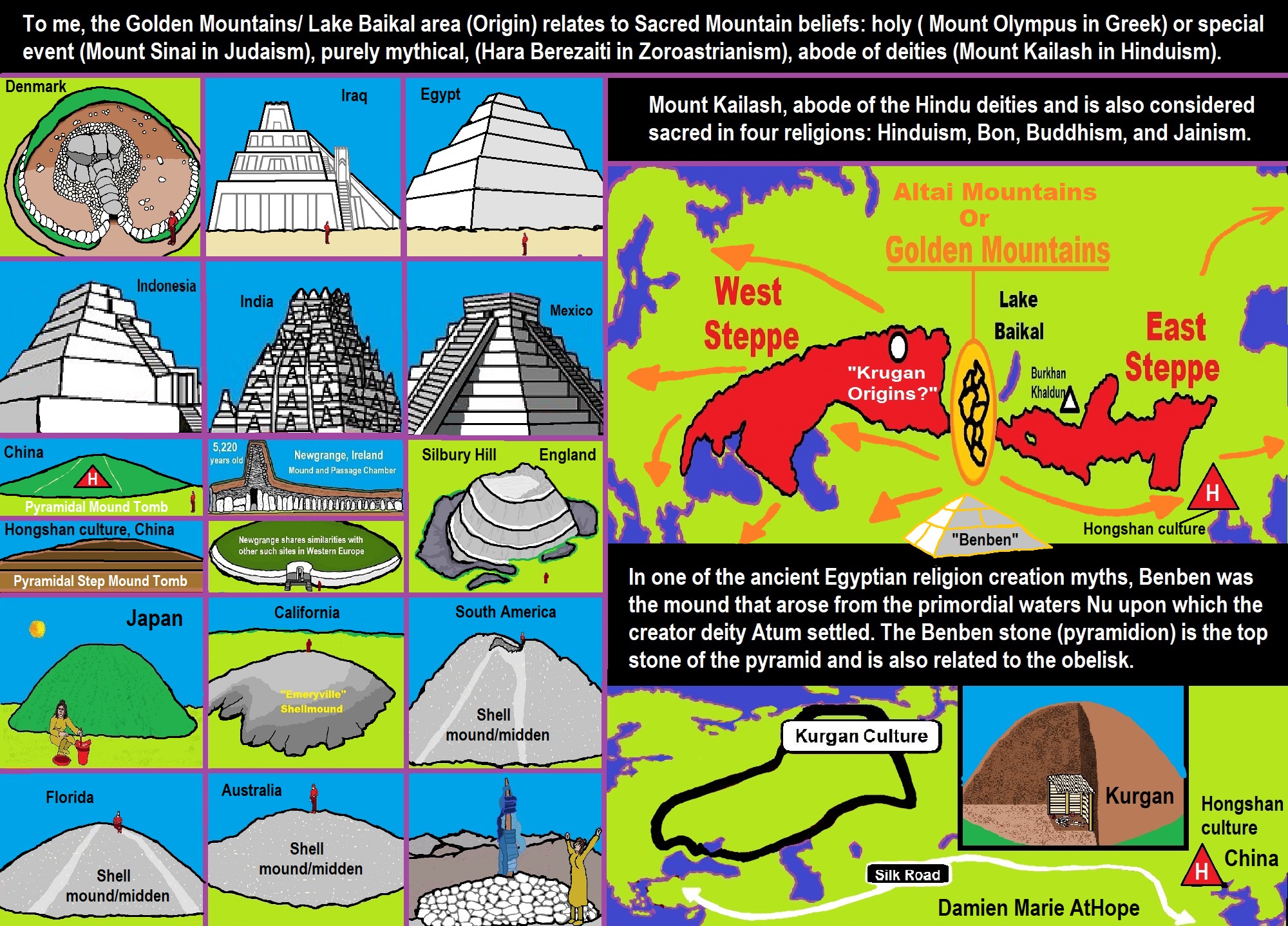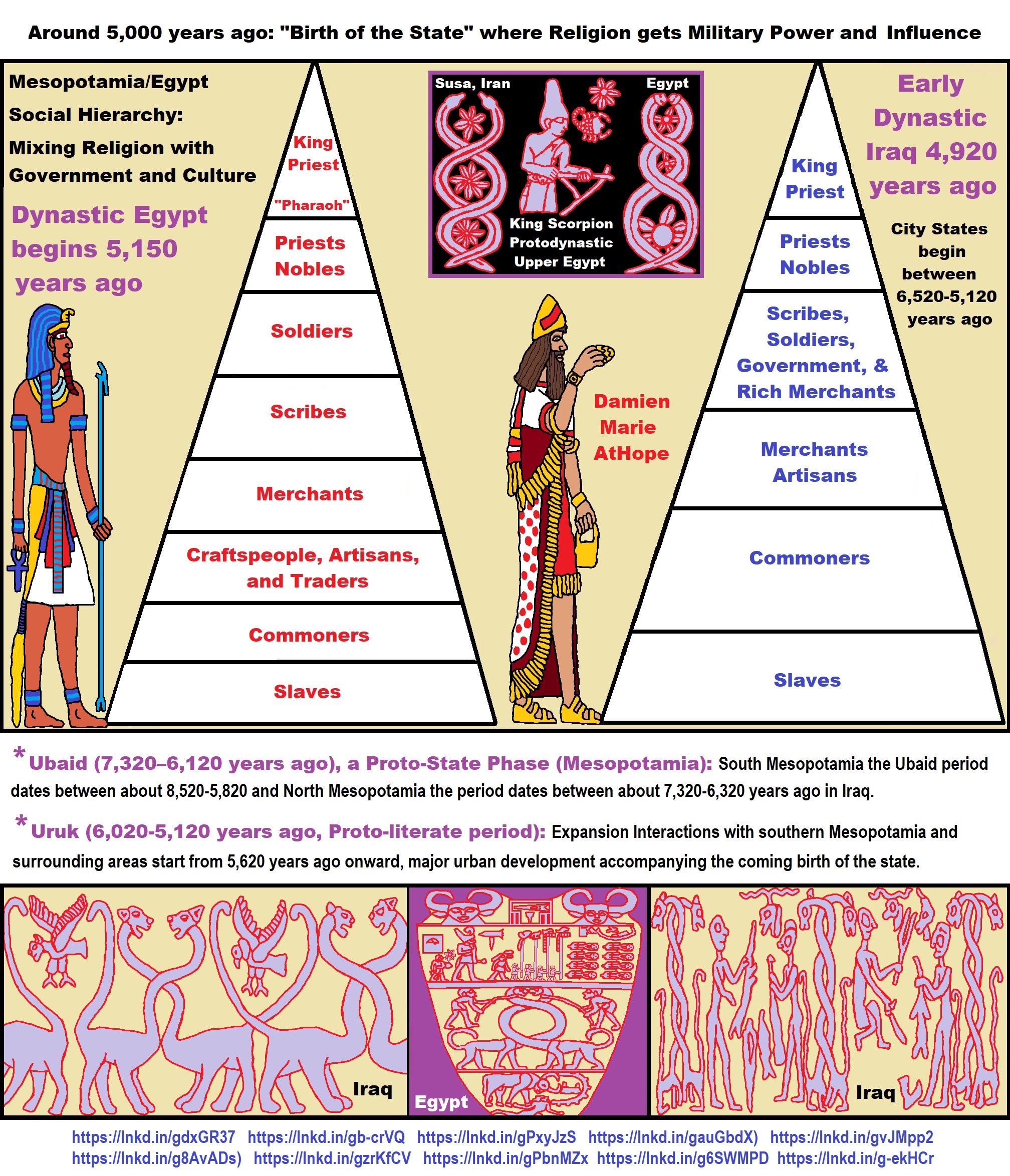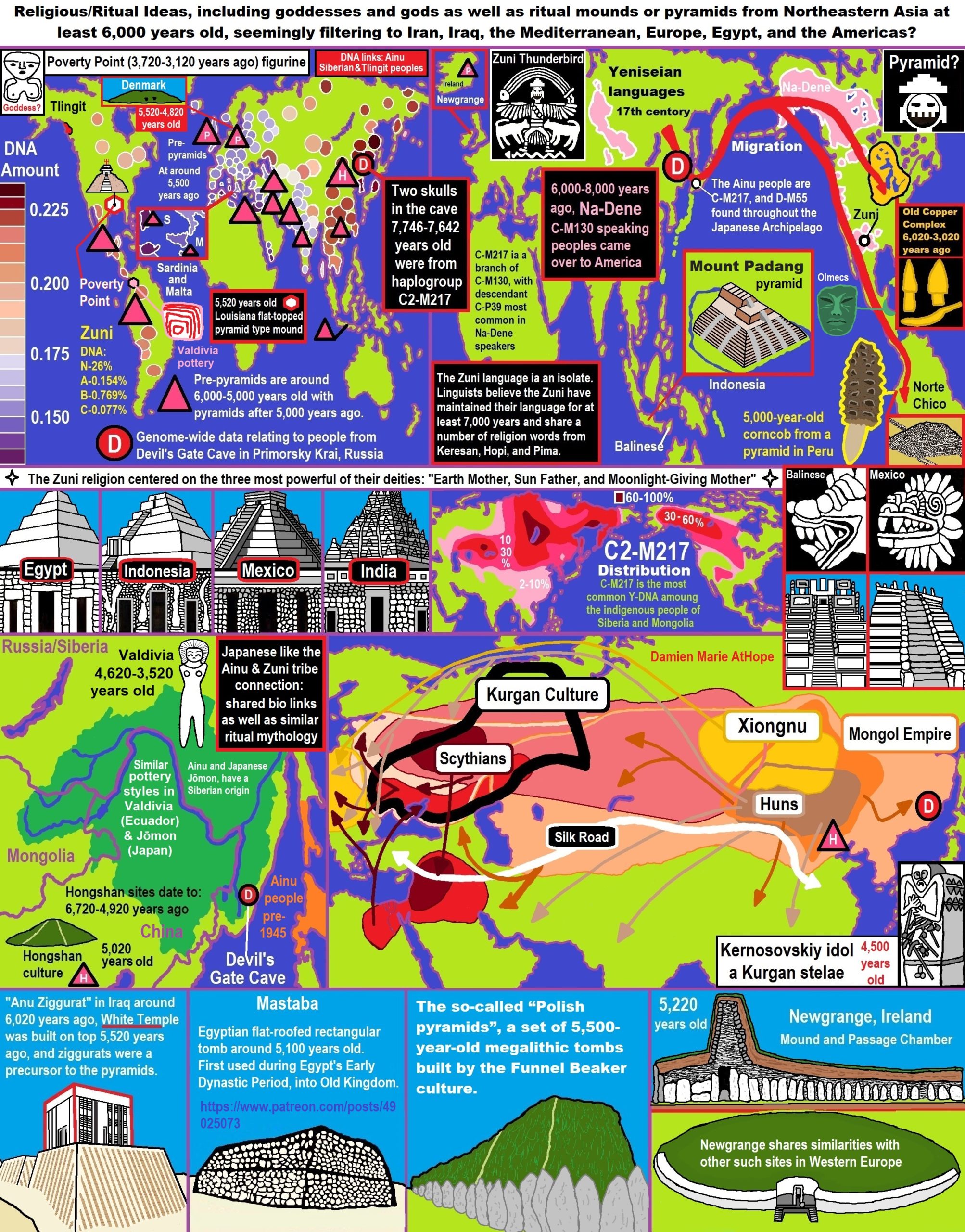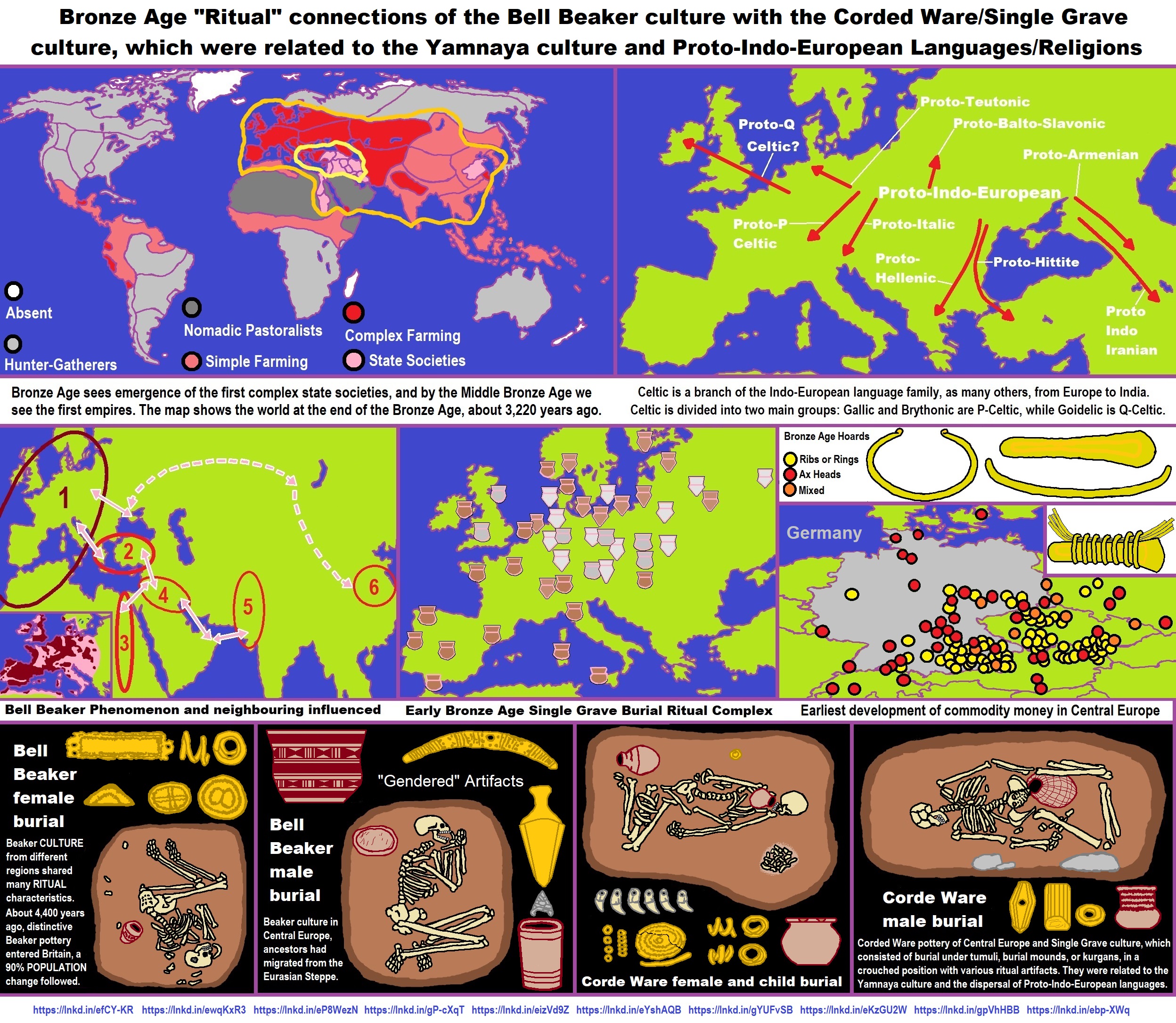
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
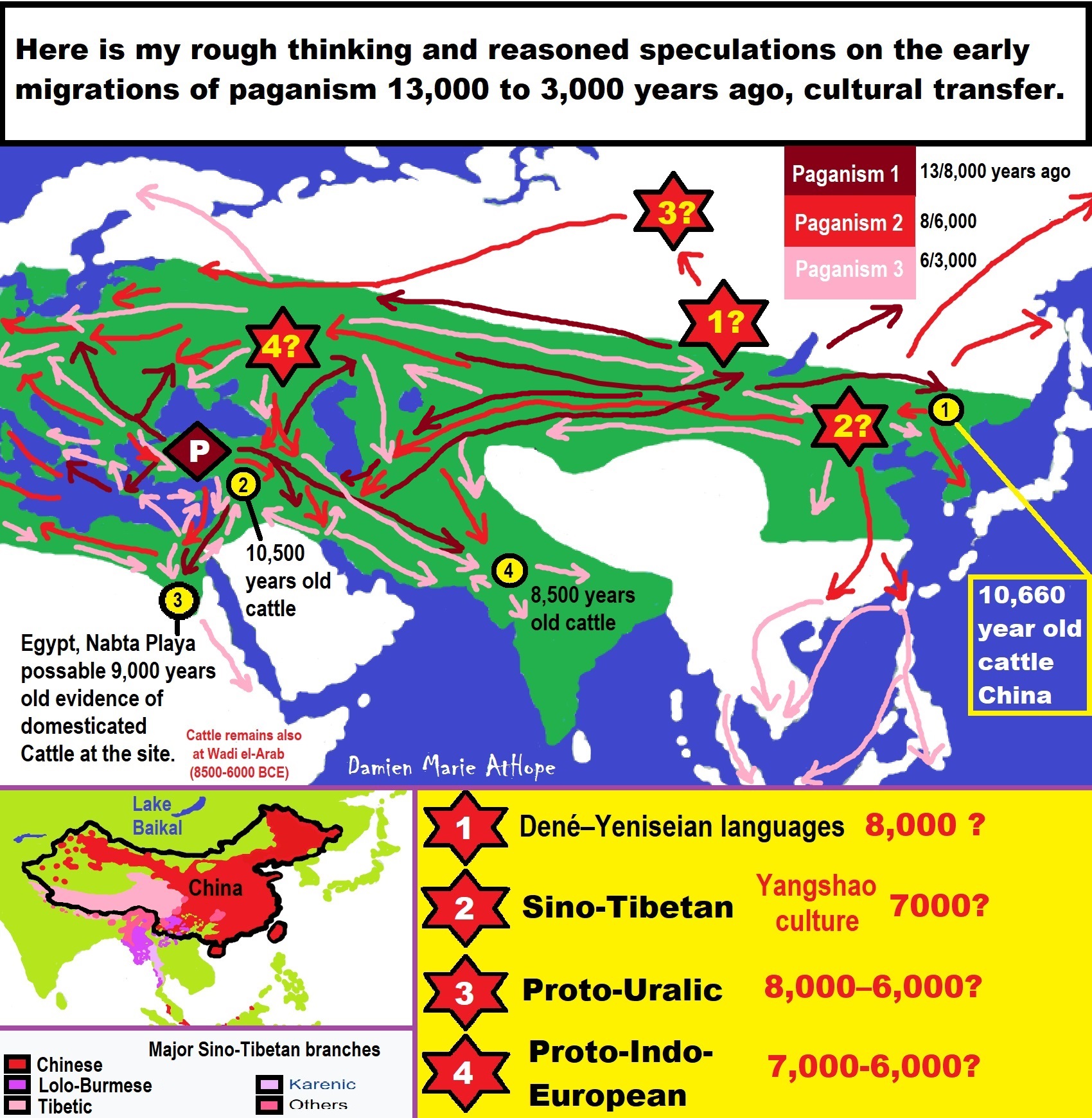
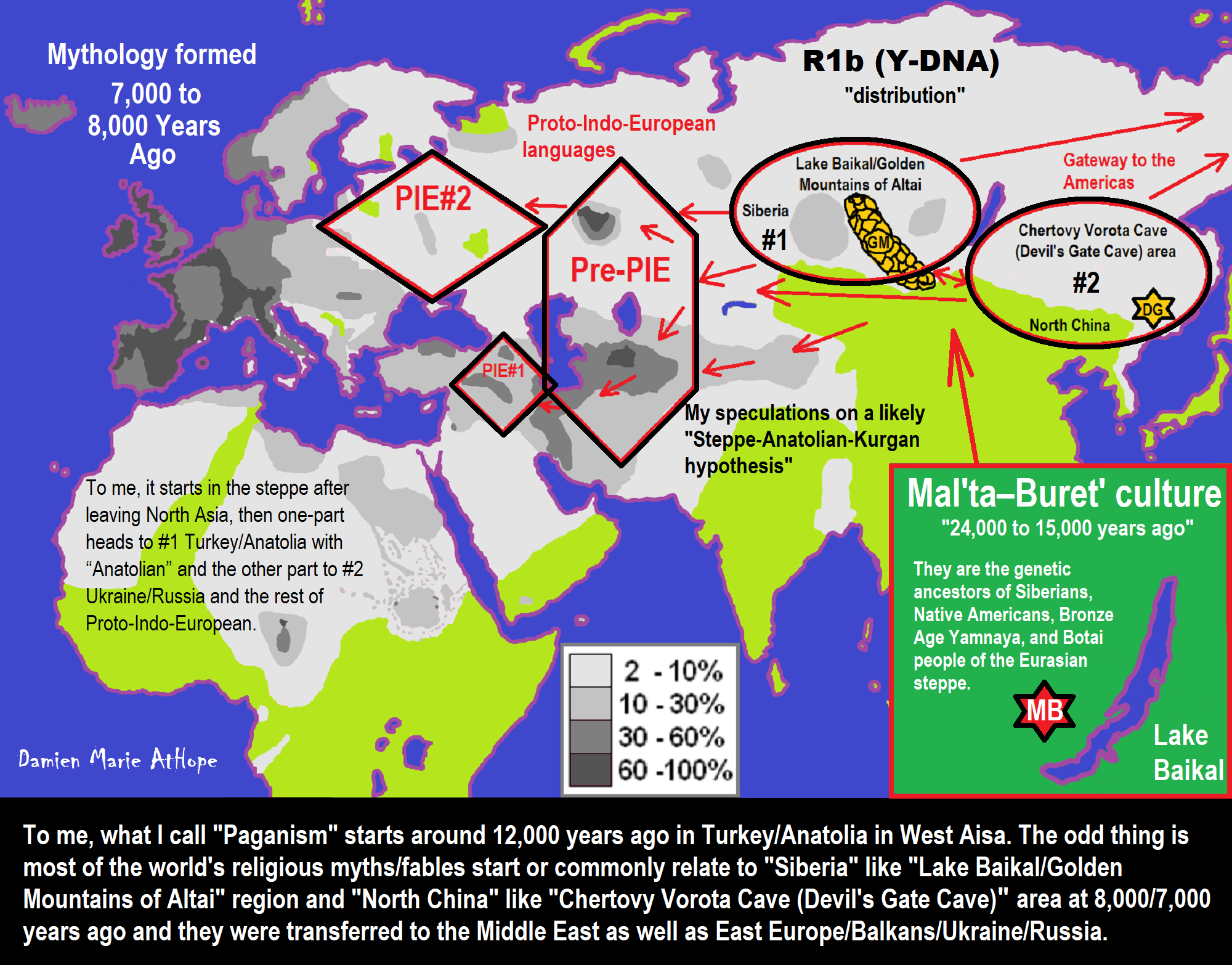
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
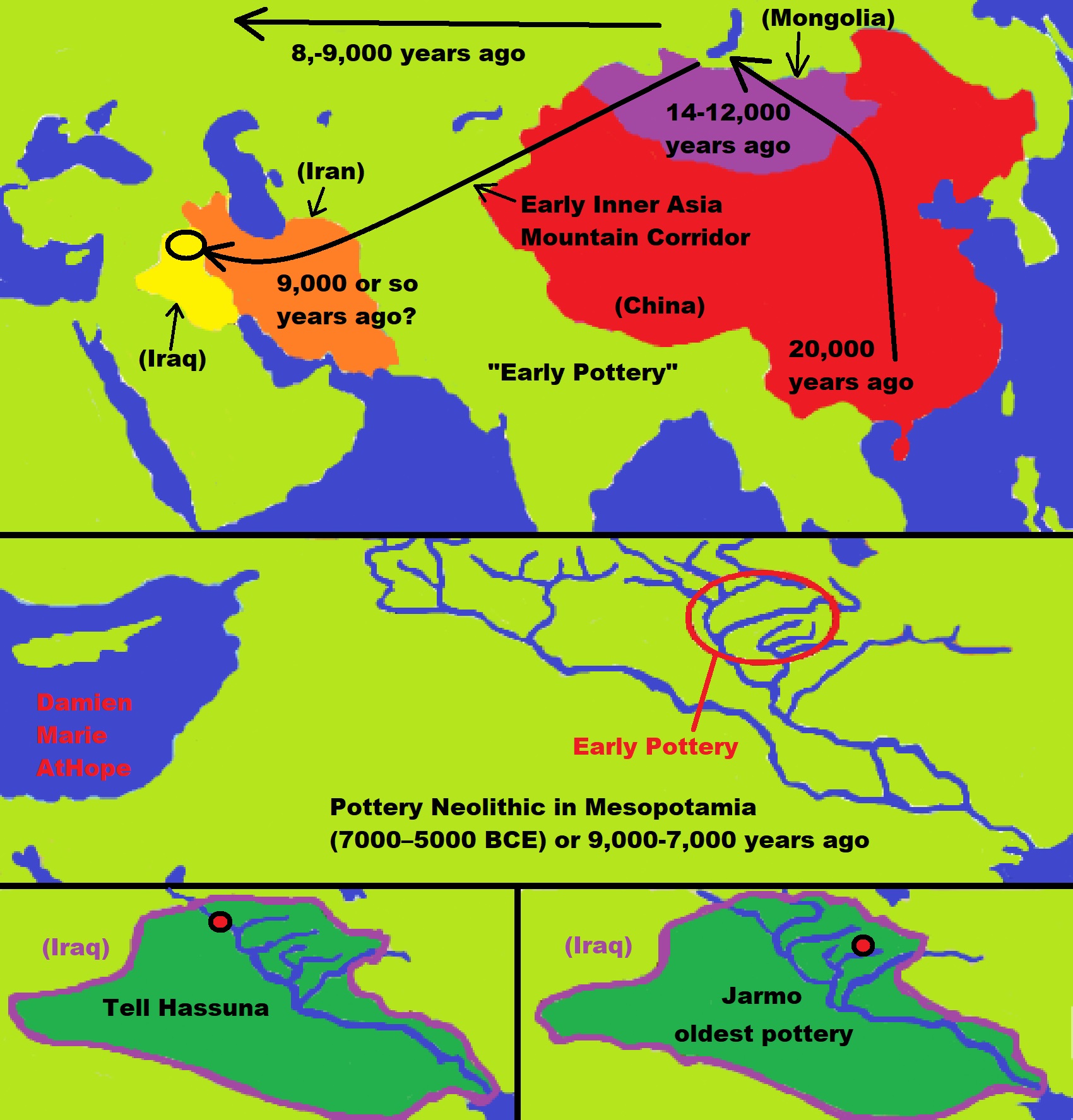
New evidence discredits my Speculation millet started in China, then migrates to Europe, and thus may have been related to Proto-indo-europian languages like it was with seemingly both the Transeurasian (Altaic) languages and Sino-Tibetan languages.
“Millet farming, pictured in a field in Yonghe Village in northern China, may have spurred the spread of the Transeurasian languages out of the Liao River Valley some 9000 years ago.” ref
“The Sino-Tibetan family which is one of the most diverse language families in the world originated among millet farmers in North China around 7200 years ago, new research shows. This analysis suggested an origin of the Sino-Tibetan family in northern Chinese communities of millet farmers of the Neolithic cultures of late Cishan and early Yangshao.” ref
“Millet began to be cultivated in Europe not 7,000 years ago in the Neolithic period as previously thought, but in the Bronze Age, about 3.5 thousand years ago.” ref
“Broomcorn millet was domesticated in northeast China by 6000 BCE. In Europe, millet was reported in Early Neolithic contexts formed by 6000 BCE, but recent radiocarbon dating of a dozen ‘early’ grains cast doubt on these claims. Archaeobotanical evidence reveals that millet was common in Europe from the 2nd millennium BCE, when major societal and economic transformations took place in the Bronze Age. We conducted an extensive program of AMS-dating of charred broomcorn millet grains from 75 prehistoric sites in Europe. Our Bayesian model reveals that millet cultivation began in Europe at the earliest during the sixteenth century BCE, and spread rapidly during the fifteenth/fourteenth centuries BCE.” ref
“Strikingly, not a single word for millet can be reconstructed for Proto-Indo-European. Intriguingly, it is evident that many agricultural meanings that have habitually been reconstructed for Proto-Indo-European are effectively post-Anatolian. Questions on the timing and the center of the Indo-European language dispersal are central to debates on the formation of the European and Asian linguistic landscapes and are deeply intertwined with questions on the archaeology and population history of these continents. Recent palaeogenomic studies support scenarios in which the core Indo-European languages spread with the expansion of Early Bronze Age Yamnaya herders that originally inhabited the East European steppes. Questions on the Yamnaya and Pre-Yamnaya locations of the language community that ultimately gave rise to the Indo-European language family are heavily dependent on linguistic reconstruction of the subsistence of Proto-IndoEuropean speakers. A central question, therefore, is how important the role of agriculture was among the speakers of this protolanguage. In this study, we perform a qualitative etymological analysis of all previously postulated Proto-Indo-European terminology related to cereal cultivation and cereal processing. On the basis of the evolution of the subsistence strategies of consecutive stages of the protolanguage, we find that one or perhaps two cereal terms can be reconstructed for the basal Indo-European stage, also known as IndoAnatolian, but that core Indo-European, here also including Tocharian, acquired a more elaborate set of terms. Thus, we linguistically document an important economic shift from a mostly non-agricultural to a mixed agro-pastoral economy between the basal and core IndoEuropean speech communities. It follows that the early, eastern Yamnaya of the Don-Volga steppe, with its lack of evidence for agricultural practices, does not offer a perfect archaeological proxy for the core Indo-European language community and that this stage of the language family more likely reflects a mixed subsistence as proposed for western Yamnaya groups around or to the west of the Dnieper River.” ref
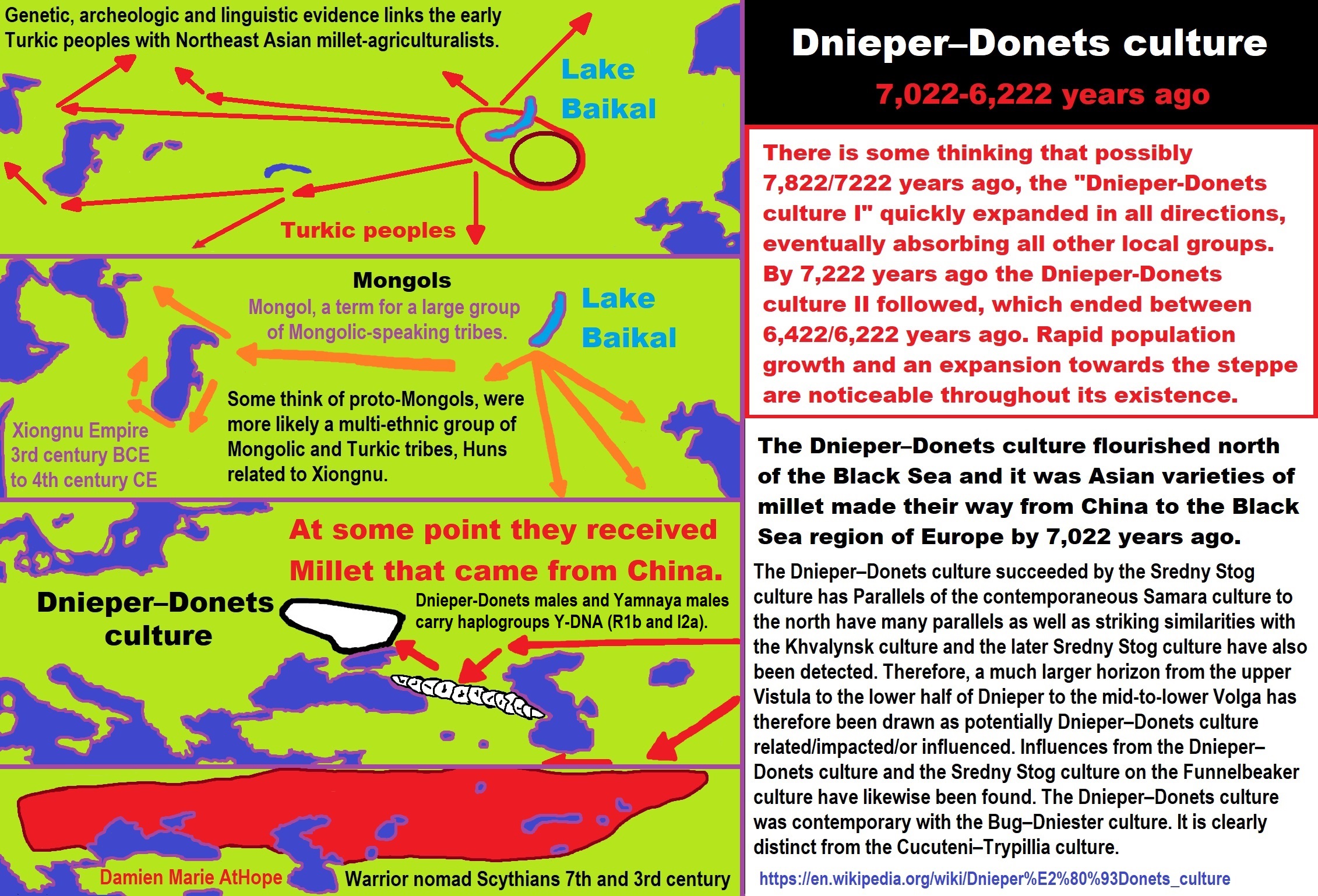
Dnieper–Donets culture
“The Dnieper–Donets culture (ca. 5th—4th millennium BCE) was a Mesolithic and later Neolithic culture which flourished north of the Black Sea ca. 5000-4200 BCE. It has many parallels with the Samara culture, and was succeeded by the Sredny Stog culture. There are parallels with the contemporaneous Samara culture to the north. Striking similarities with the Khvalynsk culture and the Sredny Stog culture have also been detected. A much larger horizon from the upper Vistula to the lower half of Dnieper to the mid-to-lower Volga has therefore been drawn. Influences from the Dnieper–Donets culture and the Sredny Stog culture on the Funnelbeaker culture have been detected. An origin of the Funnelbeaker culture from the Dnieper–Donets culture has been suggested, but this is very controversial. The Dnieper–Donets culture was contemporary with the Bug–Dniester culture. It is clearly distinct from the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture.” ref
“From around 5200 BCE, the Dnieper-Donets people began keeping cattle, sheep, and goats. Other domestic animals kept included pigs, horses, and dogs. During the following centuries, domestic animals from the Dnieper further and further east towards the Volga–Ural steppes, where they appeared ca. 4700-4600 BCE. From about 4200 BCE, the Dnieper–Donets culture adopted agriculture. Domestic plants that have been recovered include millet, wheat, and pea. Evidence from skeletal remains suggest that plants were consumed. The presence of exotic goods in Dnieper-Donets graves indicates exchange relationships with the Caucasus. In later times the deceased in the Dnieper–Donets culture were sometimes buried individually. This shift has been suggested as evidence of a shift towards increasing individualism. Dnieper–Donets burials have been found near the settlement of Deriivka, which is associated with the Sredny Stog culture.” ref
“Certain Dnieper-Donets burials are accompanied with copper, crystal or porphyry ornaments, shell beads, bird-stone tubes, polished stone maces or ornamental plaques made of boar’s tusk. The items, along with the presence of animal bones and sophisticated burial methods, appear to have been a symbol of power. Certain deceased children were buried with such items, which indicates that wealth was inherited in Dnieper-Donets society. Very similar boar-tusk plaques and copper ornament have been found at contemporary graves of the Samara culture in the middle Volga area. Maces of a different type than those of Dnieper-Donets have also been found. The wide adoption of such a status symbol attests to a change in the politics of power. The physical remains recovered from graves of the Dnieper–Donets culture have been classified as “Proto-Europoid“, with large and more massive features than the gracile Mediterranean peoples of the Balkan Neolithic. Males averaged 172 cm in height, which is much taller than contemporary Neolithic populations. Its rugged physical traits are thought to have genetically influenced later Indo-European peoples.” ref
“Dnieper-Donets pottery was initially pointed-based, but in later phases flat-based wares emerge. Their pottery is completely different from those made by the nearby Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. The importance of pottery appears to have increased throughout the existence of the Dnieper–Donets culture, which implies a more sedentary lifestyle. The early use of typical point base pottery interrelates with other Mesolithic cultures that are peripheral to the expanse of the Neolithic farmer cultures. The special shape of this pottery has been related to transport by logboat in wetland areas. Especially related are Swifterbant in the Netherlands, Ellerbek and Ertebølle in Northern Germany and Scandinavia, “Ceramic Mesolithic” pottery of Belgium and Northern France (including non-Linear pottery such as La Hoguette, Bliquy, Villeneuve-Saint-Germain), the Roucadour culture in Southwest France and the river and lake areas of Northern Poland and Russia.” ref
“In accordance with the Kurgan hypothesis, J. Mallory (1997) suggested that the Dnieper-Donets people were Pre–Indo-European-speakers who were absorbed by Proto-Indo-Europeans expanding westwards from steppe-lands further east. David Anthony (2007) believes that the Dnieper-Donets people almost certainly spoke a different language from the people of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. The areas of the upper Dniester in which the Dnieper–Donets culture was situated have mostly Baltic river names. That and the close relationship between the Dnieper–Donets culture and contemporary cultures of northeast Europe have caused the Dnieper–Donets culture to be identified with the later Balts. The precise role of the culture and its language to the derivation of the Pontic-Caspian cultures, such as Sredny Stog and Yamnaya culture, is open to debate, but the display of recurrent traits points to longstanding mutual contacts or to underlying genetic relations.” ref
DNA of Bronze Age Proto-Indo-Europeans
“The so-called Kurgan hypothesis, which postulates that the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language arose in the Pontic steppe. During the Yamna period, one of the world’s first Bronze Age cultures, Proto-Indo-European speakers migrated west towards Europe and east towards Central Asia, then South Asia, spreading with them the Indo-European languages spoken today in most of Europe, Iran, and a big part of the Indian subcontinent. The Kurgan model is the most widely accepted scenario of Indo-European origins. Most linguists agree that PIE may have been spoken as a single language (before divergence began) around 3500 BCE, which coincides with the beginning of the Yamna culture in the Pontic-Caspian steppe, and of the related Maykop culture in the northwest Caucasus. .” ref
“There is now compelling genetic evidence that haplogroups R1a and R1b, the most common paternal lineages in Europe, Central Asia, and parts of South Asia, were mainly propagated by the Indo-European migrations during the Bronze Age. A sizeable part of European maternal lineages also seem to be of Indo-European origin, although the proportion varies a lot across Europe, but generally correlating to a large extent with the proportion of Y-haplogroups R1a and R1b. Other paternal lineages, such as G2a3b, J2b2, and T1a, are thought to have spread the Copper Age from the Balkans to modern Ukraine, then to have been absorbed by the expansion of R1a and R1b people respectively from central Russia (Volga basin) and southern Russia (Kuban, northwest Caucasus).” ref
“The first PIE expansion into Europe was the Corded Ware culture, which so far have yielded only R1a samples. R1b is thought to have invaded the Balkans, then followed the Danube until Germany, from where it spread to western Europe and Scandinavia. The Asian branch originated around the Volga basin, then expanded across the Urals with the Sintashta culture, then over most of Central Asia and southern Siberia.” ref
“In the Chalcolithic (5,022-4,022 years ago), a series of complex cultures developed that would give rise to the peninsula’s first civilizations and to extensive exchange networks reaching to the Baltic, Middle East, and North Africa. Around 4,822 – 4,722 years ago, the Beaker culture, which produced the Maritime Bell Beaker, probably originated in the vibrant copper-using communities of the Tagus estuary in Portugal and spread from there to many parts of western Europe.” ref
“R1b is the most common haplogroup in Western Europe, reaching over 80% of the population in Ireland, the Scottish Highlands, western Wales, the Atlantic fringe of France, the Basque country, and Catalonia. It is also common in Anatolia and around the Caucasus, in parts of Russia, and in Central and South Asia. Besides the Atlantic and North Sea coast of Europe, hotspots include the Po valley in north-central Italy (over 70%), Armenia (35%), the Bashkirs of the Urals region of Russia (50%), Turkmenistan (over 35%), the Hazara people of Afghanistan (35%), the Uyghurs of North-West China (20%) and the Newars of Nepal (11%). R1b-V88, a subclade specific to sub-Saharan Africa, is found in 60 to 95% of men in northern Cameroon.” ref
“The oldest forms of R1b (M343, P25, L389) are found dispersed at very low frequencies from Western Europe to India, a vast region where could have roamed the nomadic R1b hunter-gatherers during the Ice Age. The three main branches of R1b1 (R1b1a, R1b1b, R1b1c) all seem to have stemmed from the Middle East. The southern branch, R1b1c (V88), is found mostly in the Levant and Africa. The northern branch, R1b1a (P297), seems to have originated around the Caucasus, eastern Anatolia, or northern Mesopotamia, then to have crossed over the Caucasus, from where they would have invaded Europe and Central Asia. R1b1b (M335) has only been found in Anatolia/Turkey.” ref
Neolithic cattle herders
“It has been hypothesized that R1b people (perhaps alongside neighboring J2 tribes) were the first to domesticate cattle in northern Mesopotamia some 10,500 years ago. R1b tribes descended from mammoth hunters, and when mammoths went extinct, they started hunting other large game such as bisons and aurochs. With the increase of the human population in the Fertile Crescent from the beginning of the Neolithic (starting 12,000 years ago), selective hunting and culling of herds started replacing indiscriminate killing of wild animals. The increased involvement of humans in the life of aurochs, wild boars, and goats led to their progressive taming. Cattle herders probably maintained a nomadic or semi-nomadic existence, while other people in the Fertile Crescent (presumably represented by haplogroups E1b1b, G and T) settled down to cultivate the land or keep smaller domesticates.” ref
“The analysis of bovine DNA has revealed that all the taurine cattle (Bos taurus) alive today descend from a population of only 80 aurochs. The earliest evidence of cattle domestication dates from circa 8,500 BCE in the Pre-Pottery Neolithic cultures in the Taurus Mountains. The Taurus Mountains (Turkish: Toros Dağları), are a mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean coastal region of southern Turkey from the central Anatolian Plateau. The two oldest archaeological sites showing signs of cattle domestication are the villages of Çayönü Tepesi in southeastern Turkey and Dja’de el-Mughara in northern Iraq, two sites only 250 km away from each others. This is presumably the area from which R1b lineages started expanding – or in other words the “original homeland” of R1b.” ref, ref
“The early R1b cattle herders would have split in at least three groups. One branch (M335) remained in Anatolia, but judging from its extreme rarity today wasn’t very successful, perhaps due to the heavy competition with other Neolithic populations in Anatolia, or to the scarcity of pastures in this mountainous environment. A second branch migrated south to the Levant, where it became the V88 branch. Some of them searched for new lands south in Africa, first in Egypt, then colonizing most of northern Africa, from the Mediterranean coast to the Sahel. The third branch (P297), crossed the Caucasus into the vast Pontic-Caspian Steppe, which provided ideal grazing grounds for cattle. They split into two factions: R1b1a1 (M73), which went east along the Caspian Sea to Central Asia, and R1b1a2 (M269), which at first remained in the North Caucasus and the Pontic Steppe between the Dnieper and the Volga. It is not yet clear whether M73 actually migrated across the Caucasus and reached Central Asia via Kazakhstan, or if it went south through Iran and Turkmenistan.” ref
“In any case, M73 would be a pre-Indo-European branch of R1b, just like V88 and M335. R1b-M269 (the most common form in Europe) is closely associated with the diffusion of Indo-European languages, as attested by its presence in all regions of the world where Indo-European languages were spoken in ancient times, from the Atlantic coast of Europe to the Indian subcontinent, which comprised almost all Europe (except Finland, Sardinia, and Bosnia-Herzegovina), Anatolia, Armenia, European Russia, southern Siberia, many pockets around Central Asia (notably in Xinjiang, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Afghanistan), without forgetting Iran, Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal. The history of R1b and R1a are intricately connected to each others.” ref
The British Isles’ introduction of Farming around 7,000 years ago began Radical Change
“The British Isles have been populated by human beings for hundreds of thousands of years, but it was the introduction of farming around 7,000 years ago that began a process of radical change. Over the millennia there were phases of extreme cold, when large areas of Britain were covered in ice, followed by warmer times. Around 10,000 years ago, the latest ice age came to an end. Sea levels rose as the ice sheets melted, and Britain became separated from the European mainland shortly before 8,000 years ago. The people living on the new islands of Britain were descendants of the first modern humans, or Homo sapiens, who arrived in northern Europe around 30,000 – 40,000 years ago. Like their early ancestors, they lived by hunting and gathering. The introduction of farming, when people learned how to produce rather than acquire their food, is widely regarded as one of the biggest changes in human history. This change happened at various times in several different places around the world. The concept of farming that reached Britain between about 7,000 – 6,500 years ago had spread across Europe from origins in Syria and Iraq between about 13,000 -11,000 years ago.” ref
“So the majority of early farmers were probably Mesolithic people who adopted the new way of life and took it with them to other parts of Britain. This was not a rapid change – farming took about 2,000 years to spread across all parts of the British Isles. The ‘Neolithic revolution according to radiocarbon dates, shows that the transition from hunter-gatherer to farmer was relatively gradual. We know, for example, that hunters in the Mesolithic ‘managed’ or tended their quarry. They would make clearings in woodland around sources of drinking water, and probably made efforts to see that the herds of deer and other animals they hunted were not over-exploited.” ref
“The switch from managed hunting to pastoral farming was not a big change. The first farmers brought the ancestors of cattle, sheep, and goats with them from the continent. Domestic pigs were bred from wild boars, which lived in the woods of Britain. Neolithic farmers also kept domesticated dogs, which were bred from wolves. It is probable that the earliest domesticated livestock were allowed to wander, and may be tended by a few herders. Sheep, goats, and cattle are fond of leaves and bark, and pigs snuffle around roots. These domestic animals may have played a major role in clearing away the huge areas of dense forest that covered most of lowland Britain.” ref
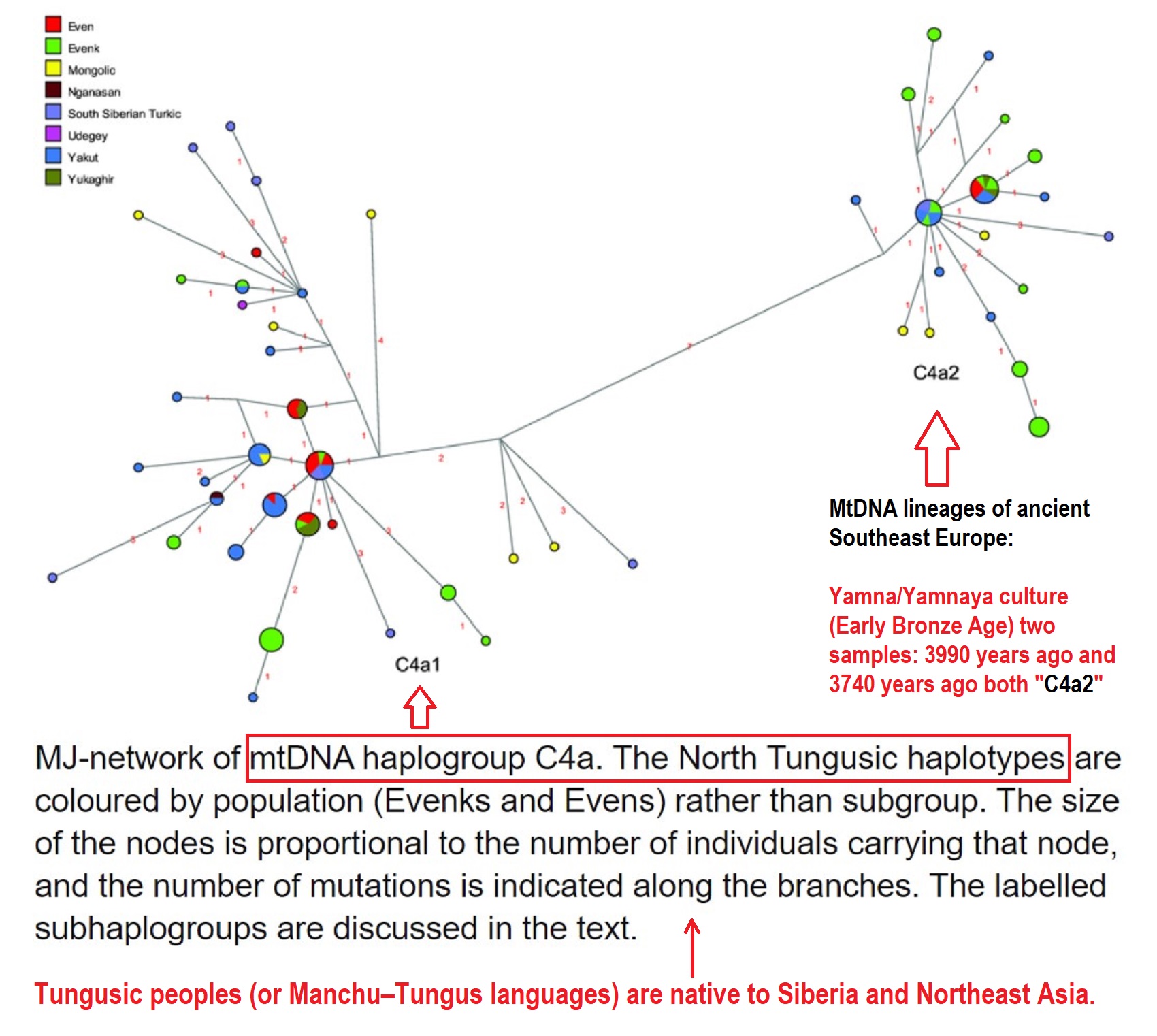
MtDNA haplogroup C4a belongs to North Tungusic haplotypes (Evenks and Evens)
North Aisains’ C4a in MtDNA lineages of ancient Southeast Europe (Yamnaya/Yamna culture C4a2)
“MJ-network of mtDNA haplogroup C4a. The North Tungusic haplotypes are colored by population (Evenks of North Asia: Russia, China, or Mongolia and Evens from Siberia and the Russian Far East) rather than a subgroup. The size of the nodes is proportional to the number of individuals carrying that node, and the number of mutations is indicated along the branches.” ref
MtDNA lineages of ancient Southeast Europe with C4a2 (seen in Yamnaya/Yamna culture)
“A distinct inclusion of lineages of east Eurasian origin belonging to mtDNA haplogroup C was observed in the Yamna group of western. The two C-bearing Yamna specimens from the L kurgan appear to possess a similar, albeit different at two nucleotide positions, SNP motif at HVR-1 in the C4a2 lineage of haplogroup C. Specimen L8, the chronologically older of the two C4a2-carrying specimens in our study, is more derived than L15, suggesting, on the one hand, an ex situ diversification of C4a2 lineages before their arrival in western NPR. On the other hand, it is equally likely that these lineages had diversified on the local substrate of the Neolithic builders of Mariupol-type cemeteries of extended burials of the Dnieper–Donets Culture Complex from the Dnieper Rapids in the central part of the NPR, specimens from which featured representatives of the C haplogroup.” ref
“In fact, both EBA lineages of C presented in this study could be viewed as derived from the lineage of the Dnieper–Donets Culture Complex specimen Ya34 from the Mariupol-type cemetery at Yasinovatka6 via the transition at 16218. Sequence matches to the HVR-1 nucleotide motif of Ya34 have been identified in modern Siberian populations from the circum-Baikal area as well as Sherpa populations from Tibetan highlands. The lack of coding region polymorphism for the C lineages in the NPR limits our understanding of their phylogenetic relationships. Anthropological data support a link between NPR’s Dnieper–Donets Culture Complex and EBA populations, as well as connecting them with northern Europe, including the Mesolithic population of the South Olenij Ostrov. The latter was featured as a part of the Mesolithic North European population in our PCA and genetic distance analyses, both indicating a mtDNA haplogroup frequency similarity between the NPR EBA and Mesolithic North European populations. Representatives of east Eurasian mtDNA haplogroups such as C and D have been found on Olenij Ostrov.” ref
MtDNA C in ancient Ukraine extends East Eurasian genetic lineages in Neolithic Central and Eastern Europe
“Although the majority of identified mtDNA haplogroups belonged to the traditional West Eurasian lineages of H and U, three specimens were determined to belong to the lineages of mtDNA haplogroup C. This find extends the presence of East Eurasian lineages in Neolithic Europe from the Carpathian Mountains to the northern shores of the Black Sea and provides the first genetic account of Neolithic mtDNA lineages from the North Pontic Region. During the Neolithic, the North Pontic Region was home to major prehistoric cultural conglomerates, among them—the Dnieper-Donets cultural complex.” ref
“The Dnieper-Donets culture has been studied in approximately 200 sites in Ukraine and Byelorussia, including settlements and large collective cemeteries of the Mariupol-type. The main feature of Mariupol-type cemeteries is inhumation burial in the supine position. This burial rite differs from most local Mesolithic burial traditions and is characteristic of the ‘Euro-Siberian’ zone of extended burials, which are found from Lake Baikal and the forest and forest-steppe zones of the East European Plain to the northern part of Central Europe and Scandinavia. The distinct burial tradition of Neolithic populations of the North Pontic Region as well as their anthropological characteristics suggests an influx of external population sources.” ref
Mariupol culture
“The Mariupol culture (Mariupol-type cemeteries) was a transitional culture of the Neolithic and Eneolithic (Copper Age) in the Pontic Steppe during the second half of the 5th millennium BCE. The final stages of this culture are described as the Post-Mariupol culture. The Post-Mariupol culture was superseded by Sredny Stog culture. In older works, it is referred to as a part of wider Dnieper-Donetsk culture also known as the Mariupol type cultures. D. Ya. Telegin, an expert on Neolithic and Eneolithic Eastern Europe, asserts that the Mariupol-type cemeteries seem to have had their origins in the late Mesolithic and endured into the Copper Age: a period of more than two thousand years (c. 6500–4000 cal BCE). They were primarily fisher-hunter-gatherers familiar with livestock through exchange or pastoralism. In terms of biological anthropology, Mariupol remains appear to be Caucasoid and physically larger than their contemporaries.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
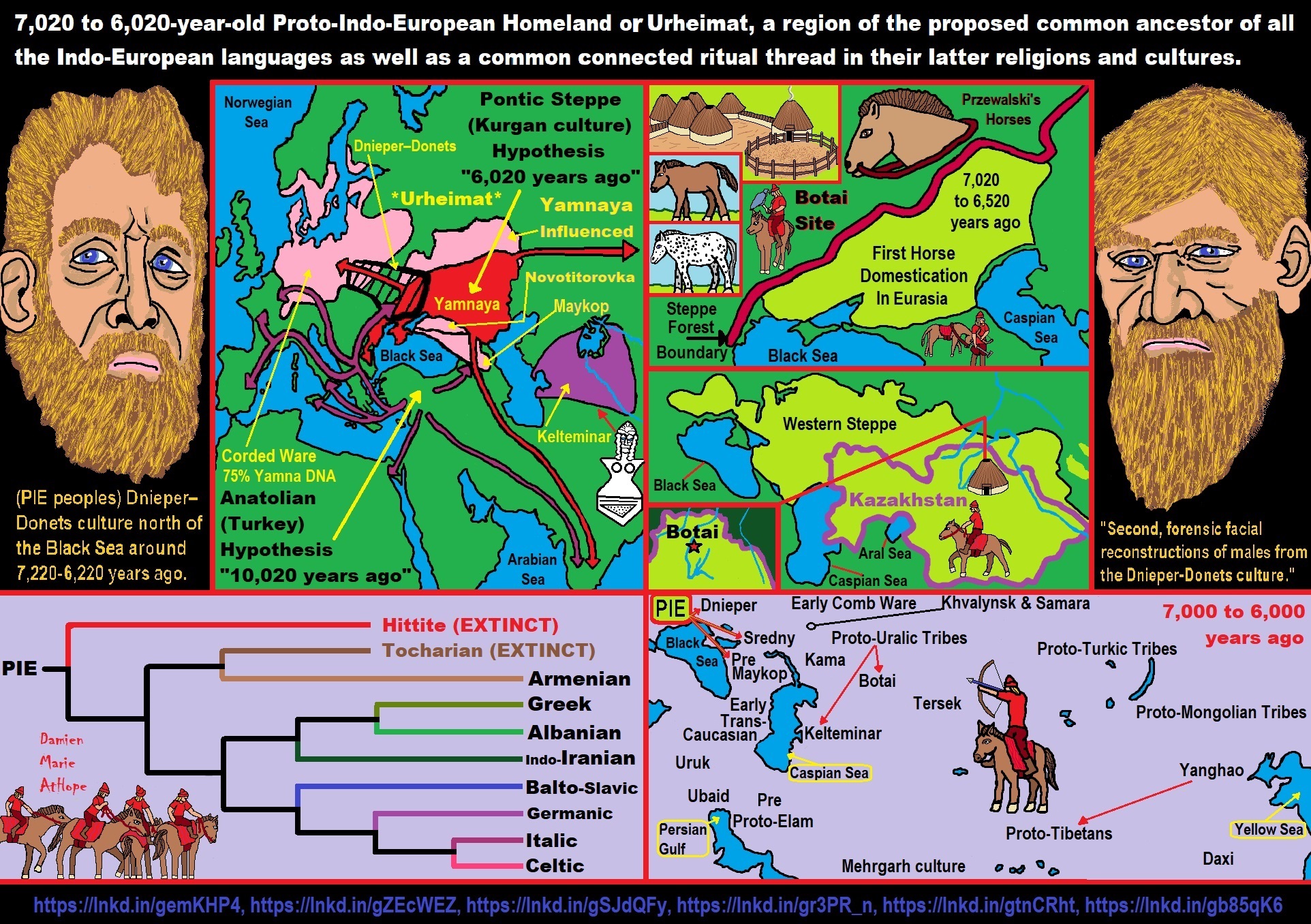
Proto-Indo-Europeans: Western Steppe Herders
“The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BCE. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eastern Europe (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia).” ref
“Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BCE or 7,522-6,522 years ago) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BCE or 9,522-7,522 years ago), and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BCE, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded Ware culture), the edges of Central Asia (Yamnaya culture), and southern Siberia (Afanasievo culture).” ref
“While ‘Proto-Indo-Europeans’ is used in scholarship to designate the group of speakers associated with the reconstructed proto-language and culture, the term ‘Indo-Europeans’ may refer to any historical people that speak an Indo-European language. In the words of philologist Martin L. West, “If there was an Indo-European language, it follows that there was a people who spoke it: not a people in the sense of a nation, for they may never have formed a political unity, and not a people in any racial sense, for they may have been as genetically mixed as any modern population defined by language.” ref
“Using linguistic reconstruction from old Indo-European languages such as Latin and Sanskrit, hypothetical features of the Proto-Indo-European language are deduced. Assuming that these linguistic features reflect the culture and environment of the Proto-Indo-Europeans, the following cultural and environmental traits are widely proposed:
- pastoralism, including domesticated cattle, horses, and dogs
- agriculture and cereal cultivation, including technology commonly ascribed to late-Neolithic farming communities, e.g., the plow
- transportation by or across water
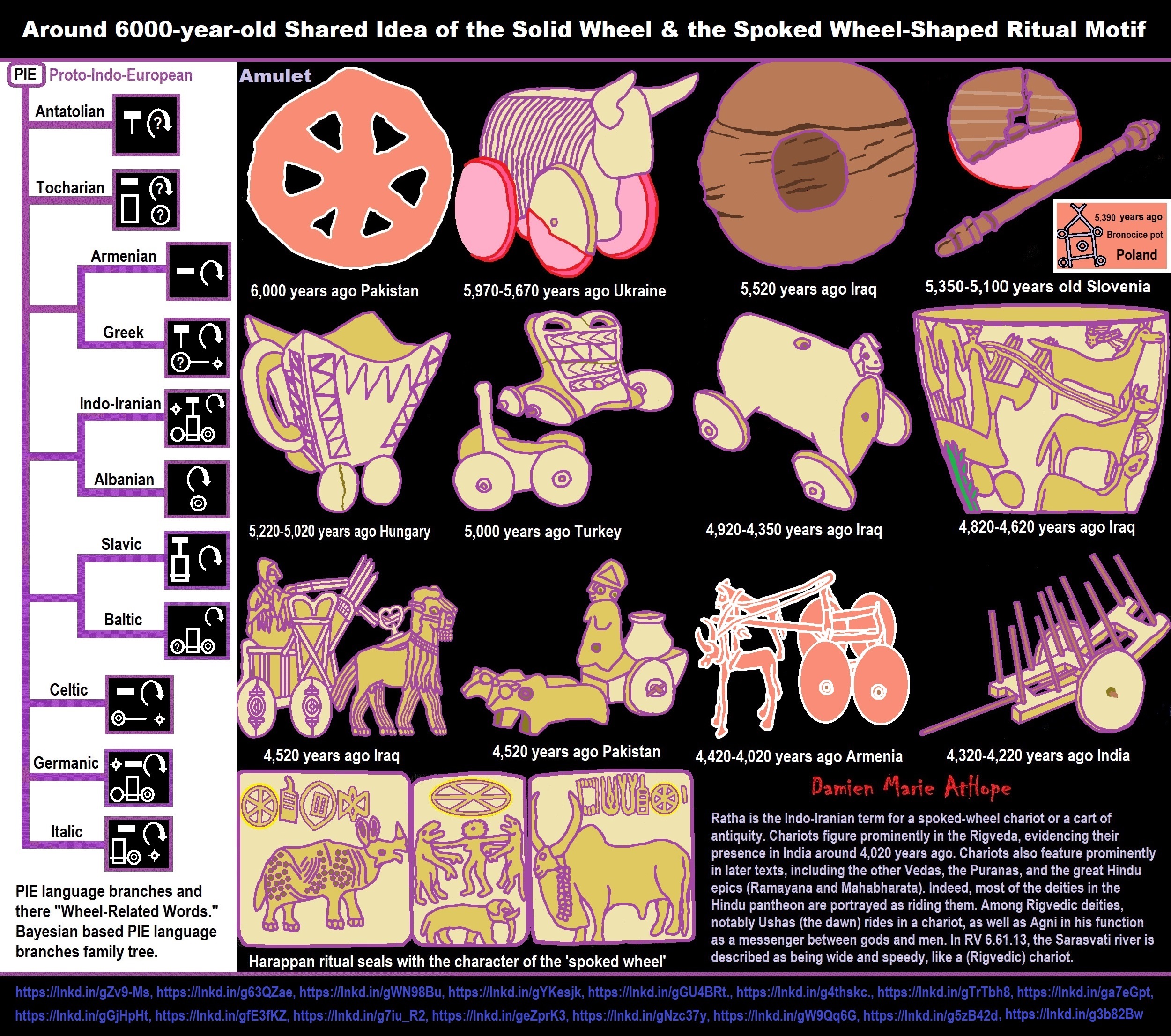
- the solid wheel, used for wagons, but not yet chariots with spoked wheels
- worship of a sky god, *Dyḗus Ph2tḗr (lit. “sky father”; > Vedic Sanskrit Dyáuṣ Pitṛ́, Ancient Greek Ζεύς (πατήρ) / Zeus (dyeus)), vocative *dyeu ph2ter (> Latin Iūpiter, Illyrian Deipaturos)
- oral heroic poetry or song lyrics that used stock phrases such as imperishable fame (*ḱléwos ń̥dʰgʷʰitom) and the wheel of the sun (*sh₂uens kʷekʷlos).
- a patrilineal kinship-system based on relationships between men” ref
“A 2016 phylogenetic analysis of Indo-European folktales found that one tale, The Smith and the Devil, could be confidently reconstructed to the Proto-Indo-European period. This story, found in contemporary Indo-European folktales from Scandinavia to India, describes a blacksmith who offers his soul to a malevolent being (commonly a devil in modern versions of the tale) in exchange for the ability to weld any kind of materials together. The blacksmith then uses his new ability to stick the devil to an immovable object (often a tree), thus avoiding his end of the bargain. According to the authors, the reconstruction of this folktale to PIE implies that the Proto-Indo-Europeans had metallurgy, which in turn “suggests a plausible context for the cultural evolution of a tale about a cunning smith who attains a superhuman level of mastery over his craft.” ref
“Researchers have made many attempts to identify particular prehistoric cultures with the Proto-Indo-European-speaking peoples, but all such theories remain speculative. The scholars of the 19th century who first tackled the question of the Indo-Europeans’ original homeland (also called Urheimat, from German), had essentially only linguistic evidence. They attempted a rough localization by reconstructing the names of plants and animals (importantly the beech and the salmon) as well as the culture and technology (a Bronze Age culture centered on animal husbandry and having domesticated the horse).” ref
“The scholarly opinions became basically divided between a European hypothesis, positing migration from Europe to Asia, and an Asian hypothesis, holding that the migration took place in the opposite direction. In the early 20th century, the question became associated with the expansion of a supposed “Aryan race“, a now-discredited theory promoted during the expansion of European empires and the rise of “scientific racism“. The question remains contentious within some flavors of ethnic nationalism (see also Indigenous Aryans).” ref
“A series of major advances occurred in the 1970s due to the convergence of several factors. First, the radiocarbon dating method (invented in 1949) had become sufficiently inexpensive to be applied on a mass scale. Through dendrochronology (tree-ring dating), pre-historians could calibrate radiocarbon dates to a much higher degree of accuracy. And finally, before the 1970s, parts of Eastern Europe and Central Asia had been off-limits to Western scholars, while non-Western archaeologists did not have access to publications in Western peer-reviewed journals.” ref
“The pioneering work of Marija Gimbutas, assisted by Colin Renfrew, at least partly addressed this problem by organizing expeditions and arranging for more academic collaboration between Western and non-Western scholars. The Kurgan hypothesis, as of 2017 the most widely held theory, depends on linguistic and archaeological evidence, but is not universally accepted. It suggests PIE origin in the Pontic–Caspian steppe during the Chalcolithic. A minority of scholars prefer the Anatolian hypothesis, suggesting an origin in Anatolia during the Neolithic. Other theories (Armenian hypothesis, Out of India theory, Paleolithic Continuity Theory, Balkan hypothesis) have only marginal scholarly support.” ref
“In regard to terminology, in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term Aryan was used to refer to the Proto-Indo-Europeans and their descendants. However, Aryan more properly applies to the Indo-Iranians, the Indo-European branch that settled parts of the Middle East and South Asia, as only Indic and Iranian languages explicitly affirm the term as a self-designation referring to the entirety of their people, whereas the same Proto-Indo-European root (*aryo-) is the basis for Greek and Germanic word forms which seem only to denote the ruling elite of Proto-Indo-European (PIE) society.” ref
“In fact, the most accessible evidence available confirms only the existence of a common, but vague, socio-cultural designation of “nobility” associated with PIE society, such that Greek socio-cultural lexicon and Germanic proper names derived from this root remain insufficient to determine whether the concept was limited to the designation of an exclusive, socio-political elite, or whether it could possibly have been applied in the most inclusive sense to an inherent and ancestral “noble” quality which allegedly characterized all ethnic members of PIE society. Only the latter could have served as a true and universal self-designation for the Proto-Indo-European people.” ref
“By the early twentieth century, this term had come to be widely used in a racist context referring to a hypothesized white, blonde, and blue-eyed “master race” (Herrenrasse), culminating with the pogroms of the Nazis in Europe. Subsequently, the term Aryan as a general term for Indo-Europeans has been largely abandoned by scholars (though the term Indo-Aryan is still used to refer to the branch that settled in Southern Asia).” ref
Proto-Indo-European Urheimat hypotheses and Indo-European migrations
“According to some archaeologists, PIE speakers cannot be assumed to have been a single, identifiable people or tribe, but were a group of loosely related populations ancestral to the later, still partially prehistoric, Bronze Age Indo-Europeans. This view is held especially by those archaeologists who posit an original homeland of vast extent and immense time depth. However, this view is not shared by linguists, as proto-languages, like all languages before modern transport and communication, occupied small geographical areas over a limited time span, and were spoken by a set of close-knit communities—a tribe in the broad sense. Researchers have put forward a great variety of proposed locations for the first speakers of Proto-Indo-European. Few of these hypotheses have survived scrutiny by academic specialists in Indo-European studies sufficiently well to be included in modern academic debate.” ref
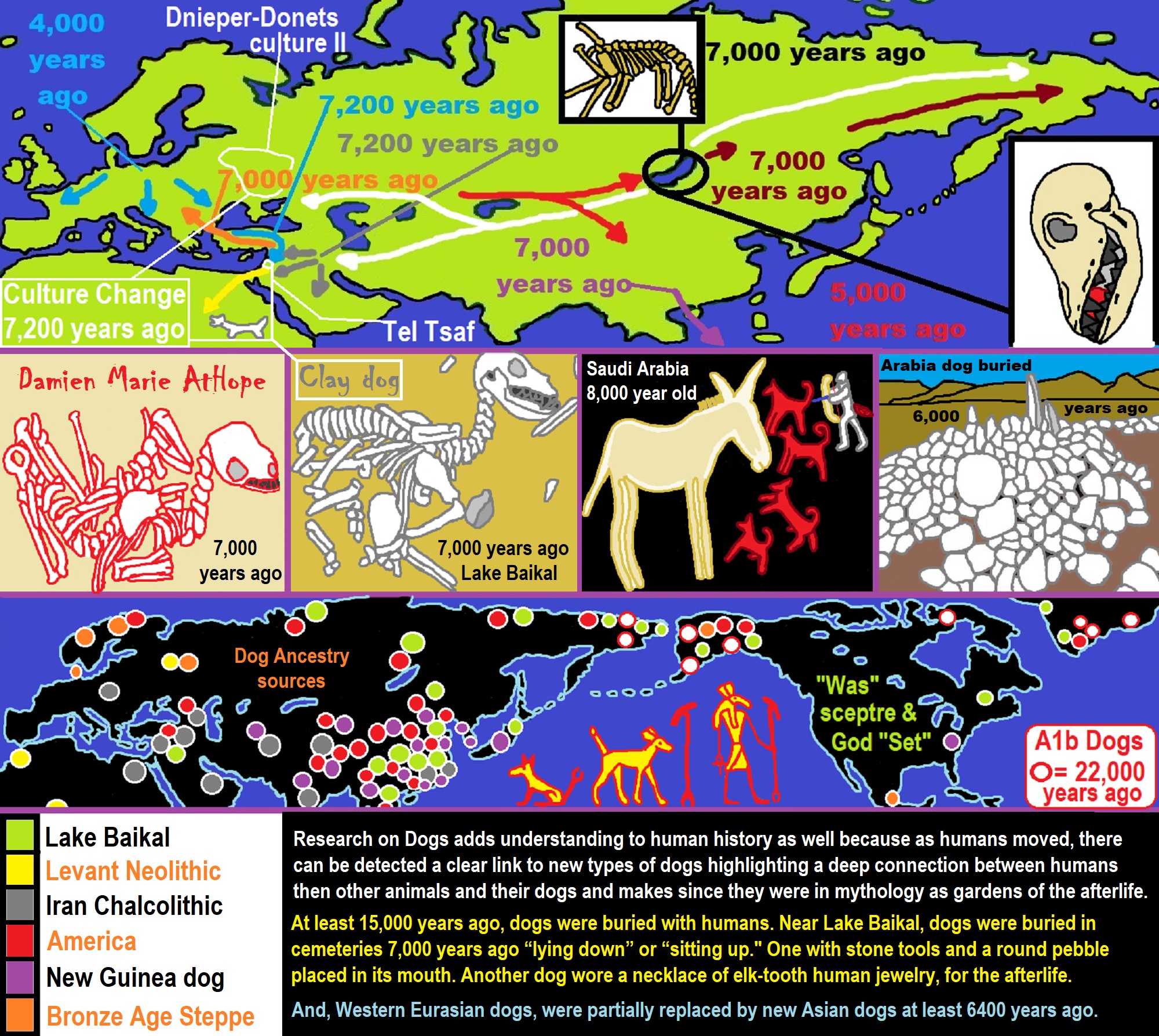

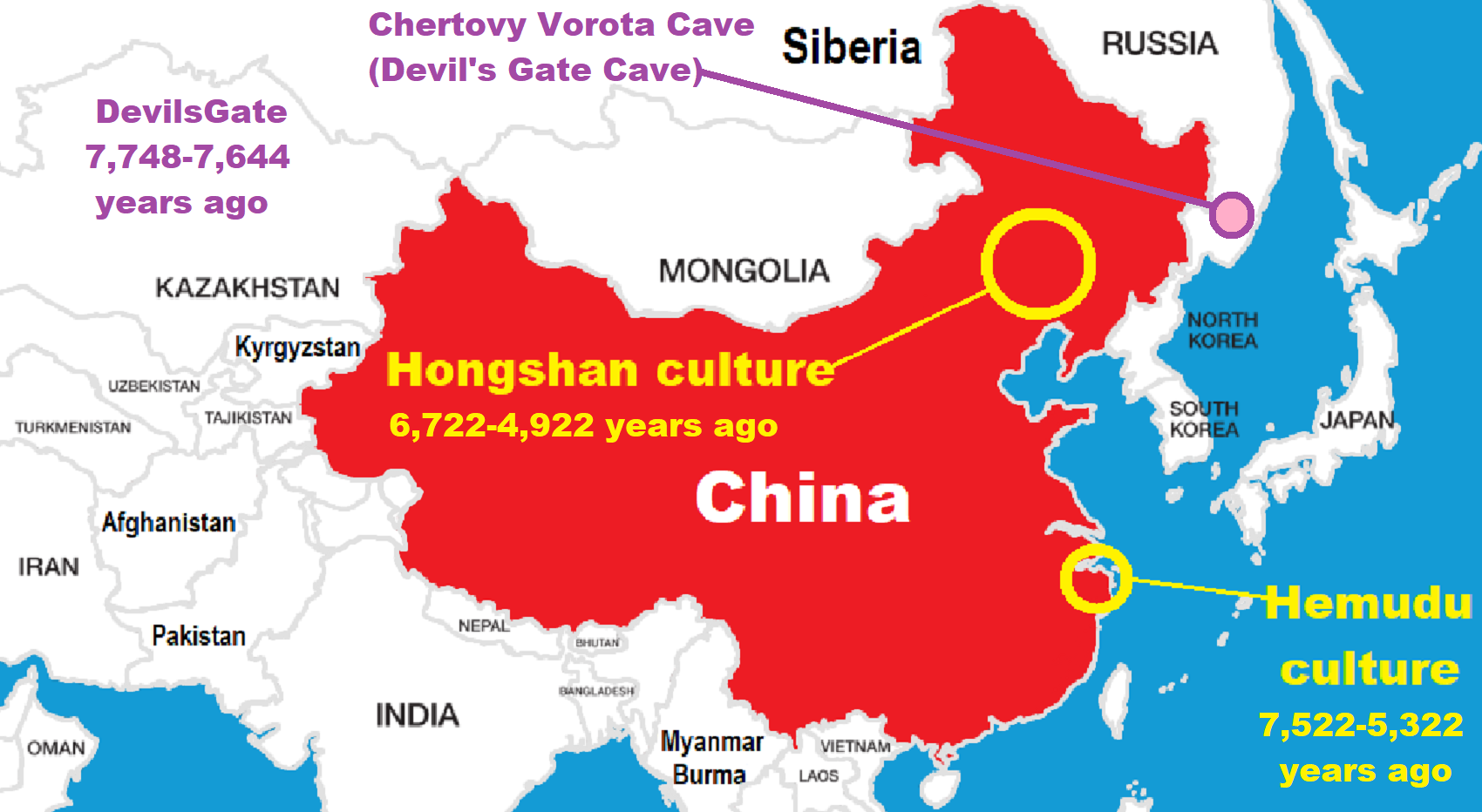
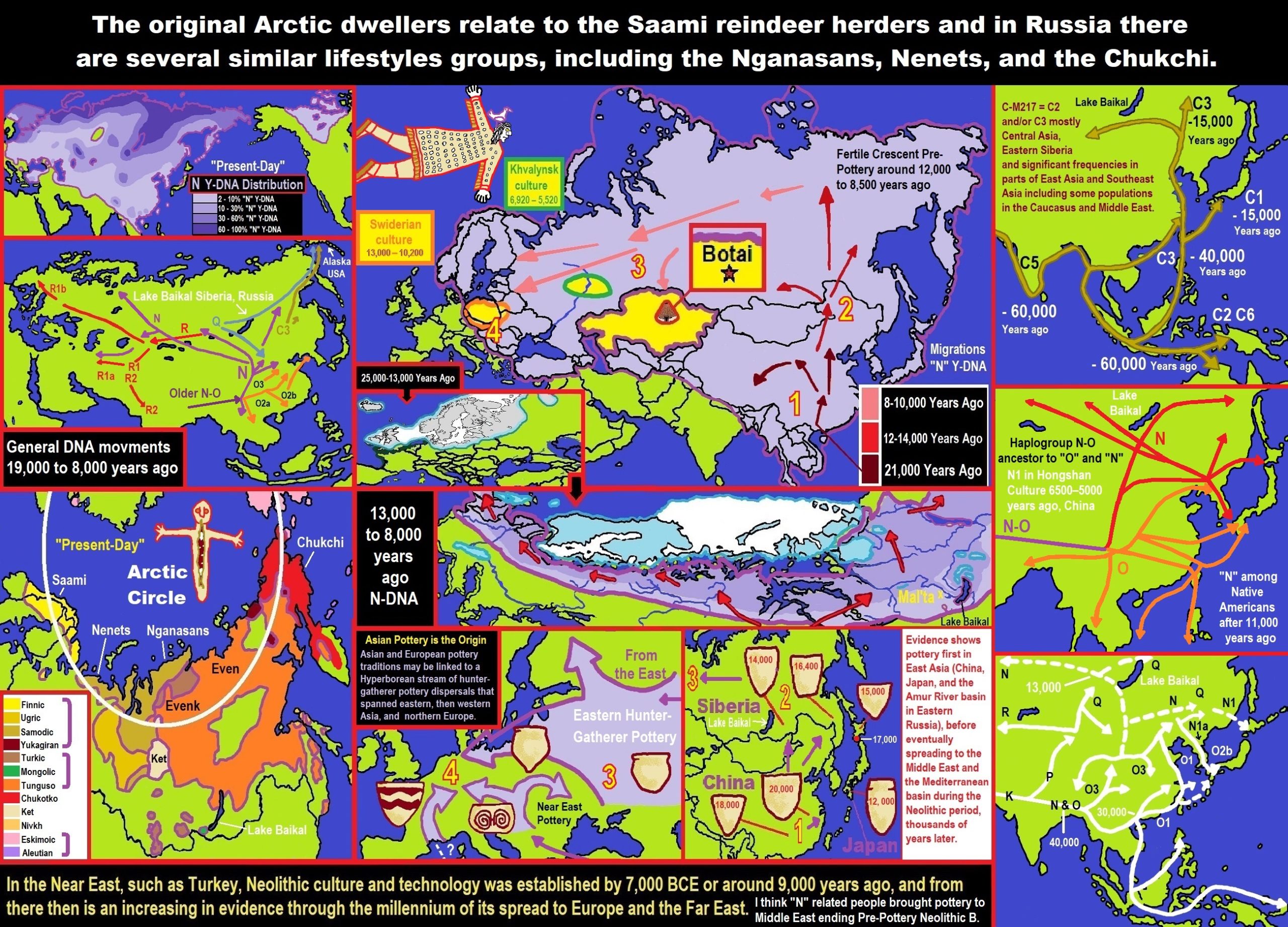
There is some thinking that possibly 7,822/7222 years ago, the “Dnieper-Donets culture I” quickly expanded in all directions, eventually absorbing all other local groups. By 7,222 years ago the Dnieper-Donets culture II followed, which ended between 6,422/6,222 years ago. Rapid population growth and an expansion towards the steppe are noticeable throughout its existence. ref
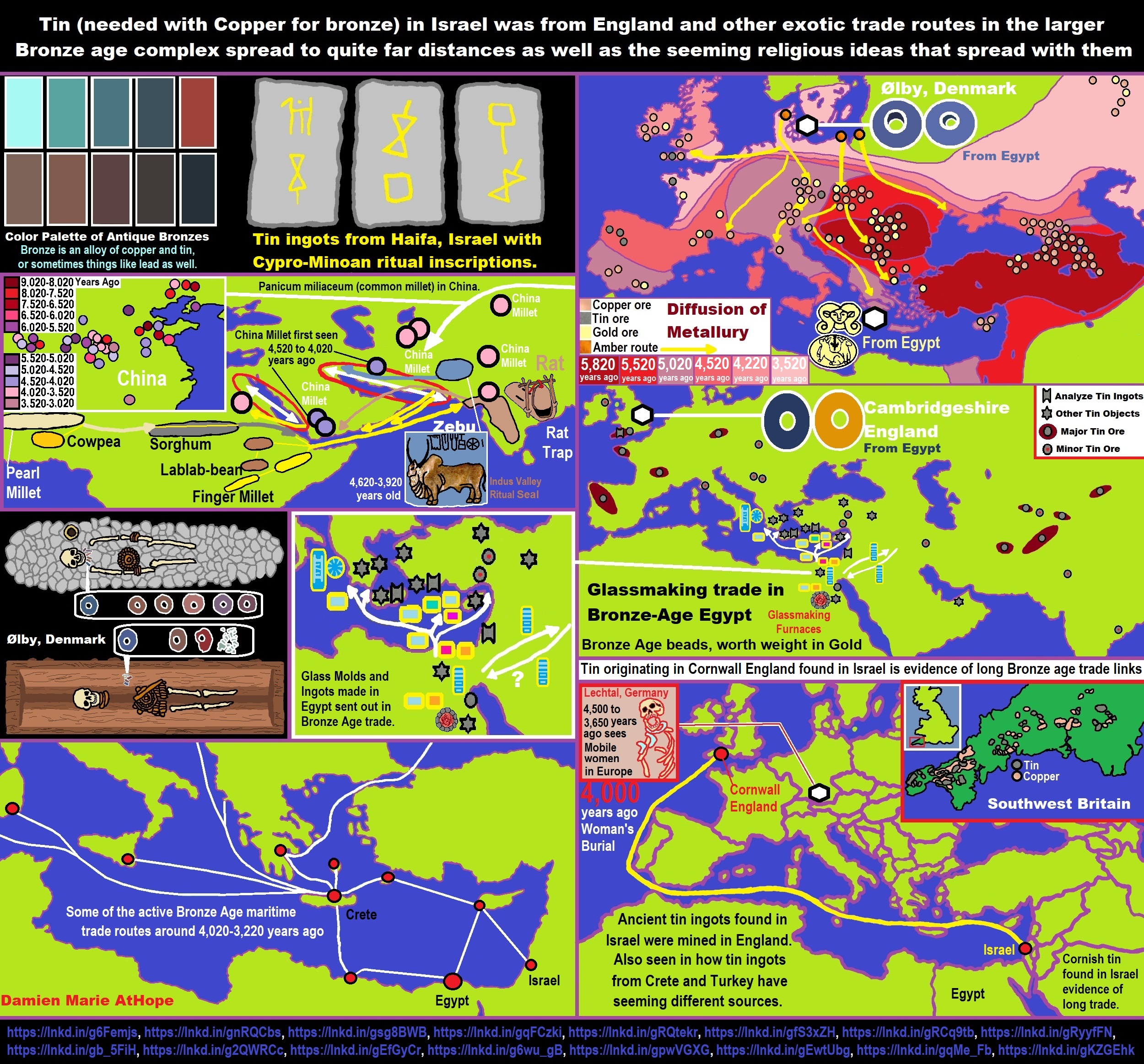
“The Dnieper–Donets culture flourished north of the Black Sea and it was Asian varieties of millet made their way from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago.” ref, ref
“The Dnieper–Donets culture succeeded by the Sredny Stog culture has Parallels of the contemporaneous Samara culture to the north have many parallels as well as striking similarities with the Khvalynsk culture and the later Sredny Stog culture have also been detected. Therefore, a much larger horizon from the upper Vistula to the lower half of Dnieper to the mid-to-lower Volga has therefore been drawn as potentially Dnieper–Donets culture related/impacted/or influenced. Influences from the Dnieper–Donets culture and the Sredny Stog culture on the Funnelbeaker culture have likewise been found. The Dnieper–Donets culture was contemporary with the Bug–Dniester culture. It is clearly distinct from the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture.” ref
“From around 5200 BCE or 7,222 years ago, the Dnieper-Donets people began keeping cattle, sheep, and goat. Other domestic animals kept included pig, horse, and dog. During the following centuries, domestic animals from the Dnieper further and further east towards the Volga–Ural steppes, where they appeared ca. 4700-4600 BCE or 6,722-6,622 years ago. From about 4200 BCE or 6,222 years ago, the Dnieper–Donets culture adopted agriculture. Domestic plants that have been recovered include millet, wheat, and pea. Evidence from skeletal remains suggests that plants were consumed. The presence of exotic goods in Dnieper-Donets graves indicates exchange relationships with the Caucasus.” ref
“The Dnieper–Donets culture is known from more than 200 sites. Few settlements from the Dnieper–Donets culture are known, but a few semi-subterranean huts have been found. These huts were covered in bark. The Dnieper–Donets culture was originally a hunter-gatherer culture. The economic evidence from the earliest stages is almost exclusively from hunting and fishing. Among the sources of food hunted and foraged by the Dnieper-Donets people were aurochs, elk, red deer, roe, wild boar, fox, wildcat, hare, bear, and onager. Their diet was primarily high protein, with meat, fish, and nuts being consumed.” ref
“The Dnieper–Donets culture produced no female figurines. The Dnieper–Donets culture continued using Mesolothic technology, but later phases see the appearance of polished stone axes, later flint, and the disappearance of microliths. These tools were sometimes deposited in graves. The Dnieper–Donets culture is well known for about thirty of its cemeteries that have been discovered. These contain around 800 individuals. It is evident that funerals were complex events that had several phases.” ref
“Burials are mostly in large pits where the deceased were periodically placed and covered with ocher. The deceased was typically exposed for a time before their bones were collected and buried. On other occasions, the ceased was buried in the flesh without exposure. Deceased Dnieper-Donets people sometimes had only their skulls buried, at other times the entire bodies. The variants of Dnieper-Donets burial often appear in the same pits. Animal bones has also been found in the graves.” ref
“Certain Dnieper-Donets burials are accompanied with copper, crystal, or porphyry ornaments, shell beads, bird-stone tubes, polished stone maces, or ornamental plaques made of boar’s tusk. The items, along with the presence of animal bones and sophisticated burial methods, appear to have been a symbol of power. Certain deceased children were buried with such items, which indicates that wealth was inherited in Dnieper-Donets society. Very similar boar-tusk plaques and copper ornament have been found at contemporary graves of the Samara culture in the middle Volga area. Maces of a different type than those of Dnieper-Donets have also been found. The wide adoption of such a status symbol attests to a change in the politics of power.” ref
“In later times the deceased in the Dnieper–Donets culture were sometimes buried individually. This shift has been suggested as evidence of a shift towards increasing individualism. Dnieper–Donets burials have been found near the settlement of Deriivka, which is associated with the Sredny Stog culture. In accordance with the Kurgan hypothesis, J. Mallory (1997) suggested that the Dnieper-Donets people were Pre–Indo-European-speakers who were absorbed by Proto-Indo-Europeans expanding westwards from steppe-lands further east.” ref
“David Anthony (2007) believes that the Dnieper-Donets people almost certainly spoke a different language from the people of the Cucuteni–Trypillia culture. The areas of the upper Dniester in which the Dnieper–Donets culture was situated have mostly Baltic river names. That and the close relationship between the Dnieper–Donets culture and contemporary cultures of northeast Europe have caused the Dnieper–Donets culture to be identified with the later Balts.” ref
“The precise role of the culture and its language to the derivation of the Pontic-Caspian cultures, such as Sredny Stog and Yamnaya culture, is open to debate, but the display of recurrent traits points to longstanding mutual contacts or to underlying genetic relations. The physical remains recovered from graves of the Dnieper–Donets culture have been classified as “Proto-Europoid“. They are predominantly characterized as late Cro-Magnons with large and more massive features than the gracile Mediterranean peoples of the Balkan Neolithic.” ref
“Males averaged 172 cm in height, which is much taller than contemporary Neolithic populations. Its rugged physical traits are thought to have genetically influenced later Indo-European peoples. Physical anthropologists have pointed out similarities in the physical type of the Dnieper-Donets people with the Mesolithic peoples of Northern Europe. The peoples of the neighboring Sredny Stog culture, which eventually succeeded the Dnieper–Donets culture, were of a more gracile appearance.” ref
“Mathieson et al. (2018) analyzed 32 individuals from three Eneolithic cemeteries at Deriivka, Vilnyanka, and Vovnigi, which Anthony (2019a) ascribed to the Dnieper–Donets culture. These individuals belonged exclusively to the paternal haplogroups R and I (mostly R1b and I2), and almost exclusively to the maternal haplogroup U (mostly U5, U4, and U2). This suggests that the Dnieper-Donets people were “distinct, locally derived population” of mostly of Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) descent, with Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) admixture. The WHG admixture appears to have increased in the transition from the Mesolithic to the Neolithic.” ref
“Unlike the Yamnaya culture, whose genetic cluster is known as Western Steppe Herder (WSH), in the Dnieper–Donets culture no Caucasian Hunter-Gatherer (CHG) or Early European Farmer (EEF) ancestry has been detected. At the Vilnyanka cemetery, all the males belong to the paternal haplogroup I, which is common among WHGs. David W. Anthony suggests that this influx of WHG ancestry might be the result of EEFs pushing WHGs out of their territories to the east, where WHG males might have mated with EHG females.” ref
“Dnieper-Donets males and Yamnaya males carry the same paternal haplogroups (R1b and I2a), suggesting that the CHG and EEF admixture among the Yamnaya came through EHG and WHG males mixing with EEF and CHG females. According to Anthony, this suggests that the Indo-European languages were initially spoken by EHGs living in Eastern Europe. The Dnieper–Donets culture was succeeded by the Sredny Stog culture, its eastern neighbor, with whom it co-existed for a time before being finally absorbed. The Dnieper–Donets culture and the Sredny Stog culture were in turn succeeded by the Yamnaya culture. The Mikhaylovka culture, the Novodanilovka group, and the Kemi Oba culture displays evidence of continuity from the Dnieper–Donets culture.” ref
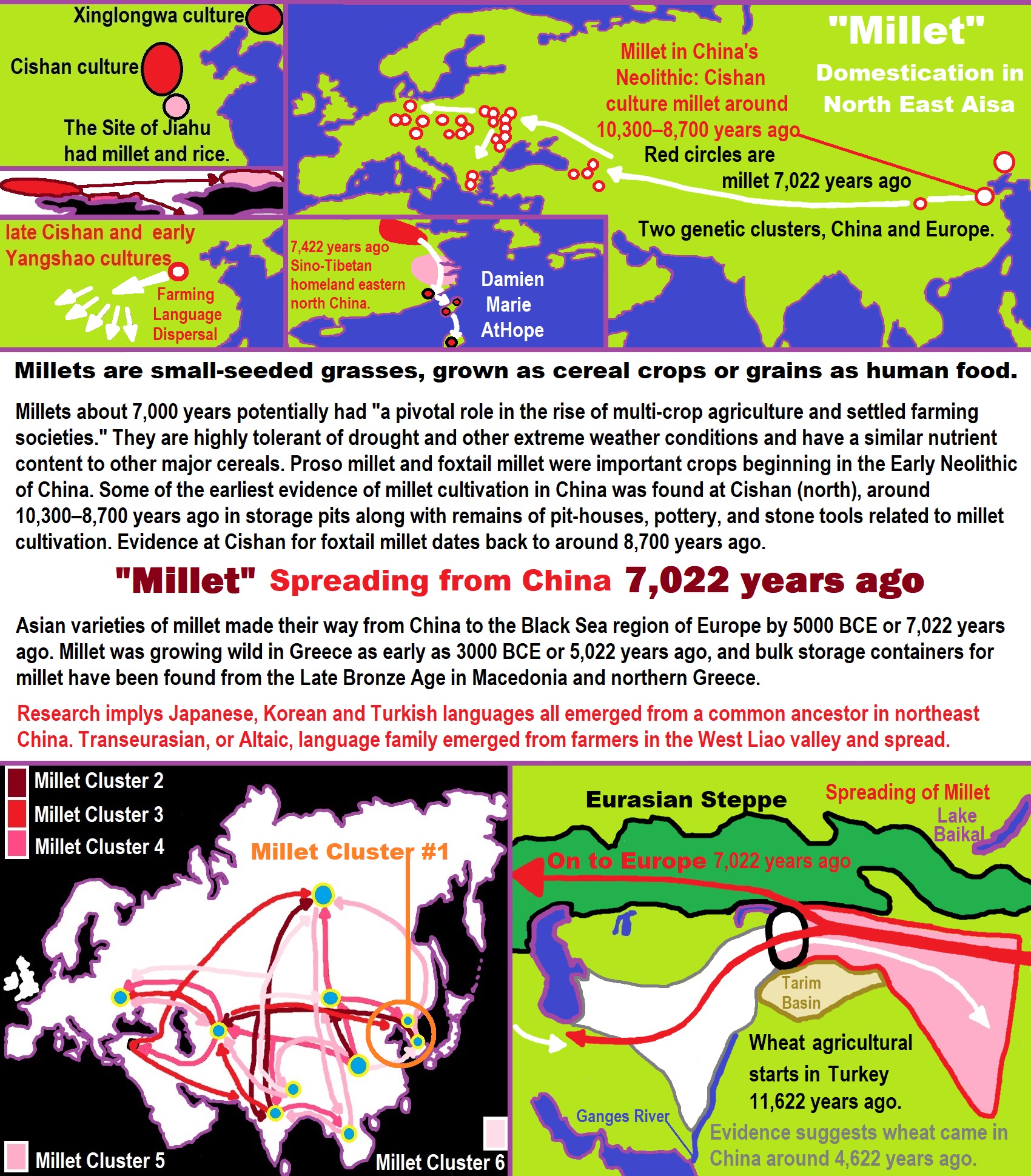
“Asian varieties of millet made their way from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 5000 BCE or 7,000 years ago.” https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Millet
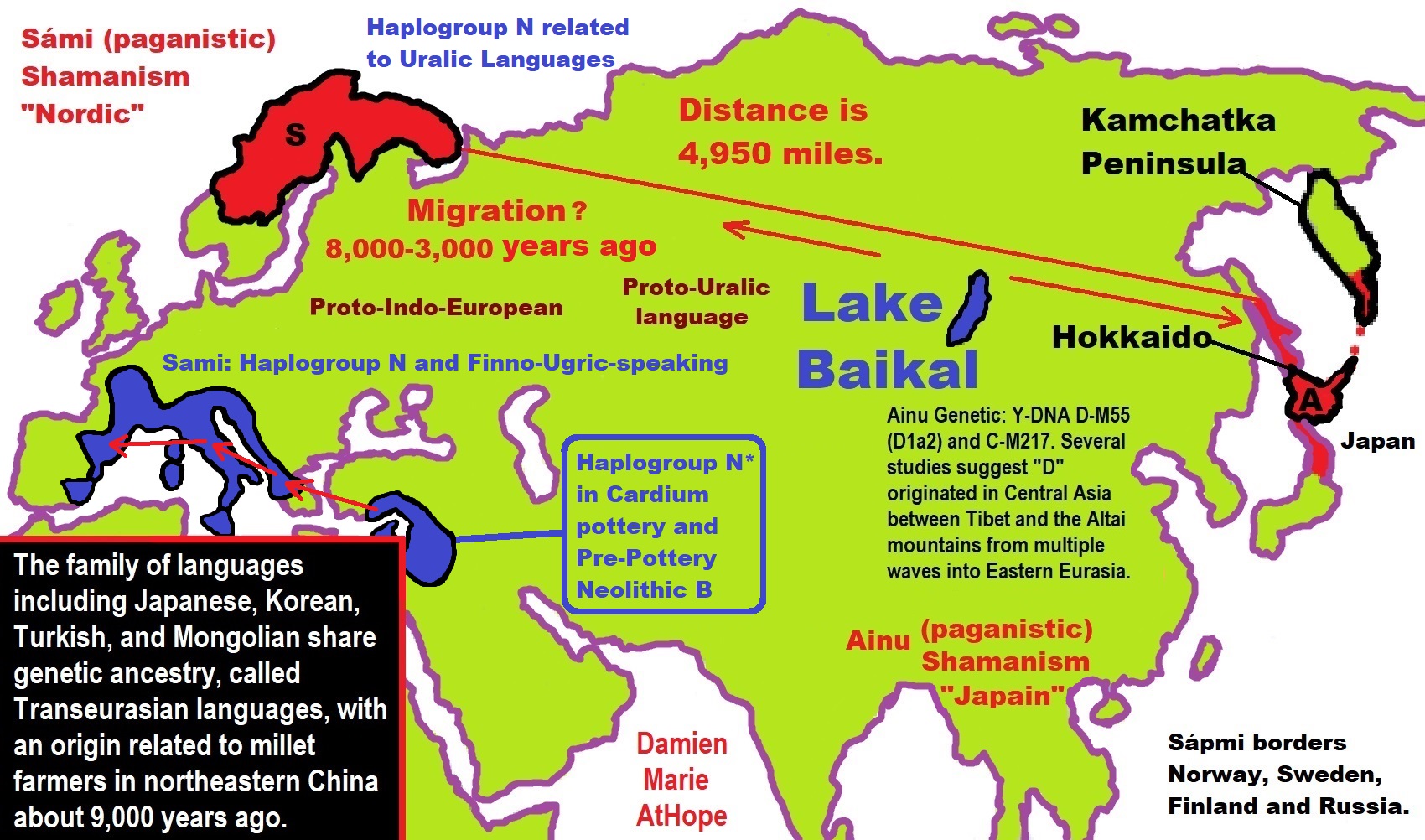
Origins of ‘Transeurasian’ languages traced to Neolithic millet farmers in north-eastern China about 9,000 years ago
“A study combining linguistic, genetic, and archaeological evidence has traced the origins of a family of languages including modern Japanese, Korean, Turkish and Mongolian and the people who speak them to millet farmers who inhabited a region in north-eastern China about 9,000 years ago. The findings outlined on Wednesday document a shared genetic ancestry for the hundreds of millions of people who speak what the researchers call Transeurasian languages across an area stretching more than 5,000 miles (8,000km).” ref
“Millet was an important early crop as hunter-gatherers transitioned to an agricultural lifestyle. There are 98 Transeurasian languages, including Korean, Japanese, and various Turkic languages in parts of Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, and Siberia, various Mongolic languages, and various Tungusic languages in Manchuria and Siberia. This language family’s beginnings were traced to Neolithic millet farmers in the Liao River valley, an area encompassing parts of the Chinese provinces of Liaoning and Jilin and the region of Inner Mongolia. As these farmers moved across north-eastern Asia over thousands of years, the descendant languages spread north and west into Siberia and the steppes and east into the Korean peninsula and over the sea to the Japanese archipelago.” ref
So new evidence supports my Speculation pottery started in China, then migrates to Siberia, and then to Europe. And other evidence discredits my Speculation millet started in China, then migrates to Europe, and thus may have been related to Proto-indo-europian languages like it was with seemingly both the Transeurasian (Altaic) languages and Sino-Tibetan languages.
“Millet farming, pictured in a field in Yonghe Village in northern China, may have spurred the spread of the Transeurasian languages out of the Liao River Valley some 9000 years ago.” ref
“The Sino-Tibetan family which is one of the most diverse language families in the world originated among millet farmers in North China around 7200 years ago, new research shows. This analysis suggested an origin of the Sino-Tibetan family in northern Chinese communities of millet farmers of the Neolithic cultures of late Cishan and early Yangshao.” ref
Supported Speculation
First, the supported speculation-evidence I theorized from that years later was found accurate
Discredited Speculation
Second, the speculation-evidence I theorized from later changed and was found inaccurate
Discrediting evidence against my previous speculations
Millet from China was related to the Proto-Indo-European language
“Millet began to be cultivated in Europe not 7,000 years ago in the Neolithic period as previously thought, but in the Bronze Age, about 3.5 thousand years ago.” ref
“Broomcorn millet was domesticated in northeast China by 6000 BCE. In Europe, millet was reported in Early Neolithic contexts formed by 6000 BCE, but recent radiocarbon dating of a dozen ‘early’ grains cast doubt on these claims. Archaeobotanical evidence reveals that millet was common in Europe from the 2nd millennium BCE, when major societal and economic transformations took place in the Bronze Age. We conducted an extensive program of AMS-dating of charred broomcorn millet grains from 75 prehistoric sites in Europe. Our Bayesian model reveals that millet cultivation began in Europe at the earliest during the sixteenth century BCE, and spread rapidly during the fifteenth/fourteenth centuries BCE.” ref
“Strikingly, not a single word for millet can be reconstructed for Proto-Indo-European. Intriguingly, it is evident that many agricultural meanings that have habitually been reconstructed for Proto-Indo-European are effectively post-Anatolian. Questions on the timing and the center of the Indo-European language dispersal are central to debates on the formation of the European and Asian linguistic landscapes and are deeply intertwined with questions on the archaeology and population history of these continents. Recent palaeogenomic studies support scenarios in which the core Indo-European languages spread with the expansion of Early Bronze Age Yamnaya herders that originally inhabited the East European steppes. Questions on the Yamnaya and Pre-Yamnaya locations of the language community that ultimately gave rise to the Indo-European language family are heavily dependent on linguistic reconstruction of the subsistence of Proto-IndoEuropean speakers. A central question, therefore, is how important the role of agriculture was among the speakers of this protolanguage. In this study, we perform a qualitative etymological analysis of all previously postulated Proto-Indo-European terminology related to cereal cultivation and cereal processing. On the basis of the evolution of the subsistence strategies of consecutive stages of the protolanguage, we find that one or perhaps two cereal terms can be reconstructed for the basal Indo-European stage, also known as IndoAnatolian, but that core Indo-European, here also including Tocharian, acquired a more elaborate set of terms. Thus, we linguistically document an important economic shift from a mostly non-agricultural to a mixed agro-pastoral economy between the basal and core IndoEuropean speech communities. It follows that the early, eastern Yamnaya of the Don-Volga steppe, with its lack of evidence for agricultural practices, does not offer a perfect archaeological proxy for the core Indo-European language community and that this stage of the language family more likely reflects a mixed subsistence as proposed for western Yamnaya groups around or to the west of the Dnieper River.” ref
Pic ref
Ancient Human Genomes…Present-Day Europeans – Johannes Krause (Video)
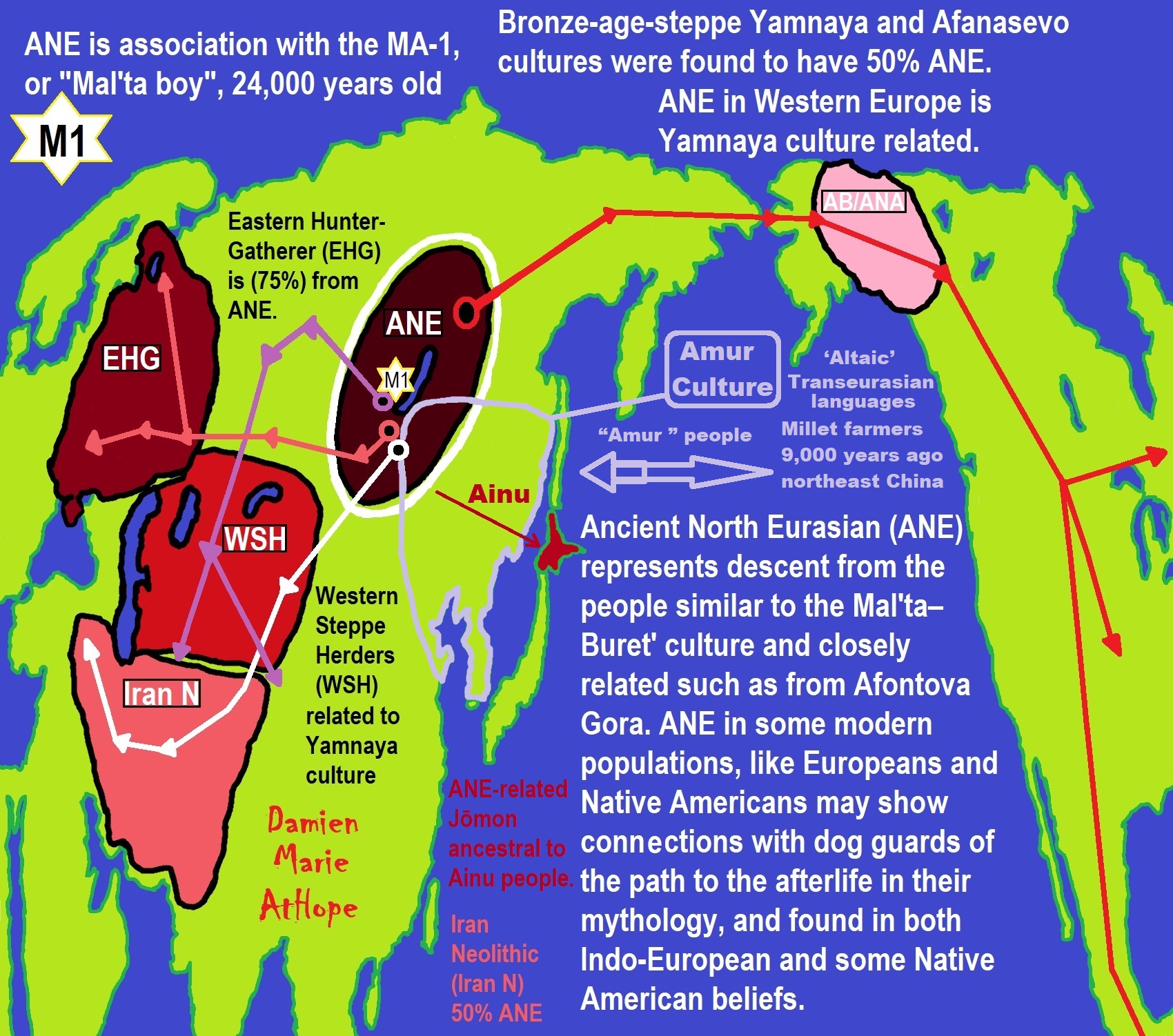
Ancient North Eurasian (ANE)
Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG)
Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG)
Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG)
Early European Farmers (EEF)
A quick look at the Genetic history of Europe
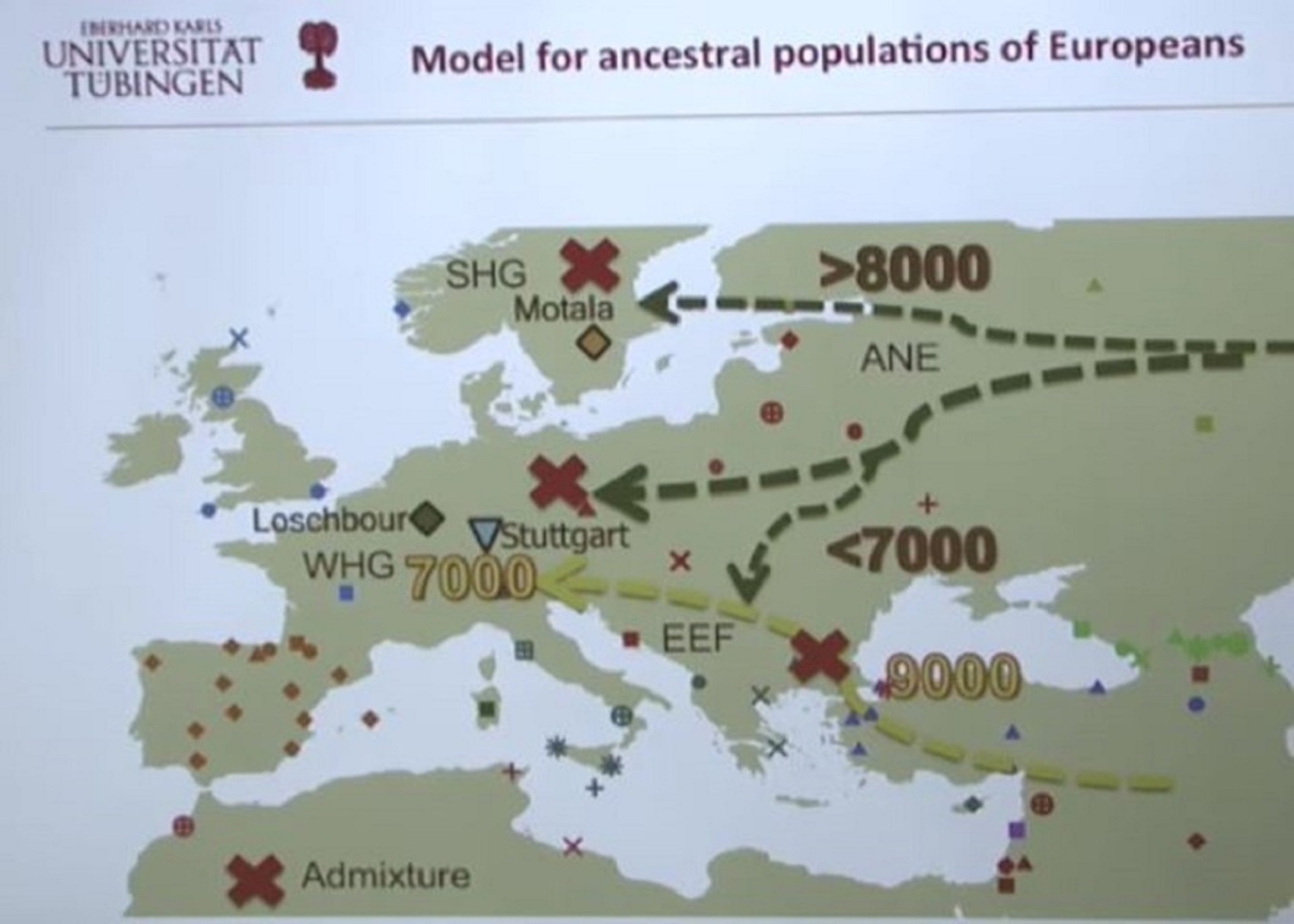
“The most significant recent dispersal of modern humans from Africa gave rise to an undifferentiated “non-African” lineage by some 70,000-50,000 years ago. By about 50–40 ka a basal West Eurasian lineage had emerged, as had a separate East Asian lineage. Both basal East and West Eurasians acquired Neanderthal admixture in Europe and Asia. European early modern humans (EEMH) lineages between 40,000-26,000 years ago (Aurignacian) were still part of a large Western Eurasian “meta-population”, related to Central and Western Asian populations. Divergence into genetically distinct sub-populations within Western Eurasia is a result of increased selection pressure and founder effects during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, Gravettian). By the end of the LGM, after 20,000 years ago, A Western European lineage, dubbed West European Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) emerges from the Solutrean refugium during the European Mesolithic. These Mesolithic hunter-gatherer cultures are substantially replaced in the Neolithic Revolution by the arrival of Early European Farmers (EEF) lineages derived from Mesolithic populations of West Asia (Anatolia and the Caucasus). In the European Bronze Age, there were again substantial population replacements in parts of Europe by the intrusion of Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) lineages from the Pontic–Caspian steppes. These Bronze Age population replacements are associated with the Beaker culture archaeologically and with the Indo-European expansion linguistically.” ref
“As a result of the population movements during the Mesolithic to Bronze Age, modern European populations are distinguished by differences in WHG, EEF, and ANE ancestry. Admixture rates varied geographically; in the late Neolithic, WHG ancestry in farmers in Hungary was at around 10%, in Germany around 25%, and in Iberia as high as 50%. The contribution of EEF is more significant in Mediterranean Europe, and declines towards northern and northeastern Europe, where WHG ancestry is stronger; the Sardinians are considered to be the closest European group to the population of the EEF. ANE ancestry is found throughout Europe, with a maximum of about 20% found in Baltic people and Finns. Ethnogenesis of the modern ethnic groups of Europe in the historical period is associated with numerous admixture events, primarily those associated with the Roman, Germanic, Norse, Slavic, Berber, Arab and Turkish expansions. Research into the genetic history of Europe became possible in the second half of the 20th century, but did not yield results with a high resolution before the 1990s. In the 1990s, preliminary results became possible, but they remained mostly limited to studies of mitochondrial and Y-chromosomal lineages. Autosomal DNA became more easily accessible in the 2000s, and since the mid-2010s, results of previously unattainable resolution, many of them based on full-genome analysis of ancient DNA, have been published at an accelerated pace.” ref
Kurgan Hypothesis
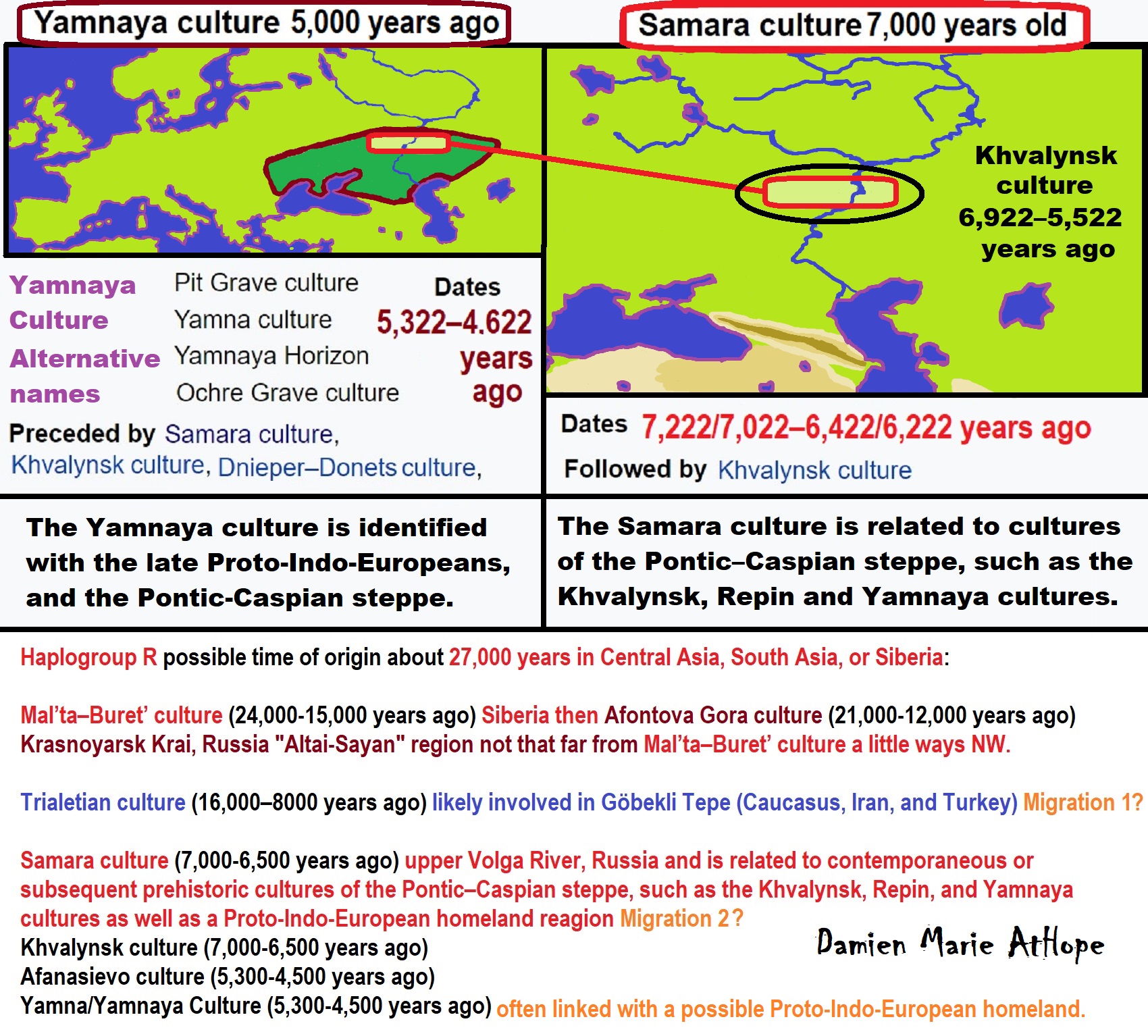
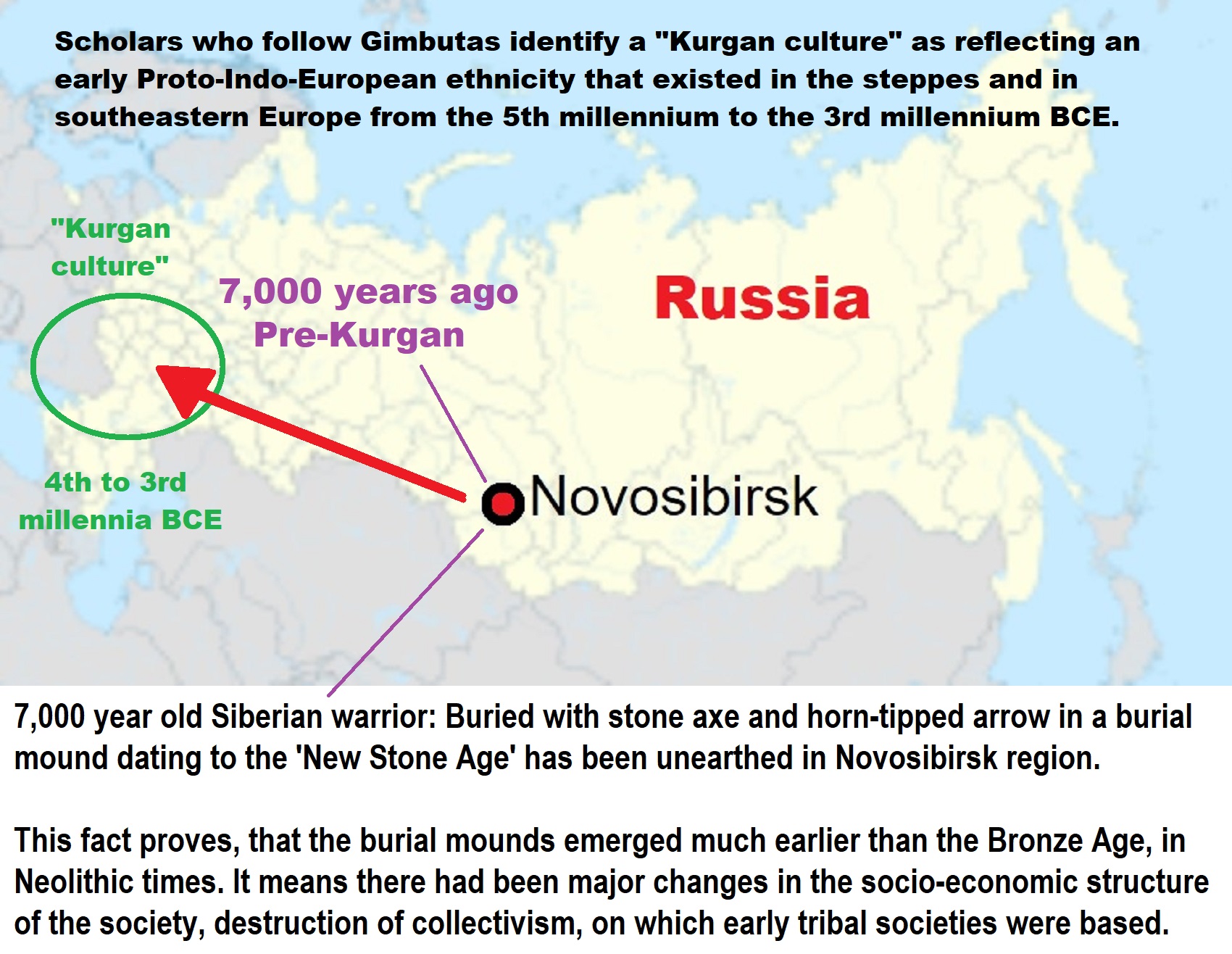
“The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory or Kurgan model) or Steppe theory is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian kurgan (курга́н), meaning tumulus or burial mound. The Steppe theory was first formulated by Otto Schrader (1883) and V. Gordon Childe (1926), then systematized in the 1950s by Marija Gimbutas, who used the term to group various prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and its relationship with other cultures as a point of reference.” ref
“Gimbutas defined the Kurgan culture as composed of four successive periods, with the earliest (Kurgan I) including the Samara and Seroglazovo cultures of the Dnieper–Volga region in the Copper Age (early 4th millennium BCE). The people of these cultures were nomadic pastoralists, who, according to the model, by the early 3rd millennium BCE had expanded throughout the Pontic–Caspian steppe and into Eastern Europe. Recent genetics studies have demonstrated that populations bearing specific Y-DNA haplogroups and a distinct genetic signature expanded into Europe and South Asia from the Pontic-Caspian steppe during the third and second millennia BCE. These migrations provide a plausible explanation for the spread of at least some of the Indo-European languages, and suggest that the alternative Anatolian hypothesis, which places the Proto-Indo-European homeland in Neolithic Anatolia, is less likely to be correct.” ref
“Cultures that Gimbutas considered as part of the “Kurgan culture”:
- Bug–Dniester (6th millennium)
- Samara (5th millennium)
- Khvalynsk (5th millennium)
- Dnieper–Donets (5th to 4th millennia)
- Sredny Stog (mid-5th to mid-4th millennia)
- Maikop–Dereivka (mid-4th to mid-3rd millennia)
- Yamnaya (Pit Grave): This is itself a varied cultural horizon, spanning the entire Pontic–Caspian steppe from the mid-4th to the 3rd millennium.
- Usatovo culture (late 4th millennium)” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
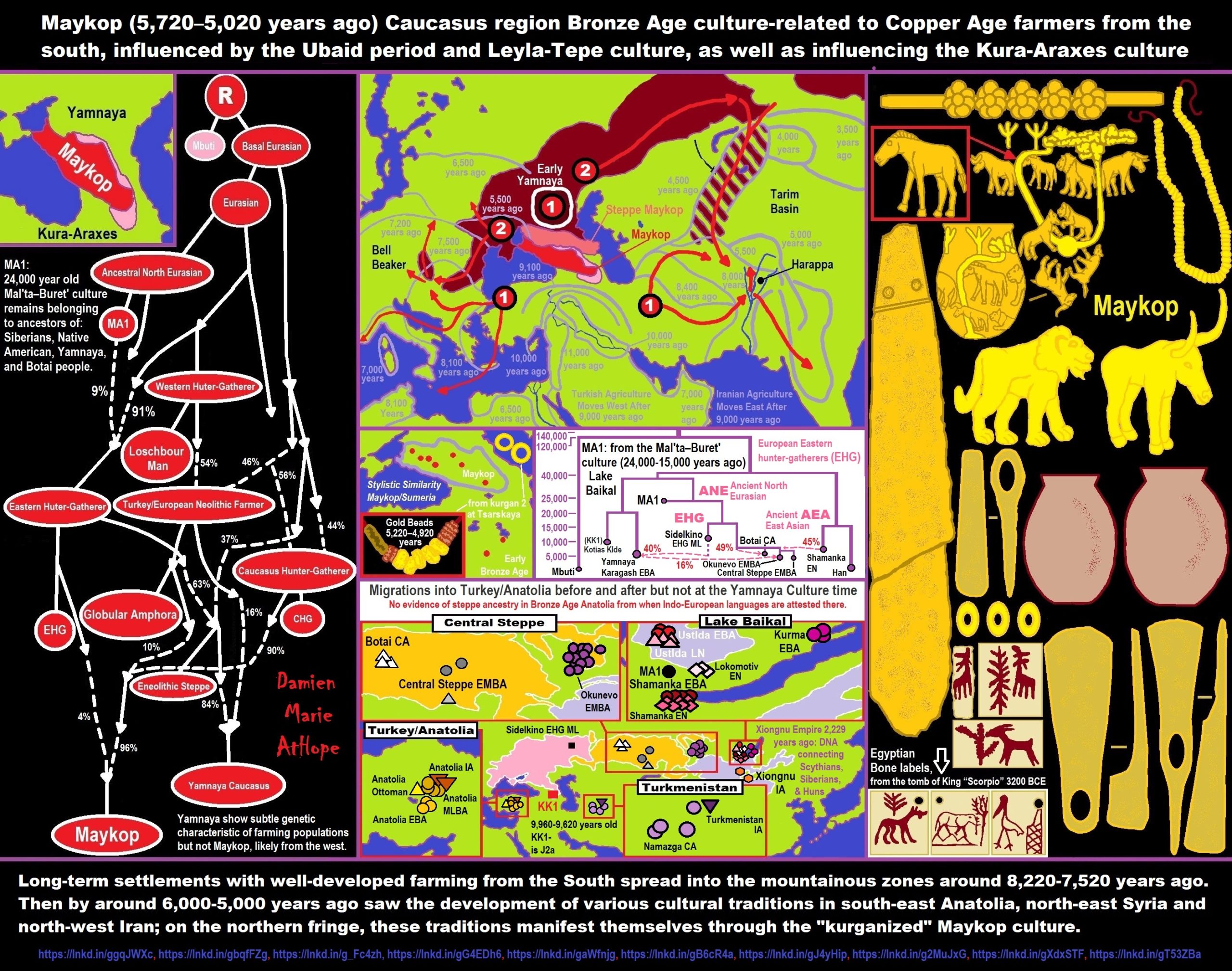
The Maykop culture, the R1b link to the Steppe?
“The Maykop culture (3700-2500 BCE) in the north-west Caucasus was culturally speaking a sort of southern extension of the Yamna horizon. Although not generally considered part of the Pontic-Caspian steppe culture due to its geography, the North Caucasus had close links with the steppes, as attested by numerous ceramics, gold, copper, and bronze weapons and jewelry in the contemporaneous cultures of Mikhaylovka, Sredny Stog, and Kemi Oba. The link between the northern Black Sea coast and the North Caucasus is older than the Maykop period. Its predecessor, the Svobodnoe culture (4400-3700 BCE), already had links to the Suvorovo-Novodanilovka and early Sredny Stog cultures. The even older Nalchik settlement (5000-4500 BCE) in the North Caucasus displayed a similar culture as Khvalynsk in the Caspian Steppe and Volga region. This may be the period when R1b started interacting and blending with the R1a population of the steppes.” ref
“The Yamna and Maykop people both used kurgan burials, placing their deads in a supine position with raised knees and oriented in a north-east/south-west axis. Graves were sprinkled with red ochre on the floor, and sacrificed domestic animal buried alongside humans. They also had in common horses, wagons, a heavily cattle-based economy with a minority of sheep kept for their wool, use of copper/bronze battle-axes (both hammer-axes and sleeved axes), and tanged daggers. In fact, the oldest wagons and bronze artefacts are found in the North Caucasus, and appear to have spread from there to the steppes.” ref
“Maykop was an advanced Bronze Age culture, actually one of the very first to develop metalworking, and therefore metal weapons. The world’s oldest sword was found at a late Maykop grave in Klady kurgan 31. Its style is reminiscent of the long Celtic swords, though less elaborated. Horse bones and depictions of horses already appear in early Maykop graves, suggesting that the Maykop culture might have been founded by steppe people or by people who had close link with them. However, the presence of cultural elements radically different from the steppe culture in some sites could mean that Maykop had a hybrid population. Without DNA testing it is impossible to say if these two populations were an Anatolian R1b group and a G2a Caucasian group, or whether R1a people had settled there too. The two or three ethnicities might even have cohabited side by side in different settlements. The one typical Caucasian Y-DNA lineage that does follow the pattern of Indo-European migrations is G2a-L13, which is found throughout Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the Balkans, the Danube basin, and Central Europe its frequency is somewhat proportional to the percentage of R1b.” ref
“Maykop people are the ones credited for the introduction of primitive wheeled vehicles (wagons) from Mesopotamia to the Steppe. This would revolutionize the way of life in the steppe, and would later lead to the development of (horse-drawn) war chariots around 2000 BCE. Cavalry and chariots played an vital role in the subsequent Indo-European migrations, allowing them to move quickly and defeat easily anybody they encountered. Combined with advanced bronze weapons and their sea-based culture, the western branch (R1b) of the Indo-Europeans from the Black Sea shores are excellent candidates for being the mysterious Sea Peoples, who raided the eastern shores of the Mediterranean during the second millennium BCE.” ref
“The rise of the IE-speaking Hittites in Central Anatolia happened a few centuries after the disappearance of the Maykop and Yamna cultures. Considering that most Indo-European forms of R1b found in Anatolia today belong to the R1b-Z2103 subclade, it makes little doubt that the Hittites came to Anatolia via the Balkans, after Yamna/Maykop people invaded Southeast Europe. The Maykop and Yamna cultures were succeeded by the Srubna culture (1600-1200 BCE), possibly representing an advance of R1a-Z282 people from the northern steppes towards the Black Sea shores, filling the vacuum left by the R1b tribes who migrated to Southeast Europe and Anatolia.” ref
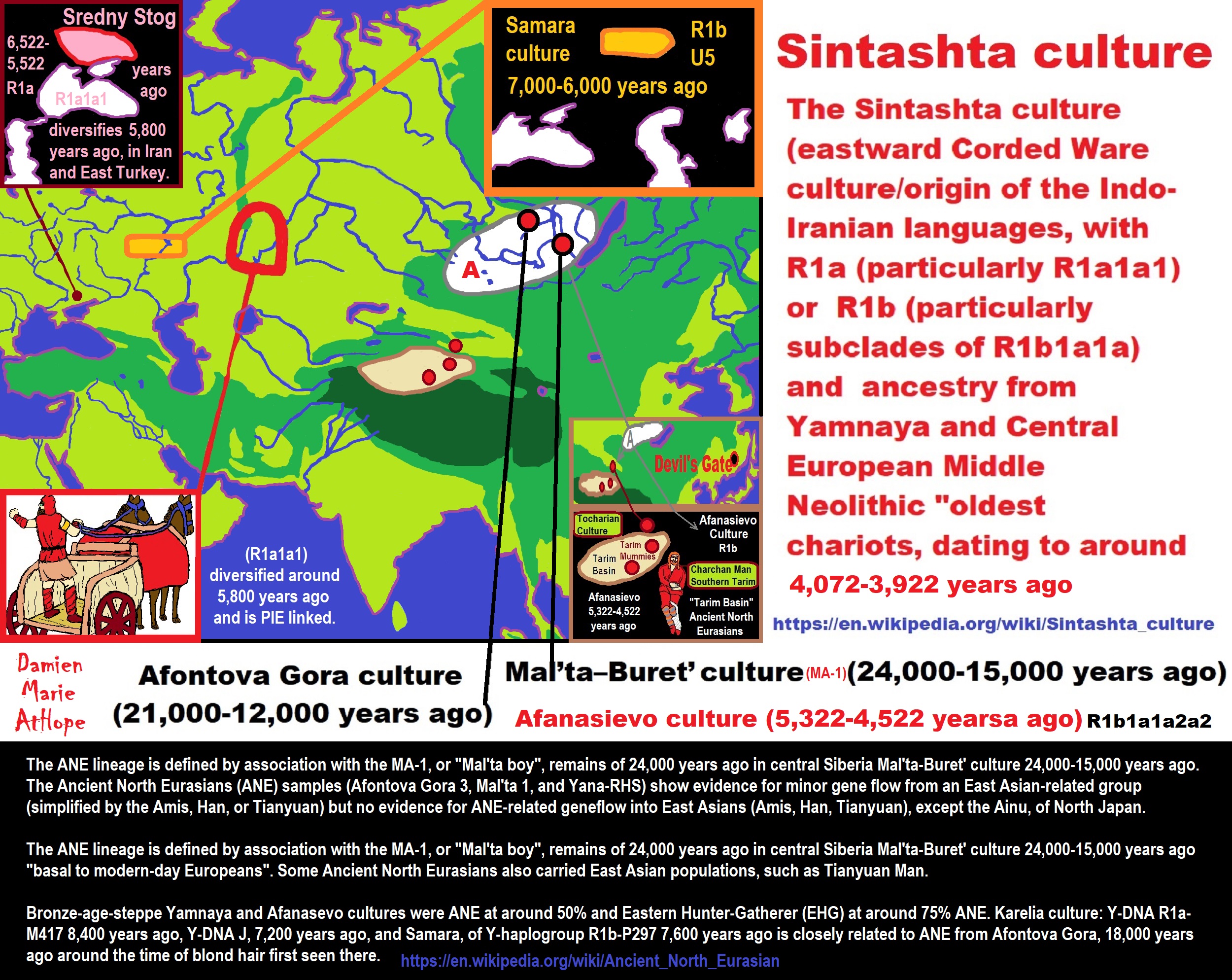
The Siberian & Central Asian branch corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“When R1b crossed the Caucasus in the Late Neolithic, it split into two main groups. The western one (L51) would settle the eastern and northern of the Black Sea. The eastern one (Z2103) migrated to the Don-Volga region, where horses were domesticated circa 4600 BCE. R1b probably mixed with indigenous R1a people and founded the Repin culture (3700-3300 BCE) a bit before the Yamna culture came into existence in the western Pontic Steppe. R1b would then have migrated with horses along the Great Eurasian Steppe until the Altai mountains in East-Central Asia, where they established the Afanasevo culture (c. 3600-2400 BCE). Afanasevo people might be the precursors of the Tocharian branch of Indo-European languages. In 2014, Clément Hollard of Strasbourg University tested three Y-DNA samples from the Afanasevo culture and all three turned out to belong to haplogroup R1b, including two to R1b-M269.” ref
“The R1b people who stayed in the Volga-Ural region were probably the initiators of the Poltavka culture (2700-2100 BCE), then became integrated into the R1a-dominant Sintashta-Petrovka culture (2100-1750 BCE) linked to the Indo-Aryan conquest of Central and South Asia (=> see R1a for more details). Nowadays in Russia R1b is found at higher frequencies among ethnic minorities of the Volga-Ural region (Udmurts, Komi, Mordvins, Tatars) than among Slavic Russians. R1b is also present in many Central Asian populations, the highest percentages being observed among the Uyghurs (20%) of Xinjiang in north-west China, the Yaghnobi people of Tajikistan (32%), and the Bashkirs (47%, or 62.5% in the Abzelilovsky district) of Bashkortostan in Russia (border of Kazakhstan). R1b-M73, found primarily in North Asia (Altai, Mongolia), Central Asia, and the North Caucasus is thought to have spread during the Neolithic from the Middle East to Central and North Asia, and therefore can be considered to be pre-Indo-European.” ref
The European & Middle Eastern branch corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The Indo-Europeans’s bronze weapons and the extra mobility provided by horses would have given them a tremendous advantage over the autochthonous inhabitants of Europe, namely the native haplogroup C1a2, F, and I (descendants of Cro-Magnon) and the early Neolithic herders and farmers (G2a, H2, E1b1b, and T1a). This allowed R1a and R1b to replace most of the native male lineages (=> see How did R1b come to replace most of the older lineages in Western Europe?), although female lineages seem to have been less affected.” ref
“A comparison with the Indo-Iranian invasion of South Asia shows that 40% of the male linages of northern India are R1a, but less than 10% of the female lineages could be of Indo-European origin. The impact of the Indo-Europeans was more severe in Europe because European society 4,000 years ago was less developed in terms of agriculture, technology (no bronze weapons), and population density than that of the Indus Valley civilization. This is particularly true of the native Western European cultures where farming arrived much later than in the Balkans or Central Europe. Greece, the Balkans and the Carpathians were the most advanced of European societies at the time and were the least affected in terms of haplogroup replacement. neolithic lineages survived better in regions that were more difficult to reach or less hospitable to horse breeders, like the Alps, the Dinaric Alps, the Apennines, and Sardinia.” ref
The Conquest of “Old Europe” and Central Europe (4200-2500 BCE) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The first forays of Steppe people into the Balkans happened between 4200 BCE and 3900 BCE, when cattle herders equipped with horse-drawn wagons crossed the Dniester and Danube and apparently destroyed the towns of the Gumelnița, Varna, and Karanovo VI cultures in Eastern Romania and Bulgaria. A climatic change resulting in colder winters during this exact period probably pushed steppe herders to seek milder pastures for their stock, while failed crops would have led to famine and internal disturbance within the Danubian and Balkanic communities. The ensuing Cernavodă culture (Copper Age, 4000-3200 BCE), Coțofeni/Usatovo culture (Copper to Bronze Age, 3500-2500 BCE), Ezero culture (Bronze Age, 3300-2700 BCE), in modern Romania, seems to have had a mixed population of steppe immigrants and people from the old tell settlements. These Steppe immigrants were likely a mixture of both R1a and R1b lineages, with a probably higher percentage of R1a than later Yamna-era invasions.” ref
“The Steppe invaders would have forced many Danubian farmers to migrate to the Cucuteni-Trypillian towns in the eastern Carpathians, causing a population boom and a north-eastward expansion until the Dnieper valley, bringing Y-haplogroups G2a, I2a1 (probably the dominant lineage of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture), E1b1b, J2a, and T1a in what is now central Ukraine. This precocious Indo-European advance westward was fairly limited, due to the absence of Bronze weapons and organized army at the time, and was indeed only possible thanks to climatic catastrophes which reduced the defenses of the towns of Old Europe. The Carphatian, Danubian, and Balkanic cultures were too densely populated and technologically advanced to allow for a massive migration.” ref
“In comparison, the forest-steppe R1a people successfully penetrated into the heart of Europe with little hindrance, due to the absence of developed agrarian societies around Poland and the Baltic. The Corded Ware culture (3200-1800 BCE) was a natural northern and western expansion of the Yamna culture, reaching as far west as Germany and as far north as Sweden and Norway. DNA analysis from the Corded Ware confirmed the presence of R1a and R1b in Poland c. 2700 BCE and R1a central Germany around 2600 BCE. The Corded Ware tribes expanded from the northern fringe of the Yamna culture where R1a lineages were prevalent over R1b ones.” ref
“The expansion of R1b people into Old Europe was slower, but proved inevitable. In 2800 BCE, by the time the Corded Ware had already reached Scandinavia, the Bronze Age R1b cultures had barely moved into the Pannonian Steppe. They established major settlements in the Great Hungarian Plain, the most similar habitat to their ancestral Pontic Steppes. Around 2500 BCE, the western branch of Indo-European R1b were poised for their next major expansion into modern Germany and Western Europe. By that time, the R1b immigrants had blended to a great extent with the indigenous Mesolithic and Neolithic populations of the Danubian basin, where they had now lived for 1,700 years.” ref
“The strongly patriarchal Indo-European elite remained almost exclusively R1b on the paternal side, but absorbed a high proportion of non-Indo-European maternal lineages. Hybridized, the new Proto-Indo-European R1b people would have lost most of their remaining Proto-Europoid or Mongolid features inherited from their Caspian origins (which were still clearly visible in numerous individuals from the Yamna period). Their light hair, eye and skin pigmentation, once interbred with the darker inhabitants of Old Europe, became more like that of modern Southern Europeans. The R1a people of the Corded Ware culture would come across far less populous societies in Northern Europe, mostly descended from the lighter Mesolithic population, and therefore retained more of their original pigmentation (although facial traits evolved considerably in Scandinavia, where the I1 inhabitants were strongly dolicocephalic and long-faced, as opposed to the brachycephalic and broad-faced Steppe people).” ref
The Conquest of Western Europe (2500-1200 BCE) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The R1b conquest of Europe happened in two phases. For nearly two millennia, starting from circa 4200 BCE, Steppe people limited their conquest to the rich Chalcolithic civilizations of the Carpathians and the Balkans. These societies possessed the world’s largest towns, notably the tell settlements of the Cucuteni-Tripolye culture. Nothing incited the R1b conquerors to move further into Western Europe at such an early stage, because most of the land north and west of the Alps was still sparsely populated woodland. The Neolithic did not reach the British Isles and Scandinavia before circa 4000 BCE. Even northern France and most of the Alpine region had been farming or herding for less than a millennium and were still quite primitive compared to Southeast Europe and the Middle East.” ref
“North-west Europe remained a tribal society of hunter-gatherers practicing only limited agriculture for centuries after the conquest of the Balkans by the Indo-Europeans. Why would our R1b “conquistadors” leave the comfort of the wealthy and populous Danubian civilizations for the harsh living conditions that lie beyond? Bronze Age people coveted tin, copper, and gold, of which the Balkans had plenty, but that no one had yet discovered in Western Europe.” ref
“R1b-L51 is thought to have arrived in Central Europe (Hungary, Austria, Bohemia) around 2500 BCE, approximately two millennia after the shift to the Neolithic lifestyle in these regions. Agrarian towns had started to develop. Gold and copper had begun to be mined. The prospects of a conquest were now far more appealing.” ref
“The archeological and genetic evidence (distribution of R1b subclades) point at several consecutive waves towards eastern and central Germany between 2800 BCE and 2300 BCE. The Unetice culture was probably the first culture in which R1b-L11 lineages played a major role. It is interesting to note that the Unetice period happen to correspond to the end of the Maykop (2500 BCE) and Kemi Oba (2200 BCE) cultures on the northern shores of the Black Sea, and their replacement by cultures descended from the northern steppes. It can therefore be envisaged that the (mostly) R1b population from the northern half of the Black Sea migrated westward due to pressure from other Indo-European people (R1a) from the north, for example that of the burgeoning Proto-Indo-Iranian branch, linked to the contemporary Poltavka and Abashevo cultures.” ref
“It is doubtful that the Bell Beaker culture (2900-1800 BCE) in Western Europe was already Indo-European because its attributes are in perfect continuity with the native Megalithic cultures. The Beaker phenomenon started during the Late Neolithic and Early Chalcolithic in Portugal and propagated to the north-east towards Germany. During the same period Bronze Age Steppe cultures spread from Germany in the opposite direction towards Iberia, France and Britain, progressively bringing R1b lineages into the Bell Beaker territory. It is more likely that the beakers and horses found across Western Europe during that period were the result of trade with neighboring Indo-European cultures, including the first wave of R1b into Central Europe. It is equally possible that the Beaker people were R1b merchants or explorers who traveled across Western Europe and brought back tales of riches poorly defended by Stone Age people waiting to be to be conquered. This would have prompted a full-scale Indo-European (R1b) invasion from about 2500 BCE in Germany, reaching the Atlantic (north of the Pyrenees at least) around 2200 BCE.” ref

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
By day the LORD went ahead of them in a pillar of cloud to guide them on their way and by night in a pillar of fire to give them light, so that they could travel by day or night.
- By day the “Bible God” was in a cloud pillar.
- By night the “Bible God” was in a fire pillar.

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref


My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
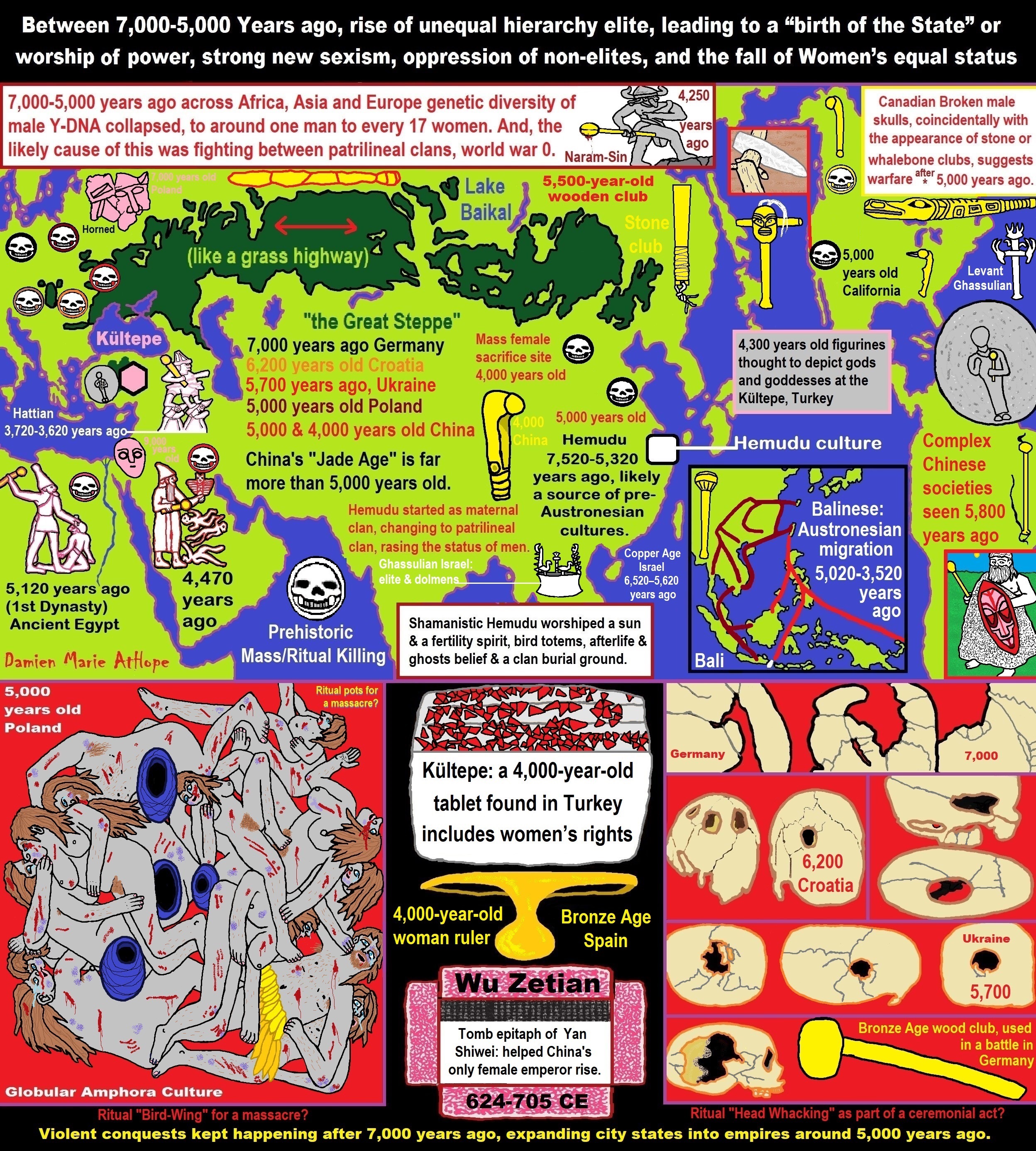
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


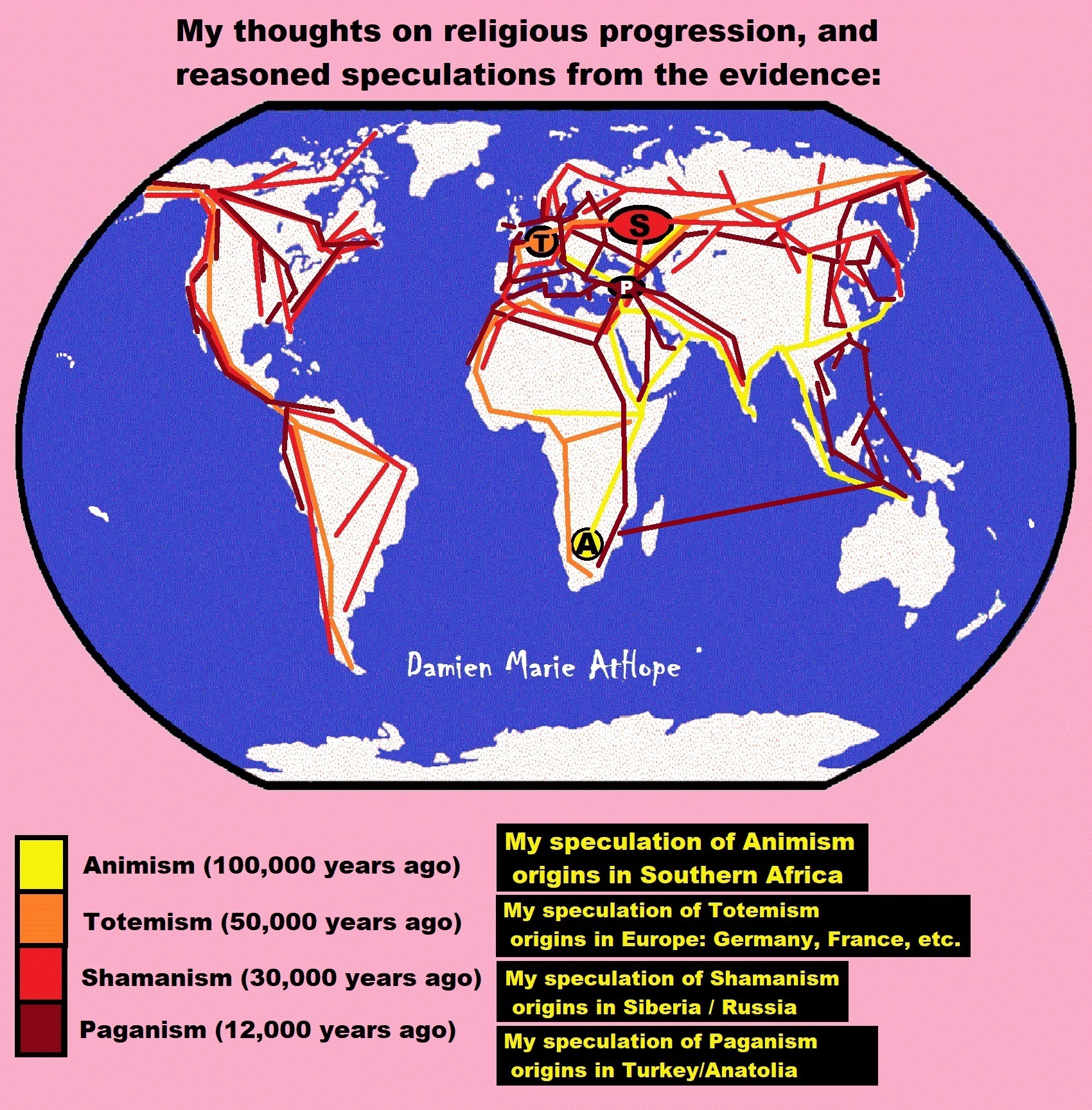




ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.



While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com