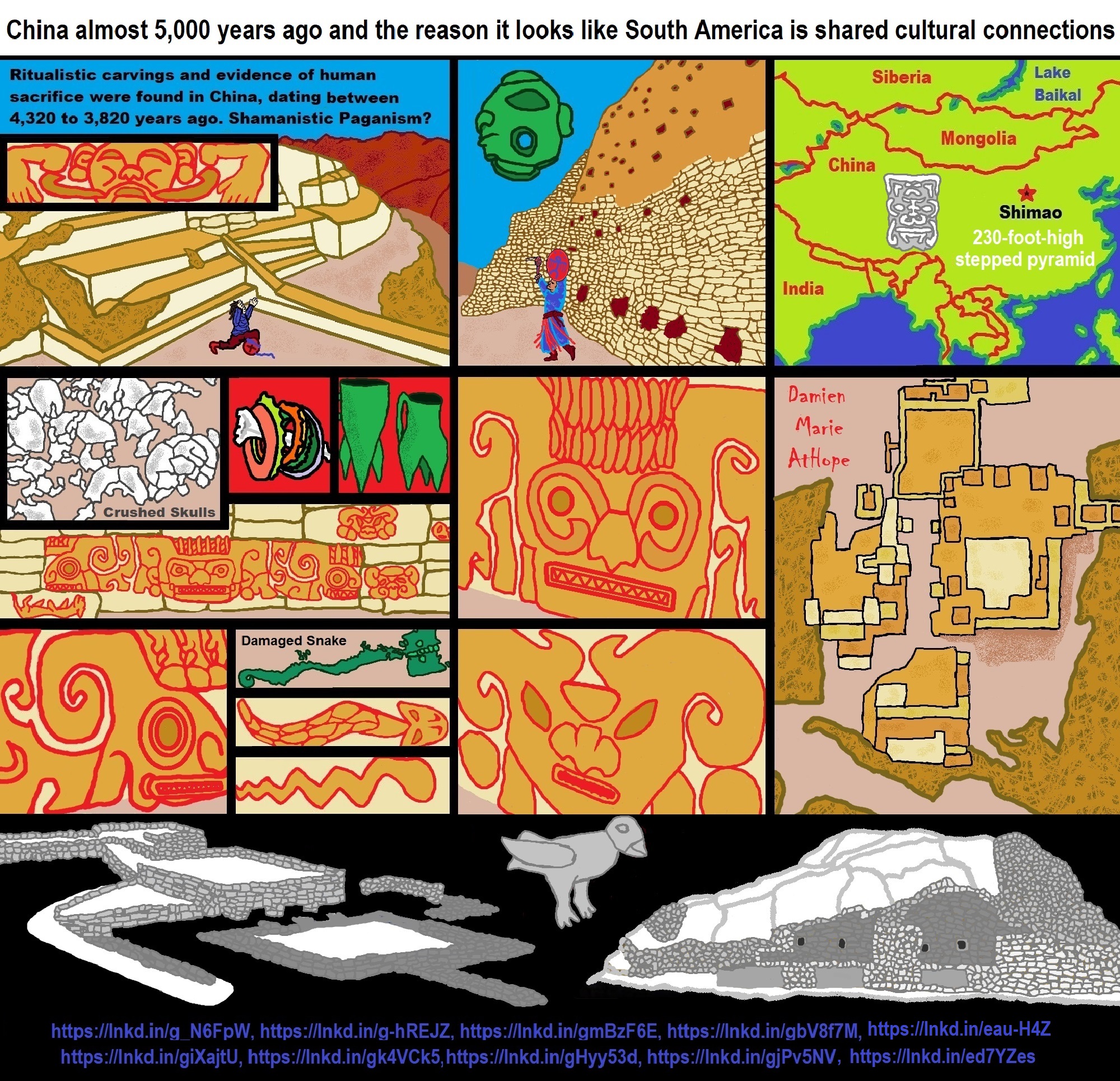
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.

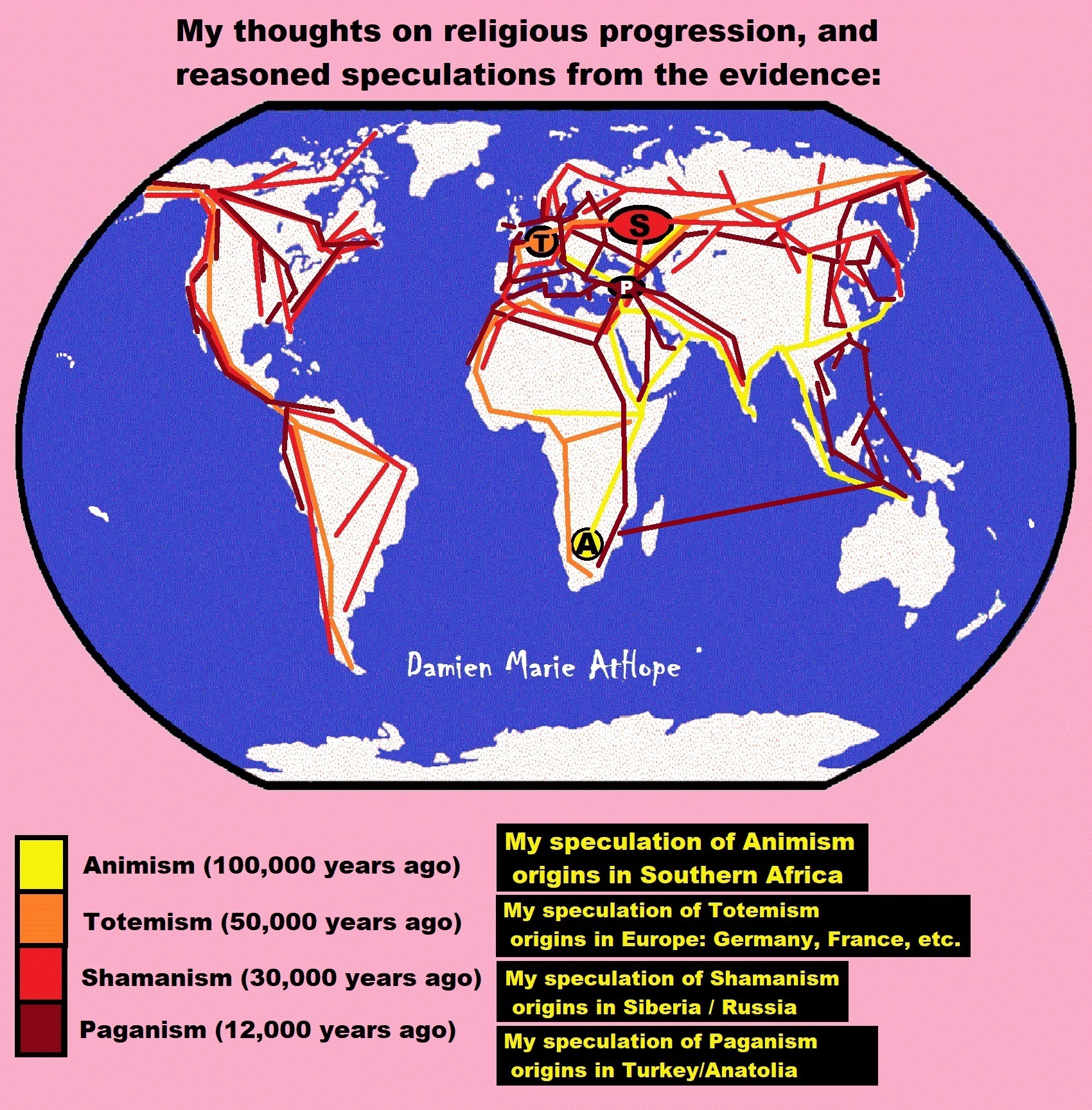




ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.



While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com