Understanding Religion Evolution per Damien’s speculations from the evidence:
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) possibly Africa, Middle East, and Eurasia
Animism (at least 100,000 years ago) possibly Southern Africa or maybe Central Africa
Totemism (at least 50,000/45,000 years ago) possibly around Germany, France, or somewhere in West Europe
Shamanism (at least 30,000/35,000 years ago) possibly West Siberia or East Russia
Paganism (at least 12,000/13,000 years ago) Turkey And/or Levant: “Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestine, Syria”
Progressed organized religion (at least 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
I think animism started 100,000 years ago, totemism 50,000-45,000 years ago, and shamanism 30,000-35,000 years ago.
Animism (simplified to me as a belief in a perceived spirit world) passably by at least 100,000 years ago “the primal stage of early religion” To me, Animistic Somethingism: You just feel/think there has to be something supernatural/spirit-world or feel/think things are supernatural/spirit-filled.
Totemism (simplified to me, as a belief that these perceived spirits could be managed or related with by created physical expressions) passably by at least 50,000 years ago “progressed stage of early religion” A totem is a representational spirit being, a sacred object, or symbol of a group of people, clan, or tribe.
Shamanism (simplified to me as a belief that some special person can commune with these perceived spirits on the behalf of others by way of rituals) passably by at least 30,000 years ago Shamanism is an otherworld connection belief thought to heal the sick, communicate with spirits/deities, and escort souls of the dead.

Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art at least 300,000-year-old
Rock Art Museum’s, Art Collection as well as their take on animism: Link
Here is Rock Art Museum’s, main gallery is here Link
- First Sculpture: Handaxe to Figure Stone
- Lower Paleolithic ‘figure (ANCESTOR?) stones’
- Similar stone tools of a later date with ‘Right eye open, left eye missing’ carved stone head
Lower Paleolithic Figure (ANCESTOR?) Stones?
Face made around 450,000 to 300,000 years before present, The Netherlands. ref
Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art at least 300,000-year-old some possibly up to 500,000 years ago. This Pre-Animism, to me, involves “animistic superstitionism”, I surmise, which leads to the animistic somethingism or animistic supernaturalism that is presented in today’s religions and is a representation of general Animism that is at least 100,000 years old.
Five types of ancient art sculpture
Flint ‘portrait’ from the Ohle gravel pit which is likely 423,000 -524,000 years old Similar profile heads from the Ohle pit. Center is the primary piece which is sometimes called ‘Sorrowful Man.’ Height, 13.2cm; Width, 9.6cm. ref
One of the most productive sites for Early Paleolithic figurines is the Ohle gravel pit, Groß Pampau, near Hamburg, Germany, from Elster glacial moraine basal gravels and the artifacts from these gravels can be dated to 478,000 -524,000 years ago, 423,000 -478,000, or generally about 500,000 to 400,000 years ago. There appears to be some reworking of artifacts suggests a time around 362,000 -423,000 years ago with associated tools from the Middle Acheulian style and early Later Acheulian quality, suggesting that some are around 500,000 years ago or older. The preponderance of Abbevillian and early Later Acheulian type tools at Pampau and their setting in the Elster moraine suggest that the Pampau palaeo-art is basically Later Acheulian period and thus the Ohle Elster gravels palaeo-art might be considered one of the oldest examples of palaeo-art in the world. It at least puts the Ohle site in a time frame comparable to the accepted Later Acheulian figurines from Tan-Tan, Morocco, 300,000 -500,000 years ago or older and Berekhat Ram, from Israel, dates to around 233,000-470,000. ref
The Venus of Berekhat Ram is a seeming female figure, anthropomorphic red tufic pebble, 35 mm (1.4 in) long found at Berekhat Ram on the Golan Heights, Israel between two layers of ash, at least 230,000 years ago and likely 300,000 years ago or older maybe up to 500,000 years ago. Rather than being made by modern humans, it would have been made by Neanderthals or perhaps by Homo erectus, hunter-gatherers and Acheulean tool users. ref
Tan-Tan sculpture from Morocco, North Africa part of the Acheulian stone tool culture, dating to 500,000-300,000 years old, resembling a human figure and was found near stone tools seeming to express its cultural importance. ref
My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
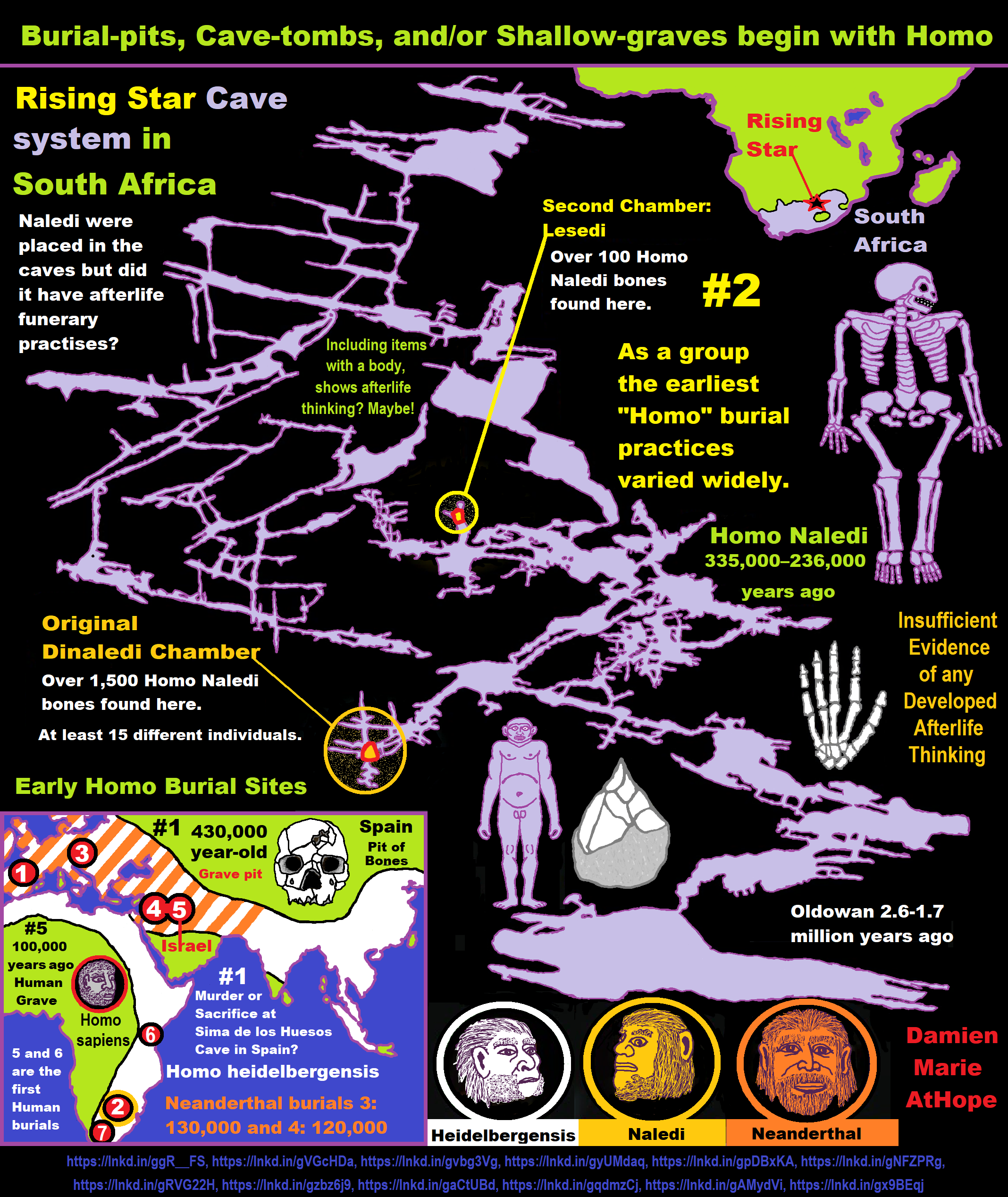
Homo naledi may have lit fires in underground caves at least 236,000 years ago
“Remnants of small fireplaces found in South African cave system, researchers announce. An ancient hominid dubbed Homo naledi may have lit controlled fires in the pitch-dark chambers of an underground cave system, new discoveries hint. Researchers have found remnants of small fireplaces and sooty wall and ceiling smudges in passages and chambers throughout South Africa’s Rising Star cave complex, paleoanthropologist Lee Berger announced in a December 1 lecture hosted by the Carnegie Institution of Science in Washington, D.C. “Signs of fire use are everywhere in this cave system,” said Berger, of the University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref ,ref ,ref ,ref ,ref, ref, ref
Homo Naledi
“Homo Naledi is a species of archaic human discovered in the Rising Star Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa dating to the Middle Pleistocene 335,000–236,000 years ago. The initial discovery comprises 1,550 specimens, representing 737 different elements, and at least 15 different individuals. Despite this exceptionally high number of specimens, their classification with other Homo remains unclear.” ref
“Along with similarities to contemporary Homo, they share several characteristics with the ancestral Australopithecus and early Homo as well (mosaic anatomy), most notably a small cranial capacity of 465–610 cm3 (28.4–37.2 cu in), compared to 1,270–1,330 cm3 (78–81 cu in) in modern humans. They are estimated to have averaged 143.6 cm (4 ft 9 in) in height and 39.7 kg (88 lb) in weight, yielding a small encephalization quotient of 4.5. Nonetheless, Homo Naledi’s brain anatomy seems to have been similar to contemporary Homo, which could indicate equatable cognitive complexity. The persistence of small-brained humans for so long in the midst of bigger-brained contemporaries revises the previous conception that a larger brain would necessarily lead to an evolutionary advantage, and their mosaic anatomy greatly expands the known range of variation for the genus.” ref
“Homo Naledi anatomy indicates that, though they were capable of long-distance travel with a humanlike stride and gait, they were more arboreal than other Homo, better adapted to climbing and suspensory behavior in trees than endurance running. Tooth anatomy suggests consumption of gritty foods covered in particulates such as dust or dirt. Though they have not been associated with stone tools or any indication of material culture, they appear to have been dextrous enough to produce and handle tools, and likely manufactured Early or Middle Stone Age industries. It has also been controversially postulated that these individuals were given funerary rites, and were carried into and placed in the chamber.” ref
Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art at least 300,000-year-old
Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art at least 300,000-year-old some possibly up to 500,000 years ago.
This Pre-Animism, to me, involves “animistic superstitionism”, I surmise, which leads to the animistic somethingism or animistic supernaturalism that is presented in today’s religions and is a representation of general Animism that is at least 100,000 years old.
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
Around a million years ago, I surmise that Pre-Animism, “animistic superstitionism”, began, Around 400,000 Years ago shows Sociocultural Evolution, and then led to the animistic somethingism or animistic supernaturalism, which is at least 300,000 years old and about 100,00 years ago, it evolves to a representation of general Animism, which is present in today’s religions. There is also Homo Naledi and an Intentional Cemetery “Pre-Animism” dating to around 250,000 years ago. And, Neanderthals “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” Mystery Cave Rings 175,000 Years Ago. Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, around 130,000 years ago at sites such as Krapina in Croatia.
Pre-animism ideas can be seen in rock art such as that expressed in portable anthropomorphic art, which may be related to some kind of ancestor veneration. This magical thinking may stem from a social or non-religious function of ancestor veneration, which cultivates kinship values such as filial piety, family loyalty, and continuity of the family lineage. Ancestor veneration occurs in societies with every degree of social, political, and technological complexity and it remains an important component of various religious practices in modern times.
Humans are not the only species, which bury their dead. The practice has been observed in chimpanzees, elephants, and possibly dogs. Intentional burial, particularly with grave goods, signify a “concern for the dead” and Neanderthals were the first human species to practice burial behavior and intentionally bury their dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. The earliest undisputed human burial dates back 100,000 years ago with remains stained with red ochre, which show ritual intentionality similar to the Neanderthals before them. ref, ref
Animism (such as that seen in Africa: 100,000 years ago)
Did Neanderthals teach us “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” 120,000 Years Ago? Homo sapiens – is known to have reached the Levant between 120,000 and 90,000 years ago, but that exit from Africa evidently went extinct. 100,000 years ago, in Qafzeh, Israel, the oldest intentional burial had 15 African individuals covered in red ocher was from a group who visited and returned back to Africa. 100,000 to 74,000 years ago, at Border Cave in Africa, an intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament, which may have possible connections to the Africans buried in Qafzeh.
Animism is approximately a 100,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden animist.
The following is evidence of Animism: 100,000 years ago, in Qafzeh, Israel, the oldest intentional burial had 15 African individuals covered in red ocher was from a group who visited and returned back to Africa. 100,000 to 74,000 years ago, at Border Cave in Africa, an intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament, which may have possible connections to the Africans buried in Qafzeh, Israel. 120,000 years ago, did Neanderthals teach us Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism) as they too used red ocher and burials? ref, ref
It seems to me, it may be the Neanderthals who may have transmitted a “Primal Religion (Animism)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife. The Neanderthals seem to express what could be perceived as a Primal “type of” Religion, which could have come first and is supported in how 250,000 years ago, the Neanderthals used red ochre, and 230,000 years ago shows evidence of Neanderthal burial with grave goods and possibly a belief in the afterlife. ref
Do you think it is crazy that the Neanderthals may have transmitted a “Primal Religion”? Consider this, it appears that 175,000 years ago, the Neanderthals built mysterious underground circles with broken-off stalactites. This evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel, and Krapina in Croatia. Other evidence may suggest the Neanderthals had it transmitted to them by Homo heidelbergensis, 350,000 years ago, by their earliest burial in a shaft pit grave in a cave that had a pink stone ax on the top of 27 Homo heidelbergensis individuals and 250,000 years ago, Homo Naledi had an intentional cemetery in South Africa cave. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Anthropomorphic Pre-animism “Human Face” Art
Figure-stones present in additional objects from the same context as the Belgian Kempen, Belgium, like these stone faces dated to around 450,000 to 300,000 years old. They indicate the eye concavities are natural features but the overall shape of the piece possibly was worked to the final head shape. ref
“Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife may have been transferred from Neanderthals to arcane humans when they bread with them. Neanderthals, also interbred with Homo erectus, the “upright walking man,” Homo habilis, the “tool-using man,” and possibly others which means they could have possibly learned some pre-animism ideas from one of them like that expressed in portable anthropomorphic art that could have related to so kind of ancestor veneration as well. ref
The earliest European hominin crania associated with Acheulean handaxes are at the sites of Arago, Atapuerca Sima de los Huesos, and Swanscombe, dating to around 500,000 to 400,000 years ago. The Atapuerca fossils and the Swanscombe cranium belong to the Neandertal clade, whereas the Arago hominins have been attributed to an incipient stage of Neandertal evolution, to Homo heidelbergensis, or to a subspecies of Homo erectus A recently discovered cranium (Aroeira 3) from the Gruta da Aroeira (Almonda karst system, Portugal) dating to 436,000 to 390,000 years ago provides important evidence on the earliest European Acheulean-bearing hominins as well as could show a transfer of ideas. ref
Homo erectus, the “upright walking man,” Lived: Between about 1.89 million and 143,000 years ago, whereas, early African Homo erectus fossils (sometimes called Homo ergaster) are the oldest known early humans to have possessed modern human-like. The earliest evidence of hearths (campfires) occur during the time range of Homo erectus. While we have evidence that hearths were used for cooking (and probably sharing) food, they are likely to have been places for social interaction, and also used for warmth and to keep away large predators, possibly even relating to Primal Religion “Pre-Animism, which may have included Fire Sacralizing and/or Worship. ref
Neanderthals used fire 400,000 years ago and there is evidence of a 300,000-year-old ‘campfire’ from Israel not that surprising after our human ancestors controlled fire from 1.5 million to 300,000 years ago and beyond. The benefits of fire are not only to cook food and fend off predators, but also extended their day and added to the community by how a fire in the middle of the darkness mellows and also flames excite people, possibly inspiring pre-animism’s “animistic superstitionism.” Sun-worshipping baboons rise early to catch the African sunrise and race each other to the top for the best spots. Thus, we may rightly ponder how much did fireside tales aid to the socio-cultural-religious transformations or evolution. In the dark under flickering lights both above and below, was the scene a mix of wonder, fear, and mystery that superstition was expanded and religion further imagined? It would seem that superstition was expanded and religion further imagined because both heavenly lights and flickering fire have been sacralized. Which does seem to be somewhat supported by a researcher who spent 40 years studying African Bushmen who gathered evidence of the importance of gathering around a nighttime campfire might be a universally applicable time for bonding, social information, many shared emotions, in fireside tales if we can ascertain a correlation that our prehistoric ancestors likely lived in a similar way to how the Bushmen current do.
Although, we cannot directly peer into the past, or fully know the past from the indigenous Bushmen, these people do live in a way that our ancient ancestors lived for around 99% of our evolution. Therefore, we can somewhat draw some reasonable parallels such as how daytime conversations focused mainly on social relationships with only a small percentage of stories, whereas the evening conversations around campfires centered on storytelling, especially the adding of stories about the spirit world adding possible credence to the thinking that nighttime and its darkness full of fear and or wonder in the flickering lights of fireside allows for more mystical thinking and the tales such an environment can produce which could have aided in socio-cultural-religious transformations or evolution. The importance of water and fire can be a set of hidden factors to human evolution and socio-cultural-religious transformations and involved in many religious themes; lingering primitive animism still seen in current religions.
Fire as sacred or magic can be seen in consuming fire, volcanos/lightning as gods power/vengeance, holy fire, fire as a means of transformation or magical purification or just a magical being itself as well as used in fire worship/worshiping the sun or punishment (hell: lake of fire which could be seen as mixing fire and water if only symbolically) used in ceremonies like bonfires, eternal flames, or sacred candles/incense/lights/lamps are in one form or another incorporated in many faiths such as Judaism, Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, Bahaism, Shintoism, Taoism, etc. All this worship of fire/sun are hardly special certain primates worship thunderstorms, others fire or sunrises. We have forgotten how nature worship, animistic superstitionism, animistic somethingism, or animistic supernatralism is presented in today’s religion. The mega religions now think they are removed from animistic superstitionism, which they have not. Their rituals, beliefs, and prayers have a connection to animism nature worship but are more hidden or stylized, such as burning candles which is worshipping fire. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
* “animist” Believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife (you are a hidden animist/Animism : an approximately 100,000-year-old belief system
Qafzeh: Oldest Intentional Burial of 15 individuals with red ocher and Border Cave: intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament (possibly extending to or from Did Neanderthals teach us “Primal Religion (Animism?)” 120,000 Years Ago, as they too used red ocher?
Well it seems to me it may be Neanderthals who may have transmitted a “Primal Religion (Animism?)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife they seem to express what could be perceived as a Primal “type of” Religion.
Which could have come first is supported in how 250,000 years ago Neanderthals used red ochre and 230,000 years ago shows evidence of Neanderthal burial with grave goods and possibly a belief in the afterlife. Think the idea that Neanderthals who may have transmitted a “Primal Religion” as crazy then consider this, it appears that Neanderthals built mystery underground circles 175,000 years ago.
Evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. Or maybe Neanderthals had it transmitted to them Evidence of earliest burial: a 350,000-year-old pink stone axe with 27 Homo heidelbergensis. As well as the fact that the oldest Stone Age Art dates to around 500,000 to 233,000 Years Old and it could be of a female possibly with magical believed qualities or representing something that was believed to)
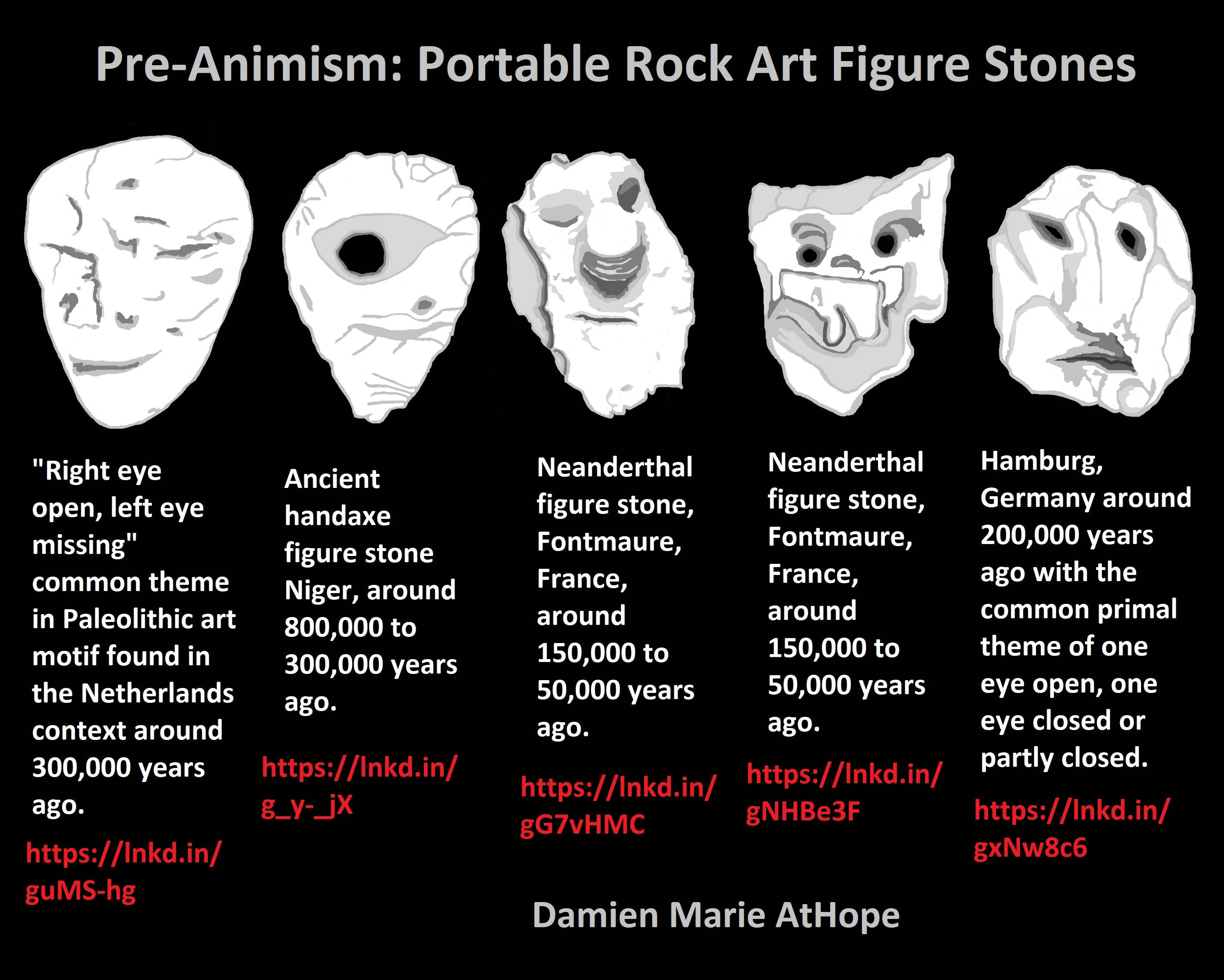
Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art Figure Stones
Neanderthal figure stone, Fontmaure, France, around 150,000 to 50,000 years ago. ref, ref
Hamburg, Germany around 200,000 years ago with the common primal theme of one eye open, one eye closed or partly closed. ref
Ancient handaxe figure stone Niger, around 800,000 to 300,000 years ago. ref
“Right eye open, left eye missing”a common theme in Paleolithic art motif found in the Netherlands context around 300,000 years ago. ref
The world’s oldest sculpture; archaeology reveals the earliest sculptures discovered and enhanced by hominid hand. To date, the oldest known human three-dimensional representation is the Tan-Tan sculpture (above left), discovered in Morocco, in an open site in ancient river deposits of the Draa river. It is Acheulian, and has been dated between 500,000 to 300,000 years old. It is almost 6 cms in height and just over 1 cm wide. The overall shape of this small quartzite pebble resembles a human figure. Found near stone tools, it is possible that the pebble was simply collected and kept by someone who noticed its human shape. It is entirely natural yet appears to have been modified by human action; examination under a microscope suggests this shape may have been emphasised by deliberate alteration of the natural grooves which run across the body. It was found at the Berekhat Ram site on the Golan Heights, a pebble of volcanic rock 35mm in length. The pebble was noticeable because it resembled a female human form. ref
The Berekhat Ram sculpture (above right) has a groove around the neck and on the sides which have been shown to be deliberate modifications absent from other scoria found in the area. The archaeologist Alexander Marshak examined the pebble using an electron microscope. He concluded that it had been made, or enhanced, by hominid hand, the hominins who found and worked on their respective pieces would have been unaware of their future significance. The Venus of Berekhat Ram is a pebble found at Berekhat Ram on the Golan Heights, Israel. The base object is an anthropomorphic red tufic pebble, 35 mm (1.4 in) long, which has had at least three grooves, possibly incised on it by a sharp-edged stone. One is a deep groove that encircles the narrower, more rounded end of the pebble, two shallower, curved grooves run down the sides. These grooves can be interpreted as marking the neck and arms of a figure. Because it was found between two layers of ash, it has been dated by tephrochronology to at least 230,000 years before the present but is at a range of 500,000 – 233,000 Years Ago.
The venus of Berekhat Ram is a red stone figure with symbolic intent and possibly intended to represent an anthropomorphic female figure. The surface is a bright high red with a large hole lined with black volcanic glass is at the approximate position of a ‘navel.’ Venus figurines are often found in different elements or mediums from limestone, serpentine, ivory, clay, and bone ash and are dispersed from western Europe to Siberia. These figurines are often faceless with downturned heads, large breasts, buttocks (many-extreme fat), some possibly pregnant, several stuck into the ground, and found near cave walls or in hearths. So what are the possible explanations of venus figurines? They could be some kind of good luck charms (evidence of polish), symbols of fertility, cult objects, art, Paleolithic porn, or representations of women by women or men (some look like modern pregnant bodies and some very skinny) but overall there may be no one reason. These figurines may have been created for several different reasons depending on time, place, and people but we just do not know.
Though calling them all goddesses or venus is at least misleading if not outright uncalled for because of mythologizing motivated by current projections and this is true even if a few were seen as some kind of goddesses. However, the venus of Berekhat Ram even if just anthropomorphic art (i.e. ascribing human form or attributes to a thing not human) could be seen as possibly the earliest known archaeological manifestations of any kind of elements that later become more defined religious belief systems. This is reasonable because anthropomorphic character design in art is a symbolic use of design to portray personality and thus, natural objects resembling the human body (or parts of it) which have received minor amounts of intentional modification in order to bring out the similarity further for a desired purpose. One could possibly even surmise that for some, there may have been a character that can play a possible part in telling stories. Thus, anthropomorphic art, such as venus figurines, may connect or be a larger growing fantasy of symbolism, superstitions, and supernaturalism thus to socio-cultural-religious transformations or evolution.
Although one cannot at present rule out a purely fortuitous association with the venus of Berekhat Ram and the piece can hardly be described as artistic, the possibility remains that it can be placed in the figures category as unambiguous indicators of early symbolism, let alone ritual, and we should not write it off as casual ‘lithic art’. Instead, the appearance of precocious lithic technologies such as end-scrapers and stone chisels at Berekhat Ram, symbolism (and by extension perhaps ritual) drifted in and out of use over evolutionary time. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Ref: Insoll, T. (2012). The Oxford handbook of the archaeology of ritual and religion. Oxford, United Kingdom. Oxford University Press.
Read more in the Art of the Ice Age section: Link
Are these “Art Pieces” just art or a form of Ancestor Veneration?
Pre-animism ideas seen in rock art, such as that expressed in portable anthropomorphic art that could have related to so kind of ancestor veneration, which may be a magical thinking but stem from social or non-religious function of ancestor veneration is to cultivate kinship values, such as filial piety, family loyalty, and continuity of the family lineage. Ancestor veneration occurs in societies with every degree of social, political, and technological complexity, and it remains an important component of various religious practices in modern times.
Ancestor reverence is not the same as the worship of a deity or deities. In some Afro-diasporic cultures, ancestors are seen as being able to intercede on behalf of the living, often as messengers between humans and the gods. As spirits who were once human themselves, they are seen as being better able to understand human needs than would a divine being. In other cultures, the purpose of ancestor veneration is not to ask for favors but to do one’s filial duty. Some cultures believe that their ancestors actually need to be provided for by their descendants, and their practices include offerings of food and other provisions.
Others do not believe that the ancestors are even aware of what their descendants do for them, but that the expression of filial piety is what is important. Although there is no generally accepted theory concerning the origins of ancestor veneration, this social phenomenon appears in some form in all human cultures documented so far. David-Barrett and Carney claim that ancestor veneration might have served a group coordination role during human evolution, and thus it was the mechanism that led to religious representation fostering group cohesion. Humans are not the only species which bury their dead; the practice has been observed in chimpanzees, elephants, and possibly dogs.
Intentional burial, particularly with grave goods, signify a “concern for the dead” and Neanderthals were the first human species to practice burial behavior and intentionally bury their dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. The earliest undisputed human burial dates back 100,000 years with remains stained with red ochre showing ritual intentionality similar to the Neanderthals before them. ref, ref
Chimpanzees Sacralizing Trees?
There is evidence currently limited to West Africa where chimpanzees mainly adult males but also females or juveniles are observed creating a kind of shrine of accumulated stone piles beside, or inside trees as well as regularly visiting these trees picking up these stones and then throwing them at these trees accompanied with vocalization “performativity” which is (speech, gestures) to communicate an action.
Chimpanzees have been observed engaging in “social learning,” both teaching and learning such as tool use as well as communication signals: vocal and gestures. Such social learning is seen as playing an important and unique role in the development of human language, culture, and mythologizing. Altogether such things observed in these West Africa where chimpanzees could indicate some kind of what could be perceived as magical thinking or at least quasi-magical thinking in the sacralizing of trees as it does not seem connected to some utilitarian or food foraging practice of which rocks or tools would make sense.
This at first may sound too complex for a nonhuman animal but what needs to be understood is that chimpanzees have been known to exhibit “metacognition,” or think about thinking. Also, chimpanzees have the greatest variation in tool-use behaviors of any animal, second only to humans, where humans seem to have magical thinking or irrational beliefs are hardwired in our brains at a very ancient level because they involve mentally-fabricated patterns of thinking.
Moreover, such processing abilities are somewhat common among non-human primates if not lower mammals as well to some extent and can be seen as a part of evolutionary survival fitness and thus not uniquely human. It can be thought that different emotions evolved at different times with fear being ancient care for offspring relatively next later followed likely by extended social emotions, such as guilt and pride, evolved among social primates. Why this could be important is it is believed that emotions evolved to reinforce memories of patterns adding to survival and reproduction as well as responses to internal or external events and in such remapping facilitated by emotions could involve mentally-fabricated patterns of thinking which could superstitionize things in the world that do not truly limit it to the way it is possibly adding a kind of animism or the like involving some amount of magical thinking such as sacralizing of trees.
Magical thinking such as beliefs that there are relationships between behaviors or sounds thought to have the ability to directly affect other events in the world. Whereas quasi-magical thinking is acting as if there is a false belief that action influences the outcome, even though they may not really actualize or intentionally hold such a belief. Now I doubt West African chimpanzees are fully mythologizing the trees to a human magical thinking extent but we can see some possibilities of what about them could be inspired by magical thinking.
Magical thinking may lead to a type of causal reasoning or causal fallacy that looks for meaningful relationships of grouped phenomena (coincidence) between acts and events. Moreover, magical thinking when applied to trees are significant as believed sacred totems and natural sacred representations in many of the world’s oldest myths possibly because of using magical thinking when observing the growth and annual death and then revival of their foliage, seen them as symbolic representations of growth, death, and rebirth. As well as trees may be conceived as existing in three realms the underworld or death with the roots the world of the living the trunk existing in our world above the ground and its branches reaching to the heavens thus existing in the realm of the spirits, ancestors or gods. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
*Pre-Animism (belief in objects containing spiritual energy: magical Anthropomorphism thinking/possibly a form of Ancestor worship/Veneration of the dead) possibly by at least 300,000 years ago “the most primal stage before Animism’s early religion”
- Animism (belief in a perceived spirit world) possibly by at least 100,000 years ago “the primal stage of early religion”
- Totemism (belief that these perceived spirits could be managed with created physical expressions) possibly by at least 50,000 years ago “progressed stage of early religion”
- Shamanism (belief that some special person can commune with these perceived spirits on the behalf of others by way rituals) possibly by at least 30,000 years ago
- Paganism “Early organized nature-based religion” mainly like an evolved shamanism with gods (possibly by at least 13,000 years ago).
- Institutional religion “organized religion” as a social institution with official dogma usually set in a hierarchical/bureaucratic structure that contains strict rules and practices dominating the believer’s life. And to me paganism and Institutional religion categorized into the following stages:
*primal stage of organized religion is 13,000 years ago.
*proto-stage of organized religion is around 10,000 years ago.
*progressed stage of organized religion is around 7,000 years ago.
*developed stage of organized “Institutional” religion is around 5,000 years ago.
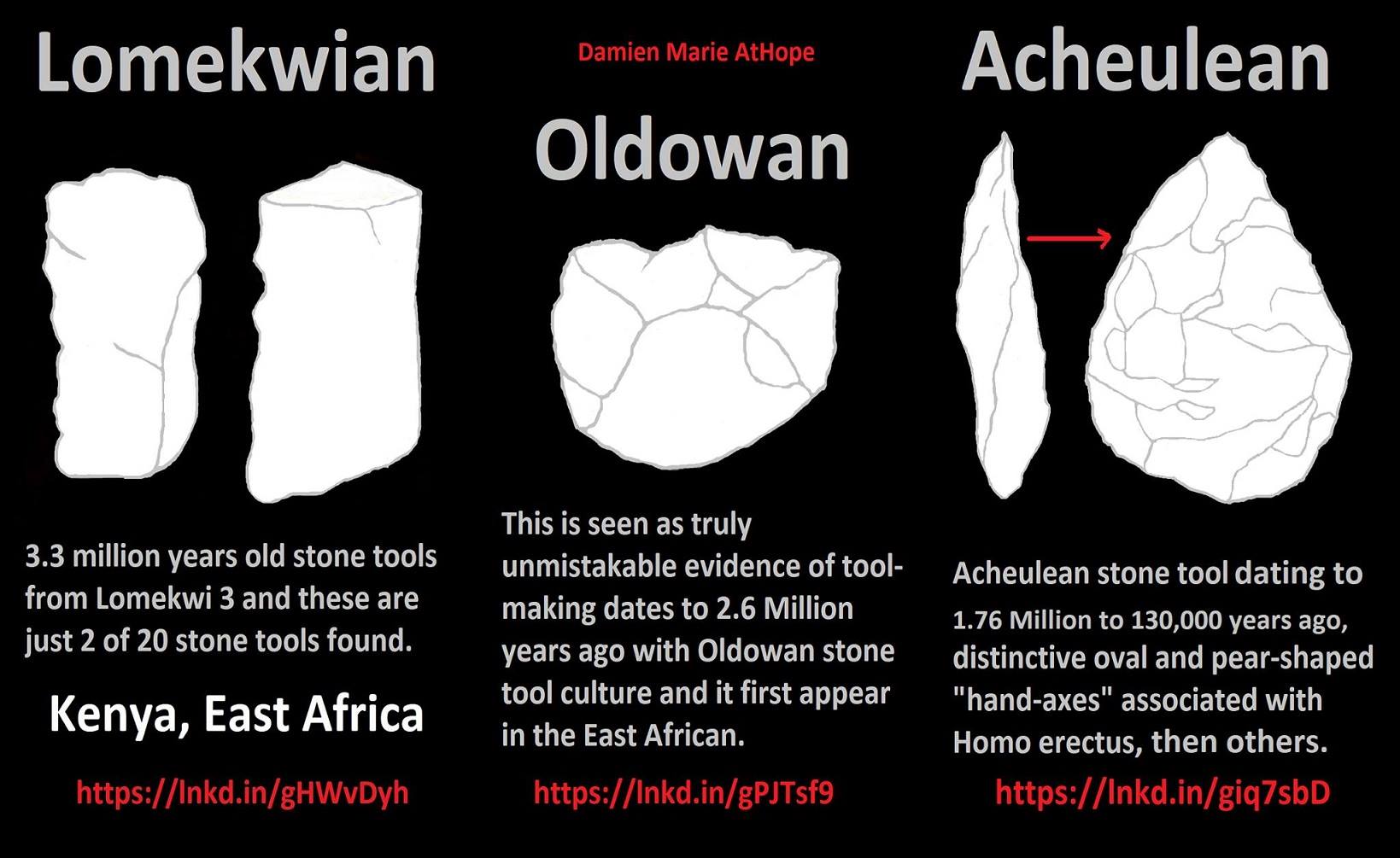
“Two parallel marks that look like cut marks on a 3.4-million-year-old bone from a buffalo-sized creature from Ethiopia in East Africa. Along with scores of crude stone tools discovered at Lomekwi 3 in Kenya are East Africa that date back 3.3 million years. And more interesting is Kenyanthropus a hominin genus identified from the Lomekwi site by Lake Turkana, Kenya, dated to 3.3 to 3.2 million years ago.” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“Statistical assessment of the temporal and cultural relationship between the Lomekwian 3 dates to 3.3 million years ago and Oldowan 2.58 million years ago to 1.6 stone tool cultures. Results suggest the Lomekwian and Oldoan result from the same cultural process. Both should currently be considered part of the same cultural evolutionary process.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352409X23000093
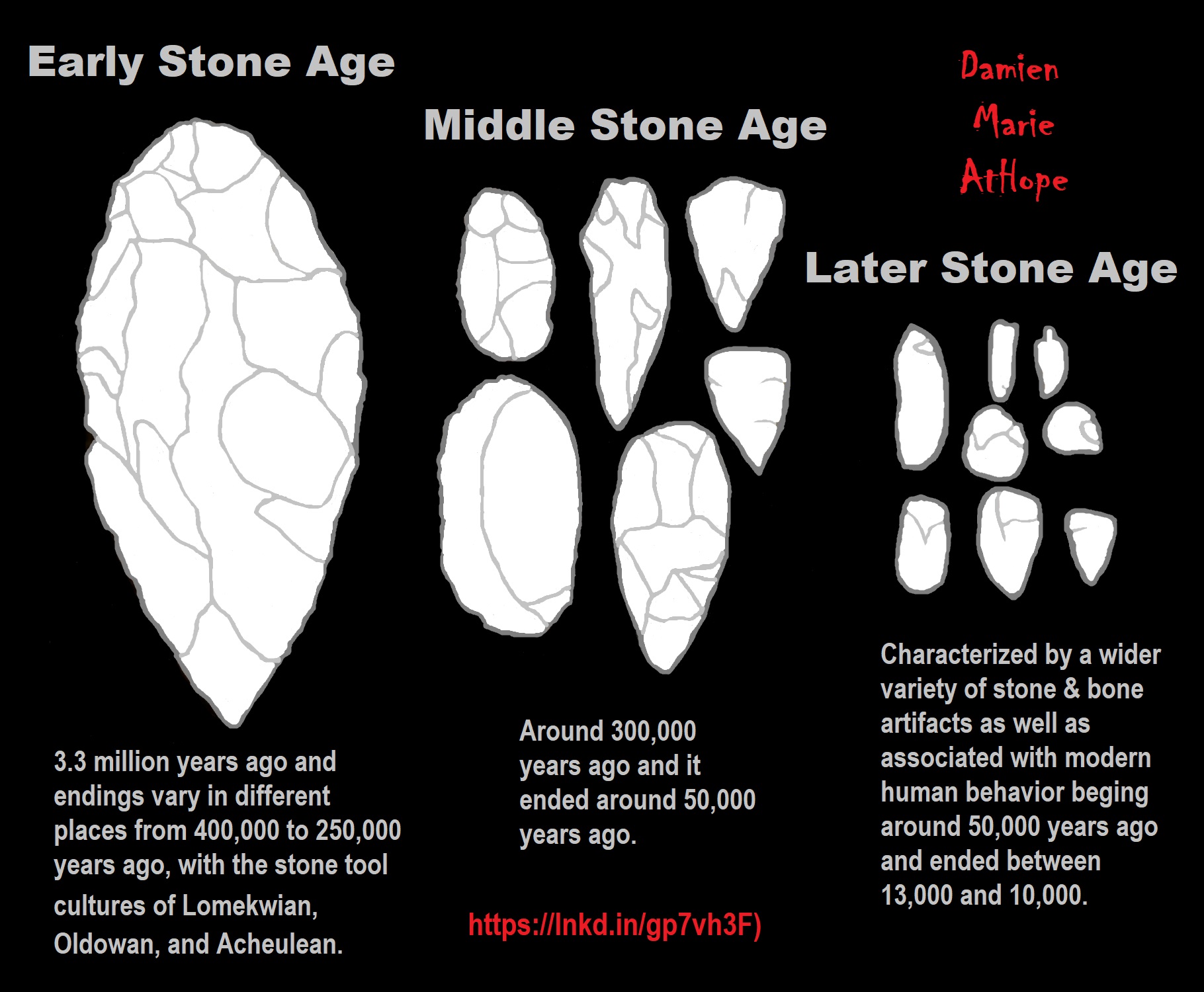
Early Stone Age (Lower Paleolithic): “The Lower Paleolithic is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in the current archaeological record, until around 300,000 years ago, spanning the Oldowan (“mode 1”) and Acheulean (“mode 2”) lithics industries. In African archaeology, the time period roughly corresponds to the Early Stone Age, the earliest finds dating back to 3.3 million years ago, with Lomekwian stone tool technology, spanning Mode 1 stone tool technology, which begins roughly 2.6 million years ago and ends between 400,000 and 250,000 years ago, with Mode 2 technology.” ref
Middle Stone Age (Middle Paleolithic): “The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa, and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleolithic in African archeology. The Middle Paleolithic broadly spanned from 300,000 to 30,000 years ago. There are considerable dating differences between regions. The Middle Paleolithic was succeeded by the Upper Paleolithic subdivision which first began between 50,000 and 40,000 years ago. Pettit and White date the Early Middle Paleolithic in Great Britain to about 325,000 to 180,000 years ago (late Marine Isotope Stage 9 to late Marine Isotope Stage 7), and the Late Middle Paleolithic as about 60,000 to 35,000 years ago. According to the theory of the recent African origin of modern humans, anatomically modern humans began migrating out of Africa during the Middle Stone Age/Middle Paleolithic around 125,000 years ago and began to replace earlier pre-existent Homo species such as the Neanderthals and Homo erectus.” ref
“Middle Paleolithic burials at sites such as Krapina in Croatia (dated to c. 130,000 BP) and the Qafzeh and Es Skhul caves in Israel (c. 100,000 BP) have led some anthropologists and archeologists (such as Philip Lieberman) to believe that Middle Paleolithic cultures may have possessed a developing religious ideology which included concepts such as an afterlife; other scholars suggest the bodies were buried for secular reasons. According to recent archeological findings from Homo heidelbergensis sites in the Atapuerca Mountains, the practice of intentional burial may have begun much earlier during the late Lower Paleolithic, but this theory is widely questioned in the scientific community.” ref
“The earliest undisputed evidence of artistic expression during the Paleolithic period comes from Middle Paleolithic/Middle Stone Age sites such as Blombos Cave in the form of bracelets, beads, art rock, ochre used as body paint and perhaps in ritual, though earlier examples of artistic expression such as the Venus of Tan-Tan and the patterns found on elephant bones from Bilzingsleben in Thuringia may have been produced by Acheulean tool-users such as Homo erectus prior to the start of the Middle Paleolithic period. Activities such as catching large fish and hunting large game animals with specialized tools indicate increased group-wide cooperation and more elaborate social organization. In addition to developing advanced cultural traits, humans also first began to take part in long-distance trade between groups for rare commodities (such as ochre (which was often used for religious purposes such as ritual) and raw materials during the Middle Paleolithic as early as 120,000 years ago. Inter-group trade may have appeared during the Middle Paleolithic because trade between bands would have helped ensure their survival by allowing them to exchange resources and commodities such as raw materials during times of relative scarcity (i.e., famine or drought).” ref
Later Stone Age (Upper Paleolithic): “The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning of the Holocene), according to some theories coinciding with the appearance of behavioral modernity in early modern humans, until the advent of the Neolithic Revolution and agriculture. Anatomically modern humans (i.e. Homo sapiens) are believed to have emerged in Africa around 300,000 years ago, it has been argued by some that their ways of life changed relatively little from that of archaic humans of the Middle Paleolithic, until about 50,000 years ago, when there was a marked increase in the diversity of artifacts found associated with modern human remains. This period coincides with the most common date assigned to an expansion of modern humans from Africa throughout Asia and Eurasia, which contributed to the extinction of the Neanderthals. The Upper Paleolithic has the earliest known evidence of organized settlements, in the form of campsites, some with storage pits. Artistic work blossomed, with cave paintings, petroglyphs, carvings, and engravings on bone or ivory.” ref
“The first evidence of human fishing is also found, from artifacts in places such as Blombos cave in South Africa. More complex social groupings emerged, supported by more varied and reliable food sources and specialized tool types. This probably contributed to increasing group identification or ethnicity. The peopling of Australia most likely took place before c. 60,000 years ago. Europe was peopled after c. 45,000 years ago. Anatomically modern humans are known to have expanded northward into Siberia as far as the 58th parallel by about 45 ka (Ust’-Ishim man). The Upper Paleolithic is divided by the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), from about 25,000 to 15,000 years ago. The peopling of the Americas occurred during this time, with East and Central Asia populations reaching the Bering land bridge after about 35 ka, and expanding into the Americas by about 15,000 years ago. In Western Eurasia, the Paleolithic eases into the so-called Epipaleolithic or Mesolithic from the end of the LGM, beginning 15 ka. The Holocene glacial retreat begins 11.7,00 years ago (10th millennium BCE), falling well into the Old World Epipaleolithic, and marking the beginning of the earliest forms of farming in the Fertile Crescent.” ref

Acheulean Stone Tools
Acheulean tools date to about 1.76 million to 130,000 years ago, are typically found with Homo erectus remains and were produced during the Lower Palaeolithic era across Africa and much of West Asia, South Asia, and Europe, and are typically found with Homo erectus remains. It is thought that Acheulean technologies developed from the more primitive Oldowan technology associated with Homo habilis. ref
Homo ergaster or early Homo erectus is the likely the earliest user of Acheulean tools. It appears that Acheulean originated in Africa and spread to Asian, Middle Eastern, and European areas sometime between 1.5 million years ago and about 800 thousand years ago. Later, used by Homo heidelbergensis (the common ancestor of both Neanderthals and Homo sapiens). ref
Tool types found in Acheulean assemblages include pointed, cordate, ovate, ficron, and bout-coupé hand-axes (referring to the shapes of the final tool), cleavers, retouched flakes, scrapers, and segmental chopping tools. Materials used were determined by available local stone types; flint is most often associated with the tools but its use is concentrated in Western Europe; in Africa sedimentary and igneous rock such as mudstone and basalt were most widely used, for example. Other source materials include chalcedony, quartzite, andesite, sandstone, chert, and shale. Even relatively soft rock such as limestone could be exploited. In all cases the toolmakers worked their handaxes close to the source of their raw materials, suggesting that the Acheulean was a set of skills passed between individual groups. ref
The symmetry of the hand-axes has been used to suggest that Acheulean tool users possessed the ability to use language; the parts of the brain connected with fine control and movement are located in the same region that controls speech. The wider variety of tool types compared to earlier industries and their aesthetically as well as functionally pleasing form could indicate a higher intellectual level in Acheulean tool users than in earlier hominines. ref
Acheulean artifacts, such as the Venus of Berekhat Ram, have been used to argue for artistic expression among this Acheulean stone tool culture users. The incised elephant tibia from Bilzingsleben in Germany, and ochre finds from Kapthurin in Kenya and Duinefonteinin South Africa, are sometimes cited as being some of the earliest examples of an aesthetic sensibility in human history. There are numerous other explanations put forward for the creation of these artefacts, however; and there is no unequivocal evidence of human art until around 50,000 years ago, after the emergence of modern Homo sapiens. ref
Ethnographic study of flint-knapping populations of the Irian Jaya, demonstrated it require long-term memory, spatial or procedural cognition, advanced planning, and procedural ‘know-how’ or social cognition. Other research contends that higher order cognitive function is tied to motor action and that these processes and must be in order to make an Acheulean tool. Therefore, Homo erectus may have had an enlargement of neural areas relevant to tool-making cognitive processes. Thus, the Acheulean actually could signal both innovations in social cognition and technological creativity. ref
Acheulean culture spread throughout Europe, Africa, and Asia. It flourished around 400,000–100,000 years ago. The Homo erectus and early Homo sapiens of the Acheulean culture lived in primitive communities in caves and in the open. They were hunters and gatherers who had discovered the use of fire. Known Acheulean sites in Ukraine are the Kiik-Koba, Zhytomyr, and Luka-Vrublivetska. ref

“Wonderwerk Cave is an archaeological site, in the Kuruman Hills, situated between Danielskuil and Kuruman in the Northern Cape Province, South Africa, dating suggests that basal sediment entered the cave some 2 million years ago. Evidence within Wonderwerk cave has been called the oldest controlled fire with what is thought to be Fire-Making by about 1.7 Million Years Ago. Moreover, evidence for fire-making ranges from the end of the Later Stone Age to the very base of the Acheulean. That discovery is seen to be in accord with findings from four other regional sites, which together provide evidence that can be construed as support for fire-making over almost the same time span.” ref, ref
“A handaxe (or hand ax) is a prehistoric stone tool with two faces that is the longest-used tool in human history. Hand axe tools were possibly used to butcher animals; to dig for tubers, animals, and water; to chop wood and remove tree bark; and/or process vegetal materials. Other scholars have proposed that hand axes were used to throw at prey; for a ritual or social purpose; or possibly as a source for flake tools. Moreover, No academic consensus describes their use, but it is commonly agreed that the hand axe was some form of unhafted all-purpose tool. The pioneers of Palaeolithic tool studies first suggested that bifaces were used as axes despite the fact that they have a sharp border all around. Other uses seem to show that hand axes were a multi-functional tool, leading some to describe them as the “Acheulean Swiss Army knife“. Other academics have suggested that the hand axe was simply a byproduct of being used as a core to make other tools, a weapon, and/or was perhaps used ritually.” ref
“Evidence for unusual symbolic activity in Wonderwerk date to around 400,000–500,000 years ago, which predates Middle Stone Age sites like Blombos Cave deposits that currently date at between c. 100,000 and 70,000 years ago.” ref, ref
Figure Stones
“A shell etched by Homo erectus is by far the oldest engraving ever found, challenging what we know about the origin of art and complex human thought. A right-handed individual and used a shark’s tooth. They had a remarkably steady hand and a strong arm. Half a million years ago, on the banks of a calm river in central Java, they scored a deep zigzag into a fossilised freshwater clam, by far the oldest engraving ever found. The date also means it was made two to three hundred thousand years before our own species evolved, by a more ancient hominin, Homo erectus.” ref
If the artifact was intended to replicate a female figure, it would be the earliest example of representational art in the archaeological record. Rather than being made by modern humans, it would have been made by Homo erectus, hunter-gatherers and Acheulean tool users. There is some other evidence of an aesthetic sensibility during the period although compelling examples do not appear in the archaeological record until the emergence of behaviorally modern humans around 50,000 years ago. ref
Subjectivity in Stone Age art works such as figure stones, engravings, sculptures, effigies and curated manuports. See how images and icons have been realized in portable rock media since the dawn of humanity. Here, archaeologists and art historians are becoming aware of these forsaken artifacts. “And this our life, exempt from public haunt, finds tongues in trees, books in the running brooks, sermons in stones, and good in every thing.” -in W. Shakespeare, As You Like It, 1599.
One common primal theme of one eye open, one eye closed or partly closed on stones. Below, compare the eyes and the shape of the mouth of the German figure with those on a sandstone petroglyph at Day’s Knob. Ursel Benekendorff’s Stone Age Art website displays some of her extensive collection of Figure Stones from northern Germany and the Canary Islands. Many of the motifs characterizing this material closely resemble those in the artifacts from the much more recent 33GU218 site in Ohio, in some cases almost to the point of being identical, although of different lithic material. In addition to anthropomorphic imagery, a readily identifiable bird motif is well represented. Figure Stones and Acheulean handaxes, some of which have now been confirmed as artifacts by professional archaeologists and by Dr. Eric Law, petrologist and professor of geology, who examined the Venus figure at Muskingum University in Ohio. Faces on customized stones seem to indicate it had symbolic significance. To me the nose and eyes look like possible fire starting holes but then there is the mouth and the odd hole at the top. Maby it represents a loved one or ancestor or magical significance…is it an idol of some sort or symbol of something? Homo erectus was the first to use fire and sophisticated tools. Unlike earlier hominids that developed crude choppers and flakes,
Homo erectus produced sophisticated stone axes and used sharp stone cleavers and finger-size scrapers used slice off chewable sizes of meat. “Tools gave them access to elephants, wildebeest—bonanzas so big they couldn’t eat it all,” Nick Toth, an archaeologist from Indiana University told National Geographic. Blades dated to 240,000 year ago made from long slivers of stones in the Rift Valley are so skillfully crafted from difficult-to-work obsidian and lava, that some anthropologists argue that they required abstract thought to make. Some tools associated with Homo erectus however were also relatively primitive. The tools found at sites Dmanisi, Georgia consisted of rock “cores” and primitive choppers, not much sophisticated than those made by Homo habilis and possibly Australopithecus. Hand axes are usually associated with Homo erectus. Ones found at Konso-Gardula, Ethiopia are believed to be between 1.37 and 1.7 million year old.
Describing a primitive 1.5- to 1.7-million-year-old ax, Ethiopian archaeologist Yonas Beyene told National Geographic, “You don’t see much refinement here. They’ve only been knapped away a few flakes to make the edge sharp.” After displaying a beautifully-crafted ax from a perhaps a 100,000 year later he said, “See how refined and straight the cutting edge has become. It was an artform for them. It wasn’t just for cutting. Making these is time-consuming working.” Thousands of primitive hand 1.5-million- to 1.4-million-year-old hand axes have been Olduvai Gorge, Tanzania and Ubeidya, Israel. Carefully-crafted, sophisticated 780,000-year-old hand axes have been unearthed in Olorgesaile, near the Kenya and Tanzania border. Scientists believe they were used to butcher, dismember and deflesh large animals like elephants. Sophisticated Homo erectus teardrop-shaped stone axes that fit snugly in the hand and had a sharp edged created by careful shearing of the rock on both sides.
The tool could be used to cut, smash and beat. Big symmetrical hand axes, known as Acheulan tools, endured for more than 1 million years little changed from the earliest versions found. Since few advances were made one anthropologists described the period in which Homo erectus lived as a time of “almost unimaginable monotony.” Acheulan tools are named after 300,000-year-old hand axes and other tools found in St. Acheul, France. In Eastern sites in China, India and Indonesia, numerous choppers and flakes have been discovered but no hand axes. This has lead scientists to speculate that larger tools may have been made from bamboo or wood. The oldest tools found in Asia include a 1.7-million-year-old flakes found in Nihewan, near Beijing and a crude 600,000-year-old biface found in Yuxian, China.
Homo erectus learned to control fire about one million years ago. Sophisticated stone tools found at the 780,000-year-old site of Bose Basin in southern China near the Vietnam border seems to indicate that homonids in Asia developed tools just as advanced as tools made by their cousins in Africa and Europe. For a long time Asian homonids were depicted as being inferior and less sophisticated than homonids in Africa and Europe but the teardrop-shaped tools with double sharp edges found at Bose basin are as developed as this made 500,000 years ago in Europe. A 116,000-year-old core tool has been found in Jimminum, north Australia. Skulls dated to be 500,000 years old found in caves in Longgushan China appear to have been severed from the body and preserved, presumably as trophies. The purpose of this may have been to obtain the strength of the deceased. Critics of these claim say the marks made on the skulls were more likely made by giant hyenas than other hominids. Cut marks made on human bones, similar to those made with Homo erectus tools on butchered animals, have been found in sites ranging from South Africa to Croatia.
Homo Erectus ritual/culture and thinking: At the 350,000-year-old site in Bilzingsleben, archaeologists found pieces of bone and smooth stones arranged in a 27-foot-wide circle. “They intentionally paved this area for cultural activities,” Dietrich Mania off the University of Jena, told National Geographic. “We found here a large anvil of quartzite set between the horns of a huge bison. Near it were fractured human skulls.” Describing an elephant tibia engraved with a series a regular lines found at Bilzingsleben, Mania said, “Seven lines go in one direction, 21 go in the other. We have found other pieces of bone with cut lines that are also too regular to be accidental. They are graphic symbols. To us they are evidence of abstract thinking and human language.” The tibia was dated at around 400,000 years ago. Scientists debate whether 400,000-year-old hominids were capable of symbolic thinking, often regarded as hallmark of language. If Mania’s conjectures are correct, then ancient hominids could have been much more advanced than previously thought.
In Zambia, scientists found what they said were 350,000-year-old ocher crayons. If these crayons had in fact been used to make drawings or markings they could be regarded as the oldest known attempt to paint, suggests that early man attempted create art much earlier than people thought. Some scientists have theorized that Homo erectus must have possessed some form of rudimentary language because it needed to communicate to organize hunts and pass on information about tool making. The parts of the Homo erectus brain associated with reasoning, symbolism and imagination though were relatively undeveloped. The frontal lobe, where complex thinking takes place in modern humans, was relatively small. The small hole in its vertebrae probably meant that not enough information was transferred from the brain to the lungs, neck and mouth to make speech possible. Ann MacLarson, an anthropologist at Roehampton Institute in London, told National Geographic: “With simple grunts you can communicate a lot. But he couldn’t have produced anything like modern speech.”
Scientists believe that man may have been able to speak as early as 400,000 years based on studies of the hypoglossal canal, an opening on the skull through which nerve fibers pass from the brain to the tongue. Humans have a larger hypoglossal canal than chimpanzees and evidence from 400,000 fossils seems to indicate that early man had a canal closer in size to a human canal than a chimpanzee canal. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Religions continuing in our modern world, full of science and facts, should be seen as little more than a set of irrational conspiracy theories of reality. Nothing more than a confused reality made up of unscientific echoes from man’s ancient past. Rational thinkers must ask themselves why continue to believe in religions’ stories. Religion myths which are nothing more than childlike stories and obsolete tales once used to explain how the world works, acting like magic was needed when it was always only nature. These childlike religious stories should not even be taken seriously, but sadly too often they are.
Often without realizing it, we accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives. In order to bring about awareness, we need to be willing to alter skewed beliefs. Rational thinkers must examine the facts instead of blindly following beliefs or faith. Below is a collection of researched information such as archaeology, history, linguistics, genetics, art, science, sociology, geography, psychology, philosophy, theology, biology, and zoology. It will make you question your beliefs with information, inquiries, and ideas to ponder and expand on. The two main goals are to expose the evolution of religion starting by around 100,000 years ago and to offer challenges to remove the rationale of faith. It is like an intervention for belief in myths that have plagued humankind for way too long. We often think we know what truth is nevertheless this can be but a vantage point away from losing credibility if we are not willing to follow valid and reliable reason and evidence.
The door of reason opens not once but many times. Come on a journey to free thought where the war is against ignorance and the victor is a rational mind. Understanding Religion Evolution: Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago), * Animism (such as that seen in Africa: 100,000 years ago), *Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago), * Shamanism (beginning around 30,000 years ago), *Paganism (beginning around 12,000 years ago), * Progressed organized religion (around 5,000 years ago), * CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago), and * Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by around 2,600 Years Ago)
“Religion is an Evolved Product”
In a general way, it all starts with Animism (a theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits) and this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (a theoretical belief in a mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to perform this worship and believed interaction as Shamanism (a theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through rituals). In addition, there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above, which is Paganism and is often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking from which it stems.
My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theoretical house (modern religions development). It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe by superstition perceived as good and evil”, and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul”, which was thought to affect the still living and led to ancestor worship. Presumably, this ancestor worship led to the belief in supernatural beings, which some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived idea that was “made from nothing into something over and over, changing again and again, taking on more as they evolve, and all the while, they are thought to be special.” However, it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Historically, around 5,000 years ago, in large city-state societies such as Egypt or Iraq culminated to make religion into something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine. However, this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent, it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine. These magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed and many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere, even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence. This amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion that started at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. This message of how religion and gods are intertwined with humans is clearly a man-made idea that was developed slowly as it was invented, reinvented, and implemented piece by piece, which discredits them all. This seems to be a simple point, which some are just not grasping how devastating this is to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.

Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Around 500,000 – 233,000 years ago, Oldest Anthropomorphic art (Pre-animism) is Related to Female
- 400,000 Years Old Sociocultural Evolution
- Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art at least 300,000-year-old
- Homo Naledi and an Intentional Cemetery “Pre-Animism” dating to around 250,000 years ago?
- Oldowan stone tool Culture (2.6–1.7 Million years ago)
- Acheulean stone tool culture (1.76–0.1 Million years ago)
- Acheulo-Yabrudian stone tool culture (400-200,000 years ago)
- Mousterian stone tool culture (160,000–35-30,000 years ago)
- Aterian (145,000–c. 20,000 years ago)
First, there was Pre-Animism: Portable Rock Art
Around a million years ago, I surmise that Pre-Animism, “animistic superstitionism”, began and led to the animistic somethingism or animistic supernaturalism, which is at least 300,000 years old and about 100,00 years ago, it evolves to a representation of general Animism, which is present in today’s religions.
Anthropology states that Pre-animism is “A stage of religious development supposed to have preceded animism, in which material objects were believed to contain spiritual energy.” ref
To me, it is a kind of “Primal Pre-Religion (Pre-Animism/Proto-Animism” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife, may have been transferred from the Neanderthals to arcane humans when they bred with them. Neanderthals, also interbred with Homo erectus, the ‘upright walking man,’ Homo habilis, the ‘tool-using man” and possibly others, which means they could have possibly learned some pre-animism ideas from one of the other hominids thas is expressed in portable anthropomorphic art, which could have been related to some kind of ancestor veneration as well. ref
Around 500,000 to 400,000 years ago, the earliest European hominin crania associated with Acheulean handaxes are at the sites of Arago, Atapuerca Sima de los Huesos, and Swanscombe. The Atapuerca fossils and the Swanscombe cranium belong to the Neandertals whereas the Arago hominins have been attributed to Homo heidelbergensis or to a subspecies of Homo erectus, which is an incipient stage of Neandertal evolution. A cranium (Aroeira 3) from the Gruta da Aroeira (Almonda karst system, Portugal) dating to 436,000 to 390,000 years ago provides important evidence on the earliest European Acheulean-bearing hominins as well as could show a transfer of ideas. ref
Homo erectus, the “upright walking man,” lived between 1.89 million and 143,000 years ago, whereas early African Homo erectus and sometimes called Homo ergaster are the oldest known early humans to have possessed modern human-like attributes. The earliest evidence of campfires occurred during the time of Homo erectus. While there is evidence that campfires were used for cooking, and probably sharing food, they are likely to have been placed for social interaction, used for warmth, to keep away large predators, and possibly even relating to Primal Religion, “Pre-Animism,” which may have included Fire Sacralizing and/or Worship. ref
Neanderthals used fire 400,000 years ago and there is evidence of a 300,000-year-old ‘campfire’ from Israel, which is not that surprising since our human ancestors have controlled fire from 1.5 million to 300,000 years ago and beyond. The benefits of fire are not only to cook food and fend off predators, but also extended their day and added to the community by how a fire in the middle of the darkness mellows and also excite people, which possibly inspire pre-animism’s “animistic superstitionism.” ref
Forkhead box P2 (FOXP2) is implicated in human speech and language playing important roles in the plasticity of the developing brain and that of modern populations suggests that it has been the target of positive (Darwinian) selection during recent human evolution. The first mutations in exon 7 more than around 400,000 years ago, prior to the human-Neandertal split, and impacted FOXP2 function. The second event, beginning within the last 200,000 years, did not involve further FOXP2 amino acid changes (because the Neandertal and human FOXP2 are identical) but might have instead affected FOXP2. Overall, there was strong evidence of selection of FOXP2 targets in Europeans, but not in the Han Chinese, Japanese, or Yoruba populations. Analyses of ancient DNA samples have revealed that the amino acid differences were shared with Neandertals, who split from modern humans 300,000–400,000 years ago, and the haplotypes extended across the amino acid changes. And, Neanderthals and humans share two changes in FOXP2 compared with chimpanzees and the possibilities range from interaction gene flow to that of a common ancestor to both or changes and selective sweep occurred before the divergence that could mean Neanderthals had language and or other type capabilities. ref, ref
There was a primitive Homo sapiens skull found at Jebel Irhoud in Morocco dated to around 300,000 years ago. With remarkable similarities between the Moroccan skull and one found in China dated to around 260,000 years ago. ref, ref
Sun-worshipping baboons rise early to catch the African sunrise and race each other to the top for the best spots. Thus, we may rightly ponder how much did fireside tales aid to the socio-cultural-religious transformations or evolution. In the dark under flickering lights from the stars above and the fire below was the scene of wonder, fear, and mystery. Was superstition expanded and religion further imagined? It would seem that superstition was expanded and religion further imagined because both heavenly lights and flickering fire have been sacralized. This does seem to be somewhat supported by a researcher who spent 40 years studying African Bushmen who gathered evidence of the importance of gathering around a nighttime campfire as a time for bonding, social information, and shared emotions with fireside tales. This may provide a correlation that our prehistoric ancestors likely lived in a similar way to how the Bushmen currently do. Although we cannot directly peer into the past or fully know the past from the indigenous Bushmen, these people do live in a way that our ancient ancestors lived for around 99% of our evolution.
Fire, as sacred or magic, can be seen in:
- Consuming fire as volcanos/lightning as gods and gods’power/vengeance.
- Holy fire as a means of transformation or magical purification.
- A magical being as used in worshipping the sun or punishment such as hell/lake of fire, which could be seen as mixing fire and water, if only symbolically.
- Ceremonies such as bonfires, eternal flames, or sacred candles/incense/lights/lamps are in one form or another incorporated in many faiths such as judaism, christianity, islam, hinduism, buddhism, sikhism, bahaism, shintoism, taoism, etc. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
All this worship of fire/sun is hardly special to humans since many other primates worship thunderstorms, others fire, or sunrises. We have forgotten how nature worship, animistic superstitionism, animistic somethingism, or animistic supernatralism is presented in today’s religion. The mega religions now think they are removed from animistic superstitionism, which they are not. Their rituals, beliefs, and prayers have a connection to animism nature worship but are more hidden or stylized such as burning candles, which is worshipping fire.
Archaeology reveals that the world’s oldest sculpture was enhanced by hominid hand. To date, the oldest known human three-dimensional representation is the Tan-Tan sculpture, which is an anthropomorific human form from Morocco was found in ancient river deposits of the Draa river. It is Acheulian and has been dated between 500,000 to 300,000 years old. 500,000 to 233,000 years ago, in Israel, another sculpture, which may be the oldest Stone Age Art was found at the Berekhat Ram site on the Golan Heights that consist of a small quartzite pebble, which resembles a human female figure with magical believed qualities or representing something that was believed to be magical. ref
Is this just art or a form of ancestor veneration?
Pre-animism ideas can be seen in rock art such as that expressed in portable anthropomorphic art, which may be related to some kind of ancestor veneration. This magical thinking may stem from a social or non-religious function of ancestor veneration, which cultivates kinship values such as filial piety, family loyalty, and continuity of the family lineage. Ancestor veneration occurs in societies with every degree of social, political, and technological complexity and it remains an important component of various religious practices in modern times.
Humans are not the only species, which bury their dead. The practice has been observed in chimpanzees, elephants, and possibly dogs. Intentional burial, particularly with grave goods, signify a “concern for the dead” and Neanderthals were the first human species to practice burial behavior and intentionally bury their dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. The earliest undisputed human burial dates back 100,000 years ago with remains stained with red ochre, which show ritual intentionality similar to the Neanderthals before them. ref, ref
- “300,000 years ago: the first possible appearance of Homo sapiens, in Jebel Irhoud, Morocco.
- 270,000 years ago: age of Y-DNA haplogroup A00(“Y-chromosomal Adam“).
- 250,000 years ago: the first appearance of Homo neanderthalensis (Saccopastore skulls)
- 250,000-200,000 years ago: modern human presence in West Asia (Misliya cave)
- 230,000–150,000 years ago: age of mt-DNA haplogroup L (“Mitochondrial Eve“)
- 195,000 years ago: Omo remains (Ethiopia), the emergence of anatomically modern humans.
- 160,000 years ago: Homo sapiens idaltu
- 170,000 years ago: humans are wearing clothing by this date.
- 150,000 years ago: Peopling of Africa: Khoisanid separation, an age of mtDNA haplogroup L0
- 125,000 years ago: the peak of the Eemian interglacial period.
- 120,000–90,000 years ago: Abbassia Pluvial in North Africa—the Sahara desert region is wet and fertile.” ref
130,000 years ago – Earliest undisputed evidence for intentional burial and it is Neanderthals…
Evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead and possibly doing cannibalism which could be evidence of a death ritual, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. 130,000 years ago – Earliest undisputed evidence for intentional burial. Neanderthals bury their dead at sites such as Krapina in Croatia. There was a total of 876 single Neanderthal fossil remnants found at the Hušnjak hill. The Bones belonged to several dozen different individuals, of different sex, from 2 to 40 years of age. Over a thousand pieces of various stone tools and weapons from the Paleolithic era were found, all witnessing to the material culture of the Krapina proto-human. This rich locality is approximately 130.000 years old. Numerous fossil remnants of the cave bear, wolf, moose, large deer, warm climate rhinoceros, wild cattle and many other animals were also found. Moreover, there is bird skeletons, with some of the parts modified, are found in association with the Neanderthal bones. Here are some talons and foot bones from the white-tailed eagle. There appears to be cut marks in the talons and foot bones to which they were attached, suggesting that Neanderthals were using the talons and bones as jewelry. This is supported by recent findings of gut “fiber” tied around part of a talon. Here are a foot bone and a talon that have been modified by having grooves cut in them. Neanderthals were largely carnivores, though we know they also used medicinal plants. ref, ref, ref
Did Neanderthals teach us “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” 120,000 Years Ago?
Homo sapiens – is known to have reached the Levant between 120,000 and 90,000 years ago, but that exit from Africa evidently went extinct. Homo sapiens – is known to have reached the Levant between 120,000 and 90,000 years ago, but that exit from Africa evidently went extinct. ref, ref
A population that diverged early from other modern humans in Africa contributed genetically to the ancestors of Neanderthals from the Altai Mountains roughly 100,000 years ago. By contrast, we do not detect such a genetic contribution in the Denisovan or the two European Neanderthals. In addition to later interbreeding events, the ancestors of Neanderthals from the Altai Mountains and early modern humans met and interbred, possibly in the Near East, many thousands of years earlier than previously thought. ref
In 2005, a set of 7 teeth from Tabun Cave in Israel were studied and found to most likely belong to a Neandertal that may have lived around 90,000 years ago. And another Neandertal (C1) from Tabun Cave was estimated to be in northern Israel. The limb bones are characteristic of Neanderthals, whereas the lower jaw has a combination of Neanderthal and earlier features. These fossils date from more than 150,000 years ago ref, ref
A fossilized human jawbone in a collapsed cave in Israel that they said is between 177,000 and 194,000 years old. The Tabun Cave contains a Neanderthal-type female, dated to about 120,000 years ago. It is one of the most ancient human skeletal remains found in Israel. Objects at Tabun suggests that ancestral humans used fire at the site on a regular basis since about 350,000 years ago. ref, ref, ref
The absolute chronology of the Levantine (Israel and local surrounding areas) Middle Paleolithic (300–45 ka) fossils indicates that Humans existed there between 120,000 to 90,000 years ago (possibly leaving the area due to climate change), making things colder and again migrating and staying from 55,000 years ago until the present. The genomic evidence suggests gene flow from early Humans to the eastern Altai Neandertals around 100,000 years ago and flow from Neandertals to Humans between around 60,000 and 50,000 years ago. In the Levant, the archaeological record cannot distinguish between these two Middle Paleolithic populations. The broad array of stone tool techniques and styles variability observed in the Levantine Middle Paleolithic is not clearly taxonomy related. The two populations left similar material culture remains—in particular, lithic industries that include the Levallois technology. In addition, the populations seem to have had similar, settlement and mobility patterns with respect to the use of caves for habitation and burials; at Tabun, these populations used the same cave diachronically. Therefore, it was also difficult to determine these species’ settlement patterns and territorial behavior within the Levant. ref
The remains of seven adults and three children were found, some of which (Skhul;1,4, and 5) are claimed to have been burials. Assemblages of perforated Nassarius shells (a marine genus) significantly different from local fauna have also been recovered from the area, suggesting that these people may have collected and employed the shells as bead as they are unlikely to have been used as food. Skhul Layer B has been dated to an average of 81,000-101,000 years ago with the electron spin resonance method, and to an average of 119,000 years ago with the thermoluminescence method. ref, ref, ref
Skhul 5 had the mandible of a wild boar on its chest. The skull displays prominent supraorbital ridges and jutting jaw, but the rounded braincase of modern humans. When found, it was assumed to be an advanced Neanderthal, but is today generally assumed to be a modern human, if a very robust one. ref, ref
It is possible that Neandertals and early moderns did make contact in the region and it may be possible that the Skhul and Qafzeh hominids are partially of Neandertal descent. Non-African modern humans contain 1-4% Neandertal genetic material, with hybridization possibly having taken place in the Middle East. ref
It has been suggested, however, that the Skhul/Qafzeh hominids represent an extinct lineage. If this is the case, modern humans would have re-exited Africa around 70,000 years ago, crossing the narrow Bab-el-Mandeb strait between Eritrea and the Arabian Peninsula. ref
Modern humans were present in Arabia and South Asia earlier than currently believed, and probably coincident with the presence of Homo sapiens in the Levant between ca 130 and 70,000 years ago. This is the same route proposed to have been taken by the people who made the modern tools at Jebel Faya. This Neandertal girl’s toe bone had ancient DNA her ancestors picked up by mating with modern humans more than 100,000 years ago. ref, ref, ref
If the Skhul burials took place within a relatively short time span, then the best age estimate lies between 100 and 135 ka. However, we cannot exclude the possibility that the material associated with the Skhul IX burial is older than those of Skhul II and Skhul V. These and other recent age estimates suggest that the three burial sites, Skhul, Qafzeh and Tabun are broadly contemporaneous, falling within the time range of 100 to 130 ka. The presence of early representatives of both early modern humans and Neanderthals in the Levant during Marine Isotope Stage 5 inevitably complicates attempts at segregating these populations by date or archaeological association. Nevertheless, it does appear that the oldest known symbolic burials are those of early modern humans at Skhul and Qafzeh. This supports the view that, despite the associated Middle Palaeolithic technology, elements of modern human behavior were represented at Skhul and Qafzeh prior to 100 ka. ref
As some of the first bands of modern humans moved out of Africa, they met and mated with Neandertals about 100,000 years ago—perhaps in the fertile Nile Valley, along with the coastal hills of the Middle East, or in the once-verdant Arabian Peninsula. These early modern humans’ own lineages died out, and they are not among the ancestors of living people. But a small bit of their DNA survived in the toe bone of a Neandertal woman who lived more than 50,000 years ago in Denisova Cave in the Altai Mountains of Siberia, Russia. ref
100,000 years ago – The oldest known ritual burial of modern humans at Qafzeh in Israel: a double burial of what is thought to be a mother and child. The bones have been stained with red ochre. By 100,000 years ago anatomically modern humans migrated to the middle east from Africa. However, the fossil record of these humans ends after 100kya, leading scholars to believe that population either died out or returned to Africa. 100,000 to 50,000 years ago – Increased use of red ochre at several Middle Stone Age sites in Africa. Red Ochre is thought to have played an important role in ritual. The human skeletons were associated with red ochre which was found only alongside the bones, suggesting that the burials were symbolic in nature. ref
Within Israel’s Qafzeh Cave, researchers found evidence of a sophisticated culture and remains of modern humans that are up to 100,000 years old. About 100,000 years ago, tall, long-limbed humans lived in the caves of Qafzeh, east of Nazareth, and Skhul, on Israel’s Mount Carmel. The Skhul-Qafzeh people gathered shells from a shoreline more than 20 miles away, decorated them and strung them as jewelry. They buried their dead, most likely with grave goods, and cared for their living: A child born with hydrocephalus, sometimes called water on the brain, lived with a profound disability until the age of 3 or so, a feat only possible with a patient, loving care. The Qafzeh humans were around 92,000 years old, and the Skhul people were even older, averaging about 115,000 years. Around 75,000 years ago, close to the time, the Homo sapiens of Skhul and Qafzeh disappear from the fossil record, the climate in the Levant shifted in Neanderthals’ favor. Rapid glaciation left the region both cooler and drier. Steppe-deserts advanced, and forests retreated. Neanderthal bodies were adapted for colder conditions. Their stocky, barrel-chested build lost less heat and offered plenty of insulating muscle, and their systems were streamlined to extract calories from food and turn them into body heat. The Skhul-Qafzeh people’s slender physiques were better at getting rid of heat than making it. Or, as Shea says, “Neanderthals liked cold and dry. Our ancestors liked warm and wet. It got cold, and humans retreated.” ref, ref
At some point between 195,000 and 123,000 years ago, the population size of Homo sapiens plummeted, thanks to cold, dry. A late human population bottleneck is postulated by some scholars at approximately 70,000 years ago, during the Toba catastrophe, when Homo sapiens population may have dropped to as low as between 1,000 and 10,000 individuals. Everyone alive today is descended from a group of people from a single region who survived this catastrophe. The southern coast of Africa would have been one of the few spots where humans could survive during this climate crisis. Estimates all indicate that everyone alive today is descended from a small population that lived in one region of Africa sometime during this global cooling phase. ref, ref
At Blombos Cave, South Africa, revealed a processing workshop where a liquefied ochre-rich mixture was produced and stored in two Haliotis midae (abalone) shells 100,000 years ago. Ochre, bone, charcoal, grindstones, and hammerstones form a composite part of this production toolkit. The application of the mixture is unknown, but possibilities include decoration and skin protection. At Pinnacle Point on the southern coast of South Africa at cave Cave PP13B held the earliest evidence for human consumption of shellfish – dated to around 164,000 years ago. Cave shelter PP5-6, containing possibly the earliest evidence for projectile points around 71,000 years ago, and to make those microliths they focused on heat treatment to improve the stone. The types of innovations that have been revealed by the excavations in the Pinnacle Point complex share some major traits: cooperation, organization, and planning,” says Leonard. And these were critical to the later development of agriculture and urbanization, basic elements of civilization. 75,000-year-old pieces of ochre engraved with abstract designs, 75,000-year-old beads made from Nassarius (sea tick) shells, and 80,000-year-old bone tools, as well as human teeth with crown diameters that suggested that the people in the cave were likely anatomically modern. Moreover, at the Pinnacle Point complex, there were deposits dating to around 110,000 years ago include both red ochre and seashells that were clearly collected for their aesthetic appeal seeming to show that humans had begun to embed in their worldview and rituals. ref, ref, ref
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
Around a million years ago, I surmise that Pre-Animism, “animistic superstitionism”, began, Around 400,000 Years ago shows Sociocultural Evolution, and then led to the animistic somethingism or animistic supernaturalism, which is at least 300,000 years old and about 100,00 years ago, it evolves to a representation of general Animism, which is present in today’s religions. There is also Homo Naledi and an Intentional Cemetery “Pre-Animism” dating to around 250,000 years ago. And, Neanderthals “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” Mystery Cave Rings 175,000 Years Ago. Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, around 130,000 years ago at sites such as Krapina in Croatia.
Pre-animism ideas can be seen in rock art such as that expressed in portable anthropomorphic art, which may be related to some kind of ancestor veneration. This magical thinking may stem from a social or non-religious function of ancestor veneration, which cultivates kinship values such as filial piety, family loyalty, and continuity of the family lineage. Ancestor veneration occurs in societies with every degree of social, political, and technological complexity and it remains an important component of various religious practices in modern times.
Humans are not the only species, which bury their dead. The practice has been observed in chimpanzees, elephants, and possibly dogs. Intentional burial, particularly with grave goods, signify a “concern for the dead” and Neanderthals were the first human species to practice burial behavior and intentionally bury their dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. The earliest undisputed human burial dates back 100,000 years ago with remains stained with red ochre, which show ritual intentionality similar to the Neanderthals before them. ref, ref
Animism (such as that seen in Africa: 100,000 years ago)
Did Neanderthals teach us “Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism?)” 120,000 Years Ago? Homo sapiens – is known to have reached the Levant between 120,000 and 90,000 years ago, but that exit from Africa evidently went extinct. 100,000 years ago, in Qafzeh, Israel, the oldest intentional burial had 15 African individuals covered in red ocher was from a group who visited and returned back to Africa. 100,000 to 74,000 years ago, at Border Cave in Africa, an intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament, which may have possible connections to the Africans buried in Qafzeh.
Animism is approximately a 100,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden animist.
The following is evidence of Animism: 100,000 years ago, in Qafzeh, Israel, the oldest intentional burial had 15 African individuals covered in red ocher was from a group who visited and returned back to Africa. 100,000 to 74,000 years ago, at Border Cave in Africa, an intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament, which may have possible connections to the Africans buried in Qafzeh, Israel. 120,000 years ago, did Neanderthals teach us Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism) as they too used red ocher and burials? ref, ref
It seems to me, it may be the Neanderthals who may have transmitted a “Primal Religion (Animism)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife. The Neanderthals seem to express what could be perceived as a Primal “type of” Religion, which could have come first and is supported in how 250,000 years ago, the Neanderthals used red ochre and 230,000 years ago shows evidence of Neanderthal burial with grave goods and possibly a belief in the afterlife. ref
Do you think it is crazy that the Neanderthals may have transmitted a “Primal Religion”? Consider this, it appears that 175,000 years ago, the Neanderthals built mysterious underground circles with broken off stalactites. This evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. Other evidence may suggest the Neanderthals had it transmitted to them by Homo heidelbergensis, 350,000 years ago, by their earliest burial in a shaft pit grave in a cave that had a pink stone axe on the top of 27 Homo heidelbergensis individuals and 250,000 years ago, Homo naledi had an intentional cemetery in South Africa cave. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
Did Neanderthals Help Inspire Totemism? Because there is Art Dating to Around 65,000 Years Ago in Spain? Totemism as seen in Europe: 50,000 years ago, mainly the Aurignacian culture. Pre-Aurignacian “Châtelperronian” (Western Europe, mainly Spain and France, possible transitional/cultural diffusion between Neanderthals and Humans around 50,000-40,000 years ago). Archaic–Aurignacian/Proto-Aurignacian Humans (Europe around 46,000-35,000). And Aurignacian “classical/early to late” Humans (Europe and other areas around 38,000 – 26,000 years ago).
Totemism is approximately a 50,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden totemist.
Toetmism may be older as there is evidence of what looks like a Stone Snake in South Africa, which may be the “first human worship” dating to around 70,000 years ago. Many archaeologists propose that societies from 70,000 to 50,000 years ago such as that of the Neanderthals may also have practiced the earliest form of totemism or animal worship in addition to their presumably religious burial of the dead. Did Neanderthals help inspire Totemism? There is Neanderthals art dating to around 65,000 years ago in Spain. ref, ref
Shamanism (beginning around 30,000 years ago)
Shamanism (such as that seen in Siberia Gravettian culture: 30,000 years ago). Gravettian culture (34,000–24,000 years ago; Western Gravettian, mainly France, Spain, and Britain, as well as Eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians, which include the Pavlovian culture). And, the Pavlovian culture (31,000 – 25,000 years ago such as in Austria and Poland). 31,000 – 20,000 years ago Oldest Shaman was Female, Buried with the Oldest Portrait Carving.
Shamanism is approximately a 30,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden shamanist.
Around 29,000 to 25,000 years ago in Dolní Vestonice, Czech Republic, the oldest human face representation is a carved ivory female head that was found nearby a female burial and belong to the Pavlovian culture, a variant of the Gravettian culture. The left side of the figure’s face was a distorted image and is believed to be a portrait of an elder female, who was around 40 years old. She was ritualistically placed beneath a pair of mammoth scapulae, one leaning against the other. Surprisingly, the left side of the skull was disfigured in the same manner as the aforementioned carved ivory figure, indicating that the figure was an intentional depiction of this specific individual. The bones and the earth surrounding the body contained traces of red ocher, a flint spearhead had been placed near the skull, and one hand held the body of a fox. This evidence suggests that this was the burial site of a shaman. This is the oldest site not only of ceramic figurines and artistic portraiture but also of evidence of early female shamans. Before 5,500 years ago, women were much more prominent in religion.
Archaeologists usually describe two regional variants: the western Gravettian, known namely from cave sites in France, Spain, and Britain, and the eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians include the Pavlovian culture, which were specialized mammoth hunters and whose remains are usually found not in caves but in open air sites. The origins of the Gravettian people are not clear, they seem to appear simultaneously all over Europe. Though they carried distinct genetic signatures, the Gravettians and Aurignacians before them were descended from the same ancient founder population. According to genetic data, 37,000 years ago, all Europeans can be traced back to a single ‘founding population’ that made it through the last ice age. Furthermore, the so-called founding fathers were part of the Aurignacian culture, which was displaced by another group of early humans members of the Gravettian culture. Between 37,000 years ago and 14,000 years ago, different groups of Europeans were descended from a single founder population. To a greater extent than their Aurignacian predecessors, they are known for their Venus figurines. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
Paganism (beginning around 12,000 years ago)
Paganism (such as that seen in Turkey: 12,000 years ago). Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” around 12,000 years ago. Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago. Pagan-Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and 12,000 – 10,000 years old Paganistic-Shamanistic Art in a Remote Cave in Egypt. Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago and Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 10,000 years ago.
Paganism is approximately a 12,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife and who are guided/supported by a goddess/god, goddesses/gods, magical beings, or supreme spirits. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden paganist.
Around 12,000 years ago, in Turkey, the first evidence of paganism is Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” and around 9,500 years ago, in Turkey, the second evidence of paganism is Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”. In addition, early paganism is connected to Proto-Indo-European language and religion. Proto-Indo-European religion can be reconstructed with confidence that the gods and goddesses, myths, festivals, and form of rituals with invocations, prayers, and songs of praise make up the spoken element of religion. Much of this activity is connected to the natural and agricultural year or at least those are the easiest elements to reconstruct because nature does not change and because farmers are the most conservative members of society and are best able to keep the old ways.
The reconstruction of goddesses/gods characteristics may be different than what we think of and only evolved later to the characteristics we know of today. One such characteristic is how a deity’s gender may not be fixed, since they are often deified forces of nature, which tend to not have genders. There are at least 40 deities and the Goddesses that have been reconstructed are: *Pria, *Pleto, *Devi, *Perkunos, *Aeusos, and *Yama.
The reconstruction of myths can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and by additional research, many of these myths have since been confirmed including some areas that were not accessible to the early writers such as Latvian folk songs and Hittite hieroglyphic tablets. There are at least 28 myths and one of the most widely recognized myths of the Indo-Europeans is the myth, “Yama is killed by his brother Manu” and “the world is made from his body”. Some of the forms of this myth in various Indo-European languages are about the Creation Myth of the Indo-Europeans.
The reconstruction of rituals can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and is estimated to have been spoken as a single language from around 6,500 years ago. One of the earliest ritual is the construction of kurgans or mound graves as a part of a death ritual. kurgans were inspired by common ritual-mythological ideas. Kurgans are complex structures with internal chambers. Within the burial chamber at the heart of the kurgan, elite individuals were buried with grave goods and sacrificial offerings, sometimes including horses and chariots.
The speakers of Pre-Proto-Indo-European lived in Turkey and it associates the distribution of historical Indo-European languages with the expansion around 9,000 years ago, with a proposed homeland of Proto-Indo-European proper in the Balkans around 7,000 years ago. The Proto-Indo-European Religion seemingly stretches at least back around 6,000 years ago or likely much further back and I believe Paganism is possibly an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system.
The earliest kurgans date to 6,000 years ago and are connected to the Proto-Indo-European in the Caucasus. In fact, around 7,000 years ago, there appears to be pre-kurgan in Siberia. Around 7,000 to 2,500 years ago and beyond, kurgans were built with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia, which display the continuity of the archaic forming methods. Kurgan cultures are divided archaeologically into different sub-cultures such as Timber Grave, Pit Grave, Scythian, Sarmatian, Hunnish, and Kuman–Kipchak. Kurgans have been found from the Altay Mountains to the Caucasus, Ukraine, Romania, and Bulgaria. Around 5,000 years ago, kurgans were used in the Ukrainian and Russian flat unforested grasslands and their use spread with migration into eastern, central, northern Europe, Turkey, and beyond. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
Progressed organized religion (around 5,000 years ago)
Progressed organized religion (such as that seen in Egypt: 5,000 years ago “The First Dynasty dates to 5,150 years ago”). This was a time of astonishing religion development and organization with a new state power to control. Around the time of 5,000 to 4,000 years ago, saw the growth of these riches, both intellectually and physically, became a source of contention on a political stage, and rulers sought the accumulation of more wealth and more power.
*The First Dynasty*
Date: 3,150 B.C.E. (5,150 years ago)
The Beginning Rise of the Unequal State Government Hierarchies, Religions and Cultures Merger
The Pharaoh in ancient Egypt was the political and religious leader holding the titles ‘Lord of the Two Lands’ Upper and Lower Egypt and ‘High Priest of Every Temple’. In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt and this reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later.
Around 4,890 years ago during the Second Dynasty, the King was linked with the divine and reign with the will of the gods. Following this, rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due to those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth, the intermediary between the gods and the people, and when he died, he was thought to become Osiris, the god of the dead. As such, in his role of ‘High Priest of Every Temple’, it was the pharaoh’s duty to build great temples and monuments celebrating his own achievements and paying homage to the gods of the land. Among the earliest civilizations that exhibit the phenomenon of divinized kings are early Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt.
In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by the king Menes (now believed to be Narmer). Menes/Narmer is depicted on inscriptions wearing the two crowns of Egypt, signifying unification, and his reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later. During the Second Dynasty of Egypt 4,890-4,670 years ago King Raneb (also known as Nebra) linked his name with the divine and his reign with the will of the gods. Following Raneb, the rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due to those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth.
The honorific title of `pharaoh’ for a ruler did not appear until the period known as the New Kingdom 3,570-3,069 years ago. Monarchs of the dynasties before the title of `pharaoh’ from the New Kingdom were addressed as `your majesty’ by foreign dignitaries and members of the court and as `brother’ by foreign rulers; both practices would continue after the king of Egypt came to be known as a pharaoh. Ref Ref
CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago). Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. Christianity around 2,000 years old. Shinto around 1,305 years old. Islam around 1407–1385 years old. Sikhism around 548–478 years old. Bahá’í around 200–125 years old.
Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
Around 2,600 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.
Religions continuing in our modern world, full of science and facts, should be seen as little more than a set of irrational conspiracy theories of reality. Nothing more than a confused reality made up of unscientific echoes from man’s ancient past. Rational thinkers must ask themselves why continue to believe in religions’ stories. Religion myths which are nothing more than childlike stories and obsolete tales once used to explain how the world works, acting like magic was needed when it was always only nature. These childlike religious stories should not even be taken seriously, but sadly too often they are. Often without realizing it, we accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives. In order to bring about awareness, we need to be willing to alter skewed beliefs. Rational thinkers must examine the facts instead of blindly following beliefs or faith.
Below is a collection of researched information such as archaeology, anthropology, ethnography, history, linguistics, genetics, art, science, sociology, geography, psychology, philosophy, theology, biology, and zoology. It will make you question your beliefs with information, inquiries, and ideas to ponder and expand on. The two main goals are to expose the evolution of religion starting 100,000 years ago and to offer challenges to remove the rationale of faith. It is like an intervention for belief in myths that have plagued humankind for way too long. We often think we know what truth is nevertheless this can be but a vantage point away from losing credibility if we are not willing to follow valid and reliable reason and evidence. The door of reason opens not once but many times. Come on a journey to free thought where the war is against ignorance and the victor is a rational mind.
If you are a religious believer, may I remind you that faith in the acquisition of knowledge is not a valid method worth believing in. Because, what proof is “faith”, of anything religion claims by faith, as many people have different faith even in the same religion?

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.

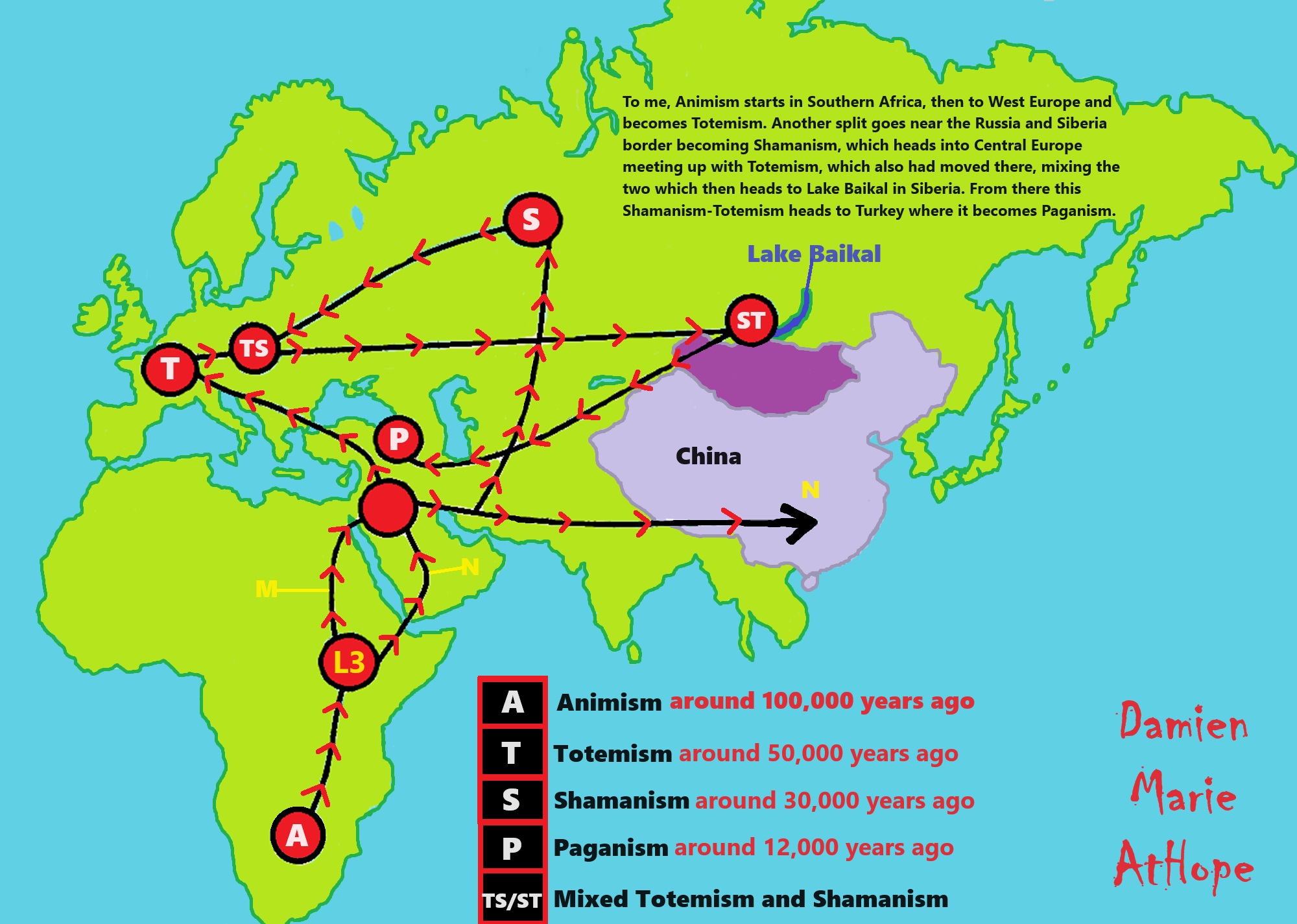
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
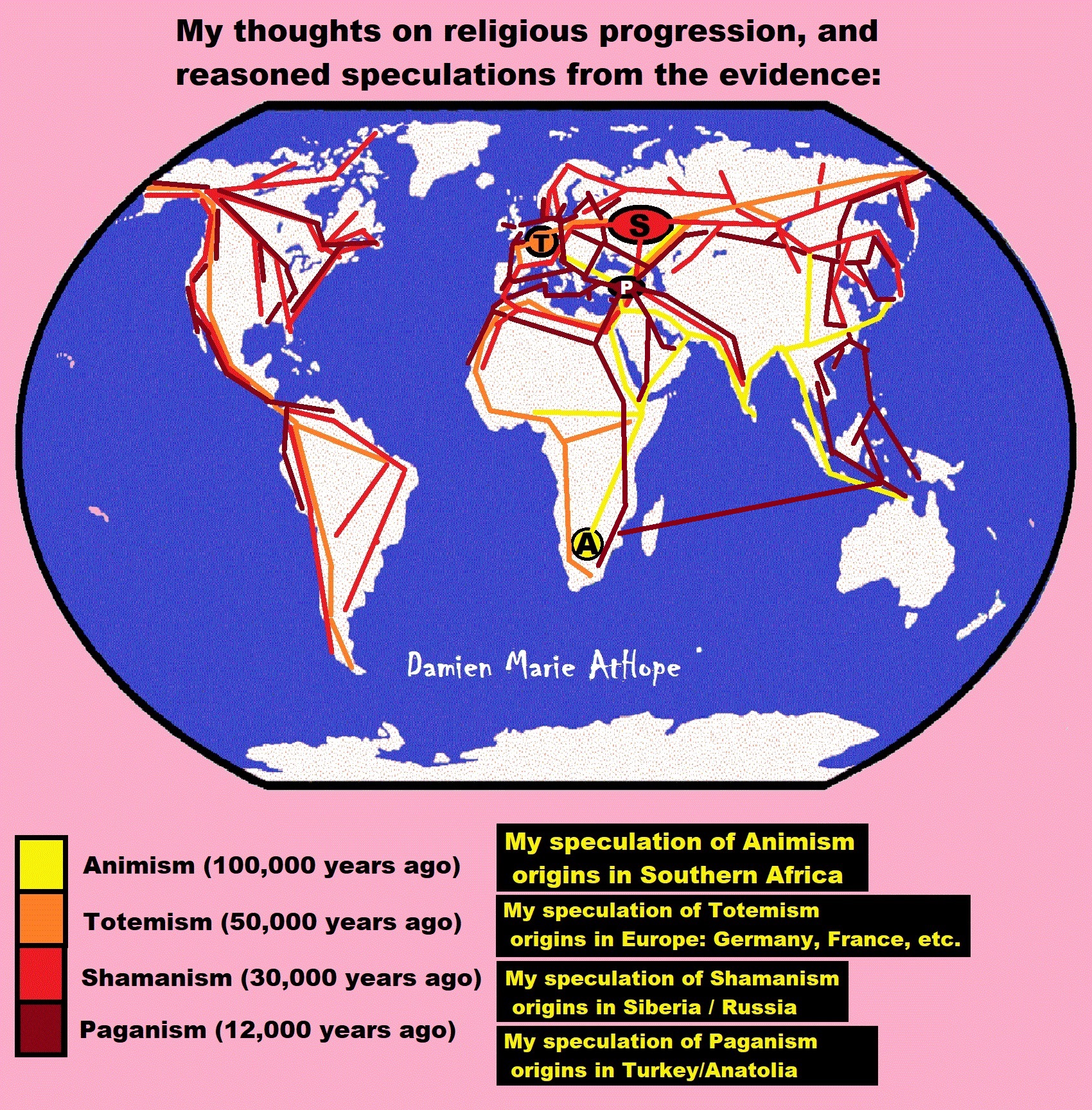


Animism (such as that seen in Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Animism: an approximately 100,000-year-old belief system?
- Rock crystal stone tools 75,000 Years Ago – (Spain) made by Neanderthals
- Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago
- Similarities and differences in Animism and Totemism
- Did Neanderthals Help Inspire Totemism? Because there is Art Dating to Around 65,000 Years Ago in Spain?
- History of Drug Use with Religion or Sacred Rituals possibly 58,000 years ago?
Animism is approximately a 100,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden animist.
The following is evidence of Animism: 100,000 years ago, in Qafzeh, Israel, the oldest intentional burial had 15 African individuals covered in red ocher was from a group who visited and returned back to Africa. 100,000 to 74,000 years ago, at Border Cave in Africa, an intentional burial of an infant with red ochre and a shell ornament, which may have possible connections to the Africans buried in Qafzeh, Israel. 120,000 years ago, did Neanderthals teach us Primal Religion (Pre-Animism/Animism) as they too used red ocher and burials? ref, ref
It seems to me, it may be the Neanderthals who may have transmitted a “Primal Religion (Animism)” or at least burial and thoughts of an afterlife. The Neanderthals seem to express what could be perceived as a Primal “type of” Religion, which could have come first and is supported in how 250,000 years ago, the Neanderthals used red ochre and 230,000 years ago shows evidence of Neanderthal burial with grave goods and possibly a belief in the afterlife. ref
Do you think it is crazy that the Neanderthals may have transmitted a “Primal Religion”? Consider this, it appears that 175,000 years ago, the Neanderthals built mysterious underground circles with broken off stalactites. This evidence suggests that the Neanderthals were the first humans to intentionally bury the dead, doing so in shallow graves along with stone tools and animal bones. Exemplary sites include Shanidar in Iraq, Kebara Cave in Israel and Krapina in Croatia. Other evidence may suggest the Neanderthals had it transmitted to them by Homo heidelbergensis, 350,000 years ago, by their earliest burial in a shaft pit grave in a cave that had a pink stone axe on the top of 27 Homo heidelbergensis individuals and 250,000 years ago, Homo naledi had an intentional cemetery in South Africa cave. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
- “120,000–90,000 years ago: Abbassia Pluvial in North Africa—the Sahara desert region is wet and fertile.
- 120,000 to 75,000 years ago: Khoisanid back-migration from Southern Africa to East Africa.
- 82,000 years ago: small perforated seashell beads from Taforalt in Morocco are the earliest evidence of personal adornment found anywhere in the world.
- 75,000 years ago: Toba Volcano supereruption that almost made humanity extinct. Populations could have been lowered to about 3000-1000 people on the Earth.
- 70,000 years ago: earliest example of abstract art or symbolic art from Blombos Cave, South Africa—stones engraved with grid or cross-hatch patterns.
- 70,000 years ago: Recent African origin: separation of sub-Saharan Africans and non-Africans.” ref
Did Neanderthals Help Inspire Totemism?
Because there is Art Dating to Around 65,000 Years Ago in Spain?
“What About Neanderthals and Religion”
Scientists have found the first major evidence that Neanderthals made cave paintings, indicating they may have had an artistic sense similar to our own. A new study led by the University of Southampton and the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology shows that paintings in three caves in Spain were created more than 64,000 years ago – 20,000 years before modern humans arrived in Europe. This means that the Palaeolithic (Ice Age) cave art – including pictures of animals, dots, and geometric signs – must have been made by Neanderthals, a ‘sister’ species to Homo sapiens, and Europe’s sole human inhabitants at the time. It also indicates that they may have had a similar artistic sense, in terms of thinking symbolically, to modern humans. Published today in the journal Science, the study reveals how an international team of scientists used a state-of-the-art technique called uranium-thorium dating to fix the age of the paintings as more than 64,000 years. Until now, cave art has been attributed entirely to modern humans, as claims to a possible Neanderthal origin have been hampered by imprecise dating techniques. However, uranium-thorium dating provides much more reliable results than methods such as radiocarbon dating, which can give false age estimates. Results show that the paintings we dated are, by far, the oldest known cave art in the world, and were created at least 20,000 years before modern humans arrived in Europe from Africa so it is assumed – therefore they may have been painted by Neanderthals. All three caves contain red (ochre) or black paintings of groups of animals, dots, and geometric signs, as well as hand stencils, handprints, and engravings. According to the researchers, creating the art must have involved such sophisticated behavior as the choice of a location, planning of light source and mixing of pigments. There is evidence that Neanderthals in Europe used body ornamentation around 40,000 to 45,000 years ago, but many researchers have suggested this was inspired by modern humans who at the time had just arrived in Europe. Study co-author Paul Pettitt, of Durham University, commented: “Neanderthals created meaningful symbols in meaningful places. The art is not a one-off accident. ref
Neanderthals are our closest extinct relative, but for a long time, they had a reputation for being pretty backward. Early modern humans, for example, made cave paintings. But even though Neanderthals used pigments and decorated themselves with eagle claws and shells, there was no clear proof that they painted caves. One theory goes that Neanderthals developed their rudimentary culture only after early modern humans arrived in Europe some 40,000 to 50,000 years ago. The most recent painting is at least 64,800 years old, according to this technique, and the oldest is more than 66,000 years old. ref
The Neanderthal was the only proven Human of Europe at the time, but was his or her brain up to the job? Or did modern humans reach Europe tens of thousands of years earlier than thought? The ancient art forms are symbolic but not figurative, explain their finders. In Spain, a cave in Maltravieso features hand stencils more than 66,000 years old, Prof. Dirk Hoffmann of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and others report in their paper, published Thursday in Science. The La Pasiega Cave in Cantabria features a ladder form composed of red horizontal and vertical lines that were created more than 64,000 years ago, they say. Further supporting the Neanderthal-as-artist theory, a related paper published Thursday in Science Advances reports that dyed and decorated seashells found in a Spanish cave dated to more than 115,000 years ago. Perforated shells found in sediments in Cueva de los Aviones that date to between 115,000 and 120,000 years. There’s no argument that there were Neanderthals in Europe 64,000 years ago. Homo sapiens, on the other hand, was thought to have reached Europe only 45,000 to 40,000 years ago. There is no evidence for modern humans in Iberia before 41,000 years ago, and there is evidence for Neanderthal presence until about 36,000 years ago in southern Spain and Portugal. Neanderthals existed for twice the time modern people have, if not more, and were once the dominant hominin in Europe. While Neanderthals may have etched a crisscross and perhaps carved a flute, look what Homo sapiens achieved, Coolidge says. The Paleolithic record is replete with exquisite works, from cave paintings to carvings done tens of thousands of years ago – such as the Lion Man sculpture found in a German cave and made of mammoth ivory some 38,000 years ago. ref
Neanderthal ritual or religious practice at around 50,000 years old burial in Sima de las Palomas in Murcia, Southeast Spain of a female covered with rocks inturned with a cut off panther paw, suggesting that Neanderthals—much like today’s bear hunters—ceremoniously cut off panther paws and kept them as totemistic trophies. This 50,000-year-old Neanderthal burial ground actually includes the remains of at least three individuals intentionally buried, with each Neanderthal’s arms folded such that the hands were close to the head. Remains of other Neanderthals have been found in this position, suggesting that it held meaning. The remains of six to seven other Neanderthals, including one baby and two juveniles, have also been excavated at the site. The tallest individual appears to have been an adult who stood around 5 feet 1 inch tall. ref, ref
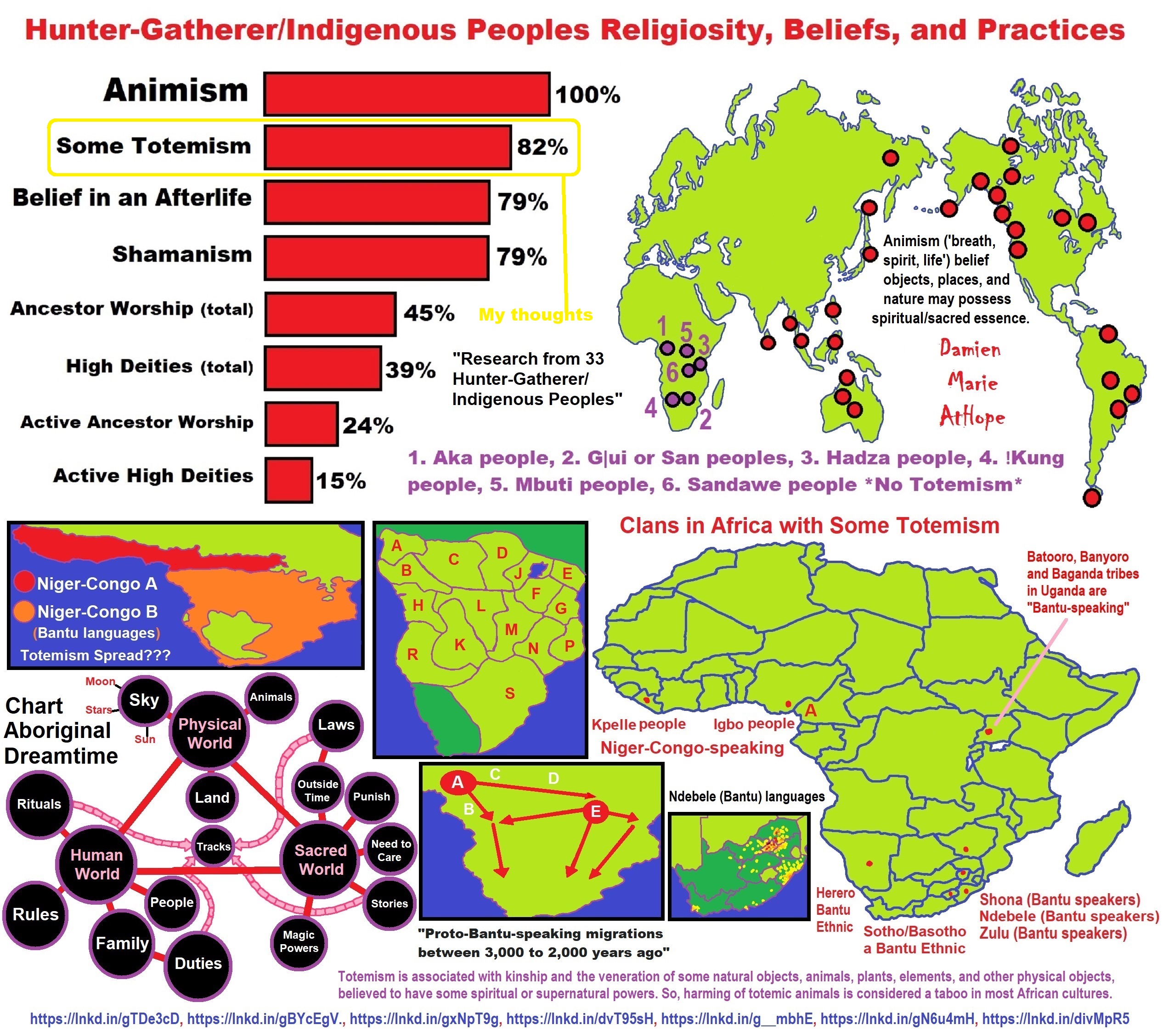
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.

Totemism as seen in Europe: 50,000 years ago, mainly the Aurignacian culture
- Pre-Aurignacian “Châtelperronian” (Western Europe, mainly Spain and France, possible transitional/cultural diffusion between Neanderthals and humans around 50,000-40,000 years ago)
- Archaic–Aurignacian/Proto-Aurignacian (Europe around 46,000-35,000)
- Aurignacian “classical/early to late” (Europe and other areas around 38,000 – 26,000 years ago)
- Totemism: an approximately 50,000-year-old belief system?
- Australia & Aboriginal Religion at least around 50,000 years old
- Modern Humans start around 50,000 years ago Helped by Feminisation
- Out of Africa: “the evolution of religion seems tied to the movement of people”
- Totemism and Shamanism Dispersal Theory Expressed around 50,000 to 30,000 years ago
- Possible Religion Motivations in the First Cave Art at around 43,000 years ago?
- 40,000 years old Aurignacian Lion Figurine Early Totemism?
- 40,000-35,000 years ago “first seeming use of a Totem” ancestor, animal, and possible pre-goddess worship?
- Prehistoric Egypt 40,000 years ago to The First Dynasty 5,150 years ago
- 38,000 Years Old Engraving of an Aurochs with Seeming Totemism Expression?
“The most significant “recent” Out of Africa wave took place about 70,000 years ago, via the so-called “Southern Route”, spreading rapidly along the coast of Asia and reaching Australia by around 65,000–50,000 years ago. While Europe was populated by an early offshoot which settled the Near East and Europe less than 55,000 years ago.” ref
There is prehistoric art possibly relating to Aurgnacien, it is similar to other Aurgnacien cultural items. Such as the “lion-human”, Löwenmensch figurine from Hohlenstein-Stadel, Germany but also in its decorating like marking on the arms in Aurgnacian times (43,000 – 28,000 years ago). This statue comes from Geißenklösterle, also in Germany, which contains traces of prehistoric art from between 43,000 to 30,000. This Ivory Art Statue is dated to around 32,500 to 38,000 years ago. There are 86 notches on the tablet, a number that has two special meanings, subtracted from a year equals the average number of days of pregnancy and the number of days that one of Orion’s two prominent stars, Betelguese, is visible. To ancient man, this might have linked human fertility with the spirits (stars) in the sky. ref, ref, ref, ref
All populations before around 40,000 years ago where way more inbred and then after that is has a great decrease, to which I hypothesize could be genetic evidence of the emergence of INCEST-PROHIBITION hints at the taboo in Totemism. ref
“The Horror of Incest” concerns incest taboos adopted by societies believing in totemism.
Totemism is a belief system scattered world-wide mainly by hunting and gathering peoples, which seems to diminish when agricultural becomes predominant. Totemism seems expressed all over the North American especially the west cost indigenous peoples, in Peru, in Guiana, what was the African Gold Coast, in India, the South Seas islands, Australia, Siberia, Egypt and Semitic regions. It is thought that the current true totemism is found only among Australian Aborigines, North, and South American indigenous peoples, in New Guinea, and parts of Africa and India. But it is Australia, America, and Africa that are the three main areas where totemism has been found in its most highly developed and widespread forms. ref
Totemism is approximately a 50,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden totemist.
Toetmism may be older as there is evidence of what looks like a Stone Snake in South Africa, which may be the “first human worship” dating to around 70,000 years ago. Many archaeologists propose that societies from 70,000 to 50,000 years ago such as that of the Neanderthals may also have practiced the earliest form of totemism or animal worship in addition to their presumably religious burial of the dead. Did Neanderthals help inspire Totemism? There is Neanderthals art dating to around 65,000 years ago in Spain. ref, ref
Based on archaeological evidence from caves around 300,000 to 50,000 years ago, suggests that a widespread Neanderthal bear-cult existed. Animal cults from 50,000 to 10,000 years ago, such as the bear cult may have had their origins in these hypothetical 300,000 to 50,000 years ago animal cults. 50,000 to 10,000 years ago, animal worship intertwined with hunting rites. For instance, archaeological evidence from art and bear remains reveals that the bear cult apparently had involved a type of sacrificial bear ceremonialism, in which a bear was shot with arrows, then was finished off by a shot in the lungs, and ritualistically buried near a clay bear statue covered with bear fur with the skull of the bear buried separately.
100,000 to 50,000 years ago, there is an increased use of red ochre at several sites in Africa. Red ochre is thought to have played an important role in rituals. 42,000 years ago, there is a ritual burial of a man covered in red ochre at Lake Mungo in Australia. Around 40,000 years ago in Europe, an abundance of fossil evidence includes elaborate burials of the dead with Venus female figurines and cave art also involving red ochre.
Around 45,000 to 30,000 years ago, the Aurignacian culture created figurines that have been found depicting faunal representations of the time period associated with now-extinct mammals, including mammoths, rhinoceros, and Tarpan, along with anthropomorphized depictions that may be interpreted as some of the earliest evidence of religion. Many 35,000-year-old animal figurines such as mammoths and horses were discovered in the Vogelherd Cave in Germany. The production of ivory beads for body ornamentation was also important to the Aurignacian.
The oldest cave art is found in the Cave of El Castillo in Spain, in early Aurignacian dated at around 40,000 years, the time when it is believed that homo sapiens migrated to Europe from Africa. The next oldest cave art is found in the Chauvet Cave in France, dating to around 37,000 to 33,500 years ago (Aurignacian period: Totemism) and the second from 31,000 to 28,000 years ago (Gravettian period: Shamanism) with most of the black drawings dating to the earlier period. What is interesting is the Neanderthals favor the color black as well that may connect to their transferring some of their ideas to modern humans.
Chauvet Cave appears to have been used by humans during two distinct periods: the Aurignacian and the Gravettian. Most of the artwork dates to the earlier Aurignacian period (30,000 to 32,000 years ago) and the later Gravettian occupation, which occurred 25,000 to 27,000 years ago. The art features a larger variety of wild animals such as lions, panthers, bears, and hyenas. There are no examples of complete human figures in these cave art. The cave art is believed to represent religious thought by modern humans. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
- “67,000 to 40,000 years ago: Neanderthal admixture to Eurasians
- 50,000 years ago: the earliest sewing needle found. Made and used by Denisovans.
- 50,000–30,000 years ago: Mousterian Pluvial in North Africa. The Sahara desert region is wet and fertile. Later Stone Age begins in Africa.
- 45,000–43,000 years ago: European early modern humans.
- 45,000–40,000 years ago: Châtelperronian culture in France.
- 42,000 years ago: Paleolithic flutes in Germany.
- 42,000 years ago: earliest evidence of advanced deep sea fishing technology at the Jerimalai cave site in East Timor—demonstrates high-level maritime skills and by implication the technology needed to make ocean crossings to reach Australia and other islands, as they were catching and consuming large numbers of big deep sea fish such as tuna.
- 41,000 years ago: Denisova hominin lives in the Altai Mountains.
- 40,000 years ago: Aurignacian culture begins in Europe.
- 40,000 years ago: oldest known figurative art the zoomorphic Löwenmensch figurine.
- 40,000–30,000 years ago: human settlement (Aboriginal Australians) in Sydney, Perth, and Melbourne.
- 40,000–20,000 years ago: oldest known ritual cremation, the Mungo Lady, in Lake Mungo, Australia.
- 35,000 years ago: one of the oldest known figurative art of a human figure as opposed to a zoomorphic figure (Venus of Hohle Fels).” ref

Shamanism (such as that seen in Siberia Gravettian culture: 30,000 years ago)
- Gravettian culture (34,000–24,000 years ago; Western Gravettian, mainly France, Spain, and Britain, as well as Eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians, which include the Pavlovian culture)
- Pavlovian culture (31,000 – 25,000 years ago such as in Austria and Poland)
- Prehistoric Child Burials Begin Around 34,000 Years Ago
- Early Shamanism around 34,000 to 20,000 years ago: Sungar (Russia) and Dolni Vestonice (Czech Republic)
- 31,000 – 20,000 years ago Oldest Shaman was Female, Buried with the Oldest Portrait Carving
- Shamanism: an approximately 30,000-year-old belief system
- ‘Sky Burial’ theory and its possible origins at least 12,000 years ago to likely 30,000 years ago or older.
- The Peopling of the Americas Pre-Paleoindians/Paleoamericans around 30,000 to 12,000 years ago
- Similarity in Shamanism?
- Black, White, and Yellow Shamanism?
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Horned female shamans and Pre-satanism Devil/horned-god Worship? at least 10,000 years ago.
- Shamanistic rock art 8,000 and 10,000 years ago from central Aboriginal Siberians and Aboriginal drums in the Americas.
Shamanism is approximately a 30,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden shamanist.
Around 29,000 to 25,000 years ago in Dolní Vestonice, Czech Republic, the oldest human face representation is a carved ivory female head that was found nearby a female burial and belong to the Pavlovian culture, a variant of the Gravettian culture. The left side of the figure’s face was a distorted image and is believed to be a portrait of an elder female, who was around 40 years old. She was ritualistically placed beneath a pair of mammoth scapulae, one leaning against the other. Surprisingly, the left side of the skull was disfigured in the same manner as the aforementioned carved ivory figure, indicating that the figure was an intentional depiction of this specific individual. The bones and the earth surrounding the body contained traces of red ocher, a flint spearhead had been placed near the skull, and one hand held the body of a fox. This evidence suggests that this was the burial site of a shaman. This is the oldest site not only of ceramic figurines and artistic portraiture but also of evidence of early female shamans. Before 5,500 years ago, women were much more prominent in religion.
Archaeologists usually describe two regional variants: the western Gravettian, known namely from cave sites in France, Spain, and Britain, and the eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians include the Pavlovian culture, which were specialized mammoth hunters and whose remains are usually found not in caves but in open air sites. The origins of the Gravettian people are not clear, they seem to appear simultaneously all over Europe. Though they carried distinct genetic signatures, the Gravettians and Aurignacians before them were descended from the same ancient founder population. According to genetic data, 37,000 years ago, all Europeans can be traced back to a single ‘founding population’ that made it through the last ice age. Furthermore, the so-called founding fathers were part of the Aurignacian culture, which was displaced by another group of early humans members of the Gravettian culture. Between 37,000 years ago and 14,000 years ago, different groups of Europeans were descended from a single founder population. To a greater extent than their Aurignacian predecessors, they are known for their Venus figurines. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
- “33,000 years ago: oldest known domesticated dog skulls show they existed in both Europe and Siberia by this time.
- 31,000–16,000 years ago: Last Glacial Maximum (peak at 26,500 years ago).
- 30,000 years ago: rock paintings tradition begins in Bhimbetka rock shelters in India, which presented as a collection is the densest known concentration of rock art. In an area about 10 km2, there are about 800 rock shelters of which 500 contain paintings.
- 29,000 years ago: The earliest ovens found.
- 28,500 years ago: New Guinea is populated by colonists from Asia or Australia.
- 28,000 years ago: the oldest known twisted rope.
- 28,000–24,000 years ago: some of the oldest known pottery—used to make figurines rather than cooking or storage vessels (Venus of Dolní Věstonice).
- 28,000–20,000 years ago: Gravettian period in Europe. Harpoons and saws invented.
- 26,000 years ago: people around the world use fibers to make baby carriers, clothes, bags, baskets, and nets.
- 25,000 years ago: a hamlet consisting of huts built of rocks and of mammoth bones is founded in what is now Dolní Věstonice in Moravia in the Czech Republic. This is the oldest human permanent settlement that has yet been found by archaeologists.
- 21,000 years ago: artifacts suggests early human activity occurred in Canberra, the capital city of Australia.
- 20,000 years ago: Kebaran culture in the Levant.
- 20,000 years ago: oldest pottery storage/cooking vessels from China.
- 20,000-10,000 years ago: Khoisanid expansion to Central Africa.
- 16,000-14,000 years ago: Minatogawa Man (Proto-Mongoloid phenotype) in Okinawa, Japan
- 16,000–13,000 years ago: the first colonization of North America.
- 16,000-11,000 years ago: Caucasian Hunter-Gatherer (Caucasoid phenotype) expansion to Europe.
- 16,000 years ago: Wisent sculpted in clay deep inside the cave now known as Le Tuc d’Audoubert in the French Pyrenees near what is now the border of Spain.
- 15,000–14,700 years ago: Earliest supposed date for the domestication of the pig.
- 14,800 years ago: The Humid Period begins in North Africa. The region that would later become the Sahara is wet and fertile, and the aquifers are full.
- 14,500-11,500: Red Deer Cave people in China, possible late survival of archaic or archaic-modern hybrid humans.
- 14,000-12,000 years ago: Oldest evidence for prehistoric warfare (Jebel Sahaba massacre, Natufian culture).
- 13,000–10,000 years ago: Late Glacial Maximum, end of the Last glacial period, climate warms, glaciers recede.
- 13,000 years ago: A major water outbreak occurs on Lake Agassiz, which at the time could have been the size of the current Black Sea and the largest lake on Earth. Much of the lake is drained in the Arctic Ocean through the Mackenzie River.
- 13,000–11,000 years ago: Earliest dates suggested for the domestication of the sheep.
- Approximately 13,000 years ago, the Younger Dryas ice age.” ref
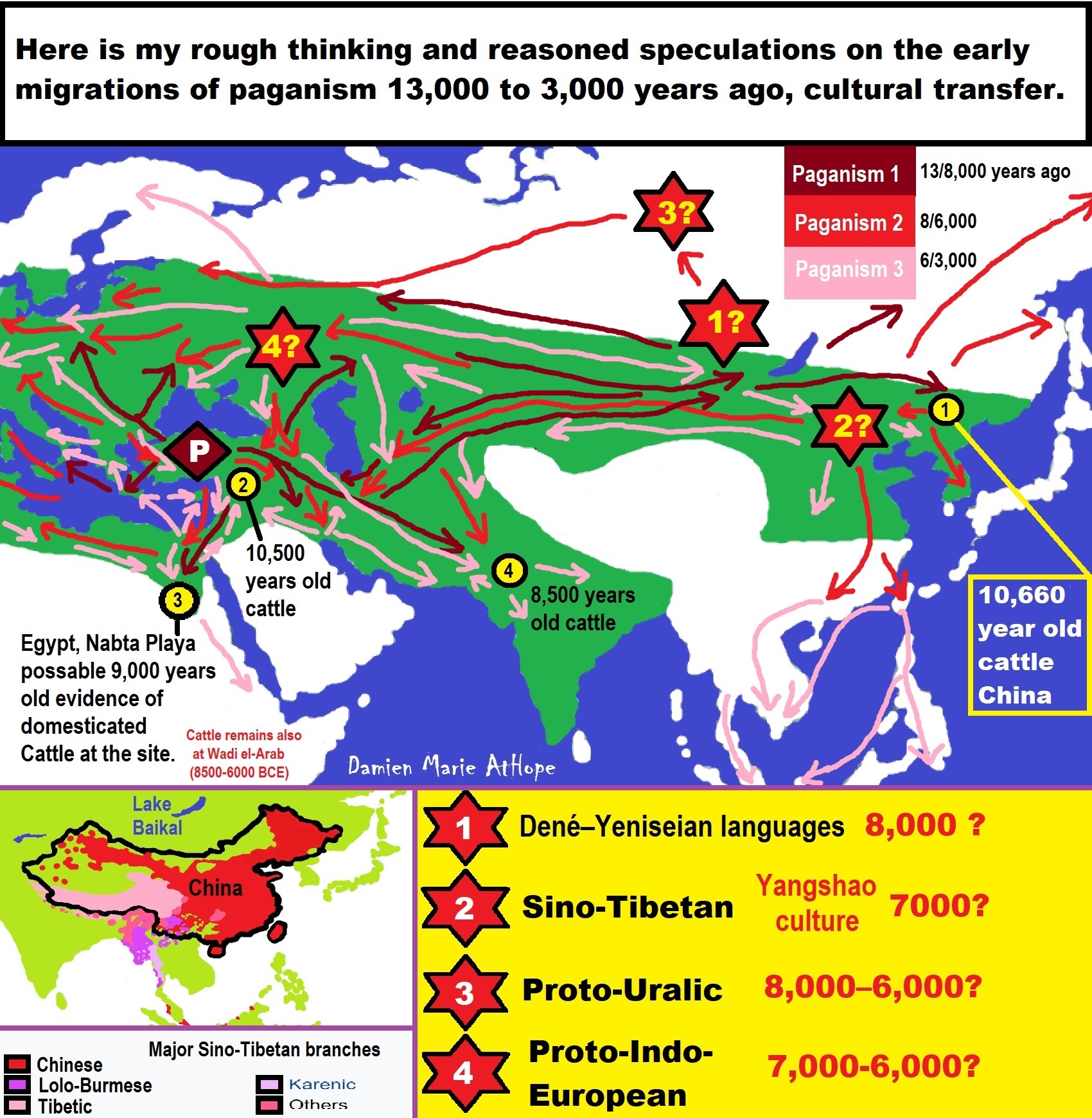
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

Paganism (such as that seen in Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
Haplogroup G2a (Y-chromosomal DNA) and the Seeming Development of Early Agriculture – “Haplogroup G descends from macro-haplogroup F, which is thought to represent the second major migration of Homo sapiens out of Africa, at least 60,000 years ago. Haplogroup G has 303 mutations confirming a severe bottleneck before splitting into haplogroups G1 and G2. G1might have originated around modern Iran around 26,000 years ago. G2 would have developed around the same time in West Asia and haplogroup G2 appear to have been closely linked to the development of early agriculture in the Fertile Crescent part, around 11,500 years before present. G2a branch expanded to Anatolia, the Caucasus, and Europe, while G2b diffused from Iran across the Fertile Crescent and east to Pakistan.
There has so far been ancient Y-DNA analysis from Early Neolithic Anatolia, Iran, Israel, Jordan as well as most Neolithic cultures in Europe (Thessalian Neolithic in Greece, Starčevo culture in Hungary/Croatia, LBK culture in Germany, Remedello in Italy, and Cardium Pottery in south-west France and Spain) and all sites yielded a majority of G2a individuals, except those from the Levant. This strongly suggests that farming was disseminated by members of haplogroup G at least from Anatolia/Iran then moved to Europe. 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, and found one G2b sample dating from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic (9,250 years ago) and a G2a1 from the Early Pottery Neolithic (7,700 years ago), both from Iran. The highest genetic diversity within haplogroup G is found in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent, between the Levant and the Caucasus, which is a good indicator of its region of origin.
Çatalhöyük in south-central Anatolia/Turkey was founded by farmers who also brought domesticated goats and sheep. Also around 8,500 years ago, G2a Neolithic farmers arrived in northwest Anatolia and Thessaly in central Greece, as attested by the ancient genomes around the time that it seems cattle domestication was introduced to Çatalhöyük and other sites in Central Anatolia, presumably by trading with their eastern neighbors. Ancient skeletons from the Starčevo–Kőrös–Criș culture (8,000-6,500 years ago) in Hungary and Croatia, and the Linear Pottery culture (7,500-6,500 years ago) in Hungary and Germany, all confirmed that G2a (both G2a2a and G2a2b) remained the principal paternal lineage even after farmers intermingled with indigenous populations as they advanced. G2a farmers from the Thessalian Neolithic quickly expanded across the Balkans and the Danubian basin, reaching Serbia, Hungary, and Romania by 7,800 years ago, Germany by 7,500 years ago, and Belgium and northern France by 7,200 years ago. By 7,800 years ago, farmers making cardial pottery arrived at the Marmara coast in northwest Anatolia with ovicaprids and pigs.
These people crossed the Aegean by boat and colonized the Italian peninsula, the Illyrian coast, southern France and Iberia, where they established the Cardium Pottery culture (5000-1500 BCE). Once again, ancient DNA yielded a majority of G2a samples in the Cardium Pottery culture, with G2a frequencies above 80% (against 50% in Central and Southeast Europe). Nevertheless, substantial minorities of other haplogroups have been found on different Neolithic sites next to a G2a majority, including C1a2, H2, I*, I2a1, I2c, and J2a in Anatolia, C1a2, E-M78, H2, I*, I1, I2a, I2a1, J2 and T1a in Southeast and Central Europe (Starčevo, Sopot, LBK), as well as E-V13, H2, I2a1, I2a2a1 and R1b-V88 in western Europe (Cardium Pottery, Megalithic). H2 and T1a were found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levant and are undeniably linked to the early development of agriculture alongside G2a. That being said, C1a2 was also found in Mesolithic Spain and, as it is an extremely old lineage associated with the first Paleolithic Europeans, it could have been found all over Europe and Anatolia before the Neolithic. E1b1b was also found in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levant, but the subclades may not be E-M78 or E-V13 (more likely E1b1b1* or E-M123).
R1b-V88 surely spread from the Near East too, although through a different route, with cattle herders via North Africa, then crossing over to Iberia. The rest probably represent assimilated hunter-gatherers descended from Mesolithic western Anatolian (I*, I2c, J2) and Europeans (E-V13, I*, I1, I2a, I2a1, I2a2). It is interesting to note that many of these lineages, such as C1a2, H2 and I* are virtually extinct anywhere nowadays, and several others are now very rare in Europe (I2c, R1b-V88).” ref
Haplogroup J (mtDNA) and the Seeming Spread of Early Agriculture – “Samples have been identified from various Neolithic sites, including Linear Pottery culture (LBK) in Central Europe, the Cardium Pottery culture in southern France, Megalithic cultures in northern Spain, and the Funnelbeaker culture in Germany and Sweden. All Neolithic samples tested to date belonged to J1*, J1c or J2b1a. One question that follows is: did J1c and J2b1a lineages actually come from the Near East during the Neolithic, or whether they were already in the Balkans and just expanded from there? Both being rare in the Near East today, the second hypothesis might seem more convincing at first. However, the age of J2b1a has been estimated at 11,000 years before present, while the Neolithic started over 12,000 years ago in the Near East. In other words, it could have arrived from the Near East as J2b1* and developed into J2b1a only after reaching Europe, which would explain why this particular subclade is almost exclusively European while all other subclades of J2b1 are mostly Middle Eastern or the eastern Mediterranean. J2b1a would, therefore, have come as a maternal lineage of early agriculturalists alongside the paternal lineage G2a (and perhaps also E1b1b and T1a). J1c, however, is too old (15,000 years) for that scenario.
If it had been part of the Neolithic expansion from the Fertile Crescent, many J1c subclades would be primarily West Asian today, which isn’t the case. The only J1c individuals outside Europe belong to deep clades that clearly originated in Europe or in Anatolia. DNA of Early Neolithic farmers from western Anatolia and from the Starcevo culture in Hungary and Croatia, and found that J1c was present in both cultures, alongside other typical European Neolithic lineages like H5, K1a, N1a, T2, and X2. Of 44 ancient Near Eastern samples, including Neolithic farmers from Jordan and western Iran, and well as Chalcolithic and Bronze Age samples from Armenia and the Levant, but did not find any J1c, apart from a single sample in Neolithic Iran.
This suggests that J1c lineages were probably not found among the very first farmers of the Fertile Crescent but were rather assimilated in neighboring populations further north, notably in Anatolia and Iran, but probably also in the Balkans, which were connected to Anatolia by a land bridge during the glacial and immediate post-glacial periods. Haplogroup J has been found in Bronze Age samples from the Yamna culture (J2b), Corded Ware culture (J1c and J2b1a), the Catacomb culture (J1b1a1), the Unetice culture (J1b1a1), and the Urnfield culture (J1b1), all in Central Europe. The Corded Ware culture is associated with the expansion of Y-haplogroup R1a from the northern Russian steppe, and in light of the continuity with Neolithic samples from Central Europe it can be assumed that J1c and J2b1a maternal lineages were not brought by the newcomers, but absorbed by the male invaders. On the other hand, J1b has never been found in Europe before the Bronze Age and was very probably brought by the Indo-Europeans carrying R1b paternal lineages. Both the Unetice and the Urnfield cultures are thought to have been founded mainly by R1b men.” ref
- Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” around 12,000 years ago.
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- “36cu0190” a Historic and Prehistoric site in Pennsylvania
- 12,000 – 10,000 years old Shamanistic Art in a Remote Cave in Egypt
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”around 10,000 years ago
- 9,000-8500 year old Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- Connected “dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures?
- Stars: Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities (at least back to around 6,000 years ago)
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
Paganism is approximately a 12,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife and who are guided/supported by a goddess/god, goddesses/gods, magical beings, or supreme spirits. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden paganist.
Around 12,000 years ago, in Turkey, the first evidence of paganism is Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made temple” and around 9,500 years ago, in Turkey, the second evidence of paganism is Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”. In addition, early paganism is connected to Proto-Indo-European language and religion. Proto-Indo-European religion can be reconstructed with confidence that the gods and goddesses, myths, festivals, and form of rituals with invocations, prayers, and songs of praise make up the spoken element of religion. Much of this activity is connected to the natural and agricultural year or at least those are the easiest elements to reconstruct because nature does not change and because farmers are the most conservative members of society and are best able to keep the old ways.
The reconstruction of goddesses/gods characteristics may be different than what we think of and only evolved later to the characteristics we know of today. One such characteristic is how a deity’s gender may not be fixed, since they are often deified forces of nature, which tend to not have genders. There are at least 40 deities and the Goddesses that have been reconstructed are: *Pria, *Pleto, *Devi, *Perkunos, *Aeusos, and *Yama.
The reconstruction of myths can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and by additional research, many of these myths have since been confirmed including some areas that were not accessible to the early writers such as Latvian folk songs and Hittite hieroglyphic tablets. There are at least 28 myths and one of the most widely recognized myths of the Indo-Europeans is the myth, “Yama is killed by his brother Manu” and “the world is made from his body”. Some of the forms of this myth in various Indo-European languages are about the Creation Myth of the Indo-Europeans.
The reconstruction of rituals can be connected to Proto-Indo-European culture/language and is estimated to have been spoken as a single language from around 6,500 years ago. One of the earliest ritual is the construction of kurgans or mound graves as a part of a death ritual. kurgans were inspired by common ritual-mythological ideas. Kurgans are complex structures with internal chambers. Within the burial chamber at the heart of the kurgan, elite individuals were buried with grave goods and sacrificial offerings, sometimes including horses and chariots.
The speakers of Pre-Proto-Indo-European lived in Turkey and it associates the distribution of historical Indo-European languages with the expansion around 9,000 years ago, with a proposed homeland of Proto-Indo-European proper in the Balkans around 7,000 years ago. The Proto-Indo-European Religion seemingly stretches at least back around 6,000 years ago or likely much further back and I believe Paganism is possibly an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system.
At a mound is called Gadachrili Gora, and the Stone Age farmers who lived here 8,000 years ago were grape lovers: Their rough pottery is decorated with bunches of the fruit, and analysis of pollen from the site suggests the wooded hillsides nearby were once decked with grapevines. Combined with the grape decorations on the outside of the jars, ample grape pollen in the site’s fine soil, and radiocarbon dates from 7,800 to 8,000 years ago, the chemical analysis indicates the people at Gadachrili Gora were the world’s earliest winemakers. ref
Starting from 9,500 years ago, a new population began to settle the Balkans and the Danube valley. Evidence shows that the Neolithic newcomers mixed with the indigenous population in Lepenski Vir. Arriving from Asia Minor/Anatolia (modern-day Turkey), the immigrants had a completely different physical appearance and lifestyle. With them, they brought a knowledge of agriculture, first grain crops, and husbandry: sheep, cattle, and goats. Based on the research, Starović concluded that the blending of the population occurred almost immediately, during the first immigrant generation, which was unique as in the other parts of Europe two such different communities would live next to each other at first. He believes that this melting pot was a keystone of human development in Europe. It produced the boom of the Lepenski Vir culture, establishing the “original Balkan Neolithic, the most original occurrence in the entire prehistory in Europe, which founded all we know today – the concepts of village, square, family – which then spread over and overwhelmed the continent”. ref
The culture of Lepenski Vir is around 8,5 millennia old and is located on the right bank of the Danube in the Djerdap gorge (The Iron gates of the Danube) near the town of Donji Milanovac. It was the center of one of the most complex prehistoric cultures. Rich cultural layer reveals the traces of the highly developed culture that had complex social relations and as such was the first in Europe to organize its settlement according to a plan. Trapezoid-base houses with a primitive wooden construction which were organized in the shape of a horseshoe. The buildings surrounded an open space – the first known square, with the central building, probably some kind of a temple or a shrine. Fireplace surrounded by fishlike stone figurines took central place in every house. Stone idols found in Lepenski Vir represent the oldest monumental stone sculptures found in Europe. At first, they only had a head with a strange expression, while in later stages these figurines had anthropomorphic shapes. Besides these figurines, numerous tools and arms made of stone, bone, and antler, pottery and jewelry made of shells and pebbles were found here. Based on these pieces of evidence we can conclude that these first inhabitants of the Danube banks lived at the time of the so-called Neolithic revolution when the first communities started working the land and tamed some animals. The culture of Lepenski Vir developed in the period from 8,500 to 7,500 years ago. ref, ref
The main site consists of several archeological phases starting with Proto-Lepenski Vir, then Lepenski Vir Ia-e, Lepenski Vir II and Lepenski Vir III, whose occupation spanned from 1,500 to 2,000 years, from the Mesolithic to the Neolithic period, when it was succeeded by the Neolithic Vinča culture and Starčevo culture, both upstream the Danube, 135 km (84 mi) and 139 km (86 mi) from Lepenski Vir, respectively. The Vinca culture a Neolithic archaeological culture in Serbia and smaller parts of Romania (particularly Transylvania), dated to the period 7,700–8,500 or 7,300–6,700/6,500 years ago.
The Vinča culture occupied a region of Southeastern Europe (i.e. the Balkans) corresponding mainly to modern-day Serbia (with Kosovo), but also parts of Romania, Bulgaria, Bosnia, Montenegro, Republic of Macedonia, and Greece. This region had already been settled by farming societies of the First Temperate Neolithic, but during the Vinča period sustained population growth led to an unprecedented level of settlement size and density along with the population of areas that were bypassed by earlier settlers. it was thought, on the basis of typological similarities, that Vinča and other Neolithic cultures belonging to the ‘Dark Burnished Ware’ complex were the product of migrations from Anatolia to the Balkans but the Dark Burnished Ware complex appeared at least a millennium before Troy I, the putative starting point of the westward migration. An alternative hypothesis where the Vinča culture developed locally from the preceding Starčevo culture.
Named for its type site, Vinča-Belo Brdo, a large tell settlement. These settlements maintained a high degree of cultural uniformity through the long-distance exchange of ritual items but were probably not politically unified. Various styles of zoomorphic and anthropomorphic figurines are hallmarks of the culture, as are the Vinča symbols, which some conjecture to be the earliest form of proto-writing. Although not conventionally considered part of the Chalcolithic or “Copper Age”, the Vinča culture provides the earliest known example of copper metallurgy. A number of satellite villages belonging to the same culture and time period were discovered in the surrounding area. These additional sites include Hajdučka Vodenica, Padina, Vlasac, Ikaona, Kladovska Skela, and others. Found artifacts include tools made from stone and bones, the remains of houses, and numerous sacral objects including unique stone sculptures.
It is assumed that the people of Lepenski Vir culture represent the descendants of the early European population of the Brno–Předmostí (Czech Republic) hunter-gatherer culture from the end of the last ice age. Archeological evidence of human habitation of the surrounding caves dates back to around 20,000 BC. The first settlement on the low plateau dates back to 11,500–9,200 BC. The late Lepenski Vir (8,300–8,000 years ago) architectural development was the development of the Trapezoidal buildings and monumental sculpture.[1] The Lepenski Vir site consists of one large settlement with around ten satellite villages. Numerous piscine sculptures and peculiar architecture have been found at the site. And the sculptures of this size so early in human history and original architectural solutions, define Lepenski Vir as the specific and very early phase in the development of the prehistoric culture in Europe. ref, ref
An 8,000-YEAR-OLD VEILED MOTHER GODDESS NEAR BULGARIA’S VIDIN ‘PUSHES BACK’ NEOLITHIC REVOLUTION IN EUROPE. The head of the Neolithic Mother Goddess, the earliest deity of Europe’s first sedentary farmers was found along with and other artifacts and structures in the settlement in Mayor Uzunovo, Vidin District, close to the Danube River, in Northwest Bulgaria. Also, in Bulgaria is found one of the oldest funerals in the Balkans – an early Neolithic funeral of a person at the age of 12-13, which dates back to around 8,300-8,150 years ago. The Neolithic settlement at Dzhulyunitsa existed between 8,300 and 7,700 years ago. Bulgaria farming inhabitants of 8,000 years ago deliberately burned individual homes down, perhaps as some sort of sacrifice. It’s likely they followed a religion concerned with fertility and there are graves dating to the end of the sixth millennium BC, with one skeleton buried in a fetal position. Some of the earliest European evidence for farming is found here as the new crops and domestic animals spread from the Near East through modern-day Turkey.
The finds from the Ohoden excavations indicate that the Balkan Peninsula was the center of a prehistoric civilization which spread to the rest of Europe and we can ponder what they spread the settlement, also had a religious shrine of the sun cult. Early Neolithic pits with traces of fire were next to a northern pit, and an 8,000-year-old stone structure set at a right angle and featuring an arch has been discovered. This is one of the earliest stone structures in the Balkans. The shrine is believed to have been a fertility and sun temple as its floor was paved with U-shaped stones directed to the east; it contained dozens of clay and stone disc symbolizing the sun disc, respectively the sun cult, in early agrarian societies. At the Ohoden site with the sanctuary containing a prehistoric altar decorated with huge trophy elk horns placed 2 meters away from a ritual burial of a man. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
The earliest kurgans date to 6,000 years ago and are connected to the Proto-Indo-European in the Caucasus. In fact, around 7,000 years ago, there appears to be pre-kurgan in Siberia. Around 7,000 to 2,500 years ago and beyond, kurgans were built with ancient traditions still active in Southern Siberia and Central Asia, which display the continuity of the archaic forming methods. Kurgan cultures are divided archaeologically into different sub-cultures such as Timber Grave, Pit Grave, Scythian, Sarmatian, Hunnish, and Kuman–Kipchak. Kurgans have been found from the Altay Mountains to the Caucasus, Ukraine, Romania, and Bulgaria. Around 5,000 years ago, kurgans were used in the Ukrainian and Russian flat unforested grasslands and their use spread with migration into eastern, central, northern Europe, Turkey, and beyond. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
Y-DNA G2a, F* and J2 are what we would expect from a source in Anatolia or the Caucasus Mountains or the highlands of Iran, not the Levant or Arabia or even the lowlands of Mesopotamia (although J2 would surely be found in Mesopotamia in significant proportions). The first European farmers probably emerged from the highlands that form the Southern boundaries of Europe and West Asia, rather than from what we would conventionally think of as the “Near East” proper. And rather than being European hunter-gatherers who were assimilated into the first wave of Neolithic farmers in the Balkans, that the Pelasgians (the indigenous inhabitants of the Aegean Sea region and their cultures) may have been the first wave Neolithic farmers in the Balkans (who probably arrived around 9,000-6,000 years ago). ref
The arrival of the Neolithic culture comes from Anatolia between 9.000 and 5.000 years ago, mtDNA data from Early Neolithic farmers of the Starčevo Criş culture in Romania (Cârcea, Gura Baciului, and Negrileşti sites), confirm their genetic relationship with those of the LBK culture (Linienbandkeramik Kultur) in Central Europe, and they show little genetic continuity with modern European populations. On the other hand, populations of the Middle-Late Neolithic (Boian, Zau and Gumelniţa cultures), supposedly the second wave of Neolithic migration from Anatolia, had a much stronger effect on the genetic heritage of the European populations. In contrast, we find a smaller contribution of Late Bronze Age migrations to the genetic composition of Europeans. Based research findings, it has been proposed that permeation of mtDNA lineages from the second wave of Middle-Late Neolithic migration from North-West Anatolia into the Balkan Peninsula and Central Europe represent an important contribution to the genetic shift between Early and Late Neolithic populations in Europe, and consequently to the genetic make-up of modern European populations.
The study of the genomes of a 7,000-year-old farmer from Germany and eight ~8,000-year-old hunter-gatherers from Luxembourg and Sweden have shown that most present-day Europeans derive from at least three highly differentiated populations. Besides, authors have proposed that early European farmers had a ~44% ancestry from a ‘basal Eurasian’ population.
Archaeological data show that the Neolithic expansion from Anatolia was not a single event but was represented by several waves of migrants. In this respect, the Proto-Sesklo culture in Greece, from which directly Starčevo-Criş in the northern Balkans and indirectly LBK in Central Europe originate represents only the first great wave of Neolithisation of Europe. A later great wave of migration from North-West Anatolia led to important cultures of South-Eastern Europe such as Vinča and Boian cultures.
aDNA studies of hunter-gatherers revealed a high genetic homogeneity in the pre-Neolithic groups throughout Europe, whether from Scandinavia, Central Europe or the Iberian Peninsula. The analysis of aDNA from Early European farmer groups of the Linear Pottery Culture (LPC, also known as Linienbandkeramik Kultur or LBK) in Central Europe suggested a genetic discontinuity in Central Europe and favored instead of a process of Neolithic transition through a of population diffusion into and across the area, based on a high frequency of the N1a haplogroup (about 15%) in the LBK farmers, absent in hunter-gatherers in this same region and almost nonexistent (0.2%) in the present-day European populations. Moreover, these first farmers shared an affinity with the modern-day populations from the Near East and Anatolia, supporting a major genetic input from this area during the advent of farming in Europe. Studies of other Neolithic sites in the North of France, Hungary and the Northeast of Iberian Peninsula also supported this view. However, an ancient mtDNA study of a Neolithic site in the Mediterranean region of Europe, namely in the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal), led to the proposal of a dual model for explaining the Neolithic dispersion process in Europe: DD in Mediterranean area and CD in Central Europe. ref
- “12,000 years ago: Jericho has evidence of settlement dating back to 10,000 BC. Jericho was a popular camping ground for Natufian hunter-gatherer groups, who left a scattering of crescent microlith tools behind them.
- 12,000 years ago: Earliest dates suggested for the domestication of the goat.
- 11,600 years ago: Start of the current Holocene epoch.
- 11,000 -12,00/13,000 years ago (9,000 BC): Earliest date recorded for construction of temenoi ceremonial structures at Göbekli Tepe in southern Turkey, as possibly the oldest surviving proto-religious site on Earth.
- 11,000 years ago: Emergence of Jericho, which is now one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Giant short-faced bears and giant ground sloths go extinct. Equidae goes extinct in North America.
- 10,500 years ago: Earliest supposed date for the domestication of cattle.
- 10,000 years ago: The Quaternary extinction event, which has been ongoing since the mid-Pleistocene, concludes. Many of the ice age megafauna go extinct, including the megatherium, woolly rhinoceros, Irish elk, cave bear, cave lion, and the last of the sabre-toothed cats. The mammoth goes extinct in Eurasia and North America, but is preserved in small island populations until ~1650 BC.
- 11,000 – 9,000 years ago: Byblos appears to have been settled during the PPNB period, approximately 8800 to 7000 BC. Neolithic remains of some buildings can be observed at the site.
- 10,000 – 8,000 years ago: The post-glacial sea level rise decelerates, slowing the submersion of landmasses that had taken place over the previous 10,000 years.
- 10,000 – 9,000 years ago: In northern Mesopotamia, now northern Iraq, cultivation of barley and wheat begins. At first they are used for beer, gruel, and soup, eventually for bread. In early agriculture at this time, the planting stick is used, but it is replaced by a primitive plow in subsequent centuries. Around this time, a round stone tower, now preserved to about 8.5 meters high and 8.5 meters in diameter is built in Jericho.
- 9,500–5,900 years ago: Neolithic Subpluvial in North Africa. The Sahara desert region supports a savanna-like environment. Lake Chad is larger than the current Caspian Sea. An African culture develops across the current Sahel region.
- 9,500 years ago: Çatalhöyük urban settlement founded in Anatolia. Earliest supposed date for the domestication of the cat.
- 9,200 years ago: First human settlement in Amman, Jordan; ‘Ain Ghazal Neolithic settlement was built spanning over an area of 15 hectares.
- 9,000 years ago: Jiahu culture began in China.
- 9,000 years ago: large first fish fermentation in southern Sweden.
- 8,200–8,000 years ago: 8.2 kiloyear event: a sudden decrease of global temperatures, likely caused by the final collapse of the Laurentide Ice Sheet, which leads to drier conditions in East Africa and Mesopotamia.
- 8,000-5,000 years ago: development of proto-writing in China, Southeast Europe (Vinca symbols) and West Asia (proto-literate cuneiform).
- 8,000 years ago: Evidence of habitation at the current site of Aleppo dates to about c. 8,000 years ago, although excavations at Tell Qaramel, 25 kilometers north of the city show the area was inhabited about 13,000 years ago, Carbon-14 dating at Tell Ramad, on the outskirts of Damascus, suggests that the site may have been occupied since the second half of the seventh millennium BC, possibly around 6300 BC. However, evidence of settlement in the wider Barada basin dating back to 9000 BC exists.
- 7,500 years ago: Copper smelting in evidence in Pločnik and other locations.
- 7,200–6,000 years ago: 5200–4000 BC:Għar Dalam phase on Malta. First farming settlements on the island.
- 6,100–5,800 years ago: Żebbuġ phase. Malta.
- 6,070–6,000 years ago: Trypillian build in Nebelivka (Ukraine) settlement which reached 15,000—18,000 inhabitants.
- 6,500 years ago: The oldest known gold hoard deposited at Varna Necropolis, Bulgaria.
- 6,000 years ago: Civilizations develop in the Mesopotamia/Fertile Crescent region (around the location of modern-day Iraq). Earliest supposed dates for the domestication of the horse and for the domestication of the chicken, invention of the potter’s wheel.
- 5,900 years ago: 5.9 kiloyear event: a rapid and intense aridification event, which likely started the current Sahara Desert dry phase and a population increase in the Nile Valley due to migrations from nearby regions. It is also believed this event contributed to the end of the Ubaid period in Mesopotamia.
- 5,800 years ago: The Post Track and Sweet Track causeways are constructed in the Somerset Levels.
- 5,800 years ago: Trypillian build in Talianki (Ukraine) settlement which reached 15,600—21,000 inhabitants.
- 5,800–5,600 years ago: Mġarr phase A short transitional period in Malta’s prehistory. It is characterized by pottery consisting of mainly curved lines.
- 5,700 years ago: starts mass graves at Tell Brak in Syria.
- 5,700 years ago: Trypillian build in Maidanets (Ukraine) settlement which reached 12,000—46,000 inhabitants and built 3-story building.
- 5,700 years ago: Minoan culture begins on Crete.
- 5,600–5,200 years ago: Ġgantija phase on Malta. Characterized by a change in the way the prehistoric inhabitants of Malta lived.
- 5,500 years ago: Uruk period in Sumer. The first evidence of mummification in Egypt.
- 5,500 years ago: the oldest known depiction of a wheeled vehicle (Bronocice pot, Funnelbeaker culture)
- 5,300 years ago: Bronze Age begins in the Near East, Newgrange is built in Ireland. Hakra Phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins in the Indian subcontinent.
- 5,300–5,000 years ago: Saflieni phase in Maltese prehistory.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Progressed organized religion (such as that seen in Egypt: 5,000 years ago),
(Prehistoric Egypt 40,000 years ago to The First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
4,600 years ago: (2600 BCE): Writing is developed in Sumer
and Egypt, triggering the beginning of recorded history.
*The First Dynasty*
Date: 3,150 B.C.E. (5,150 years ago)
The Beginning Rise of the Unequal State Government Hierarchies, Religions and Cultures Merger
The Pharaoh in ancient Egypt was the political and religious leader holding the titles ‘Lord of the Two Lands’ Upper and Lower Egypt and ‘High Priest of Every Temple’. In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt and this reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later.
Around 4,890 years ago during the Second Dynasty the King was linked with the divine and reign with the will of the gods. Following this rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth, the intermediary between the gods and the people, and when he died, he was thought to become Osiris, the god of the dead. As such, in his role of ‘High Priest of Every Temple’, it was the pharaoh’s duty to build great temples and monuments celebrating his own achievements and paying homage to the gods of the land. Among the earliest civilizations that exhibit the phenomenon of divinized kings are early Mesopotamia and ancient Egypt.
In 5,150 years ago the First Dynasty appeared in Egypt with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by the king Menes (now believed to be Narmer). Menes/Narmer is depicted on inscriptions wearing the two crowns of Egypt, signifying unification, and his reign was thought to be in accordance with the will of the gods; but the office of the king itself was not associated with the divine until later. During the Second Dynasty of Egypt 4,890-4,670 years ago King Raneb (also known as Nebra) linked his name with the divine and his reign with the will of the gods. Following Raneb, the rulers of the later dynasties were equated with the gods and with the duties and obligations due those gods. As supreme ruler of the people, the pharaoh was considered a god on earth.
The honorific title of `pharaoh’ for a ruler did not appear until the period known as the New Kingdom 3,570-3,069 years ago. Monarchs of the dynasties before the title of `pharaoh’ from the New Kingdom were addressed as `your majesty’ by foreign dignitaries and members of the court and as `brother’ by foreign rulers; both practices would continue after the king of Egypt came to be known as a pharaoh. Ref Ref
“This was a time of astonishing creativity as city-states and empires emerged in a vast area stretching from the Mediterranean to the Indus Valley. The previous millennium had seen the emergence of advanced, urbanized civilizations, new bronze metallurgy extending the productivity of agricultural work, and highly developed ways of communication in the form of writing. Around the time of 5,000 to 4,000 years ago, saw the growth of these riches, both intellectually and physically, became a source of contention on a political stage, and rulers sought the accumulation of more wealth and more power. The civilizations of Sumer and Akkad in Mesopotamia became a collection of volatile city-states in which warfare was common. Uninterrupted conflicts drained all available resources, energies, and populations. Also, in Egypt, pharaohs began to posture themselves as living gods made of an essence different from that of other human beings. Even in Europe, which was still largely Neolithic during the same period, the builders of megaliths were constructing giant monuments of their own. In the Near East and the Occident around 5,000 years ago and religion developed and advanced to roughly the ways we are somewhat familiar to a large amount, limits were being pushed by architects and rulers. After lengthy wars, the Sumerians recognized the benefits of unification into a stable form of national government and became a relatively peaceful, well-organized, complex technocratic state called the 3rd dynasty of Ur. This dynasty was later to become involved with a wave of nomadic invaders known as the Amorites, who were to play a major role in the region during the following centuries.” ref
“Foreign artifacts dating to the 7,000 years ago in the Badarian culture in Egypt indicate contact with distant Syria. In predynastic Egypt, by the beginning of the 6,000 years ago, ancient Egyptians in Maadi were importing pottery as well as construction ideas from Canaan. By the 4th millennium BCE, shipping was well established, and the donkey and possibly the dromedary had been domesticated. Domestication of the Bactrian camel and use of the horse for transport then followed. Charcoal samples found in the tombs of Nekhen, which were dated to the Naqada I and II periods, have been identified as cedar from Lebanon. Predynastic Egyptians of the Naqada I period also imported obsidian from Ethiopia, used to shape blades and other objects from flakes. The Naqadans traded with Nubia to the south, the oases of the western desert to the west, and the cultures of the eastern Mediterranean to the east. Pottery and other artifacts from the Levant that date to the Naqadan-era have been found in ancient Egypt. Egyptian artifacts dating to this era have been found in Canaan and other regions of the Near East, including Tell Brak and Uruk and Susa in Mesopotamia. By the second half of the 4th millennium BCE, the gemstone lapis lazuli was being traded from its only known source in the ancient world—Badakhshan, in what is now northeastern Afghanistan—as far as Mesopotamia and Egypt. By the 3rd millennium BCE, the lapis lazuli trade was extended to Harappa, Lothal and Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley Civilization of modern-day Pakistan and northwestern India. The Indus Valley was also known as Meluhha, the earliest maritime trading partner of the Sumerians and Akkadians in Mesopotamia. The ancient harbor constructed in Lothal, India, around 4,400 years ago is the oldest seafaring harbor known. The overland route through the Wadi Hammamat from the Nile to the Red Sea was known as early as predynastic times; drawings depicting Egyptian reed boats have been found along the path dating to 6,000 years ago. Ancient cities dating to the First Dynasty of Egypt arose along both its Nile and Red Sea junctions, testifying to the route’s ancient popularity. It became a major route from Thebes to the Red Sea port of Elim, where travelers then moved on to either Asia, Arabia or the Horn of Africa.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ancient_Egyptian_trade
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
Genetic analyses shows that 7,000-8,000 years ago, a closely related group of early farmers moved into Europe from the Near East, confirming the findings of previous studies. ref
Progressed organized religion is approximately a 5,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife and who are guided/supported by a goddess/god, goddesses/gods, magical beings, or supreme spirits and are attached to a standardized and hierarchy structure of control, rules, male dominance, oppression, and lowering of women status. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden animist, shamanist, totemist, and paganist.
This was a time of astonishing creativity as city-states and empires emerged into a vast area that stretch from the Mediterranean to the Indus Valley. The previous thousand years had seen the emergence of advanced and urbanized civilizations, new bronze metallurgy that extend the productivity of agricultural work, and highly developed ways of communication in the form of writing. 5,000 years ago, the growth of these riches, both intellectually and physically, became a source of contention on a political stage, and rulers sought the accumulation of more wealth and more power. Along with this came the first appearances of mega-architecture, imperialism, organized absolutism, and internal revolution. The civilizations of Sumer and Akkad in Mesopotamia became a collection of volatile city-states where warfare was common and the uninterrupted conflicts drained all the available resources, energies, and populations.
In addition, during this period, larger empires succeeded the last and conquerors grew in stature until the great Sargon of Akkad pushed his empire to the whole of Mesopotamia and beyond. It would not be surpassed in size until Assyrian times 1,500 years later. In the Old Kingdom of Egypt, the Egyptian pyramids were constructed and would remain the tallest and largest human constructions for thousands of years. Also in Egypt, pharaohs began to posture themselves as living gods made of an essence different from that of other human beings. Even in Europe, during the same period, which was still largely primitive, the builders of megaliths were constructing giant monuments of their own. Around 5,000 years ago, in the Near East and Fertile Cresent where agriculture arose, religion developed and advanced to roughly the ways we are somewhat familiar with today, and limits were being pushed by architects and rulers. ref, ref, ref, ref
- “5,750 years ago: The Proto-Semitic people emerged from a generally accepted urheimat in the Levant. The Proto-Semitic people would migrate throughout the Near East into Mesopotamia, Egypt, Ethiopia and the eastern shore of the Mediterranean.
- 5,700 years ago: Lothal: Indus Valley trade-port city in India.
- 5,650 years ago: Minoan culture appeared on Crete.
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- 5,300 years ago: The Indus Valley Civilization (IVC) was a Bronze Age civilization (3300–1300 BCE; mature period 2600–1900 BCE) in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, noted for its cities built of brick, roadside drainage system and multi-storeyed houses, as well as for creating artifacts which could be linked to pre-Vedic religions.
- 5,200 years ago: Helladic culture and Cycladic culture both emerge in Greece.
- 5,102 years ago: This was the beginning of Kaliyuga, a new age among the followers of Indian religions.
- 5,100 years ago: The initial form of Stonehenge was completed. The circular bank and ditch enclosure, about 110 metres (360 ft) across, may have been completed with a timber circle.
- 5,100 years ago: Newgrange, the 250,000 ton (226,796.2 tonne) passage tomb aligned to the winter solstice in Ireland, was built.
- 5,000 years ago: Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt.
- 5,000 years ago: First evidence of gold being used in the Middle East.
- 5,000 years ago: Vessels from Denmark
- 5,000 years ago: Sumerian Cuneiform emerged from the proto-literate Uruk period, allowing the codification of beliefs and creation of detailed historical religious records.
- 5,000 years ago: The second phase of Stonehenge was completed and appeared to function as the first enclosed cremation cemetery in the British Isles.
- 4,900 years ago: Beginning of the Early Dynastic Period I in Sumer.
- 4,900 years ago: Sumerianpictographs evolve into phonograms.
- 4,900 years ago: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period.
- 4,900 years ago: Votive statues from the Square Temple of Eshnunna (modern Tell Ashmar, Iraq) were made.
- 4,900 years ago: Syria: Foundation of the city of Mari.
- 4,900 years ago: Semitic tribes occupy Assyria in northern part of the plain of Shinar and Akkad.
- 4,900 years ago: Phoenicians settle on Syrian coast, with centers at Tyre and Sidon.
- 4,900 years ago: Beginning of the period of the Sage Kings in China, also known as the Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors.
- 4,900 years ago: Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- 4,879 years ago: Rise of the Văn Lang Kingdom and the Hồng Bàng Dynasty in northern Viet Nam.
- 4,874 years ago: The 365-day calendar year was installed in ancient Egypt
- 4,852 years ago: The beginning of the period of the Three August Ones and Five Emperors in China.
- 4,832 years ago: Estimated germination of the Methuselah Tree, the oldest known living organism
- 4,807 years ago: Suggested date for an asteroid or comet impact occurring between Africa and Antarctica, around the time of a solar eclipse on May 10, based on an analysis of flood stories. Possibly causing the Burckle crater and Fenambosy Chevron.
- 4,800 years ago: Ur becomes one of the richest cities in Sumer
- 4,800 years ago: Harp Player, from Keros, Cyclades, was made. It is now at the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
- 4,800 years ago: Iran: Creation of the Kingdom of Elam.
- 4,800 years ago: Seated Harp Player, from Keros, Cyclades, is made.
- 4,775 years ago: Second Dynasty wars in Ancient Egypt.
- 4,773 years ago: the 365-day calendar is introduced in Egypt.
- 4,750 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic I Period, and the beginning of the Early Dynastic II Period in Mesopotamia.
- 4,750 years ago: Estimated ending of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture in the region of modern-day Romania, Moldova, and southwestern Ukraine
- 4,700 years ago: Germination of the Bristlecone pine tree “Methuselah“, one of the oldest known trees still living now.
- 4,700 years ago: Merit-Ptah is world’s first female physician mentioned by name.
- 4,700 years ago: Old Kingdom of Egypt begins. 3rd–6th Dynasties.
- 4,700 years ago: Mesoamericans begin to plant and domesticate maize.
- 4,697 years ago: The Yellow Emperor starts to reign in China.
- 4,685 years ago: Bull lyre from the tomb of Queen Puabi, Ur (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) was made.
- 4,640 years ago: The cultivation and weaving of silk starts to be a closely guarded secret in China.
- 4,630 years ago: Imhotep, Vizier of Egypt, constructs the Pyramid of Djoser The Djoser pyramid is a step pyramid (or proto-pyramid) is considered to be the earliest large-scale cut stone construction and was thought to function in both life and the afterlife, which was sealed with a 3.5 ton block after the burial. The symbolism of the step pyramid form, which did not survive the 3rd Dynasty, is unknown, but it has been suggested that it may be a monumental symbol of the crown, especially the royal mortuary cult, since seven small step pyramids (not tombs) were built in the provinces.
- 4,627 years ago: Construction of the Caral metropolis in Peru
- 4,600 years ago: Mature Harappan phase of the Indus Valley Civilisation begins. The cities of Harappa and Mohenjo-daro become large metropolises and the civilization expands to over 2,500 cities and settlements across the whole of Pakistan, much of northern India, and parts of Afghanistan and Iran, covering a region of around one million square miles, which was larger than the land area of its contemporaries Egypt and Mesopotamia combined, and also had superior urban planning and sewage systems. The civilization began using the mature Indus script for its writing system.
- 4,600 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic II Period and the beginning of the Early Dynastic IIIa Period in Mesopotamia.
- 4,600 years ago: Founding of the Chalcolithic Iberian civilizations of Los Millares and Zambujal.
- 4,600 years ago: the Indus Valley Civilisation rises to become a powerful civilization.
- 4,600 years ago: Pre-Palace Period, phase I, in Crete
- 4,600 years ago: Wild horses still provide hunting feasts in Denmark. (Clutton-Brock)
- 4,600 years ago: Large water tank, possibly a public or ritual bathing area, Mohenjo-daro, Indus Valley Civilisation, is made.
- 4,600 years ago: Butmir culture existed in Butmir, near Ilidža, Bosnia and Herzegovina, dating from the Neolithic. It is characterized by its unique pottery, and is one of the best researched European cultures from 2600-2400 BC.
- 4,600 years ago: Unified Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 4,550 years ago: Estimated date of completion of the Great Pyramid of Giza.
- 4,550 years ago: Mesannepada is king of Ur (followed by his son, A-annepadda) who founds the First Dynasty of Ur and overthrows the last king of Uruk, as well as Mesilim of Kish.
- 4,550 years ago:: Great Lyre with bull’s head, from the tomb of King Meskalamdug, Ur (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) is made.
- 4,500 years ago: Excavation and development of the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni at Paola, Malta, a subterranean temple complex subsequently used as a necropolis.
- 4,500 years ago: The legendary line of Three Sovereigns and Five Emperors of China is founded by the Yellow Emperor.
- 4,500 years ago: the construction of the stone circle at Stonehenge begins and continues for the next five hundred years.
- 4,500 years ago: Rice was first introduced to Malaysia
- 4,500 years ago: Scribal schools flourish throughout Sumer.
- 4,500 years ago: Assyria is established.
- 4,500 years ago: Cylinder seal from Sumer and its impression are made. It is now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art, New York.
- 4,500 years ago: Excavation and development of the Hypogeum of Ħal-Saflieni at Paola, Malta, a subterranean temple complex subsequently used as a necropolis.
- 4,500 years ago: Valley Temple of Khafra, Giza, is built.
- 4,500 years ago: Khafra from Giza Valley, Temple of Khafra is made. Fourth Dynasty of Egypt. Discovered by Auguste Mariette. It is now kept in Egyptian Museum, Cairo.
- 4,500 years ago: Mohenjo-daro is about 7 square miles (18 km2) in size and has a population of c. 20,000 to 50,000.
- 4, 500 years ago: Incised panel “Frying pan”, from Syros, Cyclades is made.
- 4,500 years ago: Two figures of women, from the Cyclades, are made.
- 4,494 years ago: End of Fourth Dynasty, start of Fifth Dynasty in Egypt. Construction of the Pyramids begins.
- 4,494 years ago: “Sculptors at work”, relief from Saqqara, Fifth Dynasty. It is now at Egyptian Museum, Cairo, Egypt.
- 4,494 years ago: The Seated Scribe, a sculpture found at Saqqara, Fifth Dynasty of Egypt is made.
- 4,494 years ago: The first of the oldest surviving religious texts, the Pyramid Texts, was composed in Ancient Egypt.
- 4,492 years ago: Traditional date for the legendary foundation of Armenia by Hayk.
- 4,492 years ago: The Armenian patriarch Hayk defeats the Babylonian king Bel (legendary account) and Hayk founds Armenia.
- 4,474 years ago: Golden age of Ur in Mesopotamia.
- 4,450 years ago: End of the Early Dynastic IIIa Period and beginning of the Early Dynastic IIIb Period in Sumer.
- 4,450 years ago: Kish is lost to Hamazi tribesmen of the Kurdistan mountains; Elam under the Awan dynasty occupies parts of Sumer.
- 4,419 years ago: Neferefre is pharaoh
- 4,410 years ago: By this time, kings in Sumer have ceased to be automatically high priests of the city deity. Infiltration and conquest of Mesopotamia by ancient Semitic-speaking peoples begins.
- 4,400 years ago: Construction of Stonehenge
- 4,400 years ago: Megalithic culture begins to spread through Europe and the western Mediterranean.
- 4,400 years ago: Earliest signs of Corded Ware culture from the Caucasus.
- 4,400 years ago: Southeastern Spain is settled from the Mediterranean, by people using Prehistoric Egyptian-style pottery.
- 4,400 years ago: Amorites and Canaanites occupy Syria and Lebanon.
- 4,334 years ago: Sargon of Akkad conquers Mesopotamia, establishing the Akkadian Empire.
- 4,334 years ago: City of Lothal founded under the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 4,333 years ago: According to the Korean creation story, Dangun Wanggeom established the first Korean Empire, Gojoseon
- 4,300 years ago: C-Group pastoralists arrive in Nubia.
- 4,300 years ago: Megalithic, Corded Ware culture and the Beaker flourish in Europe.
- 4,300 years ago: Sumerian poetry, lamenting the death of Tammuz, the shepherd god.
- 4,300 years ago: Sumerian cuneiform writing reduces pictographs still in use to about 550 BC.
- 4,300 years ago: Major religious festival in Sumeria celebrates the victory of god of spring over goddess of chaos.
- 4,300 years ago: Earliest Trojan culture.
- 4,300 years ago: Beginning of the Pengtoushan culture in China.
- 4,300 years ago: Indus Valley Civilization (Harappan) flourishing in modern day eastern Pakistan – western India.
- 4,300 years ago: Metals start to be used in Northern Europe.
- 4,300 years ago: Unetice culture emerges in the modern day Czech Republic.
- 4,300 years ago: Disk of Enheduanna, from Ur, (modern Muqaiyir, Iraq) is made.
- 4,300 years ago: “Head of a man from Nineveh” (modern Kuyunjik, Iraq) is made.
- 4,285 years ago: Enheduanna, high priestess of the moon god Nanna in Ur, was born.
- 4,254 years ago: Stela of Naram-Sin, probably from Sippar, discovered in Susa (modern Shush, Iran), is made.
- 4,250 years ago: Earliest evidence of maize cultivation in Central America.
- 4,240 years ago: Akkad, capital of the Akkadian Empire, becomes the largest city in the world, surpassing Memphis, capital of Egypt.
- 4,220 years ago: Scord of Brouster farmstead established in Shetland, Scotland
- 4.2 kiloyear event – a severe aridification event that probably lasted the entire 22nd century BC and caused the collapse of several Old World civilizations.
- 4,217 years ago: Nomadic invasions of Akkad.
- 4,200 years ago: The Minoan Civilization developed in Crete. Citizens worshipped a variety of goddesses.
- 4,150 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh—originally titled He who Saw the Deep (Sha naqba īmuru) or Surpassing All Other Kings (Shūtur eli sharrī)—were written.
- 4,104 years ago: Approximate date of the Biblical flood according to the Hebrew Calendar.
- 4,070 years ago: Xia Dynasty, first Chinese dynasty and government system established.
- 4,000 years ago: Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- 3,700 years ago: The oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,600 years ago: The ancient development of Stonehenge came to an end.
- 3,500 years ago: The Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation.
- 3,450 years ago: This is the traditionally accepted period in which, according to legend, the Israelite lawgiver Moses gave the Ten Commandments.
- 3,351 years ago: The reign of Akhenaten, sometimes credited with starting the earliest known recorded monotheistic religion, in Ancient Egypt
- 3,300 years ago: The “standard” Akkadian version of the Epic of Gilgamesh was edited by Sin-liqe-unninni.
- 3,250 years ago: The Upanishads (Vedic texts) were composed, containing the earliest emergence of some of the central religious concepts of Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com