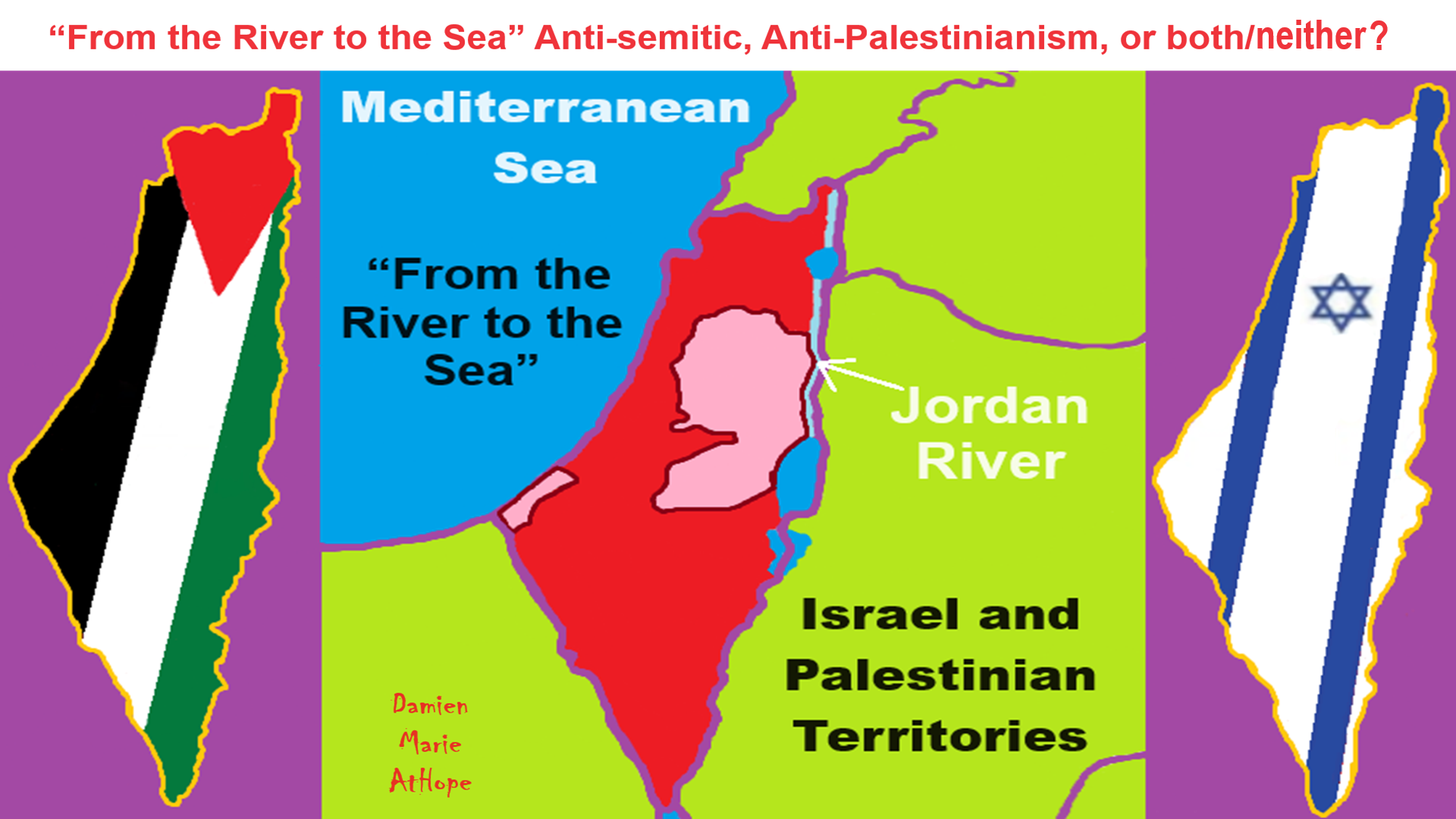
“From the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea“
‘From the river to the sea’: related to the Bible
Genesis 17:7-8 “I will establish my covenant as an everlasting covenant between me and you and your descendants after you for the generations to come, to be your God and the God of your descendants after you. The whole land of Canaan, where you now reside as a foreigner, I will give as an everlasting possession to you and your descendants after you; and I will be their God.”
Psalm 72:8 “He (king’s rule) shall have dominion also from sea to sea, and from the river unto the ends of the earth.”
Deuteronomy 11:24 “Every place where you set your foot will be yours: Your territory will extend from the desert to Lebanon, and from the Euphrates River to the Mediterranean Sea.”
Joshua 23:4 “Remember how I have allotted as an inheritance for your tribes all the land of the nations that remain—the nations I conquered—between the Jordan and the Mediterranean Sea in the west.”
The Land of Canaan (Heb. אֶרֶץ]כְּנַעַן ,כְּנָעַן]), was promised to the Israelites by God (e.g., Gen. 17:8; Ex. 6:4)
“The name “Canaan” appears throughout the Bible as a geography associated with the “Promised Land.” The demonym “Canaanites” serves as an ethnic catch-all term covering various indigenous populations—both settled and nomadic-pastoral groups—throughout the regions of the southern Levant or Canaan. It is by far the most frequently used ethnic term in the Bible. Biblical scholar Mark Smith, citing archaeological findings, suggests “that the Israelite culture largely overlapped with and derived from Canaanite culture… In short, Israelite culture was largely Canaanite in nature. Canaan was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region of the Southern Levant in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BCE) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni, and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur, and Gezer.” ref
“
“However, the mention of a Canaanite among other foreigners in a merchant list from Ugarit from around 1200 B.C.E. suggests, therefore, that at that time Ugarit was not considered a part of Canaan. According to the detailed description of the borders of the land of Canaan in Numbers 34:2–12, the southern border began at the southern tip of the Dead Sea and continued southwest to the ascent of Akrabbim and Kadesh-Barnea, reaching to the Brook of Egypt (probably Wadi El-Arish). On the west was the Mediterranean. The northern border started at the coast near a place known as Mount Hor and extended east to Lebo-Hamath, the present-day Labwa in the valley of Lebanon (the Biqāʿ), north of Baalbek (ancient Heliopolis).” ref
“From there, the border continued east to Zedad, the present-day Ṣadad, about 65½ miles (c. 100 km.) north-northeast of Damascus. The northeast corner of Canaan was marked by the settlements of Ziphronah and Hazar-Enan, identified today with Ḥawārīn and Qaryatayn, southeast of Ṣadad. The eastern boundary included the region of Damascus and the Hauran to the east and the Bashan and the Golan to the south, touching the southeast corner of the Sea of Galilee and continuing south along the Jordan River to the Dead Sea (cf. Ezek. 47:17–18). Neither Numbers 34 nor other biblical passages include Transjordan within the land of Canaan (Num. 33:51; 35:10; Josh. 22:10–11).” ref
“It is reasonable to assume that the political and demographic realities reflected broken in the boundaries of Canaan given in Numbers 34 are roughly similar to those existing at the time of Egyptian rule in Ereẓ Israel and Syria in the third quarter of the second millennium BCE. This area is given in one instance, in a and doubtful context, as [p-i?]-ḫati ša ki-na-ḫi, which would mean “the province (?) of Canaan.” According to certain biblical passages, the name Canaan applied to an area along the coast of the Mediterranean, including the important cities of Tyre and Sidon (e.g., Num. 13:29; Josh. 5:1; Isa. 23:11).” ref
“Canaan’s population was not homogeneous. The names of various peoples living in Canaan are given in Genesis 10:15–18. In some passages, the Canaanites are only one of several peoples settled in the land allocated to the Israelites (Ex. 3:8; 34:11). At times, the term *Amorite occurs as a general name for the inhabitants of Canaan (Gen. 15:16; I Sam. 7:14). Canaan’s population was primarily Semitic, as is indicated by place-names such as Jericho, Megiddo, Gebal, and Sidon, and by documents from the first half of the second millennium BCE. containing names of places and rulers. During the first centuries of the second millennium, West-Semitic tribes known in the sources as Amurru penetrated into Canaan. The movement of the Hyksos brought considerable change to the ethnic composition of the population, since in its wake, Hurrian and Indo-European elements penetrated the country during the 17th and 16th centuries. The ethnic heterogeneity of Canaan’s population is illustrated by the names of rulers of the country, appearing in the *El-Amarna letters and in Egyptian documents from the time of the New Kingdom.” ref
“Canaan was never consolidated into a unified political whole. Rather, it was split up into small political units, each usually under the rule of a king. Many Canaanite city-states are mentioned in inscriptions of the Egyptian pharaohs; most of the Tell el-Amarna letters were sent by Canaanite kings to the pharaoh. Thirty-one kings whom the Israelites fought during the conquest of the country are listed in Joshua 12. The most important city-states were Gebal, Sidon, Amurru,

ref From (7:17 / 14:30)
Israeli/Jewish “From the River to the Sea”
“The precise origins of the phrase are disputed. According to American historian Robin D. G. Kelley, the phrase “began as a Zionist slogan signifying the boundaries of Eretz Israel.” Israeli-American historian Omer Bartov notes that Zionist usage of such language predates the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 and began with the Revisionist movement of Zionism led by Vladimir Jabotinski, which spoke of establishing a Jewish state in all of Palestine and had a song which includes: “The Jordan has two banks; this one is ours, and the other one too,” suggesting a Jewish state extending even beyond the Jordan River. In 1977, the concept appeared in an election manifesto of the Israeli political party Likud, which stated that “between the sea and the Jordan there will be only Israeli sovereignty.” ref
“Middle East scholar Elliott Colla says that the relevant historical context for understanding ‘from the river to the sea’ is the history of partition and fragmentation in Palestine, along with Israeli appropriation and annexation of Palestinian lands. In his opinion these include: the 1947 UN Partition plan for Palestine, which proposed to divide the land between the river and the sea; the 1948 Nakba, in which that plan materialized; the 1967 War, in which Israel occupied the West Bank and Gaza; the Oslo Accords, that (in his view) fragmented the West Bank into Palestinian enclaves (that he describes as “an archipelago of Bantustans surrounded by Israeli settlements, bases, and checkpoints”); and the Israeli separation wall first erected after the Second Intifada.” ref
“The phrase was also used by the Israeli ruling Likud party as part of their 1977 election manifesto which stated “Judea and Samaria will not be handed to any foreign administration; between the Sea and the Jordan there will only be Israeli sovereignty.” This slogan was repeated by Menachem Begin. Similar wording has also been used more recently by other Israeli politicians, like Gideon Sa’ar and also Uri Ariel of The Jewish Home. In 2014 Ariel said, “Between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea there will be only one state, which is Israel.” The phrase has been used by the Israeli Prime Minister, Likud’s Benjamin Netanyahu, in speeches. Similar wording has also been used more recently by other Israeli politicians.
“Similar formulations have been used by Zionists and Israelis. Omer Bartov notes the song “The East Bank of the Jordan” by the Revisionist Zionist leader Vladimir Jabotinsky used the formulation שתי גדות לירדן: זו שלנו, זו גם כן “The Jordan has two banks; this one is ours, and the other one too.” The phrase appeared in a 2021 B’Tselem report entitled “A Regime of Jewish Supremacy from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea: This Is Apartheid” that described Israel’s de facto rule over the territory from the river to the sea, through its occupation of the West Bank and blockade of the Gaza Strip, as a regime of apartheid. The Likud Party used the formulation בין הים לירדן תהיה רק ריבונות ישראלית “Between the sea and the Jordan, there will only be Israeli sovereignty.” Most recently, this has been stated by Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on 18 January 2024.” ref
Palestinian “From the River to the Sea”
“From the river to the sea” is a political phrase that refers geographically to the area between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, an area described as Palestine, which today includes Israel and the Israeli-occupied Palestinian territories, including the West Bank, East Jerusalem, and the Gaza Strip. The phrase was popularised among the Palestinian population in the 1960s as a call for liberation from living under Israeli, Jordanian and Egyptian control. In the 1960s, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) used it to call for an Arab state encompassing the entirety of Mandatory Palestine, which was initially stated to only include the Palestinians and the descendants of Jews who had lived in Palestine before 1947, although this was later revised to only include descendants of Jews who had lived in Palestine before the first Aliyah (1881).” ref
“Many Palestinian activists have called it “a call for peace and equality” after decades of Israeli military rule over Palestinians while for most Jews it has been “a clear demand for Israel’s destruction.” Islamist militant faction Hamas used the phrase in its 2017 charter. Usage of the phrase by such Palestinian militant groups has led critics to argue that it advocates for the dismantling of Israel, and calls for the removal or extermination of the Jewish population of the region.” ref
“An old Zionist slogan, envisaged statehood extending over the two banks of the Jordan river, and when that vision proved impractible, it was substituted by the idea of a Greater Israel, an entity conceived as extending from the Jordan to the sea. The Palestinian phrase has also been used by Israeli politicians. The 1977 election manifesto of the right-wing Israeli Likud party said: “Between the sea and the Jordan there will only be Israeli sovereignty.” Similar wording, such as referring to the area “west of the Jordan river”, has also been used more recently by other Israeli politicians, including Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on 18 January 2024. Some countries have considered criminalizing use of the phrase. On 16 April 2024, the U.S. House of Representatives adopted a resolution condemning the phrase as antisemitic.” ref
“Palestinian usage of this phrase is also unclear. Kelley writes that the phrase was adopted by the Palestine Liberation Organization in the mid-1960s; while Elliott Colla notes that “it is unclear when and where the slogan “from the river to the sea,” first emerged within Palestinian protest culture.” In November 2023, Colla wrote that he had not encountered the phrase – in either Standard nor Levantine Arabic – in Palestinian revolutionary media of the 1960s and 1970s and noted that “the phrase appears nowhere in the Palestinian National Charters of 1964 or 1968, nor in the Hamas Charter of 1988.” From the river to the sea, Palestine will be free”—the translation of min an-nahr ʾilā l-baḥr / Filasṭīn sa-tatḥarrar—is the version that has circulated among English speakers expressing solidarity with Palestine since at least the 1990s.” ref
“The 1964 charter of the PLO’s Palestinian National Council called for “the recovery of the usurped homeland in its entirety”. The 1964 charter stated that “Jews who are of Palestinian origin shall be considered Palestinians if they are willing to live peacefully and loyally in Palestine”, specifically defining “Palestinian” as those who had “normally resided in Palestine until 1947”. In the 1968 revision, the charter was further revised, stating that “Jews who had resided normally in Palestine until the beginning of the Zionist invasion” would be considered Palestinian. In 1979, the phrase was invoked by delegates attending the Palestine Congress of North America. The concept of “from the river to the sea” has appeared in various pro-Palestinian protest chants, typically as the first line of a rhyming couplet.” ref
“Colla notes that activists of the First Intifada (1987-1993) “remember hearing variations of the phrase in Arabic from the late 1980s onwards” and that the phrases have been documented in graffiti from the period in works such as Saleh Abd al-Jawad’s “Faṣā’il al-ḥaraka al-waṭaniyya al-Filasṭīniyya fi-l-arāḍī al-muḥtalla wa-shu’ārāt al-judrān” (1991) and Julie Peteet’s “The Writing on the Walls: The Graffiti of the Intifada” (1996). The phrase appeared in a 2021 B’Tselem report entitled “A Regime of Jewish Supremacy from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea: This Is Apartheid” that described Israel’s de facto rule over the territory from the river to the sea, through its occupation of the West Bank and blockade of the Gaza Strip, as a regime of apartheid.” ref
“Hamas, as part of its revised 2017 charter, rejected “any alternative to the full and complete liberation of Palestine, from the river to the sea”, referring to all areas of former Mandatory Palestine and by extension, the end of Jewish sovereignty in the region. Islamic Jihad declared that “from the river to the sea – [Palestine] is an Arab Islamic land that [it] is legally forbidden from abandoning any inch of, and the Israeli presence in Palestine is a null existence, which is forbidden by law to recognize. Islamists have used a version “Palestine is Islamic from the river to the sea.” ref
“The phrase was used as part of its 2017 revised platform where they state “Hamas rejects any alternative to the full and complete liberation of Palestine, from the river to the sea […] along the lines of the 4th of June 1967”. Among the materials recovered by American forces during the killing of al-Qaeda founder Osama bin Laden was a speech addressed to the American people, in which bin Laden proposed economic and security guarantees in exchange for a “roadmap that returns the Palestine land to us, all of it, from the sea to the river, it is an Islamic land not subject to being traded or granted to any party.” ref
“On September 27, 2008, Hezbollah secretary-general Hassan Nasrallah stated at a rally “Palestine, from the sea to the river is the property of Arabs and Palestinians, and no one has the right to give up even a single grain of earth or one stone, because every grain of the land is holy. The entire land must be returned to its rightful owners.” Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi, in 2023, used the phrase, saying “The only solution is a Palestinian state from the river to the sea,” meaning that the only solution to the conflict would be a Palestinian state encompassing all of Israel and the Palestinian territories.” ref
“In 2003, then Iraqi President Saddam Hussein, during a speech commemorating the anniversary of the Iraqi Army‘s establishment, referred to the Palestinian people and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, stating “Long live Palestine, free and Arab, from the sea to the river. ” ref
“On 30 October 2023, British Member of Parliament Andy McDonald was suspended from the Labour Party after stating in a pro-Palestine rally speech: “We won’t rest until we have justice, until all people, Israelis, and Palestinians, between the river and the sea can live in peaceful liberty”. The party described McDonald’s comment as “deeply offensive”. McDonald said at the time, “These words should not be construed in any other way than they were intended, namely as a heartfelt plea for an end to killings in Israel, Gaza, and the occupied West Bank, and for all peoples in the region to live in freedom without the threat of violence.” ref
“As of 1 November 2023, the UK Football Association barred the use of the phrase by its players, stating they made clear to teams “that this phrase is considered offensive to many” and that the league will seek police guidance on how [they] should treat it and respond” if players have used it. On November 5 the Met Police stopped working with an adviser who chanted the slogan during a protest saying this appears “antisemitic and contrary with our values.” ref
“On November 30, 2018, CNN fired American academic Marc Lamont Hill from his position as a political commentator after he delivered a speech at the United Nations on the International Day of Solidarity with the Palestinian People ending with the words: “…we have an opportunity, to not just offer solidarity in words, but to commit to political action, grassroots action, local action, and international action that will give us what justice requires. And that is a free Palestine, from the river to the sea.” Critics focused on his use of the phrase ‘from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free’ because Hamas also uses it. The ADL accused Hill of using the phrase “from the river to the sea” as code for the destruction of Israel. Hill apologized, but later tweeted “You say “River to the Sea” is “universally” understood to mean the destruction of the Jewish State? On what basis do you make this claim? Did it signify destruction when it was the slogan of the Likud Party? Or when currently used by the Israeli Right?” ref
“On 7 November 2023, United States Representative Rashida Tlaib was censured by the House of Representatives in part for using the phrase, which Tlaib defended as “an aspirational call for freedom, human rights, and peaceful coexistence, not death, destruction or hate”. Before the vote, House Democratic leader Hakeem Jeffries criticized the phrase as something which is “widely understood as calling for the complete destruction of Israel”. On 8 November 2023, the White House condemned Tlaib for using the phrase. White House Press Secretary Karine Jean-Pierre said that “when it comes to the phrase that was used, ‘from the river to the sea,’ it is divisive, it is hurtful, many find it hurtful, and many find it antisemitic,” and added that the White House “categorically reject[s] applying the term to the (2023 Israel–Hamas) conflict.” ref
“The phrase has been used across social media, including on TikTok. On November 15, 2023, Jewish influencers and celebrities confronted TikTok executives in a private call, to press them to moderate use of the phrase on the platform. Adam Presser, head of operations for TikTok, stated that only content “where it is clear exactly what they mean…that content is violative and we take it down,” adding that if “someone is just using it casually, then that has been considered acceptable speech.” In a statement, TikTok said that content using the phrase “in a way that threatens violence and spreads hate” is not allowed on the platform. A report by Fortune described an additional Zoom call between “about 40 mostly Jewish tech leaders,” including Anthony Goldbloom, and TikTok executives, on November 16, claiming that the platform’s algorithm favored “content that supports Palestine over pro-Israel content” and pushing the platform to “reexamine its community guidelines”, with the company rejecting “blunt comparisons” of hashtags on the platform and stating that the imbalance of content is not the result of “any kind of intended or unintended bias in its algorithms.” ref
“On November 17, 2023, Elon Musk, the owner of Twitter, announced a policy change, stating that users who use terms like “decolonization” and “from the river to the sea,” or similar expressions would be suspended. He claimed these terms were used as euphemisms for extreme violence or genocide. Musk’s announcement came after he was criticized for “endorsing an antisemitic post” on the platform two days before, and companies such as IBM, Comcast, Apple, Paramount Global, Disney, and Lionsgate announced a pause of ads on the platform.” ref
“Jonathan Greenblatt, the CEO of the Anti-Defamation League, applauded Musk’s action on November 17, calling it “an important and welcome move” and praising his “leadership in fighting hate.” Greenblatt’s statement was reported by The Guardian as being part of an effort to gain influence on the far right, and that the head of the ADL’s Center for Technology and Society (CTS), Yael Eisenstat, quit her position in protest. Other ADL staffers expressed their opposition to Greenblatt’s move. Rolling Stone stated that it was “doubtful” that Twitter users would be suspended for “repeating either phrase.” Noah Lanard of Mother Jones wrote that the new policy would “presumably apply only to those who use the phrase [from the river to the sea] in support of Palestinians” and argued that Musk is “trying to cover up for his own bigotry.” Pro-Palestinian users criticized Musk’s new policy, arguing he was conflating legitimate political speech with “calls for violence” and was “limiting free speech.” ref
“The phrase has been used widely in pro-Palestinian protest movements. It has often been chanted at pro-Palestinian demonstrations, usually followed or preceded by the phrase “Palestine will be free” (the phrase rhymes in English, not Arabic). Interpretations differ amongst its supporters. In a survey conducted by the Arab World for Research and Development on November 14, 74.7% Palestinians agreed that they support a single Palestinian state “from the river to the sea”, while only 5.4% of respondents supported a “one-state for two peoples” solution.” ref
“Civic figures, activists, and progressive publications have said that the phrase calls for a one-state solution: a single, secular state in all of Historic Palestine where people of all religions have equal citizenship. This stands in contrast to the two-state solution, which envisions a Palestinian state existing alongside a Jewish state. This usage has been described as speaking out for the right of Palestinians “to live freely in the land from the river to the sea”, with Palestinian writer Yousef Munayyer describing the phrase as “a rejoinder to the fragmentation of Palestinian land and people by Israeli occupation and discrimination.” Others have said it stands for “the equal freedom and dignity of the Palestinian people.” Elliott Colla traces the first evidence of use of the phrase in Palestinian protest culture to the First Intifada (1987-1993), with documentation in graffiti from the period.” ref
“On November 8, 2023, Amazon told Newsweek that they would not be removing pro-Palestinian merchandise, including garments bearing the phrase, stating that the items do not “contravene our policies,” which prohibit sale of products which “promote, incite, or glorify hatred, violence, racial, sexual, or religious intolerance.” ref
November 10, 2023 ‘From the river to the sea’: Why is the Palestinian nationalist slogan about Gaza a flashpoint?
“When the House this week voted to censure Democratic Rep. Rashida Tlaib, accusing her of calling for Israel‘s destruction, her critics said it was, in part, because she repeated the Palestinian nationalist slogan, “from the river to the sea.” The phrase, perhaps unfamiliar to many Americans, has been around for decades, before the militant group Hamas even existed, and continues with the words, “Palestine will be free.” It has now become both a rallying cry for Palestinian rights chanted by supporters worldwide — and what others consider offensive code for wiping Israel off the map, between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea, as Hamas has vowed to do. Hamas, designated a terrorist organization by the U.S., adopted the phrase in its 2017 charter. The group’s brutal attack on Israel on Oct. 7 caused the horrific deaths of 1,400 men, women, and children, according to Israeli officials. That, as the world has seen in grim detail since, set off the current war in the neighboring Gaza Strip, where more than 10,000 people have been killed, many of them innocent civilians, including thousands of children buried under blasts from Israeli bombs, according to the Hamas-run Gaza Health Ministry.” ref
Is ‘From the river to the sea’ hate speech?
“From the river to the sea, Palestine will be free” is a slogan echoing through pro-Palestinian rallies across the United States and elsewhere, including those observed on the campuses of the University of Southern California and the University of California, Los Angeles this week. Like all aspects of the Middle East conflict, the phrase is polarizing, and interpretations vary. For the Anti-Defamation League, however, it’s clear. “What it connotes to the Jewish people, a vast majority of whom have an intrinsic tie between their Judaism and the State of Israel, ‘From the river to the sea’ means eradicating that piece of land and all Jewish life,” says Jeffrey Abrams, the ADL’s Los Angeles regional director. “That’s what we saw on October 7 by Hamas, a terrorist organization, which committed the greatest atrocity against the Jewish people since the Holocaust.” ref
For context, the State of Israel and the Palestinian territories lie between the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea. The river, spanning over 200 miles, forms a natural border between the Jewish state, the Palestinian-controlled West Bank, and neighboring Jordan and Syria. The ADL and other Jewish advocacy groups insist that “From the river to the sea” is blatantly antisemitic and crosses the line between freedom of speech and hate speech. They argue that those who chant it are advocating for genocide rather than simply supporting the plight of Palestinians. Not true, says Palestinian-American writer and political analyst Yousef Munayyer. “When we talk about ‘From the river to the sea,’ we’re talking about a place that we call home,” Munayyer told the CBC. He argues that the phrase expresses a desire for Palestinian independence and freedom, not the eradication of Jews.” ref
“From the river to the sea today, there is one state, an Israeli state, that rules over millions of people: Palestinians who don’t have equal rights, who are not free. That’s what has to change. It doesn’t mean that there should be any violence against Israelis,” he says. What many Jews hear, of course, is something different. Their belief that the phrase is antisemitic is shared by many political leaders who can point to its adoption by Hamas over a decade ago. “Palestine is ours from the river to the sea and from the south to the north,” Khaled Mashaal, the militant group’s former leader, said in a 2012 speech in Gaza celebrating the 25th anniversary of the founding of Hamas. “There will be no concession on any inch of the land.” ref
“When Rep. Rashida Tlabi (D-Michigan) used ‘From the river to the sea’ in speeches and on social media last year, she was censured by the U.S. House of Representatives. In October 2023, Vienna police banned a pro-Palestinian demonstration, citing the phrase “From the river to the sea” mentioned in invitations and characterizing it as a call to violence. In the United States, law enforcement and universities have largely avoided addressing whether the slogan constitutes hate speech that incites violence, focusing instead on the actions of the protesters rather than their words.” ref
“At USC, demonstrators were removed for pitching tents and erecting banners, which violates the private school’s policy. Activists at UCLA, however, were unchecked as they took over a large plaza on the public university’s campus with tents and barricades and displayed signs with the slogan. While the ADL condemns the use of “From the river to the sea,” Abrams says his organization is more concerned with these disruptions on college campuses and the threats, both real and perceived, targeting Jewish students. “It’s not an issue of free speech. With free speech, there are obligations to each other,” he says. “Just because one group has a right doesn’t mean they have the right to trample on the rights of others, which, unfortunately, is what’s been happening across our country when it comes to the rights of Jewish students on these campuses.” ref
“Some politicians and advocacy groups such as the Anti-Defamation League and American Jewish Committee consider the phrase to be antisemitic, hate speech and incitement to genocide, suggesting that it denies the right of Jews for self-determination in their ancestral homeland, or advocates for their removal or extermination. Such critics of the phrase claim that it has been explicitly used to call for the land to be placed entirely under Arab rule at the cost of the State of Israel and its Jewish citizens. ADL regional director Jonah Steinberg stated that from the time of the 1948 Arab–Israeli War and thereafter, “there was a catchphrase of ‘pushing the Jews into the sea’ and the phrase, ‘from the river to the sea’ echoes that trope in a menacing way.” ref
“Steven Lubet wrote in an opinion piece on The Hill that if the people promoting this slogan were really interested only in “freedom, human rights, and peaceful coexistence” as they claim, then they would have changed the slogan to “From the river to the sea, Palestinians will be free.” Lubet also says that, according to DEI norms, the racism of a certain speech can be determined not only by the intent of the speaker, but mainly by the impact it has on the people who feel offended or threatened by it. Therefore, he concludes, since most Jews view the slogan as hurtful and threatening, it should be avoided, regardless of what is the real intent of its chanters.” ref
“According to Susie Linfield in an interview in Salmagundi magazine, there is nothing wrong with both Jews and Palestinians “pursuing national self-determination”. In her opinion, the slogan ‘from the river to the sea’ represents a rejectionist unwillingness to compromise with the other nation on a two-state solution, which led the Palestinian leadership to reject the partition plan in 1947, ended in them losing everything so far.” ref
“On 9 November 2023, Claudine Gay, the president of Harvard University at the time, condemned the phrase. On 17 April 2024, Minouche Shafik, the president of Columbia University at the time, said that she herself hears the phrase as antisemitic, but some people do not. On 16 April 2024 the U.S. House of Representatives approved a decision that condemns the chant as antisemitic, with a majority of 377 against 44.” ref
“Oxford researcher Ahmad Khalidi has responded to those who characterize it as genocidal, “It is perfectly possible for both people to be free between the river and the sea, is ‘free’ necessarily in itself genocidal? I think any reasonable person would say no. Does it preclude the fact that the Jewish population in the area between the sea and the river cannot also be free? I think any reasonable person would also say no.” ref
“Palestinian-American writers such as Yousef Munayyer and University of Arizona professor Maha Nassar have written that accusations that the phrase is a call to genocide, rely on racist and Islamophobic assumptions about Palestinian intent. Nadia Abu El Haj notes that critics who characterize it as “threatening”, “intimidating”, or a call to “genocidal violence” when it is used in support of Palestine do not make equivalent claims when used by Israelis.” ref
“In describing the criticism of the phrase, scholar of politics in the Arab world Elliott Colla writes:
It is the first phrase of the slogan—”from the river to the sea”—that has caused so much fury. Dominant Jewish communal institutions, most prominently the ADL and AJC, have insisted that this phrase is antisemitic. Throughout recent years, they have composed new definitions of antisemitism that render many common expressions of Palestine solidarity as ipso facto instances of anti-Jewish hate speech … the slogan “from the river to the sea” figures prominently in their accusations of antisemitic doublespeak.” ref
“In 2021, over 200 scholars in various fields signed the Jerusalem Declaration on Antisemitism. The declaration discussed common manifestations of antisemitism, as well as what kinds of speech and behavior are antisemitic and what kind of speech and behavior are not, espacially regarding the Palestine-Israel conflict. According to the authors, “between the river and the sea” is not antisemitic.” ref
Antisemitism
“Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. This sentiment is a form of racism, and a person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Primarily, antisemitic tendencies may be motivated by negative sentiment towards Jews as a people or by negative sentiment towards Jews with regard to Judaism. In the former case, usually presented as racial antisemitism, a person’s hostility is driven by the belief that Jews constitute a distinct race with inherent traits or characteristics that are repulsive or inferior to the preferred traits or characteristics within that person’s society. In the latter case, known as religious antisemitism, a person’s hostility is driven by their religion’s perception of Jews and Judaism, typically encompassing doctrines of supersession that expect or demand Jews to turn away from Judaism and submit to the religion presenting itself as Judaism’s successor faith—this is a common theme within the other Abrahamic religions. The development of racial and religious antisemitism has historically been encouraged by the concept of anti-Judaism, which is distinct from antisemitism itself.” ref
“There are various ways in which antisemitism is manifested, ranging in the level of severity of Jewish persecution. On the more subtle end, it consists of expressions of hatred or discrimination against individual Jews, and may or may not be accompanied by violence. On the most extreme end, it consists of pogroms or genocide, which may or may not be state-sponsored. Although the term “antisemitism” did not come into common usage until the 19th century, it is also applied to previous and later anti-Jewish incidents. Notable instances of antisemitic persecution include the Rhineland massacres in 1096; the Edict of Expulsion in 1290; the European persecution of Jews during the Black Death, between 1348 and 1351; the massacre of Spanish Jews in 1391, the crackdown of the Spanish Inquisition, and the expulsion of Jews from Spain in 1492; the Cossack massacres in Ukraine, between 1648 and 1657; various anti-Jewish pogroms in the Russian Empire, between 1821 and 1906; the Dreyfus affair, between 1894 and 1906; the Holocaust by Nazi Germany during World War II; and various Soviet anti-Jewish policies. Historically, most of the world’s violent antisemitic events have taken place in Christian Europe. However, since the early 20th century, there has been a sharp rise in antisemitic incidents across the Arab world, largely due to the surge in Arab antisemitic conspiracy theories, which have been cultivated to an extent under the aegis of European antisemitic conspiracy theories.” ref
“In the contemporary era, a manifestation known as “new antisemitism” was identified. As the State of Israel has a Jewish-majority population, antisemitic rhetoric can be manifested in expressions of anti-Israeli sentiment. Due to the root word Semite, the term is prone to being invoked as a misnomer by those who incorrectly assert that it refers to racist hatred directed at “Semitic people” in spite of the fact that this grouping is an obsolete historical race concept. Likewise, such usage is erroneous; the compound word antisemitismus was first used in print in Germany in 1879 as a “scientific-sounding term” for Judenhass (lit. ‘Jew-hatred‘), and it has since been used to refer to anti-Jewish sentiment alone. Pseudoscientific theories concerning race, civilization, and “progress” had become quite widespread in Europe in the second half of the 19th century, especially as Prussian nationalistic historian Heinrich von Treitschke did much to promote this form of racism. He coined the phrase “the Jews are our misfortune” which would later be widely used by Nazis. According to Avner Falk, Treitschke uses the term “Semitic” almost synonymously with “Jewish”, in contrast to Renan’s use of it to refer to a whole range of peoples, based generally on linguistic criteria.” ref
“Antisemitism manifests itself in a variety of ways. René König mentions social antisemitism, economic antisemitism, religious antisemitism, and political antisemitism as examples. König points out that these different forms demonstrate that the “origins of anti-Semitic prejudices are rooted in different historical periods.” König asserts that differences in the chronology of different antisemitic prejudices and the irregular distribution of such prejudices over different segments of the population create “serious difficulties in the definition of the different kinds of anti-Semitism.” ref
Anti-Palestinianism
“Anti-Palestinianism or anti-Palestinian sentiment, also called anti-Palestinian racism, refers to prejudice, collective hatred, and discrimination directed at the Palestinian people for any variety of reasons. Since the mid-20th century, the phenomenon has largely overlapped with anti-Arab racism and Islamophobia due to the fact that the overwhelming majority of Palestinians today are Arabs and Muslims. Historically, however, anti-Palestinianism was more closely identified with European antisemitism, as far-right Europeans detested the Jewish people as undesirable foreigners from Palestine. Modern anti-Palestinianism—that is, xenophobia with regard to the Arab people of Palestine—is most common in Israel, the United States, and Lebanon, among other countries. “Pakistani author and professor Sunaina Maira, citing American professor of Islamic studies Shahzad Bashir in the context of labelling, states: “…an important aspect of anti-Palestinianism, that is, the moral panic whipped up about the “radicalization” of Muslim and Arab American youth is often accompanied by the charge that they are automatically anti-Semites if they are critical of the Israeli state’s policies.” ref
Canada Anti-Palestinianism
“In 2018, author and political activist Yves Engler criticized the New Democratic Party (NDP) for its conduct in respect of the Palestine Resolution that called for support of efforts to ban “settlement products from Canadian markets, and using other forms of diplomatic and economic pressure to end the [Israeli] occupation.” Engler said it “demonstrated the need to directly confront anti-Palestinianism within the party.” In 2020, the University of Toronto allegedly blocked the hiring of Valentina Azarova as director of the International Human Rights Program (IHRP) due to her pro-Palestinian activism. Dania Majid, president of the Arab Canadian Lawyers Association (ACLA), described this as an example that “anti-Palestinian racism is alive and well” in Canada. In 2023, the principal of Park West School in Halifax, Nova Scotia, apologized after Palestinian students were told they couldn’t wear the keffiyeh during the school’s culture day. Palestinian and pro-Palestinian activists protested the banning of the keffiyeh as an act of anti-Palestinian racism in front of the Department of Education building in Halifax.” ref
France Anti-Palestinianism
“In May 2021, the French interior minister Gérald Darmanin requested that the police ban a pro-Palestinian protest in Paris. The Parisian journalist Sihame Assbague described the decision as an expression of “French colonial solidarity with the Israeli occupation forces.” ref
Germany Anti-Palestinianism
“Mati Shemoelof in +972 Magazine said Anti-Palestinian sentiment is common in Germany. The German left, particularly the Antideutsch movement, has been noted for anti-Palestinian sentiment. Many pro-Israel non-Jewish Zionists on the German left regard being anti-Palestinian as connected to their solidarity with Jews. In 2019, the Bundestag declared the BDS movement to be a form of antisemitism. In response, the BDS movement condemned the motion as anti-Palestinian. The Palestinian B.D.S. National Committee issued a statement declaring the motion an “anti-Palestinian…McCarthyite and unconstitutional resolution passed by the German Parliament.” British musician Brian Eno has argued that pro-Palestinian artists are subjected to “censorship and inquisitorial McCarthyism” due to the actions of the German government and anti-Palestinian groups.” ref
“On the 75th anniversary of Israel’s independence, or for Palestinians the 75th anniversary of the Nakba, prominent German politician Ursula von der Leyen referred to Israel as a “vibrant democracy” in the Middle East that made “the desert bloom” in remarks criticized by the foreign ministry of the Palestinian Authority as a “propagandist discourse” propagating an “anti-Palestinian racist trope” and a ‘whitewashing‘ of Israeli occupation.” ref
“Germany’s relationship with Palestine has been highlighted as “complex.” At present, Germany’s political class exhibits a “zealous identification with Israel” that is “often explained in terms of the country’s past.” Alternative readings, however, view this trend as a “qualitatively new phenomenon in Germany largely unrelated to moral considerations pertaining to the Nazi era.” Hannah C. Tzuberi argues that German manifestations of “anti-antisemitism” (which has been described as “a defining marker of post-war German identity”) can go beyond the identification of Germans with Jews, sometimes leading to the identification of German gentiles as Jews, and the identification of Germany as Israel.” ref
Israel Anti-Palestinianism
Anti-Zionism
“Anti-Zionism is opposition to Zionism. Although anti-Zionism is a heterogeneous phenomenon, all its proponents agree that the creation of the modern State of Israel, and the movement to create a sovereign Jewish state in the region of Palestine—a region partly coinciding with the biblical Land of Israel—was flawed or unjust in some way.” ref
“Until World War II, anti-Zionism was widespread among Jews for varying reasons. Orthodox Jews opposed Zionism on religious grounds, as preempting the Messiah, while many secular Jewish anti-Zionists identified more with ideals of the Enlightenment and saw Zionism as a reactionary ideology. Opposition to Zionism in the Jewish diaspora was surmounted only from the 1930s onward, as conditions for Jews deteriorated radically in Europe and, with the Second World War, the sheer scale of the Holocaust was felt. Thereafter, Jewish anti-Zionist groups generally either disintegrated or transformed into pro-Zionist organizations, though many small groups, and bodies like the American Council for Judaism, conserved an earlier Reform tradition of rejection of Zionism. Non-Jewish anti-Zionism likewise spanned communal and religious groups, with the Arab population of Palestine largely opposed to what it considered the colonial dispossession of its homeland. Opposition to Zionism was, and continues to be, widespread in the Arab world, especially among Palestinians.” ref
“Zionism’s proponents note its success in establishing the Jewish state of Israel in the region of Palestine, and seek to portray anti-Zionism as broad opposition to Israel and a Jewish presence in the region. Some supporters of Zionism highlight that some antisemites hold anti-Zionist views. The relationship between Zionism, anti-Zionism and antisemitism is debated, with some academics and organizations that study antisemitism taking the view that anti-Zionism is inherently antisemitic or new antisemitism, while others reject any such linkage as unfounded and a method to stifle criticism of Israel and its policies, including its occupation of the West Bank and blockade of the Gaza Strip.” ref
Early Jewish anti-Zionism
“Formal anti-Zionism arose in the late 19th century as a response to Theodor Herzl‘s proposal in The Jewish State (1896) to create an independent country in Palestine for Jews subject to persecution in the “civilized nations” of Europe, but even before Herzl, the idea of Zionism – of Jews as constituting a nation rather than a people constituted by their religion – promoted by Moses Hess (1862) and Leo Pinsker (1882) elicited fierce opposition within European Orthodox Jewry. Samson Raphael Hirsch, for one, considered the active promotion of Jewish emigration to Palestine a sin. The creation of a Jewish state before the appearance of the messiah was widely interpreted in Jewish religious circles as contradicting the divine will, a programme, furthermore, that was visibly driven by Jewish secularists. Until World War I, across Central Europe, Jewish religious leaders largely perceived the Zionist movement’s aspirations for Jewish nationhood in a distant “New Judea” as a threat, in that it might encourage paradoxically the very antisemites, with their treatment of Jews in their midst as “aliens,” whose fundamental rationale Zionism itself sought to undermine.” ref
“When Herzl began to propound his proposal, many, including, secular Jews, regarded Zionism as a fanciful and unrealistic movement. Some antisemites even dismissed it as a “Jewish trick.” Many assimilationist Jewish liberals, heirs of the Enlightenment, had argued that Jews should enjoy full equality in exchange for a pledge of loyalty to their respective nation-states. Those liberal Jews who accepted integration and assimilationist principles saw Zionism as a threat to efforts to facilitate Jewish citizenship and equality within the European nation-state context. Many in the intellectual elite of the Anglo-Jewish community, for example, opposed Zionism because they felt most at home in England, where, in their view, antisemitism was neither a social or cultural norm.” ref
“The Jewish establishment in Germany, France (and its Alliance Israelite Universelle), and America strongly identified with its respective states, a sentiment that made it regard Zionism negatively. Reform rabbis in German-speaking lands and Hungary advocated the erasure of all mentions of Zion in their prayer books. Herzl’s successor, the Zionist atheist Max Nordau, whose views on race coincided with those of the antisemitic Drumont, lambasted Reform Judaism for emptying ancient Jewish prayers of their literal meaning in claiming that the Jewish diaspora was a fact of destiny.” ref
“Herzl’s proposal initially met with broad, vigorous opposition within Jewish intellectual, social, and political movements. A notable exception was the religious Mizrachi movement. In his essay Mauschel, Herzl called Jews who opposed his project “yids”, and not true Jews. Among left-wing currents within diaspora Jewish communities, strong opposition emerged in such formations as the Bundism, Autonomism, Folkism, Jewish Communists, Territorialism, and Jewish-language anarchist movements. Yevsektsiya, the Jewish section of the Communist Party in the Soviet Union created to combat “Jewish bourgeois nationalism,” targeted the Zionist movement and managed to close down its offices and place Zionist literature under a ban, but Soviet officials themselves often disapproved of anti-Zionist zeal.” ref
“Orthodox Judaism, which stressed civic responsibilities and patriotic feelings in religion, was strongly opposed to Zionism because Zionism espoused nationalism in a secular fashion and used “Zion,” “Jerusalem,” “Land of Israel,” “redemption” and “ingathering of exiles” as literal rather than sacred terms, endeavouring to achieve them in this world. According to Menachem Keren-Kratz, the situation in the United States differed, with most Reform rabbis and laypeople endorsing Zionism. Dina Porat holds the opposite view of Orthodox Jewish opinion generally.” ref
“Elaborating on the work of David N. Myers, Jonathan Judaken states that “numerous Jewish traditions have insisted that preservation of what is most precious about Judaism and Jewishness ‘demands’ a principled anti-Zionism or post-Zionism.” This tradition dwindled in the aftermath of the Holocaust and the establishment of Israel, but is still alive in religious groups such as Neturei Karta and among many intellectuals of Jewish background in Israel and the diaspora, such as George Steiner, Tony Judt, and Baruch Kimmerling.” ref
Early Arab anti-Zionism
“Arabs began paying attention to Zionism in the late Ottoman period. In 1899, compelled by a “holy duty of conscience,” Yousef al-Khalidi, mayor of Jerusalem and a member of the Ottoman Parliament, wrote a letter to Zadok Kahn, the chief rabbi of France to voice his concerns that Zionism would jeopardize the friendly associations among Muslims, Christians and Jews in the Ottoman Empire. He wrote: “Who can deny the rights of the Jews to Palestine? My God, historically it is your country!” But Khalidi suggested that, since Palestine was already inhabited, the Zionists should find another place for the implementation of their political goals: “in the name of God,” he wrote, “let Palestine be left alone.” ref
“According to Rashid Khalidi, Alexander Scholch, and Dominique Perrin, Yousef Khalidi was prescient in predicting that, regardless of Jewish historic rights, given the geopolitical context, Zionism could stir an awakening of Arab nationalism uniting Christians and Muslims. Kahn showed the letter to Theodor Herzl, who, on 19 March 1899, replied to Khalidi in French, arguing that both the Ottoman Empire and the non-Jewish population of Palestine would benefit from Jewish immigration. As to Khalidi’s concerns about the non-Jewish majority population of Palestine, Herzl replied rhetorically: “who would think of sending them away?” Rashid Khalidi notes that this was penned four years after Herzl had confided to his diary the idea of spiriting the Arab population away to make way for Jews.” ref
“The Maronite Christian Naguib Azoury, in his 1905 The Awakening of the Arab Nation, warned that the “Jewish people” were engaged in a concerted drive to establish a country in the area they believed was their homeland. Subsequently, the Palestinian Christian-owned and highly influential newspaper Falastin was founded in 1911 in the then Arab-majority city of Jaffa and soon became the area’s fiercest and most consistent critic of Zionism. It helped shape Palestinian identity and nationalism.” ref
“Palestinian and broader Arab anti-Zionism took a decisive turn, and became a serious force, with the November 1917 publication of the Balfour Declaration – which arguably emerged from an antisemitic milieu – in the face of strenuous resistance from two anti-Zionists, Lord Curzon and Edwin Montagu, then the (Jewish) Secretary of State for India. Other than assuring civil equality for all future Palestinians regardless of creed, it promised diaspora Jews territorial rights to Palestine, where, according to the 1914 Ottoman census of its citizens, 83% were Muslim, 11.2% Christian, and 5% Jewish. The majority Muslim and Christian population constituting 94% of the citizenry only had their “religious rights” recognized.” ref
“Given that Arab notables were almost unanimous in repudiating Zionism, and incidents such as the Surafend massacre (perpetrated by Australian and New Zealand troops serving alongside the British) stirred deep resentment against Britain throughout the area, the British soon came to the conclusion, which they confided to the Americans during the King–Crane Commission, that the provisions for Zionism could only be implemented by military force. To this end, the British Army calculated that a garrison of at least 50,000 troops would be required to implement the Zionist project on Palestinian soil. According to Henry Laurens, uneasiness among British troops stationed in the region over the task of ostensibly supporting Zionism, something that clashed with their customary paternalistic treatment of colonial populations, accounted for much of the anti-Zionist sentiment that UK military personnel based in Palestine expressed.” ref
Anti-Zionism in the 1920s–1930s
“Some members of the Jewish-Marxist Poale Zion, which advocated under Ber Borochov a separate Zionist organization for Jewish workers and advocated emigration to Palestine as a solution to antisemitism, found to their surprise on making aliyah that Palestine was a predominantly Arab country. By the early 1920s, the realization that Zionism would be discriminatory had turned Poale militants like Yaakov Meiersohn and Joseph Berger into anti-Zionists. In 1922 the Comintern‘s disowning of Poale Zion spurred the growth of a Jewish anti-Zionist left in Palestine, culminating with the formation of the Palestine Communist Party (PCP), which retained some residual Zionist traces. This anti-Zionist Jewish PCP was recognized by the Comintern in 1924, and, that same year, the first Palestinian Arab joined the party.” ref
“The Yiddish-speaking General Jewish Labor Union of Eastern Europe, the largest Jewish left-wing organization in Europe between the two wars, focused on a practice of doykayt (hereness) as the key to Jewish identity; that is, it advocated addressing practical issues Jews faced all over the diaspora in their respective national contexts. It dismissed its antagonist Zionism’s vision of resolving matters definitively by emigrating to Palestine as marked by a “separatist, chauvinist, clerical and conservative” outlook, values diametrically opposed to Bundism‘s secular, progressive and internationalist principles.” ref
“The Communist Party USA (CPUSA) was resolutely anti-Zionist throughout this period, believing that “that the only way Zionism would be able to emerge in Palestine was through a colonial project and through the expulsion of the indigenous Palestinians from the land.” Under CPUSA general-secretary Earl Browder, a clear distinction was drawn between anti-Jewish pogroms in Europe, which were likened to the activities of white supremacist groups in the U.S. such as the Ku Klux Klan and Black Legion, and Arab resistance to Jewish settlers in Palestine. At the time, around half of the CPUSA’s membership was Jewish, with perhaps 10% of the U.S. Jewish population joining the group over a decade. Throughout the 1930s and ’40s, members of the American Jewish left and its intelligentsia were almost all anti-Zionists, an exception being Meyer Levin. Mike Gold‘s 1930 novel Jews without Money depicts a Zionist entrepreneur’s fatal extortion of a poor Jew and can be read as a proletarian critique of both American capitalism and, tacitly in its subplot, of Zionists in both the U.S. and Palestine.” ref
“As well as left-wing critiques of Zionism, many mainstream liberal and conservative communal organizations in the diaspora continued to promote an assimilationist anti-Zionism. In Germany, for example, the Centralverein deutscher Staatsbürger jüdischen Glaubens (Central Union of German Citizens of Jewish Faith) argued that German Jews should be primarily loyal to Germany and identify as Jews only on religious terms. Soon after Hitler was appointed Chancellor in January 1933, Jews, and anti-Zionists among them, were galvanized to organize global protests against the new regime’s discrimination against their German confreres.” ref
“Similarly, as Italian fascism came to identify Zionism with enemies of the country abroad, in 1934 the Italian-Israeli Community Union responded to pressure by solemnly affirming the community’s allegiance to their country. Italian anti-Zionists such as Ettore Ovazza reacted by creating their own newspaper, La Nostra Bandiera (Our Flag), whose editorial line maintained that the establishment of a Jewish nation in Palestine was anachronistic.” ref
Anti-Zionism after World War II and the creation of Israel
“In a retrospective analysis of Arab anti-Zionism in 1978, Yehoshafat Harkabi argued, in a view reflected in the works of the anti-Zionist Russian-Jewish orientalist Maxime Rodinson, that Arab hostility to Zionism arose as a rational response in historical context to a genuine threat, and, with the establishment of Israel, their anti-Zionism was shaped as much by Israeli policies and actions as by traditional antisemitic stereotypes, and only later degenerated into an irrational attitude. Anne de Jong asserts that direct resistance to Zionism from the inhabitants of historical Palestine “focused less on religious arguments and was instead centered on countering the experience of colonial dispossession and opposing the Zionist enforcement of ethnic division of the indigenous population.” ref
“Until 1948, according to Derek Penslar, antisemitism in Palestine “grew directly out of the conflict with the Zionist movement and its gradual yet purposeful settlement of the country”, rather than the European model vision of Jews as the cause of all the ills of mankind. According to Anthony Julius, anti-Zionism, a highly heterogeneous phenomenon, and Palestinian nationalism, are separate ideologies; one need not have an opinion on the Israeli–Palestinian conflict to be an anti-Zionist. One Arab criticism of Zionism is that Islamic–Jewish relations were entirely peaceful until Zionism conquered Arab lands. Arab delegates to the United Nations also claimed that Zionists had unethically enticed Arab Jews to come to Israel. According to Gil Troy, neither claim is historically accurate, as Jews did not have the same rights as Muslims in these lands and had periodically experienced violent riots.” ref
Anti-Zionism and Allegations of Racism
“In the 1960s and 1970s, Soviets and Americans interpreted the Arab–Israeli conflict as a proxy war between the totalitarianism of the Soviet–Arab alliance and the democracies of the Western world. Israel’s victory in the Six-Day War of 1967 necessitated a diplomatic response by the Soviet–Arab alliance. The result was resolutions in the Organization for African Unity and the Non-Aligned Movement condemning Zionism and equating it with racism and apartheid during the early 1970s.” ref
“This culminated in November 1975 in the United Nations General Assembly‘s passage of Resolution 3379 by a vote of 72 to 35 (with 32 abstentions), which declared, “Zionism is a form of racism, and racial discrimination.” The passage evoked, in the words of American U.N. Ambassador Daniel Patrick Moynihan, “a long mocking applause.” U.N. representatives from Libya, Syria, and the PLO made speeches claiming that this resolution negated previous resolutions calling for land-for-peace agreements between Israel and its Arab neighbors. Israel’s U.N. representative, Chaim Herzog, interpreted the resolution as an attack on Israel’s legitimacy. African U.N. delegates from non-Arab countries also resented the resolution as a distraction from the fight against racism in places like South Africa and Rhodesia.” ref
“The decision was revoked on 16 December 1991, when the General Assembly passed Resolution 4686, repealing resolution 3379, by a vote of 111 to 25, with 13 abstentions and 17 delegations absent. Thirteen of the 19 Arab countries, including those engaged in negotiations with Israel, voted against the repeal, and another six were absent. All the ex-communist countries and most of the African countries who had supported Resolution 3379 voted to repeal it.” ref
“In 1993, philosopher Cornel West wrote: “Jews will not comprehend what the symbolic predicament and literal plight of Palestinians in Israel means to blacks…. Blacks often perceive the Jewish defense of the state of Israel as a second instance of naked group interest, and, again, an abandonment of substantive moral deliberation.” African-American support of Palestinians is frequently due to the consideration of Palestinians as people of color; political scientist Andrew Hacker writes: “The presence of Israel in the Middle East is perceived as thwarting the rightful status of people of color. Some blacks view Israel as essentially a white and European power, supported from the outside, and occupying space that rightfully belongs to the original inhabitants of Palestine.” ref
“In January 2015, the Lausanne movement published an article in its official journal comparing Christian Zionism, the crusades, and the Spanish Inquisition, and calling Zionism “apartheid on steroids.” The Simon Wiesenthal Center called this last claim “the big lie,” and rebutted the “dismissal of the validity of Israel’s right to exist as the Jewish State.” According to New York University social and cultural theorist Susie Linfield, one of the most pressing questions facing the New Left after World War II was “How can we maintain our traditional universalist values in light of the nationalist movements sweeping the formerly colonized world?” ref
“During the late 1960s, anti-Zionism became a part of a collection of sentiments within the far-left politics, including anti-colonialism, anti-capitalism, and anti-Americanism. In this environment, Zionism became a representation of Western power. Indeed, philosopher Jean Améry argued that this “Zionism” was merely a straw man redefinition of the term, used to mean world Jewry. The far-left Israeli politician Simha Flapan lamented in 1968, “The socialist world approved the ‘Holy War’ of the Arabs against Israel in the disguise of a struggle against imperialism. … Having agreed to the devaluation of its own ideals, [it] was ready to enter an alliance with reactionary and chauvinist appeals to genocide.” ref
“In his much-discussed essay Progressive Jewish Thought and the New Anti-Semitism, Alvin H. Rosenfeld writes that a “number of Jews, through their speaking and writing, are feeding a rise in virulent antisemitism by questioning whether Israel should even exist.” Rosenfeld laments that some left-wing Jews delegitimize Israel “in the name of Judaism” and make false equivalencies between Israel and Nazi Germany or apartheid South Africa.” ref
“Some Jewish organizations oppose Zionism as an integral part of their anti-imperialism. Today, some secular Jews, particularly socialists and Marxists, continue to oppose the State of Israel on anti-imperialist and human rights grounds. Many oppose it as a form of nationalism, which they argue is a product of capitalism. One secular anti-Zionist group, the International Jewish Anti-Zionist Network, a socialist, antiwar, anti-imperialist organization, calls for “the dismantling of Israeli apartheid, return of Palestinian refugees, and the ending of the Israeli colonization of historic Palestine.” ref
“In the 2000s, leaders of the Respect Party and the Socialist Workers Party of the United Kingdom met with leaders of Hamas and Hezbollah at the Cairo Anti-war Conference. The result of the 2003 conference was a call to oppose “normalization with the Zionist entity.” ref
Criticism of Israel
“Criticism of Israel is a subject of journalistic and scholarly commentary and research within the scope of international relations theory, expressed in terms of political science. Israel has faced international criticism since its establishment in 1948 relating to a variety of issues, many of which are centered around human rights violations in its occupation of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. Palestinian refugees are defined by the UN as Arabs who lived in Palestine for at least two years prior to 1948 and their descendants, and who fled or were expelled from their homes during and after the 1948 Palestine War. The causes and responsibilities of the exodus are a matter of controversy among historians and commentators of the conflict. Whereas historians now agree on most of the events of that period, there remains disagreement as to whether the exodus was the result of a plan designed before or during the war by Zionist leaders or was an unintended consequence of the war.” ref
“Significant international pressure was placed on both sides during the 1949 Lausanne Conference to resolve the refugee crisis. The parties signed a joint protocol on the framework for a comprehensive peace, which included territories, refugees, and Jerusalem, in which Israel agreed “in principle” to allow the return of all of the Palestinian refugees. According to New Historian Ilan Pappe, this Israeli agreement was made under pressure from the United States, and because the Israelis wanted United Nations membership, which required Israeli agreement to allow the return of all refugees. Once Israel was admitted to the UN, it retreated from the protocol it had signed because it was completely satisfied with the status quo and saw no need to make any concessions with regard to the refugees or on boundary questions. This led to significant and sustained international criticism.” ref
“Israel has been criticized for issues surrounding its establishment when most of Mandatory Palestine‘s Arab population fled or were expelled in 1948, the conduct of its armed forces in the Arab–Israeli conflict, establishment and expansion of illegal Israeli settlements in the Palestinian territories, its treatment of Palestinians, and the blockade of the Gaza Strip, with its impact on the economy of the Palestinian territories, the country’s nuclear weapons program, and its targeted killings program. Other criticized long-standing issues include: the refusal to allow post-war Palestinian refugees to return to their homes, and the prolonged occupation of territories gained in war and the construction of settlements therein. Israel’s status as a representative democracy has also been questioned because Israeli residents of the occupied territories are allowed to vote in Israel’s elections while Palestinian residents are not, leading to accusations of apartheid.” ref
“Criticisms of Israeli policies come from several groups: primarily from activists, within Israel and worldwide, the United Nations and other non-governmental organizations including European churches, and mass media. Media bias is often claimed by both sides of the debate. Since 2003, the UN has issued 232 resolutions with respect to Israel, 40% of all resolutions issued by the UN over the period and more than six times that of the second placed country, Sudan. Counter-criticisms include the assertion that some critics and their criticisms are aimed at delegitimizing Israel’s right to exist, which has led some to debate over the point at which criticism of Israel crosses the line into antisemitism. The term “new antisemitism” refers to criticisms deemed to have crossed this threshold.” ref
“New Historian” Ilan Pappe argued in The Ethnic Cleansing of Palestine that Israel’s policy between 1947 and 1949, when “over 400 Palestinian villages were deliberately destroyed, civilians were massacred, and around a million men, women, and children were expelled from their homes at gunpoint” is best described as ethnic cleansing. However, Pappe’s work has been subject to significant criticism and allegations of fabrication by other historians.” ref
“For example, Israeli historian Benny Morris called Pappe “At best … one of the world’s sloppiest historians; at worst, one of the most dishonest.” When asked about the 1948 Palestinian expulsion from Lydda and Ramle, he responded “There are circumstances in history that justify ethnic cleansing. I know that this term is completely negative in the discourse of the 21st century, but when the choice is between ethnic cleansing and genocide – the annihilation of your people – I prefer ethnic cleansing. […] There was no choice but to expel that population. It was necessary to cleanse the hinterland and cleanse the border areas and cleanse the main roads. It was necessary to cleanse the villages from which our convoys and our settlements were fired on.” He also added in 2008, that “There was no Zionist ‘plan’ or blanket policy of evicting the Arab population, or of ‘ethnic cleansing’. Plan Dalet (Plan D), of 10 March 1948 … was the master plan … to counter the expected pan-Arab assault on the emergent Jewish state.” ref
“The territories occupied by Israel from Egypt, Jordan, and Syria after the Six-Day War of 1967 have been designated as occupied territory by the United Nations and many other international organisations, governments and others. They consist of the West Bank and much of the Golan Heights. From the Six-Day War until 1982, the Sinai Peninsula was occupied by Israel, but it was returned to Egypt in the Egypt–Israel peace treaty. The Gaza Strip was also occupied by Israel until its unilateral disengagement. UN Security Council resolution 242, emphasized “the inadmissibility of the acquisition of territory by war,” setting the stage for controversy on the legal status of areas captured in 1967, and in 1948.” ref
“Despite the fact that Israeli security legislation for Palestinian territories does not state that, military law applies only to Arab residents of the territories, and not to Jews or to Israeli citizens. Israeli citizens are governed by Israeli law whereas Palestinians are governed by military law. Some Israeli individuals such as Avraham Burg, Ilan Pappé, Gershom Gorenberg, David Remnick, Oren Yiftachel, and Miko Peled and organisations as Human Rights Watch, B’tselem, Peace Now and others have questioned Israel’s status as a democracy. These questions focus on the lack of democracy in the Israeli-occupied territories, not Israel proper. Such criticisms are based on the belief that both Israeli citizens in settlements and Palestinians should be given the right to suffrage, considering the Palestinians are effectively under Israeli authority and thus should benefit from it. They share a concern that the occupation of the territories is not temporary, given the over forty-five year duration and the large and the permanent nature of the Israeli settlements.” ref
“The participating High Contracting Parties to the Fourth Geneva Convention, numerous UN resolutions, the International Court of Justice and other instances have ruled that Israel’s policy of establishing civilian settlements in territories considered occupied, including in East Jerusalem, is illegal. Israel disputes the notion that the West Bank and in particular East Jerusalem are occupied under international law, though this view is dismissed internationally. Israel’s settlement policy has drawn harsh criticism from the United States and the European Union. Ali Jarbawi called the policy as “one of the only remaining settler-colonial occupations in the world today”. In his book Hollow Land: Israel’s Architecture of Occupation, Eyal Weizman describes Israel’s policy as a “political system at the heart of this complex and terrifying project of late-modern colonial occupation.” The international community criticized Israel for “failing to protect the Palestinian population” from Israeli settler violence.” ref
“Human Rights Watch (HRW) has said Israel operates a “two-tier” judicial system in areas of the occupied Palestinian territories it administers, to an effect which provides preferential services, development, and benefits for Israelis living in settlements in the occupied territories while imposing harsh conditions on Palestinians and other non-Israeli citizens. In some cases, Israel has acknowledged differential treatment of Palestinians and Israelis, such as having separate roads for both communities and operating checkpoints for Palestinians, asserting that the measures are necessary to protect Israelis from attacks by Palestinian armed groups. In 2011, the Israeli parliament passed a law criminalizing participation in boycotts of Israeli settlements. The law drew criticism from the EU, the United States, and the Anti-Defamation League.” ref
“Amnesty International reported that in 2009 hundreds of Palestinians were detained and held incommunicado for extended periods of time by Israel. While most were later released without charge, hundreds were tried before military courts whose procedures often failed to meet international standards for fair trial. According to Amnesty, almost all Palestinian prisoners were held in violation of international humanitarian law, which prohibits the transfer of detainees to the territory of the occupying power (i.e., Israel proper). It claimed that about 300 minors and 550 adults were held without charge or trial for more than a year.” ref
“In 2011, UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-Moon said Israel held thousands of Palestinians as prisoners, and called on Israel to release them. Ban said the release of political prisoners would “serve as a significant confidence-building measure” and boost prospects of peace in the region. Also Amnesty International has called on Israel to release political prisoners, saying “all political prisoners held without charge or trial should be tried in fair trials or immediately released”. Israel objects to releasing prisoners, many of whom have been convicted by Israeli courts for violent crimes such as murder. However, several prisoner release deals have been conducted by Israel as a gesture in negotiations, many which involved the release of hundreds or more prisoners.” ref
“According to Amnesty International, methods of torture used by Israel on Palestinian prisoners include prolonged tying in painful stress positions, sleep deprivation, and threats to harm detainees’ families. Beatings and other ill-treatment of detainees are common during and following arrest and during transfer from one location to another. Organizations such as Amnesty International, the Association for Civil Rights in Israel (ACRI), the Israeli government-appointed Or Commission, and the United States Department of State have published reports that document racism and discrimination directed towards racial and ethnic groups in Israel.” ref
“According to a study commissioned by Israel’s Courts administration and Israel Bar Association, Arab Israelis who have been charged with certain types of crime are more likely than their Jewish counterparts to be convicted, and once convicted they are more likely to be sent to prison. The study also found differences in lengths of prison sentences given, with the average prison sentence at nine and a half months for Jews and 14 months for Arabs.” ref
“Rights groups have said that anti-discrimination employment laws in Israel are rarely enforced. A coalition of nine Israeli rights groups has opposed a practice under which companies can advertise their policy to hire only Jewish Israelis, and no Arab Israelis. Companies advertising under a “Hebrew labor” banner adhere to a segregated employment philosophy derived from a practice by Jewish immigrants in Palestine in the first half of the 20th century which was meant to strengthen emerging Israeli industry from British and Arab influence. In February 2011, Netanyahu called German Chancellor Angela Merkel to complain about Germany’s vote in favor of a resolution at the United Nations Security Council to declare Israeli settlements to be illegal and she responded “How dare you! You are the one who disappointed us. You haven’t made a single step to advance peace.” A few days later veteran Israeli diplomat Ilan Baruch resigned saying that Netanyahu’s policies were leading to Israel’s delegitimization.” ref
“Israel has enacted a Law of Return that allows Jews from anywhere in the world a fast-track to Israeli citizenship. Palestinian refugees cannot apply for Israeli citizenship under the law since they are not Jewish, though they can apply for Israeli citizenship through the conventional channel. The law has drawn criticism from the Cairo Institute for Human Rights Studies which says the law is a “main example of Israeli laws that discriminate against Palestinian Arabs”. The American-Arab Anti-Discrimination Committee says the contrast between the Law of Return and Israeli opposition to the right of return of Palestinian refugees exhibits “barefaced racism.” More than 1,000 American Jews have backed a campaign entitled “Breaking the Law of Return,” saying the Law of Return creates an ethnically exclusive citizenship, which they see as unjust. Critics claim that the guaranteed right for Jews to immigrate to Israel is discriminatory to non-Jews and, therefore, runs counter to the democratic value of equality under the law.” ref
“Comparisons between apartheid South Africa and Israel are increasingly made. Israelis recoil at the analogy, but the parallel is widely drawn in international circles. The Association for Civil Rights in Israel, a group in Israel with support from several EU states, asserted in 2008 that the separate road networks in the West Bank for Israelis and Palestinians, the expansion of Jewish settlements, restriction of the growth of Palestinian towns and discriminatory granting of services, budgets and access to natural resources are “a blatant violation of the principle of equality and in many ways reminiscent of the Apartheid regime in South Africa.” Israel has also been accused of apartheid by Michael Ben-Yair, Israel’s attorney-general from 1993 to 1996. and Shulamit Aloni, who served as Minister for Education under Yitzhak Rabin. In April 2021, Human Rights Watch accused Israeli officials of the crimes of apartheid and persecution under international law and called for an International Criminal Court investigation into these claims.” ref
“Some scholars and pundits have begun using the language of genocide in discussing the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, both to describe calls for the destruction of Israel and the indiscriminate killing of civilians by Hamas and other Palestinian extremist groups, and also to describe the cumulative effect of Israeli policies in the Gaza Strip. Since then, spokespeople for both Israel and Palestine frequently accuse the other of planning a scheme of genocide. During spikes in violence in the conflict, some scholars have described attacks by Hamas as illegal under the Genocide Convention, and others such as New Historian Ilan Pappé have compared retaliation by Israel and its overall policies in the Gaza Strip as a form of genocide, often broadening the term beyond the definitions of that convention.” ref
“Some criticisms of Israel or Israeli policies have been characterized as anti-Semitic. Proponents of the concept of New Antisemitism, such as Phyllis Chesler, Gabriel Schoenfeld and Mortimer Zuckerman, argue that, since the 1967 Six-Day War, many criticisms of Israel are veiled attacks on Jews and hence are essentially antisemitic. Abba Eban, Robert S. Wistrich, and Joschka Fischer focus on criticism of Zionism, and contend that some forms of anti-Zionism, particularly attacks on Israel’s right to exist, are anti-Semitic in nature.” ref
“Critics of this view often portray this view as an equation of criticism with anti-Semitism. Some critics of Israel or Israeli policies, including Ralph Nader, Jenny Tonge, Noam Chomsky, and Desmond Tutu suggest that equating criticism of Israel with antisemitism is inappropriate or inaccurate. Other critics, such as John Mearsheimer, Alexander Cockburn, Norman Finkelstein, and William I. Robinson, claim that supporters of Israel sometimes equate criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism in a deliberate attempt to prevent legitimate criticism of Israel and discredit critics. However, proponents of the view usually argue that the equation of criticism with antisemitism is rarely made. For example, Alvin H. Rosenfeld considers this argument to be disingenuous, dismissing it as “the ubiquitous rubric ‘criticism of Israel,'” He states that “vigorous discussion of Israeli policy and actions is not in question,” but rather statements that go well beyond legitimate criticism “and call into question Israel’s right to continued existence.” Alan Dershowitz claims that some enemies of Israel pretend to be victimized by accusations of anti-Semitism, in order to garner support for their position.” ref
“Dina Porat (head of the Institute for Study of Anti-semitism and Racism at Tel-Aviv University) characterizes some anti-Zionist ideals as anti-Semitic, because they amount to singling-out Jews for special treatment, while all other comparable groups of people are entitled to create and maintain a homeland. She contends that anti-Zionism is anti-Semitic because it is discriminatory: “…antisemitism is involved when the belief is articulated that of all the peoples on the globe (including the Palestinians), only the Jews should not have the right to self-determination in a land of their own. Hannah Rosenthal of the United States State Department said UN double standards against Israel constitute “profound anti-semitism”. However, many commentators have suggested singling out Israel for disproportionate criticism is warranted as a result of Israel’s actions.” ref
Distinguishing legitimate criticism of Israel from antisemitism?
“The European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia (EUMC) prepared a report in 2003 that distinguished criticism of Israel from anti-Semitism by testing whether “Israel is seen as being a representative of ‘the Jew'”: if the speaker is considering Israel as a representative of Jews in general, then anti-Semitism is deemed to be underlying the criticism.” ref
“Natan Sharansky, former Soviet dissident and Israeli Minister, suggested a three-part test to distinguish legitimate criticism of Israel from anti-Semitic attacks. Sharansky’s tests that identify a criticism as anti-Semitic are:
- Demonization – when Israeli actions are blown so far out of proportion that the account paints Israel as the embodiment of all evil.
- Double Standards – when Israel is criticized soundly for an action or policy that any other government would be viewed as justified in doing, like protecting its citizens from terrorism.
- Delegitimization: a denial of Israel’s right to exist or the right of the Jewish people to live securely in a homeland.” ref
“Demonization and double standards are often used as evidence of anti-Semitism in relation to criticism of Israel. Sharansky believes that some criticisms involve applying an especially high moral standard to Israel, higher than applied to other countries (particularly compared to surrounding countries), yet the only special characteristic of Israel is that it is a Jewish state, hence there is an element of anti-Semitism. Delegitimization was a factor addressed by Abba Eban, who claimed that efforts to deny “the equal rights of the Jewish people its lawful sovereignty within the community of nations” constituted anti-Semitism.” ref
European Union 2006 report on antisemitism
“The European Monitoring Centre on Racism and Xenophobia (EUMC, recently renamed to Fundamental Rights Agency) published a draft of an operational definition of antisemitism called Working Definition of Antisemitism which accompanied a report by the EUMC on report that summarized antisemitism in Europe. The EUMC working definition included five kinds of behaviors related to criticism of Israel that might be manifestations of antisemitism:
- Denying the Jewish people their right to self-determination, e.g., by claiming that the existence of a State of Israel is a racist endeavor.
- Applying double standards by requiring of it a behavior not expected or demanded of any other democratic nation.
- Using the symbols and images associated with classic antisemitism (e.g., claims of Jews killing Jesus or blood libel) to characterize Israel or Israelis.
- Drawing comparisons of contemporary Israeli policy to that of the Nazis.
- Holding Jews collectively responsible for actions of the state of Israel.” ref
“This part of the definition has proved highly contentious and is seen by many as attempting to proscribe legitimate criticism of the human rights record of the Israeli Government by attempting to bring any criticism of Israel into the category of antisemitism, and as not sufficiently distinguishing between criticism of Israeli actions and criticism of Zionism as a political ideology, on the one hand, and racially based violence towards, discrimination against, or abuse of, Jews.” ref
“Paul Igansky points out that one of the EUMC anti-Semitic behaviors, comparisons between Israeli policy and those of the Nazis, is “arguably not intrinsically antisemitic”, and that the context in which they are made is critical. Igansky illustrates this with the incident where Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Rabin was described by fellow Jewish Israelis as cooperating with the Nazis, and depicted wearing an SS uniform. According to Igansky, the “Nazi” label was merely used as “charged political rhetoric” in this case.” ref
EISCA 2009 report on criticism of Israel
“Following the 2006 EUMC report, the European Institute for the Study of Contemporary Antisemitism (EISCA) published a report in 2009 entitled Understanding and Addressing the ‘Nazi Card’ – Intervening Against Antisemitic Discourse which discussed comparisons of Israel with Nazi Germany. The 2009 report incorporated from the 2006 report the five specific kinds of criticism of Israel that should be considered as anti-Semitism (see above for a list of the five). The report does not say all criticism of Israel is anti-Semitic: “Abhorrence and protest against the policies, practices, and leaders of the Israeli state can be expressed in numerous forceful and trenchant ways, as they could against any other state – none of which would be antisemitic…”, and “Drawing attention to the consequent harms in [playing the Nazi card against Israel] should not be intended, or taken, in any way as an attempt to suppress criticism of Israel and its military practices. Antony Lerman criticized the report, and suggested that it could be used to suppress legitimate criticism of Israel, and suggests that the report’s authors do not adequately address that possibility.” ref
Objections to characterizing criticism of Israel as anti-Semitism
“Some commentators have objected to the characterization of criticisms of Israel as anti-Semitic, and have often asserted that supporters of Israel equate criticism with anti-Semitism or excessively blur the distinction between the two. Examples include Michael P. Prior, Noam Chomsky, Norman Finkelstein, Michael Lerner, Antony Lerman, Ralph Nader, Jenny Tonge, Ken Livingstone, and Desmond Tutu. They provide a variety of reasons for their objections, including stifling free expression, promoting anti-Semitism, diluting genuine anti-Semitism, and alienating Jews from Judaism or Israel.” ref
Vague and Indiscriminate to characterizing criticism of Israel as anti-Semitism
“Michael Lerner claims that the American Jewish community regularly tries to blur the distinction between legitimate criticism of Israel and anti-Semitism, and says it is a “slippery slope” to expand the definition of anti-Semitism to include legitimate criticism of Israel. Philosophy professor Irfan Khawaja asserts that it is a “false equation” to equate anti-Zionism with anti-Semitism, writing “The point is not that the charge of ‘anti-Semitism’ should never be made: some people deserve it…. But the equation of anti-Semitism with anti-Zionism is a farce that has gone on long enough, and it’s time that those who saw through the farce said so…” ref
“Palestine Monitor, a Palestinian advocacy group, is critical of what it characterizes as a modern trend to expand the definition of the term “antisemitic”, and states that the new definitions are overly vague and allow for “indiscriminate accusations”. Brian Klug argues that anti-Zionism sometimes is a manifestation of antisemitism, but that “[t]hey are separate” and that to equate them is to incorrectly “conflate the Jewish state with the Jewish people.” ref
“Earl Raab, founding director of the Nathan Perlmutter Institute for Jewish Advocacy at Brandeis University writes that “[t]here is a new surge of antisemitism in the world, and much prejudice against Israel is driven by such antisemitism,” but argues that charges of antisemitism based on anti-Israel opinions generally lack credibility. He writes that “a grave educational misdirection is imbedded in formulations suggesting that if we somehow get rid of antisemitism, we will get rid of anti-Israelism. This reduces the problems of prejudice against Israel to cartoon proportions.” Raab describes prejudice against Israel as a “serious breach of morality and good sense,” and argues that it is often a bridge to antisemitism, but distinguishes it from antisemitism as such.” ref
“Irfan Khawaja suggests that some legitimate criticisms of Israel are improperly attacked by deliberately conflating them with criticisms that are anti-Semitic in nature. Alexander Cockburn and Jeffrey St. Clair, in the book The Politics of Anti-Semitism, write “Apologists for Israel’s repression of Palestinians toss the word ‘anti-Semite’ at any critic of what Zionism has meant in practice for Palestinians on the receiving end. So some of the essays in this book address the issue of what constitutes genuine anti-Semitism – Jew-hatred – as opposed to disingenuous, specious charges of ‘anti-Semitism’ hurled at rational appraisals of the state of Israel’s political, military, and social conduct.” ref
Represents Jews as victims
“Norman Finkelstein and Steven Zipperstein (professor of Jewish Culture and History at Stanford University) suggest that criticism of Israel is sometimes inappropriately considered to be anti-Semitism due to an inclination to perceive Jews as victims. Zipperstein suggests that the common attitude of seeing Jews as victims is sometimes implicitly transferred to the perception of Israel as a victim; while Finkelstein suggests that the depiction of Israel as a victim (as a “Jew among nations”) is a deliberate ploy to stifle criticism of Israel.” ref
“Self-hating” Jews
“Sander Gilman has written, “One of the most recent forms of Jewish self-hatred is the virulent opposition to the existence of the State of Israel.” He uses the term not against those who criticize Israel’s policy, but against Jews who oppose Israel’s existence. Michael Lerner, editor of Tikkun magazine, asserts that the equation of Criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism has resulted in conflict within the Jewish community, in particular, proponents of the equation sometimes attack Jewish critics of Israeli policies as “self-hating Jews“. Lerner also claims that the equation of Criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism and the resulting charges of “self hating Jew” has resulted in the alienation of young Jews from their faith. Antony Lerman believes that many attacks on Jewish critics of Israel are “vitriolic, ad hominem and indiscriminate” and claims that anti-Zionism and anti-Semitism have been defined too broadly and without reason.” ref
“Lerman also states that the “redefinition” of anti-Semitism to include anti-Zionism has caused Jews to attack other Jews, because many Jews are leaders in several anti-Zionist organizations. Nicholas Saphir, chair of the Board of Trustees of the New Israel Fund in the UK published an open letter defending non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that operate within Israel to promote civil rights. He said that several organisations such as NGO Monitor, Israel Resource News Agency, WorldNetDaily and the Near and Middle East Policy Review “associate moral and ethical criticism of any activity by Israel or the policies of its Government as being anti-Israel, anti-Semitic and when conducted by Jews, as evidence of self-hatred.” ref
Scare tactics
“The International Jewish Anti-Zionist Network is also opposed to the use of the antisemitic label to suppress criticism, and objected to the “fear tactics” employed when the anti-Semitic label was applied to supporters of Israel Apartheid Week, claiming that it was reminiscent of the anti-Communist scare tactics of the 1950s. Michael Lerner suggests that some United States politicians are reluctant to criticize Israel because they are afraid of being labeled anti-Semitic. Lerner also states that groups that promote peace in the mid-East are afraid to form coalitions, lest they be discredited by what Lerner terms the “Jewish Establishment.” ref
Draws attention away from genuine antisemitism
“Brian Klug asserts that proponents of New Antisemitism define antisemitism so broadly that they deprive the term “antisemitism” of all meaning. Klug writes: “… when anti-Semitism is everywhere, it is nowhere. And when every anti-Zionist is an anti-Semite, we no longer know how to recognize the real thing–the concept of anti-Semitism loses its significance.” In the book The Politics of Anti-Semitism Scott Handleman writes: “Partisans of Israel often make false accusations of anti-Semitism to silence Israel’s critics. The ‘antisemite’ libel is harmful not only because it censors debate about Israel’s racism and human rights abuses but because it trivializes the ugly history of Jew-hatred.” ref
Excessive accusations of antisemitism may result in backlash
“Brian Klug argues that excessive claims of anti-Semitism (leveled at critics of Israel) may backfire and contribute to anti-Semitism, and he writes “a McCarthyite tendency to see anti-Semites under every bed, arguably contributes to the climate of hostility toward Jews” Tony Judt also suggests that Israel’s “insistent identification” of criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism is now the leading source of anti-Jewish sentiment in the world. Michael Lerner echos those thoughts and suggests that the continued “repression” of criticism of Israel may eventually “explode” in an outburst of genuine anti-Semitism.” ref
Attacking the messenger rather than the message
“Michael Lerner claims that some supporters of Israel refuse to discuss legitimate criticisms of Israel (such as comparisons with apartheid) and instead attack the people who raise such criticisms, thus deliberately “shifting the discourse to the legitimacy of the messenger and thus avoiding the substance of the criticisms.” ref
Exaggerating the equation in order to draw sympathy
“Alan Dershowitz distinguishes between legitimate criticism of Israel and anti-Semitism, but he claims that some “enemies of Israel” encourage the equation of the two, because it makes the enemies appear to be victims of false accusations of anti-Semitism, which the enemies use in an attempt to gain sympathy for their cause.” ref
“A number of commentators have debated whether public criticism of Israel is suppressed outside of Israel, particularly within the United States. Stephen Zunes writes that “assaults on critics of Israeli policies have been more successful in limiting open debate, but this gagging censorship effect stems more from ignorance and liberal guilt than from any all-powerful Israel lobby.” He goes on to explain that while “some criticism of Israel really is rooted in anti-Semitism,” it is his opinion that some members of the Israel lobby cross the line by labeling intellectually honest critics of Israel as anti-Semitic. Zunes argues that the mainstream and conservative Jewish organizations have “created a climate of intimidation against many who speak out for peace and human rights or who support the Palestinians‘ right of self-determination.” ref
“Zunes has been on the receiving end of this criticism himself: “As a result of my opposition to US support for the Israeli government’s policies of occupation, colonization and repression, I have been deliberately misquoted, subjected to slander and libel, and falsely accused of being “anti-Semitic” and “supporting terrorism”; my children have been harassed and my university’s administration has been bombarded with calls for my dismissal.” In an opinion piece for The Guardian, Jimmy Carter wrote that mainstream American politics does not give equal time to the Palestinian side of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and that this is due at least in part to AIPAC. Several commentators have asserted that supporters of Israel attempt to stifle legitimate criticism of Israel by unfairly labeling critics as antisemitic.” ref
“One of the major themes of Norman Finkelstein‘s book Beyond Chutzpah: On the Misuse of Anti-Semitism and the Abuse of History is that some supporters of Israel employ accusations of anti-Semitism to attack critics of Israel, with the goal of discrediting the critics and silencing the criticism. Professors Judy Rebick and Alan Sears, in response to Israel Apartheid Week activities at Carleton University, wrote an open letter to the university president which claimed that accusations of anti-Semitism are sometimes made with the goal of “silencing” criticism of Israel.” ref
“Journalist Peter Beaumont also claims that some proponents of the concept of New Antisemitism conflate criticism of Israel with anti-Semitism. Tariq Ali, a British-Pakistani historian and political activist, argues that the concept of new antisemitism amounts to an attempt to subvert the language in the interests of the State of Israel. He writes that the campaign against “the supposed new ‘anti-semitism'” in modern Europe is a “cynical ploy on the part of the Israeli Government to seal off the Zionist state from any criticism of its regular and consistent brutality against the Palestinians. … Criticism of Israel can not and should not be equated with anti-semitism.” He argues that most pro-Palestinian, anti-Zionist groups that emerged after the Six-Day War were careful to observe the distinction between anti-Zionism and antisemitism.” ref
“Jewish Voice for Peace has spoken against what they see as the abuse of the antisemitic label. For example, in an opinion piece, they wrote “For decades, some leaders of the Jewish community have made the preposterous claim that there is complete unity of belief and interest between all Jews and the Israeli government, no matter what its policies. They must believe their own propaganda, because they see no difference between criticism of the Israeli government and anti-Semitism, and they do everything they can to silence critical voices. If the brand of anti-Semitism is not sufficiently intimidating, the silencing has been enforced by organized phone and letter-writing campaigns, boycotts, threats of, and actual withdrawal of funding support from ‘offending’ institutions and individuals.” ref
Anti-Israel and Anti-Zionist Campaigns (Anti-Defamation League)
“ADL speaks out when anti-Israel rhetoric or activism engages in distortions or delegitimizes Israel, crosses into antisemitism when it demonizes or negates Zionism, and uses anti-Jewish assertions and tropes. There is a wide range of views on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and the vigorous debate and activism on this complex situation is an important component of public discourse and the free exchange of ideas. While criticism of Israeli policies and actions is part of that discourse, certain forms of anti-Israel rhetoric and activism delegitimize Israel and its existence, and are antisemitic when they vilify and negate Zionism – the movement for Jewish self-determination and statehood – or utilize anti-Jewish tropes or hold all Jews responsible for Israel’s actions.” ref
“ADL has seen firsthand how extreme and demonizing rhetoric and ugly expressions of anti-Zionism can be the driving force behind antisemitic discrimination against Jews in different environments, including on campus and in the workplace. Such rhetoric has even served to embolden acts of anti-Jewish violence in the U.S. and around the world. ADL believes that one can advocate for the Palestinian people and their right to self-determination while also respecting the Jewish right to self-determination.” ref
“ADL provides analysis on trends and developments within anti-Israel and anti-Zionist movements and serves as a go-to resource for stakeholders confronting these actions. We educate about how some rhetoric and activity in these spaces can be antisemitic, and/or support violence against Israel and Israelis. And we highlight how some anti-Israel campaigns, such as those orchestrated by proponents of BDS (boycott, divestment, sanctions) provide simplistic, unfair and unconstructive answers to the complex Israeli-Palestinian conflict, and do not advocate for the advancement of Israeli-Palestinian dialogue, mutual understanding and peace.” ref


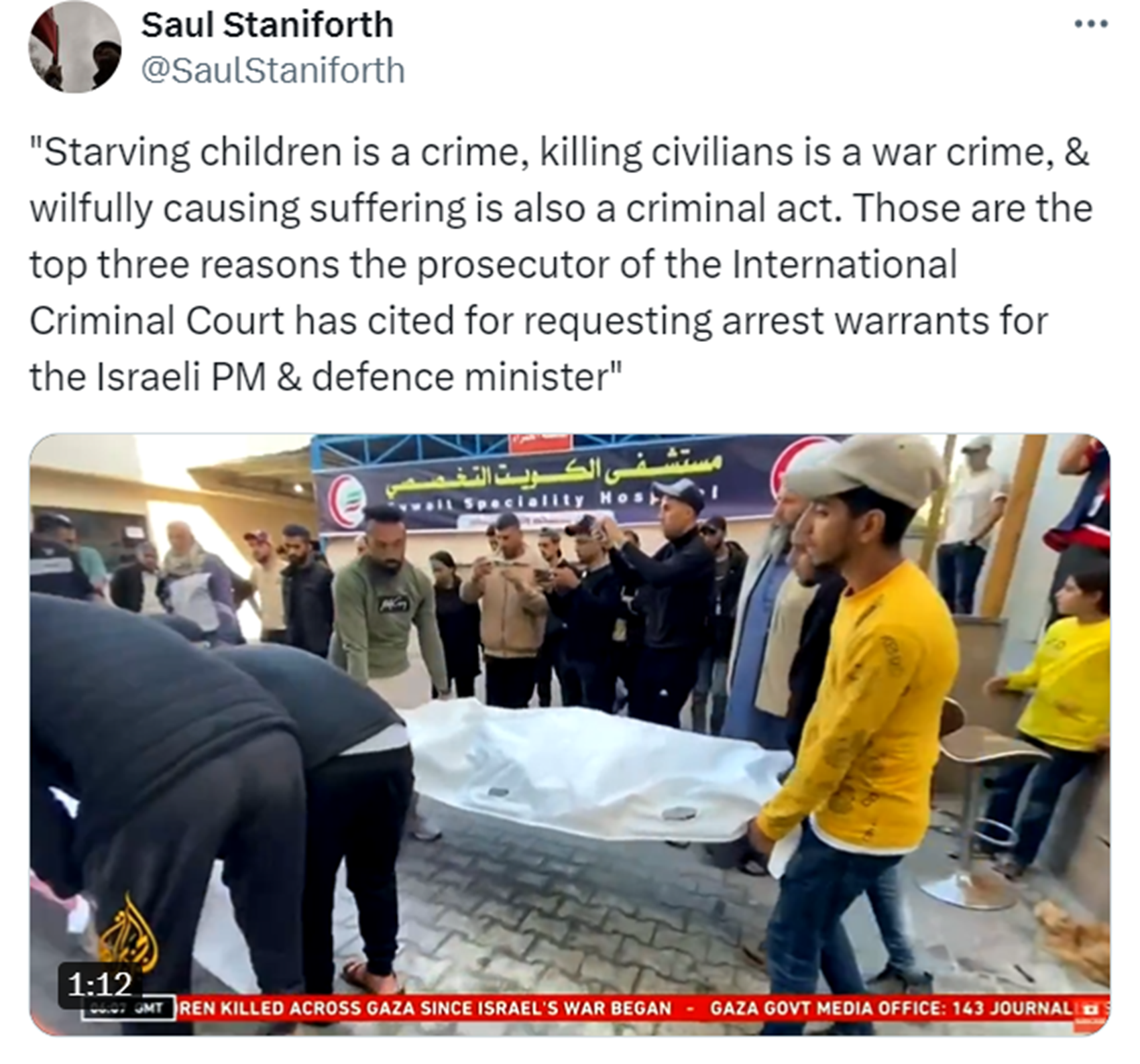
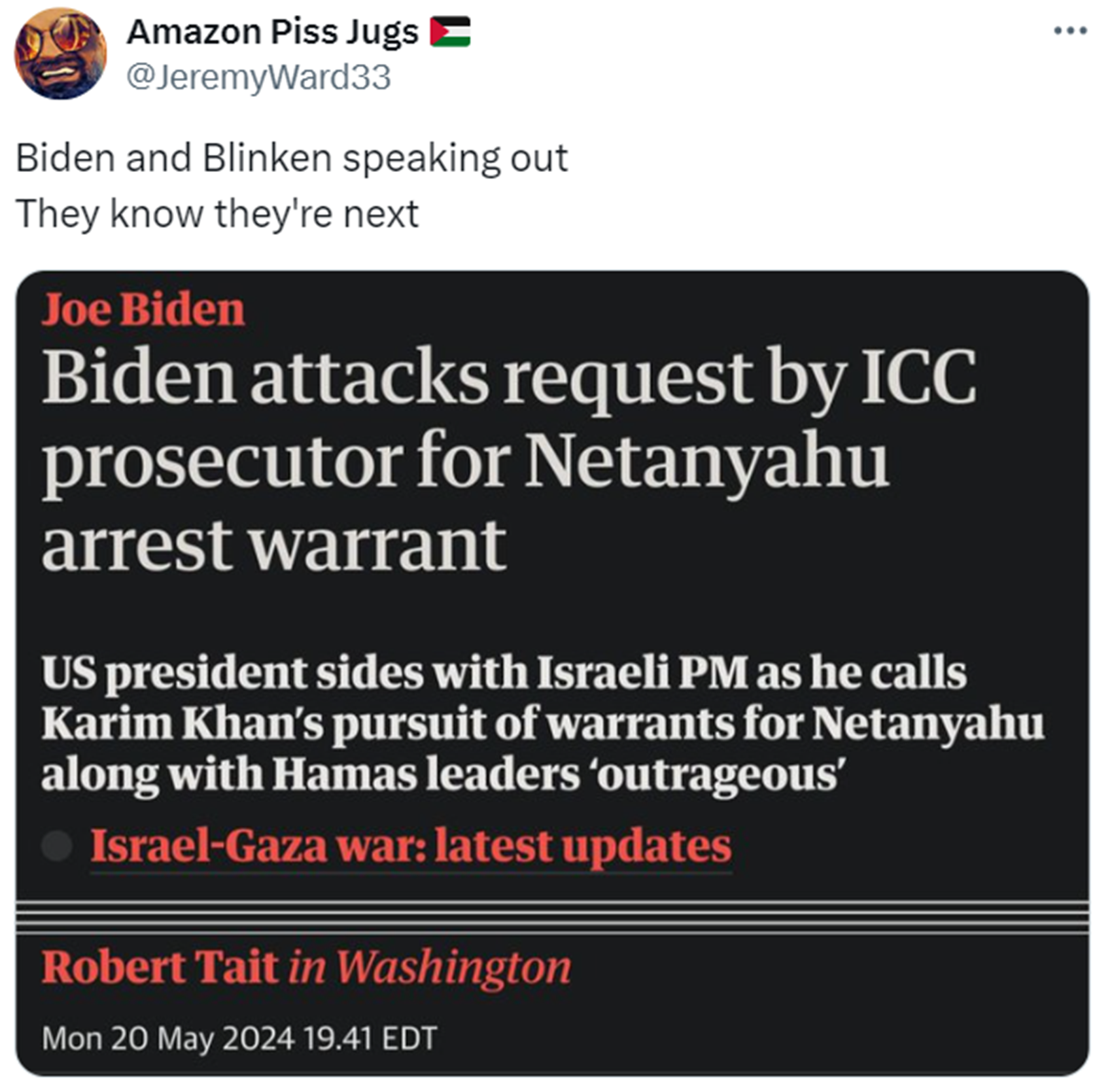
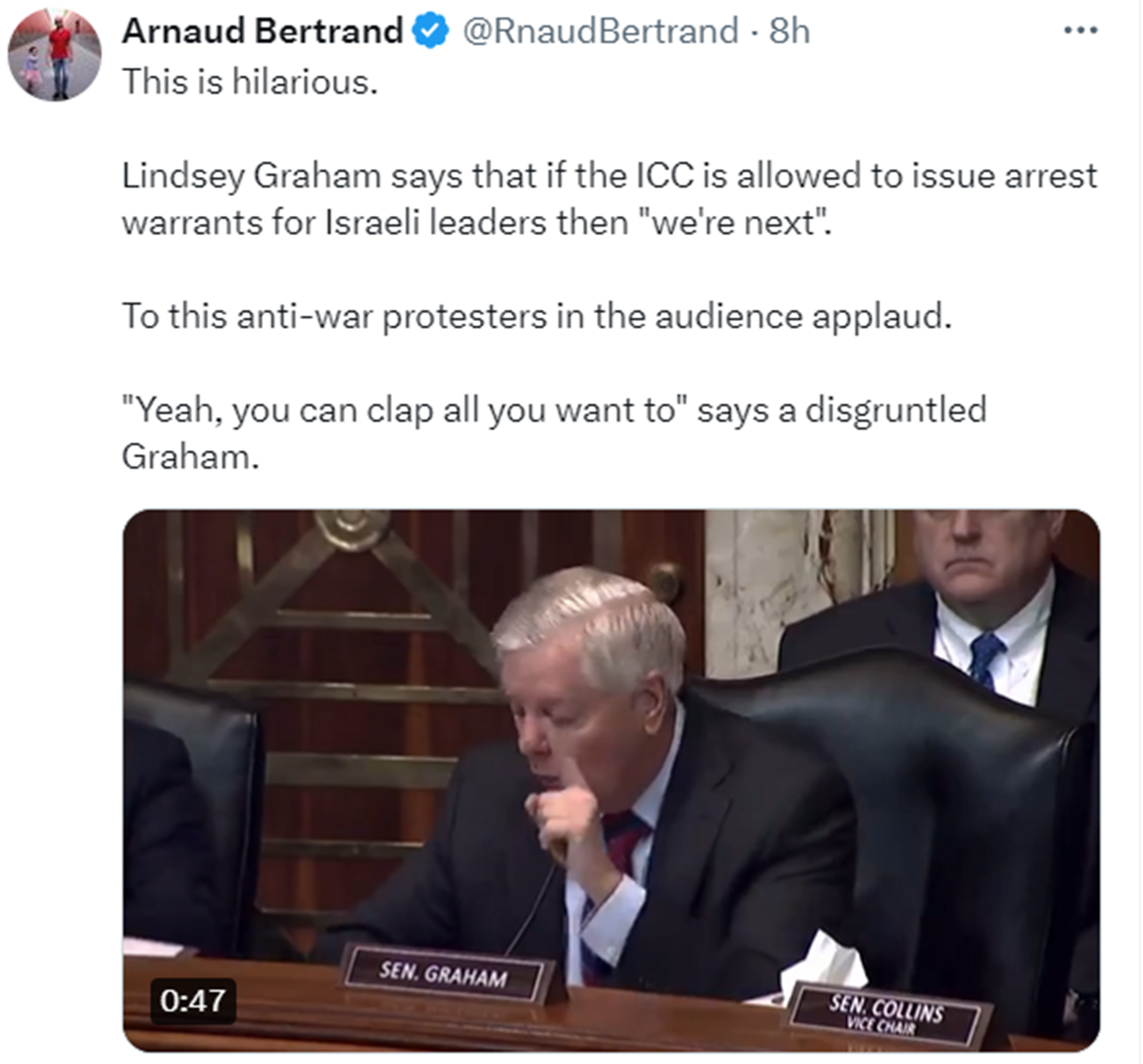
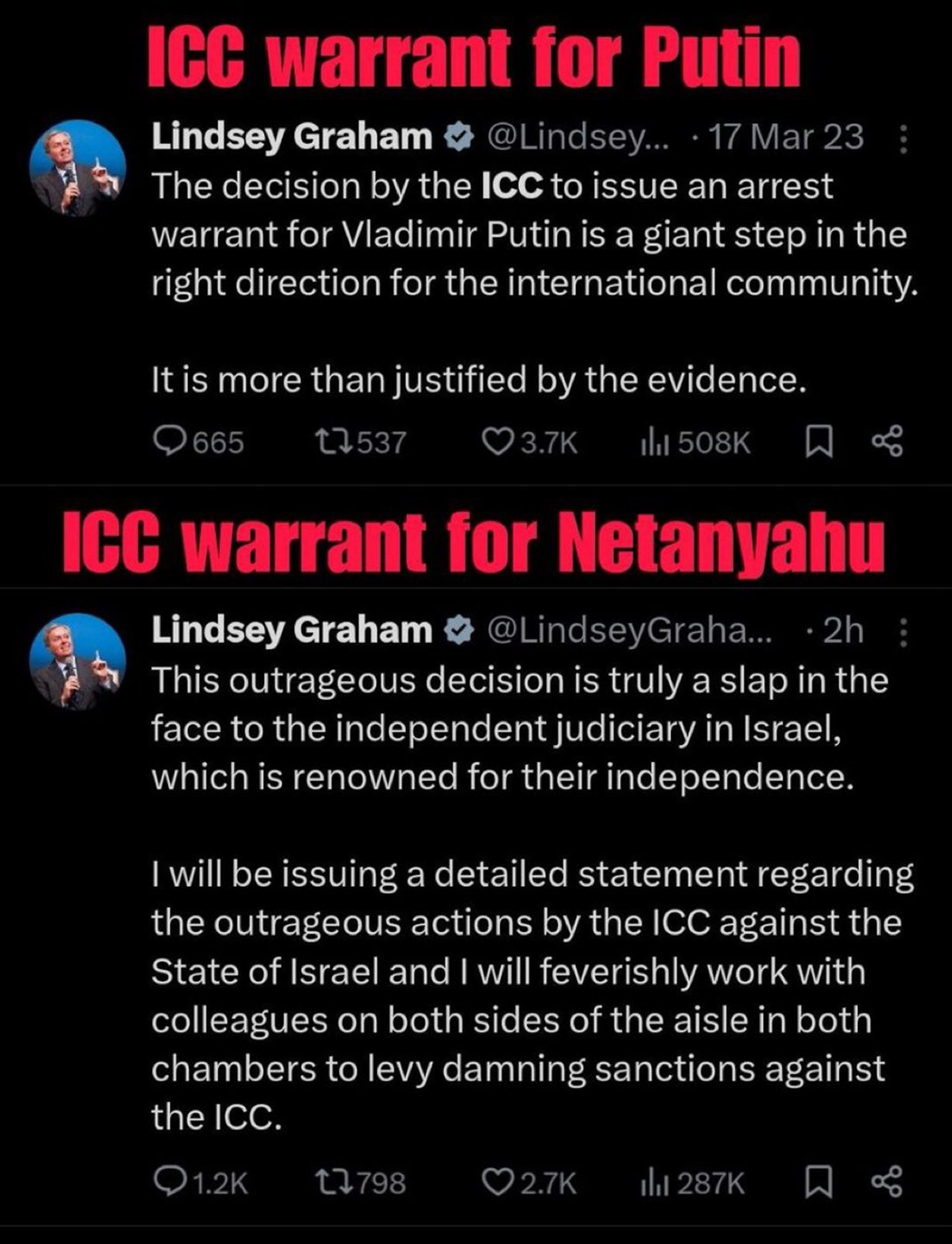
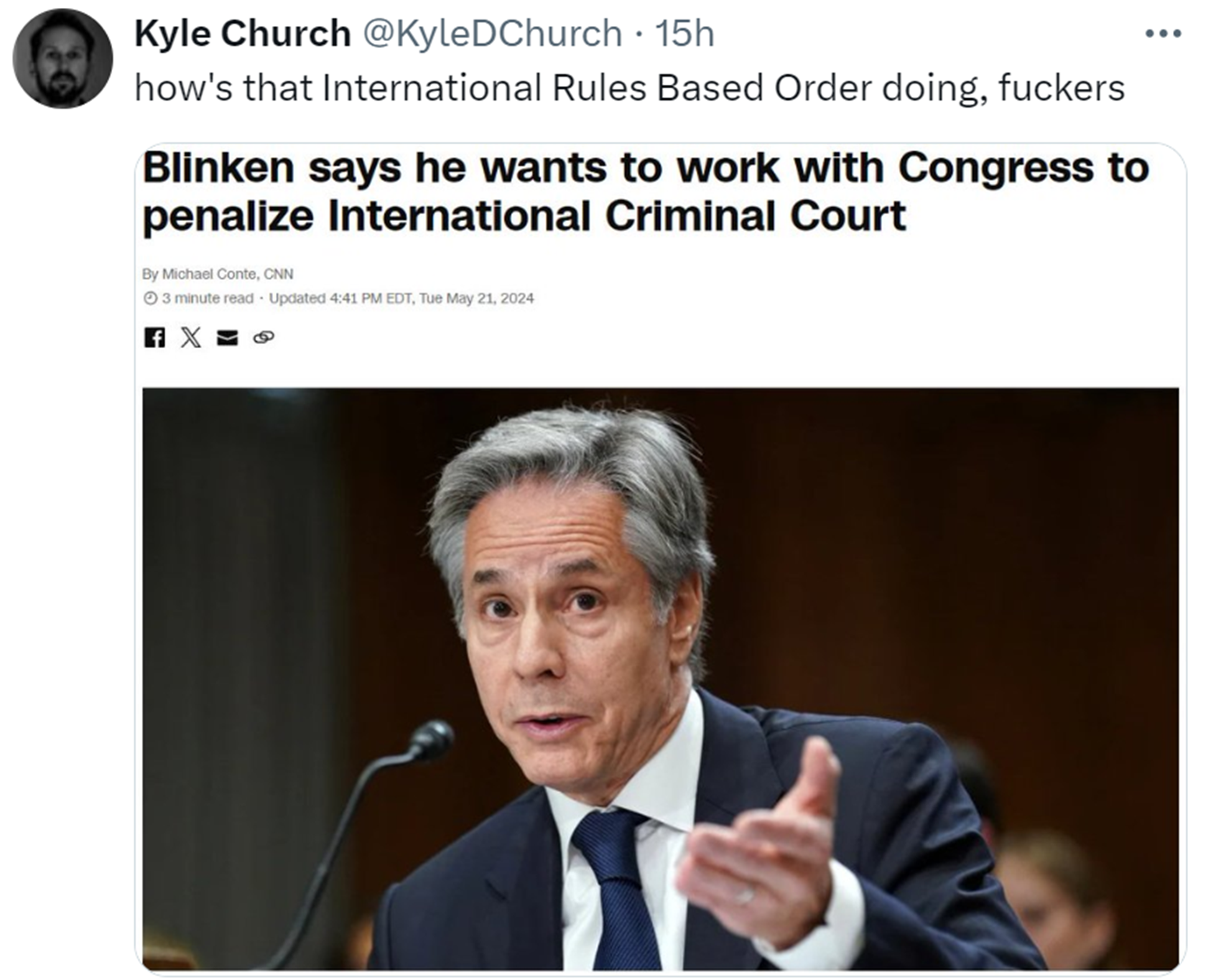
Blinken says he wants to work with Congress to penalize International Criminal Court
“US Secretary of State Antony Blinken said he wants to work with Congress on legislation to penalize the International Criminal Court after it applied for arrest warrants for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Defense Minister Yoav Gallant. “Given the events of yesterday, I think we have to look at the appropriate steps to take to deal with again, what is a profoundly wrongheaded decision,” Blinken said at a State Department budget hearing with the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. Blinken’s comments were an early indication of the Biden administration’s openness to taking action against the Netherlands-based court for its application for arrest warrants for the senior Israeli officials. The court’s chief prosecutor Karim Khan also issued warrants for senior Hamas officials, including its leader in Gaza, Yahya Sinwar.” ref
“Blinken was responding to questions by the ranking member of the committee, Republican Sen. James Risch, who asked if Blinken would work with him on legislation that “includes the question of the ICC sticking its nose in the business of countries that have an independent legitimate, democratic judicial system.” “The devil’s in the details, so let’s see what you got, and we can take from there,” said Blinken in response, adding that he wants to work with the committee “on a bipartisan basis.” In a Senate Appropriations subcommittee hearing on Tuesday afternoon, Blinken said he would “welcome” working with Sen. Lindsey Graham on “bipartisan” sanctions against the ICC.” ref
“The Biden administration came out forcefully against Khan on Monday for his decision to apply for the warrants against top Israel officials on charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. “It’s clear Israel wants to do all it can to ensure civilian protection,” said Biden at a White House reception marking Jewish American Heritage Month. “Let me be clear: What’s happening is not genocide.” Lawmakers from both parties condemned the ICC’s actions on Monday, and House Speaker Mike Johnson said that House Republicans are looking into sanctioning the ICC. “In the absence of leadership from the White House, Congress is reviewing all options, including sanctions, to punish the ICC and ensure its leadership faces consequences if they proceed.” ref
“If the ICC is allowed to threaten Israeli leaders, ours could be next,” Johnson said in a statement Monday. Meanwhile, the Biden administration has faced questions about its condemnation of the ICC’s actions while saying it continues to support the court’s investigation into Russian war crimes during its invasion of Ukraine. “Regarding the question of whether or not we’ll continue to provide support to the ICC with respect to crimes that are committed in Ukraine, yes, we continue that work,” Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said at a news conference after a virtual meeting of the Ukraine Defense Contact Group on Monday.” ref
“State Department spokesperson Matthew Miller said at a news conference on Monday that the ICC has done “important work over the years to hold people accountable for war crimes and crimes against humanity” that the US still supports. “We’ll have the time to look at it, to digest it and perhaps issue a more complete response,” Miller said about the ICC applications. The Trump administration previously sanctioned ICC officials by executive order in 2020 over its investigation of possible war crimes by US military and intelligence officials in Afghanistan, sanctions that the Biden administration lifted the next year.” ref
International Criminal Court?
“The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals for the international crimes of genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression. The ICC is distinct from the International Court of Justice, an organ of the United Nations that hears disputes between states. Established in 2002 pursuant to the multilateral Rome Statute, the ICC is considered by its proponents to be a major step toward justice, and an innovation in international law and human rights. However, it has faced a number of criticisms from governments and civil society groups, including objections to its jurisdiction, accusations of bias, Eurocentrism, and racism, questioning of the fairness of its case selection and trial procedures, and doubts about its effectiveness.” ref
“The establishment of an international tribunal to judge political leaders accused of international crimes was first proposed during the Paris Peace Conference in 1919 following the First World War by the Commission of Responsibilities. The issue was addressed again at a conference held in Geneva under the auspices of the League of Nations in 1937, which resulted in the conclusion of the first convention stipulating the establishment of a permanent international court to try acts of international terrorism. The convention was signed by 13 states, but none ratified it and the convention never entered into force.” ref
“Following the Second World War, the allied powers established two ad hoc tribunals to prosecute Axis leaders accused of war crimes. The International Military Tribunal, which sat in Nuremberg, prosecuted German leaders while the International Military Tribunal for the Far East in Tokyo prosecuted Japanese leaders. In 1948 the United Nations General Assembly first recognised the need for a permanent international court to deal with atrocities of the kind prosecuted after World War II. At the request of the General Assembly, the International Law Commission (ILC) drafted two statutes by the early 1950s but these were shelved during the Cold War, which made the establishment of an international criminal court politically unrealistic.” ref
“Benjamin B. Ferencz, an investigator of Nazi war crimes after World War II and the Chief Prosecutor for the United States Army at the Einsatzgruppen trial, became a vocal advocate of the establishment of international rule of law and of an international criminal court. In his book Defining International Aggression: The Search for World Peace (1975), he advocated for the establishment of such a court. Another leading proponent was Robert Kurt Woetzel, a German-born professor of international law, who co-edited Toward a Feasible International Criminal Court in 1970 and created the Foundation for the Establishment of an International Criminal Court in 1971.” ref
“The ICC began operations on 1 July 2002, upon the entry into force of the Rome Statute, a multilateral treaty that serves as the court’s charter and governing document. States which become party to the Rome Statute become members of the ICC, serving on the Assembly of States Parties, which administers the court. As of November 2023, there are 124 ICC member states; 41 states have neither signed nor become parties to the Rome Statute. Intended to serve as the “court of last resort”, the ICC complements existing national judicial systems and may exercise its jurisdiction only when national courts are unwilling or unable to prosecute criminals. It lacks universal territorial jurisdiction and may only investigate and prosecute crimes committed within member states, crimes committed by nationals of member states, or crimes in situations referred to the Court by the United Nations Security Council.” ref
How the International Criminal Court works
“The International Criminal Court (ICC) investigates and, where warranted, tries individuals charged with the gravest crimes of concern to the international community: genocide, war crimes, crimes against humanity and the crime of aggression. The Court is participating in a global fight to end impunity, and through international criminal justice, the Court aims to hold those responsible accountable for their crimes and to help prevent these crimes from happening again. The Court cannot reach these goals alone. As a court of last resort, it seeks to complement, not replace, national Courts. Governed by an international treaty called the Rome Statute, the ICC is the world’s first permanent international criminal court.” ref
“The Court’s founding treaty, called the Rome Statute, grants the ICC jurisdiction over four main crimes. First, the crime of genocide is characterized by the specific intent to destroy in whole or in part a national, ethnic, racial or religious group by killing its members or by other means: causing serious bodily or mental harm to members of the group; deliberately inflicting on the group conditions of life calculated to bring about its physical destruction in whole or in part; imposing measures intended to prevent births within the group; or forcibly transferring children of the group to another group.” ref
“Second, the ICC can prosecute crimes against humanity, which are serious violations committed as part of a large-scale attack against any civilian population. The 15 forms of crimes against humanity listed in the Rome Statute include offenses such as murder, rape, imprisonment, enforced disappearances, enslavement – particularly of women and children, sexual slavery, torture, apartheid, and deportation.” ref
“Third, war crimes which are grave breaches of the Geneva conventions in the context of armed conflict and include, for instance, the use of child soldiers; the killing or torture of persons such as civilians or prisoners of war; intentionally directing attacks against hospitals, historic monuments, or buildings dedicated to religion, education, art, science or charitable purposes.” ref
“Finally, the fourth crime falling within the ICC’s jurisdiction is the crime of aggression. It is the use of armed force by a State against the sovereignty, integrity or independence of another State. The definition of this crime was adopted through amending the Rome Statute at the first Review Conference of the Statute in Kampala, Uganda, in 2010. On 15 December 2017, the Assembly of States Parties adopted by consensus a resolution on the activation of the jurisdiction of the Court over the crime of aggression as of 17 July 2018.” ref
Why do we need another international court? Why not use the International Court of Justice?
“This century has seen the worst violence in the history of humankind. In the past fifty years more than 250 conflicts have erupted around the world; more than 86 million civilians, mostly women and children, have died; and over 170 million people were stripped of their rights, their property and their dignity. Most of these victims have been simply forgotten and few perpetrators have been brought to justice. In spite of rules and laws defining and forbidding war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide, along with various treaties and conventions, protocols and codicils banning everything from poison gas to chemical weapons, what has been lacking up to now, has been any system for enforcing these norms and for holding individual violators criminally responsible.” ref
“The United Nations General Assembly first recognized the need for a permanent mechanism to prosecute mass murderers and war criminals in 1948, following the Nuremberg and Tokyo trials after World War II, and it has been under discussion at the UN ever since. Until now, however, attempts to create such a mechanism have been unsuccessful despite the need for a permanent criminal court to prosecute and punish those individuals committing the most serious crimes. The International Court of Justice, the principal judicial organ of the United Nations, was designed to deal primarily with disputes between States. It has no jurisdiction over matters involving individual criminal responsibility.” ref
US Sanctions on the International Criminal Court?
“On September 2, 2020, the United States government imposed sanctions on the International Criminal Court (ICC) prosecutor, Fatou Bensouda, and another senior prosecution official, Phakiso Mochochoko. In addition, US Secretary of State Michael Pompeo announced that the United States had restricted the issuance of visas for certain unnamed individuals “involved in the ICC’s efforts to investigate US personnel.” The sanctions on Bensouda and Mochochoko implemented a sweeping executive order issued on June 11, 2020 by President Donald Trump. This order declared a national emergency and authorized asset freezes and family entry bans against ICC officials who were identified as being involved in certain activities. Earlier, the Trump administration had repeatedly threatened action to thwart ICC investigations in Afghanistan and Palestine. In a precursor step, in 2019, the Trump administration revoked the prosecutor’s US visa. The following questions and answers discuss the Trump administration’s unprecedented authorization of a sanctions program aimed at undermining the work of the ICC.” ref
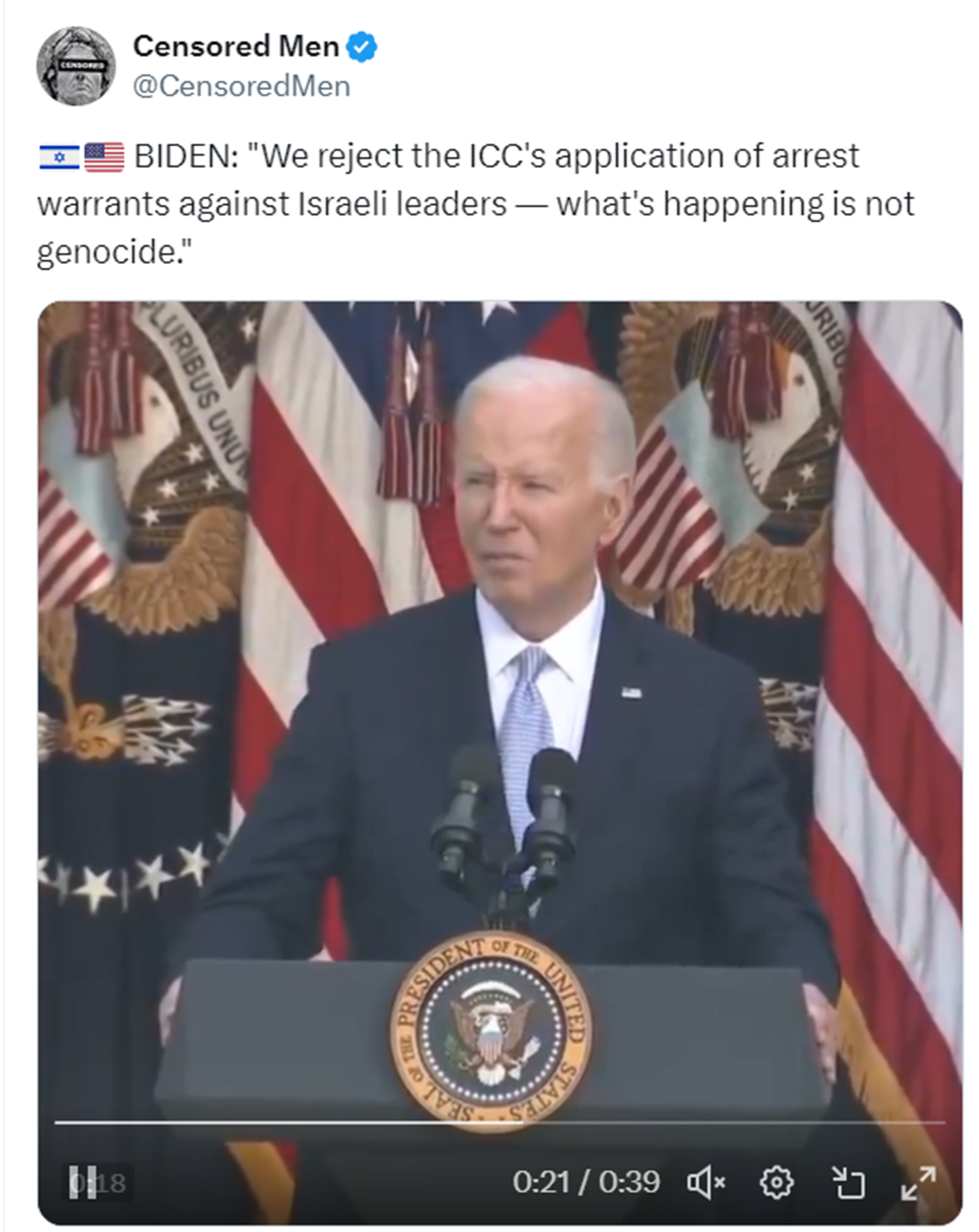

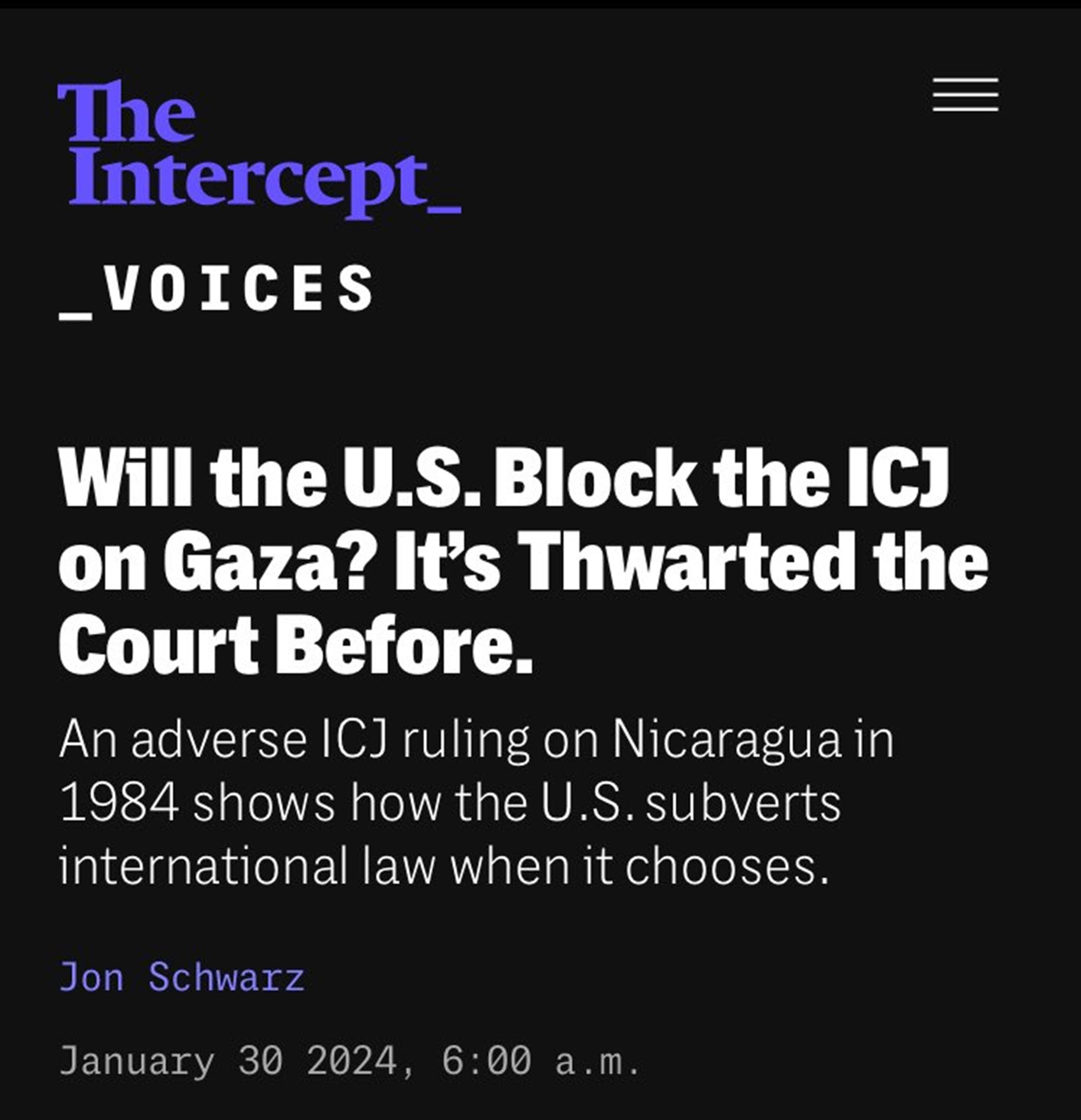

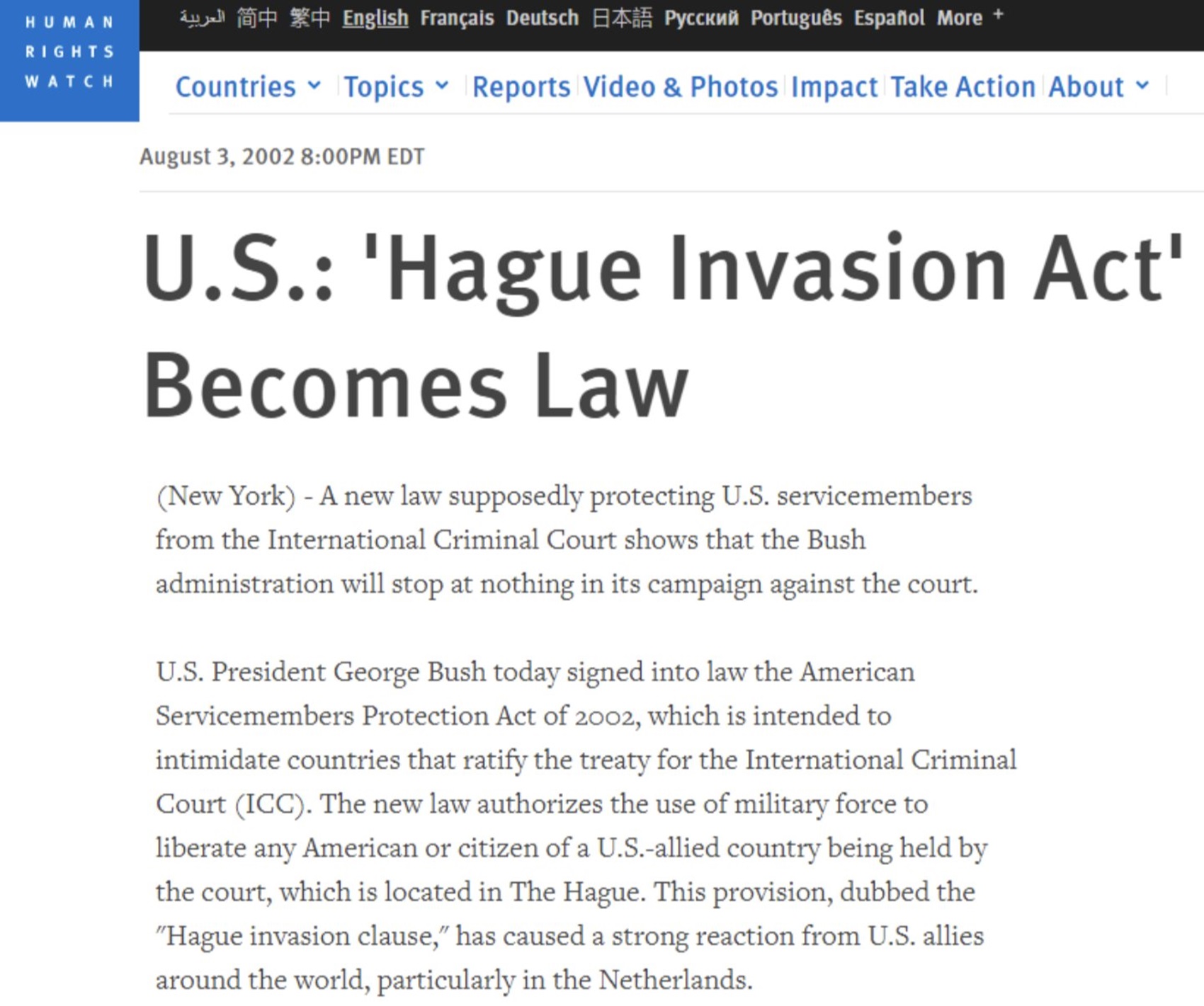
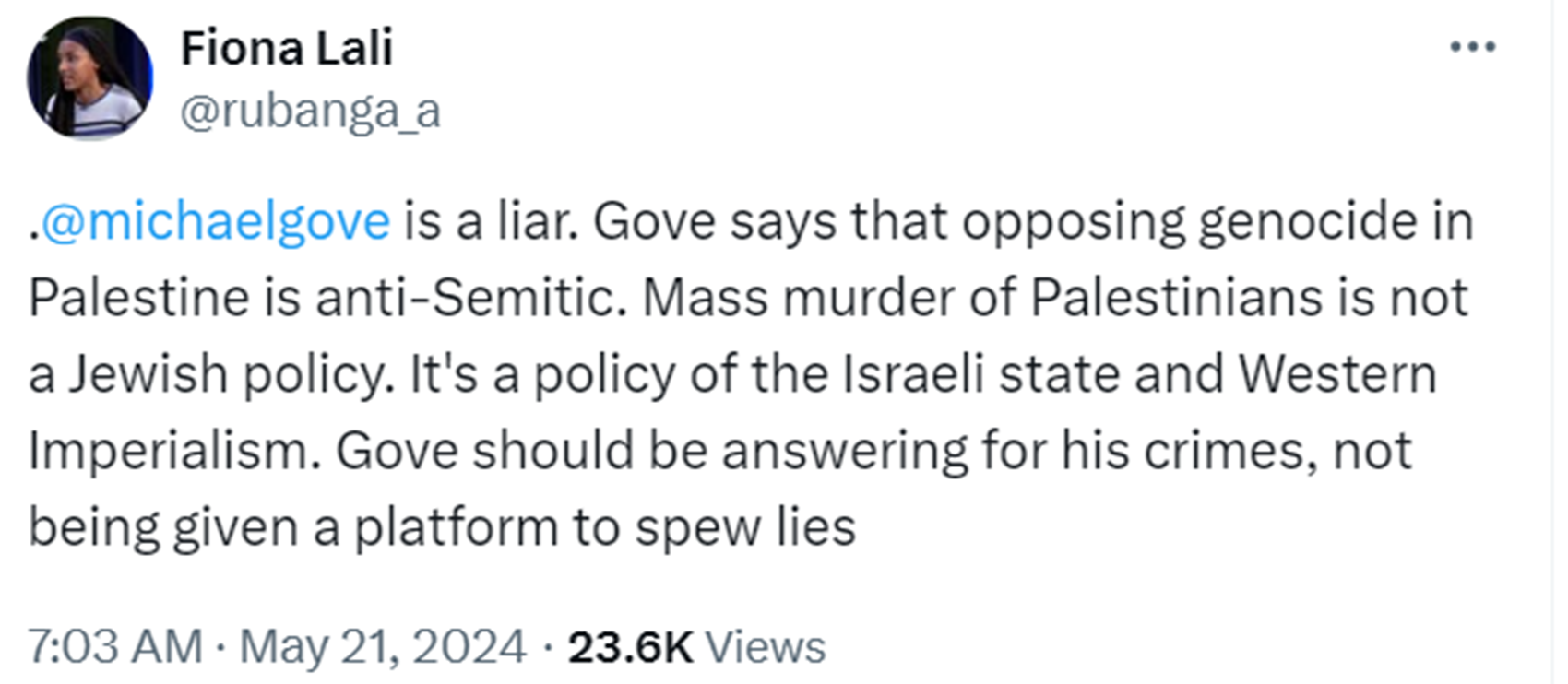
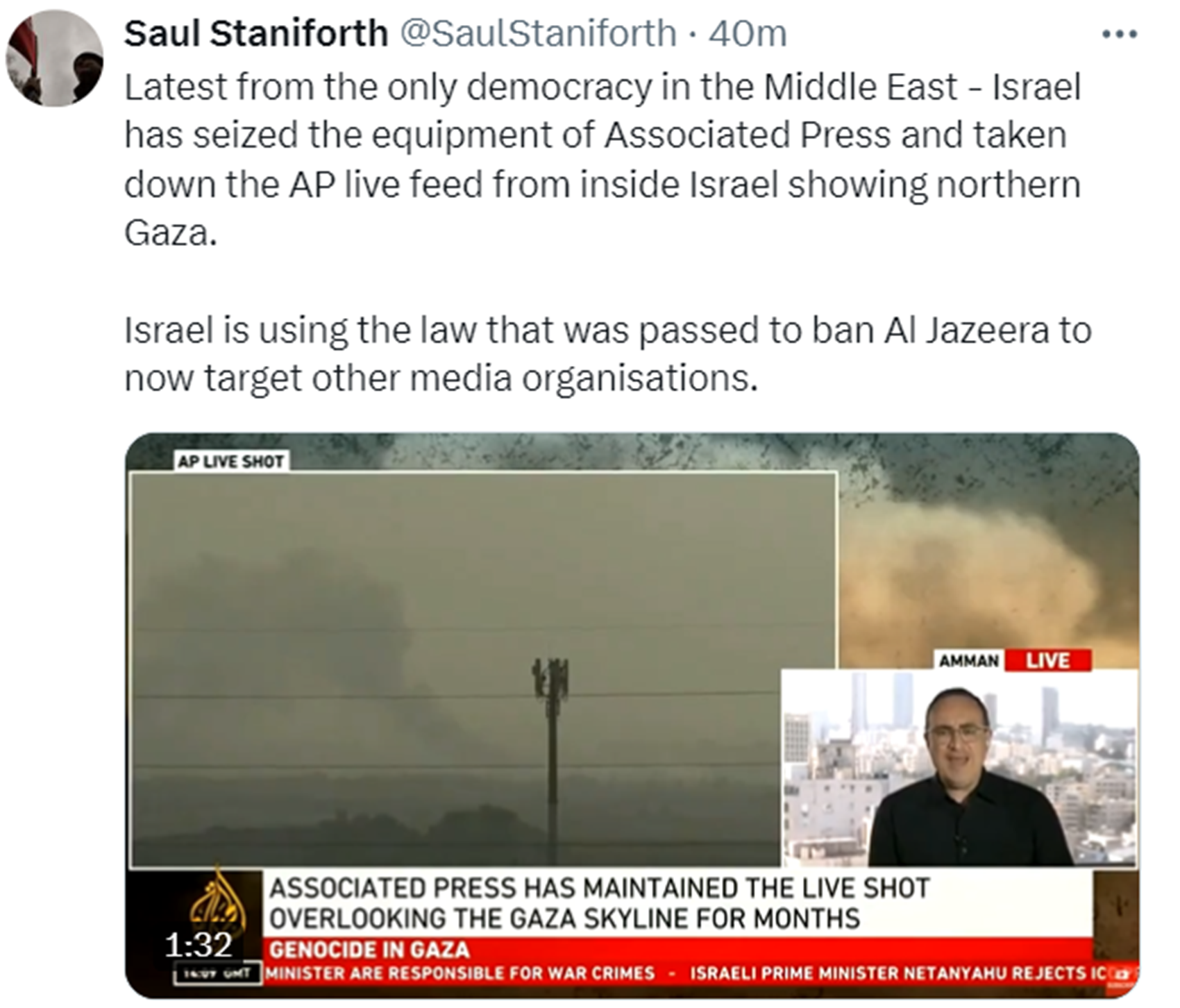
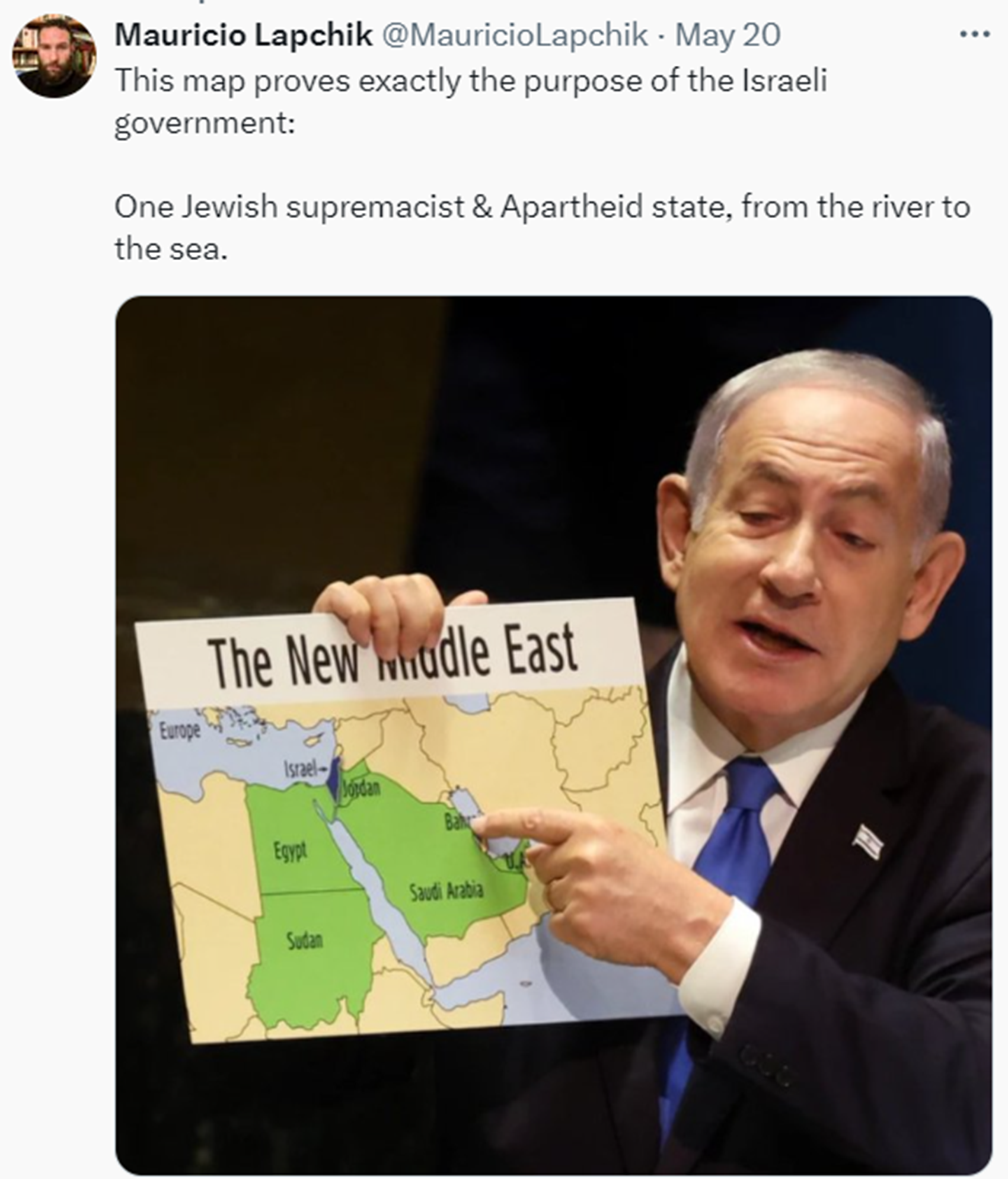
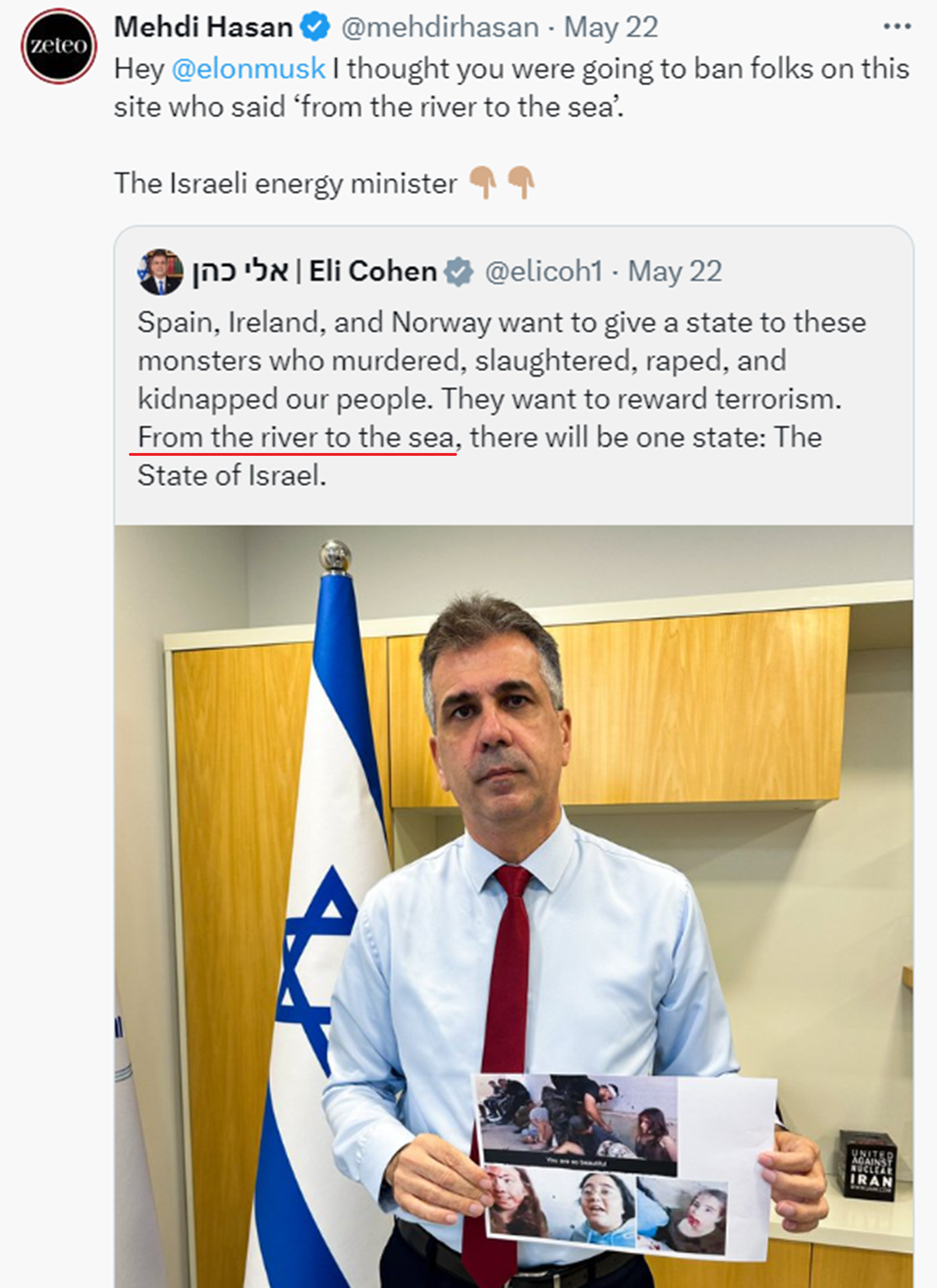
Heavy-handed NYPD on pro-Palestinian protesters
“Leaders of the NYPD sought to justify what appeared to be a heavy-handed crackdown by a controversial unit on pro-Palestinian protesters in Bay Ridge on Saturday amid mounting scrutiny about the department’s commitment to a federal settlement last year meant to protect demonstrators’ First Amendment rights and limit police violence. Video shared on social media showed police punching, shoving, and roughly engaging with the demonstrators. As part of the settlement, which went into effect in February and stemmed from the NYPD’s aggressive treatment of George Floyd protesters in 2020, the NYPD committed to working out new rules for accommodating demonstrations “whenever possible.” ref

A core value in anarchist thinking is a challenge to and the abolition of all unjust hierarchical power structures. Power can’t justify itself, and we should be very skeptical of all power. Just leaders are one of many, not one over many.
We all make a difference! Often we wait for others to be friendly, to be kind, to make a difference, or to be a leader. When we have such power all along, may I be friendly, Kind, make a difference, and be a leader of such active humanism, promoting human good…
I am wise, as I know I can be wrong. I am wise because I am open to learning from anyone. I am wise, though I am far from perfect; in fact, I am powerful as a thinker for the very reasons I challenge my thinking and eagerly work to change WHEN I SEE ERRORS.
“Responding to the application for arrest warrants by the Office of the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC) against Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Israeli Minister of Defence Yoav Gallant, as well as Hamas leaders Yahya Sinwar, Mohammed Deif and Ismail Haniyeh, for war crimes and crimes against humanity committed in Israel and in the State of Palestine, specifically in the occupied Gaza Strip, from at least 7 October 2023, Agnès Callamard, Amnesty International’s Secretary General, said:
“No one is above international law: no leaders of armed groups, no government officials – elected or not, no military officials. Regardless of the cause they are pursuing, no one is above the law. “This move by the ICC Prosecutor sends an important message to all parties to the conflict in Gaza and beyond that they will be held accountable for the devastation they have waged on the peoples of Gaza and Israel. “Those who are suspected of responsibility for crimes under international law in Israel and the OPT should face trial and accountability, no matter how powerful or how high-ranking they are.” ref
“The application for arrest warrants by the ICC’s prosecutor in the situation in the State of Palestine is also a long-awaited opportunity to end the decades-long cycle of impunity in Israel and the Occupied Palestinian Territories (OPT) and to restore the credibility of the international justice system as a whole. “All states must respect the legitimacy of the court, they must refrain from any attempts to intimidate or pressure the court to allow the judges to conduct their work with full independence and impartiality.” ref
“It is now for the Pre-Trial Chamber, while the office of the prosecutor is continuing its investigations, to promptly review and decide these first applications for arrest warrants. All states, including third states not members of the ICC, must respect this decision. If the Court’s judges approve any arrest warrants all ICC states parties must ensure the enforcement of these warrants.” The present applications for arrest warrants of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Israeli Minister of Defence Yoav Gallant allege the war crimes of starvation of civilians, attacks directed at civilians, and wilful killing and causing great suffering, as well as the crimes against humanity of extermination, including through starvation, and persecution, among others, under the Rome Statute, committed in the Gaza strip from at least 8 October 2023.” ref
“Regarding the Hamas leaders Yahya Sinwar, Mohammed Deif and Ismail Haniyeh, the Office of the Prosecutor alleges the crimes against humanity and war crimes, starting on 7 October, of extermination, murder, rape and other sexual violence, hostage-taking, and acts of torture and other cruel treatment in the context of captivity, among others. These applications still need to be reviewed and approved by a Pre-Trial Chamber of the Court, before arrest warrants can be issued. The Office of the Prosecutor also stated that investigations are ongoing. This means that further applications, both for other persons and alleged crimes, could still follow.” ref
“Amnesty International has long called for the ICC’s Prosecutor to take immediate concrete action to expedite the investigation opened in March 2021, with regard to potential crimes under the Rome Statute of the ICC committed since 13 June 2014 in Gaza and the West Bank, including East Jerusalem. On 29 October and again in November 2023, the ICC Prosecutor belatedly issued statements confirming that the ICC’s ongoing investigation into the situation in Palestine would cover acts committed by all sides in Israel and the OPT on and after 7 October. Israeli authorities have so far failed to promptly, thoroughly and independently investigate war crimes and other violations committed by the Israeli army across the OPT. And Palestinian authorities have failed to investigate crimes and violations by Hamas and other armed groups.” ref
“Evidence gathered by Amnesty International demonstrates how Israeli forces continue to flagrantly violate international humanitarian law, including since 7 October 2023, through indiscriminate or direct attacks on civilians and civilian objects in the occupied Gaza Strip, which must be investigated as war crimes. Israeli authorities have also failed to comply with measures issued by the International Court of Justice to prevent genocide by deliberately depriving access to sufficient humanitarian aid. Indiscriminate attacks or direct attacks against civilians and civilian objects by Israeli armed forces have also been documented by Amnesty International during the 2008-9, 2014, and 2021 conflicts.” ref
“Amnesty International has also documented violations of international law by Hamas and other Palestinian armed groups on and since 7 October including the deliberate killings of civilians, hostage-taking and launching indiscriminate rocket attacks on Israel. Amnesty International is calling on Hamas and Palestinian armed groups to unconditionally release all civilians who continue to be held hostage in Gaza. Hostage-taking is a war crime. Amnesty International has consistently documented violations of international law committed by Hamas and other armed groups in Gaza, including torture and ill-treatment, indiscriminate rocket attacks into Israel and those resulting in Palestinian casualties in the occupied Gaza Strip.” ref
International law and Israeli settlements
“The international community considers the establishment of Israeli settlements in the Israeli-occupied territories illegal on one of two bases: that they are in violation of Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention, or that they are in breach of international declarations. The United Nations Security Council, the United Nations General Assembly, the International Committee of the Red Cross, the International Court of Justice and the High Contracting Parties to the Convention have all affirmed that the Fourth Geneva Convention applies to the Israeli-occupied territories. Numerous UN resolutions and prevailing international opinion hold that Israeli settlements in the West Bank, East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights are a violation of international law, including UN Security Council resolutions in 1979, 1980, and 2016.” ref
“UN Security Council Resolution 446 refers to the Fourth Geneva Convention as the applicable international legal instrument, and calls upon Israel to desist from transferring its own population into the territories or changing their demographic makeup. 126 Representatives at the reconvened Conference of the High Contracting Parties to the Geneva Conventions in 2014 declared the settlements illegal as has the primary judicial organ of the UN, the International Court of Justice and the International Committee of the Red Cross. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334 of 2016, which passed 14-0 with the United States abstaining, declared that Israel’s settlement activity in the occupied Palestinian territories, including East Jerusalem, “has no legal validity and constitutes a flagrant violation under international law”, and demanded that Israel “immediately and completely cease all settlement activities.” ref
“Israel has consistently argued that the settlements are not in violation of the Fourth Geneva Convention since, in its view, Israeli citizens were neither deported nor transferred to the territories, and they cannot be considered to have become “occupied territory” since there had been no internationally recognized legal sovereign prior. Successive Israeli governments have argued that all authorized settlements are entirely legal and consistent with international law. In practice, Israel does not accept that the Fourth Geneva Convention applies de jure, but has stated that on humanitarian issues it will govern these areas de facto by its provisions, without specifying which these are.” ref
“The majority of legal scholars hold the settlements to violate international law, while others have offered dissenting views supporting the Israeli position. According to Talia Sasson, the Supreme Court of Israel, with a variety of different justices sitting, has repeatedly stated that Israel’s presence in the West Bank is in violation of international law. The establishment of settlements has been described by some legal experts as a war crime according to the Rome Statute (to which Israel is not a party), and is currently under investigation as part of the International Criminal Court investigation in Palestine. The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) holds that the establishment of Israeli settlements violate Fourth Geneva Convention. The ICRC also holds that the displacement of Palestinians that may occur due to the settlements also violates Article 49 of the Fourth Geneva Convention.” ref
“At present, based on the result of numerous UN resolutions that cite Article 49 of the Geneva Convention, the consensus view of the international community is that Israeli settlements are illegal and constitute a violation of international law. According to Tim Franks from the BBC, as of 2008 every government in the world, except Israel, considered the settlements to be illegal. In November 2019, the United States said that it no longer views them as inconsistent with international law. Since the occupation of the West Bank in 1967, numerous United Nations resolutions, including 446, 452, 465, 471, and 476 affirm unambiguously that Israel’s occupation is illegal, and, since Resolution 446 was adopted on 22 March 1979, have confirmed that its settlements there have no legal validity and pose a serious obstacle to peace. United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334 of 2016 states that Israel’s settlement activity constitutes a “flagrant violation” of international law and has “no legal validity.” It demands that Israel stop such activity and fulfill its obligations as an occupying power under the Fourth Geneva Convention.” ref
“In 2004, an advisory opinion by the primary judicial organ of the UN, the International Court of Justice, also found the settlements to be illegal under international law. The court’s finding was based on the provisions of the Fourth Geneva Convention and UN Security Council resolutions that condemned the establishment of settlements and attempts by Israel to alter the demographics of the territories under its control. The United Nations General Assembly, which regards itself as having a chief role in the process of the codification of international law, has passed several resolutions with an overwhelming majority that denounce settlements as being illegal.[citation needed] The United Nations Human Rights Council has also called the Israeli settlements and related activities a violation of international law.” ref
“According to records of the 1998 meeting of Committee on the Elimination of Racial Discrimination, Theo van Boven said
The status of the settlements was clearly inconsistent with Article 3 of the Convention, which, as noted in the Committee’s General Recommendation XIX, prohibited all forms of racial segregation in all countries. There is a consensus among publicists that the prohibition of racial discrimination, irrespective of territories, is an imperative norm of international law.” ref
“It has been observed that a double standard appears to apply with regard to Israel’s violations of UN resolutions and comparable violations by some other countries. Whereas the UNSC resolutions 660 and 687 regarding Iraq’s Invasion of Kuwait and the UNSC 1441 before the Gulf War demanded Iraq’s immediate withdrawal from land it occupied belligerently, and regarded as a casus belli its putative recourse to a program for building weapons of mass destruction, Israel, though occupying a foreign territory and reputedly having an atomic arsenal, was treated differently. The difference lies in the fact that UN Security Council resolutions against Israel are widely thought to be passed under Chapter VI of the United Nations Charter and are non-binding, being concerned with disputes that are to be resolved peacefully, whereas in the case of Iraq, the resolutions were passed under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter, which are legally binding. Resolution 242 however, while often thought to have been introduced within the framework of Chapter 6, was considered by both the Arab States and Russia at the time to be binding.” ref
“In 2004, an advisory opinion by the International Court of Justice concluded that Israel had breached its obligations under international law by establishing settlements in the West Bank, including East Jerusalem and that Israel cannot rely on a right of self-defence or on a state of necessity in order to preclude the wrongfulness of imposing a régime, which is contrary to international law. In its 2004 advisory opinion on the Legal Consequences of the Construction of a Wall in the Occupied Palestinian Territory it states, at paragraph 120, that Article 49(6) “prohibits not only deportations or forced transfers of population…but also any measures taken by an occupying Power in order to organize or encourage transfers of parts of its own population into the occupied territory.” All 13 judges were unanimous on the point. The Court also concluded that the Israeli régime violates the basic human rights of the Palestinians by impeding the liberty of movement of the inhabitants of the Occupied Palestinian Territory (with the exception of Israeli citizens) and their exercise of the right to work, to health, to education and to an adequate standard of living.” ref
International law and the Arab–Israeli conflict
“The International law bearing on issues of Arab–Israeli conflict, which became a major arena of regional and international tension since the birth of Israel in 1948, resulting in several disputes between a number of Arab countries and Israel. There is an international consensus that some of the actions of the states involved in the Arab–Israeli conflict violate international law, but some of the involved states dispute this. Israel has completed long stretches of barriers within the West Bank, separating Israel proper, Israeli settlements, and large parts of the Palestinian territories from Palestinian cities and population centers.” ref
“In the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel pre-empted what many Israeli leaders believed to be an imminent Arab attack and invaded and occupied territory that had itself been invaded and occupied by neighboring Egypt, Syria, and Jordan in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Following the peace treaties between Israel and Egypt and Israel and Jordan, in which the states relinquished their claims to the Israeli-occupied territory, the conflict today mostly revolves around the Palestinians. In 2004, the United Nations passed a number of resolutions, and the International Court of Justice issued a ruling where judges ruled 14–1 that the portions of the Israeli West Bank barrier that are located within occupied Palestinian territories are illegal under international law. Prior to the ruling, Israel had made the claim that the ICJ lacked standing to rule on the legality of the barrier, which the court unanimously rejected. On July 20, 2004, the United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution demanding that Israel obey the ICJ ruling. 150 nations voted in favor of the resolution, 7 voted against, and 10 abstained.” ref
“The main points of dispute (also known as the “core issues” or “final status issues”) are the following:
- Israel’s annexation of East Jerusalem (Israel has also annexed the Golan Heights, but that territory isn’t claimed by Palestinians), construction of Israeli settlements in the Palestinian territories, and the erection of the Israeli West Bank barrier;
- how borders should be decided between Israel and a Palestinian state;
- the right of return of the Palestinian refugees from the 1948 and 1967 wars.” ref
“Unlike a treaty agreement, customary international law is usually not written. Customs of a longstanding nature can be codified by formal treaties. The Laws and Customs of War on Land (Hague Convention IV) of 18 October 1907 and the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949 are examples of conventional laws that are declarations of customary law. To prove that a certain rule is customary one has to show that it is reflected in state practice and that there exists a conviction in the international community that such practice is required as a matter of law. In this context, “practice” relates to official state practice and therefore includes formal statements by states. A contrary practice by some states is possible because if this contrary practice is condemned by the other states, or subsequently denied by the government itself, the original rule is actually confirmed.” ref
“In accordance with article 13 of the UN Charter, the General Assembly is obligated to initiate studies and to make recommendations that encourage the progressive development of international law and its codification. Acting in that agreed-upon treaty capacity, the General Assembly affirmed the principles of international law that were recognized by the Charter of the Nuremberg Tribunal and directed that they should be codified. Many of those same principles were subsequently adopted for inclusion in draft treaties that were under development by the International Law Commission of the United Nations. They were also incorporated through the agreement of the High Contracting Parties into the Geneva Conventions of 1949.” ref
“In 1993, the UN Security Council “acting under Chapter VII of the Charter on the United Nations” established an international tribunal and approved a Statute that had been recommended in a report submitted by the UN Secretary-General. It concluded beyond doubt that the law applicable in armed conflict as embodied in the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949 and the Hague Convention (IV) of 18 October 1907 had become part of international customary law, and should be part of the subject matter jurisdiction of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia. In 1998, the United Nations Diplomatic Conference of Plenipotentiaries approved the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court. The offenses against unwritten customary international law were amenable to prosecution by international tribunals, like the Nuremberg Tribunal, long before they were codified and incorporated into the subsequent treaties.” ref
“Many provisions of international law are based upon principles and norms that were developed in the Americas during the 19th century. They include the principle of uti possidetis of 1810 and the related Monroe Doctrine of 1823, regarding non-colonization and non-intervention. In 1890, the First International Conference of American States adopted a proscription against territorial conquest and agreed upon the non-recognition of all acquisitions made by force. Those principles and regional understandings were recognized in Article 21 of the Covenant of the League of Nations. The system of mandates contained in article 22 of the Covenant was based in part upon those normative declarations and state practices. The Kellogg-Briand Pact of 1928, and the League of Nations approval of the Stimson Doctrine in 1931 were efforts designed to end the practice of coercive territorial revisionism through international law.” ref
“After World War II, the principles of international law that upheld the territorial integrity of states were incorporated in the Charter of the United Nations, and subsequently reaffirmed in the Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples, the Organization of African Unity charter respecting the integrity of inherited boundaries, and the 1975 CSCE Helsinki Final Act which contained a proscription that boundaries could only be altered by consent. The Chapter on Fundamental Rights and Duties of States in the Charter of the Organization of American States provides that:
The territory of a State is inviolable; it may not be the object, even temporarily, of military occupation or of other measures of force taken by another State, directly or indirectly, on any grounds whatever. No territorial acquisitions or special advantages obtained either by force or by other means of coercion shall be recognized.” ref
“In their relations with other peoples and countries during the colonial era the Concert of Europe adopted a fundamental legal principle that the supreme legal authority, or sovereignty, lay outside the indigenous nations. That legal principle resulted in the creation of a large number of dependent states with restricted sovereignty or colonial autonomy. Various terms were used to describe different types of dependent states, such as condominium, mandate, protectorate, colony, and vassal state. After World War II there was strong international pressure to eliminate dependencies associated with colonialism.” ref
“The vast majority of the world’s sovereign states resulted from the grant of independence to colonial peoples and dependent territories. Prior to World War II many states were formed as a result of wars that were resolved through peace treaties. Some of these peace treaties were imposed on the losing side in a war; others came about as a result of negotiations that followed wars, or were entered into under the threat of war. In these cases, the applicable law was bound in peace treaties among the states. The practice of territorial aggrandizement was prohibited by the UN Charter, a multilateral treaty, and the authoritative explanation of its legal principles contained in UN General Assembly resolution 2625 (XXV) of 24 October 1970, Declaration of Principles of International Law Concerning Friendly Relations and Co-operation Among States in Accordance with the Charter of the United Nations.” ref
“The purpose of the United Nations is the prevention and removal of threats to peace and the suppression of acts of aggression. The Charter requires that members shall refrain from the threat of, or use of force. According to communis opinio the obligations imposed by those provisions of the Charter have become part of customary international law and are binding on all States, whether they are members of the United Nations or not. After World War II, the British government decided to abandon its mandate in Palestine. A United Nations Commission (UNSCOP) was assigned to recommend a solution to the conflict to the General Assembly. The recommendation was a partition plan that would result in an Arab and a Jewish state in the remaining mandate, and Jerusalem under UN rule, was approved by the General Assembly.” ref
“However, the resolution served partially as a basis for the Declaration of the Establishment of the State of Israel to take effect when Great Britain’s mandate expired. Many states granted the State of Israel either de facto or de jure recognition. Israel was accepted as a sovereign member state in the United Nations and has diplomatic relations with many, but not all, sovereign states. The Geneva Conventions and other international tractates recognize that land: a) conquered in the course of a war; and b) the disposition of which is unresolved through subsequent peace treaties is “occupied” and subject to international laws of war and international humanitarian law. This includes special protection of individuals in those territories, limitations on the use of land in those territories, and access by international relief agencies.” ref
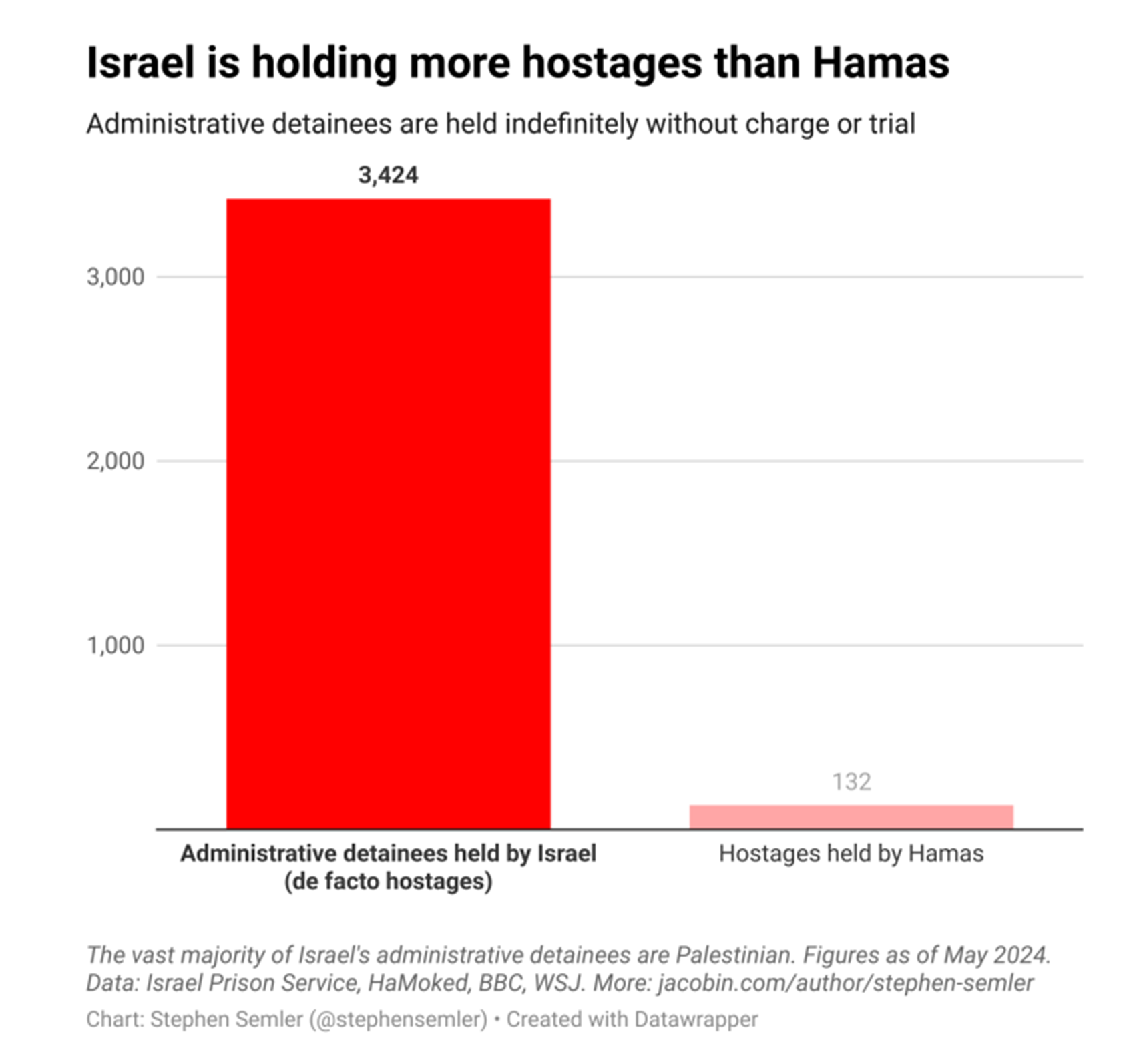
Israel’s Priority Is Killing Gazans, Not Freeing Hostages
“This war would look very different if Israel’s principal aim was to free the hostages. But Israel’s assault on Gaza was never about the hostages. The Biden administration is repeating the lie that Hamas is the only obstacle to peace in Gaza and the hostages returning home. “There would be a cease-fire tomorrow if Hamas would release the hostages,” Joe Biden said at a recent fundraiser in Seattle. “It’s up to Hamas; if they wanted to do it, we could end [Israel’s military campaign in Gaza] tomorrow.” This week, National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan said, “The world should be calling on Hamas to come back to the table and accept a deal” before reiterating the president’s claim.” ref
“Biden’s remarks came just a few days after Israel torpedoed a cease-fire and hostage release deal immediately after Hamas agreed to it. Israel then announced that it would proceed with its planned invasion of Rafah and bombed the city. After its invasion of Rafah caused a break in further negotiations, Israel fully cut off talks on May 10. Israel was never negotiating in good faith: Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu admitted on April 30 that Israel would invade Rafah “with or without a deal” to release the hostages. Israel’s official demands reflect this — the country refuses to accept a permanent cease-fire. After Netanyahu’s rejection of the latest proposal, it’s clearer than ever that Israel’s war isn’t and never was about the hostages. Biden’s continued support for Israel demonstrates that the hostages aren’t a priority for the United States, either.” ref
“If the hostages were a priority, Biden and Netanyahu would listen to the hostages’ families. Hamas has repeatedly offered to release the hostages in exchange for a cease-fire and Palestinian prisoners, including as early as October 7 and October 9. Family members of the Israeli hostages have repeatedly urged their government to accept those offers, but Israeli leaders always rebuffed them, claiming that military force is the best way to free the hostages. “We need to rely on the army that will bring them all home safely,” Israeli president Isaac Herzog said to the hostages’ families in October. Netanyahu told them, “The greater the pressure, the greater the chances [of freeing the captives].” That’s the excuse this time, too. In a statement, Netanyahu claimed invading Rafah would “apply military pressure on Hamas, with the goal of making progress on freeing the hostages and the other war aims.” ref
“The best chance of getting the hostages back is through a cease-fire and prisoner-exchange deal like the one Israel just rejected. The worst thing for the hostages’ well-being would be for Israel to continue its assault on Gaza. Israeli forces have shown that they’re more likely to kill hostages than rescue them. Hamas abducted about 250 people on October 7. As of mid-May, the group holds 132 in captivity. Hamas released four hostages in mid-October and 105 during a temporary cease-fire in late November in exchange for Palestinian prisoners. Outside of the cease-fire, Israeli forces have rescued just three hostages in seven months (one in October, and two in February) but managed to kill three in one day. In December, Israeli troops shot three hostages dead in broad daylight while they were shirtless and waving a white flag.” ref
“Israel announced that thirty-six of the remaining hostages are dead. It didn’t disclose the causes of the deaths but admitted that one was killed during a failed rescue operation (Hamas said he was killed by friendly fire; Israel hasn’t said one way or the other). Hamas claims that Israel has killed dozens more hostages by bombing Gaza. There’s good reason to believe them. Israel has prosecuted a historically destructive bombing campaign featuring carpet-bombing tactics and the prodigious use of two-thousand-pound bombs which “turn earth to liquid.” Several freed hostages said they were almost killed by Israeli bombardment.” ref
“Hamas is much more eager to release the hostages than Israel is to bring them home. After all, the main point of Hamas’s October 7 attack was to get enough hostages to eventually free in exchange for Palestinians held in Israeli prisons. This is from Hamas’s official statement on the attack:
Operation Al-Aqsa Flood on Oct. 7 targeted the Israeli military sites, and sought to arrest the enemy’s soldiers to pressure the Israeli authorities to release the thousands of Palestinians held in Israeli jails through a prisoner exchange deal.” ref
“Hostage taking and prisoner swaps in the context of Israel and Palestine date back to 1968. More recently, several exchanges have occurred between Israel and nonstate actors like Hamas and Hezbollah, including in 2004, 2008, and 2011. In March, Netanyahu slammed a proposal to exchange Israeli hostages for a thousand Palestinian prisoners as “ridiculous,” even though Israel freed more than a thousand prisoners in exchange for one Israeli soldier captured by Hamas in 2006.” ref
“Of the prisoners Israel agreed to release as part of the November cease-fire and hostage exchange, 80 percent hadn’t been convicted of any crime. Most were women and children. An NBC investigation found that they “were either charged with crimes that had not yet been prosecuted, or were detained under a practice known as administrative detention.” What’s administrative detention? B’Tselem explains:
In administrative detention, a person is held without trial without having committed an offense, on the grounds that he or she plans to break the law in the future. As this measure is supposed to be preventive, it has no time limit. The person is detained without legal proceedings, by order of the regional military commander, based on classified evidence that is not revealed to them. This leaves the detainees helpless — facing unknown allegations with no way to disprove them, not knowing when they will be released, and without being charged, tried or convicted.” ref
“In other words, administrative detainees are de facto hostages. So Israel held thousands of Palestinians hostage before Hamas took hundreds of Israelis hostage on October 7. In September, Israel broke the thirty-year record for the number of Palestinians in administrative detention, with 1,264. Now Israel holds 3,424 Palestinians hostage in administrative detention. This is only a fraction of the total 9,088 Palestinians that Israel has incarcerated as “security prisoners.” ref
“The Biden and Netanyahu administrations are colluding to make Hamas appear intransigent on releasing the hostages. This illusion depicts Israel as a reluctant hero, as opposed to an opportunistic murderer — it makes it seem like Israel has no choice but to continue its assault on Rafah and the rest of Gaza. Selling this assault as a hostage-rescue mission is dishonest and morally bankrupt. In effect, US and Israeli leaders are using the hostages as political cover for genocide.” ref
What did ICJ ruling mean in South Africa’s genocide case against Israel?
“In January, the ICJ delivered an interim judgment – and one key paragraph from the ruling drew the most attention: “In the Court’s view, the facts and circumstances… are sufficient to conclude that at least some of the rights claimed by South Africa and for which it is seeking protection are plausible.” The UN’s top court is hearing Israel’s response to a case brought by South Africa seeking an emergency halt to its offensive in Rafah. South Africa has also accused Israel of genocide in the Gaza war. Israel, which has called South Africa’s case “wholly unfounded” and “morally repugnant”, responded on Friday accusing South Africa of bringing “biased and false claims”. The words of the International Court of Justice (ICJ) have been subject to intense scrutiny since South Africa brought its case, and it’s centered around the use of the word “plausible” in the ruling. Having decided that Palestinians in Gaza had plausible rights under the Genocide convention, it concluded that they were at real risk of irreparable damage – and Israel should take steps to prevent genocide from occurring while these critical issues remain in question. The court did not rule whether Israel had committed genocide – but did its wording mean that it was convinced there was a risk of that happening?” ref
“In April, Joan Donoghue, the president of the ICJ at the time of that ruling, said, the purpose of the ruling was to declare that South Africa had a right to bring its case against Israel and that Palestinians had “plausible rights to protection from genocide” – rights which were at a real risk of irreparable damage. The judges had stressed they did not need to say for now whether a genocide had occurred but concluded that some of the acts South Africa complained about, if they were proven, could fall under the United Nations’ Convention on Genocide. Last December, South Africa launched an attempt at the ICJ to prove that, in its view, Israel was committing genocide in relation to how it was perpetrating the war against Hamas in the Gaza Strip. It alleged that the way Israel had prosecuted the war was “genocidal in nature” because, according to the South African case, there was an intention to “destroy Palestinians in Gaza”. Israel absolutely rejected these allegations, saying the entire case misrepresented what was happening on the ground. “In the Court’s view, the facts and circumstances… are sufficient to conclude that at least some of the rights claimed by South Africa and for which it is seeking protection are plausible.” ref
No genocide taking place in Gaza, Israel tells UN’s top court – as it happened (Fri 17 May 2024)
“Israel is appearing at international court of justice after South Africa asked it to urgently order end to assault on Rafah.” ref
“Israel on Friday defended the military necessity of its Gaza offensive at the International Court of Justice (ICJ) after South Africa asked judges to order it to halt operations in Rafah and completely withdraw from the Palestinian territory. Israeli justice ministry official Gilad Noam called South Africa’s case, which accuses Israel of violating the genocide convention, “completely divorced from facts and circumstances”. On Friday Noam told the ICJ that “this war, like all wars, is tragic … it has exacted a terrible human price but it is not genocide”. This week’s hearings focused only on issuing emergency measures and decision on the request is expected next week.” ref
“Noam told the ICJ hearing that South Africa’s charge of genocide was “an obscene exploitation of the most sacred convention,” referring to the international treaty banning genocide, agreed after the Holocaust in the second world war. Noam said that Israel’s military operations were not aimed at civilians, but at Hamas terrorists using Rafah as a stronghold, who have tunnel systems which could be used to smuggle hostages and militants out of Gaza.” ref
“Hearings at the International Court of Justice (ICJ) were briefly interrupted on Friday by a protester who called out “liars” as an Israeli official was presenting arguments. Reuters reported that a woman was seen being removed by court security guards.” ref
“Before Israel’s presentation at the ICJ, several dozen pro-Israeli protesters gathered outside, displaying photographs of hostages taken by Hamas on 7 October and demanding their release.” ref
“Israel must comply with international law in Gaza and address the devastating humanitarian crisis there, a group of western nations wrote in a letter to the Israeli government seen by Reuters on Friday. All countries belonging to the G7, apart from the US, signed the letter, along with Australia, South Korea, New Zealand, the Netherlands, Denmark, Sweden and Finland.” ref
“Israeli settlers attacked and burned a truck in the occupied West Bank overnight on Thursday, injuring the driver, the Israeli military said. Troops who arrived to separate the settlers from the Israeli driver were attacked and three soldiers were slightly hurt, the military said. Israel’s Kan public radio reported that the protesters believed the truck was carrying aid supplies to Gaza but the military said the truck was not.” ref
“At least 35,303 Palestinians have been killed and 79,261 have been injured in Israel’s military offensive on Gaza since 7 October, the Gaza health ministry said in a statement on Friday. The Hamas-run health ministry does not distinguish between combatants and non-combatants.” ref
U.S. report says it’s ‘reasonable to assess’ that Israel has violated humanitarian law (MAY 10, 2024)
“A U.S. State Department report said Friday it was “reasonable to assess” that Israel has violated international humanitarian law while carrying out military operations in Gaza. But the report stopped short of drawing any final or sweeping conclusions about Israeli conduct in the war against Hamas. The Biden administration voluntarily undertook this review of Israel and six other countries receiving U.S. weapons. While the administration is facing criticism at home and abroad, this report does not require it to take any specific actions. The report reflects an administration that’s become increasingly critical of Israel and frustrated with the way it’s handling the war, though President Biden insists he still supports Israel and its aim of defeating Hamas in Gaza.” ref
“The report looked at two key questions: whether Israel has violated international law while using U.S. weapons, and whether Israel is restricting humanitarian aid. On the first question, the report said: “It is reasonable to assess that [U.S.] defense articles … have been used by Israeli security forces since October 7 in instances inconsistent with its [International Humanitarian Law] obligations or with established best practices for mitigating civilian harm.” The State Department findings cited multiple examples where large numbers of Palestinian civilians were killed in Israeli airstrikes. The reports said these instances raised serious concerns, but the U.S. did not have enough evidence to reach definitive conclusions.” ref
“More than 34,000 Palestinians have been killed in Gaza, according to Palestinian health officials, adding that about two-thirds were women and children. Israel, meanwhile, has said it has killed more than 13,000 Hamas fighters in Gaza. On the question of humanitarian aid for Gaza, the report stated that Israel initially did not cooperate with the U.S. and international aid groups to let in humanitarian aid and thus “contributed significantly” to the lack of aid to the Palestinian people. Aid groups say that incoming assistance has all but halted this week after Israeli troops took over the Rafah border crossing along Gaza’s southern frontier with Egypt.” ref
“The Biden administration announced this week that the U.S. was withholding a weapons shipment to Israel consisting of more than 3,000 large bombs. And in an interview this week, Biden suggested he could pause the delivery of additional weapons as well. The U.S. has been sending large quantities of weapons to Israel for decades, and ramped up deliveries after the Hamas attack on Oct. 7 that ignited the war. The withholding of a single shipment of weapons is unlikely to have any impact on Israeli operations in Gaza, though it signals the administration’s sense that Israel should take a different approach.” ref
The UN has become a ‘terrorist entity,’ asserts Israel’s UN envoy (15 May 2024)
“The United Nations has become a “terrorist entity,” Israel’s UN Ambassador Gilad Erdan tells Army Radio, citing its alleged collaboration with Hamas in Gaza and documented cases of terror activities carried out from within UNRWA facilities. “The UN, since Israel withdrew from Gaza, has essentially become a collaborator with Hamas, and more than that, has become a terrorist entity of its own,” Erdan says.” ref
“Asked by the interviewer to elaborate on the accusation, Erdan softens his words slightly, claiming the UN has “partially” become a terrorist entity, and citing its frequent and swift condemnation of Israel upon any “unverified” accusation against it, while it declines to comment on allegations of Hamas use of UN infrastructure and fails to take action to prevent that or to fire UNRWA staff who have allegedly engaged in terrorism. “And thus the body has partially become a sort of terror organization, I have no better way of putting it,” he says.” ref
CBC has whitewashed Israel’s crimes in Gaza. I saw it firsthand (May 16 2024)
“Working for five years as a producer at the public broadcaster, I witnessed the double standards and discrimination in its coverage of Palestine—and experienced directly how CBC disciplines those who speak out. Six weeks into Israel’s siege and bombardment of the Gaza Strip, which had, at the time, killed over 11,000 Palestinians, the majority of them women and children. Legal experts were already suggesting that what was taking place could be a “potential genocide,” with an Israeli Holocaust scholar calling it “a textbook case.”” ref
Why we support ICC prosecutions for crimes in Israel and Gaza
“From Lord Justice Fulford, Judge Theodor Meron CMG, Amal Clooney, Danny Friedman KC, Baroness Helena Kennedy LT KC, Elizabeth Wilmshurst CMG KC”
- Lord Justice Fulford, retired lord justice of appeal, former vice-president of the Court of Appeal of England and Wales and former judge at the International Criminal Court
- Judge Theodor Meron CMG, visiting professor at the University of Oxford, honorary fellow, Trinity College, and former judge and former president of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia
- Amal Clooney, barrister, adjunct professor at Columbia Law School and co-founder of the Clooney Foundation for Justice
- Danny Friedman KC, barrister, expert in criminal law, international law and human rights
- Baroness Helena Kennedy LT KC, barrister, member of the House of Lords and director of the International Bar Association Human Rights Institute
- Elizabeth Wilmshurst CMG KC, former deputy legal adviser at the United Kingdom Foreign and Commonwealth Office and distinguished fellow of international law at Chatham House ref
“The attacks by Hamas in Israel on October 7 and the military response by Israeli forces in Gaza have tested the system of international law to its limits. This is why, as international lawyers, we felt compelled to assist when the prosecutor of the International Criminal Court, Karim Khan, asked us to advise whether there was sufficient evidence to lay charges of war crimes and crimes against humanity. Today, the prosecutor has taken a historic step to ensure justice for the victims in Israel and Palestine by issuing applications for five arrest warrants alleging war crimes and crimes against humanity by senior Hamas and Israeli leaders.” ref
“These include applications for a warrant of arrest against the political and military commanders of Hamas and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. For months, we have engaged in an extensive process of review and analysis. We have carefully examined each of the applications for arrest warrants, as well as underlying material produced by the prosecution team in support of the applications. This has included witness statements, expert evidence, official communications, videos and photographs. In our legal report published today, we unanimously agree that the prosecutor’s work was rigorous, fair and grounded in the law and the facts.” ref
“And we unanimously agree that there are reasonable grounds to believe that the suspects he identifies have committed war crimes and crimes against humanity within the jurisdiction of the ICC. It is not unusual for the prosecutor to invite external experts to participate in an evidence-review, under appropriate confidentiality arrangements, during the course of an investigation or trial. And this is not the first time an international prosecutor has formed a Panel of Experts to advise on potential charges related to a conflict. But this conflict is perhaps unprecedented in the extent to which it has given rise to misunderstandings about the ICC’s role and jurisdiction, a particularly fractured discourse and, in some contexts, even antisemitism and Islamophobia. It is against this backdrop that, as lawyers specialised in international law hailing from diverse personal backgrounds, we felt we had a duty to accept the invitation to provide an impartial and independent legal opinion based on evidence.” ref
“We were selected because of our expertise in public international law, international human rights law, international humanitarian law and international criminal law, and, in the case of two of us, experience as former judges of international criminal tribunals. Our common goal is advancing accountability and we have reached our conclusions based on an assessment of the warrant applications against an objective legal standard. We have reached these conclusions unanimously. And we believe it is important to publish them given the extent to which discourse has been politicised, disinformation has been rife and international media has been denied access to the front lines.” ref
“The Panel unanimously agrees with the prosecutor’s conclusion that there are reasonable grounds to believe that three of Hamas’s most senior leaders — Yahya Sinwar, Mohammed Deif and Ismail Haniyeh — have committed war crimes and crimes against humanity for the killing of hundreds of civilians, the taking of at least 245 hostages and acts of sexual violence committed against Israeli hostages. The Panel also unanimously agrees that the evidence presented by the prosecutor provides reasonable grounds to believe that Netanyahu and Israel’s minister of defence Yoav Gallant have committed war crimes and crimes against humanity. This includes the war crime of intentionally using starvation of civilians as a method of warfare and the murder and persecution of Palestinians as crimes against humanity. Our reasons for reaching these conclusions are set out in our legal report.” ref
“It is important to understand that the charges have nothing to do with the reasons for the conflict. The charges concern waging war in a manner that violates the long-established rules of international law that apply to armed groups and the armed forces in every state in the world. And, of course, the warrant applications announced today are just the first step. We hope that the prosecutor will continue to conduct focused investigations including in relation to the extensive harm suffered by civilians as a result of the bombing campaign in Gaza and evidence of sexual violence committed against Israelis on October 7. There is no doubt that the step taken today by the prosecutor is a milestone in the history of international criminal law.” ref
“There is no conflict that should be excluded from the reach of the law; no child’s life valued less than another’s. The law we apply is humanity’s law, not the law of any given side. It must protect all the victims of this conflict; and all civilians in conflicts to come. The judges of the ICC will ultimately determine which warrants, if any, should be issued. And as investigations continue, we hope that state authorities, witnesses and survivors will engage with the judicial process. Ultimately, we hope that this process will contribute to increased protections for civilians and sustainable peace in a region that has already endured too much.” ref
North Carolina Senate votes to ban people from wearing masks in public for health reasons (May 15, 2024)
“Republican supporters of the ban said it would help police crack down on protesters who wear masks — which some lawmakers called a growing concern, saying demonstrators are abusing Covid-19 pandemic-era norms to wear masks that hide their identities. “It’s about time that the craziness is at least slowed down, if not literally stopped,” said bill sponsor Buck Newton, R-Wilson. The proposal faced strong opposition from Democratic lawmakers, community activists, and advocates for people with health issues — who are concerned about the consequences of the proposal. House Bill 237 would ban everyone, not just protesters, from wearing masks in public for medical reasons if it becomes law. It passed 30-15, with every Republican in favor and every Democrat opposed.” ref
College students across the U.S. have been arrested and threatened with suspension over pro-Palestinian protests. But what legal rights do they have?
“After nearly 3,000 people were arrested at protests against the war in Gaza at 57 colleges and universities across the United States, hundreds of students were threatened with suspension or even expulsion, in addition to potential criminal charges being filed against them. As the academic year comes to an end, student protesters have continued demonstrating during graduation ceremonies. At Arizona State University, students have filed lawsuits against the school, claiming that their suspensions violated their right of free speech.” ref
“Students across the country still face severe consequences, including potential suspensions, evictions, expulsions and criminal prosecutions” according to the Appeal, a nonprofit news organization. The group reached out to hundreds of prosecutors and city attorneys to learn whether criminal cases will be filed against demonstrators. Out of the over 40 city attorney offices that responded to the Appeal, only four prosecutors confirmed they would not charge people for peacefully protesting — in Bernalillo County, N.M., where the University of New Mexico’s Albuquerque campus is; in Cook County, Ill., where the Art Institute of Chicago is; in Ithaca, N.Y., where Cornell University is; and in Ulster County, N.Y., where the State University of New York is.” ref
“In other cities, protesters still face serious criminal charges. In New Orleans three people were charged with battery, committing “hate crimes” against police and resisting an officer with force. The third charge could carry a one- to three-year prison sentence. In terms of academic penalties, some schools in California, like the University of Southern California and Cal Poly, Humboldt, have implemented interim suspensions, a punishment usually reserved for “serious and imminently dangerous misconduct,” according to the Los Angeles Times.” ref
“It’s not clear how many students have been formally suspended for participating in protests, because at some schools, like at the University of California, San Diego, students can appeal their suspensions and have them overturned. Do students have a claim to the First Amendment following the campus protests? Yahoo News spoke to legal experts to break down the rights of students.” ref
Public school campuses are protected as public spaces under the First Amendment
“Lee Rowland, the executive director of the National Coalition Against Censorship (NCAC), an activist group dedicated to supporting free speech, told Yahoo News that the First Amendment protects people from government censorship. “You have a right to engage in protected speech in areas where you’re allowed to be,” Rowland said, referring to public spaces. “The First Amendment fully protects you from censorship by the government, which includes public schools — whether they’re high schools or colleges or universities.” ref
“Robert Kleinfeldt, a senior counsel at New York City-based law firm Romano Law, emphasized that these rights are “strongest” in what is known as “traditional public forums,” such as streets, sidewalks and parks. The protection isn’t limited to just students — it’s any participant in a public campus protest.” ref
Private school campuses have different rules
“A private school on the other hand, like Columbia, has more “ability to control” who is on its property, which sets up trespassing violations to those who don’t abide by the school’s rules, Rowland said. “A private property owner can set [rules] and say, ‘Everyone here is trespassing’ and they have the right to make a legal complaint about trespassing or to call in the police,” she explained. “It would not be a First Amendment violation for the school to shut down an encampment — it doesn’t mean, however, that it is the correct or wise thing to do for free expression more broadly.” ref
What type of protesting isn’t protected by the First Amendment?
“Violence is not protected by the First Amendment. Some forms of civil disobedience aren’t protected either, such as occupying a building or staying overnight in a place that has a closing time. “Police generally cannot break up a demonstration or gathering unless there is … [an] immediate threat to public safety,” Kleinfeldt said.” ref
“There are also “time, place and manner” restrictions, which are laws that allow institutions of any kind to set general limits, such as start and end times for protests or capping the number of allowed demonstrators in one area. Rowland said that these laws make it constitutional for a school to call the police if protesters violate these restrictions. It becomes unconstitutional if the school calls the police in response to the message behind the protests.” ref
Protesters who get arrested need to have known ahead of time they were violating the law
“Private schools are allowed to come up with new rules that make it constitutional for them to punish protesters who violate them, Rowland said. For example, a school can decide that any student who participates in a walkout will be disciplined. The American Civil Liberties Union explained that for this example schools can enact new policies about missing classes, but they can’t punish students more harshly because of the message behind the walkout.” ref
“Rowland emphasizes that before anyone can be arrested or charged, they need to have known they were violating a law. “What we often see are announcements from police to [protesters], something to the effect of, ‘This has been declared an unlawful assembly; you have 20 minutes to pack up,’” Rowland said. “That warning is usually given to ensure that if police decide to issue an arrest, there is some evidence that the people arrested knew that they were breaking some rule or law.” ref
Grand jury ignores felony disguise charges against pro-Palestinian protesters at Xavier (May 13, 2024)
“A Xavier University student and a recent graduate arrested in connection with a campus protest were charged with felonies under a law that officials say had never been used in Hamilton County before. The pair appeared in court Monday on charges they committed a crime while wearing disguises. Witnesses said they were wearing medical face masks. They are also charged with trespassing, a misdemeanor.” ref
“By Monday afternoon, the charges against Sophia Dempsey and Julia Lankisch, both 22, had been ignored by a grand jury. In Ohio, grand juries are held in secret, so details about why the charges were so quickly brought before the jurors and why they were ignored is not known. The law that was used against students was a law that dates to the 1800s, but there is no record of its use in Hamilton County.” ref
“The protesters were initially charged under an 1800s-era law used to target the Ku Klux Klan and other similar violent, vigilante groups. Attorney General Dave Yost pointed out the law in a letter to Ohio university presidents in response to the recent pro-Palestinian protests. It carries a maximum sentence of 18 months in prison. Hamilton County Prosecutor’s Office spokesman Matthew Broo said staff at his office could find no records or recall anyone else ever being charged under this law in this county.” ref
“Dempsey and Lankisch were protesting Saturday in support of Palestine in reference to the ongoing war between Israel and Hamas, according to the student group XU Free Palestine. The protesters were “peacefully protesting the university’s investments in Israel and academic trips and its complicity in continuing to fund genocide,” the group said in its statement following the arrests.” ref
“While non-violent campus demonstrations by Xavier students, faculty and staff are welcome, University policy states it may limit the time, place and manner of demonstrations to ensure disruptions to campus operations are avoided,” the university said in a statement Saturday. He said he believes the “strong show of force” was influenced by the nationwide protests but pointed out this was not a major encampment. While there have been national stories about major conflicts between university administrations and students, Zolides said other schools have handled things differently.” ref
“There have been other schools that have addressed this more peacefully,” Zolides said. “It doesn’t have to be that way. Ethan Nichols, a rising Xavier University senior and leader in the XU Free Palestine group said the group is calling for Chief Warfel’s removal, an investigation into the arrests and for the faculty committee to hold a vote of no confidence in President Colleen Hanycz.” ref
‘Israelism’ Documentary, About Jewish Attitudes Toward Israel, Lands U.S. Distributor (May 10, 2024)
“The film centers on two young American Jews, Simone Zimmerman and Eitan, who are raised to defend the state of Israel at all costs. Eitan joins the Israeli military, while Zimmerman supports Israel on “the other battlefield:” America’s college campuses. When they witness Israel’s mistreatment of the Palestinian people with their own eyes, they are horrified and heartbroken. The two join the movement of young American Jews battling the old guard over Israel’s centrality in American Judaism and demanding freedom for the Palestinian people.” ref
“Their stories reveal a generational divide in the American Jewish community as more young Jews question the narratives their synagogues and Hebrew school teachers delivered them as children. The doc includes voices including Sami Awad, Peter Beinart, Jeremy Ben-Ami, Noam Chomsky, Noura Erakat, Abe Foxman and Cornel West, with the filmmakers describing it as being an “urgent, crucial examination of how we got here, what the debate in the Jewish community is like at this moment, and where it might go from here.” ref
Will the US adopt IHRA’s anti-Semitism definition? What’s the controversy? (8 May 2024)
“The United States House of Representatives passed a bill on May 1 that could expand the federal definition of anti-Semitism, and the Senate – the upper house of Congress – is now expected to debate and vote on the legislation. The Democratic Party’s Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer said on Thursday that the bill faced objections from some Democrats and Republicans. At the heart of the debate and controversy over the bill is the definition of anti-Semitism that it seeks to adopt – despite opposition from several civil liberties groups.” ref
“The bill codifies a definition drafted by the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance (IHRA) that has been accused of conflating criticism of the state of Israel and Zionism with anti-Semitism. Critics of the bill warn the non-legally binding working definition was developed as a tool for monitoring anti-Semitic incidents worldwide and was never intended to serve as a legal framework. As protests against Israel’s war in Gaza continue to roil US campuses, concern is rising over the possible use of a new definition to stifle dissent and curb academic freedom.” ref
“The IHRA definition consists of a four-line description as follows: “Anti-Semitism is a certain perception of Jews, which may be expressed as hatred toward Jews. Rhetorical and physical manifestations of anti-Semitism are directed toward Jewish or non-Jewish individuals and/or their property, toward Jewish community institutions and religious facilities.” ref
“It goes on to provide 11 “contemporary examples of anti-Semitism” to illustrate its application, seven of which deal with the State of Israel. One of the examples states that anti-Semitism is embodied in “denying the Jewish people their right to self-determination, i e, by claiming that the existence of a State of Israel is a racist endeavor.” It is also anti-Semitic to apply “double standards by requiring of [Israel] a behavior not expected or demanded of any other democratic nation” and “drawing comparisons of contemporary Israeli policy to that of the Nazis.” ref
“In a letter sent to US senators on May 3, the non-profit Middle East Studies Association argued the bill “endangers the constitutionally protected right to freedom of speech as well as academic freedom at this country’s institutions of higher education.” “We believe that requiring the federal government to define anti-Semitism so broadly and vaguely will have a chilling effect on scholarly and public discussion of international affairs and current events in this country,” it said. “Indeed, it is likely to have the perverse effect of defining as anti-Semitism even criticism of Israeli policies advanced by Israeli scholars, or by Jewish students and faculty in the United States.” ref
Why is the definition controversial?
“Several Middle East experts and prominent lawyers have argued it expands the definition of anti-Semitism beyond its traditional meaning of hatred against Jews to encompass all criticism of Jewish institutions, including Israel. The slogans “Free Palestine” or “From the river to the sea, Palestine will be free” are considered anti-Semitic under the definition. As a result, monitoring organizations in several countries in the US and Europe warned of a rise in anti-Semitic incidents since the beginning of the war in Gaza on October 7.” ref
“A statement issued in 2022 by 128 scholars, including leading Jewish academics at Israeli, European, United Kingdom and United States universities, said the definition had been “hijacked” to protect the Israeli government from international criticism. Former UN Special Rapporteur on racism, E Tendayi Achiume, said it was being “wielded to prevent or suppress legitimate criticisms of the State of Israel, a State that must, like any other in the United Nations system, be accountable for human rights violations that it perpetrates.” “Those primarily harmed as a result are Palestinians, as well as human rights defenders advocating on their behalf,” Achiume added in a 2022 report.” ref
“Israeli Professor Neve Gordon, vice president of BRISMES and professor of international law and human rights at Queen Mary University in London, told Al Jazeera that by conflating anti-Zionism with anti-Semitism, the IHRA definition may result in the paradoxical branding of critical Jewish voices as anti-Semitic. “If I were to teach in a class the Human Rights Watch report stating that Israel is an apartheid state, I could be accused of anti-Semitism,” Gordon said.” ref
“In one recent example, renowned British Palestinian surgeon Ghassan Abu-Sittah was branded an anti-Semite for a post on social media equating Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to German Nazi leader Adolf Hitler, the main architect of the Holocaust. Abu-Sittah, who spent 43 days tending to the wounded in Gaza City last year, was refused entry into Germany to speak at a conference and forbidden from appearing on video link. Then, last week, he was also barred from entering France, where he was visiting to address the upper house of Parliament. “The idea that comparing policies carried out by Israel with policies carried out by the Nazi regime is anti-Semitic is crazy,” Gordon said. “What the definition tries to do is to silence legitimate critique of Israel and the genocide it is carrying out in Gaza.” ref
According to the American Jewish Committee (AJC),
“WHAT IS ANTI-ZIONISM: Zionism is derived from the word Zion, referring to the Biblical Land of Israel. In the late 19th century, Zionism emerged as a political movement to reestablish a Jewish state in Israel, the ancestral homeland of the Jewish People. Today, Zionism refers to support for the continued existence of Israel, in the face of regular calls for its destruction or dissolution. Anti-Zionism is opposition to Jews having a Jewish state in their ancestral homeland, and denies the Jewish people’s right to self-determination.” ref
“HOW IS ANTI-ZIONISM ANTISEMITIC: The belief that the Jews, alone among the people of the world, do not have a right to self-determination — or that the Jewish people’s religious and historical connection to Israel is invalid — is inherently bigoted. When Jews are verbally or physically harassed or Jewish institutions and houses of worship are vandalized in response to actions of the State of Israel, it is antisemitism. When criticisms of Israel use antisemitic ideas about Jewish power or greed, utilize Holocaust denial or inversion (i.e. claims that Israelis are the “new Nazis”), or dabble in age-old xenophobic suspicion of the Jewish religion, otherwise legitimate critiques cross the line into antisemitism. Calling for a Palestinian nation-state, while simultaneously advocating for an end to the Jewish nation-state is hypocritical at best, and potentially antisemitic.” ref
“IS ALL CRITICISM OF ISRAEL ANTISEMITIC: No. The International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance’s Working Definition of Antisemitism (“the IHRA Definition”) — employed by governments around the world — explicitly notes that legitimate criticism of Israel is not antisemitism: “Criticism of Israel similar to that leveled against any other country cannot be regarded as antisemitic.” When anti-Zionists call for the end of the Jewish state, however, that is no longer criticism of policy, but rather antisemitism.” ref
Myth: Israel (or any other state) has a right to exist
Israel Doesn’t Have a “Right to Exist” — But Israelis and Palestinians Do
“But no nation-state has an inviolable right to exist — especially not an ethnostate based on exclusion and ethnic cleansing. The mystical two-state solution also assumes that Future Independent Palestine would reclaim the territory that Israel has conquered since 1967 but not formally annexed. So, realistically, a “Palestinian state” wouldn’t take up all of the West Bank and Gaza (territories that add up to just 22 percent of the total land mass of Israel/Palestine as a whole).” ref
States Have No Inherent ‘Right to Exist’—but It’s a Media Fixation on Israel/Palestine
“No state has an intrinsic “right to exist.” As international relations scholar Scott Burchill points out, there is no abstract “right to exist” in international law, or in “any serious theory of international relations.” Nor is it customary, Burchill explains, for states or sub-state groups to recognize a state’s “right to exist.” “States,” writes the author Yousef Munayyer (Forward, 1/22/19), don’t exist because they have a “right” to. They exist because certain groups of people amassed enough political and material power to make territorial claims and establish governments, sometimes with the consent of those already living there and, oftentimes, at their expense.” ref
“In stories on Israel/Palestine, however, media outlets regularly draw attention to whether Palestinians and their supporters recognize an Israeli “right to exist.” I used the media aggregator Factiva to search for “Israel’s right to exist” in material the New York Times, Wall Street Journal and Washington Post have run between January 1, 2000, and February 2, 2021, the time of writing. Between these three newspapers, the phrase appears in a combined 1,358 pieces. Given the frequency with which it appears, this aspect of discussions about Israel/Palestine merits examination.” ref
“In the Washington Post (1/20/21), to take one recent example, Daniel W. Drezner wrote a deeply critical assessment of Trump’s legacy but said, “Are there positive accomplishments the Trump administration can take credit for? Sure. Every administration has their concrete achievements.” Among these, Drezner asserted, is that “a few more countries recognize Israel’s right to exist than before.” ref
“As I’ve shown in FAIR (9/26/20), Trump’s chief “achievements” in these deals were opening the door to weapons proliferation, escalating the risk of war and entrenching colonialism: The United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and, more recently, Morocco and Sudan “recognizing Israel’s right to exist” meant cementing a belligerent military alliance against Iran, and facilitating the further dispossession of and violence against Palestinians—and, in Morocco’s case, the Saharawis of Western Sahara (Haaretz, 12/11/20).” ref
“In a similar case of goalpost shifting, Newsweek (11/30/20) ran a piece by Gilad Erdan, Israel’s ambassador to the United Nations and now also Israel’s ambassador to the United States. Erdan asserted that the United Nations insists on “only” referring to the Temple Mount by its Muslim name, Haram al-Sharif. (Search “Temple Mount” on the UN’s webpage and you get 254 results compared to 329 for Haram al-Sharif; most UN documents seem to use both its Jewish and its Muslim name.)” ref
“On the basis of this false claim, Erdan wrote that “by ignoring our 3,000-year link to the Temple Mount, the UN validates the Palestinian refusal to recognize our right to exist as the world’s only Jewish state.” Here Erdan suggests that Jewish peoples’ connection to the Temple Mount necessarily translates not only into Israel having a “right to exist,” but a “right to exist as the world’s only Jewish state.” ref
“This approach suggests that the “right to exist” extends to the right to be an ethno-state: At present, the state to which Erdan refers is “the world’s only Jewish state” in the sense that it discriminates against the indigenous inhabitants of the land because they are not Jewish. Perhaps most notably, it minimizes the non-Jewish population by preventing Palestinian refugees from exercising their legally protected right to return to their homes, while guaranteeing any Jewish person on Earth the right to settle the land and become Israeli citizens.” ref
“Erdan is hardly the only one to misleadingly conflate the state of Israel’s “right to exist” with Jewish peoples’ cultural, religious and human rights: Of the above-mentioned 1,358 pieces in the Times, Journal and Post, 83 refer to “Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state,” or involve analogous phrasing. Such slippages between the Israeli state and Jewish people muddy exactly what one is being asked to recognize, which is precisely why the phrase “Israel’s right to exist” operates as an emotional sledgehammer.” ref
“As Munayyer (Forward, 1/22/19) noted: Factors like the unfortunate though all-too-often-commonplace conflation of the State of Israel with Judaism and world Jewry, coupled with the awful history of persecution Jews have faced, mean that anyone who doesn’t answer the question about Israel’s right to exist with an unequivocal “yes” risks being portrayed as an eliminationist radical worthy of labels like “antisemite.” ref
“Author and scholar Steven Salaita (Mondoweiss, 12/10/19) pushes back against this approach, saying that there are plenty of reasons to eschew the demand [to recognize Israel’s “right to exist”]. The first reason is practical: We don’t advocate for the destruction of human communities, but of ideologies conducive to racism and inequality. It’s both insidious and unethical to conflate Jewish people (of any national origin) with the existence of a violent, rapacious polity. That sort of conflation is a grave disservice to activists and intellectuals devoted to a better world—and to the communities for whom a better world is a necessity of survival….” ref
“Steven Salaita stated, I am happy, eager even, to affirm the right of Jewish people to live in peace and security, wherever that may be, a right all humans deserve in no particular order of worthiness. But I won’t ratify Israel’s bloody founding or its devotion to racial supremacy. Ultimately, when Zionists demand that you affirm Israel’s right to exist, what they really seek is affirmation of Palestinian nonexistence.” ref
“This manifestation of the “right to exist” issue is especially live in coverage of the movement to boycott, divest from and levy sanctions against Israel (BDS). NPR (11/19/20), for example, wrote that “some supporters of BDS deny Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state, which has led Israel’s leaders to label the movement both antisemitic and an existential threat.” The article gave voice to BDS activists pointing out that mislabeling the campaign in general as antisemitic “has been condemned by dozens of Jewish groups worldwide and by hundreds of leading Jewish and Israeli scholars, including world authorities on antisemitism and the Holocaust.” However, the specific claim from “Israel’s leaders” that “deny[ing] Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state” is antisemitic was not explicitly challenged.” ref
“It was, however, challenged days ago in a mainstream Israeli newspaper (Haaretz, 1/30/21), when journalist Gideon Levy wrote: One can regard Zionism as racism without being suspected of being antisemitic. It’s inconceivable that those combating racism be condemned as racists of the antisemitic brand. From the Law of Return to the nation-state law, from the ethnic cleansing of 1948 to the ethnic cleansing of the Jordan Valley and the southern Hebron hills in 2021, this is the brief summary of Zionist history. Is this not racism?” ref
“The reality of apartheid and Jewish supremacy from the Jordan River to the sea is hidden only from the blind, the ignorant, the propagandists and the liars. The BDS movement does not wish to destroy Israel, only to replace its regime of Jewish supremacy; the Palestinian right of return is not meant to throw the Jews into the sea; the one-state solution is not meant to repatriate the Jews to Europe. All of these only wish to partially and belatedly repair an historic wrong wrought by Zionism, deliberately or not, a correction without which no belated justice will ever be established here.” ref
“In contrast, the New York Times (12/12/20) published an article about artists and intellectuals in Germany who questioned the effects of the German Parliament’s May 2019 resolution designating BDS a form of antisemitism and “call[ing] on all Germany’s states and municipalities to deny public funding to any institution that ‘actively supports’ the movement, or questions the right of the state of Israel to exist.” This is one of three passages in the article connecting the questioning of Israel’s “right to exist” with antisemitism,, the other two being statements from German officials.” ref
“The piece’s only counterpoint was its account of Yehudit Yinhar, a Jewish-Israeli student at a German art school who was accused of antisemitism for helping organize a project called “School for Unlearning Zionism.” Yinhar’s case illustrates the pitfall of assuming that the state of Israel is an essential feature of Judaism—comparable, perhaps, to assuming that the state of Myanmar embodies Theravada Buddhism. Readers who know that opposing Zionism is more or less equivalent to challenging Israel’s “right to exist as a Jewish state” will glean that Yinhar’s story functions to partially balance the assertions that critics of Zionism are inherently antisemitic. Yet there is no voice in the article that directly questions that repeated equation.” ref
“Coverage that asks whether Palestinians and pro-Palestinians acknowledge Israel’s “right to exist” poses an unhelpful question. The far more concrete, constructive and urgent one is: What is a fair arrangement under which all the peoples of historic Palestine can live? Borders shift, states come into and out of being—did Yugoslavia have a “right to exist”?—and countries change political systems. Jim Crow once existed in the American South, and apartheid once existed in South Africa, but these systems have been replaced.” ref
“Yet, as Munayyer (Forward, 1/22/19) writes: White and Black populations [continue to exist in each place], and they both exercise self-determination through equal rights to the vote. What no longer exists are the overt and systemic policies of Apartheid and Jim Crow…even though much work remains to achieve real equality in both places. We should fight for that outcome in Israel/Palestine, where the rights of all people to freedom, justice and equality come before the so-called “rights” of any state to deny them.” ref
USA House passes resolution reaffirming Israel’s right to exist
“ H.Res. 888—Reaffirming the State of Israel’s right to exist: Israel is the only state in the world whose fundamental right to exist, within any borders at all, is openly denied by other states. Some of them including Iran even call for Israel’s complete destruction and support transnational terrorist organizations to work toward its destruction. It is also the only state in the world whose fundamental right to exist is constantly undermined and challenged by intergovernmental organizations—such as, most shamefully of all, the United Nations. The antisemitism motivating those who deny Israel’s right to exist is apparent, but it is important to connect, as this resolution does, the denial of Israel’s right to exist to antisemitism and to connect them both, as enabling causes, to the monstrous crimes Hamas has unleashed on Israel. Make no mistake, antisemitic bigotry is at the root of the UN’s hostility toward Israel, which is ugly, evil, and manifests itself in almost every UN entity.” ref
Israel’s “Right to Exist” Is a Rhetorical Trap
No country has a right to exist, so what do people really mean when they say Israel does?
“There can be no genuine peace in the Middle East until the Arab states abandon the policy of hostility to Israel and show by deeds and words readiness to accept Israel’s right to exist,” Abba Eban, Israel’s ambassador to the United States, told the Overseas Writers Club in Washington in 1955. Sixty-six years later, Dani Dayan, the Israeli consul general in New York, wrote in The New York Times, “The day Palestinians accept Israel’s right to exist as the legitimate homeland of the Jewish people, a real peace process will begin.” Through the intervening years of wars, invasions, occupation, peace processes, and treaties, Israel’s right to exist has stubbornly endured. Just last month, the House of Representatives passed a resolution that “denying Israel’s right to exist is a form of antisemitism.” The phrase and its long history compels us to ask: What does it mean for a nation to “exist,” and who judges its right to do so?” ref
“Republican Congressman Chris Smith of New Jersey said recently that “Israel is the only state in the world whose fundamental right to exist, within any borders at all, is openly denied by other states.” But Israel is the only nation with a “right to exist,” as the phrase is not commonly attached to any other country. And that’s the tell: This is not a legal concept, but a political one, available for broad interpretation and rhetorical weaponization. The “right to exist” as a nation is, as the Palestinian scholar Edward Said once wearily dismissed it, “a formula hitherto unknown in international or customary law.” Rights pertain to individuals, not countries. And universal rights can’t, by definition, belong to some peoples and not others. It’s one of the great ironies, then, of the Israel-Palestine conflict that Israel seems untouchable by international law as it actually exists—it suffers no sanctions for routine violations of Geneva Convention prohibitions against settlements in the occupied West Bank—but is so fulsomely protected by a statute of international law that is basically made up.” ref
“However intensely Israel feels under threat, its right to exist is meaningless as a matter of law. Its realest meaning is as a flexible piece of political rhetoric. One consistency in its use over the years is that Israel’s “right to exist” is always invoked negatively, as a thing someone somewhere denies or won’t accept. It’s most typically used to characterize Arab and Palestinian intransigence or dogmatism. After Israel’s resounding victory in the 1967 Six-Day War against Egypt, Syria, and Jordan, Egypt’s foreign minister told the press in obvious exasperation: Perhaps we have not said this loudly enough or plainly enough…. That this document [the Egyptian-Israeli Armistice Agreement of 1949] would guarantee the right of Israel to exist is self-evident. We do know Israel exists, we have signed a piece of paper. We did not sign it with shadows.” ref
“Palestine Liberation Organization President Yasir Arafat sounded a similar note in 1988, after an official statement that the Palestinian National Council “accepted the existence of Israel as a state in the region.” “The PNC accepted two states, a Palestinian state and a Jewish state, Israel,” Arafat said. “Is that clear enough?” Apparently, it was not. The specific meaning of the phrase relies a lot on things unsaid or implied: Both the nature of the supposed refusal and the implication that denying Israel’s “right to exist” means denying Jews’. It also depends a lot on the dependent clauses that come after that word: “as a state,” “in peace and security,” or “as a Jewish state?” ref
Right to Exist
“The right to exist is said to be an attribute of nations. According to an essay by the 19th-century French philosopher Ernest Renan, a state has the right to exist when individuals are willing to sacrifice their own interests for the community it represents. Unlike self-determination, the right to exist is an attribute of states rather than of peoples. It is not a right recognized in international law. The phrase has featured prominently in the Arab–Israeli conflict since the 1950s. The right to exist of a de facto state may be balanced against another state’s right to territorial integrity. Proponents of the right to exist trace it back to the “right of existence”, said to be a fundamental right of states recognized by writers on international law for hundreds of years.” ref
“Thomas Paine (1737–1809) used the phrase “right to exist” to refer to forms of government, arguing that representative government has a right to exist, but that hereditary government does not. In 1823, Sir Walter Scott argued for the “right to exist in the Greek people.” (The Greeks were then revolting against Turkish rule.) According to Renan’s “What is a Nation?” (1882), “So long as this moral consciousness [called a nation] gives proof of its strength by the sacrifices which demand the abdication of the individual to the advantage of the community, it is legitimate and has the right to exist. If doubts arise regarding its frontiers, consult the populations in the areas under dispute.” Existence is not a historical right, but “a daily plebiscite, just as an individual’s existence is a perpetual affirmation of life,” Renan said. The phrase gained enormous usage in reference to the breakup of the Ottoman Empire in 1918. “If Turkey has a right to exist – and the Powers are very prompt to assert that she has – she possesses an equally good right to defend herself against all attempts to imperil her political existence,” wrote Eliakim and Robert Littell in 1903. In many cases, a nation’s right to exist is not questioned, and is therefore not asserted.” ref
Israel/Palestine
“In 1947, a United Nations General Assembly resolution provided for the creation of an “Arab State” and a “Jewish State” to exist within Palestine in the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. The Jewish Agency, precursor to the Israeli government, agreed to the plan, but the Palestinians rejected it and fighting broke out. After Israel’s 14 May 1948 unilateral declaration of independence, support from neighboring Arab states escalated the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine into the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The legal and territorial status of Israel and Palestine is still hotly disputed in the region and within the international community. According to Ilan Pappé, Arab recognition of Israel’s right to exist was part of Folke Bernadotte‘s 1948 peace plan. The Arab states gave this as their reason to reject the plan. In the 1950s UK MP Herbert Morrison cited then Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser as saying “Israel is an artificial State which must disappear.” The issue was described as the central one between Israel and the Arabs.” ref
“After the June 1967 war, Egyptian spokesman Mohammed H. el-Zayyat stated that Cairo had accepted Israel’s right to exist since the signing of the Egyptian–Israeli armistice in 1949. He added that this did not imply recognition of Israel. In September, the Arab leaders adopted a hardline “three nos” position in the Khartoum Resolution: No peace with Israel, no recognition of Israel, and no negotiations with Israel. But In November, Egypt accepted UN Security Council Resolution 242, which implied acceptance of Israel’s right to exist. At the same time, Nasser urged Yasser Arafat and other Palestinian leaders to reject the resolution. “You must be our irresponsible arm,” he said. King Hussein of Jordan also acknowledged that Israel had a right to exist at this time. Meanwhile, Syria rejected Resolution 242, saying that it, “refers to Israel’s right to exist and it ignores the right of the [Palestinian] refugees to return to their homes.” ref
“Upon assuming the premiership in 1977, Menachem Begin spoke as follows: Our right to exist—have you ever heard of such a thing? Would it enter the mind of any Briton or Frenchman, Belgian or Dutchman, Hungarian or Bulgarian, Russian or American, to request for its people recognition of its right to exist? … Mr. Speaker: From the Knesset of Israel, I say to the world, our very existence per se is our right to exist! As reported by The New York Times, in 1988 Yasser Arafat declared that the Palestinians accepted United Nations Security Council Resolutions 242 and 338, which would guarantee “the right to exist in peace and security for all”. In June 2009, US president Barack Obama said “Israelis must acknowledge that just as Israel’s right to exist cannot be denied, neither can Palestine’s.” ref
“In 1993, there was an official exchange of letters between Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and chairman Arafat, in which Arafat declared that “the PLO affirms that those articles of the Palestinian Covenant which deny Israel’s right to exist, and the provisions of the Covenant which are inconsistent with the commitments of this letter are now inoperative and no longer valid.” In 2009 Prime Minister Ehud Olmert demanded the Palestinian Authority‘s acceptance of Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state, which the Palestinian Authority rejected. The Knesset plenum gave initial approval in May 2009 to a bill criminalising the public denial of Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state, with a penalty of up to a year in prison. In 2011 Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas said in a speech to the Dutch Parliament that the Palestinian people recognise Israel’s right to exist and they hope the Israeli government will respond by “recognizing the Palestinian state on the borders of the land occupied in 1967.” ref
“Israeli government ministers Naftali Bennett and Danny Danon have repeatedly rejected the creation of a Palestinian state, with Bennett stating “I will do everything in my power to make sure they never get a state.” In June 2016 a poll showed that only 4 out of 20 Israeli ministers accepted the state of Palestine’s right to exist. John V. Whitbeck argued that Israel’s insistence on a right to exist forces Palestinians to provide a moral justification for their own suffering. Noam Chomsky has argued that no state has the right to exist, that the concept was invented in the 1970s, and that Israel’s right to exist cannot be accepted by the Palestinians. International law scholar Anthony Carty observed in 2013 that “the question whether Israel has a legal right to exist might appear to be one of the most emotively charged in the vocabulary of international law and politics. It evokes immediately the ‘exterminationist’ rhetoric of numerous Arab and Islamic politicians and ideologues, not least the present President of Iran.” (referring to then president Mahmoud Ahmadinejad)” ref
Self-determination and the State?
“Self-determination refers to a people‘s right to form its own political entity, and internal self-determination is the right to representative government with full suffrage. Self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law, binding, as such, on the United Nations as an authoritative interpretation of the Charter‘s norms. The principle does not state how the decision is to be made, nor what the outcome should be (whether independence, federation, protection, some form of autonomy or full assimilation), however, and the right of self-determination does not necessarily include a right to an independent state for every ethnic group within a former colonial territory. Further, no right to secession is recognized under international law.” ref
“The concept emerged with the rise of nationalism in the 19th century and came into prominent use in the 1860s, spreading rapidly thereafter. During and after World War I, the principle was encouraged by both Soviet Premier Vladimir Lenin and United States President Woodrow Wilson. Having announced his Fourteen Points on 8 January 1918, on 11 February 1918 Wilson stated: “National aspirations must be respected; people may now be dominated and governed only by their own consent. ‘Self determination’ is not a mere phrase; it is an imperative principle of action.” During World War II, the principle was included in the Atlantic Charter, jointly declared on 14 August 1941 by Franklin D. Roosevelt, President of the United States, and Winston Churchill, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, who pledged The Eight Principal points of the Charter. It was recognized as an international legal right after it was explicitly listed as a right in the UN Charter.” ref
“Implementing the right to self-determination can be politically difficult, in part because there are multiple interpretations of what constitutes a people and which groups may legitimately claim the right to self-determination. As World Court judge Ivor Jennings put it: “The people cannot decide until somebody decides who the people are.” The norm of self-determination can be originally traced to the American and French revolutions, and the emergence of nationalism. The European revolutions of 1848, the post-World War I settlement at Versailles, and the decolonization movement after World War II shaped and established the norm in international law.” ref
“The American Revolution has been seen as the earliest assertion of the right of national and democratic self-determination, as well as the concepts of consent and sovereignty by the people governed. These ideas were inspired particularly by John Locke‘s writings of the previous century. Thomas Jefferson further promoted the notion that the will of the people was supreme, especially through authorship of the United States Declaration of Independence, which became an inspiration for European nationalist movements during the 19th century. The French Revolution legitimatized the ideas of self-determination on that Old World continent.” ref
“Nationalist sentiments emerged inside traditional empires: Pan-Slavism in Russia; Ottomanism, Kemalist ideology, and Arab nationalism in the Ottoman Empire; State Shintoism and Japanese identity in Japan; and Han identity in juxtaposition to the Manchurian ruling class in China. Meanwhile, in Europe itself, the rise of nationalism led to Greece, Hungary, Poland, and Bulgaria all seeking or winning independence. Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels supported some of these nationalist movements, believing nationalism might be a “prior condition” to social reform and international alliances. In 1914 Vladimir Lenin wrote: “[It] would be wrong to interpret the right to self-determination as meaning anything but the right to existence as a separate state.” ref
“Woodrow Wilson revived America’s commitment to self-determination, at least for European states, during World War I. When the Bolsheviks came to power in Russia in the October Revolution, they called for Russia’s immediate withdrawal as a member of the Allies of World War I. They also supported the right of all nations, including colonies, to self-determination.” The 1918 Constitution of the Soviet Union acknowledged the right of secession for its constituent republics.” ref
“This presented a challenge to Wilson’s more limited demands. In January 1918, Wilson issued his Fourteen Points of January 1918, which, among other things, called for adjustment of colonial claims, insofar as the interests of colonial powers had equal weight with the claims of subject peoples. The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk in March 1918 led to Soviet Russia‘s exit from the war and the nominal independence of Armenia, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Ukraine, Lithuania, Georgia and Poland, though in fact those territories were under German control. The end of the war led to the dissolution of the defeated Austro-Hungarian Empire and Czechoslovakia and the union of the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs and the Kingdom of Serbia as new states out of the wreckage of the Habsburg empire. However, this imposition of states where some nationalities (especially Poles, Czechs, and Serbs and Romanians) were given power over nationalities who disliked and distrusted them was eventually used as a pretext for German aggression in World War II.” ref
“Wilson publicly argued that the agreements made in the aftermath of the war would be a “readjustment of those great injustices which underlie the whole structure of European and Asiatic society,” which he attributed to the absence of democratic rule. The new order emerging in the postwar period would, according to Wilson, place governments “in the hands of the people and taken out of the hands of coteries and of sovereigns, who had no right to rule over the people.” The League of Nations was established as the symbol of the emerging postwar order; one of its earliest tasks was to legitimize the territorial boundaries of the new nation-states created in the territories of the former Ottoman Empire, Asia, and Africa. The principle of self-determination did not extend so far as to end colonialism; under the reasoning that the local populations were not civilized enough, the League of Nations was to assign each of the post-Ottoman, Asian, and African states and colonies to a European power by the grant of a League of Nations mandate.” ref
“One of the German objections to the Treaty of Versailles was a somewhat selective application of the principle of self-determination as the Republic of German-Austria, which included the Sudetenland, was seen as representing the will to join Germany in those regions, while the majority of people in Danzig wanted to remain within the Reich. However, the Allies ignored the German objections; Wilson’s 14 Points had called for Polish independence to be restored and Poland to have “secure access to the sea,” which would imply that the German city of Danzig (modern Gdańsk, Poland), which occupied a strategic location where the Vistula River flowed into the Baltic Sea, be ceded to Poland. At the Paris Peace Conference in 1919, the Polish delegation led by Roman Dmowski asked for Wilson to honor point 14 of the 14 points by transferring Danzig to Poland, arguing that the city was rightfully part of Poland because it was Polish until 1793, and that Poland would not be economically viable without it.” ref
“During the First Partition of Poland in 1772, the inhabitants of Danzig fought fiercely for it to remain a part of Poland, but as a result of the Germanisation process in the 19th century, 90% of the people in Danzig were German by 1919, which made the Allied leaders at the Paris peace conference compromise by creating the Free City of Danzig, a city-state in which Poland had certain special rights. Through the city of Danzig was 90% German and 10% Polish, the surrounding countryside around Danzig was overwhelmingly Polish, and the ethnically Polish rural areas included in the Free City of Danzig objected, arguing that they wanted to be part of Poland. Neither the Poles nor the Germans were happy with this compromise and the Danzig issue became a flash-point of German-Polish tension throughout the interwar period.” ref
“During the 1920s and 1930s there were some successful movements for self-determination in the beginnings of the process of decolonization. In the Statute of Westminster the United Kingdom granted independence to Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland, the Commonwealth of Australia, and the Union of South Africa after the British parliament declared itself as incapable of passing laws over them without their consent. Although the Irish Free State had already gained internationally recognized independence at the conclusion of the Irish War of Independence, as established in the Anglo-Irish Treaty, it was still included in the Statute of Westminster. This statute built on the Balfour Declaration of 1926 which recognized the autonomy of these British dominions, representing the first phase of the creation of the British Commonwealth of Nations. Egypt, Afghanistan, and Iraq also achieved independence from Britain. Other efforts were unsuccessful, like the Indian independence movement. And Italy, Japan and Germany all initiated new efforts to bring certain territories under their control, leading to World War II. In particular, the National Socialist Program invoked this right of nations in its first point (out of 25), as it was publicly proclaimed on 24 February 1920 by Adolf Hitler.” ref
“In Asia, Japan became a rising power and gained more respect from Western powers after its victory in the Russo-Japanese War. Japan joined the Allied Powers in World War I and attacked German colonial possessions in the Far East, adding former German possessions to its own empire. In the 1930s, Japan gained significant influence in Inner Mongolia and Manchuria after it invaded Manchuria. It established Manchukuo, a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia. This was essentially the model Japan followed as it invaded other areas in Asia and established the Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere. Japan went to considerable trouble to argue that Manchukuo was justified by the principle of self-determination, claiming that people of Manchuria wanted to break away from China and asked the Kwantung Army to intervene on their behalf. However, the Lytton commission which had been appointed by the League of Nations to decide if Japan had committed aggression or not, stated the majority of people in Manchuria who were Han Chinese who did not wish to leave China.” ref
“In 1912, the Republic of China officially succeeded the Qing Dynasty, while Outer Mongolia, Tibet and Tuva proclaimed their independence. Independence was not accepted by the government of China. By the Treaty of Kyakhta (1915) Outer Mongolia recognized China’s sovereignty. However, the Soviet threat of seizing parts of Inner Mongolia induced China to recognize Outer Mongolia’s independence, provided that a referendum was held. The referendum took place on October 20, 1945, with (according to official numbers) 100% of the electorate voting for independence. Many of East Asia‘s current disputes to sovereignty and self-determination stem from unresolved disputes from World War II. After its fall, the Empire of Japan renounced control over many of its former possessions including Korea, Sakhalin Island, and Taiwan. In none of these areas were the opinions of affected people consulted, or given significant priority. Korea was specifically granted independence but the receiver of various other areas was not stated in the Treaty of San Francisco, giving Taiwan de facto independence although its political status continues to be ambiguous.” ref
“In 1941 Allies of World War II declared the Atlantic Charter and accepted the principle of self-determination. In January 1942 twenty-six states signed the Declaration by United Nations, which accepted those principles. The ratification of the United Nations Charter in 1945 at the end of World War II placed the right of self-determination into the framework of international law and diplomacy.
- Chapter 1, Article 1, part 2 states that purpose of the UN Charter is: “To develop friendly relations among nations based on respect for the principle of equal rights and self-determination of peoples, and to take other appropriate measures to strengthen universal peace.”
- Article 1 in both the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (ICCPR) and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR) reads: “All peoples have the right of self-determination. By virtue of that right they freely determine their political status and freely pursue their economic, social and cultural development. “
- The United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights article 15 states that everyone has the right to a nationality and that no one should be arbitrarily deprived of a nationality or denied the right to change nationality.” ref
“On 14 December 1960, the United Nations General Assembly adopted United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1514 (XV) subtitled “Declaration on the Granting of Independence to Colonial Countries and Peoples“, which supported the granting of independence to colonial countries and people by providing an inevitable legal linkage between self-determination and its goal of decolonization. It postulated a new international law-based right of freedom to exercise economic self-determination. Article 5 states: Immediate steps shall be taken in Trust and Non-Self-Governing Territories, or all other territories which have not yet attained independence, to transfer all powers to the people of those territories, without any conditions or reservations, in accordance with their freely expressed will and desire, without any distinction as to race, creed or color, in order to enable them to enjoy complete independence and freedom.” ref
“On 15 December 1960 the United Nations General Assembly adopted United Nations General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV), subtitled “Principles which should guide members in determining whether or nor an obligation exists to transmit the information called for under Article 73e of the United Nations Charter in Article 3″, which provided that “[t]he inadequacy of political, economic, social and educational preparedness should never serve as a pretext for delaying the right to self-determination and independence.” To monitor the implementation of Resolution 1514, in 1961 the General Assembly created the Special Committee referred to popularly as the Special Committee on Decolonization to ensure decolonization complete compliance with the principles of self-determination in General Assembly Resolution 1541 (XV).” ref
“However, the charter and other resolutions did not insist on full independence as the best way of obtaining self-government, nor did they include an enforcement mechanism. Moreover, new states were recognized by the legal doctrine of uti possidetis juris, meaning that old administrative boundaries would become international boundaries upon independence if they had little relevance to linguistic, ethnic, and cultural boundaries. Nevertheless, justified by the language of self-determination, between 1946 and 1960, thirty-seven new nations in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East gained independence from colonial powers. The territoriality issue inevitably would lead to more conflicts and independence movements within many states and challenges to the assumption that territorial integrity is as important as self-determination.” ref
“Since the early 1990s, the legitimatization of the principle of national self-determination has led to an increase in the number of conflicts within states, as sub-groups seek greater self-determination and full secession, and as their conflicts for leadership within groups and with other groups and with the dominant state become violent. The international reaction to these new movements has been uneven and often dictated more by politics than principle. The 2000 United Nations Millennium Declaration failed to deal with these new demands, mentioning only “the right to self-determination of peoples which remain under colonial domination and foreign occupation.” In an issue of Macquarie University Law Journal Associate Professor Aleksandar Pavkovic and Senior Lecturer Peter Radan outlined current legal and political issues in self-determination.” ref
Defining “peoples” and Self-determination
“There is not a recognized legal definition of “peoples” in international law. Indeed, Ivor Jennings called Wilson’s doctrine “ridiculous” because, though on the surface it seems reasonable to “let the people decide”, in practice “the people cannot decide until someone decides who are the people”. Reviewing various international judgements and UN resolutions, Vita Gudeleviciute of Vytautas Magnus University Law School finds that, in cases of non-self-governing peoples (colonized and/or indigenous) and foreign military occupation, “a people” is defined as the entire population of the occupied territorial unit, no matter their other differences. Meanwhile, in cases where people lack representation by a state’s government, the unrepresented become a defined as a separate people. Present international law does not recognize ethnic and other minorities as separate peoples, with the notable exception of cases in which such groups are systematically disenfranchised by the government of the state they live in.” ref
“Other definitions offered are “peoples” as self-evident (from ethnicity, language, history, etc.), or defined by “ties of mutual affection or sentiment” (“loyalty”, or by mutual obligations among peoples). Professor Uriel Abulof suggests that self-determination entails the “moral double helix” of duality: 1. personal right to align with a people, and the people’s right to determine their politics; and 2. and mutuality (the right is as much the other’s as the self’s). Thus, self-determination grants individuals the right to form “a people,” which then has the right to establish an independent state, as long as they grant the same to all other individuals and peoples.” ref
Self-Determination versus Territorial Integrity
“National self-determination appears to challenge the principle of territorial integrity (or sovereignty) of states as it is the will of the people that makes a state legitimate. This implies a people should be free to choose their own state and its territorial boundaries. However, there are far more self-identified nations than there are existing states and there is no legal process to redraw state boundaries according to the will of these peoples. According to the Helsinki Final Act of 1975, the UN, ICJ and international law experts, there is no contradiction between the principles of self-determination and territorial integrity, with the latter taking precedence.” ref
“Allen Buchanan, author of seven books on self-determination and secession, supports territorial integrity as a moral and legal aspect of constitutional democracy. However, he also advances a “Remedial Rights Only Theory” where a group has “a general right to secede if and only if it has suffered certain injustices, for which secession is the appropriate remedy of last resort.” He also would recognize secession if the state grants, or the constitution includes, a right to secede. Vita Gudeleviciute holds that in cases of non-self-governing peoples and foreign military occupation the principle of self-determination trumps that of territorial integrity. In cases where people lack representation by a state’s government, they also may be considered a separate people, but under current law cannot claim the right to self-determination. On the other hand, she finds that secession within a single state is a domestic matter not covered by international law. Thus, there are no on what groups may constitute a seceding people.” ref
“A number of states have laid claim to territories, which they allege were removed from them as a result of colonialism. This is justified by reference to Paragraph 6 of UN Resolution 1514(XV), which states that any attempt “aimed at partial or total disruption of the national unity and the territorial integrity of a country is incompatible with the purposes and principles of the Charter.” This, it is claimed, applies to situations where the territorial integrity of a state had been disrupted by colonization so that the people of a territory subject to a historic territorial claim are prevented from exercising a right to self-determination. This interpretation is rejected by many states, who argue that Paragraph 2 of UN Resolution 1514(XV) states that “all peoples have the right to self-determination,” and Paragraph 6 cannot be used to justify territorial claims.” ref
“The original purpose of Paragraph 6 was “to ensure that acts of self-determination occur within the established boundaries of colonies, rather than within sub-regions.” Further, the use of the word attempt in Paragraph 6 denotes future action and cannot be construed to justify territorial redress for past action. An attempt sponsored by Spain and Argentina to qualify the right to self-determination in cases where there was a territorial dispute was rejected by the UN General Assembly, which re-iterated the right to self-determination was a universal right. In order to accommodate demands for minority rights and avoid secession and the creation of a separate new state, many states decentralize or devolve greater decision-making power to new or existing subunits or autonomous areas.” ref
“Self-determination can be at odds with the principle of majority rule and equal rights, especially when there is a sizable minority group. In democratic societies, majority rule is often used to determine the outcome in electoral and voting processes. However, a major critique of majority rule is that it may result in the tyranny of the majority, especially in cases in which a simple majority is used in order to determine outcome. This flaw is particularly poignant when there is a large minority group whose interests are not being represented, and who may then seek to secede.” ref
“The right to self-determination by a minority has long been contested in democracies with majority rule. For instance, in his first inaugural speech Abraham Lincoln argued that:
Plainly the central idea of secession is the essence of anarchy. A majority held in restraint by constitutional checks and limitations, and always changing easily with deliberate changes of popular opinions and sentiments, is the only true sovereign of a free people. Whoever rejects it does of necessity fly to anarchy or to despotism. Unanimity is impossible. The rule of a minority, as a permanent arrangement, is wholly inadmissible; so that, rejecting the majority principle, anarchy or despotism in some form is all that is left.” ref
“However, liberal proponents for the right to self-determination by minority groups contradict this notion by arguing that, in cases where the minority is not able to become the majority, and that minority is territorially concentrated and does not want to be governed by the majority, it may serve the best interest of the state to allow the secession of this group. Most sovereign states do not recognize the right to self-determination through secession in their constitutions. Many expressly forbid it. However, there are several existing models of self-determination through greater autonomy and through secession.” ref
“In liberal constitutional democracies the principle of majority rule has dictated whether a minority can secede. In the United States Abraham Lincoln acknowledged that secession might be possible through amending the United States Constitution. The Supreme Court in Texas v. White held secession could occur “through revolution, or through consent of the States.” The British Parliament in 1933 held that Western Australia only could secede from Australia upon vote of a majority of the country as a whole; the previous two-thirds majority vote for secession via referendum in Western Australia was insufficient.” ref
“The Chinese Communist Party followed the Soviet Union in including the right of secession in its 1931 constitution in order to entice ethnic nationalities and Tibet into joining. However, the Party eliminated the right to secession in later years and had anti-secession clause written into the Constitution before and after the founding the People’s Republic of China. The 1947 Constitution of the Union of Burma contained an express state right to secede from the union under a number of procedural conditions. It was eliminated in the 1974 constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma (officially the “Union of Myanmar”). Burma still allows “local autonomy under central leadership.” ref
“As of 1996 the constitutions of Austria, Ethiopia, France, and Saint Kitts and Nevis have express or implied rights to secession. Switzerland allows for the secession from current and the creation of new cantons. In the case of proposed Quebec separation from Canada the Supreme Court of Canada in 1998 ruled that only both a clear majority of the province and a constitutional amendment confirmed by all participants in the Canadian federation could allow secession.” ref
“The 2003 draft of the European Union Constitution allowed for the voluntary withdrawal of member states from the union, although the State which wanted to leave could not be involved in the vote deciding whether or not they can leave the Union. There was much discussion about such self-determination by minorities before the final document underwent the unsuccessful ratification process in 2005. As a result of the successful constitutional referendum held in 2003, every municipality in the Principality of Liechtenstein has the right to secede from the Principality by a vote of a majority of the citizens residing in this municipality.” ref
“In determining international borders between sovereign states, self-determination has yielded to a number of other principles. Once groups exercise self-determination through secession, the issue of the proposed borders may prove more controversial than the fact of secession. The bloody Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s were related mostly to border issues because the international community applied a version of uti possidetis juris in transforming the existing internal borders of the various Yugoslav republics into international borders, despite the conflicts of ethnic groups within those boundaries. In the 1990s indigenous populations of the northern two-thirds of Quebec province opposed being incorporated into a Quebec nation and stated a determination to resist it by force.” ref
“The border between Northern Ireland and the Irish Free State was based on the borders of existing counties and did not include all of historic Ulster. A Boundary Commission was established to consider re-drawing it. Its proposals, which amounted to a small net transfer to the Free State, were leaked to the press and then not acted upon. In December 1925, the governments of the Irish Free State, Northern Ireland, and the United Kingdom agreed to accept the existing border. There have been a number of notable cases of self-determination. For more information on past movements see list of historical separatist movements and lists of decolonized nations. Also see list of autonomous areas by country and lists of active separatist movements.” ref
‘Anti-Zionism is antisemitism,’ US House asserts in ‘dangerous’ resolution
Palestinian rights advocates denounce a Republican-led measure as a push to smear Israel’s critics amid the war in Gaza.
“Washington, DC – Palestinian rights advocates are denouncing a congressional resolution that equates anti-Zionism with anti-Semitism, calling it a “dangerous” measure that aims to curb free speech and distract from the war in Gaza. The Republican-controlled House of Representatives passed the measure on Tuesday in a 311-14 vote, with 92 Democratic members abstaining by voting “present.” The symbolic resolution was framed as an effort to reject the “drastic rise of anti-Semitism in the United States and around the world.” But it contained language saying that the House “clearly and firmly states that anti-Zionism is antisemitism.” It also condemned the slogan “From the River to the Sea,” which rights advocates understand to be an aspirational call for equality in historic Palestine.” ref
“Instead, the resolution described it as a “rallying cry for the eradication of the State of Israel and the Jewish people”. It also characterised demonstrators who gathered in Washington, DC, last month to demand a ceasefire as “rioters”. They “spewed hateful and vile language amplifying antisemitic themes”, the resolution alleges. Husam Marajda, an organiser with the US Palestinian Community Network (USPCN), said the resolution is an effort to “cancel” Palestinian rights advocates by accusing them of bigotry and labelling their criticism of Israeli policies as hate speech. “It’s super dangerous. It sets a really, really bad precedent. It’s aiming to criminalise our liberation struggle and our call for justice and peace and equality,” Marajda told Al Jazeera.” ref
“Zionism is a nationalist ideology that helped establish the state of Israel in 1948. It contends that the Jewish people have a right to self-determination in historic Palestine, which Zionists view as their ancestral homeland. The rise of Zionism in the late 1800s was partly in response to anti-Semitism in Europe. But many Palestinians reject Zionism as a driver of the settler colonialism that dispossessed them during the founding of Israel. Israel’s establishment coincided with the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians who were forcibly driven from their homes in what is known as the Nakba, the Arabic word for “catastrophe.” While Palestinians view themselves as the native people of the land, Zionists say Jewish people have historic and biblical claims to what is today Israel.” ref
“Some hardline Zionists, including members of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu’s government, argue that the present-day Palestinian territories — the West Bank and Gaza — also belong to Israel. At a United Nations General Assembly speech in November, Netanyahu held up a map of Israel that showed the country stretching from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea, encompassing the West Bank, Gaza and Syria’s Golan Heights. Some Palestinians also blame Zionism for Israeli abuses against them, which amount to apartheid, according to leading human rights groups like Amnesty International. In the US, Palestinian rights supporters have long rejected conflations of Zionism with Judaism, noting that many Jewish Americans identify as anti-Zionist.” ref
“Opposing the policies of the government of Israel and Netanyahu’s extremism is not antisemitic. Speaking up for human rights and a ceasefire to save lives should never be condemned,” Palestinian American Congresswoman Rashida Tlaib said in a social media post on Tuesday, explaining her vote against the resolution. Marajda stressed that Palestinians have a right to oppose Zionism, a position he said has nothing to do with prejudice. “This resolution is saying that if you’re critical of this Israeli government, essentially you hate Jewish people,” he said. “I didn’t choose — the Palestinians didn’t choose — their occupiers.” The resolution is one of several pro-Israel motions approved by Congress since October 7. Most US legislators have expressed unwavering support for Israel amid its offensive in Gaza, which has killed more than 16,000 Palestinians.” ref
“Yasmine Taeb, the legislative and political director at MPower Change, a Muslim American advocacy group, called the resolution “extremely dangerous”. “It unequivocally equates any criticism of the Israeli government with anti-Semitism. Essentially it smears millions and millions of people demonstrating globally in support of a lasting ceasefire, including Jewish-American organisations,” Taeb told Al Jazeera. The advocacy group Jewish Voice for Peace (JVP) was also quick to denounce the congressional measure. “Falsely stating that anti-Zionism is antisemitism conflates all Jews with the Israeli state and endangers our communities. It fuels deadly violence and censorship campaigns against Palestinians,” JVP Action said in a social media post. “We are proud anti-Zionists Jews. We refuse to pit communities against one another.” ref
“All House Republicans but one — Congressman Thomas Massie — voted in favor of the resolution. But Democrats were split on the measure: 13 voted against it and 95 for it, on top of the 92 who abstained with a “present” vote. Jerrold Nadler, a key Jewish House Democrat, had decried the resolution on Monday, noting that some Jewish communities oppose Zionism for religious reasons and should not be branded as anti-Semitic. “While most anti-Zionism is indeed anti-Semitic, the authors, if they were at all familiar with Jewish history and culture, should know about Jewish anti-Zionism that was, and is, expressly not anti-Semitic,” he said. Nadler accused Republicans of using support for Israel to advance “partisan wedging at the expense of the Jewish community.” Still, he did not vote against the resolution on Tuesday. He opted for “present.” The vote highlighted the divisions among the Democrats over Israel’s military campaign in Gaza. While the party’s progressive wing has pressed for a ceasefire, President Joe Biden and the majority of congressional Democrats have avoided such calls. But that could signal a disconnect from the party base. A Reuters/Ipsos poll in November indicated 62 percent of Democratic voters considered Israel’s response “excessive.” Two in three survey respondents backed a ceasefire.” ref
“Republicans, meanwhile, have led motions that critics say are designed to bring the Democratic schism to the fore. Last month, for instance, they moved to censure Congresswoman Tlaib, the only Palestinian in the House, over her comments on the Gaza war. Conservatives have accused Democrats who vote against such measures of being anti-Israel, if not anti-Semitic. That creates a political dilemma for Democratic lawmakers. If they support the bills, they risk upsetting large segments of their base, but if they oppose them, they open themselves to Republican attacks. Taeb said the lawmakers who voted “present” did not want to go on the record as equating anti-Semitism with anti-Zionism, but at the same time, they wanted to be seen as countering anti-Semitism. “It’s just politics,” she told Al Jazeera.” ref
“Tuesday’s resolution was co-sponsored by Congressman Max Miller, who has faced outrage in recent weeks for saying, “We’re going to turn [Palestine] into a parking lot.” Taeb said the fact that lawmakers who have promoted anti-Palestinian hate are championing such resolutions shows that Tuesday’s measure is not about combating prejudice. “The intent of these members is to smear and silence peace activists calling to end the massacre of Palestinian children and families.” ref
‘Good Jews oppose Zionism’: French Jewish students say campus no longer a safe space (5 May 2024)
Post-October 7 anti-Israel agitation and the antisemitism it unleashed are pushing promising candidates away from French schools. Last week’s protests may be the tipping point
“A student in her final year of high school, Esther is within reach of her first life goal as an adult: Getting accepted into the law or geopolitics program of the ultra-prestigious Paris Institute of Political Studies, or Sciences Po. In recent months, however, Esther (who requested that her last name be withheld due to the sensitivity of the subject) has cooled off the goal that had guided her for years. She cites aggressive and protracted anti-Israel agitation on campus that she and many other critics (French-language link) say is spilling over to antisemitism without a firm response from authorities. Esther now considers Sciences Po unsuitable for a Jew who does not wish to hide their identity or support of Israel. “It used to be my dream,” Esther tells The Times of Israel about studying at Sciences Po. “But now, honestly, I wouldn’t go even if I’m accepted.” ref
“Esther’s disillusionment with Sciences Po is shared widely among the French-Jewish community. Like many American Jews who are horrified by the anti-Israel mobilization on US campuses, French Jews perceive this development — and the antisemitism they say characterizes it — as portending a shift in their ability to prosper in France. The anti-Israel mobilization has been simmering for years at many French campuses, and Jewish student groups see it as linked to an increase in antisemitism. In a poll (French) from September, 91% of French Jewish students sampled said they had encountered an antisemitic incident during their studies. But the problem exploded after October 7, when about 3,000 Hamas terrorists murdered some 1,200 Israelis and abducted another 252. Israel’s ongoing incursion into Gaza to topple Hamas has prompted a global wave of protest, as well as a spike in antisemitic incidents in France and beyond.” ref
“In France, many fear this wave means that anti-Jewish attitudes have returned to universities that for decades after World War II had been the main vehicle for upward social mobility by Jews and others. Higher education has been key to the success of France’s Jewish community, where most members were born to Holocaust survivors or impoverished immigrants from North Africa. At Sciences Po, anti-Israel activists began staging in March what they call “blockages,” occupying campus buildings, sometimes for days. That month, the protesters prevented one Jewish student leader from entering a Sciences Po campus building as other students were let through, prompting the UEJF Jewish student association to accuse the protesters of antisemitism.” ref
“The blockages — there have been dozens across French campuses — feature multiple calls for a “global intifada,” a term many interpret as a call to harm Jews, and chants of “From the river to the sea, Palestine will be free,” which critics say is a call for ethnic cleansing. In January, three Jewish students in Strasbourg were assaulted (French) for putting up posters raising awareness for the hostages in Gaza. Signs reading “no entry to Zionists” have become commonplace in French campuses, according to the UEJF. This development is occurring against an explosion of antisemitic hate crimes, of which the Jewish community watchdog SPCJ recorded in 2023 a total of 1,676 cases (more than the tallies of the previous three years combined). Nearly 75% of all cases recorded last year happened after October 7. French Prime Minister Gabriel Attal in an April 27 speech said that blockages would not be tolerated in France.” ref
“Yet the handling of the blockages at Sciences Po, the flagship of French academia, and beyond left many feeling that the blockers had gotten a free pass. On April 30, students at Sciences Po agreed to end their weeklong blockage after obtaining from the university administration an amnesty on any disciplinary action and a promise to arrange a campus debate about the war in Gaza. Despite the compromise, dozens of protesters returned to Sciences Po on Friday, prompting police to evacuate them from the campus building they had occupied. The compromise by Sciences Po’s administration, which had vowed (French) initially to be “uncompromising” in its actions against antisemitic intimidation and blockages, set it apart from some counterpart institutions in the United States, and especially Columbia University, where the administration called police to break up campus occupation actions, and arrest participants.” ref
“At Sciences Po, “the administration lay down before the anti-Israel crowd and its antisemitism,” said historian Marc Knobel, who is a graduate of Sciences Po and who researches modern-day antisemitism. Jean Bassères, the caretaker director of Sciences Po, defended (French) the compromise in an interview published in Le Monde. An intervention by law enforcement “would be a difficult operation and not result in an end to the blockages,” he said. The Paris region authority punished Sciences Po for the compromise. On Tuesday, the Île-de-France government suspended its annual funding of about $1 million for Sciences Po “until calm and security have been restored at the school,” region president Valerie Pecresse wrote on X. Sciences Po is heavily subsidized — taxpayers provide 37% of its annual budget of about $214 million — but most of the funding comes from the central government, which has not suspended it.” ref
“The message that came out of the blockages, Knobel said, was: “You can disrupt studies, harass Jewish students and intimidate faculty into concessions — and get away with it.” At Sciences Po and other French universities, some Jewish students feel unsafe. Lea Hanoune, a leader of the Union of French Jewish Students in France and a student at the Sorbonne University, said: “Many Jewish students like me feel unsafe when we hear slogans about intifada.” She added: “We have to be the ‘good Jews’ and oppose Zionism. If we’re ‘bad Jews’ who support Israel, we will be intimidated — or worse.” Sophie B., who also asked her last name be withheld from this article, recalled avoiding a certain bathroom on the campus of her Université Paris Cité because it had been defaced with the words “Free Palestine” in large letters and slogans accusing Israel of murdering children on the walls. The graffiti was removed following Sophie’s complaint, but it made her feel uneasy.” ref
“I try not to show my identity. I’m a secular Jew, so for me it’s normal,” she told The Times of Israel. At her university, she added, “I have never seen anyone wear a kippa or any religious Jewish sign.” The response to her initiatives in November to go with other Jews and hang up posters of the hostages were lukewarm. “People said they’re too scared,” she said. Knobel, the historian, is among the many French Jews who view the campus blockages and riots as an orchestrated push by one of France’s main political forces, the far-left LFI party of Jean-Luc Melenchon. “What we’re seeing isn’t a grassroots explosion of sentiment, although it’s sometimes framed this way,” Knobel said. “At Sciences Po and other campuses, we see the fingerprint of LFI’s incessant weaponization, by its top members and campus activists, of the Palestinian issue to strengthen its base with young voters.” ref
“Melenchon, a former communist who won 19% of the vote in the previous presidential elections and whom the CRIF umbrella of French Jewish communities has accused of stoking antisemitism, has called (French) Israel’s actions in Gaza “genocide.” His party has placed Rima Hassan, a French-Palestinian activist who is under a police investigation for justifying the October 7 onslaught, on its ticket for the European Parliament elections next month. She visited the Sciences Po blockage and danced and sang with the protesters. Melenchon, who in a 2017 speech had said about French Jews that “France is the opposite of aggressive communities that lecture to the rest of country,” has dismissed claims that he is encouraging antisemitism as an attempt to besmirch him. Melenchon and LFI have been vocal supporters of the blockages, advertising them on social media and announcing each new blockage approvingly. “After Columbia, Sciences Po and hundreds of faculties worldwide, the Sorbonne joins the vast movement of student solidarity with the Palestinian people,” LFI wrote on X recently, in a post that Melenchon shared (French) on his own X account.” ref
“In her heavily Jewish and affluent suburb of Paris, Esther is weighing options along with her two brothers. Her older brother is preparing to study at the École Polytechnique, where he hopes to get on an exchange program with MIT or Harvard. But now, studying on an American campus seems much less desirable to him than it did before October 7, says Esther. “London, New York, Montreal: It’s the same, so I’m not sure how to choose. None of us do,” said Esther. Studying in Israel would solve the antisemitism issue, she said, but she doesn’t see herself living in Israel. “We’re kind of lost. We’re asking ourselves where to go, where will we encounter problems,” she says. “Now safety is suddenly a major criterion. It’s kind of crazy.” ref
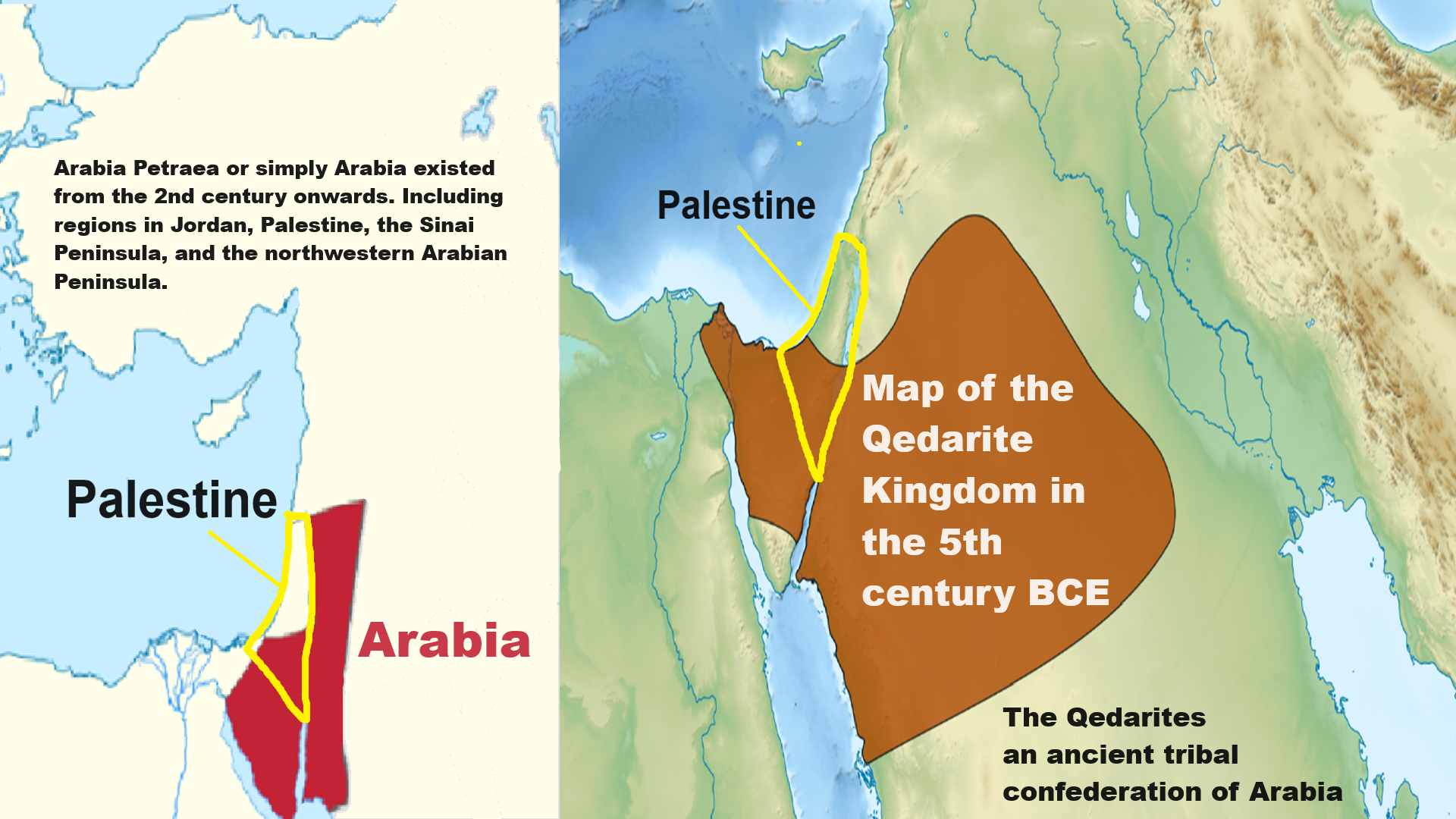
Arabs?
“The Arabs, also known as the Arab people (الشَّعْبَ الْعَرَبِيّ), are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Arabic is a Semitic language that belongs to the Afroasiatic language family. The majority of scholars accept the “Arabian peninsula” has long been accepted as the original Urheimat (linguistic homeland) of the Semitic languages. Central Semitic is a branch of the Semitic language includes Arabic, Aramaic, Canaanite, Phoenician, Hebrew, and others. The origins of Proto-Semitic may lie in the Arabian Peninsula, with the language spreading from there to other regions.” ref
“According to Arab–Islamic–Jewish traditions, Ishmael, the son of Abraham and Hagar was “father of the Arabs”. The Book of Genesis narrates that God promised Hagar to beget from Ishmael twelve princes and turn his descendants into a “great nation”. Ishmael was considered the ancestor of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the founder of Islam. The tribes of Central West Arabia called themselves the “people of Abraham and the offspring of Ishmael.” Ibn Khaldun, an Arab scholar in the 8th century, described the Arabs as having Ishmaelite origins. According to the Samaritan book Asaṭīr adds: “And after the death of Abraham, Ishmael reigned twenty-seven years; And all the children of Nebaot ruled for one year in the lifetime of Ishmael; And for thirty years after his death from the river of Egypt to the river Euphrates; and they built Mecca.” Josephus also lists the sons and states that they “…inhabit the lands which are between Euphrates and the Red Sea, the name of which country is Nabathæa.” ref
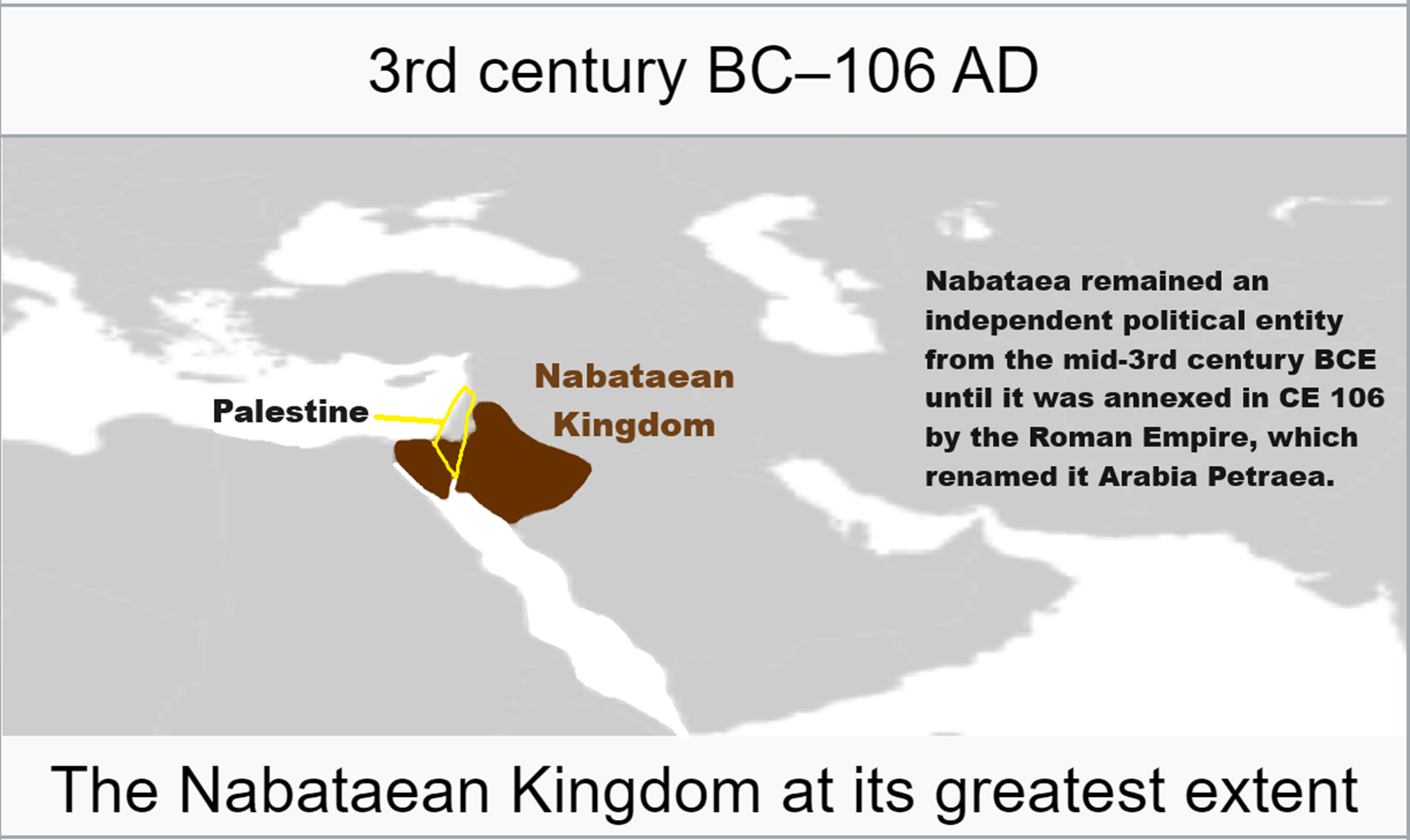
“The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin Arab tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. The precise origin of the specific tribe of Arab nomads remains uncertain. One hypothesis locates their original homeland in today’s Yemen, in the southwest of the Arabian peninsula, but their deities, language and script share nothing with those of southern Arabia. Another hypothesis argues that they came from the eastern coast of the peninsula. The suggestion that they came from the Hejaz area is considered to be more convincing, as they share many deities with the ancient people there; nbṭw, the root consonant of the tribe’s name, is found in the early Semitic languages of Hejaz.” ref
“Similarities between the late Nabataean Arabic dialect and the ones found in Mesopotamia during the Neo-Assyrian period, as well as a group with the name of “Nabatu” being listed by the Assyrians as one of several rebellious Arab tribes in the region, suggests a connection between the two. The Nabataeans might have originated from there and migrated west between the 6th and 4th centuries BC into northwestern Arabia and much of what is now modern-day Jordan. Nabataeans have been falsely associated with other groups of people. A people called the “Nabaiti”, who were defeated by the Assyrian king Ashurbanipal, were associated by some with the Nabataeans because of the temptation to link their similar names. Another misconception is their identification with the Nebaioth of the Hebrew Bible, the descendants of Ishmael, Abraham‘s son. Unlike the rest of the Arabian tribes, the Nabataeans later emerged as vital players in the region during their times of prosperity. However, their influence then faded, and the Nabataeans were forgotten.” ref
“In a 2003 genetic study, Bedouins showed the highest rates (62.5%) of the subclade Haplogroup J-M267 among all populations tested, followed by Palestinian Arabs (38.4%), Iraqis (28.2%), Ashkenazi Jews (14.6%) and Sephardic Jews (11.9%), according to Semino et al. Semitic-speaking populations usually possess an excess of J1 Y chromosomes compared to other populations harboring Y-haplogroup J. The haplogroup J1, the ancestor of subclade M267, originates south of the Levant and was first disseminated from there into Ethiopia and Europe in Neolithic times. J1 is most common in Palestine, as well as Syria, Iraq, Algeria, and Arabia, and drops sharply at the border of non-semitic areas like Turkey and Iran. A second diffusion of the J1 marker took place in the 7th century CE when Arabians brought it from Arabia to North Africa.” ref
“According to a 2010 study by Behar et al. titled “The genome-wide structure of the Jewish people”, in one analysis, Palestinians tested clustered genetically close to Bedouins, Jordanians, and Saudi Arabians which was described as “consistent with a common origin in the Arabian Peninsula”. In another analysis of West Eurasians only, Palestinians fell between Saudis (and more distantly, Bedouins) on one side and Jordanians and Syrians on the other. Admixture analysis in the same study inferred that the Palestinian and Jordanian DNA largely resembled the mixture of Syrians, Lebanese, Druze and Samaritans. They differed from the Saudi profile, which almost completely lacked a European-like component and had a smaller proportion of the component typical of more northerly West Asian populations, both of which were more prominently present in Palestinians and other Levantine populations. Palestinians differed from Druze and Samaritans in having more sub-Saharan African-related admixture.” ref
“A 2013 study by Haber et al. found that “The predominantly Muslim populations of Syrians, Palestinians and Jordanians cluster on branches with other Muslim populations as distant as Morocco and Yemen.” The authors explained that “religious affiliation had a strong impact on the genomes of the Levantines. In particular, conversion of the region’s populations to Islam appears to have introduced major rearrangements in populations’ relations through admixture with culturally similar but geographically remote populations leading to genetic similarities between remarkably distant populations.” The study found that Christians and Druze became genetically isolated following the arrival of Islam. The authors reconstructed the genetic structure of pre-Islamic Levant and found that “it was more genetically similar to Europeans than to Middle Easterners.” ref
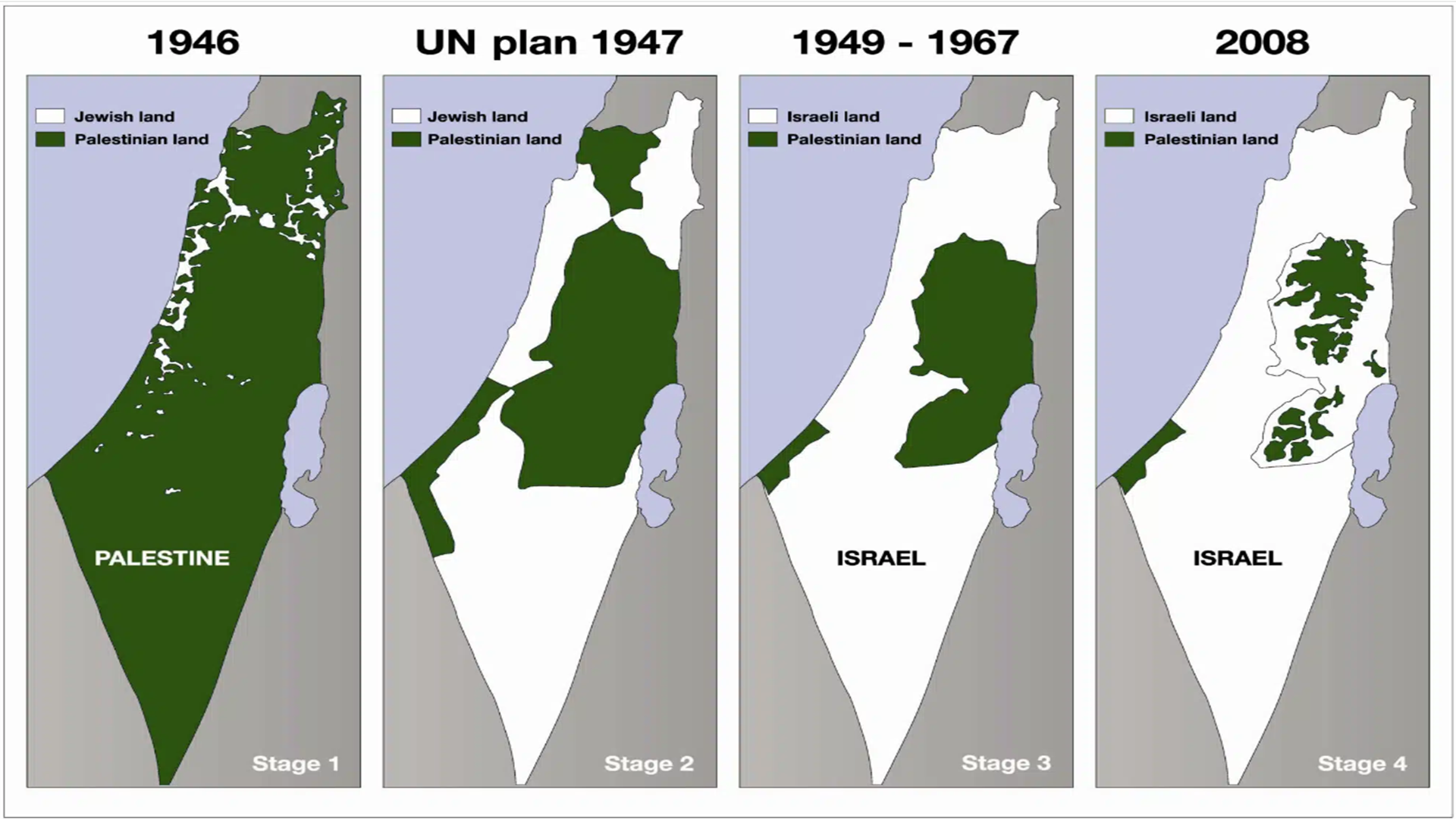
So, Palestinians had South Palestine; Jews had North Palestine, and that is why I think Jews are allowed an area in the north and Palestinians in the south. And Jews never had Gaza, not even at its kingdom’s largest extent.
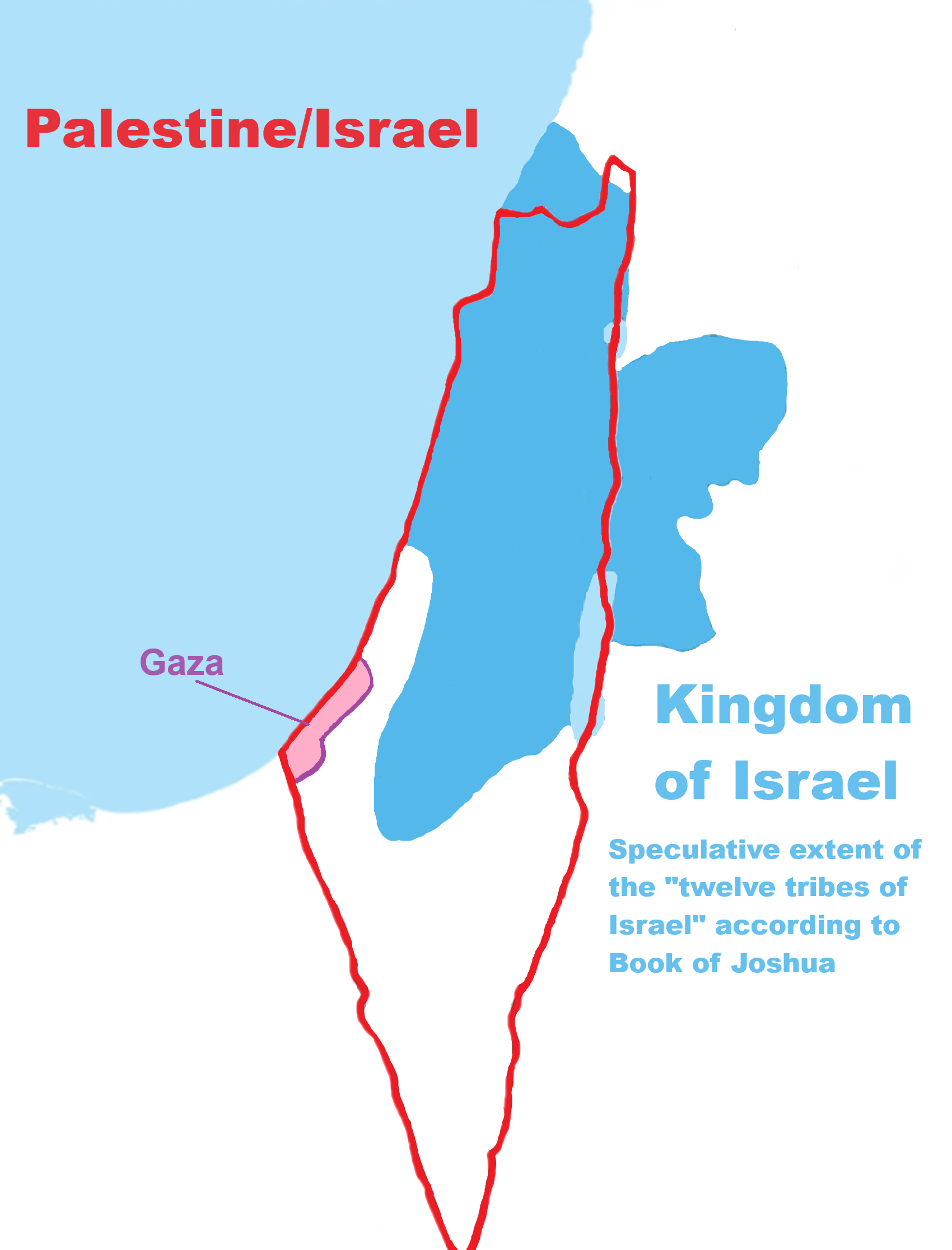
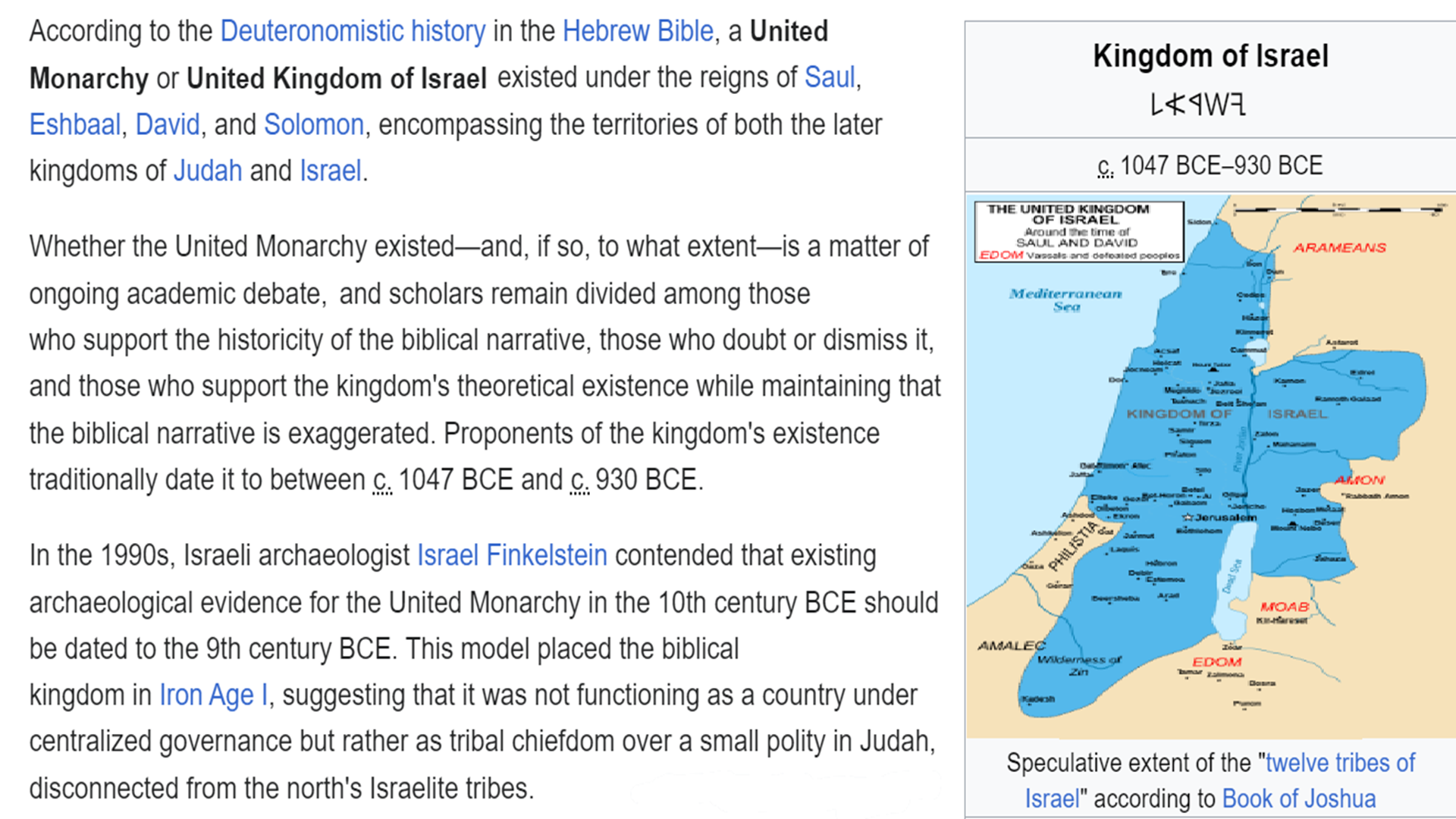
Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy)
“According to the Deuteronomistic history in the Hebrew Bible, a United Monarchy or United Kingdom of Israel existed under the reigns of Saul, Eshbaal, David, and Solomon, encompassing the territories of both the later kingdoms of Judah and Israel. Whether the United Monarchy existed—and, if so, to what extent—is a matter of ongoing academic debate, and scholars remain divided among those who support the historicity of the biblical narrative, those who doubt or dismiss it, and those who support the kingdom’s theoretical existence while maintaining that the biblical narrative is exaggerated. Proponents of the kingdom’s existence traditionally date it to between c. 1047 BCE and c. 930 BCE. In the 1990s, Israeli archaeologist Israel Finkelstein contended that existing archaeological evidence for the United Monarchy in the 10th century BCE should be dated to the 9th century BCE. This model placed the biblical kingdom in Iron Age I, suggesting that it was not functioning as a country under centralized governance but rather as tribal chiefdom over a small polity in Judah, disconnected from the north’s Israelite tribes.” ref
“The rival chronology of Israeli archaeologist Amihai Mazar places the relevant period beginning in the early 10th century BCE and ending in the mid-9th century BCE, addressing the problems of the traditional chronology while still aligning pertinent findings with the time of Saul, David, and Solomon. Mazar’s chronology and the traditional one have been fairly widely accepted, though there is no current consensus on the topic. Recent archaeological discoveries by Israeli archaeologists Eilat Mazar and Yosef Garfinkel in Jerusalem and Khirbet Qeiyafa, respectively, seem to support the existence of the United Monarchy, but the dating and identifications are not universally accepted. According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon’s son Rehoboam, the United Monarchy would have split into two separate kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel in the north, containing the cities of Shechem and Samaria; and the Kingdom of Judah in the south, containing Jerusalem and the Jewish Temple.” ref
What we don’t understand, we can come to fear. That which we fear, we often learn to hate. Things we hate, we usually seek to destroy. It is thus, upon us, to try and understand the unknown or unfamiliar, not letting fear drive us into the unreasonable arms of hate and harm.
“Israel is a country in Palestine that is bordered by Lebanon to the north, by Syria to the northeast, by Jordan to the east, by the Red Sea to the south, by Egypt to the southwest, by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, and by the Palestinian territories – the West Bank along the east and the Gaza Strip along the southwest. The area historically was called Canaan, which also involved the Land of Israel, Palestine, and the Holy Land.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Israel
“The Palestinian territories are the two regions of the former British Mandate for Palestine that have been militarily occupied by Israel since the Six-Day War of 1967, namely: the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. The International Court of Justice (ICJ) has referred to the West Bank, including East Jerusalem, as “the Occupied Palestinian Territory”, and this term was used as the legal definition by the ICJ in its advisory opinion of July 2004. The term occupied Palestinian territory was used by the United Nations and other international organizations between October 1999 and December 2012 to refer to areas controlled by the Palestinian National Authority, but from 2012, when Palestine was admitted as one of its non-member observer states, the United Nations started using exclusively the name State of Palestine. The European Union (EU) also adopts the term occupied Palestinian territory, with a parallel term Palestinian Authority territories also occasionally used. The government of Israel and its supporters use the label “disputed territories” instead.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palestinian_territories
“The Gaza Strip and the West Bank had been occupied by Egypt and Jordan, respectively, since the 1948 Arab–Israeli War until the Six-Day War of 1967. Israel occupied the West Bank and the Gaza Strip in 1967 and has since maintained control. In 1980, Israel officially absorbed East Jerusalem and proclaimed the whole of the city to be its capital. The inclusion, though never formally amounting to legal annexation, was condemned internationally and declared “null and void” by the United Nations Security Council. The Palestinian National Authority, the United Nations, the international legal and humanitarian bodies, and the international community regard East Jerusalem as part of the West Bank, and consequently a part of the Palestinian territories. The Palestinian National Authority never exercised sovereignty over the area, although it housed its offices in Orient House and several other buildings as an assertion of its sovereign interests. Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem has not been recognized by the International community, on the grounds that the unilateral annexation of territory occupied during war contravenes the Fourth Geneva Convention.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Palestinian_territories
It is amazing that the USA can find war crimes done in Ukraine by Russians on an American but seems oblivious to war crimes it has done or that of allies like Israel. America’s justice has always been lacking in justice.
Support Freedom
I am glad some hostages are being freed. They all should be freed immediately and never should have been taken to begin with. We all deserve freedom, including the West Bank and Gasa from occupation, apartheid, and oppression.

Cultural Genocide
“Cultural genocide or culturicide, as the Armenian Genocide Museum defines it as “acts and measures undertaken to destroy nations’ or ethnic groups’ culture through spiritual, national, and cultural destruction.” ref
Some Palestinians seem to want a Cultural genocide to remove Israel as if Jews have no rights to the land culturally. Cultural genocide may be part of the Israel state’s not supporting a two-state solution and wanting all the land in Palestine thus removing Palestinians’ culture.
Anarchist Atheist
I am an anti-religionist, and I also don’t want any states. But as a secularist, I don’t force my anti-religion on others, though I wish for a world where religion is finally seen for the mythology it is. Being a secularist is an ethical way of honoring the rights of others who may think differently but respect each other. I am not for forced atheism. Rather I wish to inspire others to atheism. I offer thoughtful education on prehistory and religion with the goal of helping people see religion was and always will be just a product of culture, not more than, like languages, completely human-made. We are capable of great empathy as well as love and these are as great a force as our negative features or failures. Really is not one-sided and we have the power to change and choose better. I want to make a difference in the world and try to bring hope and new thinking to others where I can. I also wish to champion kindness as often as I champion challenges in thinking and hope for wisdom as much as reason or doubt. Humanity is a worthy cause, and we all benefit from its advancement. Don’t let ANGER become an unethical behavior.
Religion has been a reason for violence and harm and at times a promoter of peace. Science does not need to fill the gap of religion. We need to remove it as it was always an abstraction not a realistic thing to being with. Not one thing religion offers that is thought of as good cannot be done by persons not following any religion. Atheist generally is simply life with religion removed, all its pseudo meaning as well as pseudoscience, pseudohistory, and pseudo-morality. We have real science, and realistic history and can access real morality with a blend of philosophy, anthropology, psychology, sociology, and cognitive science.
To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” is important.
Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.
Reject Antisemitism and Islamophobia hate.
I am anti-bigotry.
Condemn governments and terrorists when they do wrong,
don’t hate regular people, not related to either.
Hating people is wrong.
I am an anti-nationalist and anti-capitalist to my core. I stand in solidarity with humanity, not borders or nations, rather it is the humans from every single plot of dirt they happen to currently live on. We are all one. Don’t let imaginary borders tell you who to love or hate.

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
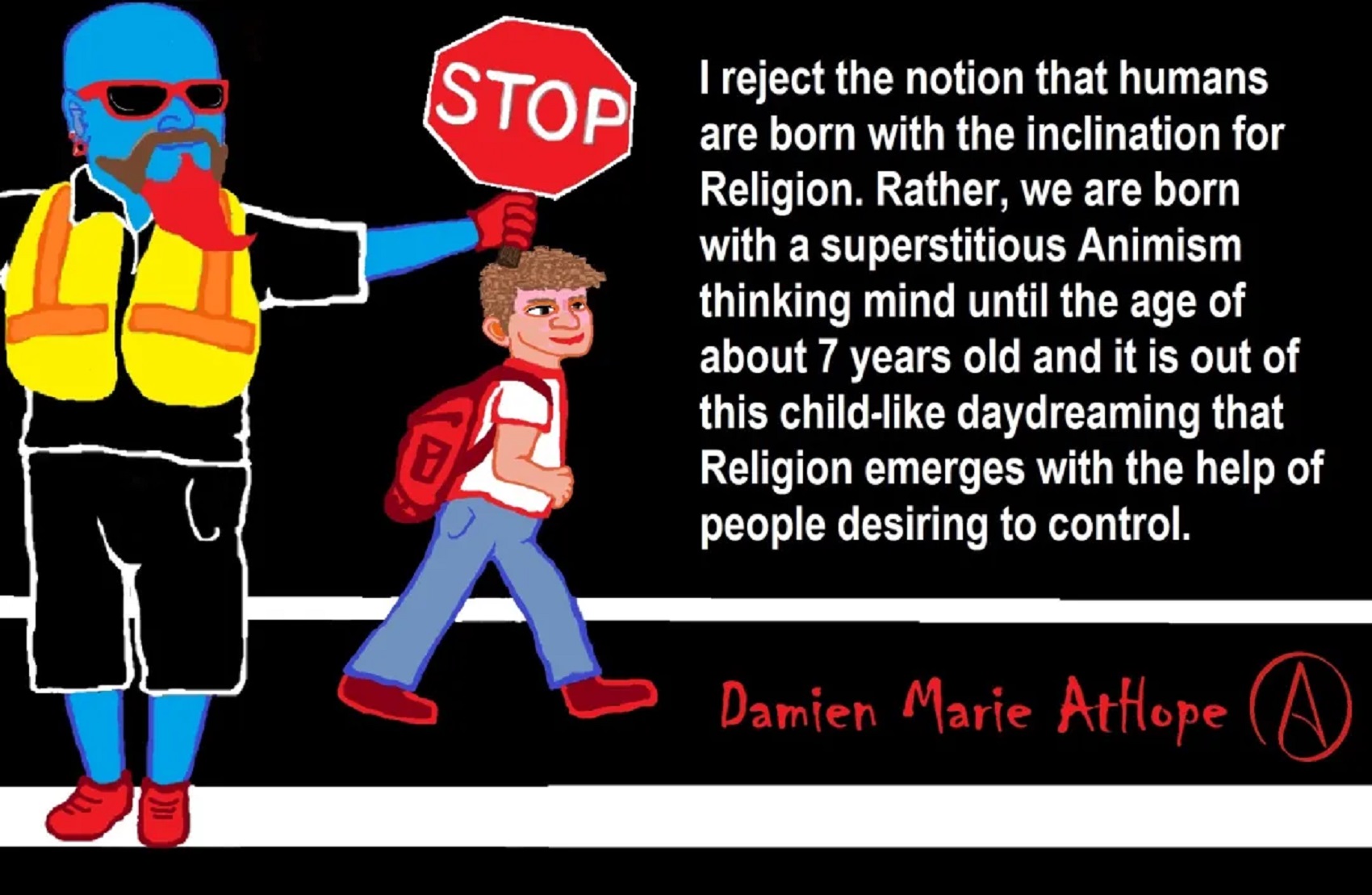
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


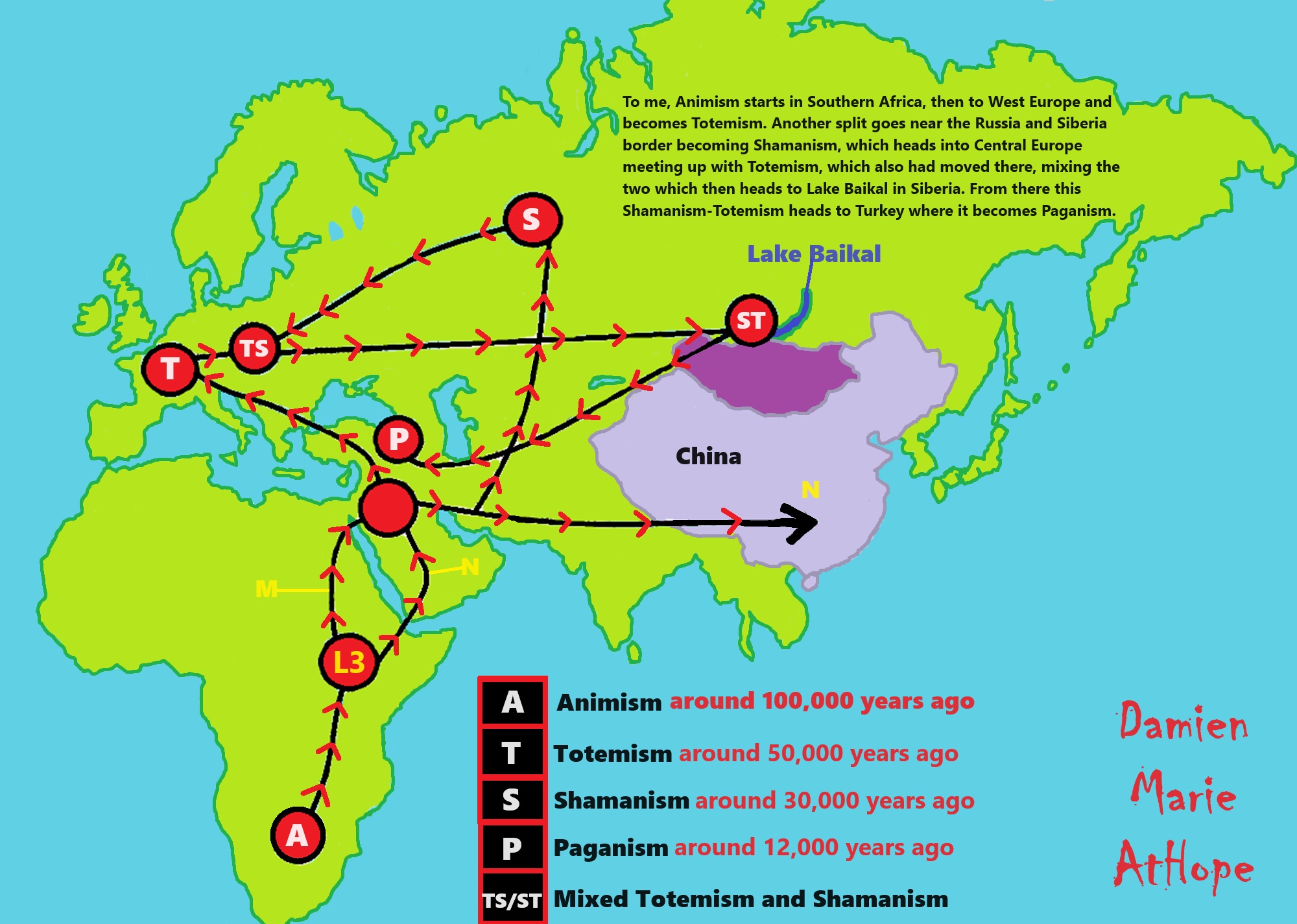
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
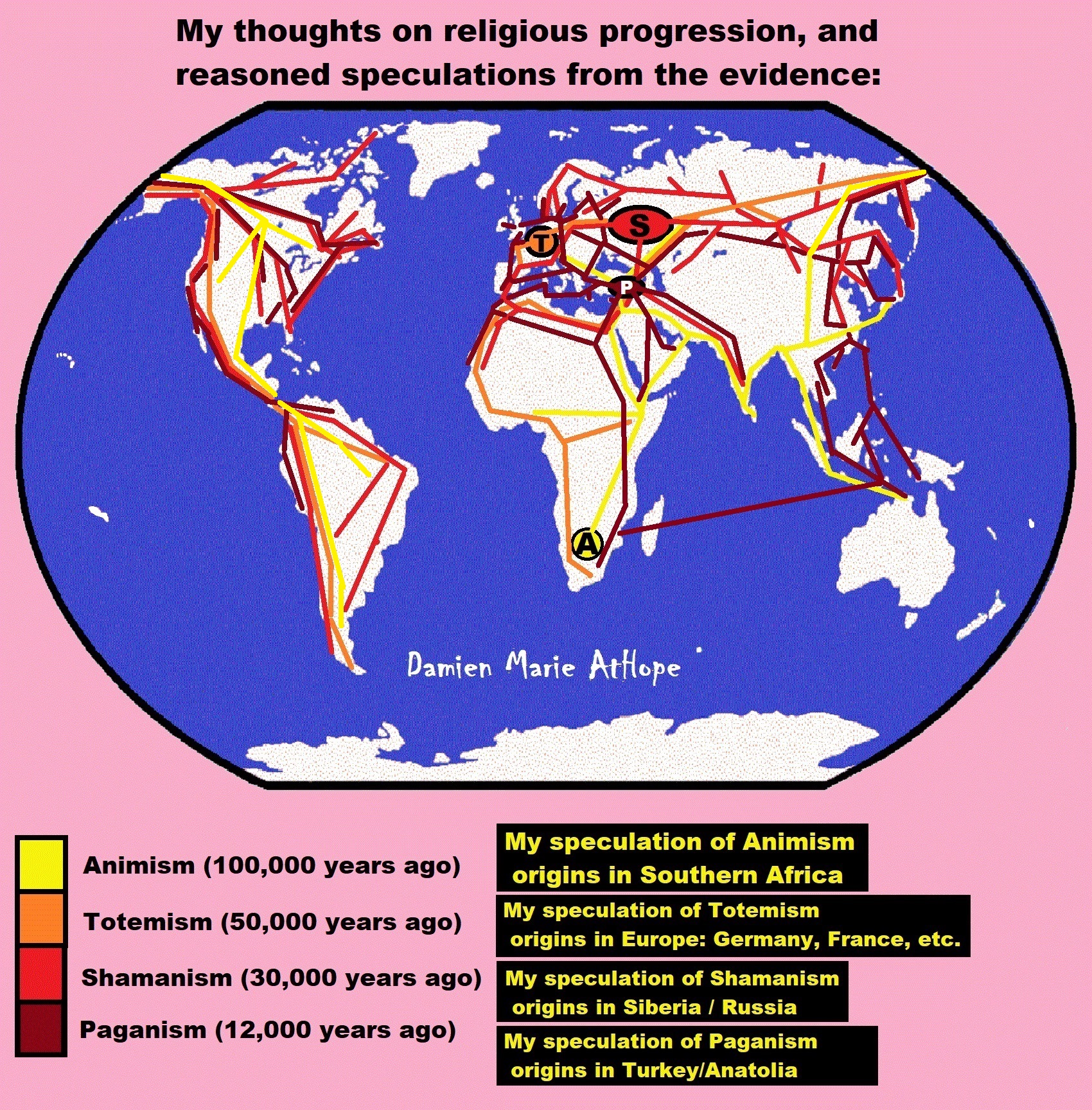



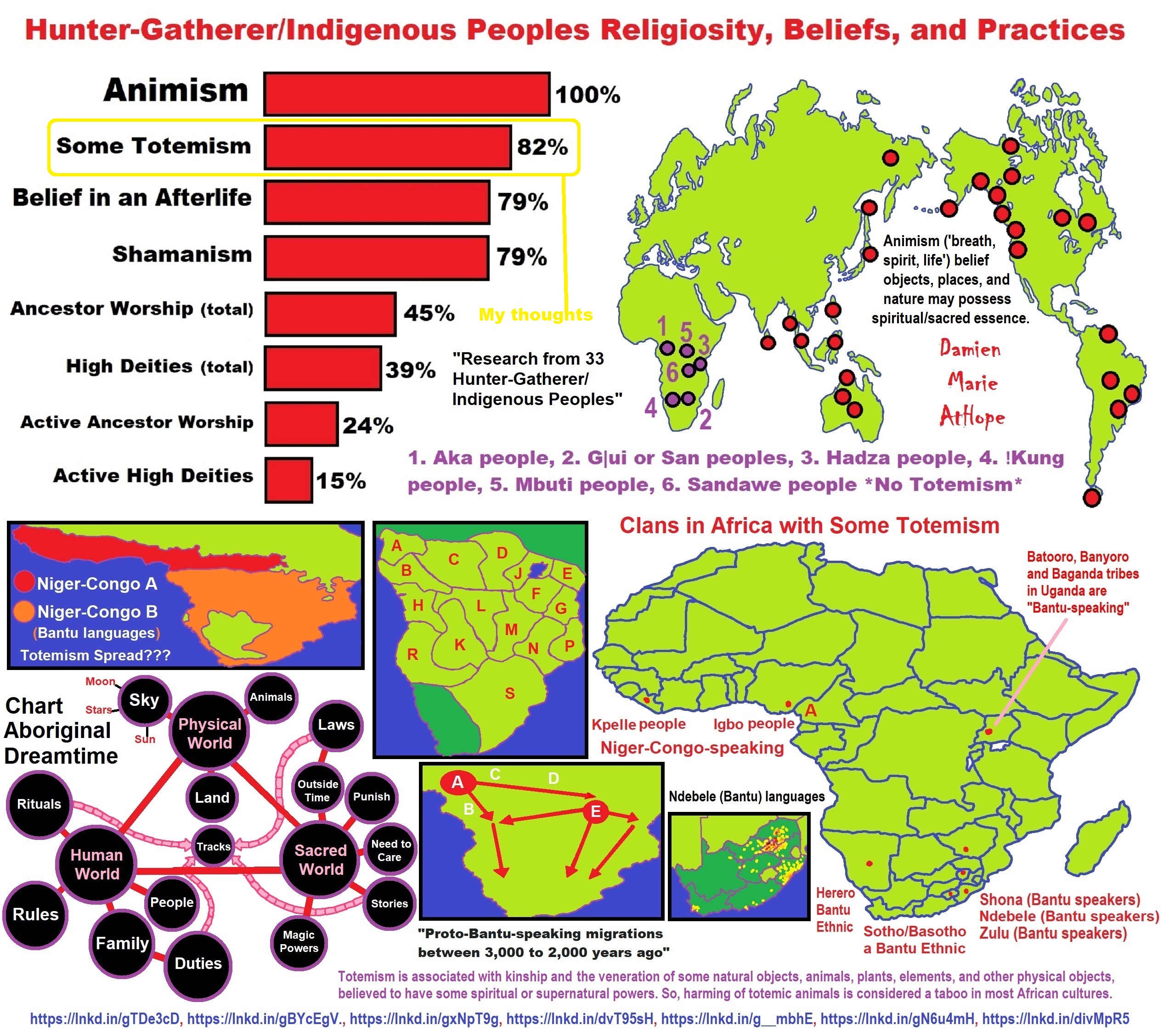
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.


Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com
