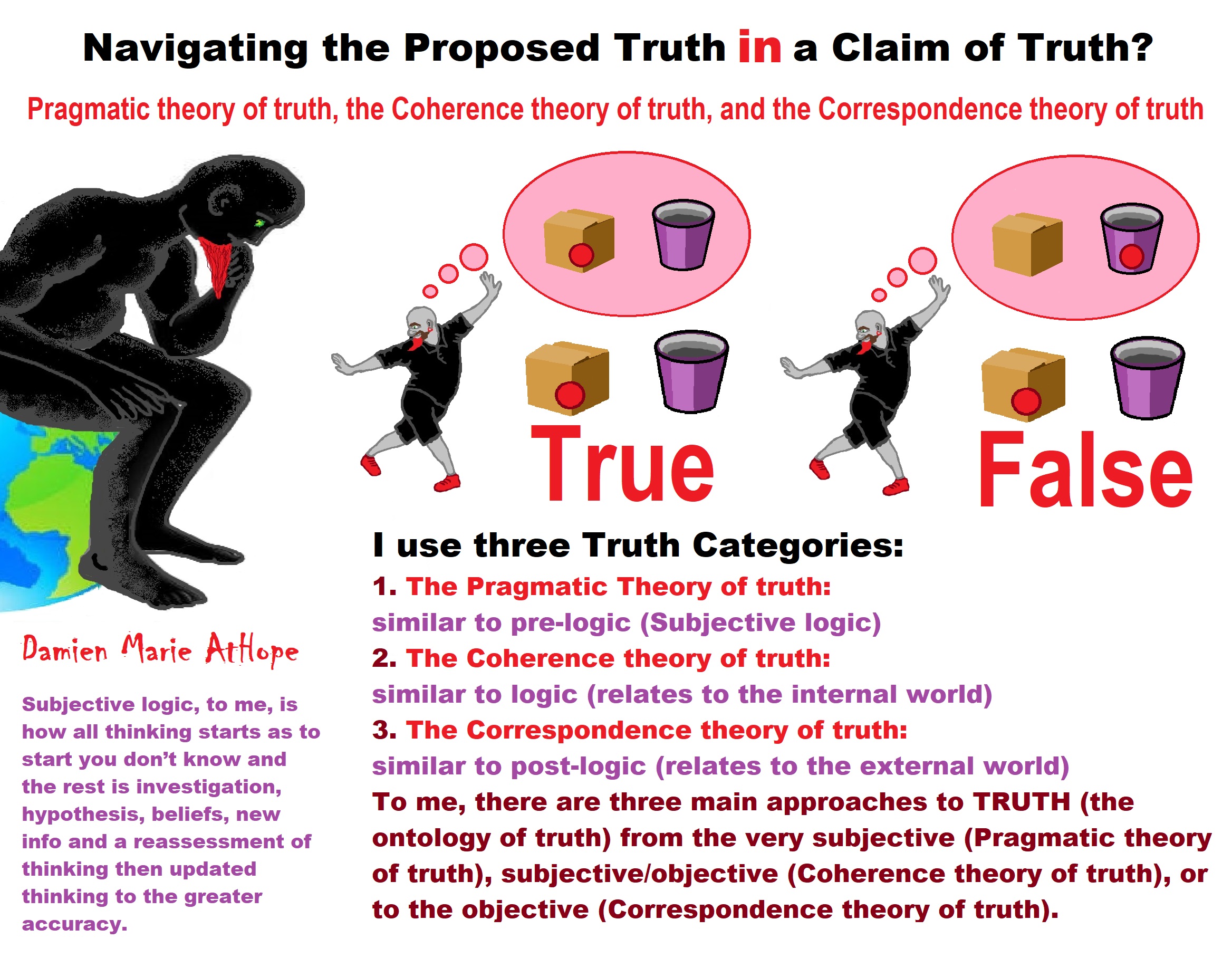

Grasping the Status of Truth (Ontology of Truth): pre-logic, logic, and post-logic?
- The Pragmatic Theory of truth: similar to pre-logic (Subjective logic)
- The Coherence theory of truth: similar to logic (relates to the internal world)
- The Correspondence theory of truth: similar to post-logic (relates to the external world)
Pragmatic Ethical/Axiology Driven Assumptions, Overcome the Weight of Solipsism Doubt
Words from a Friend: Marquis Amon
Subjective logic to me is reasoning that is in the pragmatic truth theory stage and or the internal truth theory stage of truth coherence. It can be used for problem-solving and it can also contain ideologies as well(internal truth theory context). It fails in the objective or reality stage of truth coherence(external truth coherence). In other words, it fails to get definitive real-world results because mostly, it doesn’t specifically seek it out. It also could contain thinking errors such as ideology versus reality, or misinterpreting data, ect. “How can you reach objective logic using only subjective logic.” (Paraphrasing you Damien AtHope.
Objective logic contains the pragmatic and internal aspects of thinking but also it works out the external, reality-based constituents of the issues. It still may contain thinking errors but it works in the direction of consciously trying to solve them.
You were speaking with someone who believed that cultural lifestyle should be put before humanism. The person claimed that cultural lifestyle is equal to humanism. It is not. Quite simply the objective stance says cultural lifestyle is acceptable so long as it does not harm to people.
One of the examples in the conversation was that it is acceptable to sacrifice people to gods, because people believe it is okay. This is flawed in objective reality. There are no gods and killing people outside of defense is wrong, period. Therefore people are dying for no real reason other than a very bad idea that is demonstrably wrong.
Unfortunately in our country even in modern times children have been denied medical care based on religious belief and died. As a humanist to deny any human medical treatment is unethical, period. It again is objectively wrong. I have no problem with sane adults refusing it but everyone should have the option, regardless of belief. Under no circumstance should anyone be denied it, it is a human right and doing otherwise is inhumane.
Next another example touched upon by Dawkins and Dennett, in particular, is a cultural lifestyle of tribes living in an antiquated lifestyle. It was argued that they are not spectacles to be observed for uniqueness. That they are equal humans that should be offered modern technology. Of course they shouldn’t be forced to accept it, but we are all humans on this planet and naturally interact with each other…It is part of life.
In short, universal ethics and humanism aren’t subjective, they are superior because their benefits clearly support humanity in reality. So as you address, all thinking starts with pre logic, I was using corresponding concepts to say that subjective logic is part of the pragmatic and internal truth coherence, I did not mean to say it was exclusive.
– Marquis Amon
Guest post: Atheism’s Conclusion by Rational Thinking” by Marquis Amon
Here is why “Reason is my only master”
The most Base Presupposition begins in reason. Reason is needed for logic (logic is realized by the aid of reason enriching its axioms). Logic is needed for axiology/value theory (axiology is realized by the aid of logic). Axiology is needed for epistemology (epistemology is realized by aid of axiology value judge and enrich its value assumptions as valid or not). Epistemology is needed for a good ontology (ontology is realized by the aid of epistemology justified assumptions/realizations/conclusions). Then when one possesses a good ontology (fortified with valid and reliable reason and evidence) they can then say they know the ontology of that thing. In a general way, all reality, in a philosophic sense, is an emergent property of reason, and knowing how reason accrues does not remove its warrant. Feelings are experienced then perceived, leading to thinking, right thinking is reason, right reason is logic, right logic is mathematics, right mathematics is physics and from there all science. Science is understanding what is, while religion is wishing on what is not. So, I think, right thinking is reason. Right reason is logic. Right logic, can be used for mathematics and from there we can get to science. And, by this methodological approach, we get one of the best ways of knowing the scientific method.
When assessing belief, one should think about reliabilism.
What is knowledge: reliabilism?
I usually try to use a reliabilism approach to epistemology, which emphasizes the truth-conduciveness of a belief-forming process, method, or other epistemologically relevant factors. The reliability theme appears in theories of knowledge, of justification, and of evidence. “Reliabilism” is sometimes used broadly to refer to any theory that emphasizes truth-getting or truth indicating properties. Ref We conceptualize epistemological attitudes and beliefs as components of meta-cognitive knowledge. As such, they serve an important function in regulating the use of epistemic strategies such as knowledge-based validation of information and checking arguments for internal consistency. Ref Epistemic Attitudes: Belief, Disbelief and Suspended Judgement. Here is an interesting but complicated article on this subject: Ref
Truth is a Value (axiological) Judgment.
Real Truth Seekers?
Authoritarian Truth Seekers and Anti-Authoritarian Truth Seekers?
To me “truth” is a value judgment we place as a label on what we believe is evidence. Thus, we should be compelled to validate the warrant to believe value judgment we label as “truth” is actually supported with valid and reliable reason and evidence.
Faith is the thinking error of assuming feelings demonstrate external evidence for made-up-magic of all kinds, the pseudoscience hopes of the indoctrinated, confused, or deluded. Faith is not reasoned thinking in the genuine prosses of trying to know things. Faith as processed though is the unthinking the faith drunk tend to do, rather, be a rationalist instead and reject thinking pathways to falsehood, like faith, which is literally like the glory hole of bad beliefs, so be willing to look and be a real truth seeker instead. Faith is evidence of mental intoxication because faith is basically the Gloryhole of bad unjustified beliefs as well as a profoundly inaccurate way to say one knows anything.
Faith is not a reasoned, be a rationalist willing to look and be a truth seeker.
Rise, my friend, come to the defense of truth.
This charge is required of all honest thinkers. I repeat, rise and let your voice be heard, as this not a time of slumber. No, this is a time of fighting for truth and a time where the truth is in much need as we are literally in a post-truth nation. Rise, become a truth-crusader and support truth in a world of lies.
Likelihood of “Truth,” the power behind any thought or belief being true or having a high likelihood of being true, is often limited to the weakest link in its reason and evidence. Therefore, truth is what can be trusted after surviving critical inquiry. What makes some believed Truth actually True? To me truth is a value judgment we place on what we think or believe is is evidence. Therefore, the rational imperative on us is to demonstrate that the proposed evidence or reasoned assumption is actually of a high epistemic standard with as much valid and reliable reason and evidence as possible from as credible a sore as possible which then makes some believed “Truth” actually worthy to be seen as Epistemologically True thus a “justified true belief”.
Broadly, epistemic means “relating to knowledge (itself) or to the degree of its validation” and epistemological means ” critical study of knowledge validity, methods, as well as limits to knowledge and the study or theory of various aspects of or involved in knowledge”. Truth or Lies? Religious people love to unjustifiablely claim truth but what they say does not correspond to the real world, nor does most of it have anything close to facts.
Some nonreligious people claim they don’t value truth because people can claim things true which are not, like the religious people do. So instead these nonreligious say they only use facts. To me the issue is not truth but that the religious are telling lies and have no right to call it truth. There is such thing as objective truth. But yes I feel truth is basically a value judgment we place on what we believe is evidence. The definition of “FACT” is something that actually exists, is reality or truth. A fact is something known to exist or to have happened. A fact is a truth known by “actual” experience or observation; such as something known to be true, containing the ontological qualities needed. A fact something said to be true or supposed to have happened. Dictionary on the word “fact”
I use the correspondence theory of truth, to help validate what I call truth. The correspondence theory of truth, states that the truth or falsity of a statement is determined only by how it relates to the world and whether it accurately describes (i.e., corresponds with) that world. The Correspondence Theory of Truth
A General Thinking in all My Epistemology Theorizing is Justificationism
By claiming to know something by faith is to act in a way mirroring a dishonest thinker, as intellectually honest thinkers don’t claim knowledge without justification.
In my paper “Constructing a Comprehensively Anti-justificationist Position” I expound and endorse anti-justificationism and contrast it with justificationism. In that paper, on pp. 120–123, I summarise the key components of justificationism in seven theses; an overview of that account is included here.
| (1) | Knowledge is defined as justified true belief |
Bartley takes this standard analysis to be the unique determining feature of justificationism. Justificationists think this real definition of knowledge is important and many of them are seriously troubled by examples which show that it is flawed. (If you are unclear about the difference between essentialist and abbreviatory definitions, look at my page on real and nominal definitions.)
| (2) | Knowledge is subjective |
The epistemological focus for justificationism is the knowledge that some individual or other has. There is, certainly, knowledge in this sense, but Popper has persuasively argued that it should not be the primary concern of epistemology; that should be objective knowledge.
| (3) | Knowledge is understood as being certain |
This has led many epistemologists to engage in what Popper, following Dewey, calls “the quest for certainty”. I write in my paper: “Anti-justificationists can have a lot of fun with any philosopher who claims that a particular class of statements or some specific proposition is certain and, therefore, immune from criticism, because, with a little effort, luck and creativity, it is possible to find a way of criticising any given statement.”
| (4) | Justificationists are much concerned by what counts as a justification |
In recent years the idea of justification has become increasingly important in analytical philosophy.
| (5) | Criticism is fused with justification |
Bartley was the first to realize this. He distinguished two ways in which such criticism can operate. In the first a theory is rejected if it cannot be justified from already justified statements and in the second a theory is rejected if it conflicts with justified statements.
| (6) | Some statements cannot be criticised |
A justification has to proceed from a collection of foundational statements that cannot themselves be justified logically. The collection of foundational statements, therefore, has to be thought of as being immune from criticism.
| (7) | Knowledge grows incrementally |
Knowledge is seen as growing in a non-evolutionary and non-revolutionary manner. This is because, if something is granted the status of knowledge, then, as it is certainly true, there is no way that it could turn out to be false. Once something is accepted as knowledge, it remains knowledge forever.
In my paper I also characterise anti-justificationism; if you click here this characterisation will open in a new browser window or tab, so that you can compare the two easily.
Reference
- Antoni Diller, “Constructing a Comprehensively Anti-justificationist Position”, in Ian Jarvie, Karl Milford and David Miller (eds.), Karl Popper: A Centenary Assessment, vol. II, Metaphysics and Epistemology, [London, Ashgate, 2006, ISBN 0-7546-5376-5], pages 119–129. This paper was presented at the Karl Popper 2002 Centenary Congress; a PDF version of it is available on this website, as is the original abstract. Note that the title of the abstract is slightly different from that of the published paper.
The Scientific Method and its Philosophy Axioms
Scientific Values: fallibilism, realism, & rationalism
Pragmatic theory of truth, Coherence theory of truth, and Correspondence theory of truth
Here is more on fallibilism:
Fallibilism applies that assessment even to science’s best-entrenched claims and to people’s best-loved commonsense views. Some epistemologists have taken fallibilism to imply skepticism, though, it is fallibilist epistemologists (which is to say, the majority of epistemologists) who tend not to be skeptics about the existence of knowledge or justified belief. Generally, those fallibilist epistemologists see themselves as thinking about knowledge and justification in a comparatively realistic way — by recognizing the fallibilist realities of human cognitive capacities, even while accommodating those fallibilities within a theory that allows perpetually fallible people to have knowledge and justified beliefs. Epistemologists generally seek to understand knowledge and justification in a way that permits fallibilism to describe a benign truth about how we can gain knowledge and justified beliefs. The difference between fallibilism and skepticism lies in their beliefs about what constitutes knowledge. Fallibilists and skeptics both believe that we can never establish the truth of a proposition with 100% certainty. However, skeptics believe that we don’t know what we cannot confirm with 100% certainty, while fallibilists have a more moderate view where 100% certainty is not required for knowledge. When I state “fallibilists and skeptics both believe that we can never establish the truth of a proposition with 100% certainty.””, what I as a thinker using Fallibilism, believe that we can never establish the truth of a proposition with 100% certainty is referring to how it could be later found to be in error and may need adapting to the increase in epistemic accuracy tempered with Epistemic Humility. We are 100% certain all the time (certainty is a belief state), what most who doubt 100% certainty, likely are referring to is our ability to validate a kind of certainty or level of certainty as there is not one universal thinking on certainty with the two main types being psychological certainty or Epistemic Certainty. Certainty is connected to a belief state or level of sureness, so we can be 100% psychologically certain of things we state normatively. As in If I or you take a piece of text and know things about it as in is it written in a language legible to the general group of english only speakers to know it is written in english, as well as many other things with 100% logically certain belief. But I am open to new information to prove some thinking could be found in error in some way need updating to a more accurate view as a general epistemic persuasion. Ref Ref
Rationalism and the Enlightenment
Rationalist thinkers vs Skeptic thinkers
If I made the statement that the following proposition was 100% true and certain today and for all time that,
“There is a chance that Damien AtHope will either reply or not reply to his posts on FB”
I think people like to only talk as if there is one type of certainty as a universal true class. When I hold that there are different kinds of certainty such as first needing to know what type of certainty that I am referring, as in what is expressed in this statement:
“There is a chance that Damien AtHope will either reply or not reply to his posts on FB”
This is a kind of normative statement so to me normative thinking standards apply. As such, we can know that I proposed an “hedge one’s bets trying to keep from being wrong by saying you believe two contrary propositions at the same time which could be an unintentional oddity but just as likely is used as a form of intellectual dishonesty involving a rhetoric claim used as a red herring evasion.” Moreover, with further understanding we can also know that by accepting such an openness to all possibilities, what it is telling us, beyond its not making an open strong opinion on one side in its options, other than the thinking logically certain that accepting all possible outcomes of a being’s behavior is also maybe unwittingly confirming a stance to all, the possible presuppositions hidden in that, or that it seems “hedge one’s bets” possibly trying to avoid the possibility of making a claim that offers a thinking that is outside of challenge may not work that well unless you accept the belief in the reality of a world with free agents or even unthinking agents doing the choosing. But believing in as well as epistemically certain about the reality of a world, is not doing anything that strange assuming a lot we all do all the time. But that’s the only thing we can do in a sense is unwittingly confirm a stance for the possible presuppositions hidden in much that we think or say as it seems we often express a belief in the reality of a world presupposition (which I believe we have extensive epistemic certainty, thus deserves 100% psychological certainty until shown otherwise.
What do you mean by god Evidence?
Atheistic Null Hypothesis: There is no God/Gods
Folk Logic: YOU CAN’T PROVE A NEGATIVE because you can PROVE A NEGATIVE
No there is No gods and No we are not a Brain in a Vat
In reality, the world is quite logical, tangible, and natural in how it operates although as it’s devoid of magic or mind it thus is unaware of its absurdity and cruelty. Reality is logical in that things are fixed there is not a person one day and a horse another day. Reality is logical and that is why it is predictable and quantifiable. Whereas in the religious mind, they seem to think the world is illogical, unreal, unnatural, filled with reality-defying magical dreams. Dreams in which their chosen made up reality supposedly operates with magic and mind (god or whatever) some claims even hold that this god or somethingism magic is fully aware of our perceivable reality’s absurdity and cruelty, as well as reportedly planned that our “proven” reality was meant to be this way. And though that may sound thrilling to some such ridiculousness is not in evidence in our true rational “naturalistic” reality devoid of all magic or mind.
Wisdom as Epistemic Humility?
When would skepticism NOT be reasonable?
Knowledge can be classified in several ways. Firstly, it can be either explicit (self-conscious) or implicit (tacit, hidden from self-consciousness). Secondly, it can be either propositional or non-propositional (something which cannot be represented by propositions, e.g. knowing how to do something?).
Simply the scientific method requires certain a priori assumptions of epistemology and metaphysics in order to even get out of the starting gate. It assumes you are not a brain in a vat. The scientific method means that supernatural entities or concepts that are meaningless or logically contradictory cannot be included in a scientific hypothesis (not least because you can’t put a sample of a god in a test-tube). Consequently, when carrying out investigations scientists assume a position of methodological naturalism.
The idea that scientific evidence can disprove the notion of god is scientific realism. Scientific realism is also a priori rationalism about the accepted natural reality of nature. The point is a thing cannot validate itself science accepts what is reasoned, it may forget the philosophy it uses and cannot live without but it is still there. I can reasonably likewise assume a priori rationalism about the natural world that has no rational validity to a supernatural being called god.
“The Hammer of Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
Scientific knowledge
To be scientific the knowledge must be
. communicable: It is something which is discussed.
. general: generalized vs. separate fragments of knowledge
. conceptual: represented by concepts vs. intuitive ideas (i.e. explicit and propositional knowledge)
. true or probable
. argumented: It can be proved or demonstrated.
The scientific methods should also fill some criteria, which try to guarantee quality of scientific knowledge. (These are important and quite permanent part of the general paradigm of science):
. progressive: knowledge base is expanded by using this method
. self-correcting: the errors get corrected by this method.
. publicity: arguments are public for anyone
. justifiable: the arguments are satisfactory
BETWEEN NATURALISM AND RATIONALISM
My Methodological Skepticism Style
Philosophical Skepticism, Solipsism and the Denial of Reality or Certainty
“String theory, the multiverse and other ideas of modern physics are potentially untestable. At a historic meeting in Munich, scientists and philosophers asked: should we trust them anyway? And, as many in Munich were surprised to learn, falsificationism is no longer the reigning philosophy of science. Massimo Pigliucci, a philosopher at the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, pointed out that falsifiability is woefully inadequate as a separator of science and nonscience, as Popper himself recognized. Astrology, for instance, is falsifiable — indeed, it has been falsified ad nauseam — and yet it isn’t science. Physicists’ preoccupation with Popper “is really something that needs to stop,” Pigliucci said. “We need to talk about the current philosophy of science. We don’t talk about something that was current 50 years ago.” Nowadays, as several philosophers at the workshop said, Popperian falsificationism has been supplanted by Bayesian confirmation theory, or Bayesianism, a modern framework based on the 18th-century probability theory of the English statistician and minister Thomas Bayes. Bayesianism allows for the fact that modern scientific theories typically make claims far beyond what can be directly observed — no one has ever seen an atom — and so today’s theories often resist a falsified-unfalsified dichotomy. Instead, trust in a theory often falls somewhere along a continuum, sliding up or down between 0 and 100 percent as new information becomes available. “The Bayesian framework is much more flexible” than Popper’s theory, said Stephan Hartmann, a Bayesian philosopher at LMU. “It also connects nicely to the psychology of reasoning.” Gross concurred, saying that, upon learning about Bayesian confirmation theory from Dawid’s book, he felt “somewhat like the Molière character who said, ‘Oh my God, I’ve been talking prose all my life!’” Another advantage of Bayesianism, Hartmann said, is that it is enabling philosophers like Dawid to figure out “how this non-empirical evidence fits in, or can be fit in.”” Ref
My “Methodological Rationalism” approach
Basics of my Methodological Rationalism Epistemology Approach
Truth Navigation: Techniques for Discussions or Debates
by Lawrence Lerner
It is standard intelligent design creationist jargon to deliberately confuse and misuse the terms ontological (philosophical) naturalism andmethodological naturalism. The former is the view that nothing supernatural exists – a point which may engender heated debate among theologians and philosophers but is irrelevant to the pursuit of science. Methodological naturalism is not a “doctrine” but an essential aspect of the methodology of science, the study of the natural universe. If one believes that natural laws and theories based on them will not suffice to solve the problems attacked by scientists – that supernatural and thus nonscientific principles must be invoked from time to time – then one cannot have the confidence in scientific methodology that is prerequisite to doing science. The spectacular successes over four centuries of science based on methodological naturalism cannot be gainsaid. On the other hand, a scientist who, when stumped, invokes a supernatural cause for a phenomenon he or she is investigating is guaranteed that no scientific understanding of the problem will ensue. Here is an example. Let us imagine a geocentrist astronomer in the era of Newton. Newton uses his dynamics to account for the perturbation of the elliptical orbit of Mars around the Sun due to the gravitational influence of Jupiter, and cranks out numbers that are quickly verified by astronomical observation. The entire exercise makes no sense to the geocentrist, who (a) on the basis of the central importance of mankind in the eyes of God, does not grant the ellipticity of the orbit of Mars around the Sun but insists that the Earth be the center of the universe; (b) insists that the orbits of the planets (and the Sun) are guided by angels. The intelligent design creationist arguments may be couched more subtly and elusively than this geocentric view, but they are of the same kind. As for the phraseology, “not designed,” there is here a slipping around the need to define the term “design.” Living things certainly have organs and systems that are best described in terms of Aristotle’s “final cause” – that is, the function which their form enables them to accomplish. But design can mean either of two things. It can mean the form itself, without reference to the way that the form came to be. No one doubts that the wings of birds are admirably designed to the function of flight, in this sense of design. What the intelligent design creationists are after, however, is the other meaning of design – the end-product of the work of a designer. Intelligent design creationists often hide the essentially theological nature of this meaning by insisting that the designer might have been some space aliens and not the God of their scriptures. But they do not maintain this position when addressing sympathetic church groups of their own or similar persuasion. Ref
More on Methodological naturalism
|
“”If a philosopher or social scientist were to try to encapsulate a single principle that yoked together the intellectual process of [civilization], it would be a gradual dismantling of presumptions of magic. Brick by brick, century by century, with occasional burps and hiccups, the wall of superstition has been coming down. Science and medicine and political philosophy have been on a relentless march in one direction only — sometimes slow, sometimes at a gallop, but never reversing course. Never has an empirical scientific discovery been deemed wrong and replaced by a more convincing mystical explanation. (“Holy cow, Dr. Pasteur! I’ve examined the pancreas of a diabetic dog, and darned if it’s NOT an insulin deficiency, but a little evil goblin dwelling inside. And he seems really pissed!”) Some magical presumptions have stubbornly persisted way longer than others, but have eventually, inexorably fallen to logic, reason and enlightenment, such as the assumption of the divine right of kings and the entitlement of aristocracy. That one took five millennia, but fall it did. —Gene Weingarten
|
|
The majority of scientists do not believe it is possible to combine methodological naturalism with theistic or supernatural philosophical belief systems. Even in the United States, a majority of scientists embrace full philosophical naturalism — although a significant minority (40%-45%) describe themselves as “theistic evolutionists” or hold other religious beliefs. Methodological naturalism has become an important buzz word in the culture wars with the anti-science movement. The battle hinges around intelligent design and creationism advocates who claim the theory of evolution is a religion. The modern form of this started with Phillip Johnson and his publication of Darwin on Trial where he not only created a list of repeatedly refuted creationist claims but also tried to put forward the idea that teaching evolution was a violation of the establishment clause of the United States Constitution. Johnson’s main argument centered around confounding philosophical naturalism and methodological naturalism and claiming that teaching evolution was an endorsement of philosophical naturalism and thus impinged on the religious beliefs of students. Eugenie Scott described Johnson’s error in her review:
While Johnson and the creationists may have started the ball rolling it is the intelligent design advocates that have really embraced the rhetoric surrounding the evils of methodological naturalism. The Discovery Institute (“DI”) as the primary public relations firm for “ID” has been beating this drum in every possible direction. The DI claims many things all at once, and the fact that they may contradict each other never seems to bother them. They just like to throw a bunch of bullshitout there and see what sticks. They claim that:
All of these arguments together are pretty self-defeating, but they are also wrong individually. Methodological naturalism is a cornerstone of science, embraced by both practitioners and philosophers of science. There is always disagreement in philosophy, and that includes philosophy of science. The fact that intelligent design doesn’t talk about the designer is a major hit against it as a hypothesis, and it certainly doesn’t save it from violations of methodological naturalism. The value of methodological naturalism comes from the ability to quantify, measure, and study the causes of phenomena. Intelligent design removes our ability to predict, measure and quantify, whether the intelligent designer is supernatural or an alien. The questions that evolution answers are rooted as firmly in empirical evidence and methodological naturalism as any other science. Arguments that claim it is not are really holdover ideas from creationists, who like to claim that unless it’s directly observed in a laboratory, “it’s not science”. Sometimes the DI likes to mix in issues of morality and ethics, and claims evolution address those questions, but this is simply the naturalistic fallacy. Finally, the last argument that evolution is a religion is the same old Johnson argument — all over again — that Scott and others have had to address ad nauseum. Ref |
This article was originally published in Philo, Vol. 3, No. 2 (Fall-Winter 2000), pp. 7-29.
SCIENTIFIC VIEWS OF NATURALISM
Since methodological and philosophical naturalism are founded upon the methods and findings, respectively, of modern science, philosophical naturalism is bound to take into account the views of scientists. As Hilary Kornblith asserts, “Philosophers must be … modest … and attempt to construct philosophical theories which are scientifically well informed.” Arthur Strahler, a geologist who has taken particular interest in the claims of supernaturalists to be able to supersede naturalistic explanations of the world, points out the essentiality of naturalism to science: The naturalistic view is that the particular universe we observe came into existence and has operated through all time and in all its parts without the impetus or guidance of any supernatural agency. The naturalistic view is espoused by science as its fundamental assumption.” Clearly, the first statement refers to philosophical naturalism. Strahler’s point in the second statement, however, is that science must operate as though this is true. So philosophical naturalism serves minimally as a regulative, or methodological, principle in science, for the following reasons given by Strahler: [S]upernatural forces, if they can be said to exist, cannot be observed, measured, or recorded by the procedures of science—that’s simply what the word “supernatural” means. There can be no limit to the kinds and shapes of supernatural forces and forms the human mind is capable of conjuring up “from nowhere.” Scientists therefore have no alternative but to ignore the claims of the existence of supernatural forces and causes. This exclusion is a basic position that must be stoutly adhered to by scientists or their entire system of evaluating and processing information will collapse…. To find a reputable scientist proposing a theory of supernatural force is disturbing to the community of scientists. If the realm of matter and energy with which scientists work is being influenced or guided by a supernatural force, science will be incapable of explaining the information it has collected; it will be unable to make predictions about what will happen in the future, and its explanations of what has happened in the past may be inadequate or incomplete. This is clearly a methodological objection to supernaturalism on Strahler’s part. Introducing supernatural explanations into science would destroy its explanatory force since it would be required to incorporate as an operational principle the premise that literally anything which is logically possible can become an actuality, despite any and all scientific laws; the stability of science would consequently be destroyed. While methodological naturalism is a procedural necessity for science in its study of the natural world, it is also the rule for philosophical naturalism since the naturalist world view is constrained—and thereby stabilized—by methodological naturalism. Strahler ventures onto the turf of philosophical naturalism when he points out how supernaturalism’s lack of methodology renders it metaphysically sterile, in effect pointing out the inseparable connection between epistemology and metaphysics: In contrasting the Western religions with science, the most important criterion of distinction is that the supernatural or spiritual realm is unknowable in response to human attempts to gain knowledge of it in the same manner that humans gain knowledge of the natural realm (by experience)…. Given this fiat by the theistic believers, science simply ignores the supernatural as being outside the scope of scientific inquiry. Scientists in effect are saying: “You religious believers set up your postulates as truths, and we take you at your word. By definition, you render your beliefs unassailable and unavailable.” This attitude is not one of surrender, but simply an expression of the logical impossibility of proving the existence of something about which nothing can possibly be known through scientific investigation. Although I am generally in agreement with Strahler, I differ with him on one point. Although it is logically impossible to prove the existence of something about which nothing can be known at all, it is not logically, but procedurally, impossible to prove the existence of something about which nothing can be known through scientific investigation. Scientific investigation is a procedure based on an empiricist epistemology. The fact that there is no successful procedure for knowing the supernatural does not logically preclude its being known at all, i.e., through intuition or revelation. The problem is that there is no procedure for determining the legitimacy of intuition and revelation as ways of knowing, and no procedure for either confirming or disconfirming the supernatural content of intuitions or revelations. My objection notwithstanding, Strahler is making an essential point which the philosophical naturalist also makes: the methodology of science is the only viable method of acquiring reliable knowledge about the cosmos.
Given this fact, if there is no workable method for acquiring knowledge of the supernatural, then it is procedurally impossible to have knowledge of either a supernatural dimension or entity. In the absence of any alternative methodology, the metaphysical claims one is entitled to make are very strictly limited. The philosophical naturalist, without making any metaphysical claims over and above those warranted by science, can demand from supernaturalists the method that legitimizes their metaphysical claims. In the absence of such a method, philosophical naturalists can not only justifiably refuse assent to such claims, but can deny—tentatively, not categorically—the existence of the supernatural, and for the same reason they deny the existence of less exalted supernatural entities like fairies and ghosts: the absence of evidence. Strahler makes another point that is important to the understanding of philosophical naturalism: the metaphysical adequacy of supernaturalism is inversely proportionate to the explanatory power of science. The more science successfully explains, the less need or justification there is for the supernatural as an explanatory principle. Strahler, quoting E. O. Wilson, asserts that the explanatory power of science diminishes the metaphysical adequacy of supernaturalism by explaining even religion: Most importantly, we have come to the crucial stage in the history of biology when religion itself is subject to the explanations of the natural sciences … sociobiology can account for the very origin of mythology by the principle of natural selection acting on the genetically evolving material structure of the human brain. If this interpretation is correct, the final, decisive edge enjoyed by scientific naturalism will come from its capacity to explain traditional religion, its chief competitor, as a wholly material phenomenon….
However, many people reject the application of scientific method to the phenomenon of religion and, though they adopt the methodology of naturalism to inquire about a natural entity or object or to solve a practical problem, they simultaneously assent to existential claims about the supernatural. Sterling Lamprecht, in Naturalism and the Human Spirit, says that some philosophers “accept a kind of empiricism for purposes of scientific procedure and practical affairs, but all the time hold that the existences and occurrences thus empirically found require some further ‘explanation’ to make them ‘satisfactory’ or ‘intelligible.’” These philosophers hold that what is learned scientifically must still be explained from within a more comprehensive, non-naturalistic metaphysics, in effect adopting the supernatural as a causal explanation. Strahler, however, in his remarks about using the supernatural as a causally explanatory principle while simultaneously acknowledging the sufficiency of scientific method to provide causal explanations of the natural world, maintains that using the supernatural as an additionalcausal explanation is logically contradictory as well: A specific event of history in a specific time segment must fall into either (a) divine causation or (b) natural causation. Our logic is as follows: ‘If a [divine, supernatural causation], then not b [natural causation]. If b, then not a.’ To follow with the proposal ‘Both a and b‘ is therefore not logically possible. Moreover, one cannot get out of this bind by proposing that God is the sole causative agent of all natural causes, which in turn are the causative agents of the observed event.
This ‘First Cause/Secondary Cause’ model, long a standby of the eighteenth-century school of natural theology … adds up to 100 percent supernatural creation. Consider the analogy of cosmic history as an unbroken chain [of causal explanations] made from all possible combinations of two kinds of links, a [supernatural cause, as in religion] and b [natural cause, as in science]…. When a theist declares any link in the chain to be an a-link (whereas all the others are b-links), an element of the science set has been replaced by an element of the religion set. When this substitution has been accomplished, the entire ensuing sequence is flawed by that single antecedent event of divine creation and must be viewed as false science, or pseudoscience. The reason that replacement of a single link changed the character of all ensuing links is that each successor link is dependent upon its predecessor in a cause-effect relationship … that divine act can never be detected by the scientist because, by definition, it is a supernatural act. There exists only the claim that such an act occurred, and science cannot deal in such claims. By the same token, science must reject revelation, as a means of obtaining empirical knowledge. Under the theistic model, according to Strahler, any recognition of natural causation is logically nullified by the simultaneous assertion of supernatural intervention, either actual or merely possible.
Even while differing with Strahler on the logical impossibility of invoking both natural and supernatural explanations—it is logically conceivable if the supernatural and natural causes operate at different ontological levels—one must recognize that invoking supernatural explanations is illegitimate because of the procedural impossibility of ascertaining the facticity of the supernatural cause itself, not to mention its intervention in the chain of natural causes. This points to the metaphysical implications of methodological naturalism: if supernatural causal factors are methodologically permissible, the cosmos one is trying to explain is a non-natural cosmos. Conversely, if only natural causal factors are methodologically and epistemologically legitimate as explanations, then only a naturalist metaphysics is philosophically justifiable. Let us consider now the comments of Wesley Elsberry, in “Enterprising Science Needs Naturalism”: While the subjective appreciation of a role for supernatural causation may be important to personal fulfillment, it does not afford a basis for objective knowledge, nor can it be counted as a means of comprehending the universe in a scientific manner…. I will connote “naturalism” as “proposing only natural mechanisms for physical phenomena” rather than “asserting that only natural mechanisms have existence.”… Science is incompetent to examine those conjectures which cannot be tested in the light of inter-subjective experience or criticism.
The assertion that “only natural mechanisms have existence” is equivalent to the claim that “no supernatural causes exist.” That is an example of proving a negative, and can only be regarded as a statement of faith, since it requires omniscience on the part of the claimant…. humans cannot establish a supernatural cause by experimental reproduction of that cause. No human is capable of producing a supernatural cause…. natural and supernatural causation are confounding: suspected supernatural causation may simply be due to currently indiscernible natural causes. Because of the confounding nature of the interaction, the only way to establish supernatural causation is through the elimination of all natural alternatives. This is simply another case of proving a negative, which is an intractable problem…. Elsberry’s point is a methodological one: in explaining the natural world, one can not invoke the supernatural because of its methodological inaccessibility, and no successful method other than the naturalistic one is available in scientific explanation. However, Elsberry’s methodological point has metaphysical implications. If supernatural causation as a methodological principle “does not afford a basis for objective knowledge,” the implication is that methodological naturalism does afford one.
If supernatural causation cannot be “counted as a means of comprehending the universe in a scientific manner,” the implication is that methodological naturalism can be so counted upon. And comprehending the universe in a scientific manner is the goal of philosophical naturalism. Steven Schafersman, also a scientist, makes the same point as Elsberry: [N]aturalism is a methodological necessity in the practice of science by scientists, and an ontological necessity for understanding and justifying science by scientists…. The alternative to naturalism is supernaturalism…. [T]he foundations of science … will not be epistemologically reliable unless naturalism is either true or assumed to be true, since by not doing so, part of reality will remain unexplained and unexplainable. Schafersman’s point here is that, given the (procedurally but not logically) necessary exclusivity of methodological naturalism in science, any view of the cosmos other than a naturalistic one becomes unjustifiable.
The philosophical naturalist would expand upon this by adding that given the procedurally necessary exclusivity of methodological naturalism in science and the unavailability of any other workable method for grounding any claims with existential import, any metaphysical view of the cosmos other than the naturalistic one is epistemologically unjustifiable. The point is not that supernaturalism is logically impossible; rather, the point is that, from both an epistemological and a methodological standpoint, supernaturalism has not proved its mettle, whereas methodological naturalism has done so consistently and convincingly. Supernaturalism has not provided the epistemology or the methodology needed to support its metaphysics, whereas naturalism has, although the invitation to supernaturalism to do likewise is a standing one, as Schafersman indicates: “except for humans, philosophical naturalists understand nature to be fundamentally mindless and purposeless….
Of course, this doesn’t eliminate the possibility of supernatural mind and purpose in nature; the only requirement would be the demonstration of its existence and mechanism, which is up to the supernaturalist to provide. We are still waiting.” Ref
THE THINKER’S GUIDE TO SCIENTIFIC THINKING
By DR. RICHARD PAUL and DR. LINDA ELDER
Based on Critical Thinking Concepts & Principles
Why Scientific Thinking? The Problem: Everyone thinks; it is our nature to do so. But much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uninformed, or down-right prejudiced. Yet the quality of our life and that of what we produce, make, or build depends precisely on the quality of our thought. Shoddy thinking is costly, both in money and in quality of life. Excellence in thought, however, must be systematically cultivated. A Definition: Scientific thinking is that mode of thinking — about any scientific subject, content, or problem — in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skillfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them. The Result: A well cultivated scientific thinker: • raises vital scientific questions and problems, formulating them clearly and precisely; • gathers and assesses relevant scientific data and information, using abstract ideas to interpret them effectively; • comes to well-reasoned scientific conclusions and solutions, testing them against relevant criteria and standards; • thinks open-mindedly within convergent systems of scientific thought, recognizing and assessing scientific assumptions, implications, and practical consequences; and • communicates effectively with others in proposing solutions to complex scientific problems. Scientific thinking is, in short, self-directed, self-disciplined, self-monitored, and self-corrective. It presupposes assent to rigorous standards of excellence and mindful command of their use. It entails effective communication and problem solving abilities as well as a commitment to developing scientific skills, abilities, and dispositions. Ref
Fibonacci sequence as scientific evidence of a creator?
That is not accurate in any way… Challenging Claims?
You can’t change people, by reason and evidence. WRONG, I do it all the time.
Challenged or Challenging? (questions of ontology)
Critical or Analytical Thinking and Suspension of Judgment, Disbelief or Belief
Grasping the status of truth (ontology of truth)
Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology argument/challenge protocol
“The Hammer if Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
The Evolution of Religion and Removing the Rationale of Faith
I personally try to use what is most reliable and the most accurate. I generally use in one way or another: Scientific Realism, Metaphysical Naturalism, Rationalism, Empiricism, Methodological Skepticism, Justificationism, Correspondence Theory of Truth, Falsafacationism, Falabalism, Reliabilism, Probabilism, and Probability Theory. Pretty much all the methods that used by the scientific method. I use the many methods that are also employed by the scientific method, which is not one thing but a group of things used in succession so its not a one method to me its a group of methods that I also use so your question then is not about my use as they are also used in the scientific method. I use them as they add to the accuracy in thinking and evidence generation and validation they are a priori tools for validation. Most if not all tools at their root will be pragmatic axioms use as they are what we have that works. I use my hammer of truth to know things that are true from that which is untrue. my hammer of truth involves three epistemological tools Questioning the ontology: “the philosophical study of the nature of being, becoming, existence, or reality, as well as the basic categories of being and their relations.” this is part of a hypothesis, testing the assumption of its truth and will be involved in the conclusion.
Ontology delineation: unpack and lay bare WHAT is being said, assumed or believed and is this valid and reliable in a reasonable amount, expression and or qualities.
Epistemology deconstruction: unpack and lay bare WHY it is being said, assumed, or believed and is this valid and reliable in a reasonable amount, expression, and or qualities.
Axiology discrediting: unpack and lay bare HOW it is being said, assumed, or believed and is this valid and reliable in a reasonable amount, expression, and or qualities.
Address Thinking (Ontology): Identity what they are talking about, investigate its thingness, its beingness, its purpose, how it works and question the elements that would be involved and their thingness, beingness, and purpose.
Then Analyze Thinking (Epistemology): Identify how they can claim to know what they think they know, as well as its detailed information, assumptions, implications, and challenge their belief etiquette on what they claim is their way of acquiring what they say they believe or know, in addition to when and how they claimed to know.
Last Assess Thinking (Axiology): Identify how they can claim worth, value, accuracy, relevance, depth, significance, logic, reason, justification, warrant, and fairness of what they think they know. This refers to the assessment of thinking or supposed evidence and is a value judging stage in the systematic inquiry which is challenging the quality of what is being offered.
The Critical Thinking Skills Cheatsheet [Infographic]
Critical thinking skills truly matter in learning. Why? Because they are life skills we use every day of our lives. Everything from our work to our recreational pursuits, and all that’s in between, employs these unique and valuable abilities. Consciously developing them takes thought-provoking discussion and equally thought-provoking questions to get it going. Begin right here with the Critical Thinking Skills Cheatsheet. It’s a simple infographic offering questions that work to develop critical thinking on any given topic. Whenever your students discover or talk about new information, encourage them to use these questions for sparking debate and the sharing of opinions and insights among each other. Together they can work at building critical thinking skills in a collaborative and supportive atmosphere. Ref
Grasping the status of truth (ontology of truth): “To say there is no difference in truth from #1 being full truth and #16 with almost no truth at all, is to not use reality for one’s thinking on truth.“







Science is quite the opposite of just common sense.
“Common sense is presumptive and at best basically a form of Naïve realism“
“Science is Methodological and at best basically a form of Scientific realism“
As a rationalist, I want you to deeply think and not just simply doubt.
“Scientific realism is a positive epistemic attitude towards the content of our best theories and models, recommending belief in both observable and unobservable aspects of the world described by the sciences.” Ref
“Scientific realism is, at the most general level, the view that the world described by science is the real world as it is, independent of what it might be taken to be. Within philosophy of science, it is often framed as an answer to the question “how is the success of science to be explained?” The debate over the success of science in this context centers primarily on the status of unobservable entities apparently talked about by scientific theories. Generally, those who are scientific realists assert that one can make valid claims about unobservables (viz., that they have the same ontological status) as observables, as opposed to instrumentalism. Scientific realism involves the two basic positions. First, it is a set of claims about the features of an ideal scientific theory; an ideal theory is the sort of theory science aims to produce. Second, it is the commitment that science will eventually produce theories very much like an ideal theory and that science has done pretty well thus far in some domains. It is important to note that one might be a scientific realist regarding some sciences while not being a realist regarding others. For example, one might hold realist attitudes toward physics, chemistry and biology, and not toward economics, psychology, and sociology.” Ref
What is Scientific Realism?
Epistemic Achievements versus Epistemic Aims
According to Anjan Chakravartty with The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, “It is perhaps only a slight exaggeration to say that scientific realism is characterized differently by every author who discusses it, and this presents a challenge to anyone hoping to learn what it is. Fortunately, underlying the many idiosyncratic qualifications and variants of the position, there exists a common core of ideas, typified by an epistemically positive attitude towards the outputs of scientific investigation, regarding both observable and unobservable aspects of the world. The distinction here between the observable and the unobservable reflects human sensory capabilities: the observable is that which can, under favorable conditions, be perceived using the unaided senses (for example, planets and platypuses); the unobservable is that which cannot be detected this way (for example, proteins and protons). This is to privilege vision merely for terminological convenience and differs from scientific conceptions of observability, which generally extend to things that are detectable using instruments (Shapere 1982). The distinction itself has been problematized (Maxwell 1962, Churchland 1985, Musgrave 1985, Dicken & Lipton 2006), but if it is problematic, this is arguably a concern primarily for certain forms of antirealism, which adopt an epistemically positive attitude only with respect to the observable. It is not ultimately a concern for scientific realism, which does not discriminate epistemically between observables and unobservables per se. Before considering the nuances of what scientific realism entails, it is useful to distinguish between two different kinds of definition in this context. Most commonly, the position is described in terms of the epistemic achievements constituted by scientific theories (and models—this qualification will be taken as given henceforth). On this approach, scientific realism is a position concerning the actual epistemic status of theories (or some components thereof), and this is described in a number of ways. For example, most define scientific realism in terms of the truth or approximate truth of scientific theories or certain aspects of theories. Some define it in terms of the successful reference of theoretical terms to things in the world, both observable and unobservable. (A note about the literature: ‘theoretical term’, prior to the 1980s, was standardly used to denote terms for unobservables, but will be used here to refer to any scientific term, which is now the more common usage.) Others define scientific realism not in terms of truth or reference, but in terms of belief in the ontology of scientific theories. What all of these approaches have in common is a commitment to the idea that our best theories have a certain epistemic status: they yield knowledge of aspects of the world, including unobservable aspects. (For definitions along these lines, see Smart 1963, Boyd 1983, Devitt 1991, Kukla 1998, Niiniluoto 1999, Psillos 1999, and Chakravartty 2007a.) Another way to think about scientific realism is in terms of the epistemic aims of scientific inquiry (van Fraassen 1980, p. 8, Lyons 2005). That is, some think of the position in terms of what science aims to do: the scientific realist holds that science aims to produce true descriptions of things in the world (or approximately true descriptions, or ones whose central terms successfully refer, and so on). There is a weak implication here to the effect that if science aims at truth and scientific practice is at all successful, the characterization of scientific realism in terms of aim may then entail some form of characterization in terms of achievement. But this is not a strict implication, since defining scientific realism in terms of aiming at truth does not, strictly speaking, suggest anything about the success of scientific practice in this regard. For this reason, some take the aspirational characterization of scientific realism to be too weak (Kitcher 1993, p. 150, Devitt 2005, n. 10, Chakravartty 2007b, p. 197)—it is compatible with the sciences never actually achieving, and even the impossibility of their achieving, their aim as conceived on this view of scientific realism. Most scientific realists commit to something more in terms of achievement, and this is assumed in what follows.” Ref
The Three Dimensions of Realist Commitment
According to Anjan Chakravartty with The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, “The description of scientific realism as a positive epistemic attitude towards theories, including parts putatively concerning the unobservable, is a kind of shorthand for more precise commitments (Kukla 1998, ch. 1, Niiniluoto 1999, ch. 1, Psillos 1999, Introduction, Chakravartty 2007a, ch. 1). Traditionally, realism more generally is associated with any position that endorses belief in the reality of something. Thus, one might be a realist about one’s perceptions of tables and chairs (sense datum realism), or about tables and chairs themselves (external world realism), or about mathematical entities such as numbers and sets (mathematical realism), and so on. Scientific realism is a realism about whatever is described by our best scientific theories—from this point on, ‘realism’ here denotes scientific realism. But what, more precisely, is that? In order to be clear about what realism in the context of the sciences amounts to, and to differentiate it from some important antirealist alternatives, it is useful to understand it in terms of three dimensions: a metaphysical (or ontological) dimension; a semantic dimension; and an epistemological dimension. Metaphysically, realism is committed to the mind-independent existence of the world investigated by the sciences. This idea is best clarified in contrast with positions that deny it. For instance, it is denied by any position that falls under the traditional heading of ‘idealism’, including some forms of phenomenology, according to which there is no world external to and thus independent of the mind. This sort of idealism, though historically important, is rarely encountered in contemporary philosophy of science, however. More common rejections of mind-independence stem from neo-Kantian views of the nature of scientific knowledge, which deny that the world of our experience is mind-independent, even if (in some cases) these positions accept that the world in itself does not depend on the existence of minds. The contention here is that the world investigated by the sciences—as distinct from “the world in itself” (assuming this to be a coherent distinction)—is in some sense dependent on the ideas one brings to scientific investigation, which may include, for example, theoretical assumptions and perceptual training; this proposal is detailed further in section 4. It is important to note in this connection that human convention in scientific taxonomy is compatible with mind-independence. For example, though Psillos (1999, p. xix) ties realism to a ‘mind-independent natural-kind structure’ of the world, Chakravartty (2007a, ch. 6) argues that mind-independent properties are often conventionally grouped into kinds (see also Boyd 1991 and Humphreys 2004, pp. 22–25, 35–36). Semantically, realism is committed to a literal interpretation of scientific claims about the world. In common parlance, realists take theoretical statements at “face value”. According to realism, claims about scientific entities, processes, properties, and relations, whether they be observable or unobservable, should be construed literally as having truth values, whether true or false. This semantic commitment contrasts primarily with those of so-called instrumentalist epistemologies of science, which interpret descriptions of unobservables simply as instruments for the prediction of observable phenomena, or for systematizing observation reports. Traditionally, instrumentalism holds that claims about unobservable things have no literal meaning at all (though the term is often used more liberally in connection with some antirealist positions today). Some antirealists contend that claims involving unobservables should not be interpreted literally, but as elliptical for corresponding claims about observables. Epistemologically, realism is committed to the idea that theoretical claims (interpreted literally as describing a mind-independent reality) constitute knowledge of the world. This contrasts with sceptical positions which, even if they grant the metaphysical and semantic dimensions of realism, doubt that scientific investigation is epistemologically powerful enough to yield such knowledge, or, as in the case of some antirealist positions, insist that it is only powerful enough to yield knowledge regarding observables. The epistemological dimension of realism, though shared by realists generally, is sometimes described more specifically in contrary ways. For example, while many realists subscribe to the truth (or approximate truth) of theories understood in terms of some version of the correspondence theory of truth (as suggested by Fine 1986 and contested by Ellis 1988), some prefer deflationary accounts of truth (including Giere 1988, p. 82, Devitt 2005, and Leeds 2007). Though most realists marry their position to the successful reference of theoretical terms, including those for unobservable entities, processes, properties, and relations (Boyd 1983, and as described by Laudan 1981), some deny that this is a requirement (Cruse & Papineau 2002, Papineau 2010). Amidst these differences, however, a general recipe for realism is widely shared: our best scientific theories give true or approximately true descriptions of observable and unobservable aspects of a mind-independent world.” Ref
No, science CAN NOT be with religion.
Science is a method to understand the world as it is, which is naturalistic only, not one shred of magic. In fact, the scientific method assumes Methodological Naturalism, because that is all that has ever been found and is the most likely thing that ever will be found. As religion is not intended to represent the world as it is but instead what it is not the stupid supernatural, which is the thing of fantasy, wishful thinking, and delusion.













I am a Methodological Rationalist, I rarely am pushed to doubt as a default, instead, I see reason as my default and at times it may be responsible to doubt, but I get to that conclusion because of reasoning. A common saying in pseudologic is “You can’t prove a negative.” This is, simply not true. This is clearly not true because any statement can be rewritten into the negation of its negation. Any provable statement can be written as a negative. For example, “X is true” can be rewritten as “X is not false”, a negative statement! If “X is true” can be proven true, then you have also proven a negative statement “X is not false”. Moreover, even if it is widely believed that you can’t prove a negative. Going so far as to have people thinking that it is a law of logic—you can’t prove that Santa Claus, unicorns, the Loch Ness Monster, God, pink elephants, WMD in Iraq, and Bigfoot don’t exist. This widespread belief is flatly, 100% wrong. In this little essay, I show precisely how one can prove a negative, to the same extent that one can prove anything at all. Evidence of absence is evidence of any kind that suggests something is missing or that it does not exist. Per the traditional aphorism, “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence”, positive evidence of this kind is distinct from a lack of evidence or ignorance of that which should have been found already, had it existed. In this regard, Irving Copi writes: “In some circumstances, it can be safely assumed that if a certain event had occurred, evidence of it could be discovered by qualified investigators. In such circumstances, it is perfectly reasonable to take the absence of proof of its occurrence as positive proof of its non-occurrence.” — Copi, Introduction to Logic (1953), p. 95
Here is why “Reason is my only master”
The most Base Presupposition begins in reason. Reason is needed for logic (logic is realized by the aid of reason enriching its axioms). Logic is needed for axiology/value theory (axiology is realized by the aid of logic). Axiology is needed for epistemology (epistemology is realized by the aid of axiology value judge and enrich its value assumptions as valid or not). Epistemology is needed for a good ontology (ontology is realized with the aid of epistemology justified assumptions/realizations/conclusions). Then when one possesses a good ontology (fortified with valid and reliable reason and evidence) they can then say they know the ontology of that thing. Thinking is good and one claiming otherwise is indeed a person erroring in reason. Which may I remind you is terrible since the most Base Presupposition in our understanding of everything begins in reason.
So, I think, right thinking is reason. Right-reason (Sound reasoning) is logic. Right logic, can be used for mathematics, and from there we can get to science. And, by this methodological approach, we get one of the best ways of knowing the scientific method. Activating experience/event occurs, eliciting our feelings/scenes. Then naive thoughts occur, eliciting emotions as a response. Then it is our emotional intelligence over emotional hijacking, which entrance us but are unavoidable, and that it is the navigating this successfully in a methodological way we call critical thinking or as In just call right thinking. So, to me, could be termed “Right” thinking, that is referring to a kind of methodological thinking. Reason is at the base of everything and it builds up from pragmatic approaches. And, to me, there are three main approaches to truth (ontology of truth) from the very subjective (Pragmatic theory of truth), to subjective (Coherence theory of truth), then onto objective (Correspondence theory of truth) but remember that this process as limited as it can be, is the best we have and we build one truth ontop another like blocks to a wall of truth.
Soundness
“In logic, more precisely in deductive reasoning, an argument is sound if it is both valid in form and its premises are true. Soundness also has a related meaning in mathematical logic, wherein logical systems are sound if and only if every formula that can be proved in the system is logically valid with respect to the semantics of the system. In deductive reasoning, a sound argument is an argument that is both valid, and all of whose premises are true (and as a consequence its conclusion is true as well). An argument is valid if, assuming its premises are true, the conclusion must be true.” ref
An example of a sound argument is the following well-known syllogism:
“All men are mortal. Socrates is a man. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.” Because of the logical necessity of the conclusion, this argument is valid; and because the argument is valid and its premises are true, the argument is sound. However, an argument can be valid without being sound. For example: “All birds can fly. Penguins are birds. Therefore, penguins can fly.” This argument is valid because, assuming the premises are true, the conclusion must be true. However, the first premise is false. Not all birds can fly (penguins, ostriches, kiwis etc.) For an argument to be sound, the argument must be valid and its premises must be true.” ref
The soundness of a deductive system is the property that any sentence that is provable in that deductive system is also true on all interpretations or structures of the semantic theory for the language upon which that theory is based. In symbols, where S is the deductive system, L the language together with its semantic theory, and P a sentence of L: if ⊢S P, then also ⊨L P.” ref
Strong soundness
“Strong soundness of a deductive system is the property that any sentence P of the language upon which the deductive system is based that is derivable from a set Γ of sentences of that language is also a logical consequence of that set, in the sense that any model that makes all members of Γ true will also make P true. In symbols where Γ is a set of sentences of L: if Γ ⊢S P, then also Γ ⊨L P. Notice that in the statement of strong soundness, when Γ is empty, we have the statement of weak soundness.” ref
Pragmatic theory of truth, Coherence theory of truth, and Correspondence theory of truth
In a general way, all reality, in a philosophic sense, is an emergent property of reason, and knowing how reason accrues does not remove its warrant. Feelings are experienced then perceived, leading to thinking, right thinking is reason, right reason is logic, right logic is mathematics, right mathematics is physics and from there all science.
Right-(SOUND)-Reason: is reasoning to the highest soundness available.
Science is quite the opposite of just common sense. To me, common sense is experience-related interpretation, relatively, as it generally relates to the reality of things in the world, which involves “naïve realism” as well as possible psychological certainty and low epistemic certainty. Whereas, most of those who are scientific thinkers, hold typically more to scientific realism or other stances far removed from the limited common sense of naive realism. Science is a multidisciplinary methodological quest for truth. Science understands what is, while religion is wishing on what is not. Scientific realism sees external reality as described by science is what is REAL and thus TRUE with the highest epistemic certainty regardless of possible psychological certainty.
Getting Real with Logic
Logic is the result of rationalism, as what do you think gets you to logic if not starting at reason? I want to hear your justification for your claims, all the presuppositions you are evading to explain the links in your claims of truth. As it is invalid to just claim this without a justification for your professed claims and the presupposing you do to get there, that is not trying to use rationalism to refuse rationalist thinking. How are you making the statement and not appearing to what is the rationale behind it? If not, you must want to think “Logic is self-generating as valid” and this understood value is to you not reducible to reason? You are devoid of an offer of your burden of proof, first just try to keep up with the thinker’s responsibility to provide more than unjustified claims. Logic is derived by axioms and thus using rationalism to validate them, think otherwise provide your proof. My Rationalism: is two things externalistic “scientific rationalism” a belief or theory that opinions and actions should be based on reason and knowledge rather than on religious belief or emotional response. And internalistic “philosophic rationalism” the theory that reason is the most base presupposition before all others, rather than simply trying to rely on experience is the foundation of certainty in knowledge. Activating experience occurs we then have thinking, right (methodological) thinking (critical thinking) is reason, right reason is logic, right logic can be used for math, right math in response to the natural world is physics, and from there all other Sciences, physics is the foundation for chemistry and chemistry is the foundation of biology. May Right-(SOUND)-Reason be your only master and may you also master reason.
Religion vs. Science, Don’t Confuse Beliefs
A basic outline of scientific epistemology:
Science: Hypotheses (Rationalism/Deductive, Inductive, or Abductive Reasoning etc.) + Testing (Empiricism/Systematic Observation) – Checking for errors (Skepticism/Fallibilism) + Interpret/Draw a Conclusion (Rationalism/Deductive, Inductive, or Abductive Reasoning etc.) *if valid* = Scientific Laws (describes observed phenomena) or Scientific Theory (substantiated and repeatedly tested explanation of phenomena) = Justified True Belief = Scientific Knowledge = Epistemic Certainty supportive of correctability
*being epistemically certain, is believing a truth has the highest epistemic status, often with warranted psychological certainty but it may not, neither is it a requirement*
“Damien, I have a question: Who/what gives humans value?”
My response, We give value, as value is an awareness and judgment, it is an emergent property of validation; the ability to use critical thinking and logic in a useful way, to conclude worth, benefit, or good.
I am the “one” you have been waiting for. I am will to power, a deep thought so true it has taken flight to the lofty aspirations dreamed for and a care transmitted to offer hope to humanity. I believe in you and will strive to champion you with all I have for you are so worthy… I am that freak of nature, a power from the anti-power crusaders, warring against the power dynamic to return it back where it belongs- the hands of the people. I am a free-thinking invader into the shell of malignancy infecting humanity which strangles reason out of the world. A proud anarchy theorist, I breathe the fire of the heathens, a thought revolutionary and mental freedom fighter. I am a humanist atheist who desires a better world for us all, one that is kinder, more just, and more rational in its pursuits.
I am a “Scientific Axiology” minded “Philosophic Axiologist.”
*Philosophic Axiology (Value Theory)
*Scientific Axiology (Formal Axiology)
Axiological atheism can be thought to involve ethical/value theory reasoned and moral argument-driven apatheism, ignosticism, atheism, anti-theism, anti-religionism, secularism, and humanism. The valuations move up the latter as the levels of evaluation is made to value judge all the elements to better understand the value or disvalue available to reach the most accurate valuation reasonable with a sound aware value conciseness. Axiological atheism can be thought to involve Ethical Atheism. Below shows the 7 axiological atheism argument flow to show the value layers and my thoughts on it:
1. Apatheism: starts at real, we are born and by the fact reality is devoid of magic removes theological desires to understand the obvious naturalistic world, until we learn otherwise. (a “presumptive-value” failure, thus no motivation to adequately start the evaluation needed to understand if there is real value for an Axiology assessment to accurately place it in the value hierarchy). = no value
2. Ignosticism: sees theological arguments and language as equivocation, contradictory, and/or un-cognitively relatable other than emotionalism or the like. I see Ignosticism as using the Theological non-cognitivism arguments of “mind understanding issues” (rationalism challenging) and an evidentialist/verificationist arguments of “lacking evidence issues” (empiricism challenging). As an atheist, I am a person who disbelieves or lacks belief in the existence of god or gods. In my non-belief, I am also ignostic feeling that every theological position assumes too much about the concept of god(s). As an ignostic, I am a person who rational no idea of anything from reality whatever to label as “a concept of god” thus I can say I have no idea of anything that can connect to the term god and no reason to think anyone else can either. (again a “presumptive-value” failure, no good Ontology of the thing for Identifying values that could influence belief but without what is needed to understand if there is real value for an axiology assessment to accurately place it in the value hierarchy). = no value
3. Atheism: How can we not reject the concept of gods, aka: supposed supreme magical beings, when not even some simple magic is supported in reality. So how then is it not even more ridiculous to claim some supreme magic aka: gods which are even further from reality. May I remind you that faith in the acquisition of knowledge is not a valid method worth believing in. Because, what proof is “faith”, of anything religion claims by faith, as many people have different faith even in the same religion? As an atheist, I am a person who disbelieves or lacks belief in the existence of god or gods. In my non-belief, I am also ignostic feeling that every theological position assumes too much about the concept of god(s). As an ignostic, I am a person who rational no idea of anything from reality whatever to label as “a concept of god” thus I can say I have no idea of anything that can connect to the term god and no reason to think anyone else can either. Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure or a firefighter talking about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victim’s of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions. If you think you believe in a god, “what do you mean by god,” saying a name tells me not one thing about the thing I am asking to know “its” beingness / thingness / attributes / qualities. Thus, what is the thing “god” to which you are talking about and I want you to explain its beingness /thingness / attributes/ qualities? Religious/theistic people with supernatural beliefs often seem as though they haven’t thought much about and that is something we can help using ontology questions about the beingness / thingness / attributes/ qualities they are trying to refer too. What do you mean by god, when you use the term god? And, I am not asking you for the name you attach to the thing you label as a god. I don’t need to know what the god you believe is known “by.” I am asking, what is the thing you are naming as a god and what that thing is, its qualities in every detail like all things have if they are real. Are you just making stuff up or guessing/hoping or just promoting unjustified ideas you want to believe, what is a god? As an atheist, I feel more wonder than I did as a theist because I thought, “big deal” to any wonder I experienced, thinking god could do anything. So with such an unrealistic mindset, everything lost its wonder but it’s the opposite as an atheist. As a theist, the world was full of superstitions and supernatural magic possibilities and thus utilized thinking that was not in the real world. As an atheist all I have now is the real world, not that all atheists seem to get this, we all are in a real world devoid of magic anything, therefore, everything adds to my feeling of awe. There should be little debate with atheist acknowledging discernable reality compared to theists with non-reality claims. Yes, I have way more awe and wonder as an atheist than I ever had as a theist because as a theist anything was possible with god. Therefore, as a theist things where not that amazing. However, as an atheist grasping what an absolute accidental or how random things are, with a 95 to 99 % of all life ever existing on this planet went extinct. I am thoroughly amazed we are even here the evolved children of ancient exploded stars, likely born in galaxies born in super-massive black holes, it’s all amazing. There is no evidence for Gods. But is their proposition outside of reason? As always start in reality from the evidence we do know, such as never in the history of scientific research or investigation has any supernatural claims shown to be true. So it is completely outside of possibility and is utterly ridiculous. Therefore, belief should be rejected as there are no warrants at all and it is axiologically unworthy to such a preponderance to demand disbelief. (yet again a “presumptive value” failure, no good Ontology of the thing not the cognitively meaningful claims relatable to reality that must be attached to all magic and gods claims for Identifying values that could influence belief but without what is needed to understand if there is real value for an axiology assessment to accurately place it in the value hierarchy).
4. Antitheism: Anti-theism requires more than either merely disbelieving in gods or even denying the existence of gods. Anti-theism requires a couple of specific and additional beliefs: first, that theism is harmful to the believer, harmful to society, harmful to politics, harmful, to culture, etc.; second, that theism can and should be countered in order to reduce the harm it causes. If a person believes these things, then they will likely be an anti-theist who works against theism by arguing that it be abandoned, promoting alternatives, or perhaps even supporting measures to suppress it. It’s worth noting here that, however, unlikely it may be in practice, it’s possible in theory for a theist to be an anti-theist.This may sound bizarre at first, but remember that some people have argued in favor of promoting false beliefs if they are socially useful. To me, I think many may have a misconception of the term. Atheism and anti-theism so often occur together at the same time and in the same person that it’s understandable if many individuals fail to realize that they aren’t the same. Making a note of the difference is important, however, because not every atheist is anti-theistic and even those who are, aren’t anti-theistic all the time. Atheism is simply the absence of belief in gods; anti-theism is a conscious and deliberate opposition to theism.Many atheists are also anti-theists, but not all and not always. To me as an antitheist, I see the concept of gods antihumanistic and wholly harmful to a free humanity and if the so-called gods somehow do end up being real that I will switch to direct opposition as I would any tyrant oppressing humanity. Antitheism (sometimes anti-theism) is a term used to describe an opposition to theism. The term has had a range of applications and definitions. In secular contexts, it typically refers to direct opposition to the validity of theism, but not necessarily to the existence of a deity. As an anti-theist, I am a person who is active in opposition to theism: both the concepts of god(s) as well as the religions that support them.This is because theistic concepts and theistic religions are harmful and that even if theistic beliefs were true, they would be undesirable. (And, again a “presumptive value” failure, of the other value challenges of the lesser evaluations and value judgments addressed in the apatheism, ignosticism, atheism value judgment conclusion and an Axiological Atheism assessment of the god concept that must be attached to all magic and gods claims Identifying a lack of value and/or disvalue that influence harm to real value in an axiology assessment to accurately place its value violations in the value hierarchy).
5. Antireligionism: Not just Atheist, axiological atheists should be antitheists but this generally will involve anti-religionism. it would generally thus hold anti-religionist thinking. Especially, I am an anti-religionist, not just an atheist, and here is why summed up in three ideas I am against. And, in which these three things are common in all religions: “pseudo-science”, “pseudo-history”, and “pseudo-morality”. And my biggest thing of all is the widespread forced indoctrination of children, violating their free choice of what to not believe or believe, I hate forced hereditary religion. And my biggest thing of all is the widespread forced indoctrination of children, violating their free choice of what to not believe or believe, I hate forced hereditary religion. As well as wish to offer strong critiques regarding the pseudo-meaning of the “three letter noise” people call “G.o.d” (group originated delusion)!As an anti-religionist, I am a person who can look at religion on the whole and see it is detrimental to the progress of humanity thus am in opposition to all and every religion, not even just opposition to organized religion. In case you were wondering, I am anti-pseudoscience, anti-supernatural, and anti-superstition as well. May I not be a silent watcher as millions of children are subjugated almost before their birth let alone when they can understand thought and are forcibly coerced, compelled, constrained, and indoctrinated in the mental pollution that religion can be. My main goal against religion is to fully stop as much as possible forced indoctrination, one could ask but then why do I challenge all adults faith?Well, who do you think is doing the lying to children in the first place. End Hereditary religion, if its a belief let them the equal right to choose to believe. “Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings… (And, one last time a “presumptive value” failure, of the other value challenges of the lesser evaluations and value judgments addressed in the apatheism, ignosticism, atheism value judgment conclusion and an Axiological Atheism assessment of the god concept and anti-theism assessment of the god show not just a lack of value but a possibly or likely harm demonstrating bot just a lack of value but a real disvalue and that includes the religions potentially removing value in an axiology assessment to accurately place it in the value hierarchy).
6. Secularism: is the only honorable way to value the dignity of others. If it was not true that there is a large unequal distribution of religion contributing to violence then there would be equal religion and atheist secularism violence. You do not see atheists bombing agnostics the very idea is laughable however even different branches of the same religion do will and have killed one another. So, violence not who we are it’s something we need to be compelled to do. Therefore, please support secularism. We are all one connected human family, proven by DNA showing we should treat each other as fellow dignity beings, supported equally (no gods and no masters). States may often have powers, but only citizens have the glue of morality we call rights. And, as they say, in my “dream society”, lots of things are free (aka. planting free food everywhere, free to everyone); but I wonder what you mean when people say you can’t just let things be free, I think, yeah, how can I take free stuff from a free earth.If one observes the virtues of (T. R. U. E. “The Rational Universal Ethics” or “The Responsible Universal Ethics”) that connect to all things as that of the connectedness equality like those which mirror the rays of the sun, fall down equally with a blind but fair indifference. (what is being expressed is that this sun shining will not favor one over another, no, the same upon everyone offering its light to all plant, animal, human, women, men, single or married, homosexual, bisexual, heterosexual, nonreligious, religious, people of means and those without, able-bodied and those which special needs, people of color, and those who are not, those with access to resources and those which out, young and elderly, etc.) All who wish to follow T. R. U. E. thus embodying a universalize equalitarian standard of ethics should strive to be like a ray of connected light to the world, shining equally and freedom to all of the world by such efforts a nonbiased unitive ethical approach is possible, one would have an increase in positive feelings to help others understanding equalitarian connectedness. If you don’t think different you will not behave differently, if you have never lived differently it is hard to see things differently and if you do not strive to understand difference one is thus unknowingly or not bound by limited encapsulation. I am for a Free Secular Society. I am not for oppression or abuse of religious believer and want a free secular society with both freedoms of religion and freedom from religion. Even though I wish the end of faith and believing in myths and superstition, I wish this by means of informing the willing and not force of the unwilling. I will openly challenge and rebuff religious falsehoods and misunderstanding as well as rebuke and ridicule harmful or unethical religious ideology or behavior.
7. Humanism: is the philosophic thinking that humans can solve human problems by human means, without feeling a need to appeal to the likes of holy books, mystical anything, nor the belief in gods or religions. But, instead, aspires to a true belief in humanity, viewing it with a persuasion of equality. This caring realist thinking found in humanism utilizes an unstated assumption or aspiration, to do no harm as much as possible and to do good whenever one can.Moreover, we are all one connected human family, proven by DNA showing we should treat each other as fellow dignity beings, supported equally. And, no one really owns the earth, we may make claims to it even draw lines on maps thinking this makes the fantasy borders, illusion supported by force and the potential for threat. Thus the ethical truth is we need to share the earth as communally as possible. And use the resources as safe and ethically as possible striving towards sharing and caring. (do no Harm and do good = Humanism). My core definition of humanism is that humans can solve human problems by human means. I am not saying other things can’t or shouldn’t be added to it but to me, a definition of humanism must always contain something coherent to such a thinking or not contradict such as I have offered. Thus, why it is appropriate to say “good without god” when one is a humanist.
Dogmatic–Propaganda vs. Disciplined-Rationality
Religionists and fideists, promote Dogmatic-Propaganda whereas atheists and antireligionists mostly promote Disciplined-Rationality. Dogmatic–Propaganda commonly is a common motivator of flawed or irrational thinking but with over seventy belief biases identified in people, this is hardly limited to just the religious or faith inclined. Let me illustrate what I am saying, to me all theists are believing lies or irrationally in that aspect of their lives relating to god belief. So the fact of any other common intellectual indexers where there may be “right” reason in beliefs cannot remove the flawed god belief corruption being committed. What I am saying is like this if you kill one person you are a killer. If you believe in one “god” I know you are a follower of Dogmatic-Propaganda and can not completely be a follower of Disciplined-Rationality. However, I am not proclaiming all atheists are always rational as irrationally is a revolving door many people believe or otherwise seem to stumble through. It’s just that god-belief does this with intentionally.
Disciplined-Rationality is motivated by principles of correct reasoning with emphasis on valid and reliable methods or theories leading to a range of rational standpoints or conclusions understanding that concepts and beliefs often have consequences thus hold an imperative for truth or at least as close to the truth as can be acquired rejecting untruth. Disciplined-Rationality can be seen as an aid in understanding the fundamentals for knowledge, sound evidence, justified true belief and involves things like decision theory and the concern with identifying the value(s), reasonableness, verification, certainties, uncertainties, and other relevant issues resulting in the clearest optimal decision/conclusion and/or belief/disbelief. Disciplined-Rationality attempts to understand the justification or lack thereof in propositions and beliefs concerning its self with various epistemic features of belief, truth, and/or knowledge, which include the ideas of justification, warrant, rationality, reliability, validity, and probability.
ps. “Sound Thinker”, “Shallow Thinker”, “Dogmatic–Propaganda” & “Disciplined-Rationality” are concepts/terms I created*
Atheists but I have faith in gravity tho, but it isn’t exactly “faith”???
My response, “No, I don’t agree, you don’t have “faith” in gravity or gravitation, as it is “a fundamental force” you have proof or if lacking some direct proof would use inference, and if even less evidence you use conjecture, not faith. Do you gauntly thinking you need faith in gravity because you wonder or worry that when walking down a set of stairs that you going to fall back up? You don’t need faith (strong belief without evidence) as there is massive proof, almost to the point that it is easily self-evident. You don’t need faith (strong belief without evidence) for anything, as if it’s warranted it will or should have evidence or it doesn’t deserve not only strong belief but any amount of belief at all as sound beliefs need something to ground their worthiness in relation to reality; the only place evidence comes. “Gravity, or gravitation, is a natural phenomenon by which all things with mass are brought toward (or gravitate toward) one another, including planets, stars, and galaxies.” Ref
“Gravity is responsible for various phenomena observed on Earth and throughout the Universe; for example, it causes the Earth and the other planets to orbit the Sun, the Moon to orbit the Earth, the formation of tides, the formation and evolution of the Solar System, stars and galaxies. Since energy and mass are equivalent, all forms of energy, including light, also cause gravitation and are under the influence of it. On Earth, gravity gives weight to physical objects and causes the ocean tides. The gravitational attraction of the original gaseous matter present in the Universe caused it to begin coalescing, forming stars – and the stars to group together into galaxies – so gravity is responsible for many of the large-scale structures in the Universe.” Ref
Axiological “Presumptive-Value”
Your god myth is an Axiological “Presumptive-Value” Failure, and I as an Axiological (value theorist) Atheist am compelled to speak out on how Claims of god are a Presumptive-Value failure. Simply, if you presume a thing is of value that you can’t justify, then you have committed an axiological presumptive value failure.
Axiological “presumptive-value” Success: Sound Thinker: uses disciplined rationality (sound axiological judgment the evaluation of evidence to make a decision) supporting a valid and reliable justification.
Axiological “presumptive-value” Failure: Shallow Thinker: undisciplined, situational, sporadic, or limited thinking (unsound axiological judgment, lacking required evidence to make a “presumptive-value” success decision) lacking the support of a needed valid and reliable justification.
Often I get disheartened to see that so many people can look at the unknown or that which is devoid of any and all understanding and claim to know that this is evidence for some god or another. How can they with all honesty even say that they somehow already know about an established scientific unknown, when all along it is what it ever was, which I will remind you, is currently holding a confirmed status of unknown. Thus, still fully intact as currently unknowable (I.e. you simply cannot justifiability claim that such unknown is god or evidence of god). What really is a god anyway? The term god equals mystery that is used to explain the mysterious leaving us with yet more mystery, thus explains nothing. Claims of god are a Presumptive-Value failure. Simply, if you presume a thing is of value that you can’t justify, then you have committed an axiological presumptive value failure. Axiological “presumptive-value” Success: Sound Thinker: uses disciplined rationality (sound axiological judgment the evaluation of evidence to make a decision) supporting a valid and reliable justification.
“Ok, So basically, the difference between reasoning with evidence and without?” – Questioner
My response, Well with or without valid justification because of evidence. As in you can’t claim to know the value of something you can’t demonstrate as having good qualities to attach the value claim too so if you lack evidence of the thing in question then you cannot validate its value. So it’s addressing a kind of justificationism (uncountable) Theory of justification, An (philosophy standard) approach that regards the justification of a claim as primary, while the claim itself is secondary; thus, criticism consists of trying to show that a claim cannot be reduced to the authority or criteria that it appeals to. Think of is as a use-matrix. If I say this is of great use for that, can you validate its use or value, and can I use this as a valid method to state a valid justification for my claims without evidence to value judge from? No, thus an axiological presumptive-value failure as a valid anything.
Theory of justification is a part of epistemology that attempts to understand the justification of propositions and beliefs. Epistemologists are concerned with various epistemic features of belief, which include the ideas of justification, warrant, rationality, and probability. Loosely speaking, justification is the reason that someone (properly) holds a belief. When a claim is in doubt, justification can be used to support the claim and reduce or remove the doubt. Justification can use empiricism (the evidence of the senses), authoritative testimony (the appeal to criteria and authority), or reason. – Wikipedia
“Presumptions are things that are credited as being true until evidence of their falsity is presented. Presumptions have many forms and value (Axiology) is just one. In ethics, value denotes the degree of importance of something or action, with the aim of determining what actions are best to do or what way is best to live (normative ethics), or to describe the significance of different actions. It may be described as treating actions as abstract objects, putting VALUE to them.
It deals with right conduct and living a good life, in the sense that a highly, or at least relatively high valuable action may be regarded as ethically “good” (adjective sense), and that an action of low value, or relatively low in value, may be regarded as “bad”. What makes an action valuable may, in turn, depend on the ethical values of the objects it increases, decreases, or alters. An object with “ethic value” may be termed an “ethic or philosophic good” (noun sense). Values can be defined as broad preferences concerning appropriate courses of actions or outcomes. As such, values reflect a person’s sense of right and wrong or what “ought” to be.
“Equal rights for all”, “Excellence deserves admiration”, and “People should be treated with respect and dignity” are representatives of values. Values tend to influence attitudes and behavior and these types include ethical/moral values, doctrinal/ideological(religious, political) values, social values, and aesthetic values. It is debated whether some values that are not clearly physiologically determined, such as altruism, are intrinsic, and whether some, such as acquisitiveness, should be classified as vices or virtues.” ref, ref
The Way of a Sound Thinker?
“Sound thinking to me, in a general way, is thinking, reasoning, or belief that tends to make foresight a desire to be as accurate as one can with valid and reliable reason and evidence.”
Sound axiological judgment, to me, a “presumptive-value” success, is value judged opinions expressed as facts with a valid and reliable justification. In an informal and psychological sense, it is used in reference to the quality of cognitive faculties and adjudicational (relating to adjudication) capabilities of particular individuals, typically called wisdom or discernment. In a legal sense, – used in the context of a legal trial, to refer to a final finding, statement, or ruling, based on a considered weighing of evidence, called, “adjudication“.
A shallow thinker (i.e. not a Deep Thinker, a person whose thoughts are reasoned, methodological, logical, empirical, profound; an intellectual) quickly talks, often with boastful postulations, likely just as often pushed strongly and loudly as if this adds substance, and they do this before fully understanding what’s is really involved. Whereas, a Sound Thinker is reasoned (comparative more reasoned, superlative most reasoned) generally based on reasoning; being the result of logical thought. As a first debate process, a Sound Thinker commonly poses Questions to understand slowing down and assessing all the facts or factors involved and then builds their argument or ideas. In classical logic, the law of non-contradiction (LNC) (also known as the law of contradiction, the principle of non-contradiction (PNC), or the principle of contradiction) states that contradictory statements cannot both be true in the same sense at the same time, e.g. the two propositions “A is B” and “A is not B” are mutually exclusive. It is the second of the three classic laws of thought.
Here are examples of theoretical philosophy subjects I delve into:
Ontology
Epistemology
Axiology
Ignosticism
Atheism
Rationalism
Antitheism
Antireligion
Anarchism
Secularism
Secular humanism
Humanism
Theories of truth
Questions on knowledge
Practical philosophy
Logic
Questions on Morality
Feminist philosophy
Philosophy of science
Philosophy of language
Philosophy of mind
Metaphysics
Axiology and Value Theory?
“Value theory is a range of approaches to understanding how, why, and to what degree persons value things; whether the object or subject of valuing is a person, idea, object, or anything else. This investigation began in ancient philosophy, where it is called axiology or ethics.”– Wikipedia
“The term “Value Theory” is used in at least three different ways in philosophy. In its broadest sense, “value theory” is a catch-all label used to encompass all branches of moral philosophy, social and political philosophy, aesthetics, and sometimes feminist philosophy and the philosophy of religion — whatever areas of philosophy are deemed to encompass some “evaluative” aspect. In its narrowest sense, “value theory” is used for a relatively narrow area of normative ethical theory particularly, but not exclusively, of concern to consequentialists. In this narrow sense, “value theory” is roughly synonymous with “axiology”. Axiology can be thought of as primarily concerned with classifying what things are good, and how good they are. – (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
For instance, a traditional question of axiology concerns whether the objects of value are subjective psychological states or objective states of the world. But in a more useful sense, “value theory” designates the area of moral philosophy that is concerned with theoretical questions about value and goodness of all varieties — the theory of value. The theory of value, so construed, encompasses axiology, but also includes many other questions about the nature of value and its relation to other moral categories. – (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
The division of moral theory into the theory of value, as contrasting with other areas of investigation, cross-cuts the traditional classification of moral theory into normative and metaethical inquiry, but is a worthy distinction in its own right; theoretical questions about value constitute a core domain of interest in moral theory, often cross the boundaries between the normative and the metaethical, and have a distinguished history of investigation.” – (Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy)
Normative Philosophy? – Wikipedia
“Normative generally means relating to an evaluative standard. Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good or desirable or permissible and others as bad or undesirable or impermissible. A norm in this normative sense means a standard for evaluating or making judgments about behavior or outcomes. – Wikipedia
Normative is sometimes also used, somewhat confusingly, to mean relating to a descriptive standard: doing what is normally done or what most others are expected to do in practice. In this sense a norm is not evaluative, a basis for judging behavior or outcomes; it is simply a fact or observation about behavior or outcomes, without judgment. Many researchers in this field try to restrict the use of the term normative to the evaluative sense and refer to the description of behavior and outcomes as positive, descriptive, predictive, or empirical. – Wikipedia
In philosophy, normative statements make claims about how things should or ought to be, how to value them, which things are good or bad, and which actions are right or wrong. Normative claims are usually contrasted with positive (i.e. descriptive, explanatory, or constative) claims when describing types of theories, beliefs, or propositions. Positive statements are (purportedly) factual statements that attempt to describe reality. Normative statements and norms, as well as their meanings, are an integral part of human life. – Wikipedia
They are fundamental for prioritizing goals and organizing and planning. Thought, belief, emotion, and action are the basis of much ethical and political discourse; indeed, normativity is arguably the key feature distinguishing ethical and political discourse from other discourses (such as natural science). Much modern moral/ethical philosophy takes as its starting point the apparent variance between peoples and cultures regarding the ways they define what is considered to be appropriate/desirable/praiseworthy/valuable/good etc. (In other words, variance in how individuals, groups, and societies define what is in accordance with their normative standards.) – Wikipedia
This has led philosophers such as A.J. Ayer and J.L. Mackie (for different reasons and in different ways) to cast doubt on the meaningfulness of normative statements. Philosophers, such as Christine Korsgaard, have argued for a source of normative value which is independent of individuals’ subjective morality and which consequently attains (a lesser or greater degree of) objectivity. In the social sciences, the term “normative” has broadly the same meaning as its usage in philosophy, but may also relate, in a sociological context, to the role of cultural ‘norms‘; the shared values or institutions that structural functionalists regard as constitutive of the social structure and social cohesion. – Wikipedia
These values and units of socialization thus act to encourage or enforce social activity and outcomes that ought to (with respect to the norms implicit in those structures) occur, while discouraging or preventing social activity that ought not to occur. That is, they promote social activity that is socially valued. While there are always anomalies in social activity (typically described as “crime” or anti-social behavior, see also normality (behavior)) the normative effects of popularly endorsed beliefs (such as “family values” or “common sense“) push most social activity towards a generally homogeneous set.” – Wikipedia
Theoretical philosophy? – Wikipedia
“The division of philosophy into a practical and a theoretical discipline has its origin in Aristotle‘s moral philosophy and natural philosophy categories. Theoretical philosophy is sometimes confused with Analytic philosophy, but the latter is a philosophical movement, embracing certain ideas and methods but dealing with all philosophical subject matters, while the former is a way of sorting philosophical questions into two different categories in the context of a curriculum. – Wikipedia
Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
“The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
Hammer of Truth: Investigate (ONTOLOGY), Expose (EPISTEMOLOGY), and Judge (AXIOLOGY)
Hammer of Truth: Yes, you too, have lots of beliefs…
“The Hammer of Truth” Process
“Hammer of Truth” response to “Do you Believe in god?”
“The Hammer of Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
Error Crushing Force of the Dialectic Questions and the Hammer of Truth
Atheist Rationalist Talking on “TRUTH” with a Spiritualist Philosopher
Damien AtHope: Pre-Historical Writer/Researcher chats with Lisa For Truth: Origins of Religion and Anthropology of Religion
Truth Navigation: “Belief-Etiquette”
Truth Navigation and the fallacy of Fideism “faith-ism”
Truth Navigation: Techniques for Discussions or Debates
Science and the word “TRUTH”
Truth Navigation and the fallacy of Fideism “faith-ism”
Truth is a Value (axiological) Judgment.
Why are lies more appealing than the truth?
The Battle of Truth
To Find Truth You Must First Look
Pragmatic theory of truth, Coherence theory of truth, and Correspondence theory of truth
I use a kind of Dialectical Rhetoric = truth persuasion (motivational teaching)
Religion is not about truth
#rationalism #philosapgy #atheism


My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.

While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com