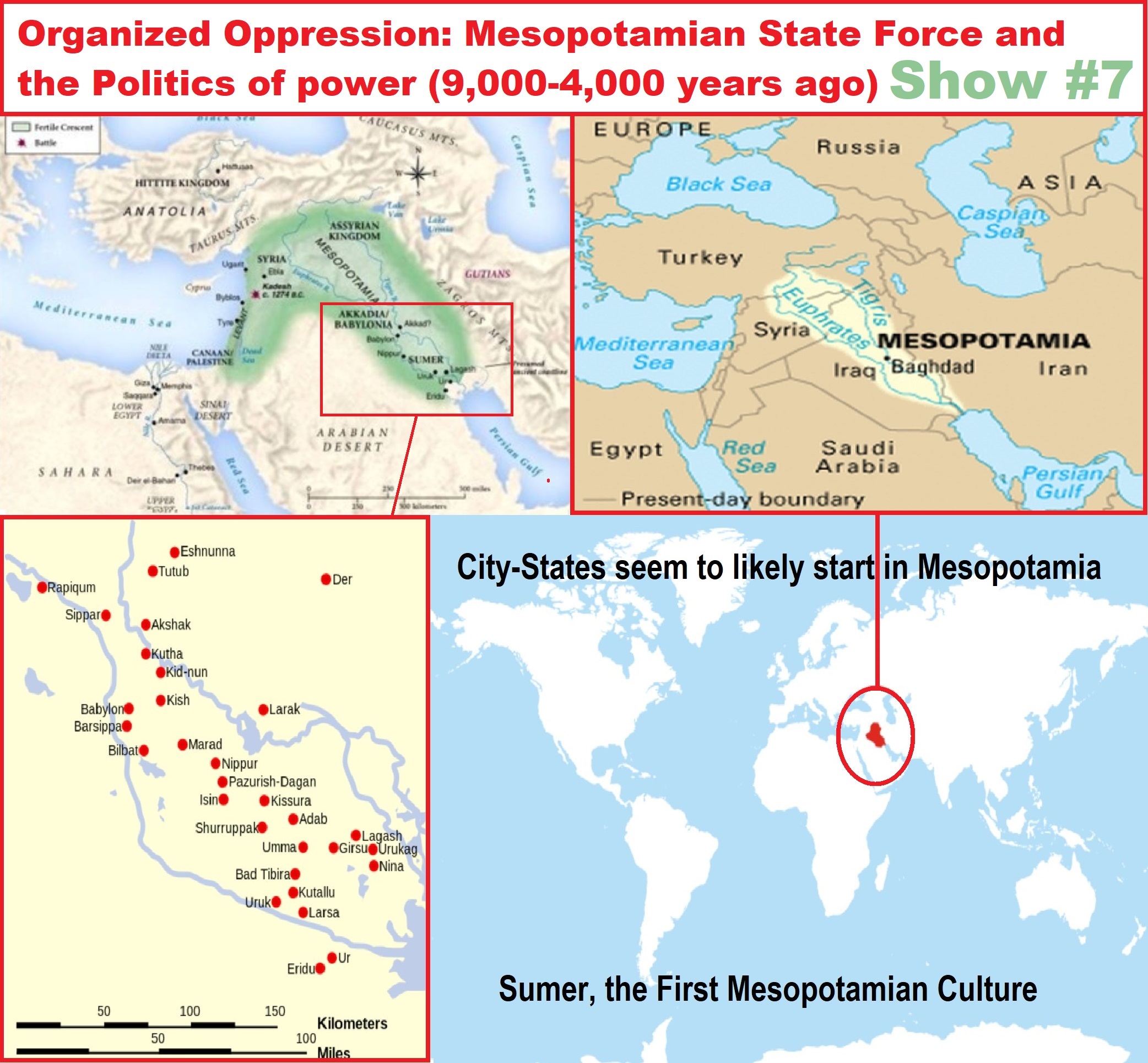
“Mesopotamia is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Mesopotamia occupies most of present-day Iraq and Kuwait. The historical region includes the head of the Persian Gulf and parts of present-day Iran, Syria, and Turkey.” ref
“The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history (c. 3100 BCE or 5,121 years ago) to the fall of Babylon in 539 BCE or 2,560 years ago, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BCE or 2,353 years ago, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (900 BCE – 270 CE).” ref
“Around 150 BCE or 2,171 years ago, Mesopotamia was under the control of the Parthian Empire. Mesopotamia became a battleground between the Romans and Parthians, with western parts of Mesopotamia coming under ephemeral Roman control. In 226 CE, the eastern regions of Mesopotamia fell to the Sassanid Persians. The division of Mesopotamia between Roman (Byzantine from 395 AD) and Sassanid Empires lasted until the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia of the Sasanian Empire and Muslim conquest of the Levant from Byzantines.” ref
“A number of primarily neo-Assyrian and Christian native Mesopotamian states existed between the 1st century BCE and 3rd century BCE, including Adiabene, Osroene, and Hatra. Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BCE or 12,021 years ago. It has been identified as having “inspired some of the most important developments in human history, including the invention of the wheel, the planting of the first cereal crops, and the development of cursive script, mathematics, astronomy, and agriculture“. It has been known as one of the earliest civilizations to ever exist in the world.” ref
City-States seem to likely start in Mesopotamia
“As time went on, many small villages became the first cities, one of them being Eridu, according to the Mesopotamians themselves. Scholars, however, consider Uruk to be the first city in history. Other Sumerian cities include Ur, Lagash, Adab, Kish, Larsa, Nippur, Kullah, and Adab among others.” ref
“In 4000 BCE or 6,021 years ago. came the first villages and the beginning of towns. By 3,500 BCE or 5,521 years ago, the Sumerian city-states began forming, all centered around temples to the gods. By this time, Sumerian people had invented writing, the wheel, irrigation and water control, and sailboats. One of the names for Mesopotamia is the “cradle of civilization,” as the land between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers was the birthplace of civilization as we know it.” ref
“Sumer’s city-states were first ruled by priest-kings, known as Ensi. As society grew more complex, however, and city-states began battling over land and water rights, a secular kingship began, with the rule of a city-state in the hands of a Lugal, or strong man. The Lugal supervised wars and oversaw important trade with other lands. Trade brought in goods such as metal ores that were unobtainable in Sumer itself. It was probably the necessity of record-keeping in long-distance trade that spurred the development of cuneiform writing.” ref
“While the archeological record reveals the life of common Sumerians, the Sumerian King List provides some detail of Sumer’s kings. The King List, a cuneiform document that lists and briefly describes all the kings of the region beginning with Etana of Kish, who ruled c. 3100 BCE or 5,121 years ago. A scribe in the city of Lagash wrote the document around 2100 BCE or 4,121 years ago at the instigation of a king who wished to legitimate his rule by connecting his name with the known kings and their great deeds.” ref
“Sumer’s city-states warred with each other continually for land, water rights, and other natural resources. One king might create a larger alliance, but no one managed to rule them all until Eannutum of Lagash, who managed to subdue most of the city-states of Sumer under his rule. Lugalzagesi of Umma then held that proto-empire together until he was overthrown by Sargon the Great circa 2234 BCE or 4,255 years ago. Sargon, a Semite rather than a Sumerian, originated from northern Mesopotamia.” ref
“The Akkadian Empire dominated Sumer for the next 150 years. Sumer, however, would rise again during the Sumerian Renaissance of 2047-1750 BCE or 4,068 years ago. Sumer’s civilization provided the world with many firsts: first legal codes, court system, schools, proverbs, moral and ethical ideas, mathematical systems, libraries, bronze, writing, astrological signs, our division of time into hours and minutes and many technological innovations.” ref
Divine right of Kings
“Historically, many Notions of rights have been authoritarian and hierarchical, with different people granted different rights and some having more rights than others. For instance, the right of a father to receive respect from his son did not indicate a right for the son to receive a return from that respect. Analogously, the divine right of kings, which permitted absolute power over subjects, provided few rights for the subjects themselves.” ref
Pre-Christian conceptions of the Divine Right of Kings
Divine Right of Kings and Zoroastrianism (Iranian world)
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family.
“Khvarenah “Ahura Mazda the god reportedly gives divine kingship to Ardashir.” Khvarenah is an Iranian and Zoroastrian concept, which literally means glory, about the divine right of the kings. This may stem from early Mesopotamian culture, where kings were often regarded as deities after their death. Shulgi of Ur was among the first Mesopotamian rulers to declare himself to be divine. In the Iranian view, kings would never rule, unless Khvarenah is with them, and they will never fall unless Khvarenah leaves them. For example, according to the Kar-namag of Ardashir, when Ardashir I of Persia and Artabanus V of Parthia fought for the throne of Iran, on the road Artabanus and his contingent are overtaken by an enormous ram, which is also following Ardashir. Artabanus’s religious advisors explain to him that the ram is the manifestation of the khwarrah of the ancient Iranian kings, which is leaving Artabanus to join Ardashir.” ref
Roman Empire (Italic languages)
Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken on the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BCE.
“The Imperial cult of ancient Rome identified Roman emperors and some members of their families with the “divinely sanctioned” authority (auctoritas) of the Roman State. The official offer of cultus to a living emperor acknowledged his office and rule as divinely approved and constitutional: his Principate should therefore demonstrate pious respect for traditional Republican deities and mores. Many of the rites, practices, and status distinctions that characterized the cult to emperors were perpetuated in the theology and politics of the Christianised Empire.” ref
Christian conceptions of the Divine Right of Kings
“In European Christianity, the divine right of kings, divine right, or God’s mandation is a political and religious doctrine of political legitimacy of a monarchy. It stems from a specific metaphysical framework in which a monarch is, before birth, pre-ordained to inherit the crown. According to this theory of political legitimacy, the subjects of the crown have actively (and not merely passively) turned over the metaphysical selection of the king’s soul – which will inhabit the body and rule them – to God. In this way, the “divine right” originates as a metaphysical act of humility and/or submission towards God. The Divine Right has been a key element of the legitimation of many absolute monarchies.” ref
“Significantly, the doctrine asserts that a monarch is not accountable to any earthly authority (such as a parliament) because their right to rule is derived from divine authority. Thus, the monarch is not subject to the will of the people, of the aristocracy, or of any other estate of the realm. It follows that only divine authority can judge a monarch, and that any attempt to depose, dethrone or restrict their powers runs contrary to God’s will and may constitute a sacrilegious act. It is often expressed in the phrase by the Grace of God, which has historically been attached to the titles of certain reigning monarchs. Note, however, that such accountability only to God does not per se make the monarch a sacred king.” ref

Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power Show #7
41:57 Sargon and Akkadian Rule of Sumer Video Used
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

Pic ref
“King of Sumer and Akkad”
southern (Sumer) and northern (Akkad) Mesopotamia
“Although Sargon of Akkad is often referred to as the “founder” of Akkad, the city itself probably existed before his rule; a pre-Sargonic inscription refers to it by name and the name “Akkad” itself is not actually of the Akkadian language of Sargon and his successors. Sargon’s reign does however mark the transition of Akkad from a city-state into the first known great empire, with the Akkadian king ruling all Mesopotamia. His rise to power began with the defeat of the Sumerian king Lugal-zage-si, who had ruled Lower Mesopotamia from Uruk, and the conquest of his empire. Through military campaigns, Sargon subjugated regions as far west as the Mediterranean and as far north as Assyria, which he boasted of in his inscriptions.” ref
“Akkadian was an East Semitic language, now extinct, that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia (Akkad, Assyria, Isin, Larsa, and Babylonia) from the third millennium BCE or around 5,000 years ago until its gradual replacement by Akkadian-influenced Old Aramaic among Mesopotamians by the 8th century BCE or 2,822 years ago. It is the earliest documented Semitic language. It used the cuneiform script, which was originally used to write the unrelated, and also extinct, Sumerian (which is a language isolate). Akkadian is named after the city of Akkad, a major center of Mesopotamian civilization during the Akkadian Empire (c. 2334–2154 BCE or 4,356-4,176 years ago).” ref
“Semitic languages occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic Akkadian and Eblaite texts (written in a script adapted from Sumerian cuneiform) appearing from the 30th century BCE and the 25th century BCE or 5,022-4,522 years ago in Mesopotamia and the north eastern Levant respectively. The only earlier attested languages are Sumerian and Elamite (2800 BCE to 550 BCE or 4,822-2,572 years ago), both language isolates, and Egyptian (a sister branch of the Afroasiatic family, related to the Semitic languages but not part of them). Amorite appeared in Mesopotamia and the northern Levant circa 2000 BCE or 4,022 years ago, followed by the mutually intelligible Canaanite languages (including Hebrew, Phoenician, Moabite, Edomite and Ammonite, and perhaps Ekronite, Amalekite, and Sutean), the still spoken Aramaic, and Ugaritic during the 2nd millennium BCE.” ref
“The king of Akkad was the ruler of the city of Akkad and its empire, in ancient Mesopotamia. In the 3rd millennium BC, from the reign of Sargon of Akkad to the reign of his great-grandson Shar-Kali-Sharri, the Akkadian Empire represented the dominant power in Mesopotamia and the first known great empire. The empire would rapidly collapse following the rule of its first five kings, owing to internal instability and foreign invasion, probably resulting in Mesopotamia re-fracturing into independent city-states, but the power that Akkad had briefly exerted ensured that its prestige and legacy would be claimed by monarchs for centuries to come. Ur-Nammu of Ur, who founded the Neo-Sumerian Empire and reunified most of Mesopotamia, created the title “King of Sumer and Akkad” which would be used until the days of the Achaemenid Empire.” ref
“Sargon’s successors consolidated his vast realm and continued expanding the borders of the Akkadian Empire. Sargon’s grandson and the fourth king of Akkad, Naram-Sin, brought the empire to its greatest extent and assumed a new title to illustrate his great power, King of the Four Quarters, which referenced the entire world. He was also the first king in Mesopotamia to be deified in his lifetime, being addressed as “the god of Akkad”. Although at least seven kings would rule Akkad after him, the Akkadian Empire quickly collapsed after Naram-Sin’s reign and prominent central authority under a single king would not be restored in Mesopotamia until the rise of the Neo-Sumerian Empire. It’s likely that the region reverted to local governance under kings of city-states in the time between the two empires. A major cause of this collapse was the invasion of Mesopotamia by a people referred to as the Gutians, who would be defeated and driven away by the founder of the Neo-Sumerian Empire, Ur-Nammu.” ref
“Ur-Nammu (or Ur-Namma, Ur-Engur, Ur-Gur, ruled c. 2112 – 2094 BCE or 4,134-4,116 years ago middle chronology, or possibly c. 2048–2030 BCE or 4,070-4,052 years ago short chronology) founded the Sumerian Third Dynasty of Ur, in southern Mesopotamia, following several centuries of Akkadian and Gutian rule. His main achievement was state-building, and Ur-Nammu is chiefly remembered today for his legal code, the Code of Ur-Nammu, the oldest known surviving example in the world. He held the titles of “King of Ur, and King of Sumer and Akkad.” ref
“The final kings to rule Akkad, Dudu, and Shu-turul are assumed to have been related to the original ruling dynasty and as such are often regarded as members of the Sargonic dynasty. Although Akkad and what remained of its empire was destroyed, its power and prominence led to rulers of later Mesopotamian empires wishing to claim its prestige and legacy for themselves. Ur-Nammu, who founded the Neo-Sumerian Empire in the aftermath of the Gutian rule of Mesopotamia assumed the title “King of Sumer and Akkad”. Although the title was meant to justify his rule over both southern (Sumer) and northern (Akkad) Mesopotamia, it also clearly connected Ur-Nammu to the old Akkadian kings, who may have been against linking Sumer and Akkad in such a fashion even though they had ruled both regions.” ref
“Ur-Nammu’s title would endure for more than 1,500 years. It was assumed by Hammurabi, founder of the Old Babylonian Empire, and used by Babylonian kings up until the 8th century BCE or around 2,800 years ago. It was also prominently used in the Middle and Neo-Assyrian Empires and in the Neo-Babylonian Empire. For Assyrian kings, “King of Sumer and Akkad” was used as a marker of their control of Babylon (which was in the South, e.g. Sumer), and only those Assyrian kings who actually controlled Babylon used the title in their inscriptions. The final king to assume the title of “King of Sumer and Akkad” was Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire, who reigned from 559 to 530 BCE or 2,581-2,552 years ago. In the Cyrus Cylinder, written in Akkadian cuneiform script following Cyrus’s conquest of Babylon, he assumed several traditional Mesopotamian royal titles, most of which were not used by his successors.” ref
Akkadian Empire
“The Akkadian Empire (/əˈkeɪdiən/) was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad (/ˈækæd/) and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire exercised influence across Mesopotamia, the Levant, and Anatolia, sending military expeditions as far south as Dilmun and Magan (modern Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, and Oman) in the Arabian Peninsula.” ref
“The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BCE, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad. Under Sargon and his successors, the Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam and Gutium. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though the meaning of this term is not precise, and there are earlier Sumerian claimants. After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the people of Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian-speaking nations: Assyria in the north, and Babylonia in the south.” ref
“Trade extended from the silver mines of Anatolia to the lapis lazuli mines in modern Afghanistan, the cedars of Lebanon, and the copper of Magan. This consolidation of the city-states of Sumer and Akkad reflected the growing economic and political power of Mesopotamia. The empire’s breadbasket was the rain-fed agricultural system and a chain of fortresses was built to control the imperial wheat production.” ref
“Images of Sargon were erected on the shores of the Mediterranean, in token of his victories, and cities and palaces were built at home with the spoils of the conquered lands. Elam and the northern part of Mesopotamia were also subjugated, and rebellions in Sumer were put down. Contract tablets have been found dated in the years of the campaigns against Canaan and against Sarlak, king of Gutium. He also boasted of having subjugated the “four-quarters” — the lands surrounding Akkad to the north, the south (Sumer), the east (Elam), and the west (Martu). Some of the earliest historiographic texts (ABC 19, 20) suggest he rebuilt the city of Babylon (Bab-ilu) in its new location near Akkad.” ref
“Sargon, throughout his long life, showed special deference to the Sumerian deities, particularly Inanna (Ishtar), his patroness, and Zababa, the warrior god of Kish. He called himself “The anointed priest of Anu” and “the great ensi of Enlil” and his daughter, Enheduanna, was installed as priestess to Nanna at the temple in Ur.” ref
“Troubles multiplied toward the end of his reign. A later Babylonian text states:
In his old age, all the lands revolted against him, and they besieged him in Akkad (the city) [but] he went forth to battle and defeated them, he knocked them over and destroyed their vast army.” ref
“It refers to his campaign in “Elam”, where he defeated a coalition army led by the King of Awan and forced the vanquished to become his vassals.” ref
“Also shortly after, another revolt took place:
the Subartu the upper country—in their turn attacked, but they submitted to his arms, and Sargon settled their habitations, and he smote them grievously.” ref
“Sargon had crushed opposition even at old age. These difficulties broke out again in the reign of his sons, where revolts broke out during the nine-year reign of Rimush (2278–2270 BCE), who fought hard to retain the empire, and was successful until he was assassinated by some of his own courtiers. According to his inscriptions, he faced widespread revolts, and had to reconquer the cities of Ur, Umma, Adab, Lagash, Der, and Kazallu from rebellious ensis: Rimush introduced mass slaughter and large scale destruction of the Sumerian city-states, and maintained meticulous records of his destructions. Most of the major Sumerian cities were destroyed, and Sumerian human losses were enormous.” ref
Pre-Sargonic Akkad
“The Akkadian Empire takes its name from the region and the city of Akkad, both of which were localized in the general confluence area of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers. Although the city of Akkad has not yet been identified on the ground, it is known from various textual sources. Among these is at least one text predating the reign of Sargon. Together with the fact that the name Akkad is of non-Akkadian origin, this suggests that the city of Akkad may have already been occupied in pre-Sargonic times.” ref
Sargon of Akkad: Sargon of Akkad
“Sargon of Akkad defeated and captured Lugal-zage-si in the Battle of Uruk and conquered his empire. The earliest records in the Akkadian language date to the time of Sargon. Sargon was claimed to be the son of La’ibum or Itti-Bel, a humble gardener, and possibly a hierodule, or priestess to Ishtar or Inanna.” ref
“One legend related to Sargon in Assyrian times says that:
My mother was a changeling, my father I knew not. The brothers of my father loved the hills. My city is Azurpiranu (the wilderness herb fields), which is situated on the banks of the Euphrates. My changeling mother conceived me, in secret she bore me. She set me in a basket of rushes, with bitumen she sealed my lid. She cast me into the river which rose not over me. The river bore me up and carried me to Akki, the drawer of water. Akki, the drawer of water, took me as his son and reared me. Akki the drawer of water, appointed me as his gardener. While I was gardener Ishtar granted me her love, and for four and (fifty?) … years I exercised kingship.” ref
Later claims made on behalf of Sargon were that his mother was an “entu” priestess (high priestess). The claims might have been made to ensure a pedigree of nobility, since only a highly placed family could achieve such a position.” ref
“Originally a cupbearer (Rabshakeh) to a king of Kish with a Semitic name, Ur-Zababa, Sargon thus became a gardener, responsible for the task of clearing out irrigation canals. The royal cupbearer at this time was in fact a prominent political position, close to the king and with various high-level responsibilities not suggested by the title of the position itself. This gave him access to a disciplined corps of workers, who also may have served as his first soldiers. Displacing Ur-Zababa, Sargon was crowned king, and he entered upon a career of foreign conquest. Four times he invaded Syria and Canaan, and he spent three years thoroughly subduing the countries of “the west” to unite them with Mesopotamia “into a single empire.” ref
“However, Sargon took this process further, conquering many of the surrounding regions to create an empire that reached westward as far as the Mediterranean Sea and perhaps Cyprus (Kaptara); northward as far as the mountains (a later Hittite text asserts he fought the Hattian king Nurdaggal of Burushanda, well into Anatolia); eastward over Elam; and as far south as Magan (Oman) — a region over which he reigned for purportedly 56 years, though only four “year-names” survive. He consolidated his dominion over his territories by replacing the earlier opposing rulers with noble citizens of Akkad, his native city where loyalty would thus be ensured.” ref

Pic ref
Sargon of Akkad
“Sargon of Akkad (/ˈsɑːrɡɒn/; Akkadian: ???????????? Šarrugi), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BCE. He is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire. He was the founder of the “Sargonic” or “Old Akkadian” dynasty, which ruled for about a century after his death until the Gutian conquest of Sumer. The Sumerian king list makes him the cup-bearer to king Ur-Zababa of Kish.” ref
“His empire is thought to have included most of Mesopotamia, parts of the Levant, besides incursions into Hurrite and Elamite territory, ruling from his (archaeologically as yet unidentified) capital, Akkad (also Agade). Sargon appears as a legendary figure in Neo-Assyrian literature of the 8th to 7th centuries BCE. Tablets with fragments of a Sargon Birth Legend were found in the Library of Ashurbanipal.” ref
“The Akkadian name is normalized as either Šarru-ukīn or Šarru-kēn. The name’s cuneiform spelling is variously LUGAL–ú-kin, šar-ru-gen6, šar-ru-ki-in, šar-ru-um-ki-in. In Old Babylonian tablets relating the legends of Sargon, his name is transcribed as ???????????????????? (Šar-ru-um-ki-in). In Late Assyrian references, the name is mostly spelled as LUGAL-GI.NA or LUGAL-GIN, i.e. identical to the name of the Neo-Assyrian king Sargon II. The spelling Sargon is derived from the single mention of the name (in reference to Sargon II) in the Hebrew Bible, as סַרְגוֹן, in Isaiah 20:1.” ref
“The first element in the name is šarru, the Akkadian (East Semitic) for “king” (c.f. Hebrew sár שַׂר). The second element is derived from the verb kīnum “to confirm, establish” (related to Hebrew kūn כּוּן). A possible interpretation of the reading Šarru-ukīn is “the king has established (stability)” or “he [the god] has established the king”. Such a name would, however, be unusual; other names in -ukīn always include both a subject and an object, as in Šamaš-šuma-ukīn “Shamash has established an heir”. There is some debate over whether the name was an adopted regnal name or a birth name. The reading Šarru-kēn has been interpreted adjectivally, as “the king is established; legitimate”, expanded as a phrase šarrum ki(e)num.” ref
“The terms “Pre-Sargonic” and “Post-Sargonic” were used in Assyriology based on the chronologies of Nabonidus before the historical existence of Sargon of Akkad was confirmed. The form Šarru-ukīn was known from the Assyrian Sargon Legend discovered in 1867 in Library of Ashurbanipal at Nineveh. A contemporary reference to Sargon thought to have been found on the cylinder seal of Ibni-sharru, a high-ranking official serving under Sargon. Joachim Menant published a description of this seal in 1877, reading the king’s name as Shegani-shar-lukh, and did not yet identify it with “Sargon the Elder” (who was identified with the Old Assyrian king Sargon I). In 1883, the British Museum acquired the “mace-head of Shar-Gani-sharri”, a votive gift deposited at the temple of Shamash in Sippar. This “Shar-Gani” was identified with the Sargon of Agade of Assyrian legend. The identification of “Shar-Gani-sharri” with Sargon was recognised as mistaken in the 1910s. Shar-Gani-sharri (Shar-Kali-Sharri) is, in fact, Sargon’s great-grandson, the successor of Naram-Sin.” ref
“It is not entirely clear whether the Neo-Assyrian king Sargon II was directly named for Sargon of Akkad, as there is some uncertainty whether his name should be rendered Šarru-ukīn or as Šarru-kēn(u). Primary sources pertaining to Sargon are sparse; the main near-contemporary reference is that in the various versions of the Sumerian King List. Here, Sargon is mentioned as the son of a gardener, former cup-bearer of Ur-Zababa of Kish. He usurped the kingship from Lugal-zage-si of Uruk and took it to his own city of Akkad. Various copies of the king list give the duration of his reign as either 54, 55, or 56 years. Numerous fragmentary inscriptions relating to Sargon are also known.” ref
“In absolute years, his reign would correspond to c. 2334–2279 BCE in the middle chronology. His successors until the Gutian conquest of Sumer are also known as the “Sargonic Dynasty” and their rule as the “Sargonic Period” of Mesopotamian history. Foster (1982) argued that the reading of 55 years as the duration of Sargon’s reign was, in fact, a corruption of an original interpretation of 37 years. An older version of the king list gives Sargon’s reign as lasting for 40 years. Thorkild Jacobsen marked the clause about Sargon’s father being a gardener as a lacuna, indicating his uncertainty about its meaning. Ur-Zababa and Lugal-zage-si are both listed as kings, but separated by several additional named rulers of Kish, who seem to have been merely governors or vassals under the Akkadian Empire.” ref
“The claim that Sargon was the original founder of Akkad has been called into question with the discovery of an inscription mentioning the place and dated to the first year of Enshakushanna, who almost certainly preceded him. The Weidner Chronicle (ABC 19:51) states that it was Sargon who “built Babylon in front of Akkad.” The Chronicle of Early Kings (ABC 20:18–19) likewise states that late in his reign, Sargon “dug up the soil of the pit of Babylon, and made a counterpart of Babylon next to Agade.” Van de Mieroop suggested that those two chronicles may refer to the much later Assyrian king, Sargon II of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, rather than to Sargon of Akkad.” ref
“Some of the regnal year names of Sargon are preserved, and throw some light in the events of his reign, particularly the conquest of the surrounding territories of Simurrum, Elam, and Mari, and Uru’a, thought to be a city in Elam:
Year in which Sargon went to Simurrum
Year in which Sargon destroyed Uru’a
Year in which Uru’a was destroyed
Year in which Sargon destroyed Elam
Year in which Mari was destroyed
— Known regnal year names of Sargon.” ref
Language and script used in records
“Sargon appears to have promoted the use of Semitic (Akkadian) in inscriptions. He frequently calls himself “king of Akkad” first, after he apparently founded the city of Akkad. He appears to have taken over the rule of Kish at some point, and later also much of Mesopotamia, referring to himself as “Sargon, king of Akkad, overseer of Inanna, king of Kish, anointed of Anu, king of the land [Mesopotamia], governor (ensi) of Enlil“.” ref
“During Sargon’s reign, East Semitic was standardized and adapted for use with the cuneiform script previously used in the Sumerian language into what is now known as the “Akkadian language“. A style of calligraphy developed in which text on clay tablets and cylinder seals was arranged amidst scenes of mythology and ritual.” ref
Year names
“While various copies of the Sumerian king list credit Sargon with a 56, 55, or 54-year reign, dated documents have been found for only four different year-names of his actual reign. The names of these four years describe his campaigns against Elam, Mari, Simurrum (a Hurrian region), and Uru’a (an Elamite city-state).” ref
Nippur inscription
“Among the most important sources for Sargon’s reign is a tablet of the Old Babylonian period recovered at Nippur in the University of Pennsylvania expedition in the 1890s. The tablet is a copy of the inscriptions on the pedestal of a statue erected by Sargon in the temple of Enlil. Its text was edited by Arno Poebel (1909) and Leon Legrain (1926).” ref
Conquest of Sumer
“In the inscription, Sargon styles himself “Sargon, king of Akkad, overseer (mashkim) of Inanna, king of Kish, anointed (guda) of Anu, king of the land [Mesopotamia], governor (ensi) of Enlil”. It celebrates the conquest of Uruk and the defeat of Lugalzagesi, whom Sargon brought “in a collar to the gate of Enlil”:
Sargon, king of Akkad, overseer of Inanna, king of Kish, anointed of Anu, king of the land, governor of Enlil: he defeated the city of Uruk and tore down its walls, in the battle of Uruk he won, took Lugalzagesi king of Uruk in the course of the battle, and led him in a collar to the gate of Enlil.— Inscription of Sargon (Old Babylonian copy from Nippur).” ref
“Sargon then conquered Ur and E-Ninmar and “laid waste” the territory from Lagash to the sea, and from there went on to conquer and destroy Umma:
Sargon, king of Agade, was victorious over Ur in battle, conquered the city and destroyed its wall. He conquered Eninmar, destroyed its walls, and conquered its district and Lagash as far as the sea. He washed his weapons in the sea. He was victorious over Umma in battle, [conquered the city, and destroyed its walls]. [To Sargon], lo[rd] of the land the god Enlil [gave no] ri[val]. The god Enlil gave to him [the Upper Sea and] the [Lower (Sea).— Inscription of Sargon.” ref
Conquest of Upper Mesopotamia, as far as the Mediterranean sea
“Submitting himself to the (Levantine god) Dagan, Sargon conquered territories of Upper Mesopotamia and the Levant, including Mari, Yarmuti (Jarmuth?), and Ibla “up to the Cedar Forest (the Amanus) and up to the Silver Mountain (Aladagh?)”, ruling from the “upper sea” (Mediterranean) to the “lower sea” (Persian Gulf).
Sargon the King bowed down to Dagan in Tuttul. He (Dagan) gave to him (Sargon) the Upper Land: Mari, Iarmuti, and Ebla, as far as the Cedar Forest and the Silver Mountains— Nippur inscription of Sargon.” ref
Conquests of Elam and Marhashi
“Sargon also claims in his inscriptions that he is “Sargon, king of the world, conqueror of Elam and Parahshum“, the two major polities to the east of Sumer. He also names various rulers of the east whom he vanquished, such as “Luh-uh-ish-an, son of Hishibrasini, king of Elam, king of Elam” or “Sidga’u, general of Parahshum”, who later also appears in an inscription by Rimush. Sargon triumphed over 34 cities in total. Ships from Meluhha, Magan, and Dilmun, rode at anchor in his capital of Akkad. He entertained a court or standing army of 5,400 men who “ate bread daily before him.” ref
Sargon Epos
“A group of four Babylonian texts, summarized as “Sargon Epos” or Res Gestae Sargonis, shows Sargon as a military commander asking the advice of many subordinates before going on campaigns. The narrative of Sargon, the Conquering Hero, is set at Sargon’s court, in a situation of crisis. Sargon addresses his warriors, praising the virtue of heroism, and a lecture by a courtier on the glory achieved by a champion of the army, a narrative relating a campaign of Sargon’s into the far land of Uta-raspashtim, including an account of a “darkening of the Sun” and the conquest of the land of Simurrum, and a concluding oration by Sargon listing his conquests.” ref
“The narrative of King of Battle relates Sargon’s campaign against the Anatolian city of Purushanda in order to protect his merchants. Versions of this narrative in both Hittite and Akkadian have been found. The Hittite version is extant in six fragments, the Akkadian version is known from several manuscripts found at Amarna, Assur, and Nineveh. The narrative is anachronistic, portraying Sargon in a 19th-century milieu. The same text mentions that Sargon crossed the Sea of the West (Mediterranean Sea) and ended up in Kuppara, which some authors have interpreted as the Akkadian word for Keftiu, an ancient locale usually associated with Crete or Cyprus.” ref
“Famine and war threatened Sargon’s empire during the latter years of his reign. The Chronicle of Early Kings reports that revolts broke out throughout the area under the last years of his overlordship:
Afterward in his [Sargon’s] old age all the lands revolted against him, and they besieged him in Akkad; and Sargon went onward to battle and defeated them; he accomplished their overthrow, and their widespreading host he destroyed. Afterward he attacked the land of Subartu in his might, and they submitted to his arms, and Sargon settled that revolt, and defeated them; he accomplished their overthrow, and their widespreading host he destroyed, and he brought their possessions into Akkad. The soil from the trenches of Babylon he removed, and the boundaries of Akkad he made like those of Babylon. But because of the evil which he had committed, the great lord Marduk was angry, and he destroyed his people by famine. From the rising of the sun unto the setting of the sun they opposed him and gave him no rest.” ref
“A. Leo Oppenheim translates the last sentence as “From the East to the West he [i.e. Marduk] alienated (them) from him and inflicted upon (him as punishment) that he could not rest (in his grave).” ref
Chronicle of Early Kings
“Shortly after securing Sumer, Sargon embarked on a series of campaigns to subjugate the entire Fertile Crescent. According to the Chronicle of Early Kings, a later Babylonian historiographical text:
[Sargon] had neither rival nor equal. His splendor, over the lands it diffused. He crossed the sea in the east. In the eleventh year he conquered the western land to its farthest point. He brought it under one authority. He set up his statues there and ferried the west’s booty across on barges. He stationed his court officials at intervals of five double hours and ruled in unity the tribes of the lands. He marched to Kazallu and turned Kazallu into a ruin heap, so that there was not even a perch for a bird left.” ref
“In the east, Sargon defeated four leaders of Elam, led by the king of Awan. Their cities were sacked; the governors, viceroys, and kings of Susa, Waraḫše, and neighboring districts became vassals of Akkad.” ref
Origin legends
“Sargon became the subject of legendary narratives describing his rise to power from humble origins and his conquest of Mesopotamia in later Assyrian and Babylonian literature. Apart from these secondary, and partly legendary, accounts, there are many inscriptions due to Sargon himself, although the majority of these are known only from much later copies. The Louvre has fragments of two Sargonic victory steles recovered from Susa (where they were presumably transported from Mesopotamia in the 12th century BCE).” ref
Sumerian legend
“The Sumerian-language Sargon legend contains a legendary account of Sargon’s rise to power. It is an older version of the previously known Assyrian legend, discovered in 1974 in Nippur and first edited in 1983.” ref
“The extant versions are incomplete, but the surviving fragments name Sargon’s father as La’ibum. After a lacuna, the text skips to Ur-Zababa, king of Kish, who awakens after a dream, the contents of which are not revealed on the surviving portion of the tablet. For unknown reasons, Ur-Zababa appoints Sargon as his cup-bearer. Soon after this, Ur-Zababa invites Sargon to his chambers to discuss a dream of Sargon’s, involving the favor of the goddess Inanna and the drowning of Ur-Zababa by the goddess.” ref
“Deeply frightened, Ur-Zababa orders Sargon murdered by the hands of Beliš-tikal, the chief smith, but Inanna prevents it, demanding that Sargon stop at the gates because of his being “polluted with blood.” When Sargon returns to Ur-Zababa, the king becomes frightened again and decides to send Sargon to king Lugal-zage-si of Uruk with a message on a clay tablet asking him to slay Sargon. The legend breaks off at this point; presumably, the missing sections described how Sargon becomes king. The part of the interpretation of the king’s dream has parallels to the biblical story of Joseph, the part about the letter with the carrier’s death sentence has similarities to the Greek story of Bellerophon and the biblical story of Uriah.” ref
Birth legend
“A Neo-Assyrian text from the 7th century BCE purporting to be Sargon’s autobiography asserts that the great king was the illegitimate son of a priestess. Only the beginning of the text (the first two columns) is known, from the fragments of three manuscripts. The first fragments were discovered as early as 1850.” ref
“Sargon’s birth and his early childhood are described thus:
My mother was a high priestess, my father I knew not. The brothers of my father loved the hills. My city is Azupiranu, which is situated on the banks of the Euphrates. My high priestess mother conceived me, in secret she bore me. She set me in a basket of rushes, with bitumen she sealed my lid. She cast me into the river which rose over me. The river bore me up and carried me to Akki, the drawer of water. Akki, the drawer of water, took me as his son and reared me. Akki, the drawer of water, appointed me as his gardener. While I was a gardener, Ishtar granted me her love, and for four and … years I exercised kingship.” ref
“Similarities between the Sargon Birth Legend and other infant birth exposures in ancient literature, including Moses, Karna, and Oedipus, were noted by psychoanalyst Otto Rank in his 1909 book The Myth of the Birth of the Hero. The legend was also studied in detail by Brian Lewis, and compared with many different examples of the infant birth exposure motif found in European and Asian folktales. He discusses a possible archetype form, giving particular attention to the Sargon legend and the account of the birth of Moses. Joseph Campbell has also made such comparisons.” ref
“Sargon is also one of the many suggestions for the identity or inspiration for the biblical Nimrod. Ewing William (1910) suggested Sargon based on his unification of the Babylonians and the Neo-Assyrian birth legend. Yigal Levin (2002) suggested that Nimrod was a recollection of Sargon and his grandson Naram-Sin, with the name “Nimrod” derived from the latter.” ref
Legacy
“Sargon of Akkad is sometimes identified as the first person in recorded history to rule over an empire (in the sense of the central government of a multi-ethnic territory), although earlier Sumerian rulers such as Lugal-zage-si might have a similar claim. His rule also heralds the history of Semitic empires in the Ancient Near East, which, following the Neo-Sumerian interruption (21st/20th centuries BCE), lasted for close to fifteen centuries until the Achaemenid conquest following the 539 BCE Battle of Opis.” ref
“Sargon was regarded as a model by Mesopotamian kings for some two millennia after his death. The Assyrian and Babylonian kings who based their empires in Mesopotamia saw themselves as the heirs of Sargon’s empire. Sargon may indeed have introduced the notion of “empire” as understood in the later Assyrian period; the Neo-Assyrian Sargon Text, written in the first person, has Sargon challenging later rulers to “govern the black-headed people” (i.e. the indigenous population of Mesopotamia) as he did. An important source for “Sargonic heroes” in oral tradition in the later Bronze Age is a Middle Hittite (15th century BCE) record of a Hurro-Hittite song, which calls upon Sargon and his immediate successors as “deified kings” (dšarrena).” ref
“Sargon shared his name with two later Mesopotamian kings. Sargon I was a king of the Old Assyrian period presumably named after Sargon of Akkad. Sargon II was a Neo-Assyrian king named after Sargon of Akkad; it is this king whose name was rendered Sargon (סַרְגוֹן) in the Hebrew Bible (Isaiah 20:1). Neo-Babylonian king Nabonidus showed great interest in the history of the Sargonid dynasty and even conducted excavations of Sargon’s palaces and those of his successors.” ref

“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.

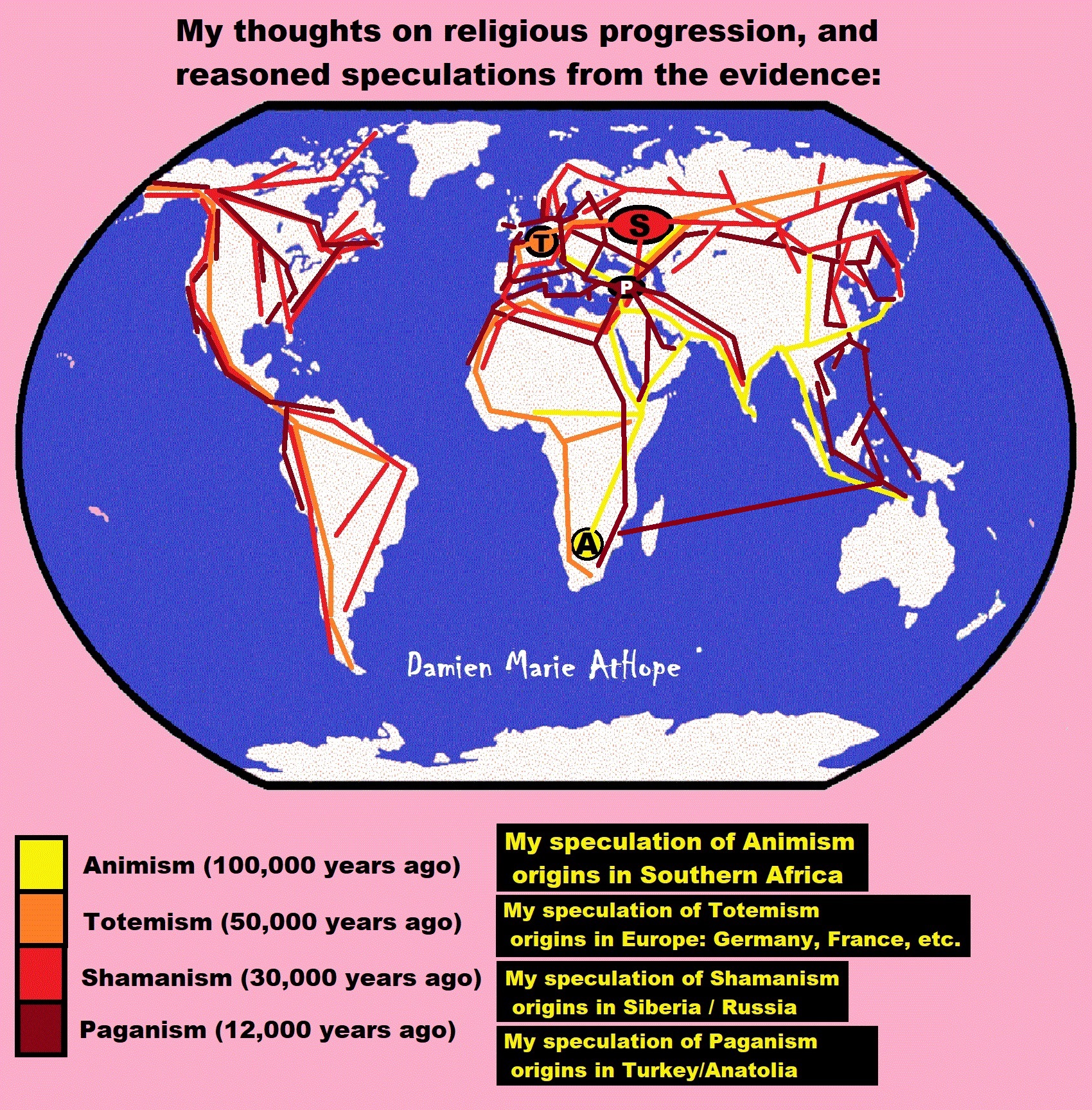
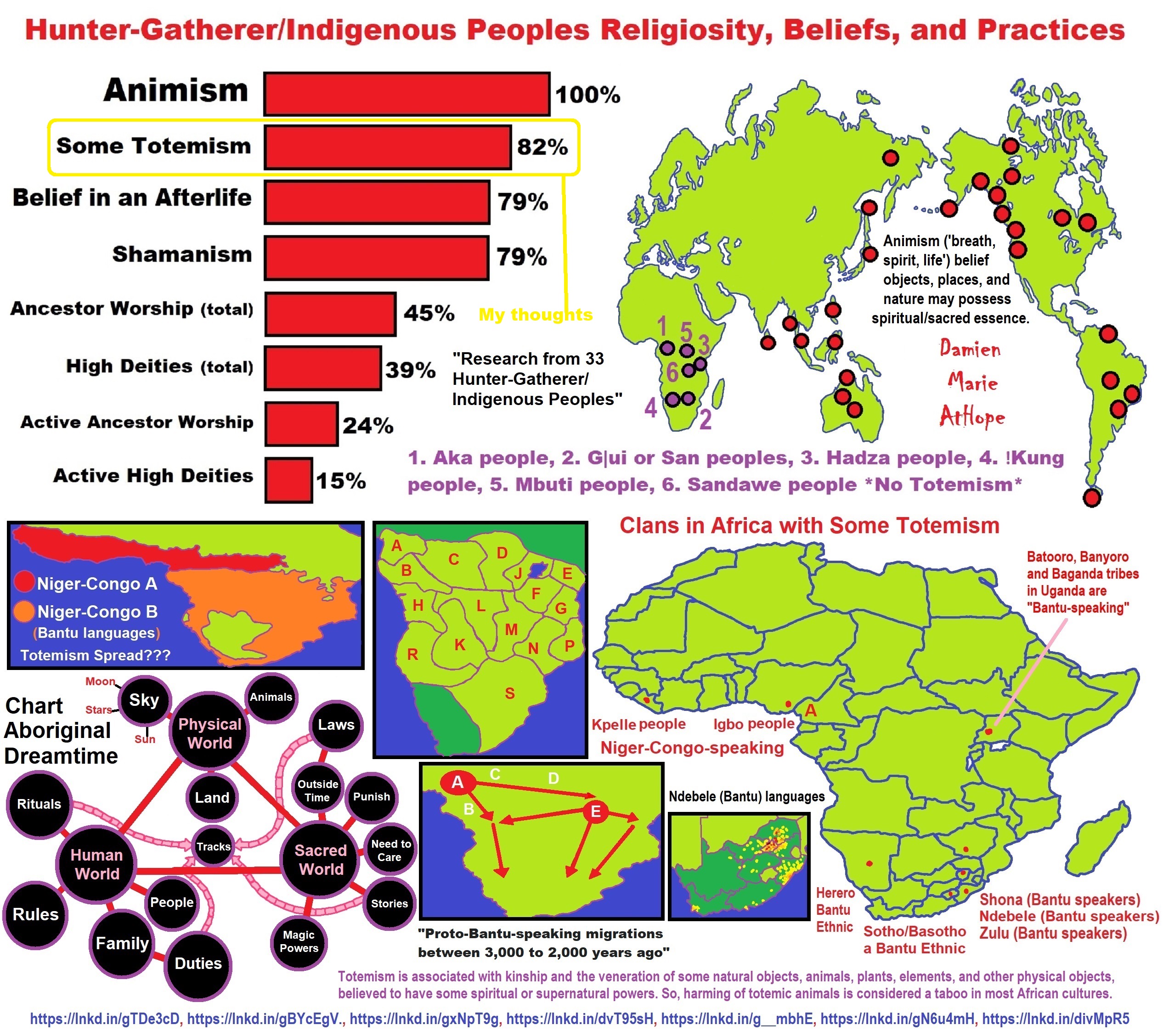
My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
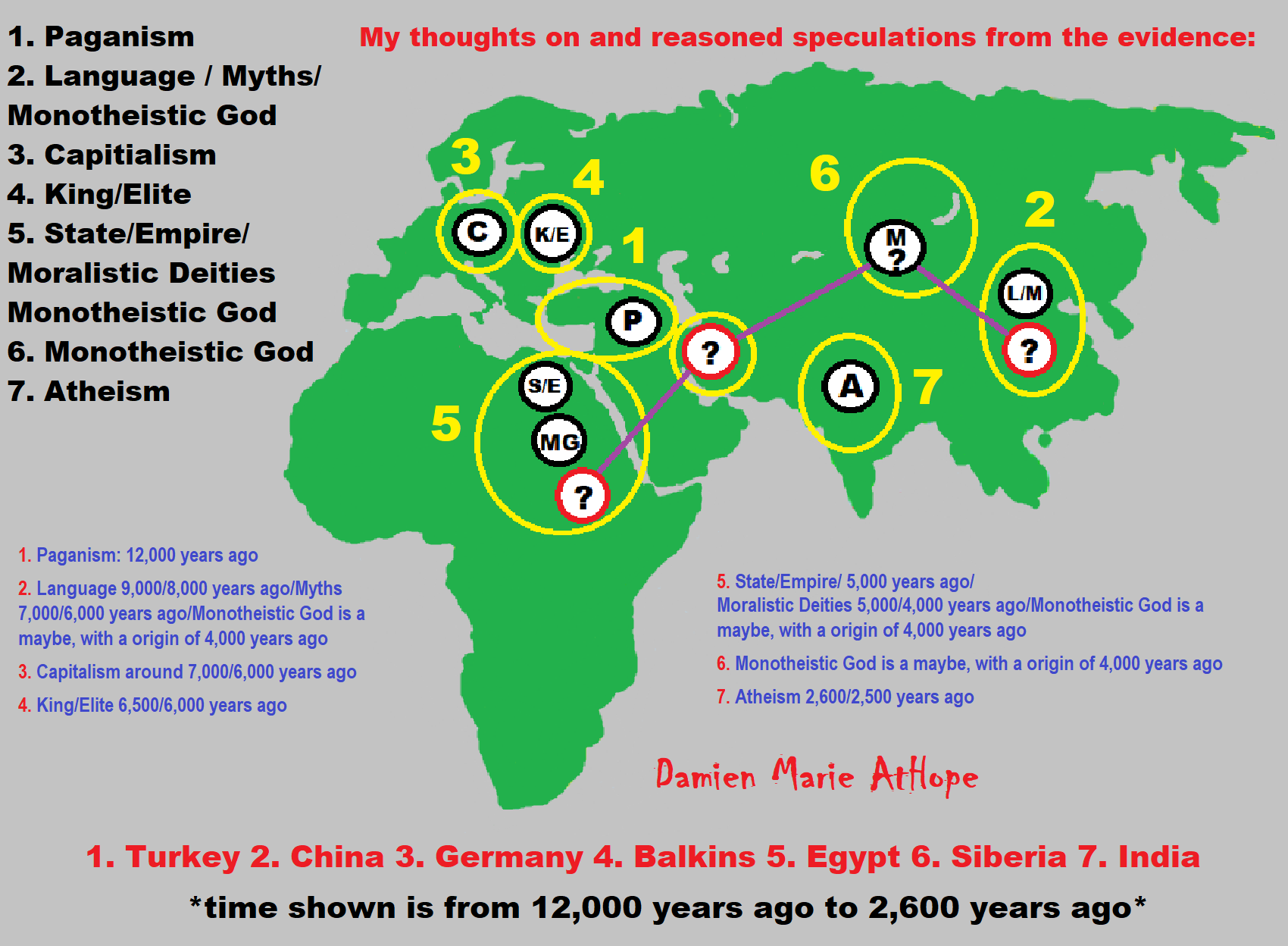
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
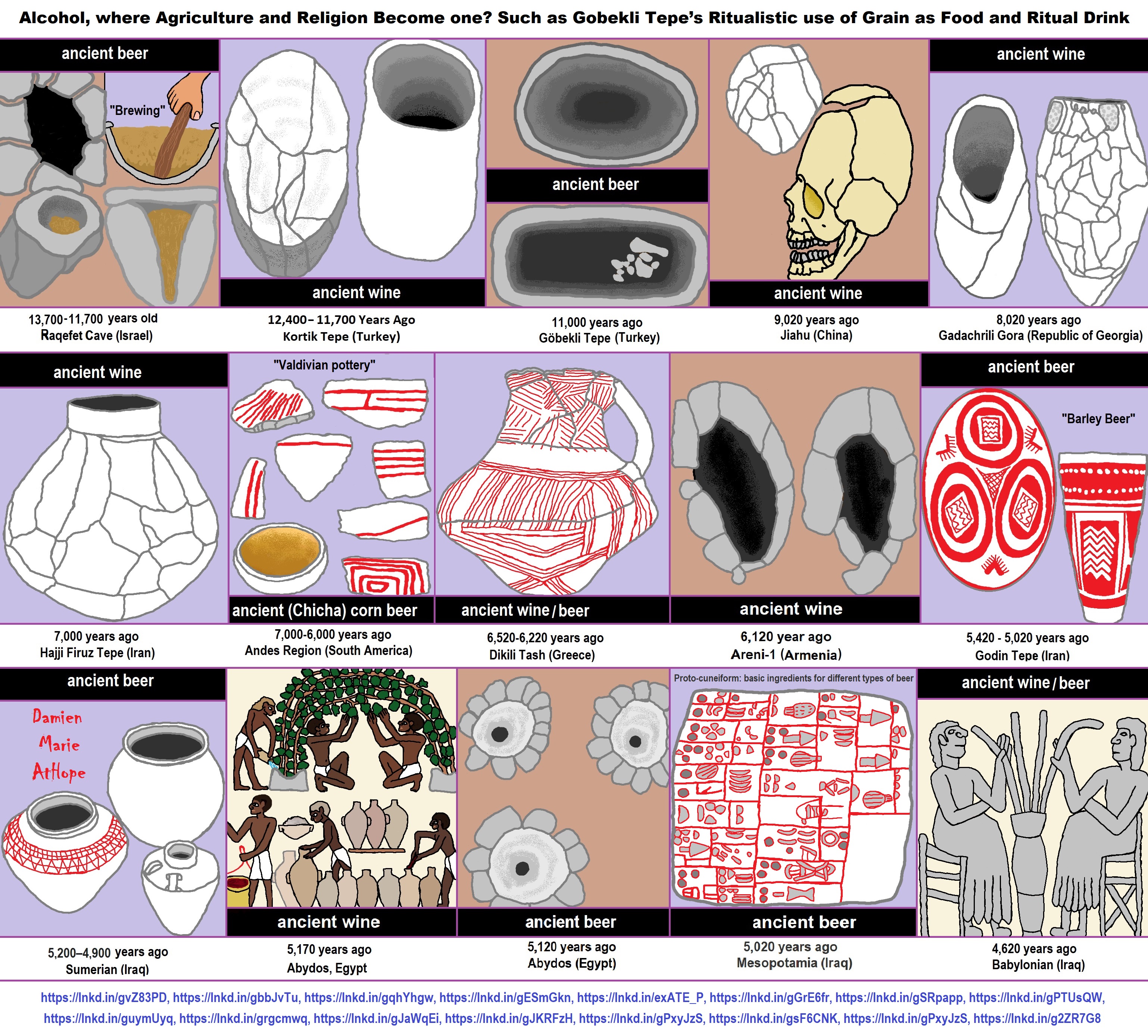
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
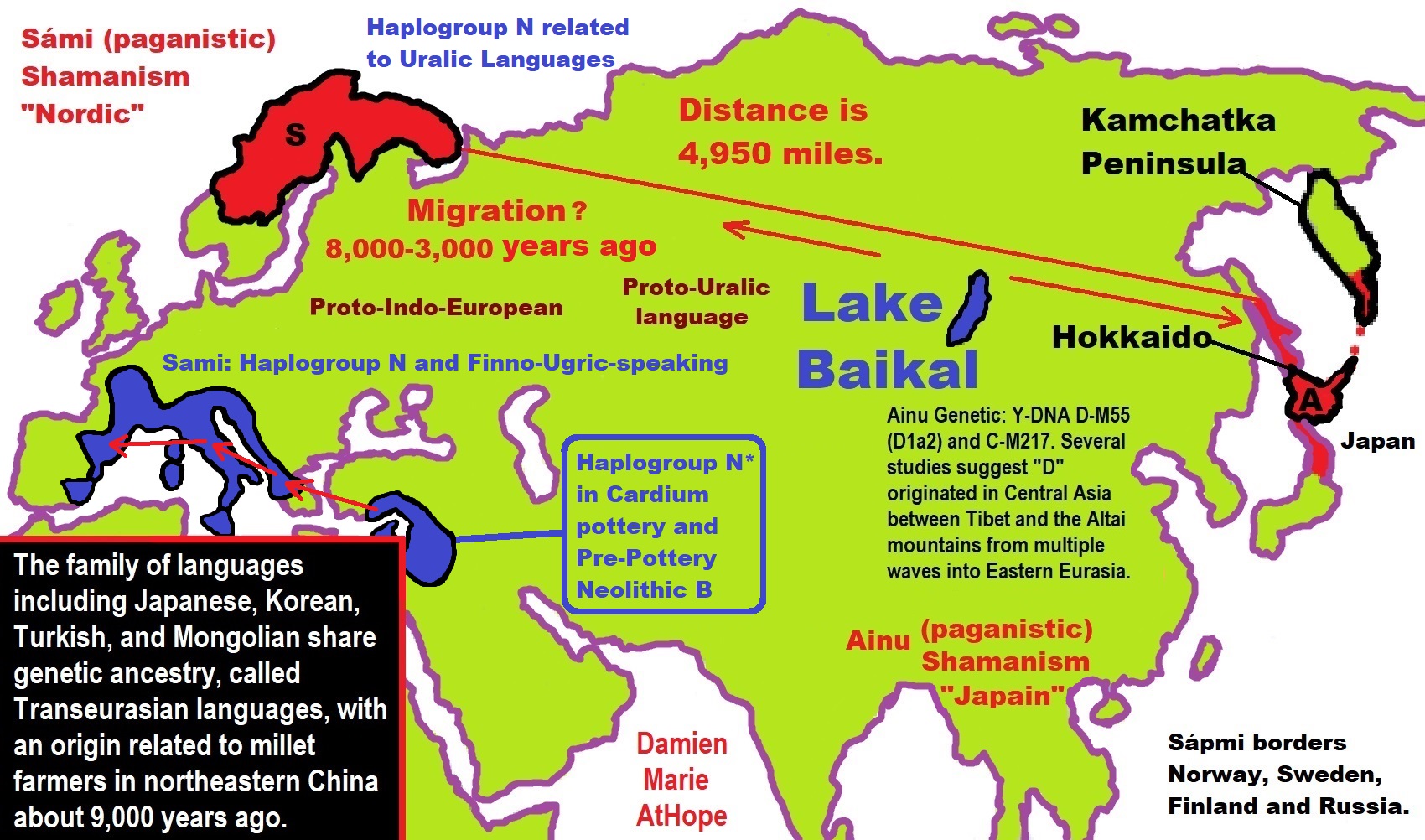
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
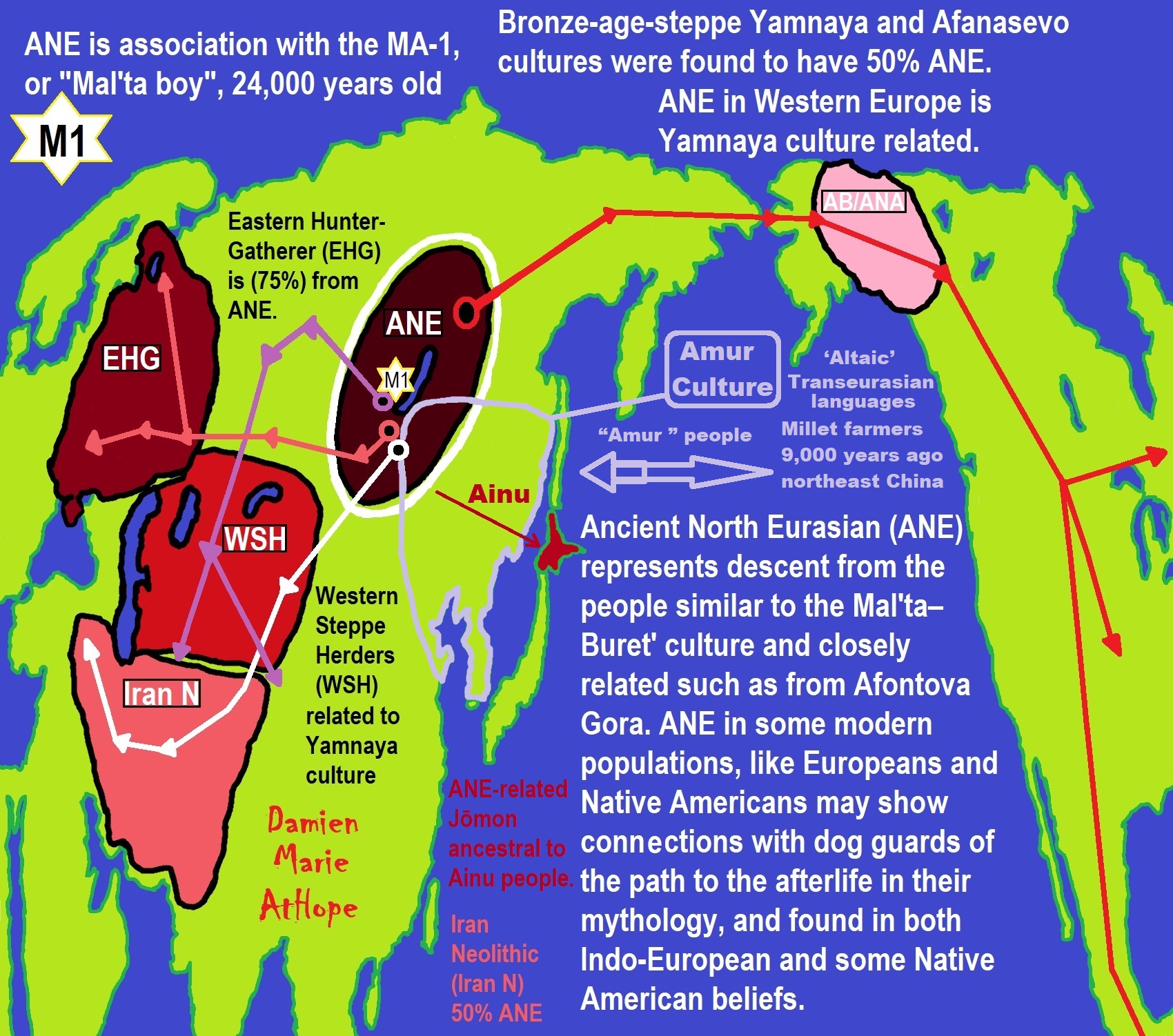
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
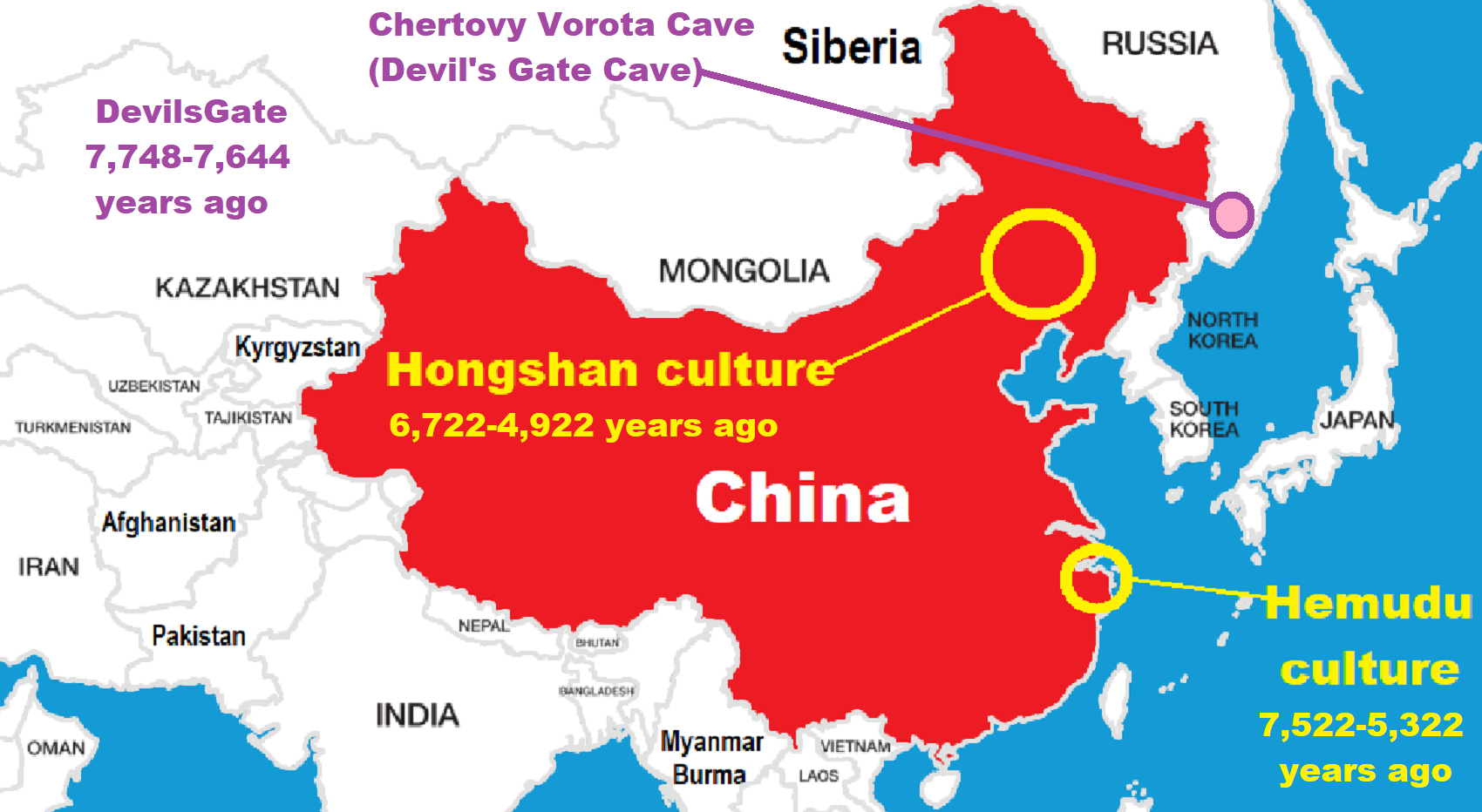
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
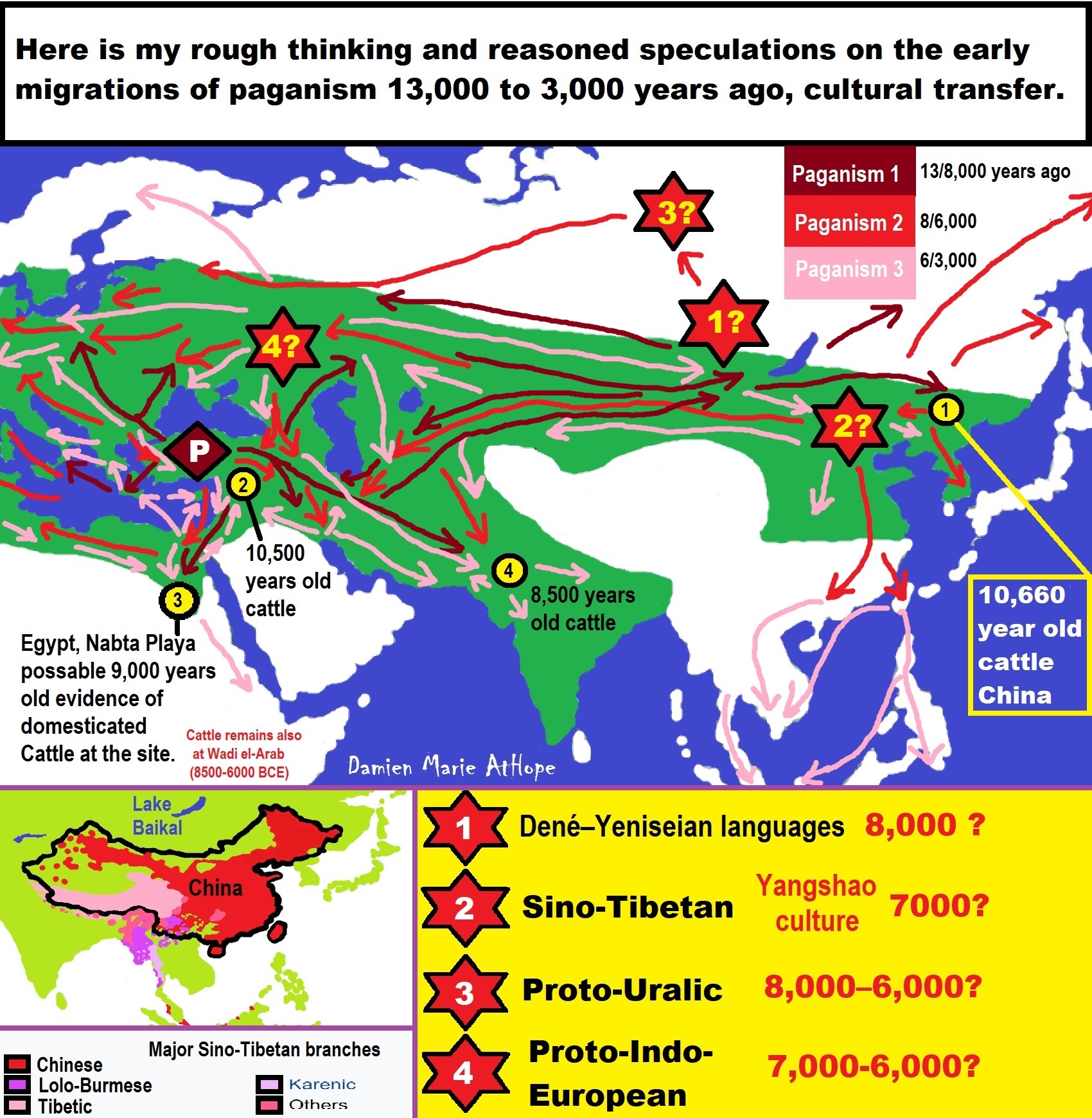
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
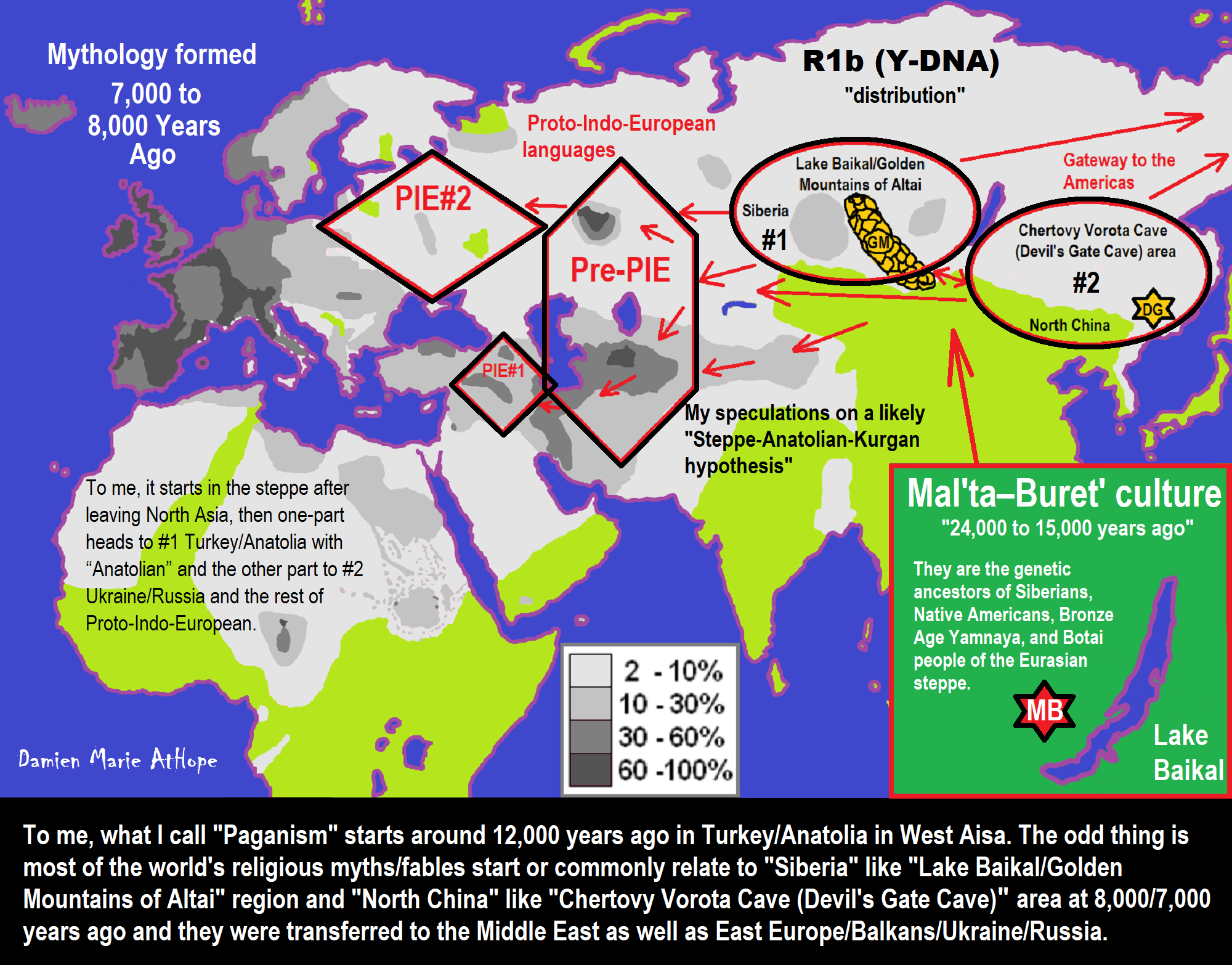
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
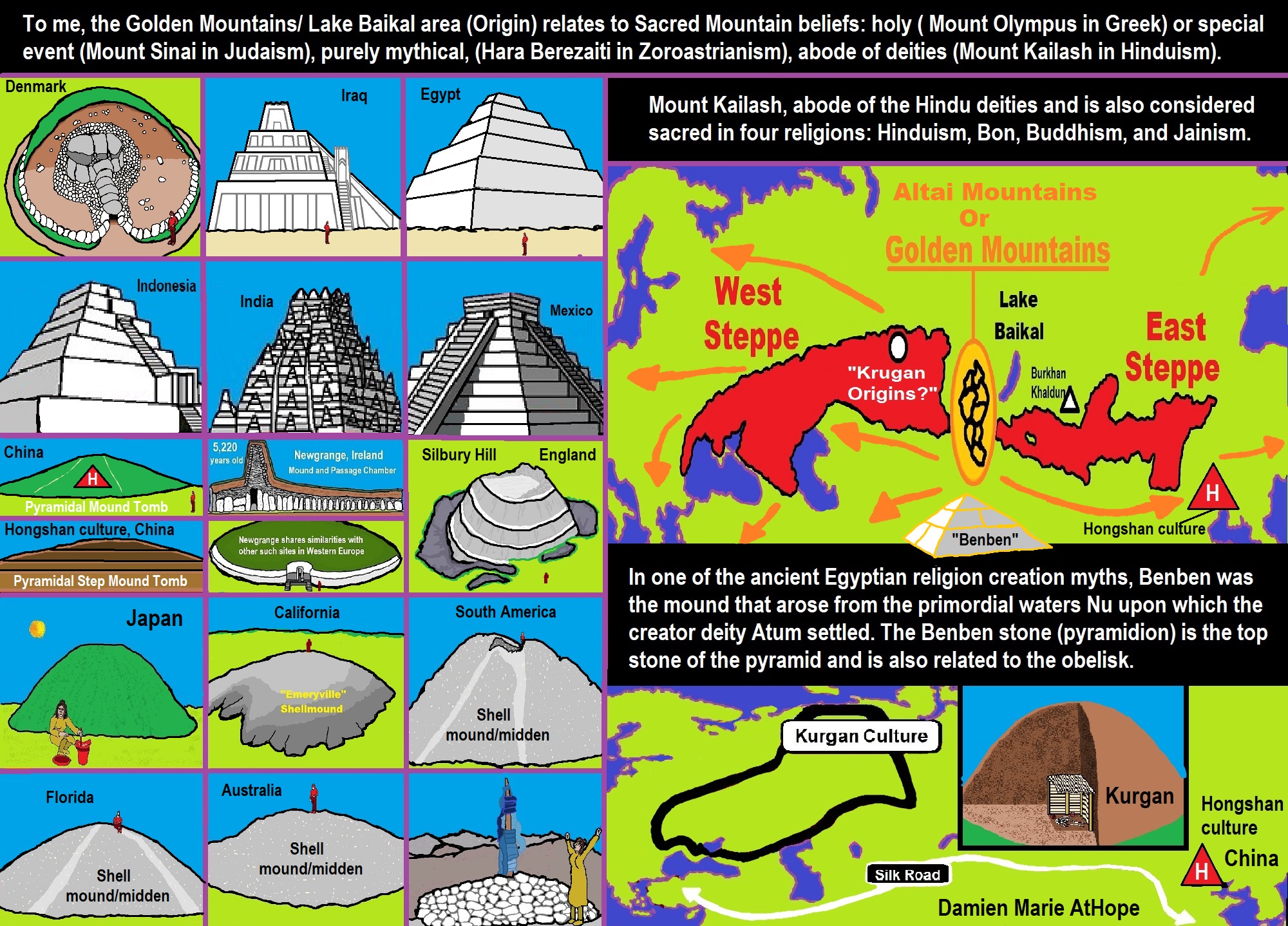
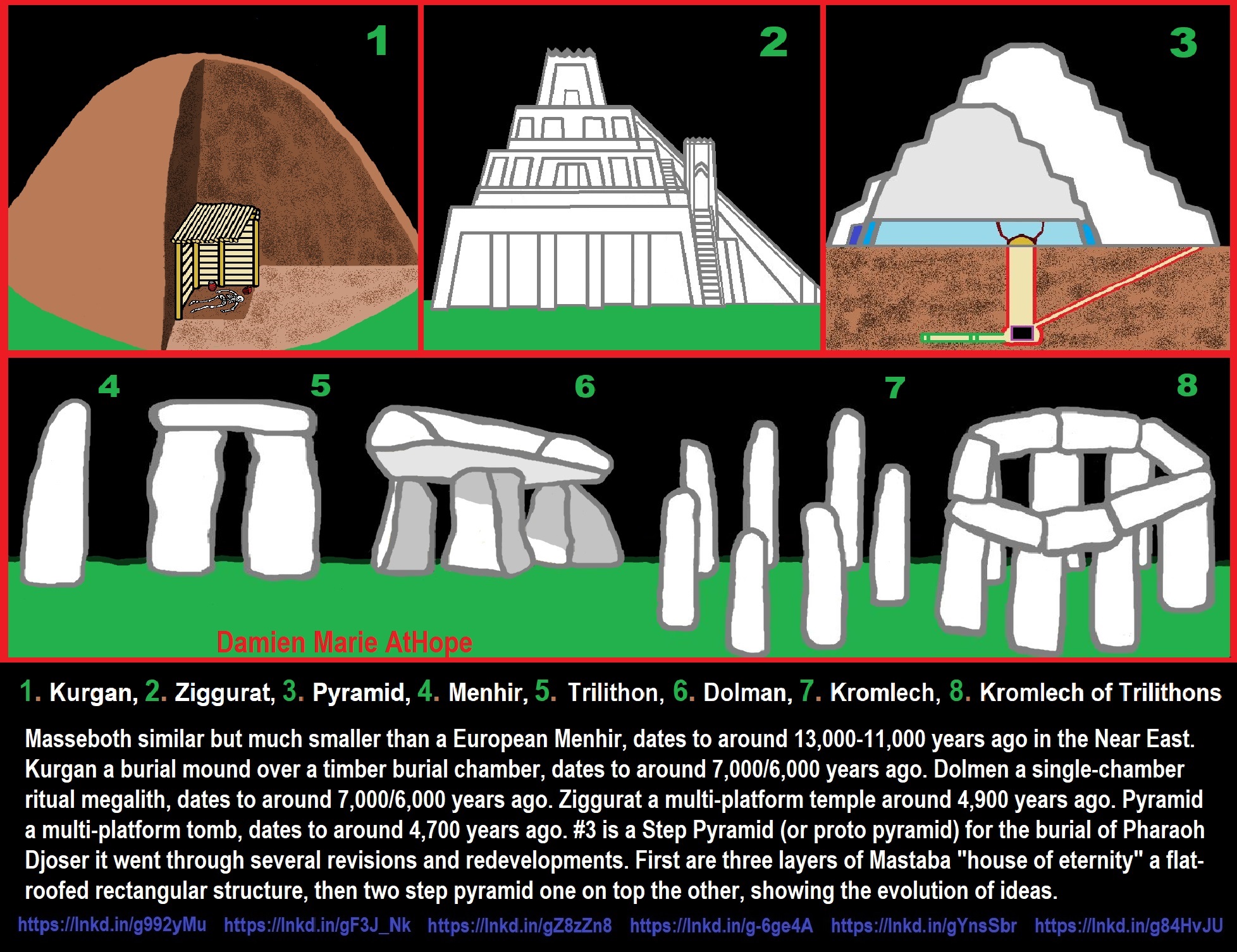
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
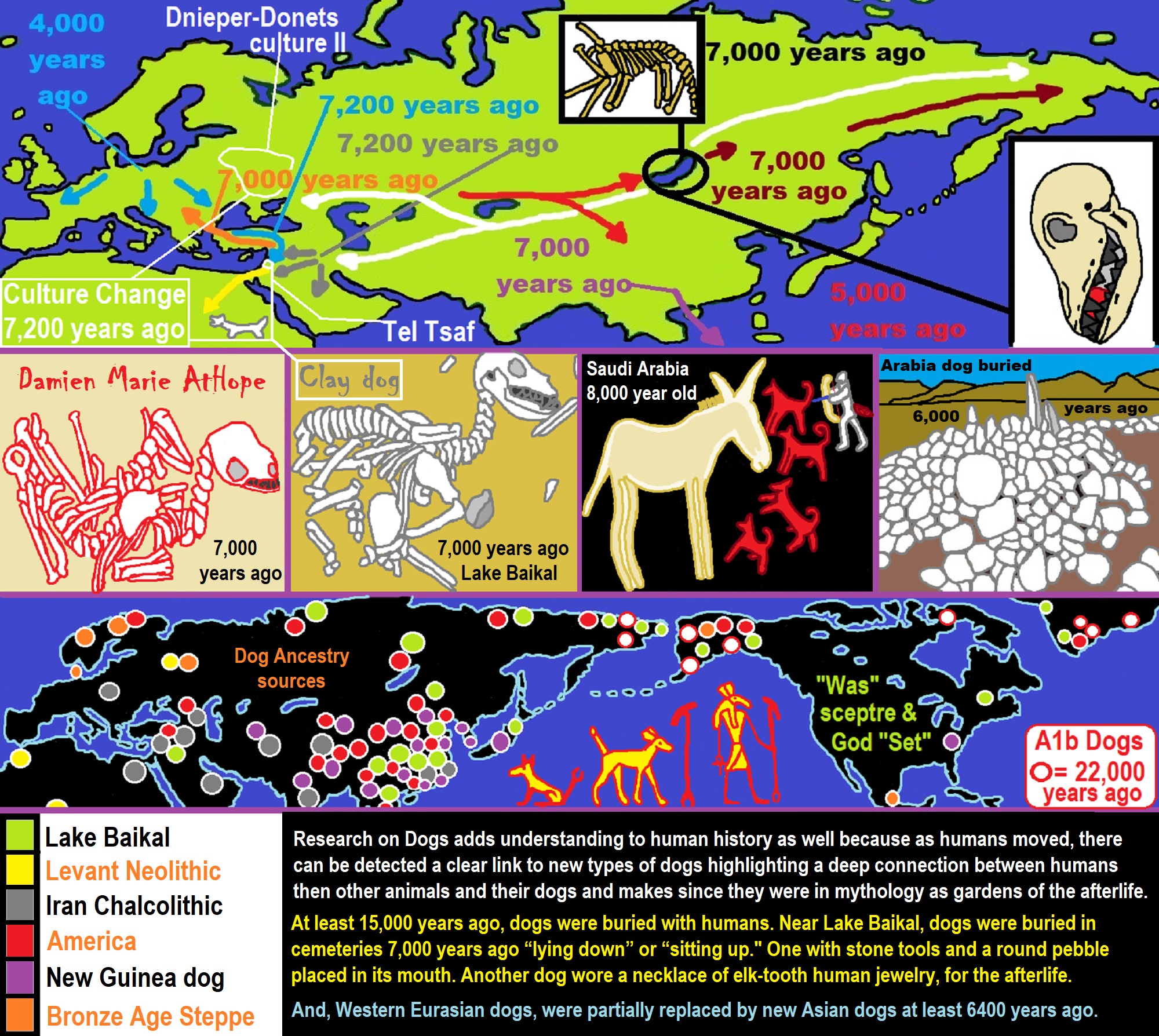
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
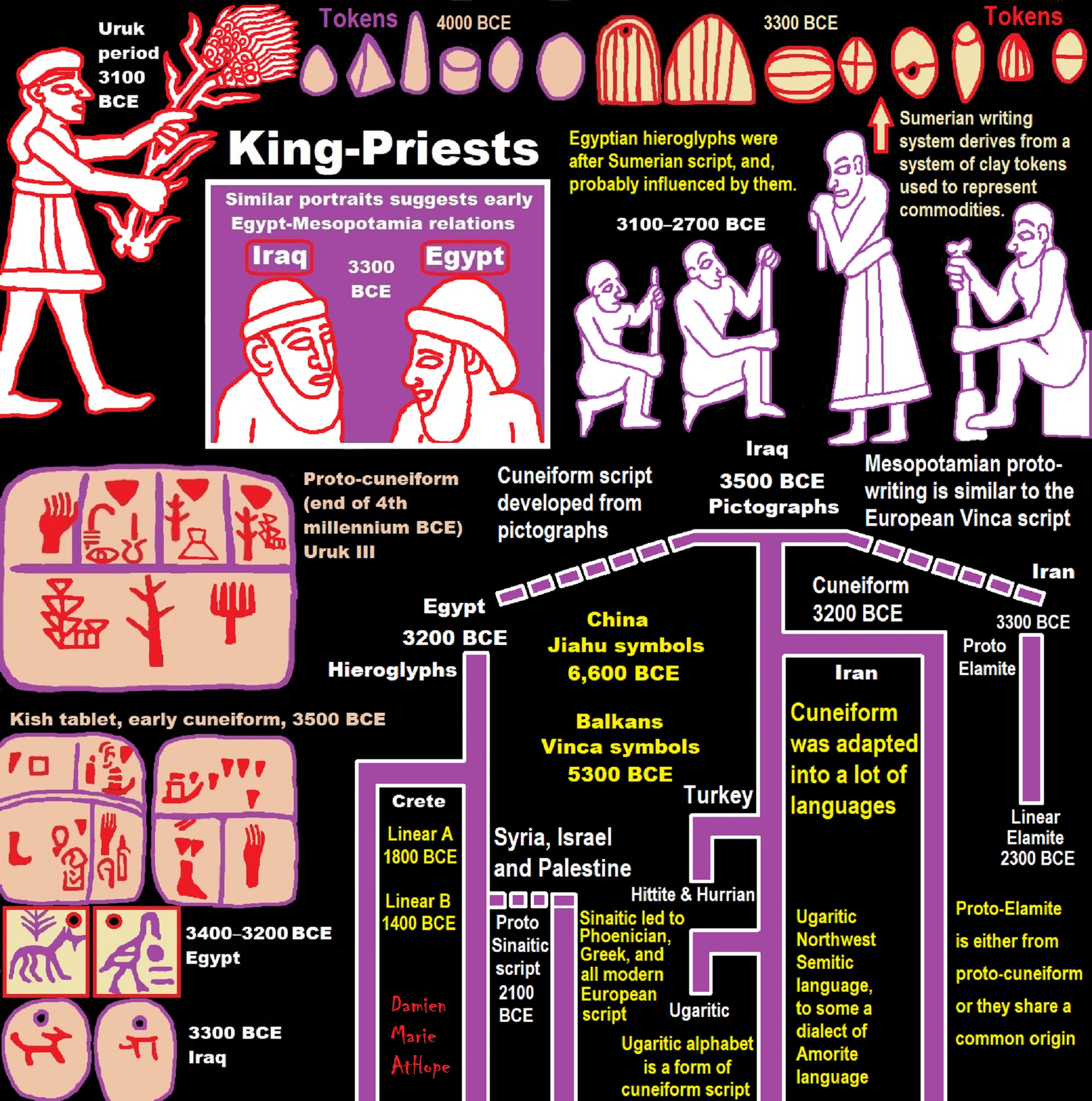
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
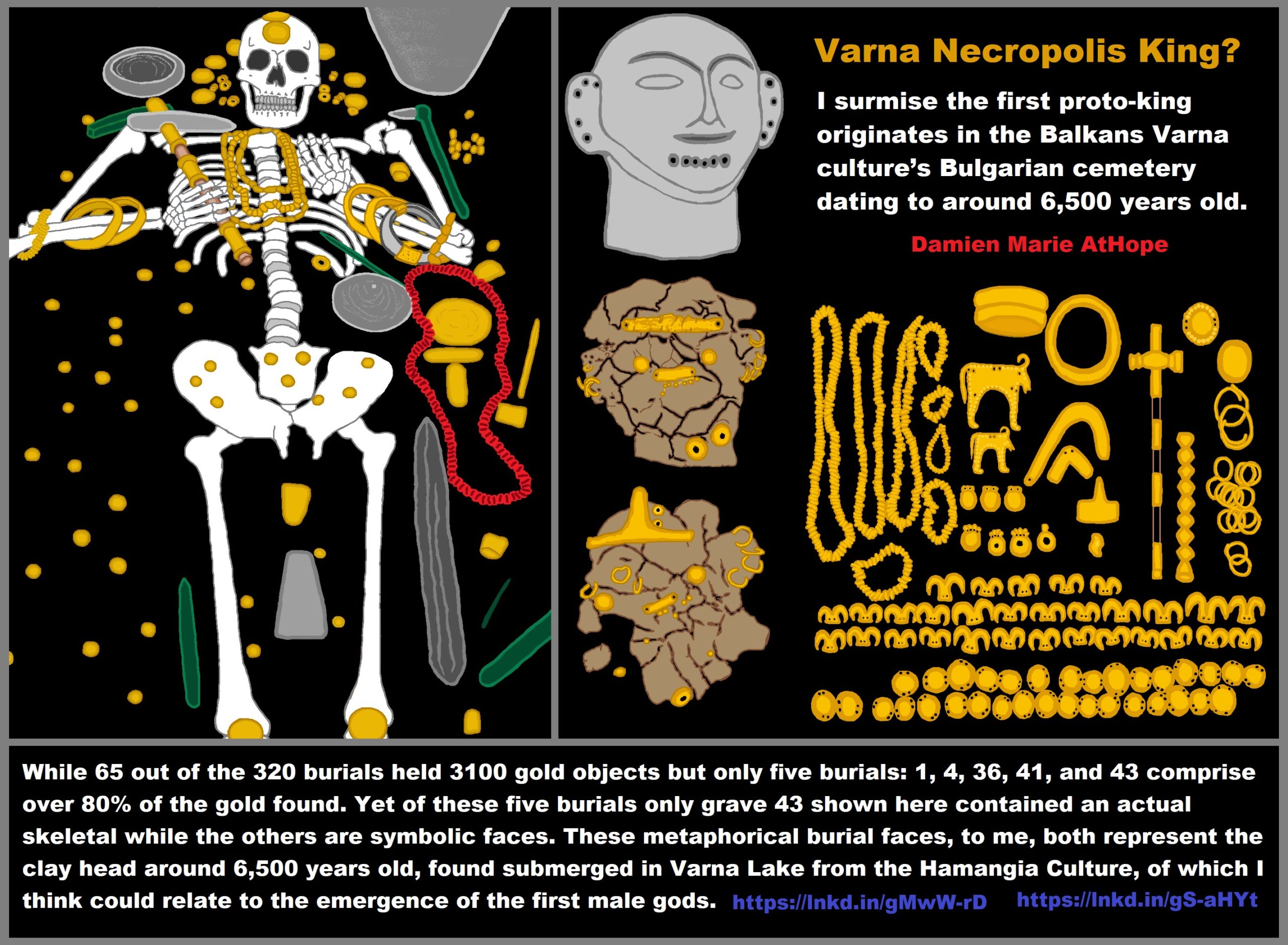
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
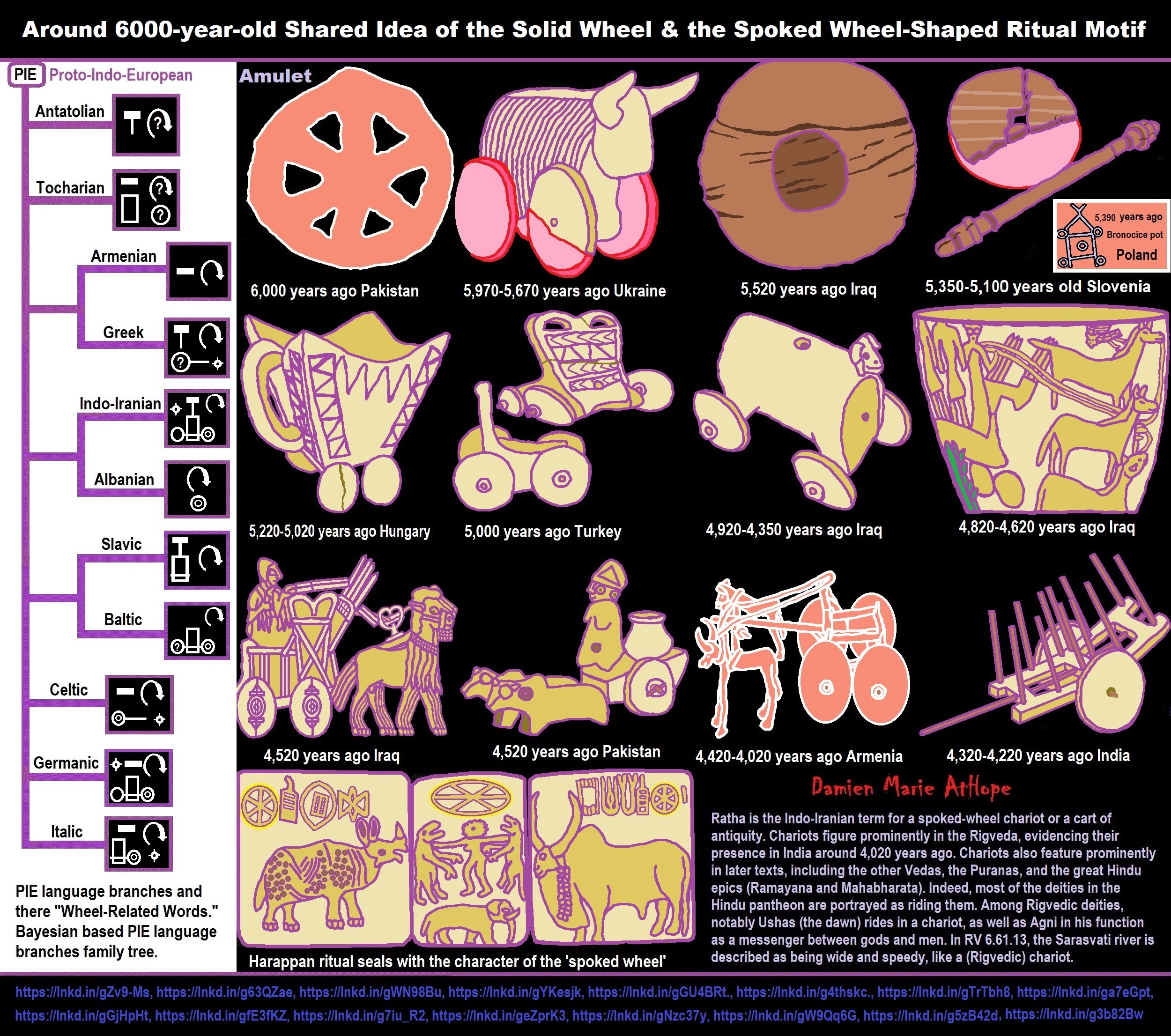
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
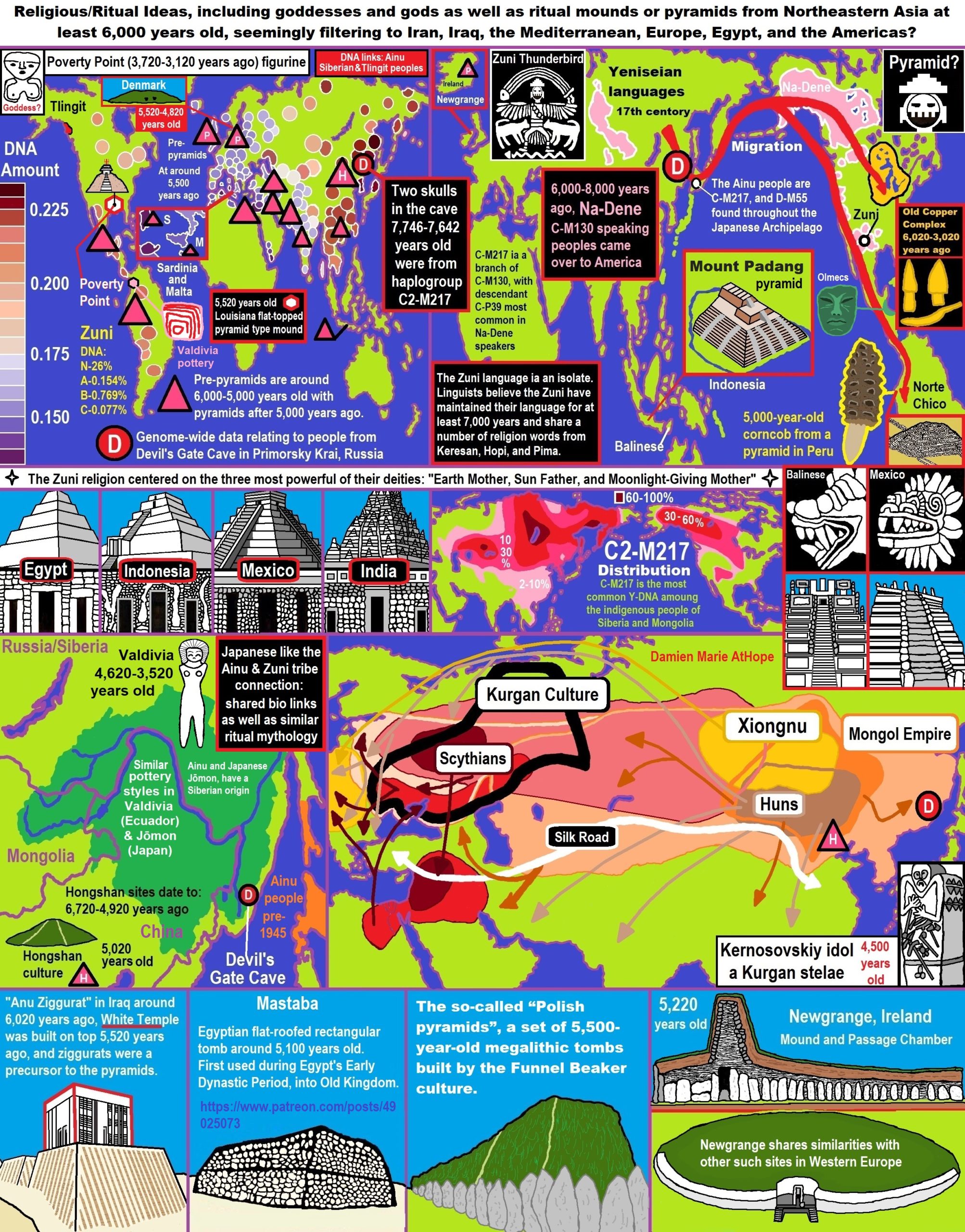
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
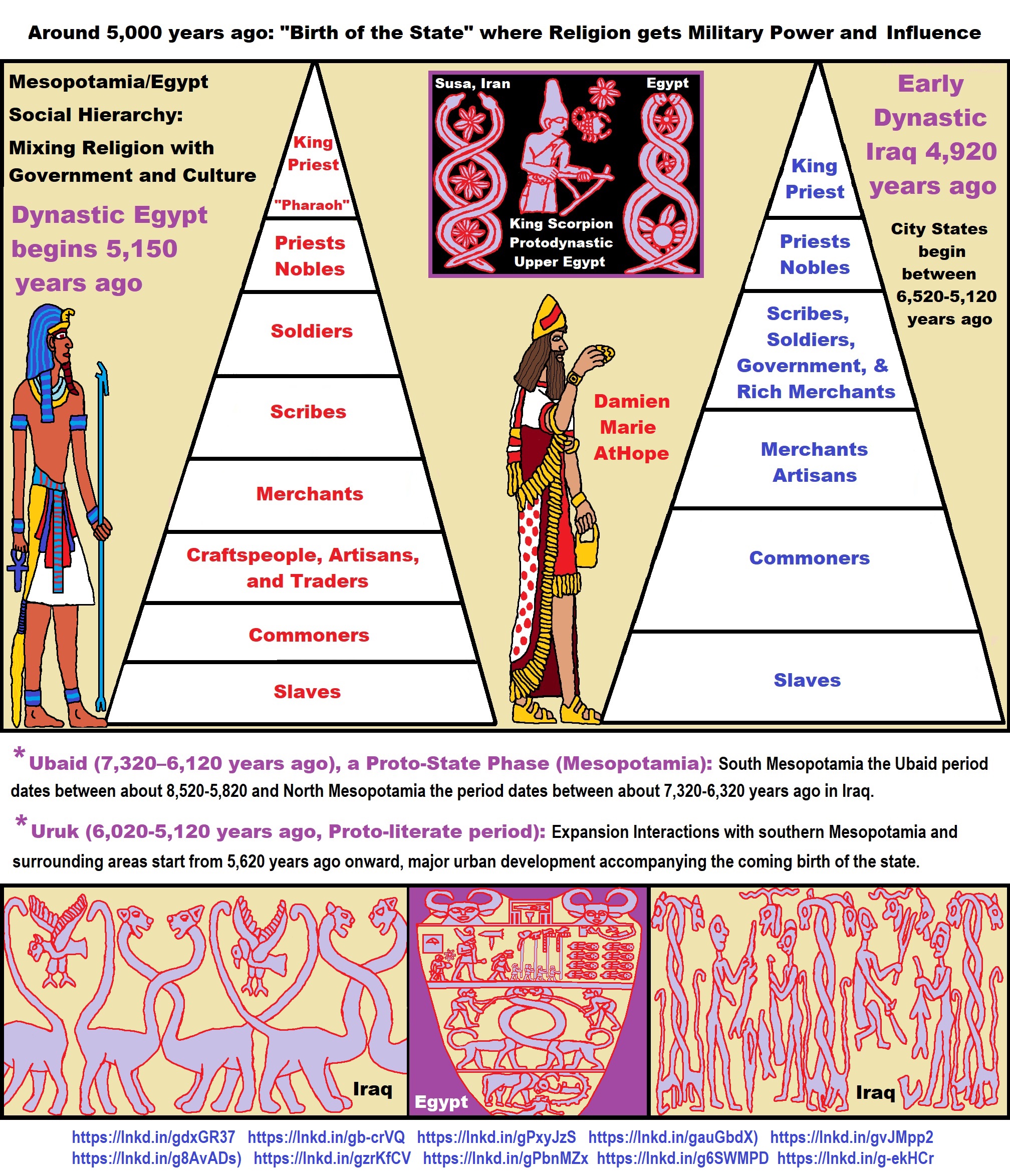
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
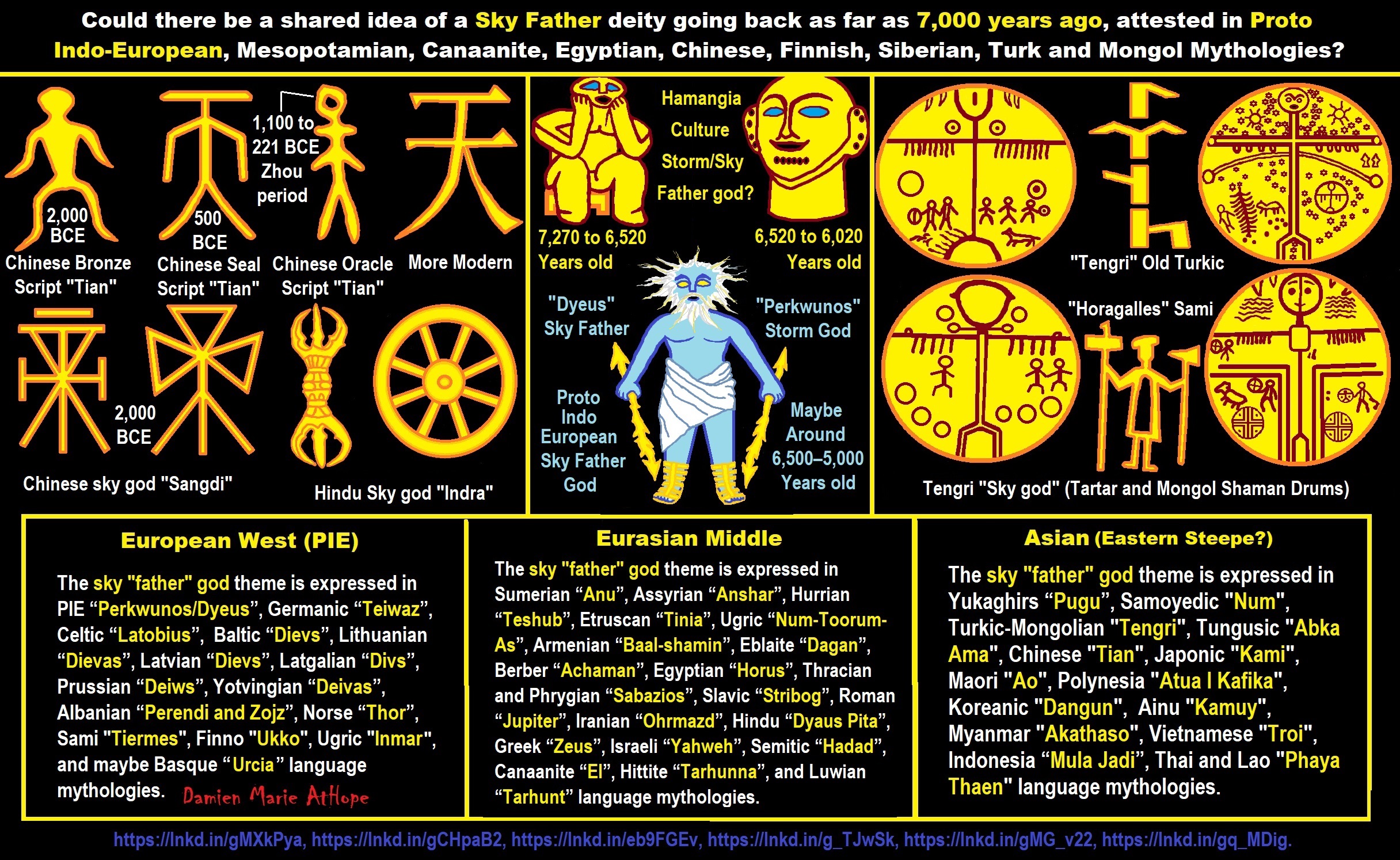
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
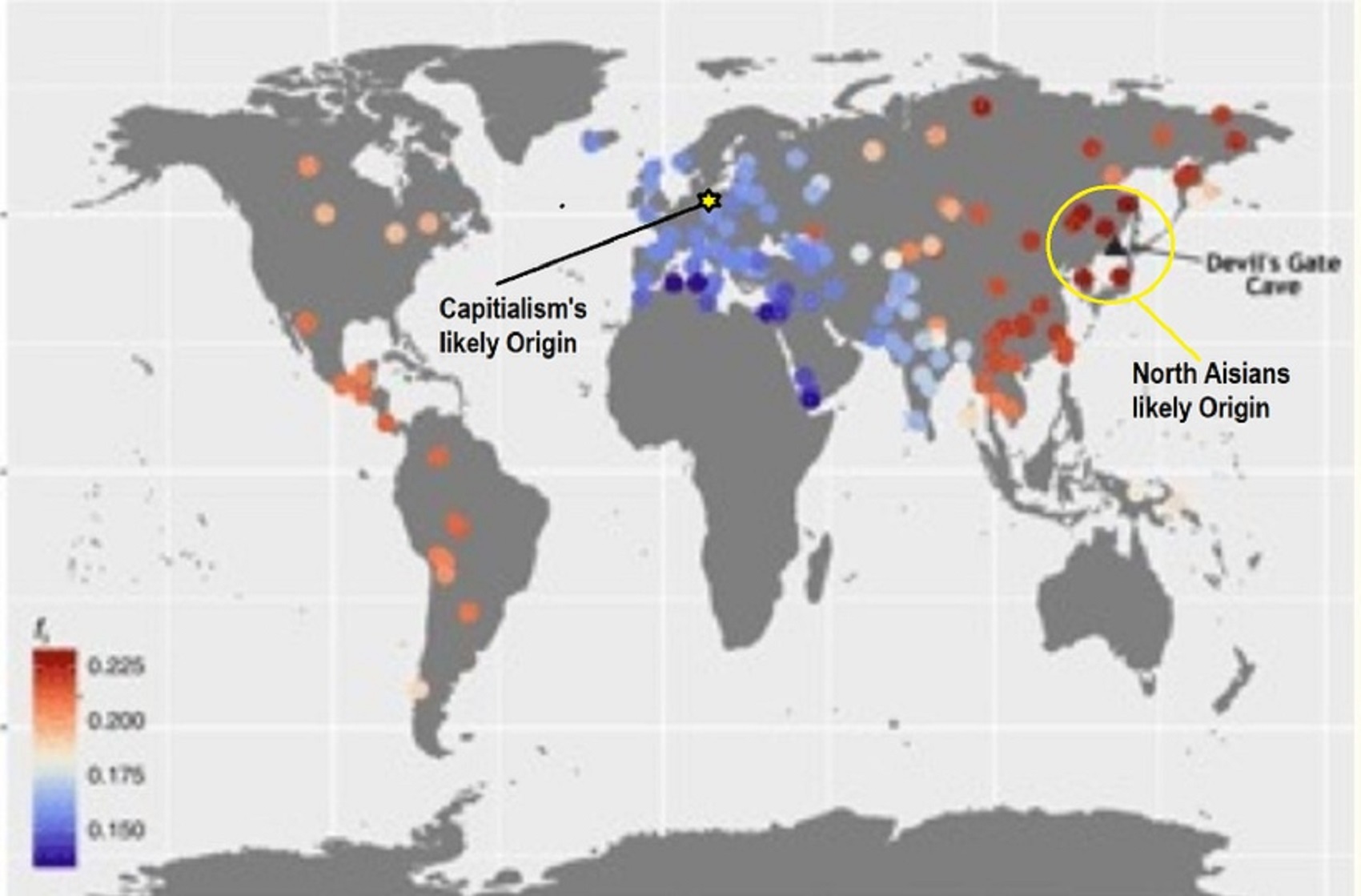
Pic ref
Abstract
“Ancient genomes have revolutionized our understanding of Holocene prehistory and, particularly, the Neolithic transition in western Eurasia. In contrast, East Asia has so far received little attention, despite representing a core region at which the Neolithic transition took place independently ~3 millennia after its onset in the Near East. We report genome-wide data from two hunter-gatherers from Devil’s Gate, an early Neolithic cave site (dated to ~7.7 thousand years ago) located in East Asia, on the border between Russia and Korea. Both of these individuals are genetically most similar to geographically close modern populations from the Amur Basin, all speaking Tungusic languages, and, in particular, to the Ulchi. The similarity to nearby modern populations and the low levels of additional genetic material in the Ulchi imply a high level of genetic continuity in this region during the Holocene, a pattern that markedly contrasts with that reported for Europe.” ref
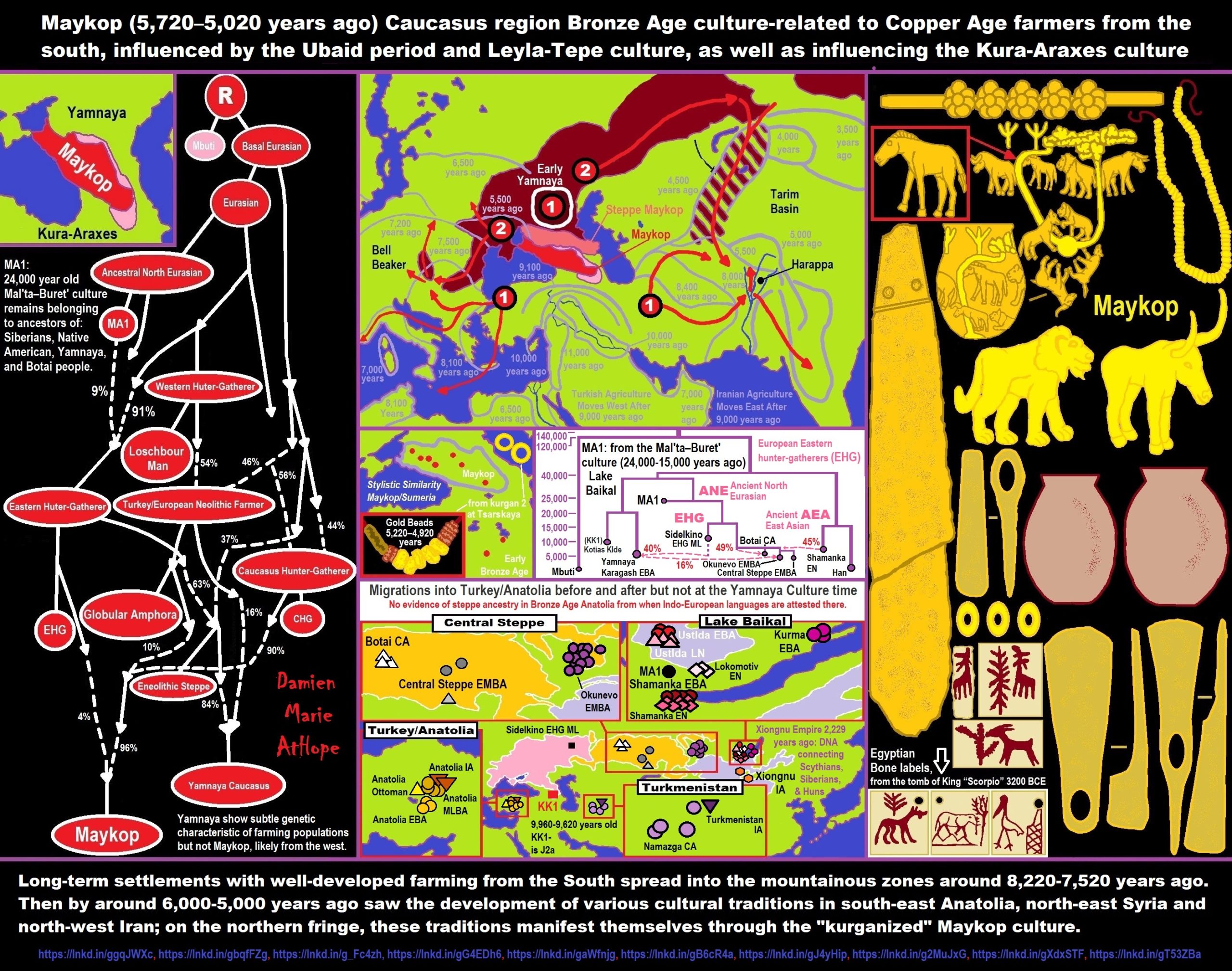
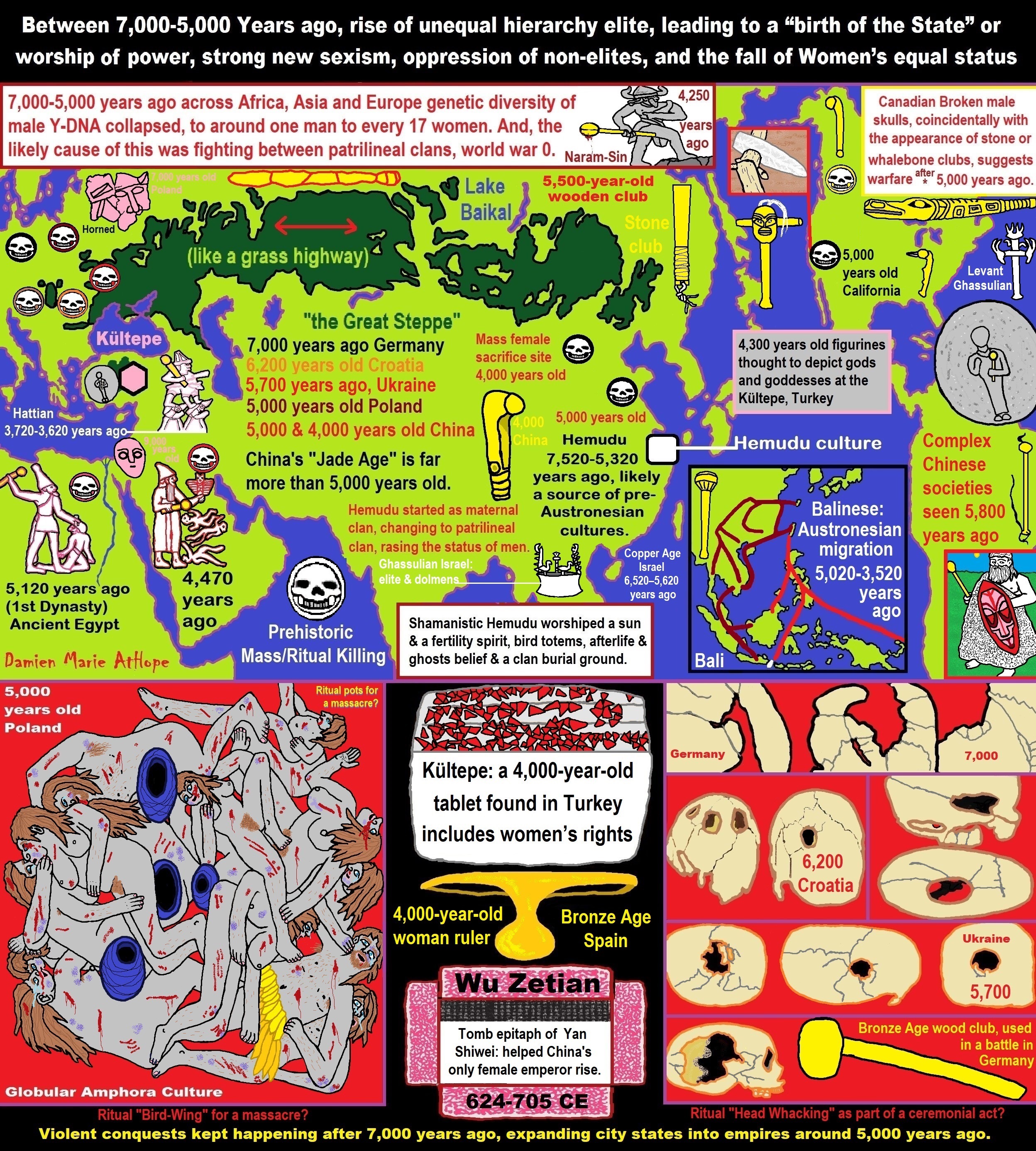
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
A First Male expression of a god?
I think so, and we see a lowering of the goddess that came before, as I believe, he now sits on her old birthing stool of power (sacred throne). To me, this represents the male and female duality and the first possible god sitting on a birthing stool to signify the male on the throne previously reserved only for women. I think the bent arms of both may possibly signify metaphoric “Bull Horns.” Part of the Hamangia culture (Romania and Bulgaria) between the Danube and the Black Sea and Muntenia in the south.
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
The Hamangia culture began around 7,250-7,200 years ago and lasted until around 6,550-6,500 years ago It was absorbed by the expanding Boian culture in its transition towards the Gumelnitsa. Its cultural links with Anatolia suggest that it was the result of a settlement by people from Anatolia, unlike the neighboring cultures, which appear descended from an earlier Neolithic settlement. ref
Goddess relating to the three realms: heaven, earth, and the underworld.
I surmise that there is an expression in goddess representation that relates to the three realms sky goddess with the upturned arms relating to the waxing crescent, the fat sitting goddess is a representation to the full moon and the arms turned down are a representation of the waning crescent. And it this way both up and down arms represent metaphorical bullhorns and why goddesses are associated with bulls or as bulls. Especially, with paganism.
My Thought on the Evolution of God?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Then Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago.
Several Kemetuic statuettes of goddesses with vulture-shaped heads and upraised arms are known from around 6,200-5,400 years ago. Ancient ivory amulet of a bearded man “phallus” from the Gerzeh culture. ref
The Colossus of Min Dynasty 0 (around 5,300 years ago). This big statue (in brown) is one of a pair found in the re-mains of the temple in Coptos in Upper Egypt. ref
Nagada, also known as Naqada, is the type site of the prehistoric Egyptian Amratian culture (“Naqada I”), Gerzeh culture (“Naqada II”), and Naqada III (“Dynasty 0”) predynastic cultures. Naqada existed before and during the union of Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, the Naqada III or “protodynastic” period. The process of unification apparently started from Nagada. ref

While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Eridu “Tell Abu Shahrain”)
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (King/Ruler Lugalzagesi)
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com