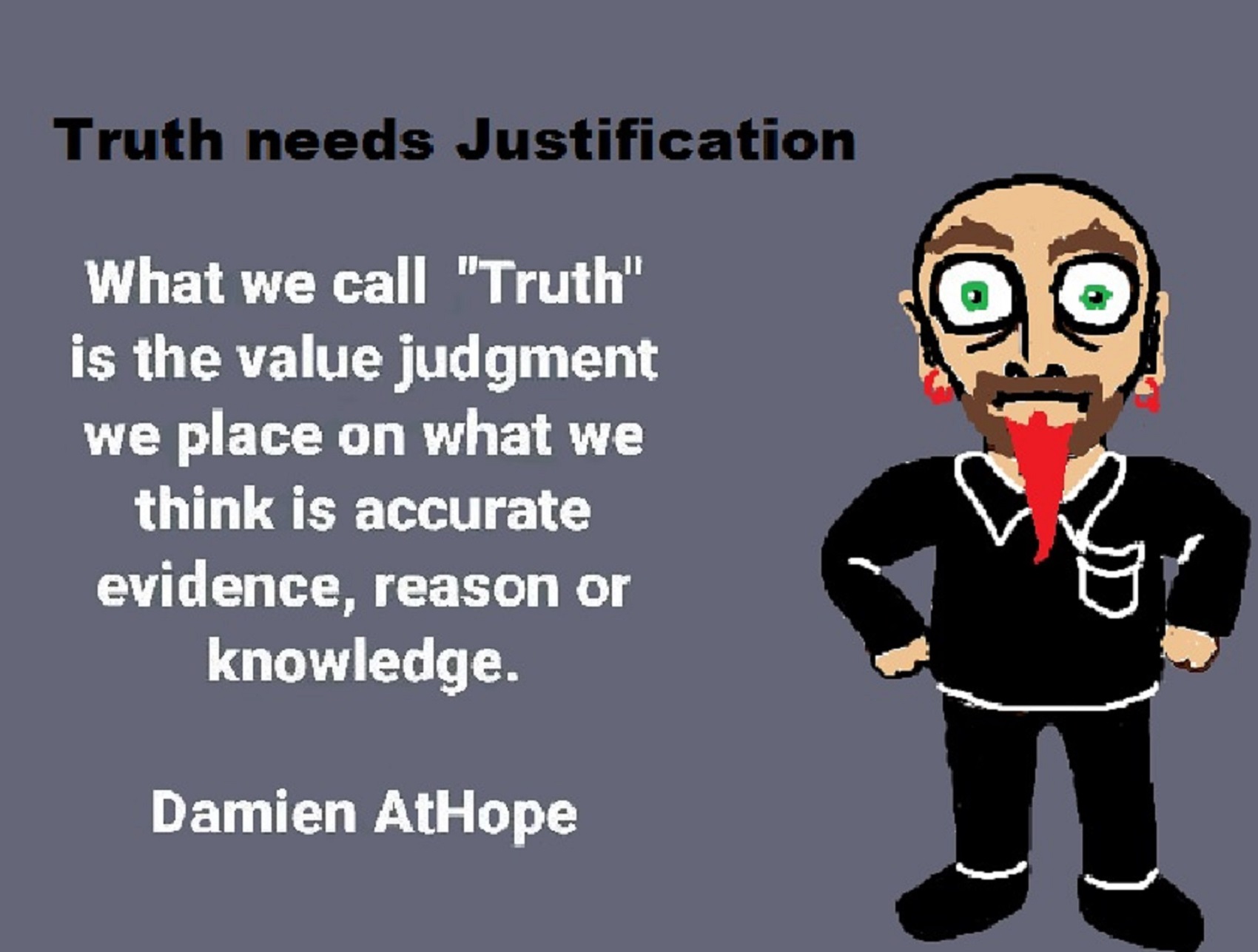


My “Methodological Rationalism” approach:
(REMS) Reason, Evidence & Methodological Skepticism
We don’t really defend atheism, to me as much as present reason and evidence to why theism is unjustified, unwarranted and found baseless to the point that atheism is almost like a default conclusion; it is reasonable when the belief proposition of theism fails as it always will. I have been told that me challenging or correcting people’s religious falsehoods was harmful. I say, “what”, ((sarcastically)) then responded, “yes”, just like challenging or correcting people’s lies is harmful…. Well, ok it’s harmful to falsehoods keeping their unjustified persuasive power.
My style, when doing atheist outreach, is basically to challenge with valid and reliable reason and evidence with a “reflective equilibrium” to what appears to be, has some high likelihood of being or has some strong confirmation.
The rationale of why reason is first, is because if you can’t reason with them and at times this is obviously a factor with some people, just stop as all things revolve around reason. Thus, roughly stated as rationalism (which for me is reasonable use or application of things in philosophy methods or tools like reason, logic, axiology, ontology and epistemology, etc.), and empiricism (which for me is reasonable use or application of things in philosophy methods or tools like evidence ie. facts like science, history, and archeology, etc.) as well as navigating all this with “methodological skepticism” is stead of (Philosophical skepticism) which is an approach that subjects all knowledge claims to scrutiny with the goal of sorting out true from false claims.
The Rational Imperative, How Does One Know Things?
I am aggressive with ideas, but I am kind to people. My motto is attack thinking not people. I do not respect religion, but I respect people. I do not believe in religion as it has a high potential for bad, but I believe in the potential for good in people. That is my style as a Firebrand Atheist that is a Humanistic Person.
My Atheist Activism Acknowledged in College Paper: Link
I often say to believers on the street, no, you don’t believe in god or religion. What you do or did was were told, (most often by family) this is what you need to believe or this is what we believe and you say ok, only after that as an adult, (especially when challenged) you try to support this post-acceptance commitment as if it has a rationalization. You are attempting to support that you did not choose wrong overlooking any faults or defects in order to feel justified and the psychological desire to stay consistent to that commitment. So, what you likely have now is a kind of Post-purchase rationalization. Which is also known as Buyer’s Stockholm Syndrome, a cognitive bias whereby someone who has purchased an expensive product or service overlooks any faults or defects in order to justify their purchase. It is a special case of choice-supportive bias. This rationalization is based on the Principle of Commitment and the psychological desire to stay consistent to that commitment. (6)
Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology Debating Tools
(REMS) Reason, Evidence & Methodological Skepticism
We don’t really defend atheism, to me as much as present reason and evidence to why theism is unjustified, unwarranted and found baseless to the point that atheism is almost like a default conclusion; it is reasonable when the belief proposition of theism fails as it always will. I have been told that me challenging or correcting people’s religious falsehoods was harmful. I say, “what”, ((sarcastically)) then responded, “yes”, just like challenging or correcting people’s lies is harmful…. Well, ok it’s harmful to falsehoods keeping their unjustified persuasive power.
My style when doing atheist outreach is basically to challenge with valid and reliable reason and evidence with a “reflective equilibrium” to what appears to be, has some high likelihood of being or has some strong confirmation.
The rationale of why reason is first, is because if you can’t reason with them and at times this is obviously a factor with some people, just stop as all things revolve around reason. Thus, roughly stated as rationalism (which for me is reasonable use or application of things in philosophy methods or tools like Reason “rationalism” tools: ontology, epistemology, and axiology, etc.), and Evidence “empiricism” tools: (which for me is reasonable use or application of things in philosophy methods or tools like evidence ie. facts like science, history, and archeology, etc.) as well as navigating all this with “methodological skepticism” is stead of (Philosophical skepticism) which is an approach that subjects all knowledge claims to scrutiny with the goal of sorting out true from false claims.
Legal burden of proof and Philosophic burden of proof: Understanding and utilizing evidence and evidence critique. There is a common need to grasp the issues surrounding “evidence”, deconstructing evidence-based claims and the pathways in thinking needed to control what is offered or accepted as evidence, is it really even evidence or does it matter to supporting a assertion.Evidence, broadly construed, is anything presented in support of an assertion. This support may be strong or weak. The strongest type of evidence is that which provides direct proof of the truth of an assertion. At the other extreme is evidence that is merely consistent with an assertion but does not rule out other, contradictory assertions, as in circumstantial evidence. In law, rules of evidence govern the types of evidence that are admissible in a legal proceeding. Types of legal evidence include testimony, documentary evidence, and physical evidence. The parts of a legal case which are not in controversy are known, in general, as the “facts of the case.” Beyond any facts that are undisputed, a judge or jury is usually tasked with being a trier of fact for the other issues of a case. Evidence and rules are used to decide questions of fact that are disputed, some of which may be determined by the legal burden of proof relevant to the case. Evidence in certain cases (e.g. capital crimes) must be more compelling than in other situations (e.g. minor civil disputes), which drastically affects the quality and quantity of evidence necessary to decide a case. Scientific evidence consists of observations and experimental results that serve to support, refute, or modify a scientific hypothesis or theory, when collected and interpreted in accordance with the scientific method. In philosophy, the study of evidence is closely tied to epistemology, which considers the nature of knowledge and how it can be acquired.
The burden of proof is the obligation of a party in an argument or dispute to provide sufficient evidence to shift the other party’s or a third party’s belief from their initial position. The burden of proof must be fulfilled by both establishing confirming evidence and negating oppositional evidence. Conclusions drawn from evidence may be subject to criticism based on a perceived failure to fulfill the burden of proof. Two principal considerations are: 1) On whom does the burden of proof rest? Or 2) To what degree of certitude must the assertion be supported? The latter question depends on the nature of the point under contention and determines the quantity and quality of evidence required to meet the burden of proof. In epistemology, the burden of proof (Latin: onus probandi (shorthand for Onus probandi incumbit ei qui dicit, non ei qui negat)) is the obligation on a party in a dispute to provide sufficient warrant for their position. Holder of the burden: When two parties are in a discussion and one asserts a claim that the other disputes, the one who asserts has a burden of proof to justify or substantiate that claim. An argument from ignorance occurs when either a proposition is assumed to be true because it has not yet been proved false or a proposition is assumed to be false because it has not yet been proved true. This has the effect of shifting the burden of proof to the person criticizing the proposition. While certain kinds of arguments, such as logical syllogisms, require mathematical or strictly logical proofs, the standard for evidence to meet the burden of proof is usually determined by context and community standards and conventions.
In public discourse: Burden of proof is also an important concept in the public arena of ideas. Once participants in discourse establish common assumptions, the mechanism of burden of proof helps to ensure that all parties contribute productively, using relevant arguments.
Proving a negative: A negative claim is a colloquialism for an affirmative claim that asserts the non-existence or exclusion of something. There are many proofs that substantiate negative claims in mathematics, science, and economics including Arrow’s impossibility theorem. A negative claim may or may not exist as a counterpoint to a previous claim. A proof of impossibility or an evidence of absenceargument are typical methods to fulfill the burden of proof for a negative claim. Example: Atheist internet personality Matt Dillahunty gives the example of a large jar full of gumballs to illustrate the burden of proof. The number of whole gumballs in the jar is either even or odd, but the degree of personal acceptance or rejection of claims about that characteristic may vary. We can choose to consider two claims about the situation, given as: 1. The number of gumballs is even. or 2. The number of gumballs is odd. Either claim could be explored separately; however, both claims represent the same propositionand do in fact ask the same question. Odd in this case means “not even” and could be described as a negative claim. Before we have any information about the number of gumballs, we have no means of checking either of the two claims. When we have no evidence to resolve the proposition, we may suspend judgment. From a cognitive sense, when no personal preference toward opposing claims exists, one may be either skeptical of both claims or ambivalent of both claims. If there is a claim proposed and that claim is disputed, the burden of proof falls onto the proponent of the claim. If there is no agreeably adequate evidence to support a claim, the claim could be considered to be an argument from ignorance. Ref, Ref
Rationalism is any view appealing to intellectual and deductive reason (as opposed to sensory experience or any religious teachings) as the source of knowledge or justification. I personally lean to a type of modern rationalism similar to what was held during the middle of the 20th Century where there was a strong tradition of organized Rationalism (represented in Britain by the Rationalist Press Association, for example), which was particularly influenced by free thinkers and intellectuals.
However, Rationalism in this sense has little in common with traditional Continental Rationalism, and is marked more by a reliance on empirical science. It accepted the supremacy of reason but insisted that the results be verifiable by experience and independent of all arbitrary assumptions or authority. (1)
Rationalism, since the Enlightenment, historically emphasized a “politics of reason” centered upon rational choice,utilitarianism, secularism, and irreligion – the latter aspect’s antitheism later ameliorated by utilitarian adoption of pluralistic rationalist methods practicable regardless of religious or irreligious ideology. In this regard, rationalism, as a methodology, became socially conflated with atheism, In the past, particularly in the 17th and 18th centuries, the term ‘rationalist’ was often used to refer to free thinkers of an anti-clerical and anti-religious outlook. The use of the label ‘rationalist’ to characterize a world outlook which has no place for the supernatural is becoming less popular today; terms like ‘humanist‘ or ‘materialist‘ seem largely to have taken its place.(2)
Moreover, both rationalism and empiricism are known as two major approaches to natural philosophy. Empiricism involved the method of inductive reasoning, which was applied on experience, including observation and experimentation. Rationalism, while not discounting induction entirely, maintained that deductive reasoning was the means to establish true knowledge. Deduction is reasoning from given premises to necessary conclusions. (3)
The modern scientific method synthesizes rationalism and empiricism. The logic of the rationalist is combined with the observational experience of the empiricist. There is an overwhelming consensus, though, that empiricism is the main emphasis. No matter how much logical deduction and mathematical analysis is used, at some point the world must be checked for the confirmation of a belief. The modern scientific method synthesizes rationalism and empiricism. The logic of the rationalist is combined with the observational experience of the empiricist. There is an overwhelming consensus, though, that empiricism is the main emphasis. No matter how much logical deduction and mathematical analysis is used, at some point the world must be checked for the confirmation of a belief. Historically, however, spurred on by the power of mathematics and the tendency to conclude that we know something even though complete empirical observations are not available, rationalism has played both a constructive and creative role in development of science.
The criticism of those who are too rationalistic and who create ivory-tower fantasies from speculative logic, overlooks the fact that many great discoveries have been made by scientists sitting at desks or standing in front of chalkboards. It is difficult for many people today to imagine that the Earth is moving and not the Sun. We do not experience ourselves moving at 1,000 miles per hour; instead we “observe” the Sun to move. That a belief is inconsistent with our common observational experience is not by itself a conclusive argument that it is false. Empirical scientists do believe in the ability of the human mind to figure things out. Any fundamental inconsistency between common sense and reason is seen as nature’s way of taunting us, of revealing one of her important secrets. The confidence in the logical and mathematical powers of human thinking has been a key ingredient in the development of modern science. “Theory Must Agree With Reality” (4)
Radical skepticism cannot be reasonable, we should nonetheless take his method seriously enough that we remain diffident in our judgments – that we not take things dogmatically, but rather critically, ready to recognize evidence that can challenge the rational acceptability of those judgments. So long as we do not take ‘clear’ and ‘distinct’ as rigidly, it is not a bad rule to include nothing more in one’s judgments than what presents itself to one’s mind so clearly and distinctly that one has no reason to doubt it. This is what reasonable persons do, to many it is now the norm. (5)
A question to believers: “if your religion was false would you want to know about it?” If you’re sure of your response is that truly coming from a place of open honesty. We must never forget that just because an idea or belief has mass approval or a wide acceptance, this tells nothing of its truth status, its accuracy, or any provable validity.
My Methodological Rationalism: investigate (ontology), expose (epistemology) and judge (axiology)
Ontology: what is the nature of being or what can rightly even be claimed as existing as a being, thing, or a defined idea’s qualities including what potentially can be said to contain the qualities for truth, facts, or evidence to be seen a real, existing in reality, or even possibly real concepts (Ontology)?
Epistemology: what is the nature of knowledge or what can rightly even be claimed as existing as truth, facts, or evidence including what potentially can be said to contain the conditions for truth, facts, or evidence to be seen a knowledge (Epistemology)?
Axiology: And lastly, what is the nature of value, good, worth, or beneficialness or what can rightly even be claimed as existing as good, worth, or beneficial including what potentially can be said to contain the conditions as well as the qualities for truth, facts, or evidence to be seen a knowledge of value, good, worth, or beneficialness (Axiology).
Ontology and language: Using Ontology to Attack Theistic Errors
ONTOLOGY is the philosophical study of the nature of being, becoming, existence or reality as well as the basic categories of being and their relations. Traditionally listed as a part of the major branch of philosophy known as metaphysics, ontology often deals with questions concerning what entities exist or may be said to exist and how such entities may be grouped, related within a hierarchy, and subdivided according to similarities and differences. Although ontology as a philosophical enterprise is highly theoretical, it also has practical application in information science and technology, such as ontology engineering.
Some philosophers suggest that the question of “What is?” is (at least in part) an issue of usage rather than a question about facts. Suppose a person refers to a “spirit” as a “demon” or “god” and makes some comments pertinent to a spirit, but uses the word “demon” consistently throughout instead of some “god” one listening may get confused yet possibly also catch on that this person simply calls a spirit, demon or a god the same thing and the oddity is thus somewhat understood even though we don’t know why or what they are trying to assert ‘there are’ such-and-such by referring to more unproven/disproven ‘such-and-such’ still tells nothing about the positive anything exist, we might conclude that these people are confused, trying to misinform, or are not thinking enough about that which they refer to, they simply use empty claims of ‘there are’ this or that such-and-such. The question of What is being said, assumed, or believed and is this valid and reliable in a reasonable amount, expression, and/or qualities. “What is being talked about,” is at least partially a topic in the philosophy of language, and yet is not entirely about ontology itself and it is the ontology of what is being said is what I see is of importance.
Why are lies more appealing than the truth?
No there is No gods and No we are not a Brain in a Vat
“Dead is Dead” no ghosts, spirits or souls…
Psychological certainty and Epistemic certainty?
Basics of my Methodological Rationalism Epistemology Approach
I was asked about the The Gettier Problem, well, to me Edmund Gettier only points out that more than just JTB is needed as there may be some beliefs outside of simply JTB which I do, I feel all stages need analysis and support not just some simple use of JTB. With my Methodological Rationalism Epistemology Approach, I try to show how to build accuracy in beliefs, of course there are always many non-accurate ways beliefs may be arrived at, analize or maintained, as well as updated or remove beliefs if found to be in error. We conceptualize epistemological attitudes and beliefs as components of metacognitive knowledge. As such, they serve an important function in regulating the use of epistemic strategies such as knowledge-based validation of information and checking arguments for internal consistency. Ref Epistemic Attitudes: Belief, Disbelief and Suspended Judgement. click here is an interesting but complicated article on this subject. To me when assessing belief, one should think about reliabilism.I usually try to use a reliabilism approach to epistemology which emphasizes the truth-conduciveness of a belief-forming process, method, or other epistemologically relevant factors. The reliability theme appears in theories of knowledge, of justification, and of evidence. “Reliabilism” is sometimes used broadly to refer to any theory that emphasizes truth-getting or truth indicating properties. Ref
The Scientific Method & Naturalistic Rationalism
Why not Find Out if what you believe is True?
Scientific Thinking not Faith Thinking
The Rational Imperative, How Does One Know Things?
I am aggressive with ideas, but I am kind to people. My motto is attack thinking not people. I do not respect religion, but I respect people. I do not believe in religion as it has a high potential for bad, but I believe in the potential for good in people. That is my style as a Firebrand Atheist that is a Humanistic Person.
My Atheist Activism Acknowledged in College Paper: Link
I often say to believers on the street, no, you don’t believe in god or religion. What you do or did was were told, (most often by family) this is what you need to believe or this is what we believe and you say ok, only after that as an adult, (especially when challenged) you try to support this post-acceptance commitment as if it has a rationalization. You are attempting to support that you did not choose wrong overlooking any faults or defects in order to feel justified and the psychological desire to stay consistent to that commitment.
So, what you likely have now is a kind of Post-purchase rationalization. Which is also known as Buyer’s Stockholm Syndrome, a cognitive bias whereby someone who has purchased an expensive product or service overlooks any faults or defects in order to justify their purchase. It is a special case of choice-supportive bias. This rationalization is based on the Principle of Commitment and the psychological desire to stay consistent to that commitment. (6)
I am a rationalist and support reasonable skepticism, thus, I am not a skeptic though I somewhat am a fan. Lol
I do not call myself a skeptic, I do not doubt that which is unreasonable to require doubt. I am a rationalist who uses methodological skepticism and also may utilize scientific skepticism. Methodological skepticism is a way of using the process of doubting in order to arrive at certainty. And scientific skepticism is the practice of questioning whether claims are supported by empirical research and have reproducibility, as part of a methodological norm pursuing “the extension of certified knowledge” Some people who doubt what is rational or proven say they are skeptics or being skeptical they are denialists or possibly using philosophic skepticism. Philosophical skepticism is distinguished from methodological skepticism in that philosophical skepticism is an approach that questions the possibility of certainty in knowledge. Whereas methodological skepticism is an approach that subjects all knowledge claims to scrutiny with the goal of sorting out true from false claims. Methodological skepticism, is a systematic process of being skeptical about (or doubting) the truth of one’s beliefs, it is similar to scientific skepticism.
Likewise, scientific skepticism is different from philosophical skepticism, which questions our ability to claim any knowledge about the nature of the world and how we perceive it. Scientific skeptics believe that empirical investigation of reality leads to the truth, and that the scientific method is best suited to this purpose. Scientific skeptics attempt to evaluate claims based on verifiability, reliability, and often adhering to falsifiability discouraging acceptance of claims on faith or anecdotal evidence. There does seem to be a lot of improper use of the term skeptic attached to conspiracy theories and denialism. In human behavior, denialism is exhibited by individuals choosing to deny reality as a way to avoid dealing with an uncomfortable truth. Then again, I have skepticism for “extreme philosophical skepticism or universal skepticism philosophy”. Radical skepticism about the external world is the idea that we cannot have accurate knowledge about the physical world outside of our minds. That idea, if true, would block the truth-seeker’s attempt to gain knowledge by assessing the natural world. Sure, reasonable skepticism gets us to a good solid starting point to remove flawed beliefs but there is a need to move beyond skepticism if it removes any sureness of things that are actually demonstrative as true then to me it can become pseudo-skeptic and denialist thinking.
Granted I do think all claims or beliefs we think are true should be open to challenge and reassessment and if found wanting corrected or abandoned. Scientific skepticism is also called rational skepticism, and it is sometimes referred to as skeptical inquiry. I see philosophy as a set of tools, some are viral, some not needed as much but still useful, other not very useful but still needed and others just some gimmick people were conned into buying that is entirely unusual and even harmful. I am not anti-skeptical or anti-skeptic it is just not the accurate label for my thinking. if the term “Skeptic” was limited to only methodological skepticism I would champion the term as well. I think skeptic should automatically infer the methodological skepticism approach and likewise, denialist thinking should not be seen as a true philosophical approach to skepticism as there is a difference between a skeptic and denialist. Denialist “pseudo-skeptics” are often religionists, magical thinkers, conspiracy theorist, supporters of woo-woo, and other whack jobs these days. Religion and other magical thinking woo-woo distorts reality. How can we expect people to make rational decisions when they believe in non-reality as if it is reality? Reasonable skepticism to me is or should be more about the process of applying reason and critical thinking to determine validity or reliable reason or evidence. It’s the process of finding a supported conclusion, not the justification of a preconceived conclusion. 1, 2, 3, 4
Rationalism, Freethinker, Humanism & Secular humanism?
I am a am a rationalist, freethinker, humanist and a secularist.
*Rationalism is a philosophy in which a high regard is given to reason (specifically logic) and to empirical observation.
*Freethinker a person who forms his or her own opinions about important subjects (such as religion and politics) instead of accepting what other people say.
*Humanism is a philosophical and ethical stance that emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, individually and collectively, and generally prefers critical thinking and evidence (rationalism, empiricism) over established doctrine or faith (fideism).
*Secular humanism is a comprehensive, nonreligious life stance incorporating: A naturalistic philosophy. A cosmic outlook rooted in science. A consequentialist ethical system.
My Methodological Skepticism Style
Rationalist through and through
Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology argument/challenge protocol
“The Hammer of Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
“Hammer of Truth” response to “Do you Believe in god?”
Why not Find Out if what you believe is True?
Scientific Thinking not Faith Thinking
Scientific Values: fallibilism, realism, & rationalism
The Scientific Method & Naturalistic Rationalism
The Evolution of Religion and Removing the Rationale of Faith
You can’t change people, by reason and evidence. WRONG, I do it all the time.
“The Age of Enlightenment: Rationalism, Revolution, and Irreligion”
Skepticism and or Rationalism Leads to Humanism and Atheism?
Rationalism, Freethinker, Humanism & Secular humanism?
Below is Info gathered from From Wikipedia
The Enlightenment has long been hailed as the foundation of modern Western political and intellectual culture. The Enlightenment brought political modernization to the West, in terms of introducing democratic values and institutions and the creation of modern, liberal democracies. This thesis has been widely accepted by Anglophone scholars and has been reinforced by the large-scale studies by Robert Darnton, Roy Porter and most recently by Jonathan Israel. The Enlightenment has always been contested territory. According to Keith Thomas, its supporters “hail it as the source of everything that is progressive about the modern world. For them, it stands for freedom of thought, rational inquiry, critical thinking, religious tolerance, political liberty, scientific achievement, the pursuit of happiness, and hope for the future”. Areas of study such as literature, philosophy, science and the fine arts increasingly explored subject matter that the general public in addition to the previously more segregated professionals and patrons could relate to. Thomas adds that its detractors accuse it of shallow rationalism, naïve optimism, unrealistic universalism and moral darkness. From the start, conservative and clerical defenders of traditional religion attacked materialism and skepticism as evil forces that encouraged immorality.
By 1794, they pointed to the Terror during the French Revolution as confirmation of their predictions. As the Enlightenment was ending, Romantic philosophers argued that excessive dependence on reason was a mistake perpetuated by the Enlightenment because it disregarded the bonds of history, myth, faith, and tradition that were necessary to hold society together. One of the primary elements of the culture of the Enlightenment was the rise of the public sphere, a “realm of communication marked by new arenas of debate, more open and accessible forms of urban public space and sociability, and an explosion of print culture”, in the late 17th century and 18th century. Elements of the public sphere included: it was egalitarian, it discussed the domain of “common concern” and argument was founded on reason. Habermas uses the term “common concern” to describe those areas of political/social knowledge and discussion that were previously the exclusive territory of the state and religious authorities, now open to critical examination by the public sphere. The values of this bourgeois public sphere included holding reason to be supreme, considering everything to be open to criticism (the public sphere is critical) and the opposition of secrecy of all sorts. In philosophy, rationalism is the epistemological view that “regards reason as the chief source and test of knowledge” or “any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification”. More formally, rationalism is defined as a methodology or a theory “in which the criterion of the truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive”. Generally speaking, intuition is a priori knowledge or experiential belief characterized by its immediacy; a form of rational insight. We simply just “see” something in such a way as to give us a warranted belief. Beyond that, the nature of intuition is hotly debated. In the same way, generally speaking, deduction, is the process of reasoning from one or more general premises to reach a logically certain conclusion. Using valid arguments, we can deduce from intuited premises.
For example, when we combine both concepts, we can intuit that the number three is prime and that it is greater than two. We then deduce from this knowledge that there is a prime number greater than two. Thus, it can be said that intuition and deduction combined to provide us with a priori knowledge – we gained this knowledge independently of sense experience. Empiricists such as David Hume have been willing to accept this thesis for describing the relationships among our own concepts. In this sense, empiricists argue that we are allowed to intuit and deduce truths from knowledge, that has been obtained a posteriori. By injecting different subjects into the Intuition/Deduction thesis, we are able to generate different arguments. Most rationalists agree mathematics is knowable by applying the intuition and deduction. Some go further to include ethical truths into the category of things knowable by intuition and deduction. Furthermore, some rationalists also claim metaphysics is knowable in this thesis. In addition to different subjects, rationalists sometimes vary the strength of their claims by adjusting their understanding of the warrant. Some rationalists understand warranted beliefs to be beyond even the slightest doubt; others are more conservative and understand the warrant to be believed beyond a reasonable doubt. Rationalists also have different understanding and claims involving the connection between intuition and truth. Some rationalists claim that intuition is infallible and that anything we intuit to be true is as such. More contemporary rationalists accept that intuition is not always a source of certain knowledge – thus allowing for the possibility of a deceiver who might cause the rationalist to intuit a false proposition in the same way a third party could cause the rationalist to have perceptions of nonexistent objects. Naturally, the more subjects the rationalists claim to be knowable by the Intuition/Deduction thesis, the more certain they are of their warranted beliefs, and the more strictly they adhere to the infallibility of intuition, the more controversial their truths or claims and the more radical their rationalism. To argue in favor of this thesis, Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, a prominent German philosopher, says, “The senses, although they are necessary for all our actual knowledge, are not sufficient to give us the whole of it, since the senses never give anything but instances, that is to say, particular or individual truths. Now all the instances which confirm a general truth, however numerous they may be, are not sufficient to establish the universal necessity of this same truth, for it does not follow that what happened before will happen in the same way again.
From which it appears that necessary truths, such as we find in pure mathematics, and particularly in arithmetic and geometry, must have principles whose proof does not depend on instances, nor consequently on the testimony of the senses, although without the senses it would never have occurred to us to think of them…”The Enlightenment (also known as the Age of Enlightenment or the Age of Reason; in French: le Siècle des Lumières, lit. ‘”the Century of Lights”‘; and in German: Aufklärung, “Enlightenment”) was an intellectual and philosophical movement which dominated the world of ideas in Europe during the 18th century, “The Century of Philosophy”. The Enlightenment included a range of ideas centered on reason as the primary source of authority and legitimacy—and came to advance ideals like liberty, progress, tolerance, fraternity, constitutional government and separation of church and state. In politics, rationalism, since the Enlightenment, historically emphasized a “politics of reason” centered upon rational choice, utilitarianism, secularism, and irreligion – the latter aspect’s antitheism later softened by politic adoption of pluralistic rationalist methods practicable regardless of religious or irreligious ideology. In this regard, the philosopher John Cottingham noted how rationalism, a methodology, became socially conflated with atheism, a worldview: “In the past, particularly in the 17th and 18th centuries, the term ‘rationalist’ was often used to refer to free thinkers of an anti-clerical and anti-religious outlook, and for a time the word acquired a distinctly pejorative force (thus in 1670 Sanderson spoke disparagingly of ‘a mere rationalist, that is to say in plain English an atheist of the late edition…’). The use of the label ‘rationalist’ to characterize a world outlook which has no place for the supernatural is becoming less popular today; terms like ‘humanist’ or ‘materialist’ seem largely to have taken its place. But the old usage still survives.”
French historians traditionally place the Enlightenment between 1715 (the year that Louis XIV died) and 1789 (the beginning of the French Revolution). Some recent historians begin the period in the 1620s, with the start of the scientific revolution. Les philosophes (French for “the philosophers”) of the period widely circulated their ideas through meetings at scientific academies, Masonic lodges, literary salons, coffee houses and printed books and pamphlets. The ideas of the Enlightenment undermined the authority of the monarchy and the Church—and paved the way for the political revolutions of the 18th and 19th centuries. A variety of 19th-century movements, including liberalism and neo-classicism, trace their intellectual heritage back to the Enlightenment. The Age of Enlightenment was preceded by and closely associated with the scientific revolution. Earlier philosophers whose work influenced the Enlightenment included Francis Bacon, René Descartes, John Locke and Baruch Spinoza. The major figures of the Enlightenment included Cesare Beccaria, Voltaire, Denis Diderot, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, David Hume, Adam Smith and Immanuel Kant. Some European rulers, including Catherine II of Russia, Joseph II of Austria and Frederick II of Prussia, tried to apply Enlightenment thought on religious and political tolerance, which became known as enlightened absolutism. Benjamin Franklin visited Europe repeatedly and contributed actively to the scientific and political debates there and brought the newest ideas back to Philadelphia. Thomas Jefferson closely followed European ideas and later incorporated some of the ideals of the Enlightenment into the Declaration of Independence (1776). One of his peers, James Madison, incorporated these ideals into the United States Constitution during its framing in 1787.
The most influential publication of the Enlightenment was the Encyclopédie (Encyclopaedia). Published between 1751 and 1772 in thirty-five volumes, it was compiled by Denis Diderot, Jean le Rond d’Alembert (until 1759) and a team of 150 scientists and philosophers. It helped spread the ideas of the Enlightenment across Europe and beyond. Other landmark publications were Voltaire’s Dictionnaire philosophique (Philosophical Dictionary; 1764) and Letters on the English (1733); Rousseau’s Discourse on Inequality (1754) and The Social Contract (1762); Adam Smith’s The Wealth of Nations (1776); and Montesquieu’s The Spirit of the Laws (1748). The ideas of the Enlightenment played a major role in inspiring the French Revolution, which began in 1789. René Descartes’ rationalist philosophy laid the foundation for enlightenment thinking. His attempt to construct the sciences on a secure metaphysical foundation was not as successful as his method of doubt applied in philosophic areas leading to a dualistic doctrine of mind and matter. His skepticism was refined by John Locke’s Essay Concerning Human Understanding (1690) and David Hume’s writings in the 1740s. His dualism was challenged by Spinoza’s uncompromising assertion of the unity of matter in his Tractatus (1670) and Ethics (1677). These laid down two distinct lines of Enlightenment thought: the moderate variety, following Descartes, Locke and Christian Wolff which sought accommodation between reform and the traditional systems of power and faith and the radical enlightenment, inspired by the philosophy of Spinoza, advocating democracy, individual liberty, freedom of expression and eradication of religious authority. The moderate variety tended to be deistic whereas the radical tendency separated the basis of morality entirely from theology.
Both lines of thought were eventually opposed by a conservative Counter-Enlightenment, which sought a return to faith. In the mid-18th century, Paris became the center of an explosion of philosophic and scientific activity challenging traditional doctrines and dogmas. The philosophic movement was led by Voltaire and Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who argued for a society based upon reason rather than faith and Catholic doctrine, for a new civil order based on natural law and for science based on experiments and observation. The political philosopher Montesquieu introduced the idea of a separation of powers in a government, a concept which was enthusiastically adopted by the authors of the United States Constitution. While the Philosophes of the French Enlightenment were not revolutionaries, and many were members of the nobility, their ideas played an important part in undermining the legitimacy of the Old Regime and shaping the French Revolution. Mary Wollstonecraft was one of England’s earliest feminist philosophers. She argued for a society based on reason and that women as well as men should be treated as rational beings. She is best known for her work A Vindication of the Rights of Woman (1791). Science played an important role in Enlightenment discourse and thought. Many Enlightenment writers and thinkers had backgrounds in the sciences and associated scientific advancement with the overthrow of religion and traditional authority in favor of the development of free speech and thought. Scientific progress during the Enlightenment included the discovery of carbon dioxide (fixed air) by the chemist Joseph Black, the argument for deep time by the geologist James Hutton and the invention of the steam engine by James Watt. The experiments of Lavoisier were used to create the first modern chemical plants in Paris and the experiments of the Montgolfier Brothers enabled them to launch the first manned flight in a hot-air balloon on 21 November 1783 from the Château de la Muette, near the Bois de Boulogne. Broadly speaking, Enlightenment science greatly valued empiricism and rational thought and was embedded with the Enlightenment ideal of advancement and progress.
The study of science, under the heading of natural philosophy, was divided into physics and a conglomerate grouping of chemistry and natural history, which included anatomy, biology, geology, mineralogy and zoology. As with most Enlightenment views, the benefits of science were not seen universally: Rousseau criticized the sciences for distancing man from nature and not operating to make people happier. Science during the Enlightenment was dominated by scientific societies and academies, which had largely replaced universities as centers of scientific research and development. Societies and academies were also the backbone of the maturation of the scientific profession. Another important development was the popularization of science among an increasingly literate population. Philosophes introduced the public to many scientific theories, most notably through the Encyclopédie and the popularization of Newtonianism by Voltaire and Émilie du Châtelet. Some historians have marked the 18th century as a drab period in the history of science. However, the century saw significant advancements in the practice of medicine, mathematics and physics; the development of biological taxonomy; a new understanding of magnetism and electricity; and the maturation of chemistry as a discipline, which established the foundations of modern chemistry. Scientific academies and societies grew out of the Scientific Revolution as the creators of scientific knowledge in contrast to the scholasticism of the university. During the Enlightenment, some societies created or retained links to universities, but contemporary sources distinguished universities from scientific societies by claiming that the university’s utility was in the transmission of knowledge while societies functioned to create knowledge. As the role of universities in institutionalized science began to diminish, learned societies became the cornerstone of organized science. Official scientific societies were chartered by the state in order to provide technical expertise. Most societies were granted permission to oversee their own publications, control the election of new members and the administration of the society. After 1700, a tremendous number of official academies and societies were founded in Europe and by 1789 there were over seventy official scientific societies. In reference to this growth, Bernard de Fontenelle coined the term “the Age of Academies” to describe the 18th century. Hume and other Scottish Enlightenment thinkers developed a “science of man”, which was expressed historically in works by authors including James Burnett, Adam Ferguson, John Millar and William Robertson, all of whom merged a scientific study of how humans behaved in ancient and primitive cultures with a strong awareness of the determining forces of modernity.
Modern sociology largely originated from this movement and Hume’s philosophical concepts that directly influenced James Madison (and thus the U.S. Constitution) and as popularised by Dugald Stewart, would be the basis of classical liberalism. In 1776, Adam Smith published The Wealth of Nations, often considered the first work on modern economics as it had an immediate impact on British economic policy that continues into the 21st century. It was immediately preceded and influenced by Anne-Robert-Jacques Turgot, Baron de Laune drafts of Reflections on the Formation and Distribution of Wealth (Paris, 1766). Smith acknowledged indebtedness and possibly was the original English translator. John Locke, one of the most influential Enlightenment thinkers, based his governance philosophy in social contract theory, a subject that permeated Enlightenment political thought. The English philosopher Thomas Hobbes ushered in this new debate with his work Leviathan in 1651. Hobbes also developed some of the fundamentals of European liberal thought: the right of the individual; the natural equality of all men; the artificial character of the political order (which led to the later distinction between civil society and the state); the view that all legitimate political power must be “representative” and based on the consent of the people; and a liberal interpretation of law which leaves people free to do whatever the law does not explicitly forbid. Both Locke and Rousseau developed social contract theories in Two Treatises of Government and Discourse on Inequality, respectively. While quite different works, Locke, Hobbes and Rousseau agreed that a social contract, in which the government’s authority lies in the consent of the governed, is necessary for man to live in civil society. Locke defines the state of nature as a condition in which humans are rational and follow natural law, in which all men are born equal and with the right to life, liberty and property.
However, when one citizen breaks the Law of Nature both the transgressor and the victim enter into a state of war, from which it is virtually impossible to break free. Therefore, Locke said that individuals enter into civil society to protect their natural rights via an “unbiased judge” or common authority, such as courts, to appeal to. Contrastingly, Rousseau’s conception relies on the supposition that “civil man” is corrupted, while “natural man” has no want he cannot fulfill himself. Natural man is only taken out of the state of nature when the inequality associated with private property is established. Rousseau said that people join into civil society via the social contract to achieve unity while preserving individual freedom. This is embodied in the sovereignty of the general will, the moral and collective legislative body constituted by citizens. Locke is known for his statement that individuals have a right to “Life, Liberty and Property” and his belief that the natural right to property is derived from labor. Tutored by Locke, Anthony Ashley-Cooper, 3rd Earl of Shaftesbury wrote in 1706: “There is a mighty Light which spreads its self over the world especially in those two free Nations of England and Holland; on whom the Affairs of Europe now turn”. Locke’s theory of natural rights has influenced many political documents, including the United States Declaration of Independence and the French National Constituent Assembly’s Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen. The philosophes argued that the establishment of a contractual basis of rights would lead to the market mechanism and capitalism, the scientific method, religious tolerance and the organization of states into self-governing republics through democratic means. In this view, the tendency of the philosophes in particular to apply rationality to every problem is considered the essential change. Though much of Enlightenment political thought was dominated by social contract theorists, both David Hume and Adam Ferguson criticized this camp. Hume’s essay Of the Original Contract argues that governments derived from consent are rarely seen and civil government is grounded in a ruler’s habitual authority and force. It is precisely because of the ruler’s authority over-and-against the subject, that the subject tacitly consents, and Hume says that the subjects would “never imagine that their consent made him sovereign”, rather the authority did so. Similarly, Ferguson did not believe citizens built the state, rather polities grew out of social development. In his 1767 An Essay on the History of Civil Society, Ferguson uses the four stages of progress, a theory that was very popular in Scotland at the time, to explain how humans advance from a hunting and gathering society to a commercial and civil society without “signing” a social contract.
Both Rousseau and Locke’s social contract theories rest on the presupposition of natural rights, which are not a result of law or custom, but are things that all men have in pre-political societies and are therefore universal and inalienable. The most famous natural right formulation comes from John Locke in his Second Treatise, when he introduces the state of nature. For Locke, the law of nature is grounded on mutual security or the idea that one cannot infringe on another’s natural rights, as every man is equal and has the same inalienable rights. These natural rights include perfect equality and freedom, as well as the right to preserve life and property. Locke also argued against slavery on the basis that enslaving yourself goes against the law of nature because you cannot surrender your own rights, your freedom is absolute, and no one can take it from you. Additionally, Locke argues that one person cannot enslave another because it is morally reprehensible, although he introduces a caveat by saying that enslavement of a lawful captive in time of war would not go against one’s natural rights. Enlightenment era religious commentary was a response to the preceding century of religious conflict in Europe, especially the Thirty Years’ War. Theologians of the Enlightenment wanted to reform their faith to its generally non-confrontational roots and to limit the capacity for religious controversy to spill over into politics and warfare while still maintaining a true faith in God. For moderate Christians, this meant a return to simple Scripture. John Locke abandoned the corpus of theological commentary in favor of an “unprejudiced examination” of the Word of God alone. He determined the essence of Christianity to be a belief in Christ the redeemer and recommended avoiding more detailed debate. In the Jefferson Bible, Thomas Jefferson went further and dropped any passages dealing with miracles, visitations of angels and the resurrection of Jesus after his death, as he tried to extract the practical Christian moral code of the New Testament. Enlightenment scholars sought to curtail the political power of organized religion and thereby prevent another age of intolerant religious war. Spinoza determined to remove politics from contemporary and historical theology (e.g., disregarding Judaic law). Moses Mendelssohn advised affording no political weight to any organized religion, but instead recommended that each person follow what they found most convincing. A good religion based in instinctive morals and a belief in God should not theoretically need force to maintain order in its believers and both Mendelssohn and Spinoza judged religion on its moral fruits, not the logic of its theology. A number of novel ideas about religion developed with the Enlightenment, including deism and talk of atheism.
According to Thomas Paine, deism is the simple belief in God the Creator, with no reference to the Bible or any other miraculous source. Instead, the deist relies solely on personal reason to guide his creed, which was eminently agreeable to many thinkers of the time. Atheism was much discussed, but there were few proponents. Wilson and Reill note: “In fact, very few enlightened intellectuals, even when they were vocal critics of Christianity, were true atheists. Rather, they were critics of orthodox belief, wedded rather to skepticism, deism, vitalism, or perhaps pantheism”. Some followed Pierre Bayle and argued that atheists could indeed be moral men. Many others like Voltaire held that without belief in a God who punishes evil, the moral order of society was undermined. That is, since atheists gave themselves to no Supreme Authority and no law and had no fear of eternal consequences, they were far more likely to disrupt society. Bayle (1647–1706) observed that in his day that “prudent persons will always maintain an appearance of [religion]” and he believed that even atheists could hold concepts of honor and go beyond their own self-interest to create and interact in society. Locke said that if there were no God and no divine law, the result would be moral anarchy: every individual “could have no law but his own will, no end but himself. He would be a god to himself, and the satisfaction of his own will the sole measure and end of all his actions”. The “Radical Enlightenment” promoted the concept of separating church and state, an idea that is often credited to English philosopher John Locke (1632–1704). According to his principle of the social contract, Locke said that the government lacked authority in the realm of individual conscience, as this was something rational people could not cede to the government for it or others to control.
For Locke, this created a natural right in the liberty of conscience, which he said must therefore remain protected from any government authority. These views on religious tolerance and the importance of individual conscience, along with the social contract, became particularly influential in the American colonies and the drafting of the United States Constitution. Thomas Jefferson called for a “wall of separation between church and state” at the federal level. He previously had supported successful efforts to disestablish the Church of England in Virginia and authored the Virginia Statute for Religious Freedom. Jefferson’s political ideals were greatly influenced by the writings of John Locke, Francis Bacon and Isaac Newton whom he considered the three greatest men that ever lived. Several Americans, especially Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson, played a major role in bringing Enlightenment ideas to the New World and in influencing British and French thinkers. Franklin was influential for his political activism and for his advances in physics. The cultural exchange during the Age of Enlightenment ran in both directions across the Atlantic. Thinkers such as Paine, Locke and Rousseau all take Native American cultural practices as examples of natural freedom. The Americans closely followed English and Scottish political ideas, as well as some French thinkers such as Montesquieu. As deists, they were influenced by ideas of John Toland (1670–1722) and Matthew Tindal (1656–1733). During the Enlightenment there was a great emphasis upon liberty, and here was no respect for monarchy or inherited political power. Ref, Ref
Why I Am A Rationalist
by Bertrand Russell
The Rational Habit Of Mind Is A Rare One
![]()
I am, in this age when there are a great many appeals to unreason, an unrepentant Rationalist. I have been a Rationalist ever since I can remember, and I do not propose to cease to be so whatever appeals to unreason may be made. We have listened to a speech, by which I think we were all much moved, about the pioneers in the past who have done what they could to promote the cause of freedom of thought. I suppose it is for me to speak about the great need of continuing this work in our own day, and about how much there is that remains for all who sympathize with its objects to accomplish. We are not yet, and I suppose men and women never will be, completely rational. Perhaps, if we were, we should not have all the pleasures that we have at present; but I think complete rationality is so distant a prospect that we need not be much alarmed by it, and the nearest approach that we are likely to get is sure to be all to the good. I certainly find that there is a very great deal of irrationality still about in the world. While Professor Graham Wallas was speaking about the bequests that have been made to the Rationalist Press Association I was thinking: What is its creed, what is its dogma, and what is going to be the, so to speak, doctrine that these benefactions are going to be devoted to propagating? You have, of course, to be a little careful, when you find yourself landed with endowments and benefactions, lest you should become another endowed church. (Laughter.)
As far as I can see, the view to which we are committed, one which I have stated on a former occasion, is that we ought not to believe, and we ought not to try to cause others to believe, any proposition for which there is no evidence whatever. That seems a modest proposition, and if you can stick to that you will be fairly sure that you are not going to become a sort of ossified endowed church. We ought not to commit ourselves to dogmatic negations any more than to dogmatic affirmations; we ought merely to say that there are a great many propositions about which men and women feel pretty certain, but, concerning which they have no right to feel certain, and it is our business as Rationalists to try to make them see that those things are not certain. I am told that that is a very wicked position to maintain. I have here a book recently published which I commend to your attention. You may or may not know that some little time ago, under the auspices of the National Secular Society, I delivered a lecture on “Why I am Not a Christian.” Now, It appears that I did not know why it is that I am not a Christian; and here is a book which will tell you why I am not — by Mr. H. G. Wood, who is a somewhat eminent member of the Society of Friends, a body for which I have the greatest respect. His book is called Why Mr. Bertrand Russell is Not a Christian.
It seems that the reasons are not those which I thought they were. He says in one sentence: “The main reason why he is not a Christian is that he simply does not know what religion is.” One might say that Mr. Wood is not an Agnostic because he does not know what Agnosticism is. After all, I had all the benefits of a Christian education, and he did not have the benefits of an Agnostic education; so that possibly the argument might be considered two-edged. Nevertheless, I commend the book to your attention, and you will then know why it is that I am not a Christian. There is a very large amount of Rationalist work required in the world. I think the battle is quite as fierce as ever it was. Take, for example America. America is a very important country. What America thinks today the rest of the world will be forced to think tomorrow, and therefore what America thinks is important. There are some hopeful features about America. I was recently on a boat going to America, and a minister of religion on the boat invited me to speak to his congregation about my views on religion. I said: “Yours must be a very broad-minded congregation”; and this minister of religion, somewhat to my surprise, replied: “Oh, of course, I do not believe in God.” I met other ministers of religion in America who took the same line.
That, I must say, somewhat surprised me; but they are, I am afraid, rather a small minority, and the great bulk of Americans are still extremely theological. Moreover, we have to face the very serious position due to the growth of the Roman Catholic Church in America, because, as far as I can see, the Roman Catholic Church is likely to dominate America in another fifty or a hundred years by the sheer increase of numbers, and not by rational propaganda. That is a very grave matter, and a matter which I think will affect the whole of the civilized world very much. Of course, you know that already in Boston, which was once the home of advanced Protestantism, the Roman Catholics rule the whole place; and there is a censorship upon literature more severe than in any other part of America. I expect you know that in America men are still sent to prison for Atheism, not only in Fundamentalist States, but even in States of the East, and altogether there is in that part of the world an enormous need of propaganda on these matters. It is very important to all of us, because the Americans tend more and more to rule the world, and we shall find ourselves in a very difficult position unless we can more or less liberalize them — a mission, I may say, in which I have done what I can, and my wife has also. We have to realize that the attitude of Rationalism, which I defined as that of not believing a proposition or causing others to believe it unless there is at least some reason for supposing it to be true, is by no means widespread.
Take the matter of education, concerning which Professor Graham Wallas spoke. In most countries of the world a great many extremely dubious propositions are taught to the young with great emphasis, and the young grow up accepting those extremely dubious propositions. If by any chance you attempt, as my wife and I are attempting at this moment, to bring up a small number of young people free from superstition, you find yourself in a very difficult situation. You find, of course, that the public money which goes to education will not be given to any education that involves no element of superstition; you find that support is extremely difficult to obtain; you find that altogether it is thought that, whatever grown men and women may be allowed to think, the young, at any rate, ought to believe a whole lot of absurdities, and that it is quite impossible for the young to attain the necessary minimum of virtues unless you produce an extremely large number of very bad arguments in favor of that virtue-arguments which, of course, they will see through as soon as they get a little older; but it is thought that what they do then when they see through them does not so much matter. I cannot quite take that view. I think that any virtue that you may believe in should be one that you can support from the very first without appealing to anything that you do not yourself believe.
Education will have to be quite enormously transformed if that view is accepted. I believe that it is at present illegal in every country of the world except Russia to teach children in the kind of way which skilled medical practitioners would consider the best for their mental health. That is one point upon which irrational convictions as generally held interfere, and there are a number of ways in which it is at present impossible to educate rationally without coming up against the authorities. The authorities are organized upon a basis of certain irrational dogmas, and those dogmas are not all of them theological. Some are theological, and some are of other sorts; but the rational habit of mind is a very rare one. I think that we ought to do all that we can to bring before the world the importance of the attitude that we are not going to believe a thing unless there is some reason to think that it is true. I know that that is thought to be very shocking. It is supposed that there are a lot of things that you ought to believe because good people believe them, and not because there is any reason for them. I do not take that view. I think anything that is worth believing must have some positive ground in its favor.
There are always new grounds being alleged in favor of irrationality; perpetually new things come up. Take, for example, the kind of use that has been made by some people of psycho-analysis. If you read the works of the founder of psycho-analysis, you find an entirely rationalist attitude; but if you listen to some of the minor disciples you will imagine that this doctrine has swept away the idea that opinions can be based upon reason at all. That, of course, is not the truth of it. You will always find a number of clever people engaged in perversions of anything that comes up — engaged in saying that the latest results of science prove that the people who always opposed science are after all in the right. That is where there is always humbug. Anybody who tells you that the latest results of science prove something, he himself not being a scientist, you may be pretty sure is talking nonsense. Ref
Skepticism and or Rationalism Leads to Humanism and Atheism?
“My Methodological Skepticism Style, Part of My Methodological Rationalism”
I am going to give a quick and clear expression of my methodological skepticism style. It is more like critical thinking then just some act of doubt, which can be summed up as pausing when any thought is offered, ether by oneself and/or others. I mainly advocate for fallibilism (realizing that humans tend to error and lack accuracy) instead of the falsification skeptics seem to like; I also may rely on the axiomatic arguments, which rests on accepted precepts. Broadly speaking, Fallibilism (from Medieval Latin: fallibilis, “liable to err”) is the philosophical claim that no belief is free from the possibility to be in error or lacking in accuracy, knowledge does not require anything more than epistemic certainty and I believe that extends to all domains of knowledge. Roughly characterized, a belief is epistemically certain when it has the highest possible epistemic status. Epistemic certainty is the full confidence that the epistemic position offered has warrants often accompanied by psychological certainty, but it need not be. It is possible that a subject may have a belief that enjoys the highest possible epistemic status and yet be unaware that it does. In such a case, the subject may feel less than the full confidence that her epistemic position warrants.
Questions should be asked as to how any knowledge claim is “known” or thought to be true. Proof is needed to be provide the understanding of the thinking’s, reasoning’s or belief’s “knowledge representation” which is then questioned, defined, and explored. Yet that same question can be asked of the proof, and any subsequent proof. This may also be applied to weaker notions than knowledge; Things that are not (fully) justified, Things that are “probably true”, and Things that are “true most of the time.”
Then to manage these questions one employs my “Hammer of Truth” which is three philosophic categories of Ontology, Epistemology and Axiology to add accuracy in thinking, reasoning and believing. Ontology (What), Epistemology (How) and Axiology (why) questions debate/challenge philosophy tools so people easily learn how to use Ontology, Epistemology and Axiology questions to remove errors and add accuracy.
Thus, when one employs my “Hammer of Truth”, they can use the three categories of specific philosophic questions requiring precise philosophic answers with the aim of helping in this error removing and accuracy building endeavor.
*Ontology (thingness of things) questions to define or compare and contrast thingness.
*Epistemology (knowledge of things) questions to explode or establish and confirm knowledge.
*Axiology (value/worth/goodness of things) questions to valueize (value judge) or establish and confirm value or disvalue, worth or dis-worth, as well as goodness or un-good.
To understand what is being offered using My Methodological Rationalism’s “Hammer of Truth” Ontology, Epistemology and Axiology questions debate/challenge philosophy tools gatherers: “Ontology”, inquisitors: “Epistemology”, & judgers: “Axiology.”
Ontology (Greek meaning ontos, “being; that which is”; and logos meaning “discourse, study, ratio, calculation, reason”) Ontology is the philosophical study of the nature of being, becoming, existence, or reality, as well as the basic categories of being and their relations.
Epistemology (Greek episteme, meaning “knowledge, understanding”, and logos, meaning “discourse, study, ratio, calculation, reason”) it is the theory of knowledge, especially with regard to its methods, validity, and scope. Epistemology is the investigation of what distinguishes justified belief from opinion.
Axiology (Greek meaning axia, “value, worth”; and logos meaning “discourse, study, ratio, calculation, reason”) it is the philosophical study of value as well as ethics and aesthetics. Formal Axiology is a specific branch of the science of Axiology. Axiology also studies of goodness, value or worth, in the widest sense of these terms. Its significance lies in the unification that it has provided for the study of a variety of questions—economic, moral, aesthetic, and even logical—that had often been considered in relative isolation.
“The Hammer of Truth” is the use of Ontology, Epistemology and Axiology questions to remove errors and add accuracy. It is also my folk name for Scientific Philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, and Axiology”
Questions to Ponder or Pose:
*What is being offered (a good Ontology answer is needed; or understanding the “what” of the thing in question or what is the level of accuracy or understanding of “what” is being transmitted).
* How Do you know that (a good Epistemology answer is needed; or understanding the “how” of the way, manner or by what means is the justification, warrant and/or support reached needing valid and reliable reason and evidence for what is being offered.
*Why Do You think what is being offered is valuable/worthwhile/good evidence, especially if there is posable contradictory evidence or good reason/valid and reliable reasoning process” (a good Axiological answer is needed; or understanding the “why” of what is being offered is valuable, worthwhile, good, accurate, valid, and reliable reason and evidence for what is being offered.
Then one should use My Methodological Rationalism’s three belief stages for understanding or testing or updating the thinking, reasoning or belief(s) of what is being offered or its “knowledge representation” (exposing the breaking down of the different positions of beliefs or thinking or reasoning, etc. into “good belief etiquette” units assisting in evaluation and action of what is epistemically warranted as rational or that follows epistemic rationality. epistemic rationality can be thought to involve critical thinking about epistemology and the process of forming beliefs that as accurately as possible match the reality of the natural world which is current to the evidence available and only forming beliefs after rational consideration motivated by truth-conducive beliefs, constantly making reasonable efforts to avoid fallacious reasoning and always being open too new or more reality accurate reason or evidence.
Then to expose an account of belief, one should use a Belief acquisition questioning, Belief maintenance rechecking, and Belief retention updating any and all thinking, reason, and or beliefs to ensure full confidence that the epistemic position being offered has epistemic warrant or that follows epistemic rationality. Broadly, “epistemic” means “relating to knowledge (itself) or to the degree of its validation” and epistemological means; critical study of knowledge, validity, methods, as well as limits to knowledge and the study or theory of various aspects of or involved in knowledge.
“According to many analytic philosophers, a belief is a “propositional attitude”: as a proposition, it has a specific meaning that can be expressed in the form of a sentence; as an attitude, it involves a mental stance on the validity of the proposition (Schwitzgebel, 2010). Beliefs thus involve at least two properties: (i) representational content and (ii) assumed veracity (Stephens and Graham, 2004). It is important to note, however, that beliefs need not be conscious or linguistically articulated. It is likely that the majority of beliefs remain unconscious or outside of immediate awareness, and are of relatively mundane content: for example, that one’s senses reveal an environment that is physically real, that one has ongoing relationships with other people, and that one’s actions in the present can bring about outcomes in the future. Beliefs thus typically describe enduring, unquestioned ontological representations of the world and comprise primary convictions about events, causes, agency, and objects that subjects use and accept as veridical.” https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4327528/
In general, I do not care that much what others believe personally until they say it is true, ask my opinion, challenge my evidence, thinking, or beliefs, or use their beliefs to hurt, oppress, or discriminate against others or me. Often, the problem with what is labeled as personal religious belief never stays personal. It becomes a mission to spread (sometimes by force) that same religious belief as an innate factor of the belief itself. Commonly, this seems then to lead to the promotion of dogmatic magical thinking propaganda that tends to motivate beliefs with little problems in hurting, oppressing, or discriminating against others who reject the personal religious belief of the religionist, theist, or fideist. This practice of supposedly personal belief is most commonly forced on to children which shows that there is little personal about it. As for me, I do openly express my atheism, antitheism, antireligionism, and secular humanism but this is not some limiting dogmatism as I strive to be open to learn new things, if warranted and express my thinking or beliefs with justification as much as possible by utilizing valid and reliable reason as well as evidence.
Damien Marie AtHope: Caring firebrand atheist
My Written Discussions, Responses and Debates
Childhood Indoctrination is often the gateway drug,
to a life of irrational magical thinking superstitions, like ghosts, gods, or guardian spirits.
It seems, in general, the less education and higher poverty have a higher correlation to being religious.
I am an Axiological Atheist, with a Rationalist Persuasion, who Supports Anarcho-Humanism
“I often find that the quality of a person is written in their thinking and behavior.”
“Child’s Eyes”
Atheism is the reality position.
Theism is the anti-reality position!
I don’t need religion or its fake gods.
“Reason is my only master.”
I am will to power!
Here is why “Reason is my only master”
The most Base Presupposition begins in reason. Reason, is needed for logic (logic is realized by the aid of reason enriching its axioms). Logic is needed for axiology/value theory (axiology is realized by the aid of logic). Axiology is needed for epistemology (epistemology is realized by aid of axiology value judge and enrich its value assumptions as valid or not). Epistemology is needed for a good ontology (ontology is realized by the aid of epistemology justified assumptions/realizations/conclusions). Then when one possesses a good ontology (fortified with valid and reliable reason and evidence) they can then say they know the ontology of that thing. In a general way, all reality, in a philosophic sense, is an emergent property of reason, and knowing how reason accrues does not remove its warrant. Feelings are experienced then perceived, leading to thinking, right thinking is reason, right reason is logic, right logic is mathematics, right mathematics is physics and from there all science. Science is understanding what is, while religion is wishing on what is not. So, I think, right thinking is reason. Right reason is logic. Right logic, can be used for mathematics and from there we can get to science. And, by this methodological approach, we get one of the best ways of knowing the scientific method.
I am the “one” you have been waiting for I am will to power, a deep thought so true it has taken flight to the lofty aspirations dreamed for and a care transmitted to offer hope to humanity I believe in you and will strive to champion you with all I have for you are so worthy…
“Reason is my only master, whereas faith offered as reality is most defiantly not my friend.”
Theistic believers think that as an atheist, I have a life without meaning. What foolishness, I only have this one short life, how precious life is when you only have “one life” with no extra afterlives nor any reincarnation do-overs.
No, as an atheist, there is just this one valuable life, may I live it well.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, Paganism & Progressed organized religion
The Evolution of Religion and Removing the Rationale of Faith
Similarities and differences in Animism and Totemism
What do you mean by god? So, even though You may say terms like god(s), as if that term universally means anything, without a connected myth people believe in (appeals to faith Fideism “FAITH-ISM”: faith is independent of reason, superior to reason, or reliance upon faith alone in some (generally religious) chosen beliefs and not others, even if reason is valued). But you don’t believe in a know-nothing theism “FAITH-ISM”, do you? You only value reason and evidence, right? Now, be honest when you think of god the influences of some god myth come in your head not an unknown and unknown possibly god somethingism, a vague unjustified theistic possibility thing you think came before the big bang. And, whatever, people can believe it’s a god but even if one could agree with you, honestly that would at best only get you the vague unjustified god nothing as your possibility before all the nature and reality we do know. However, we both get such a god does not fit a given religion hella vague something unknown before the big bang god if real has shown complete indifference to life on earth. So, all the religions are out the door or you could say almost all god claims can fit an origins unknown like what the big bang would limit and in that we find the problem. Religious holy book myth gods are well defined and not at all like the undefined something that could have been concluded as something before the big bang, which leaves us at, we don’t know but what is it about this unknown that can be believed to be a god something does nothing for you just as it tells you nothing and is most likely nothing but more nature just as everything we do know is a nature nothing magical.
What do you mean by god Evidence?
What do you mean by god? Are you just making stuff up or guessing/hoping or just promoting unjustified ideas you want to believe, what is a god? What makes you think this naturalistic reality contains unproven magic or supernatural anything and how do you know that you are not in error?
Do you want what is true or want what you believe without concern for what may actually be true?
Character is not something you get by accident. Just like caring for humanity should not be something you only do if it is not to hard or support equality if it’s convenient. One makes a choice to champion what is right because it is right, knowing that to do so will take hard work and one is proud to do so because they have character. I see a care for humanity as an honor for the direct part I play in it. Again, what do you mean by god and are you really “ok” with just pretend or do you seek to truly know, such as are you ethical in your prosses of forming, developing and maintaining beliefs?
As ethical atheists, we are not ok with pretend. So we are not silent because sacred falsehoods must end, even if the truth may offend. What is Faith but an unjustified belief that is willfully supported in violation to The Ethics of Belief, as faith holds a burden of proof until justified so faith claiming to “know” anything by this means is intellectually dishonest, uninformed on good belief etiquette or confused thinking offered as pseudo-knowledge? Theists like to confuse the understanding of atheism to lessen its obvious reason. So, here’s a definition of atheism: all offered claims of god(s) are baseless and devoid of a shred of testable or provable evidence and the claims of or about gods either don’t represent in reality or claim to represent things contrary to reality as well as contradicts each other requiring a conclusion of atheism (lack of belief or disbelief in theism). The god claim, is like a clown car in the magic big top of Fideism “faith-ism”, and Presuppositional Apologetics is Just Fascist Fideism all of which demonstrates the Theistic Reality Confusion.
What do you mean by god? Sure there are intelligent theists and that does not in any way make theism even reasonable as one can be brilliant and hold logical fallacies as their truth and that like any thinking errors like theism can happen to an otherwise sound thinker. I strive to be a sound thinker thus I am an axiological atheist and some may wonder what is that? Axiological Atheism (“philosophic” value theory/value science “formal axiology” social science” atheism) is Classed Under Anthropocentric (human-centered) arguments: “Axiological atheism favors humanity as the absolute source of ethics and values, and permits individuals to resolve moral problems without resorting to God. Marx, Nietzsche, Sartre and Freud all used this argument to some extent to convey messages of liberation, full-development, and unfettered happiness.” – Link
“Damien, your Axiological Atheism sounds Highly interesting! One point, though. Have you considered that all of this philosophizing will mean nothing when you are dead? Human ideology on the concepts of mortality have been around since the dawn of mankind and will continue until every last human being is dead.” – Challenger
My response, philosophizing like all science will mean nothing after “we” are dead but I care about more than me I want universal betterment and true humanity flourishing so philosophizing like all science matter in this goal does it not? I am Not just Atheist, I am a proud Anti-religionist as well as Anti-theist. Those atheists who still like esoteric religions or religious philosophies, that is not me at all I oppose it all. Yes, you read that right, I reject it all, every religion or even pseudo-religion like. Just so I am not misunderstood, this includes buddhism, satanism, taoism, paganism, wicca, spiritualism, etc. Don’t get me wrong I am against ALL religion. What makes some believed Truth is actually True? To me, truth, in general, is a value judgment we place on what we think or believe is evidence or reason. Therefore, the rational imperative on us as intellectually honest thinkers to demonstrate that the proposed evidence or reasoned assumption is actually of a high epistemic standard with as much valid and reliable reason and evidence as possible from a credible source as possible which then makes some believed “Truth” actually worthy to be seen as Epistemologically True thus a “justified true belief”. Broadly, epistemic means “relating to knowledge (itself) or to the degree of its validation” and epistemological means ” critical study of knowledge validity, methods, as well as limits to knowledge and the study or theory of various aspects of or involved in knowledge”.
What do you mean by god? I have justification to claim to know what I claim to know, that is proof, not faith which is unproof “Unjustified Belief.” Do you have such Justification? By claiming to know something by faith is to act in a way mirroring a dishonest thinker, as intellectually honest thinkers don’t claim knowledge without justification.
As a general thinking in all my epistemology is Justificationism:(philosophy) is an approach that regards the justification of a claim as primary, while the claim itself is secondary; thus, criticism consists of trying to show that a claim cannot be reduced to the authority or criteria that it appeals to. In a general way, “Justificationism” to me, is the presupposition that claims to knowledge must be authenticated, certified, verified, validated, confirmed, proven, corroborated, back up, show to be accurate, confirmed or in some other way shown to be justified. In other words, if a belief is knowledge, then it is in some way justified, and if a belief is unjustified then it is not knowledge. Justificationism” is the presupposition that claims to knowledge are on trial and the desire is make sure or demonstrate that (something) is true, thus in a Justificationism presupposition inquiry any claim to knowledge can be analyzed, for value by asking for its justification, and failure to provide sufficient justification is enough to reject that claim to knowledge until adequate justification is provided. In this context, a rational ethical belief (Ethics of Belief), is one which is justified, and a rational person is one who provides a rational ethical belief, with good reasons or proof to justify what is believed. For a justificationist, the purpose of philosophical investigation is not a search for faith (unjustified) belief, but only a search for justified true belief. This difference is subtle but important: while a justified belief is always rationally justified as true, it still must be realized that an unjustified belief is not necessarily always false but indeed is not justified. Failure to provide sufficient justification is enough to reject an offered claim to knowledge as unjustified belief (faith: belief without evidence or belief even up against contradictory evidence). These presuppositions constitute a reinforced justificationism uses and defines the rules by which competing proposals are evaluated, it can ensure any attempt to introduce faith (unjustified) belief(s) can be dismissed as unjustified. “Theory of justification is a part of epistemology that attempts to understand the justification of propositions and beliefs. Epistemologists are concerned with various epistemic features of belief, which include the ideas of justification, warrant, rationality, and probability. Loosely speaking, justification is the reason that someone (properly) holds a belief. When a claim is in doubt, justification can be used to support the claim and reduce or remove the doubt. Justification can use empiricism (the evidence of the senses), authoritative testimony (the appeal to criteria and authority), or logical deduction.” Ref
What do you mean by god? I have to challenge your beliefs, because you won’t. To me, every religion was new at some point and had someone who made shit up, yes all of them, every religion. As an atheist, I am a person who disbelieves or lacks belief in the existence of god or gods. In my non-belief, I am also ignostic feeling that every theological position assumes too much about the concept of god(s). As an ignostic, I am a person who rational no idea of anything from reality whatever to label as “a concept of god” thus I can say I have no idea of anything that can connect to the term god and no reason to think anyone else can either. As an anti-theist, I am a person who is active in opposition to theism: both the concepts of god(s) as well as the religions that support them. This is because theistic concepts and theistic religions are harmful and that even if theistic beliefs were true, they would be undesirable. As an anti-religionist, I am a person who can look at religion on the whole and see it is detrimental to the progress of humanity thus am in opposition to all and every religion, not even just opposition to organized religion. In case you were wondering, I am anti-pseudoscience, anti-supernatural, and anti-superstition as well. Therefore, I am a proud anti-religionist, not just atheist or even anti-theist. Yes, I am an atheist, anti-theist, and an anti-religionist. I am against flawed superstitious magical beliefs like god(s) and/or religion. However, I am not against people. I have many strong opinions and beliefs as well as my challenge of others or I am against many types of beliefs especially if they involve supernatural or superstitious, or harm. However, I am not against people nor am I against their free right to believe as they wish. To me, everyone owns themselves and their beliefs are theirs as well, and will be held accountable for those beliefs. Thus, to me, not I or anyone has the right to force people on what to believe. I as others do have the right to voice our beliefs, just as I or others then have the right to challenge voiced beliefs. Long live mental freedom. Proudly, I am an atheist, anti-theist, and an anti-religionist.
“Damien, what’s your philosophical position? Are you a materialist who believes that everything is reducible to physical? Idealism, Neutral Monist, etc.?” – Questioner
My response, I am a metaphysical naturalist (basically everything is reducible to physical) because of the universal reliable truth of the application of the scientific methods reliable and only demonstration using methodological naturalism, no magic, not even simple supernatural found in any amount ever anywhere by anyone.
“Damien, regardless of fancy wording we can not prove something is true without evidence just the same as we can not prove something is not true without evidence. Do you not agree that is the real argument?” – Questioner
My response, No, I don’t agree, it is always so. If I say I have the Nile River in my pocket you can’t see in my pocket but if you are rational and assess just what is allowable in reality, you don’t have to even look I know as you such a claim is preposterous to the point it can defy reason thus anyone would rightly reject a claim that a very limited space of a pants pocket watch can only at most fit something about 10 inches long but the Nile River is 4,258 mi long and even if it could be moved, which it can’t, more issues, but all and all it is clear that you can with certainty say that the Nile River in my pocket does not exist. I will give you another. Or say I said I have a money in my front pocket and you look finding nothing where it would be if there thus you now have negative evidence of my pocket which is empty when reasonably searched and nothing, you rightly can confirm with certainty that the pocket is, in fact, empty and not filled with money as I had claimed. You are certain there is no money in my pocket exists. There are many more examples but I think you can see what I am saying. To me even your question, while a good one exposes how the approach to reason may be used differently depending on the thinker.
What do you mean by god? I am a Methodological Rationalist, I rarely am pushed to doubt as a default, instead, I see reason as my default and at times it may be responsible to doubt, but I get to that conclusion because of reasoning. A common saying in pseudologic is “You can’t prove a negative.” This is, simply not true. This is clearly not true because any statement can be rewritten into the negation of its negation. Any provable statement can be written as a negative. For example, “X is true” can be rewritten as “X is not false”, a negative statement! If “X is true” can be proven true, then you have also proven a negative statement “X is not false”. Moreover, even if it is widely believed that you can’t prove a negative. Going so far as to have people thinking that it is a law of logic—you can’t prove that Santa Claus, unicorns, the Loch Ness Monster, God, pink elephants, WMD in Iraq and Bigfoot don’t exist. This widespread belief is flatly, 100% wrong. In this little essay, I show precisely how one can prove a negative, to the same extent that one can prove anything at all. Evidence of absence is evidence of any kind that suggests something is missing or that it does not exist. Per the traditional aphorism, “absence of evidence is not evidence of absence”, positive evidence of this kind is distinct from a lack of evidence or ignorance of that which should have been found already, had it existed. In this regard Irving Copi writes: “In some circumstances, it can be safely assumed that if a certain event had occurred, evidence of it could be discovered by qualified investigators. In such circumstances, it is perfectly reasonable to take the absence of proof of its occurrence as positive proof of its non-occurrence.” — Copi, Introduction to Logic (1953), p. 95
Here are some links about proving a negative: Link, Link, Link, Link, Link, Link We fight IDEAS, not people, so while I wish to destroy harmful or false ideas I wish to uplift and empower people by inspiring their will to reason and know REASON is often the enemy of ignorance.
My Strongest Explicit Atheism “positive” / “strong” / “hard” atheists similar to Antitheist Atheism.
My Atheism: “Axiological Atheism”
My quick definition of Axiology?
Axiology is a philosophy (value theory) and a social (value science) science (formal axiology) mainly involving the “what, why, and how” of “value” the way epistemology approaches “knowledge” as in what is of value/good/worth/beneficial/ or useful? Why is the thing in question is of value/good/worth/beneficial/ or useful? How should the value/good/worth/beneficial/ or useful thing be interacted with?
Axiology: Understanding Value Accuracy?
The value of an argument (ie. its worth) depends on its level of supporting justification in relation to assessable evidence (ie. the correspondence theory of truth). This toast picture is a good reference if we see # 1 the completely burned toast as the highest epistemic evidence possible and #16 the completely untoasted bread as devoid of any evidence at all thus no level as all to even start assessing a supporting justification, thus exposes an unwarranted argument devoid of value.
The Correspondence Theory of Truth: which states that the truth or falsity of a statement is determined only by how it relates to the world and whether it accurately describes (i.e., corresponds with) that world. Correspondence theories claim that true beliefs and true statements correspond to the actual state of affairs. http://plato.stanford.edu/entries/truth-correspondence/
- Hammer of Truth: Yes, you too, have lots of beliefs…
- “The Hammer of Truth” Process
- “Hammer of Truth” response to “Do you Believe in god?”
- “The Hammer of Truth” (scientific philosophy: Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) in action.
- Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology argument/challenge protocol
- Error Crushing Force of the Dialectic Questions and the Hammer of Truth
- Grasping the status of truth (ontology of truth)
- Challenged or Challenging? (questions of ontology)
- Truth is a Value (axiological) Judgment.
- Truth Navigation: “Belief-Etiquette”
- Truth Navigation: Techniques for Discussions or Debates
- Truth Navigation and the fallacy of Fideism “faith-ism”
- My “Methodological” approach
- I use a kind of Dialectical Rhetoric = truth persuasion (motivational teaching)
- Methodological Rationalism (Ontology, Epistemology, & Axiology) and Skepticism
- My Methodological Rationalism: investigate (ontology), expose (epistemology) and judge (axiology)
- Basics of my Methodological Rationalism Epistemology Approach
- Axiology, Naturalism, Realism and Moral Theory Ideas
- Axiological Atheism Explained
- I am a “Scientific Axiology” minded “Philosophic Axiologist Theorist” and my conclusion is Axiological atheism
- Sound thinking, Presumptive-value, Axiology, and Disciplined-Rationality
- Axiology, Morality and the Dignity Being: “Human Entity”
- Deconstructing Pseudo-Morality with Axiology Understanding?
- Pragmatic Ethical/Axiology Driven Assumptions, Overcome the Weight of Solipsism Doubt


Atheism is non-belief in god and agnosticism unless it is purposing some belief is a stating non-belief in god. Therefore agnosticism is actually a subset of atheism. Or to put it another way, all agnostics are actually atheists, unless they believe in gods. Which means we are all atheists! lol



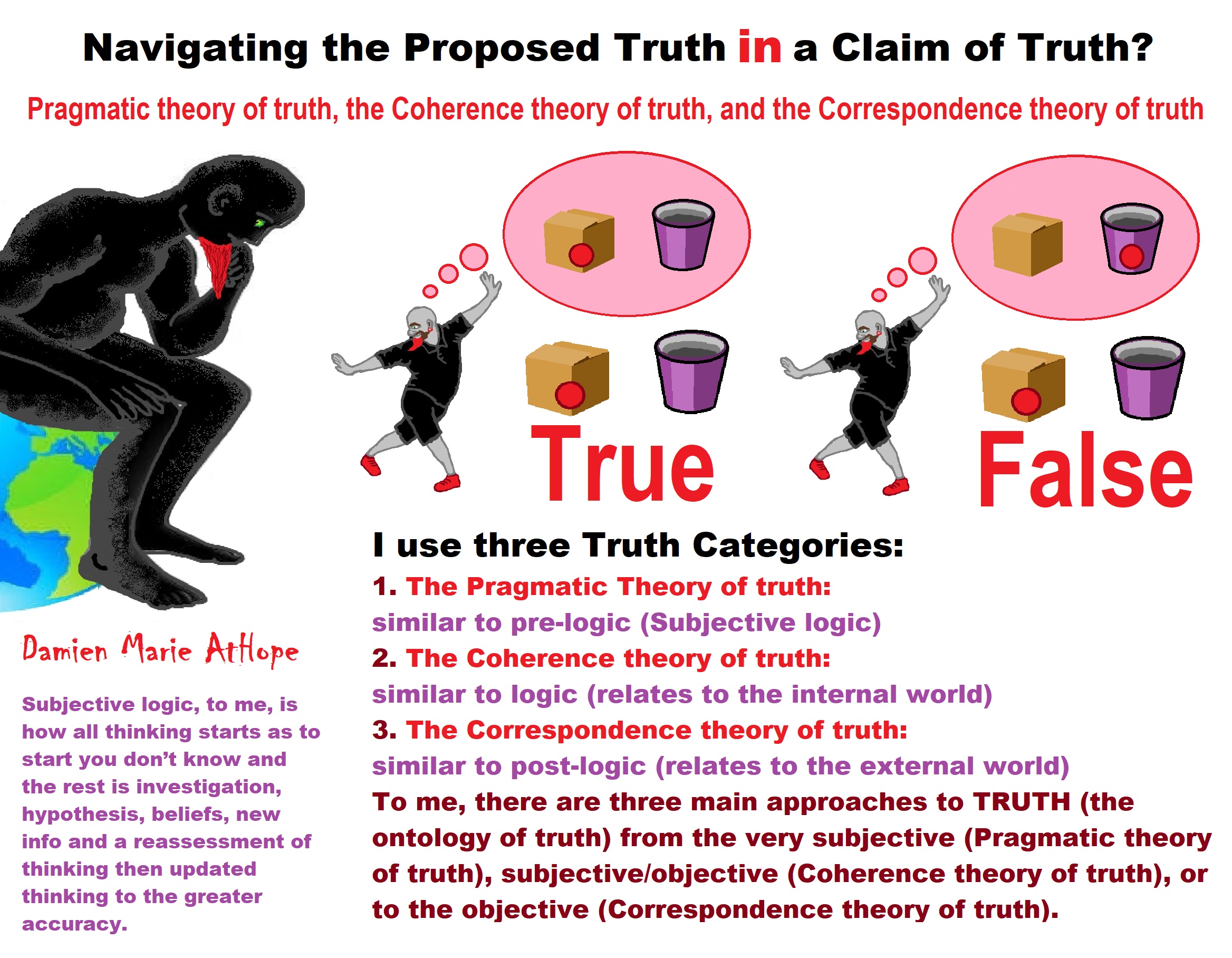















People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
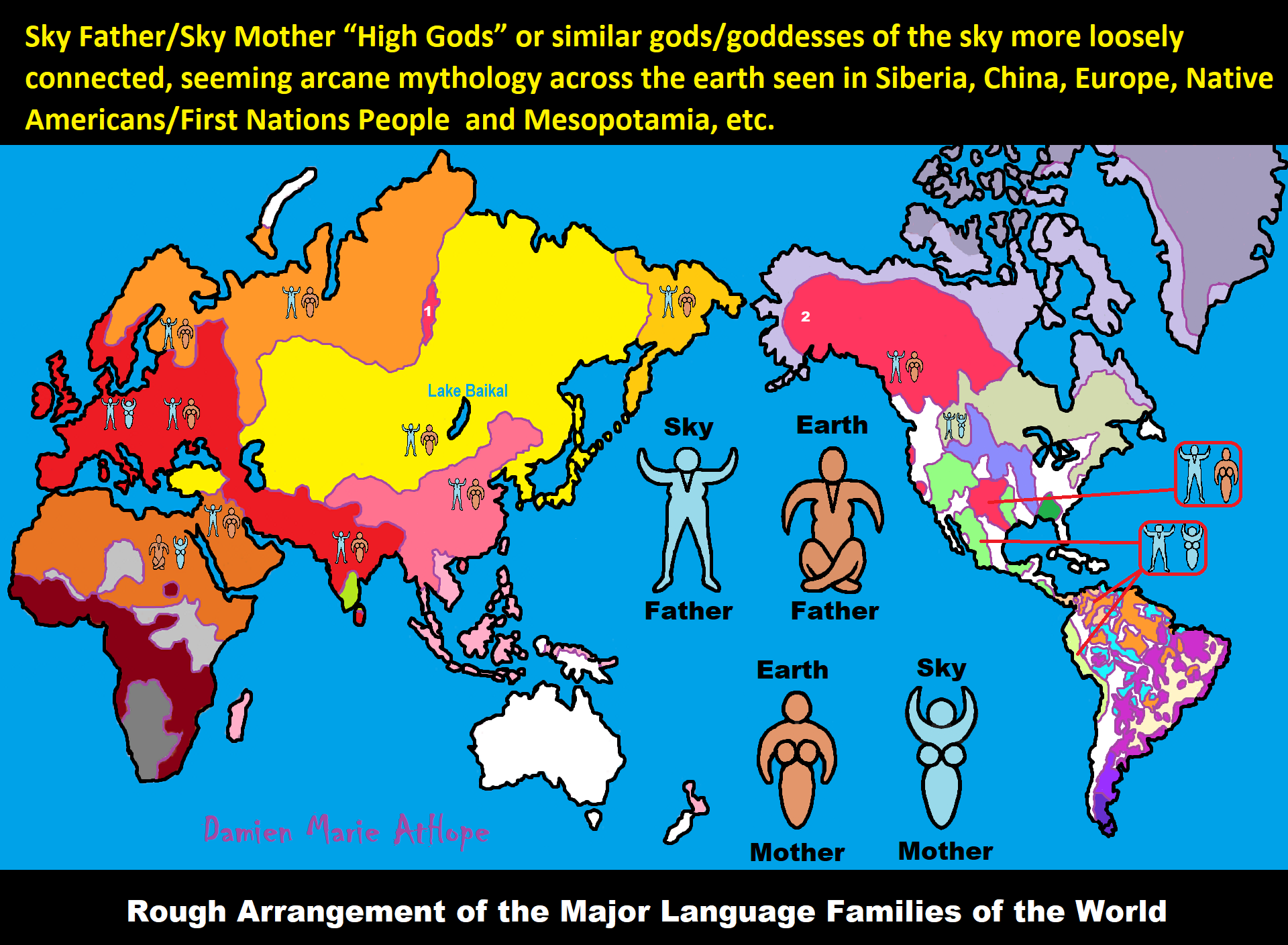
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com











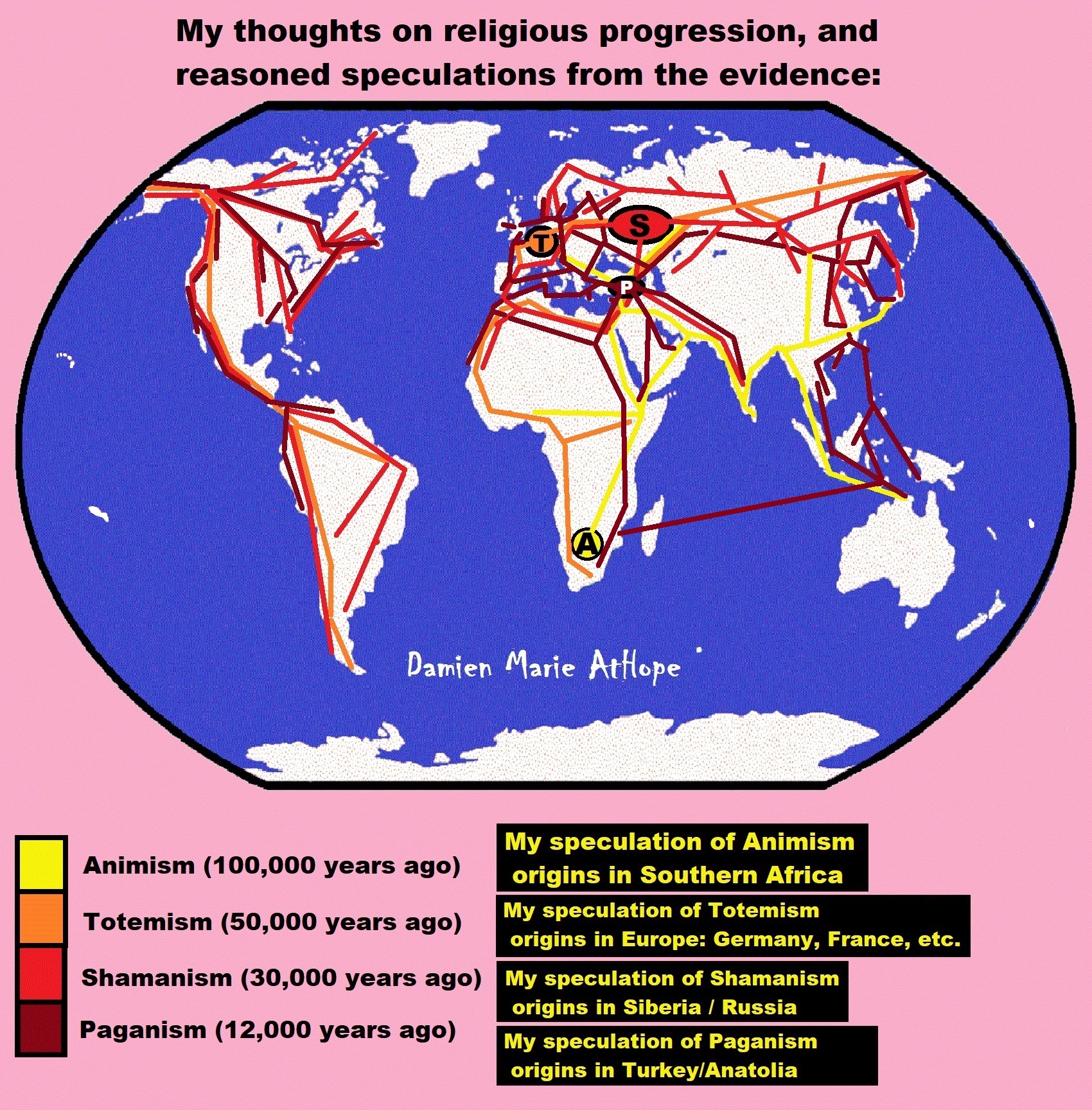



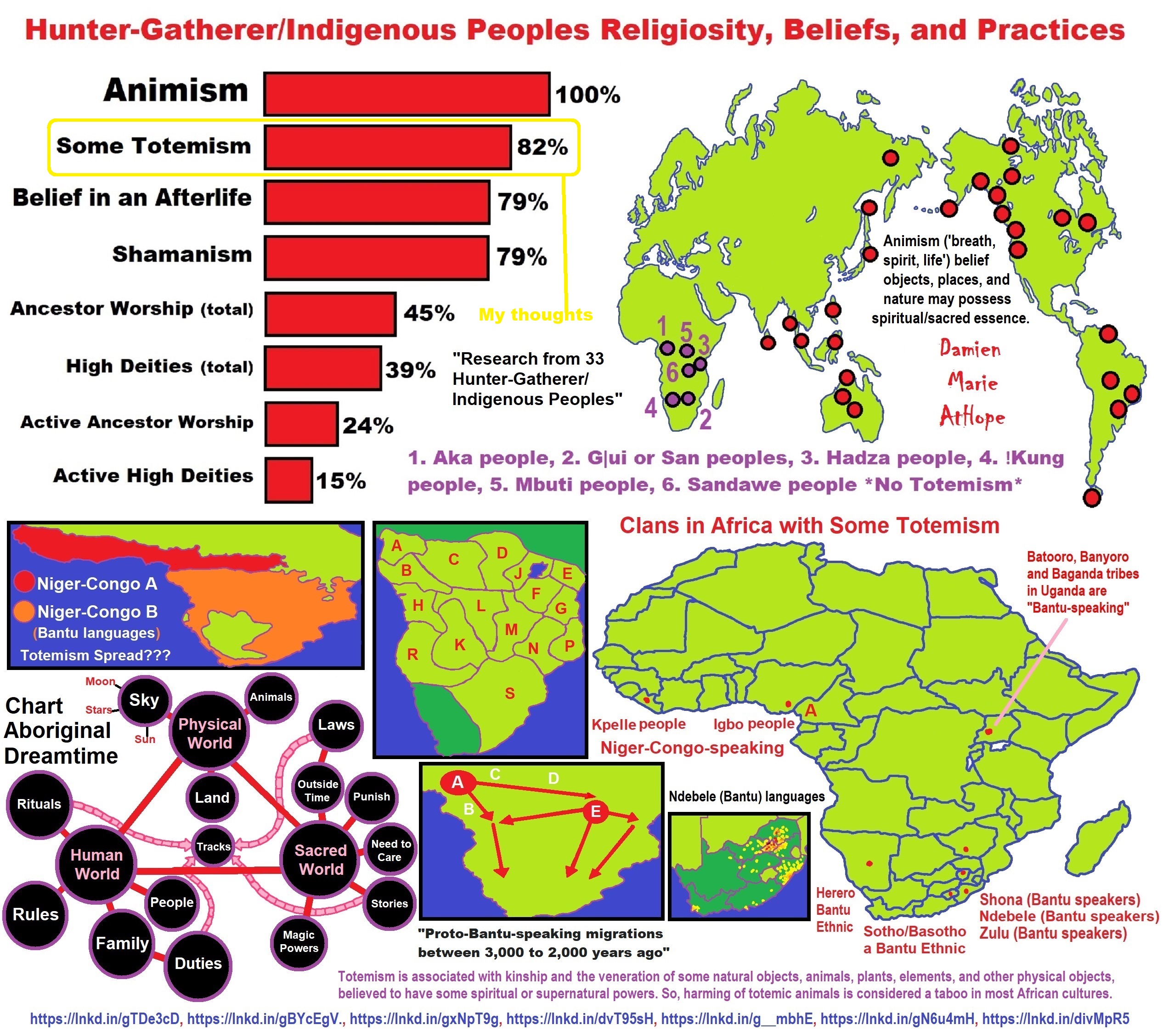
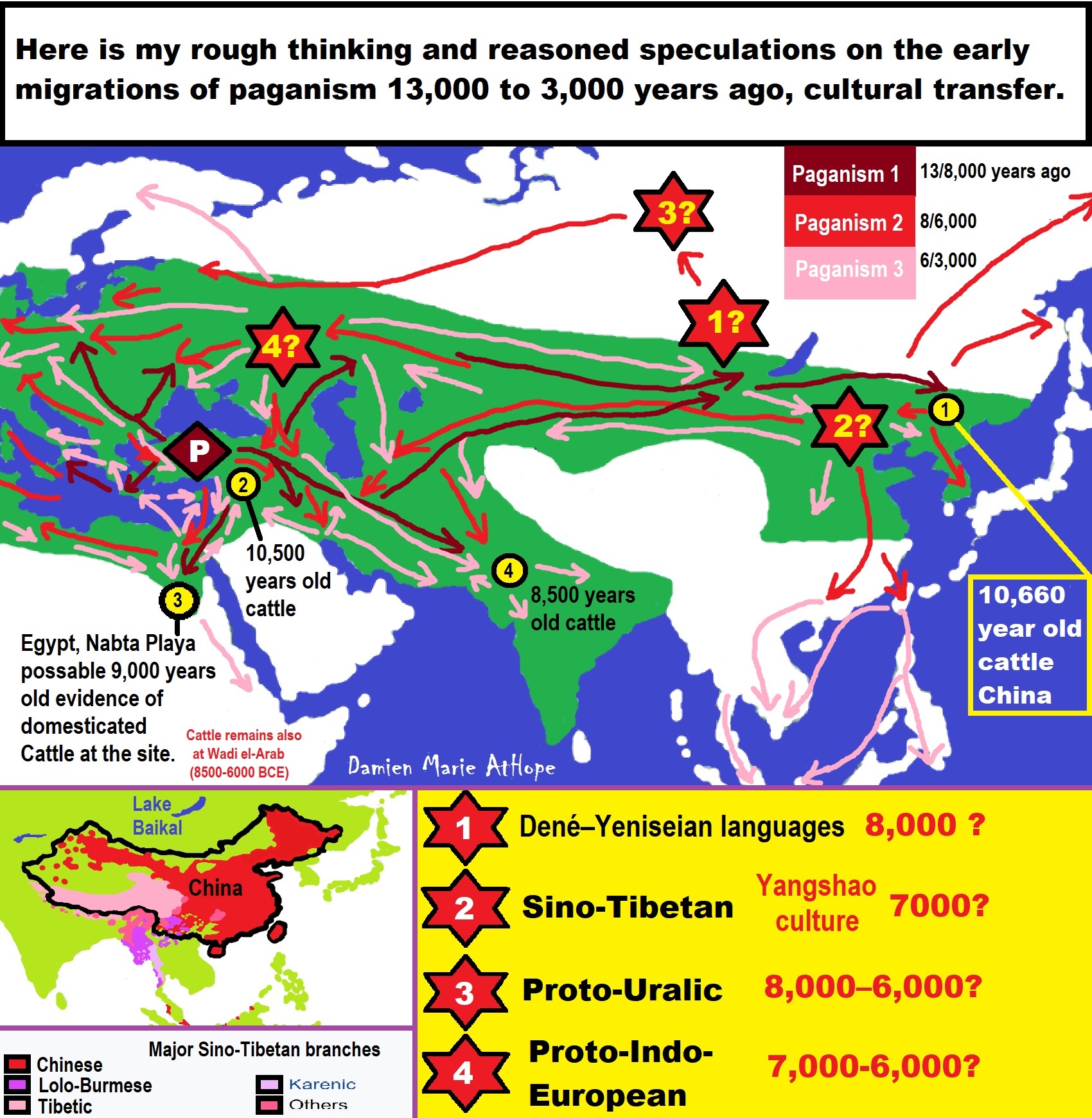



“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolves all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred. So, it all starts in a general way with Animism (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development).