I am for Non-Aggression?
I am not a pacifist, rather I am for non-aggression, I will engage in or support violence if it is direct self-defense or for other-defense.
“If you want to leave your gun with your children, go for it. People do it all the time.” – Challenger
My response, Can we kill the child if it kills my child with a gun? “Unintentional injury is a leading cause of death among U.S. children and adolescents aged 0–17 years, and firearms are a leading injury method.” ref
“What you tell your kids is not my problem or my business; whatever you want to do with your kids should be nobody else’s decision but yours.” – Challenger
My response, Are the kids yours, or someone else’s, or do they own themselves?
“The kids are mine until they are old enough to move out and take care of themselves. If I want to trans my kids, cover them in tattoos, or marry them off, it’s no one else’s business.” – Challenger
My response, Wrong, you are a caregiver, not a master, or you also don’t understand anarchist child care.
“Anarchists have long been aware of the importance of child-rearing and education. Aware that child-rearing should aim to develop “a well-rounded individuality” and not “a patient work slave, professional automaton, tax-paying citizen, or righteous moralist.” [Emma Goldman, Red Emma Speaks, p. 108]
Prioritizing Kids in the Anarchist Community
“If one accepts the thesis that the authoritarian family is the breeding ground for both individual psychological problems and political reaction, it follows that anarchists should try to develop ways of raising children that will not psychologically cripple them but instead enable them to accept freedom and responsibility while developing natural self-regulation. We will refer to children raised in such a way as “free children.” ref
“That’s a great philosophy, if you want to push your ideas on me and enforce them. You’re an authoritarian.” – Challenger
My response, But if it’s your child, then no rights for you until adulthood? Can you beat them if you want? Rape them if you want or kill them if you want?
“There is no way to force people into a certain way of raising their children without being an authoritarian non-anarchist society.” – Challenger
My response, So let you rape them? No, we will value the child owning themselves, and if you keep violating them, we will protect that fellow who owns themselves, and if you get harmed, then you learn not to harm your children.
“I know this is going to sound sick, but yes, personally, I would prefer to put them in the wood chipper, but that’s being a little bit of a tyrant. Since we are talking hypothetically.” – Challenger
My response, Then you are not an anarchist; stop calling yourself one. I understand, you do not understand ethics.
So many think a gun of war is needed to change things but look at the many uprisings around the world bringing change that guns are not used. I am for non-aggression, I am one who champions nonviolent actions, and activism to inspire change. We are more powerful than we realize. I am a far leftist and I don’t own any guns and am for reasonable gun rights and reasonable gun laws.




“Damien, aren’t you an anarchist?” – Communist
My response, Yes, and I am for reasonable rules, not rulers. I support reasonable gun laws. I am for car laws as well for the same reason, safety.
“But you still have rulers why give up your means of self-defense when the threat is still present?” – Communist
My response, I don’t own a gun, I did in the past when I was a rightist but now as a leftist, I don’t feel it necessary.
“Then you’re a liberal, not a leftist. We’re still oppressed, so long as the capitalists rule and the state remains.” – Communist
My response, So if I am not for all people having access to a type of gun but not all guns then one is not a leftist? Give me a break. lol
“Keep it to one message, and no what makes you, not a leftist is your content in your oppression. Anarchists used to assassinate monarchies and now you are protesting for a policy that directly fucks your cause. Read theory on either ideology anarchism isn’t just No government.” – Communist
My response, Is it being disarmed if I can’t have bombs and grenades? If I was OK with laws against walking around with bombs would this make me not a leftist? What if I wanted to have nuclear weapons at my home if others wanted laws against this world, they be, not leftist?
“You’re moving the goalposts, we’re dealing with guns, not world-ending devices.” – Communist
My response, As to my politics, when I take political tests I am listed as close to anarchist communist and I will trust it over your opinions.
“You trust a political compass, really? Have you read any political theory anarchist or otherwise? Wanting laws isn’t anti-leftist, but advocating for laws that restrict your access to your most direct line of democracy. Yeah I think that’s not leftist.” – Communist
“It seems like America is the only country on earth with the worst gun control laws in terms of keeping everyone safe.” – Marxist-Leninist, Atheist, No war but class war
“Communism (from Latin communis, ‘common, universal’) is a left-wing to far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology within the socialist movement, whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered around common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange that allocates products to everyone in the society. Communist society also involves the absence of private property, social classes, money, and the state. Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a more libertarian approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers’ self-management, and a more vanguardist or Communist party-driven approach through the development of a constitutional socialist state followed by the withering away of the state. As one of the main ideologies on the political spectrum, communism is placed on the left-wing alongside socialism, and communist parties and movements have been described as radical left or far left.” ref
“Variants of communism have been developed throughout history, including anarcho-communism, Marxist schools of thought, and religious communism, among others. Communism includes a variety of schools of thought, which broadly include Marxism, Leninism, and libertarian communism, as well as the political ideologies grouped around those. All of these different ideologies generally share the analysis that the current order of society stems from capitalism, its economic system, and mode of production, that in this system there are two major social classes, that the relationship between these two classes is exploitative, and that this situation can only ultimately be resolved through a social revolution. The two classes are the proletariat (the working class), who make up the majority of the population within society and must sell their labor to survive, and the bourgeoisie (the capitalist class), a small minority that derives profit from employing the working class through private ownership of the means of production. According to this analysis, a communist revolution would put the working class in power, and in turn establish common ownership of property, the primary element in the transformation of society towards a communist mode of production.” ref
“Anarchist communism is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that advocates communism. It calls for the abolition of private property but retains personal property and collectively-owned items, goods, and services. It supports social ownership of property and the distribution of resources “From each according to his ability, to each according to his needs“. Some forms of anarchist communism, such as insurrectionary anarchism, are strongly influenced by egoism and radical individualism, believing anarchist communism to be the best social system for realizing individual freedom. Most anarchist communists view the philosophy as a way of reconciling the opposition between the individual and society.” ref
I am not, nor do I support “egoism and radical individualism“, I am a pro-collectivist anarchist thinker.
“Collectivist anarchism, also called anarchist collectivism and anarcho-collectivism, is an anarchist school of thought that advocates the abolition of both the state and private ownership of the means of production. In their place, it envisions both the collective ownership of the means of production and the entitlement of workers to the fruits of their own labor, which would be ensured by a societal pact between individuals and collectives. Collectivists considered trade unions to be the means through which to bring about collectivism through a social revolution, where they would form the nucleus for a post-capitalist society.” ref
“The tendency was initially conceived as a synthesis of social equality and liberty, by the Russian revolutionary socialist Mikhail Bakunin. It is commonly associated with the anti-authoritarian sections of the International Workingmen’s Association and the early Spanish anarchist movement, with whom it continued to hold a strong influence until the end of the 19th century. Eventually, it was supplanted as the dominant tendency of anarchism by anarcho-communism, which advocated for the abolition of wages and the distribution of resources “from each according to their ability, to each according to their needs.” ref
Science like logic should follow truth devoid of political or religious/nonreligious beliefs or persuasions.
To me, to do otherwise is to move away from science and thus risks falling into pseudoscience.

“Axiology (from Greek ἀξία, axia: “value, worth”; and -λογία, -logia: “study of”) is the philosophical study of value. It includes questions about the nature and classification of values and about what kinds of things have value. It is intimately connected with various other philosophical fields that crucially depend on the notion of value, like ethics, aesthetics or philosophy of religion. It is also closely related to value theory and meta-ethics.” ref
“Axiology, also called THEORY OF VALUE, the philosophical study of goodness, or value, in the widest sense of these terms. Its significance lies (1) in the considerable expansion that it has given to the meaning of the term value and (2) in the unification that it has provided for the study of a variety of questions—economic, moral, aesthetic, and even logical—that had often been considered in relative isolation.” ref
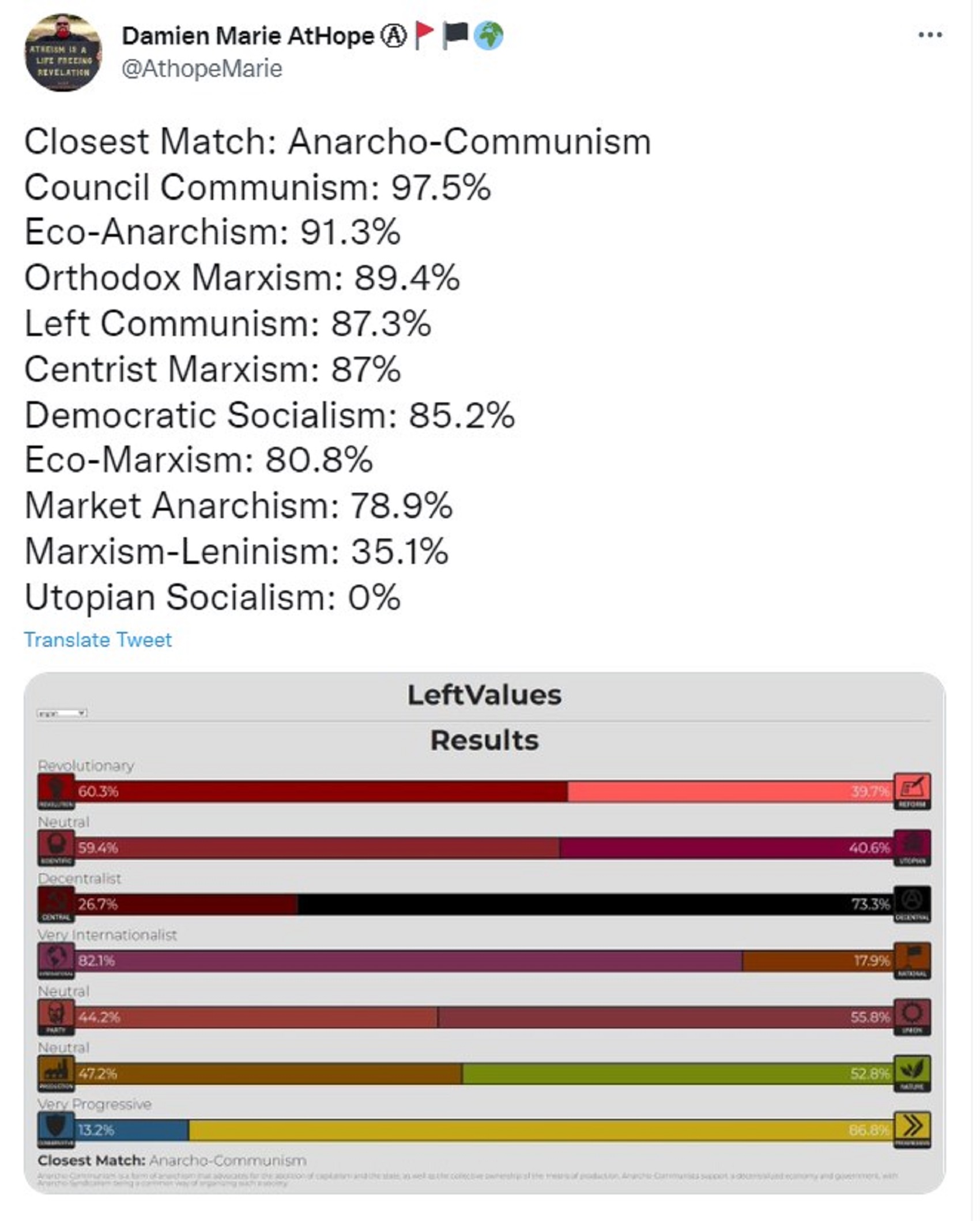
LeftValues test: Link
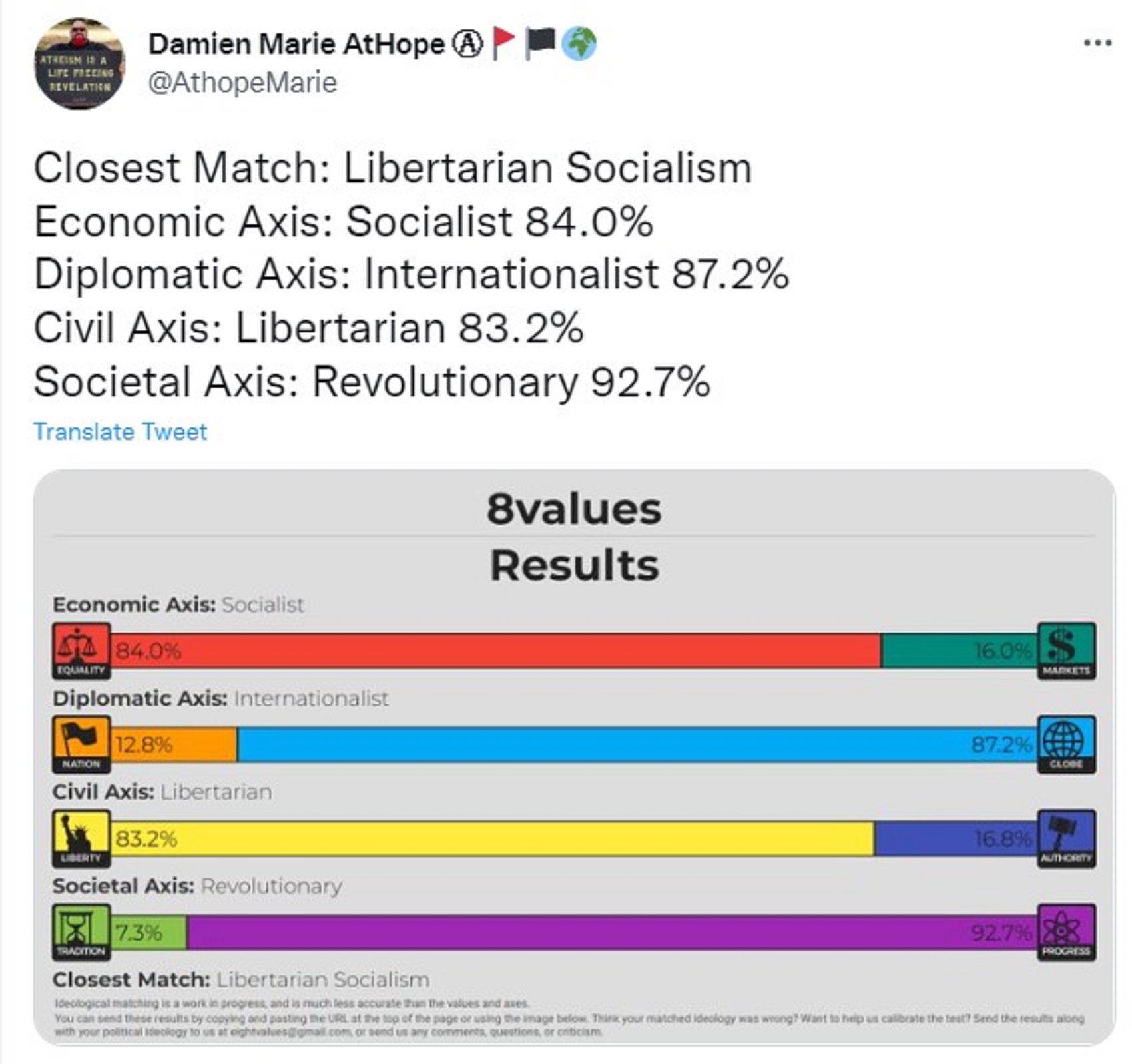
8values test: Link
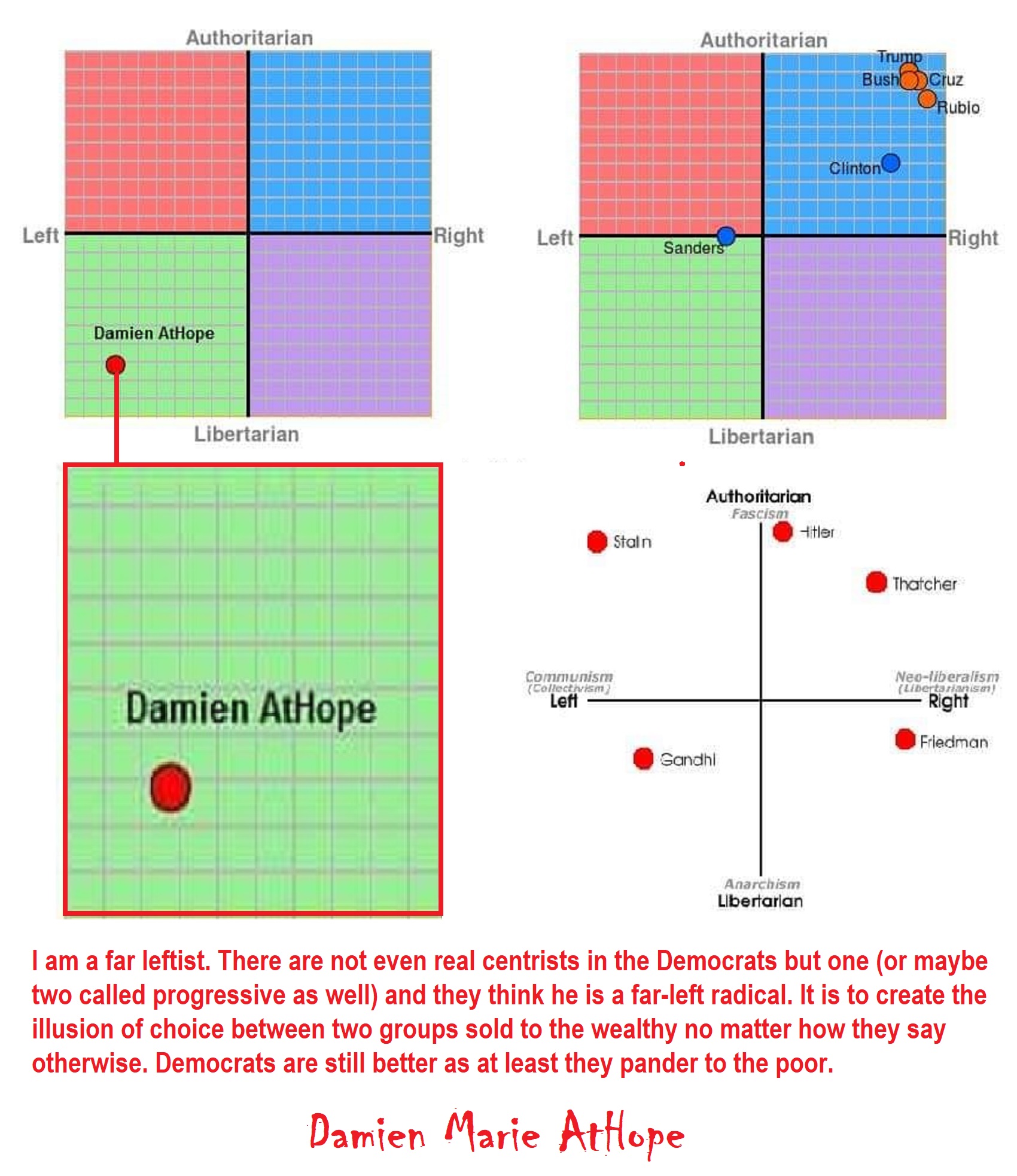
Political compass test: politicalcompass.org/test
I want people to rise up in Nonviolent Resistance/Action for Change,
so I don’t champion revolution by a gun.
“Nonviolent resistance, or nonviolent action, sometimes called civil resistance, is the practice of achieving goals such as social change through symbolic protests, civil disobedience, economic or political noncooperation, satyagraha, constructive program, or other methods, while refraining from violence and the threat of violence. This type of action highlights the desires of an individual or group that feels that something needs to change to improve the current condition of the resisting person or group.” ref
“Nonviolent resistance is often but wrongly taken as synonymous with civil disobedience. Each of these terms—nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience—has different connotations and commitments. Berel Lang argues against the conflation of nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience on the grounds that the necessary conditions for an act instancing civil disobedience are: (1) that the act violates the law, (2) that the act is performed intentionally, and (3) that the actor anticipates and willingly accepts punitive measures made on the part of the state against him in retaliation for the act. Since acts of nonviolent political resistance need not satisfy any of these criteria, Lang argues that the two categories of action cannot be identified with one another.” ref
“Furthermore, civil disobedience is a form of political action which necessarily aims at reform, rather than revolution. Its efforts are typically directed at the disputing of particular laws or groups of laws while conceding the authority of the government responsible for them. In contrast, political acts of nonviolent resistance can have revolutionary ends. According to Lang, civil disobedience need not be nonviolent, although the extent and intensity of the violence is limited by the non-revolutionary intentions of the persons engaging in civil disobedience. Lang argues the violent resistance by citizens being forcibly relocated to detentions, short of the use of lethal violence against representatives of the state, could plausibly count as civil disobedience but could not count as nonviolent resistance.” ref
“Mahatma Gandhi is the most popular figure related to this type of protest; United Nations celebrates Gandhi’s birthday, October 2, as the International Day of Non-Violence. Other prominent advocates include Khan Abdul Ghaffar Khan (affectionately called Bacha Khan), Henry David Thoreau, Etienne de la Boétie, Charles Stewart Parnell, Te Whiti o Rongomai, Tohu Kākahi, Leo Tolstoy, Alice Paul, Martin Luther King Jr., Daniel Berrigan, Philip Berrigan, James Bevel, Václav Havel, Andrei Sakharov, Lech Wałęsa, Gene Sharp, Nelson Mandela, Jose Rizal, and many others. From 1966 to 1999, nonviolent civic resistance played a critical role in fifty of sixty-seven transitions from authoritarianism.” ref
“The “Singing revolution” (1989–1991) in Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, led to the three Baltic countries‘ restoration of independence from the Soviet Union in 1991. Recently, nonviolent resistance has led to the Rose Revolution in Georgia. Research shows that non-violent campaigns diffuse spatially. Information on non-violent resistance in one country could significantly affect non-violent activism in other countries.” ref
“Many movements which promote philosophies of nonviolence or pacifism have pragmatically adopted the methods of nonviolent action as an effective way to achieve social or political goals. They employ nonviolent resistance tactics such as: information warfare, picketing, marches, vigils, leafletting, samizdat, magnitizdat, satyagraha, protest art, protest music and poetry, community education and consciousness raising, lobbying, tax resistance, civil disobedience, boycotts or sanctions, legal/diplomatic wrestling, Underground Railroads, principled refusal of awards/honors, and general strikes. Current nonviolent resistance movements include: the Jeans Revolution in Belarus, the Black Lives Matter movement in the United States, the fight of the Cuban dissidents, and internationally the Extinction Rebellion and School Strike for Climate.” ref
“Although nonviolent movements can maintain broader public legitimacy by refraining from violence, some segments of society may perceive protest movements as being more violent than they really are when they disagree with the social goals of the movement. A great deal of work has addressed the factors that lead to violent mobilization, but less attention has been paid to understanding why disputes become violent or nonviolent, comparing these two as strategic choices relative to conventional politics.” ref
“Nonviolent resistance proves a potent weapon“
“When Erica Chenoweth started her predoctoral fellowship at the Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs in 2006, she believed in the strategic logic of armed resistance. She had studied terrorism, civil war, and major revolutions — Russian, French, Algerian, and American — and suspected that only violent force had achieved major social and political change. But then a workshop led her to consider proving that violent resistance was more successful than the nonviolent kind. Since the question had never been addressed systematically, she and colleague Maria J. Stephan began a research project. For the next two years, Chenoweth and Stephan collected data on all violent and nonviolent campaigns from 1900 to 2006 that resulted in the overthrow of a government or in territorial liberation. They created a data set of 323 mass actions. Chenoweth analyzed nearly 160 variables related to success criteria, participant categories, state capacity, and more. The results turned her earlier paradigm on its head — in the aggregate, nonviolent civil resistance was far more effective in producing change. The Weatherhead Center for International Affairs (WCFIA) sat down with Chenoweth, a new faculty associate who returned to the Harvard Kennedy School this year as a professor of public policy, and asked her to explain her findings and share her goals for future research. Chenoweth is also the Susan S. and Kenneth L. Wallach Professor at the Radcliffe Institute for Advanced Study.” ref
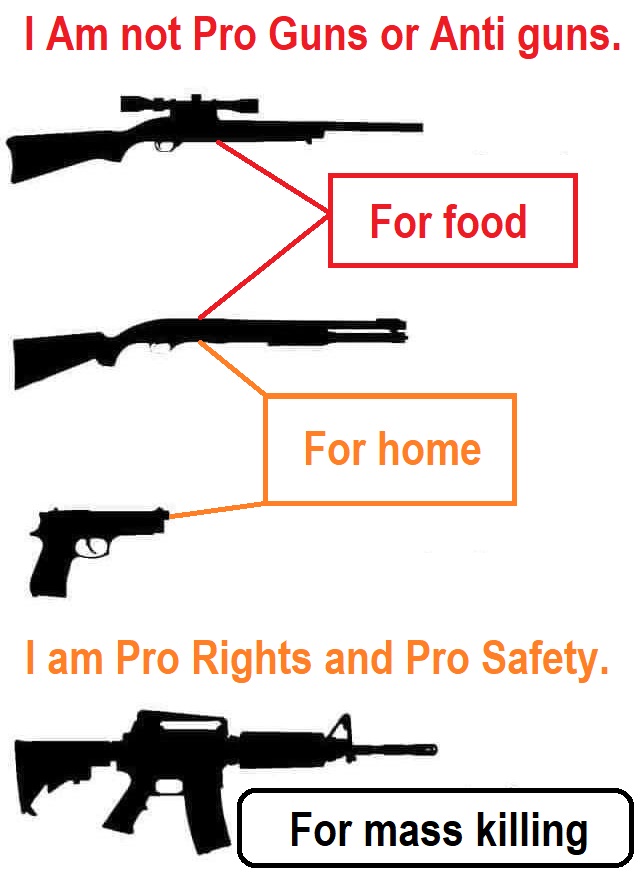
I Am not Pro Guns or Anti guns,
I am Pro Rights and Pro Safety.
I am a leftist atheist for Non-Aggression, valuing anti-violence,
unless the aggression or violence is for direct self-defense or other-defense.
Why is it a believed human right to have a gun? One has a right to self-protection, not any means or any tools and such people loudly fight to the death for this product “guns.” However, some of these same people (who believe they are champions human rights) seem oblivious to human life and its inherent rights? Some of these self-claim champions of “human rights for guns which I may remind you is only a product, tend to not think housing (also another product) is a human right, as many die homeless in the street? I would rather be one who fights for human life than a product like guns, and why is it so easy to fight for death when life is clearly in such need?
“I need a nuclear weapon to protect myself from other countries that might do me harm, I should have a right to a nuclear weapon. Humor aside, the U.S.Constitutionn does not say gun ownership is an individual right, but a collective right of citizens under state jurisdiction, this is why we have different gun laws in every state. Essentially the constitution says that you can’t outright ban gun ownership by citizens for a lawful purpose, regulation is permissible. A person is more important than a gun, objectively. Do people have the right to own guns? Yes, but with reasonable laws, as I think human ethics would move to the anarchist position.” – Marquis Amon
I am for Gun Rights and I am for Gun Laws.
I want sensible laws for all things guns are in no way special. I would like gun laws to be like vehicle license laws, such as different classes A, B, C. And similar scaling required Personal Firearms Liability Insurance per gun and gun type owned like car insurance is for vehicles by different classes A, B, C. NRA Endorsed Personal Firearms Liability Insurance (voluntary of course for the NRA; though I think it should be mandatory)
“A” Being full auto machine guns. “B” being pistols and semiautomatics, and “C” being shotguns and hunting rifles. Just like driving licenses, it should be easier to get a class “C” gun license and the hardest and have extra requirements to get a class “A” gun license just like driving licenses. And each class requires proof of training yearly registration and liability insurance for gun ownership just like vehicles. To me, the guns rights issue starts off with a confused mind about guns as I see it there is a human right to self-defense not a right to a dangerous product unencumbered by any restrictions. Guns are not special, they are a product, a very dangerous product they may or may not be employed in Self-care (for food “hunting”, safety “self-defense”/other-defense” fun “target practice”). While guns don’t have a human right, there is a human right self-defense is people seem to confuse the two. Speaking of human right self-defense, I am in support of a right to reasonable safety in society (shared right to self along with other-defense) and why I support reasonable gun laws.
The NRA once supported gun control: http://www.salon.com/
Name me laws we don’t put into practice simply because some will not follow them? I’m all for sensible laws. We need sensible laws even if getting people to follow them is a problem. Just like underage drinking, we cannot stop it but we need the laws.
Laws are why we even have a right to have guns in the first place. Thus, it is no strange thing a law is needed to govern them as well. Laws are what come from the Bill of Rights in the U.S. Constitution, that guarantees our basic freedoms like freedom of speech, religion, and the press etc.
Possible Gun Debate Fallacies
The gun debate needs a reason, not rhetoric, and logical fallacies. There are many fallacies that occur on both sides of the gun debate, this fallacy can be especially distortive in how it affects our ability to think rationally about the issue.
Appeal to Fear- used by both sides such as saying how many more gun deaths would there be if there were no guns to protect us or we must ban all or some guns as it’s the only way to protect us.
Appeal to emotion – used by both sides such as saying if we don’t ban guns, then kids will continue to be violently and gruesomely murdered. If we don’t allow more guns everywhere, then kids will continue to be violently and gruesomely murdered.
False causality – (assume that correlation must equal causation)- used by both sides such as saying remove guns and gun violence will have to drop or allow more guns everywhere and gun violence. Another way to say this is there is no evidence that making gun laws removed gun violence or there is no evidence that open carry gun laws reduce overall gun violence. There could be places in different parts of the country where either of these claims has what looks like validating statistics. This can be a fallacy because it ignores the possibility that the two things are influenced by a third factor. This is a fallacy you should look for whenever statistics are being thrown around because as one of my old dive instructors used to say, statistics can be like bikinis: what they show is revealing, but what they hide is essential.
Slippery slope – eg. If they take away our rights to any weapon soon we won’t be able to hunt at all: This tends to be more of the pro-gun side as they are supportive of maintaining the status quo. It is not a particularly useful argument for change.
Perfect solution fallacy – We can’t strengthen firearm regulations because people will still get their dirty paws on guns. But the goal is a reduction of gun deaths. There’s no reason why we shouldn’t employ a multifaceted approach to deal with this problem.
Appeal to authority – eg. The constitution says we should have guns. This is a tricky point as the validity of the constitution as an authority is rarely questioned, yet it does not necessarily represent a valid argument. This is probably a point that will never change.
Anecdotal fallacy – eg. I know of someone who stopped a robbery with a gun. One incident can always be pointed to where a gun was useful in defense. The size of this example set is usually the point of debate. The same can be said for massacres with firearms on the other side.
My Personal Mission: I champion a value-driven life not just enlightenments by valuing people and embarking to be a friend and show friendliness as a way of inspiring change. Instead of trying to attack people personally and put others down rather than putting bad ideas down. A person wishing for a value-driven life works to inform and build others up as well as hold a willingness to listen and where we see, unrest in the world try to help to offer new thinking to bring level-headedness and peace. A person wishing for a value-driven life sees this positive thinking, not just a good thing to do when convenient but see it as a way of life and compassion as a personal virtue.
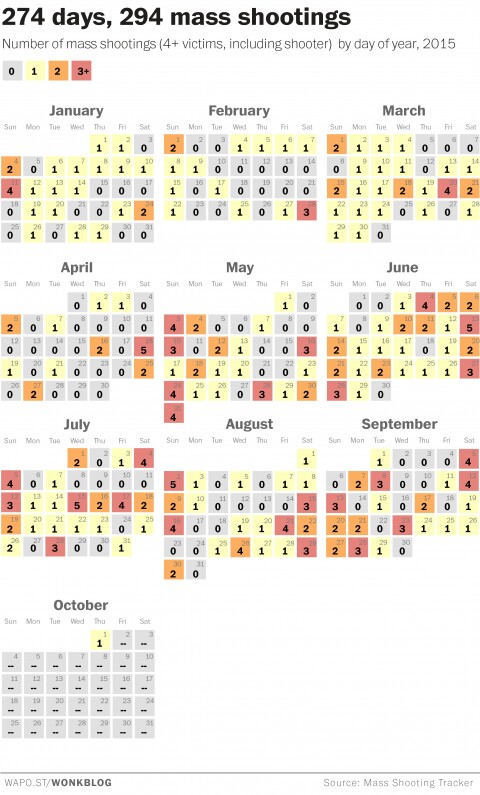
The number of mass shootings in the America this year (2015) reached 294, according to the Mass Shooting Tracker. The website defines mass shootings as incidents in which four or more people are killed or injured by gunfire. http://shootingtracker.com/wiki/Mass_Shootings_in_2015
The math of mass shootings?
50 years of U.S. mass shootings
[The number of ‘mass shootings’ in the U.S. depends on how you count]
This data — compiled from Mother Jones; Grant Duwe, author of “Mass Murder in the United States: A History,” and Washington Post research — does not include gang killings, shootings that began as other crimes such as robberies, and killings that involved only the shooter’s family.
948 victims
Each gun was used to kill an average of three people, not counting shooters. The 948 people came from nearly every imaginable race, religion and socioeconomic background, and 145 were children or teenagers.
The oldest victim
Louise De Kler, 98, still took her pool cue and boombox to the rec room at Pinelake Health and Rehab and shot pool with the “young guys,” her daughter told the Associated Press. She was shot to death on March 29, 2009, along with seven other residents and a nurse, by a man who had come to the Carthage, N.C., nursing home looking for his estranged wife.
The youngest victim
Eight-month-old Carlos Reyes was buried in a casket with his mother, Jackie, who had tried to shield him, as an unemployed father of two killed 21 and injured 19 in a busy McDonald’s in San Ysidro, Calif., on July 18, 1984. The man told his wife he was going out “hunting humans” and opened fire with an Uzi, a shotgun and a semiautomatic pistol.
271 guns
Shooters brought an average of three weapons to each shooting; the Las Vegas music festival shooter had at least 10. We don’t know how all the guns were acquired, but of the ones we know, 164 were obtained legally and 39 were obtained illegally.
9mm
Shooters in some of the deadliest mass shootings in U.S. history carried models of the country’s most popular types of weapons. The gunman who killed 32 students and teachers at Virginia Tech on April 16, 2007, used a 9mm semiautomatic Glock 19 (and a .22-caliber Walther P22, another popular caliber). These guns, used by many law enforcement officers, are generally light, inexpensive, easy to conceal and require little strength to control. In this tally of weapons, 9mm semiautomatic handguns show up more than any other weapon.
AK-47
A drifter carrying a Chinese variant of an AK-47 and a semiautomatic handgun fired more than 100 rounds into an elementary school playground in Stockton, Calif., on Jan. 17, 1989, killing five children and wounding 30 other students and teachers before shooting himself. The gunman had a history of crime, mental illness and drug abuse, but he bought the guns legally in Oregon and California. Five months later, California enacted the country’s first ban on assault weapons.
134 shooters
All but three of the mass shooters were male; the vast majority were age 20 to 49. More than half — 75 of them — died at or near the scene of the shooting, often by killing themselves.
An anomaly
Tashfeen Malik, the 27-year-old Pakistani mother who helped kill 14 partygoers at her husband’s workplace in San Bernardino, was an anomaly among mass shooters in two ways: She was part of a pair rather than a lone gunman, and she was a woman. The other two women in this data set are Jennifer San Marco, who in 2006 killed a former neighbor and six employees at a Goleta, Calif., mail-processing facility where she once worked; and Cherie Rhoades, who killed her brother and three others at a tribal council meeting in 2014.
Two middle-schoolers
Andrew Golden, 11, and Mitchell Johnson, 13, pulled a fire alarm to flush students and teachers out of their Jonesboro, Ark., middle school on March 24, 1998, and began shooting, killing four girls and a teacher and wounding 10 others. Between them, they had nine guns including two semiautomatic assault pistols. Both were released from prison when they turned 21.
40 states and the District
Twenty-seven percent of the mass shootings occurred in workplaces, and 1 in 8 took place at schools. Others took place in religious, military, retail and restaurant or other locations. California has had more mass shootings than any other state, with 21. While some locations have simply become shorthand for the tragedies that occurred there, others have added tragic phrases to the national vocabulary.
Post offices
One of the most notorious workplace shootings was carried out by an ex-Marine in an Edmond, Okla., post office on Aug. 20, 1986. The 44-year-old part-time mail carrier, who had gotten a poor performance review the day before, entered the post office wearing his mailman’s uniform and carrying three handguns in his bag. He killed 14 and wounded six before shooting himself. It was the deadliest in a series of rage-fueled killings by current and former postal employees that gave rise to the phrase “going postal.”
Schools
The April 20, 1999, killing of 12 students and a teacher by two disgruntled seniors at Columbine High School in Littleton, Colo., became a turning point after which school shootings could no longer be considered unthinkable aberrations. After a confused response that played out over several hours while a teacher bled to death, U.S. law enforcement agencies overhauled procedures and officer training to create protocols for stopping an “active shooter.”
People killed in mass shootings make up less than half of 1 percent of the people shot to death in the United States. More than half of gun deaths every year are suicides. In 2015, more than 12,000 people have been killed by guns, according to the Gun Violence Archive.
We ethically must do something, as to doing nothing likely means more will suffer.
Reasonable anarchist gun laws?
“Damien, you say you agree with reasonable gun laws, but you say you are an anarchist. How can you have gun control without a government?” – Questioner
My response, As if “government” is the only form of governance…
“Explain to me how it works then.” – Questioner
My response, What governance?
“Controlling gun ownership without a state, how would that work.” – Questioner
My response, We the People are the management, and we should support all reasonable personal freedom but still have laws we directly vote on like free People. Direct democracy (also known as pure democracy) is a form of democracy in which people decide (e.g. vote on, form consensus on) policy initiatives directly. Guns are not some human right it’s a dangerous product and like all hazardous products need reasonable regulations just as bomb-making.
“Who enforces the regulations?” – Questioner
My response, I hope you don’ wrongly think I am anti-society. No, I am for ethical Governance, I just oppose the abusive hierarchal governments and one over many rules removing our rights then only giving them back in small peaces and demanding we thank and praise them, some almost as if gods but I am not so fooled, as to me much of what we have now is similar such as fire departments and all other reasonable services we as a community pay for in taxes. I am not against reasonable taxes for desirable social services. From “Big Government” to “Big Governance”?
Australian Gun Stats?
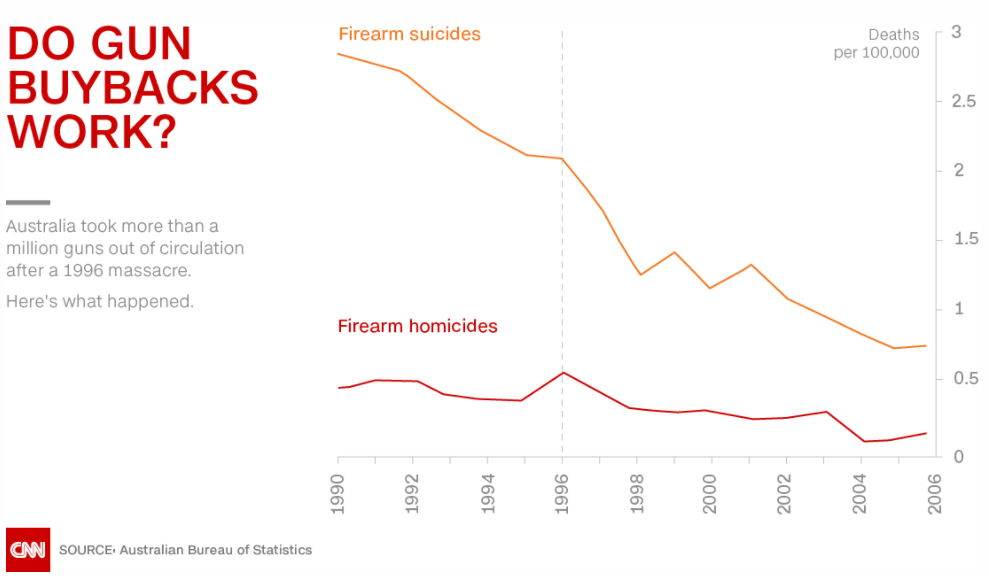
In a peer-reviewed paper published by American Law and Economics Review in 2012, researchers Andrew Leigh of Australian National University and Christine Neill of Wilfrid Laurier University found that in the decade following the NFA, firearm homicides (both suicides and intentional killings) in Australia had dropped significantly:
In 1997, Australia implemented a gun buyback program that reduced the stock of firearms by around one-fifth (and nearly halved the number of gun-owning households). Using differences across states, we test[ed] whether the reduction in firearms availability affected homicide and suicide rates. We find that the buyback led to a drop in the firearm suicide rates of almost 80%, with no significant effect on non-firearm death rates. The effect on firearm homicides is of similar magnitude but is less precise [somewhere between 35% and 50%].
Similarly, Dr. David Hemenway and Mary Vriniotis of the Harvard Injury Control Research Center found in 2011 that the NFA had been “incredibly successful in terms of lives saved”:
For Australia, the NFA seems to have been incredibly successful in terms of lives saved. While 13 gun massacres (the killing of 4 or more people at one time) occurred in Australia in the 18 years before the NFA, resulting in more than one hundred deaths, in the 14 following years (and up to the present), there were no gun massacres.
The NFA also seems to have reduced firearm homicide outside of mass shootings, as well as firearm suicide. In the seven years before the NFA (1989-1995), the average annual firearm suicide death rate per 100,000 was 2.6 (with a yearly range of 2.2 to 2.9); in the seven years after the buyback was fully implemented (1998-2004), the average annual firearm suicide rate was 1.1 (yearly range 0.8 to 1.4). In the seven years before the NFA, the average annual firearm homicide rate per 100,000 was .43 (range .27 to .60) while for the seven years post NFA, the average annual firearm homicide rate was .25 (range .16 to .33)
Additional evidence strongly suggests that the buyback causally reduced firearm deaths. First, the drop in firearm deaths was largest among the type of firearms most affected by the buyback. Second, firearm deaths in states with higher buyback rates per capita fell proportionately more than in states with lower buyback rates.
While there is no doubt that firearms deaths in Australia have decreased substantially in the years since the implementation of the NFA, how much of that decrease is directly attributable to the NFA is still subject to debate. Much of that debate focuses on the fact that the gun death rate in Australia was already decreasing prior to the time the NFA was introduced:
For Australia, a difficulty with determining the effect of the law was that gun deaths were falling in the early 1990s. No study has explained why gun deaths were falling, or why they might be expected to continue to fall. Yet most studies generally assumed that they would have continued to drop without the NFA. Many studies still found strong evidence for a beneficial effect of the law.
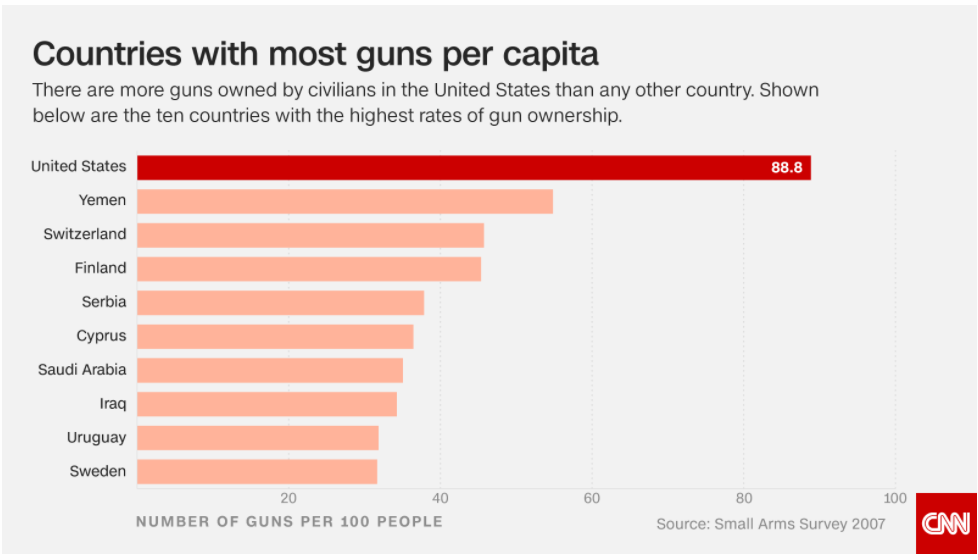
It’s also true that in both cases, the authors of studies cautioned that NFA-like plans wouldn’t necessarily achieve (and have not achieved) the same results in the United States, in large part because Australia’s geography makes it much easier to control the flow of arms into the country:
Several factors are important in assessing the extent to which the results from the Australian buyback can be extrapolated to other countries. Australian borders are more easily controlled than in countries that have land borders. In addition, Australia’s government in general and its policing and customs services in particular are highly organized and effective. The NFA also had an extremely high degree of political support and was quite competently executed. And the buyback was accompanied by a uniform national system for licensing and registration of firearms. These factors should be borne in mind in considering the extent to which the results from the Australian NFA might generalize to other countries.
It does not appear that the Australian experience with gun buybacks is fully replicable in the United States. Levitt provides three reasons why gun buybacks in the United States have apparently been ineffective: (a) the buybacks are relatively small in scale (b) guns are surrendered voluntarily, and so are not like the ones used in crime; and (c) replacement guns are easy to obtain. These factors did not apply to the Australian buyback, which was large, compulsory, and the guns on this island nation could not easily be replaced. For example, compared to the buyback of 650,000 firearms, annual imports after the law averaged only 30,000 per year, with many of these bought by law enforcement agencies.
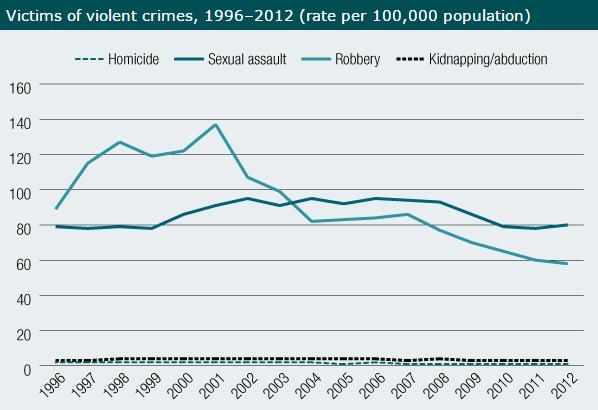
Regardless of how much of a cause-and-effect relationship there might be between the NFA and gun deaths in Australia, it’s undeniable that the firearms homicide rate in that country has decreased substantially since the implementation of the NFA. It’s not the case, however, as suggested by the misleading and long out-of-date online piece quoted in the Example block above (which was written way back in 2001) that the overall crime rate in Australia has shot up since the NFA was introduced. The rates of various types of violent crimes (sexual assault, kidnapping, homicides of all types) have scarcely changed at all, and while the robbery rate rose substantially in the 1998-2001 timeframe, it dropped below its pre-NFA level by 2004 and has continually declined since then:
Australia, 30,000 guns handed in?
“There is nothing in Australian law that stops a person from buying hundreds of guns and creating what are in effect private arsenals in suburban Sydney or Brisbane,” Shoebridge said. “This is a hole in the current laws that needs an urgent fix.”
More than 30,000 firearms are expected to have been handed in during Australia’s first national firearms amnesty since the national gun buyback prompted by the Port Arthur massacre in 1996. Figures for most states and territories are yet to be finalised, but New South Wales police said they had received more than 20,000 guns between 1 July 1 and 30 September. Of those, more than 5,000 were surrendered in the past month. Western Australian authorities announced on Monday that they had received 1,242 surrendered firearms during the amnesty period, including 186 shotguns, 860 rifles, 196 handguns and 65,628 rounds of ammunition. The surrendered weapons included first world war rifles and handguns, a second world war sub-machine gun and luger pistols, as well as three guns from the 19th century. Tasmanian police collected 1,924 firearms, comprising 754 shotguns, 1,071 rifles and 109 handguns. The surrendered firearms included two SKS military-style semi-automatic rifles, a 150-year-old Belgian Lefaucheux 9mm pin-fire revolver plus a tin of original rounds, which had been used to guard the mail coach between Richmond and Hobart, and two guns that had been reported stolen since 1995: a .222 calibre rifle and a Norinco NZ759mm pistol. While it is the first national firearms amnesty since the buyback scheme in 1996, under which more than 650,000 guns were collected and melted down, there have been a number of smaller, state-based amnesty periods. WA police ran a statewide gun amnesty in 2013, which collected 1,281 firearms and 80,000 rounds of ammunition. South Australia has held five gun amnesties between 1997 and 2017, amassing a total of 13,252 firearms. In the most recent amnesty period, between December 2015 and June 2017, just before the national amnesty began, 5,472 firearms were surrendered. Queensland has held amnesties in 2004 and 2013, collecting and destroying 2,835 and 2,000 guns respectively. NSW reportedly collected 63,000 guns in two amnesties in 2001 and 2003 and a further 4,323 in 2009. Tasmania and Victoria have had standing gun amnesties since 1997, meaning that a person can at any time surrender an unregistered firearm to a police station or gun dealer. All firearms surrendered in the national amnesty will be destroyed, with the exception of a few antiques that have been passed on to state museums. University of Sydney emeritus professor Simon Chapman, who has researched the decline in gun deaths since the national firearms agreement was put in place six weeks after the Port Arthur massacre, said he suspected many of the guns surrendered in 2017 should have been surrendered 20 years ago. Chapman’s research found there had been no fatal mass shootings since the national firearms agreement was put in place and gun deaths had declined at an accelerated rate, from a 3% decline annually prior to 1996 to a 5% annual decline in the 20 years since. “The guns which have been handed in in the most recent one are guns that people kept in defiance of the law since 1996,” he told Guardian Australia. “At the time I can recall going on to gun blogging sites such as they were at that stage, and people talking about hiding them and burying them and all that sort of stuff … there are obviously more out there.” Chapman said the initial gun buyback and rolling gun amnesties were an important part of Australia’s gun control system because they reduced the likelihood that unregistered and unaccounted for guns would be available to people who had no proper purpose to have them. Under Australia’s gun laws, semi-automatic or automatic firearms of the type suspected to have been used in the Las Vegas massacre cannot be legally owned and possession of one of these weapons, or any other unregistered firearm, carries a potential fine of $280,000 or 14 years imprisonment.
“Obviously there will always be some guns that come in illegally, but the world looks on to Australia’s gun laws with great envy,” Chapman said. The NSW Greens MP David Shoebridge questioned the effectiveness of gun amnesties, which he said did not balance out the number of guns being imported, legally or illegally, into Australia. “NSW alone is on track to have a record 1 million registered firearms by 2020,” he said. Shoebridge said the 2017 national firearms agreement, which resulted from the 20-year review of the Port Arthur laws, was focused on reducing red tape for gun owners. “There is nothing in Australian law that stops a person from buying hundreds of guns and creating what are in effect private arsenals in suburban Sydney or Brisbane,” Shoebridge said. “This is a hole in the current laws that needs an urgent fix.”
A History Of Gun Control Laws Shows US Citizens Don’t Have An Absolute Right To Bear Arms?
By Abby Rogers
The Second Amendment, which was added to the Constitution in 1791, gives everyone an inalienable right to bear arms, gun enthusiasts have argued.
But does that right allow people to walk around with assault weapons?
As we remember the 27 people killed during the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting and await an assault weapons ban bill, we decided to take a look at the history of gun control laws:
- 1860s — Many southern states passed “Black Codes” around this time, which severely limited African-American southerners’ rights, including their right to own guns.
- 1927 — Congress passed the Mailing of Firearms Act, also known as the Miller Act, which banned mailing concealable firearms.
- 1934 — The National Firearms Act of 1934 taxed the manufacture and transfer of certain firearms specified in the act. It also taxed people who imported, manufactured, or dealt in firearms and required registration of all firearms.
- 1938 — The Federal Firearms Act of 1938 regulated interstate commerce in firearmsand banned criminals from receiving or sending firearms in interstate or foreign commerce.
- 1968 — The Gun Control Act of 1968, passed after the assassinations of John F. Kennedy and Martin Luther King, regulated gun ownership, defined who wasn’t allowed to own a gun (including felons), and barred anyone under 21 years old from buying a handgun.
- 1976 — The Washington D.C. Council voted 12 to 1 in favor of a bill restricting residents’ access to handguns, the Washington Post reported in 2008. According to the vote, all firearms other than rifles and shotguns had to be kept unloaded and disassembled.
- 1986 — The Armed Career Criminal Act increased penalties for felons in possession of firearms.
- 1989 – California became the first state to pass a law restricting the use of assault rifles, which have a “high rate of fire and fire capacity.”
- 1993 — The Brady Act imposed a waiting period of up to five days when buying a handgun and forced purchasers to undergo a background check. The bill was named for Jim Brady, the press secretary to Ronald Reagan who was seriously injured by John Hinckley Jr..
- 1994 — Congress passed HR 4296, which made it illegal to own or transfer many semiautomatic weapons, which fire more quickly because they reload new rounds automatically.
- 2004 — The 1994 assault weapons ban expired.
- 2005 — The Protection of Lawful Commerce in Arms Act was passed, which saved the gun industry from being held legally responsible if a crime was committed with its weapons.
- 2010 — During President Barack Obama’s first term the federal government lifted restrictions on guns in national parks, The Washington Post reported at the time.
The Ku Klux Klan, Ronald Reagan, and, for most of its history, the NRA all worked to control guns. The Founding Fathers? They required gun ownership—and regulated it. And no group has more fiercely advocated the right to bear loaded weapons in public than the Black Panthers—the true pioneers of the modern pro-gun movement. In the battle over gun rights in America, both sides have distorted history and the law, and there’s no resolution in sight.
No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.
The key phrase, in Bingham’s view, was privileges or immunities of citizens—and those “privileges or immunities,” he said, were “chiefly defined in the first eight amendments to the Constitution.” Jacob Howard of Michigan, the principal sponsor of Bingham’s amendment in the Senate, reminded his colleagues that these amendments guaranteed “the freedom of speech and of the press,” “the right to be exempt from unreasonable searches and seizures,” and “the right to keep and bear arms.” Whether or not the Founding Fathers thought the Second Amendment was primarily about state militias, the men behind the Fourteenth Amendment—America’s most sacred and significant civil-rights law—clearly believed that the right of individuals to have guns for self-defense was an essential element of citizenship. As the Yale law professor Akhil Reed Amar has observed, “Between 1775 and 1866 the poster boy of arms morphed from the Concord minuteman to the Carolina freedman.” The Fourteenth Amendment illustrates a common dynamic in America’s gun culture: extremism stirs a strong reaction. The aggressive Southern effort to disarm the freedmen prompted a constitutional amendment to better protect their rights. A hundred years later, the Black Panthers’ brazen insistence on the right to bear arms led whites, including conservative Republicans, to support new gun control. Then the pendulum swung back. The gun-control laws of the late 1960s, designed to restrict the use of guns by urban black leftist radicals, fueled the rise of the present-day gun-rights movement—one that, in an ironic reversal, is predominantly white, rural, and politically conservative. Today, the NRA is the unquestioned leader in the fight against gun control. Yet the organization didn’t always oppose gun regulation. Founded in 1871 by George Wingate and William Church—the latter a former reporter for a newspaper now known for hostility to gun rights, The New York Times—the group first set out to improve American soldiers’ marksmanship. Wingate and Church had fought for the North in the Civil War and been shocked by the poor shooting skills of city-bred Union soldiers. In the 1920s and ’30s, the NRA was at the forefront of legislative efforts to enact gun control. The organization’s president at the time was Karl T. Frederick, a Princeton- and Harvard-educated lawyer known as “the best shot in America”—a title he earned by winning three gold medals in pistol-shooting at the 1920 Summer Olympic Games. As a special consultant to the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws, Frederick helped draft the Uniform Firearms Act, a model of state-level gun-control legislation. (Since the turn of the century, lawyers and public officials had increasingly sought to standardize the patchwork of state laws. The new measure imposed more order—and, in most cases, far more restrictions.) Frederick’s model law had three basic elements. The first required that no one carry a concealed handgun in public without a permit from the local police. A permit would be granted only to a “suitable” person with a “proper reason for carrying” a firearm. Second, the law required gun dealers to report to law enforcement every sale of a handgun, in essence creating a registry of small arms. Finally, the law imposed a two-day waiting period on handgun sales. The NRA today condemns every one of these provisions as a burdensome and ineffective infringement on the right to bear arms. Frederick, however, said in 1934 that he did “not believe in the general promiscuous toting of guns. I think it should be sharply restricted and only under licenses.” The NRA’s executive vice president at the time, Milton A. Reckord, told a congressional committee that his organization was “absolutely favorable to reasonable legislation.” According to Frederick, the NRA “sponsored” the Uniform Firearms Act and promoted it nationwide. Highlighting the political strength of the NRA even back then, a 1932 Virginia Law Review article reported that laws requiring a license to carry a concealed weapon were already “in effect in practically every jurisdiction.” When Congress was considering the first significant federal gun law of the 20th century—the National Firearms Act of 1934, which imposed a steep tax and registration requirements on “gangster guns” like machine guns and sawed-off shotguns—the NRA endorsed the law. Karl Frederick and the NRA did not blindly support gun control; indeed, they successfully pushed to have similar prohibitive taxes on handguns stripped from the final bill, arguing that people needed such weapons to protect their homes. Yet the organization stood firmly behind what Frederick called “reasonable, sensible, and fair legislation.” One thing conspicuously missing from Frederick’s comments about gun control was the Second Amendment. When asked during his testimony on the National Firearms Act whether the proposed law violated “any constitutional provision,” he responded, “I have not given it any study from that point of view.” In other words, the president of the NRA hadn’t even considered whether the most far-reaching federal gun-control legislation in history conflicted with the Second Amendment. Preserving the ability of law-abiding people to have guns, Frederick would write elsewhere, “lies in an enlightened public sentiment and in intelligent legislative action. It is not to be found in the Constitution.” In the 1960s, the NRA once again supported the push for new federal gun laws. After the assassination of President John F. Kennedy in 1963 by Lee Harvey Oswald, who had bought his gun through a mail-order ad in the NRA’s American Rifleman magazine, Franklin Orth, then the NRA’s executive vice president, testified in favor of banning mail-order rifle sales. “We do not think that any sane American, who calls himself an American, can object to placing into this bill the instrument which killed the president of the United States.” Orth and the NRA didn’t favor stricter proposals, like national gun registration, but when the final version of the Gun Control Act was adopted in 1968, Orth stood behind the legislation. While certain features of the law, he said, “appear unduly restrictive and unjustified in their application to law-abiding citizens, the measure as a whole appears to be one that the sportsmen of America can live with.” A growing group of rank-and-file NRA members disagreed. In an era of rising crime rates, fewer people were buying guns for hunting, and more were buying them for protection. The NRA leadership didn’t fully grasp the importance of this shift. In 1976, Maxwell Rich, the executive vice president, announced that the NRA would sell its building in Washington, D.C., and relocate the headquarters to Colorado Springs, retreating from political lobbying and expanding its outdoor and environmental activities. Rich’s plan sparked outrage among the new breed of staunch, hard-line gun-rights advocates. The dissidents were led by a bald, blue-eyed bulldog of a man named Harlon Carter, who ran the NRA’s recently formed lobbying arm, the Institute for Legislative Action. In May 1977, Carter and his allies staged a coup at the annual membership meeting. Elected the new executive vice president, Carter would transform the NRA into a lobbying powerhouse committed to a more aggressive view of what the Second Amendment promises to citizens. The new NRA was not only responding to the wave of gun-control laws enacted to disarm black radicals; it also shared some of the Panthers’ views about firearms. Both groups valued guns primarily as a means of self-defense. Both thought people had a right to carry guns in public places, where a person was easily victimized, and not just in the privacy of the home. They also shared a profound mistrust of law enforcement. (For years, the NRA has demonized government agents, like those in the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives, the federal agency that enforces gun laws, as “jack-booted government thugs.” Wayne LaPierre, the current executive vice president, warned members in 1995 that anyone who wears a badge has “the government’s go-ahead to harass, intimidate, even murder law-abiding citizens.”) For both the Panthers in 1967 and the new NRA after 1977, law-enforcement officers were too often representatives of an uncaring government bent on disarming ordinary citizens. A sign of the NRA’s new determination to influence electoral politics was the 1980 decision to endorse, for the first time in the organization’s 100 years, a presidential candidate. Their chosen candidate was none other than Ronald Reagan, who more than a decade earlier had endorsed Don Mulford’s law to disarm the Black Panthers—a law that had helped give Reagan’s California one of the strictest gun-control regimes in the nation. Reagan’s views had changed considerably since then, and the NRA evidently had forgiven his previous support of vigorous gun control. In 2008, in a landmark ruling, the U.S. Supreme Court declared that the government cannot ever completely disarm the citizenry. In District of Columbia v. Heller, the Supreme Court clearly held, for the first time, that the Second Amendment guarantees an individual’s right to possess a gun. In an opinion by Justice Antonin Scalia, the Court declared unconstitutional several provisions of the District’s unusually strict gun-control law, including its ban on handguns and its prohibition of the use of long guns for self-defense. Indeed, under D.C.’s law, you could own a shotgun, but you could not use it to defend yourself against a rapist climbing through your bedroom window. Gun-rights groups trumpeted the ruling as the crowning achievement of the modern gun-rights movement and predicted certain victory in their war to end gun control. Their opponents criticized the Court’s opinion as right-wing judicial activism that would call into question most forms of gun control and lead inevitably to more victims of gun violence. So far, at least, neither side’s predictions have come true. The courts have been inundated with lawsuits challenging nearly every type of gun regulation; in the three years since the Supreme Court’s decision, lower courts have issued more than 200 rulings on the constitutionality of gun control. In a disappointment to the gun-rights community, nearly all laws have been upheld. The lower courts consistently point to one paragraph in particular from the Heller decision. Nothing in the opinion, Scalia wrote, should be taken to cast doubt on longstanding prohibitions on the possession of firearms by felons and the mentally ill, or laws forbidding the carrying of firearms in sensitive places such as schools and government buildings, or laws imposing conditions and qualifications on the commercial sale of arms. This paragraph from the pen of Justice Scalia, the foremost proponent of constitutional originalism, was astounding. True, the Founders imposed gun control, but they had no laws resembling Scalia’s list of Second Amendment exceptions. They had no laws banning guns in sensitive places, or laws prohibiting the mentally ill from possessing guns, or laws requiring commercial gun dealers to be licensed. Such restrictions are products of the 20th century. Justice Scalia, in other words, embraced a living Constitution. In this, Heller is a fine reflection of the ironies and contradictions—and the selective use of the past—that run throughout America’s long history with guns. – The Atlantic




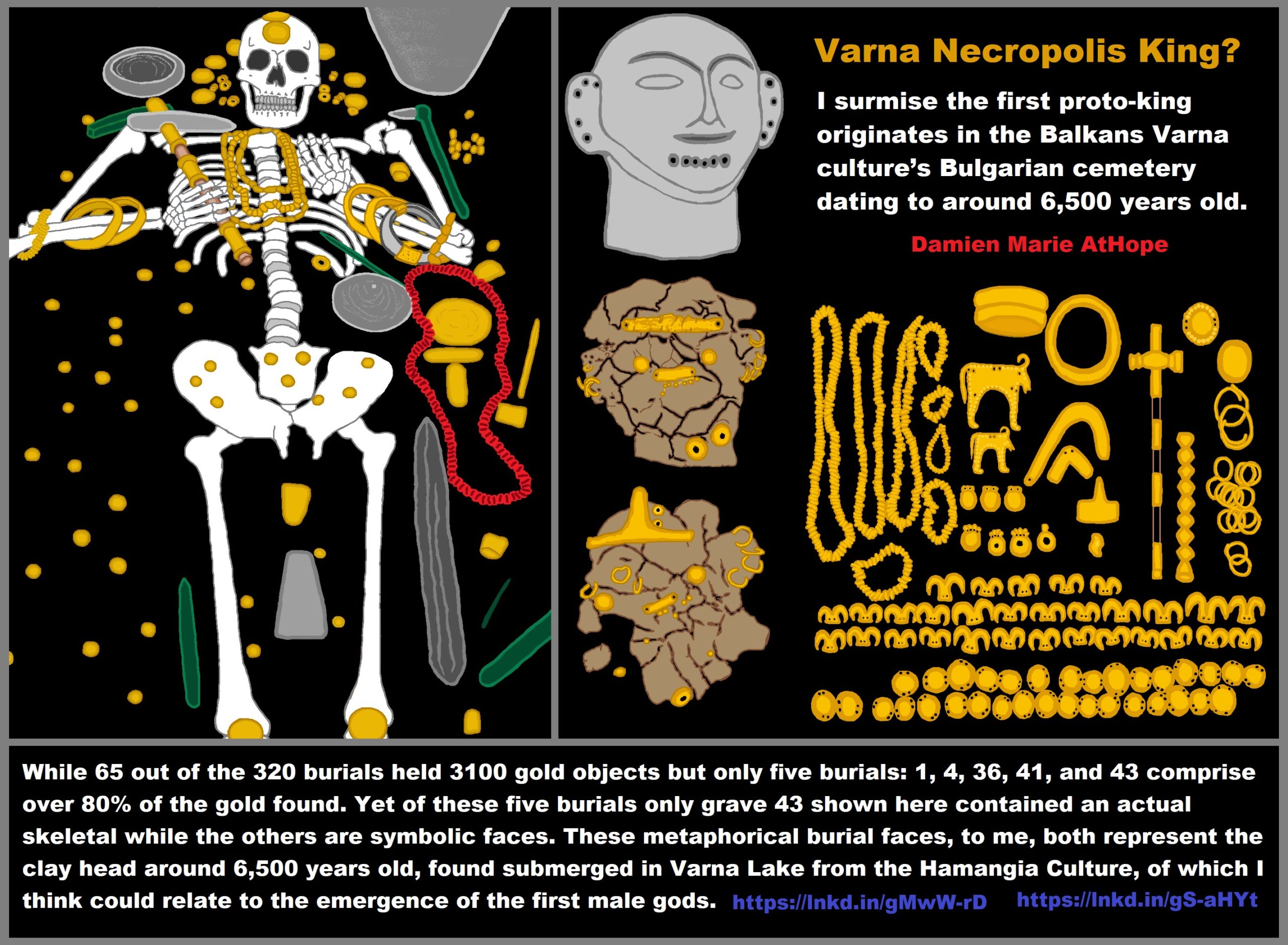
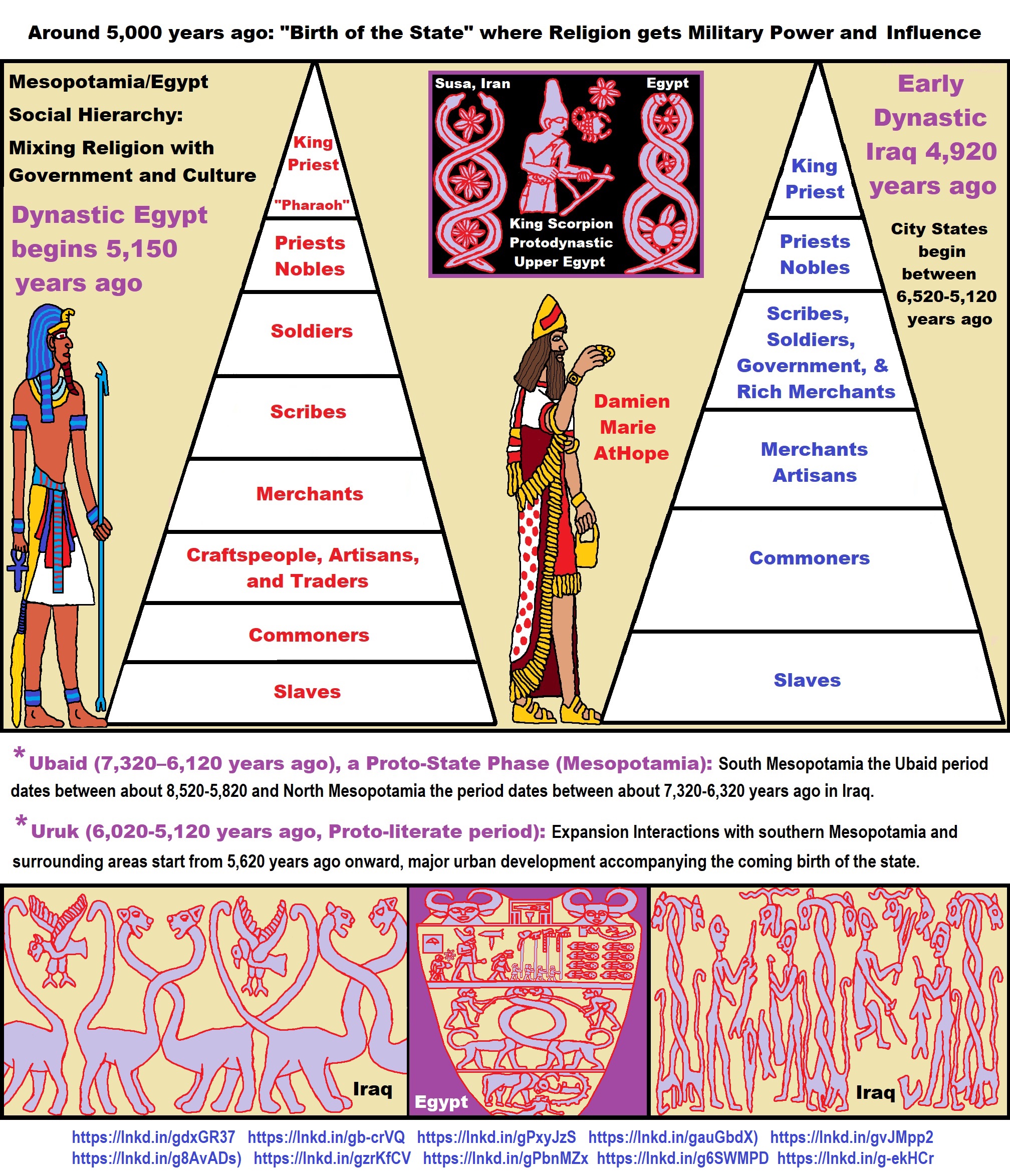
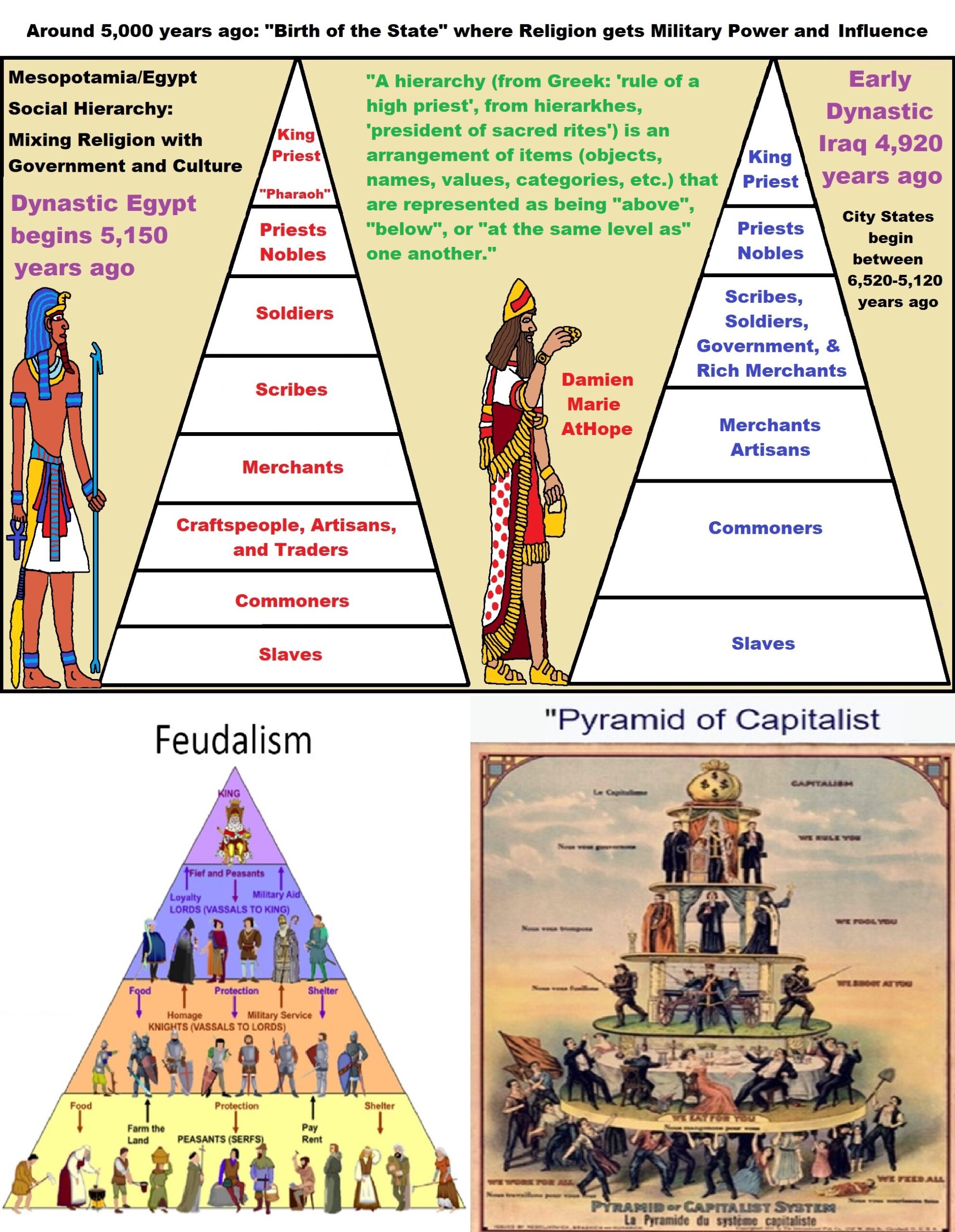
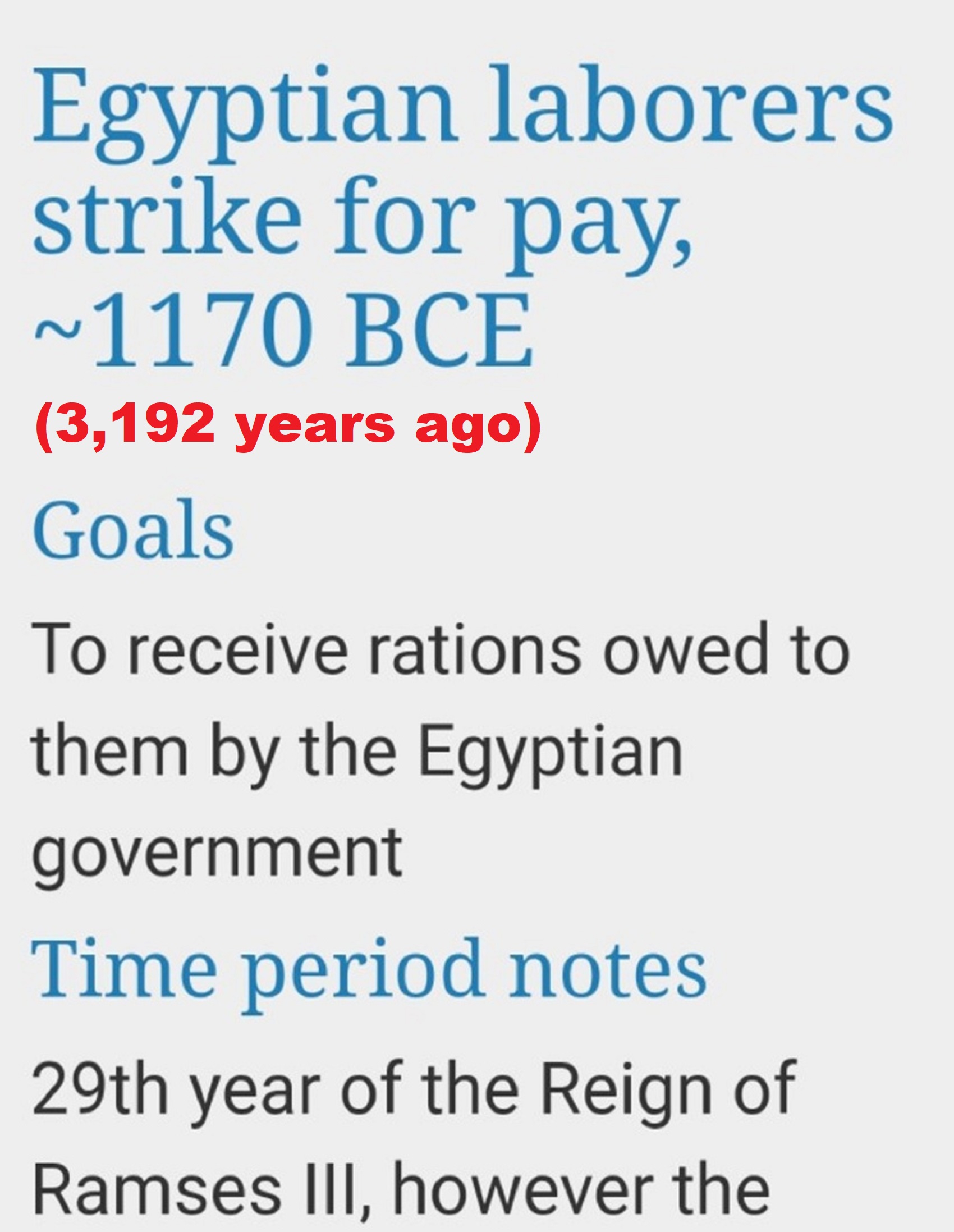
I surmise the first proto-king originates in the Balkans Varna culture’s Bulgarian cemetery dating to around 6,500 years old. Moreover, while 65 out of the 320 burials held 3100 gold objects but only five burials: 1, 4, 36, 41, and 43 comprise over 80% of the gold found. Yet of these five burials only grave 43 shown here contained an actual skeletal while the others are symbolic faces. These metaphorical burial faces, to me, both represent the clay head around 6,500 years old, found submerged in Varna Lake from the Hamangia Culture, of which I think could relate to the emergence of the first male gods.
“The oldest gold treasure in the world, belonging to the Varna culture, was discovered in the Varna Necropolis and dates to 6,600-6,200 years ago. Varna is the third-largest city in Bulgaria and the largest city and seaside resort on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast. Situated strategically in the Gulf of Varna, the city has been a major economic, social and cultural center for almost three millennia. Varna, historically known as Odessos (Ancient Greek: Ὀδησσός), grew from a Thracian seaside settlement to a major seaport on the Black Sea.” ref, ref
“The Varna culture belongs to the later Neolithic of northeastern Bulgaria, is contemporary and closely related with Gumelnița in southern Romania, often considered as local variants. It is characterized by polychrome pottery and rich cemeteries, the most famous of which are Varna Necropolis, the eponymous site, and the Durankulak complex, which comprises the largest prehistoric cemetery in southeastern Europe.” ref
“The culture had sophisticated religious beliefs about afterlife and developed hierarchical status differences: it constitutes the oldest known burial evidence of an elite male. The end of the fifth millennium BC is the time that Marija Gimbutas, founder of the Kurgan hypothesis claims the transition to male dominance began in Europe. The high status male was buried with remarkable amounts of gold, held a war axe or mace and wore a gold penis sheath. The bull-shaped gold platelets perhaps also venerated virility, instinctive force, and warfare. Gimbutas holds that the artifacts were made largely by local craftspeople.” ref
“Burials at Varna have some of the world’s oldest gold jewelry. There are crouched and extended inhumations. Some graves do not contain a skeleton, but grave gifts (cenotaphs). The symbolic (empty) graves are the richest in gold artifacts. Around 3000 gold artifacts were found, with a weight of approximately 6 kilograms. Grave 43 contained more gold than has been found in the entire rest of the world for that epoch. Three symbolic graves contained masks of unfired clay. The weight and the number of gold finds in the Varna cemetery exceeds by several times the combined weight and number of all of the gold artifacts found in all excavated sites of the same millenium, 5000-4000 BC, from all over the world, including Mesopotamia and Egypt”.” ref
“Varna Culture Decline: The discontinuity of the Varna, Karanovo, Vinča and Lengyel cultures in their main territories and the large scale population shifts to the north and northwest are indirect evidence of a catastrophe of such proportions that cannot be explained by possible climatic change, desertification, or epidemics. Direct evidence of the incursion of horse-ridingwarriors is found, not only in single burials of males under barrows, but in the emergence of a whole complex of Indo-European cultural traits.” ref
Copper Age migrations likely motivated to escape war/violence and climate caused problems brought waves of migration from Turkey and Iran as well as ideas or possibly people as well from the Balkans to north Israel as well small parts of Jordan around 6,500–5,800 years ago.
“The Funnel Beaker Culture – “First Farmers of Scandinavia” around 6,200-4,650 years ago marks the arrival of Megalithic structures in Scandinavia from western Europe. At graves, the people sacrificed ceramic vessels that contained food along with amber jewelry and flint-axes. Flint-axes and vessels were also deposed in streams and lakes near the farmlands, and virtually all Sweden’s 10,000 flint axes that have been found from this culture were probably sacrificed in water. Ancient DNA and the peopling of the British Isles – pattern and process of the Neolithic transition 6000 years ago.” ref
The first human-caused climate change, dramatically changed how nature works, such as the way plant and animal communities were structured on Earth around 6,000 years ago.
The first human migrations spread the first plague is believed to have contributed to the plunge of Europe’s settlements around. As well as the close contact between humans and animals and the accumulation of food, likely led to poorer sanitary conditions and an increased risk of pathogen around 6,000-5,000 years ago.
The first passage tomb thought to lead to the afterlife from Ireland, close to when people first began farming in the region that seems to mark a transition towards a time when religion played a greater role in people’s lives 5,800-5,500 years ago.
The first birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status 5,500-5,000 years ago. And more than 5,000 years ago a nomadic group of shepherds rode out of the steppes of eastern Europe to conquer the rest of the continent. The group, today is known as the Yamna or Kurgan/Pit Grave culture, brought with them an innovative new technology, wheeled carts, which enabled them to quickly occupy new lands.
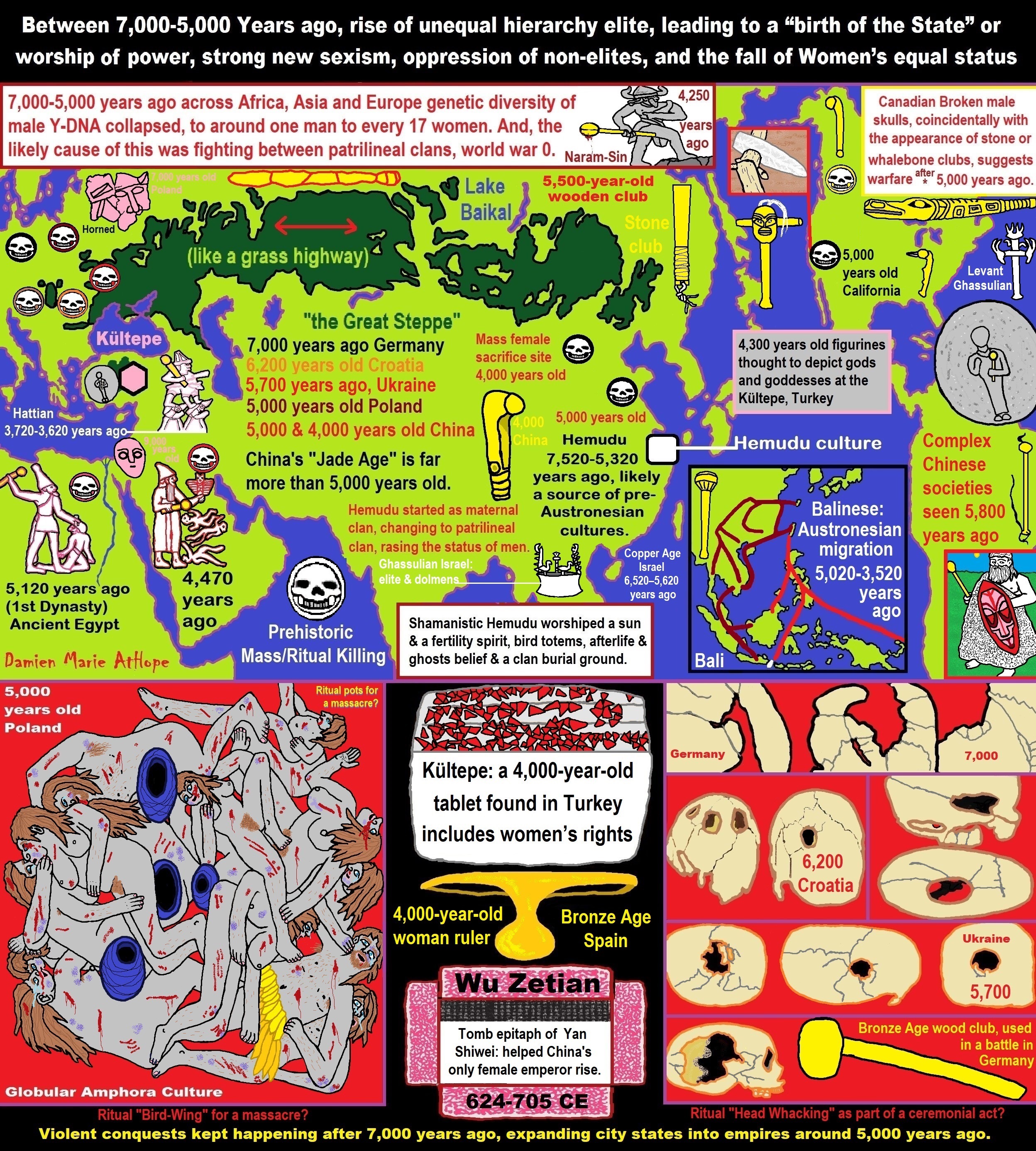
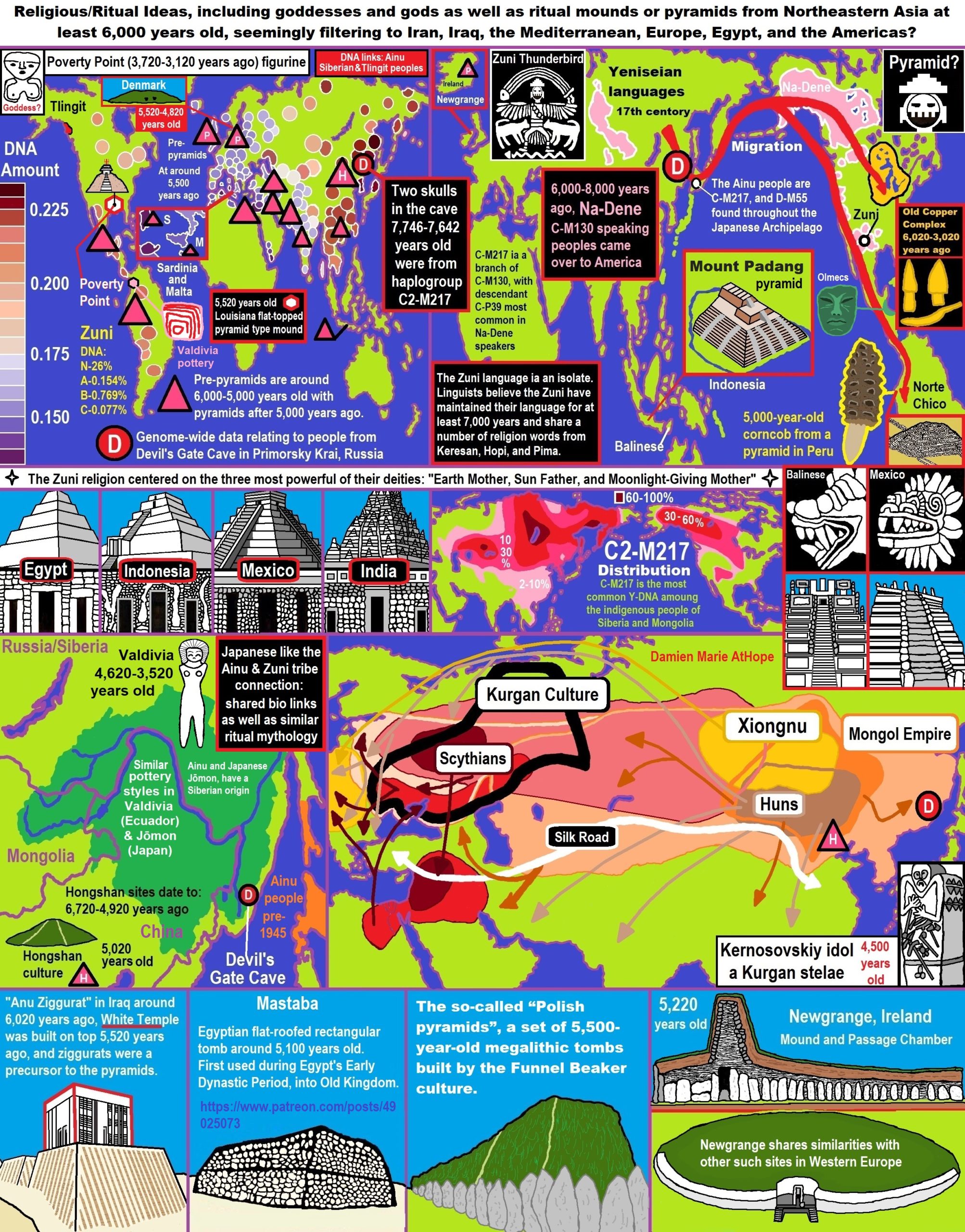
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
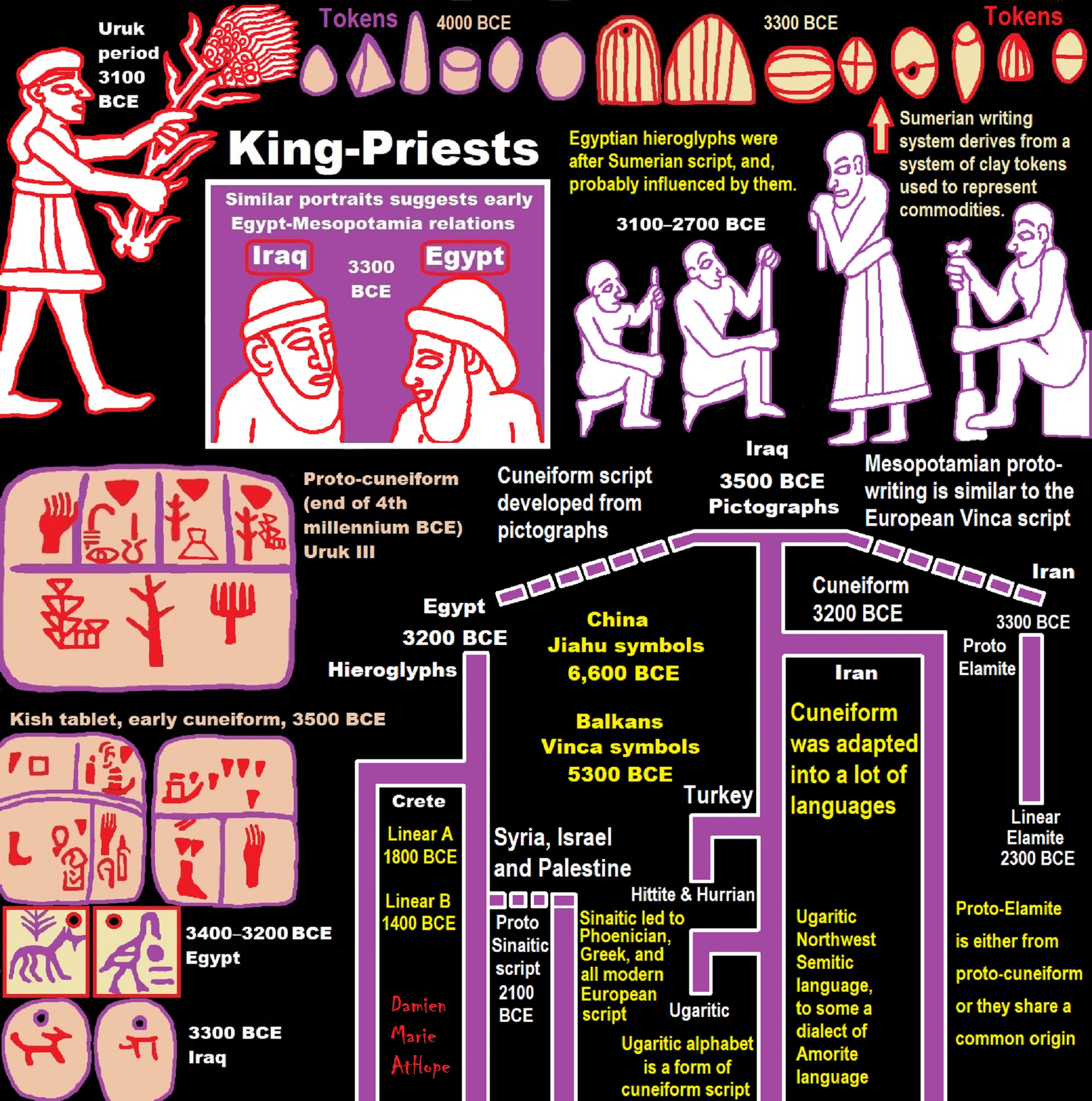
Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
Priest-King (at least by 6,000 to 5,000 they emerge)
“A sacred king, a monarch with prominent religious attributes. A theocrat, a sovereign high priest.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE or 4,022-5,122 years ago; also known as Protoliterate period) is known to have had “Priest-Kings” and this period existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. The late Uruk period (34th to 32nd centuries) saw the gradual emergence of the cuneiform script and corresponds to the Early Bronze Age; it has also been described as the “Protoliterate period.” ref
The cylinder seals of Susa I and Susa II in Iran near the border with southern Iraq had a very rich iconography, uniquely emphasizing scenes of everyday life, although there is also some kind of local potentate which P. Amiet sees as a ‘proto-royal figure,’ preceding the ‘priest-kings’ of Late Uruk. These cylinder seals, as well as bullae and clay tokens, indicate the rise of administration and of accounting techniques at Susa during the second half of the 4th millennium BCE. The Uruk period levels at Susa are called Susa I (c. 4000–3700 BCE) and Susa II (c. 3700–3100 BCE), during which the site became an urban settlement. Susa I saw the beginning of monumental architecture on the site, with the construction of a ‘High Terrace’, which was increased during Susa II to measure roughly 60 x 45 metres.” ref
“Mesopotamian king as Master of Animals on the Gebel el-Arak Knife, dated circa 3300-3200 BCE, Abydos, Egypt. This work of art suggests early Egypt-Mesopotamia relations, showing the influence of Mesopotamia on Egypt at an early date, and the state of Mesopotamian royal iconography during the Uruk period. A similar portrait of a probable Uruk King-Priest with a brimmed round hat and large beard, excavated in Uruk and dated to 3300 BCE.” ref
“The Uruk period provides the earliest signs of the existence of states in the Near East. The monumental architecture is more imposing than that of the preceding period; ‘Temple D’ of Eanna covers around 4600 m2—a substantial increase compared to the largest known temple of the Ubayd period, level VI of Eridu, which had an area of only 280 m2—and the Eanna complex’s other buildings cover a further 1000 m2, while the Ubayd temple of Eridu was a stand-alone structure. The change in size reflects a step-change in the ability of central authorities to mobilize human and material resources. Tombs also show a growing differentiation of wealth and thus an increasingly powerful elite, who sought to distinguish themselves from the rest of the population by obtaining prestige goods, through trade if possible, and by employing increasingly specialized artisans. The idea that the Uruk period saw the appearance of a true state, simultaneously with the appearance of the first cities (following Gordon Childe), is generally accepted in scholarship but has been criticized by some scholars, notably J.D. Forest who prefers to see the Empire of Akkad in the 24th century BCE as the first true state and considers Late Uruk to have known only “city-states” (which are not complete states in his view). Regardless, the institution of state-like political structures is concomitant with several other phenomena of the Uruk period.” ref
“What kind of political organization existed in the Uruk period is debated. No evidence supports the idea that this period saw the development of a kind of ‘proto-empire’ centered on Uruk, as has been proposed by Algaze and others. It is probably best to understand an organization in ‘city-states’ like those that existed in the 3rd millennium BCE. This seems to be corroborated by the existence of ‘civic seals’ in the Jemdet Nasr period, which bear symbols of the Sumerian cities of Uruk, Ur, Larsa, etc. The fact that these symbols appeared together might indicate a kind of league or confederation uniting the cities of southern Mesopotamia, perhaps for religious purposes, perhaps under the authority of one of them (Uruk?). It is clear that there were major changes in the political organization of society in this period. The nature of the powerholders is not easy to determine because they cannot be identified in the written sources and the archaeological evidence is not very informative: no palaces or other buildings for the exercise of power have been identified for sure and no monumental tomb for a ruler has been found either. Images on steles and cylinder-seals are a little more evocative. An important figure who clearly holds some kind of authority has long been noted: a bearded man with a headband who is usually depicted wearing a bell-shaped skirt or as ritually naked.” ref
“He is often represented as a warrior fighting human enemies or wild animals, e.g. in the ‘Stele of the Hunt’ found at Uruk, in which he defeats lions with his bow. He is also found in victory scenes accompanied by prisoners or structures. He also is shown leading cult activities, as on a vase from Uruk of the Jemdet Nasr period which shows him leading a procession towards a goddess, who is almost certainly Inanna. In other cases, he is shown feeding animals, which suggests the idea of the king as a shepherd, who gathers his people together, protects them, and looks after their needs, ensuring the prosperity of the kingdom. These motifs match the functions of the subsequent Sumerian kings: war-leader, chief priest, and builder. Scholars have proposed that this figure should be called the ‘Priest-King’. This ruler may be the person designated in Uruk III tablets by the title of en. He could represent a power of a monarchic type, like that would subsequently exist in Mesopotamia.” ref
“It is perhaps at the end of the Uruk period that the first signs of anthropomorphism of divinities that became the norm in subsequent periods emerge. The Uruk vase undoubtedly represents the goddess Inanna in human form. Additionally, real and fantastic animals were always present on seals, often as the principal subject of the scene. A very widespread motif is that of the ‘cycle’ representing a series of animals in a continuous line, exploiting the new possibilities offered by the cylinder seal. Sculpture followed the style and themes of seals. Small statues were made representing gods or ‘priest-kings.’ The artists of Uruk created many remarkable works, represented above all by the works in the Sammelfund (hoard) of level III of Eanna (Jemdet Nasr period). Some bas-reliefs are found on steles like the ‘Hunt stele’ or the great alabaster vase representing a scene of a man giving an offering to a goddess, undoubtedly Inanna. These works also foreground an authority figure who carries out military exploits and manages religious cults.” ref
The king as Priest and Seer
“Religious duties quite often are connected with the office of chieftain, who is also priest or seer and rainmaker—all in one. Correspondingly, in nontribal societies, cultic functions belong to the office of the king. In the 3rd dynasty of Uruk, Lugalzaggisi is described as king of the country, priest of the god Anu (the god of the heavens), and prophet of Nisaba (goddess of grasses and writing). When a division of functions evolved, the intrinsically royal priestly and other cultic functions were transferred to priests, seers, and other servants of the cult; the old concept of the king as priest, however, survived in some fashion for thousands of years. In Mesopotamia, the king was viewed as the cultic mediator between god and man. As head of all of the priests of the country, he had important cultic functions at the New Year’s festival. In critical situations, the king might issue an oracle of blessing; through him the land would be promised salvation, which was often accompanied by the words, “Fear not!” ref
“The Egyptian king was the chief priest of the land and the superior of all priests and other cult functionaries. In many images he is portrayed as presiding over the great festivals and bringing offerings to the gods. Later priests carried out their functions as his representative. The Persian king performed the sacrifice at the horse offering and was also the “guardian of the fire.” In all questions of religion he was the highest authority; he was also the most cultivated of the magicians. The king in Ugarit (in Canaan) also carried out priestly functions and as prophet was the receiver of revelations. Like other ancient Middle Eastern monarchs, the Hittite king was the chief priest. The relationship between sacred kingship and priestly cultic functions has extended over widespread geographic areas and historical eras: East Asia, China, Japan, India, Europe (among the Germanic and Scandinavian kings), Africa (in the great empires), and Madagascar. Sometimes the division of functions brought about a transfer of the royal title to those who carried out cultic functions.” ref
“In Africa from the earliest times, there was a type of king who was called lord of the earth; he originally combined political and cultic functions but, with changing times, retained only the cultic ones. The strict separation of the priestly office from that of the king, as in India, where king and priest belong to different castes—Kshatriya and Brahman, respectively—is an unusual exception, however. The king may be the recipient of a direct revelation of the will of a god. Thus, in Egypt, the pharaoh received a divine oracle through dreams in the temple (a practice known as incubation). In Mesopotamia the duty of the king to ascertain the will of the gods was more strongly emphasized; a directive of the gods could result from omens, dreams, or reading the entrails of offerings. All major undertakings of the king were dependent on directives of the god, who was to be consulted in advance. A direct divine revelation to a king is related in the Hebrew Bible in I Kings, chapter 3, which tells of a dream of the 10th-century-BC Israelite Solomon in which he received the promise of the gift of wisdom. Likewise in Genesis, chapter 41, Yahweh, god of the Hebrews, gives the pharaoh a directive in a dream.” ref
“Although a pharaonic cult occasionally existed in Egypt, the ruler cult differs entirely from sacred kingship because the former came into being from political impulses. The ruler cult, generally developed in a country or empire with many peoples and many religions, was one of the ruler’s means of power. Syncretism, the fusing of various beliefs and practices, often succeeded in bringing together completely different religious and nonreligious motives. Alexander the Great (who established an empire of many peoples and religions), for example, revealed a conscious effort at continuity with the Egyptian kingdom, inasmuch as the oracle of the Egyptian god Amon at Sīwah designated him as the son of Amon and thus the successor of the pharaohs. Among the diadochoi (successors to Alexander) of the first generation, the ruler cult remained limited, but, under Ptolemy II Philadelphus of Egypt (reigned 285–246 BCE), it became an established institution that was connected with the deified Alexander.” ref “When the ruler cult was carried over to Rome, the emperor Augustus (reigned 27 BCE–CE 14) allowed it to be practiced only in the east in connection with the worship of the goddess Roma—though he allowed it to be pursued with fewer restrictions in the newly conquered western provinces; the adaptation of honouring the divine Caesar (or emperor of Rome) soon became, however, an important expression of the unity of the empire. Serious resistance to the imperial cult was encountered only among the two radical monotheistic religions: Judaism (e.g., against Antiochus IV Epiphanes of Syria in the mid-2nd century BCE) and Christianity. The Hellenistic and Roman ruler cults never generated a strong religious movement. The sacrifices brought to the king (emperor) date to the ancient custom of bringing tribute to the king (or chief). From this practice, the custom of bringing offerings to the deceased king developed.” refThe king as the Center of Ruler Cults
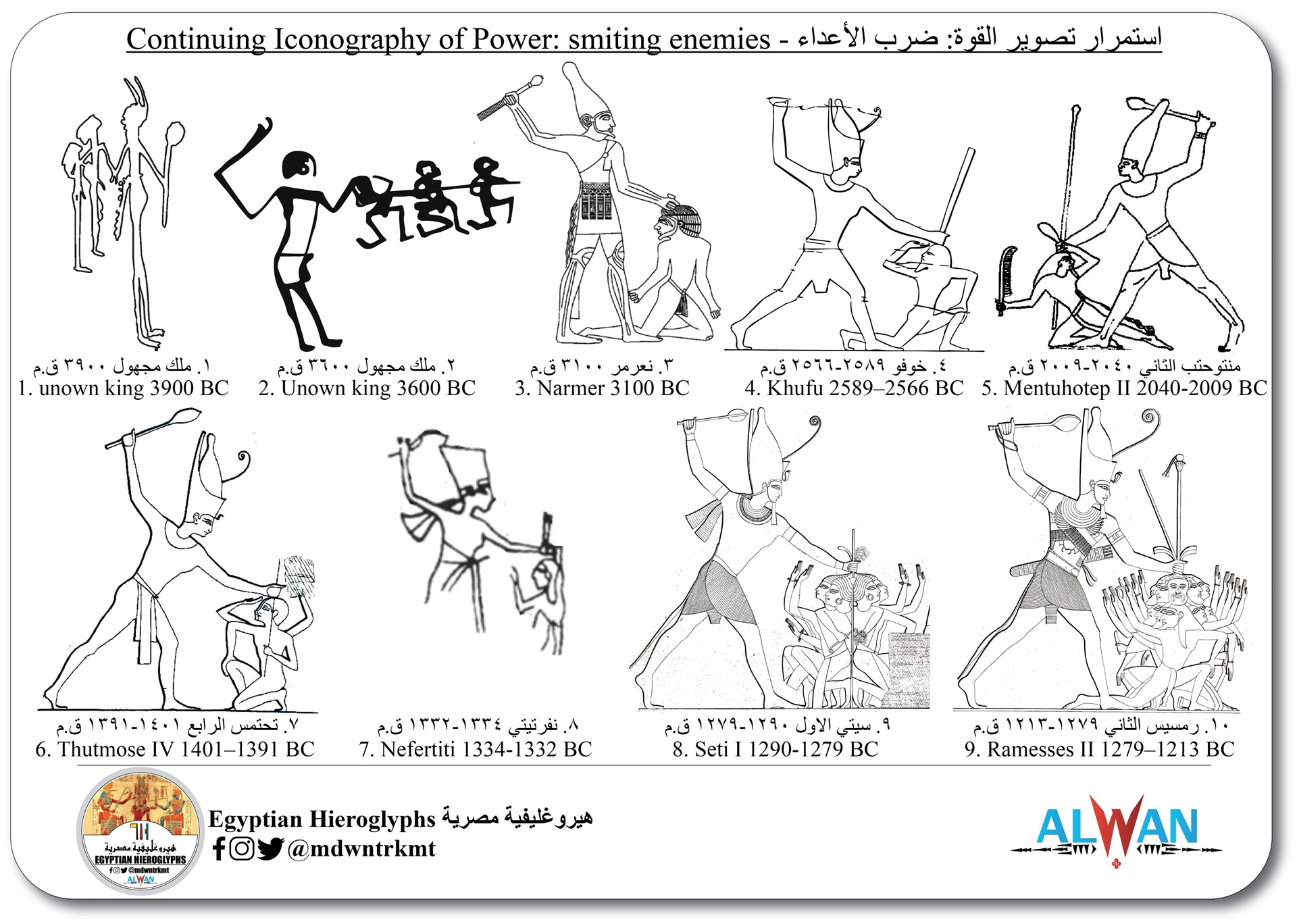
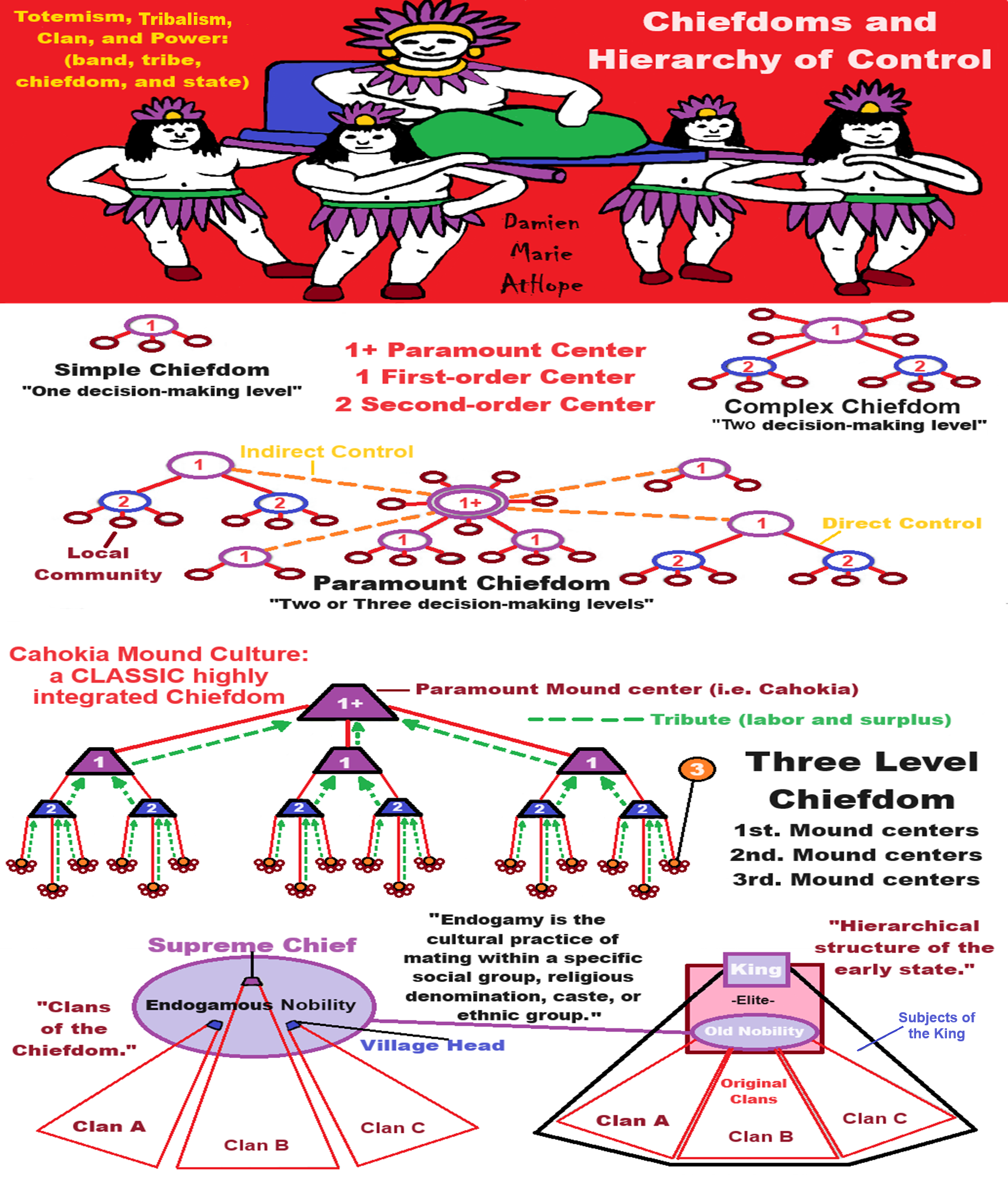
It is hierarchy oppression from the earliest proto-kings (powerful chieftains?).
Continuing Iconography of Power: smiting enemies

(List of matrilineal or matrilocal societies) “Matrilineal means kinship is passed down through the maternal line, the mother’s lineage, which can involve the inheritance of property and titles.” ref, ref
Chiefdoms are powers that are often believed to mobilize due to surplus labor, food, and prestige items. However, I see it as a cultural package that started with hunter-gather/fisher-foragers in west Siberia with the switch from a Matrilineal society to a patrilineal society from 8,000 to 7,000 years ago and from there spread this new war and powerful male thinking, but some Matrilineal societies changed to the war and power modal as well but kept being female-centered. I often talk as if they were completely wiped out by male clans, but not all were, and some became as horrible as male clans. One such major transfer of such ideas, which I think relates to the Tlingit (Matrilineal Na-Dene language connected to patrilineal Yeniseian languages such as the Ket People of Siberia with mostly to Y-DNA haplogroup Q-M242 linking Tlingit and South America) of the Pacific Northwest Coast of North America, were a Slaveholding, matrilineal clan chiefdom. And like 90% of South America shares their DNA and also, to me, likely somewhat influenced all Mesoamerican cultures and Moundbuilding cultures that had “Big Men/Big Women” pre/proto-chiefdoms, chiefdoms, and then clan monarchs: Kings/Empresses.






Hopewell Mound Builder culture (200 BCE–500 CE)
“The Hopewell inherited from their Adena Mound Building culture (500 BCE–100 CE) forebears an incipient social stratification.” ref
“These cultures likely accorded certain families a special place of privilege. Some scholars suggest that these societies were marked by the emergence of “big-men/women”, leaders whose influence depended on their skill at persuasion in important matters such as trade and religion. They also perhaps augmented their influence by cultivating reciprocal obligations with other important community members. The emergence of “big-men/women” was a step toward the development of these societies into highly structured and stratified chiefdoms.” ref
On the Significance of Matrilineal Chiefship
” UNDER the term chiefship as here used we include only that civil office in which the incumbent is the head of a family and has under his rule a band of families, a tribe, or a nation. Such chiefs are, for example, the band chiefs of the north and east Algonkian, the chiefs of the households of the Nootka, of the households or matrilineal “families” of the Iroquois; the tribal head chiefs of the Nootka, Coast, and Delt Salish, Tsimshian, etc., and the kings of the Natchez, man African states, modern European nations, etc. The first essential fact we have to note about this office is that universally it is the prerogative of an adult male. Occasionally, it is held by a child, the functions of pending the child chief’s maturity, being exercise warmer” or regent. Occasionally also, which is more the office is held by a female. A child holds office those peoples with whom the chiefship has become hereditary, and the heir presumptive may not be A woman holds office only where the office is strictly a given family, and when no eligible male heir is near enough in blood to be considered acceptable in a closely related female who can be expected soon son and so perpetuate the chiefship through the descent.” ref
“An example of the type of situation which gave rise to the installation of queens even among so-called “primitive” folk may
well be noted at length at this point, in part because of certain remarkable features which will interest us more in a moment. In the year 1660 the Piscottoways (Ganawagas, Conoys) of Maryland applied to the governor of the province for ratification of their choice of an “emperor,” and to his inquiry as to their customs relative to succession they replied that the office went, on the death of an incumbent, to his brother, “and for want of such, to a sister’s son,” and stated that in such wise the office had descended from their first emperor-who had been some one come to rule over them from the eastern Shore of Maryland-for thirteen generations, without interruption, until the time of the emperor Kittamaqund who preceded the emperor just deceased.” ref
“Kittamaqund had died without having brother or sister, (and, presum without a sister’s son) to succeed him, and took it upon him, therefore, to appoint his daughter to be “queen.” The perejected this appointment, however, as contrary to tribal custom and chose as emperor, Weghucasso, who was descended “from of the brothers, which one, they knew not, of the first emperor “And Weghucasso at his death appointed to be king some descendant of one of the first kings.” This appointee was Jan Wizous, which in their language signifies a true king [they] would not suffer us to call him Towzin, which is the they give to the sons of their kings who by their custom ar to succeed in rule, but his brothers, or the sons of his sisters.” To avoid possible misconceptions it is perhaps at this point to consider a practice prevailing among
Kwakiutl of British Columbia.” ref
“For them Boas patrilineal inheritance is the rule for certain circumstances the annual or winter ceremonies of the secret societies, such as that of master-of-ceremonies, those of caretaker of the drum, of the batons, of the eagle-down, etc. Civil privileges also are sometimes so inherited but much the larger number of these are given by a father to his son-in-law expressly in trust for the donor’s grandson. Hill-Tout has noted for the not-distant Siciatl that the chiefship, a civil “privilege” on the Northwest Coast, maybe so inherited, or bestowed; regularly it goes to the eldest son of a chief but where there is no son the son-in-law will succeed,5 as a consequence of which in the third generation the reigning chief will be the grandson of the chief whose son-in-law succeeded, the chiefship, thereby descending in the direct line of succession just as if the daughter herself had actually succeeded to the office and exercised its functions. It has been suggested that the practice of the southern Kwakiutl indicates an adaptation of a former patrilineal inheritance to concepts diffused from the tribes farther up the coast with whom all privileges and property including the privilege of chiefship descend matrilineally.” ref
“However, it has also been pointed out that the kinship terms of the Kwakiutl correspond to a loose organization in which relationship is reckoned bilaterally, as is the case with the closely related Nootka. For the Nootka Sapir has shown that privileges are inherited through both the male and female lines, with a preference for the male line, the inheritance of privileges being in a measure conditioned by the fact that privileges are not only personally owned but also definitely associated with the local group among whom they originate. More data, especially on the inheritance of the particular of chiefship, is desirable, but it seems evident that the Kwa represent simply a people reckoning bilaterally, but who, like peoples whose developing institution of chiefship has not be affected by the influence of a matrilineal kinship reckoning, the develop a patrilineal inheritance of office.” ref
“Rather than an indication of influences from the northern tribes and an addition to the idea of a matrilineal reckoning, the peculiar Kwa inheritance practice we have noted is simply an indication of Kwakiutl concern that privileges, in general, should descend patrilineally. And, in case a chief only has daughters, the Kw, like the Society, with the son-in-law arrangement, are able to the chiefship in the direct line of descent and, at the same, avoid having a woman chief or queen. We may now confine ourselves to the actual chiefship. Typically, though not always, it is cor the mother-sib. Despite the fact that with many whom the sib, and, specifically, the mother-sib, is a institution-such as the Iroquois, the Haida, etc.-this does not include the concept of even a fictitious kin its members, it yet remains obvious that sib member
patrilineally or matrilineally reckoned, is acquired the blood relationship to a father or a mother member obvious, and is perhaps superfluous to observe, also, whether transmitted matrilineally or patrilineally inherited by virtue of actual blood relationship cumbent of the office.” ref
“But a matrilineal reckoning for an which is universally the prerogative of a male and his male cessors appears as a noteworthy phenomenon, particularly of the fact that different types of inheritance reckonings for ent prerogatives, privileges, things, relationships, etc. contained within the same cultural considered in connection with the processes by which chiefship undoubtedly evolved. Definitely, instituted chiefship is itself an office which cannot be placed too far back in social evolution; and the concept and practice of the inheritance of the office exclusively within some one family of the group of families concerned must be placed reltively later, in that obviously intermediary developments remain on record as the existing practice of many peoples-though very definite records of this gradual evolution for any one people are hardly available. This evolution of the concept of ban and higher chiefships as hereditary within a given family and even as with many peoples, through an inflexible rule of picture took place of course concurrently with the of concepts of the inheritance of other things such ship, real, and personal property, songs, names, other office, etc.” ref
The Real Mound Builders of North America: matrilineal chiefdom
Mississippian Chiefdoms
“Although groups speaking several different languages produced Mississippian societies, they shared many cultural traits. The most spectacular features of these societies were the temple- and burial-mound centers they constructed. The largest such site is at Cahokia in what is now Collinsville, Illinois, just east of St. Louis, Missouri; the village area extended for six miles along the Illinois River, contained eighty-five temple and burial mounds, and sustained a population perhaps as high as seventy-five thousand persons. Being master farmers allowed the Mississippians to develop such large societies, although most chiefdoms were much smaller than Cahokia. All Mississippian sites utilized maize or corn as a primary staple and supplemented it with other plants and meats.” ref
“Chiefdoms. Mississippian societies are called chiefdoms because they were governed by small groups of elites or even by a single individual, called a paramount chief. Commoners and outlying satellite villages paid tributes of corn, deer meat, animal skins, and prestige items to the principal town. In some cases new towns joined a chiefdom by military conquest. The labor of commoners built the mounds and suggests that elites held the power to assemble large bodies of people to do their bidding. Leadership passed through hereditary lines in at least some of these chiefdoms, but high status was most likely based upon command of spiritual forces. The general population recognized the large amounts of power that leaders manipulated and honored them with positions of prestige. Matrilineal kinship characterized Mississippian culture, and female paramount chiefs greeted Spanish expeditions, such as the “Lady of Cofitachequi” from the chiefdom of Cofitachequi in present-day South Carolina who welcomed Hernando de Soto in the 1540s.” ref
“Decline. Mississippian chiefdoms still existed in the mid 1500s when de Soto and others traveled through the Southeast, but just a century later, the mound sites were abandoned. Because of this timing, scholars looked to the de Soto campaign as the cause of this phenomenon. It is probable that some of de Soto’s men, or maybe the horses and pigs that accompanied them, carried diseases to which the Indians had no immunity. Pandemics may have wiped the Mississippians from the map, replacing them with refugee groups of survivors who banded together for protection but lacked the numbers to maintain the mounds. Many Mississippian sites became vacant before European contact, however, which suggests that local reasons contributed to abandonment. Perhaps Mississippians overused their resources, depleting the soil for corn and cutting down trees necessary for their buildings and fires. Possibly, climatic changes resulted in drought or a shorter growing season, thus reducing the food supply. Political conflict and war between chiefdoms could have weakened some to the point of being unsustainable. Likely, all of the above factors contributed to the abandonment of the mound sites. The Choctaws, Creeks, Chickasaws, Cherokees, and Seminoles descended from the Mississippian peoples and held many traits in common with their ancestors.” ref
“Although the first people entered what is now the Mississippi about 12,000 years ago, the earliest major phase of earthen mound construction in this area did not begin until some 2100 years ago. Mounds continued to be built sporadically for another 1800 years, or until around 1700 CE. Archeologists, the scientist who study the evidence of past human lifeways, classify moundbuilding Indians of the Southeast into three major chronological/cultural divisions: the Archaic, the Woodland, and the Mississippian traditions. To date, no mounds of the Archaic period (7000 to 1000 BCE) have been positively identified in Mississippi; the mounds described herein all date to the last two cultural periods.” ref
“The Middle Woodland period (100 BCE to 200 CE) was the first era of widespread mound construction in Mississippi. Middle Woodland peoples were primarily hunters and gatherers who occupied semipermanent or permanent settlements. Some mounds of this period were built to bury important members of local tribal groups. These burial mounds were rounded, dome-shaped structures that generally range from about three to 18 feet high, with diameters from 50 to 100 feet. Distinctive artifacts obtained through long-distance trade were sometimes placed with those buried in the mounds. The construction of burial mounds declined after the Middle Woodland, and only a few were built during the Late Woodland period (circa 400 to 1000 CE). Woodland burial mounds can be visited at the Boyd, Bynum, and Pharr sites and at Chewalla Lake in Holy Springs National Forest. (The Chewalla Mound is not included in this itinerary because it is not listed in the National Register of Historic Places).” ref
“The Mississippian period (1000 to 1700 CE) saw a resurgence of mound building across much of the southeastern United States. Most Mississippian mounds are rectangular, flat-topped earthen platforms upon which temples or residences of chiefs were erected. These buildings were constructed of wooden posts covered with mud plaster and had thatched roofs. Mississippian platform mounds range in height from eight to almost 60 feet and are from 60 to as much as 770 feet in width at the base. Mississippian period mounds can be seen at the Winterville, Jaketown, Pocahontas, Emerald, Grand Village, Owl Creek, and Bear Creek sites.” ref
“Mississippian period mound sites mark centers of social and political authority. They are indicators of a way of life more complex than that of the Woodland and earlier periods. In contrast to the relatively simple, egalitarian tribal organization of most societies of the Woodland period, regional Mississippian populations were typically organized into chiefdoms–territorial groups with hereditary, elite leadership classes. Across the Southeast, the chiefdom system of political organization arose as a means of managing increased social complexity caused by steady population growth. This population growth was sustained by agriculture (corn, beans, and squash)–a revolutionary new means of subsistence that became an economic mainstay during the Mississippian period.” ref
“Mound construction was once again in decline by the time the first Europeans came to this region in the 1500s. Shortly thereafter, epidemic diseases introduced by early European explorers decimated native populations across the Southeast, causing catastrophic societal disruption. As a result, by the time sustained contact with European colonists began about 1700 CE, the long tradition of mound building had nearly ended.” ref
Ancient Colombian chiefdoms
“Chiefdoms in Central America were small groups who developed unique art forms in order to distinguish themselves and compete with one another. c. 500 B.C.E.–1600 C.E.” ref
Tribe versus Chiefdom in Lower Central America
“Abstract: It has commonly been argued that chiefdoms were the dominant form of prehispanic political organization in Lower Central America. Reexamination of the data base, however, reveals that tribal forms of organization were also present in Lower Central America at the time of Spanish contact and before. The salient characteristics of both tribes and chiefdoms are discussed, and criteria for identifying tribes and chiefdoms in the archaeological record are outlined. Data from the Central Provinces of Panama and the Gulf of Nicoya are then examined in light of these criteria. We argue that while a chiefdom form of organization prevailed in Panama, the Gulf of Nicoya was occupied by tribal groups immediately prior to contact with the Spanish.” ref
“The customs and social systems of South American peoples are closely and naturally related to the environments in which they live. These environmental relationships are mediated by the systems of technology that the people use to exploit their resources. Four basic types of social and cultural organization of South American peoples emerge from the archaeological and historical records: (1) central Andean irrigation civilizations, (2) chiefdoms of the northern Andes and the circum-Caribbean, (3) tropical-forest farming villages, and (4) nomadic hunters and gatherers. Each type developed in its own fashion during thousands of years, and since the 16th century each has made a distinctive adjustment to the impact of European civilization. The original migrants to the New World had no knowledge of the domestication of plants or animals, with the exception of dogs, which were used in hunting. Recent discoveries in Mexico indicate that agriculture was independently discovered in the New World in roughly the same era that it was established in the Middle East (about 7000–8000 BCE) and that New World civilizations were built on an indigenous agricultural base.” ref
“The evidence on early hunting and gathering peoples in Peru is still sparse. It is not yet possible to reconstruct social patterns, since most of the remains consist only of shellfish middens and small, widely scattered campsites along the coast. It was a period of thousands of years’ duration, however, toward the end of which some knowledge of plant domestication reached the Peruvian coast. The next major era is set off by incipient agriculture and also is characterized by the remains of small, hamlet-type communities along the Pacific Ocean near river mouths, where the alluvial soil was able to support crops. Technology remained simple, irrigation was not practiced, and population remained small.” ref
“After the passage of 1,000 years or so, marked developments appear in the archaeological record. These include many new crops, irrigation ditches that extended the arable area and controlled the supply of water, more and larger communities that attest to a growing population, and important temple mounds that formed the symbolic centres of theocratic government controlled by a priestly class. The formative era saw the development of the basic technologies and life-styles that were to become elaborated into even more complex cultural forms and state institutions. The emergence of city-states and empires in the central Andes is the result of local cultural-ecological adjustments of this sort, based on an irrigation agriculture that supported growing populations and necessitated controls in the hands of priests and nobles, with a warrior class subservient to the state.” ref
Subsistence Economy and Chiefdom Emergence in the Muisca Area
“ABSTRACT: Muisca societies located in the central mountains of Colombia impressed early Spanish arrivals in the sixteenth century with the power and level of respect commanded by their chiefs and the quality and variety of the crafts their artisans produced, sometimes from raw materials obtained from other regions. Early Spanish accounts especially emphasize the “advanced” economic development of Muisca societies, with what seemed to European eyes especially well-organized and flourishing trade and dense populations that were well-provisioned despite the fairly cold, wet, high-elevation zone they inhabited. As several regional chiefdoms in northern South America have been studied archaeologically, it has often turned out that their subsistence and craft economies do not involve very high degrees of trade, tribute, or household interdependence. This emerging pattern contrasts with sixteenth-century descriptions of the Muisca.” ref
“The archaeological evidence of Muisca societies has provided at best only incomplete confirmation of the descriptions in historical sources, particularly in regard to the development of local, regional, and supra-regional patterns of economic interdependence and the importance of such an economy to the emergence of chiefly power. One aspect of economic interdependence specifically discussed in the historical sources, however, has been subject to very little archaeological investigation. This is the agricultural exploitation of warmer low-elevation zones located quite close to some of the principal Muisca chiefly centers. In these areas higher temperatures led to greater productivity as well as protection from the frosts that were a constant risk to agriculture in the Muisca heartland. There are detailed sixteenth-century historical accounts of the importance of these resources for sustaining the very high population densities of the Muisca heartland, high densities fully attested to by both historical and archaeological information.” ref
“Under the supervision of Dr. Robert D. Drennan, Pedro Argüello will carry out a systematic regional survey of some 100 sq km in the Tena region on the slopes leading down from the western edge of the Muisca heartland toward the valley of the Magdalena River. The Tena region, which ranges from 2200 m above sea level down to about 700 m, is specifically mentioned in sixteenth-century documents as a major source of agricultural produce for the Bogotá chiefdom. If its agricultural resources were increasingly intensively exploited as Muisca chiefdoms emerged and developed and population levels in the high-elevation Muisca heartland grew, this will be reflected in changing patterns of distribution of human occupation in the Tena region. Such a result would provide stronger support for the historical accounts of one of the economic foundations of Muisca chiefly power than has been forthcoming from archaeological investigations of other aspects of Muisca economy. It would help to explain the relatively late but extremely rapid development of the Muisca chiefdoms and to position these societies properly in comparative analysis of the pathways toward the consolidation of political power in general.” ref
“The societies of the Muisca area in the eastern highlands of Colombia were described by early Spanish conquerors as among the richest and most highly developed societies they encountered in northern South America. Chiefs were rich and powerful, and controlled regional populations engaged in well-organized intensive agricultural production to sustain quite high population densities. Archaeological evidence tends to agree that these societies developed vigorously during the last few hundred years before the sixteenth-century arrival of the Spanish, but evidence available to date provides conflicting views about their earlier trajectories of development. In several ways archaeological evidence has failed to convincingly substantiate sixteenth-century written accounts. One aspect of Muisca demography and agricultural production is described in these accounts in particular detail. It involves the expansion by Muisca populations from the high-elevation Bogotá Savannah down the slopes toward the Magdalena River at the expense of Panche people who had previously occupied the zone. The driving force behind this expansion was said to be the need to increase and intensify agricultural production in the warmer Tena region in order to sustain burgeoning populations in the Bogotá Savannah.” ref
“The archaeological research confirmed that Muisca people did, in fact, live in the Tena region, not only in the last few hundred years before the Spanish Conquest but in much earlier times as well. The history of this occupation goes back at least 2400 years to the initial period of sedentary farming. During the earliest occupation of the Tena region—during the Herrera period (400 BCE–800 CE)—the majority of the population lived in widely scattered dispersed farmsteads, although a cluster of occupation more like a nucleated village also occurred. This settlement pattern continued in similar form during the next period—Early Muisca (800–1200 CE)—during which the region witnessed quite substantial population growth. During the last prehispanic period—Late Muisca (1200–1550 CE)—a combination of dispersed farmsteads and nucleated villages persisted, but in sharp contrast to the implications of the sixteenth-century accounts, population actually decreased somewhat, making the Tena region extremely unusual among the demographic patterns for the Muisca area at this time.” ref
“The region’s inhabitants, like those of earlier periods, were Muisca farmers living there year-round, and practicing relatively extensive agriculture. There is no sign of a major influx of seasonal occupation by people whose permanent residences were in the higher-elevation Bogotá Savannah. Nor is there indication of more intensive agricultural production. These results question literal interpretations of sixteenth-century written accounts of late Muisca expansion beyond the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and of the intensive and organized exploitation of the agricultural resources of adjacent lower-elevation zones as a source of chiefly wealth and power. They thus add to our knowledge of the variety of pathways followed in the development of very early complex societies, in which the foundations of much modern human social organization were constructed.” ref
Chiefdoms in northern South America
“Abstract: The multiple and varied trajectories of chiefdom development in northern South America (and adjacent Central America) offer a rich opportunity for evaluating generalizations about the processes of chiefdom development. Sequences of the south coast of Ecuador, the Alto Magdalena, Calima, the Muisca region, Barinas, and the Tairona region are well enough documented to attempt to use in this way. Although centralized, hierarchical societies develop in all these regions, there are many differences in the character of centralization and hierarchy and in the pacing of the development, and none of the traditionally proposed forces of social change is entirely adequate to account for these cases. Attention to the role played by competition between aspiring chiefs and their factions offers promise for more satisfactory generalizations that could be evaluated through further comparative study.” ref
Precolumbian Chiefdom Settlements with Stone Spheres of the Diquís
“The property includes four archaeological sites located in the Diquís Delta in southern Costa Rica, which are considered unique examples of the complex social, economic, and political systems of the period CE 500–1500. They contain artificial mounds, paved areas, burial sites, and, most significantly, a collection of stone spheres between 0.7 m and 2.57 m in diameter, whose meaning, use, and production remain largely a mystery. The spheres are distinctive for their perfection, number, size and density, and placement in original locations. Their preservation from the looting that befell the vast majority of archaeological sites in Costa Rica has been attributed to the thick layers of sediment that kept them buried for centuries.” ref
“Four archaeological sites (Finca 6, Batambal, El Silencio, and Grijalba-2) located in the Diquís Delta in southern Costa Rica illustrates a collection of unique stone spheres located in chiefdom settlement structures of the Precolumbian period. The four sites represent different settlement structures of chiefdom societies (500-1500 CE) containing artificial mounds, paved areas, and burial sites. Special objects of wonder and admiration are the distinctive Diquís stone spheres, which are rare in their perfection of large-sized (up to 2.57m diameter) spherical structures but are also distinct for their number and location in their original positions within residential areas.” ref
“The Precolumbian Chiefdom Settlements with Stone Spheres of the Diquís illustrate the physical evidence of the complex political, social, and productive structures of the Precolumbian hierarchical societies. The chiefdoms which inhabited the Diquís Delta created hierarchical settlements expressing the division of different levels of power centers, presented by the different serial components. Likewise, the exceptional stone spheres, which continue to leave researchers speculating about the method and tools of their production, represent an exceptional testimony to the artistic traditions and craft capabilities of these Precolumbian societies.” ref
https://sites.santafe.edu/~bowles/SimpleChiefdoms.ppt
Elite Status and Gender: Women Leaders in Chiefdom Societies of the Southeastern U.S.
“ABSTRACT: This dissertation presents an ethnohistorical study of women chiefs in the Southeastern United States. Women chiefs were a recurring feature of Southeastern chiefdom societies at and following European contact. Knowledge of how and why women filled these public roles helps explain how chiefdom societies were organized, their political structure, and how gender roles were defined. Chiefdom structure, political economy, and chiefly succession are examined to provided a framework for understanding how chiefdoms operate and how chiefs come to power. Ethnohistoric data are presented and analyzed, supporting the conclusion that women chiefs were present at the very dawn of European contact, even when there were high ranking men available to fill the office. Women sometimes served as regents, usually for an immature child, but some of the women identified as regents were actually chiefs. Women chiefs are present because their elite status takes precedence over their gender. Chiefly offices may not necessarily be gendered male or female, since women accessed them regularly. This analysis shows that elite status, personal ability, and strong support from a faction are needed for both women and men to become chiefs, regardless of gender. Women chiefs were present in both matrilineal and patrilineal societies, so the form of kinship reckoning is not a critical or limiting variable for determining the likelihood of women chiefs being present. The most salient variable is the presence of ascribed, elite statuses that women can access. Therefore, the innate structure of chiefdom societies themselves makes it likely that women chiefs will be present. Baseline comparative data from chiefdom societies having women chiefs from outside the U.S.–Tonga and Taíno –are used to generate a hypothesis about the presence of women chiefs.” ref
Paramount Chief
“A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and archaeological theory to refer to the rulers of multiple chiefdoms or the rulers of exceptionally powerful chiefdoms that have subordinated others. Paramount chiefs were identified by English-speakers as existing in Native American confederacies and regional chiefdoms, such as the Powhatan Confederacy and Piscataway Native Americans encountered by European colonists in the Chesapeake Bay region of North America. During the Victoria era, paramount chief was a formal title created by British colonial administrators in the British Empire and applied in Britain’s colonies in Asia and Africa. They used it as a substitute for the word “king” to ensure that only the British monarch held that title. Since the title “chief” was already used in terms of district and town administrators, the addition of “paramount” was made so as to distinguish between the ruling monarch and the local aristocracy.” ref
In Asia
“Khan, alternately spelled lowercase as khan and sometimes spelled as Han, Xan, Ke-Han, Turkic: khān, Mongolian: qāān, Chinese: 可汗 or 汗, kehan or han) is an originally Central Asian title for a sovereign or military ruler, first used by medieval Turko-Mongol nomadic tribes living to the north of China. ‘Khan’ is first seen as a title in the Xianbei confederation for their chief between 283 and 289 and was used as a state title by the Rouran confederation. It was subsequently adopted by the Göktürks before Turkic peoples and the Mongols brought it to the rest of Asia. In the middle of the sixth century it was known as “Kagan – King of the Turks” to the Persians. It now has many equivalent meanings such as commander, leader, or ruler. The most famous khan was the Great Khan of Mongols: Genghis Khan. Another famous Manchu khan was Nurhachi.” ref
“Sabah, Malaysian Borneo, Huguan Siou is the paramount leader for the Kadazandusun Murut indigenous community in Sabah. The current and the second Huguan Siou is Joseph Pairin Kitingan. The office is near sacred and can be left vacant if no one is deemed worthy to hold the title.” ref
In Oceania
“New Zealand, Ariki Nui of Ngati Tuwharetoa, a Māori tribe in the central North Island – a hereditary chieftainship which still has great influence. In the 1850s the Māori King Movement resulted in the election of a Waikato chief as Māori King.” ref
“Cook Islands, the paramount chief of the Cook Islands was an ariki of the Makea Nui dynasty, a chiefdom of the Te Au O Tonga tribe in Rarotonga, the Kingdom of Rarotonga was established in 1858 and ended in 1888.” ref
“Fiji, during the October–December 1987 secession agitation on one island, known as the Republic of Rotuma, led by Henry Gibson (remained in New Zealand), his style was Gagaj Sau Lagfatmaro, rendered as Paramount chief or King of the Molmahao Clan. NB: This title was not recognized by the Rotuma Island Council as the titles Gagaja and Sau have never been used together. The closest thing to a paramount chief is the position of Fakpure, currently belonging to the district chief (gagaj ‘es itu’u) of Noa’tau. The British Sovereign was recognized as “Paramount Chief“, even after the country became a republic on 7 October 1987; however, this was not an office of state.” ref
“Polynesia, Rapa Nui (Easter Island) paramount chief or king, the ariki henua or ariki mau*. Samoa, paramount titles in the fa’amatai chiefly system include; Malietoa, Mata’afa, Tupua Tamasese, and Tuimaleali’ifano. American Samoa, paramount chief titles in the fa’amatai chiefly system include; Tui Manu’a, Le’iato.” ref
In Africa
“Eastern African paramount chieftainships and titles, Kenya: Title since 1904 of the former laibon of all the Maasai in Kenya (not in Tanzania), Kenya: Title held by supreme ruler Lago Ogom, after the advent of British colonial rule in Northern Kenya. Sudan: In South Sudan, the title of the chief responsible for a payam (district) elected by the chiefs of each buma (village). The Paramount Chief works with the government-appointed Payam Director, both of whom report to a county Commissioner.” ref
“West African paramount chieftains and their countries, Cameroon: Charles Atangana, Nigeria: Ladapo Ademola, Sierra Leone: Bai Bureh, and Ghana: Otumfuo Nana Osei Tutu II.” ref
“Southern African paramount chieftainships and titles,
- Kgôsi
- In present Lesotho since it emerged as a polity in 1822, a British protectorate as Basutoland since 12 March 1868 (11 August 1871 – 18 March 1884 Annexed to Cape Colony as Basutoland territory, then as a separate colony, as one of the High Commission Territories). The title changed to king on 4 October 1966, which was the date of the country’s independence from the British Empire.
- In Namibia
- In Swaziland the term paramount chief was imposed by the British government over Swazi royal objections in 1903, was never recognized by the Swazi royalty, and was changed to “king” in English upon independence in 1968. The SiSwati name for the office is Ngwenyama, a ceremonial term for “lion.”
- In South Africa
- Khosikulu of the vhaVenda; after the people’s split, (only?) of the haMphaphuli
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the Xhosa people’s following polities: amaGcaleka, amaMbalu, amaRharhabe, amaNdlambe, imiDushane, imiQhayi, amaGasela, amaGwali, amaHleke, imiDange, amaNtinde, amaGqunukhwebe
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the amaBhaca (until 1830 called abakwaZelemu)
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the amaKhonjwayo (currently ruled by Dumisani Gwadiso)
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the amaMpondo, currently ruled by Ndamase NDAMASE (West) and Jongilanga Sigcau (East) .
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the amaMpondomise
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the abaThembu, currently ruled by Buyelekhaya Zwelinbanzi Dalindyebo.
- title Inkosi Enkhulu of the Nhlangwini, currently ruled by Melizwe Dlamini” ref
Former chiefdoms in North America
“A Chiefdom of Ameca, C Cahokia polity, Casqui, Chiefdoms of Hispaniola, and Coosa chiefdom, G Guale, J Jaega, M Mocoso, O Ocute, P Pohoy, S Saturiwa, T Tacatacuru, Tocobaga, U Utinahica, Uzita (Florida).”
Chiefdoms and Chieftaincy in the Americas
“Much has been learned about the ways chiefdoms were organized, their origins, and their ultimate fates from poring over historical accounts, sifting through archaeological sites, and observing contemporary peoples. This book, which focuses on the Americas, includes general statements on the development of chiefdoms (Elsa Redmond, Robert Carniero, and Pita Kelekna) and case studies of groups in South America (Elsa Redmond, Charles Spencer, William Sturtevant, Neil Whitehead, and Doris Kurella), the Caribbean (William Keegan and coauthors), and the United States (Winifred Creamer and Jonathan Haas, Helen Rountree and Randolph Turner, and Jerald Milanich).” ref
“These authors concentrate on the societies that gave rise to chiefdoms and the process of chiefdom formation. Redmond introduces chieftaincy to cover short-term leadership achieved by especially capable and charismatic people within the context of essentially autonomous villages. A chieftain is like a Melanesian big man, but without the latter’s geographical and cultural connotations. Chieftains exercise some control over their fellow villagers, the scope and duration of their authority are determined by the exigencies of various situations, and their reputation and influence extend to neighboring settlements. A chieftaincy is thus a society with recognized leaders, but their influence is short-lived, limited, and tied to particular circumstances. In contrast, chiefdoms are kin-based societies with social hierarchies headed by permanent chiefs, who inherit their positions of authority over the inhabitants of multiple villages. Chieftaincies came and went over time; only some of them developed into full-blown chiefdoms.” ref
“Whatever the merits of new sociopolitical categories, classification systems reveal nothing about the processes behind cultural change. What is really of interest are the circumstances that led to the crystallization of situationally advantageous leadership positions and intervillage alliances to form institutionalized social hierarchies, including chiefs, and permanent ties among dominant and subordinate villages. Carneiro refers to this transformation as the “flashpoint,” which is appropriate considering its likely suddenness. It makes considerable sense to argue that under the right conditions politically autonomous villages with presumptive leadership positions—Redmond’s chieftaincies—developed into multicommunity societies with fixed chiefly positions embedded within kin-based social hierarchies. But just what combination of circumstances gave rise to chiefdoms? Carneiro argues that whatever factors were behind chiefdom formation, they were few in number. Separate explanations are not needed in all of the many places where these societies arose. His position is arguably the most important and provocative point in this book. It is a challenge to look for ultimate causes, rather than being content with an uninterpretable hotchpotch of context-specific details.” ref
“Simplifying greatly, most scenarios for chiefdom origins invoke either warfare or economic relations, especially the role of chiefs as managers of critical resources or as major players in exchanges of highly coveted prestige goods. Contributors to this book emphasize the part played by warfare in chiefdom development. These societies arose in places where there was little chance of flight to escape severe endemic warfare. This position is argued strongly by Carneiro in an elaboration of his thirty-year-old environmental circumscription and warfare model. In short, the first chief was a highly successful and influential war leader who was determined to hold onto his position of dominance in the affairs of multiple villages located in places where the pressure on resources and harrassment by enemies could not be relieved by movement elsewhere.” ref
The Origin of State Societies in South America
“Abstract: The earliest states developed in the central Andean highlands and along the central Pacific coast of western South America. The consensus in the archaeological literature is that state societies first developed in the central Andes in the early part of the first millennium CE. A minority opinion holds that first-generation states developed as early as the late second millennium BCE in the same area. The Andean region constitutes one of a few areas of first-generation state development in the world. This area, therefore, represents an important case study for the comparative analysis of state formation. This article outlines the arguments for state formation in South America, presents the evidence, analyzes the underlying assumptions about these arguments, and assesses the South American data in terms of contemporary anthropological theory of state evolution.” ref
MATRILINY AND PATRILINY BETWEEN COHABITATION EQUILIBRIUM AND MODERNITY IN THE CAMEROON GRASSFIELDS
“ABSTRACT: The paper explores the principles in the kinship structure of the cluster of speakers of the Ring Group of Grassfield Bantu, who are at once matrilineal and patrilineal, living in the south-western edge of the western Cameroon highlands. Although operating in an inverted mirror image, the seemingly opposed kinship structures have a common logic where the basic kinship unit is residential (household). There is an attempt to strike a balance between descent groups without constituting double descent, and women occupy positions that stress symmetry rather than subordination, although there is patriarchy. The impact of modernity on matriliny in a context of generalized patriliny is also examined with the conclusion that the drift towards “patrilineal” practices does not imply a change of system but implies adaptations that leave the system unmodified.” ref
Traditional leaders in Zambia shift gender norms and strengthen women’s land rights
How community-level dialogues uprooted harmful gender norms that hinder women’s rights to land.
“Across much of Africa, land is not allocated and inherited under statutory law but through customary practices rooted in kinship. In patrilineal systems, land belongs to men’s families and is inherited through the paternal line. In Zambia, many ethnic groups follow a matrilineal system, where women own land and pass it down the maternal line. But ownership does not necessarily translate into access, use and control of land. Even in matrilineal societies, social and gender norms undermine women’s decision-making power. Traditionally – regardless of patrilineal or matrilineal systems − men have authority over household resources, including land − so when it comes to land rights, women are left out.In Zambia’s customary systems chiefs and their advisors – known as indunas – and village headpersons allocate land. These customary leaders are usually men and, as custodians of tradition and culture, heavily influence whether harmful gender norms and practices persist or change.” ref
“A woman headperson in the Nyamphande chiefdom addressed a pressing form of gender-based violence related to land: the use of traditional funeral rites to deny widows’ access to their deceased spouse’s land. Indunas and village headpersons who participated in the dialogues encouraged men in their communities to include their wives in land documentation. And the indunas led by example, committing to share their own land with their wives and children, both boys and girls. Induna Jacob Phiri, from Mnukwa chiefdom, was the first to share his land after the first dialogue session, saying “My wife had access to my land and planted crops of her own choice, but I never thought about what could happen to her if I died. I knew I needed to act while I was still alive, so I gave her a portion of land to be her own. After that, I felt empowered to tell people in my village to do the same.” ref
“Not all indunas embrace change. Despite promising shifts in behaviors and gender norms, many indunas did not support change − taking a backseat or even attempting to block and discourage those willing to drive it forward. Although bringing together indunas from different chiefdoms intended to foster collaboration, the pilot initiative found that individual action by the indunas was much more successful than collective action. Some of the indunas resisted changes in social norms, and it is important to invest more time in supporting the indunas and headpersons to have a deeper understanding of existing gender norms that should be changed before moving to planning and implementation. Change starts with community. The pilot showed that shifting harmful gender norms at the community level is crucial in supporting women to access land rights. Given their role in regulating local culture and advising the traditional authority on land administration, customary leaders like indunas and village headpersons are a key entry point for that shift. Change can be slow. But spaces for dialogue, critical reflection, and support for action-planning enabled the indunas to not only change their own beliefs, but also begin to see their role and their communities in a different light.” ref
Powhatan Complex paramount chiefdom (male) or, more rarely, a (female)
“The Powhatan were a matrilineal society, so his right to be chief was inherited from his mother.” ref
“The Powhatan people are Native Americans who belong to member tribes of the Powhatan Confederacy, or Tsenacommacah. They are Algonquian peoples whose historic territories were in eastern Virginia, and their Powhatan language is an Eastern Algonquian language. All of Virginia’s Native peoples practiced agriculture. Powhatans made offerings and prayed at sunrise. Although, they also prayed and made offerings to specific gods, who were believed to be in control of the harvest. They used the land differently, and their religion was a Native one. Significantly, one of the major duties of Powhatan priests was controlling the weather. Various tribes each held some individual powers locally, and each had a chief known as a weroance (male) or, more rarely, a weroansqua (female), meaning “commander. As early as the era of John Smith, the individual tribes of this grouping were recognized by English colonists as falling under the greater authority of the centralized power led by the chiefdom of Powhatan (c. 1545 – c. 1618), whose proper name was Wahunsenacawh or (in 17th century English spelling) Wahunsunacock.” ref
“In 1607, when the first permanent English colonial settlement in North America was founded at Jamestown, he ruled primarily from Werowocomoco, which was located on the northern shore of the York River. This site of Werowocomoco was rediscovered in the early 21st century; it was central to the tribes of the Confederacy. The improvements discovered at the site during archaeological research have confirmed that Powhatan had a paramount chiefdom over the other tribes in the power hierarchy. Anthropologist Robert L. Carneiro in his The Chiefdom: Precursor of the State. The Transition to Statehood in the New World (1981), deeply explores the political structure of the chiefdom and confederacy. Powhatan (and his several successors) ruled what is called a complex chiefdom, referred to by scholars as the Powhatan Paramount Chiefdom. Research work continues at Werowocomoco and elsewhere that deepens understanding of the Powhatan world. Wahunsenacawh had inherited control over six tribes but dominated more than 30 by 1607 when the English settlers established their Virginia Colony at Jamestown. The original six tribes under Wahunsenacawh were: the Powhatan (proper), the Arrohateck, the Appamattuck, the Pamunkey, the Mattaponi, and the Chiskiack.” ref
“He added the Kecoughtan to his fold by 1598. Some other affiliated groups included the Rappahannock, Moraughtacund, Weyanoak, Paspahegh, Quiyoughcohannock, Warraskoyack, and Nansemond. Another closely related tribe of the same language group was the Chickahominy, but they managed to preserve their autonomy from the Powhatan Paramount Chiefdom. The Accawmacke, located on the Eastern Shore across the Chesapeake Bay, were nominally tributary to the Powhatan Chiefdom but enjoyed autonomy under their own Paramount Chief or “Emperor”, Debedeavon (aka “The Laughing King”). Half a million Native Americans were living in the Allegheny Mountains around the year 1600. 30,000 of those 500,000 lived in the Chesapeake region under Powhatan’s rule, by 1677 only five percent of his population remained. The huge jump in deaths was caused by exposure and contact with Europeans. In his Notes on the State of Virginia (1781–82), Thomas Jefferson estimated that the Powhatan Confederacy occupied about 8,000 square miles (20,000 km2) of territory, with a population of about 8,000 people, of whom 2400 were warriors. Later scholars estimated the total population of the paramountcy as 15,000.” ref
“Powhatan (died April 1618, Virginia [U.S.]) was a North American Indian leader, father of Pocahontas. He presided over the Powhatan empire at the time the English established the Jamestown Colony (1607). Powhatan had inherited rulership of an empire of six tribes from his father. After succeeding his father, Powhatan brought about two dozen other tribes into the empire that was named for him; at the peak of his power, he is estimated to have ruled between 13,000 and 34,000 people. Powhatan was an astute and energetic ruler, but he was also noted as being strict and occasionally cruel toward his subjects. In the Algonquian language of his people, his title as emperor was mamanatowick, and his territory was known as Tsenacommacah. Each tribe within the Powhatan empire had its own chief, or weroance, and Powhatan ruled as the chief of these chiefs.” ref
“English colonists established a settlement, known as Jamestown, on an uninhabited peninsula within his territory in 1607. The Powhatan empire at the time of the colonists’ arrival essentially covered present-day eastern Virginia, extending from the Potomac River to the Great Dismal Swamp, and its capital was at the village of Werowocomoco. Powhatan initially acted ambivalently toward the English settlement, sometimes ordering or permitting attacks against the colonists while at other times trading tribal food for sought-after English goods such as metal tools. During the colony’s early years, he appears to have viewed the English as potential allies against his own enemies—namely, the Monacan, Mannahoac, and Massawomeck tribes to the north and west. In his trading and negotiation with the colony in those years, the English were generally represented by John Smith, with whom Powhatan played a cat-and-mouse game as each side assessed the other’s capabilities and intentions.” ref
“Among the Algonquian-speaking Virginia Indians, succession to the status of chief, or weroance, was matrilineal, meaning that Wahunsonacock must have been the son of a sister of a Powhatan weroance, taking his place as chief on the death of his uncle. Despite his status, Wahunsonacock’s childhood likely was no different from other boys; until he was about five, he went to the gardens, marshes, and forests with his mother, probably practicing archery, with her encouragement, on any creature that moved there. As an adolescent, having proved himself a proficient hunter, he endured the huskanaw ritual initiating him into manhood, after which he returned to his family and joined the ranks of the tribe’s warriors and hunters. His status as an heir to the rank of chief probably made him a cockarouse, or member of his uncle’s council.” ref
“Powhatan’s given name was Wahunsenacawh, also spelled Wahunsunacock. Little of his early life is known apart from what we can assume. We know that he came to power in the town of Powhatan, which was located near present-day Richmond. As a boy he would have aided his mother in tasks like farming and gathering useful plants. As a teenager, he would undergo a coming-of-age ritual called a huskanaw. Now considered an adult, he would have joined the other men in hunting, and might have also served as a member of the chief’s council due to his high rank. At an unknown age, he became the weroance, or chief, of Powhatan. In order to become a weroance in a matrilineal, or female-based system of inheritance, he could have been the son of the previous weroance’s sister. The new weroance of the Powhatan people would expand his political influence using several methods. One such method was force. Warfare was an expected and frequent reality of life in Powhatan’s time, and all men would have been trained as warriors.” ref
Proto-Oceanic Society was Matrilineal
“This article considers the distribution of matrilineality in the daughters of Proto Oceanic (POc) society and asserts that this distribution is most conveniently explained by Per Hage’s (1998) suggestion that POc society/Ancestral Lapita society may have been matrilineal. Proto Oceanic was the Austronesian interstage ancestral to all the Austronesian languages in Oceania with the exception of two—the Western Micronesian languages Palauan (Palau Island) and Chamorro (Mariana Islands). POc speakers were the bearers of Early Western Lapita culture which appears in the archaeological record in the Bismarck Archipelago between 3400 and 3300 years ago.” ref
Matrilineality and the Melanesian Origin of Polynesian Y Chromosomes
“Linguists and archaeologists are in general agreement that the Austronesian languages originated in Southeast Asia on or near Taiwan around 3000 b.c. and that Austronesian-speakers dispersed through Island Southeast Asia, reaching Melanesia by 1450 b.c. and Western Polynesia by 950 BCE. This model is supported by genetic data showing a predominantly Asian origin of Polynesian mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). Recently, however, Kayser et al. (2000) have shown a Melanesian origin of Polynesian Y chromosomes favoring a Slow Boat to Polynesia model with substantial population interaction components in relation to indigenous non-Austronesian (Papuan) populations in Melanesia. Our hypothesis is that the predominance of maternally transmitted mtDNA of Asian origin and the significant presence of paternally transmitted Y chromosomes of Melanesian origin in Polynesian ancestry can be accounted for as an effect of matrilocal residence and matrilineal descent in ProtoOceanic society.” ref
“For present purposes matrilineal descent groups are lineages or clans in which membership is traced exclusively through female links to a founding ancestor. In matrilocal residence a married couple lives “with or near the female matrilineal kinsmen of the wife”. In a matrilineal chiefdom, as hypothesized for Proto-Oceanic, a man is succeeded by his sister’s son. In a patrilineal descent, group membership is traced exclusively through male links to a founding ancestor, and a man is succeeded by his son. In patrilocal residence a married couple lives “with or near the male patrilineal kinsmen of the husband.” In a cognatic descent group membership is traced through either male or female links. Double descent (not to be confused with cognatic descent) refers to the presence of both matrilineal and patrilineal descent groups in the same society.” ref
There are three lineages of Polynesian mtDNA. The predominant lineage, accounting for 90–95% of Polynesian mtDNA, is a haplotype possessing a 9-base-pair intergenic deletion shared with Asian populations. The greater diversity of this haplotype in Indonesia, the Philippines, and Taiwan implies an Asian origin and an eastward expansion of Austronesian-speakers into Polynesia. A second haplotype, accounting for 3.5% of Polynesian mtDNA, is also found in Melanesia, in Vanuatu and in coastal New Guinea. Kayser et al. (2000) have discovered three haplotypes (lineages) of Polynesian Y chromosomes. The dominant haplotype, DYS 390.3del/RPS4Y711T, accounts for 82% of Cook Island, 70% of Western Samoan, 26% of Coastal Papua New Guinean, and 9–12% of Indonesian Y chromosomes. This haplotype is not found in any other Southeast Asian or Asian population.” ref
“It originated in Melanesia an estimated 11,500 years ago, long before the intrusion of Austronesian-speakers into Melanesia about 3,500 years ago. A second haplotype, M122C/M9G, is infrequent in Polynesia, accounting for 7.1–10.7% of Polynesian Y chromosomes, but frequent in East and Southeast Asia. It probably originated in Asia on the order of 11,000 years ago. Kayser et al. conclude from the Y-chromosome data that the express-train model should be replaced by a slow-boat model in which the Austronesian-speaking (Oceanic) ancestors of the Polynesians moved slowly across Melanesia, “mixing extensively” with indigenous non-Austronesian-speaking (Papuan) populations, leaving behind their genes and “incorporating” many Melanesian non-Austronesian genes. This model is consistent with cultural and archaeological evidence of Austronesian–non-Austronesian interaction and with the linguistic “pause” in the spread of the Austronesian languages between the arrival of the Lapita archaeological culture in 1450 BCE and about 1100 BCE.” ref
“On general comparative grounds, some century or centuries of change would seem to be required to account for the common linguistic innovations that mark all Austronesian Oceanic languages (and no other [living] Austronesian languages) matrilocal residence and matrilineal descent in proto-oceanic society Kayser et al.’s model does not specify the type of “intermixing” between Austronesian- and non-Austronesian-speaking populations in Melanesia, but we suggest that it took place in the framework of matrilocal residence and matrilineal descent in Proto-Oceanic society. By “Proto-Oceanic” we mean the language at the end point of its common development in the Bismarcks before the various incremental and abrupt dispersals that led to more localized varieties of speech. By “Proto-Oceanic society” we mean, formally, what can be reconstructed, linguistically, about the social vocabulary of Proto-Oceanic-speakers and what we infer from that about their society.” ref
By “Lapita society” the archaeologists mean what was surely the same community and what can be inferred about it through archaeology, comparative ethnography, and comparative linguistics. Proto-Oceanic (Lapita) society was a sophisticated maritime and horticultural society of Austronesian origin that developed in the region of the Bismarck Archipelago in western Melanesia around 1500 BCE. The society was based on an extensive voyaging and exchange network. By 1100 to 1200 BCE daughter societies were expanding eastward, arriving in the Fiji-Tonga-Samoa area by 950 BCE. After a “long pause” in Western Polynesia of as much as 1,000 years, as evidenced by numerous innovations in ProtoPolynesian, colonization resumed, reaching all islands in Eastern Polynesia by 1000 BCE.” ref
Trobriander people
“Trobriander, any of the Melanesian people of the Kiriwina (Trobriand) Islands, lying off eastern New Guinea. Subsistence is based on yams and other vegetables, domesticated pigs, and fish. Storage houses for yams and the chief’s house stand in the middle of the village, surrounded by dwellings arranged in circles. Each hut is occupied by a single family. Trobrianders are divided into totemic clans, the members of which trace their descent matrilineally (i.e., from a common ancestor through the female line). The village is the major social unit; members make their gardens together under the guidance of a garden magician, perform ceremonies, and travel together on trading expeditions. Each village has a headman, and high-ranking headmen, or chiefs, may have authority over several villages.” ref
“Wealth is extremely important as a sign of power and the means of exercising it. The Trobrianders are noted for their elaborate intertribal trading system, the kula (q.v.), which was described in the anthropological classic Argonauts of the Western Pacific (1922) by Bronisław Malinowski. Red shell necklaces are traded between permanent trading partners in a clockwise direction around a ring of islands; white shell bracelets are traded counterclockwise. Large seagoing dugout canoes are constructed for the interisland trading expeditions.” ref
Daughter Preference and Contraceptive-use in Matrilineal Tribal Societies in Meghalaya, India
“Abstract: Although son preference in patrilineal society is an established fact, daughter preference in matrilineal society is not thoroughly examined. Very few studies have been carried out on the issue. This paper attempts to explore the daughter preference and contraceptive-use in matrilineal tribal societies in Meghalaya, India. Data from the National Family Health Survey 1998-1999 have been used in this study because, among the large-scale surveys, only this dataset allows identification of matrilineal sample. Mean, percentage, and standard deviation are computed in the present study. Further, the data have been cross-tabulated, and logistic regression has been run through SPSS (version 15). Among the ever-married matrilineal women, 17% desired more sons than daughters but 18.2% desired more daughters than sons. About 11% of ever-married women could achieve their desired sex composition of children. However, a very striking finding suggests that, even after achieving desired sex composition of children, as high as 61.8% of women were still not using contraception mainly because of programme factors while one-fourth were still depending on temporary methods. The rest 13.2% adopted terminal method of contraception, which calls for immediate attention of planners. With the increase in the number of sons but without daughter, contraceptive-use drastically decreased. The most desired sex composition of children seems to be two daughters and a son. Absence of daughter with increase in the total number of sons increased the desire for additional children. Every woman with two or more sons but without daughter wanted the next child to be a daughter. Thus, there are ample evidences to draw the conclusion that there is, in fact, a daughter preference in the matrilineal tribal societies in Meghalaya, India. Policy-makers may, thus, target the women who have achieved fertility and should ensure that daughter preference does not lead to the negligence to sons.” ref
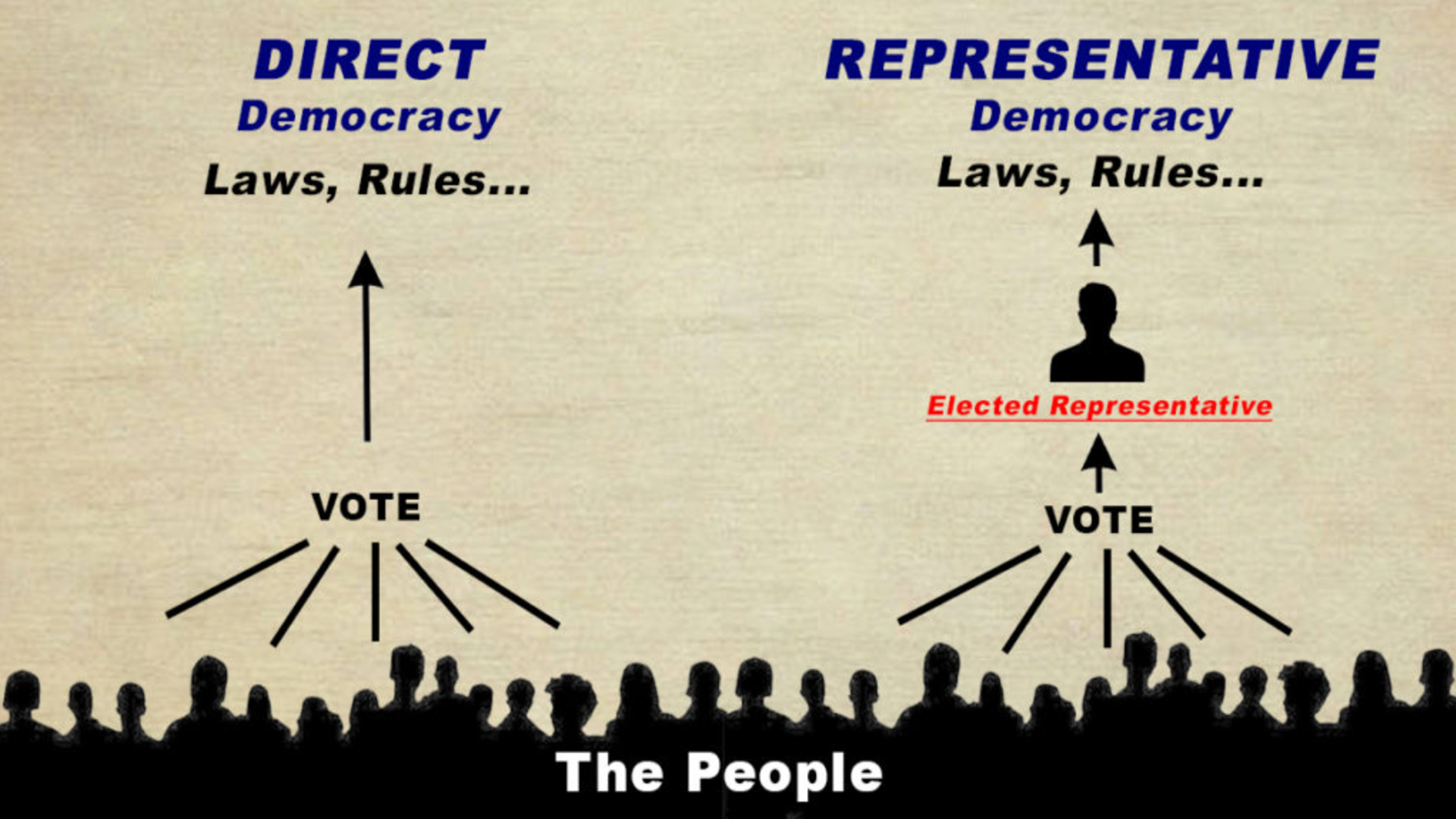
The Need for Social Justice is nothing new.
“Nanshe (Sumerian c. 4,000 to 3,100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) was a Mesopotamian goddess in various contexts associated with social justice and social welfare.” ref
Damien does not make art to demonstrate Damien’s highest skill as an artist. No, Damien’s art is Damien’s favorite way to do activism. Damien makes art for reason and evidence, not if Damien thinks people will think it is trying to just be artistic. Damien wants to help make a difference in the world, and Damien’s art helps in this.
But is Atlantis real?
No. Atlantis (an allegory: “face story” interpreted to reveal a hidden meaning) can’t be found any more than one can locate the Jolly Green Giant that is said to watch over frozen vegetables. Lol

May Reason Set You Free
There are a lot of truly great things said by anarchists in history, and also some deeply vile things, too, from not supporting Women’s rights to Anti-Semitism. There are those who also reject those supporting women’s rights as well as fight anti-Semitism. This is why I push reason as my only master, not anarchist thinking, though anarchism, to me, should see all humans everywhere as equal in dignity and rights.
We—Cory and Damien—are following the greatness that can be found in anarchist thinking.
As an Anarchist Educator, Damien strives to teach the plain truth. Damien does not support violence as my method to change. Rather, I choose education that builds Enlightenment and Empowerment. I champion Dignity and Equality. We rise by helping each other. What is the price of a tear? What is the cost of a smile? How can we see clearly when others pay the cost of our indifference and fear? We should help people in need. Why is that so hard for some people? Rich Ghouls must End. Damien wants “billionaires” to stop being a thing. Tax then into equality. To Damien, there is no debate, Capitalism is unethical. Moreover, as an Anarchist Educator, Damien knows violence is not the way to inspire lasting positive change. But we are not limited to violence, we have education, one of the most lasting and powerful ways to improve the world. We empower the world by championing Truth and its supporters.
Anarchism and Education
“Various alternatives to education and their problems have been proposed by anarchists which have gone from alternative education systems and environments, self-education, advocacy of youth and children rights, and freethought activism.” ref
“Historical accounts of anarchist educational experiments to explore how their pedagogical practices, organization, and content constituted a radical alternative to mainstream forms of educational provision in different historical periods.” ref
“The Ferrer school was an early 20th century libertarian school inspired by the anarchist pedagogy of Francisco Ferrer. He was a proponent of rationalist, secular education that emphasized reason, dignity, self-reliance, and scientific observation. The Ferrer movement’s philosophy had two distinct tendencies: non-didactic freedom from dogma and the more didactic fostering of counter-hegemonic beliefs. Towards non-didactic freedom from dogma, and fulfilled the child-centered tradition.” ref

Teach Real History: all our lives depend on it.
Damien sees lies about history as crimes against humanity. And we all must help humanity by addressing “any and all” who make harmful lies about history.

My favorite “Graham Hancock” Quote?
“In what archaeologists have studied, yes, we can say there is NO Evidence of an advanced civilization.” – (Time 1:27) Joe Rogan Experience #2136 – Graham Hancock & Flint Dibble

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
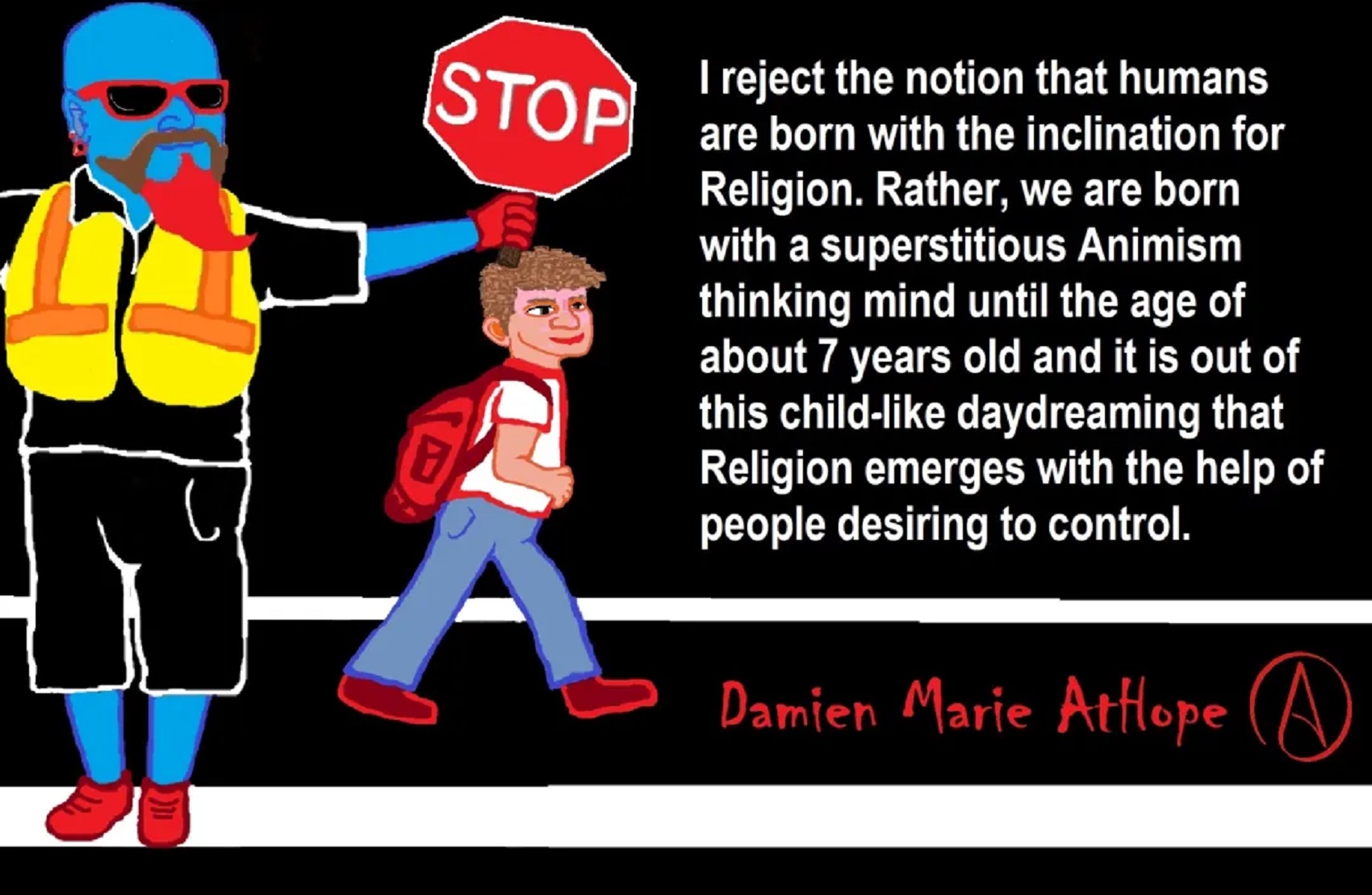
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


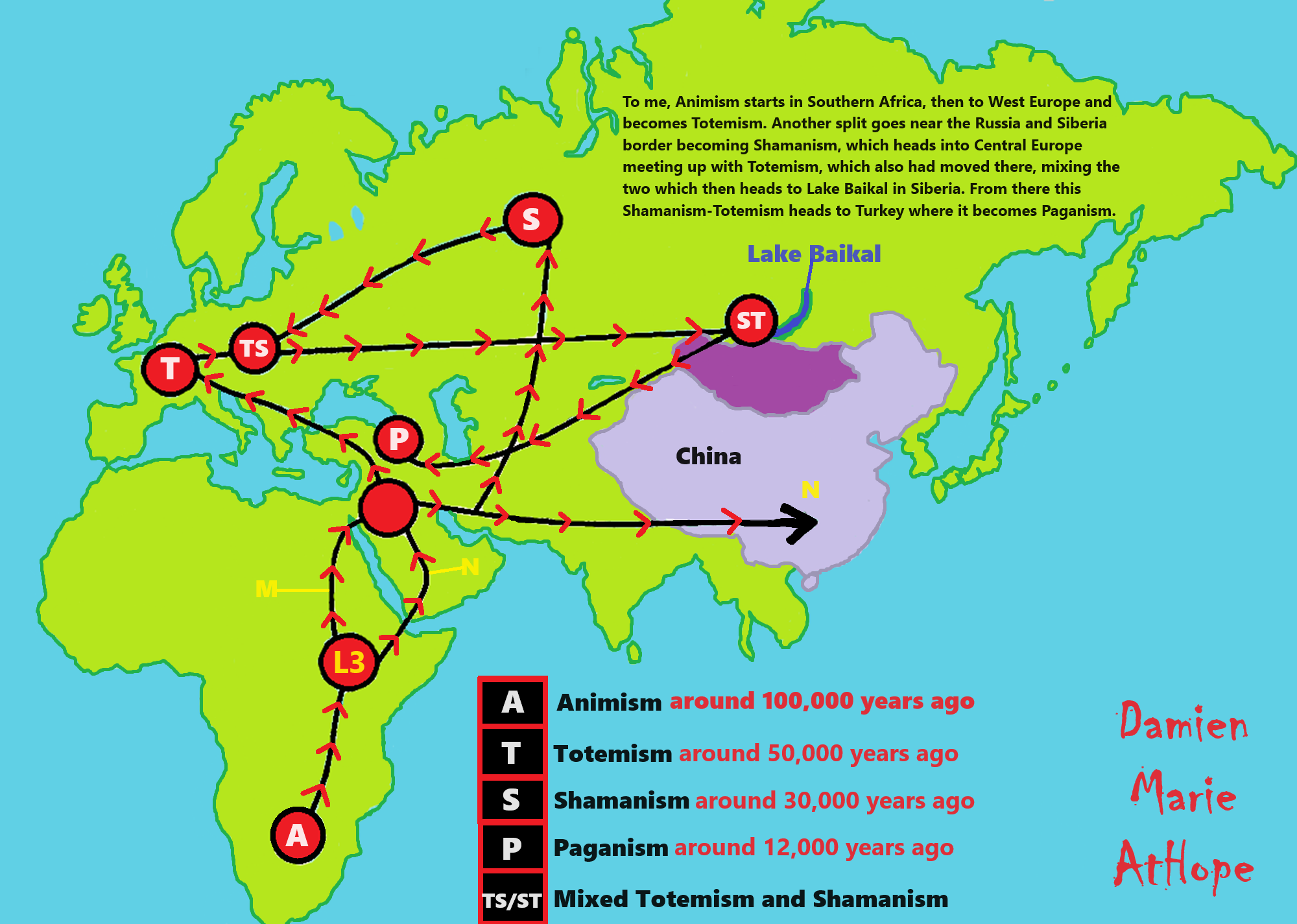
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
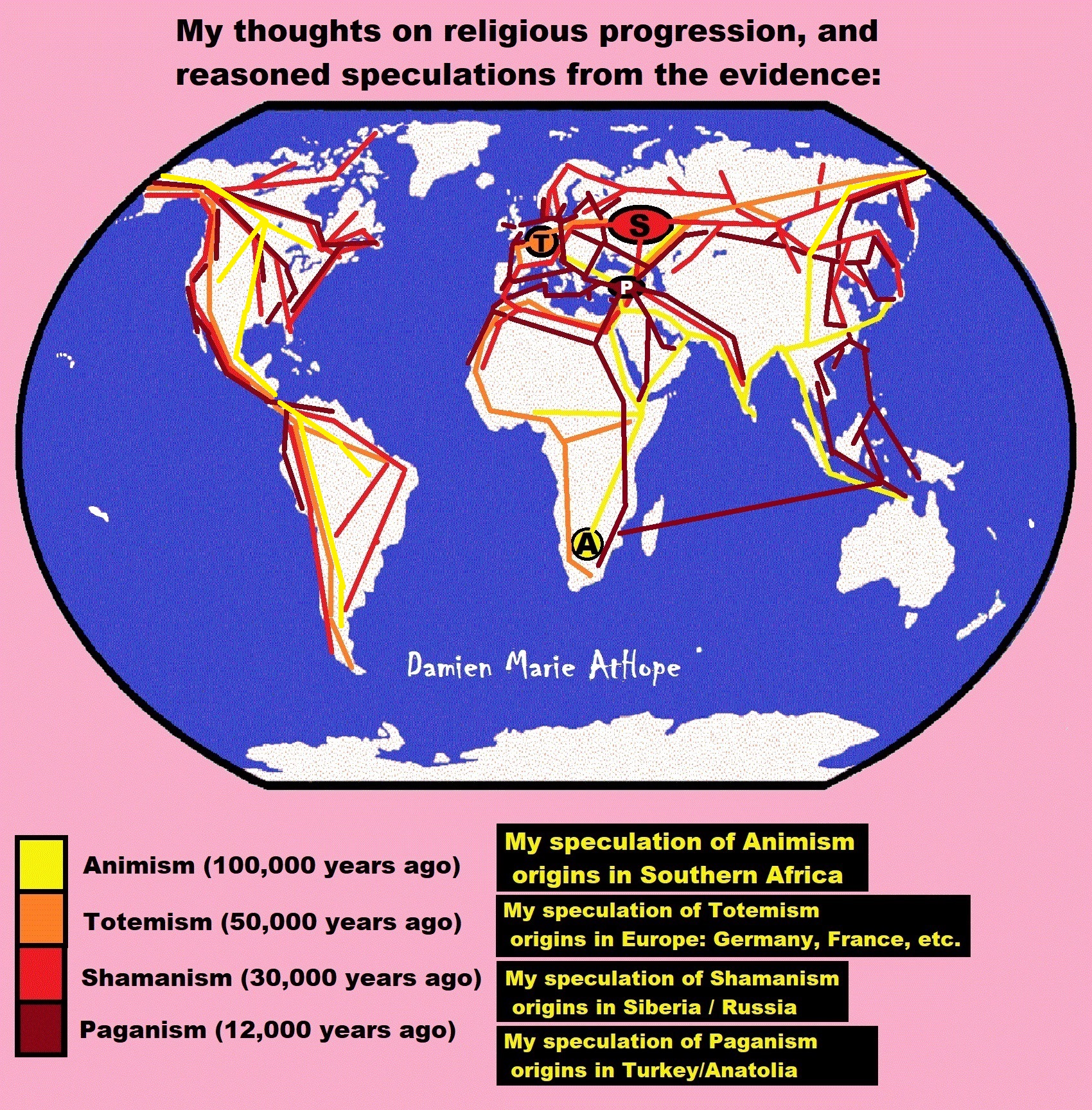



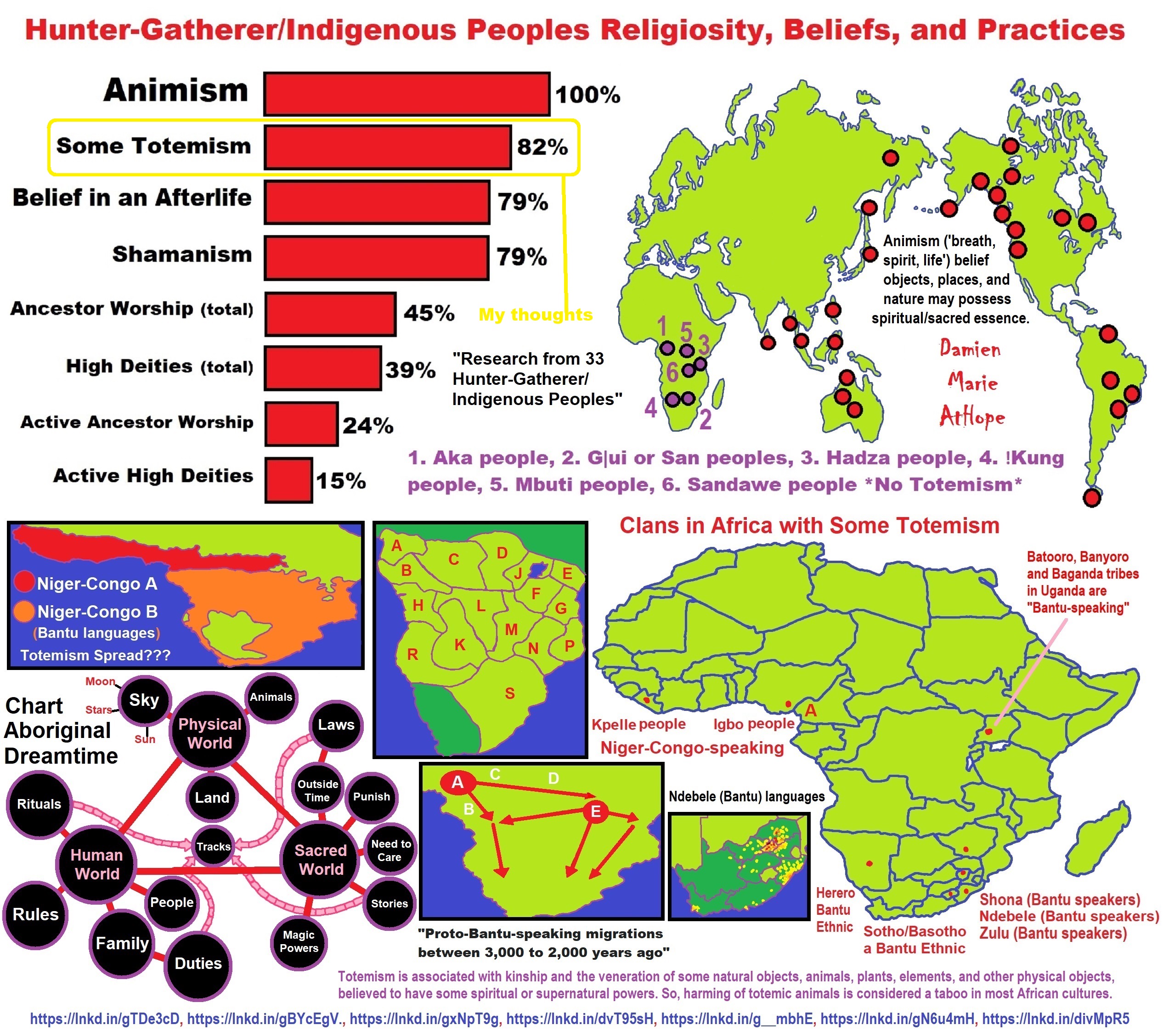
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
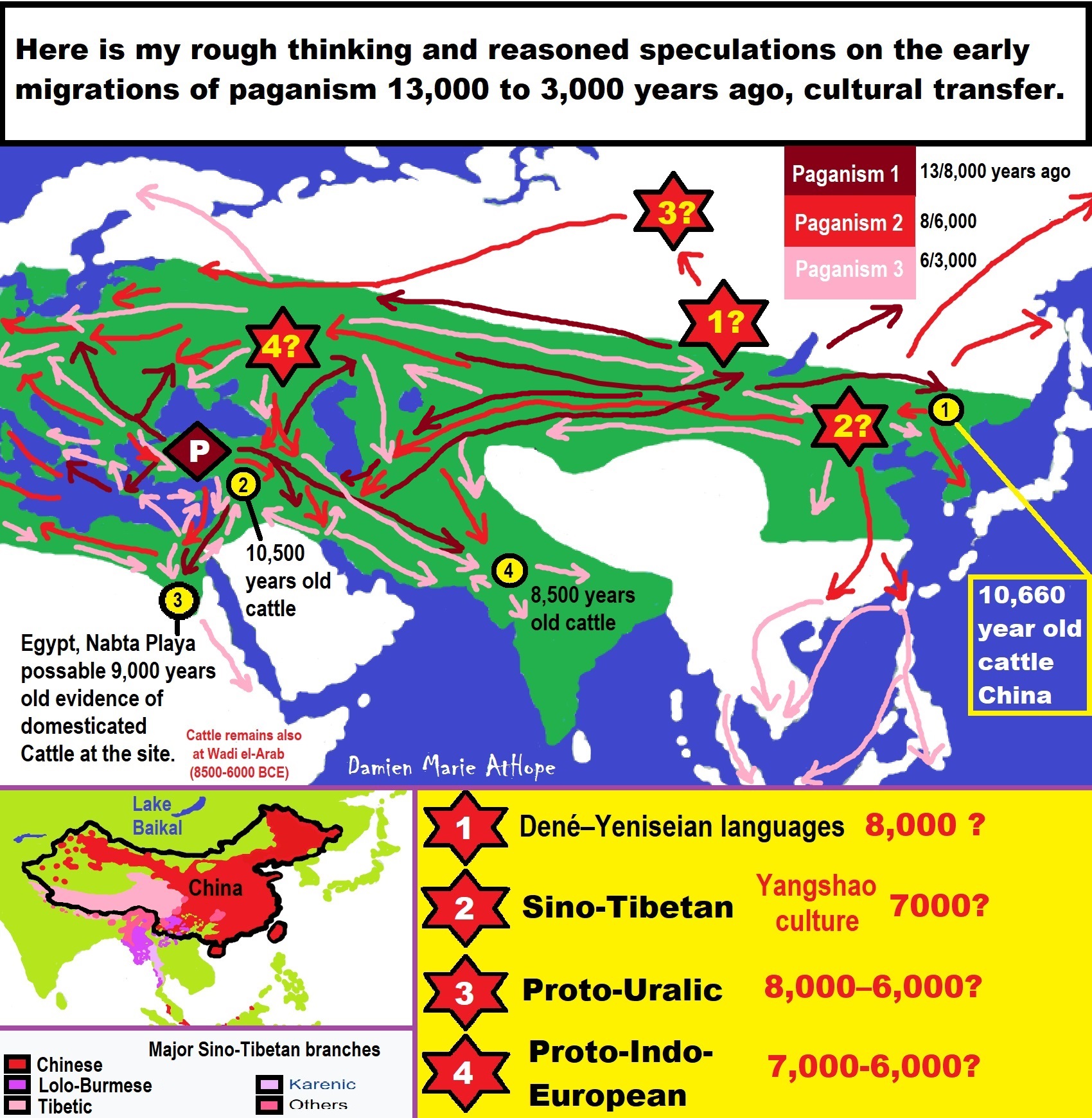
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
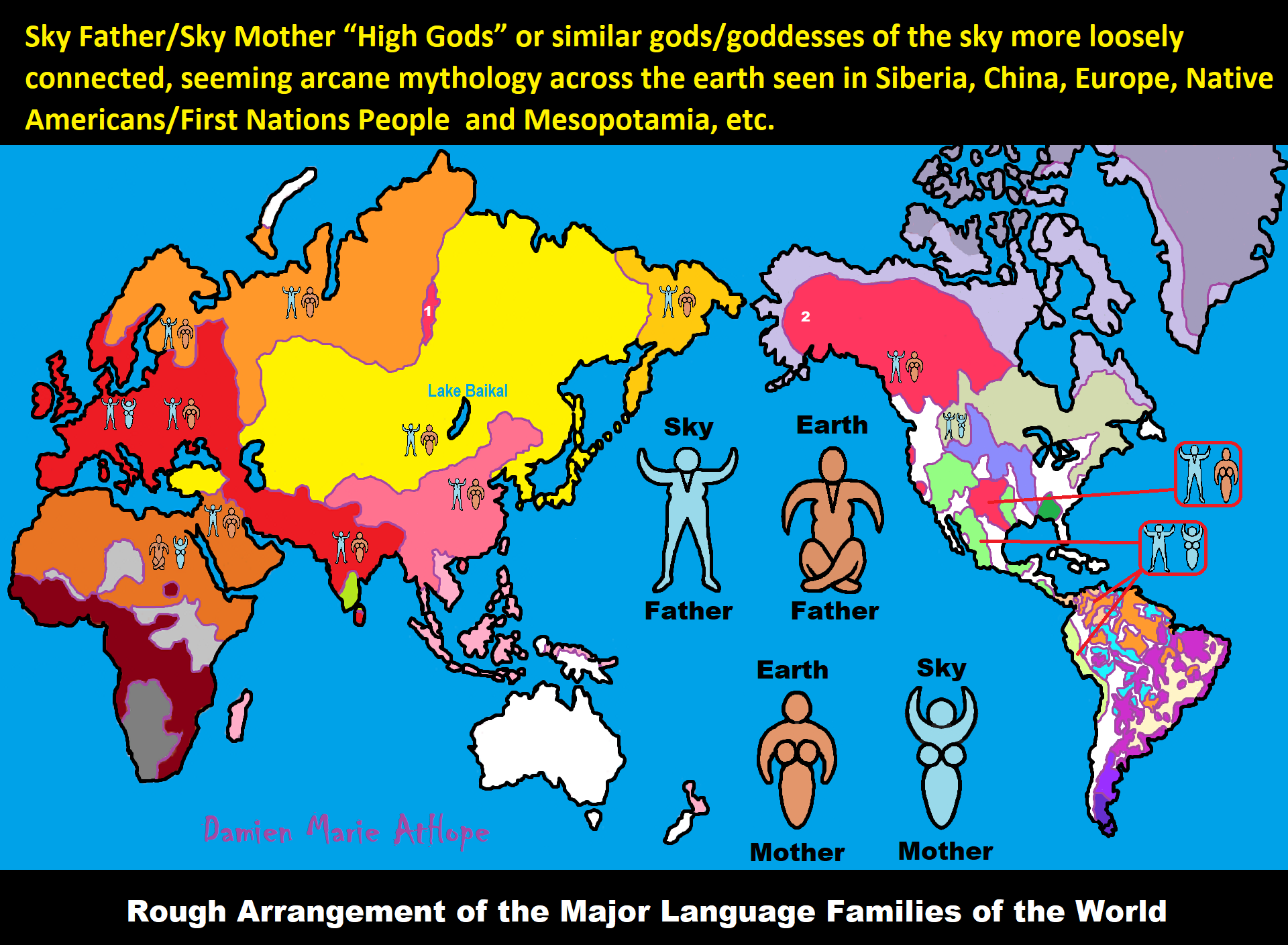
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.


Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com