ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
The Mystery Of The Lost Red Paint People (VIDEO)
Secrets Of The Lost Red Paint People (VIDEO)
“The Red Paint People are a Pre-Columbian culture indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America. They were named after their burials, which used large quantities of ochre, normally red, to cover both the bodies of the dead and grave goods. They flourished between 5,000-3,000 years ago. Alternatively, they can be called by the period in which they lived, either the “Maritime Archaic” (emphasizing a coastal and seafaring culture) or “Late Archaic” (emphasizing time and leaving open the possibility of living inland seasonally), although these terms often cover the longer period from 9,000 years ago to 1000 CE. Multiple hypotheses exist as to which if any later peoples might be their descendants and there is little archaeological evidence to support any hypothesis. The Red Paint People lived, fished, and hunted along the coasts and rivers. Some coastal sites show evidence of year-round occupation, discrediting an older theory that these people were seasonal nomads, living the summers on the coast and the winters inland. Their diet included sea and migratory fish, shellfish, meat, berries, acorns, nuts, and roots. The Red Paint People had stone and bone tools, as well as boats capable of catching swordfish. No pottery or metal tools have been found in sites associated with this culture. Their trading range is known to have extended from Labrador to the New York side of Lake Champlain.” ref
The Swordfish Hunters: The History and Ecology of an Ancient American Sea People (VIDEO)
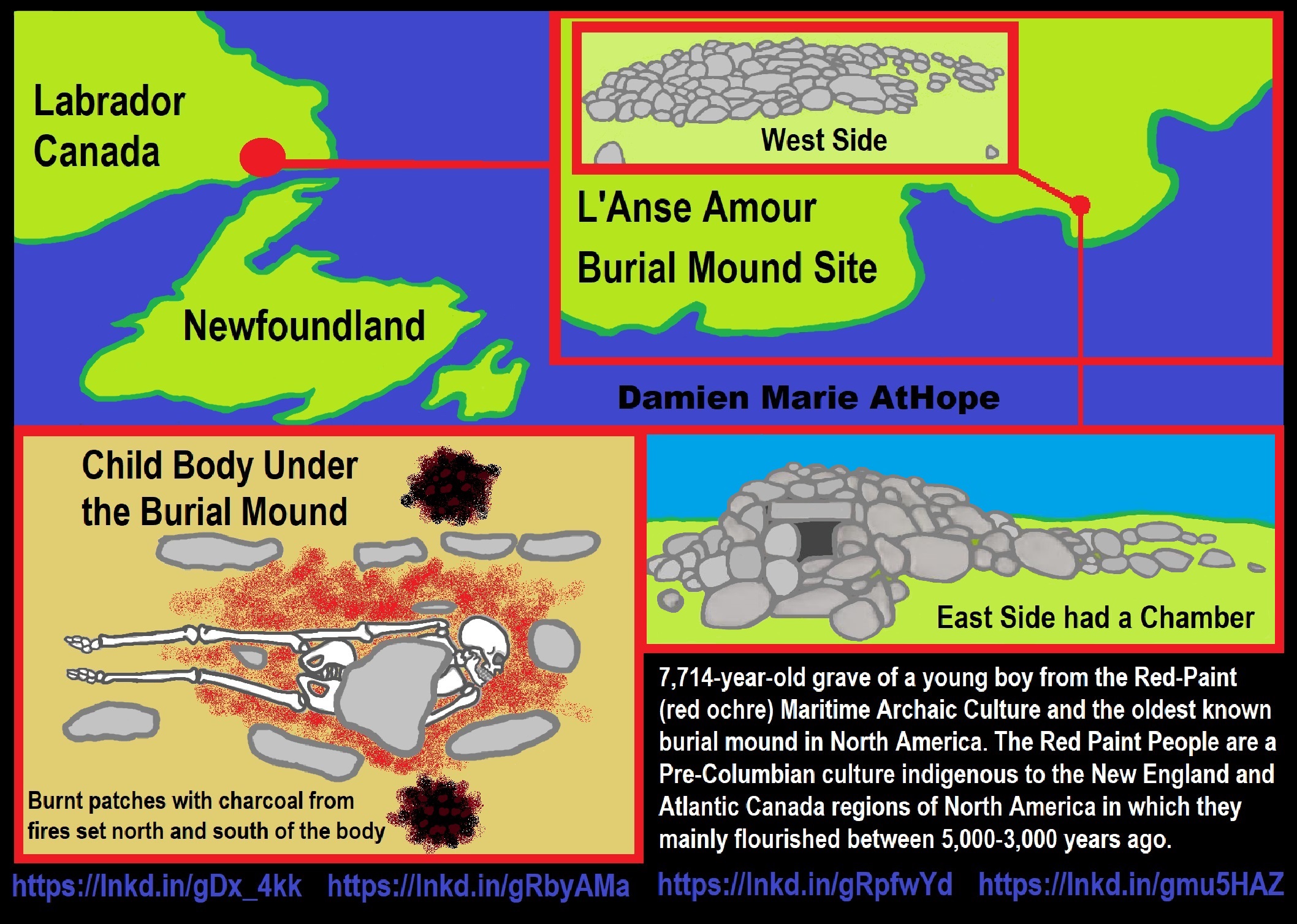
7,714-year-old grave of a young boy from the Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture and the L’Anse Amour Site in Labrador Canada is oldest known burial mound in North America. The body was wrapped in a shroud of bark or hide and placed face down in the grave with his head facing to the west. At that point, a large mound of rocks was erected over his burial place. The burnt patches on either side of the body under the mound is charcoal from fires that would have been set north and south of the body in a sacred ritual. The Red Paint People are a Pre-Columbian culture indigenous to the New England and Atlantic Canada regions of North America in which they mainly flourished between 5,000-3,000 years ago. On the west side, it looks like a mound of rocks but from the East Side, there is a small dolmen-like chamber opening. A dolmen is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, with a large flat stone laid on upright ones and the oldest known are found in Western Europe, dating from around 7,000 years ago. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Earth diver mythology or something similar??? Could be. In a way, snails are a kind of mound shape, thus similar to turtle shells, both may represent a mound of creation in the earth-diver myth. In Peru, there were snail shells, and snail shells are also used in the earth diver.
My thoughts on Dolmen origins and migrations, as well as Snail Shell Middens or Snail Burials/Turtle Shell Burials, and links from “Y-DNA R (R1a, R1b, and R2a)” migrations, maybe R2a leading to Proto-Indo-European, transferring it to R1b, taking it to the steppe 7,500 years ago.
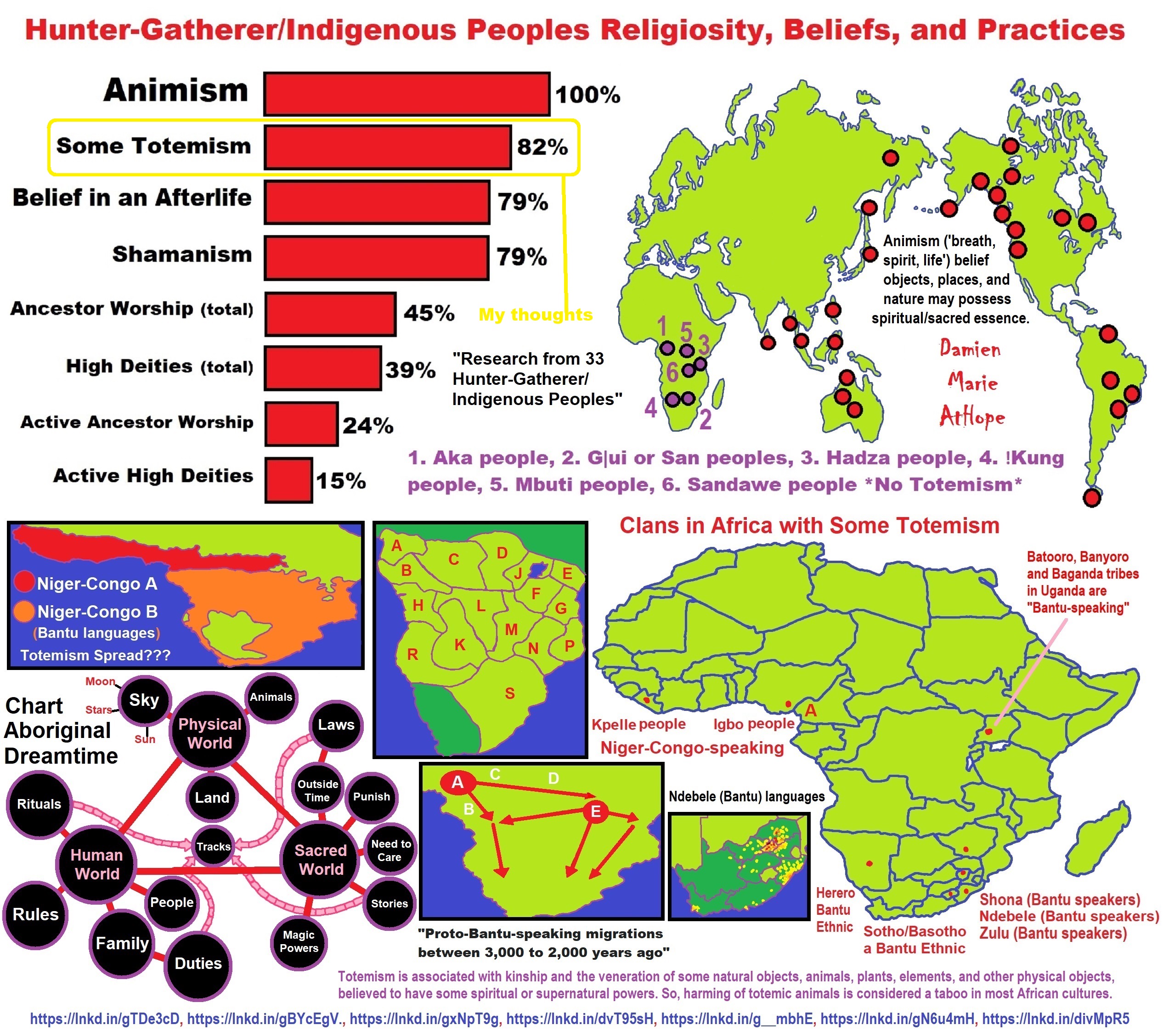
Religion is a cultural product. So, it has been part of the human experience, similar to languages, from before we left Africa, spreading humanity across the world.
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
My Speculations are in Comparative Mythologies?
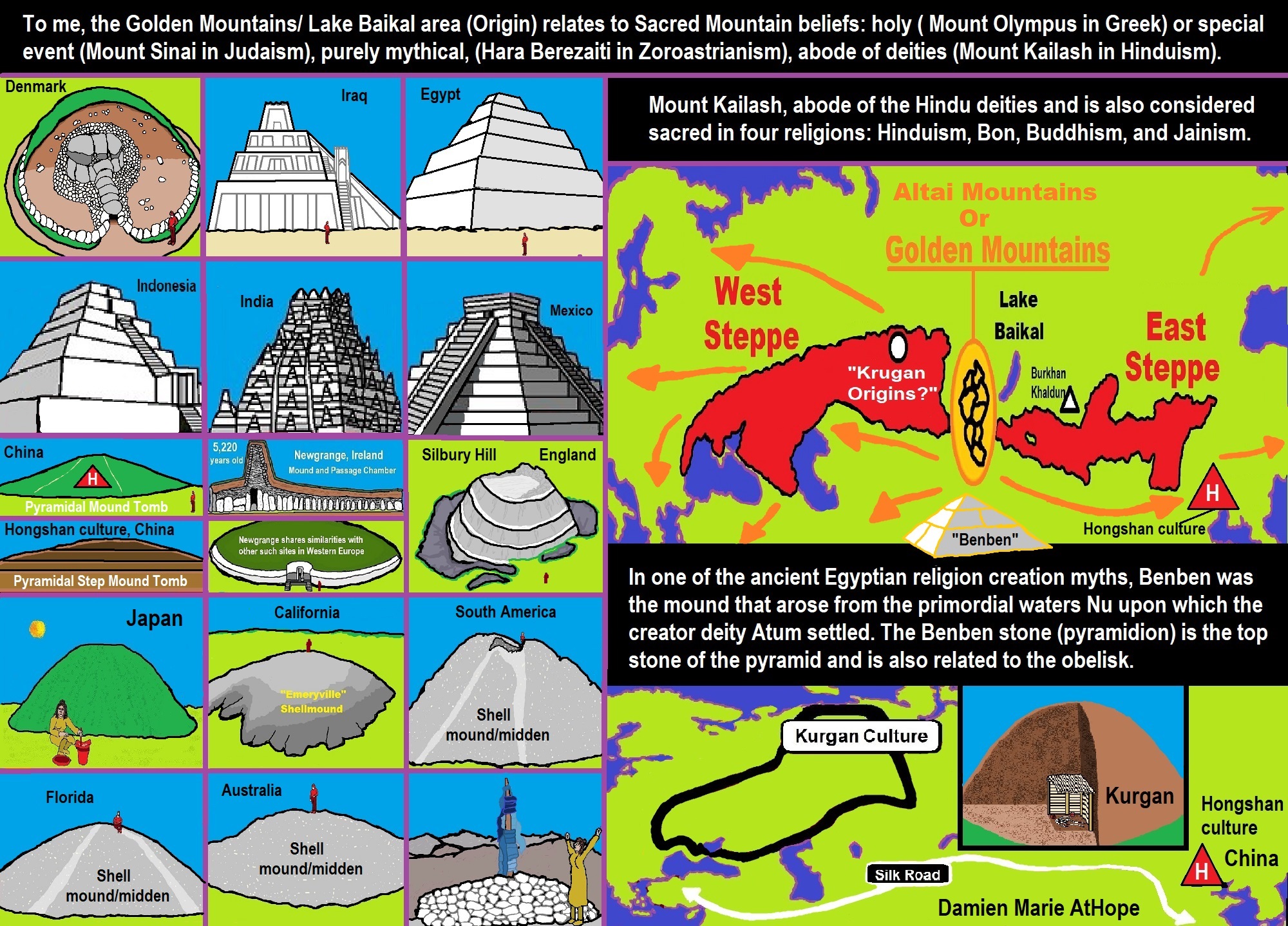
For instance, the mytheme of an ancient belief that is seemingly shared though changed and adapted, a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure seems to be shared a common relation with mountains/ancestors/gods or sacred animals with Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids.
Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep Mythology connections?
Damien thinks the “Mound of Creation” mythology ((Axis Mundi) is a “myth” reason for mounds/pyramids.
Think ancient Hunter-Gathers were unskilled and primitive? Well, think again, because they were downright amazing! CHECK OUT THIS VIDEO: Primitive Technology: Woven bark fiber
Damien thinks Egypt and Sumerian mounds are connected and evolved somewhat related but different. A similar situation happened, to me, in the Americas. North started in mounds that later evolved into something Pryamid like. This is matched by Mesoamerica. Mounds later evolved into Pryamids. In Peru, Pryamids and mounds may have been transferred together or mounds quickly evolved into Pryamids.
Link for Pictures: link
“The L’Anse Amour burial was a circular mound, constructed of large flagstones. Careful excavation revealed the skeleton of a young boy, lying buried several meters below the surface, at the heart of the mound. Offerings buried with the boy included what appeared to be a set of hunting tools – perhaps for hunting walrus. The kit contained stone and bone spearheads, a walrus ivory toggling harpoon head and hand toggle, ceremonial paint objects and a bird-bone whistle. It is intriguing to suppose that the boy may have been killed while on a walrus hunt.” ref
“Megalithic “dolmen” tomb in the Golan, it is possible that the megalithic landscape of the Golan is analogous to the megalithic landscapes of Europe, which developed as palimpsests of short, disparate episodes of megalithic construction over long periods of time. Focusing on dolmens in Jordan, there is a distinct spatial relationship between dolmen fields and settlement sites that were occupied in the Early Bronze I. Furthermore, there is also a clear correspondence in size, where small dolmen fields are found near small Early Bronze I settlement sites, and large dolmen fields are found near large sites. Yet this correlation is not absolute. While dolmens are always found near Early Bronze I settlements, not all Early Bronze I settlements are found near dolmens. Dolmen cemeteries are separated by large areas such as the Wadi Yarmouk that were also settled in the 4th millennium BCE, but in which no dolmens are found. If the distribution of dolmens was solely related to the Early Bronze I settlement landscape, then why are dolmens found close to some Early Bronze I settlement sites but not others?” ref
“‘An answer lies in understanding the distribution of dolmens within the geological landscape. The Golan and Leja are characterized by hard lava flows. And Dolmens are found in areas dominated by hard sandstone, limestone and basalt formations that are conducive to the extraction of large slabs, and are absent in areas dominated by softer chalks and marls that are suitable for the excavation of subterranean chambers. In short, there’s a distinct correlation between dolmens and Early Bronze I settlements in areas dominated by microcrystalline strata, and a marked absence of dolmens in areas where softer strata are found, even if these areas were also settled in the 4th millennium BCE.” ref

I am rather sure about the Mound order but not sure about the order of the mythology as mounds can be set in time by archaeology. To me, mounds relate mainly to the “Mound of Creation,” primeval mound/hill/mountain (that emerges out of water) or the “Axis Mundi” thinking: cosmic axis, world axis, world pillar, the center of the world, World tree, Sacred Mountain/World Mountain, etc. “(such as Mount Olympus in Greek mythology) or are related to famous events (like Mount Sinai in Judaism and descendant religions or Mount Kailash, Mount Meru in Hinduism). In some cases, the sacred mountain is purely mythical, like the Hara Berezaiti in Zoroastrianism. Mount Kailash is believed to be the abode of the deities Shiva and Parvati, and is considered sacred in four religions: Hinduism, Bon, Buddhism, and Jainism. Volcanoes, such as Mount Etna in Italy, were also considered sacred; Mount Etna is believed to have been the home of Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and the forge.” ref
I explain how all mounds shared similar myths and world views thus this is why so many seem similar. I explain how Ancient Egypt, Sumerians, and Hinduism all have something similar to a Mound of Creation, and what the Shell mounds/Kurgans/Dolmens/Earth Mounds/Pyramids relate. In Siberia/Americas it is more related to Earth Diver myths, but they also have animals build a Mound of Creation. Also, many Connect to the Axis mundi which can and often does relate to a world mountain/mound of creation.

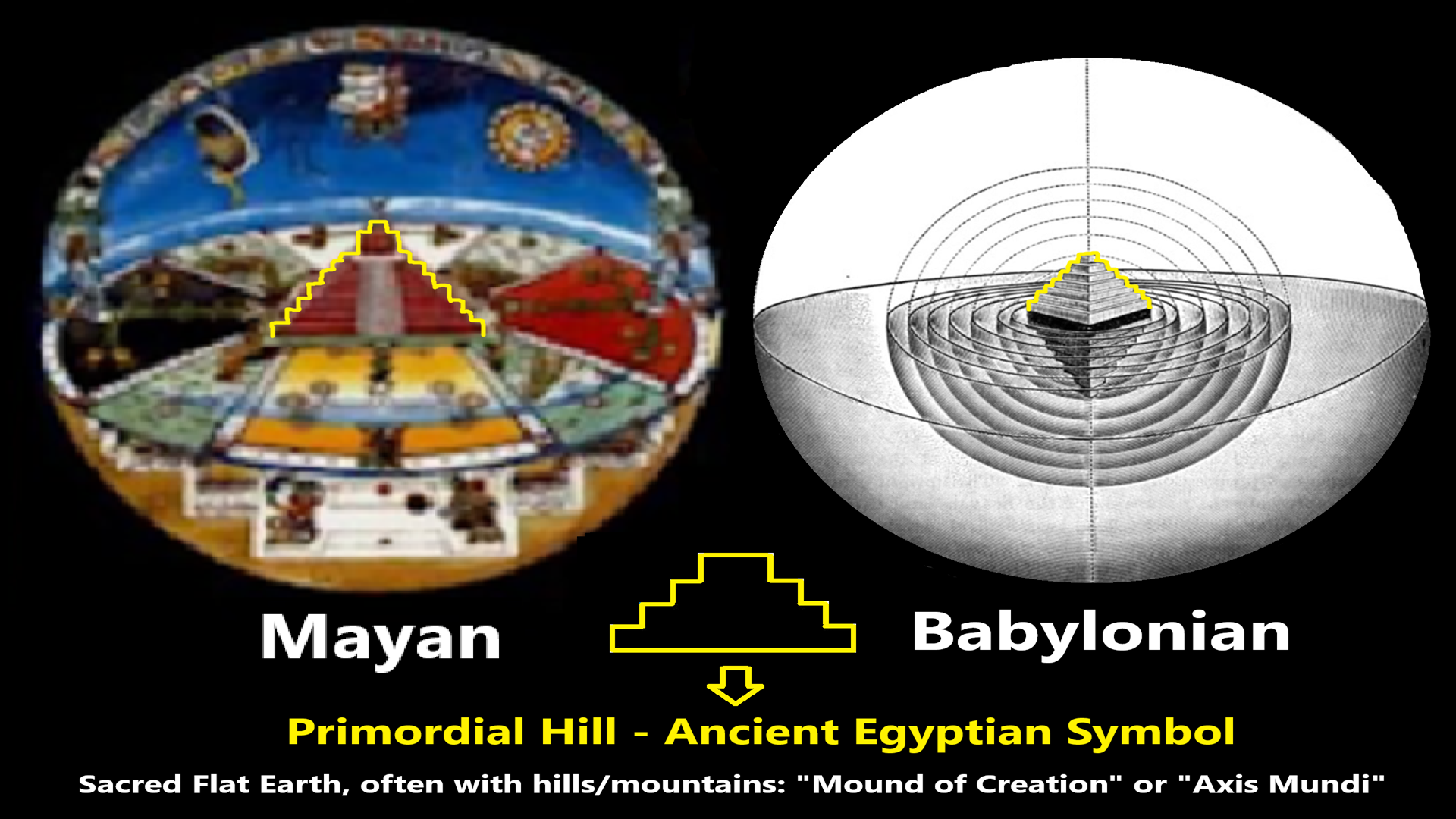
Flat Earth Mythology (a kind of square base for a mound/pyramid)?

Ancient Cosmology Shaped Everyone’s Theology
Sacred Flat Earth, often with hills/mountains: “Mound of Creation” or “Axis Mundi.”
“Cosmology in the ancient Near East (ANE) refers to the plurality of cosmological beliefs in the Ancient Near East, covering the period from the 4th millennium BCE to the formation of the Macedonian Empire by Alexander the Great in the second half of the 1st millennium BCE. These beliefs include the Mesopotamian cosmologies from Babylonia, Sumer, and Akkad; the Levantine or West Semitic cosmologies from Ugarit and ancient Israel and Judah (the biblical cosmology); the Egyptian cosmology from Ancient Egypt; and the Anatolian cosmologies from the Hittites. This system of cosmology went on to have a profound influence on views in early Greek cosmology, later Jewish cosmology, patristic cosmology, and Islamic cosmology (including Quranic cosmology). Until the modern era, variations of ancient near eastern cosmology survived with Hellenistic cosmology as the main competing system. Ancient near eastern cosmology can be divided into its cosmography, the physical structure and features of the cosmos; and cosmogony, the creation myths that describe the origins of the cosmos in the texts and traditions of the ancient near eastern world. The cosmos and the gods were also related, as cosmic bodies like heaven, earth, the stars were believed to be and/or personified as gods, and the sizes of the gods were frequently described as being of cosmic proportions.” ref
Cosmography
“Ancient Near Eastern civilizations held to a fairly uniform conception of cosmography. This cosmography remained remarkably stable in the context of the expansiveness and longevity of the ancient Near East, but changes were also to occur. Widely held components of ancient near eastern cosmography included:
- a flat earth and a solid heaven (firmament), both of which are disk-shaped
- a primordial cosmic ocean. When the firmament is created, it separates the cosmic ocean into two bodies of water:
- the heavenly upper waters located on top of the firmament, which act as a source of rain
- the lower waters that the earth is above and that the earth rests on; they act as the source of rivers, springs, and other earthly bodies of water
- the region above the upper waters, namely the abode of the gods
- the netherworld, the furthest region in the direction downwards, below the lower waters.” ref
“Keyser, categorizing ancient near eastern cosmology as belonging to a larger and more cross-cultural set of cosmologies he describes as a “cradle cosmology,” offers a longer list of shared features. Some cosmographical features have been misattributed to Mesopotamian cosmologies, including the idea that ziggurats represented cosmic objects reaching up to heaven or the idea of a dome- or vault-shaped (as opposed to a flat) firmament. Another controversy concerns if the ancient near eastern cosmography was purely observational or phenomenological. However, a number of lines of evidence, including descriptions from the cosmological texts themselves, presumptions of this cosmography in non-cosmological texts (like incantations), anthropological studies of contemporary primitive cosmologies, and cognitive expectations that humans construct mental models to explain observation, support that the ancient near eastern cosmography was not phenomenological.” ref
Cosmogony
“Ancient near eastern cosmogony also included a number of common features that are present in most if not all creation myths from the ancient near east. Widespread features included:
- Creatio ex materia from a primordial state of chaos; that is, the organization of the world from pre-existing, unordered and unformed (hence chaotic) elements, represented by a primordial body of water
- the presence of a divine creator
- the Chaoskampf motif: a cosmic battle between the protagonist and a primordial sea monster
- the separation of undifferentiated elements (to create heaven and earth)
- the creation of mankind.” ref
“Lisman uses the broader category of “Beginnings” to encompass three separate though inter-related categories: the beginning of the cosmos (cosmogony), the beginning of the gods (theogony), and the beginning of humankind (anthropogeny). There is evidence that Mesopotamian creation myths reached as far as Pre-Islamic Arabia.” ref
Overview of the whole cosmos
“The Mesopotamian cosmos can be imagined along a vertical axis, with parallel planes of existence layered above each other. The uppermost plane of existence was heaven, being the residence of the god of the sky Anu. Immediately below heaven was the atmosphere. The atmosphere extended from the bottom of heaven (or the lowermost firmament) to the ground. This region was inhabited by Enlil, who was also the king of the gods in Sumerian mythology. The cosmic ocean below the ground was the next plane of existence, and this was the domain of the sibling deities Enki and Ninhursag. The lowest plane of existence was the underworld. Other deities inhabited these planes of existence even if they did not reign over them, such as the sun and moon gods. In later Babylonian accounts, the god Marduk alone ascends to the top rank of the pantheon and rules over all domains of the cosmos. The three-tiered cosmos (sky-earth-underworld) is found in Egyptian artwork on coffin lids and burial chambers.” ref
“A variety of terms or phrases were used to refer to the cosmos as a whole, acting as rough equivalents to contemporary terms like “cosmos” or “universe”. This included phrases like “heaven and earth” or “heaven and underworld”. Terms like “all” or “totality” similarly connoted the entire universe. These motifs are found in temple hymns and royal inscriptions located in temples. The temples symbolized cosmic structures that reached heaven at their height and the underworld at their depths/foundations. Surviving evidence does not specify the exact physical bounds of the cosmos or what lies beyond the region described in the texts.” ref
Three Heavens and Earths
“In Mesopotamian cosmology, heaven and earth both had a tripartite structure: a Lower Heaven/Earth, a Middle Heaven/Earth, and an Upper Heaven/Earth. The Upper Earth was where humans existed. Middle Earth, corresponding to the Abzu (primeval underworldly ocean), was the residence of the god Enki. Lower Earth, the Mesopotamian underworld, was where the 600 Anunnaki gods lived, associated with the land of the dead ruled by Nergal. As for the heavens: the highest level was populated by 300 Igigi (great gods), the middle heaven belonged to the Igigi and also contained Marduk’s throne, and the lower heaven was where the stars and constellations were inscribed into. The extent of the Babylonian universe therefore corresponded to a total of six layers spanning across heaven and Earth. Notions of the plurality of heaven and earth are no later than the 2nd millennium BC and may be elaborations of earlier and simpler cosmographies.” ref
“One text (KAR 307) describes the cosmos in the following manner, with each of the three floors of heaven being made of a different type of stone:
30 “The Upper Heavens are Luludānītu stone. They belong to Anu. He (i.e. Marduk) settled the 300 Igigū (gods) inside. 31 The Middle Heavens are Saggilmud stone. They belong to the Igīgū (gods). Bēl (i.e. Marduk) sat on the high throne within, 32 the lapis lazuli sanctuary. And made a lamp? of electrum shine inside (it). 33 The Lower Heavens are jasper. They belong to the stars. He drew the constellations of the gods on them. 34 In the … …. of the Upper Earth, he lay down the spirits of mankind. 35 [In the …] of the Middle earth, he settled Ea, his father. 36 […..] . He did not let the rebellion be forgotten. 37 [In the … of the Lowe]r earth, he shut inside 600 Anunnaki. 38 […….] … […. in]side jasper.” ref
“Another text (AO 8196) offers a slightly different arrangement, with the Igigi in the upper heaven instead of the middle heaven, and with Bel placed in the middle heaven. Both agree on the placement of the stars in the lower heaven. Exodus 24:9–10 identifies the floor of heaven as being like sapphire, which may correspond to the blue lapis lazuli floor in KAR 307, chosen potentially for its correspondence to the visible color of the sky. One hypothesis holds that the belief that the firmament is made of stone (or a metal, such as iron in Egyptian texts) arises from the observation that meteorites, which are composed of this substance, fall from the firmament.” ref
Seven heavens and earths
“Some texts describe seven heavens and seven earths, but within the Mesopotamian context, this is likely to refer to a totality of the cosmos with some sort of magical or numerological significance, as opposed to a description of the structural number of heavens and Earth. Israelite texts do not mention the notion of seven heavens or earths.” ref
Unity of the cosmos
“Mythical bonds, akin to ropes or cables, played the role of cohesively holding the entire world and all its layers of heaven and Earth together. These are sometimes called the “bonds of heaven and earth”. They can be referred to with terminology like durmāhu (typically referring to a strong rope made of reeds), markaṣu (referring to a rope or cable, of a boat, for example), or ṣerretu (lead-rope passed through an animals nose). A deity can hold these ropes as a symbol of their authority, such as the goddess Ishtar “who holds the connecting link of all heaven and earth (or netherworld)”. This motif extended to descriptions of great cities like Babylon which was called the “bond of [all] the lands,” or Nippur which was “bond of heaven and earth,” and some temples as well.” ref
Center of the cosmos
“The idea of a center to the cosmos played a role in elevating the status of whichever place was chosen as the cosmic center and in reflecting beliefs of the finite and closed nature of the cosmos. Babylon was described as the center of the Babylonian cosmos. In parallel, Jerusalem became “the navel of the earth” (Ezekiel 38:12). The finite nature of the cosmos was also suggested to the ancients by the periodic and regular movements of the heavenly bodies in the visible vicinity of the Earth.” ref
Firmament: Firmament
“The firmament was believed to be a solid boundary above the Earth, separating it from the upper or celestial waters. In the Book of Genesis, it is called the raqia. In ancient Egyptian texts, and from texts across the Near East generally, the firmament was described as having special doors or gateways on the eastern and western horizons to allow for the passage of heavenly bodies during their daily journeys. These were known as the windows of heaven or the gates of heaven. Canaanite text describe Baal as exerting his control over the world by controlling the passage of rainwater through the heavenly windows in the firmament. In Egyptian texts particularly, these gates also served as conduits between the earthly and heavenly realms for which righteous people could ascend. The gateways could be blocked by gates to prevent entry by the deceased as well. As such, funerary texts included prayers enlisting the help of the gods to enable the safe ascent of the dead. Ascent to the celestial realm could also be done by a celestial ladder made by the gods. Multiple stories exist in Mesopotamian texts whereby certain figures ascend to the celestial realm and are given the secrets of the gods.” ref
“Four different Egyptian models of the firmament and/or the heavenly realm are known. One model was that it was the shape of a bird: the firmament above represented the underside of a flying falcon, with the sun and moon representing its eyes, and its flapping causing the wind that humans experience. The second was a cow, as per the Book of the Heavenly Cow. The cosmos is a giant celestial cow represented by the goddess Nut or Hathor. The cow consumed the sun in the evening and rebirthed it in the next morning. The third is a celestial woman, also represented by Nut. The heavenly bodies would travel across her body from east to west. The midriff of Nut was supported by Shu (the air god) and Geb (the earth god) lay outstretched between the arms and feet of Nut. Nut consumes the celestial bodies from the west and gives birth to them again in the following morning. The stars are inscribed across the belly of Nut and one needs to identify with one of them, or a constellation, in order to join them after death. The fourth model was a flat (or slightly convex) celestial plane which, depending on the text, was thought to be supported in various ways: by pillars, staves, scepters, or mountains at the extreme ends of the Earth. The four supports give rise to the motif of the “four corners of the world.” ref
Earth: Flat Earth, Topography of the earth
“The ancient near eastern earth was a single-continent disk resting on a body of water sometimes compared to a raft. An aerial view of the cosmography of the earth is pictorially elucidated by the Babylonian Map of the World. Here, the city Babylon is near the Earth’s center and it is on the Euphrates river. Other kingdoms and cities surround it. The north is covered by an enormous mountain range, akin to a wall. This mountain range was traversed in some hero myths, such as the Epic of Gilgamesh where Gilgamesh travels past it to an area only accessible by gods and other great heroes. The furthest and most remote parts of the earth were believed to be inhabited by fantastic creatures. In the Babylonian Map, the world continent is surrounded by a bitter salt-water Ocean (called marratu, or “salt-sea”) akin to Oceanus described by the poetry of Homer and Hesiod in early Greek cosmology, as well as the statement in the Bilingual Creation of the World by Marduk that Marduk created the first dry land surrounded by a cosmic sea. Egyptian cosmology appears to have also shared this view, as one of the words used for sea, shen-wer, means “great encircler”. World-encircling oceans are also found in the Fara tablet VAT 12772 from the 3rd millennium BC and the Myth of Etana.” ref
Four corners of the earth (Four Mountains)
“A common honorific that many kings and rulers ascribed to themselves was that they were the rulers of the four quarters (or corners) of the Earth. For example, Hammurabi (ca. 1810–1750 BCE or around 3,810 to 3,750 years ago) received the title of “King of Sumer and Akkad, King of the Four Quarters of the World”. Monarchs of the Assyrian empire, like Ashurbanipal, also took on this title. (Although the title implies a square or rectangular shape, in this case, it is taken to refer to the four quadrants of a circle, which is joined at the world’s center.) Likewise, the ‘four corners’ motif would also appear in some biblical texts, such as Isaiah 11:12.” ref
Cosmic mountain
Further information: Sacred mountains, Mashu, Axis mundi, and World tree
“According to iconographic and literary evidence, the cosmic mountain, known as Mashu in the Epic of Gilgamesh, was thought to be located at or extend to both the westernmost and easternmost points of the earth, where the sun could rise and set respectively. As such, the model may be called a bi-polar model of diurnal solar movement. The gates for the rising and setting of the sun were also located at Mashu. Some accounts have Mashu as a tree growing at the center of the earth with roots descending into the underworld and a peak reaching to heaven. The cosmic mountain is also found in Egyptian cosmology, as Pyramid Text 1040c says that the mountain ranges on the eastern and western sides of the Nile act as the “two supports of the sky.” In the Baal Cycle, two cosmic mountains exist at the horizon acting as the point through which the sun rises from and sets into the underworld (Mot). The tradition of the twin cosmic mountains may also lie behind Zechariah 6:1.” ref
Heavenly bodies
Sun
“The sun god (represented by the god Utu in Sumerian texts or Shamash in Akkadian texts) rises in the day and passes over the earth. Then, the sun god falls beneath the earth in the night and comes to a resting point. This resting point is sometimes localized to a designated structure, such as the chamber within a house in the Old Babylonian Prayer to the Gods of the Night. To complete the cycle, the sun comes out in the next morning. Likewise, the moon was thought to rest in the same facility when it was not visible. A similar system was maintained in Egyptian cosmology, where the sun travelled beneath the surface of the earth through the underworld (known among ancient Egyptians as Duat) to rise from the same eastern location each day. These images result from anthropomorphizing the sun and other astral bodies also conceived as gods. For the sun to exit beneath the earth, it had to cross the solid firmament: this was thought possible by the existence of opening ways or corridors in the firmament (variously illustrated as doors, windows or gates) that could temporarily open and close to allow astral bodies to pass across them. The firmament was conceived as a gateway, with the entry/exit point as the gates; other opening and closing mechanisms were also imagined in the firmament like bolts, bars, latches, and keys. During the sun’s movement beneath the earth, into the netherworld, the sun would cease to flare. This enabled the netherworld to remain dark. But when it rose, it would flare up and again emit light.” ref
“This model of the course of the sun had an inconsistency that later models evolved to address. The issue was to understand how, if the sun came to a resting point beneath the earth, could it also travel beneath the earth the same distance under it that it was observed to cross during the day above it such that it would rise periodically from the east. One solution that some texts arrived at was to reject the idea that the sun had a resting point. Instead, it remained unceasing in its course. Overall, the sun god’s activities in night according to Sumerian and Akkadian texts proceeds according to a regular and systematic series of events: (1) The western door of heaven opens (2) The sun passes through the door into the interior of heaven (3) Light falls below the western horizon (4) The sun engages in certain activities in the netherworld like judging the dead (5) The sun enters a house, called the White House (6) The sun god eats the evening meal (7) The sun god sleeps in the chamber agrun (8) The sun emerges from the chamber (9) The eastern door opens and the sun passes through as it rises. In many ancient near eastern cultures, the underworld had a prominent place in descriptions of the sun journey, where the sun would carry out various roles including judgement related to the dead.” ref
“In legend, many hero journeys followed the daily course of the sun god. These have been attributed to Gilgamesh, Odysseus, the Argonauts, Heracles and, in later periods, Alexander the Great. In the Epic of Gilgamesh, Gilgamesh reaches the cosmic mountain Mashu, which is either two mountains or a single twin-peaked mountain. Mashu acts as the sun-gate, from where the sun and sets in its path to and from the netherworld. In some texts, the mountain is called the mountain of sunrise and sunset. According to the Epic:
The name of the mountain was Mashu. When [he] arrived at Mount Mashu, which daily guards the rising [of the sun,] – their tops [abut] the fabric of the heavens, their bases reach down to Hades – there were scorpion-men guarding its gate, whose terror was dread and glance was death, whose radiance was terrifying, enveloping the uplands – at both sunrise and sunset they guard the sun…” ref
“Other texts describing the relationship between the sun and the cosmic mountain reads:
O Shamash, when you come forth from the great mountain, When you come forth from the great mountain, the mountain of the deep, When you come forth from the holy hill where destinies are ordained, When you [come forth] from the back of heaven to the junction point of heaven and earth… A number of additional texts share descriptions like these.” ref
Moon
“Mesopotamians believed the moon to be a manifestation of the moon god, known as Nanna in Sumerian texts or Sîn in Akkadian texts, a high god of the pantheon, subject to cultic devotion, and father of the sun god Shamash and the Venus god Inanna. The path of the moon in the night sky and its lunar phases were also of interest. At first, Mesopotamia had no common calendar, but around 2000 BCE, the semi-lunar calendar of the Sumerian center of Nippur became increasingly prevalent. Hence, the moon god was responsible for ordering perceivable time. The lunar calendar was divided into twelve months of thirty days each. New months were marked by the appearance of the moon after a phase of invisibility.” ref
“The Enuma Elish creation myth describes Marduk as arranging the paths of the stars and then spends considerable space on Marduk’s ordering of the moon:
12 He made Nannaru (=the moon-god) appear (and) entrusted the night to him. 13 He assigned him as the jewel of the night to determine the days. 14 Month by month without cease, he marked (him) with a crown: 15 “At the beginning of the month, while rising over the land, 16 you shine with horns to reveal six days. 17 On the seventh day, (your) disc shall be halved. 18 On the fifteenth day, in the middle of each month, you shall stand in opposition. 19 As soon as Šamaš (= the sun-god) sees you on the horizon, 20 reach properly your full measure and form yourself back. 21 At the day of disappearance, approach the path of Šamaš. 22 [… 3]0. day you shall stand in conjunction. You shall be equal to Šamaš.” ref
“The ideal course of the moon was thought to form one month every thirty days. However, the precise lunar month is 29.53 days, leading to variations that made the lunar month counted as 29 or 30 days in practice. The mismatch between the predictions and reality of the course of the moon gave rise to the idea that the moon could act according to its expected course as a good omen or deviate from it as a bad omen. In the 2nd millennium BCE, Mesopotamian scholars composed the Enūma Anu Enlil, a collection of at least seventy tablets concerned with omens. The first fourteen (1–14) relate to the appearance of the moon, and the next eight (15–22) deal with lunar eclipses. The moon was also assigned other functions, such as providing illumination during the night, and already in this period, had a known influence on the tides. During the day when the moon was not visible, it was thought that the moon descended beneath the flat disk of the earth and, like the sun, underwent a voyage through the underworld. The cosmic voyage and motion of the moon also allowed it to exert influence over the world; this belief naturally allowed for the practice of divination to arise.” ref
Stars and planets
Further information: Classical planet
“Mesopotamian cosmology would differ from the practice of astronomy in terms of terminology: for astronomers, the word “firmament” was not used but instead “sky” to describe the domain in which the heavenly affairs were visible. The stars were located on the firmament. The earliest texts attribute to Anu, Enlil, and Enki (Ea) the ordering of perceivable time by creating and ordering the courses of the stars. Later, according to the Enuma Elish, the stars were arranged by Marduk into constellations representing the images of the gods. The year was fixed by organizing the year into twelve months, and by assigning (the rising of) three stars to each of the twelve months. The moon and zenith were also created. Other phenomena introduced by Marduk included the lunar phases and lunar scheme, the precise paths that the stars would take as they rose and set, the stations of the planets, and more.” ref
“Another account of the creation of the heavenly bodies is offered in the Babyloniaca of Berossus, where Bel (Marduk) creates stars, sun, moon, and the five (known) planets; the planets here do not help guide the calendar (a lack of concern for the planets also shared in the Book of the Courses of the Heavenly Luminaries, a subsection of 1 Enoch). Concern for the establishment of the calendar by the creation of heavenly bodies as visible signs is shared in at least seven other Mesopotamian texts. A Sumerian inscription of Kudur-Mabuk, for example, reads “The reliable god, who interchanges day and night, who establishes the month, and keeps the year intact.” Another example is to be found in the Exaltation of Inanna. The word “star” (mul in Sumerian; kakkabu in Akkadian) was inclusive to all celestial bodies, stars, constellations, and planets. A more specific term for planets existed however (udu.idim in Sumerian; bibbu in Akkadian, literally “wild sheep”) to distinguish them from other stars (of which they were a subcategory): unlike the stars thought to be fixed into their location, the planets were observed to move.” ref
“By the 3rd millennium BCE, the planet Venus was identified as the astral form of the goddess Inanna (or Ishtar), and motifs such as the morning and evening star were applied to her. Jupiter became Marduk (hence the name “Marduk Star”, also called Nibiru), Mercury was the “jumping one” (in reference to its comparatively fast motion and low visibility) associated with the gods Ninurta and Nabu, and Mars was the god of pestilence Nergal and thought to portend evil and death. Saturn was also sinister. The most obvious characteristic of the stars were their luminosity and their study for the purposes of divination, solving calendrical calculations, and predictions of the appearances of planets, led to the discovery of their periodic motion. From 600 BC onwards, the relative periodicity between them began to be studied.” ref
Upper waters
Main article: Cosmic ocean
“Above the firmament was a large, cosmic body of water which may be referred to as the cosmic ocean or celestial waters. In the Tablet of Shamash, the throne of the sun god Shamash is depicted as resting above the cosmic ocean. The waters are above the solid firmament that covers the sky. In the Enuma Elish, the upper waters represented the waters of Tiamat, contained by Tiamat’s stretched out skin. Canaanite mythology in the Baal Cycle describes the supreme god Baal as enthroned above the freshwater ocean. Egyptian texts depict the sun god sailing across these upper waters. Some also convey that this body of water is the heavenly equivalent of the Nile River.” ref
Lower waters
“Both Babylonian and Israelite texts describe one of the divisions of the cosmos as the underworldly ocean. In Babylonian texts, this is coincided with the region/god Abzu. In Sumerian mythology, this realm was created by Enki. It was also where Enki lived and ruled over. Due to the connection with Enki, the lower waters were associated with wisdom and incantational secret knowledge. In Egyptian mythology, the personification of this subterranean body of water was instead Nu. The notion of a cosmic body of water below the Earth was inferred from the realization that much water used for irrigation came from under the ground, from springs, and that springs were not limited to any one part of the world. Therefore, a cosmic body of water acting as a common source for the water coming out of all these springs was conceived.” ref
Underworld
Main articles: Ancient Mesopotamian underworld and Egyptian underworld
“The Underworld/Netherworld (kur or erṣetu in Sumerian) is the lowest region in the direction downwards, below even Abzu (the primeval ocean/lower waters). It is geographically parallel with the plane of human existence, but was so low that both demons and gods could not descend to it. One of its names was “Earth of No Return”. It was, however, inhabited by beings such as ghosts, demons, and local gods. The land was depicted as dark and distant: this is because it was the opposite of the human world and so did not have light, water, fields, and so forth. According to KAR 307, line 37, Bel cast 600 Annunaki into the underworld. They were locked away there, unable to escape, analogous to the enemies of Zeus who were confined to the underworld (Tartarus) after their rebellion during the Titanomachy. During and after the Kassite period, Annunaki were largely depicted as underworld deities; a hymn to Nergal praises him as the “Controller of the underworld, Supervisor of the 600”. In Canaanite religion, the underworld was personified as the god Mot. In Egyptian mythology, the underworld was known as Duat and was ruled by Osiris, the god of the afterlife. It was also the region where the sun (manifested by the god Ra) made its journey from west (where it sets) to the east (from where it would rise again the next morning).” ref
Origins of the cosmos
“The world was thought to be created ex materia. That is, out of pre-existing, and unformed, eternal matter. This is in contrast to the later notion of creation ex nihilo, which asserts that all the matter of the universe was created out of nothing. The primeval substance had always existed, was unformed, divine, and was envisioned as an immense, cosmic, chaotic mass of water or ocean (a representation that still existed in the time of Ovid). In the Mesopotamian theogonic process, the gods would be ultimately generated from this primeval matter, although a distinct process is found in the Hebrew Bible where God is initially distinct from the primeval matter. For the cosmos and the gods to ultimately emerge from this formless cosmic ocean, the idea emerged that it had to be separated into distinct parts and therefore be formed or organized. This event can be imagined of as the beginning of time. Furthermore, the process of the creation of the cosmos is coincident or equivalent to the beginning of the creation of new gods.” ref
“In the 3rd millennium BCE, the goddess Nammu was the one and singular representation of the original cosmic ocean in Mesopotamian cosmology. From the 2nd millennium BCE onwards, this cosmic ocean came to be represented by two gods, Tiamat and Abzu who would be separated from each other to mark the cosmic beginning. The Ugaritic god Yam from the Baal Cycle may also represent the primeval ocean. Sumerian and Akkadian sources understand the matter of the primordial universe out of which the cosmos emerges in different ways. Sumerian thought distinguished between the inanimate matter that the cosmos was made of and the animate and living matter that permeated the gods and went on to be transmitted to humans. In Akkadian sources, the cosmos is originally alive and animate, but the deaths of Abzu (male deity of the fresh waters) and Tiamat (female sea goddess) give rise to inanimate matter, and all inanimate matter is derived from the dead remains of these deities.” ref
Origins of the gods
“The core Mesopotamian myth to explain the gods’ origins begins with the primeval ocean, personified by Nammu, containing Father Sky and Mother Earth within her. In the god-list TCL XV 10, Nammu is called ‘the mother, who gave birth to heaven and earth’. The conception of Nammu as mother of Sky-Earth is first attested in the Ur III period (early 2nd millennium BCE), though it may go back to an earlier Akkadian era. Earlier in the 3rd millennium BCE, Sky and Earth were the starting point with little apparent question about their own origins. The representation of Sky as male and Earth as female may come from the analogy between the generative power of the male sperm and the rain that comes from the sky, which respectively fertilize the female to give rise to newborn life or the Earth to give rise to vegetation. In the desert-dweller milieu, life depended on pastureland.” ref
“Sky and Earth are in a union. Because they are the opposite sex, they inevitably reproduce and their offspring are successive pairs or generations of gods known as the Enki-Ninki deities. The name comes from Enki and Ninki (“Lord and Lady Earth”) being the first pair in all versions of the story. The only other consistent feature is that Enlil and Ninlil are the last pair. In each pair, one member is male (indicated by the En- prefix) and the other is female (indicated by the Nin- prefix). The birth of Enlil results in the separation of heaven and earth as well as the division of the primordial ocean into the upper and lower waters. Sky, now Anu, can mate with other deities after being separated from Earth: he mates with his mother Nammu to give birth to Enki (different from the earlier Enki) who takes dominion over the lower waters. The siblings Enlil and Ninlil mate to give birth to Nanna (also known as Sin), the moon god, and Ninurta, the warrior god. Nanna fathers Utu (known as Shamash in Akkadian texts), the sun god, and Inanna (Venus). By this point, the main features of the cosmos had been created/born. A variation of this myth existed in Egyptian cosmology. Here, the primordial ocean is given by the god Nu. The creation act neither takes its materials from Nu, unlike in Mesopotamian cosmology, nor is Nu eliminated by the creation act.” ref
Separation of heaven and earth
“3rd millennium BCE texts speak of the cosmic marriage or union of Heaven and Earth. Only one towards the end of this era, the Song of the hoe, mentions their separation. By contrast, 2nd millennium texts entirely shift in focus to their separation. The tradition spread into Sumerian, Akkadian, Phoenician, Egyptian, and early Greek mythology. The cause of the separation involves either the agency of Enlil or takes place as a spontaneous act. One recovered Hittite text states that there was a time when they “severed the heaven from the earth with a cleaver”, and an Egyptian text refers to “when the sky was separated from the earth” (Pyramid Text 1208c). OIP 99 113 ii and 136 iii says Enlil separated Earth from Sky and separated Sky from Earth. Enkig and Ninmah 1–2 also says Sky and Earth were separated in the beginning. The introduction of Gilgamesh, Enkidu, and the Netherworld says that heaven is carried off from the earth by the sky god Anu to become the possession of the wind god Enlil. Several other sources also present this idea.” ref
“There are two strands of Mesopotamian creation myths regarding the original separation of the heavens and earth. The first, older one, is evinced from texts in the Sumerian language from the 3rd millennium BC and the first half of the 2nd millennium BCE. In these sources, the heavens and Earth are separated from an original solid mass. In the younger tradition from Akkadian texts, such as the Enuma Elish, the separation occurs from an original water mass. The former usually has the leading gods of the Sumerian pantheon, the King of Heaven Anu and the King of Earth Enlil, separating the mass over a time-frame of “long days and nights”, similar to the total timeframe of the Genesis creation narrative (six days and nights). The Sumerian texts do not mention the creation of the cosmic waters, but it may be surmised that water was one of the primordial elements.” ref
Stretching out the heavens
“The idiom of the heavens and earth being stretched out plays both a cultic and cosmic role in the Hebrew Bible where it appears repeatedly in the Book of Isaiah (40:22; 42:5; 44:24; 45:12; 48:13; 51:13, 16), with related expressions in the Book of Job (26:7) and the Psalms (104:2). One example reads “The one who stretched out the heavens like a curtain / And who spread them out like a tent to dwell in” (Is 40:22). The idiom is used in these texts to identify the creative element of Yahweh‘s activities and the expansion of the heavens signifies its vastness, acting as Yahweh’s celestial shrine. In Psalmic tradition, the “stretching” of the heavens is analogous to the stretching out of a tent. The Hebrew verb for the “stretching” of the heavens is also the regular verb for “pitching” a tent. The heavens, in other words, may be depicted as a cosmic tent (a motif found in many ancient cultures). This finds architectural analogy in descriptions of the tabernacle, which is itself a heavenly archetype, over which a tent is supposed to have been spread. The phrase is frequently followed by an expression that God sits enthroned above and ruling the world, paralleling descriptions of God being seated in the Holy of Holies of the Tabernacle where he is stated to exercise rule over Israel. Biblical references to stretching the heavens typically occur in conjunction with statements that God made or laid the foundations of the earth.” ref
“Similar expressions may be found elsewhere in the ancient near east. A text from the 2nd millennium BC, the Ludlul Bēl Nēmeqi, says “Wherever the earth is laid, and the heavens are stretched out”, though the text does not identify the creator of the cosmos. The Enuma Elish also describes the phenomena, in IV.137–140:
137 He split her into two like a dried fish: 138 One half of her he set up and stretched out as the heavens. 139 He stretched the skin and appointed a watch. 140 With the instruction not to let her waters escape. In this text, Marduk takes the body of Tiamat, who he has killed, and stretches out Tiamat’s skin to create the firmamental heavens which, in turn, comes to play the role of preventing the cosmic waters above the firmament from escaping and being unleashed onto the earth. Whereas the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible states that Yahweh stretched heaven like a curtain in Psalm 104:2, the equivalent passage in the Septuagint instead uses the analogy of stretching out like “skin”, which could represent a relic of Babylonian cosmology from the Enuma Elish. Nevertheless, the Hebrew Bible never identifies the material out of which the firmament was stretched. Numerous theories about what the firmament was made of sprung up across ancient cultures.” ref
Origins of humanity
“Many stories emerged to explain the creation of humanity and the birth of civilization. Earlier Sumerian language texts from the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC can be divided into two traditions: those from the cities of Nippur or Eridu. The Nippur tradition asserts that Heaven (An) and Earth (Ki) were coupled in a cosmic marriage. After they are separated by Enlil, Ki receives semen from An and gives rise to the gods, animals, and man. The Eridu tradition says that Enki, the offspring of An and Namma (in this tradition, the freshwater goddess) is the one who creates everything. Periodical relations between Enki and Ninhursaga (in this tradition, the personification of Earth) gives rise to vegetation. With the help of Namma, Enki creates man from clay. A famous work of the Eridu tradition is Eridu Genesis.” ref
“A minority tradition in Sumerian texts, distinct from Nippur and Eridu traditions, is known from KAR 4, where the blood of a slaughtered deity is used to create humanity for the purpose of making them build temples for the gods. Later Akkadian language tradition can be divided into various minor cosmogonies, cosmogonies of significant texts like Enuma Elish and Epic of Atrahasis, and finally the Dynasty of Dunnum placed in its own category. In the Atrahasis Epic, the Anunnaki gods force the Igigi gods to do their labor. However, the Igigi became fed up with this work and rebel. To solve the problem, Enlil and Mami create humanity by mixing the blood of gods with clay, who in the stead of the Igigi are assigned the gods’ work. In the Enuma Elish, divine blood alone is used to make man.” ref
Picture Link: ref
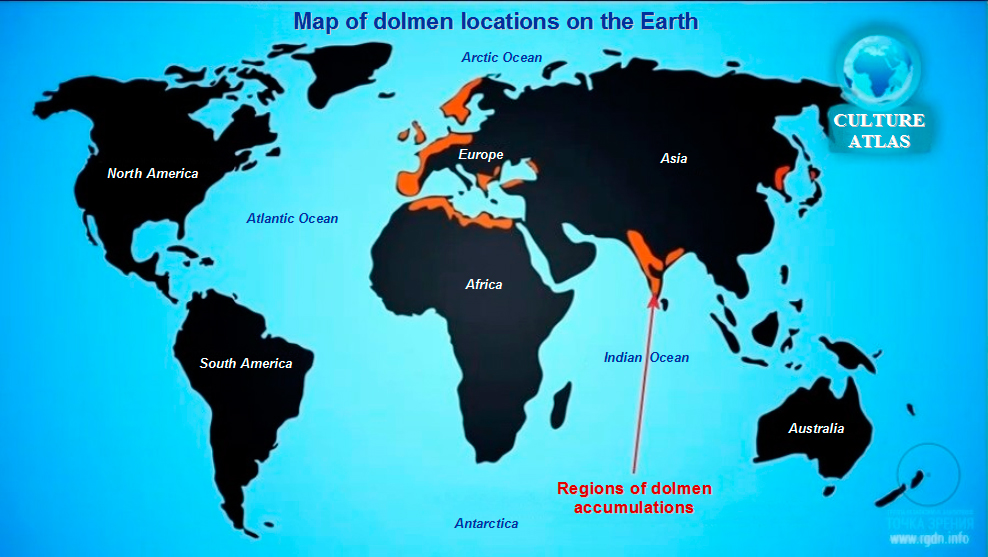
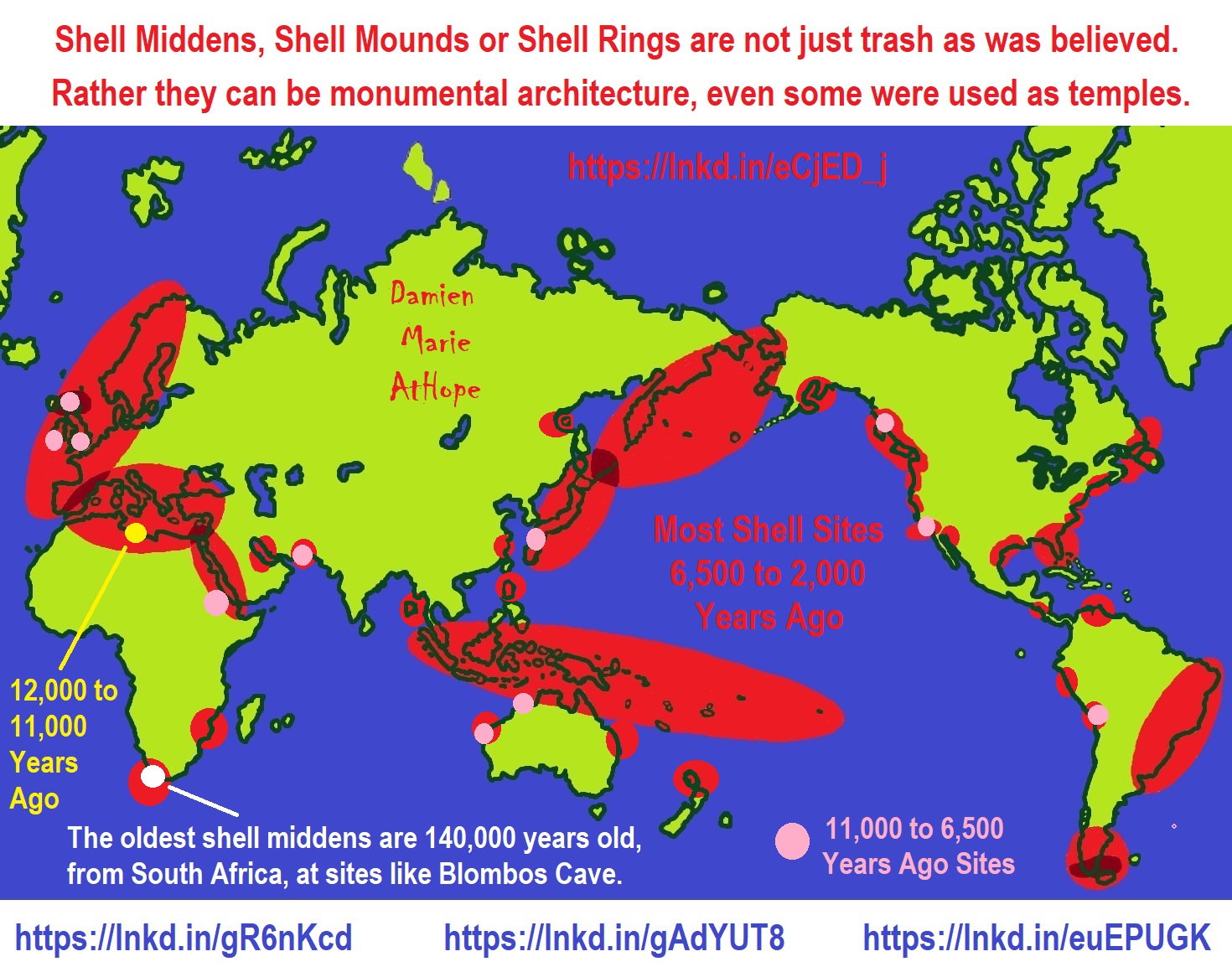
“There are ∼35,000 presently extant European megaliths, a term which is derived from Greek μέγας (mégas), “big,” and λίϑος (líthos), “stone.” These include megalithic tombs, standing stones, stone circles, alignments, and megalithic buildings or temples. Most of these were constructed during the Neolithic and the Copper Ages and are located in coastal areas. Their distribution is along the so-called Atlantic façade, including Sweden, Denmark, North Germany, The Netherlands, Belgium, Scotland, England, Wales, Ireland, northwest France, northern Spain, and Portugal, and in the Mediterranean region, including southern and southeastern Spain, southern France, the Islands of Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily, Malta and the Balearics, Apulia, northern Italy, and Switzerland. Interestingly, they share similar or even identical architectonic features throughout their distribution. Megalithic graves were built as dolmens and as passage or gallery graves. Thousands of anthropogenic erected stones either stand isolated in the landscapes or were arranged as circles or in rows. There is evidence all across Europe for an orientation of the graves toward the east or southeast in the direction of the rising Sun. The question therefore arises whether there was a single, original source from which a megalithic movement spread over Europe or regional phenomena developed independently due to a similar set of conditions.” ref
“According to study was conducted by Bettina Schulz Paulsson, a prehistoric archaeologist at the University of Gothenburg in Sweden, European megaliths can be traced back to a single hunter-gatherer culture that originated nearly 7,000 years ago in what’s today the Brittany region of northwestern France.” ref
“From 10,000-8,000 years ago, Sweden as a whole became populated by people who lived by hunting, gathering and fishing, and who used simple stone tools. Dwelling places and graves dating from the Stone Age, lasting until about 3,800 years ago, are found today in increasing numbers. The Bronze Age was marked in the Nordic region – especially in Denmark but also in Sweden – by a high level of culture, shown by the artifacts found in graves. After 2,500 years ago, such artifacts become increasingly rare as iron came into more general use. During the early Iron Age, the population of Sweden became settled, and agriculture came to form the basis of the economy and society.” ref
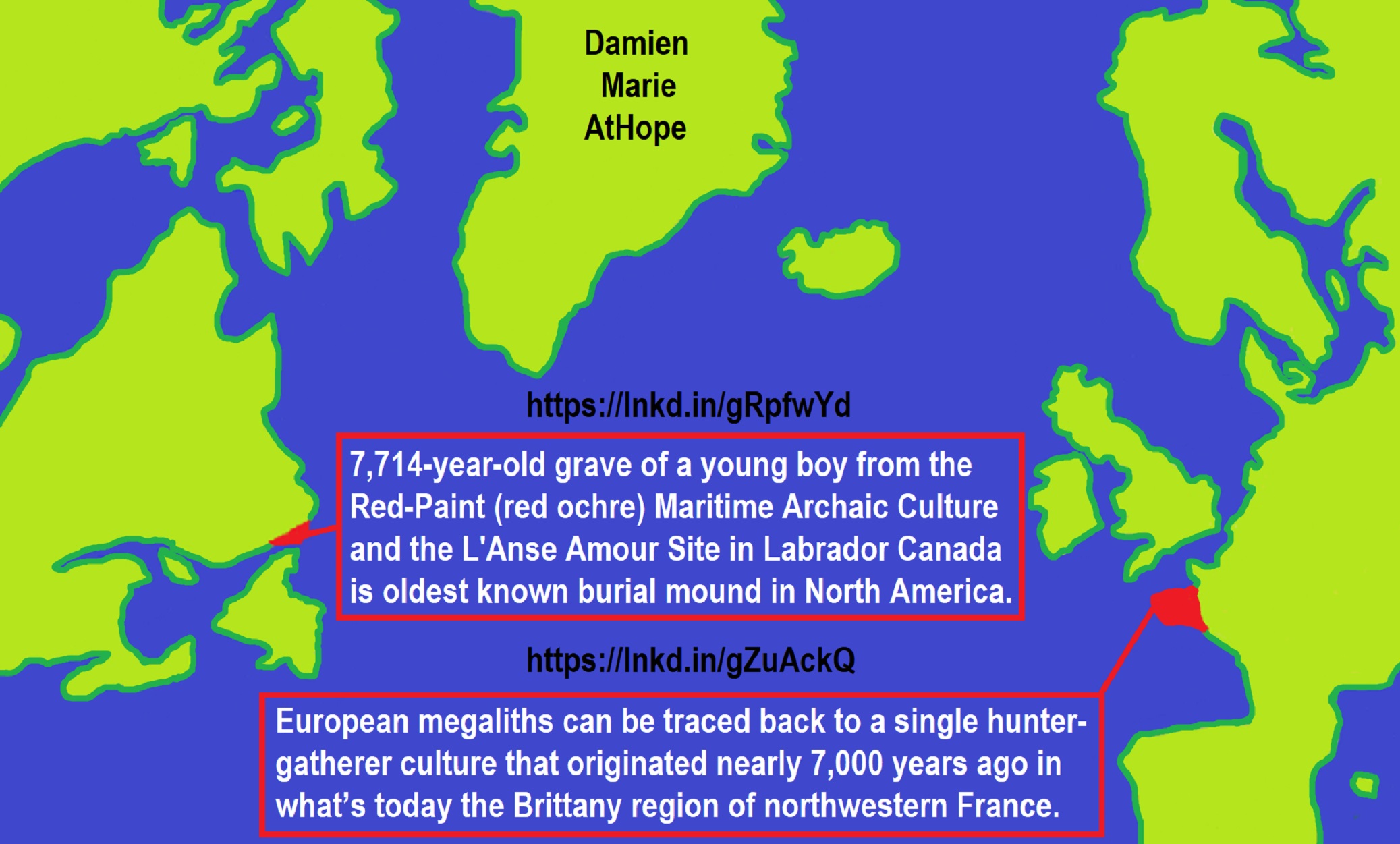
I don’t think they crossed the Atlantic Ocean across the water but by land going both directions from Asia west to Europe as well as east crossing the Bering Strait, between Asia and The Americas.
Megalithic tombs in western and northern Neolithic Europe were linked to a kindred society
“A new phenomenon of constructing distinctive funerary monuments, collectively known as megalithic tombs, emerged around 4500 BCE along the Atlantic façade. The megalithic phenomenon has attracted interest and speculation since medieval times. In particular, the origin, dispersal dynamics, and the role of these constructions within the societies that built them have been debated. We generate genome sequence data from 24 individuals buried in five megaliths and investigate the population history and social dynamics of the groups that buried their dead in megalithic monuments across northwestern Europe in the fourth millennium BCE. Our results show kin relations among the buried individuals and an overrepresentation of males, suggesting that at least some of these funerary monuments were used by patrilineal societies.” ref
“Paleogenomic and archaeological studies show that Neolithic lifeways spread from the Fertile Crescent into Europe around 9000 BCE, reaching northwestern Europe by 4000 BCE. Starting around 4500 BCE, a new phenomenon of constructing megalithic monuments, particularly for funerary practices, emerged along the Atlantic façade. While it has been suggested that the emergence of megaliths was associated with the territories of farming communities, the origin and social structure of the groups that erected them has remained largely unknown. We generated genome sequence data from human remains, corresponding to 24 individuals from five megalithic burial sites, encompassing the widespread tradition of megalithic construction in northern and western Europe, and analyzed our results in relation to the existing European paleogenomic data. The various individuals buried in megaliths show genetic affinities with local farming groups within their different chronological contexts. Individuals buried in megaliths display (past) admixture with local hunter-gatherers, similar to that seen in other Neolithic individuals in Europe. In relation to the tomb populations, we find significantly more males than females buried in the megaliths of the British Isles. The genetic data show close kin relationships among the individuals buried within the megaliths, and for the Irish megaliths, we found a kin relation between individuals buried in different megaliths. We also see paternal continuity through time, including the same Y-chromosome haplotypes reoccurring. These observations suggest that the investigated funerary monuments were associated with patrilineal kindred groups. Our genomic investigation provides insight into the people associated with this long-standing megalith funerary tradition, including their social dynamics.” ref
Radiocarbon dates and Bayesian modeling support maritime diffusion model for megaliths in Europe
“The radiocarbon dates suggest that the first megalithic graves in Europe were closed small structures or dolmens built aboveground with stone slabs and covered by a round or long mound of earth or stone. These graves emerge in the second half of the fifth millennium calibrated years (cal) BC within a time interval of 4794 cal BC to 3986 cal BC (95.4%; 4770 cal BC to 4005 cal BC, 68.2%) (Dataset S3, M7-2 to M29-4), which can be reduced most probably to 200 y to 300 y, in northwest France, the Channel Islands, Catalonia, southwestern France, Corsica, and Sardinia. Taking the associated cultural material into consideration, megalithic graves from Andalusia, Galicia, and northern Italy presumably belong to this first stage (Fig. 3). There are no radiocarbon dates available from the early megalithic graves in these regions, or their calibrated ranges show an onset extending into the fourth millennium cal BC, as is the case for Galicia. Of these regions, northwest France is the only one which exhibits monumental earthen constructions before the megaliths (SI Appendix, Fig. S2).” ref
“The Passy graves in the Paris Basin have no megalithic chamber yet, but are impressive labor-intensive structures with a length of up to 280 m. These graves seem to be the earliest monumental graves in Europe; the first individual buried in the Passy necropolis died in 5061 cal BC to 4858 cal BC (95.4%; 5029 cal BC to 4946 cal BC, 68.2%) (Dataset S3, M1-4). Somewhat later, the first monumental graves emerge in Brittany, and especially in the region of Carnac, in the form of round tumuli covering pit burials, stone cists, and dry-wall chambers. The first building phase of the tumulus St. Michel in Carnac is dated to the time interval 4782 cal BC to 4594 cal BC (95.4; 4724 cal BC to 4618 cal BC, 68.2%) (Dataset S3, M4-2 to M4-4). The earliest megalithic grave chambers in Brittany, such as Tumiac, Kervinio, Castellic, St. Germain, Manio 5, Mané Hui, and Kerlescan (14–16), emerge within this horizon as an architectonic feature of monumental long and round mounds. For these early megaliths, no radiocarbon determinations are available. It is only possible to limit the time interval of construction to the Ancient Castellic horizon based on the typochronological considerations of the grave goods and according to Ancient Castellic contexts with associated radiocarbon results ranging from 4794 cal BC to 3999 cal BC (95.4%; 4770 cal BC to 4034 cal BC, 68.2%) (Dataset S3, M7-2 to M7-7).” ref
“In the Seine-Yonne basin at around 4500 B.C. numerous cemeteries appeared, including giant “enclosures” which as a funerary manifestation would have no later equivalent in Europe. These constructions, whether tumuli, palisade enclosures, or mixed systems, sometimes exceed 300 m in length but contain very few burials. Beyond the classic interpretation, which sees high investment in a few individuals as reflecting a hierarchical society, structural analysis of these cemeteries shows the repetition of an elementary module, associated with consistent attributes, evoking hunting and more broadly, the wild. An exercise of association and exclusion brings into play the morphology and arrangements of the monuments, the gender of the inhumed individuals and their attributes. In the male monuments, a central figure is thus distinguished, sometimes with original physical characteristics and accompanied by an enigmatic insignia: a pointed bone instrument with a wide base, trivially called an “Eiffel Tower”. This figure is surrounded by other individuals interpreted as hunters on the basis of the accompanying objects. Other individuals probably served as no more than passive figurants, rather like foils. In any case, the monumental cemeteries of the 5th millennium correspond to the earliest human groups for which we can identify diverse and repetitive statuses.” ref
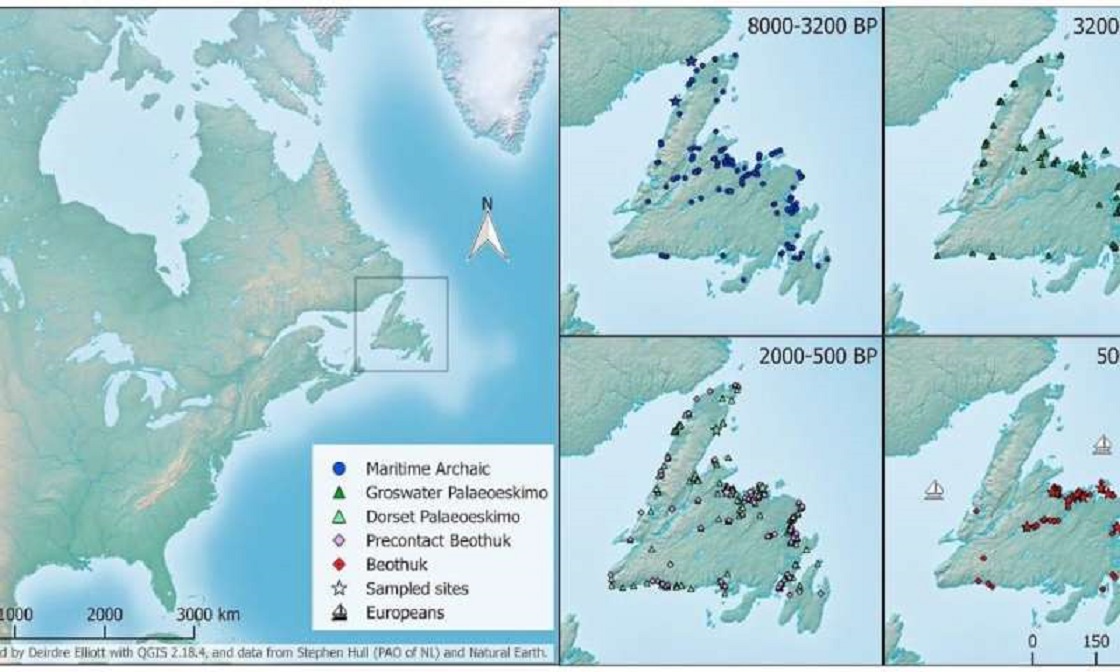
No ‘lost tribes’ or aliens: what ancient DNA reveals about American prehistory
“New genetics research settles questions about the peoples of Newfoundland and Labrador. Genetic Discontinuity between the Maritime Archaic and Beothuk Populations in Newfoundland, Canada which addresses the genetic diversity within three different ancient groups who lived in Newfoundland and Labrador. One reason this region is of particular interest is that it’s on the furthest northeastern margin of North America and so was one of the last areas in the Americas to be peopled. It appears to have been occupied successively by three culturally distinct groups beginning about 10,000 years ago in Labrador and 6,000 years ago in Newfoundland: the Maritime Archaic, the Paleo-Inuit (also referred to as the Paleo-Eskimo), and the indigenous peoples that Europeans called the Beothuk. Today the region is home to several indigenous groups, including the Inuit, the Innu, the Mi’kmaq and the Southern Inuit of NunatuKavut.” ref
“The members of the Maritime Archaic tradition created the oldest known burial mounds in North America (dating to 7,714 years ago) and subsisted upon coastal marine resources. Approximately 3,400 years ago they seem to have abandoned Newfoundland, either in response to the appearance of Paleo-Inuit in the region or because of climate changes. The Paleo-Inuit’s presence on the island overlapped with the peoples referred to as the Beothuk beginning around 2,000 years ago. The Beothuk encountered European settlers in 1500 AD, and in response to their presence gradually moved to the interior of the island, where their populations declined. Apart from that single exception, the Maritime Archaic, Paleo-Inuit, and Beothuk are clearly genetically distinctive from one another. However, it’s important to note that this study was done on mitochondrial DNA, which is exclusively matrilineally inherited, and so we can only say that the three groups were not maternally related.” ref
“In the case of Newfoundland, the three groups were genetically distinct; they do not share any maternal haplogroups except for haplogroup X2a, lineages of which were found in both the Maritime Archaic and Beothuk. (The presence of haplogroup X2a in North American populations has sometimes been cited as evidence for European ancestry in ancient Americans. If you’re interested in why I and most other geneticists specializing in Native American populations disagree with that, you can read about it here).” ref
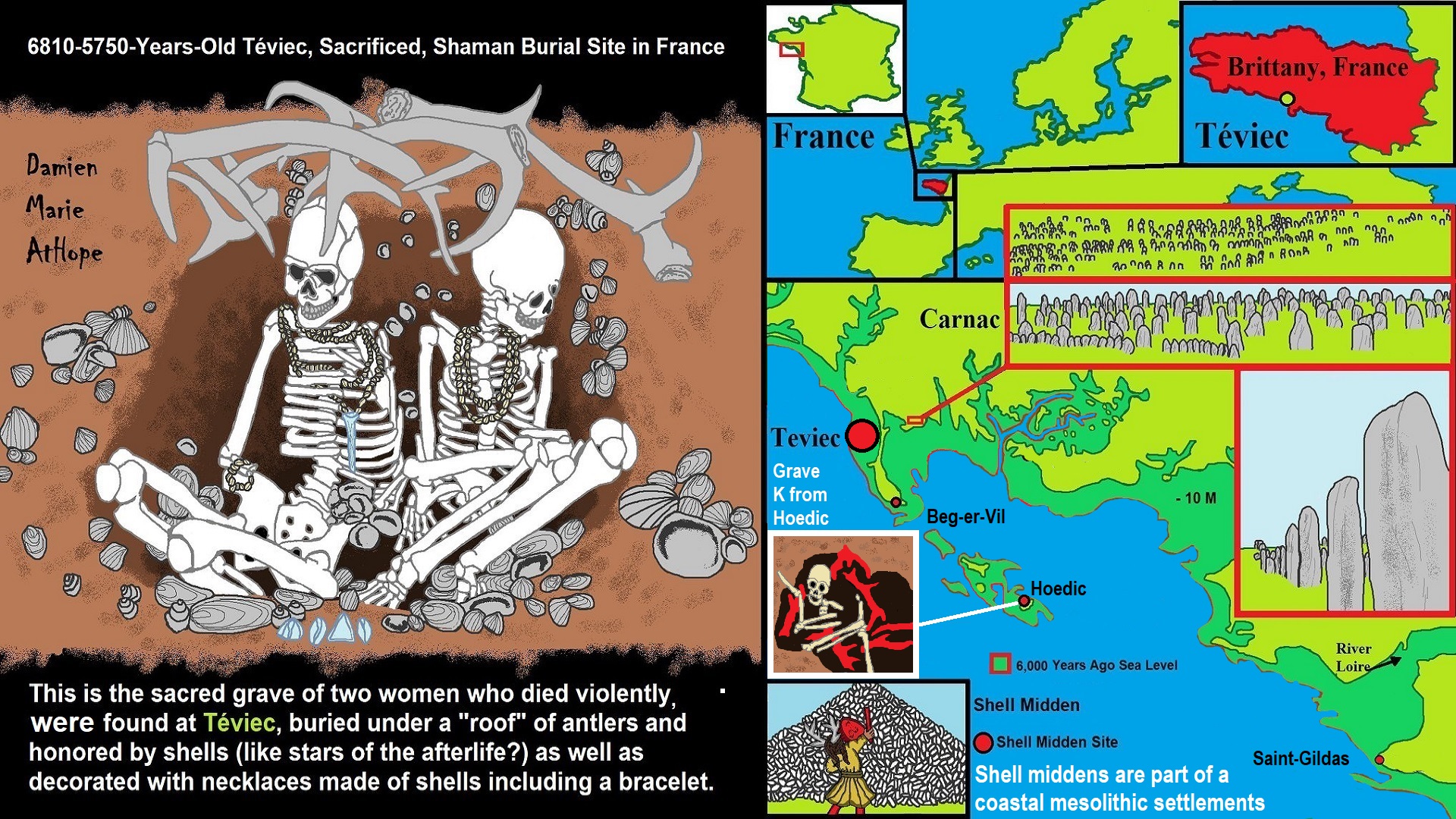
6810-5750-Years-Old Teviec, Sacrificed, Shaman Burial Site in France
This is the sacred grave of two women who died violently, were found at Teviec, buried under a “roof” of antlers and honored by shells (like stars of the afterlife?) as well as decorated with necklaces made of shells including a bracelet. ref
“The island is one of only a few known Mesolithic sites in Brittany, along with Pointe de la Torche, Hoëdic and Beg er Vil on the Quiberon peninsula. During the Mesolithic period, the sea level was much lower and it was possible to walk from France to England, and Téviec was situated in a lagoon.” ref
“Extensive middens were found near places of habitation on the island, containing the remains of shellfish, crustaceans, squid, fish, birds, cetaceans, and terrestrial mammals including wild boar, red deer, roe deer, dogs, and so on. The hunter-gatherers of Téviec buried their own dead in the middens. This helped to preserve the graves, as the carbonates from the shells in the middens insulated human bones from the acid soil.” ref
“Many tools made of bone and antler were found along with numerous flint microliths. They were originally believed to date to between 6740 and 5680 years BP. This indicates a longer occupation than previously thought, with its end coming at the beginning of the Neolithic period. Ten multiple graves were discovered at Téviec containing a total of 23 individuals, including adults and children.” ref
“Some of the remains were scattered between different locations. Several of those interred appear to have died violent deaths. One individual was found to have a flint arrowhead stuck in a vertebra. In another grave, the skeletons of two women aged 25–35, dubbed the “ladies of Téviec”, were found with signs of violence on both. One had sustained five blows to the head, two of which would have been fatal, and had received at least one arrow shot between the eyes. The other had also traces of injuries. However, this diagnosis is disputed by some archaeologists, who have suggested that the weight of earth above the grave may have been responsible for damaging the skeletons.” ref
“The bodies had been buried with great care in a pit that was partly dug into the ground and covered over with debris from the midden. They had been protected by a roof made of antlers and provided with a number of grave goods including pieces of flint and boar bones, and jewelry made of seashells drilled and assembled into necklaces, bracelets, and ringlets for the legs. The grave assemblage was excavated from the site in one piece and is now on display at the Muséum de Toulouse, where its restoration in 2010 earned a national award.” ref
- Medicine Wheel
- Serpent Mound
- Mesa Verde
- Chaco Canyon
- Casas Grandes/Paquime
- Ciudad Perdida “lost city”; Teyuna
- Ingapirca “Inca”
- Chavín de Huántar “pre-Inca”
- Sacred City of Caral-Supe *Caral culture developed between 3000 – 1800 BCE*
- Machu Picchu
- Nazca Lines
- Sacsayhuamán
- Tiwanaku/Tiahuanaco
- Atacama Giant/Lines
- Pucará de Tilcara “pre-Inca”
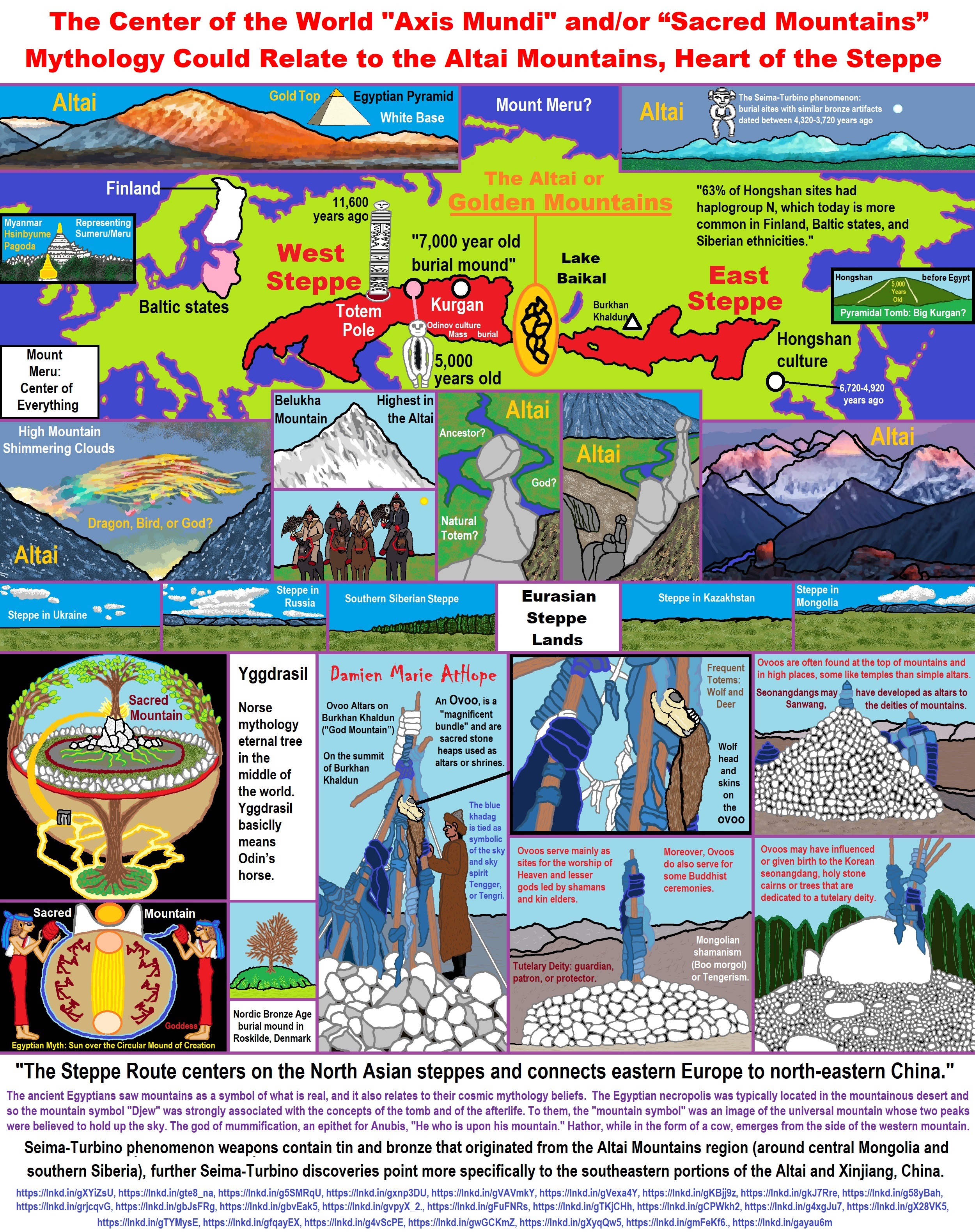
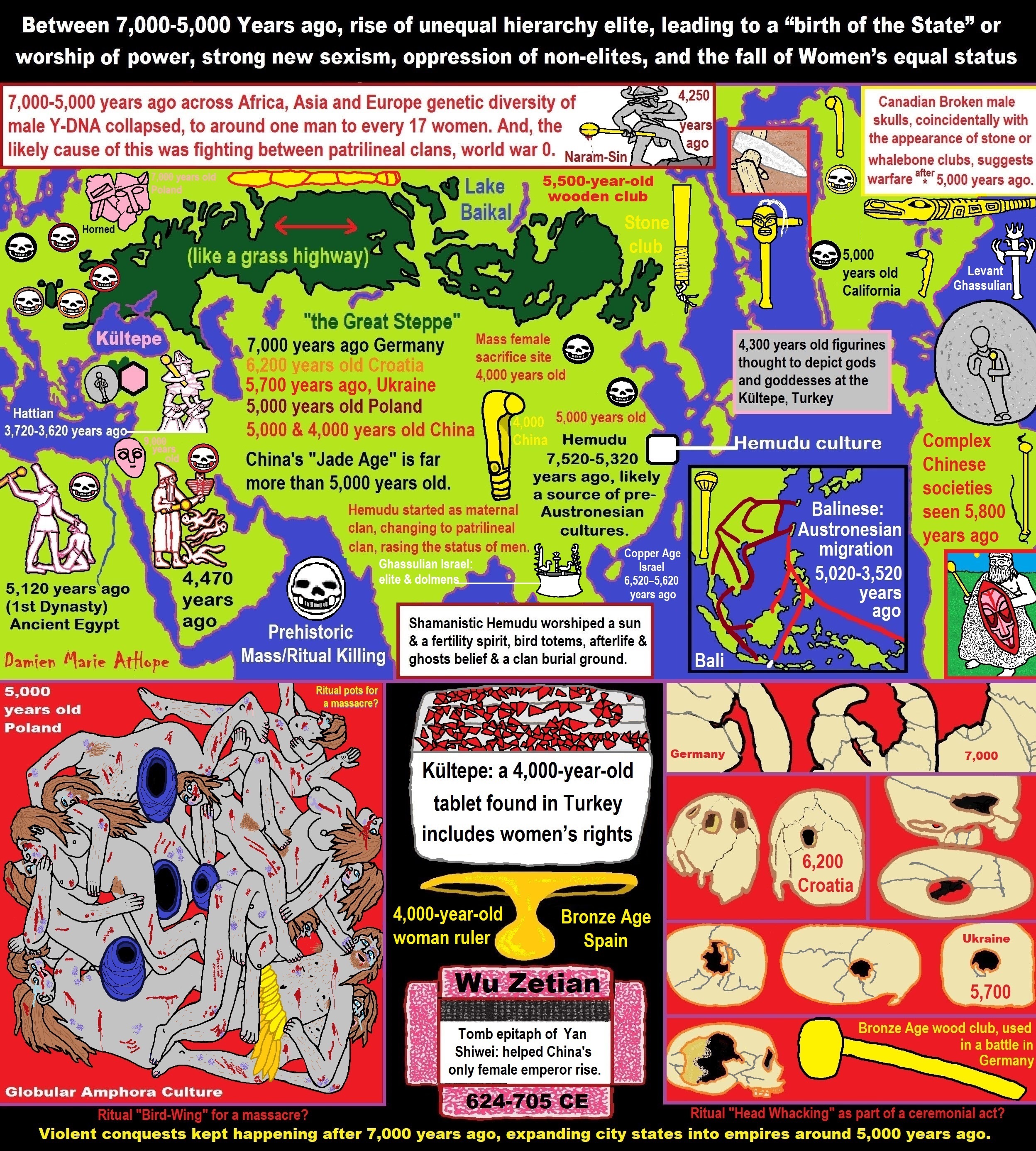
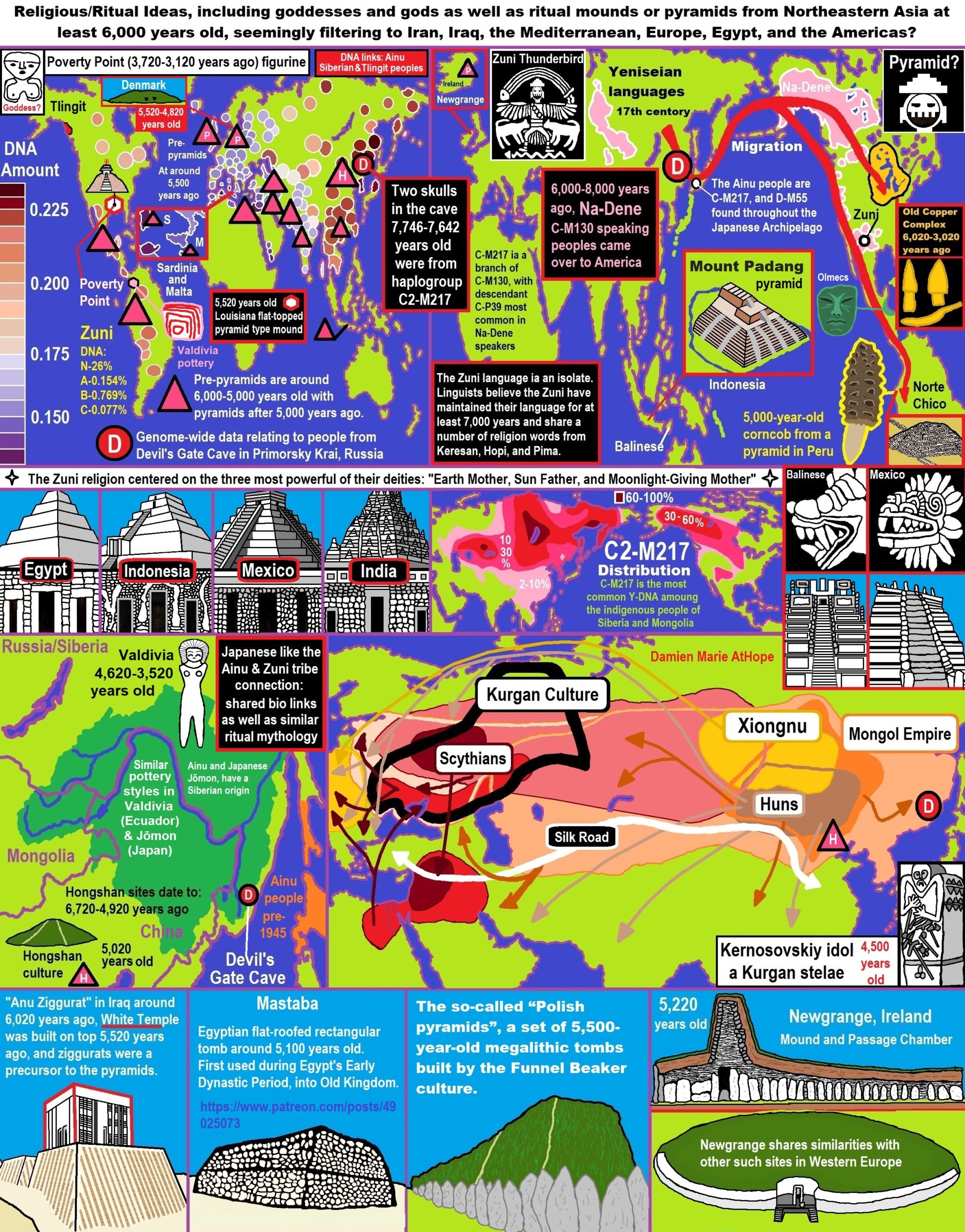
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
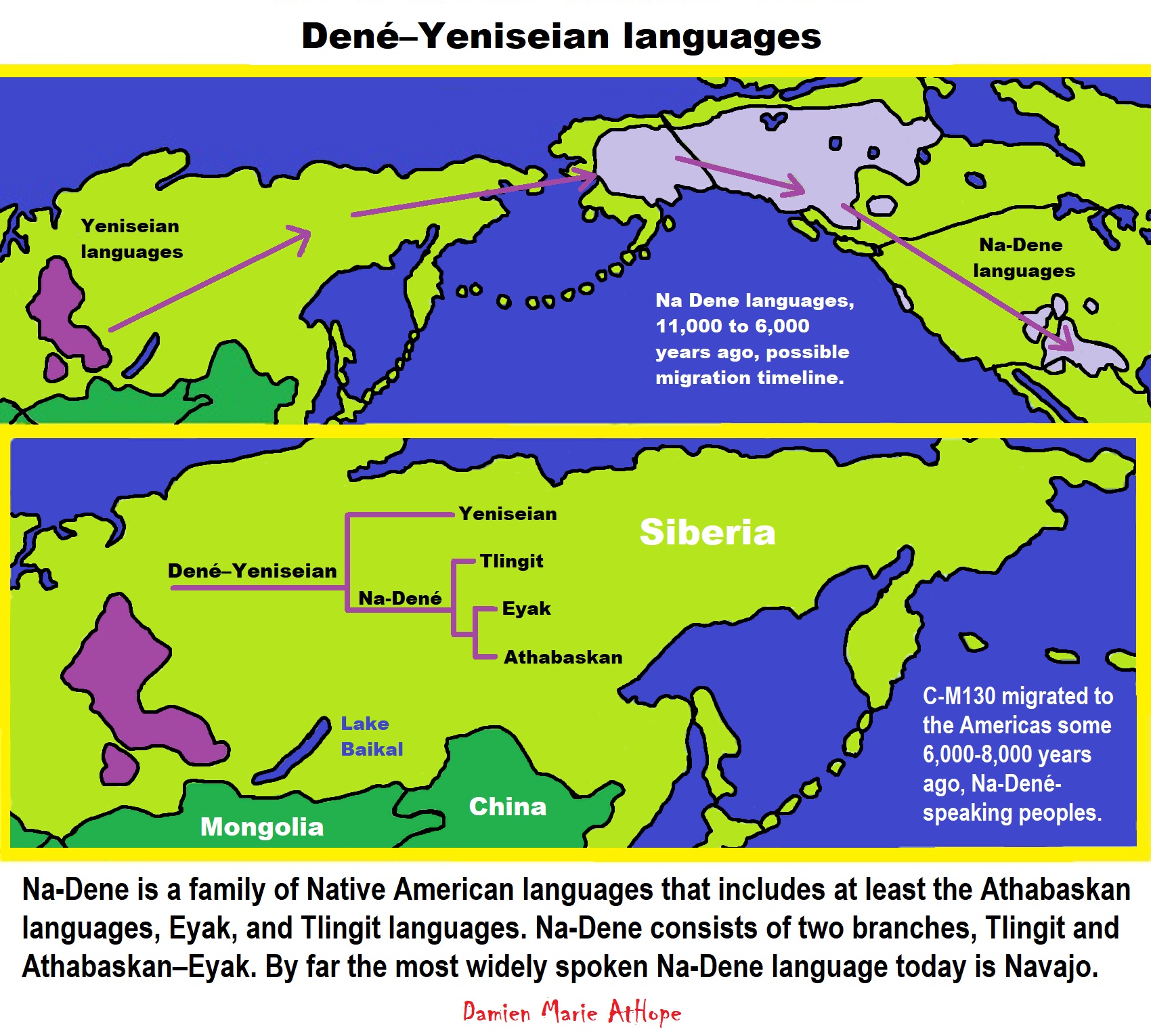
Dené–Yeniseian languages? (I think similar to the Sami or Ainu peoples, Dené–Yeniseian peoples who migrated related to beliefs that were likely “paganistic” Shamanism, with heavy totemism themes)
“Dené–Yeniseian is a proposed language family consisting of the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia and the Na-Dené languages of northwestern North America. Reception among experts has been somewhat favorable; thus, Dené–Yeniseian has been called “the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative–historical linguistics,” besides the Eskimo–Aleut languages spoken in far eastern Siberia and North America.” ref
“Na-Dene (/ˌnɑːdɪˈneɪ/; also Nadene, Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit, Tlina–Dene) is a family of Native American languages that includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. Haida was formerly included, but is now considered doubtful. By far the most widely spoken Na-Dene language today is Navajo. In February 2008, a proposal connecting Na-Dene (excluding Haida) to the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia into a Dené–Yeniseian family was published and well-received by a number of linguists. It was proposed in a 2014 paper that the Na-Dene languages of North America and the Yeniseian languages of Siberia had a common origin in a language spoken in Beringia, between the two continents.” ref
“Proto-Algic is the proto-language from which the Algic languages (Wiyot language *of Humboldt Bay, California*, Yurok language *of Del Norte County and Humboldt County on the far north coast of California*, and Proto-Algonquian) *estimated to have been spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago, usually divided into three subgroups: Eastern Algonquian *of the Atlantic coast of North America from Canada to North Carolina*, which is a genetic subgroup, and Central Algonquian *Eastern Great Lakes*, and Plains Algonquian are descended. Proto-Algic is estimated to have been spoken about 7,000 years ago somewhere in the American Northwest, possibly around the Columbia Plateau of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. Sergei Nikolaev has argued in two papers for a systematic relationship between the Nivkh language of Sakhalin *the largest island of Russia north of the Japanese archipelago*, and the Amur river basin *of the Russian Far East and Northeastern China*, and the Algic languages, and a secondary relationship between these two together and the Wakashan languages.*of British Columbia around and on Vancouver Island, and in the northwestern corner of the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state*.” ref, ref, ref
Genetics Reveal Movements of Ancient Siberians
“DNA reveals the previously unknown degree of mixture between Japan, North America, and the Eurasian mainland. Ancient DNA preserved in the icy climate of Siberia has revealed new insights about how ancient humans migrated five to seven thousand years ago.” ref
“In a study published recently in Current Biology, the researchers examined the DNA from 10 different ancient humans, which is quite a lot considering most of them date from 5,500 to 7,500 years old. These remains came from three locations in Siberia — the Altai Mountains, the Kamchatka Peninsula, and the Russian Far East.” ref
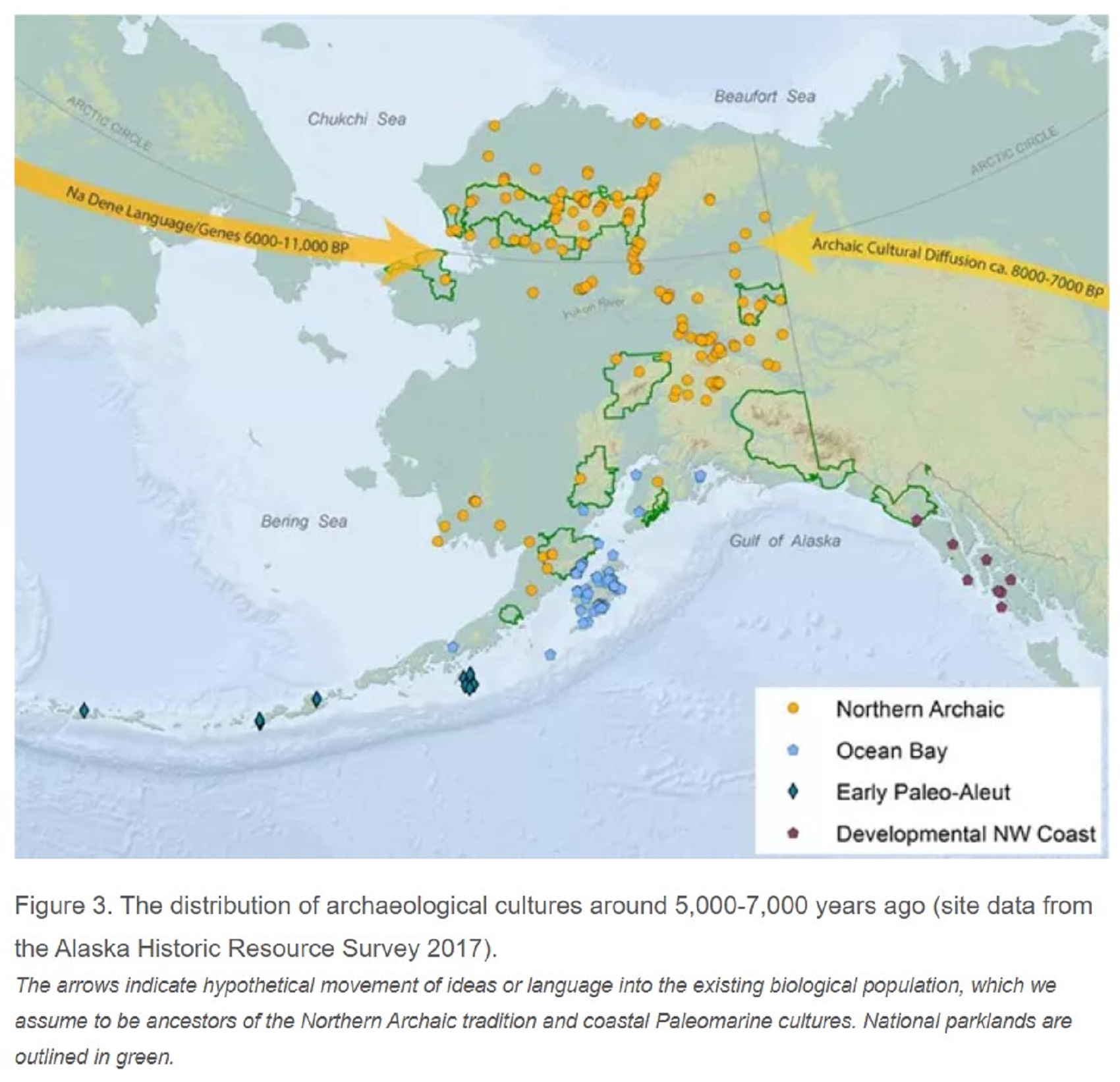
Human Migration from Asia into Alaska (North America) (11,000 to 6,000 years ago)
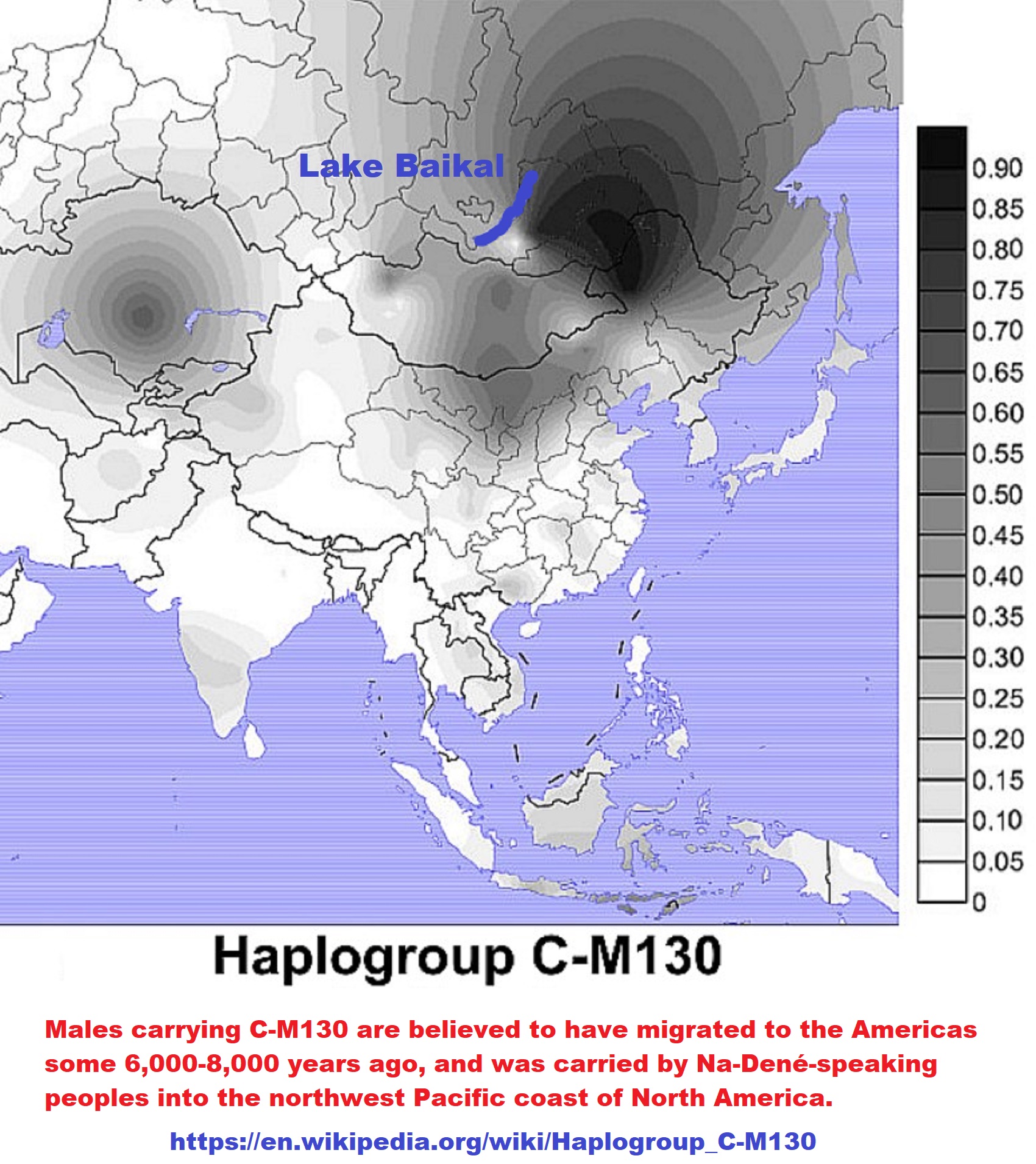
“likely relates to the Na-Dene languages described as C-M217/C2/C3/C-M130 DNA lineage”
Archaic period: 8000 BC– 1000 BCE
This C-M217/C2/C3/C-M130 DNA lineage is also in the Mound Builders (some of which are pyramid-like) such as the Adena (800 BCE–100 CE), Hopewell (200 BCE–500 CE), and the Maya civilization with pyramids.
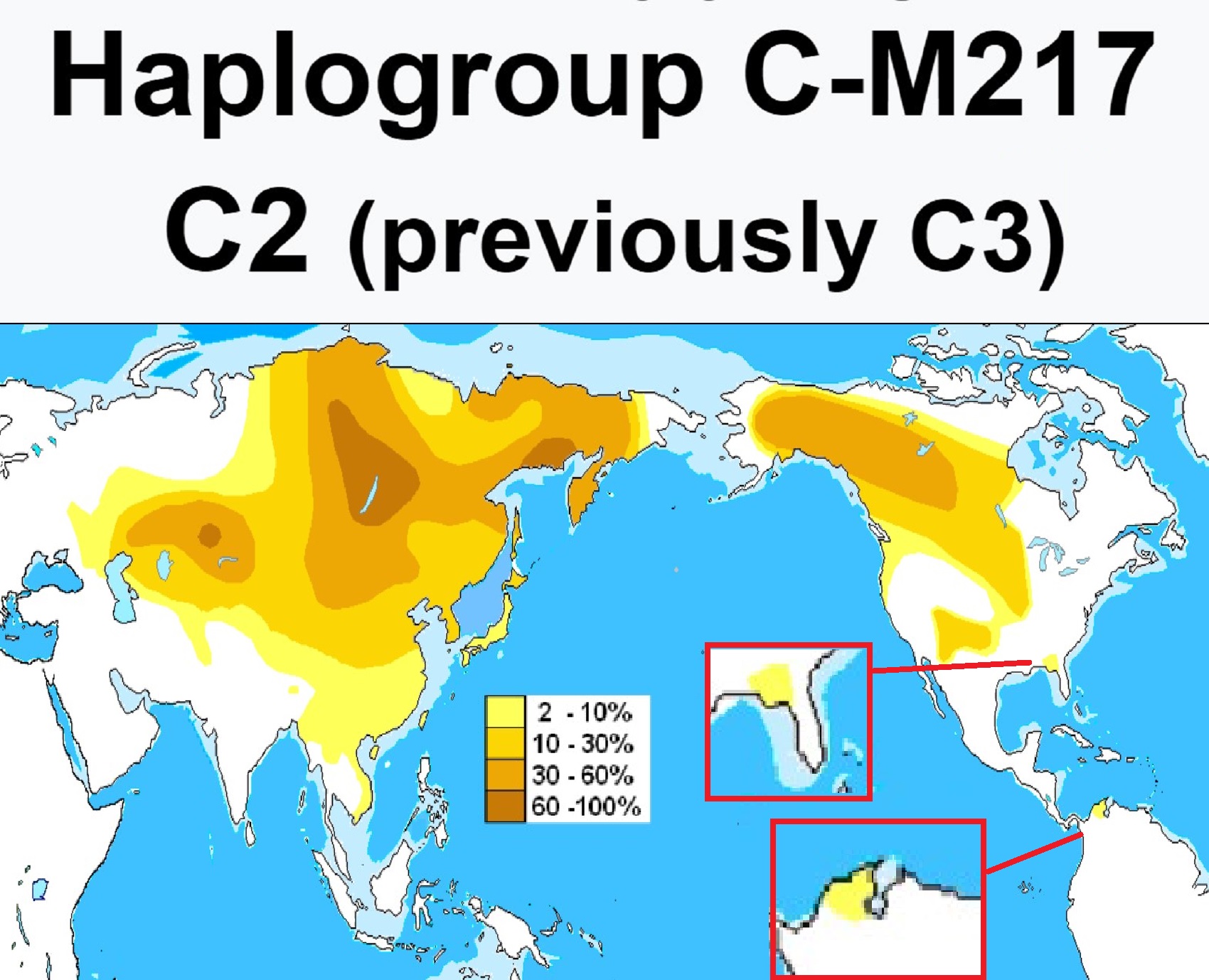
“Y DNA projects for C-M217 here, C-P39 here, and the main C project here. Please note that on the latest version of the ISOGG tree, M217, P44, and Z1453 are now listed as C2, not C3. In the Messavilla study (1962), fourteen individuals from the Kichwa and Waorani populations of South America were discovered to carry haplogroup C3* (M217). Most of the individuals within these populations carry variants of expected haplogroup Q, with the balance of 26% of the Kichwa samples and 7.5% of the Waorani samples carrying C3* (M217). MRCA estimates between the groups are estimated to be between 5.0-6.2 years ago, or years before the present.” ref
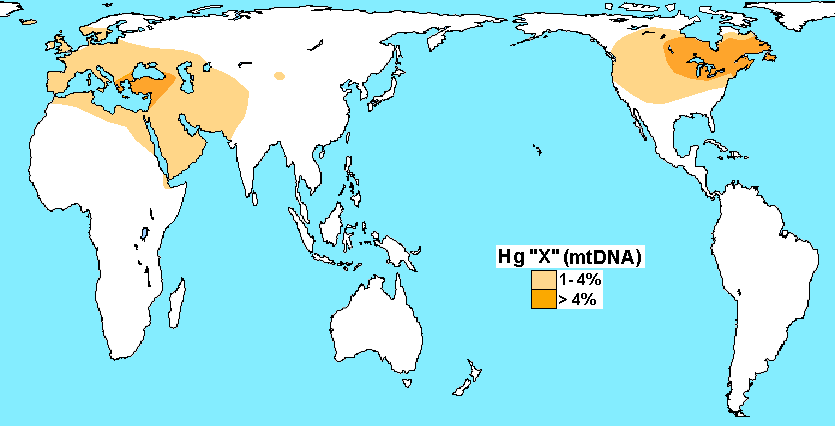
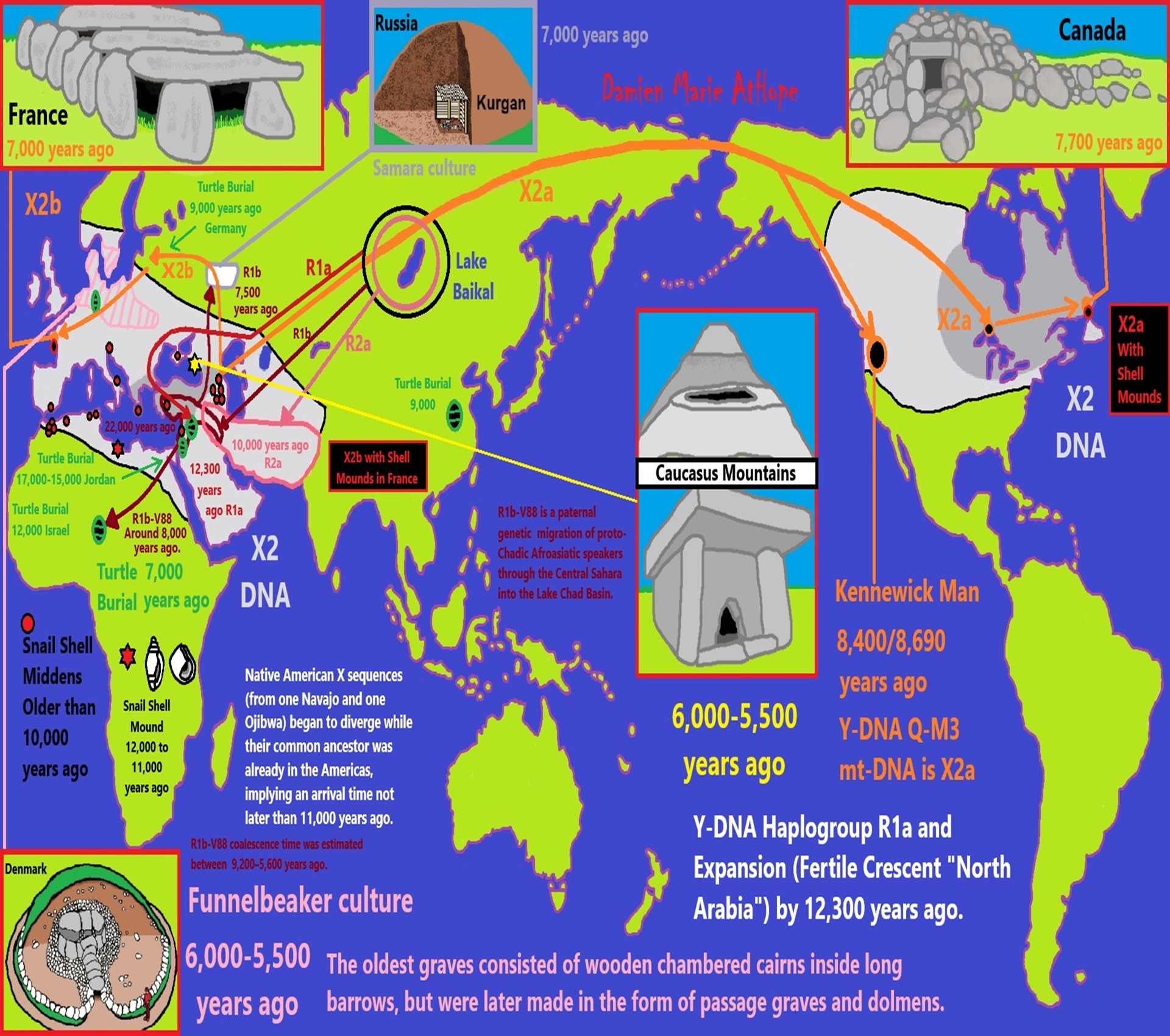
“Haplogroup X is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is found in America, Europe, Western Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa. The genetic sequences of haplogroup X diverged originally from haplogroup N. They subsequently further diverged thousands of years ago, forming two sub-groups, X1 and X2. Sub-group X2 appears to have undergone extensive population expansion and dispersal around or soon after the Last Glacial Maximum, about 21,000 years ago. It is more strongly present in the Near East, the Caucasus, and Southern Europe and somewhat less strongly present in the rest of Europe. Particular concentrations appear in Georgia(8%), Orkney (in Scotland) (7%), and amongst the Israeli Druze community (27%). Subclades X2a and X2g are found in North America. Haplogroup X is also one of the five haplogroups found in the indigenous peoples of the Americas of which the subclades X2a and X2g are found in North America. Discoveries of haplogroup X2a and subgroups have been more widely geographically dispersed.” ref
“The position of X2a in the phylogenetic tree suggests an early split from the other X2 clades, likely at the very beginning of their expansion and spread from the Near East. It is notable that X2 includes the two complete Native American X sequences that constitute the distinctive X2a clade, a clade that lacks close relatives in the entire Old World, including Siberia.” ref
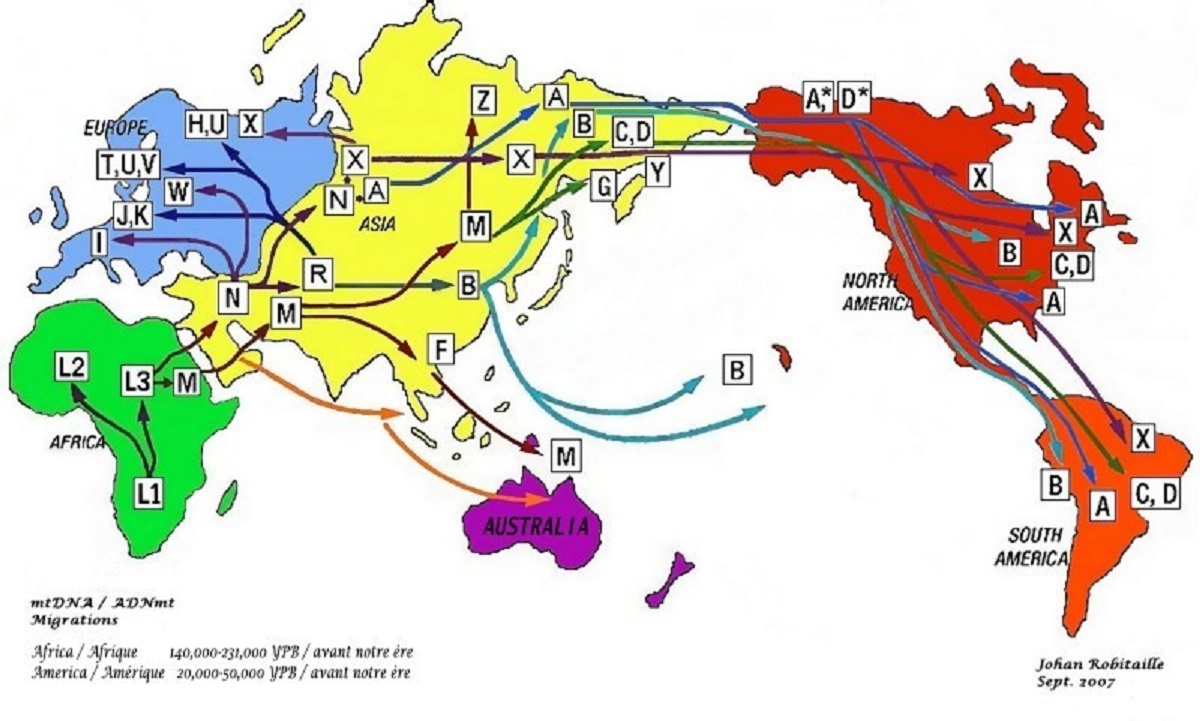
“Without conflicting evidence the most convincing explanation of Subclades X2a migration is the “Beringian model”, and X2a has not been found anywhere in Eurasia, and phylogeography gives us no compelling reason to think it is more likely to come from Europe than from Siberia. Furthermore, analysis of the complete genome of Kennewick Man, who belongs to the most basal lineage of X2a yet identified, gives no indication of recent European ancestry and moves the location of the deepest branch of X2a to the West Coast, consistent with X2a belonging to the same ancestral population as the other founder mitochondrial haplogroups. Nor have any high-resolution studies of genome-wide data from Native American populations yielded any evidence of Pleistocene European ancestry or trans-Atlantic gene flow.” ref
“X2a (and the related, rare haplogroup X2g) is a uniquely North American haplogroup, found at the highest frequencies in Great Lakes populations and at lower frequencies in the Plains and Pacific Northwest. It appears to be completely absent in populations from Central and South America. “Distinctive Paleo-Indian migration routes from Beringia marked by two rare mtDNA haplogroups. Its presence in pre-European contact skeletal remains confirms that it was not the result of post-1492 admixture.” ref
“However, unlike the other American mitochondrial haplogroups (A–D), which have clear parental haplotypes persisting in contemporary Siberian populations, there is no clear record of the evolutionary history of X2a in any population. X2a’s “grand-parental” haplogroup, X2, is found throughout, at low levels today throughout much of the world, including in the Near East (where X is more common and therefore thought to have initially evolved), South Caucasus, Europe, Siberia, Central Asia, and North Africa. It is important to note that while the Altai people in southern Siberia exhibit X2, their lineages are not ancestral to those of North Americans, and the presence of X2 there today appears to be the result of recent gene flow from the west.” ref
“Thus, the intermediate lineages linking X2 and X2a appear to have been lost in contemporary populations, or are so rare that they have not yet been well studied. We might expect to find them in ancient populations, but our temporal and spatial coverage of ancient populations is still quite sparse. X2a in North America has been cited as evidence for two different trans-Atlantic migrations before European contact. X2a is not found in the Middle East, and none of the X2 lineages present in the Middle East are immediately ancestral to X2a, the date of coalescence for X2a (14,200–17,000 years ago). The highest percentages of the X2 clade, higher even than Native American populations, is found in the Orkney Islands off the coast of Scotland. However, the X2 haplotypes found in the Orkney Islands was not the same nor ancestral to X2a, so this particular observation is irrelevant to the genetic prehistory of the Americas. And at this time, there is simply no evidence that X2a evolved in the Near East, Europe, or anywhere in West Eurasia.” ref
- X2a: found among Native North Americans
- X2a1
- X2a1a: found among the Sioux and Tanoan speakers
- X2a1a1
- X2a1b: found among the Ojibwe people
- X2a1b1
- X2a1b1a
- X2a1b1
- X2a1c: found among the Ojibwe people
- X2a1a: found among the Sioux and Tanoan speakers
- X2a2: found in Nova Scotia and Newfoundland
- X2a1
- X2g: found among the Ojibwe people ref
“The Native American–specific clade X2a appears to be defined by five mutations, three in the coding region (8913, 12397, and 14502) and two in the control region (200 and 16213) (fig). The transition at np 200 was seen in virtually all previously analyzed Native American haplogroup X mtDNAs, whereas the transition at np 16213 was absent in some of the Ojibwa. We surveyed our Old World haplogroup X mtDNAs for the five diagnostic X2a mutations (table) and found a match only for the transition at np 12397 in a single X2* sequence from Iran.” ref
“In a parsimony tree, this Iranian mtDNA would share a common ancestor with the Native American clade (fig). Yet, the nonsynonymous substitution at np 12397 converting threonine to alanine cannot be regarded a conservative marker, as it has also been observed in two different phylogenetic contexts—in haplogroups J1 and L3e—among 794 complete mtDNA sequences. Therefore, the scenario that the threonine to alanine change in the haplogroup X background is indeed due to recurrence appears most plausible.” ref
These findings leave unanswered the question of the geographic source of Native American X2a in the Old World, although our analysis provides new clues about the time of the arrival of haplogroup X in the Americas. Indeed, if we assume that the two complete Native American X sequences (from one Navajo and one Ojibwa) began to diverge while their common ancestor was already in the Americas, we obtain a coalescence time of 18,000 ± 6,800 YBP, implying an arrival time not later than 11,000 YBP. ” ref
Brittany; Breton is a cultural region in the west of France
Picture Link: ref
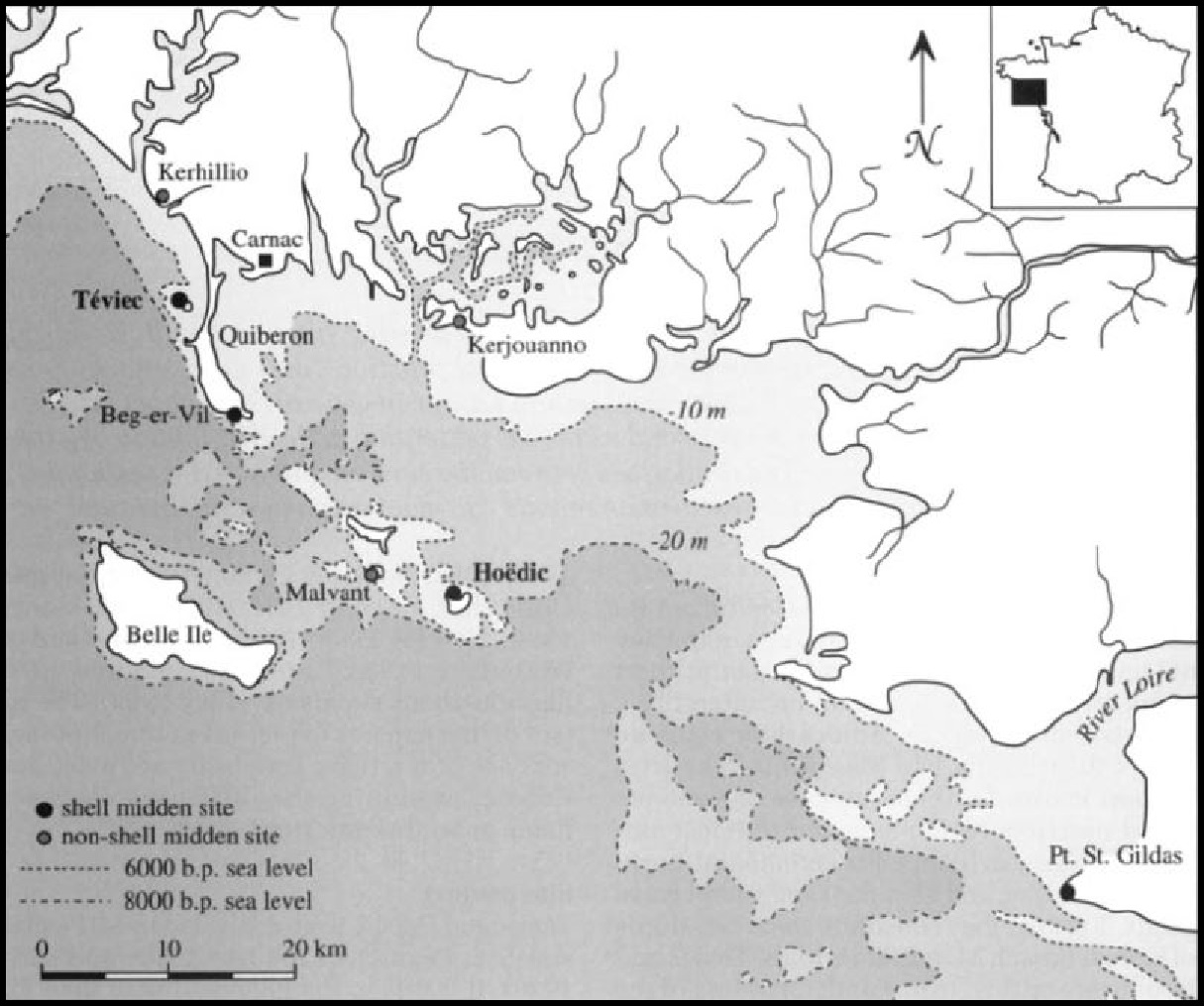
“The late Mesolithic sites of Tdviec and Hoedic, located on what are now small islands off the Breton coast, provide evidence for elaborate burial practices, and may be precursors of the megalithic tradition of Brittany and western Europe in general. The shell middens TQviec and Hoedic are located on what are now small islands in the Bay of Quiberon in Brittany, off the Atlantic coast of northwest France. An abundant microlithic industry and a single radiocarbon estimate places them in the late Mesolithic. Teviec and Hoedic are roughly contemporaneous, based on similarities in tool typology and burial practices. A single radio-carbon determination on charcoal from a hearth in the lower part of the midden at Hoedic provides an estimate of 6575+350 years ago.” ref
“The sites are best known for their evidence of elaborate burial practices, with stone and red-deer antler structures, evidence for ceremonial burning and feasting, and abundant and varied grave goods. Together they constitute some two-thirds of known French Mesolithic burials. Teviec and Hoedic are critical to our understanding of the late Mesolithic and the transition to the Neolithic. The sites are part of the phenomenon of increasing ‘complexity’ in the late Mesolithic of northwest Europe: they also fill a geographical gap between the cemeteries of south-central Portugal and those of southern Scandinavia.” ref
The burials themselves mainly remain undated. The large standard error of this date limits its usefulness; at two standard deviations it overlaps dates for Breton early Neolithic passage-graves and long mounds at around 5,700 years ago. No stratigraphic breaks were noted within the Mesolithic levels at either site, and the materials recovered were described as homogeneous throughout the 0.5 to 1.0 m of deposits. Neolithic deposits were encountered at Hoedic, but the 0.3 to 0.5 m of Mesolithic deposits were apparently entirely sealed by a layer of sterile gravel. Unfortunately, the rise in sea-levels from Atlantic times means that the sites must be looked at in isolation the now-submerged coastal plain on which they were high points was undoubtedly the focus of Mesolithic settlement in the area. Additional Mesolithic sites in Brittany include both shell-midden sites and many more non-shell-midden sites. With a 10-m drop in sea level around 6,000 years ago
“Many tools made of bone and antler were found along with numerous flint microliths dated to between 6,740-5,680 years ago. The hunter-gatherers of Téviec often buried their own dead in the middens. Extensive middens were found near places of habitation on the island, containing the remains of shellfish, crustaceans, squid, fish, birds, cetaceans and terrestrial mammals including wild boar, red deer, roe deer, dogs and so on. During the Mesolithic period, the sea level was much lower – it was possible to walk from France to England– and Téviec was situated in a lagoon.” ref
“Ten multiple graves were discovered at Téviec containing a total of 23 individuals, including adults and children. Some of the remains were scattered between different locations. Several of those interred appear to have died violent deaths. One individual was found to have a flint arrowhead stuck in a vertebra. In another grave, the skeletons of two women aged 25–35, dubbed the “ladies of Téviec”, were found with signs of violence on both. One had sustained five blows to the head, two of which would have been fatal, and had received at least one arrow shot between the eyes. The other had also traces of injuries. However, this diagnosis is disputed by some archaeologists, who have suggested that the weight of earth above the grave may have been responsible for damaging the skeletons. The bodies had been buried with great care in a pit that was partly dug into the ground and covered over with debris from the midden. They had been protected by a roof made of antlers and provided with a number of grave goods including pieces of flint and boar bones, and jewellery made of sea shells drilled and assembled into necklaces, bracelets and ringlets for the legs.” ref
Picture Links: ref
“The sample set included a Maritime Archaic subadult more than 7,700 years old found in the L’Anse Amour burial mound, the oldest known burial mound in North America and one of the first manifestations of the Maritime Archaic tradition. Indigenous people have been on the far northeastern edge of Canada for most of the last 10,000 years, moving in shortly after the ice retreated from the Last Glacial Maximum. Archaeological evidence suggests that people with distinct cultural traditions inhabited the region at least three different times with a possible hiatus for a period between 2,000 and 3,000 years ago. And based purely on mitochondrial DNA, that the Maritime Archaic were not the direct ancestors of the Beothuk and that the two groups did not share a very recent common ancestor, implying that the island of Newfoundland was populated multiple times by distinct groups. These data clearly suggest that the Maritime Archaic people are not the direct maternal ancestors of the Beothuk and thus that the population history of the island involves multiple independent arrivals by indigenous peoples followed by habitation for many generations.” ref
“Situated at the furthest northeastern edge of Canada, the island of Newfoundland (approximately 110,000 km2 ) and Labrador (approximately 295,000 km2 ) today constitute a province characterized by abundant natural resources but low population density. Both landmasses were covered by the Laurentide ice sheet during the Last Glacial Maximum (18,000 years ago); after the glacier retreated, ice patches remained on the island until ca. 9,000 years ago. Nevertheless, indigenous peoples, whose ancestors had trekked some 5,000 km/3107 miles from the west coast, arrived approximately 10,000 years ago in Labrador and around 6,000 years ago in Newfoundland. Differential features in material culture indicate at least three settlement episodes by distinct cultural groups, including the Maritime Archaic, Palaeoeskimo, and Beothuk. Newfoundland has remained home to indigenous peoples until present day with only one apparent hiatus (3,400–2,800 years ago). This record suggests abandonment, severe constriction, or local extinction followed by subsequent immigrations from single or multiple source populations, but the specific dynamics and the cultural and biological relationships, if any, among these successive peoples remain enigmatic. By examining the mitochondrial genome diversity and isotopic ratios of 74 ancient remains in conjunction with the archaeological record, we have provided definitive evidence for the genetic discontinuity between the maternal lineages of these populations. This northeastern margin of North America appears to have been populated multiple times by distinct groups that did not share a recent common ancestry, but rather one much deeper in time at the entry point into the continent.” ref
“Research into the mitochondrial diversity of indigenous peoples of the Americas has identified four major haplogroups found throughout North, Central, and South America: A2, B2, C1 (specifically C1b, C1c, and C1d, which are distinct from the C1e and C1f haplogroups found in Northern Europe), and D1. There are additional minor founding lineages with more restricted distributions, such as haplogroup X2, found exclusively in North America; haplogroups D2 and D3, associated with Arctic populations; and other low-frequency haplogroups, such as C4c and D4h3a. Importantly, the sum of the genetic studies to date make it clear that these primary founder lineages migrated southward from Beringia, (defined as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada) sometime before 14,000 years ago, most likely by way of a coastal or interior route made available by receding ice sheets.” ref

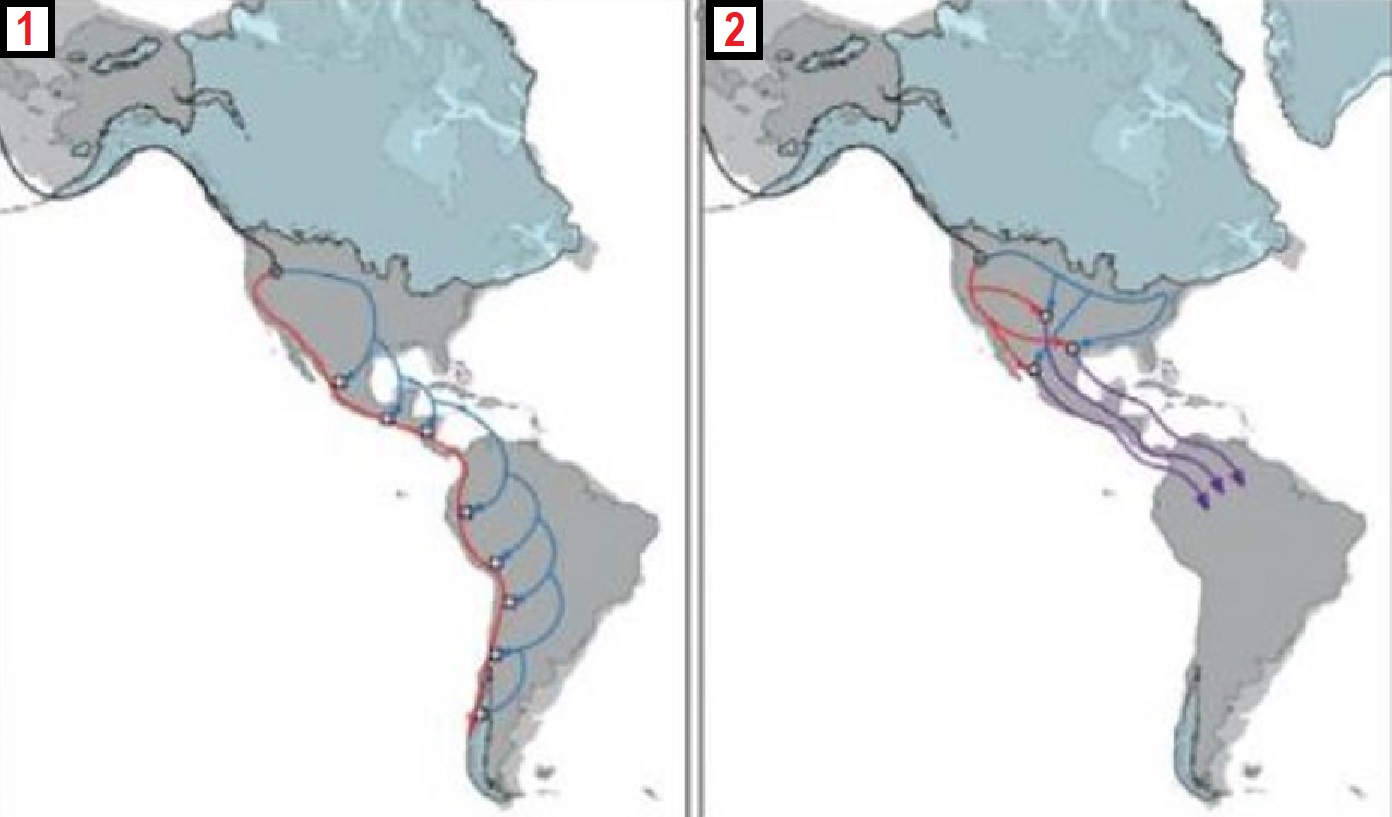
“Two ancient populations that diverged later ‘reconverged’ in the Americas. A new genetic study of ancient individuals in the Americas and their contemporary descendants finds that two populations that diverged from one another 18,000 to 15,000 years ago remained apart for millennia before mixing again. This historic; reconvergence; occurred before or during their expansion to the southern continent.” ref
“A 12,700-year-old Anzick Child, the remains of Paleo-Indian male infant found in south-central Montana, United States. The child was found with more than 115 tools made of stone and antlers and dusted with red ocher, suggesting an honorary burial. Similar to an ancient burial pit in Alaska with a girl was just six weeks old when she died. Her body was buried on a bed of antler points and red ocher, and she lay undisturbed for 11,500 years. The child’s genome from her remains. The second-oldest human genome ever found in North America, it sheds new light on how people — among them, the ancestors of living Native Americans — first arrived in the Western Hemisphere and strongly supports the idea that the Americas were settled by migrants from Siberia. Atop a hearth dating back 11,500 years were the cremated bones of a 3-year-old child. Digging into the hearth itself, archaeologists discovered the remains of two infants.” ref, ref
“They found that Anzick-1’s mtDNA belongs to the haplogroup D4h3a, a “founder” haplogroup that might represent people taking an early coastal migration route into the Americas. The D haplogroup is also found in modern Native American populations, which provides a link between Anzick-1 and modern Native Americans. Although it is rare in most of today’s Native Americans in the US and Canada, D4h3a genes are more common in native people of South America. Moreover, Anzick-1 was sequenced, and researchers determined that his y-chromosome haplogroup is Q-L54*(xM3), one of the major founding lineages of the Americas.” ref
“However, the manner in which the first indigenous peoples spread throughout the American continents and their shifting occupations of various regions after their arrival remains, not surprisingly, much less clear. Each of the mtDNA genomes recovered from the samples included in this study belongs to one of the well-established founder lineages. The haplogroup diversity in the Maritime Archaic and Beothuk is high. In this respect, they contrast sharply with Dorset Palaeoeskimo, who occupied a wider geographic range but seem to have carried only a single haplogroup. Notably, although no comparative data of similar scale are available from ancient indigenous populations of the Americas, populations for which multiple samples have been sequenced also appear to have limited genetic diversity. Most strikingly, the Maritime Archaic and Beothuk populations do not share a single haplotype, and they have no direct descent relationship, with the possible exception of the X2a1-X2a1b lineage. In this context, the recovery of several lineages of X2a from these samples is noteworthy. The mtDNA of Kennewick Man from Washington State, dated to ca. 8,800 years ago, has recently been typed as a basal, ancestral variant of X2a. Though this basal variant is not present in any of our Newfoundland samples, derived variants of it are found in both the Maritime Archaic and Beothuk. These data support an ancient origin of X2a in an early northern indigenous population whose descendants had expanded from the northern Pacific to the northern Atlantic coasts of North America as early as ca. 4,000 years ago.” ref
“8,500-year-old Kennewick Man, found in Washington state showed that he belonged to haplogroup X2a but had no indication of recent European ancestry throughout the rest of his genome.” ref
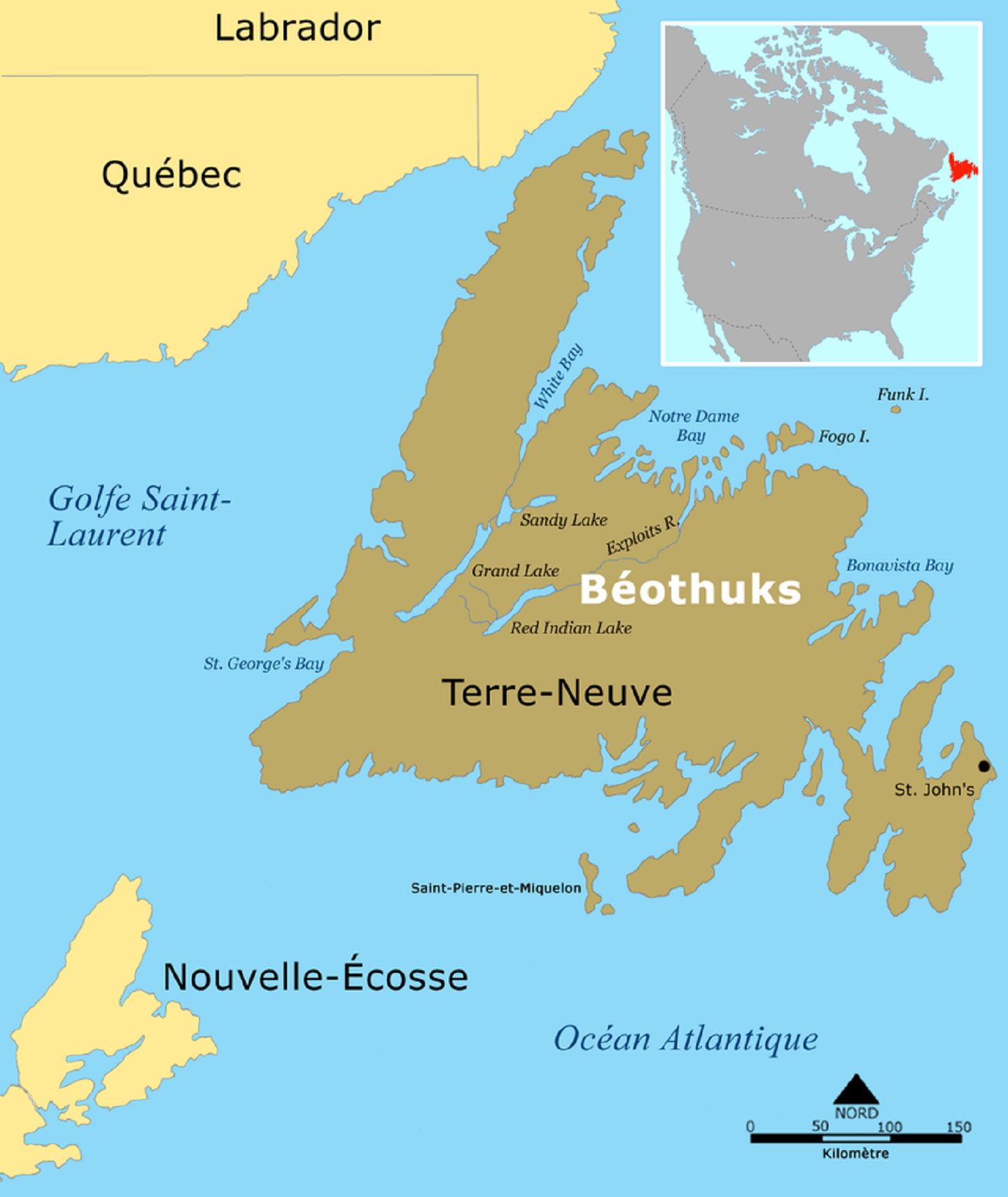
Picture Links: ref
“Beginning around 3,500 years ago, the Beothuk culture formed. This appeared to be the most recent cultural manifestation of peoples who first migrated from Labrador to present-day Newfoundland around AD 1. The ancestors of this group had three earlier cultural phases, each lasting approximately 500 years. DNA from the teeth of Demasduit and her husband Nonosabasut, two Beothuk individuals who had died in the 1820s. The results assigned them to Haplogroup X (mtDNA) and Haplogroup C (mtDNA), respectively, which are also found in current Mi’kmaq populations in Newfoundland. It also demonstrated they were solely of First Nation indigenous maternal ancestry, unlike some earlier studies that suggested European admixture. However, the analysis also showed that although the two Beothuk and living Mi’kmaq occur in the same haplogroups, SNP differences between Beothuk and Mi’kmaq individuals indicated that they were dissimilar within those groups, and that a “close relationship” was not supported.” ref
Maritime Archaic Tradition
“The Maritime Archaic is a North American cultural complex of the Late Archaic along the coast of Newfoundland, the Canadian Maritimes and northern New England. The culture consisted of sea-mammal hunters in the subarctic who used wooden boats. Maritime Archaic sites have been found as far south as Maine and as far north as Labrador. Their settlements included longhouses, and boat-topped temporary or seasonal houses. They engaged in long-distance trade, as shown by white chert from northern Labrador being found as far south as Maine. The Maritime Archaic is one cultural complex among several of the Archaic stage for North American peoples. Archaeogenetic research established, that the Maritime Archaic people had nothing in common with the Inuit, nor with Beothuk Indians, who later inhabited the same area after the climatic conditions changed.” ref
“Another significant Maritime Archaic find are the “Red Ochre Culture” burials throughout the Northeast United States. They may represent the last phases of the Maritime Archaic, as they contain significant finds of white chert artifacts common to other Maritime Archaic sites. This issue is currently debated among scholars. If the hypothesis of the Red Ochre as the last state of the Maritime Archaic period is accepted, then the latter is best known from a mortuary site in Newfoundland at Port au Choix. This site revealed over 100 graves embellished with red ochre. The graves contained many elaborate artifacts, including barbed bone points; daggers of ivory, antler, or bone; toggling harpoons; shell-beaded clothing; and a burial suit made from more than 200 skins of the now-extinct great auk. These finds indicated a stratified society with trade and some level of social complexity.” ref
Archaeologists recognize two variants of the Maritime Archaic tradition called the Northern and Southern branches.
*The Northern Branch
“Northern branch people were the earlier of the two variants to arrive in the province. They are descended from the earliest people along the Labrador Straits and their maritime adaptation is obvious by about 7,500 years ago. Excavation of a burial mound at L’Anse Amour in southern Labrador revealed a walrus tusk, fish bones, a true toggling harpoon, an antler toggle or handle and other objects that indicate a reliance on marine resources by this time. Both the mound and the harpoon are among the oldest in the world. Once established in southern Labrador, Maritime Archaic people continued to spread northward until, by about 5,000 years ago they had reached Saglek and Ramah Bays in far northern Labrador. In the latter area they discovered the source of a distinctive stone called “Ramah chert”, from which they fashioned their chipped stone tools and weapons for the next 2,500 years. A series of archaeological “complexes” dating between 7,500 and 3,500 years ago indicates a long in situ evolution along most of the coast of Labrador.” ref
“Throughout this time, skillfully flaked stone spear points with narrow blades and long, tapering stems for hafting were made from Ramah chert. Other chipped stone tools include knives and scrapers, some of the former of truly impressive proportions. Stone was ground and polished to make axes, adzes and gouges for working wood. Polished slate lance points were used to dispatch wounded sea mammals. Ulus, or half-moon shaped knives, and knives of more familiar forms were used to prepare skins and dress game. We can only imagine what objects were made from bone, antler, ivory wood, skin, bark, and other organic materials. They must have included frames for dwellings, harpoon and spear shafts, tailored clothing, bark and wood containers and many others. Some authorities believe that the Maritime Archaic people may have made large dugout boats in areas where wood was available or could be traded for. Ornaments include cut mica, soapstone pendants, or plummets, and large blades made from Ramah chert that must have served ceremonial, rather than utilitarian, functions.” ref
“Although very few traces of food bone remain in the acid soils of Labrador, those that have been recovered and the location of Maritime Archaic campsites and villages all indicate a reliance on marine resources. Fish, seals, seabirds, walrus, and perhaps even small whales were hunted regularly. Land mammals, particularly caribou, seem also to have been important for food, antler, bone and skins. At least one large seasonal village, at Nulliak in northern Labrador, seems to have been established for communal caribou hunting. “Drive lanes” consisting of rows of piled rocks may have channeled migrating caribou virtually into the hunters’ campsite. In suitable areas houses were made by excavating depressions into boulder beaches. At some sites, where the retreating sea level left a series of raised beaches, house forms can be seen to have evolved from single family dwellings to communal dwellings consisting of a number of “rooms” arranged in a linear fashion along the beach. These dwellings reached their peak at the Nulliak site, where “longhouses” as long as 100m have been discovered.” ref
“About 4,000 years ago a new people – the Palaeo-Eskimos – arrived in northern Labrador. As these strangers became more familiar with Labrador and continued to expand southward, the Maritime Archaic people seem to disappear at the same time. Although the two events could be coincidental, many archaeologists believe that the Palaeo-Eskimos were more successful in competing for resources and the best campsites. Whatever the cause, the Northern Branch Maritime Archaic people disappear from the archaeological record not long after 3,500 years ago. If any groups survived after that time, their whereabouts has escaped the intensive archaeological research on the Labrador coast.” ref
*The Southern Branch
“The origins of the Southern Branch Maritime Archaic people are obscure. Shortly before 6,000 years ago a new stone tool complex appears in southern Labrador. The people who made these tools preferred locally-available cherts and rhyolites to the quartz, quartzite and Ramah chert of the Northern branch people. By about 5,000 or 4,500 years ago these people had become established on the coast of southern Labrador and parts of the central coast. They made spear points with broad blades and side-notches for hafting. Flaked knives, scrapers and expedient tools were made from the same local materials. A few sites have produced ground stone axes, adzes and gouges, as well as polished slate spears and lances. Their house types are not known; only traces of stone fireplaces, sometimes arranged in a row along ancient beach terraces, have been found.” ref
“The Southern branch people were the first humans to colonize the Island of Newfoundland. By at least 5,000 years ago they had established themselves on the Northern Peninsula and within a millennium their campsites are to be found virtually around the entire Newfoundland coastline. In general it is hard to escape the conclusion that the Maritime Archaic people were remarkably well adapted to life in Newfoundland – from their technology and economy to their intellectual culture.” ref
“The most instructive Maritime Archaic site yet excavated is that at Port au Choix where the regular arrival of migrating harp seals each spring provided a reliable and predictable food source. In 1968 a large site containing hundreds of artifacts was excavated. In contrast to most other locations, the soil at Port au Choix permits the preservation of organic material. Artifacts of bone, ivory and antler provide some indication of the elaborate and sophisticated technology of the Southern branch Maritime Archaic people. Toggling and barbed harpoons, bird darts and fish spears of bone and antler, and a series of polished bone and slate spear and lance points, all suggest a technology perfectly suited to the Newfoundland environment. Scrapers and “beamers” of caribou bone, bone awls and fine needles made from split bird bones were used to prepare and sew hides into clothing. Stone gouges, axes and adzes, as well as small chisels and knives made from beaver incisors, were used to fell trees and convert the wood into products that we can only imagine.” ref
“Many ornaments and magical or religious objects were also found at Port au Choix. The bills and feet of birds, teeth of bears, foxes, wolves and beaver, pins and pendants carved to resemble birds, a bear and even a human form were also recovered. Shell beads, pendants resembling swords and paddles, crystals of quartz, calcite and amethyst and any number of unusually-shaped stones may have served religious, as well as decorative, purposes. Many of these objects relate to the sea, for example a carved stone killer whale, a tooth from the same animal, and depictions of gulls, ducks, loons and the now-extinct great auk. It is difficult to escape the conclusion that certain individuals must have had some special symbolic relationships with these birds and mammals.” ref
“In central and southern Labrador this successful adaptation seems to have persisted into the succeeding Intermediate Indian and Recent Indian periods. Some archaeologists believe that the Southern branch Maritime Archaic people may have been, in some way, the distant ancestors of today’s Innu. Despite the apparent success of the Southern branch people in Labrador, and the apparently well adjusted nature of their culture in Newfoundland, the residents of the Island of Newfoundland disappear from the archaeological record about 3,000 years ago. Archaeologists can cite no convincing influx of a new population at this time, as was the case with the Palaeo-Eskimos in northern Labrador. For the present the disappearance of the maritime Archaic people, and what seems to be a complete absence of Indian people from Newfoundland between 3,000 and 2,000 years ago remains one of the most puzzling mysteries in the Native history of the province.” ref


The Swordfish Hunters: The History and Ecology of an Ancient American Sea People – amazon.com
by Bruce Bourque (Author)
“Thousands of years ago, Maine’s Red Paint People, so called because of the red ochre in their burial sites, were among the first maritime cultures in the Americas. They could have subsisted on easily caught cod, but they chose to capture dangerous and elusive swordfish. This book explains beautifully the prehistory of these people, the evolution of archaeological thinking about them, and the myriad new scientific threads that shed new light on this old culture.” ref
“In the closing years of the nineteenth century, strange objects began to come out of the ground in Hancock County, Maine. They were quickly recognized as prehistoric artifacts of stone, but they were very unlike the spear tips and other small artifacts collectors gathered from coastal sites as they eroded into the sea. Many were large and finely crafted, some made of beautiful stone from far-off places. Strangest of all, they came from pits filled with a brilliant red powder called red ocher. These were ancient graves clustered into large cemeteries. Local naturalists brought these finds to the attention of a new breed of scientist–archaeologists who were busy developing their new science at the Peabody Museum of American Archaeology and Ethnography at Harvard University.” ref
“They began to visit and to excavate these sites and introduced them to the world in 1893 at Chicago’s World’s Columbian Exposition. Between then and 1920, other archaeologists became involved, searching for and discovering more than a dozen new cemeteries. Museum collections grew quickly, but so did confusion about what kind of culture could have produced these wonderful objects. Then interest in the so-called Red Paint cemeteries waned as American archaeologists began to broaden their horizons to other continents. The mystery of the Red Paint People was left hanging. A half century later, as Maine archaeology was undergoing a revival, a new generation of archaeologists, armed with the analytical tools of modern science, once again turned their attention to the Red Paint People and reached some surprising conclusions.” ref
“This book tells the story of the Red Paint People and the archaeologists who have tried to understand them for over a century. Interwoven with that story is one of scientific growth and evolution, as archaeologists have adopted new research models in collaboration with a broad range of natural scientists to flesh out the life story of a remarkable prehistoric culture: the swordfish hunters. Thousands of years ago, Maine’s Red Paint People were among the first maritime cultures in the Americas. They could have subsisted on easily caught cod, but they chose to capture dangerous and elusive swordfish.” ref
Shamanism (beginning around 30,000 years ago)
Shamanism (such as that seen in Siberia Gravettian culture: 30,000 years ago). Gravettian culture (34,000–24,000 years ago; Western Gravettian, mainly France, Spain, and Britain, as well as Eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians, which include the Pavlovian culture). And, the Pavlovian culture (31,000 – 25,000 years ago such as in Austria and Poland). 31,000 – 20,000 years ago Oldest Shaman was Female, Buried with the Oldest Portrait Carving.
Shamanism is approximately a 30,000-year-old belief system and believe in spirit-filled life and/or afterlife that can be attached to or be expressed in things or objects and these objects can be used by special persons or in special rituals that can connect to spirit-filled life and/or afterlife. If you believe like this, regardless of your faith, you are a hidden shamanist.
Around 29,000 to 25,000 years ago in Dolní Vestonice, Czech Republic, the oldest human face representation is a carved ivory female head that was found nearby a female burial and belong to the Pavlovian culture, a variant of the Gravettian culture. The left side of the figure’s face was a distorted image and is believed to be a portrait of an elder female, who was around 40 years old. She was ritualistically placed beneath a pair of mammoth scapulae, one leaning against the other. Surprisingly, the left side of the skull was disfigured in the same manner as the aforementioned carved ivory figure, indicating that the figure was an intentional depiction of this specific individual. The bones and the earth surrounding the body contained traces of red ocher, a flint spearhead had been placed near the skull, and one hand held the body of a fox. This evidence suggests that this was the burial site of a shaman. This is the oldest site not only of ceramic figurines and artistic portraiture but also of evidence of early female shamans. Before 5,500 years ago, women were much more prominent in religion.
Archaeologists usually describe two regional variants: the western Gravettian, known namely from cave sites in France, Spain, and Britain, and the eastern Gravettian in Central Europe and Russia. The eastern Gravettians include the Pavlovian culture, which were specialized mammoth hunters and whose remains are usually found not in caves but in open air sites. The origins of the Gravettian people are not clear, they seem to appear simultaneously all over Europe. Though they carried distinct genetic signatures, the Gravettians and Aurignacians before them were descended from the same ancient founder population. According to genetic data, 37,000 years ago, all Europeans can be traced back to a single ‘founding population’ that made it through the last ice age. Furthermore, the so-called founding fathers were part of the Aurignacian culture, which was displaced by another group of early humans members of the Gravettian culture. Between 37,000 years ago and 14,000 years ago, different groups of Europeans were descended from a single founder population. To a greater extent than their Aurignacian predecessors, they are known for their Venus figurines. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, & ref
If you are a religious believer, may I remind you that faith in the acquisition of knowledge is not a valid method worth believing in. Because, what proof is “faith”, of anything religion claims by faith, as many people have different faith even in the same religion?
But is Atlantis real?
No. Atlantis (an allegory: “fake story” interpreted to reveal a hidden meaning) can’t be found any more than one can locate the Jolly Green Giant that is said to watch over frozen vegetables. Lol

May Reason Set You Free
There are a lot of truly great things said by anarchists in history, and also some deeply vile things, too, from not supporting Women’s rights to Anti-Semitism. There are those who also reject those supporting women’s rights as well as fight anti-Semitism. This is why I push reason as my only master, not anarchist thinking, though anarchism, to me, should see all humans everywhere as equal in dignity and rights.
We—Cory and Damien—are following the greatness that can be found in anarchist thinking.
As an Anarchist Educator, Damien strives to teach the plain truth. Damien does not support violence as my method to change. Rather, I choose education that builds Enlightenment and Empowerment. I champion Dignity and Equality. We rise by helping each other. What is the price of a tear? What is the cost of a smile? How can we see clearly when others pay the cost of our indifference and fear? We should help people in need. Why is that so hard for some people? Rich Ghouls must End. Damien wants “billionaires” to stop being a thing. Tax then into equality. To Damien, there is no debate, Capitalism is unethical. Moreover, as an Anarchist Educator, Damien knows violence is not the way to inspire lasting positive change. But we are not limited to violence, we have education, one of the most lasting and powerful ways to improve the world. We empower the world by championing Truth and its supporters.
Anarchism and Education
“Various alternatives to education and their problems have been proposed by anarchists which have gone from alternative education systems and environments, self-education, advocacy of youth and children rights, and freethought activism.” ref
“Historical accounts of anarchist educational experiments to explore how their pedagogical practices, organization, and content constituted a radical alternative to mainstream forms of educational provision in different historical periods.” ref
“The Ferrer school was an early 20th century libertarian school inspired by the anarchist pedagogy of Francisco Ferrer. He was a proponent of rationalist, secular education that emphasized reason, dignity, self-reliance, and scientific observation. The Ferrer movement’s philosophy had two distinct tendencies: non-didactic freedom from dogma and the more didactic fostering of counter-hegemonic beliefs. Towards non-didactic freedom from dogma, and fulfilled the child-centered tradition.” ref

Teach Real History: all our lives depend on it.
Damien sees lies about history as crimes against humanity. And we all must help humanity by addressing “any and all” who make harmful lies about history.

My favorite “Graham Hancock” Quote?
“In what archaeologists have studied, yes, we can say there is NO Evidence of an advanced civilization.” – (Time 1:27) Joe Rogan Experience #2136 – Graham Hancock & Flint Dibble

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


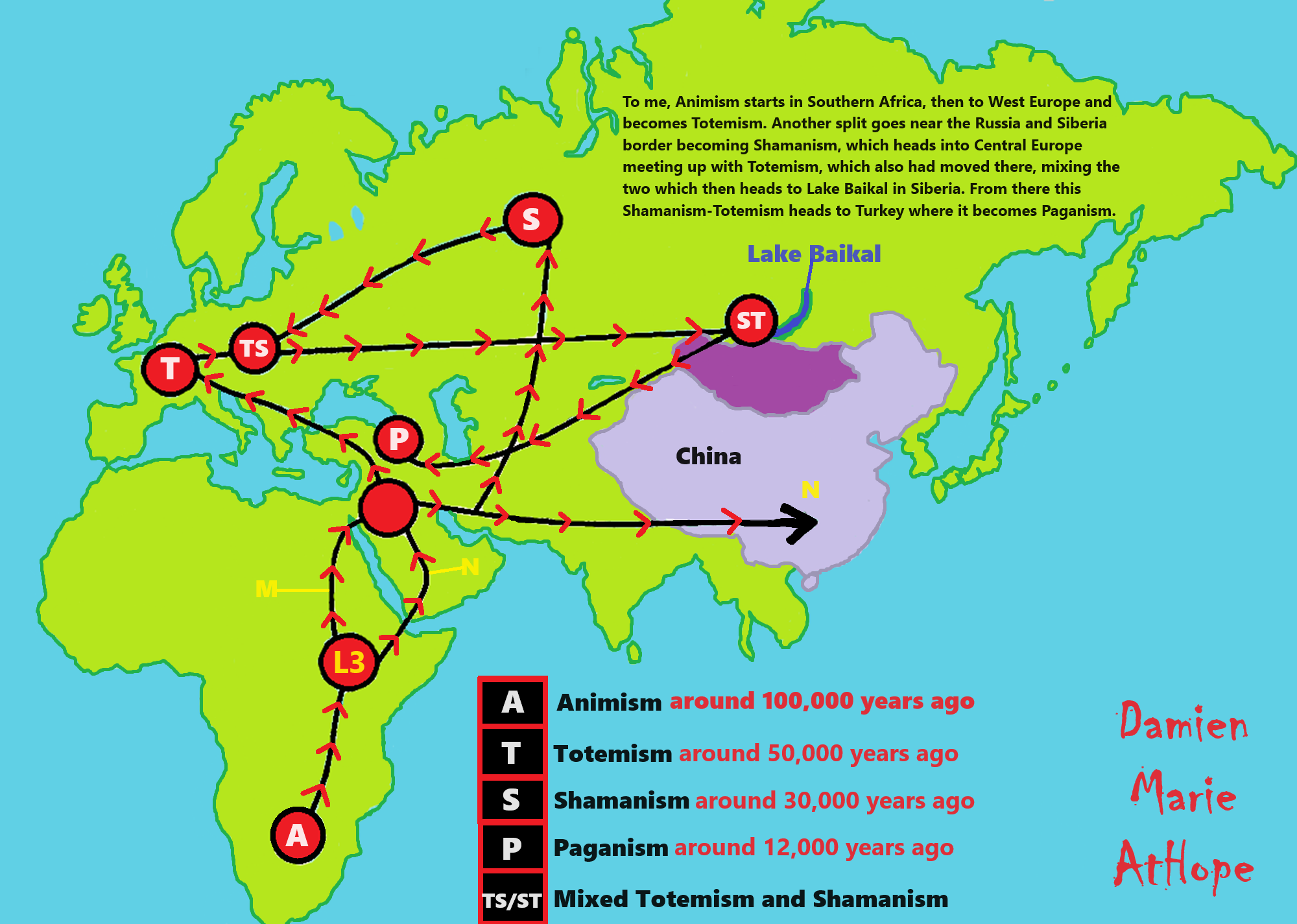
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
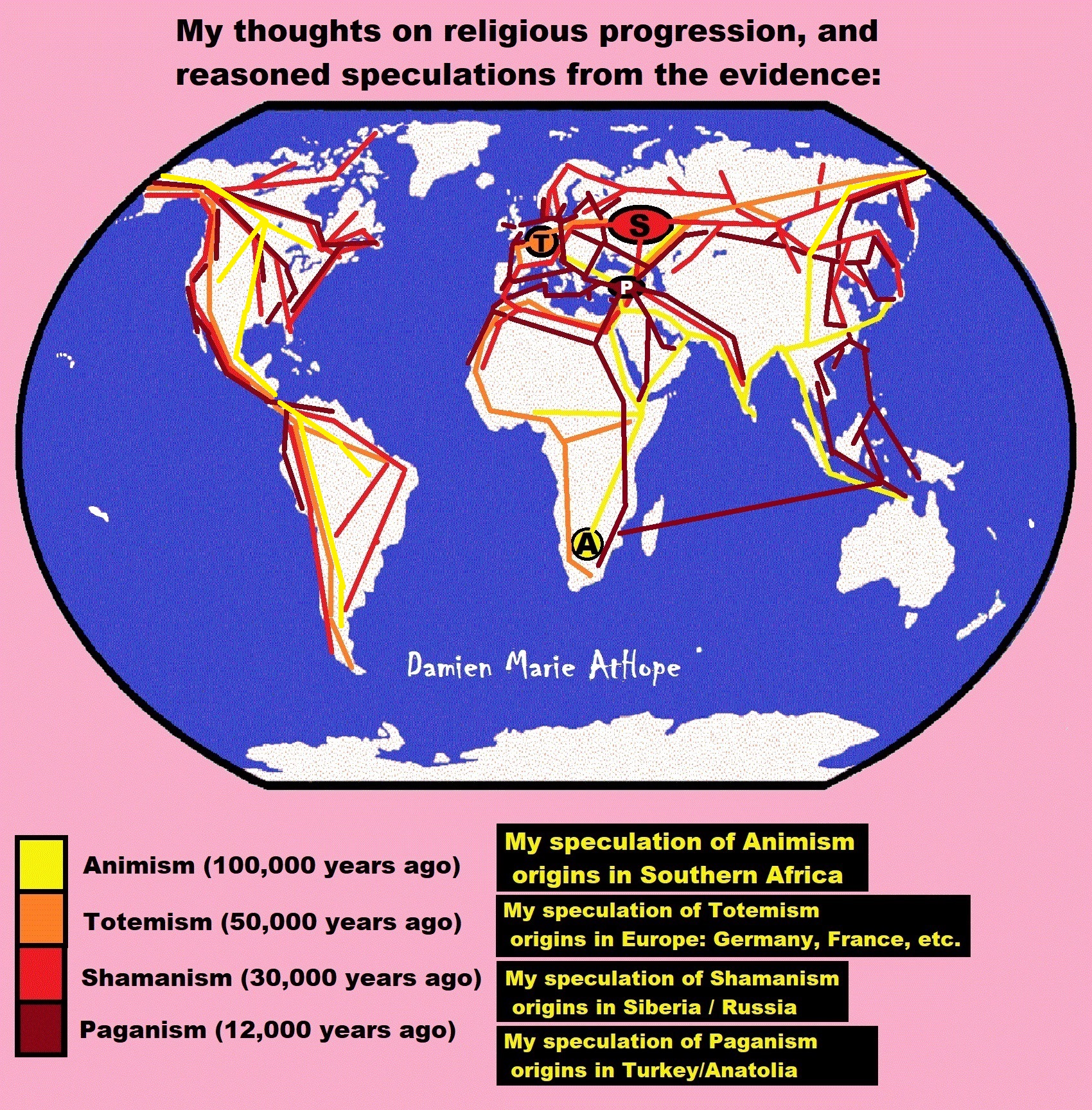



Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
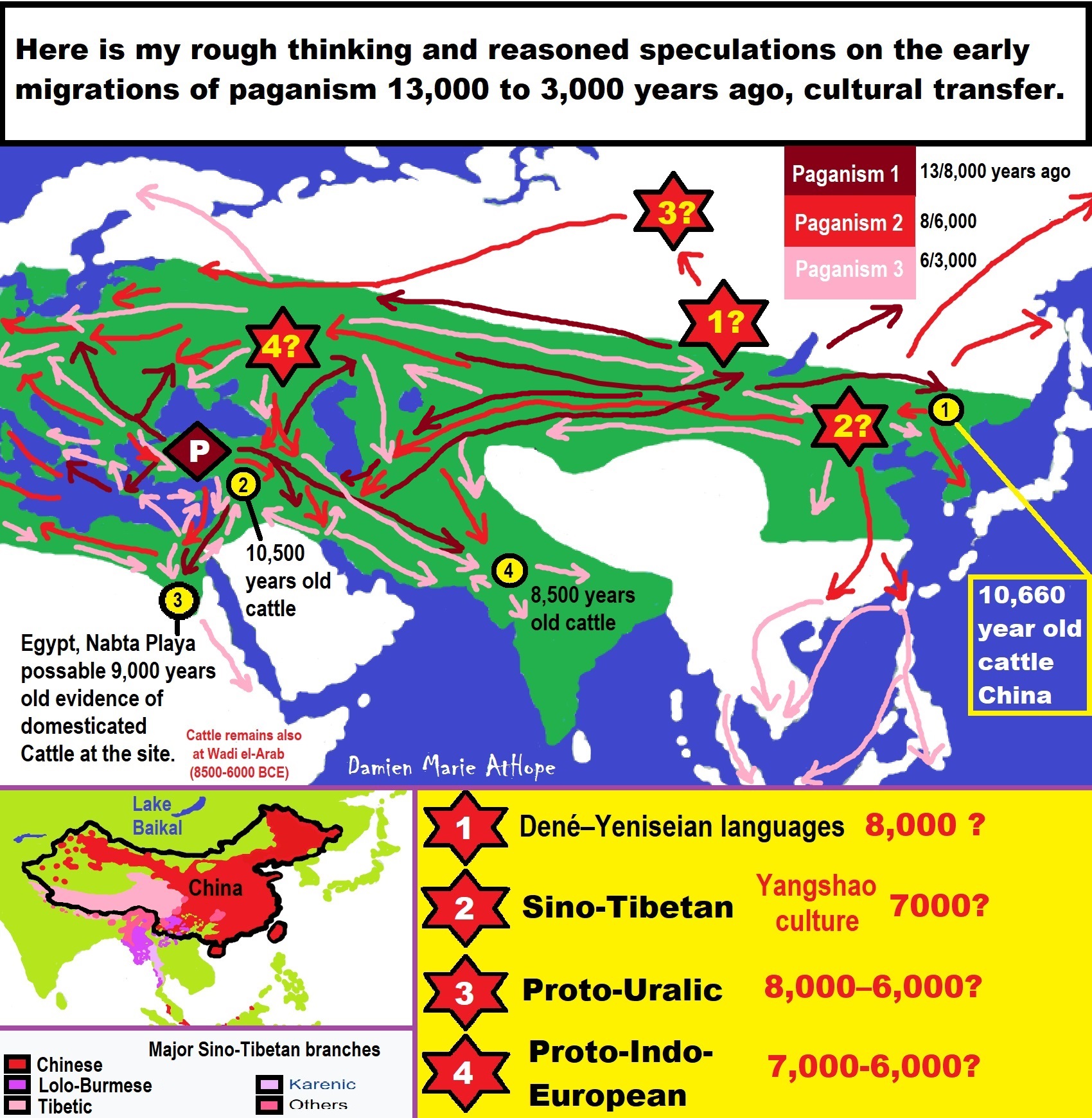
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
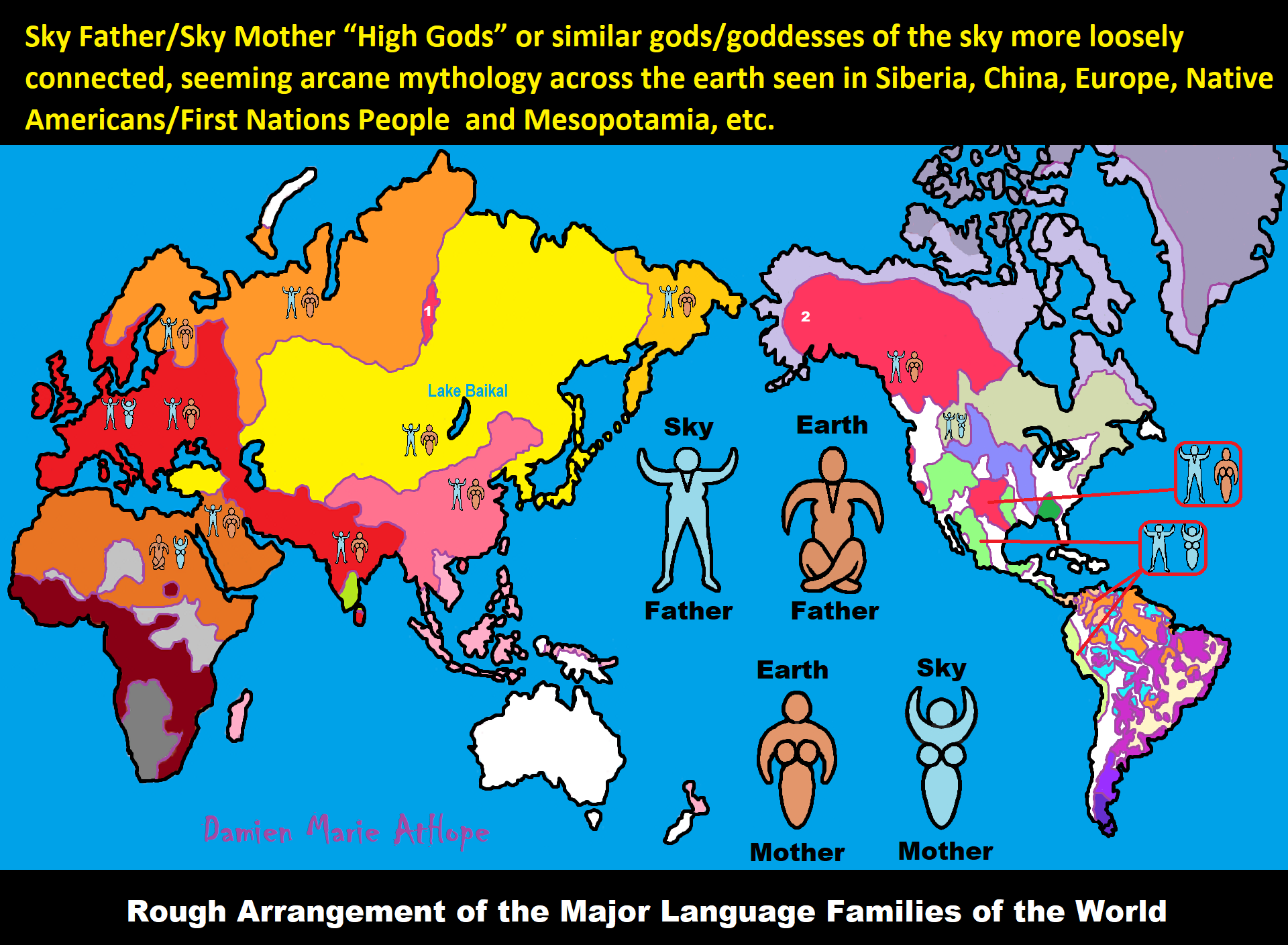
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.


Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com