“Mesopotamia is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Mesopotamia occupies most of present-day Iraq and Kuwait. The historical region includes the head of the Persian Gulf and parts of present-day Iran, Syria, and Turkey.” ref
“The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BCE or 5,121 years ago) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BCE or 2,560 years ago, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BCE or 2,353 years ago, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (900 BCE – 270 CE).” ref
“Around 150 BCE or 2,171 years ago, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with western parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In 226 CE, the eastern regions of Mesopotamia fell to the Sassanid Persians. The division of Mesopotamia between Roman (Byzantine from 395 AD) and Sassanid Empires lasted until the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire and Muslim conquest of the Levant from Byzantines.” ref
“A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BCE and 3rd century BCE, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BCE or 12,021 years ago. It has been identified as having “inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, and the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture“. It has been known as one of the earliest civilizations to ever exist in the world.” ref
City-States seem to likely start in Mesopotamia
“As time went on, many small villages became the first cities, one of them being Eridu, according to the Mesopotamians themselves. Scholars, however, consider Uruk to be the first city in history. Other Sumerian cities include Ur, Lagash, Adab, Kish, Larsa, Nippur, Kullah, and Adab among others.” ref
“In 4000 BCE or 6,021 years ago. came the first villages and the beginning of towns. By 3,500 BCE or 5,521 years ago, the Sumerian city-states began forming, all centered around temples to the gods. By this time, Sumerian people had invented writing, the wheel, irrigation and water control, and sailboats. One of the names for Mesopotamia is the “cradle of civilization,” as the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers was the birthplace of civilization as we know it.” ref
“Sumer’s city-states were first ruled by priest-kings, known as Ensi. As society grew more complex, however, and city-states began battling over land and water rights, a secular kingship began, with the rule of a city-state in the hands of a Lugal, or strong man. The Lugal supervised wars and oversaw important trade with other lands. Trade brought in goods such as metal ores that were unobtainable in Sumer itself. It was probably the necessity of record-keeping in long-distance trade that spurred the development of cuneiform writing.” ref
“While the archeological record reveals the life of common Sumerians, the Sumerian King List provides some detail of Sumer’s kings. The King List, a cuneiform document that lists and briefly describes all the kings of the region beginning with Etana of Kish, who ruled c. 3100 BCE or 5,121 years ago. A scribe in the city of Lagash wrote the document around 2100 BCE or 4,121 years ago at the instigation of a king who wished to legitimate his rule by connecting his name with the known kings and their great deeds.” ref
“Sumer’s city-states warred with each other continually for land, water rights, and other natural resources. One king might create a larger alliance, but no one managed to rule them all until Eannutum of Lagash, who managed to subdue most of the city-states of Sumer under his rule. Lugalzagesi of Umma then held that proto-empire together until he was overthrown by Sargon the Great circa 2234 BCE or 4,255 years ago. Sargon, a Semite rather than a Sumerian, originated from northern Mesopotamia.” ref
“The Akkadian Empire dominated Sumer for the next 150 years. Sumer, however, would rise again during the Sumerian Renaissance of 2047-1750 BCE or 4,068 years ago. Sumer’s civilization provided the world with many firsts: first legal codes, court system, schools, proverbs, moral and ethical ideas, mathematical systems, libraries, bronze, writing, astrological signs, our division of time into hours and minutes and many technological innovations.” ref
Divine right of Kings
“Historically, many Notions of rights have been authoritarian and hierarchical, with different people granted different rights and some having more rights than others. For instance, the right of a father to receive respect from his son did not indicate a right for the son to receive a return from that respect. Analogously, the divine right of kings, which permitted absolute power over subjects, provided few rights for the subjects themselves.” ref
Pre-Christian conceptions of the Divine Right of Kings
Divine Right of Kings and Zoroastrianism (Iranian world)
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family.
“Khvarenah “Ahura Mazda the god reportedly gives divine kingship to Ardashir.” Khvarenah is an Iranian and Zoroastrian concept, which literally means glory, about the divine right of the kings. This may stem from early Mesopotamian culture, where kings were often regarded as deities after their death. Shulgi of Ur was among the first Mesopotamian rulers to declare himself to be divine. In the Iranian view, kings would never rule, unless Khvarenah is with them, and they will never fall unless Khvarenah leaves them. For example, according to the Kar-namag of Ardashir, when Ardashir I of Persia and Artabanus V of Parthia fought for the throne of Iran, on the road Artabanus and his contingent are overtaken by an enormous ram, which is also following Ardashir. Artabanus’s religious advisors explain to him that the ram is the manifestation of the khwarrah of the ancient Iranian kings, which is leaving Artabanus to join Ardashir.” ref
Roman Empire (Italic languages)
Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BCE.
“The Imperial cult of ancient Rome identified Roman emperors and some members of their families with the “divinely sanctioned” authority (auctoritas) of the Roman State. The official offer of cultus to a living emperor acknowledged his office and rule as divinely approved and constitutional: his Principate should therefore demonstrate pious respect for traditional Republican deities and mores. Many of the rites, practices, and status distinctions that characterized the cult to emperors were perpetuated in the theology and politics of the Christianised Empire.” ref
Christian conceptions of the Divine Right of Kings
“In European Christianity, the divine right of kings, divine right, or God’s mandation is a political and religious doctrine of political legitimacy of a monarchy. It stems from a specific metaphysical framework in which a monarch is, before birth, pre-ordained to inherit the crown. According to this theory of political legitimacy, the subjects of the crown have actively (and not merely passively) turned over the metaphysical selection of the king’s soul – which will inhabit the body and rule them – to God. In this way, the “divine right” originates as a metaphysical act of humility and/or submission towards God. The Divine Right has been a key element of the legitimation of many absolute monarchies.” ref
“Significantly, the doctrine asserts that a monarch is not accountable to any earthly authority (such as a parliament) because their right to rule is derived from divine authority. Thus, the monarch is not subject to the will of the people, of the aristocracy, or of any other estate of the realm. It follows that only divine authority can judge a monarch, and that any attempt to depose, dethrone or restrict their powers runs contrary to God’s will and may constitute a sacrilegious act. It is often expressed in the phrase by the Grace of God, which has historically been attached to the titles of certain reigning monarchs. Note, however, that such accountability only to God does not per se make the monarch a sacred king.” ref

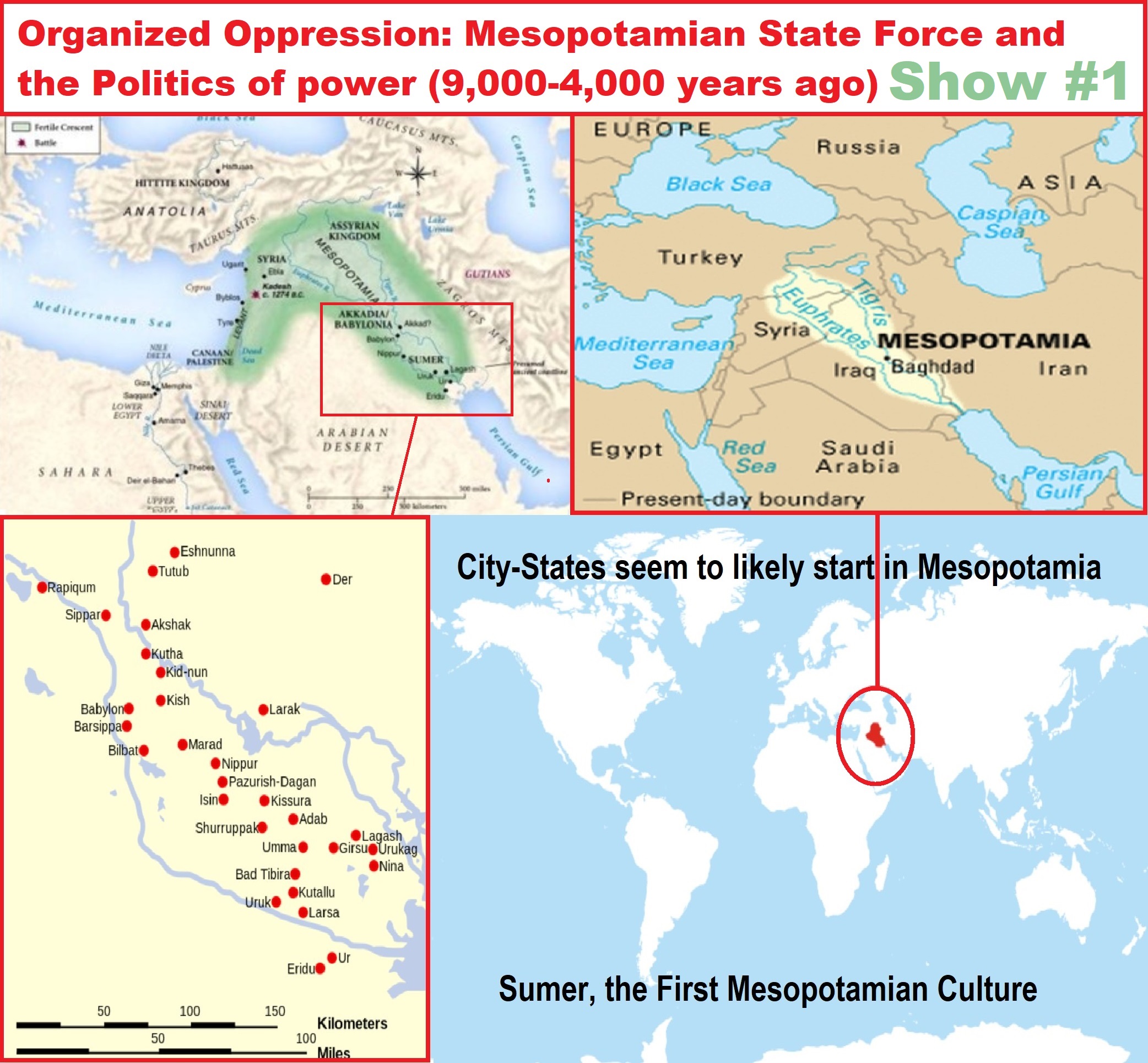
Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power Show #1 (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid) (Video)
03:21 Early Farming Communities (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid) Video Used
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)
Pic ref
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic (10000 – 6500 BCE) and Pottery Neolithic (7000–5000 BCE)
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
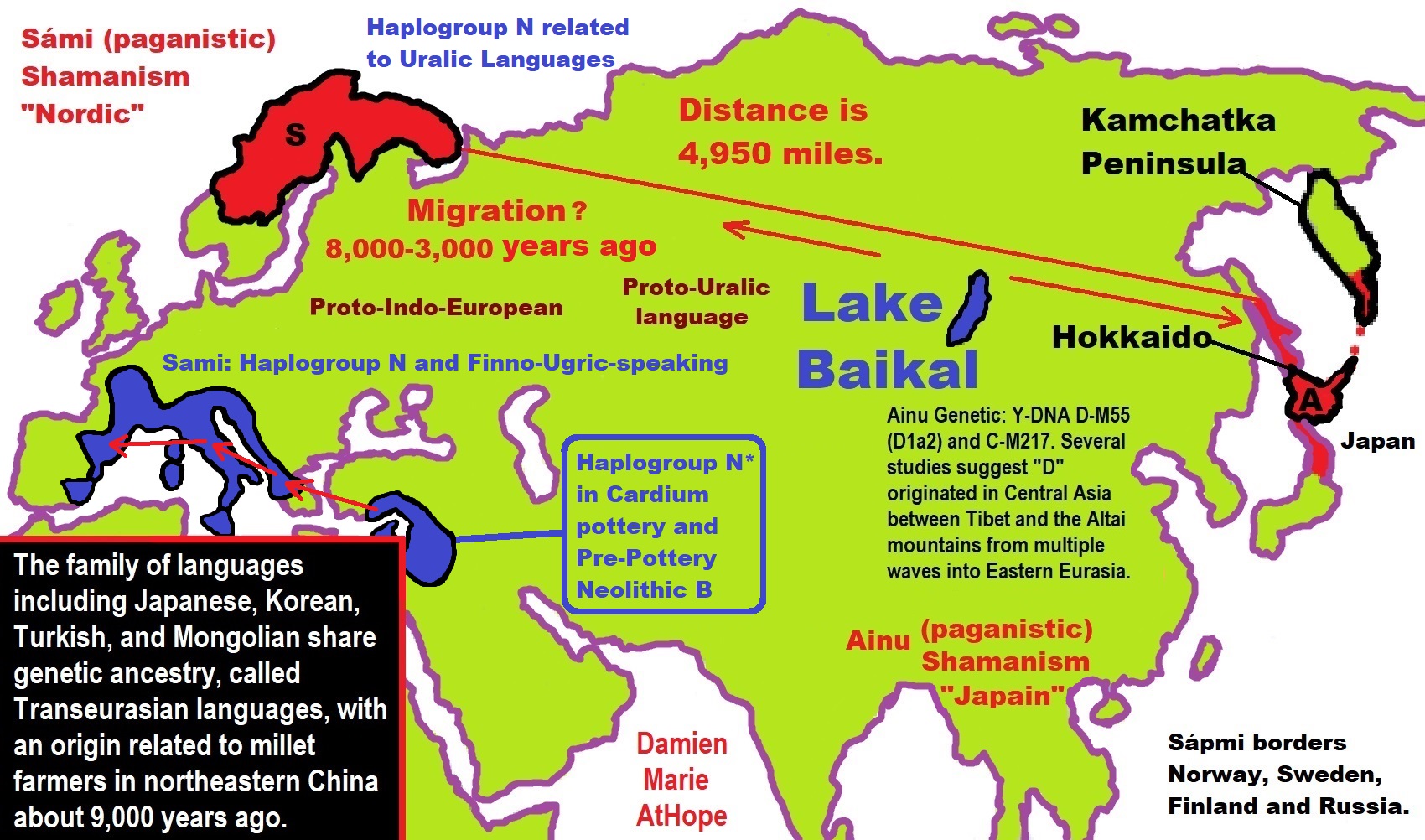
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
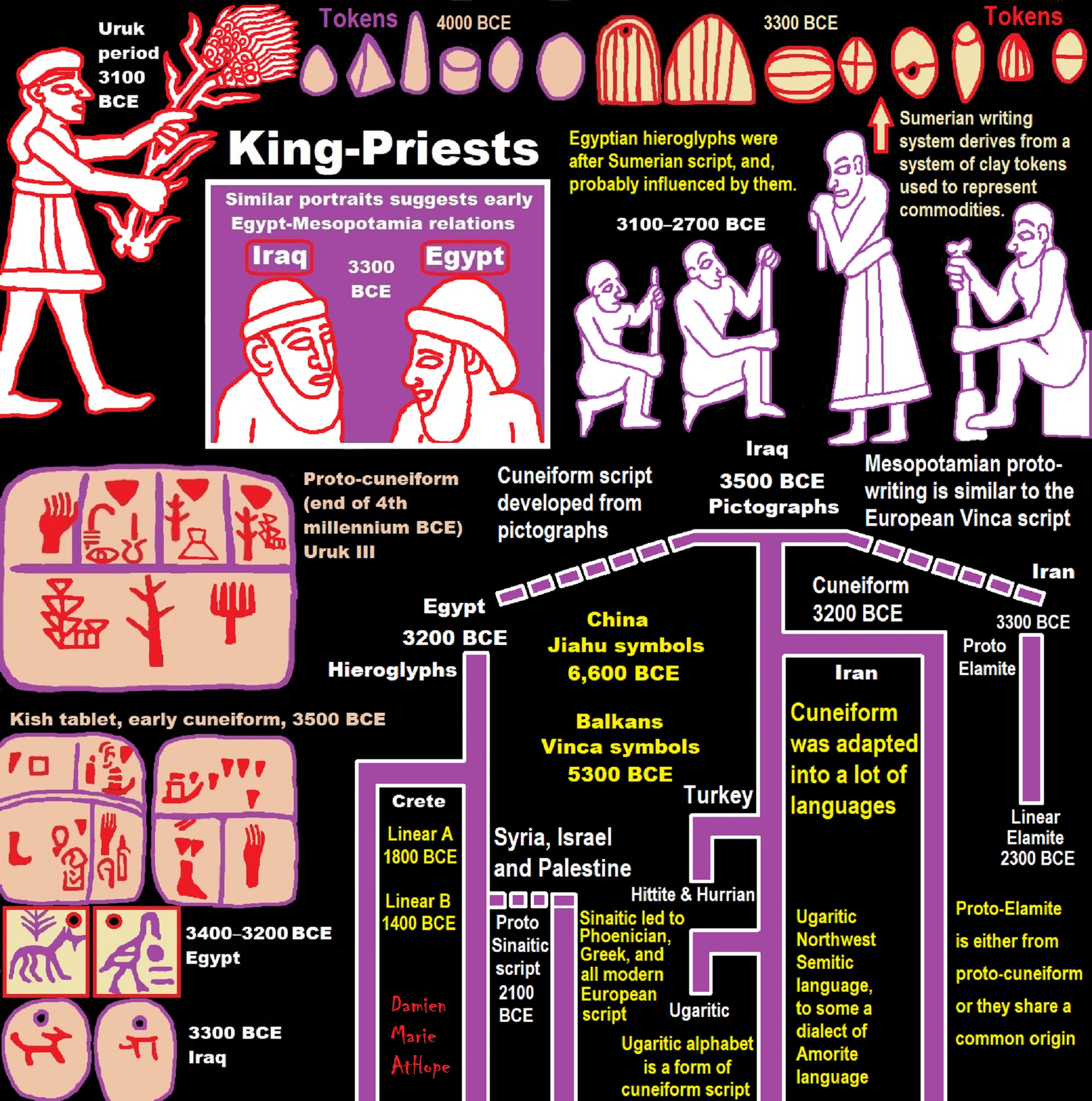
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
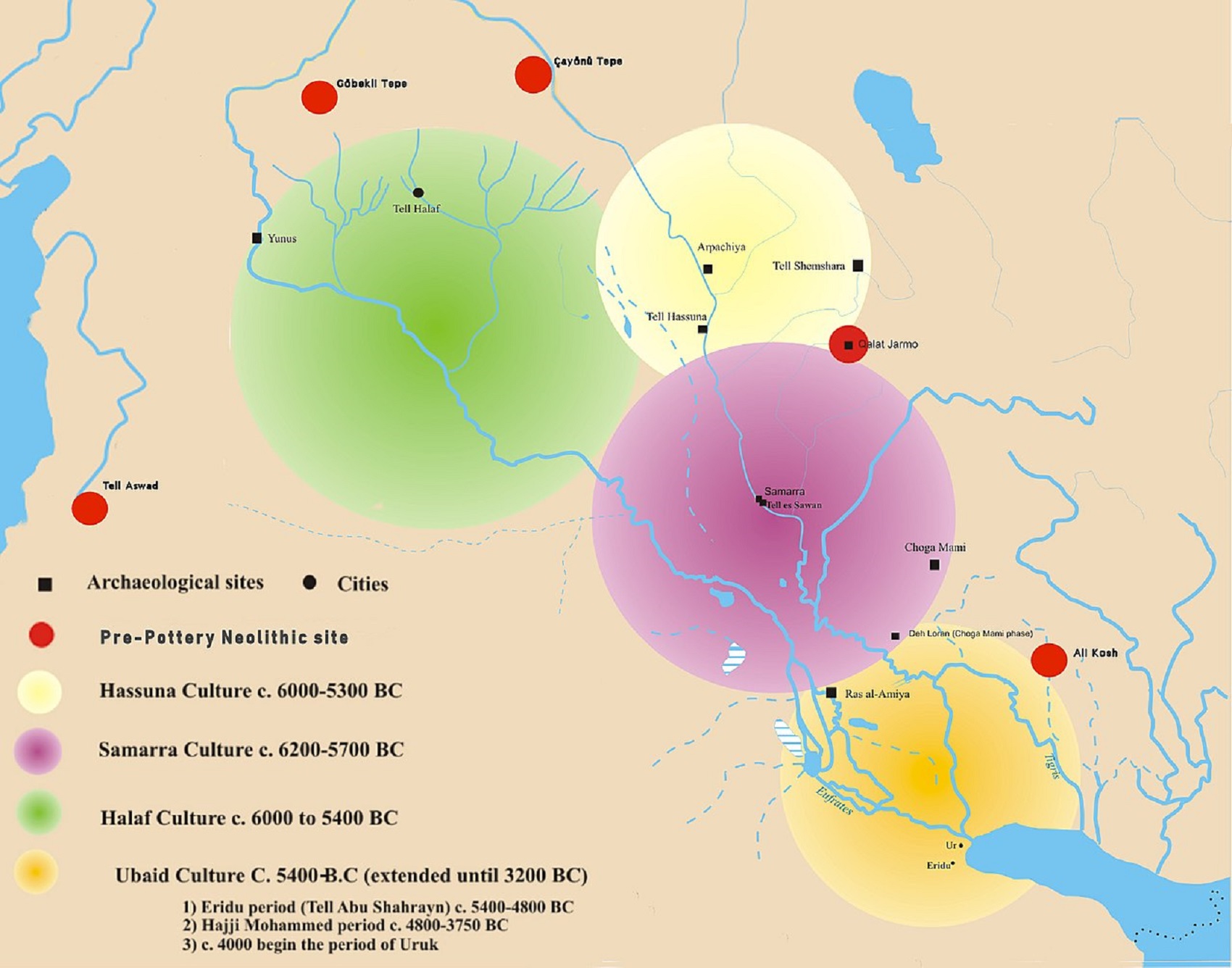
Samarra Culture
“The Samarra culture is a Late Neolithic archaeological culture of northern Mesopotamia, roughly dated to between 6200 and 4800 BCE or 8,222-6,822 years ago. It partially overlaps with Hassuna and early Ubaid. Samarran material culture was first recognized during excavations by German Archaeologist Ernst Herzfeld at the site of Samarra. Other sites where Samarran material has been found include Tell Shemshara, Tell es-Sawwan, and Yarim Tepe.” ref
“At Tell es-Sawwan, evidence of irrigation—including flax—establishes the presence of a prosperous settled culture with a highly organized social structure. The culture is primarily known for its finely made pottery decorated with stylized animals, including birds, and geometric designs on dark backgrounds. This widely exported type of pottery, one of the first widespread, relatively uniform pottery styles in the Ancient Near East, was first recognized at Samarra. The Samarran Culture was the precursor to the Mesopotamian culture of the Ubaid period.” ref
“At Tell Sabi Abyad and other Late Neolithic sites in Syria, scholars adopt increasingly vague terms such as Samarra “influenced”, Samarra-“related” or even Samarra “impulses”, largely because we do not understand the relationships with the traditional Samarra heartlands. The term may be extended to include sites in Syria such as Tell Chagar Bazar, Tell Boueid II, Tell Sabi Abyad, or Tell Halula, where similar pottery is currently being excavated in Pre-Halaf to Early Halaf Transitional contexts.” ref
Halaf culture
“The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 to 5100 BCE or 8,122-7,122 years ago. The period is a continuous development out of the earlier Pottery Neolithic and is located primarily in the fertile valley of the Khabur River (Nahr al-Khabur), of south-eastern Turkey, Syria, and northern Iraq, although Halaf-influenced material is found throughout Greater Mesopotamia. While the period is named after the site of Tell Halaf in north Syria, the earliest Halaf period material was excavated at the site of Sakce Gözü, then in Syria but now part of Turkey. Small amounts of Halaf material were also excavated at Carchemish, on the Turkish/Syrian border. However, the most important site for the Halaf tradition was the site of Tell Arpachiyah, now located in the suburbs of Mosul, Iraq.
The Halaf period was succeeded by the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period which comprised the late Halaf (c. 5400–5000 BCE or 7,422-7,022 years ago), and then by the Ubaid period. Previously, the Syrian plains were not considered as the homeland of Halaf culture, and the Halafians were seen either as hill people who descended from the nearby mountains of southeastern Anatolia/Turkey, or herdsmen from northern Iraq. A formerly unknown transitional culture between the pre-Halaf Neolithic‘s era and Halaf’s era was uncovered in the Balikh valley, at Tell Sabi Abyad (the Mound of the White Boy). The new archaeology demonstrated that Halaf culture was not sudden and was not the result of foreign people, but rather a continuous process of indigenous cultural changes in northern Syria, that spread to the other regions.” ref
“And Halaf pottery has been found in other parts of northern Mesopotamia, such as at Nineveh and Tepe Gawra, Chagar Bazar, Tell Amarna, and at many sites in Anatolia (Turkey) suggesting that it was widely used in the region. Halaf culture ended by 5000 BCE or 7,022 years ago, after entering the so-called Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period. Many Halafian settlements were abandoned, and the remaining ones showed Ubaidian characters. The new period is named Northern Ubaid to distinguish it from the proper Ubaid in southern Mesopotamia, and two explanations were presented for the transformation. The first maintain an invasion and a replacement of the Halafians by the Ubaidians, however, there is no hiatus between the Halaf and northern Ubaid which excludes the invasion theory. The most plausible theory is a Halafian adoption of the Ubaid culture, which is supported by most scholars including Oates, Breniquet, and Akkermans.” ref
Ubaid period
“The Ubaid period (c. 6500–3800 BCE or 8,522-5,822 years ago) is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. In South Mesopotamia, the period is the earliest known period on the alluvial plain although it is likely earlier periods exist obscured under the alluvium. In the south, it has a very long duration between about 6500 to 3800 BCE when it is replaced by the Uruk period. In Northern Mesopotamia the period runs only between about 5300 to 4300 BCE or 7,322-6,322 years ago. It is preceded by the Halaf period and the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period and succeeded by the Late Chalcolithic period or Copper Age.” ref
Uruk period
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE or 6,022-5,122 years ago; also known as the Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. The late Uruk period (34th to 32nd centuries) saw the gradual emergence of the cuneiform script and corresponds to the Early Bronze Age; it has also been described as the “Protoliterate period”. During this period, pottery painting declined as copper started to become popular, along with cylinder seals. However, the Anu/ White Temple ziggurat at Uruk. The original pyramidal structure, the “Anu Ziggurat” dates to around 4000 BCE or 6,022 years ago, and the White Temple was built on top of it circa 3500 BCE or 5,522 years ago.” ref
The 7th millennium BCE spanned the years 7000 to 6000 BCE or 9,022-8,022 years ago
“Neolithic culture and technology were established in the Near East by 7000 BCE or 9,022 years ago and there is increasing evidence through the millennium of its spread or introduction to Europe and the Far East. In most of the world, however, including north and western Europe, people still lived in scattered Palaeolithic hunter-gatherer communities. The Mehrgarh chalcolithic civilization began around 7000 BCE or 9,022 years ago. The world population is believed to have been stable and slowly increasing. It has been estimated that there were perhaps ten million people worldwide at the end of this millennium, growing to forty million by 5000 BCE or 7,022 years ago and 100 million by 1600 BCE or 3,622 years ago, an average growth rate of 0.027% p.a. from the beginning of the Neolithic to the Middle Bronze Age. Towards the end of this millennium, the islands of Great Britain, and Ireland were severed from continental Europe by rising seawater.” ref
Europe
“Neolithic culture and technology reached modern Turkey and Greece c. 7000 BCE or 9,022 years ago, and Crete at about the same time. The innovations, including the introduction of farming, spread from the Middle East through Turkey and Egypt. There is evidence of domesticated sheep or goats, pigs, and cattle together with grains of cultivated bread wheat. The domestication of pigs in Eastern Europe is believed to have begun c. 6800 BCE or 8,822 years ago. The pigs may have descended from European wild boar or were probably introduced by farmers migrating from the Middle East. There is evidence, c. 6200 BCE or 8,222 years ago, of farmers from the Middle East reaching the Danube and moving into Romania and Serbia. Farming gradually spread westward and northward over the next four millennia, finally reaching Great Britain and Scandinavia c. 3000 BCE or 5,022 years ago to complete the transition of Europe from the Mesolithic to the Neolithic.” ref
Near East
“The Ubaid period (c. 6500–3800 BCE or 8,522-5,822 years ago) began in Mesopotamia, its name derived from Tell al-‘Ubaid where the first significant excavation took place. By the end of this millennium, Tell es-Sultan (Jericho) had become a large agricultural settlement with some eight to ten acres within its walls. Kathleen Kenyon reckoned that it was home to about three thousand people. Construction was done using stone implements to mold clay into bricks. The main crop was wheat.” ref
Geologic and climatic change
“The early Holocene sea level rise (EHSLR), which began c.10,000 BCE or 12,022 years ago, tailed off during the 6th millennium. Global water levels had risen by about 60 meters due to the deglaciation of ice masses since the end of the Last Ice Age. Accelerated rises in sea-level rise, called meltwater pulses, occurred three times during the EHSLR. The last one, Meltwater Pulse 1C, which peaked c. 6000 BCE, produced a rise of 6.5 meters in only 140 years. It is believed that the cause was a major ice sheet collapse in Antarctica. Approximately 8,022 years ago (c. 6000 BCE), a massive volcanic landslide off Mount Etna, Sicily, caused a megatsunami that devastated the eastern Mediterranean coastline on the continents of Asia, Africa, and Europe.” ref
“In South America, a large eruption occurred at Cueros de Purulla c. 5870 BCE or 7,892 years ago, forming a buoyant cloud and depositing the Cerro Paranilla Ash in the Calchaquí Valleys. A cataclysmic volcanic eruption occurred c. 5700 BCE in Oregon when 12,000-foot (3,700 m) high Mount Mazama created Crater Lake as the resulting caldera filled with water. Another major eruption occurred c. 5550 BCE on Mount Takahe, Antarctica, possibly creating an ozone hole in the region. The carbon-14 content in tree rings created c. 5480 BCE indicates an abnormal level of solar activity.” ref
The Northgrippian
In the geologic time scale, the “Northgrippian” succeeded the “Greenlandian” c. 6236 BCE (to c. 2250 BCE or 4,272 years ago). The starting point for the Northgrippian is the so-called 8.2 kiloyear event, which was an abrupt climate change lasting some four centuries in which there was a marked decrease in global temperatures, possibly caused by an influx of glacial meltwater into the North Atlantic Ocean.” ref
“In climatology, the so-called “8.2-kiloyear event” was a sudden decrease in global temperatures that occurred approximately 8,222 years ago, or c. 6,200 BCE. It defines the start of the Northgrippian age in the Holocene epoch. Milder than the Younger Dryas cold period before it but more severe than the Little Ice Age after it, the 8.2-kiloyear cooling was a significant exception to general trends of the Holocene climatic optimum. During the event, atmospheric methane concentration decreased by 80 ppb, an emission reduction of 15%, by cooling and drying at a hemispheric scale.” ref
“Drier conditions were notable in North Africa, and East Africa was significantly affected by five centuries of general drought. In West Asia, especially Mesopotamia, the 8.2-kiloyear event was a 300-year aridification and cooling episode, which may have provided the natural force for Mesopotamian irrigation agriculture and surplus production, which were essential for the earliest formation of classes and urban life. However, changes taking place over centuries around the period are difficult to link specifically to the approximately 100-year abrupt event, as recorded most clearly in the Greenland ice cores. In particular, in Tell Sabi Abyad, Syria, significant cultural changes are observed at c. 6200 BCE or 8,222 years ago; the settlement was not abandoned at the time.” ref
Creation of Great Britain and Ireland
“The influx is believed to be one factor in the creation of Great Britain and Ireland as islands separate from the European continent. After the Last Ice Age ended c. 9700 BC, increasing sea levels gradually inundated Doggerland, a land bridge that linked Great Britain to Denmark and the Netherlands. This process began with the formation of the North Sea and the English Channel. Further west, another low-lying land area was being flooded to form the Irish Sea and create Ireland. Sometime in the second half of the 7th millennium, the Storegga Slides occurred off Norway to generate a huge tsunami which completely overwhelmed Doggerland and its Mesolithic community of an estimated 5,000 hunter-gatherers. By about 6100 BC, Great Britain had become an island.” ref

Pic ref
“In the Aceramic Neolithic (PPN) period of the Near East, many economic and societal changes took place. During the PPNA is when we recognize a process of agglomeration of hundreds of people in big sites such as Jericho. The archaeological record proves more than likely contacts between the contemporary societies of the Levant and some Eastern and Central Anatolian sites. The extent of those far contacts is hard to estimate, but we assume that such contacts and the trade network, which we can study mainly through the obsidian trade, using terrestrial and maritime routes, with the interaction of big villages though a few intermediary steps, already full operating at that time, must have helped to transform the local hierarchies, economic interdependencies, and rituals, and for instance, it could accelerated the end of Göbekli Tepe around mid-PPNB. And therefore during the Late PPNB consolidated the central villages, key nodes in the trade networks, and these, in different ecological regions, reached between 10 and 15 ha, v. gr. in Basta, Beisamoun or ‘Ain Ghazal. And in such a way, those built interdependent Ancient “World” Systems. Key words: Aceramic Neolithic, Göbekli Tepe, Çayönü, Aşikli, Jericho, ritual places, sedentary villages, obsidian, trade, surplus, Ancient World Systems.” ref
Pic ref
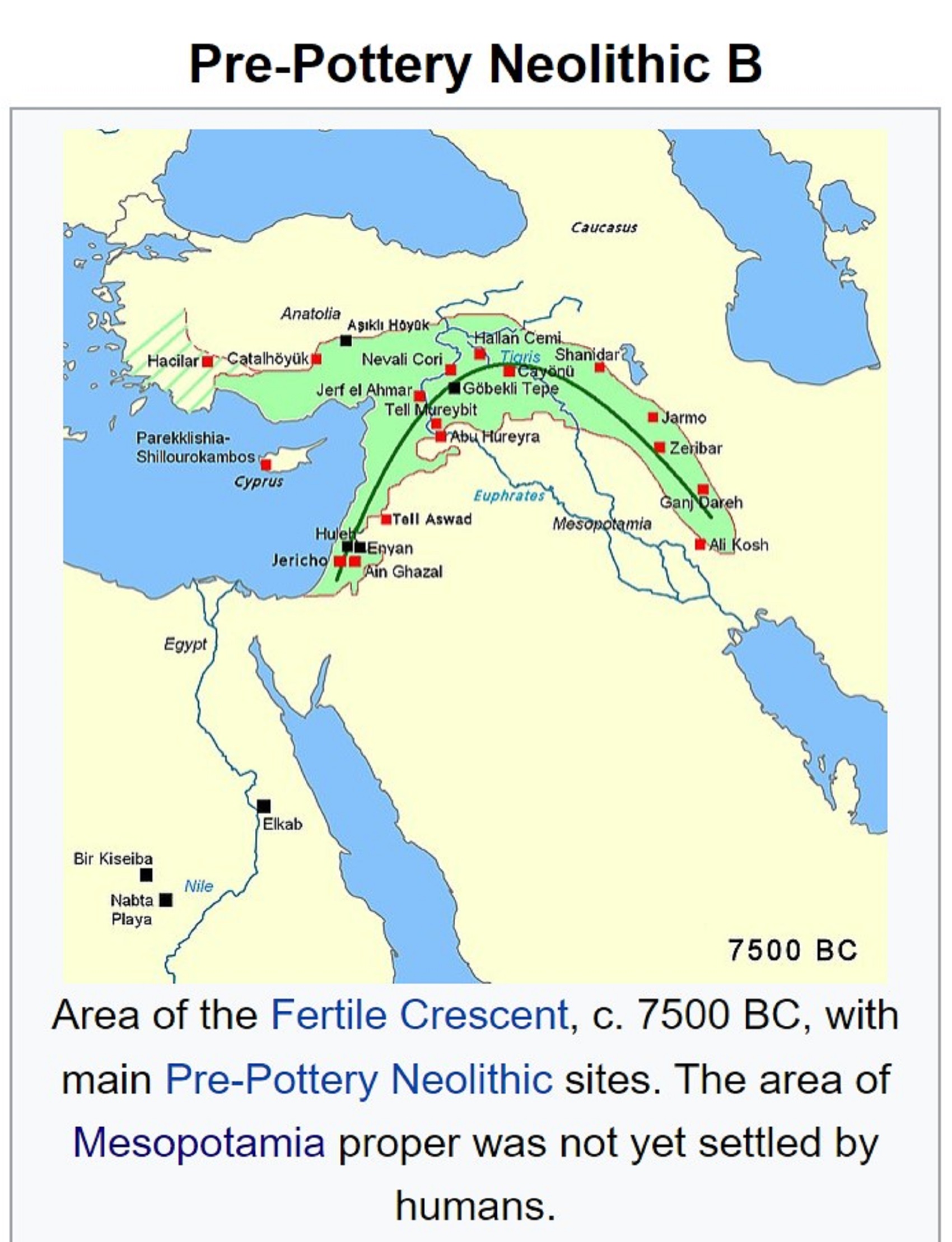
Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB)
“Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) is part of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, a Neolithic culture centered in upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, dating to c. 10,800 – c. 8,500 years ago, that is, 8800–6500 BCE. It was typed by British archaeologist Kathleen Kenyon during her archaeological excavations at Jericho in the West Bank. Like the earlier PPNA people, the PPNB culture developed from the Mesolithic Natufian culture. However, it shows evidence of a northerly origin, possibly indicating an influx from the region of northeastern Anatolia.” ref
“Cultural tendencies of this period differ from that of the earlier Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) period in that people living during this period began to depend more heavily upon domesticated animals to supplement their earlier mixed agrarian and hunter-gatherer diet. In addition, the flint tool kit of the period is new and quite disparate from that of the earlier period. One of its major elements is the naviform core. This is the first period in which architectural styles of the southern Levant became primarily rectilinear; earlier typical dwellings were circular, elliptical, and occasionally even octagonal. Pyrotechnology, the expanding capability to control fire, was highly developed in this period. During this period, one of the main features of houses is a thick layer of white clay plaster flooring, highly polished and made of lime produced from limestone.” ref
“It is believed that the use of clay plaster for floor and wall coverings during PPNB led to the discovery of pottery. The earliest proto-pottery was White Ware vessels, made from lime and gray ash, built up around baskets before firing, for several centuries around 7000 BCE or 9,022 years ago at sites such as Tell Neba’a Faour (Beqaa Valley). Sites from this period found in the Levant utilizing rectangular floor plans and plastered floor techniques were found at Ain Ghazal, Yiftahel (western Galilee), and Abu Hureyra (Upper Euphrates). The period is dated to between c. 10,722 and c. 8,022 years ago or 7000–6000 BCE.” ref
“Plastered human skulls were reconstructed human skulls that were made in the ancient Levant between 9000 and 6000 BCE or 8,022 years ago in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B period. They represent some of the oldest forms of art in the Middle East and demonstrate that the prehistoric population took great care in burying their ancestors below their homes. The skulls denote some of the earliest sculptural examples of portraiture in the history of art.” ref
“The Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN) represents the early Neolithic in the Levantine and upper Mesopotamian region of the Fertile Crescent, dating to c. 12,000 – c. 8,500 years ago, (10,000 – 6,500 BCE). And Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (PPNB) ends 6,500 BCE or so becoming the Pottery Neolithic, also known the Late Neolithic, first experiments with pottery, around 7000 BCE or 9,000 years ago, that is the final part of the Neolithic period.” ref, ref
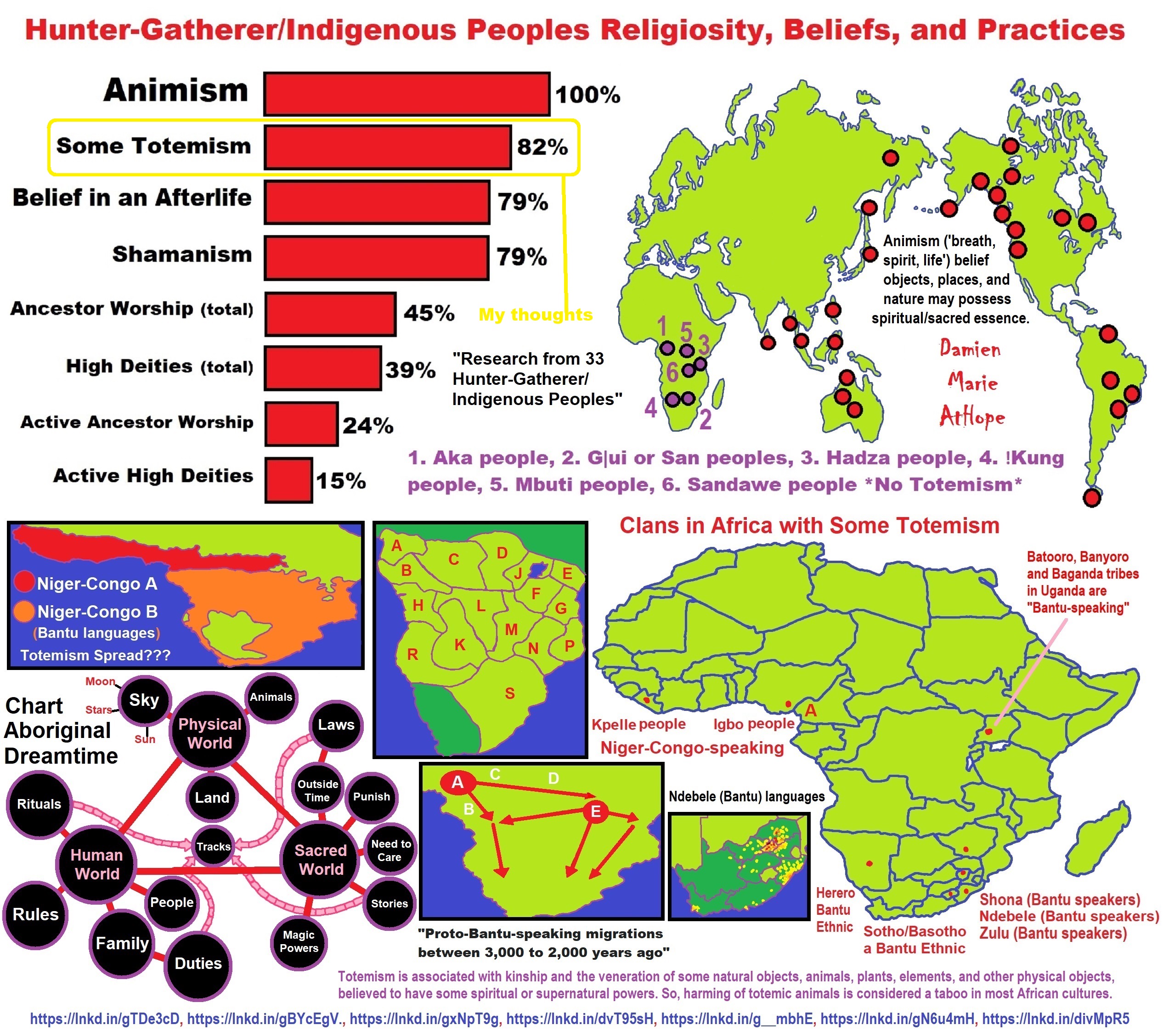
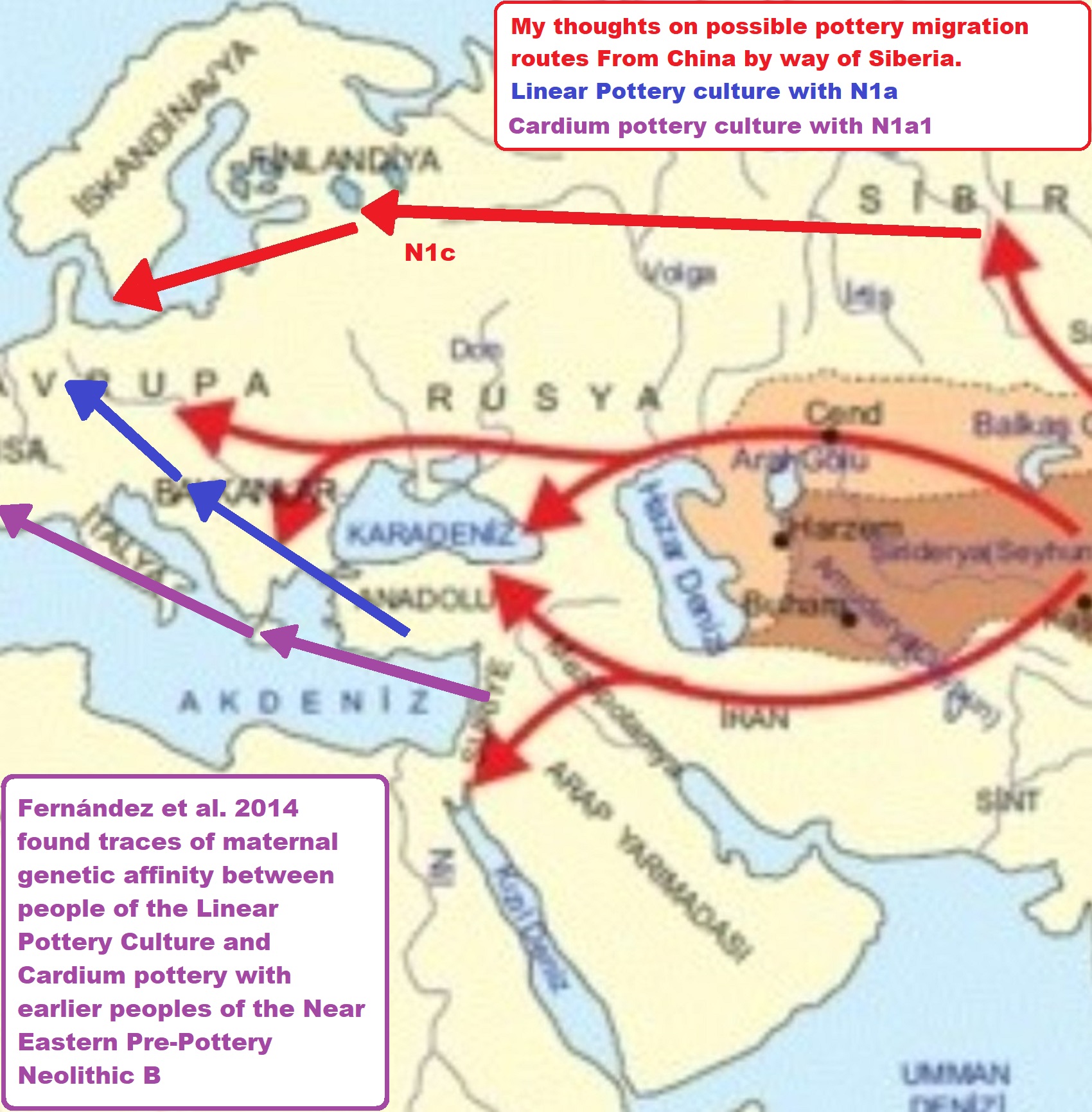
“Rare haplogroup (M-DNA “Women”) N has been found among fossils belonging to the (Cardium pottery 6400 – 5500 BCE) and the Pre-Pottery Neolithic B. HaplogroupN1a is seen in the Arabian Peninsula and Northeast Africa. Also found in Central Asia and Southern Siberia. This branch is well attested in ancient people from various cultures of Neolithic Europe, from Hungary to Spain, and among the earliest farmers with pottery of Anatolia/Turkey, like those related to the Linear Pottery culture 5500–4500 BCE of Germany and related areas. It is the Linear Pottery culture with haplogroup N1a which Damien thinks is the origins of arcane capitalism. Haplogroup N1b – found in Middle East, Egypt, Caucasus, and Europe.” ref
“Haplogroup N1a evidence supports the notion that the descendants of Neolithic Linear Pottery culture5500–4500 BCE who lack of haplogroup U5 seen in Mesolithic Europe before them supports the notion that U5 at this time is uniquely associated with non-farmers of Mesolithic European cultures who lack N1a seen in the Early farmers from Turkey. Ancient DNA suggested the Linear Pottery culture population had affinities to populations from the Near East and Anatolia/Turkey. Thus, Linear Pottery culture carrying haplogroup N, supports an early Neolithic inland colonization of Mainland Europe through Balkans and the central Europe by Near-Eastern farmers.” ref
“Early Neolithic impressed pottery (origin of Cardium pottery 6400 – 5500 BCE) is found in the Levant (i.e. Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel), and certain parts of Anatolia/Turkey. Cardium pottery carrying haplogroup N, supports an early Neolithic maritime colonization of Mainland Europe through Cyprus and the Aegean Islands by Near-Eastern farmers.” ref
Abstract: “Researchers suggest that a comparative perspective indicates that some of the most enduring themes of Neolithic studies need to be reconsidered, namely: (1) the idea of a Neolithic package consisting of a number of associated traits (including, among other things, agriculture, sedentary sites, and pottery) that developed and spread together, (2) the notion of the Neolithic as a revolutionary event marking a sharp break from the preceding Palaeolithic period, and (3) the enduring impact of the Neolithic on later periods.” ref
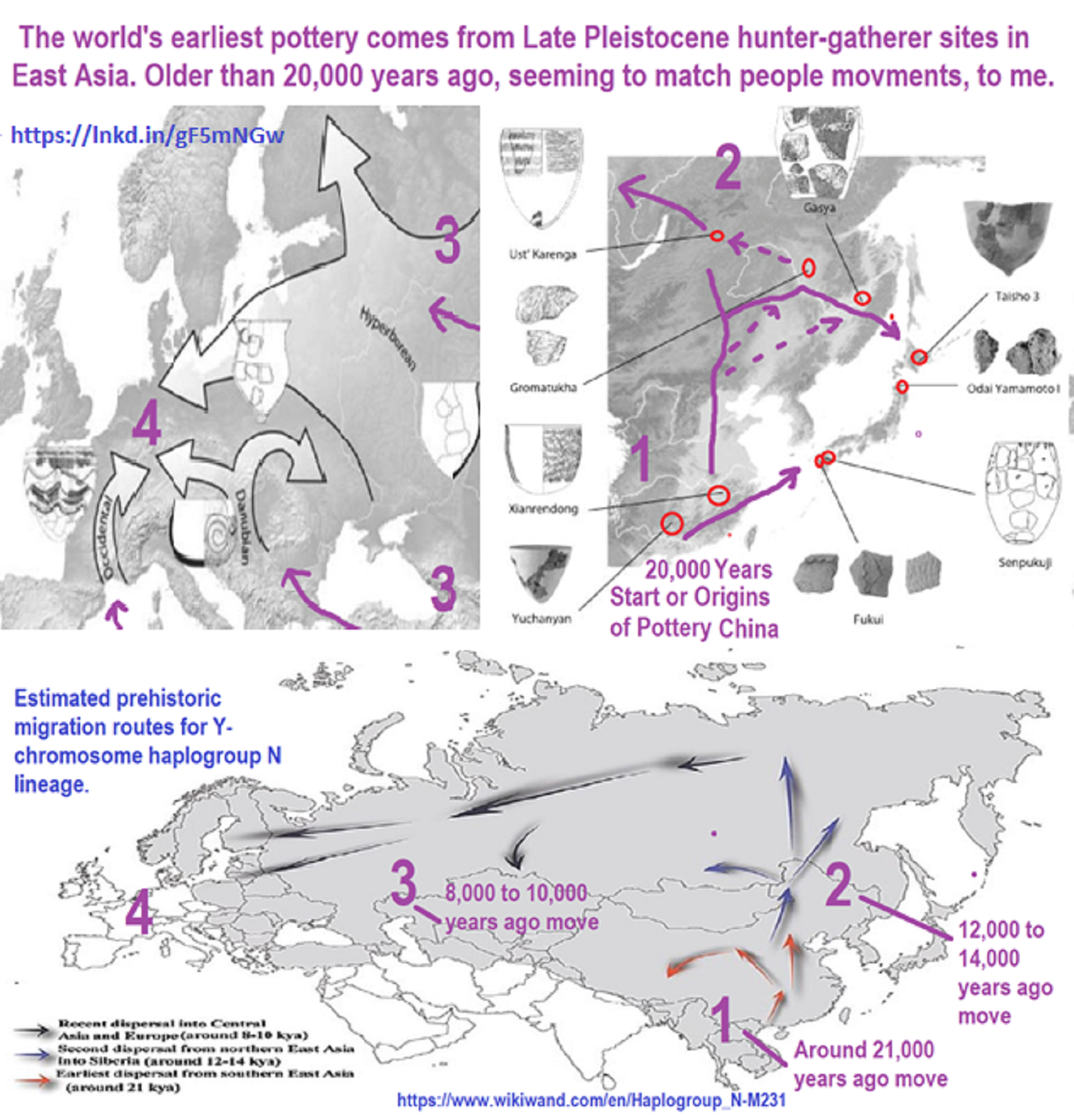
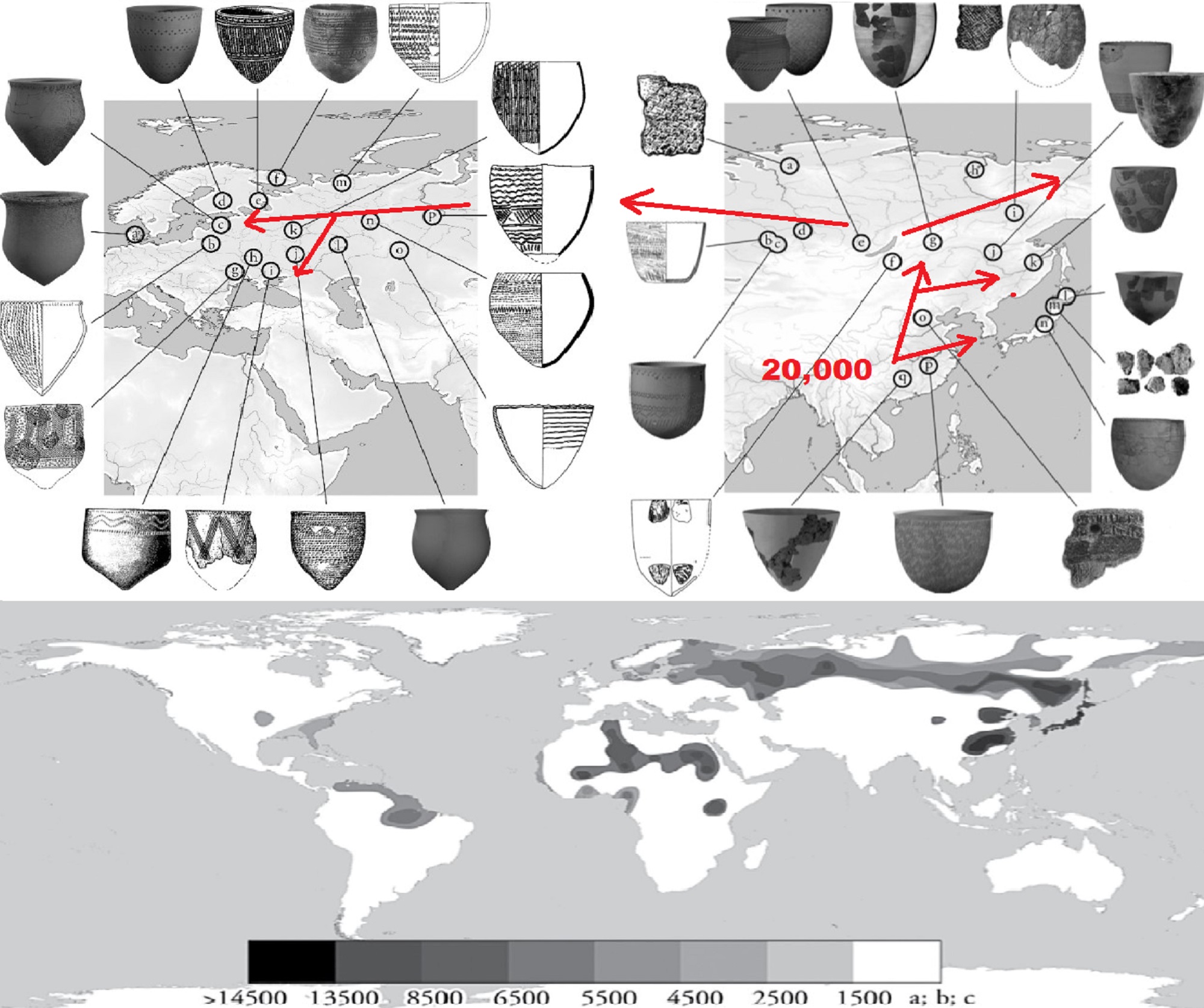
“Clay pots in China are 20,000 years old – baked 10,000 years before humans settled down and became farmers in Mesopotamia.” ref
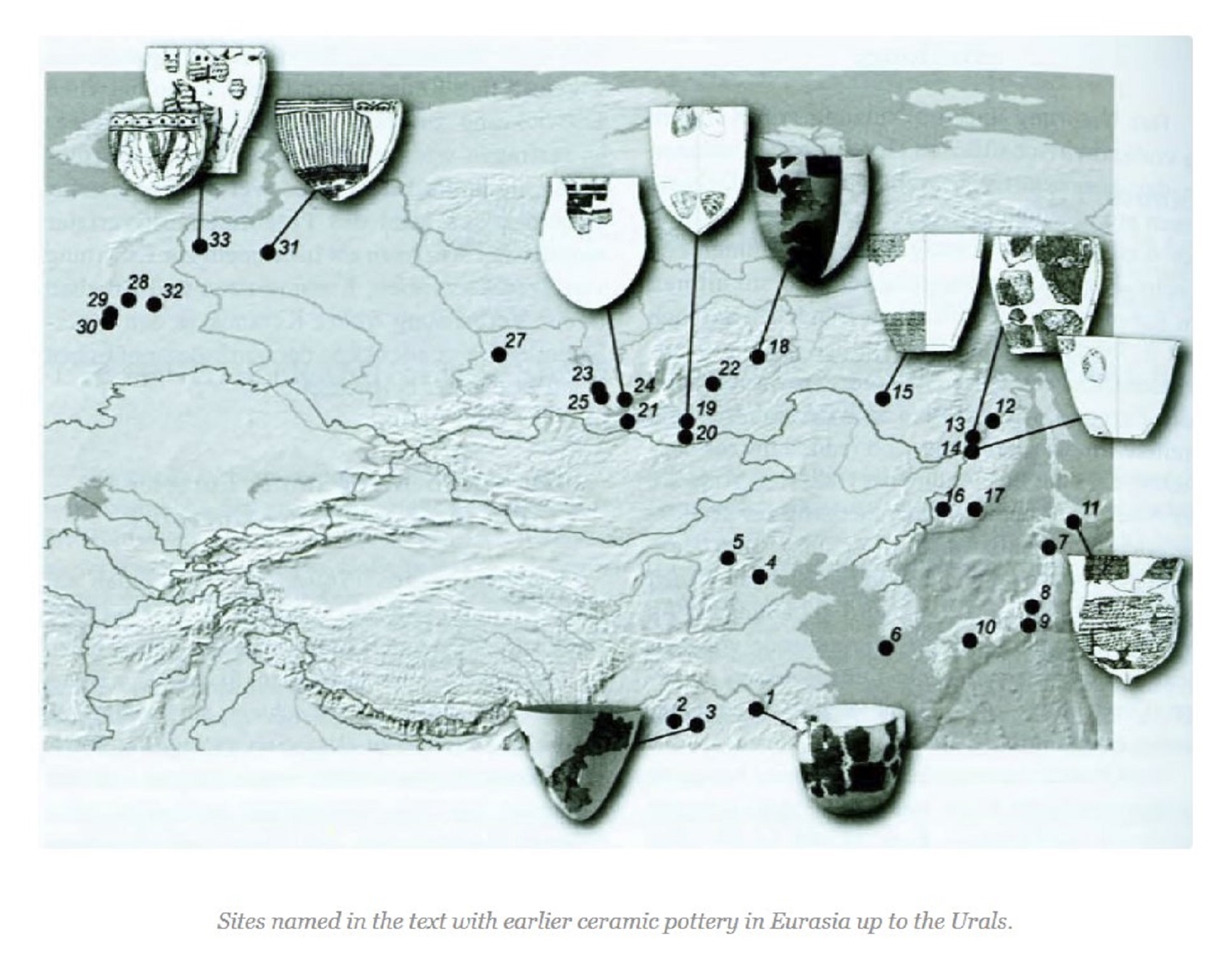
Pic ref
Globalization and the Emergence of Ceramic-using Hunter-gatherers in Northern Eurasia
“It is generally considered that Haplogroup (Y-DNA “Men”) N arose in East Asia approximately 19,400 (±4,800) years ago and populated northern Eurasia after the Last Glacial Maximum. Males carrying the marker apparently moved northwards from southern China, migrating in a counter-clockwise path, to eventually become concentrated in areas as far away as Finland-Scandinavia and the. It is suggested that Y-DNA N, reached southern Siberia from 12,000 -14,000 years ago. From there it reached southern Europe 8,000 -10,000 years ago. Haplogroup N forms two distinctive subclusters of Asian and European, the latter mostly distributed among Finno-Ugric-speaking peoples and related populations.” ref
Carbon Dating Catal Hoyuk Pottery 6700 to 5600 BCE or 8,722-7,672 years ago
“The site of Catal Hoyuk in Turkey, allows researchers to learn more about the origins of animal domestication. It could also reveal when changes in prehistoric diets, such as the adoption of dairy products, took place” ref, ref
Catal Hoyuk
“Catal Hoyuk in Turkey was a very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-city settlement in southern Anatolia/Turkey, which existed from approximately 7500 to 6400 BCE, and flourished around 7000 BCE. As a part of ritual life, the people of Çatalhöyük buried their dead within the village. Human remains have been found in pits beneath the floors and, especially, beneath hearths, the platforms within the main rooms, and under beds. Disarticulated bones in some graves suggest that bodies may have been exposed in the open air (Sky Burials) for a time before the bones were gathered and buried.” ref
“In some cases, graves were disturbed, and the individual’s head was removed from the skeleton. These heads may have been used in rituals, as some were found in other areas of the community. In a woman’s grave, spinning whorls were recovered, and in a man’s grave, stone axes. Some skulls were plastered and painted with ochre to recreate faces, a custom more characteristic of Neolithic sites in Syria and at Neolithic Jericho than at sites closer by.” ref
“All individuals tested from Catal Hoyuk in Turkey were assigned to different mtDNA lineages, present in ancient neighboring Neolithic and Chalcolithic populations and common among modern-day Eurasian populations. Three individuals were assigned to X, Haplogroup N, and W lineages.” ref
“The early Neolithic (Linear Pottery culture) in Europe featured burials of women and children under the floors of personal residences. Remains of adult males are missing. Probably, Neolithic culture featured sex discrimination in funerary customs, and women and children were important in ideology concerning the home. Burials beneath the floors of homes continued until about 4000 BCE.” ref
Linear Pottery Culture Violence
“Investigation of the Neolithic skeletons found in the Talheim Death Pit suggests that prehistoric men from neighboring tribes were prepared to fight and kill each other in order to capture and secure women. The mass grave at Talheim in southern Germany is one of the earliest known sites in the archaeological record that shows evidence of organized violence in Early Neolithic Europe, among various LBK tribes.” ref
Talheim Death Pit
“The Talheim Death Pit, was a mass grave found in a Linear Pottery Culture settlement, also known as a Linearbandkeramik (LBK) culture. It dates back to about 5000 BCE or 7,022 years ago. The pit takes its name from its site in Talheim, Germany. The pit contained the remains of 34 bodies and evidence points toward the first signs of organized violence in Early Neolithic Europe. Warfare is thought to have been more prevalent in primitive, ungoverned regions than in civilized states. The massacre at Talheim supports this idea by giving evidence of habitual warfare between Linear Pottery culture settlements. It is most likely that the violence occurred among Linear Pottery culture populations since the head wounds indicate the use of weapons from Linear Pottery cultures and all skeletons found to resemble those of Linear Pottery culture settlers.” ref
Mass burial at Schletz-Asparn
“The mass grave near Schletz, part of Asparn an der Zaya, was located about 33 kilometres (roughly 20 miles) to the north of Vienna, Austria, and dates back about 7,500 years ago. Schletz, just like the Talheim death pit, is one of the earliest known sites in the archaeological record that shows proof of genocide in Early Neolithic Europe, among various Linear Pottery culture tribes. The site was not entirely excavated, but it is estimated that the entire ditch could contain up to 300 individuals. The remains of 67 people have been uncovered, all showing multiple points of trauma. Scientists have concluded that these people were also victims of genocide. Since the weapons used were characteristic of Linear Pottery culture peoples, the attackers are believed to be members of other Linear Pottery culture tribes. In similar proportions to those found at Talheim, fewer young women were found than men at Schletz. Because of this scarcity of young women among the dead, it is possible that other women of the defeated group were kidnapped by the attackers. The site was enclosed, or fortified, which serves as evidence of violent conflict among tribes and means that these fortifications were built as a form of defense against aggressors. The people who lived there had built two ditches to counter the menace of other Linear Pottery culture communities.” ref
Mass burial at Herxheim
Main article: Herxheim (archaeological site)
“Another Early Neolithic mass grave was found at Herxheim, near Landau in the Rhineland-Palatinate dates from between 5300 and 4950 BCE or 7,322 years ago. The site, unlike the mass burials at Talheim and Schletz, serves as proof of ritual cannibalism rather than of the first signs of violence in Europe. Herxheim contained 173 skulls and skull-plates, and the scattered remains of at least 450 individuals. Two complete skeletons were found inside the inner ditch. The crania from these bodies were discovered at regular intervals in the two defensive ditches surrounding the site. After the victims were decapitated, their heads were either thrown into the ditch or placed on top of posts that later collapsed inside the ditch. The heads showed signs of trauma from axes and one other weapon. Moreover, the organized placing of the skulls suggests a recurrent ritual act, instead of a single instance. Herxheim also contained various high-quality pottery artifacts and animal bones associated with the human remains. Unlike the mass burial at Talheim, scientists have concluded that instead of being a fortification, Herxheim was an enclosed center for ritual.” ref
Mass burial at Schöneck-Kilianstädten
“This Neolithic mass grave, also in modern-day Germany, may exhibit signs of deliberate mutilation and/or torture. Skeletal analysis of the interred remains showed a remarkably high percentage of long bones (especially in the lower leg) that were broken around the time of the individuals’ deaths, which insinuates a deliberate targeting of these areas of the body, possibly as the victims were still alive. The mass grave dates to 5207–4849 BCE or 7,229-6,851 years ago and has been referred to as “indisputable evidence for another massacre.” ref

Something Weird Happened to Men 7,000 Years Ago, And We Finally Know Why
“Around 7,000 years ago – all the way back in the Neolithic – something really peculiar happened to human genetic diversity. Over the next 2,000 years, and seen across Africa, Europe, and Asia, the genetic diversity of the Y chromosome collapsed, becoming as though there was only one man for every 17 women.” ref
“Now, through computer modeling, researchers believe they have found the cause of this mysterious phenomenon: fighting between patrilineal clans. Drops in genetic diversity among humans are not unheard of, inferred based on genetic patterns in modern humans. But these usually affect entire populations, probably as the result of a disaster or other event that shrinks the population and therefore the gene pool.” ref
“But the Neolithic Y-chromosome bottleneck, as it is known, has been something of a puzzle since its discovery in 2015. This is because it was only observed on the genes on the Y chromosome that get passed down from father to son – which means it only affected men.” ref
“This points to a social, rather than an environmental, cause, and given the social restructures between 12,000 and 8,000 years ago as humans shifted to more agrarian cultures with patrilineal structures, this may have had something to do with it. In fact, a drop in genetic diversity doesn’t mean that there was necessarily a drop in population. The number of men could very well have stayed the same, while the pool of men who produced offspring declined.” ref
Why Do Genes Suggest Most Men Died Off 7,000 Years Ago?
“Modern men’s genes suggest that something peculiar happened 5,000 to 7,000 years ago: Most of the male population across Asia, Europe, and Africa seems to have died off, leaving behind just one man for every 17 women.” ref
“This so-called population “bottleneck” was first proposed in 2015, and since then, researchers have been trying to figure out what could’ve caused it. One hypothesis held that the drop-off in the male population occurred due to ecological or climatic factors that mainly affected male offspring, while another idea suggested that the die-off happened because some males had more power in society, and thus produced more children.” ref
“Now, a new paper, published May 25 in the journal Nature Communications, offers yet another explanation: People living in patrilineal clans (consisting of males from the same descent) might have fought with each other, wiping out entire male lineages at a time. [Image Gallery: Our Closest Human Ancestor]” ref
“That ratio of 17 females for every one male “struck us as being very extreme, and there must be another explanation,” said senior study author Marcus Feldman, a population geneticist at Stanford University in California. According to their new explanation, the male population didn’t take a nosedive, but rather the diversity of the Y chromosome decreased due to the way people lived and fought with each other. In other words, there weren’t actually fewer males, just less diversity among the males.” ref
“Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes that carry most of our genes. Of these, the 23rd pair is what determines our sex: Whereas females have two X chromosomes, males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.” ref
“Because offspring inherit one chromosome from each parent, genes usually get shuffled around, increasing the diversity across species. But the Y chromosome, having no female counterpart, doesn’t get shuffled, so it stays pretty much the same from grandfather to father to son (save for any mutations that occur, which explains why the Y chromosome does differ among males).” ref
War might’ve caused the Y chromosome bottleneck
“To test their theory, the researchers conducted 18 simulations in which they created different scenarios for the bottleneck that included factors such as Y chromosome mutations, competition between groups, and death. Their simulations showed that warfare between patrilineal clans could have caused this so-called “Y chromosome bottleneck,” because the members of each patrilineal clan would have very similar Y chromosomes to each other. So, if one clan killed off another, it would also slash the chance of that family’s Y chromosome moving on to offspring.” ref
“In the researchers’ simulations in which patrilineal clans didn’t exist, however, the bottleneck didn’t occur.” ref
“What’s more, there was no such bottleneck in the women of the time, as is shown by mitochondrial DNA — a type of DNA that’s passed down only from mother to child. “In that same group, the women could have come from anywhere,” Feldman told Live Science. “They would’ve been brought into the group from either the victories that they had over other groups, or they could’ve been females who were residing in that area before.” ref
“As an example, he added, if you look at colonization throughout history, people generally “killed all the men and kept the women for themselves.” ref
“Monika Karmin, a population geneticist at the University of Tartu in Estonia who was not part of the new study, told Live Science that the “beauty of their study” is the way the researchers framed their hypothesis and demonstrated that “fighting clans are indeed likely to cause a drastic drop in male genetic diversity. [Gallery: Ancient Chinese Warriors Protect Secret Tomb]” ref
“However, we do have to keep in mind that there is very little information on the actual societal organization from that time,” said Karmin, who was the lead author of the 2015 study that first proposed the bottleneck. So, there could have been other “sociocultural” forces at play, she said.” ref
“The researchers did “careful computer simulations, whereas the previous papers had not,” said Chris Tyler-Smith, an evolutionary geneticist at the Sanger Institute in the United Kingdom who was not involved with the study. “The assumption that [the cause of the bottleneck] was warfare is a reasonable one,” especially given the time period, he added.” ref
“People were still living in small clans doing small-scale farming 5,000 to 7,000 years ago, a time right before people moved into larger societies and built large cities. It was a “transition between early farming using stone tools and later farming in societies using metal tools,” Tyler-Smith told Live Science.” ref
“But after this bottleneck, “you see the start of societal organizations and the shift from small-scale societies to having cities and organizations of people into groups that are not so intent on maintaining the Y chromosome lineage,” Feldman said. During this time, the male population bounced back, he added.” ref
“Normally, researchers focus on behavior that may have a genetic basis but not on behavior that influences genes, Feldman said. The new finding is “an example of what a cultural preference can do in changing the level of genetic variation.” ref
Northern Mesopotamia and Southern Mesopotamia
“While in the Paleolithic and early Neolithic periods only parts of Upper Mesopotamia or Northern Mesopotamia were occupied, the Southern Mesopotamia where the Sumerians emerge from was settled during the late Neolithic period or Pottery Neolithic age. Mesopotamia has been home to many of the oldest major civilizations, entering history from the Early Bronze Age, for which reason it is often called the cradle of civilization.” ref
“Sumer is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the first civilizations in the world, along with ancient Egypt, Elam, the Caral-Supe civilization, the Indus Valley civilisation, the Minoan civilization, and ancient China. Living along the valleys of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers, Sumerian farmers grew an abundance of grain and other crops, the surplus from which enabled them to form urban settlements. Proto-writing dates back before 3000 BCE or 5,022 years ago. The earliest texts come from the cities of Uruk and Jemdet Nasr, and date to between around 3500 to 3000 BCE.” ref
War in Ancient Mesopotamia
“If we decided to go back to a time period such as Ancient Mesopotamia, the time period from around 2900 to 2200 BCE, War was an enormous part of daily life in Ancient Mesopotamia. Much of the artifacts left behind from this time period are war-related. Nearly every civilization and king of the time believed in expansionism, which they justified by saying they were commanded by the gods to conquer cities, or the gods gave them cities (which they would have to take by force). This was a way of life — conquering and avoiding being conquered. It is easy to deduce these ideas from the written accounts, the iconography, and the excavated weaponry from Akkad and Sumer.” ref
Ancestor Worship
“Ancestor worship refers to rituals designed to commemorate and venerate the spirits of one’s deceased forebears. Ancestor worship crosses the boundaries of religious traditions, geographical regions, and socioeconomic groups.” ref
Tutelary Deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. Tutelary expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship.” ref
Household Deity
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world.” ref
Dog Sacrifice
“Sacrificing dogs to appease supernatural forces has been a part of religious traditions as different as those of ancient Greece, where the Spartans slaughtered dogs to ensure victory in battle, and Shang Dynasty China.” ref
“Ritual Sacrifice May Have Shaped Dog Domestication. An ancient Arctic site suggests a complex relationship between humans and canines.” ref
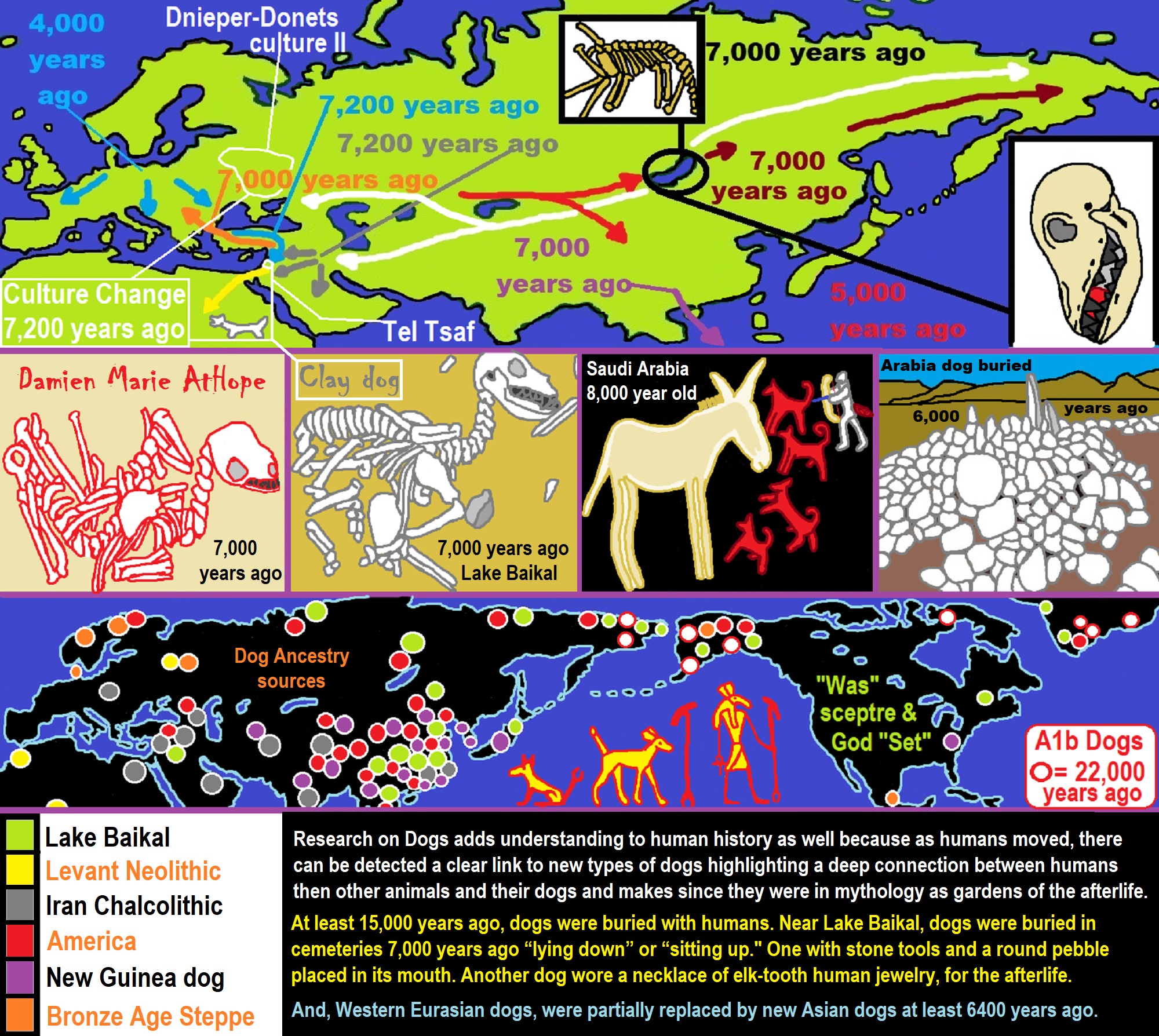
“Ancient dog burials in the Lake Baikal region of Eastern Siberia. Cemeteries first appear here ∼8000 years ago at the start of the Early Neolithic period, marked by the use of pottery (but not agriculture).” ref
“In Koryak (indigenous people of the Russian Far East) dog sacrifice, a pole is thrust under the dog’s lower jaw so that its muzzle points up to the sky, Dogs sacrificed to the village guardian are sometimes hung up on the guardian totem itself.” ref
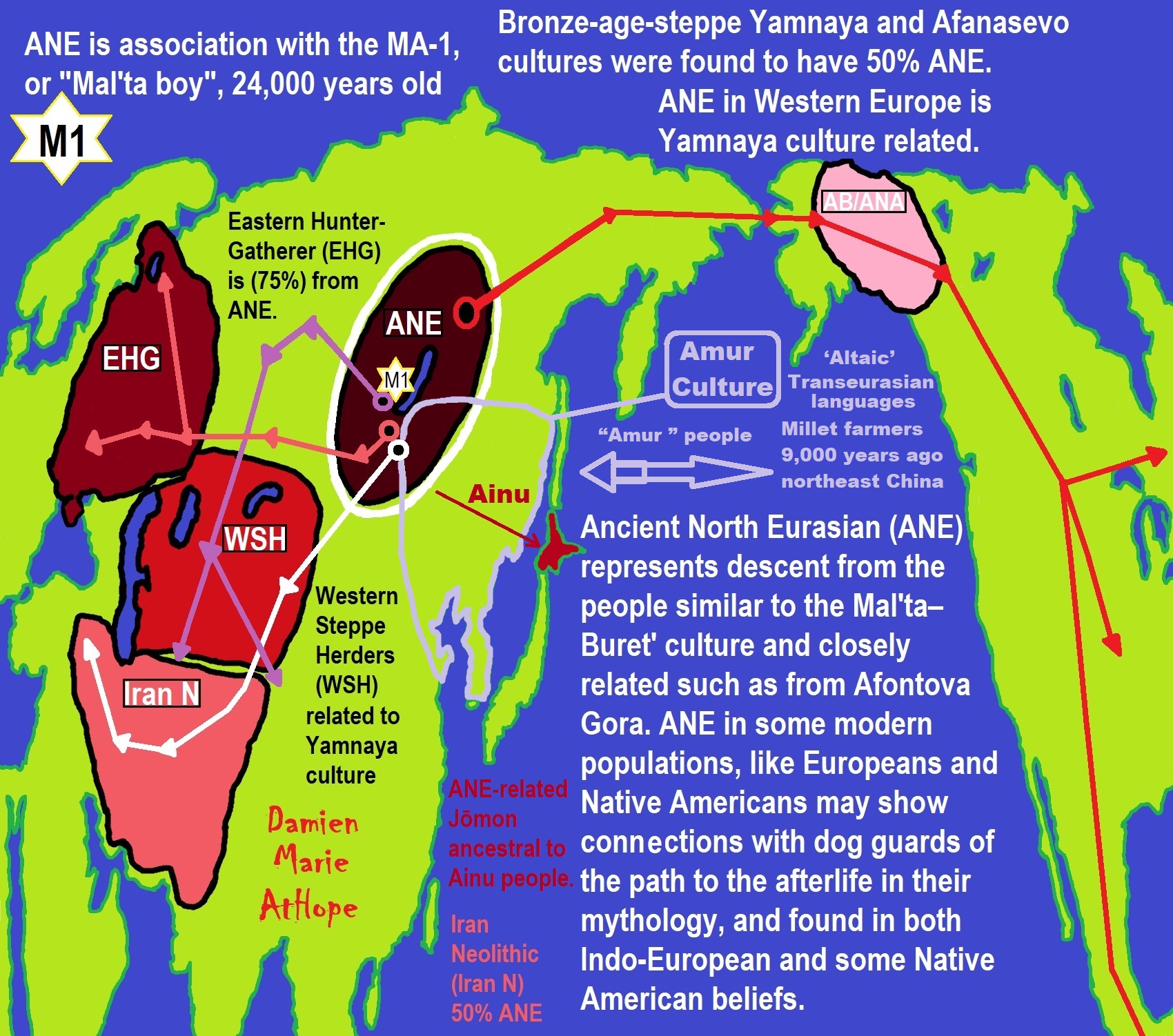
Ancient North Eurasians and Dog Sacrifice Mythology
“Ancient North Eurasian, refers to a genetic bridge of connected mating networks; scholars of comparative mythology have argued that they probably shared myths and beliefs that could be reconstructed via the comparison of stories attested within cultures that were not in contact for millennia and stretched from the Pontic–Caspian steppe to the American continent.” ref
“For instance, the mytheme of the dog guarding the Otherworld possibly stems from an older Ancient North Eurasian belief, as suggested by similar motifs found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian mythology. In Siouan, Algonquian, Iroquoian, and in Central and South American beliefs, a fierce guard dog was located in the Milky Way, perceived as the path of souls in the afterlife, and getting past it was a test. The Siberian Chukchi and Tungus believed in a guardian-of-the-afterlife dog and a spirit dog that would absorb the dead man’s soul and act as a guide in the afterlife. In Indo-European myths, the figure of the dog is embodied by Cerberus, Sarvarā, and Garmr. Anthony and Brown note that it might be one of the oldest mythemes recoverable through comparative mythology.” ref
“A second canid-related series of beliefs, myths, and rituals connected dogs with healing rather than death. For instance, Ancient Near Eastern and Turkic–Kipchaq myths are prone to associate dogs with healing and generally categorized dogs as impure. A similar myth-pattern is assumed for the Eneolithic site of Botai in Kazakhstan, dated to 3500 BCE, which might represent the dog as an absorber of illness and guardian of the household against disease and evil. In Mesopotamia, the goddess Nintinugga, associated with healing, was accompanied or symbolized by dogs. Similar absorbent-puppy healing and sacrifice rituals were practiced in Greece and Italy, among the Hittites, again possibly influenced by Near Eastern traditions.” ref
Groups partially derived from the Ancient North Eurasians
“Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) is a lineage that derived significant ancestry from ANE, ranging between 9% to up to 75%, with the remaining ancestry from a group more closely related to, but distinct from, Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHGs). It is represented by two individuals from Karelia, one of Y-haplogroup R1a-M417, dated c. 8,400 years ago, the other of Y-haplogroup J, dated c. 7,200 years ago; and one individual from Samara, of Y-haplogroup R1b-P297, dated c. 7,600 years ago. After the end of the Last Glacial Maximum, the Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG) and EHG lineages merged in Eastern Europe, accounting for early presence of ANE-derived ancestry in Mesolithic Europe. Evidence suggests that as Ancient North Eurasians migrated West from Eastern Siberia, they absorbed Western Hunter-Gatherers and other West Eurasian populations as well.” ref
“Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG) is represented by several individuals buried at Motala, Sweden ca. 8,000 years ago. They were descended from Western Hunter-Gatherers who initially settled Scandinavia from the south, and later populations of EHG who entered Scandinavia from the north through the coast of Norway.” ref
“Ancient Beringian/Ancestral Native American are specific archaeogenetic lineages, based on the genome of an infant found at the Upward Sun River site (dubbed USR1), dated to 11,500 years ago. The AB lineage diverged from the Ancestral Native American (ANA) lineage about 20,000 years ago.” ref
“West Siberian Hunter-Gatherer (WSHG) are a specific archaeogenetic lineage, first reported in a genetic study published in Science in September 2019. WSGs were found to be of about 30% EHG ancestry, 50% ANE ancestry, and 20% to 38% East Asian ancestry.” ref
“Western Steppe Herders (WSH) is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent closely related to the Yamnaya culture of the Pontic–Caspian steppe. This ancestry is often referred to as Yamnaya ancestry or Steppe ancestry.” ref
“Late Upper Paeolithic Lake Baikal – Ust’Kyakhta-3 (UKY) 14,050-13,770 years ago were mixture of 30% ANE ancestry and 70% East Asian ancestry.” ref
“Lake Baikal Holocene – Baikal Eneolithic (Baikal_EN) and Baikal Early Bronze Age (Baikal_EBA) derived 6.4% to 20.1% ancestry from ANE, while rest of their ancestry was derived from East Asians. Fofonovo_EN near by Lake Baikal were mixture of 12-17% ANE ancestry and 83-87% East Asian ancestry.” ref
“Hokkaido Jōmon people specifically refers to the Jōmon period population of Hokkaido in northernmost Japan. Though the Jōmon people themselves descended mainly from East Asian lineages, one study found an affinity between Hokkaido Jōmon with the Northern Eurasian Yana sample (an ANE-related group, related to Mal’ta), and suggest as an explanation the possibility of minor Yana gene flow into the Hokkaido Jōmon population (as well as other possibilities). A more recent study by Cooke et al. 2021, confirmed ANE-related geneflow among the Jōmon people, partially ancestral to the Ainu people. ANE ancestry among Jōmon people is estimated at 21%, however, there is a North to South cline within the Japanese archipelago, with the highest amount of ANE ancestry in Hokkaido and Tohoku.” ref
Torii gate
“A torii is a traditional Japanese gate most commonly found at the entrance of or within a Shinto shrine, where it symbolically marks the transition from the mundane to the sacred. The torii, a gateway erected on the approach to every Shinto shrine, may be derived from the Indian word torana. While the Indian term denotes a gateway, the Japanese characters can be translated as “bird perch.” Ancient Indian torana sacred gateway architecture has influenced gateway architecture across Asia, especially where Buddhism was transmitted from India; Chinese paifang gateways, Japanese torii gateways, Korean Hongsalmun gateways, Vietnam Tam quan gateways, and Sao Ching Cha in Thailand have been derived from the Indian torana.” ref
“The functions of all are similar, but they generally differ based on their respective architectural styles. According to several scholars, the vast evidence shows how the torii, both etymologically and architecturally, were originally derived from the torana, a free-standing sacred ceremonial gateway which marks the entrance of a sacred enclosure, such as Hindu–Buddhist temple or shrine, or city. The origins of the torii are unknown, and there are several different theories on the subject, none of which has gained universal acceptance. Because the use of symbolic gates is widespread in Asia—such structures can be found for example, in India, China, Thailand, Korea, and within Nicobarese and Shompen villages—historians believe they may be an imported tradition.” ref
“Another hypothesis takes the name literally: the gate would originally have been some kind of bird perch. This is based on the religious use of bird perches in Asia, such as the Korean sotdae (솟대), which are poles with one or more wooden birds resting on their top. Commonly found in groups at the entrance of villages together with totem poles called jangseung, they are talismans that ward off evil spirits and bring the villagers good luck. “Bird perches” similar in form and function to the sotdae exist also in other shamanistic cultures in China, Mongolia, and Siberia. Although they do not look like torii and serve a different function, these “bird perches” show how birds in several Asian cultures are believed to have magic or spiritual properties, and may therefore help explain the enigmatic literal meaning of the torii’s name (“bird perch”).” ref
“Bird Perches,” I think, relate to older “Sky Burials”
“Sky burial (“bird-scattered”) is a funeral practice in which a human corpse is placed on a mountaintop to decompose while exposed to the elements or to be eaten by scavenging animals, especially carrion birds. It is a specific type of the general practice of excarnation. It is practiced in the Chinese provinces and autonomous regions of Tibet, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Inner Mongolia, as well as in Mongolia, Bhutan, and parts of India such as Sikkim and Zanskar. The locations of preparation and sky burial are understood in the Vajrayana Buddhist traditions as charnel grounds. Comparable practices are part of Zoroastrian burial practices where the deceased are exposed to the elements and scavenger birds on stone structures called Dakhma. Few such places remain operational today due to religious marginalization, urbanization, and the decimation of vulture populations. The majority of Tibetan people and many Mongols adhere to Vajrayana Buddhism, which teaches the transmigration of spirits.” ref
“The shaman is, above all, a connecting figure, bridging several worlds for his people, traveling between this world, the underworld, and the heavens. He transforms himself into an animal and talks with ghosts, the dead, the deities, and the ancestors. He dies and revives. He brings back knowledge from the shadow realm, thus linking his people to the spirits and places which were once mythically accessible to all.–anthropologist Barbara Meyerhoff” ref
“(4500–4000 BCE), Proto-Indo-European language, the common ancestor of Indo-European languages, relates to the Khvalynsk culture. 4500–4200 BCE, copper, exotic ornamental shells, and stone maces were exchanged from Varna, in the eastern Balkans, to Khvalynsk, near the Volga River in Russia. (3500–2500 BCE), in its dialectal period due to the spread of the Yamnaya horizon over a large area.” ref
Ps. This show and its post are the most complicated as it is all over the place trying to aid in understanding how it all started and then became Mesopotamian as people think of it as the so-called cradle of civilization which we say is the beginning of the oppression of statism.
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
My religious family had me believing my anarchism nature was some demonic possession when it has always been a call for freedom and equality.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
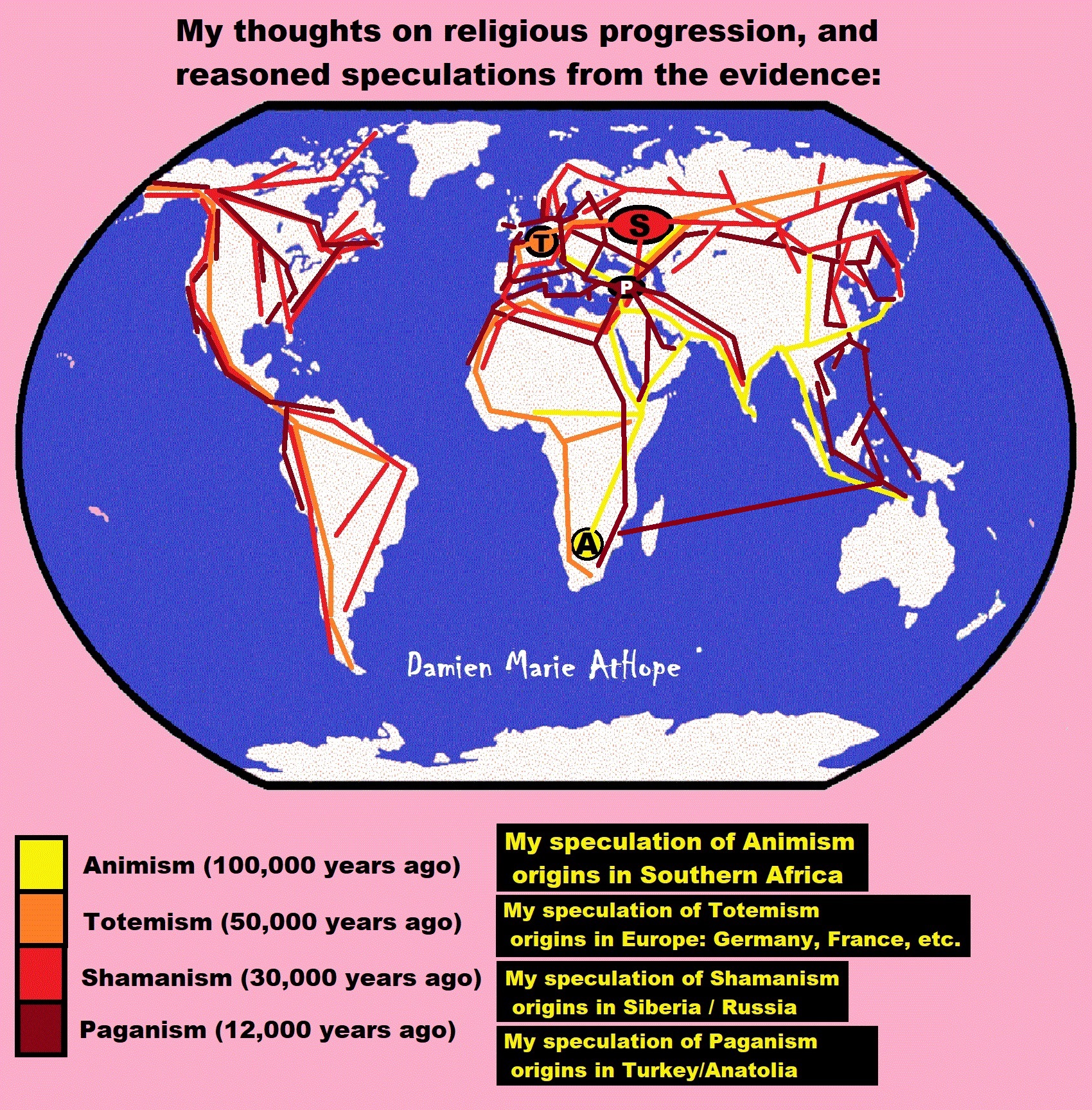
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
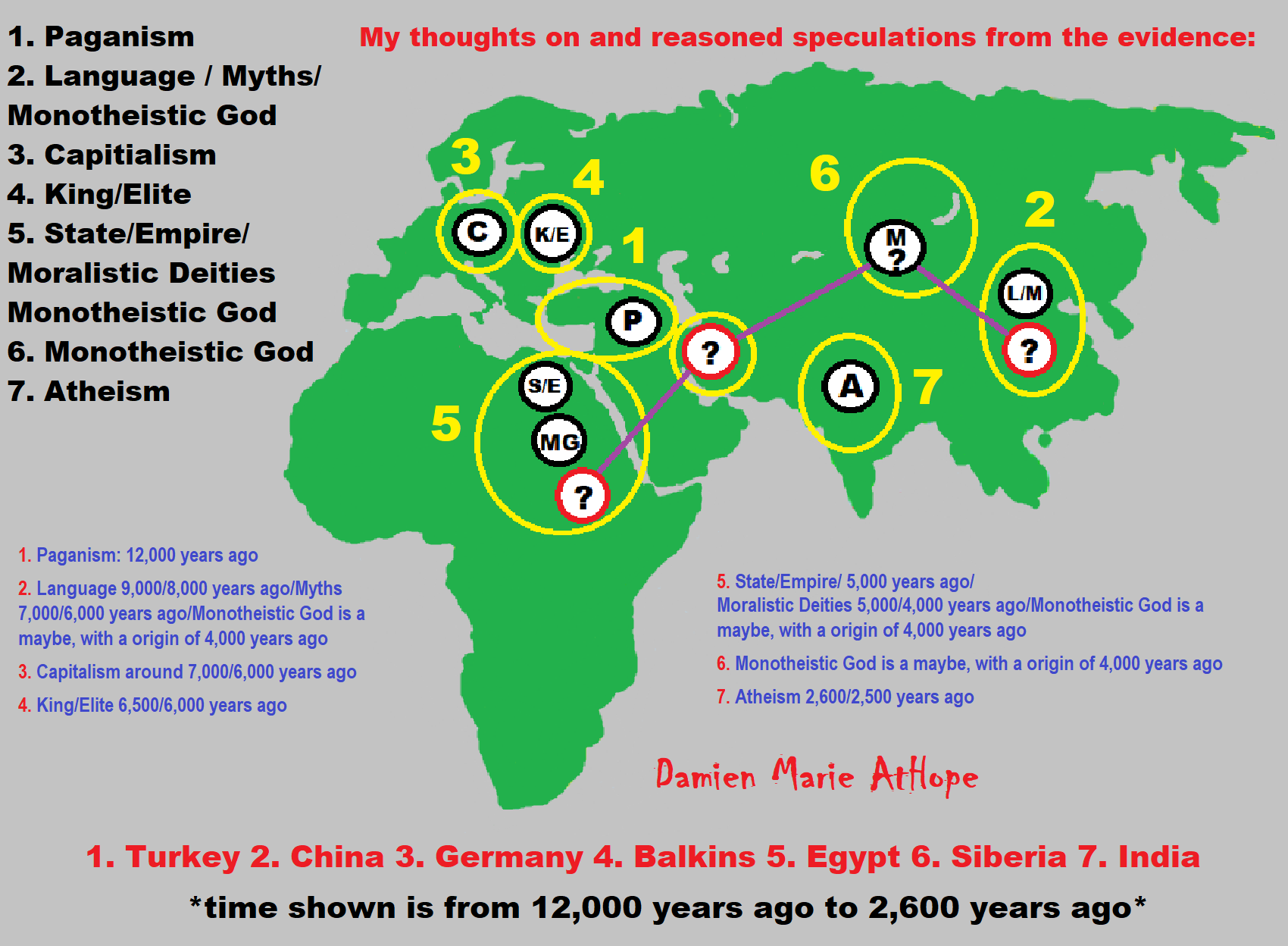
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
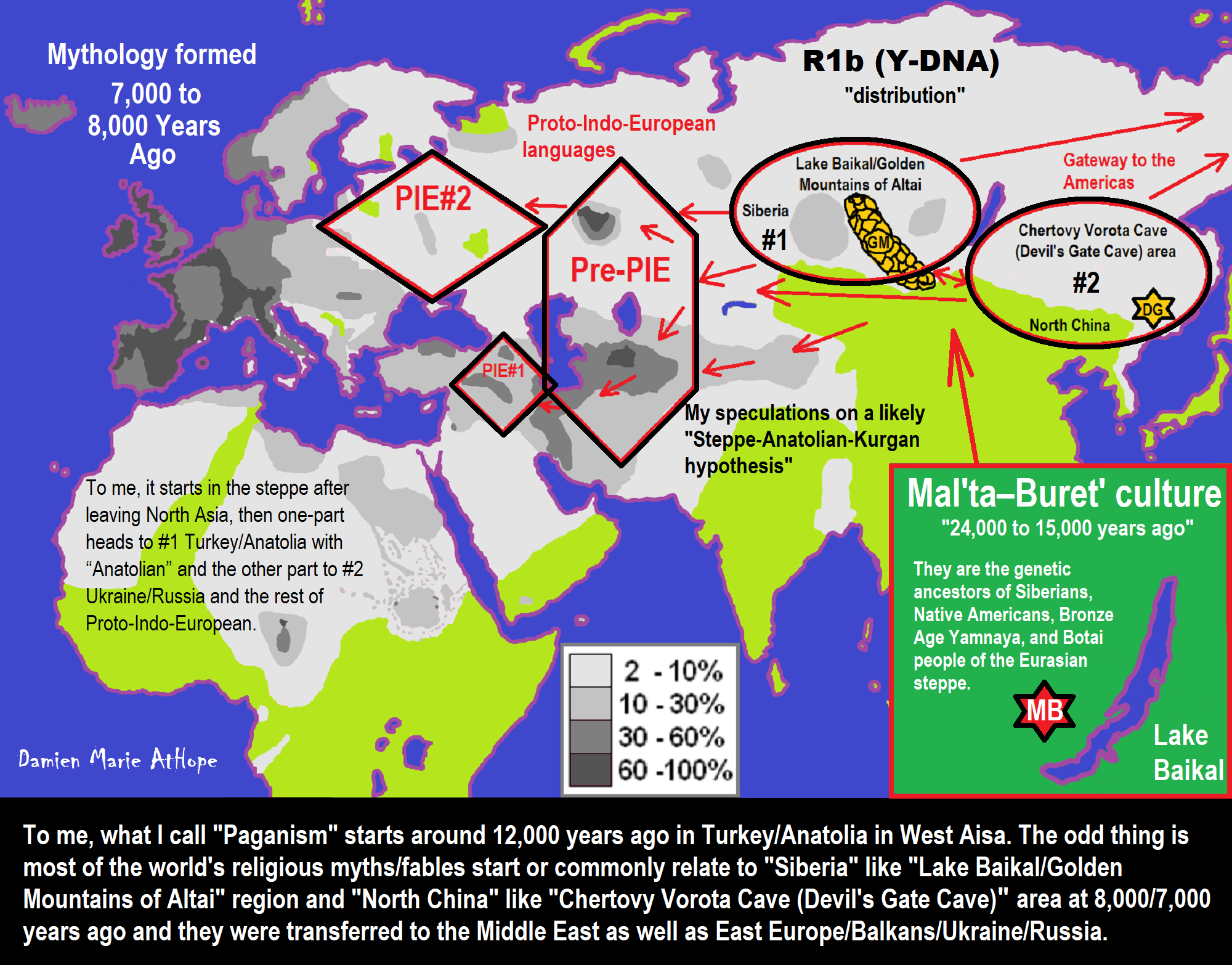
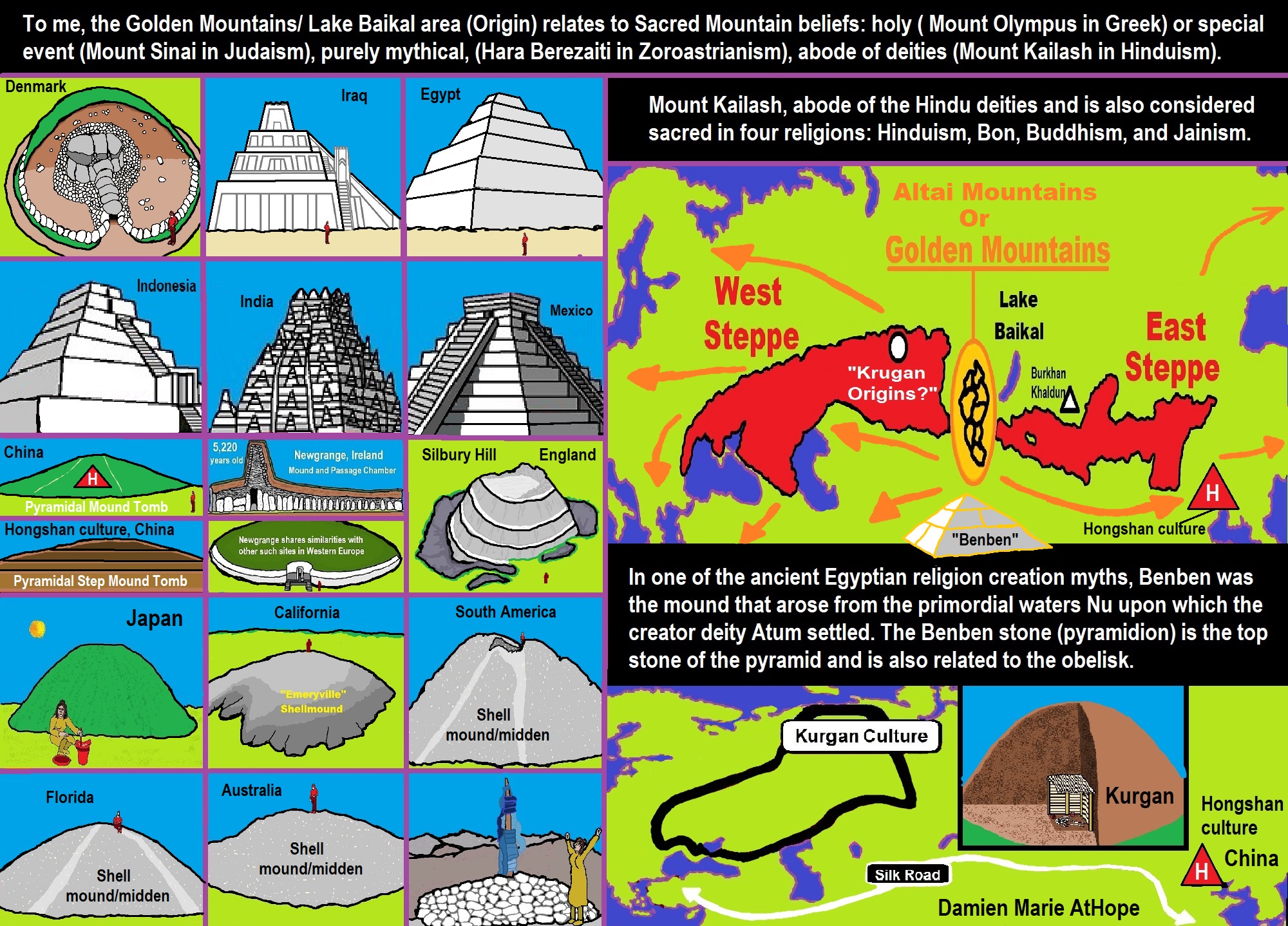
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
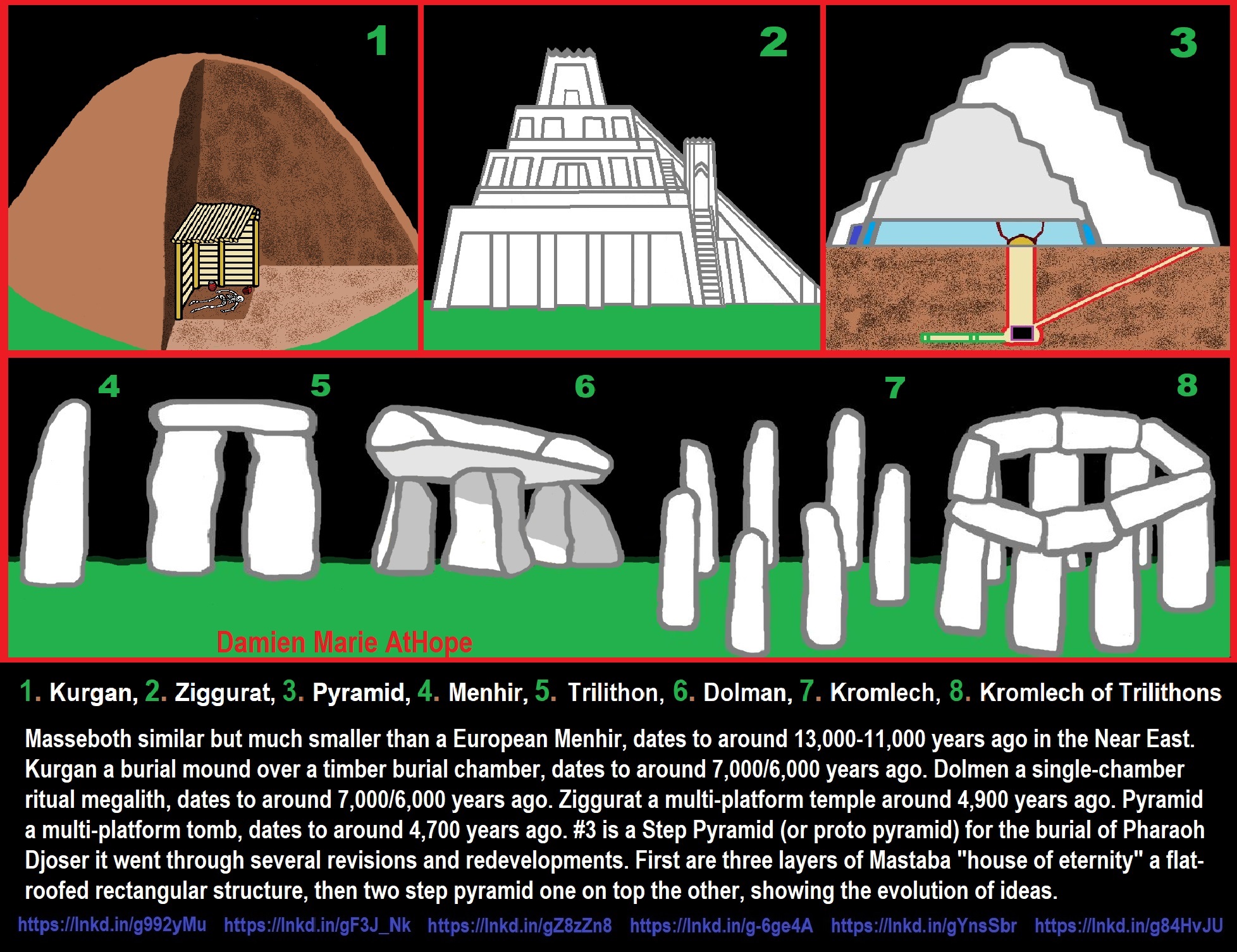
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
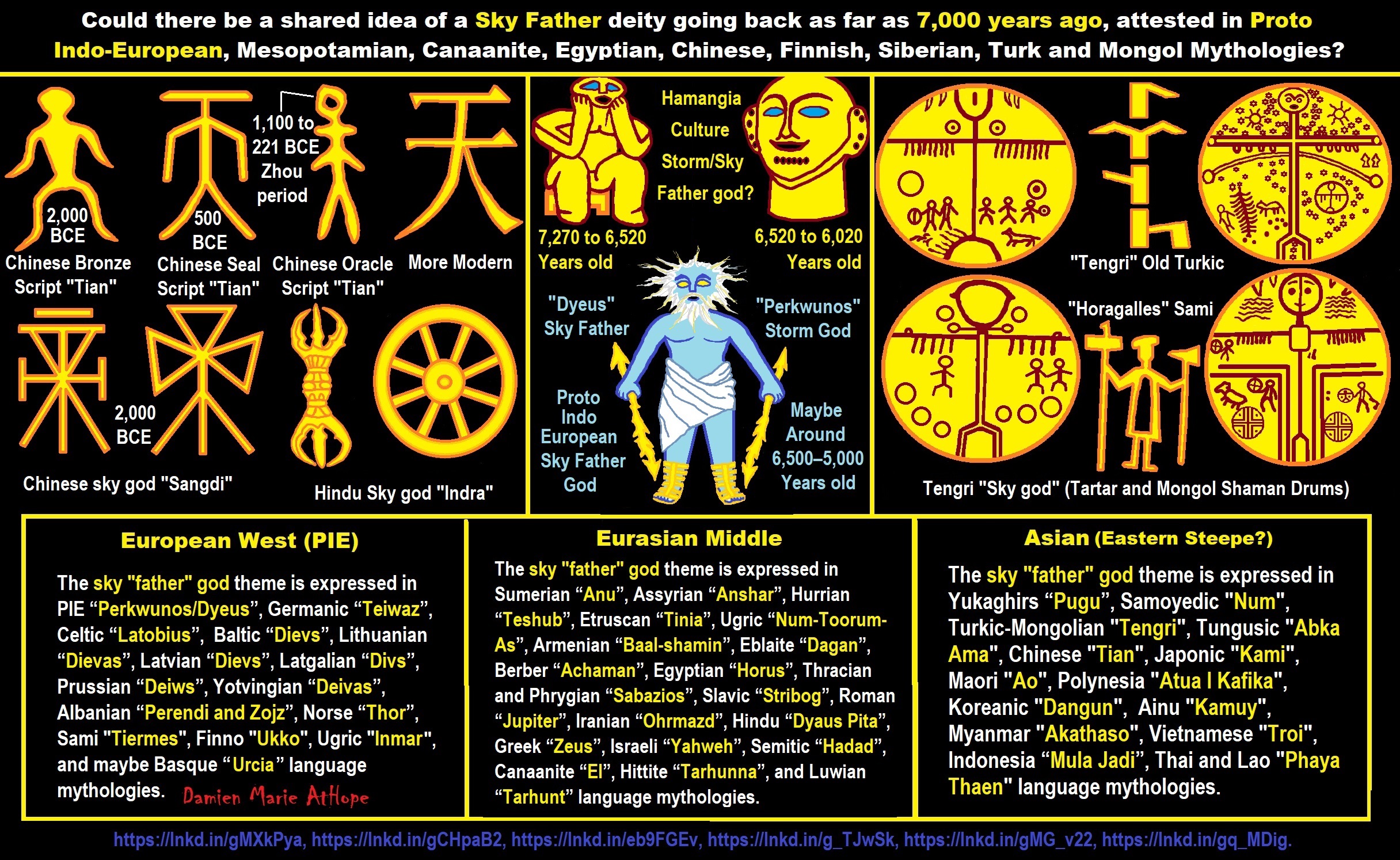
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
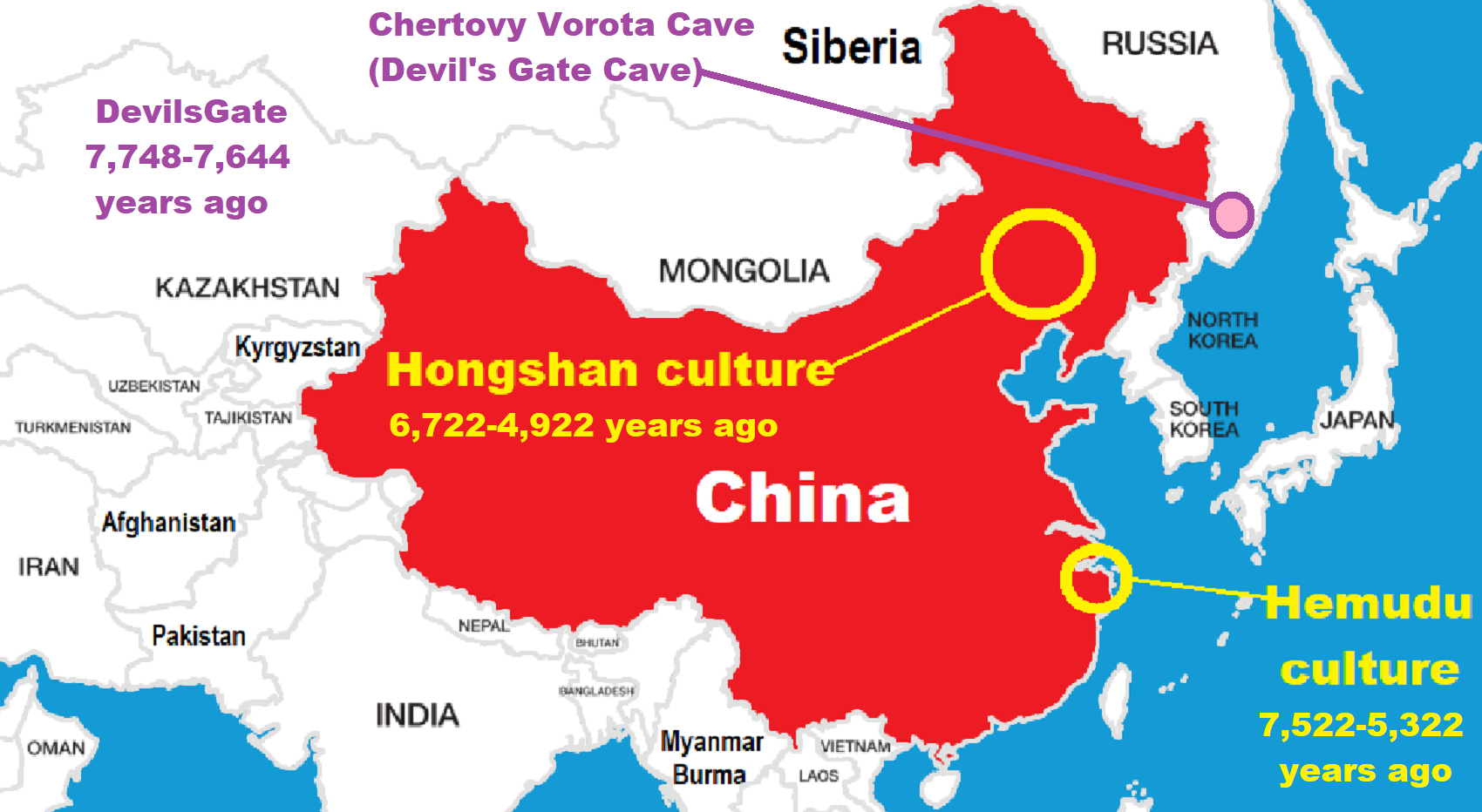
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
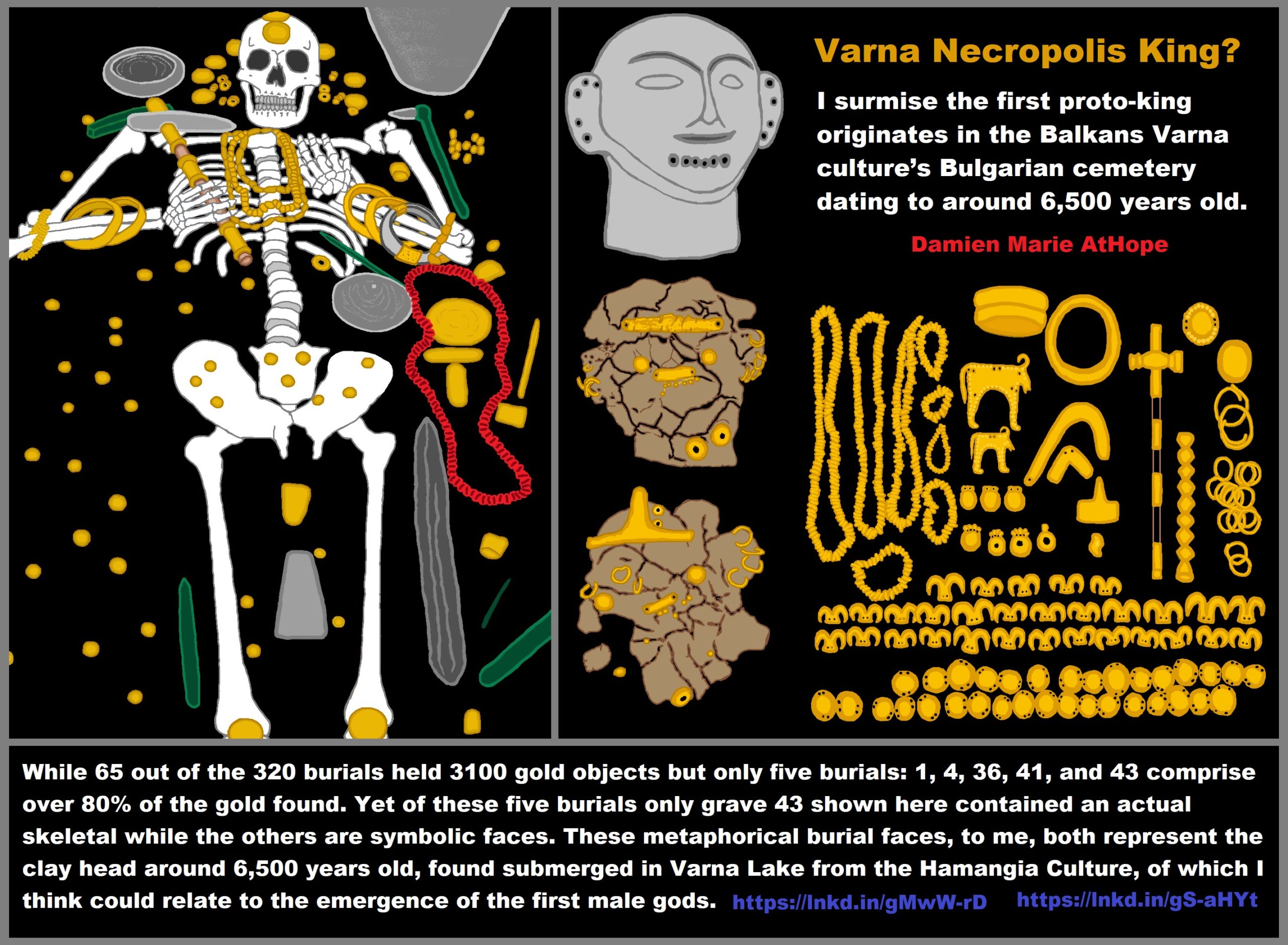
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
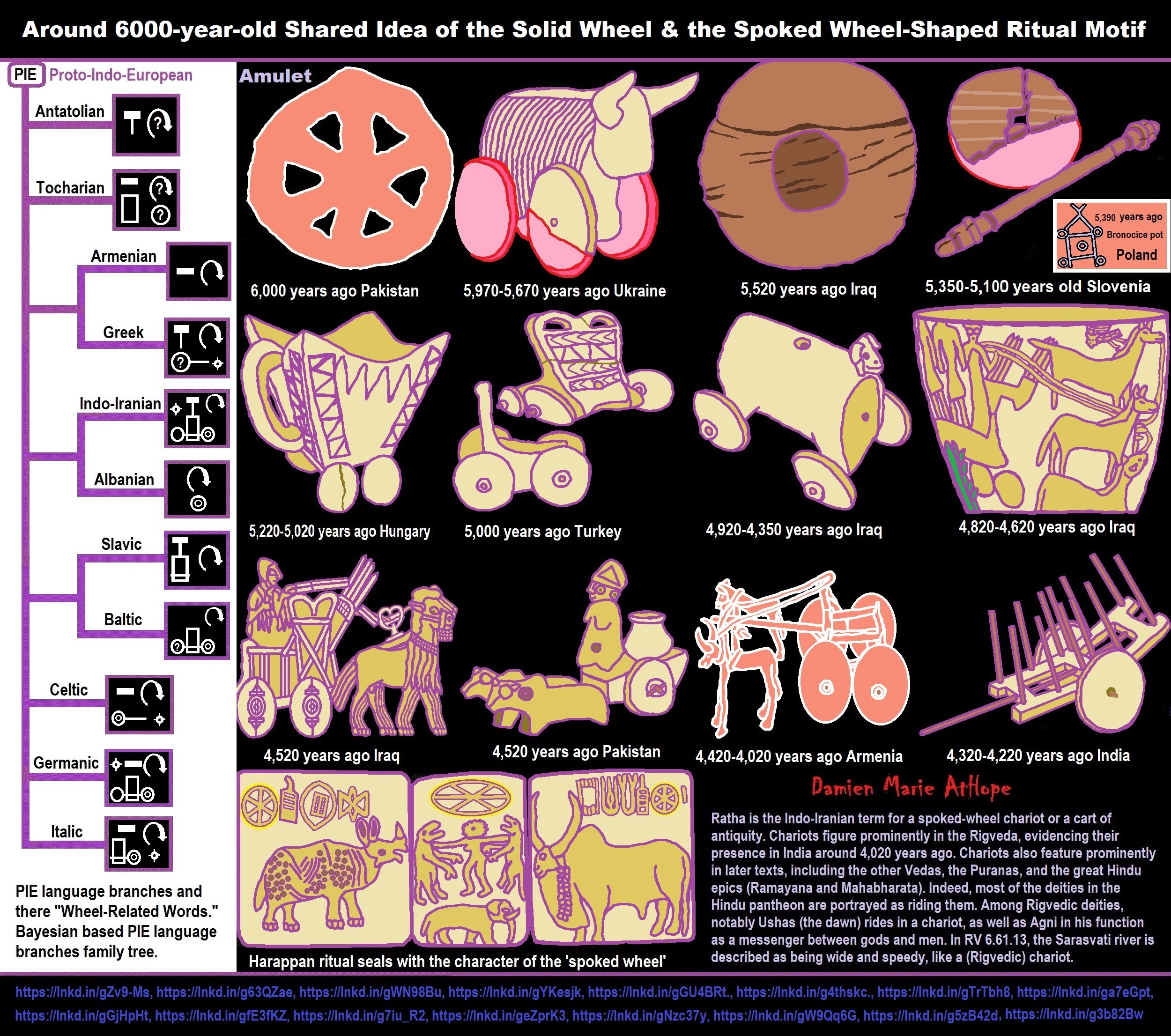
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
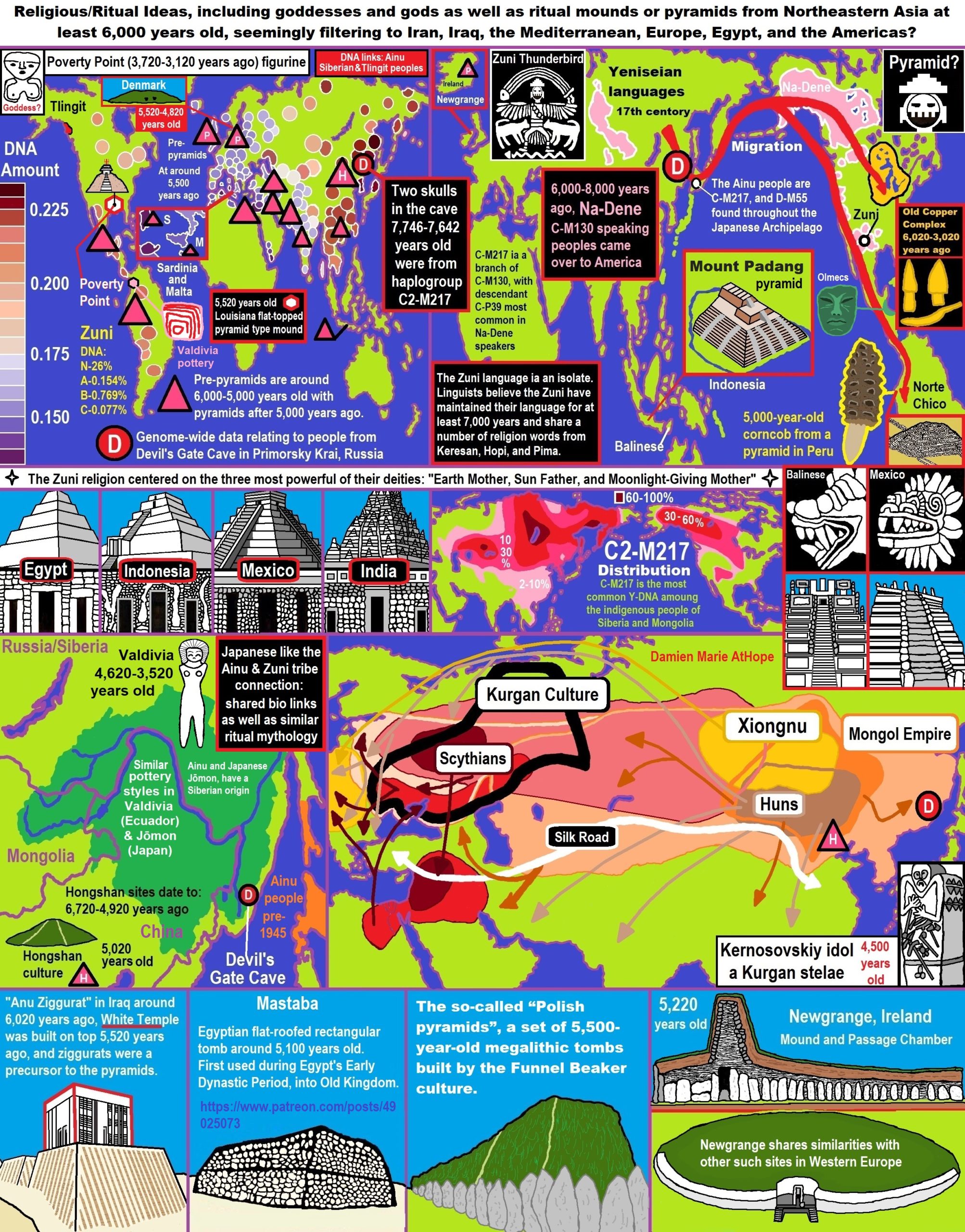
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
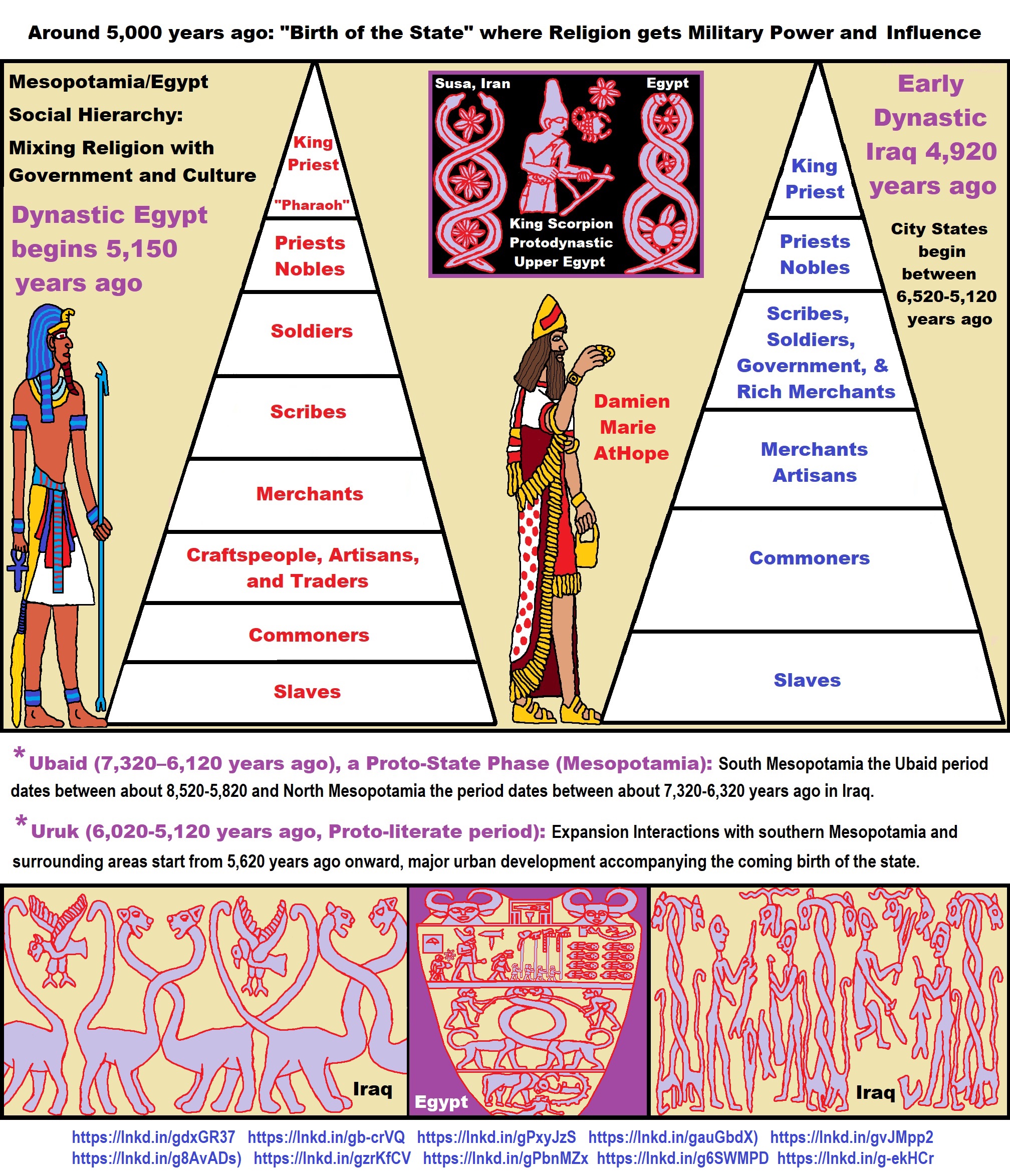
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.
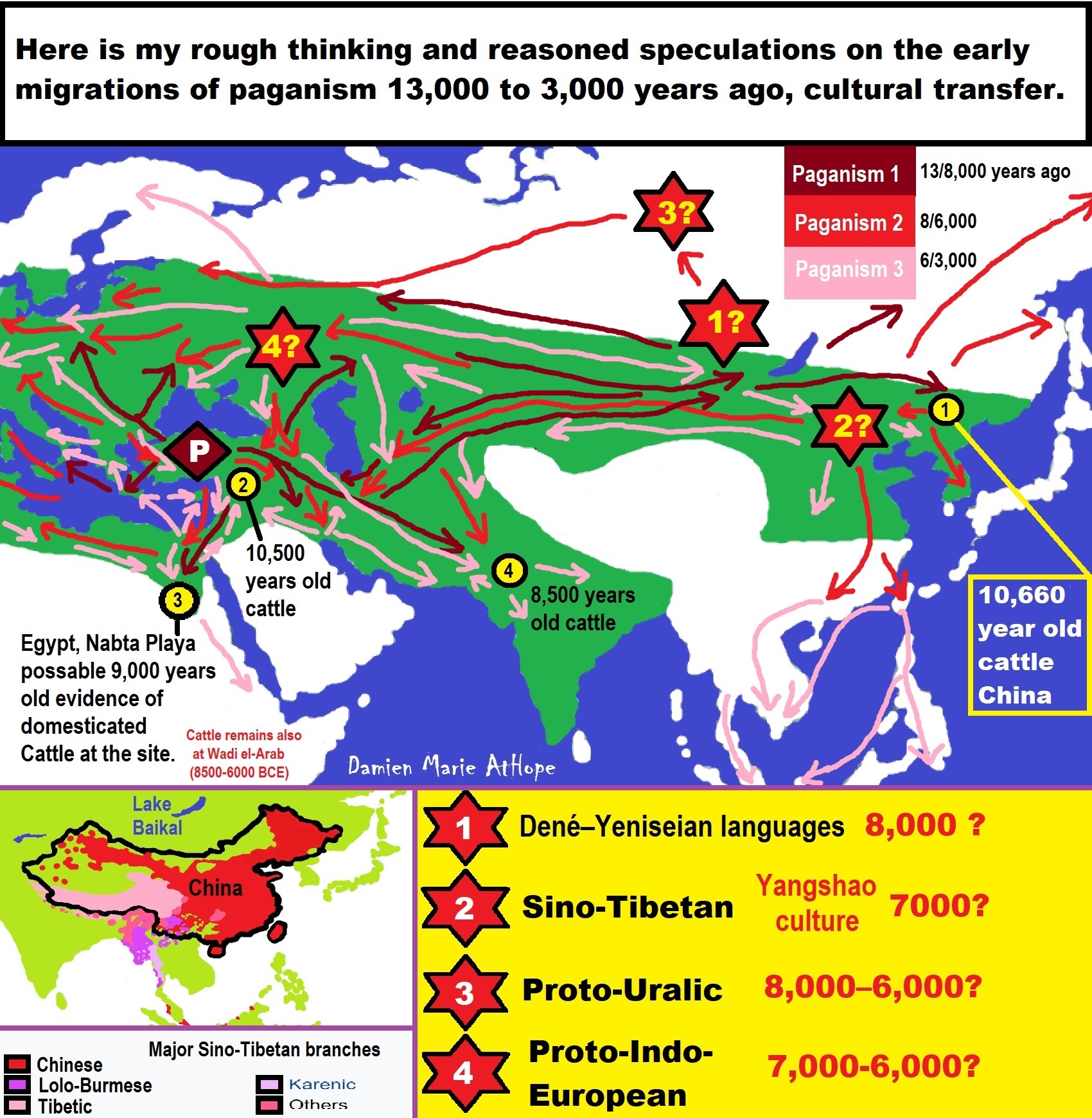

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
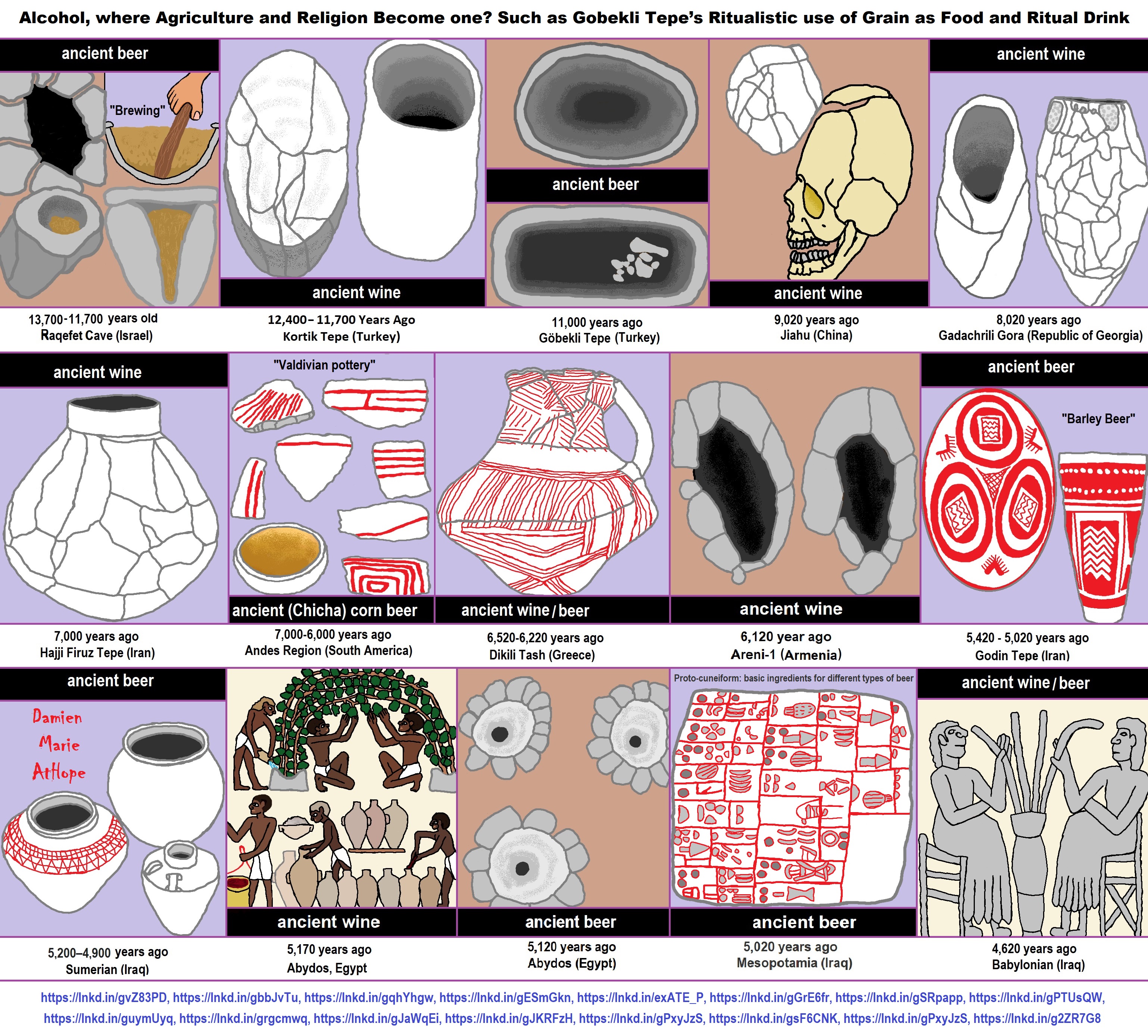
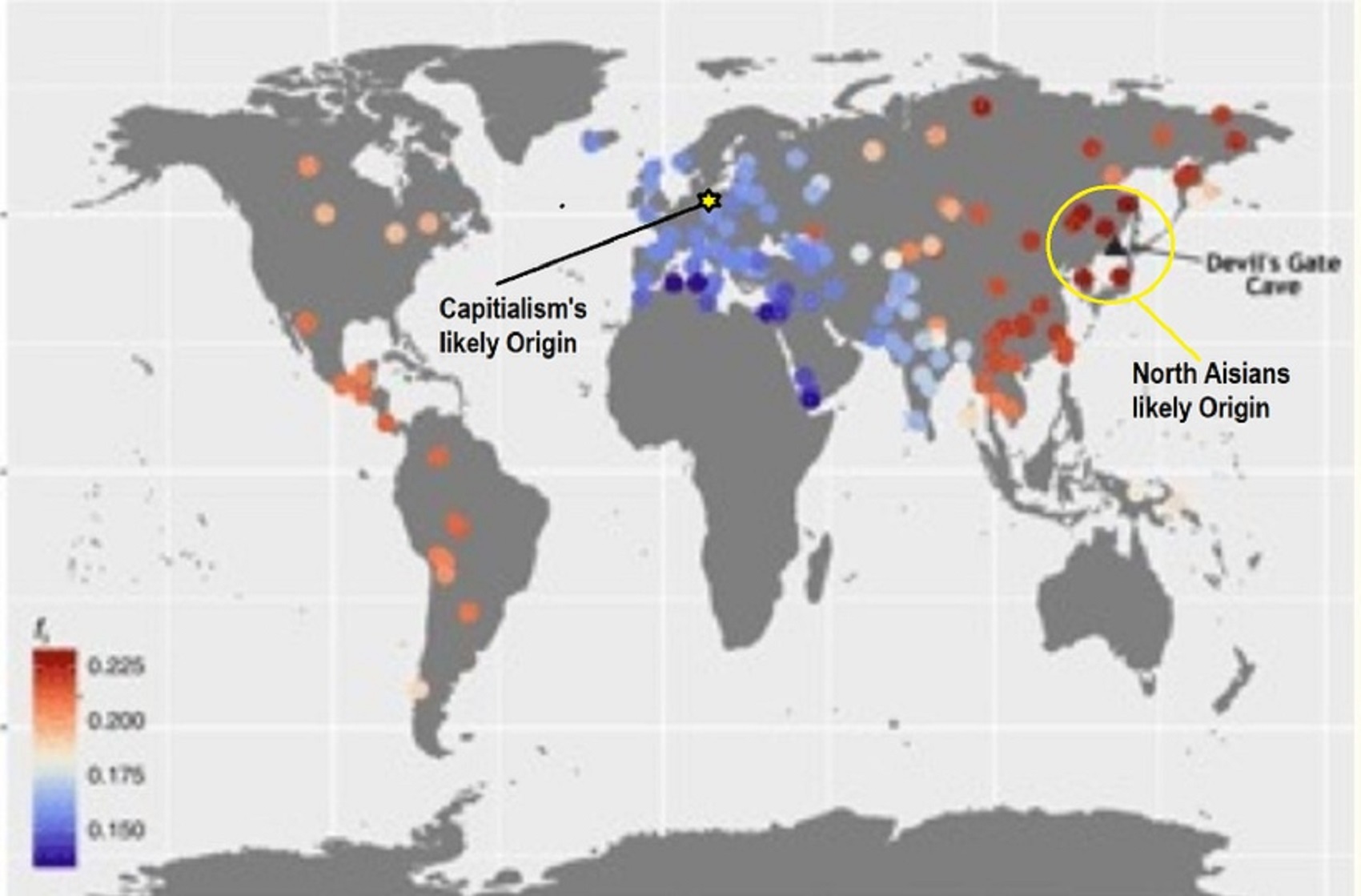
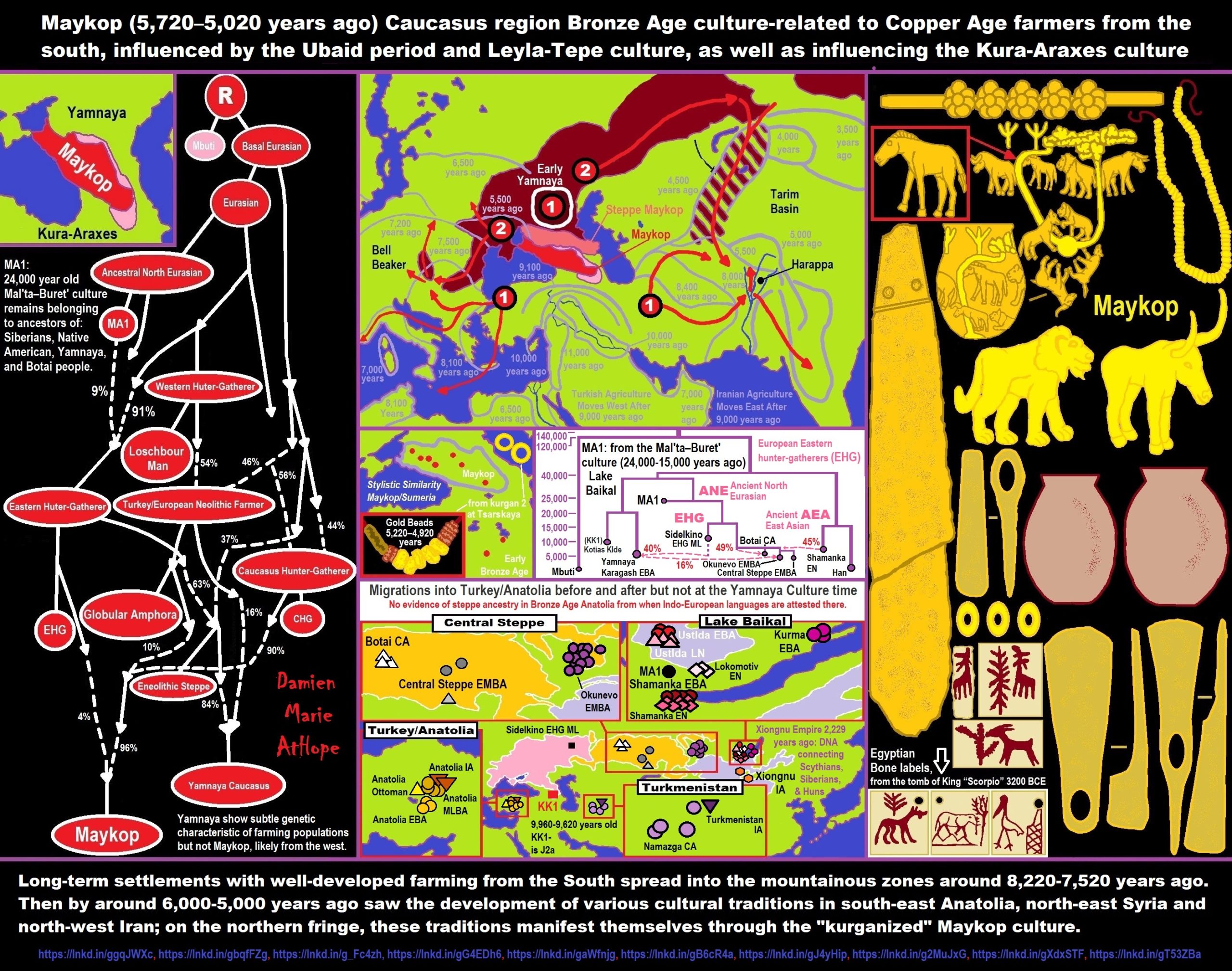
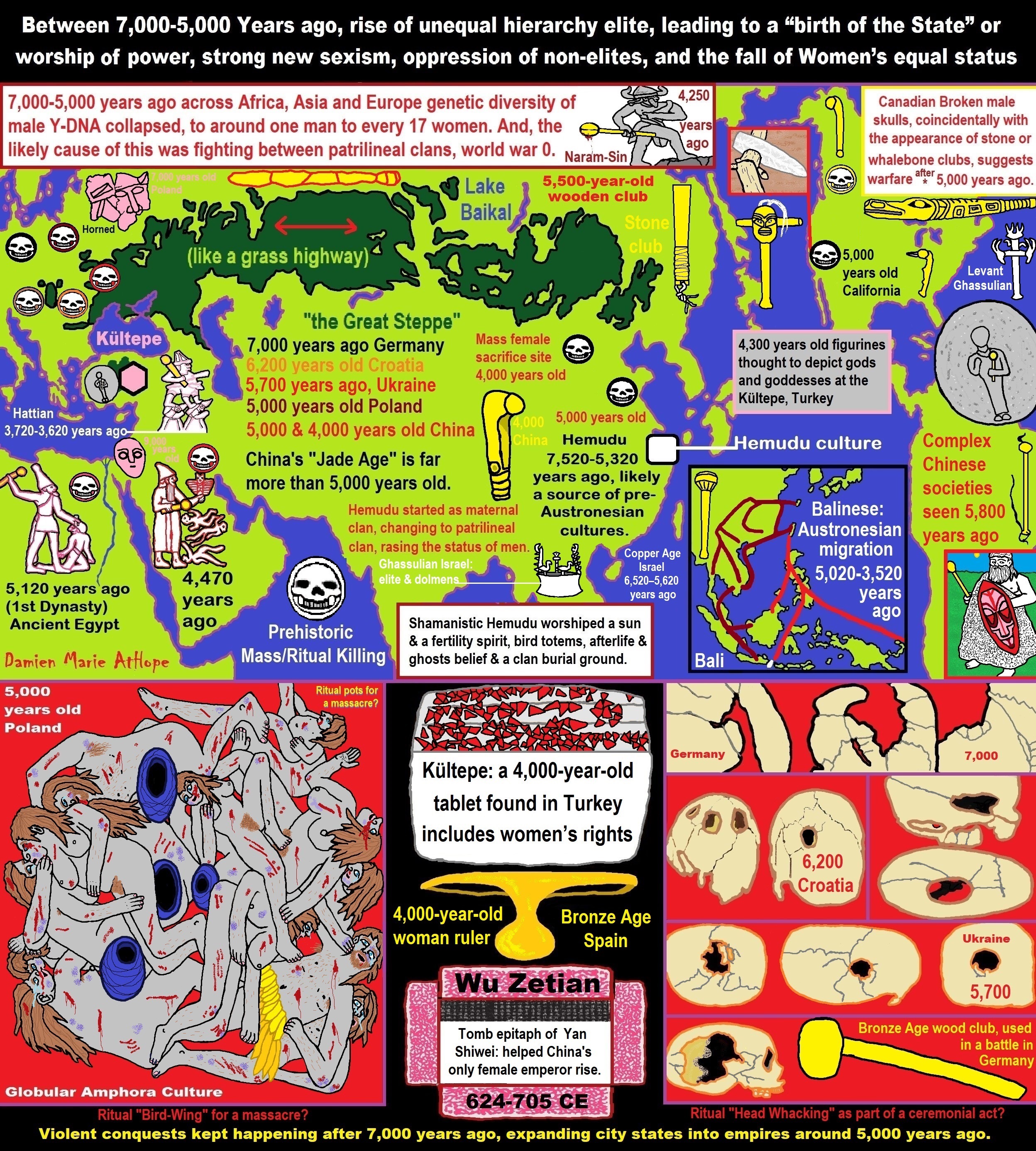
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
A First Male expression of a god?
I think so, and we see a lowering of the goddess that came before, as I believe, he now sits on her old birthing stool of power (sacred throne). To me, this represents the male and female duality and the first possible god sitting on a birthing stool to signify the male on the throne previously reserved only for women. I think the bent arms of both may possibly signify metaphoric “Bull Horns.” Part of the Hamangia culture (Romania and Bulgaria) between the Danube and the Black Sea and Muntenia in the south.
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
The Hamangia culture began around 7,250-7,200 years ago and lasted until around 6,550-6,500 years ago It was absorbed by the expanding Boian culture in its transition towards the Gumelnitsa. Its cultural links with Anatolia suggest that it was the result of a settlement by people from Anatolia, unlike the neighboring cultures, which appear descended from an earlier Neolithic settlement. ref
Goddess relating to the three realms: heaven, earth, and the underworld.
I surmise that there is an expression in goddess representation that relates to the three realms sky goddess with the upturned arms relating to the waxing crescent, the fat sitting goddess is a representation to the full moon and the arms turned down are a representation of the waning crescent. And it this way both up and down arms represent metaphorical bullhorns and why goddesses are associated with bulls or as bulls. Especially, with paganism.
My Thought on the Evolution of God?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Then Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago.
Several Kemetuic statuettes of goddesses with vulture-shaped heads and upraised arms are known from around 6,200-5,400 years ago. Ancient ivory amulet of a bearded man “phallus” from the Gerzeh culture. ref
The Colossus of Min Dynasty 0 (around 5,300 years ago). This big statue (in brown) is one of a pair found in the re-mains of the temple in Coptos in Upper Egypt. ref
Nagada, also known as Naqada, is the type site of the prehistoric Egyptian Amratian culture (“Naqada I”), Gerzeh culture (“Naqada II”), and Naqada III (“Dynasty 0”) predynastic cultures. Naqada existed before and during the union of Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, the Naqada III or “protodynastic” period. The process of unification apparently started from Nagada. ref

While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com