In my prehistory art in this blog, I offer my speculations relating to art with possible religious/supernatural thinking which I think are loose, justified, or reasoned speculations/conjectures.
“My cloud thinking is the loose speculations/conjectures.”
My thoughts on speculations/conjectures:
Unreasoned speculations/conjectures
Wild speculations/conjectures
Loose speculations/conjectures
Justified speculations/conjectures
Reasoned speculations/conjectures
Sound/proven speculations/conjectures

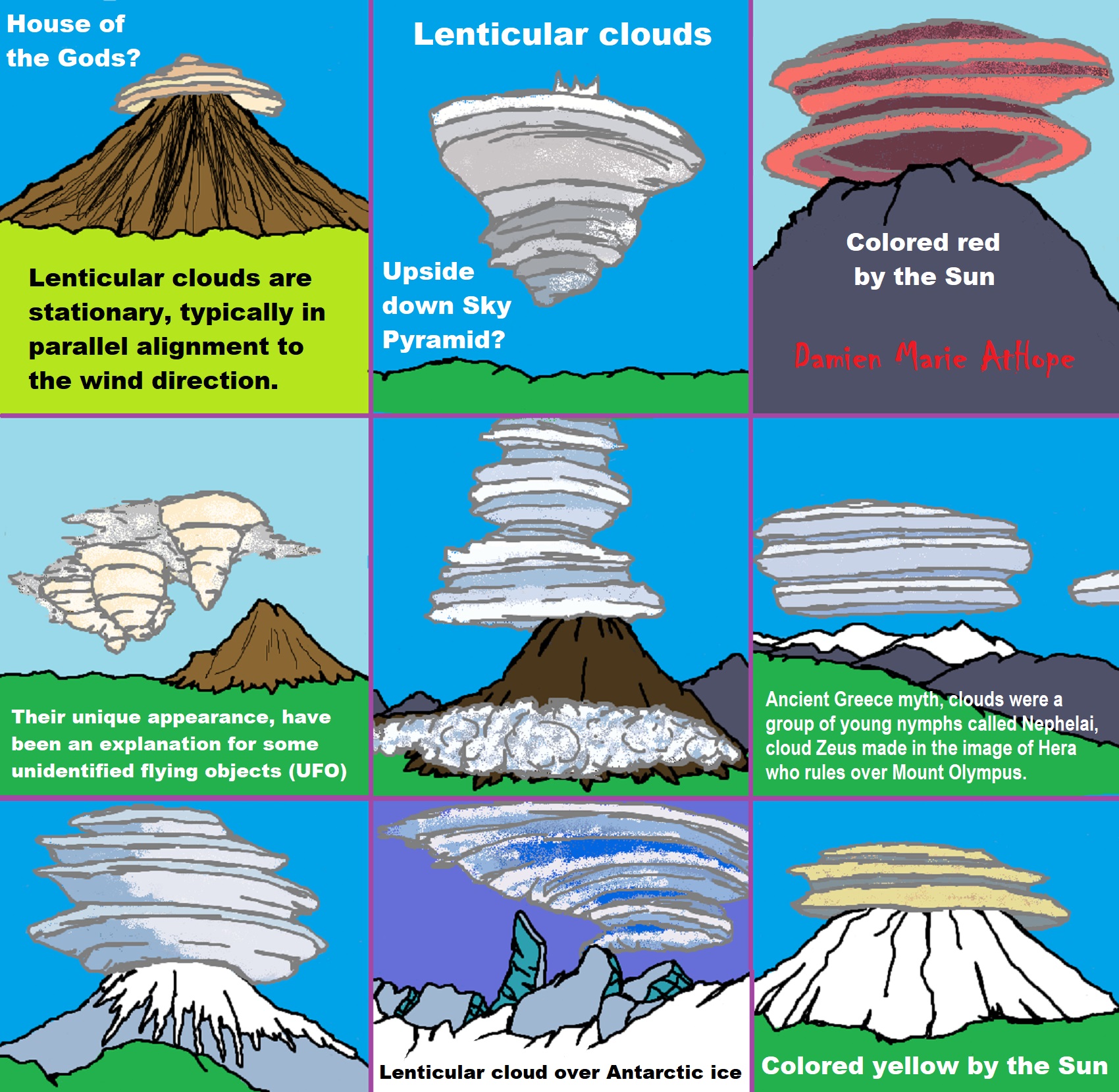
Lenticular Clouds
“Lenticular clouds (Latin: Lenticularis lentil-shaped, from lenticula lentil) are stationary clouds that form mostly in the troposphere, typically in parallel alignment to the wind direction. They are often comparable in appearance to a lens or saucer. Nacreous clouds that form in the lower stratosphere sometimes have lenticular shapes.” ref
“There are three main types of lenticular clouds: altocumulus standing lenticular (ACSL), stratocumulus standing lenticular (SCSL), and cirrocumulus standing lenticular (CCSL), varying in altitude above the ground. Because of their unique appearance, they have been suggested as an explanation for some unidentified flying object (UFO) sightings.” ref
Formation and appearance
“As air travels along the surface of the Earth, obstructions are often encountered. These include both natural features of the Earth, such as mountains or hills, and artificial structures, such as buildings and other structures. These disrupt the flow of air into “eddies”, or areas of turbulence influenced by these obstructions.” ref
“When moist, stable air flows over a larger eddy, such as those caused by mountains, a series of large-scale standing waves form on the leeward side of the mountain. If the temperature at the crest of the wave drops below the local dew point, moisture in the air may condense to form lenticular clouds. Under certain conditions, long strings of lenticular clouds may form near the crest of each successive wave, creating a formation known as a “wave cloud“. These wave systems can produce large updrafts, occasionally enough for water vapour to condense and produce precipitation.” ref
“Lenticular clouds have been said to be mistaken for UFOs; as many of these clouds have the shape of a “flying saucer”, with a characteristic “lens” or smooth, “saucer-like” shape. Because lenticular clouds generally do not form over low-lying or flat terrain, many people may have never seen one before and don’t know that they can exist. Bright colors (called iridescence) are sometimes seen along the edge of lenticular clouds.” ref
“Lenticular clouds have continuously mystified, more than “mystified” since clouds typically high above the ground are the most creative and artistic forms of water that never failed to launch human thoughts and imagination to other dimensions of creativity and this is particularly so cloud formation, the lenticular clouds, has a more profound effect on the human mind. More often they are viewed in the extraterrestrial context. They, more often, represent or are seen as the majestic but mythic flying saucer.” ref
“Lenticular clouds (Altocumulus lenticularis, meaning “shaped like a lentil” in Latin) mostly develop among the crests and valleys of mountainous terrain. They are associated with waves in the atmosphere that form when moist air flow is forced up, over, and partway down a mountaintop. The moist air cools, causing it to condense into a disk-shaped cloud.” ref
“Often a lenticular cloud resembles a spaceship hovering near a mountain’s summit. Sometimes, however, multiple clouds will pile on top of each other like a stack of pancakes. Not only do lenticulars look unique but they also behave differently than other clouds by not moving with the wind flow. By reforming over and over again in the crest of the mountain wave, they can stay in one location for several hours.” ref
“Atmospheric waves generate turbulence, so pilots avoid flying near lenticular clouds. Also, because they’re a sign that rain or snow is on the way, one glance offers an instant and visually spectacular weather forecast. Mount Rainier, located southeast of Seattle, is a magnet for this type of cloud. Numerous news stories tell of lenticulars hovering atop the mountain.” ref
“Although the clouds seem unearthly, most onlookers recognize them for what they are. Even so, a sighting by a pilot in 1947 launched a flying saucer craze, according to the book “Meteorology Today” by C. Ahrens and R. Henson. Thanks to studies of the atmosphere, lenticular clouds may look mysterious, but the way they’re formed is far from a mystery.” ref
Evidence of an alien invasion? No – the rare phenomenon of eerily beautiful lenticular clouds captured by a Russian photographer
“Russian photographer Denis Budkov, 33, captured formations the over the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia. The rare phenomenon occurs when strong winds are blocked by large geographical features such as mountains. The clouds are often mistaken for flying saucers or cover for UFOS because of their unusual shape. Hovering high above the mountains these unusual, saucer-like white masses resemble a creature or vehicle from another world – but they are in fact clouds.” ref
“The natural phenomenon, known as lenticular clouds, tends to form at high altitudes, such as above mountains. The lens-shaped formations are scientifically known as ‘altocumulus lenticularis’ and are the result of moist air that has condensed at a high altitude. They are formed when the air temperature drops and moisture droplets are pushed up a steep slope by high winds.” ref
“This unique atmospheric condition creates the interesting lens-shaped form that defines a lenticular cloud. Mountains act as natural barriers forcing clouds to condense quickly as they are pushed to cooler altitudes. This is why a large or particularly tall mountain range will experience a moist climate on one side but an arid one on the other.” ref
“He said: ‘These clouds are very special as they do not move, they stay in one place and it’s only their shape that changes. ‘There needs to be at least two factors for these clouds to appear, a very strong wind and a very high object, so Klyuchevskaya Sopka is a perfect place to find lenticular clouds.” ref
“Kamchatka is a very special and beautiful land. ‘With every new day, I seem to discover more areas of natural beauty that I didn’t even know existed. ‘I was born and raised in Kamchatka, the so-called ‘land of fire breathing mountains’ and there is nowhere else like it on Earth. You can walk to the top of a volcano, find the Pacific Ocean by following the mountain rivers and see the first sunrise over all of Russia.” ref
Lenticular Clouds
“Lenticular clouds form due to the wind blowing across the top of a mountain at a pretty good speed. The wind on the windward side is pushed up and then pulled back down on the downwind side. This process results in a slight drop in pressure on the downwind side of the mountain. This drop in pressure results in a drop in temperature (thanks Bernouli). The slight drop in temperature forces moisture in the air to condense and form a cloud. Given that the air quickly returns back to normal pressure and temperature in a short distance, the water then goes back to vapor and you do not see the cloud continuing on the downwind side of the mountain. This is different from normal clouds as we generally think of a cloud as a single parcel of air. In this case, the “cloud” we see actually has tons of air rushing through it. It is not one stationary parcel of air, but rather a stationary zone of low pressure and low temperature causing moisture to become visible momentarily before it flows on by. It typically takes very stable air blowing at 40 knots or more to generate these type of clouds.” ref
Rotor Clouds
“Rotor clouds are caused by the same weather pattern as lenticular clouds, stable air blowing perpendicularly across a mountain range. A rotor cloud will contain severe turbulence and is generally found just below the lenticular clouds, at or below the top altitude of the mountain tops. Rotor clouds form down here as a result of the surface friction with the wind blowing over the mountain. Take a look at the two pictures below to get a better understanding.” ref
Mountain Wave Turbulence
“So it seems obvious with all this air circulating around very quickly we can expect some pretty good turbulence. We refer to this as mountain wave turbulence and it can be even nastier than the regular bumps that bang you around. The trouble with mountain wave turbulence is, when air is flowing perpendicular to a mountain range, it is going to be creating updrafts as it flows up one side and downdrafts down the other. These vertical air currents are so strong in fact some aircraft could shut down their engine and still not be able to descend on the upwind side of the mountain as they get “picked up” in the updrafts. The same is true and much worse on the other side of the mountains. You NEVER want to approach a mountain range on the downwind side of it! Especially if you are flying low and in a smaller airplane without a whole lot of excess power (basically if you don’t have the ability to climb at 4,000+ fpm you should rethink your approach).” ref
“As you see in the diagram below, as you approach the mountain from the downwind side, you are going to get pushed down towards the ground, and despite your best efforts, it is doubtful your airplane will have enough power to climb up faster than the downdraft is pushing you down. Pilots who are unwise and unlucky enough to find themselves in such a situation generally either wind up flying right into the side of the mountain or stalling trying to climb more than the airplane can and falling into the side of the mountain. Either is a very bad option. Don’t try to cross a mountain range with a headwind of any strength, if you do encounter unexpected downdrafts, hopefully, you will have enough margin of error with the altitude you are flying at to execute a 180-degree turn and use that tailwind to help you get back to where you came from extra fast!” ref
The Mythology of Clouds
“What could be more whimsical and imagination-stirring than a cloud? These transient puffs of air laced with water particles take on mysterious shapes we naturally recognize as children. In recent months alone I’ve watched in awe as clouds morphed into giraffes, turtles, Coke bottles, and top hats. With their infinite changeability and frustratingly untouchable height, it’s no wonder clouds have been imbued with mythological and folkloric qualities by many cultures, for hundreds of years.” ref
“We’ll start in Ancient Greece. According to myth, clouds were not clouds at all but a group of young nymphs called Nephelai, the daughters of two titans, Oceanus and Tethys. These cloud spirits, depicted as beautiful and transparent, spent their days collecting water from the rivers in cloudy pitchers, then floating up to the heavens. When these pitchers were full, they poured water down from the sky, nourishing the earth and feeding the streams of their brothers, the Potamoi (river gods). Nephelai were thought to sail through the sky in billowing white robes, much like the way that clouds drift across the heavens.” ref
“An ancient Hindu tradition said that elephants brought the rain, and that clouds themselves were the celestial relatives of the white elephants that roamed the earth. An elephant’s body was thought to be representative of a cloud, and they would use their trunks to shower the earth with rain.” ref
“Native Americans also created myths and folklore around clouds. According to the Skidi Pawnee tribe, who lived in Nebraska, clouds were the clothing of the gods of heaven. A god spreading its arms would cause the clouds to stretch across the entire sky. And the early Navajo people believed that clouds were formed when a great white swan flapped its wings.” ref
“Even today, cloud myths endure. The Pueblo of Southwest America worship the Cloud People, supernatural beings from the Underworld who bring rain and moisture to the earth. These Cloud People are the spirits of the deceased who lived a good life, thereby taking on the form of clouds in the afterlife. By properly honoring the dead, the Pueblo – an agricultural people – believe that the Cloud People will grant them rain, thereby nourishing their land.” ref
“Since we’re into etymology (and when I see ‘we’, I mean ‘me’) – ‘cloud’ comes from the old English ‘clud’ or ‘clod,’ meaning a hill or a mass of rock. In the beginning of the 13th century, the word came to be used to refer to clouds in the sky. And in other news, the official scientific definition of a cloud is ‘a visible accumulation of water droplets or solid ice crystals that floats in the Earth’s troposphere’.” ref
“There’s no doubt about it – there’s just something about clouds that is utterly magical seeming. And it’s not just you and I that have that feeling – it’s a universal phenomenon throughout history. In fact, a Cloud Appreciation Society formed in 2005 now has more than 35,000 members worldwide. The society quite romantically calls clouds ‘Nature’s poetry’ in its manifesto.” ref
Nephele: Cloud Goddess of hospitality and Member of the Athamantian Royal House
“In Greek mythology, Nephele was a cloud nymph who figured prominently in the story of Phrixus and Helle. Greek myth has it that Nephele is the cloud whom Zeus created in the image of Hera to trick Ixion to test his integrity after displaying his lust for Hera during a feast as a guest of Zeus. Ixion’s restraint failed him, and he coupled with Nephele, eventually fathering the Centaurs (through Imbros or Centauros).” ref
“Nephele married Athamas, and had twins, a son, Phrixus, and a daughter, Helle. Athamas then divorced her for Ino, who hatched a devious plot to get rid of the twins, roasting all the town’s crop seeds so they would not grow. The local farmers, frightened of famine, asked a nearby oracle for assistance. Inobribed the men sent to the oracle to lie and tell the others that the oracle required the sacrifice of Phrixus. Before he was killed though, Phrixus and Helle were rescued by a flying golden ram sent by their natural mother Nephele.” ref
“Phrixus and Helle were instructed to not look down to Earth for the duration of their flight. Helle, though, did look down, and fell off the ram into the Hellespont (which was named after her, meaning Sea of Helle) and drowned. Phrixus survived all the way to Colchis, where King Aeetes took him in and treated him kindly, giving Phrixus his daughter, Chalciope, in marriage. In gratitude, Phrixus gave the king the Golden Fleece of the Golden Ram, which Aeetes hung in a tree in his kingdom. The Golden Fleece would later be taken by Jason and his Argonauts.” ref
Hera
“Hera (/ˈhɛrə, ˈhɪərə/; Greek: Ἥρα, translit. Hḗrā; Ἥρη, Hḗrē in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of women, marriage, family, and childbirth in ancient Greek religion and mythology, one of the twelve Olympians and the sister and wife of Zeus. She is the daughter of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. Hera rules over Mount Olympus as queen of the gods. A matronly figure, Hera served as both the patroness and protectress of married women, presiding over weddings and blessing marital unions. One of Hera’s defining characteristics is her jealous and vengeful nature against Zeus’ numerous lovers and illegitimate offspring, as well as the mortals who cross her.” ref
“Hera is commonly seen with the animals she considers sacred, including the cow, lion, and the peacock. Portrayed as majestic and solemn, often enthroned, and crowned with the polos (a high cylindrical crown worn by several of the Great Goddesses), Hera may hold a pomegranate in her hand, emblem of fertile blood and death and a substitute for the narcotic capsule of the opium poppy. Her Roman counterpart is Juno.” ref
“The name of Hera has several possible and mutually exclusive etymologies; one possibility is to connect it with Greek ὥρα hōra, season, and to interpret it as ripe for marriage and according to Plato ἐρατή eratē, “beloved” as Zeus is said to have married her for love. According to Plutarch, Hera was an allegorical name and an anagram of aēr (ἀήρ, “air”). So begins the section on Hera in Walter Burkert‘s Greek Religion. In a note, he records other scholars’ arguments “for the meaning Mistress as a feminine to Heros, Master.” ref
“John Chadwick, a decipherer of Linear B, remarks “her name may be connected with hērōs, ἥρως, ‘hero’, but that is no help since it too is etymologically obscure.” A. J. van Windekens, offers “young cow, heifer”, which is consonant with Hera’s common epithet βοῶπις (boōpis, “cow-eyed”). R. S. P. Beekes has suggested a Pre-Greek origin. Her name is attested in Mycenaean Greek written in the Linear B syllabic script as e-ra, appearing on tablets found in Pylos and Thebes, as well in the Cypriotic dialect in the dative e-ra-i.” ref
Hera may have been the first deity to whom the Greeks dedicated an enclosed roofed temple sanctuary, at Samos about 800 BCE. It was replaced later by the Heraion of Samos, one of the largest of all Greek temples (altars were in front of the temples under the open sky). There were many temples built on this site so evidence is somewhat confusing and archaeological dates are uncertain.” ref
“The temple created by the Rhoecus sculptors and architects was destroyed between 570–560 BCE. This was replaced by the Polycratean temple of 540–530 BCE. In one of these temples we see a forest of 155 columns. There is also no evidence of tiles on this temple suggesting either the temple was never finished or that the temple was open to the sky.” ref
“Earlier sanctuaries, whose dedication to Hera is less certain, were of the Mycenaean type called “house sanctuaries”. Samos excavations have revealed votive offerings, many of them late 8th and 7th centuries BCE, which show that Hera at Samos was not merely a local Greek goddess of the Aegean: the museum there contains figures of gods and suppliants and other votive offerings from Armenia, Babylon, Iran, Assyria, Egypt, testimony to the reputation which this sanctuary of Hera enjoyed and to the large influx of pilgrims. Compared to this mighty goddess, who also possessed the earliest temple at Olympia and two of the great fifth and sixth century temples of Paestum, the termagant of Homer and the myths is an “almost… comic figure”, according to Burkert.” ref
“Though greatest and earliest free-standing temple to Hera was the Heraion of Samos, in the Greek mainland Hera was especially worshipped as “Argive Hera” (Hera Argeia) at her sanctuary that stood between the former Mycenaean city-states of Argos and Mycenae, where the festivals in her honor called Heraia were celebrated. “The three cities I love best,” the ox-eyed Queen of Heaven declares in the Iliad, book iv, “are Argos, Sparta, and Mycenae of the broad streets.” There were also temples to Hera in Olympia, Corinth, Tiryns, Perachora, and the sacred island of Delos. In Magna Graecia, two Doric temples to Hera were constructed at Paestum, about 550 BCE and about 450 BCE. One of them, long called the Temple of Poseidon was identified in the 1950s as a second temple there of Hera.” ref
“In Euboea, the festival of the Great Daedala, sacred to Hera, was celebrated on a sixty-year cycle. Hera’s importance in the early archaic period is attested by the large building projects undertaken in her honor. The temples of Hera in the two main centers of her cult, the Heraion of Samos and the Heraion of Argos in the Argolis, were the very earliest monumental Greek temples constructed, in the 8th century BCE.” ref
Importance of Hera
“According to Walter Burkert, both Hera and Demeter have many characteristic attributes of Pre-Greek Great Goddesses. In the same vein, British scholar Charles Francis Keary suggests that Hera had some sort of “Earth Goddess” worship in ancient times, connected to her possible origin as a Pelasgian goddess (as mentioned by Herodotus).” ref
“According to Homeric Hymn III to Delian Apollo, Hera detained Eileithyia to prevent Leto from going into labor with Artemis and Apollo, since the father was Zeus. The other goddesses present at the birthing on Delos sent Iris to bring her. As she stepped upon the island, the divine birth began. In the myth of the birth of Heracles, it is Hera herself who sits at the door, delaying the birth of Heracles until her protégé, Eurystheus, had been born first.” ref
“The Homeric Hymn to Pythian Apollo makes the monster Typhaon the offspring of archaic Hera in her Minoan form, produced out of herself, like a monstrous version of Hephaestus, and whelped in a cave in Cilicia. She gave the creature to Python to raise.” ref
“In the Temple of Hera, Olympia, Hera’s seated cult figure was older than the warrior figure of Zeus that accompanied it. Homer expressed her relationship with Zeus delicately in the Iliad, in which she declares to Zeus, “I am Cronus‘ eldest daughter, and am honorable not on this ground only, but also because I am your wife, and you are king of the gods.” ref
Hera and Matriarchy
“There has been considerable scholarship, reaching back to Johann Jakob Bachofen in the mid-nineteenth century, about the possibility that Hera, whose early importance in Greek religion is firmly established, was originally the goddess of a matriarchal people, presumably inhabiting Greece before the Hellenes. In this view, her activity as goddess of marriage established the patriarchal bond of her own subordination: her resistance to the conquests of Zeus is rendered as Hera’s “jealousy”, the main theme of literary anecdotes that undercut her ancient cult.” ref
“However, it remains a controversial claim that an ancient matriarchy or a cultural focus on a monotheistic Great Goddess existed among the ancient Greeks or elsewhere. The claim is generally rejected by modern scholars as insufficiently evidenced.” ref
Youth and Hera
“Hera was most known as the matron goddess, Hera Teleia; but she presided over weddings as well. In myth and cult, fragmentary references and archaic practices remain of the sacred marriage of Hera and Zeus. At Plataea, there was a sculpture of Hera seated as a bride by Callimachus, as well as the matronly standing Hera.” ref
“Hera was also worshipped as a virgin: there was a tradition in Stymphalia in Arcadia that there had been a triple shrine to Hera the Girl (Παις [Pais]), the Adult Woman (Τελεια [Teleia]), and the Separated (Χήρη [Chḗrē] ‘Widowed’ or ‘Divorced’). In the region around Argos, the temple of Hera in Hermione near Argos was to Hera the Virgin. At the spring of Kanathos, close to Nauplia, Hera renewed her virginity annually, in rites that were not to be spoken of (arrheton). The Female figure, showing her “Moon” over the lake is also appropriate, as Hebe, Hera, and Hecate; new moon, full moon, and old moon in that order and otherwise personified as the Virgin of Spring, The Mother of Summer, and the destroying Crone of Autumn.” ref
Emblems of Hera
“In Hellenistic imagery, Hera’s chariot was pulled by peacocks, birds not known to Greeks before the conquests of Alexander. Alexander’s tutor, Aristotle, refers to it as “the Persian bird.” The peacock motif was revived in the Renaissance iconography that unified Hera and Juno, and which European painters focused on. A bird that had been associated with Hera on an archaic level, where most of the Aegean goddesses were associated with “their” bird, was the cuckoo, which appears in mythic fragments concerning the first wooing of a virginal Hera by Zeus.” ref
“Her archaic association was primarily with cattle, as a Cow Goddess, who was especially venerated in “cattle-rich” Euboea. On Cyprus, very early archaeological sites contain bull skulls that have been adapted for use as masks (see Bull (mythology)). Her familiar Homeric epithet Boôpis, is always translated “cow-eyed”. In this respect, Hera bears some resemblance to the Ancient Egyptian deity Hathor, a maternal goddess associated with cattle. Scholar of Greek mythology Walter Burkert writes in Greek Religion, “Nevertheless, there are memories of an earlier aniconic representation, as a pillar in Argos and as a plank in Samos.” ref
Hera Epithets
“Hera bore several epithets in the mythological tradition, including:
- Ἀλέξανδρος (Alexandros) ‘Protector of Men’ (Alexandros) (among the Sicyonians)
- Αἰγοφάγος (Aigophágos) ‘Goat-Eater’ (among the Lacedaemonians)
- Ἀκραῖα (Akráia) ‘(She) of the Heights’
- Ἀμμωνία (Ammonia)
- Ἄνθεια (Antheia), meaning flowery
- Ἀργεία (Argéia) ‘(She) of Argos‘
- Βασίλεια (Basíleia) ‘Queen’
- Βουναία (Bounáia) ‘(She) of the Mound’ (in Corinth)
- Βοῶπις (Boṓpis) ‘Cow-Eyed’ or ‘Cow-Faced’
- Λευκώλενος (Leukṓlenos) ‘White-Armed’
- Παῖς (Pais) ‘Child’ (in her role as virgin)
- Παρθένος (Parthénos) ‘Virgin’
- Τελεία (Teléia) (as goddess of marriage)
- Χήρη (Chḗrē) ‘Widowed’
- Τελχινία (Telchinia), Diodorus Siculus write that she was worshiped by the Ialysians and the Cameirans (both were on the island of Rhodes). She was named liked that because according to a legend, Telchines (Τελχῖνες) were the first inhabitants of the island and also the first who created statues of gods.” ref
Hera Mythology
Hera’s Birth
“Hera is the daughter of the youngest Titan Cronus and his wife, and sister, Rhea. Cronus was fated to be overthrown by one of his children; to prevent this, he swallowed all of his newborn children whole until Rhea tricked him into swallowing a stone instead of her youngest child, Zeus. Zeus grew up in secret and when he grew up he tricked his father into regurgitating his siblings, including Hera. Zeus then led the revolt against the Titans, banished them, and divided the dominion over the world with his brothers Poseidon and Hades.” ref
Hera’s Marriage with Zeus
“Hera is the goddess of marriage and childbirth rather more than of motherhood, and much of her mythology revolves around her marriage with her brother Zeus. She is charmed by him and she seduces him; he cheats on her and has many children by other goddesses and mortal women; she is intensely jealous and vindictive towards his children and their mothers; he is threatening and violent to her.” ref
“In the Iliad, Zeus implies their marriage was some sort of elopement, as they lay secretly from their parents. Pausanias records a tale of how they came to be married in which Zeus transformed into a cuckoo bird to woo Hera. She caught the bird and kept it as her pet; this is why the cuckoo is seated on her scepter. According to a scholion on Theocritus‘ Idylls, when Hera was heading toward Mount Thornax alone, Zeus created a terrible storm and transformed himself into a cuckoo bird who flew down and sat on her lap.” ref
“When Hera saw him, she covered him with her cloak. Zeus then transformed back and took hold of her; because she was refusing to sleep with him due to their mother, he promised to marry her. In one account Hera refused to marry Zeus and hid in a cave to avoid him; an earthborn man named Achilles convinced her to give him a chance, and thus the two had their first sexual intercourse. According to Callimachus, their wedding feast lasted three thousand years. The Apples of the Hesperides that Heracles was tasked by Eurystheus to take were a wedding gift by Gaia to the couple.” ref
Heracles and Hera
“Hera is the stepmother and enemy of Heracles. The name Heracles means “Glory of Hera”. In Homer’s Iliad, when Alcmene was about to give birth to Heracles, Zeus announced to all the gods that on that day a child by Zeus himself, would be born and rule all those around him. Hera, after requesting Zeus to swear an oath to that effect, descended from Olympus to Argos and made the wife of Sthenelus (son of Perseus) give birth to Eurystheus after only seven months, while at the same time preventing Alcmene from delivering Heracles. This resulted in the fulfilment of Zeus’s oath in that it was Eurystheus rather than Heracles.” ref
“In Pausanias’ recounting, Hera sent witches (as they were called by the Thebans) to hinder Alcmene’s delivery of Heracles. The witches were successful in preventing the birth until Historis, daughter of Tiresias, thought of a trick to deceive the witches. Like Galanthis, Historis announced that Alcmene had delivered her child; having been deceived, the witches went away, allowing Alcmene to give birth. Hera’s wrath against Zeus’ son continues and while Heracles is still an infant, Hera sends two serpents to kill him as he lies in his cot. Heracles throttles the snakes with his bare hands and is found by his nurse playing with their limp bodies as if they were a child’s toy.” ref
“One account of the origin of the Milky Way is that Zeus had tricked Hera into nursing the infant Heracles: discovering who he was, she pulled him from her breast, and a spurt of her milk formed the smear across the sky that can be seen to this day. Unlike any Greeks, the Etruscans instead pictured a full-grown bearded Heracles at Hera’s breast: this may refer to his adoption by her when he became an Immortal. He had previously wounded her severely in the breast.” ref
“When Heracles reached adulthood, Hera drove him mad, which led him to murder his family and this later led to him undertaking his famous labors. Hera assigned Heracles to labor for King Eurystheus at Mycenae. She attempted to make almost all of Heracles’ twelve labors more difficult. When he fought the Lernaean Hydra, she sent a crab to bite at his feet in the hopes of distracting him. Later Hera stirred up the Amazons against him when he was on one of his quests. When Heracles took the cattle of Geryon, he shot Hera in the right breast with a triple-barbed arrow: the wound was incurable and left her in constant pain, as Dione tells Aphrodite in the Iliad, Book V. Afterwards, Hera sent a gadfly to bite the cattle, irritate them and scatter them.” ref
“Hera then sent a flood which raised the water level of a river so much that Heracles could not ford the river with the cattle. He piled stones into the river to make the water shallower. When he finally reached the court of Eurystheus, the cattle were sacrificed to Hera. Eurystheus also wanted to sacrifice the Cretan Bull to Hera. She refused the sacrifice because it reflected glory on Heracles. The bull was released and wandered to Marathon, becoming known as the Marathonian Bull.” ref
“Some myths state that in the end, Heracles befriended Hera by saving her from Porphyrion, a giant who tried to rape her during the Gigantomachy, and that she even gave her daughter Hebe as his bride. Whatever myth-making served to account for an archaic representation of Heracles as “Hera’s man” it was thought suitable for the builders of the Heraion at Paestum to depict the exploits of Heracles in bas-reliefs.” ref
Leto and the Twins: Apollo and Artemis
“When Hera discovered that Leto was pregnant and that Zeus was the father, she convinced the nature spirits to prevent Leto from giving birth on terra-firma, the mainland, any island at sea, or any place under the sun. Poseidon gave pity to Leto and guided her to the floating island of Delos, which was neither mainland nor a real island where Leto was able to give birth to her children. Afterward, Zeus secured Delos to the bottom of the ocean. The island later became sacred to Apollo. Alternatively, Hera kidnapped Eileithyia, the goddess of childbirth, to prevent Leto from going into labor. The other gods bribed Hera with a beautiful necklace nobody could resist and she finally gave in.” ref
“Either way, Artemis was born first and then assisted with the birth of Apollo. Some versions say Artemis helped her mother give birth to Apollo for nine days. Another variation states that Artemis was born one day before Apollo, on the island of Ortygia and that she helped Leto cross the sea to Delos the next day to give birth to Apollo. Later, Tityos attempted to rape Leto at the behest of Hera. He was slain by Artemis and Apollo. This account of the birth of Apollo and Artemis is contradicted by Hesiod in Theogony, as the twins are born prior to Zeus’ marriage to Hera.” ref
Io and Argus
“The myth of Io has many forms and embellishments. Generally, Io was a priestess of Hera at the Heraion of Argos. Zeus lusted after her and either Hera turned Io into a heifer to hide her from Zeus, or Zeus did so to hide her from Hera but was discovered. Hera had Io tethered to an olive-tree and set Argus Panoptes (lit. ‘all-seeing’) to watch over her, but Zeus sent Hermes to kill him. Infuriated, Hera then sent a gadfly (Greek oistros, compare oestrus) to pursue and constantly sting Io, who fled into Asia and eventually reached Egypt. There Zeus restored her to human form and she gave birth to his son Epaphus.” ref
Judgment of Paris
“A prophecy stated that a son of the sea-nymph Thetis, with whom Zeus fell in love after gazing upon her in the oceans off the Greek coast, would become greater than his father. Possibly for this reasons, Thetis was betrothed to an elderly human king, Peleus son of Aeacus, either upon Zeus’ orders, or because she wished to please Hera, who had raised her. All the gods and goddesses as well as various mortals were invited to the marriage of Peleus and Thetis (the eventual parents of Achilles) and brought many gifts. Only Eris, goddess of discord, was not invited and was stopped at the door by Hermes, on Zeus’ order. She was annoyed at this, so she threw from the door a gift of her own: a golden apple inscribed with the word καλλίστῃ (kallistēi, “To the fairest”). Aphrodite, Hera, and Athena all claimed to be the fairest, and thus the rightful owner of the apple.” ref
“The goddesses quarreled bitterly over it, and none of the other gods would venture an opinion favoring one, for fear of earning the enmity of the other two. They chose to place the matter before Zeus, who, not wanting to favor one of the goddesses, put the choice into the hands of Paris, a Trojan prince. After bathing in the spring of Mount Ida where Troy was situated, they appeared before Paris to have him choose. The goddesses undressed before him, either at his request or for the sake of winning. Still, Paris could not decide, as all three were ideally beautiful, so they resorted to bribes. Hera offered Paris political power and control of all of Asia, while Athena offered wisdom, fame, and glory in battle, and Aphrodite offered the most beautiful mortal woman in the world as a wife, and he accordingly chose her. This woman was Helen, who was, unfortunately for Paris, already married to King Menelaus of Sparta. The other two goddesses were enraged by this and through Helen’s abduction by Paris, they brought about the Trojan War.” ref
The Iliad
“Hera plays a substantial role in The Iliad, appearing in a number of books throughout the epic poem. She hates the Trojans because of Paris’ decision that Aphrodite was the most beautiful goddess, and so supports the Greeks during the war. Throughout the epic, Hera makes many attempts to thwart the Trojan army. In books 1 and 2, Hera declares that the Trojans must be destroyed. Hera persuades Athena to aid the Achaeans in battle and she agrees to assist with interfering on their behalf.” ref
“In book 5, Hera and Athena plot to harm Ares, who had been seen by Diomedes in assisting the Trojans. Diomedes called for his soldiers to fall back slowly. Hera, Ares’ mother, saw Ares’ interference and asked Zeus, Ares’ father, for permission to drive Ares away from the battlefield. Hera encouraged Diomedes to attack Ares and he threw his spear at the god. Athena drove the spear into Ares’ body, and he bellowed in pain and fled to Mount Olympus, forcing the Trojans to fall back.” ref
“In book 8, Hera tries to persuade Poseidon to disobey Zeus and help the Achaean army. He refuses, saying he doesn’t want to go against Zeus. Determined to intervene in the war, Hera and Athena head to the battlefield. However, seeing the two flee, Zeus sent Iris to intercept them and make them return to Mount Olympus or face grave consequences. After prolonged fighting, Hera sees Poseidon aiding the Greeks and giving them the motivation to keep fighting.” ref
“In book 14 Hera devises a plan to deceive Zeus. Zeus set a decree that the gods were not allowed to interfere in the mortal war. Hera is on the side of the Achaeans, so she plans a Deception of Zeus where she seduces him, with help from Aphrodite, and tricks him into a deep sleep, with the help of Hypnos, so that the Gods could interfere without the fear of Zeus.” ref
“In book 21, Hera continues her interference with the battle as she tells Hephaestus to prevent the river from harming Achilles. Hephaestus sets the battlefield ablaze, causing the river to plead with Hera, promising her he will not help the Trojans if Hephaestus stops his attack. Hephaestus stops his assault and Hera returns to the battlefield where the gods begin to fight amongst themselves.” ref
Minor stories
Semele and Dionysus
“When Hera learned that Semele, daughter of Cadmus King of Thebes, was pregnant by Zeus, she disguised herself as Semele’s nurse and persuaded the princess to insist that Zeus show himself to her in his true form. When he was compelled to do so, having sworn by Styx, his thunder and lightning destroyed Semele. Zeus took Semele’s unborn child, Dionysus, and completed its gestation sewn into his own thigh.” ref
“In another version, Dionysus was originally the son of Zeus by either Demeter or Persephone. Hera sent her Titans to rip the baby apart, from which he was called Zagreus (“Torn in Pieces”). Zeus rescued the heart; or, the heart was saved, variously, by Athena, Rhea, or Demeter.[74] Zeus used the heart to recreate Dionysus and implant him in the womb of Semele—hence Dionysus became known as “the twice-born”. Certain versions imply that Zeus gave Semele the heart to eat to impregnate her. Hera tricked Semele into asking Zeus to reveal his true form, which killed her. Dionysus later managed to rescue his mother from the underworld and have her live on Mount Olympus.” ref
Lamia
“Lamia was a lovely queen of Libya, whom Zeus loved and slept with. Hera in jealousy, caused Lamia to kill her own children; out of grief for her actions, Lamia was turned into a misshapen creature that would therefore snatch and murder other people’s children.” ref
Gerana
“Gerana was a queen of the Pygmies who boasted she was more beautiful than Hera. The wrathful goddess turned her into a crane and proclaimed that her bird descendants should wage eternal war on the Pygmy folk.” ref
Cydippe
“Cydippe, a priestess of Hera, was on her way to a festival in the goddess’ honor. The oxen which were to pull her cart were overdue and her sons, Biton and Cleobis, pulled the cart the entire way (45 stadia, 8 kilometers). Cydippe was impressed with their devotion to her and Hera so asked Hera to give her children the best gift a god could give a person. Hera ordained that the brothers would die in their sleep. This honor bestowed upon the children was later used by Solon, as a proof while trying to convince Croesus that it is impossible to judge a person’s happiness until they have died a fruitful death after a joyous life.” ref
Tiresias
“Tiresias was a priest of Zeus, and as a young man, he encountered two snakes mating and hit them with a stick. He was then transformed into a woman. As a woman, Tiresias became a priestess of Hera, married, and had children, including Manto. After seven years as a woman, Tiresias again found mating snakes; depending on the myth, either she made sure to leave the snakes alone this time, or, according to Hyginus, trampled on them and became a man once more.” ref
“As a result of his experiences, Zeus and Hera asked him to settle the question of which sex, male or female, experienced more pleasure during intercourse. Zeus claimed it was women; Hera claimed it was men. When Tiresias sided with Zeus, Hera struck him blind. Since Zeus could not undo what she had done, he gave him the gift of prophecy.” ref
“An alternative and less commonly told story has it that Tiresias was blinded by Athena after he stumbled onto her bathing naked. His mother, Chariclo, begged her to undo her curse, but Athena could not; she gave him prophecy instead.” ref
Chelone
“At the marriage of Zeus and Hera, a nymph named Chelone was disrespectful or refused to attend the wedding. Zeus thus, turned her into a tortoise.” ref
The Golden Fleece
“Hera hated Pelias because he had killed Sidero, his step-grandmother, in one of the goddess’s temples. She later convinced Jason and Medea to kill Pelias. The Golden Fleece was the item that Jason needed to get his mother freed.” ref
Ixion
“When Zeus had pity on Ixion and brought him to Olympus and introduced him to the gods, instead of being grateful, Ixion grew lustful for Hera. Zeus found out about his intentions and made a cloud in the shape of Hera, who was later named Nephele, and tricked Ixion into coupling with it, and from their union came Centaurus. So Ixion was expelled from Olympus and Zeus ordered Hermes to bind Ixion to a winged fiery wheel that was always spinning. Therefore, Ixion was bound to a burning solar wheel for all eternity, at first spinning across the heavens, but in later myth transferred to Tartarus.” ref
Mount Olympus
“Mount Olympus (/oʊˈlɪmpəs, əˈlɪm-/;[6] Greek: Όλυμπος, romanized: Ólympos, also Ólimbos, IPA: [ˈoli(m)bos]) is the highest mountain in Greece. It is part of the Olympus massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located in the Olympus Range on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, between the regional units of Larissa and Pieria, about 80 km (50 mi) southwest from Thessaloniki. Mount Olympus has 52 peaks and deep gorges. The highest peak, Mytikas (Μύτικας Mýtikas), meaning “nose”, rises to 2,917 metres (9,570 ft). It is one of the highest peaks in Europe in terms of topographic prominence.” ref
“Olympus is notable in Greek mythology as the home of the Greek gods, on Mytikas peak. It is also noted for its exceptional biodiversity and rich flora. It has been a National Park, the first in Greece, since 1938. It is also a World Biosphere Reserve. Every year, thousands of visitors admire its fauna and flora, tour its slopes, and climb its peaks. Organized mountain refuges and various mountaineering and climbing routes are available. The usual starting point for climbing Olympus is the town of Litochoro, on the eastern foothills of the mountain, 100 km (62 mi) from Thessaloniki.” ref
“The shape of Olympus was formed by rain and wind, which produced an isolated tower almost 3,000 meters (9,800 ft) above the sea, which is only 18 kilometers (11 mi) away at Litochoro. Olympus has many peaks and an almost circular shape. The mountain has a circumference of 150 kilometers (93 mi), an average diameter of 26 kilometers (16 mi), and 500 square kilometers (190 sq mi) of area. To the northwest lies the Aromanian village of Kokkinopilos. The Makryrema stream separates Olympus from the massif of Voulgara. The villages Petra, Vrontou, and Dion lie to the northwest, while on the eastern side there is the town of Litochoro, where Enipeas bisects the massif of Olympus.” ref
“On its southeastern side, the Ziliana gorge divides Mount Olympus from Kato Olympos (Lower Olympus), while on its southwestern foothills, there are the villages Sykaminea and Karya. The Agia Triada Sparmou Monastery and the village Pythion lie to the west. Olympus’s dry foothills, known as the Xirokampi, are covered in chaparral and provides habitat for animals such as wild boar. Further east, the plain of Dion is fertile and watered by the streams which originate on Olympus.” ref
“The origin of the name Όλυμπος (Olympos) is unknown. One theory suggests that it’s compounded of lyma (λύμα) and pous (πούς), meaning “pure foot”, conforming to Hesiod‘s description of the earth as a sort of footstool for heaven up from which rise the “Blessed Gods”. According to Robert S.P. Beekes the word is of pre-Greek origin and he speculates that it originally meant “mountain”. It is worth noting that the word is also probably cognate with the Mycenean Greek word (u-ru-pi-ja-jo) which is, most likely, a term used to describe people, or possibly an ethnic group. In Homeric Greek (Odyssey 6.42), the variant Οὔλυμπος Oulumpos occurs, conceived of as the seat of the gods (and not identified with any specific peak). Homer (Iliad 5.754, Odyssey 20.103) also appears to be using οὔλυμπος as a common noun, as a synonym of οὐρανός ouranos “sky”. Mount Olympus was historically also known as Mount Belus,] after Iliad 1.591, where the seat of the gods is referred to as βηλ[ός] θεσπεσίο[ς] “heavenly threshold”.” ref
“In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, “Olympus” was the name of the home of the Twelve Olympian gods. This was conceived of as a lofty mountaintop, and in all regions settled by Greek tribes, the highest local elevation tended to be so named; among the numerous peaks called Olumpos in antiquity are mountains in Mysia, Laconia, Lycia, Cyprus, Attica, Euboea, Ionia and Lesbos, and others. Thessalian Olympus is the highest peak in any territory with Greek settlement and came to be seen as the “Pan-Hellenic” representative of the mythological seat of the gods, by at least the 5th century BC, as Herodotus (1.56) identifies Olympus as the peak in Thessaly. In Pieria, at Olympus’s northern foot, the mythological tradition had placed the nine Muses, patrons of the Fine Arts, daughters of Zeus, and the Titanide Mnemosyne.” ref
Mount Olympus History
“In antiquity, the Olympus massif formed the border between Thessaly and Macedon. The history of the surrounding area is consequently of interest in the context of the Rise of Macedon, the Chremonidean War, and the Macedonian Wars during the 4th to 2nd centuries BCE. In the period of the Ottoman Empire the mountain was a hiding place and base of operations for klephts and armatoloi. It was known as Semavatevi in Turkish during the nearly 400 years of Ottoman rule.” ref
“In Olympus, the second armatoliki was founded, led by Kara Michalis in 1489. The action of the klephts in Olympus led the Turks to visit their outrage on the klephts’ ally-village of Milia (in the late 17th century), which they destroyed. In that period Livadi in Olympus became the seat of the armatoliki of Olympus and Western Macedonia, with their first renowned commander Panos Zidros. In the 18th century the Turks had to replace the armatoloi (who very often joined the klephts) with Muslim Albanian armatoloi who ravaged the countryside of Macedonia.” ref
“However, Olympus’s armatoloi, even after their capitulation to Ali Pasha, never ceased fighting on land and at sea. Among them who were active there and in nearby regions were Nikotsaras, Giorgakis Olympios, and the legendary family of Lazaioi. In the early 20th century, even for some time after the liberation from the Ottoman Empire (1912), robbers were active in the region – the best known of them the notorious Giagoulas, while during the German invasion in 1941 the Royal Hellenic Army fought significant battles along with units of New Zealanders and Australians. During the German Occupation (1941–1944) the mountain was one of the centers of the Greek Resistance, while a little later the Greek Civil War (1946–49) started there, in Litochoro.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
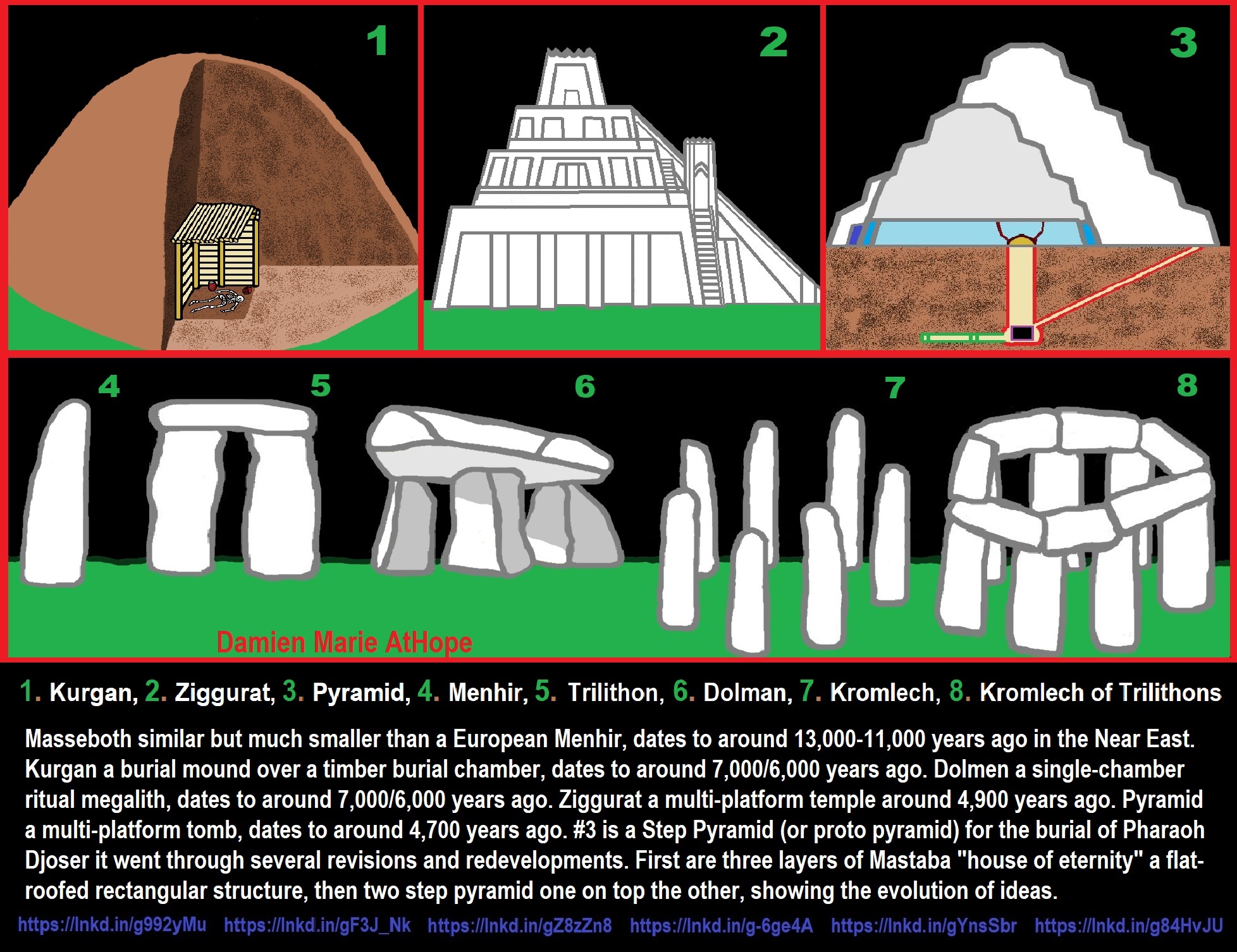
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Masseboth similar but much smaller than a European Menhir, dates to around 13,000-11,000 years ago in the Near East. Kurgan a burial mound over a timber burial chamber, dates to around 7,000/6,000 years ago. Dolmen a single-chamber ritual megalith, dates to around 7,000/6,000 years ago. Ziggurat a multi-platform temple around 4,900 years ago. Pyramid a multi-platform tomb, dates to around 4,700 years ago. #3 is a Step Pyramid (or proto pyramid) for the burial of Pharaoh Djoser it went through several revisions and redevelopments. First are three layers of Mastaba “house of eternity” a flat-roofed rectangular structure, then two step pyramid one on top the other, showing the evolution of ideas.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
By day the LORD went ahead of them in a pillar of cloud to guide them on their way and by night in a pillar of fire to give them light, so that they could travel by day or night.
- By day the “Bible God” was in a cloud pillar.
- By night the “Bible God” was in a fire pillar.

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref


My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
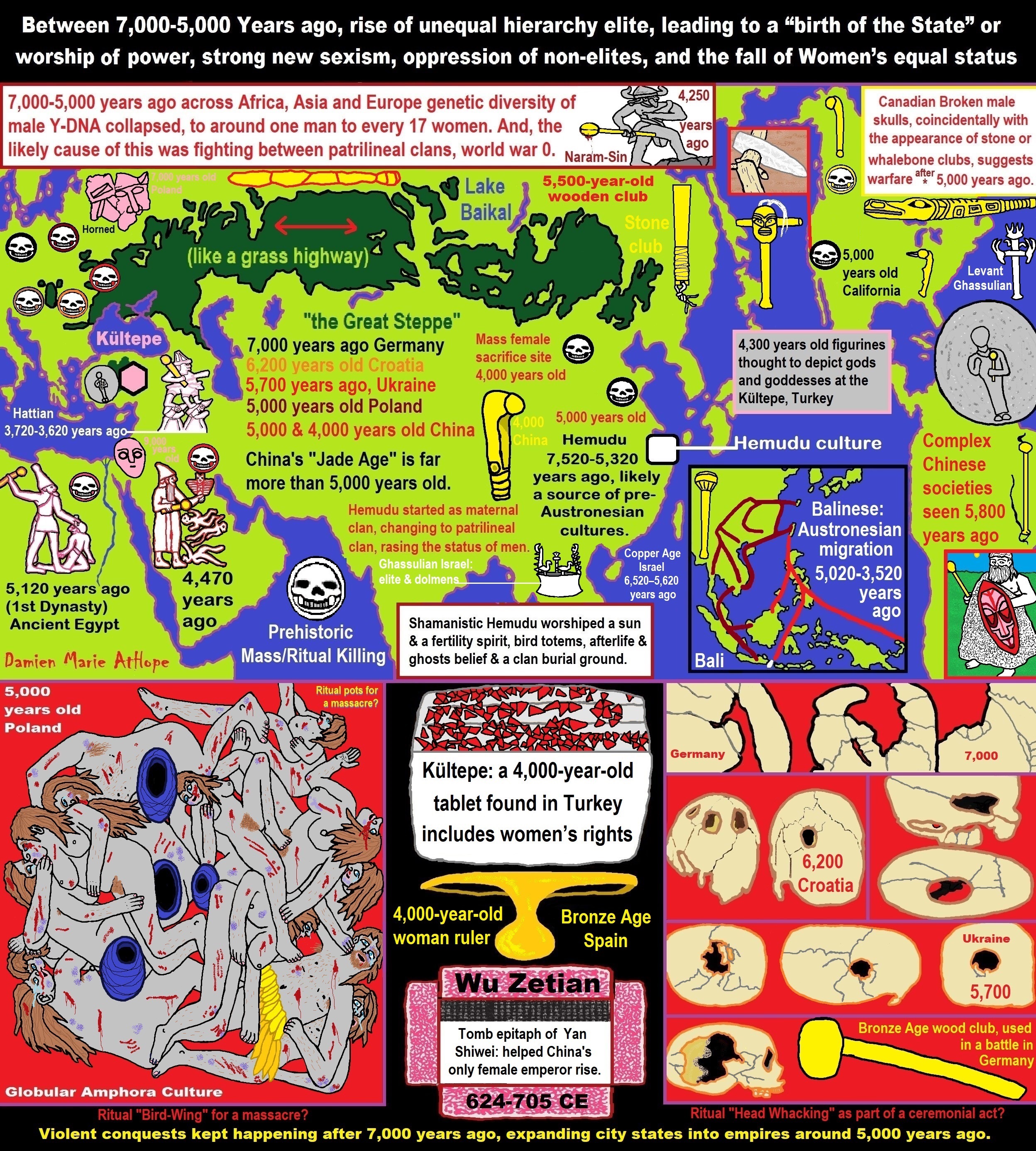
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
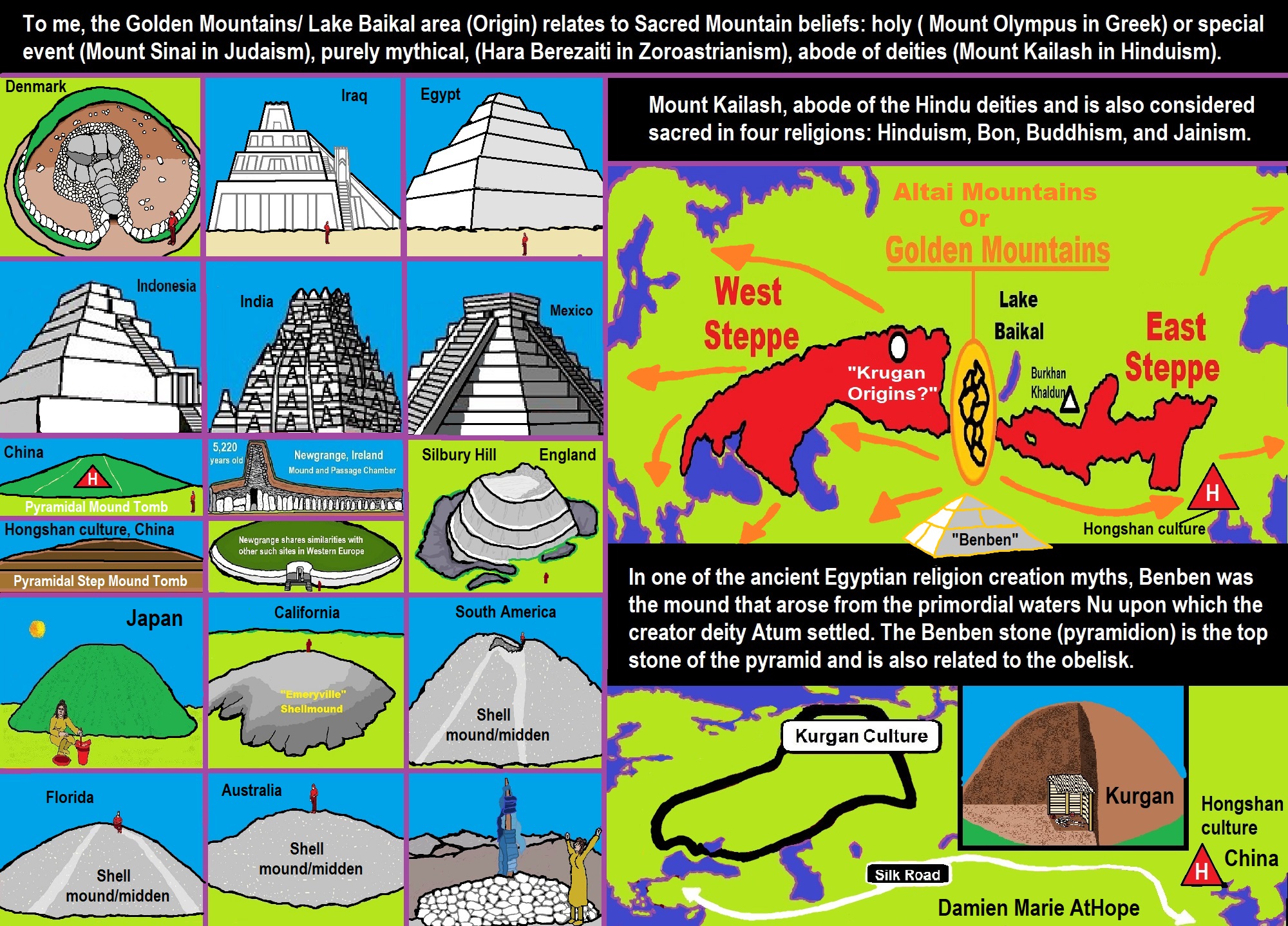
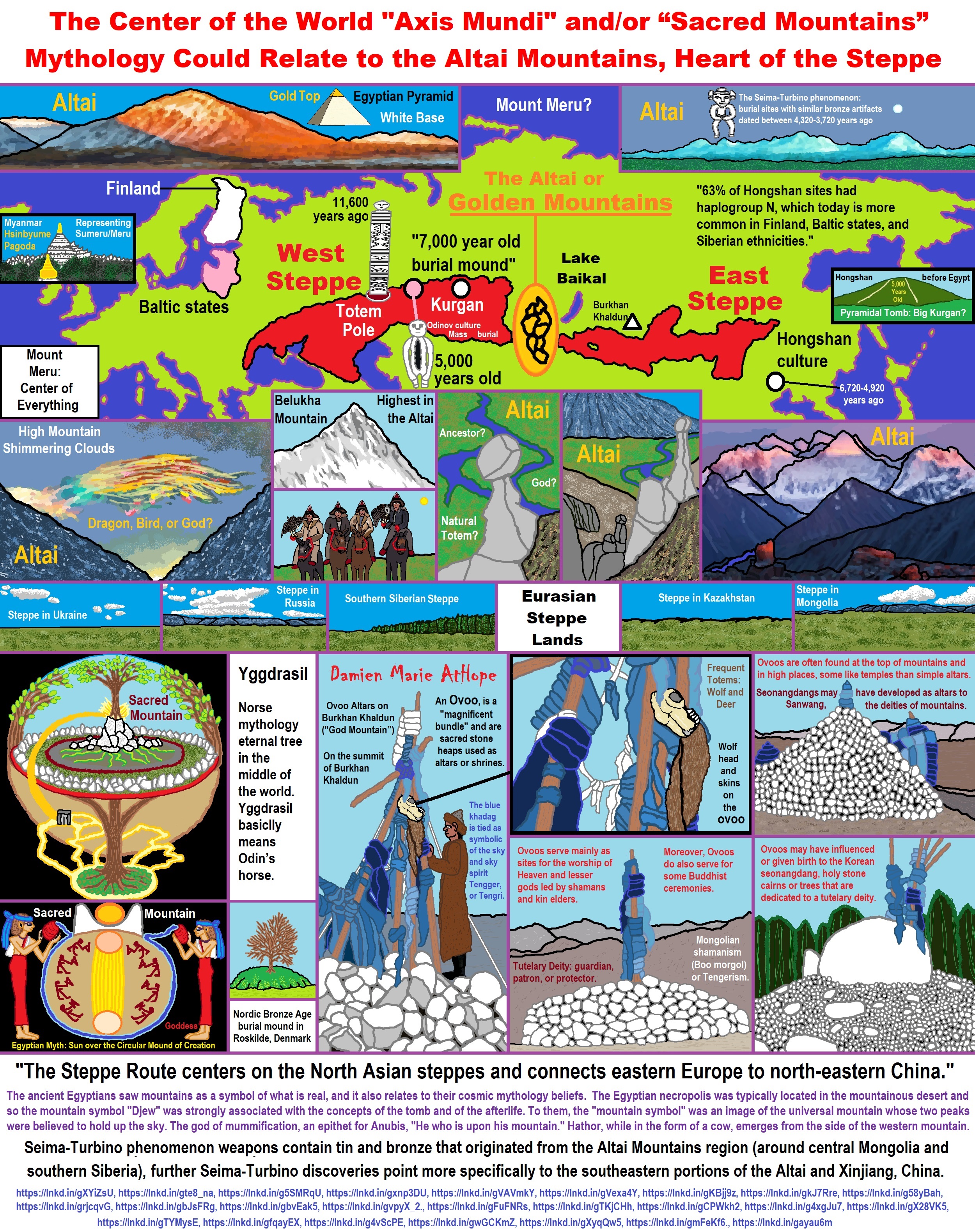
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
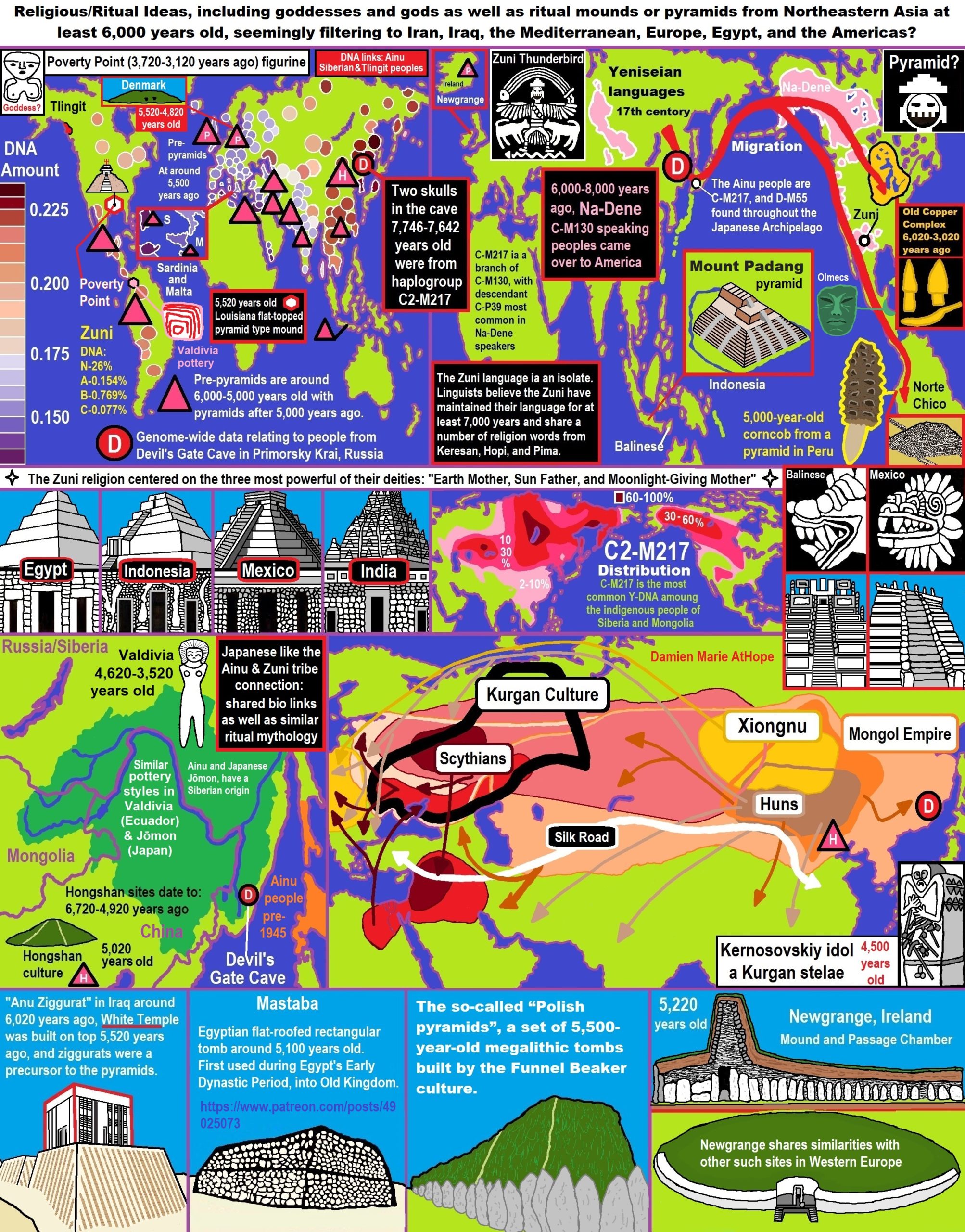
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
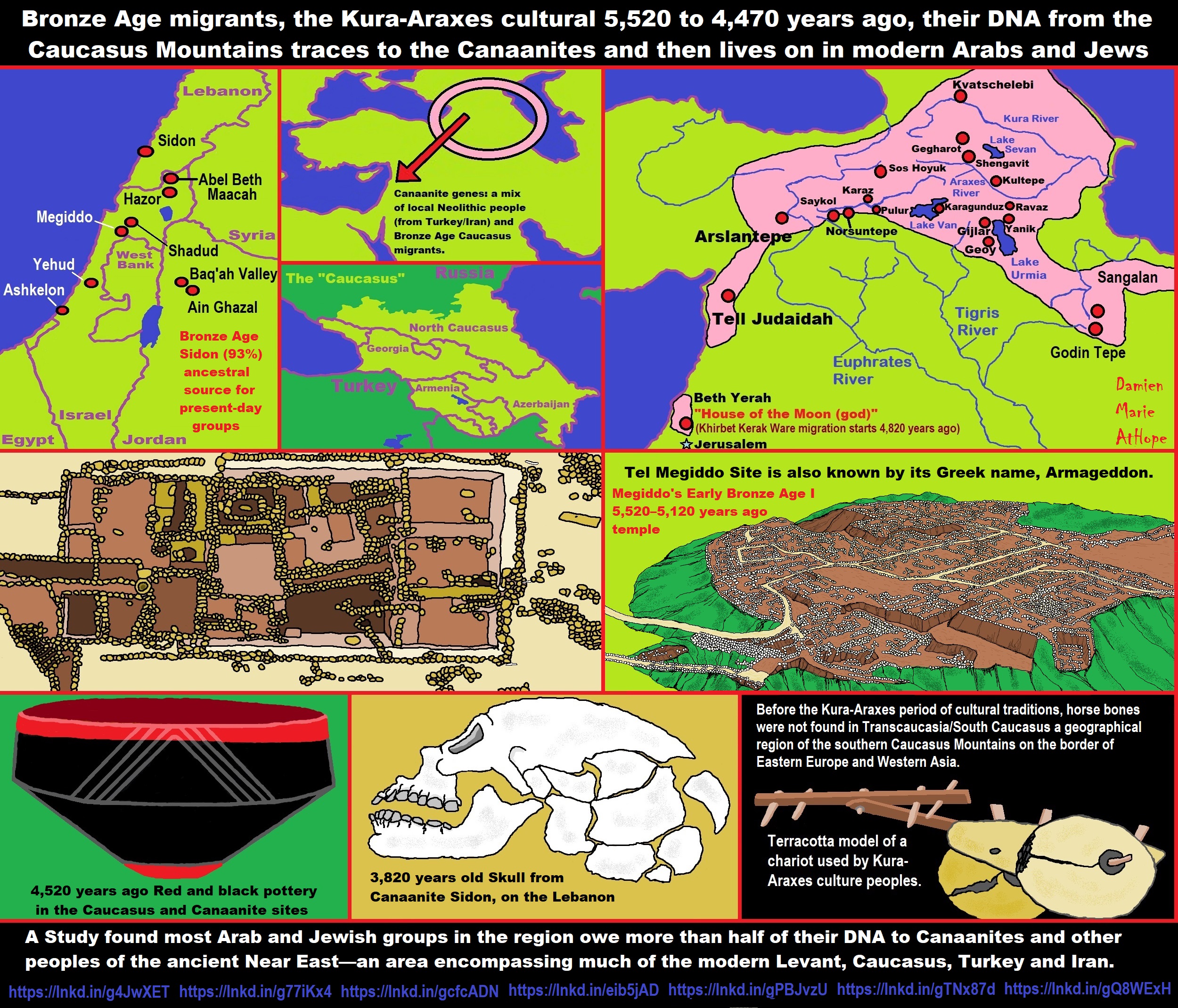
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
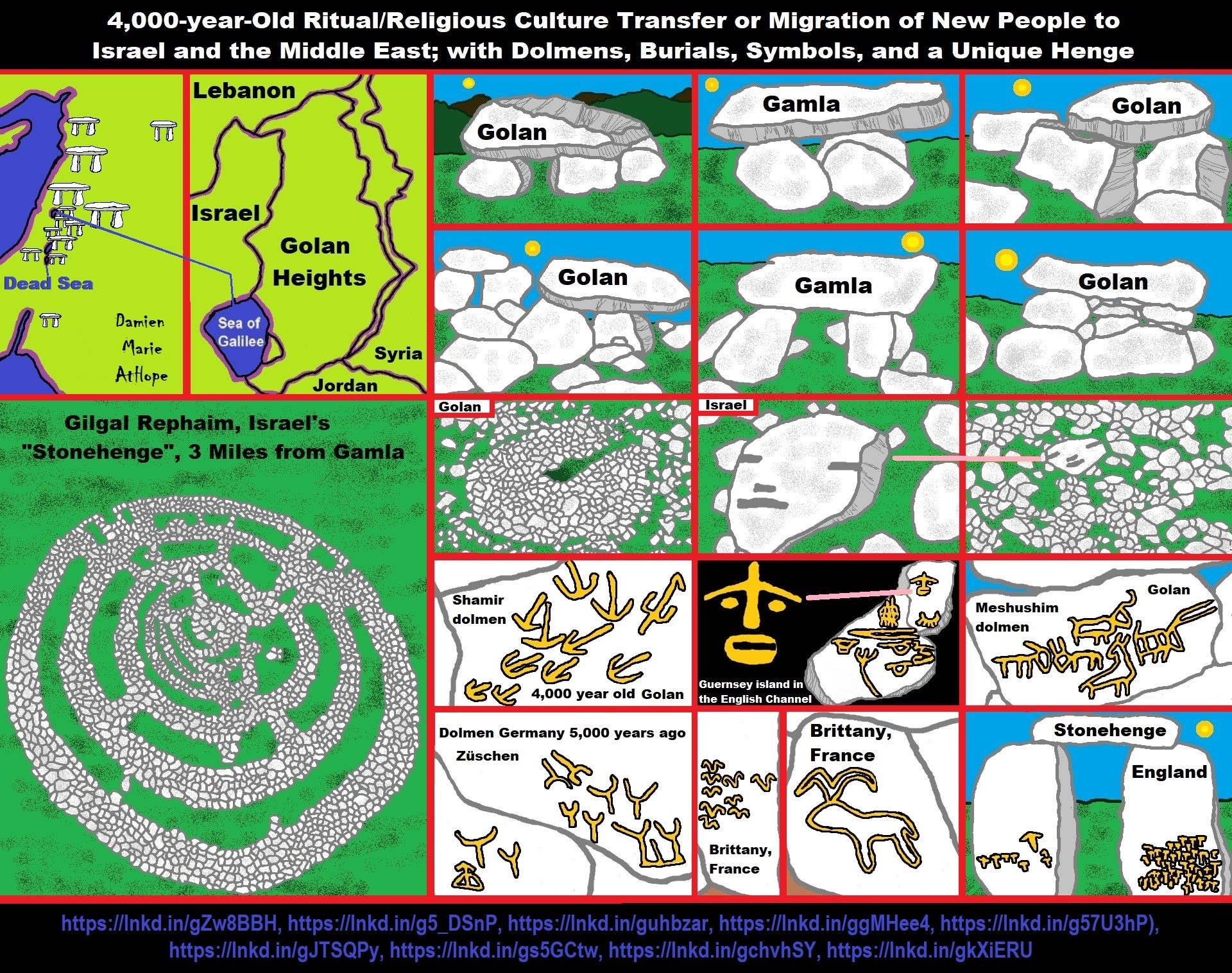
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


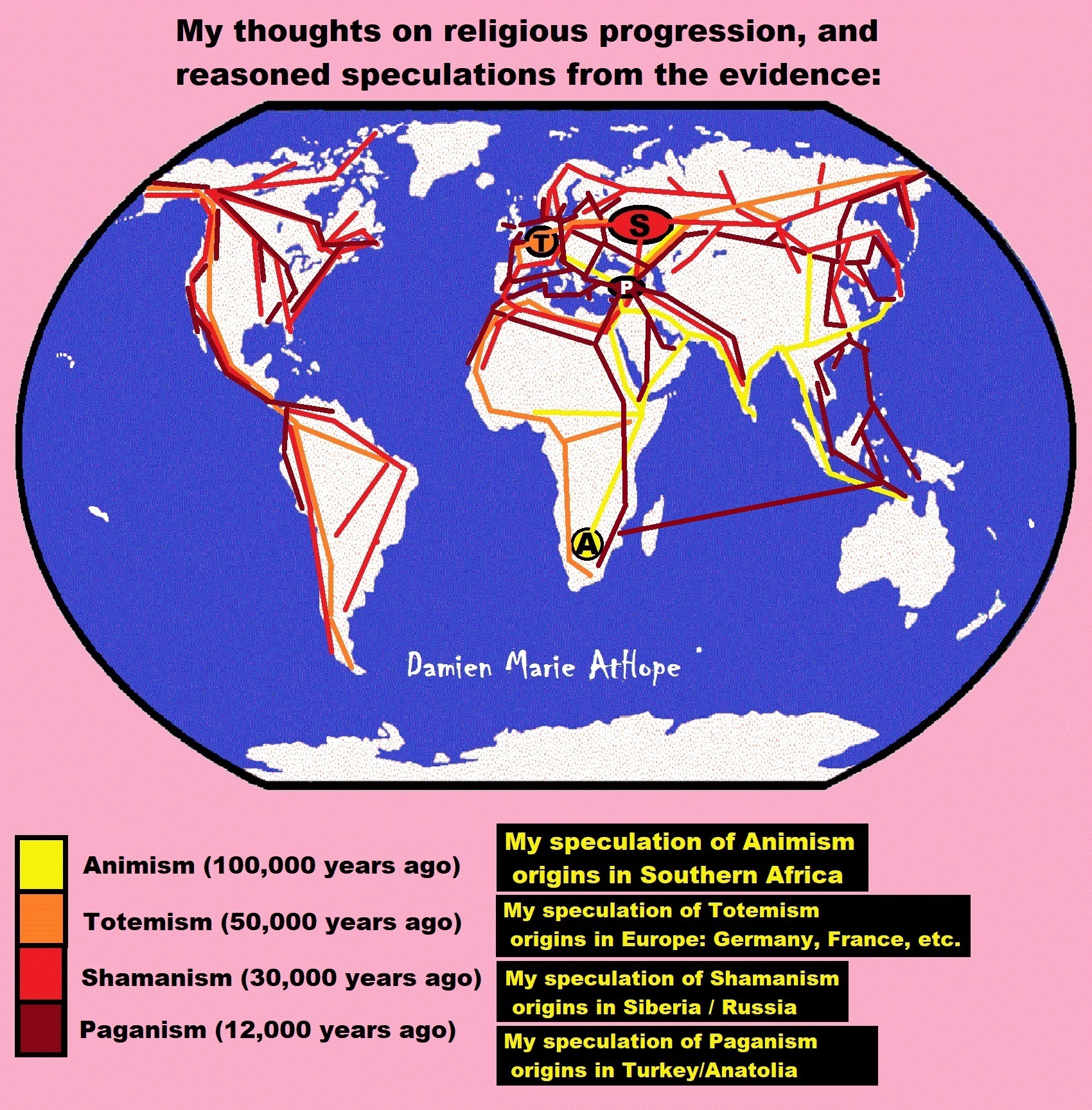



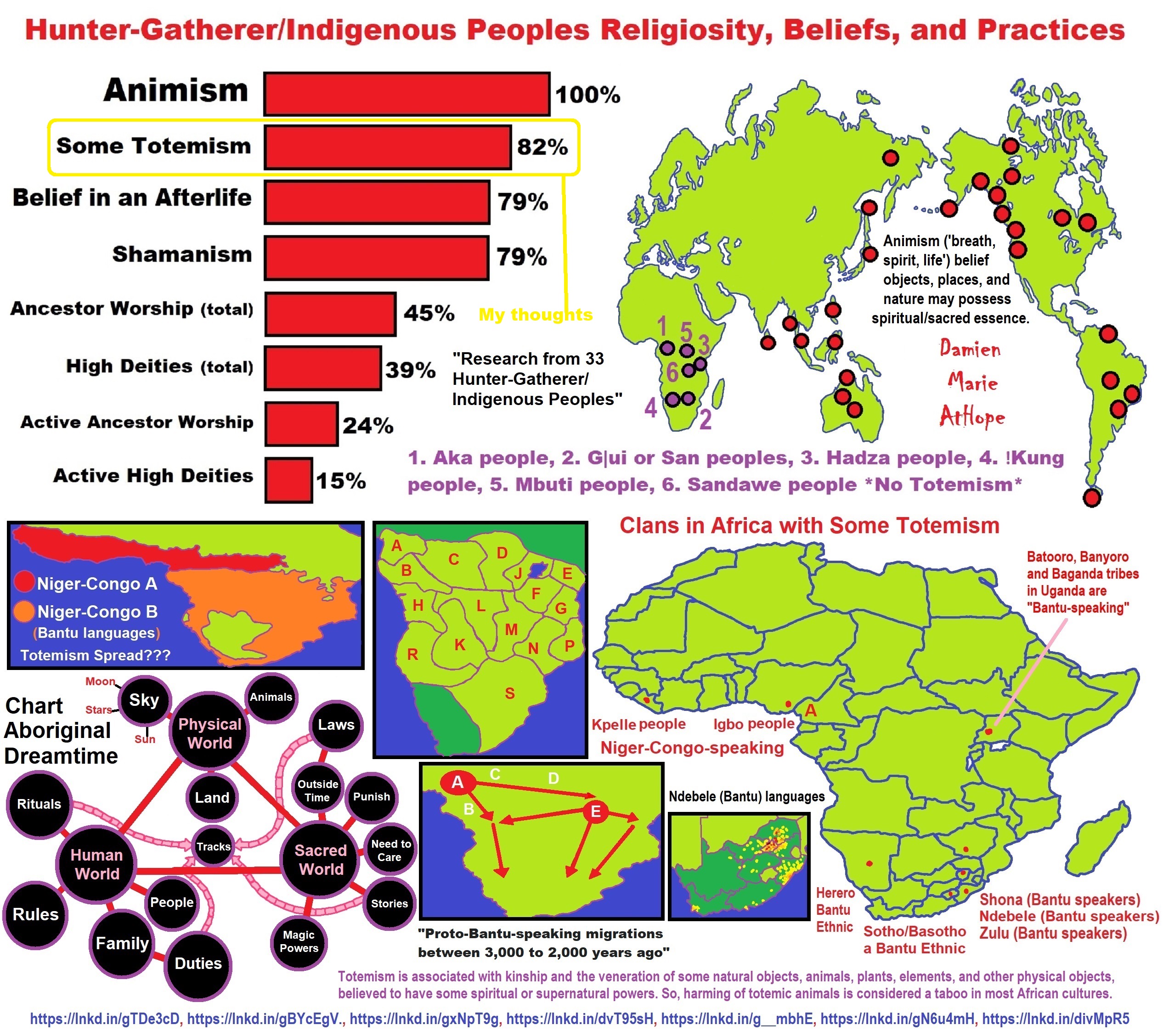
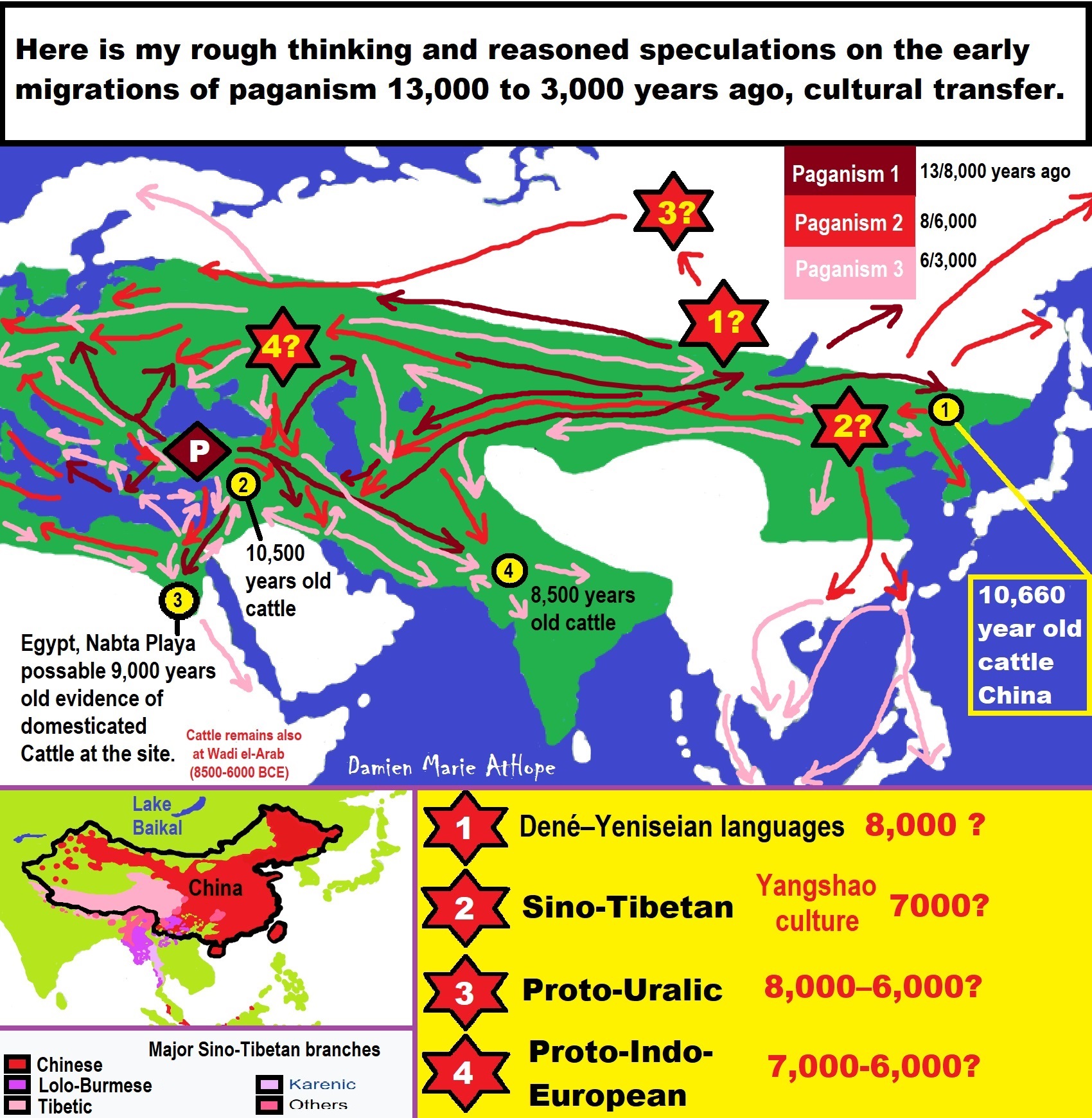

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com