ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
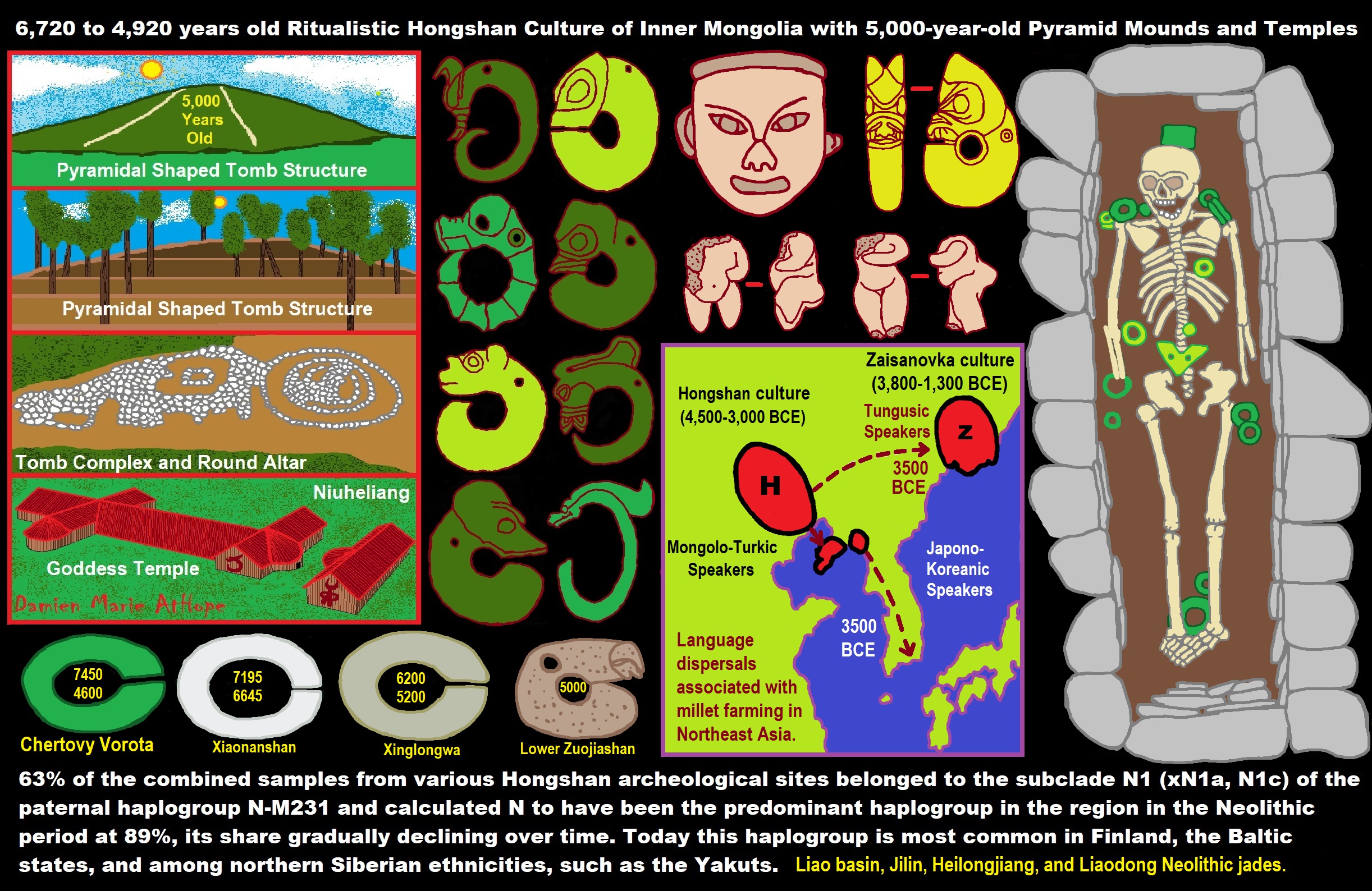
6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- Millet agriculture dispersed from Northeast China to the Russian Far East: Integrating archaeology, genetics, and linguistics
- Language dispersals associated with millet farming in Neolithic Northeast Asia: “Hongshan Neolithic Culture”
- The Development of Complexity in Prehistoric Northern China: “Hongshan Neolithic Culture”
- Hongshan Neolithic Culture of China
- 5,000-year-old “Pyramid” Found in Inner Mongolia
The Hongshan Culture
“As an important part of the Neolithic Age in Northern China, the Hongshan Culture covers an area from the Wuerjimulun River valley of Chifeng, Inner Mongolia in the north to Chaoyang, Lingyuan and the northern part of Hebei Province in the south, and extends eastward to cover Tongliao and Jinzhou. Hongshan Culture is characterized primarily by the ancient painted potteries, the “Z”-stripped potteries, and the unique digging tools-stone spades and laurel leave-shaped two-holed stone knives. The potteries of Hongshan Culture fall into two types-clay potteries and sand-mixed potteries, both manually made. The clay potteries are mostly red, usually in the forms of bowl, basin, jar, and pots, etc., most of which are containers with small flat bottoms. Most of the clay potteries are decorated with black or purple stripes arranged mainly in parallel lines, triangles, scale-shaped patterns, and occasionally in “Z”-shaped pressed stripes. The stoneware of Hongshan Culture is made by grinding with the blades of stone knives finely ground and the edges and backs in curved symmetry, indicating a fairly developed agricultural economy of the culture. Within the area of Hongshan Culture, bones of oxen, lambs, pigs, deer, and river deer have been unearthed, though in small numbers. The oxen, lambs, and pigs, which are presumably domestic animals, vaguely indicate that the early inhabitants of Hongshan Culture lived a settled life supplemented by animal husbandry, fishery, and hunting.” ref
“More than 20 cirrus-shaped jade articles have been unearthed at the site of Hongshan Culture, and each of them represents two fundamental themes-cirrus-shaped angles and minor convexities. A combination of cirrus-shaped angles and minor convexities in different ways constitute the various patterns and designs of the cirrus-shaped jade articles of Hongshan Culture, which is best demonstrated by the enormous blackish-green jade dragon unearthed at Sanxingtala Township of Wengniute Banner. The dragon is 26 cm in height with the head of a swine and the body of a serpent, coiling like cirrus. Similar dragons were found later in Balin Right Banner and the Antiques Store of Liaoning Province. These cirrus-shaped jade articles can be classified into four types by analyzing their patterns and designs: decorative articles, tools, animals, and special ones, of which the hoop-shaped articles are among the typical pieces of the jade ware of Hongshan Culture. The association of the shapes of these jade articles with their cultural context indicates that the special articles and the tools were made to meet the needs of religious ceremonies. The discovery of cirrus-shaped jade dragon at Hongshan Culture strongly suggests Inner Mongolia as one of the essential sites to trace the worship for dragons by the Chinese people.” ref
“From religious relics of Hongshan Culture like the “Goddess Temple” and stone-pile tombs have been found at Dongshanzui of Kazuo County and Niuheliang at the juncture of Lingyuan County and Jianping County of Liaoning Province. The central part of Dongshanzui relics is the foundation of a large-scaled square structure built of stone. The overall layout of the bilateral symmetry of the foundation to a south-north axis, which is characteristic of the traditional Chinese architectural style, is the first of its kind ever discovered at the site of Neolithic Age. The pottery figures unearthed at the relics indicate that the sites used to be places for sacrificial ceremonies or similar activities. In the first place, archeological studies show that Hongshan Culture was developed on the basis of Xinglongwa Culture and Zhaobaogou Culture, and the inheritance and development in religious traditions between the three cultures are evident. No sites devoted exclusively to sacrificial rites have been found so far in Xinglongwa Culture and Zhaobaogou Culture. The discovery of Niulianghe Relics indicates that large-scaled centers for sacrificial rites had shown up by the end of Hongshan Culture. This is not only a breakthrough in the study of Hongshan Culture but a discovery of great significance to the exploration of the origin of the Chinese civilization.” ref
“Secondly, Hongshan Culture is credited with remarkable achievements in architecture, pottery-making, jade-carving, and pottery sculptures which are at higher levels than those of Xinglongwa Culture and Zhaobaogou Culture. The duet of square pottery molds unearthed at the relics of a house of Hongshan Culture at Xitai, Aohan Banner, which is the earliest mold for metal casting, shows that the early people of Hongshan Culture had mastered the technology of bronze casting. Next, hunting was in the dominant position in Xinglongwa Culture and Zhaobaogou Culture, while by contrast, agriculture played an essential role in the economy of Hongshan Culture. Judging from the position of Hongshan Culture in the archeological culture of ancient Northern China and China in the Neolithic Age, we can well assume that Hongshan Culture is one of the most advanced cultures among the ranks of its peers in both southern and northern China at that time when the smelting of bronze had made appearance, the earliest cities surrounded by ditches had shown up, and the division between urban and rural areas had taken shape. Religious activities characterized by worshiping dragon and jade and respecting the ancestors were in vogue. The conflicts among social groups and the subsequent fights for the unification of religious beliefs had become the fundamental social issue. This is another proof to the assumption that the people of Hongshan Culture had marched from the clan society into the historical phase of ancient kingdoms. Therefore, we can say that by laying a foundation for the development of the Chinese civilization of five thousand years and formulating and influencing the layout of the origin and the progress of the protocol-dominating culture of China, Hongshan Culture plays an extremely essential role in the evolution of the Chinese civilization.” ref
“The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture. Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an altar—and also cairns in Niuheliang. The temple was constructed of stone platforms, with painted walls. Archaeologists have given it the name Goddess Temple due to the discovery of a clay female head with jade inlaid eyes. It was an underground structure, 1m deep. Included on its walls are mural paintings. Housed inside the Goddess Temple are clay figurines as large as three times the size of real-life humans. The exceedingly large figurines are possibly deities, but for a religion not reflective in any other Chinese culture. The existence of complex trading networks and monumental architecture (such as pyramids and the Goddess Temple) point to the existence of a “chiefdom“ in these prehistoric communities.” ref
“Painted pottery was also discovered within the temple. Over 60 nearby tombs have been unearthed, all constructed of stone and covered by stone mounds, frequently including jade artifacts. Cairns were discovered atop two nearby two hills, with either round or square stepped tombs, made of piled limestone. Entombed inside were sculptures of dragons and tortoises. It has been suggested that religious sacrifice might have been performed within the Hongshan culture.” ref
“Niuheliang is a Neolithic archaeological site in Liaoning Province, Northeast China, along the middle and upper reaches of the Laoha River and the Yingjin River (presently on the border of Chaoyang and Jianping County). The Niuheliang site belongs to the Hongshan culture (4,700 – 2,900 BC 6,720 to 4,9320 years ago). It includes evidence of religion, such as a temple, an altar, and a cairn. Niuheliang is a large burial site scattered over hilltops over a 50 square kilometer area. The altitude of Niuheliang ranges between 550 meters and 680 meters above sea level. Niuheliang dates to 3,500-3,000 BCE. It was a burial and sacrificial center in the late Hongshan period. No residential settlements have been discovered here so far. The site features a unique temple on a loam platform, with an altar and cairn complex, covering an area of around 5 km². The altar at Niuheliang was made of stone platforms, supported by painted, clay cylinders. A north-south axis connects this temple complex with a central peak of the Zhushan mountains, otherwise known as “Pig Mountain”. The subterranean ritual complex was built on a ridge and decorated with painted walls, referred to by Chinese archaeologists as the Goddess Temple, due to the discovery of a clay female head with jade inlaid eyes. Pig dragons and large, nude, clay figurines were also found at Niuheliang. Some of the figurines are up to three times the size of real-life humans; the interior of the figurines was structured from wood and straw. Six groups of cairns were discovered nearby, south, and west of the temple site. The primary burial goods accompanying the graves were jade artifacts, although most of the excavated graves had already been looted.” ref
Interpretations?
“According to the excavator of this site, Guo Dashun, there are in fact two varieties of animals represented in the jades. One is a boar with narrow eyes and flat snout; the other is a bear, represented by round eyes and short perky ears. He also found similar boar and bear symbolism in the vessels found at Xiaoheyan site. The bear has been widely worshipped in Northeast Asia, such as by the Ainu in northern Japan, and in Siberia. Thus, Guo Dashun sees this site in the wider Northeast Asian context. Some similarities with Xinglongwa culture (6200-5400 BC) of northeastern China have also been pointed out.” ref
Pyramidal structure?
“One year after the temple-cairns complex was discovered nearby a pyramidal structure “disguised” as a hill known as Zhuanshanzi, which was included during the Han dynasty (-206~220) in a section of the Great Wall. Built with earth and imported stone, its structure is more elaborate than the cairns. This site contains some of the essential elements, temples, cairns, and platforms, present in later ancestor worship of the Chinese such as the Ming tombs 5000 years later.” ref
“63% of the combined samples from various Hongshan archeological sites belonged to the subclade N1 (xN1a, N1c) of the paternal haplogroup N-M231 and calculated N to have been the predominant haplogroup in the region in the Neolithic period at 89%, its share gradually declining over time. Today this haplogroup is most common in Finland, the Baltic states, and among northern Siberian ethnicities, such as the Yakuts.” ref
“Chinese archaeologists discovered a pyramid-shaped building, dating back more than 5,000 years ago, in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, in north China. The “pyramid”, located on a mountain ridge one kilometer north of Sijiazi Township in the Aohan Banner (county), is a three-storied stone building, with the bottom layer being more than 30 meters long and 15 meters wide. The “pyramid” belongs to the Hongshan Culture period of 5,000 to 6,000 years ago, according to Guo Dashun, a famous Chinese archaeologist who works in Liaoning Archaeological Research Institute. Seven tombs and ruins of an altar were found on the top of the “pyramid.” ref
“At the site of the altar, there are many fragments of broken pottery carved with the Chinese character “mi” (rice). Archaeologists said that the character “mi” may have something to do with people’s understanding of astrology in ancient times. In one of the tombs, archaeologists found a bone flute and a stone ring, and they unearthed a stone sculpture of a goddess the size of a human body in another tomb. Archaeologists were surprised to find a stone-carved linga on the wall of a tomb and a small stone statue of a goddess below the linga in the same tomb.” ref
“Archaeologist Guo said that many of the relics were first-time discoveries and they are of great significance in studying the burial customs, religious and sacrifice rituals, and the social structure of the Hongshan Culture. He pointed out, the discovery of the “pyramid” is also of great significance in exploring the origin of the Chinese civilization. The Hongshan Culture, belonging to the Neolithic culture, is mainly distributed in the juncture area between Inner Mongolia, Liaoning and Hebei provinces.” ref
“In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BC), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BC), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. Moreover, the Yangshao culture was in the larger area and contemporary with Hongshan culture. These two cultures interacted with each other.” ref
Pyramids in China (pyramidal shaped tomb structures: 5,000 years old)
In the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in northern China, Chinese archeologists have discovered a pyramid which they have dated to be more than 5,000 years old. Archaeologist Guo Dashun stated that the three-stepped pyramid belongs to the Hongshan culture period of 5,000 to 6,000 years ago, during the Stone Age. At the top of the pyramid, the archeologists found seven tombs and the ruins of an altar. Also found were many fragments of broken pottery carved with the Chinese character mi (rice). They also discovered a bone flute, a stone ring, and a life-sized sculpture of a goddess. The term Chinese pyramids refers to pyramidal shaped structures in China, most of which are ancient mausoleums and burial mounds built to house the remains of several early emperors of China and their imperial relatives. About 38 of them are located around 16 to 22 mi) north-west of Xi’an, on the Guanzhong Plains in Shaanxi Province. The most famous is the Mausoleum of the First Qin Emperor, northeast of Xi’an and 1.7 km west of where the Terracotta Warriors were found. The earliest tombs in China are found just north of Beijing in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region and in Liaoning. They belong to the Neolithic Hongshan culture (6,700 to 2,900 years ago) a culture in northeastern China. The site of Niuheliang in Liaoning contains a pyramidal structure.culture in northeastern China. Hongshan burial artifacts include some of the earliest known examples of jade working. The Hongshan culture is known for its jade pig dragons and embryo dragons. Clay figurines, including figurines of pregnant women, are also found throughout Hongshan sites. Small copper rings were also excavated. Origin of the mysterious Yin-Shang bronzes in China indicate they contain lead with puzzlingly highly radiogenic isotopic compositions appeared suddenly in the alluvial plain of the Yellow River around 3,400 years ago. Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an altar—and also cairns in Niuheliang. The temple was constructed of stone platforms, with painted walls. Archaeologists have given it the name Goddess Temple due to the discovery of a clay female head with jade inlaid eyes. It was an underground structure, 1m deep. Included on its walls are mural paintings. Housed inside the Goddess Temple are clay figurines as large as three times the size of real-life humans. The exceedingly large figurines are possibly deities, but for a religion not reflective in any other Chinese culture. The existence of complex trading networks and monumental architecture (such as pyramids and the Goddess Temple) point to the existence of a “chiefdom“ in these prehistoric communities. Painted pottery was also discovered within the temple. Over 60 nearby tombs have been unearthed, all constructed of stone and covered by stone mounds, frequently including jade artifacts. Cairns were discovered atop two nearby two hills, with either round or square stepped tombs, made of piled limestone. Entombed inside were sculptures of dragons and tortoises. It has been suggested that religious sacrifice might have been performed within the Hongshan culture. In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BC), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BC), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. Yangshao culture was in the larger area and contemporary with Hongshan culture (see map). These two cultures interacted with each other. Just as suggested by evidence found at early Yangshao culture sites, Hongshan culture sites also provide the earliest evidence for feng shui. The presence of both round and square shapes at Hongshan culture ceremonial centers suggests an early presence of the gaitian cosmography (“round heaven, square earth”). The three exceptional pyramids around Xi’an, constructed using three different methods:
1. The Qian Shi Huang pyramid (Qin Dynasty) constructed of clay bricks
The first and largest “burial pyramid” is thought to be that of the first Emperor Qin Shi Huang, who unified China as a country and founded the Qin Dynasty. It lies in the huge mausoleum at the foot of the Qing Ling Shan Mountains, 80 km southwest of Xi’an. He began construction as soon as he ascended the throne at the tender age of 13 in 246 BC. It was to be of tremendous dimensions – its base was 354 x 357 meters, and its original height was 200 meters, making it the largest “pyramid” in the world (for comparison, the great pyramid in Giza is 230 x 230 meters and 147 meters high). For the 36 years that work went on, up to 700,000 people were employed at the site at a time to construct the pyramid and the subterranean complexes over an area of several thousand square meters. Construction was completed in 210 BC.
2. Qian Ling pyramid (Tang Dynasty), formed from a hill
This pyramid and the burial complexes are located on the slopes of Mount Liang, 6 km north of Quianling, the county seat, 80 km northwest of Xi’an. It is the mausoleum of the third Tang emperor, Gaozong (650-683 AD) and his wife, who became the Empress Wu Zetian (684-704, seventh daughter of Emperor Zhongzong (Li Xian), who was buried there in 684 or 706. The “pyramid” was not made by piling up material, however, but by shaping an existing hill (resulting in a “shaped pyramid”) which is not square and has large differences in its base lengths. What is special is the emperor’s subterranean burial chambers, which belie influences that are atypical for early China (see Fig. ??). Of the 18 Tang emperor burial sites in the Guanzhong Plain, it is the only complex that was not found and plundered by grave robbers. The enormous stairway access is almost 2 km long with two bulwark towers in front of the “pyramid” and is flanked by figures of animals and people that are up to 4 meters high and by monolithic stone pillars. Among these are armed guards, winged horses (yima), stone lions (shishi) and the Shusheng Tablets and Uncharactered Stele (wuzibei).
3. Earthen Pyramid of Princess Yongtai (Tang Dynasty)
Princess Yongtai (Huang Ti) was the granddaughter of Emperor Gaozong and Empress Wu Zetian, and died in 701 AD at only 17 years of age. She was buried near the Qianling Mausoleum in 706, together with Prince Duwei Wu Yanhin, a nephew of Wu Zetian who had died one year earlier (this delayed burial was possible because the bodies had been mummified). Yongtai‘s grave is surrounded by strong, 3-meters-tall walls, oriented to the four cardinal directions. They are 275 meters long from north to south and 220 meters wide from east to west. The pyramidal hill is located in the middle of the mausoleum. Today, it is only 14 meters high, with a respectable side length of 56 meters. An arched corridor 88 meters long, almost 4 meters wide and 6 meters high leads from the southern entrance to an antechamber and from there to the actual burial chamber. This one impressed and surprised me even more than that of Emperor Gaozong; it corresponds almost exactly to the Egyptian construction method. These similarities are not limited to the long corridors leading below the pyramid, but also include the chamber‘s shape and especially the outer sarcophagus. It is made of black basalt and is almost identical to the 24 sarcophagi in the Serapeum of Sakkara (see page 92). The frescoes are also exceptionally well preserved. The burial chamber‘s east and west walls are covered with depictions of black dragons, white tigers and an honor guard, and the ceiling features astronomical motifs. The antechamber‘s east and west walls bear depictions of waiting servants. This tomb is believed to have been plundered very early. Nevertheless, more than 1,300 items have been discovered in the vicinity during the past 50 years, including gold- and silverware, glazed figurines, porcelain and copperware.
3. Earthen Pyramid of Mao Ling (Han Dynasty)
This burial site is located 40 km from Xi‘an, near the village of Maoling, northeast of the city of Xingping. The mausoleum of Mao Ling, the burial pyramid of Emperor Wudi of the Han Dynasty (141-87 BC) is the largest of the five mausoleums built during the Western Han Dynasty and is also called the “Pyramid of the East”. Its construction is thought to have begun in 139 BC and lasted 53 years. It was surrounded by a square bulwark wall almost 6 meters thick, 431 meters long east to west and 415 meters long north to south. There was one gate in the middle of each section of the wall, one for every cardinal point. The central burial mound is a truncated pyramid, eroded to a height of 46.5 meters, with a base of about 217 x 222 meters. Around the central mausoleum are over 20 other tombs for Wudi’s family, ministers and generals, such as the burial pyramid of generals Huo Qubing, Wei Qing and Jin Midi, located between 1 and 2 km east of the emperor‘s tomb. Today, the complex also features the Mao Ling Museum, where splendid burial objects are displayed; historical records claim that the emperor spent one third of all tax income for several decades on the mausoleum‘s construction and his family’s burial goods.
Finding feng shui?
Early feng shui relied on astronomy to find correlations between humans and the universe. The culture may also have contributed to the development of settlements in ancient Korea. A group called “Qiang” were mentioned in ancient Chinese texts as well as in inscriptions on oracle bones 3000 years ago. The Qiang people who practice Qiang folk religion are an ethnic group in Chin mainly in a mountainous region in the northwestern part of Sichuan on the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. It is possible that the modern Qiang might be descendants of one of the groups referred to as Qiang in ancient times. Many of the peoples formerly designated as “Qiang” were gradually removed from this category in Chinese texts as they become sinicized or reclassified, and by the Ming and Qing dynasties, the term “Qiang” denoted only non-Han people living in the upper Min River Valley and Beichuan area, the area now occupied by the modern Qiang. Qiang territory lies between the Han Chinese and historical Tibet, and the Qiang would fall under the domination of both. Each village may have one or more stone towers in the past, and the Himalayan Towers remains a distinctive feature of some Qiang villages. Himalayan Towers are also called Stone star-shaped towers, are a series of stone towers located mostly in Kham, a province of premodern Tibet, and in Sichuan. The towers are located principally in the Changtang and Kongpo regions of Tibet as well as in the area inhabited by the modern Qiang people and in the historical region inhabited by the Western Xia. These towers can be found both in cities and in uninhabited regions. Many of the towers use a star pattern of walls as opposed to a strictly rectangular method and heights can exceed 200 ft. The Qiang worship five major gods, twelve lesser gods, some tree gods, and numerous stones were also worshiped as representatives of gods. A special god is also worshiped in every village and locality, who are mentioned by name in the sacred chants of the Qiang priests. Mubyasei, also known Abba Chi, is the supreme god of the universe and the same name is also used to refer to a male ancestor god, Abba Sei. In certain places, Shanwang, the mountain god, is considered to represent the supreme god. Archaeologists have released a photograph of a skull found in an ancient tomb in Alaer (Aral) in Southern Xinjiang, China. The skull shows an unusual characteristic in which the teeth are vertically oriented instead of horizontally. In addition, the researchers have revealed that the skeleton recovered from the tomb measured a massive 2.3 metres (7 feet 6 inches) which researchers have said that skeleton is 4,000 years old and belonged to the Qiang people. The Qiang people have been recognized as a ‘first ancestor’ culture due to their ancient roots – they were mentioned in ancient Chinese texts as well as inscriptions on the oracle bones of 3,000 years ago. However, the ancient Qiang people referred to in these ancient texts were a broad group of nomadic people and the ancestors of the modern Tibeto-Burman speakers, they are therefore not the equivalent of the modern Qiang people who are a small branch of the ancient Qiangs. The Qiangs were also not a single distinctive ethnic group in the past. According to historical records, a clan group made their homes in what is today’s Sichuan Province. During 600 to 900 AD when the Tibetan Regime gradually expanded its rule over the region, some Qiangs were assimilated by the Tibetans and others by the Hans, leaving a small number unassimilated. These developed into the distinctive ethnic group of today. Prehistoric transport and trade nvolved migrations out of the Fertile Crescent would carry early agricultural practices to neighboring regions—westward to Europe and North Africa, northward to Crimea, and eastward to Mongolia. Interestingly, the region where the tomb was uncovered is in the same region where the well-known Tarim mummies with Caucasoid features were recovered. The mummies were found to have typical Europoid body features (elongated bodies, angular faces, recessed eyes), and many of them have their hair physically intact, ranging in color from blond to red to deep brown. Like the Qiang skeleton, the Tarim mummies were also found to be very tall. Could there be a link between them? The ancient people of the Sahara imported domesticated animals from Asia between 6000 and 4000 BCE. In Nabta Playa by the end of the 7th millennium BCE, prehistoric Egyptians had imported goats and sheep from Southwest Asia. Foreign artifacts dating to the 5th millennium BCE in the Badarian culture in Egypt indicate contact with distant Syria. In predynastic Egypt, by the beginning of the 4th millennium BCE, ancient Egyptians in Maadi were importing pottery as well as construction ideas from Canaan. By the 4th millennium BCE shipping was well established, and the donkey and possibly the dromedary had been domesticated. Domestication of the Bactrian camel and use of the horse for transport then followed. Charcoal samples found in the tombs of Nekhen, which were dated to the Naqada I and II periods, have been identified as cedar from Lebanon. Predynastic Egyptians of the Naqada I period also imported obsidian from Ethiopia, used to shape blades and other objects from flakes. The Naqadans traded with Nubia to the south, the oases of the western desert to the west, and the cultures of the eastern Mediterranean to the east. Pottery and other artifacts from the Levant that date to the Naqadan era have been found in ancient Egypt. Egyptian artifacts dating to this era have been found in Canaan and other regions of the Near East, including Tell Brak and Uruk and Susa in Mesopotamia. By the second half of the 4th millennium BCE, the gemstone lapis lazuli was being traded from its only known source in the ancient world—Badakhshan, in what is now northeastern Afghanistan—as far as Mesopotamia and Egypt. By the 3rd millennium BCE, the lapis lazuli trade was extended to Harappa, Lothal and Mohenjo-daro in the Indus Valley Civilization (Ancient India) of modern-day Pakistan and northwestern India. The Indus Valley was also known as Meluhha, the earliest maritime trading partner of the Sumerians and Akkadians in Mesopotamia. The ancient harbor constructed in Lothal, India, around 2,400 years ago is the oldest seafaring harbor known. Ancient Egyptian trade consisted of the gradual creation of land and sea trade routes connecting the Ancient Egyptian civilization with the Fertile Crescent, Arabia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and India. are circular and stepped and were made of clay. structures of Igbo culture was the Nsude Pyramids, at the Nigerian town of Nsude, northern Igboland. Ten pyramidal structures were built of clay/mud. The first base section was 60 ft. in circumference and 3 ft. in height. The next stack was 45 ft. in circumference. Circular stacks continued, till it reached the top. The structures were temples for the god Ala/Uto, who was believed to reside at the top. A stick was placed at the top to represent the god’s residence. The structures were laid in groups of five parallel to each other. Because it was built of clay/mud like the Deffufa of Nubia, time has taken its toll requiring periodic reconstruction. These pyramids bear a different but somewhat similar resemblance to the Step Pyramid of Saqqara, in Egypt and could have possibly, derive from the same cultural/religious/philosophical tradition that inspired this ancient Egyptian monument also similar to Nubian-like pyramids thousands of miles away from the Nubian area in the heart of Igboland. Evidence like this could show some correlation between the ancient Egyptians and the ancient Igbo. There is an existing ideology amongst the Yorubas of Nigeria and other writers of Yoruba history that the original ancestors of the Yorubas originated in ancient Egypt hence there was migration between Egypt and Yorubaland. This researcher contends that even if there was migration between Egypt and Nigeria, such migration did not take place during the predynastic and dynastic period as speculated by some scholars. No one knows precisely the origins of the methods of specialized bronze and brass castings in Nigeria, and the reasons for the similarities between the Nok terracottas (as old as 2,500 years), the art from Igbo-Ukwu near Enugu, and the Yoruba art that produced the famous Ife bronze heads and those of ancient Egyptians. These arts found in Nigeria might have been produced independently of any foreign culture. The ancient Egyptians were not known to be too keen about traveling and to adapt so much to foreign cultures. Trade, adventure, and escape from wars might have led some of them to travel to other parts of the world, but traveling to stay in other countries seemed not to be one of their preferences. Furthermore, the absence of a known and generally acceptable descendant of Egyptians in Nigeria suggests that the Egyptians did
not live in Nigeria permanently. The Nubian dynasty of Egypt (the 25th Dynasty of Egypt) saw the first widespread construction of pyramids (many in modern Sudan) since the Middle Kingdom. Amongst the Yorubas of Nigeria, are of the opinion that there were migrations between Egypt and Yorubaland. There is some thinking that there is some linkage between the Egyptians to the Yorubas, like the various forms of spirits, gods and ancestors worshipped. A royal pyramidal tomb, located in Ji’an, Jilin, was built by the Goguryeo Kingdom. The site includes archaeological remains of 40 tombs which were built by Goguryeo, which was founded by Jumong in a region called Jolbon Buyeo, thought to be located in the middle Amrok River and Tongjia River basin, overlapping the current China–North Korea border located in and around the city of Ji’an in China. Some of the tombs have elaborate ceilings designed to roof wide spaces without columns and carry the heavy load of a stone or earth tumulus (mound) was placed above them. The paintings in the tombs, while showing artistic skills and specific style, are also an example of strong influence from various cultures. located in and around the city of Ji’an in China. Koguryo (or Goguryeo, 2,037 years ago to 668 CE) was an ancient kingdom located in what is now Manchuria and the northern Korean Peninsula. Goguryeo was a Korean kingdom with a religion makeup of Buddhism, Taoism, and Shamanism. In the geographic monographs of the Book of Han, the word Goguryeo was first mentioned around 2,113 to 1,349 years ago, as a region under the jurisdiction of the Xuantu Commandery, page 33. Capital Cities and Tombs of the Ancient Goguryo Kingdom located in and around the city of Ji’an in China and located in the northern and central parts of the Korean Peninsula and the southern and central parts of inner and outer Manchuria. Goguryeo was an active participant in the power struggle for control of the Korean peninsula and was also associated with the foreign affairs of neighboring polities in China and Japan. Jumong, the founder of Goguryeo, was worshipped and respected among the people. There was even a temple in Pyongyang dedicated to Jumong. At the annual Dongmaeng Festival, a religious rite was performed for Jumong, ancestors, and gods. Other pyramids in China, built using different construction methods, and not simply made of piled-up earth. What may deserve more attention than the earthen pyramids of Xi’an, as they are actual layered stone block pyramids, much like those in South America.
Layered stone pyramid of Jian/Zangkunchong (Goguryeo Dynasty)
There are two isolated layered pyramids near the city of Ji’an in Jangxi province in southeastern China. The perfectly preserved Ji’an pyramid is built of precisely cut stone blocks and contains a large burial chamber. Each base has a length of exactly 31.60 meters on every side, and the height is 12.4 meters. It is made up of seven layers, the first of four layers of stone, and all others of three. This layout is surprisingly similar to that of the layered pyramids in South America. The twelve monoliths that were placed so as to lean against the outer walls’ lower layers – the largest of which is 2.7 meters wide and 4.5 meters high – also set this one apart from other Chinese pyramids. Of these twelve monoliths, four are so-called guardian stones, but only “Paechong” (Korean for “warden‘s tomb”) is still intact. Interestingly, the pyramid is oriented to the cardinal points, while the heads of the stone sarcophagi in the chamber pointed precisely to the mystical volcanic crater of Paektusan (Mount Paektu) on the horizon with its beautiful crater lake at an altitude of 2,500 meters. There are three hypotheses about who built it: The first hypothesis suggests that it was built during the ancient Goguryeo empire, which briefly ruled Korea and parts of eastern China, as a stone mausoleum for King Kwangkaeto the Great (Gwangaeto, 374-413 AD). He is also credited with the construction of the nearby stone pyramid that is almost completely destroyed. The foundation walls, with their base lengths of almost 40 meters, are all that remain of that pyramid, which is thought to be his tomb. The second hypothesis posits that the remaining pyramid is the tomb of King Zangsu (Jangsu), which is why it is called “Zangkunchong”. It is also called Juni Ten (the general’s tomb) and “Pyramid of the East”. This name comes from the 20th regent of Goguryeo, the northernmost of the three Korean kingdoms, whose capital was Ji’an. Historical documents state that king Jansu was crowned king in 413 AD at the young age of 19 and went on to lead the kingdom, stretching from Korea to Mongolia, to its golden age. He died in 491 AD. But how did the Goguryeo Dynasty acquire the knowledge necessary for the construction of such flawless layered pyramids, the likes of which had never been seen in the area, and were not seen there again? The third hypothesis posits that the pyramids were built during the Kokuryo period, around 500 AD. That theory does not name the ruler who is buried there.
Xia Pyramids (Xia Dynasty), made of clay bricks
The Xia pyramids are located in western China, on the eastern slope of the Helan mountains, about 35 kilometers west of Yinchuan, the capital of the autonomous region of Ningxia Hui. They consist of pyramidal mausoleums for the imperial family with heights of between 9 and 20 meters, and 207 documented stone tombs for nobles and higher magistrates, all scattered over an area of 40 km2. Chinese researchers have conducted archaeological and scientific analyses on these tombs since the 1980s, but the sudden rise and fall of the western Xia dynasty (also referred to as the Tangut Empire, 1038-1227) remains a mystery. One theory suggests that they were overrun and largely eradicated by invading Mongols under Genghis Khan. The best-preserved burial pyramid (Mausoleum No. 3) is the only one to have been excavated and explored. It was attributed to the first Xia emperor, Jingzong (1003-1048), whose birth name was Li Yuanhao. The pyramids were built with clay tiles, and the construction method used combines elements from the construction of pyramids, towers and traditional temple-mausoleums, while the chambers feature Buddhist elements and paintings, although these might have been added later.
Stone and earth Xituanshan Pyramid near Jiaohe
The ruins of Xituanshan, near the city of Jiaohe, on the border of the Taklamakan Desert, were excavated in 1950 after water erosion exposed the first two tombs (see sunken desert cities on page 586). The entire complex spans an area of 1,000 meters x 500 meters for a total area of 500,000 m2. Historical accounts state that it was the capital of the Chesi Empire from about 108 BC to 450 AD. But in 2006, Chinese archaeologists dug deeper and uncovered a group of six much older tombs that are thought to date back to the Bronze Age, or 1,000 BC, making them 3,000 years old, or almost 1,000 years older than the Chesi empire. For five of the pyramidal structures, only parts of the foundations and first layers remain, but these still reveal their original shape and size. The largest pyramidal tomb has been clearly identified as a three-layered pyramid made of stones and earth. It has a square base of 50 meters x 30 meters and an oval platform of 15 meters x 10 meters at its apex, on which stood a stone sarcophagus covered with a granite plate and surrounded by four engraved stone tablets. This mysterious sarcophagus and the pyramidal tombs were attributed to the “king of an earlier tribe”. I am certain that this complex was built by the legendary Sand People.
Stone and earth Hongshan Pyramids near Sijiazi
In the autonomous province of Inner Mongolia in northeastern China, a 5,000-year-old, three-tiered pyramid was discovered on a shaped-hill pyramid north of the city of Sijiazi in Aohan County. Even Chinese archaeologists immediately recognized it as a man-made pyramid, specifically as a burial complex from the Hongshan Culture (4,500-2,250 BC). The tiered pyramid is said to be about 30 meters long and 15 meters wide, and an altar and seven graves were found on its platform. In the graves, besides the remains, were various vaults containing a bone flute, a stone ring and the stone statue of a goddess. The archaeologists also discovered clay fragments with small stars scratched into their interiors which they believed to indicate either an early culture’s astronomical knowledge or a mythology that indicated that they would one day return to the stars.
What is the oldest Chinese dynasty?
The Shang dynasty is the oldest Chinese dynasty whose existence is supported by archaeological finds, but more evidence for the existence of the Xia dynasty may yet emerge. It’s estimated that the Shang ruled the Yellow River Valley of China for most of the second millennium BCE—so about 1766 to 1046 BCE. For centuries, people found what they called dragon bones—bones and shells with mysterious inscriptions—in many parts of China. Excavations of the ancient city of Anyang in the early twentieth century revealed tens of thousands of these bone fragments and bronze vessels, many of which had inscriptions in proto-Chinese characters. These artifacts contained records dating back to the Shang dynasty, allowing scholars to learn much about Shang life, such as their agricultural methods, medical treatments, legal system, and craft making styles. The Shang built huge cities with strong social class divisions, expanded earlier irrigation systems, excelled in the use of bronze, and developed a writing system. Shang kings fulfilled a sacred, not political, role, while a council of chosen advisers and bureaucrats—official administrators—organized and ran the government. The oldest surviving form of Chinese writing is found as inscriptions of divination records on the bones or shells of animals, called oracle bones; oracle, from a similar Latin root as the English word orator, means holy messenger or speaker. The writing found on oracle bones shows complexity, indicating that this language had existed for a long time. Writing allowed science in the Shang dynasty to advance, as observations could be recorded more accurately. The Oracle Scripts are accounts of eclipses and other celestial events written by astronomers of the Shang period. Shang astronomers’ works also showed advances in mathematics, the development of odd and even numbers, and principles of accounting. The I-Ching—also known as The Book of Changes—was either written or compiled at this same time, around 3,250 to 3,150 years ago. The I-Ching is a book of divination with roots going back to the fortune tellers of the rural areas and their oracle bones. Musical instruments were also developed by the Shang. At Yin Xu, near Angyang, excavations have revealed instruments from the Shang period such as the ocarina—a wind instrument—drums, and cymbals. Bells, chimes, and bone flutes have been discovered elsewhere. The Shang created a lunar calendar, based on the cycles of the moon, that was used to predict and record important events, especially planting and harvesting of crops. Because lunar years are shorter than solar years, which are based on the Earth’s orbit of the sun, Shang kings employed specially-trained astronomers who made adjustments and maintained the precision of the calendar. Bronze, an alloy of copper and tin, was a hugely important metal during the Shang period. Shang metal workers developed a highly sophisticated method for casting bronze and used it to make ceremonial objects and weapons. Bronze swords and spearheads were stronger than other available metals, giving Shang soldiers an advantage in battle. The influence of the Early Shang extended hundreds of kilometers away from the capital, and many of the Shang bronze techniques diffused over large areas. The Shang in turn adopted skills, ideas, and even crops from some neighboring societies, such as wheat and axes, which may have come from Western Asia. However—because natural barriers like the ocean, mountain ranges, deserts, and steppes kept the Shang in relative isolation—the Shang dynasty as well as later dynasties evolved in unique and insular ways. The first Shang ruler supposedly founded a new capital for his dynasty at a town called Shang, near modern-day Zhengzhou on the Yellow River, is in east-central China Henan province notable as the ancient Shang dynasty capital, whose earthen walls still stand in the city center. Shang, along with other ancient Chinese cities, had two city walls—one inner and one outer wall. The common residents could live within the outer wall, but could not go past the inner wall, which enclosed a temple area, cemetery sites, bronze foundries, bronze casting areas, and bone workshops. The inner walls thus encircled an area of political elite and craft specialists, who together were the engineers of the important ritual performances. In this way, the architecture of these cities was designed to separate different social classes. However, it seems that there were many capitals aside from this one, and rulers may have moved from one to the other because of religious rituals, military strategy, or food requirements. That suggests that the power of the dynasty was concentrated in the king, whose political authority was reinforced by the Shang religion. Anyang, another Shang capital, also in modern-day Henan Province, is another important—but slightly later—Shang city that has been excavated. It was located at the intersection between lowland agricultural areas of the North China Plain and mountains which acted as a defensive border. This site yielded large numbers of oracle bones that describe the travels of eleven named kings. The names and timeframes of these kings match traditional lists of Shang kings. Anyang was a huge city, with an extensive cemetery of thousands of graves and 11 large tombs—evidence of the city’s labor force, which may have belonged to the 11 Shang kings. Cities were crucial to political and religious affairs, and they were the seats of administrative affairs, royal tombs, palaces, and shrines. Common people were concentrated in the agricultural areas outside the cities. The border territories of Shang rule were led by chieftains who gained the right to govern through connections with royalty. Shang relied heavily on neighboring fiefs for raw materials, much of which was devoted to ceremonial performances. The Shang enacted a feudal system, a system in which duties are tied to land ownership, with sharp class divisions based on clan birthright. The aristocracy were centered around Anyang, which was the seat of governmental affairs for the surrounding areas. Regional territories farther from the capital were also controlled by the wealthy. There were many local rulers who held hereditary titles. In this imperial system, elite classes benefitted from the production of peasants and large-scale projects under elite control, usually operated using various forms of unfree labor. There is also evidence of a class of proto-bureaucrats, many of whom were titled officials, who had managerial roles and kept extensive records. Shang religion was incredibly important, and it extended into the political and economic spheres. The Shang religion and state power were closely connected; state power was consolidated through a sense of reverence for royal Shang ancestors. Further, by the end of the Shang dynasty, the king was the only one who could interpret the oracle bones, thereby making him the head shaman. The Shang religion was characterized by a combination of animism, the idea that everything has a soul; shamanism, the belief in shamans who have the ability to communicate with the spiritual world; ancestor worship; and divination. Different gods represented natural and mythological symbols, such as the moon, the sun, the wind, the rain, the dragon, and the phoenix. Peasants prayed to these gods for bountiful harvests. Festivals to celebrate gods were also common. In particular, the Shang kings, who considered themselves divine rulers, consulted the great god Shangdi—the Supreme Being who ruled over humanity and nature—for advice and wisdom. The Shang believed that the ancestors could also confer good fortune; the Shang would consult ancestors through oracle bones in order to seek approval for any major decision, and to learn about future success in harvesting, hunting, or battle. It appears that there was belief in the afterlife during the Shang dynasty. Archaeologists have found Shang tombs surrounded by the skulls and bodies of human sacrifices. Some of these contain jade, which was thought to protect against decay and grant immortality. Archaeologists believe that Shang tombs were very similar to those found in the Egyptian pyramids in that they buried servants with them. Chinese archaeologists theorize that the Shang, like the ancient Egyptians, believed their servants would continue to serve them in the afterlife. Because of this belief, aristocrats’ servants would be killed and buried with them when they died. Another interpretation is that these were enemy warriors captured in battle. One elaborate tomb which has been unearthed was that of Lady Hao, a consort of a Shang king who reigned around 1200 BCE. The artifacts found in her tomb indicate that she had a high social status and a great deal of power in Shang society, which makes historians speculate about the role of women in the Shang dynasty. Based on the artifacts found in Lady Hao’s tomb, it seems that she had her own wealth and political influence, and it is possible that she also had a prominent role in the military, as many bronze weapons were found buried with her. The 16 other skeletons in Fu Hao’s tomb are believed to have been slaves, who were buried alive in order to serve her in the afterlife. The Chinese Bronze Age had begun by 3,700 years ago in the kingdom of the Shang dynasty and ancient DNA reveals a migration of the ancient Di-qiang populations into Xinjiang as early as the early Bronze Age. Moreover, in the Chinese Bronze Age it was believed the king’s right to rule was based on his good relations with the spirits of his ancestors who controlled the destiny of the domain. The king continually posed questions to his ancestors about policy. He did this by instructing his scribe to write the question on an “oracle bone” — that is, an animal shoulder blade or the breast bone of a turtle. A priest then held a hot rod to the bone until it cracked and interpreted the pattern of the cracks for the answer. It was also the king’s duty to please the great forces of nature — the sun and rain gods — who controlled the outcome of the harvest. So that these gods and his ancestor spirits would look favorably on his kingdom, the king made regular sacrifices of wine and cereals, which were placed in elaborate bronze vessels and heated over the fires on the temple altar. During the Shang dynasty bronze vessels were the symbol of royalty. At times the Shang kings make animal and human sacrifices as well; and when the king and powerful members of the royal court died, it was not unusual that their wives, servants, bodyguards, horses and dogs were killed and buried with them. During the Zhou Dynasty people gradually turned away from this custom and substituted clay figures for real people and animals. The Zhou Dynasty (Chinese folk religion, Ancestor worship, and Heaven worship) lasted longer than any other dynasty in Chinese history with capitals in Fenghao (3,046 to 2,771 years ago), Luoyang (2,510 to 314 years ago). The Zhou emulated extensively Shang cultural practices, perhaps to legitimize their own rule, and became the successors to Shang culture. At the same time, the Zhou may also have been connected to the Xirong, a broadly defined cultural group to the west of the Shang, which the Shang regarded as tributaries. In about 1050 BC the Shang dynasty was defeated in battle by armies from Zhou, a rival state to the west, which seems both to have inherited cultural traditions from the Neolithic cultures of the northwest and to have absorbed most of the material culture of the Shang. The conquerors retained their homeland in the Wei River valley in present-day Shaanxi province and portioned out the rest of their territory among their relatives and local chiefs, creating a number of local courts or principalities. The culture of the early Zhou is known to us not solely through archaeological evidence, but also through transmitted texts, such as the Book of Documents (Shujing), which describes the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the victory of just and noble warriors over a decadent and dissolute king. In these texts and bronze inscriptions alike, the rule of the Zhou kings was linked to heaven, conceived of as the sacred moral power of the cosmos. A king and a dynasty could rule only so long as they retained heaven’s favor. Zhou rulers introduced what was to prove one of East Asia’s most enduring political doctrines. The concept of the “Mandate of Heaven”. They did this so by asserting that their moral superiority justified taking over Shang wealth and territories, also that heaven had imposed a moral mandate on them to replace the Shang and return good governance to the people. The Mandate of Heaven was presented as a religious compact between the Zhou people and their supreme god in heaven (literally the ‘sky god’). The Zhou agreed that since worldly affairs were supposed to align with those of the heavens, the heavens conferred legitimate power only one person, the Zhou ruler. In return, the ruler was duty-bound to uphold heaven’s principles of harmony and honor. Any ruler who failed in this duty, who let instability creep into earthly affairs, or who let his people suffer, would lose the mandate. Under this system, it was the prerogative of spiritual authority to withdraw support from any wayward ruler and to find another, more worthy one. In this way, the Zhou sky god legitimated regime change. In using this ccreed, nthe Zhou rulers had to acknowledge that any group of rulers, even they themselves could be ousted if they lost the mandate of haven because of improper practices. The book of odes, written during the Zhou period clearly intoned this caution. The early Zhou kings contended that heaven favored their triumph because the last Shang kings had been evil men whose policies brought pain to the people through waste and corruption. After the Zhou came to power, the mandate became a political tool. Like in Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus River valley, civilization in China developed around a great river. The Yellow River carried floodwater and sediment to the land around it, making the area incredibly fertile, and thus an excellent place for the Stone Age inhabitants of the area to experiment with agriculture. While the Yellow River was the main cradle of Chinese civilization, people also settled around other rivers, such as the Huai and the Yangtze. By around 4000 BC, villages began to appear. They cultivated a number of crops, but most important was a grain called millet (two types of millet: proso and foxtail millet). The Chinese, even up to modern times, revere the Wǔgǔ, the Five Sacred Grains, which are traditionally considered soybeans, wheat, hemp, and the two types of millet. Rice was also cultivated in this period, but it was not yet the important staple that it would later become in the Chinese diet. The Neolithic Chinese domesticated animals such as pigs, dogs, and chickens. Silk production, through the domestication of silk worms, probably also began in this early period. During the Neolithic period in China, there were multiple groups of people, mostly around the Yellow River, with separate emerging cultures. Some of these various cultures include the Yangshao culture (ca. 4800 – ca. 3000 BC), the Majiayao culture (ca. 3800 – ca. 2000 BC), the Dawenkou culture (ca. 4300 – ca. 2400 BC), the Qijia culture (ca. 2200 – ca. 1800 BC), and the Longshan culture (ca. 2600 – ca. 2000 BC). Over time, they influenced each other more and more, and pottery, art, and artifacts recovered by archaeologists show greater homogenization as time went on. By 2000 BC a more unified Chinese culture was developing, and there is also evidence of urbanism and the use of early writing among the Chinese. Archaeologists have discovered advanced Bronze Age culture in China, which they call the Erlitou culture. Its capital, Erlitou, was a huge city around 2000 BC, with two possible palaces, a drainage system, and what seems to have been a very high population. This may be the people referred to in Chinese mythology as the Xia. ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Shimao pyramid: ‘Pyramid of eyes’ at heart of 4300-year-old city
A 4,300-year-old city, which has a massive step pyramid that is at least 230 feet (70 meters) high and spans 59 acres (24 hectares) at its base, has been excavated in China. The pyramid was decorated with eye symbols and “anthropomorphic,” or part-human, part-animal faces. Those figures “may have endowed the stepped pyramid with special religious power and further strengthened the general visual impression on its large audience,” the archaeologists wrote in the article. The pyramid contains 11 steps, each of which was lined with stone. On the topmost step, there “were extensive palaces built of rammed earth, with wooden pillars and roofing tiles, a gigantic water reservoir. The city’s rulers lived in these palaces, and art and craft production were carried out nearby. The stepped pyramid complex seems to possibly have functioned not only as a residential space for ruling Shimao elites, but also as a space for artisanal or industrial craft production. Shimao is a Neolithic site in Shenmu County, Shaanxi, China. The site in located in the northern part of the Loess Plateau, on the southern edge of the Ordos Desert. Unusual features include jade embedded in the city walls, possibly to provide spiritual protection, and paintings of geometrical patterns on the inner walls. Many human skulls were found under the city gate, suggesting ritual sacrifices during construction. For five centuries, a city flourished around the pyramid. At one time, the city encompassed an area of 988 acres (400 hectares), making it one of the largest in the world, the archaeologists wrote. Today, the ruins of the city are called “Shimao,” but its name in ancient times is unknown. A series of stone walls with ramparts and gates were built around the pyramid and the city. “At the entrance to the stepped pyramid were sophisticated bulwarks [defensive walls] whose design suggests that they were intended to provide both defense and highly restricted access. The remains of numerous human sacrifices have been discovered at Shimao. “In the outer gateway of the eastern gate on the outer rampart alone, six pits containing decapitated human heads. Some of the victims may be from another archaeological site called Zhukaigou, which is located to the north of Shimao, and the people of Shimao may have conquered the neighboring site. “Morphological analysis of the human remains suggests that the victims may have been related to the residents of Zhukaigou, which could further suggest that they were taken to Shimao as captives during the expansion of the Shimao polity,” the study said. While archaeologists have known about Shimao for many years, it was once thought to be part of the Great Wall of China, a section of which is located nearby. It wasn’t until excavations were carried out in recent years that archaeologists realized that Shimao is far older than the Great Wall, which was built between 2,700 and 400 years ago. ref, ref
|
Ancient Jade Artifacts Found in Inner Mongolia |
| “In North China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region archaeologists have excavated jade artifacts dating back more than 8,000 years, the earliest discovered in China. The priceless relics were discovered during excavations around the Xinglonggou Ruins of Aohan Banner in Chifeng City, and their discovery was one of the pinnacles of achievement for archaeological research in the region in 2001. Of particular interest is the discovery of an ancient funeral custom in which jade was embedded into one of the eye sockets of the dead before they were buried. No one can yet explain why this was done. One theory is that the jade pieces may have been ear adornments previously but were moved into the eye socket later to brighten the eyes of the dead who might have suffered from eye disease. Also of interest were 296 clam-shell artifacts excavated from an ash pit, showing contact and ancient cultural exchanges between Inner Mongolia and central China. Another find was the country’s earliest sculpture. Made of red clay, the finely-designed pottery sculpture consists of three women group closer together. In the Dong Ujimqin Banner on the Xilin Gol Plain, archaeologists have also found ruins of a cave inhabited by ancient-people about 100,000 years ago. As most of the fossils were from wild horses experts believe that the ancient people living on the plain may have survived by hunting wild horses.” ref |
- Proto-Transeurasian/Altaic languages
- Proto-Tungusic-Mongolo
- Proto-Koreanic-Japano
- Proto-Tungusic
- Proto-Turkic
- Proto-Mongolic
- Proto-Koreanic
- Proto-Japonic
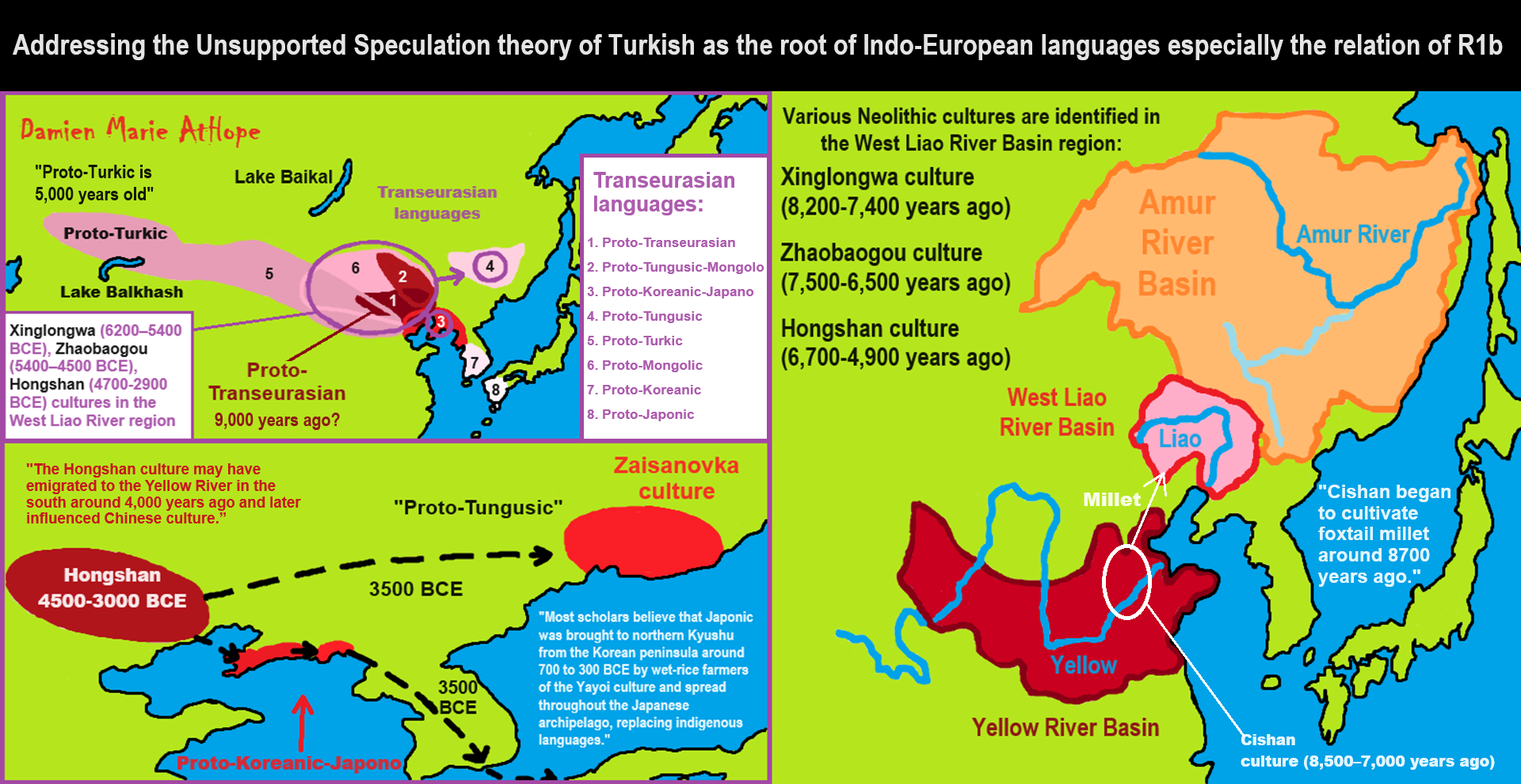
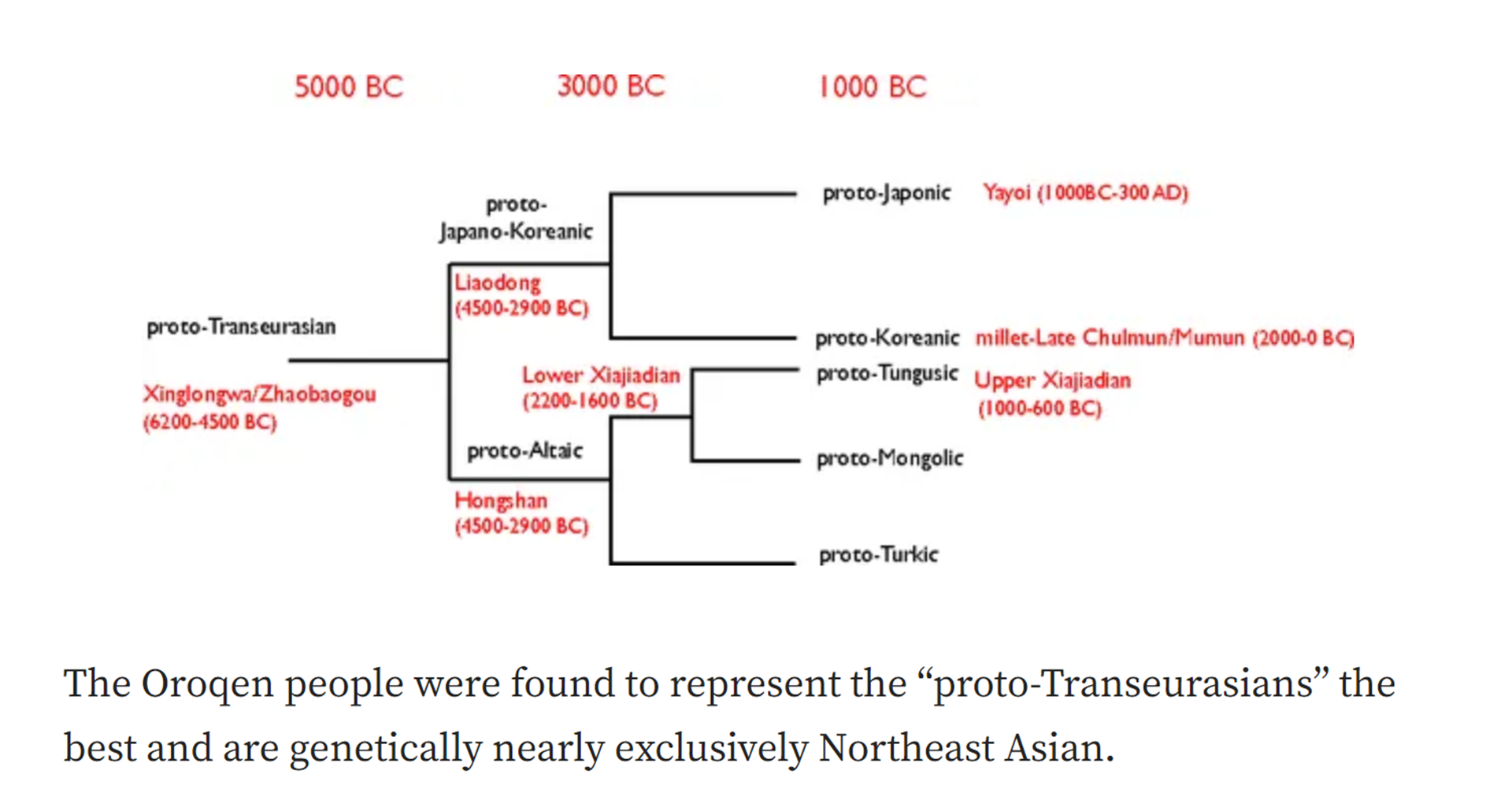
“Xinglongwa (6200–5400 BCE), Zhaobaogou (5400–4500 BCE) Hongshan (4700-2900 BCE) cultures in the West Liao River region.” ref, ref, ref, ref
“Integrating linguistic and archaeological evidence, we support the hypothesis that the expansion of the Transeurasian language system in the Amur River basin is related to the agricultural development and expansion of the southern Hongshan culture.” ref
“The Liao Civilization or Liao River Civilization (Chinese: 遼河文明), named after the Liao River, is an umbrella term for several ancient civilizations that originated in the Liao basin. It is thought to have first formed in 6,200 BCE. This civilization was discovered when the Hongshan culture was discovered. Large-scale pit-type houses, graves and temples with altars were excavated. It is thought that the Liao civilization may have been “a country” of the prehistoric age. A model of the feng shui were excavated from remains of the Hongshan culture. Ball products such as the jade which made the precursors of Chinese dragon were discovered in remains of Xinglongwa culture. In addition, the oldest pit-comb ware and Liaoning bronze dagger (biwa form bronze sword) were excavated. Since it was contemporaneous with the Yellow River civilization and Yangtze civilization, it is thought to have been a part of ancient Chinese culture. This region was thought to have been desert for the past 1 million years. However, a 2015 study found that the region once featured rich aquatic resources and deep lakes and forests that existed from 12,000 years ago to 4,000 years ago. It was changed into desert by climate change which began approximately 4,200 years ago. Therefore, people of the Hongshan culture may have emigrated to the Yellow River in the south approximately 4,000 years ago and later influenced Chinese culture.” ref
“The most ancient populations of the West Liao River valley exhibited a high frequency of Haplogroup N-M231. A study by Yinqiu Cui et al. from 2013 found that 63% of the combined samples from various Hongshan archeological sites belonged to the subclade N1 (xN1a, N1c) of the paternal haplogroup N-M231 and calculated N to have been the predominant haplogroup in the region in the Neolithic period at 89%, its share gradually declining over time. Today, this haplogroup is most common in Finland, the Baltic states, and among northern Siberian ethnicities, such as the Yakuts. Individuals at the Liao civilization were assigned into five different Y sub-haplogroups using diagnostic single nucleotide polymorphisms, namely N1 (xN1a, N1c), N1c, C/C3e, O3a (O3a3) and O3a3c. Ancient samples of the Jinggouzi site situated to the northwest of the Liao civilization were assigned to Haplogroup C-M217. Northern nomads from Jinggouzi might have entered the West Liao River valley, but these Jinggouzi people (closely related to Xianbei and Oroqen) were culturally and genetically distinct from the original people of the West Liao River valley, who carried the characteristic Haplogroup N-M231 lineage. The Haplogroup O-M122 that was observed among Liao individuals is believed to have spread to the Liao civilization from the Yellow River civilization in the southwest. This lineage is most commonly associated with speakers of Sino-Tibetan languages (such as the Han Chinese). However, its frequency only began to rise in the Bronze Age, and the ancient Liao River population was different from the Yellow River population. This means the Liao civilization was occupied by a diverse sequence of human cultures that were originally distinct from both the farming populations of the Yellow River and the nomads of the Eurasian steppe.” ref
“The formation and development of the Lower Xiajiadian culture population was likely a complex process affected by admixture of ethnically different people. The Lower Xiajiadian culture of the West Liao River included people carrying haplogroups from northern Asia, but there was genetic evidence of the migration of millet farming people from the Central Plains (Zhongyuan). The climate of the West Liao River valley was warmer at the beginning of the Early Bronze Age, which may be one of the driving forces for the northward migration of the Central Plains farming population. An archaeological study showed that the painted potteries of the Lower Xiajiadian were influenced by the Erlitou culture. The people of the Dadianzi site of Inner Mongolia received the haplogroup O3 from the immigrants of the Central Plains, and a Lower Xiajiadian individual was identified to possess both the maternal lineage of D4 and paternal lineage of O3-M122. Due to a cooling climate, part of the Lower Xiajiadian culture population migrated to the south and influenced the Central Plains. Among the Yin Ruins relics of Shang Dynasty, artefacts with northern cultural influences have been identified. The Upper Xiajiadian culture and Bronze Age West Liao River farmers (WLR_BA) can be modeled as deriving their ancestry from both Amur hunter-gatherers and Yellow River farmers. This particular ancestral lineage has been associated with Proto-Korean-speakers, and the Upper Xiajiadian culture. They displayed primarily subclades of the paternal haplogroups O and C, with a smaller minority of N.” ref
“Various Neolithic cultures have been identified in the Xiliao River / West Liao River region. Broomcorn millet and foxtail millet were the main cereal crops, while pigs and dogs were the main domesticated animals found at Neolithic archaeological sites.
- Xiaohexi culture (9,000-8,500 years ago)
- Xinglongwa culture (8,200-7,400 years ago)
- Zhaobaogou culture (7,500-6,500 years ago)
- Fuhe culture (7,200-7,000 years ago)
- Xinle culture (7,200-6,800 years ago)
- Hongshan culture (6,700-4,900 years ago)
- Xiaoheyan culture (5,000-4,000 years ago)” ref
“Bronze Age cultures of the Xiliao River region are:
- Lower Xiajiadian culture (4,000-3,200 years ago)
- Upper Xiajiadian culture (3,200-2,600 years ago)” ref
Bioarchaeological perspective on the expansion of Transeurasian languages in Neolithic Amur River basin
“Abstract: Owing to the development of sequencing technology, paleogenomics has become an important source of information on human migration and admixture, complementing findings from archaeology and linguistics. In this study, we retrieved the whole genome and Y chromosome lineage from late Neolithic Honghe individuals in the Middle Amur region in order to provide a bioarchaeological perspective on the origin and expansion of Transeurasian languages in the Amur River basin. Our genetic analysis reveals that the population of the Amur River basin has a stable and continuous genetic structure from the Mesolithic Age up to date. Integrating linguistic and archaeological evidence, we support the hypothesis that the expansion of the Transeurasian language system in the Amur River basin is related to the agricultural development and expansion of the southern Hongshan culture. The spread of agricultural technology resulted in the addition of millet cultivation to the original subsistence mode of fishing and hunting. It played a vital role in the expansion of the population of the region, which in its turn has contributed to the spread of language.” ref
“The Russian name Amur comes from the Tungusic term for “river”. Tungusic peoples are an ethno-linguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia and Northeast Asia. Historically, it was common to refer to a river simply as “water”. There are similar words for “water” or “river” in a number of Asiatic languages: e.g. 물 mul (“water”) in Korean, muren or mörön (“river”) in Mongolian, and 水 midu > mizu (“water”) in Japanese. The name “Amur” may have evolved from a root word for water, coupled with a size modifier for “Big Water. For many centuries, inhabitants of the Amur Valley comprised the Tungusic (Evenki, Solon, Ducher, Jurchen, Nanai, Ulch), Mongol (Daur) people, some Ainu and, near its mouth, the Nivkhs.” ref
“Northern China harbored the world’s earliest complex societies based on millet farming, in two major centers in the Yellow River and West Liao River basins. Until now, their genetic histories have remained largely unknown. Here we present 55 ancient genomes dating to 7500-1700 years ago from the Yellow River, West Liao River, and Amur River regions. Contrary to the genetic stability in the Amur River, the Yellow River and West Liao River genetic profiles substantially changed over time. The Yellow River populations show a monotonic increase over time in their genetic affinity with present-day southern Chinese and Southeast Asians. In the West Liao River, intensification of farming in the Late Neolithic is correlated with increased Yellow River affinity while the inclusion of a pastoral economy in the Bronze Age was correlated with increased AR affinity. Our results suggest a link between changes in subsistence strategy and human migration, and fuel the debate about archaeolinguistic signatures of past human migration.” ref
“China is one of the earliest independent centers in the world for the domestication of cereal crops, second only to the Near East, with the rainfed rice agriculture in the Yangtze River Basin in southern China, and dryland millet agriculture in northern China. Northern China represents a large geographic region that encompasses the Central Plain in the middle-to-lower Yellow River basin, the birthplace of the well-known Yellow River civilization since the Neolithic period. However, northern China extends far beyond the Central Plain and includes several other major river systems in distinct ecoregions (Fig. 1). Especially, it is now well received that the West Liao River region in northeast China (Fig. 1) played a critical role distinct from the Yellow River region in the adoption and spread of millet farming. Both foxtail (Setaria italica) and broomcorn millets (Panicum miliaceum) were first cultivated in the West Liao River and lower reaches of the Yellow River basins since at least 6000 BCE or 8,000 years ago. In the ensuing five millennia, millets domesticated in northern China spread across east Eurasia and beyond. Millets had served as one of the main staple foods in northeast Asia, particularly until the introduction of maize and sweet potato in the 16–17th centuries.” ref
“Both the Yellow River and the West Liao River are known for rich archeological cultures that relied substantially on millet farming. By the Middle Neolithic (roughly 4000 BCE), complex societies with a substantial reliance on millet farming had developed in the West Liao River (Hongshan culture; 4500–3000 BCE) and in the Yellow River (Yangshao culture; 5000–3000 BCE) basins. For example, excavations of Hongshan societies in the West Liao River yielded public ceremonial platforms with substantial offerings including numerous jade ornaments, among which the “Goddess Temple” at the Niuheliang site is the most famous. The establishment of the Middle Neolithic complex societies appears to have been associated with rapid population growth and cultural innovation, and may have been linked to the dispersal of two major language families, Sino-Tibetan from the Yellow River and Transeurasian from the West Liao River, although some scholars debate the genealogical unity of the latter.” ref
“Compared with the Yellow River region where crop cultivation already took the status of the dominant subsistence strategy by the Middle Neolithic, the level of reliance on crops in the West Liao River region has changed frequently in association with changes in climate and archeological culture. For example, paleobotanical and isotopic evidence suggest that the contribution of millets to the diet of the West Liao River people steadily increased from the Xinglongwa to Hongshan to Lower Xiajiadian (2200–1600 BCE) cultures, but was partially replaced by nomadic pastoralism in the subsequent Upper Xiajiadian culture (1000–600 BCE). Although many archeologists associated this subsistence switch with a response to the climate change, it remains to be investigated whether substantial human migrations mediated these changes. The West Liao River region adjoins the Amur River region to the northeast, in which people continued to rely on hunting, fishing, and animal husbandry combined with some cultivation of millet, barley, and legumes into the historic era. Little is known to what extent contacts and interaction between Yellow River and West Liao River societies affected the dispersal of millet farming over northern China and surrounding regions. More generally, given the limited availability of ancient human genomes so far, prehistoric human migrations and contacts as well as their impact on present-day populations are still poorly understood in this region.” ref
“Wide-ranging datasets from these disciplines, including a comprehensive Transeurasian agropastoral and basic vocabulary; an archaeological database of 255 Neolithic–Bronze Age sites from Northeast Asia; and a collection of ancient genomes from Korea, the Ryukyu islands and early cereal farmers in Japan, complementing previously published genomes from East Asia. Challenging the traditional ‘pastoralist hypothesis’, we show that the common ancestry and primary dispersals of Transeurasian languages can be traced back to the first farmers moving across Northeast Asia from the Early Neolithic onwards, but that this shared heritage has been masked by extensive cultural interaction since the Bronze Age. As well as marking considerable progress in the three individual disciplines, by combining their converging evidence we show that the early spread of Transeurasian speakers was driven by agriculture.” ref
“In an attempt to identify the individual homelands of the five families making up the Transeurasian grouping, i.e. the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, Koreanicm and Japonic families. Combining various linguistic methods and principles such as the diversity hotspot principle, phylolinguistics, cultural reconstruction, and contact linguistics, researchers propose that the individual speech communities were originally familiar with millet agriculture, while terms for pastoralism or wetrice agriculture entered their vocabularies only at a later stage.” ref
“We further propose that the individual speech communities of Transeurasian grouping, i.e. the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, Koreanic, and Japonic families were originally familiar with millet agriculture, while terms for pastoralism or wet rice agriculture entered their vocabularies only at a later stage.” ref
“In this study, we retrieved the whole genome and Y chromosome lineage from late Neolithic Honghe individuals in the Middle Amur region in order to provide a bioarchaeological perspective on the origin and expansion of Transeurasian languages in the Amur River basin. Our genetic analysis reveals that the population of the Amur River basin has a stable and continuous genetic structure from the Mesolithic Age up to date. Integrating linguistic and archaeological evidence, we support the hypothesis that the expansion of the Transeurasian language system in the Amur River basin is related to the agricultural development and expansion of the southern Hongshan culture. The spread of agricultural technology resulted in the addition of millet cultivation to the original subsistence mode of fishing and hunting. It played a vital role in the expansion of the population of the region, which in its turn has contributed to the spread of language.” ref
“To understand the Neolithic farming expansions between the West Liao River Valley and the Yellow River Valley, we analyzed mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and the Y chromosome of 48 individuals from two archeological sites, Jiangjialiang (>3000 BCE) and Sanguan (~1500 BCE). These two sites are situated between the two farming centers and experienced a subsistence shift from hunting to farming. We did not find a significant difference in the mtDNA, but their genetic variations in the Y chromosome were different. Individuals from the Jiangjialiang belonged to two Y haplogroups, N1 (not N1a or N1c) and N1c. The individuals from the Sanguan are Y haplogroup O3. Two stages of migration are supported. Populations from the West Liao River Valley spread south at about 3000 BCE, and a second northward expansion from the Yellow River Valley occurred later (3000–1500 BCE).” ref
“The Uralic languages form a language family of 42 languages spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. Theories proposing a close relationship with the Altaic languages (Transeurasian language) were formerly popular, based on similarities in vocabulary as well as in grammatical and phonological features, in particular the similarities in the Uralic and Altaic pronouns and the presence of agglutination in both sets of languages, as well as vowel harmony in some. For example, the word for “language” is similar in Estonian (keel) and Mongolian (хэл (hel)). These theories are now generally rejected, and most such similarities are attributed to language contact or coincidence.” ref
“We show that most Uralic speakers share a distinct ancestry component of likely Siberian origin, which suggests that the spread of Uralic languages involved at least some demic component. The linguistic landscape of North Eurasia is dominated by three language families—Turkic, Indo-European (IE), and Uralic. It has recently been shown that the spread of Turkic languages was mediated by gene flow from South Siberia. Similarly, ancient DNA evidence of a major episode of gene flow from the Ponto-Caspian Steppe Belt to Central Europe and Central Asia during the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age (BA) has been interpreted as supporting the ‘Steppe Hypothesis’ of the spread of IE languages. However, while historical linguists have some level of consensus over the origin and spread of the Uralic languages and archaeologists have views about the dynamics of material culture over the relevant time and space, the genetic history of Uralic-speaking populations has remained poorly known. The Uralic family contains 40–50 different languages and covers a vast territory, mainly from the shores of the Baltic Sea in Europe to the West Siberian Plain and the Taymyr Peninsula in Asia (Fig. 1a). According to the classical view, the Uralic languages derive from a protolanguage that split into two major branches—the Finno-Ugric (FU) and the Samoyed. The suggested age of the Uralic language family is 6,000–4,000 years years ago. The most widely accepted hypotheses place the homeland of the Uralic language family into the watershed of river Volga and its tributaries Oka and Kama, while some scholars propose a Siberian homeland. Sampled populations (Estonians, Udmurts or Khanty vs others) with high versus low probability to share their patrilineal ancestry in chrY haplogroup N.” ref
“It is generally considered that N-M231 arose in East Asia approximately 19,400 (±4,800) years ago and populated northern Eurasia after the Last Glacial Maximum. Males carrying the marker apparently moved northwards as the climate warmed in the Holocene, migrating in a counter-clockwise path, to eventually become concentrated in areas as far away as Fennoscandia and the Baltic. The apparent dearth of haplogroup N-M231 amongst Native American peoples indicates that it spread after Beringia was submerged, about 11,000 years ago. It has been found with greatest frequency among indigenous peoples of Russia, including Finnic peoples, Mari, Udmurt, Komi, Khanty, Mansi, Nenets, Nganasans, Turkic peoples (Yakuts, Dolgans, Khakasses, Tuvans, Tatars, Chuvashes, etc.), Buryats, Tungusic peoples (Evenks, Evens, Negidals, Nanais, etc.), Yukaghirs, Luoravetlans (Chukchis, Koryaks), and Siberian Eskimos, but certain subclades are very common in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, and other subclades are found at low frequency in China (Yi, Naxi, Lhoba, Han Chinese, etc.). Especially in ethnic Finnic peoples and Baltic-speaking peoples of northern Europe, the Ob-Ugric-speaking and Northern Samoyed peoples of western Siberia, and Turkic-speaking peoples of Russia (especially Yakuts, but also Altaians, Shors, Khakas, Chuvashes, Tatars, and Bashkirs).” ref
“Nearly all members of haplogroup N among these populations of northern Eurasia belong to subclades of either haplogroup N-CTS6128/M2048 or haplogroup N-P43. N1(xN1a,N1c) was found in ancient bones of Liao civilization:
- Niuheliang (Hongshan Culture, 6500–5000 years ago) 66.7%
- Halahaigou (Xiaoheyan Culture, 5000–4200 years ago) 100.0%
- Dadianzi (Lower Xiajiadian culture, 4200–3600 years ago) 60.0%” ref
“A sample excavated at the Houtaomuga site in the Yonghe neighborhood of Honggangzi Township, Da’an, Jilin, China dating back to 7430–7320 years ago (Phase II of the Early Neolithic) has been found to belong to Y-DNA haplogroup N and mtDNA haplogroup B4c1a2. This sample is autosomally identical with the Neolithic Amur River Basin populations, of which Nivkh people are the closest modern representative. As the paper detected this ancestry in terminal Pleistocene USR1 specimen in Alaska, it is therefore, postulated that there was gene flow from Amur to America of a population belonging to a hypothetical Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Nivkh linguistic family. N has also been found in many samples of Neolithic human remains exhumed from Liao civilization in northeastern China, and in the circum-Baikal area of southern Siberia. It is suggested that yDNA N, reached southern Siberia from 12,000 to 14,000 years ago. From there it reached southern Europe 8,000-10,000 years ago.” ref
“Haplogroup N1c is found chiefly in north-eastern Europe, particularly in Finland (61%), Lapland (53%), Estonia (34%), Latvia (38%), Lithuania (42%) and northern Russia (30%), and to a lower extent also in central Russia (15%), Belarus (10%), eastern Ukraine (9%), Sweden (7%), Poland (4%) and Turkey (4%). N1c is also prominent among the Uralic speaking ethnicities of the Volga-Ural region, including the Udmurts (67%), Komi (51%), Mari (50%), and Mordvins (20%), but also among their Turkic neighbors like the Chuvashs (28%), Volga Tatars (21%) and Bashkirs (17%), as well as the Nogais (9%) of southern Russia. N1c represents the western extent of haplogroup N, which is found all over the Far East (China, Korea, Japan), Mongolia, and Siberia, especially among Uralic speakers of northern Siberia. Haplogroup N1 reaches a maximum frequency of approximately 95% in the Nenets (40% N1c and 57% N1b) and Nganassans (all N1b), two Uralic tribes of central-northern Siberia, and 90% among the Yakuts (all N1c), a Turkic people who live mainly in the Sakha (Yakutia) Republic in central-eastern Siberia.” ref
“Haplogroup N is a descendant of East Asian macro-haplogroup NO. It is believed to have originated in Indochina or southern China approximately 15,000 to 20,000 years ago. Haplogroup N1* and N1c were both found at high frequency (26 out of 70 samples, or 37%) in Neolithic and Bronze Age remains (4500-700 BCE) from the West Liao River valley in Northeast China (Manchuria) by Yinqiu Cui et al. (2013). Among the Neolithic samples, haplogroup N1 made up two thirds of the samples from the Hongshan culture (4700-2900 BCE) and all the samples from the Xiaoheyan culture (3000-2200 BCE), hinting that N1 people played a major role in the diffusion of the Neolithic lifestyle around Northeast China, and probably also to Mongolia and Siberia.” ref
“Ye Zhang et al. 2016 found 100% of Y-DNA N out of 17 samples from the Xueshan culture (Jiangjialiang site) dating from 3600–2900 BCE, and among those 41% belonged to N1c1-Tat. It is therefore extremely likely that the N1c1 subclade found in Europe today has its roots in the Chinese Neolithic. It would have progressively spread across Siberia until north-eastern Europe, possibly reaching the Volga-Ural region around 5500 to 4500 BCE with the Kama culture (5300-3300 BCE), and the eastern Baltic with the Comb Ceramic culture (4200-2000 BCE), the presumed ancestral culture of Proto-Finnic and pre-Baltic people. There is little evidence of agriculture or domesticated animals in Siberia during the Neolithic, but pottery was widely used. In that regard it was the opposite development from the Near East, which first developed agriculture then only pottery from circa 5500 BCE, perhaps through contact with East Asians via Siberia or Central Asia.” ref
“The phylogeny of N1c1 shows that the split between Balto-Finnic and Uralic (including Ugric) peoples took place around 4400 years ago, downstream of the L1026 mutation, almost exactly at the start of the Kiukainen culture. The Uralic branch (Z1934) formed first, around 4200 years ago, followed by the Ugric branch (Y13850) and eventually the Balto-Finnic branch (VL29) 3600 years ago. The latter immediately split between the Chudes (CTS9976), to the east, and the Balto-Finns (L550) to the west. The Fennoscandians (Y4706) and Balts (M2783) bifurcated around 2600 years ago. The Bronze Age Indo-European Fatyanovo–Balanovo culture (3200-2300 BCE) progressively took over the Baltic region and southern Finland from 2,500 BCE (see History of haplogroup R1a). The merger of the two groups, Indo-European R1a, and Proto-Uralic N1c1 gave rise to the hybrid Kiukainen culture (2300-1500 BCE). Modern Baltic people have a roughly equal proportion of haplogroup N1c1 and R1a, resulting from this merger of Proto-Uralic and Northeast Indo-European populations.” ref
“The Turkic language family is currently regarded as one of the world’s primary language families. Turkic is one of the main members of the controversial Altaic language family, but Altaic currently lacks support from a majority of linguists. Some linguists suggested a relation to Uralic languages, especially to the Ugric languages. This view is rejected and seen as obsolete by mainstream linguists. Similarities are because of language contact and borrowings mostly from Turkic into Ugric languages. Stachowski (2015) states that any relation between Turkic and Uralic must be a contact one.” ref
“Proto-Turkic (3000 – c. 500 BCE) is the linguistic reconstruction of the common ancestor of the Turkic languages that was spoken by the Proto-Turks before their divergence into the various Turkic peoples. Proto-Turkic separated into Oghur (western) and Common Turkic (eastern) branches. Candidates for the proto-Turkic homeland range from western Central Asia to Manchuria, with most scholars agreeing that it lay in the eastern part of the Central Asian steppe, while one author has postulated that Proto-Turkic originated 2,500 years ago in East Asia.” ref
“Haplogroup N is seen in Yakuts, Turkic People, Liao Civilization, Xinglonggou, Xinglongwa culture, Zhaobaogou culture, Xinle culture, Hongshan culture, Lower Xiajiadian culture, Upper Xiajiadian culture, Yangshao culture, Sino-Tibetan Languages, Cishan culture, Peiligang culture, Jiahu, Beixin culture, Houli culture, Majiayao culture, Qijia culture, Dawenkou culture, Liangzhu culture, and Hemudu culture.” ref
“The Xinglongwa culture (興隆洼文化) (6200–5400 BC) was a Neolithic culture in northeastern China, found mainly around the Inner Mongolia–Liaoning border at the Liao River basin. Xinglongwa pottery was primarily cylindrical and baked at low temperatures. The Xinglongwa culture showed several signs of communal planning. At three Xinglongwa sites, houses were built in rows. Several Xinglongwa sites also featured a large central building. In addition, several Xinglongwa sites were surrounded by ditches.” ref
“The type site at Xinglongwa is located on the southwest side of a hill at Aohan Banner, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia; the site is named after a village 1.3 km to the southeast of the site. 120 pit-houses were discovered at Xinglongwa. Each home had a hearth at its center. Xinglongwa also featured a large building in the center of the village. Xinglongwa is the earliest discovered site in China to be surrounded by a ditch. Xinglongwa also featured an unusual burial custom, as some bodies were buried directly under the houses. Jade objects were also discovered. In the most lavish grave, a man was buried with a pair of pigs, as well as jade objects.” ref
“According to the study of 34 sets of human remains from Xinglongwa in-house burials, male individuals apparently predominate over female individuals at roughly 2:1 ratio (23 males vs. 11 females). Within the male group, no individuals were identified as being over 55 in age, whereas all of females belong to middle-to-old age group (no one younger than 35 years old). The youngest individuals examined were at age 13 or 14, so it’s suspected that children before mature sex-awareness might not have been buried in-house. From examined samples, the average height of males was between 163.8 cm and 168.8 cm, while the average height of females was between 153.4 cm – 159.9 cm. According to some papers, the Xinglongwa are perhaps the distant ancestors of the present-day Northeast Asian peoples that belong to the proposed “Transeurasian” (aka Altaic) language family, but this view has also been criticized. The recently discovered site at Xinglonggou is the only site of the culture to show evidence of any sort of agriculture, with evidence of millet remains. Some of the oldest Comb Ceramic artifacts were found in the Xinglongwa culture. A bone flute with five finger holes was also found at a Xinglongwa site.” ref
“The Zhaobaogou culture (Chinese: 趙宝溝文化) (5400–4500 BCE) was a Neolithic culture in northeast China, found primarily in the Luan River valley in Inner Mongolia and northern Hebei. The culture produced sand-tempered, incised pottery vessels with geometric and zoomorphic designs. The culture also produced stone and clay human figurines. The type site at Zhaobaogou, excavated in 1986, was discovered in Aohan Banner, Chifeng, Inner Mongolia. The site covers an area of around 90,000 m2.” ref
“The Hongshan culture (simplified Chinese: 红山文化; traditional Chinese: 紅山文化; pinyin: Hóngshān wénhuà) was a Neolithic culture in the West Liao river basin in northeast China. Hongshan sites have been found in an area stretching from Inner Mongolia to Liaoning, and dated from about 4700 to 2900 BCE. In northeast China, Hongshan culture was preceded by Xinglongwa culture (6200–5400 BCE), Xinle culture (5300–4800 BCE), and Zhaobaogou culture, which may be contemporary with Xinle and a little later. A genetic study by Yinqiu Cui et al. from 2013 analyzed the Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup based N subclade; it found that DNA samples from 63% of the combined samples from various Hongshan archaeological sites belonged to the subclade N1 (xN1a, N1c) of the paternal haplogroup N-M231 and calculated N to have been the predominant haplogroup in the region in the Neolithic period at 89%, with its share gradually declining over time. Today, this haplogroup is found in northern Han, Mongols, Manchu, Oroqen, Xibe and Hezhe at low frequencies. Other paternal haplogroups identified in the study were C and O3a (O3a3), both of which predominate among the present-day inhabitants of the region.” ref
“Nelson et al. 2020 attempts to link the Hongshan culture to a “Transeurasian” (Altaic) linguistic context. According to a study on genetic distance measurements from a large scale genetic study from 2021 titled ‘Genomic insights into the formation of human populations in East Asia’, hunter-gatherers of Mongolia and the Amur River Basin have ancestry shared by Mongolic and Tungusic language speakers, but they did not carry West Liao River farmer ancestry, contradicting the Transeurasian hypothesis proposed by Martine Robbeets et al. that the expansion of West Liao River farmers spread these proto-languages. A 2020 study discovered substantial genetic changes in the West Liao River region over time. An increase in the reliance on millet farming between the Middle-to-Late Neolithic is associated with higher genetic affinity to the Yellow River basin (generally associated with speakers of the Sino-Tibetan languages), while a partial switch to pastoralism in the Bronze Age Upper Xiajiadian culture is associated with a decrease in this genetic affinity. After the Late Neolithic, there was a sharp transition from Yellow River to Amur River-related genetic profiles (associated with speakers of Tungusic languages) around the West Liao River. This increase in Amur River affinity corresponds with the transition to a pastoral economy during the Bronze Age. A 2021 study found that Yellow River millet farmers from the modern-day provinces of Henan and Shandong had played an important role in the formation of Hongshan people or their descendants via both inland and coastal northward migration routes.” ref
“The Hongshan culture region was thought to have been desert for the past 1 million years. However, a 2015 study found that the region once featured rich aquatic resources and deep lakes and forests that existed from 12,000 years ago to 4,000 years ago. It was changed into desert by climate change which began approximately 4,200 years ago. Therefore, some of the people of the Hongshan culture may have emigrated south to the Yellow River valley approximately 4,000 years ago. Archaeological evidence discovered at the Miaozigou site in Ulanqab, Inner Mongolia, a northern branch of the Yangshao culture from the Yellow River (the Yangshao culture is speculated to be the origin of the Sino-Tibetan languages) demonstrates similarities in the material cultures between the Yellow River and Liao River cultures. Three individuals from the Miaozigou site belonged to haplogroup N1(xN1a, N1c), while the main lineage of Yellow River valley cultures is O3-M122. The existence of N1(xN1a, N1c) among the Miaozigou individuals could serve as evidence for the migration of some of the Hongshan people. Some Chinese archaeologists such as Guo Da-shun see the Hongshan culture as an important stage of early Chinese civilization. Whatever the linguistic affinity of the ancient denizens, Hongshan culture is believed to have exerted an influence on the development of early Chinese civilization. The culture may have also contributed to the development of settlements in ancient Korea. However, the Hongshan culture is also commonly employed in Korean pseudohistory by some Korean scholars, who seek to contest any connections between the Hongshan culture with Chinese civilization and assert that the Hongshan culture is only related to Korean civilization.” ref
“Chinese shamanism, alternatively called Wuism (Chinese: 巫教; pinyin: wū jiào; lit. ‘wu religion’, ‘shamanism‘, ‘witchcraft‘; alternatively 巫觋宗教 wū xí zōngjiào), refers to the shamanic religious tradition of China. Its features are especially connected to the ancient Neolithic cultures such as the Hongshan culture. Chinese shamanic traditions are intrinsic to Chinese folk religion.” ref
“The archaeological site at Niuheliang is a unique ritual complex associated with the Hongshan culture. Excavators have discovered an underground temple complex—which included an altar—and also cairns in Niuheliang. The temple was constructed of stone platforms, with painted walls. Archaeologists have given it the name “Goddess Temple” (Chinese: 女神庙; pinyin: nüshenmiao) due to the discovery of a clay female head with jade inlaid eyes. It was an underground structure, 1m deep. Included on its walls are mural paintings. Housed inside the Goddess Temple are clay figurines as large as three times the size of real-life humans. The exceedingly large figurines are possibly deities, but for a religion not reflective in any other Chinese culture. The existence of complex trading networks and monumental architecture (such as pyramids and the Goddess Temple) point to the existence of a “chiefdom” in these prehistoric communities. Painted pottery was also discovered within the temple. Over 60 nearby tombs have been unearthed, all constructed of stone and covered by stone mounds, frequently including jade artifacts. Cairns were discovered atop two nearby hills, with either round or square stepped tombs, made of piled limestone. Entombed inside were sculptures of dragons and tortoises. It has been suggested that religious sacrifice might have been performed within the Hongshan culture. Just as suggested by evidence found at early Yangshao culture sites, Hongshan culture sites also provide the earliest evidence for feng shui. The presence of both round and square shapes at Hongshan culture ceremonial centres suggests an early presence of the gaitian cosmography (“round heaven, square earth”). Early feng shui relied on astronomy to find correlations between humans and the universe.” ref
“Recent research indicates a common origin and spread of the Sino-Tibetan languages with the Cishan, Yangshao, and/or Majiayao cultures. The Yangshao culture (Chinese: 仰韶文化; pinyin: Yǎngsháo wénhuà) was a Neolithic culture that existed extensively along the middle reaches of the Yellow River in China from around 5000 – 3000 BCE.” ref
“Turkic Shamanism: Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri, who is not considered a deity in the usual sense but a personification of the universe. According to some scholars, adherents of Tengrism view the purpose of life to be in harmony with the universe. It was the prevailing religion of the Göktürks, Xianbei, Bulgars, Xiongnu, Yeniseian, and Mongolic peoples and Huns, as well as the state religion of several medieval states such as the First Turkic Khaganate, the Western Turkic Khaganate, the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, Old Great Bulgaria, the First Bulgarian Empire, Volga Bulgaria, Khazaria, and the Mongol Empire. In the Irk Bitig, a ninth century manuscript on divination, Tengri is mentioned as Türük Tängrisi (God of Turks). According to many academics, Tengrism was, and to some extent still is, a predominantly polytheistic religion based on the shamanistic concept of animism, and was first influenced by monotheism during the imperial period, especially by the 12th–13th centuries. Abdulkadir Inan argues that Yakut and Altai shamanism are not entirely equal to the ancient Turkic religion.” ref
“The term tengri (compare with Kami) can refer to the sky deity Tenger Etseg – also Gök Tengri; Sky father, Blue sky – or to other deities. The name Tengri (“the Sky”) is derived from Old Turkic: Tenk (“daybreak”) or Tan (“dawn”). Meanwhile, Stefan Georg proposed that the Turkic Tengri ultimately originates as a loanword from Proto-Yeniseian *tɨŋgɨr- “high”. Mongolia is sometimes poetically called the “Land of Eternal Blue Sky” (Mönkh Khökh Tengeriin Oron) by its inhabitants. According to some scholars, the name of the important deity Dangun (also Tangol) (God of the Mountains) of the Korean folk religion is related to the Siberian Tengri (“Heaven”), while the bear is a symbol of the Big Dipper (Ursa Major).” ref
“The nature of this religion remains debatable. According to many scholars, it was originally polytheistic, but a monotheistic branch with the sky god Kök-Tengri as the supreme being evolved as a dynastical legitimation. It is at least agreed that Tengrism formed from the diverse folk religions of the local people and may have had diverse branches. It is suggested that Tengrism was a monotheistic religion only at the imperial level in aristocratic circles, and, perhaps, only by the 12th-13th centuries (a late form of development of ancient animistic shamanism in the era of the Mongol empire). Others point out that Tengri itself was never an Absolute, but only one of many gods of the upper world, the sky deity, of polytheistic shamanism, later known as Tengrism.On a scale of complexity Tengrism lies somewhere between the Proto-Indo-European religion (a pre-state form of pastoral shamanism on the western steppe) and its later form the Vedic religion. The chief god Tengri (“Heaven”) is considered strikingly similar to the Indo-European sky god *Dyḗus and the East Asian Tian (Chinese: “Sky; Heaven”). The structure of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European religion is actually closer to that of the early Turks than to the religion of any people of neolithic European, Near Eastern or Mediterranean antiquity.” ref
“The first time the name Tengri was recorded in Chinese chronicles was from the 4th century BCE as the sky god of the Xiongnu, using the Chinese form 撐犁 (chēnglí, Old Chinese /*rtʰaːŋ.riːl/). Tengrism formed from the various Turkic and Mongolic folk religions, which had a diverse number of deities, spirits and gods. Turkic folk religion was based on Animism and similar to various other religious traditions of Siberia, Central Asia and Northeast Asia. Ancestor worship played an important part in Tengrism. The cult of Heaven-Tengri is fixed by the Orkhon, or Old Turkic script used by the Göktürks (“celestial Turks”) and other early khanates during the 8th to 10th centuries. Tengrism was probably similar with the folk traditions of the Tungusic peoples, such as the Manchu folk religion. Similarities with Korean shamanism and Wuism as well as Japanese Shinto are also evident. Tengrists view their existence as sustained by the eternal blue sky (Tengri), the fertile mother-earth spirit (Eje), and a ruler regarded as the chosen one by the holy spirit of the sky. Heaven, earth, spirits of nature, and ancestors provide for every need and protect all humans. By living an upright, respectful life, a human will keep his world in balance and perfect his personal Wind Horse, or spirit.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
“A study combining linguistic, genetic and archaeological evidence has traced the origins of a family of languages including modern Japanese, Korean, Turkish and Mongolian and the people who speak them to millet farmers who inhabited a region in north-eastern China about 9,000 years ago.” ref
“The Mongolic languages possible precursor to Mongolic is the Xianbei language, heavily influenced by the Proto-Turkic (later, the Lir-Turkic) language. Pre-Proto-Mongolic has borrowed various words from Turkic languages. Pre-Proto-Mongolic, from approximately the 4th century CE until the 12th century CE, influenced by Shaz-Turkic. Proto-Mongolic, from approximately the 13th century, spoken around the time of Chinggis Khan. Middle Mongol, from the 13th century until the early 15th century or late 16th century, depending on classification spoken. (Given the almost entire lack of written sources for the period in between, an exact cutoff point cannot be established.) Again influenced by Turkic.” ref
“The Tungusic languages /tʊŋˈɡʊsɪk/ (also known as Manchu–Tungus and Tungus) form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Some linguists estimate the divergence of the Tungusic languages from a common ancestor spoken somewhere in Eastern Manchuria around 500 BCE to 500 CE. Some linguists believe there are connections between the vowel harmony of Proto-Tungusic and some of the neighboring non-Tungusic languages. For example, there are proposals for an areal or genetic correspondence between the vowel harmonies of Proto-Korean, Proto-Mongolian, and Proto-Tungusic based on an original RTR harmony. Alexander Vovin (2015) notes that Northern Tungusic languages have Eskimo–Aleut loanwords that are not found in Southern Tungusic, implying that Eskimo–Aleut was once much more widely spoken in eastern Siberia. Vovin (2015) estimates that the Eskimo–Aleut loanwords in Northern Tungusic had been borrowed no more than 2,000 years ago, which was when Tungusic was spreading northwards from its homeland in the middle reaches of the Amur River. Liu et al. (2020) revealed that Haplogroup C-F5484 and its subclades are the genetic markers of Tungusic-speaking peoples. C-F5484 emerged 3,300 years ago and began to diverge 1,900 years ago, indicating the approximate age of differentiation of Tungusic languages. Tungusic is today considered a primary language family. Especially in the past, some linguists linked Tungusic with Turkic and Mongolic languages, among others, in either the Altaic or the Transeurasian language family. However, the proposal that there are genetic rather than merely areal links remains highly controversial.” ref
“Broomcorn and foxtail millets were being cultivated in the West Liao River basin in Northeast China by at least the sixth millennium BCE. However, when and how millet agriculture spread from there to the north and east remains poorly understood. Here, we trace the dispersal of millet agriculture from Northeast China to the Russian Far East and weigh demic against cultural diffusion as mechanisms for that dispersal. We compare two routes for the spread of millet into the Russian Far East discussed in previous research—an inland route across Manchuria, and a coastal/inland route initially following the Liaodong Peninsula and Yalu River—using an archaeological dataset including millet remains, pottery, stone tools, spindle whorls, jade and figurines. We then integrate the archaeological evidence with linguistic and genetic findings in an approach we term ‘triangulation’. We conclude that an expansion of agricultural societies in northeast China during the Middle to Late Hongshan (4000-3000 BCE) coincided with the arrival of millet cultivation in eastern Heilongjiang and the Primorye province of the Russian Far East. Our findings support the inland, Manchuria route for the dispersal of millet to the Primorye and suggest that, as well as long-distance cultural exchange, demic diffusion was also involved. Our results are broadly compatible with the farming/language dispersal hypothesis and consistent with a link between the spread of millet farming and proto-Tungusic, the language ancestral to the contemporary Tungusic languages, in late Neolithic Northeast Asia.” ref
“A long history of material exchanges between the two regions led Kuzmin to suggest cultural diffusion as the most likely explanation for this process. Kuzmin (2013: 5) shows three possible routes for millet dispersals from Northeast China to the Russian Far East but does not discuss details. Vostretsov (2005) outlined two routes of millet dispersal with population migrations from Northeast China to the Primorye: the first along the valley of the Tumen river (southern route) and the second along the Razdol’naya (Suifen) river (northern route). Vostretsov linked these migrations to the appearance and expansion of the Zaisanovka culture or Zaisanovka cultural tradition.” ref
“There is currently no standard interpretation of the ‘Zaisanovka culture’ in the archaeology of the Russian Far East. There are three main terms in use for this phenomenon: ‘Zaisanovka culture’; ‘Zaisanovka Neolithic (cultural) community’. Although the latter two terms are not commonly used, the debate over terminology seems to be the result of the complicated nature of the archaeological phenomenon itself, as well as the incomplete process of analysis and systematisation. Zaisanovka was certainly a cultural community prolonged in time and space. All specialists agree that the sites belonging to this ‘culture’, or ‘cultural tradition/community’, show some variability of artifact typology, while certain permanent, stable features are also noted. However, a common explanation of this variability has not yet been adopted. In general, it is widely assumed that this cultural/archaeological phenomenon was the result of wave-like processes of population migration from Northeast China. However, concrete details of this migration and the formation of new cultural unities in the Primorye region are not yet clear. In this article we use the term ‘Zaisanovka culture’, taking into account the obvious temporal and spatial variability of this ‘culture’.” ref
“Most scholars believe that Japonic was brought to northern Kyushu from the Korean peninsula around 700 to 300 BC by wet-rice farmers of the Yayoi culture and spread throughout the Japanese archipelago, replacing indigenous languages. Proto-Japonic, Proto-Japanese, or Proto-Japanese–Ryukyuan is the reconstructed language ancestral to the Japonic language family.” ref
“There are 98 Transeurasian languages, including Korean, Japanese, various Turkic languages in parts of Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia and Siberia, various Mongolic languages and various Tungusic languages in Manchuria and Siberia. This language family’s beginnings were traced to Neolithic millet farmers in the Liao River valley, an area encompassing parts of the Chinese provinces of Liaoning and Jilin and the region of Inner Mongolia. As these farmers moved across north-eastern Asia over thousands of years, the descendant languages spread north and west into Siberia and the steppes and east into the Korean peninsula and over the sea to the Japanese archipelago.” ref
“The Cishan culture (6500–5000 BCE) was a Neolithic culture in northern China, on the eastern foothills of the Taihang Mountains. The Cishan culture was based on the farming of broomcorn millet, the cultivation of which on one site has been dated back 10,000 years. The people at Cishan also began to cultivate foxtail millet around 8700 years ago. However, these early dates have been questioned by some archaeologists due to sampling issues and lack of systematic surveying. Common artifacts from the Cishan culture include stone grinders, stone sickles and tripod pottery. The sickle blades feature fairly uniform serrations, which made the harvesting of grain easier. Cord markings, used as decorations on the pottery, was more common compared to neighboring cultures. Also, the Cishan potters created a broader variety of pottery forms such as basins, pot supports, serving stands, and drinking cups. Since the culture shared many similarities with its southern neighbor, the Peiligang culture, both cultures were sometimes previously referred to together as the Cishan-Peiligang culture or Peiligang-Cishan culture. The Cishan culture also shared several similarities with its eastern neighbor, the Beixin culture. However, the contemporary consensus among archaeologists is that the Cishan people were members of a distinct culture that shared many characteristics with its neighbors. This culture has been linked to the origin of the Sino-Tibetan language family.” ref
Millet agriculture dispersed from Northeast China to the Russian Far East: Integrating archaeology, genetics, and linguistics
“Abstract: Broomcorn and foxtail millets were being cultivated in the West Liao River basin in Northeast China by at least the sixth millennium BCE. However, when and how millet agriculture spread from there to the north and east remains poorly understood. Here, we trace the dispersal of millet agriculture from Northeast China to the Russian Far East and weigh demic against cultural diffusion as mechanisms for that dispersal. We compare two routes for the spread of millet into the Russian Far East discussed in previous research—an inland route across Manchuria, and a coastal/inland route initially following the Liaodong Peninsula and Yalu River—using an archaeological dataset including millet remains, pottery, stone tools, spindle whorls, jade and figurines. We then integrate the archaeological evidence with linguistic and genetic findings in an approach we term ‘triangulation’. We conclude that an expansion of agricultural societies in Northeast China during the Middle to Late Hongshan (4000 3000 BCE) coincided with the arrival of millet cultivation in eastern Heilongjiang and the Primorye province of the Russian Far East. Our findings support the inland, Manchuria route for the dispersal of millet to the Primorye and suggest that, as well as long-distance cultural exchange, demic diffusion was also involved. Our results are broadly compatible with the farming/language dispersal hypothesis and consistent with a link between the spread of millet farming and proto-Tungusic, the language ancestral to the contemporary Tungusic languages, in late Neolithic Northeast Asia.” ref
3000 BCE) coincided with the arrival of millet cultivation in eastern Heilongjiang and the Primorye province of the Russian Far East. Our findings support the inland, Manchuria route for the dispersal of millet to the Primorye and suggest that, as well as long-distance cultural exchange, demic diffusion was also involved. Our results are broadly compatible with the farming/language dispersal hypothesis and consistent with a link between the spread of millet farming and proto-Tungusic, the language ancestral to the contemporary Tungusic languages, in late Neolithic Northeast Asia.” ref
Tracing population movements in ancient East Asia through the linguistics and archaeology of textile production
“Abstract: The term ‘Transeurasian’ replaces the traditional label ‘Altaic’ and refers to the large group of geographically adjacent languages, stretching across Europe and Asia, presented in Figure 1. It includes five uncontroversial linguistic families: Japonic, Koreanic, Tungusic, Mongolic, and Turkic. Archaeolinguistics, a field which combines language reconstruction and archaeology as a source of information on human prehistory, has much to offer to deepen our understanding of the Neolithic and Bronze Age in Northeast Asia. So far, integrated comparative analyses of words and tools for textile production are completely lacking for the Northeast Asian Neolithic and Bronze Age. To remedy this situation, here we integrate linguistic and archaeological evidence of textile production, with the aim of shedding light on ancient population movements in Northeast China, the Russian Far East, Korea and Japan. We show that the transition to more sophisticated textile technology in these regions can be associated not only with the adoption of millet agriculture but also with the spread of the languages of the so-called ‘Transeurasian’ family. In this way, our research provides indirect support for the Language/Farming Dispersal Hypothesis, which posits that language expansion from the Neolithic onwards was often associated with agricultural colonization.” ref
Origins of ‘Transeurasian’ languages traced to Neolithic millet farmers in north-eastern China about 9,000 years ago
“A study combining linguistic, genetic, and archaeological evidence has traced the origins of a family of languages including modern Japanese, Korean, Turkish and Mongolian and the people who speak them to millet farmers who inhabited a region in north-eastern China about 9,000 years ago. The findings outlined on Wednesday document a shared genetic ancestry for the hundreds of millions of people who speak what the researchers call Transeurasian languages across an area stretching more than 5,000 miles (8,000km).” ref
“Millet was an important early crop as hunter-gatherers transitioned to an agricultural lifestyle. There are 98 Transeurasian languages, including Korean, Japanese, and various Turkic languages in parts of Europe, Anatolia, Central Asia, and Siberia, various Mongolic languages, and various Tungusic languages in Manchuria and Siberia. This language family’s beginnings were traced to Neolithic millet farmers in the Liao River valley, an area encompassing parts of the Chinese provinces of Liaoning and Jilin and the region of Inner Mongolia. As these farmers moved across north-eastern Asia over thousands of years, the descendant languages spread north and west into Siberia and the steppes and east into the Korean peninsula and over the sea to the Japanese archipelago.” ref
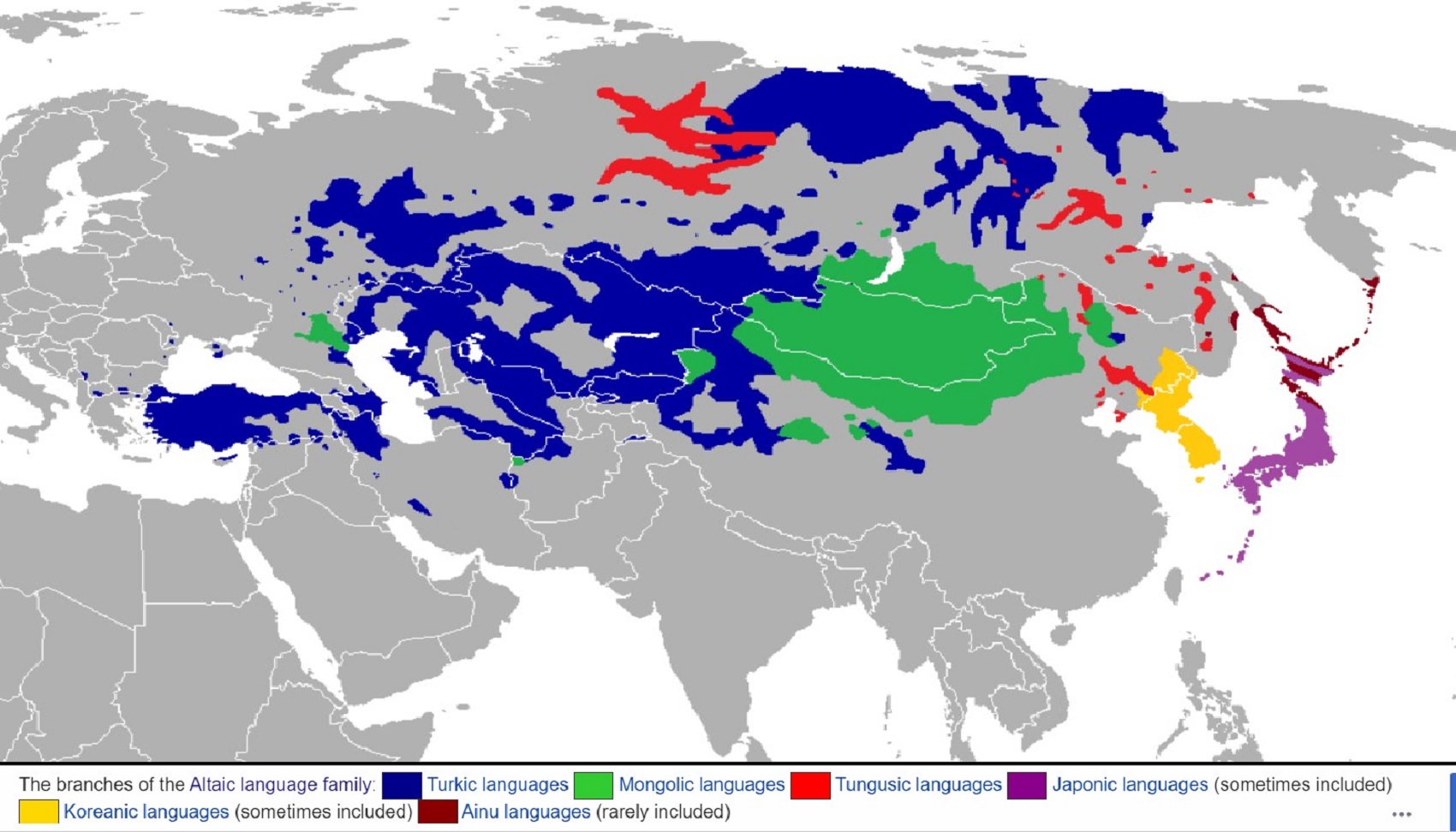
“Altaic (also called Transeurasian) is a proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are currently scattered over most of Asia north of 35 °N and in some eastern parts of Europe, extending in longitude from Turkey to Japan. The group is named after the Altai mountain range in the center of Asia.” ref
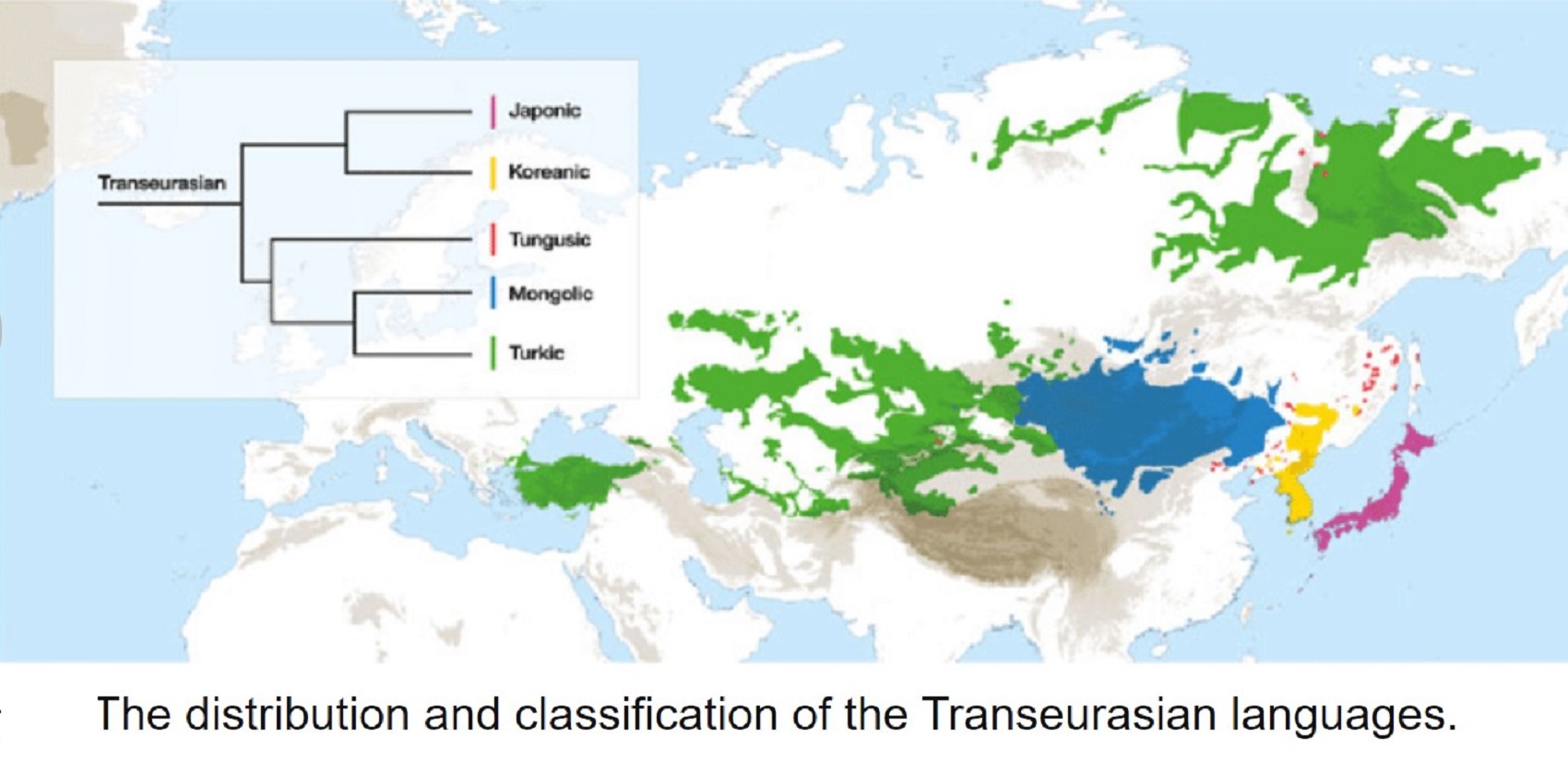
Tracing population movements in ancient East Asia through the linguistics and archaeology of textile production – 2020
Abstract
“Archaeolinguistics, a field which combines language reconstruction and archaeology as a source of information on human prehistory, has much to offer to deepen our understanding of the Neolithic and Bronze Age in Northeast Asia. So far, integrated comparative analyses of words and tools for textile production are completely lacking for the Northeast Asian Neolithic and Bronze Age. To remedy this situation, here we integrate linguistic and archaeological evidence of textile production, with the aim of shedding light on ancient population movements in Northeast China, the Russian Far East, Korea, and Japan. We show that the transition to more sophisticated textile technology in these regions can be associated not only with the adoption of millet agriculture but also with the spread of the languages of the so-called ‘Transeurasian’ family. In this way, our research provides indirect support for the Language/Farming Dispersal Hypothesis, which posits that language expansion from the Neolithic onwards was often associated with agricultural colonization.” ref
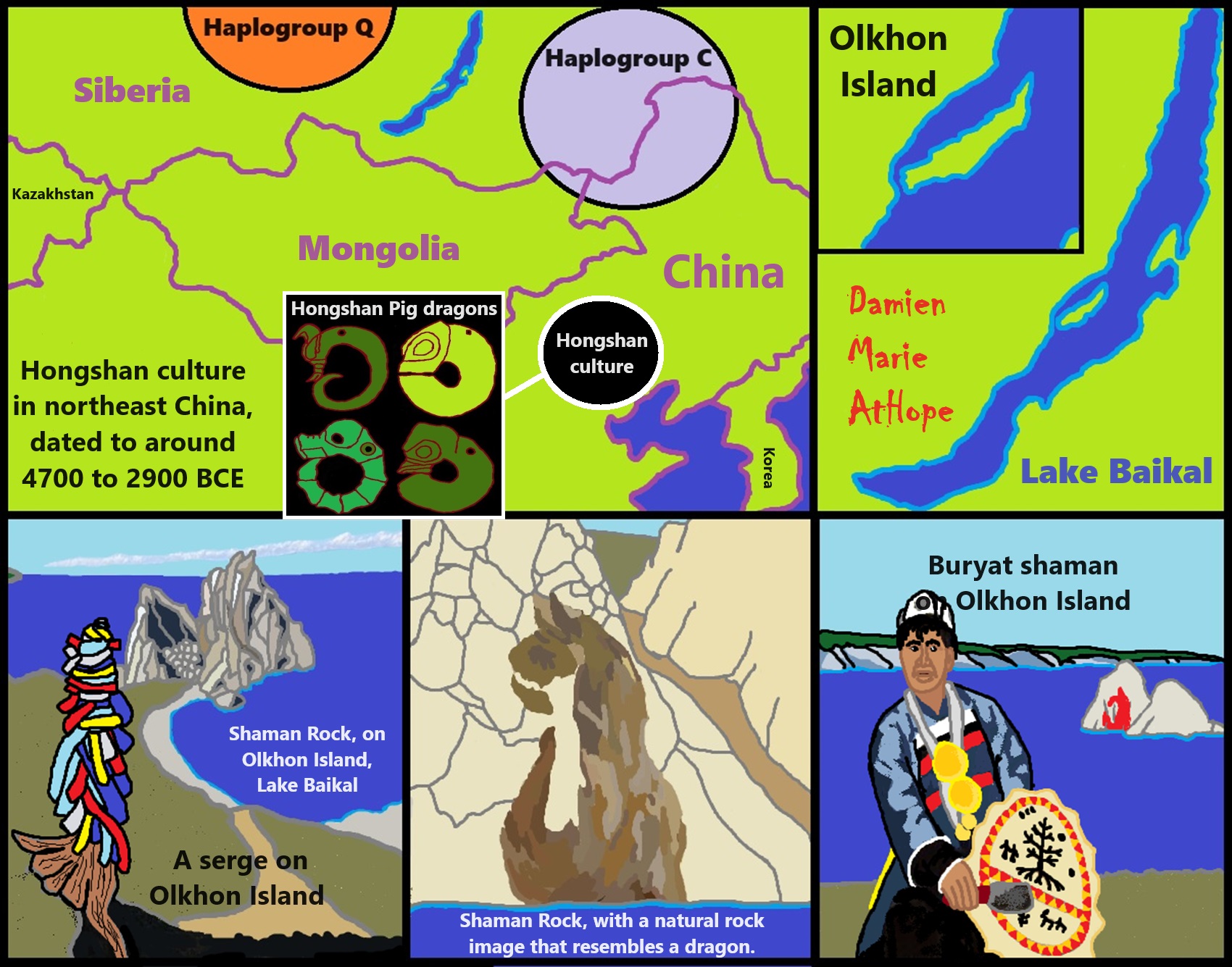
People may have first seen the Shaman Rock with the natural brown rock formation resembling a dragon between 30,000 to 25,000 years ago.
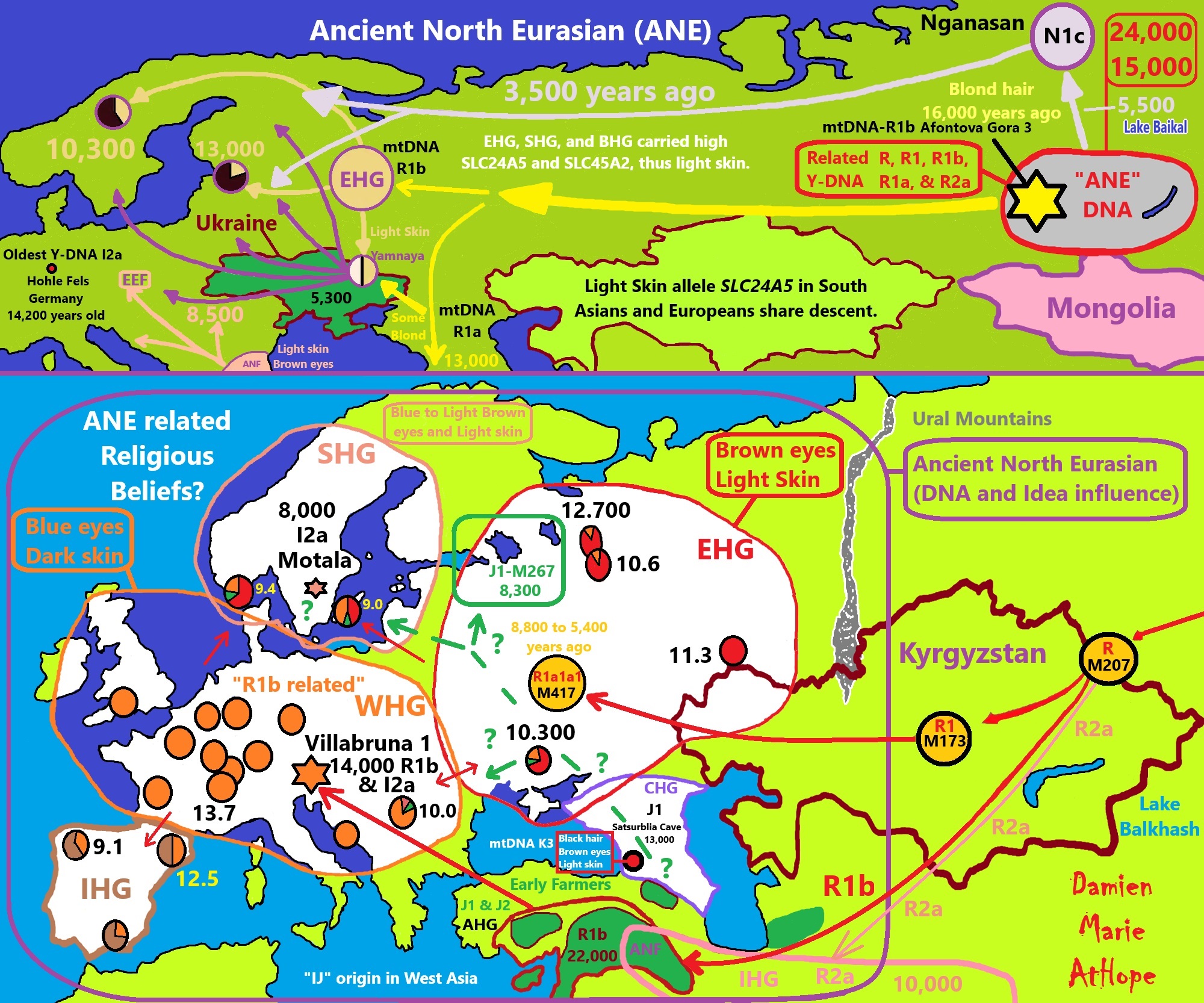
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Genetic Relations to Ancient North Eurasians (ANE):
Eastern hunter-gatherer (EHG)
Caucasus hunter-gatherer (CHG)
Zagros/Iranian Hunter-Gatherer (IHG)
Iranian Neolithic Farmers (INF)
Anatolian hunter-gatherer (AHG)
Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF)
Early European Farmers (EEF)
Yamnaya/Steppe Herders (WSH)
Villabruna 1 (burial)/Ripari Villabruna rock shelter in northern Italy (14,000 years old)
Satsurblia Cave (burial) in the Country of Georgia (13,000 years old)
Motala (burial) (8,000 years old)
“In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Northern East Asian (ANEA), also known as Northern East Asian (NEA), is used to summarize the related ancestral components that represent the Ancient Northern East Asian peoples, extending from the Baikal region to the Yellow River and the Qinling-Huaihe Line in present-day central China. They are inferred to have diverged from Ancient Southern East Asians (ASEA) around 20,000 to 26,000 BCE.” ref
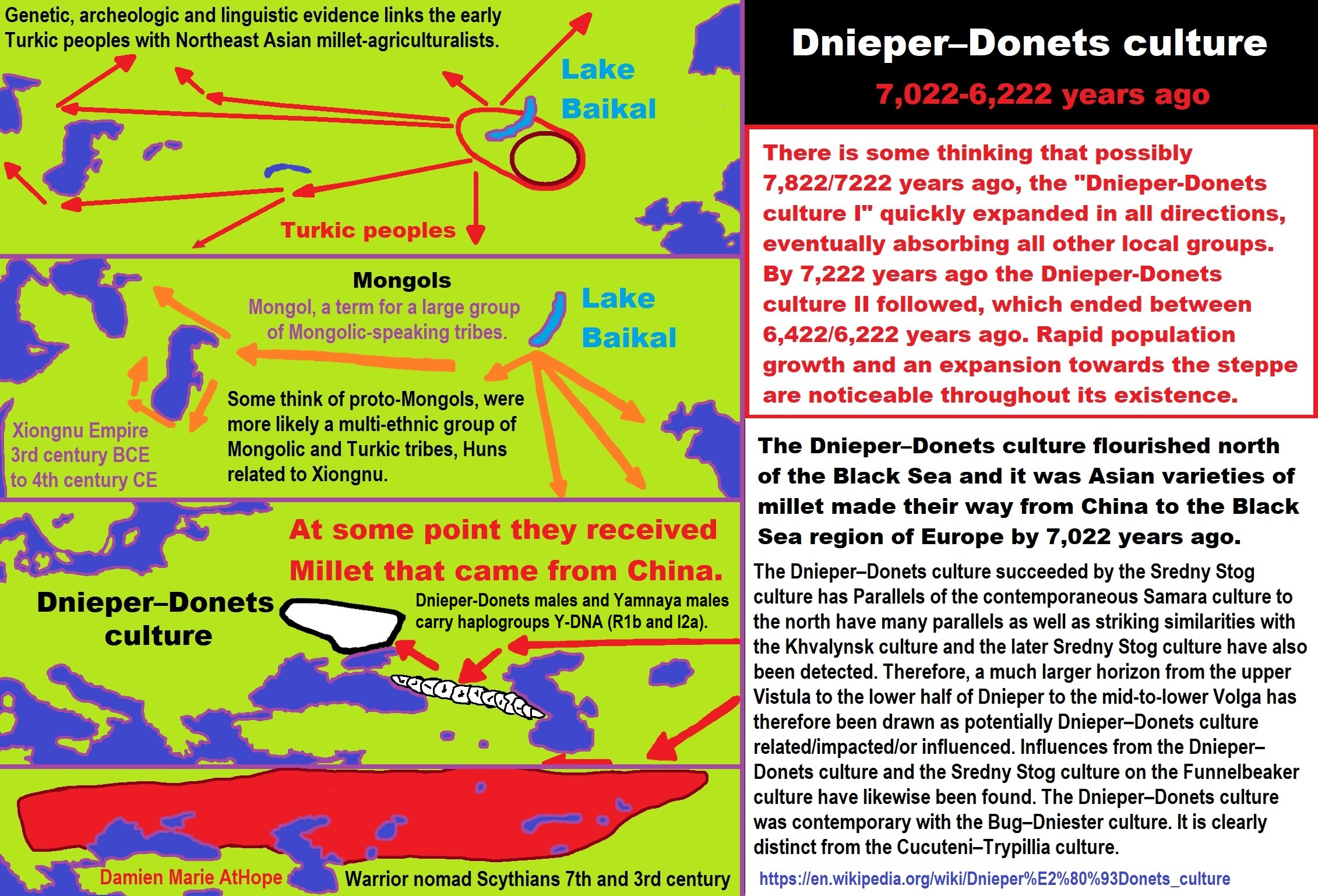
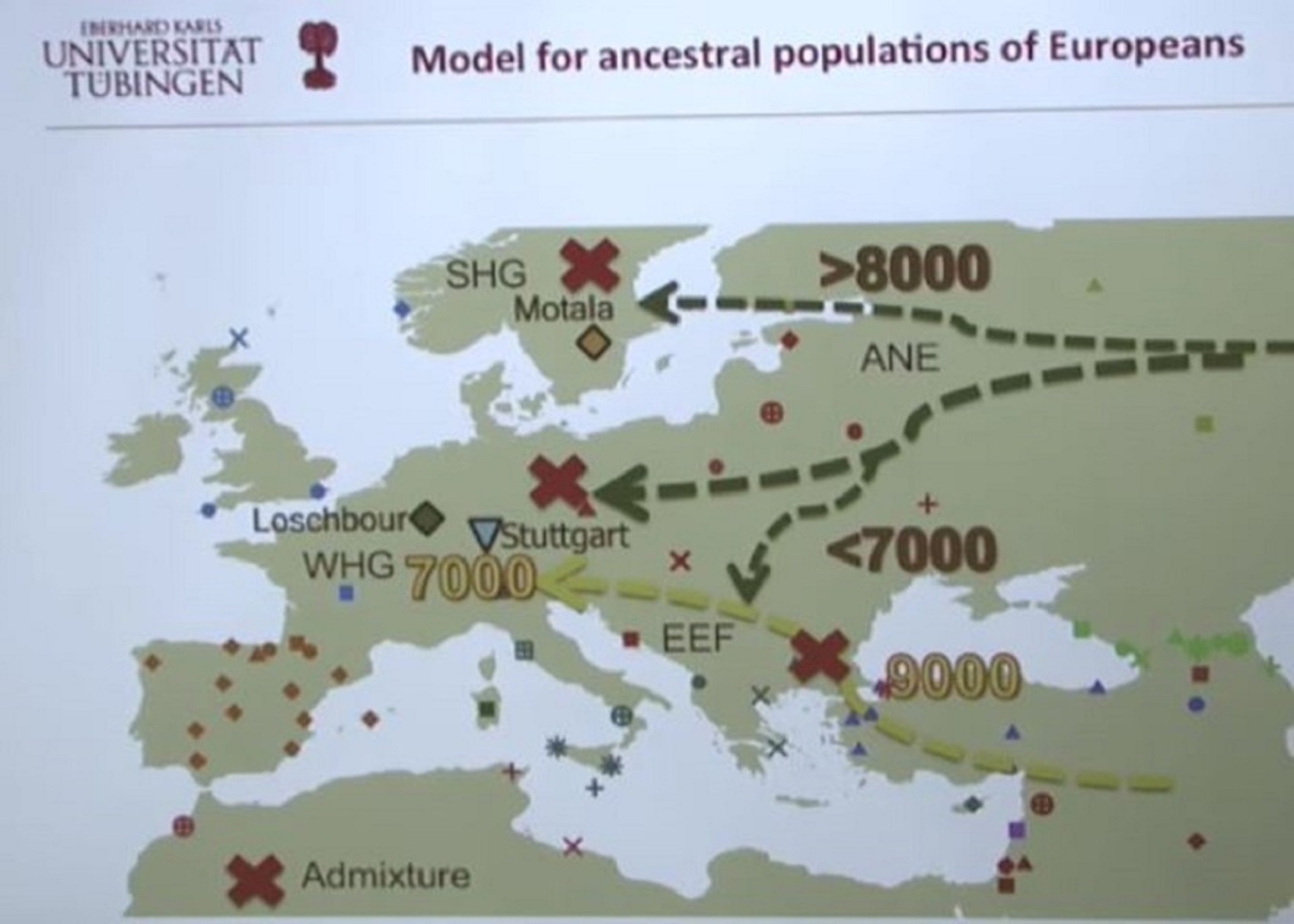
Pic ref
Ancient Human Genomes…Present-Day Europeans – Johannes Krause (Video)
Ancient North Eurasian (ANE)
Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG)
Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG)
Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG)
Early European Farmers (EEF)
A quick look at the Genetic history of Europe
“The most significant recent dispersal of modern humans from Africa gave rise to an undifferentiated “non-African” lineage by some 70,000-50,000 years ago. By about 50–40 ka a basal West Eurasian lineage had emerged, as had a separate East Asian lineage. Both basal East and West Eurasians acquired Neanderthal admixture in Europe and Asia. European early modern humans (EEMH) lineages between 40,000-26,000 years ago (Aurignacian) were still part of a large Western Eurasian “meta-population”, related to Central and Western Asian populations. Divergence into genetically distinct sub-populations within Western Eurasia is a result of increased selection pressure and founder effects during the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM, Gravettian). By the end of the LGM, after 20,000 years ago, A Western European lineage, dubbed West European Hunter-Gatherer (WHG) emerges from the Solutrean refugium during the European Mesolithic. These Mesolithic hunter-gatherer cultures are substantially replaced in the Neolithic Revolution by the arrival of Early European Farmers (EEF) lineages derived from Mesolithic populations of West Asia (Anatolia and the Caucasus). In the European Bronze Age, there were again substantial population replacements in parts of Europe by the intrusion of Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) lineages from the Pontic–Caspian steppes. These Bronze Age population replacements are associated with the Beaker culture archaeologically and with the Indo-European expansion linguistically.” ref
“As a result of the population movements during the Mesolithic to Bronze Age, modern European populations are distinguished by differences in WHG, EEF, and ANE ancestry. Admixture rates varied geographically; in the late Neolithic, WHG ancestry in farmers in Hungary was at around 10%, in Germany around 25%, and in Iberia as high as 50%. The contribution of EEF is more significant in Mediterranean Europe, and declines towards northern and northeastern Europe, where WHG ancestry is stronger; the Sardinians are considered to be the closest European group to the population of the EEF. ANE ancestry is found throughout Europe, with a maximum of about 20% found in Baltic people and Finns. Ethnogenesis of the modern ethnic groups of Europe in the historical period is associated with numerous admixture events, primarily those associated with the Roman, Germanic, Norse, Slavic, Berber, Arab and Turkish expansions. Research into the genetic history of Europe became possible in the second half of the 20th century, but did not yield results with a high resolution before the 1990s. In the 1990s, preliminary results became possible, but they remained mostly limited to studies of mitochondrial and Y-chromosomal lineages. Autosomal DNA became more easily accessible in the 2000s, and since the mid-2010s, results of previously unattainable resolution, many of them based on full-genome analysis of ancient DNA, have been published at an accelerated pace.” ref
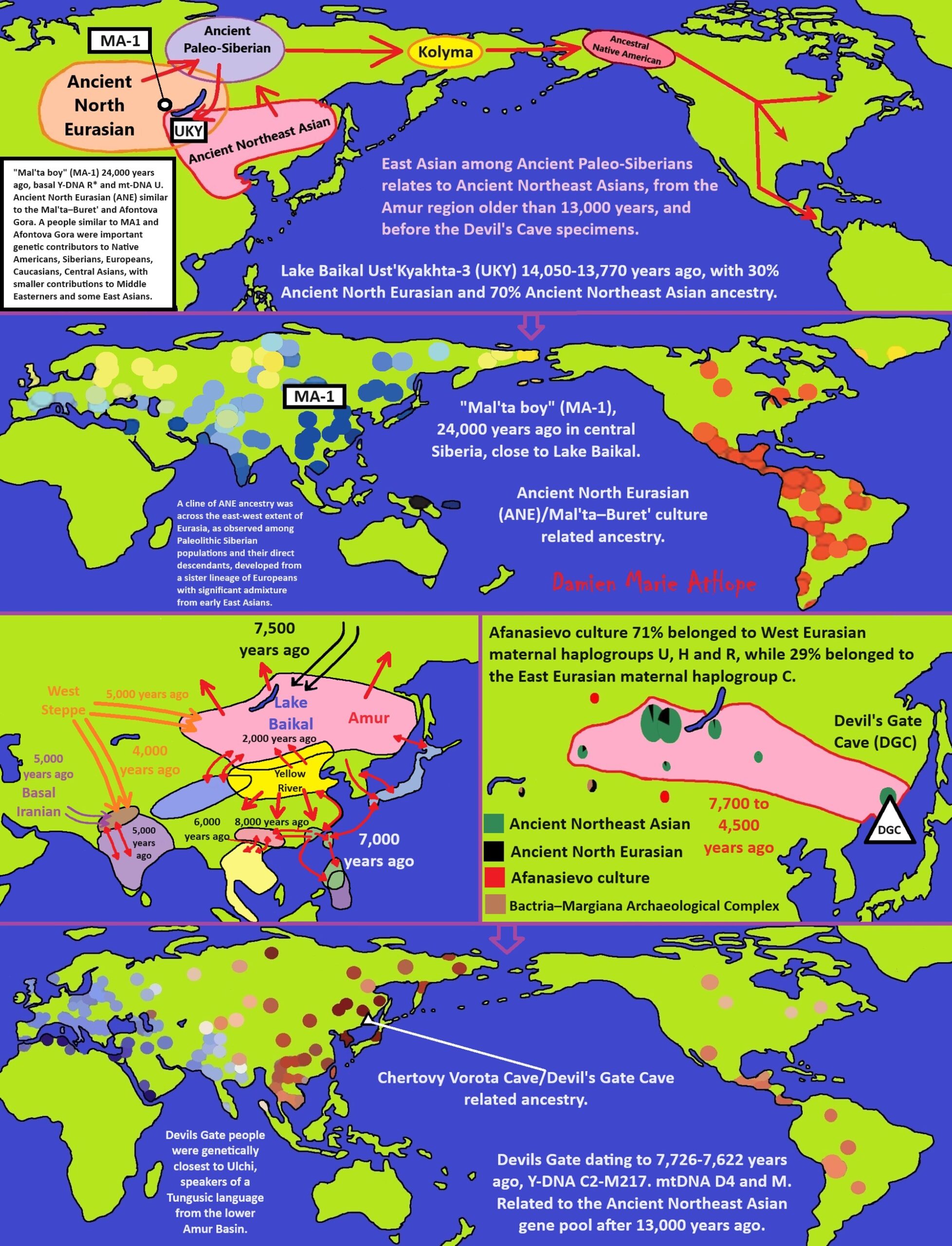
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“A 2016 study found that the global maximum of Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) ancestry occurs in modern-day Kets, Mansi, Native Americans, and Selkups. ANE ancestry has spread throughout Eurasia and the Americas in various migrations since the Upper Paleolithic, and more than half of the world’s population today derives between 5 and 42% of their genomes from the Ancient North Eurasians. Significant ANE ancestry can be found in Native Americans, as well as in regions of northern Europe, South Asia, Central Asia, and Siberia. It has been suggested that their mythology may have featured narratives shared by both Indo-European and some Native American cultures, such as the existence of a metaphysical world tree and a fable in which a dog guards the path to the afterlife.” ref
Ancient Northern East Asian/ later became Ancient Northeast Asian
Ancient Paleo-Siberian
Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (Mal’ta boy MA-1)
The Kolyma Shaitans: Legends and Reality (I only use just a small part)
“A unique “shaitan” burial was discovered on the bank of Omuk-Kuel Lake in the Middle-Kolyma ulus in Yakutia. According to the legends, buried in it are mummified remains of a shaman woman who died during a devastating smallpox epidemics in the 18th c. In an attempt to overcome the deadly disease, the shaman’s relatives used her remains as an emeget fetish. The author believes that these legends reflect the real events of those far-away years. The Arabic word “shaitan” came to the Russian language from Turkic languages. According to Islamic tradition, a shaitan is a genie, an evil spirit, a demon. During Russian colonization and Christianization of Siberia, all sacred things used by the aborigines as fetishes, patron spirits of the family, and the tribe, grew to be called “shaitans.” There are various facts, dating to the 18th and 19th cc., confirming that this word also referred to the mummified remains of outstanding shamans.” ref
“In the 1740s, a member of the Second Kamchatka Expedition Yakov Lindenau wrote, “Meat is scratched off the [shaman’s] bones and the bones are put together to form a skeleton, which is dressed in human’s clothes and worshipped as a deity. The Yukagirs place such dressed bones…in their yurts, their number can sometimes reach 10 or 15. If somebody commits even a minor sacrilege with respect to these bones, he stirs up rancor on the part of the Yukagirs… While traveling and hunting, the Yukagirs carry these bones in their sledges, and moreover, in their best sledges pulled by their best deer. When the Yukagirs are going to undertake something really important, they tell fortune using these skeletons: lift a skeleton up, and if it seems light, it means that their enterprise will have a favorable outcome. The Yukagirs call these skeletons stariks (old men), endow them with their best furs, and sit them on beds covered with deer hides, in a circle, as though they are alive.” (Lindenau, 1983, p. 155)” ref
“In the late 19th c., a famous explorer of aboriginal culture V. I. Jochelson noted the changes that occurred in the ritual in the last century and a half. So, the Yukagirs divided among themselves the shaman’s meat dried in the sun and then put it in separate tents. The dead bodies of killed dogs were left there as well. “After that,” V. I. Jochelson writes, “they would divide the shaman’s bones, dry them and wrap in clothes. The skull was an object of worshipping. It was put on top of a trunk (body) cut out of wood. A caftan and two hats – a winter and a summer one – were sewn for the idol. The caftan was all embroidered. On the skull, a special mask was put, with holes for the eyes and the mouth… The figure was placed in the front corner of the home. Before a meal, a piece of food was thrown into the fire and the idol was held above it. This feeding of the idol… was committed before each meal.” (V. I. Jochelson, 2005, pp. 236—237)” ref
“The idol was kept by the children of the dead shaman. One of them was inducted into the shamanism mysteries while his father was still alive. The idol was carried in a wooden box. Sometimes, in line with the air burial ritual, the box was erected on poles or trees, and the idol was taken out only before hunting or a long journey so that the outcome of the enterprise planned could be predicted. With time, the Yukagirs began using wooden idols as charms. V. I. Jochelson notes that by the late 19th c. the Yukagirs had developed a skeptical attitude towards idols and referred to them as “shaitans.” In this way, under the influence of Christianity, the worshipped ancestor’s spirit turned into its opposite – an evil spirit, a devil, a Satan.” ref
Ancestral Native American, Ancient Beringian
14,000-year-old Ust-Kyakhta-3 (UKY) individual found near Lake Baikal
People reached Lake Baikal Siberia around 25,000 years ago. They (to Damien) were likely Animistic Shamanists who were also heavily totemistic as well. Being animistic thinkers they likely viewed amazing things in nature as a part of or related to something supernatural/spiritual (not just natural as explained by science): spirit-filled, a sprit-being relates to or with it, it is a sprit-being, it is a supernatural/spiritual creature, or it is a great spirit/tutelary deity/goddess-god. From there comes mythology and faith in things not seen but are believed to somehow relate or interact with this “real world” we know exists.
Both areas of Lake Baikal, one on the west side with Ancient North Eurasian culture and one on the east side with Ancient Northern East Asian culture (later to become: Ancient Northeast Asian culture) areas are the connected areas that (to Damien) are the origin ancestry religion area for many mythologies and religious ideas of the world by means of a few main migrations and many smaller ones leading to a distribution of religious ideas that even though are vast in distance are commonly related to and centering on Lake Baikal and its surrounding areas like the Amur region and Altai Mountains region.
“Lakes are often mysterious bodies of water, especially if they are very deep or surrounded by mountains. No wonder legends and mysteries thrive about them, including monsters that supposedly lurk in their bottomless depths.” ref
Lake Baikal
“Lake Baikal is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast. At 31,722 km2 (12,248 sq mi)—slightly larger than Belgium—Lake Baikal is the world’s seventh-largest lake by surface area, as well as the second largest lake in Eurasia after the Caspian Sea. However, because it is also the deepest lake, with a maximum depth of 1,642 metres (5,387 feet; 898 fathoms), Lake Baikal is the world’s largest freshwater lake by volume, containing 23,615.39 km3 (5,670 cu mi) of water or 22–23% of the world’s fresh surface water, more than all of the North American Great Lakes combined. It is also the world’s oldest lake at 25–30 million years, and among the clearest. Lake Baikal is home to thousands of species of plants and animals, many of them endemic to the region. It is also home to Buryat tribes, who raise goats, camels, cattle, sheep, and horses on the eastern side of the lake, where the mean temperature varies from a winter minimum of −19 °C (−2 °F) to a summer maximum of 14 °C (57 °F). The region to the east of Lake Baikal is referred to as Transbaikalia or as the Transbaikal, and the loosely defined region around the lake itself is sometimes known as Baikalia.” ref
“Baikal is one of the clearest lakes in the world. During the winter, the water transparency in open sections can be as much as 30–40 m (100–130 ft), but during the summer it is typically 5–8 m (15–25 ft). Baikal is rich in oxygen, even in deep sections, which separates it from distinctly stratified bodies of water such as Lake Tanganyika and the Black Sea. Lake Baikal is rich in biodiversity. It hosts more than 1,000 species of plants and 2,500 species of animals based on current knowledge, but the actual figures for both groups are believed to be significantly higher. More than 80% of the animals are endemic. There are 236 species of birds that inhabit Lake Baikal, 29 of which are waterfowl. Although named after the lake, both the Baikal teal and Baikal bush warbler are widespread in eastern Asia. Fewer than 65 native fish species occur in the lake basin, but more than half of these are endemic.
“The families Abyssocottidae (deep-water sculpins), Comephoridae (golomyankas or Baikal oilfish), and Cottocomephoridae (Baikal sculpins) are entirely restricted to the lake basin. The golomyankas are the primary prey of the Baikal seal and represent the largest fish biomass in the lake. Beyond members of Cottoidea, there are few endemic fish species in the lake basin. The lake hosts a rich endemic fauna of invertebrates. The copepod Epischura baikalensis is endemic to Lake Baikal and the dominating zooplankton species there, making up 80 to 90% of the total biomass. It is estimated that they filter as much as a thousand cubic kilometers of water a year, or the lake’s entire volume every twenty-three years. Among the most diverse invertebrate groups are the amphipod and ostracod crustaceans, freshwater snails, annelid worms, and turbellarian worms. More than 350 species and subspecies of amphipods are endemic to the lake. At least 18 species of sponges occur in the lake, including about 15 species from the endemic family Lubomirskiidae (the remaining are from the nonendemic family Spongillidae), which colonized the lake about 3.4 million years ago.” ref
“The Baikal area, sometimes known as Baikalia, has a long history of human habitation. Near the village of Mal’ta, some 160 km northwest of the lake, remains of a young human male known as MA-1 or “Mal’ta Boy” are indications of local habitation by the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture ca. 24,000 years ago. An early known tribe in the area was the Kurykans. Located in the former northern territory of the Xiongnu confederation, Lake Baikal is one site of the Han–Xiongnu War, where the armies of the Han dynasty pursued and defeated the Xiongnu forces from the second century BC to the first century AD. They recorded that the lake was a “huge sea” (hanhai) and designated it the North Sea (Běihǎi) of the semimythical Four Seas. The Kurykans, a Siberian tribe who inhabited the area in the sixth century, gave it a name that translates to “much water”. Later on, it was called “natural lake” (Baygal nuur) by the Buryats and “rich lake” (Bay göl) by the Yakuts.” ref
“Little was known to Europeans about the lake until Russia expanded into the area in the 17th century. The first Russian explorer to reach Lake Baikal was Kurbat Ivanov in 1643. Lake Baikal was under the Anbei Protectorate of the Tang dynasty from 647 CE to 682 CE. Russian expansion into the Buryat area around Lake Baikal in 1628–58 was part of the Russian conquest of Siberia. It was done first by following the Angara River upstream from Yeniseysk (founded 1619) and later by moving south from the Lena River. Russians first heard of the Buryats in 1609 at Tomsk. According to folktales related a century after the fact, in 1623, Demid Pyanda, who may have been the first Russian to reach the Lena, crossed from the upper Lena to the Angara and arrived at Yeniseysk.” ref
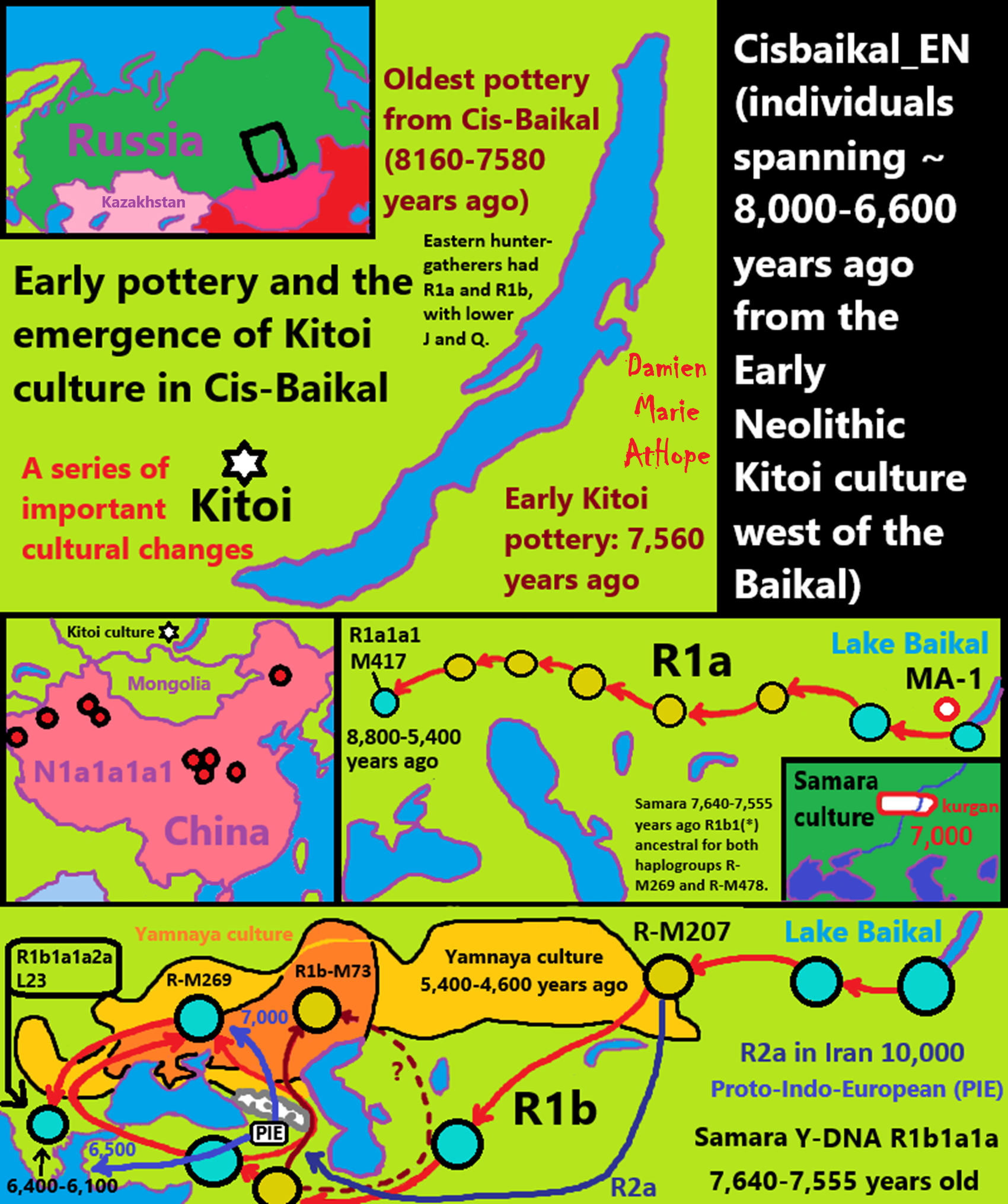
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Early Russian Pottery in Cisbaikal Kitoi culture 7,500 years ago, Samara culture 7,000 years ago, and Yamnaya culture 5,600–4,600 years ago, as well as Proto-Indo-European emergence
“The area east of Lake Baikal in Siberia is one of the few regions in Eurasia where pottery was already used during the Late Pleistocene and Early Holocene. Such early pottery complexes were identified in Ust’-Karenga XII, Studenoye 1, Ust’-Menza 1, and Ust’-Khyakhta 3, dated at about 12-000-11,000 years ago. While around 20,000 years ago East Asian hunter-gatherers were already making ceramic pots. (It seems to Damien) that ceramics spread continually from the earliest centers in China, then Japan, and next the Russian Far East, lastly towards the west, all the way to Europe.” ref
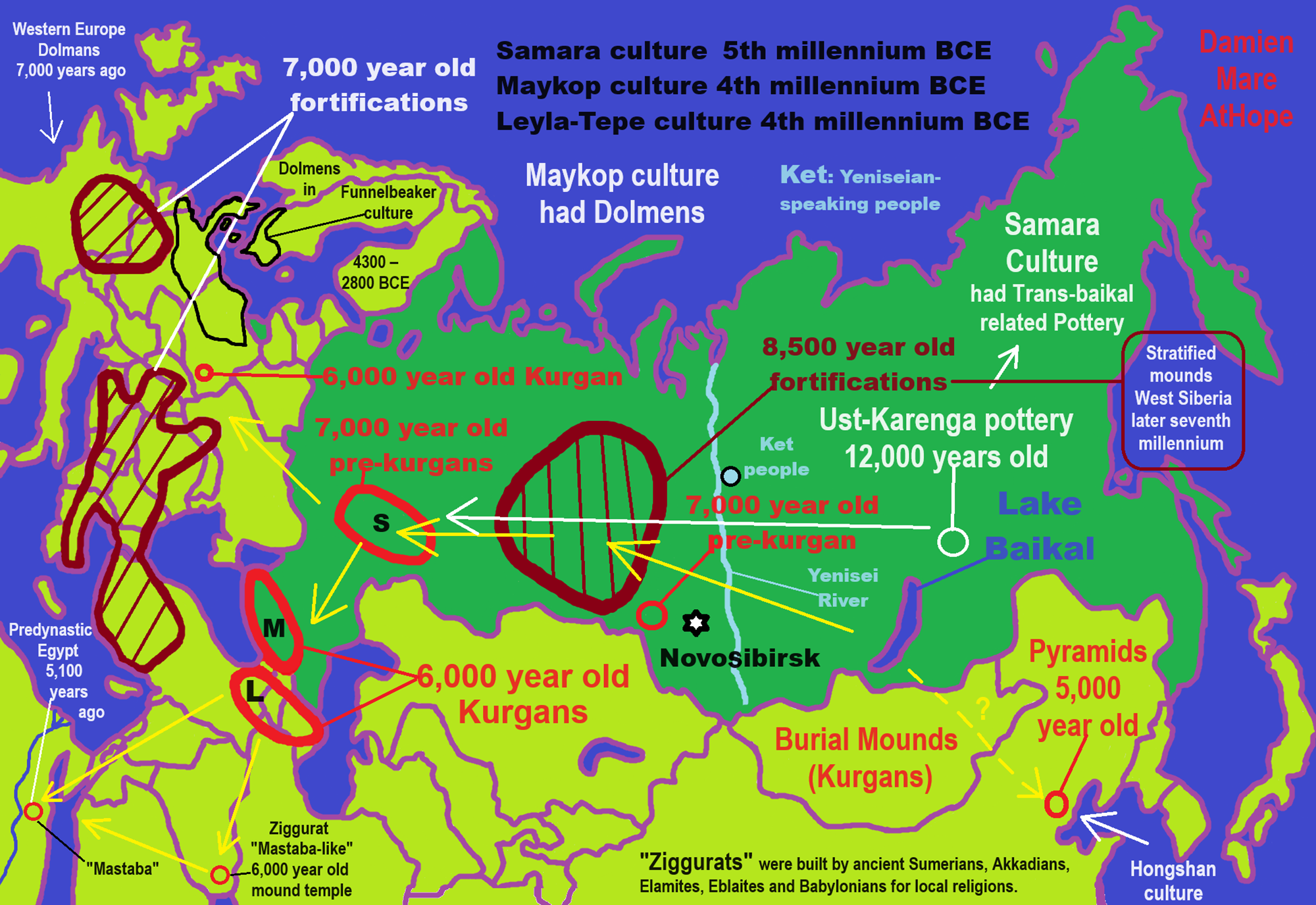
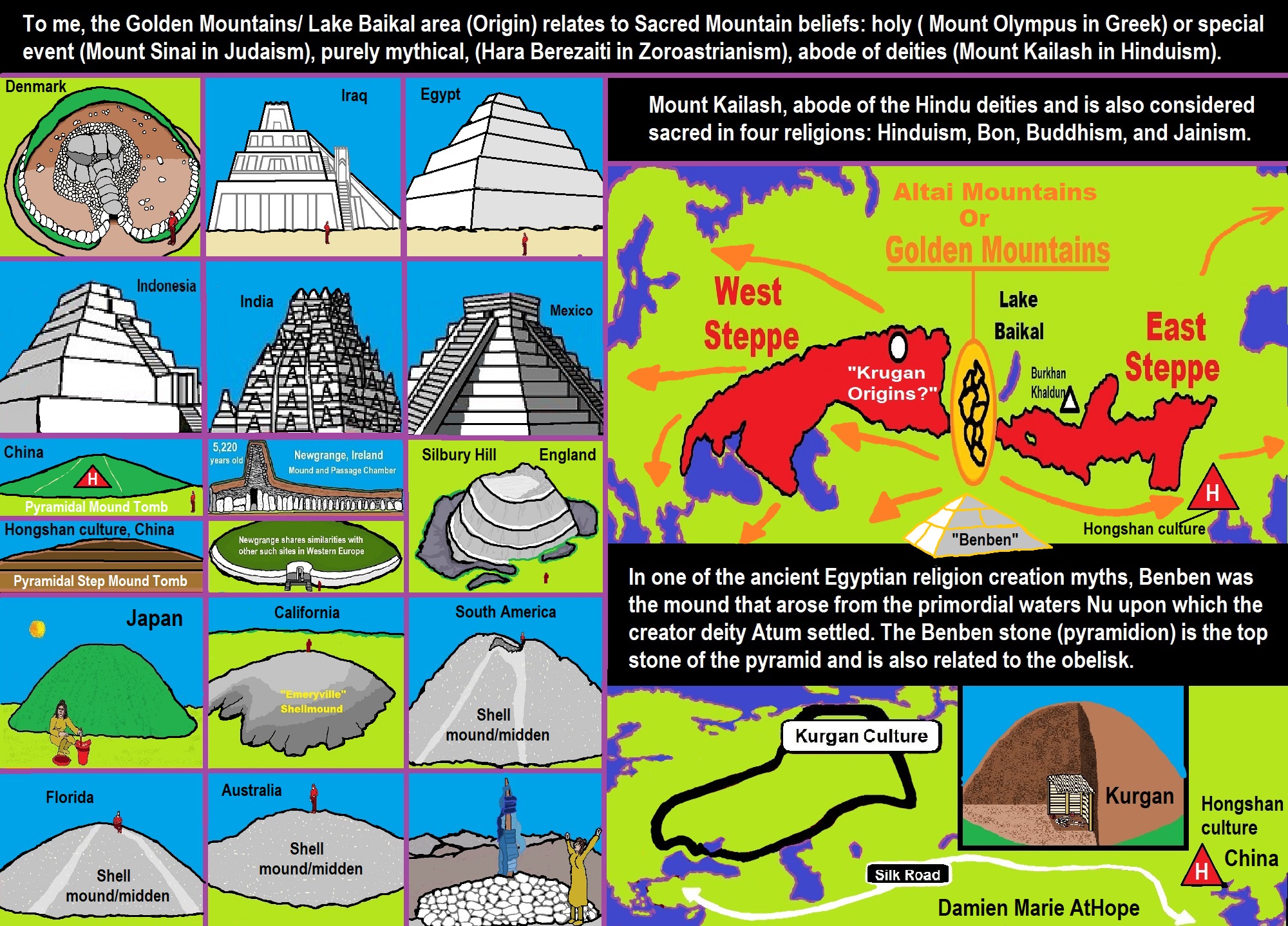
My Speculations are in Comparative Mythologies?
For instance, the mytheme of an ancient belief that is seemingly shared though changed and adapted, a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure seems to be shared a common relation with mountains/ancestors/gods or sacred animals with Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids.
Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep Mythology connections?
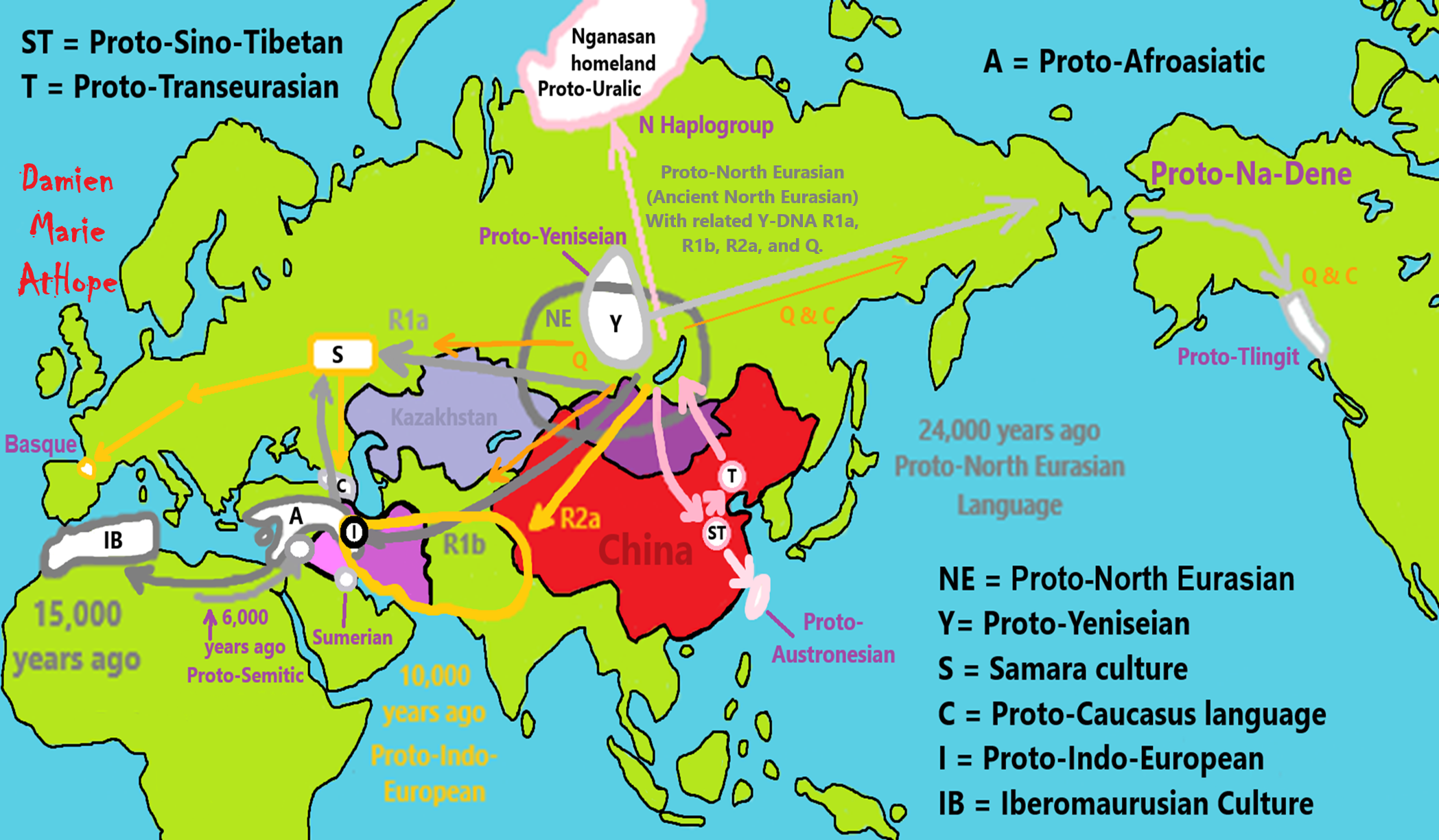
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
This art above explains my thinking from my life of investigation
I am an anarchist (Social anarchism, Left-wing anarchism, or Socialist anarchism) trying to explain prehistory as I see it after studying it on my own starting 2006. Anarchists are for truth and believe in teaching the plain truth; misinformation is against this, and we would and should fight misinformation and disinformation.
I see anarchism as a social justice issue not limited to some political issue or monetary persuasion. People own themselves, have self/human rights, and deserve freedoms. All humanity is owed respect for its dignity; we are all born equal in dignity and human rights, and no plot of dirt we currently reside on changes this.
I fully enjoy the value (axiology) of archaeology (empirical evidence from fact or artifacts at a site) is knowledge (epistemology) of the past, adding to our anthropology (evidence from cultures both the present and past) intellectual (rational) assumptions of the likely reality of actual events from time past.
I am an Axiological Atheist, Philosopher & Autodidact Pre-Historical Writer/Researcher, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Anarcho Humanist, LGBTQI, Race, & Class equality. I am not an academic, I am a revolutionary sharing education and reason to inspire more deep thinking. I do value and appreciate Academics, Archaeologists, Anthropologists, and Historians as they provide us with great knowledge, informing us about our shared humanity.
I am a servant leader, as I serve the people, not myself, not my ego, and not some desire for money, but rather a caring teacher’s heart to help all I can with all I am. From such thoughtfulness may we all see the need for humanism and secularism, respecting all as helpful servant leaders assisting others as often as we can to navigate truth and the beauty of reality.
‘Reality’ ie. real/external world things, facts/evidence such as that confirmed by science, or events taken as a whole documented understanding of what occurred/is likely to have occurred; the accurate state of affairs. “Reason” is not from a mind devoid of “unreason” but rather demonstrates the potential ability to overcome bad thinking. An honest mind, enjoys just correction. Nothing is a justified true belief without valid or reliable reason and evidence; just as everything believed must be open to question, leaving nothing above challenge.
I don’t believe in gods or ghosts, and nor souls either. I don’t believe in heavens or hells, nor any supernatural anything. I don’t believe in Aliens, Bigfoot, nor Atlantis. I strive to follow reason and be a rationalist. Reason is my only master and may we all master reason. Thinking can be random, but reason is organized and sound in its Thinking. Right thinking is reason, right reason is logic, and right logic can be used in math and other scientific methods. I don’t see religious terms Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, or Paganism as primitive but original or core elements that are different parts of world views and their supernatural/non-natural beliefs or thinking.
I am inspired by philosophy, enlightened by archaeology, and grounded by science that religion claims, on the whole, along with their magical gods, are but dogmatic propaganda, myths, and lies. To me, religions can be summed up as conspiracy theories about reality, a reality mind you is only natural and devoid of magic anything. And to me, when people talk as if Atlantis is anything real, I stop taking them seriously. Like asking about the reality of Superman or Batman just because they seem to involve metropolitan cities in their stores. Or if Mother Goose actually lived in a shoe? You got to be kidding.
We are made great in our many acts of kindness, because we rise by helping each other.
NE = Proto-North Eurasian/Ancient North Eurasian/Mal’ta–Buret’ culture/Mal’ta Boy “MA-1” 24,000 years old burial
A = Proto-Afroasiatic/Afroasiatic
S = Samara culture
ST = Proto-Sino-Tibetan/Sino-Tibetan
T = Proto-Transeurasian/Altaic
C = Proto-Northwest Caucasus language/Northwest Caucasian/Languages of the Caucasus
I = Proto-Indo-European/Indo-European
IB = Iberomaurusian Culture/Capsian culture
Natufian culture (15,000–11,500 years ago, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, the Sinai Peninsula, and the Negev desert)
Nganasan people/Nganasan language
Na-Dene languages/Dené–Yeniseian, Dené–Caucasian
Proto-Semitic/Semitic languages
24,000 years ago, Proto-North Eurasian Language (Ancient North Eurasian) migrations?
My thoughts:
Proto-North Eurasian Language (Ancient North Eurasian) With related Y-DNA R1a, R1b, R2a, and Q Haplogroups.
R1b 22,0000-15,000 years ago in the Middle east creates Proto-Afroasiatic languages moving into Africa around 15,000-10,000 years ago connecting with the Iberomaurusian Culture/Taforalt near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
R2a 10,000 years ago in Iran brings/creates Proto-Indo-European language and also a possibility is R1a in Russia around 9,000 years ago may have had a version of Proto-Indo-European language.
Around 14,000-10,000 years ago??? Proto-North Eurasian Language goes to the Yellow River basin (eventually relating with the Yangshao culture) in China creates Proto-Sino-Tibetan language.
Proto-Sino-Tibetan language then moves to the West Liao River valley (eventually relating with the Hongshan culture) in China creating Proto-Transeurasian (Altaic) language around 9,000 years ago.
N Haplogroups 9,000 years ago with Proto-Transeurasian language possibly moves north to Lake Baikal. Then after living with Proto-North Eurasian Language 24,000-9,000 years ago?/Pre-Proto-Yeniseian language 9,000-7,000 years ago Q Haplogroups (eventually relating with the Ket language and the Ket people) until around 5,500 years ago, then N Haplogroups move north to the Taymyr Peninsula in North Siberia (Nganasan homeland) brings/creates the Proto-Uralic language.
Q Haplogroups with Proto-Yeniseian language /Proto-Na-Dene language likely emerge 8,000/7,000 years ago or so and migrates to the Middle East (either following R2a to Iraq or R1a to Russia (Samara culture) then south to Iraq creates the Sumerian language. It may have also created the Proto-Caucasian languages along the way. And Q Haplogroups with Proto-Yeniseian language to a migration to North America that relates to Na-Dené (and maybe including Haida) languages, of which the first branch was Proto-Tlingit language 5,000 years ago, in the Pacific Northwest.
Sino-Tibetan language then moves more east in China to the Hemudu culture pre-Austronesian culture, next moved to Taiwan creating the Proto-Austronesian language around 6,000-5,500 years ago.
R1b comes to Russia from the Middle East around 7,500 years ago, bringing a version of Proto-Indo-European languages to the (Samara culture), then Q Y-DNA with Proto-Yeniseian language moves south from the (Samara culture) and may have been the language that created the Proto-Caucasian language. And R1b from the (Samara culture) becomes the 4,200 years or so R1b associated with the Basques and Basque language it was taken with R1b, but language similarities with the Proto-Caucasian language implies language ties to Proto-Yeniseian language.
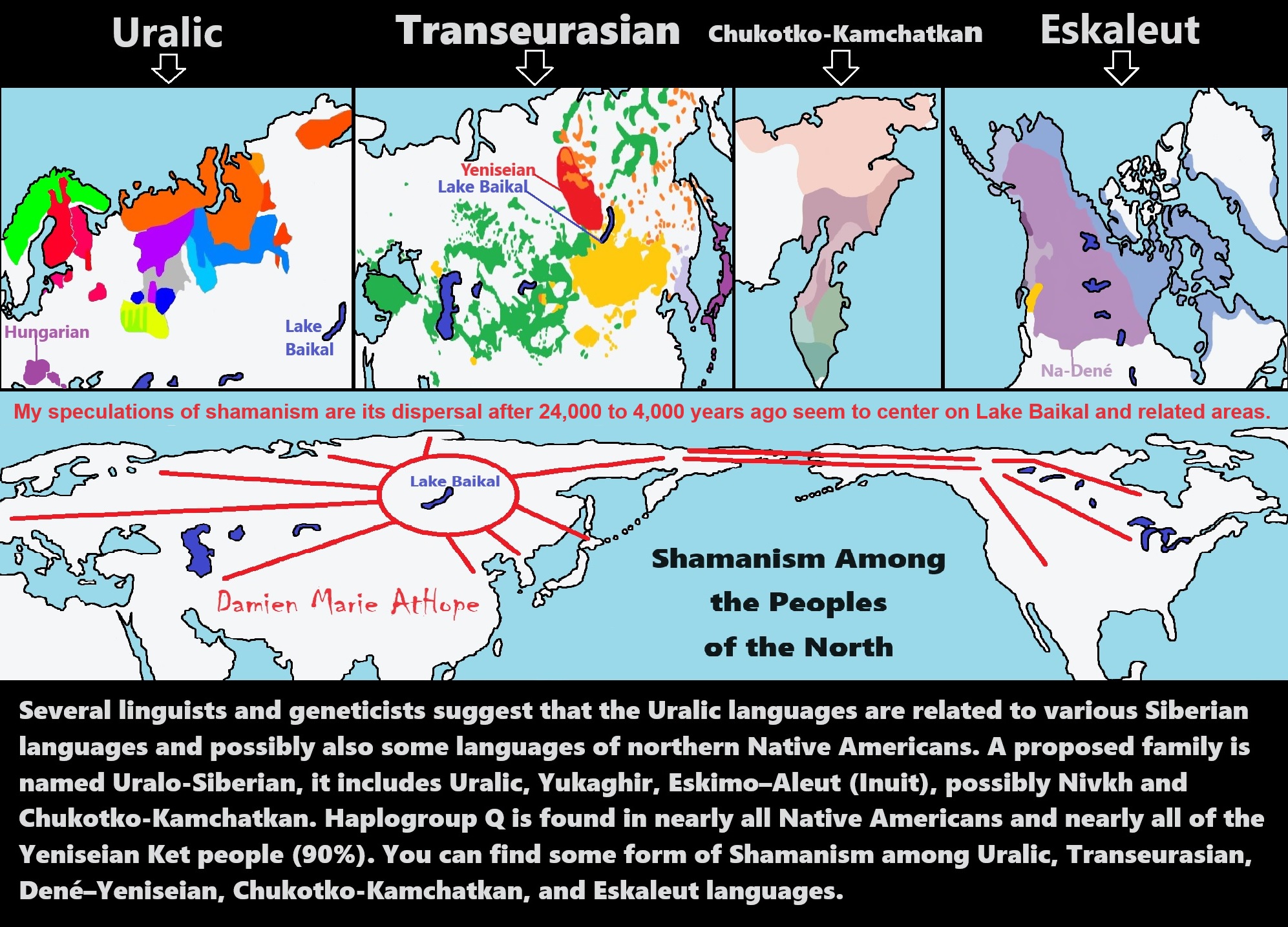
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“Several linguists and geneticists suggest that the Uralic languages are related to various Siberian languages and possibly also some languages of northern Native Americans. A proposed family is named Uralo-Siberian, it includes Uralic, Yukaghir, Eskimo–Aleut (Inuit), possibly Nivkh, and Chukotko-Kamchatkan. Haplogroup Q is found in nearly all Native Americans and nearly all of the Yeniseian Ket people (90%).” ref, ref
You can find some form of Shamanism, among Uralic, Transeurasian, Dené–Yeniseian, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskaleut languages.
My speculations of shamanism are its dispersals, after 24,000 to 4,000 years ago, seem to center on Lake Baikal and related areas. To me, the hotspot of Shamanism goes from west of Lake Baikal in the “Altai Mountains” also encompassing “Lake Baikal” and includes the “Amur Region/Watershed” east of Lake Baikal as the main location Shamanism seems to have radiated out from.
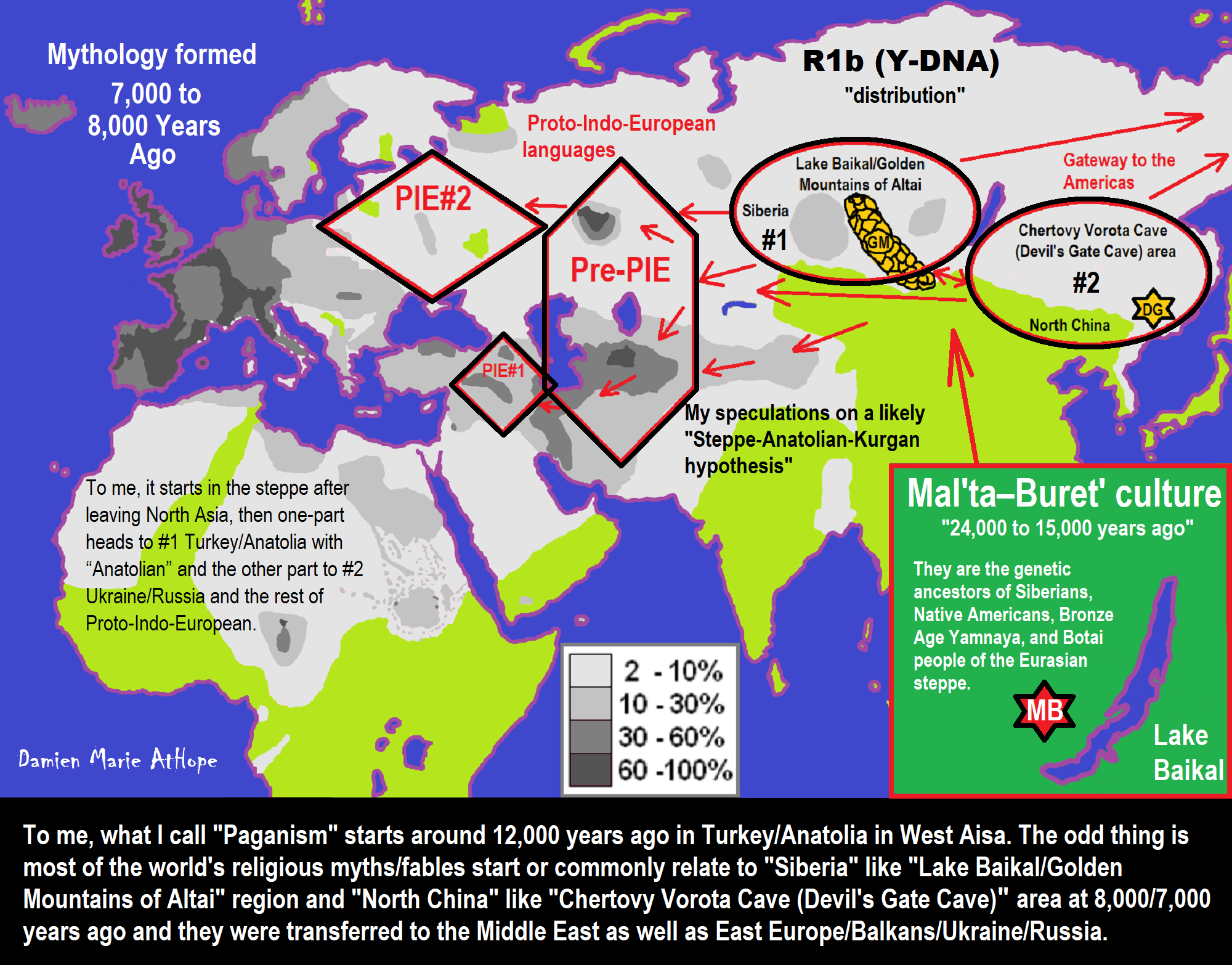
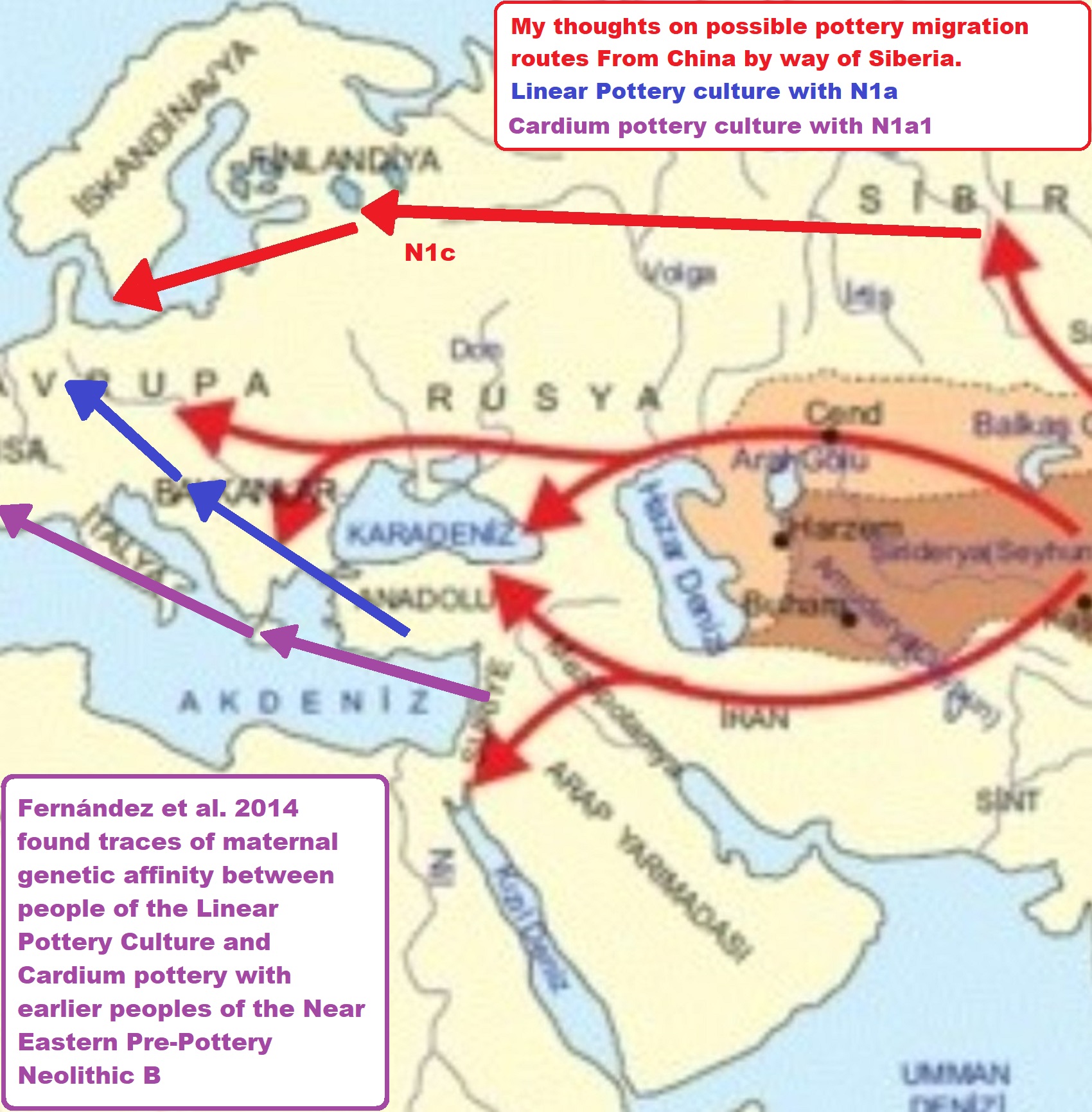
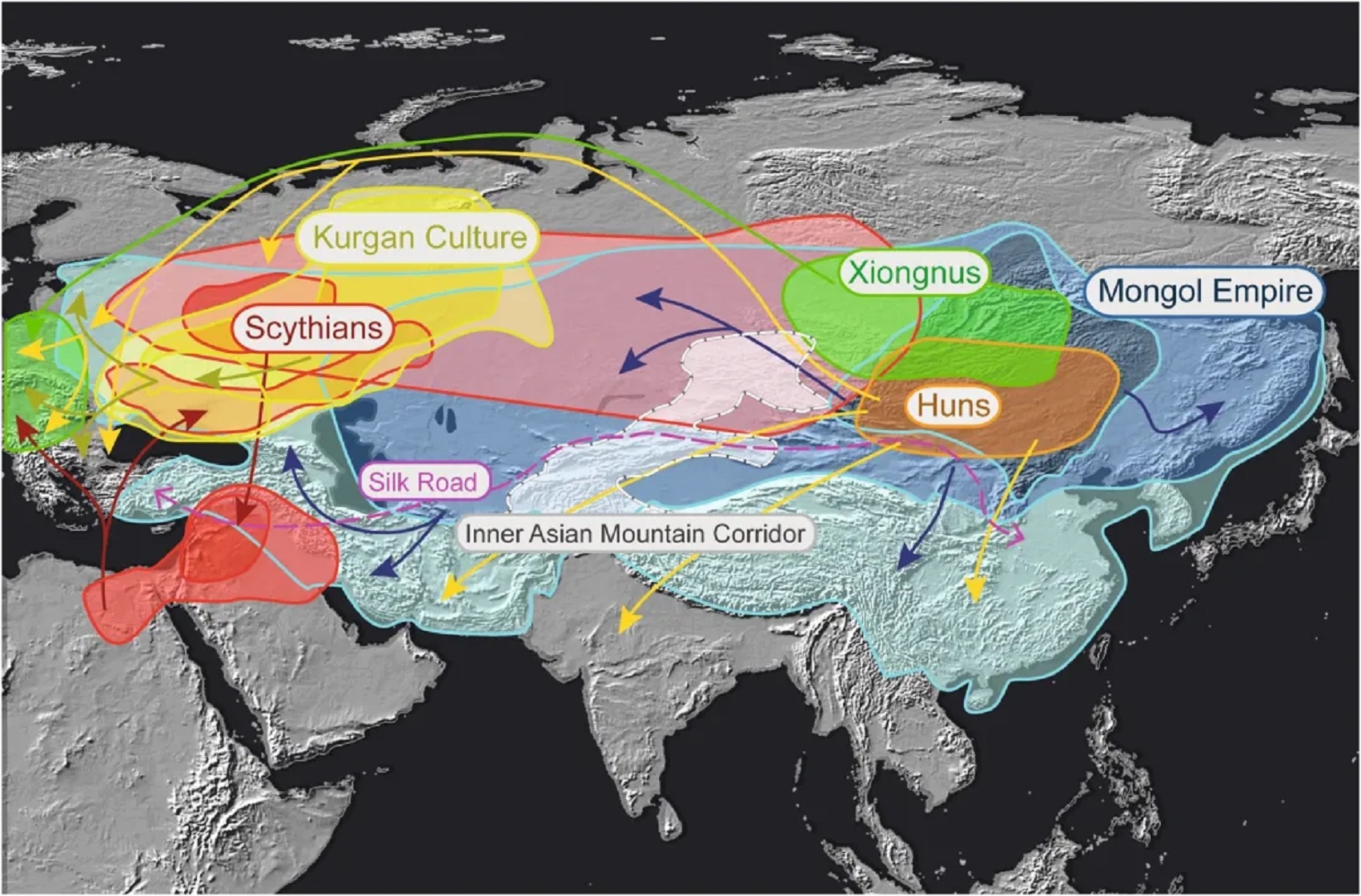
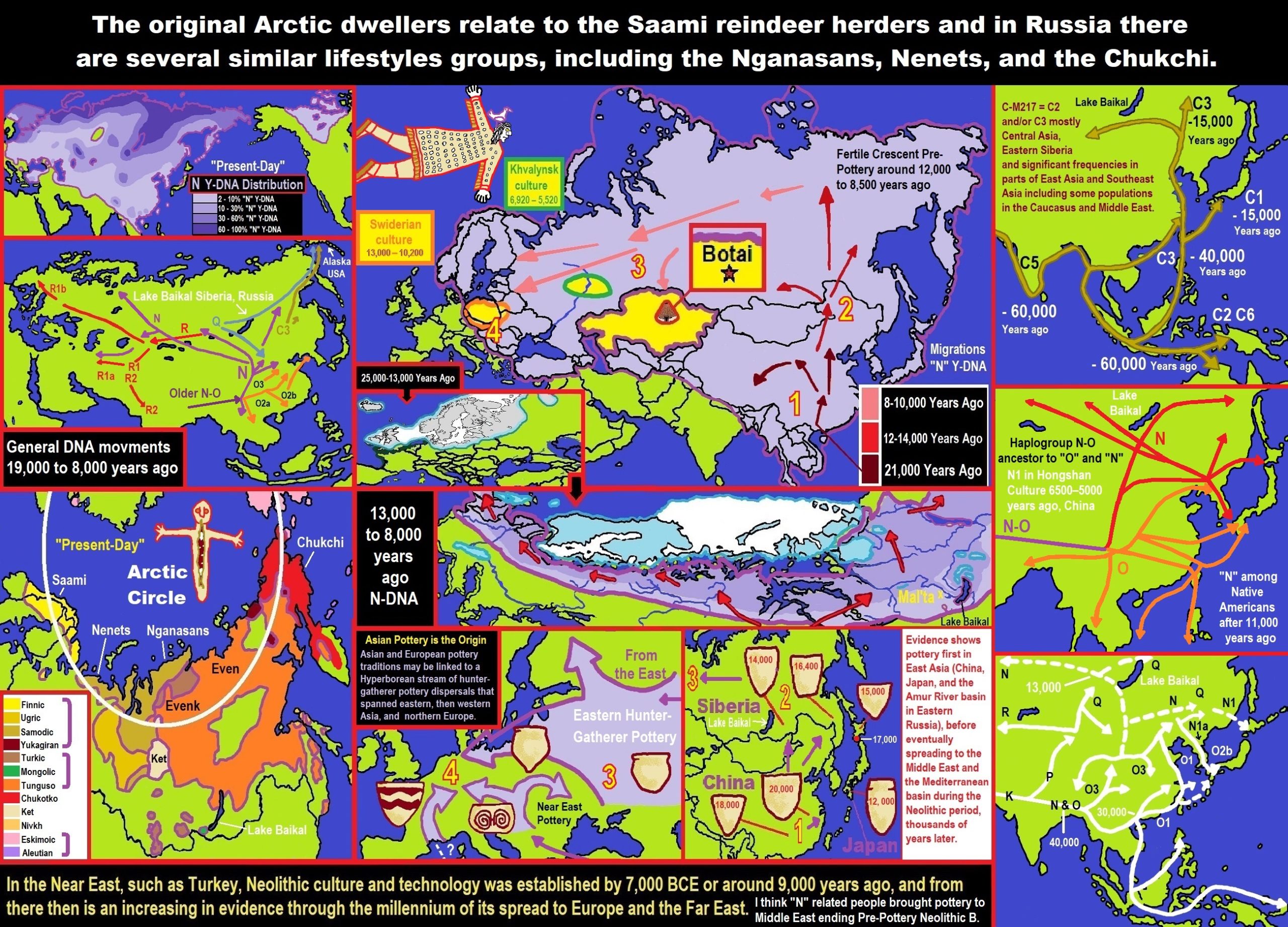
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“The shaman is, above all, a connecting figure, bridging several worlds for his people, traveling between this world, the underworld, and the heavens. He transforms himself into an animal and talks with ghosts, the dead, the deities, and the ancestors. He dies and revives. He brings back knowledge from the shadow realm, thus linking his people to the spirits and places which were once mythically accessible to all.–anthropologist Barbara Meyerhoff” ref
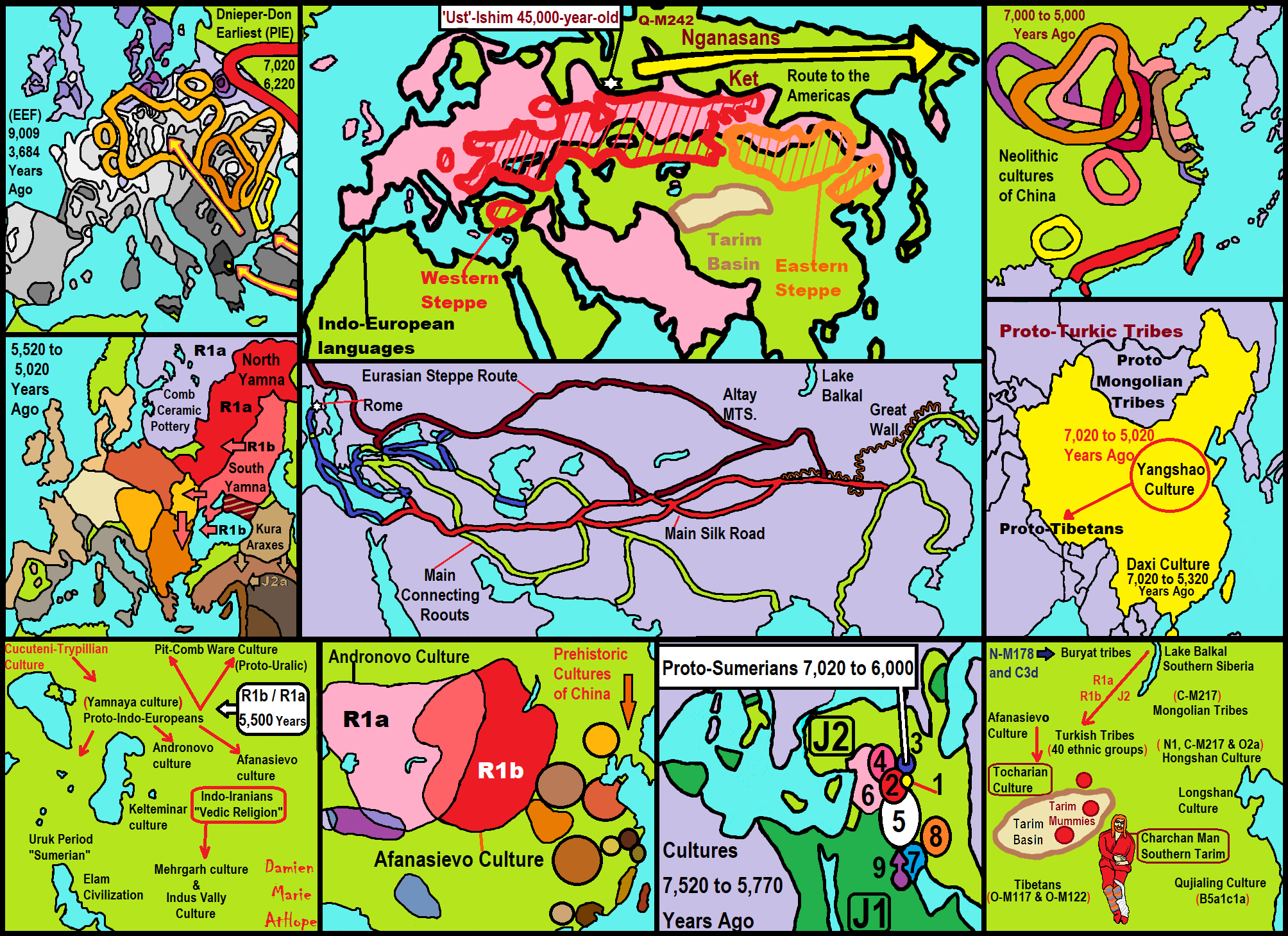
Pic ref
Ancient Women Found in a Russian Cave Turn Out to Be Closely Related to The Modern Population https://www.sciencealert.com/ancient-women-found-in-a-russian-cave-turn-out-to-be-closely-related-to-the-modern-population
Abstract
“Ancient genomes have revolutionized our understanding of Holocene prehistory and, particularly, the Neolithic transition in western Eurasia. In contrast, East Asia has so far received little attention, despite representing a core region at which the Neolithic transition took place independently ~3 millennia after its onset in the Near East. We report genome-wide data from two hunter-gatherers from Devil’s Gate, an early Neolithic cave site (dated to ~7.7 thousand years ago) located in East Asia, on the border between Russia and Korea. Both of these individuals are genetically most similar to geographically close modern populations from the Amur Basin, all speaking Tungusic languages, and, in particular, to the Ulchi. The similarity to nearby modern populations and the low levels of additional genetic material in the Ulchi imply a high level of genetic continuity in this region during the Holocene, a pattern that markedly contrasts with that reported for Europe.” ref
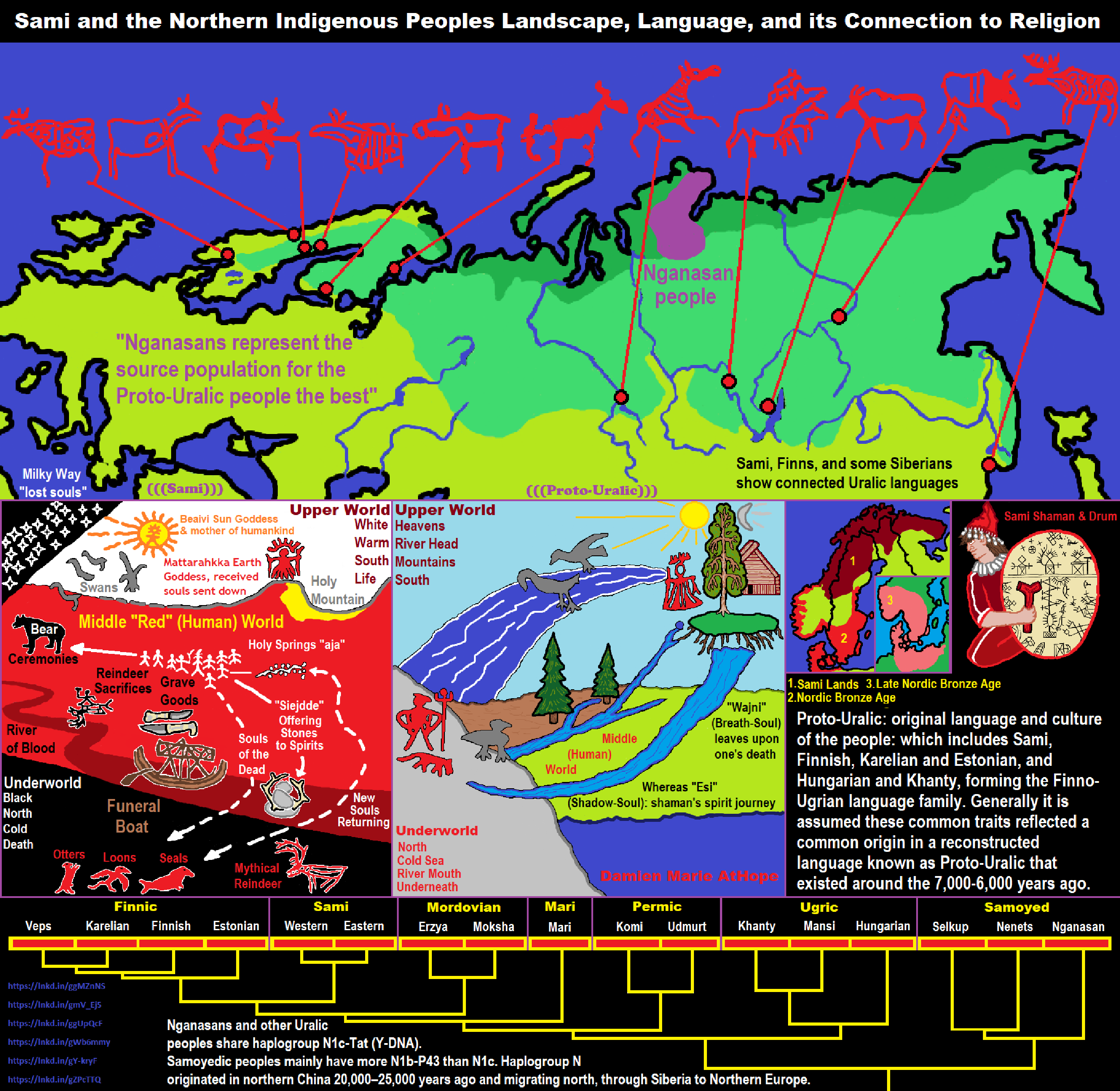
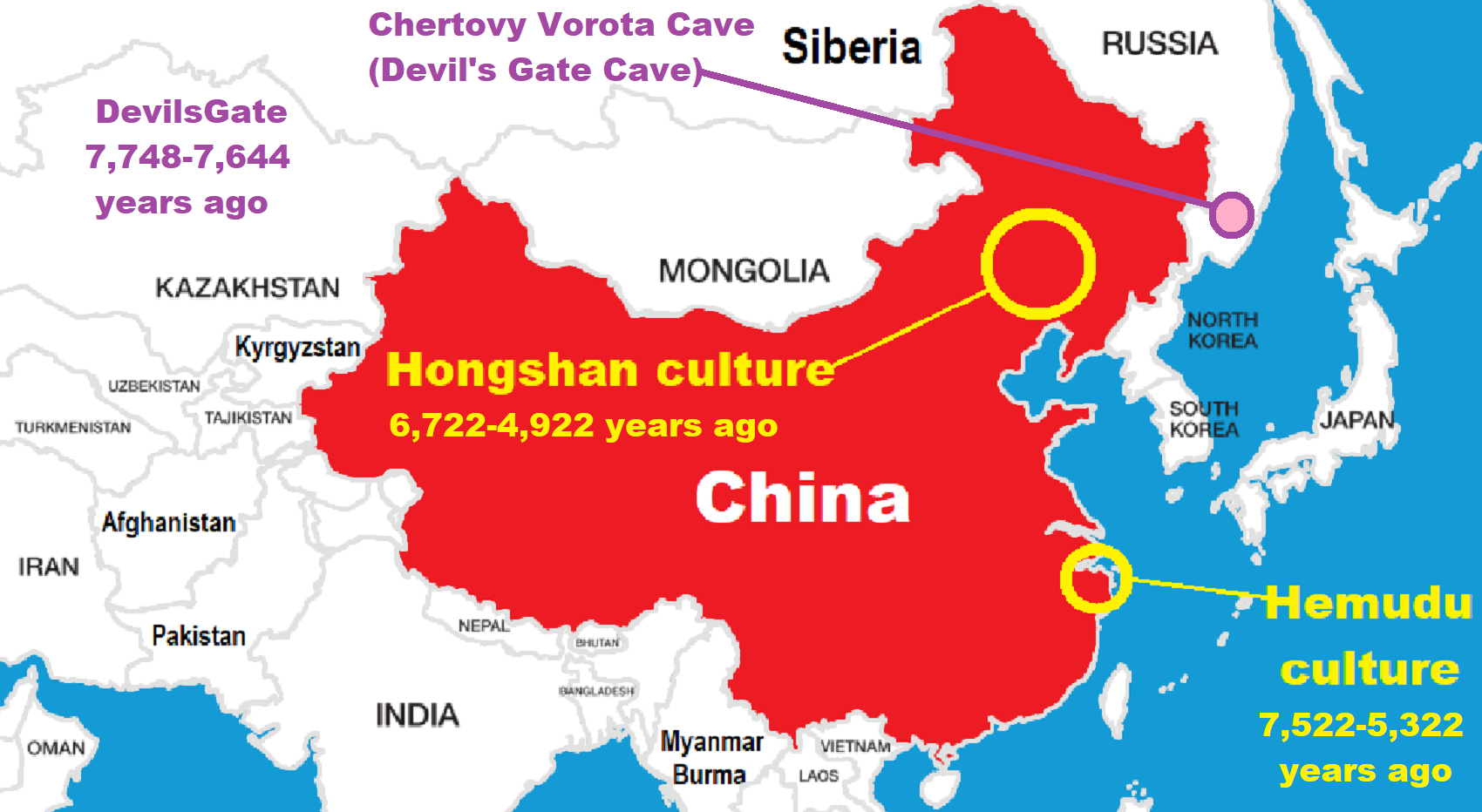
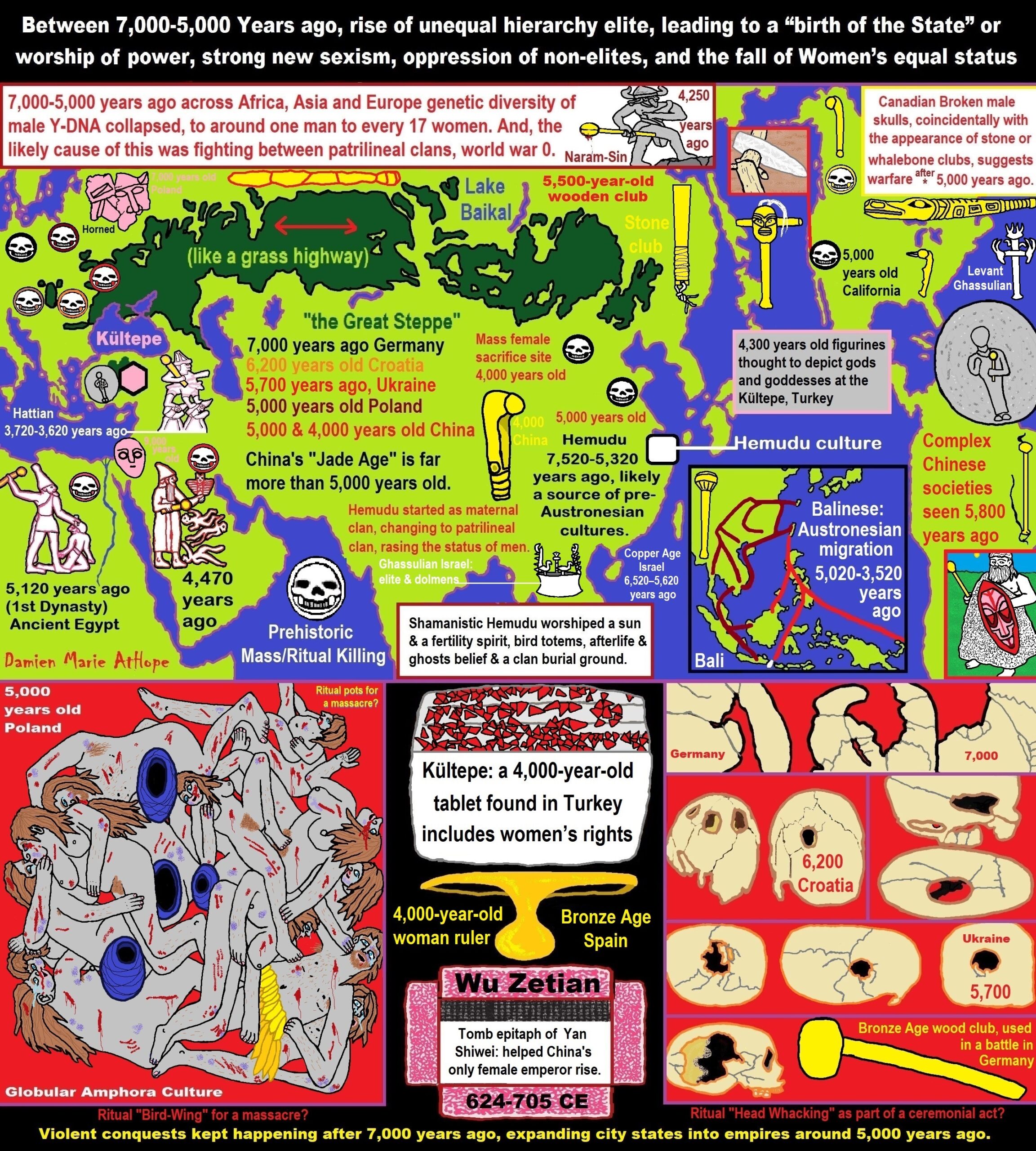
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
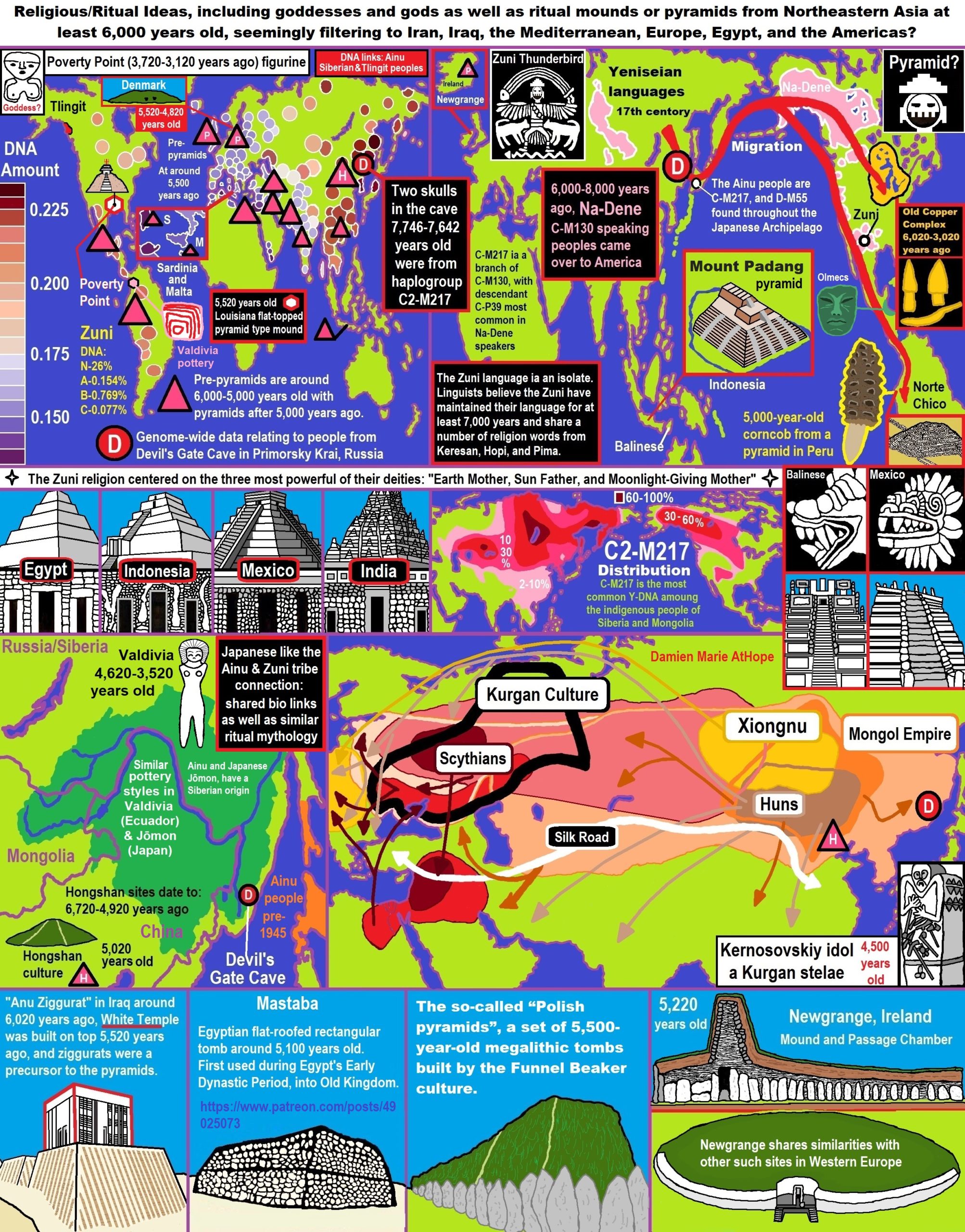
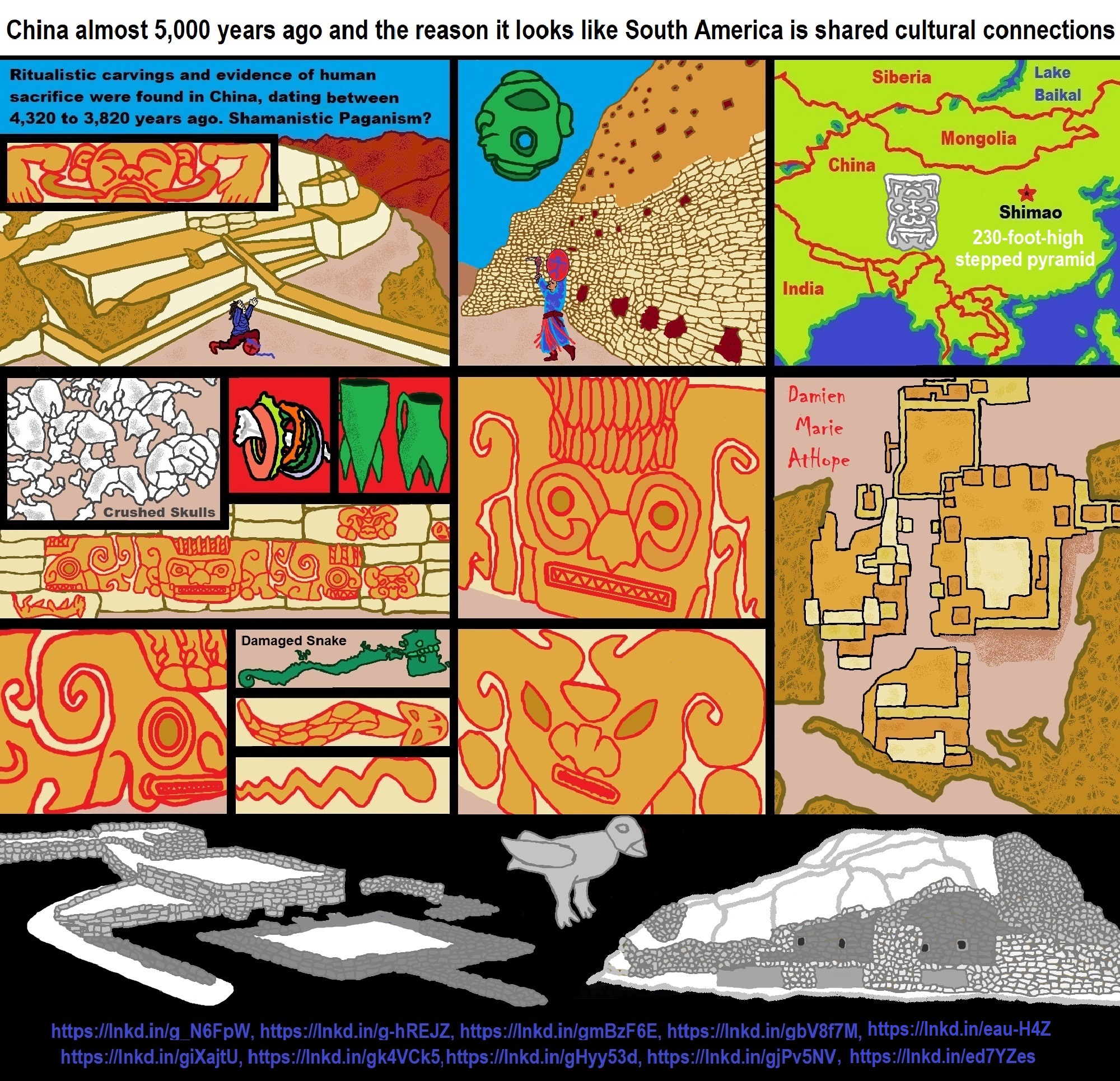
Shimao
“Shimao is a site in Shenmu County, Shaanxi, China. The site is located in the northern part of the Loess Plateau, on the southern edge of the Ordos Desert. It is dated to around 2000 BCE or around 4,000 years ago or so, near the end of the Longshan period, and is the largest known walled site of that period in China, at 400 ha. The fortifications of Shimao were originally believed by to be a section of the Great Wall of China, but the discovery of jade pieces prompted an archaeological investigation.” ref
“The city was surrounded by inner and outer stone walls, in contrast to the rammed earth walls typical of Longshan sites in the Central Plain and Shandong. The walls were 2.5 meters thick on average, with perimeters of approximately 4200 m and 5700 m respectively, and feature gates, turrets, and watchtowers. The earliest site, the “palace center”, was a large stepped pyramid based on a loess hill which had been reworked to make 11 platforms, with a height of 70m. Each of these was reinforced by stone buttresses. At the top of this pyramid palaces of rammed earth were built. The inner city contained a stone-walled platform, interpreted as a palatial complex, and densely packed residential zones, cemeteries, and craft workshops. Unusual features include jade embedded in the city walls, possibly to provide spiritual protection, relief sculptures of serpents and monsters, and paintings of geometrical patterns on the inner walls. Approximately 80 human skulls were found under the city gate, mainly of young girls, suggesting ritual sacrifice.” ref
“Developments such as bronze working, wheat, barley, sheep, goats, and cattle seem to appear here earlier than elsewhere in China, showing that its inhabitants were communicating with Eurasian Steppe peoples across extensive trade networks. Additionally, materials likely from Southern China, such as alligator skin drums, have been found, indicating a north-south commerce across what is now modern China. Thin curved bones discovered at Shimao are believed to be the earliest known evidence of the jaw harp, an instrument that has spread to over 100 different ethnic groups, suggesting possible Chinese origins.” ref
“The prevailing hypothesis concerning the abandonment of Shimao is tied to a rapid shift to a cooler, drier climate on the Loess Plateau, from 2000 to 1700 BCE. This environmental change likely led populations to shift to the Central Plain, leaving the site to be forgotten until the 21st century.” ref
- Mysterious carvings and evidence of human sacrifice uncovered in the ancient city of Shimao
- Neolithic City of Shimao in Shaanxi Province, China
- China’s Shimao ruins among top 10 archaeological finds of the past decade
- Shimao: Massive Pyramid, Lost City, and Ancient Human Sacrifices Unearthed in China
- Shimao and Erlitou: new perspectives on the origins of the bronze industry in central China
- Shimao, a 4,300-year-old Chinese City Built with Ritual Stones
- ‘Pyramid of eyes’ discovered at the heart of the 4,300-year-old city of Shimao in northern China
- Large-Scale Cemetery Of Shimao Culture Found In NW China
- Food between the country and the city: The politics of food production at Shimao and Zhaimaoliang in the Ordos Region, northern China
- The first Neolithic urban center on China’s north Loess Plateau: The rise and fall of Shimao
- Who is that Human at Shimao? China’s Ancient Belief in Metamorphic Power
Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
But is Atlantis real?
No. Atlantis (an allegory: “fake story” interpreted to reveal a hidden meaning) can’t be found any more than one can locate the Jolly Green Giant that is said to watch over frozen vegetables. Lol

May Reason Set You Free
There are a lot of truly great things said by anarchists in history, and also some deeply vile things, too, from not supporting Women’s rights to Anti-Semitism. There are those who also reject those supporting women’s rights as well as fight anti-Semitism. This is why I push reason as my only master, not anarchist thinking, though anarchism, to me, should see all humans everywhere as equal in dignity and rights.
We—Cory and Damien—are following the greatness that can be found in anarchist thinking.
As an Anarchist Educator, Damien strives to teach the plain truth. Damien does not support violence as my method to change. Rather, I choose education that builds Enlightenment and Empowerment. I champion Dignity and Equality. We rise by helping each other. What is the price of a tear? What is the cost of a smile? How can we see clearly when others pay the cost of our indifference and fear? We should help people in need. Why is that so hard for some people? Rich Ghouls must End. Damien wants “billionaires” to stop being a thing. Tax then into equality. To Damien, there is no debate, Capitalism is unethical. Moreover, as an Anarchist Educator, Damien knows violence is not the way to inspire lasting positive change. But we are not limited to violence, we have education, one of the most lasting and powerful ways to improve the world. We empower the world by championing Truth and its supporters.
Anarchism and Education
“Various alternatives to education and their problems have been proposed by anarchists which have gone from alternative education systems and environments, self-education, advocacy of youth and children rights, and freethought activism.” ref
“Historical accounts of anarchist educational experiments to explore how their pedagogical practices, organization, and content constituted a radical alternative to mainstream forms of educational provision in different historical periods.” ref
“The Ferrer school was an early 20th century libertarian school inspired by the anarchist pedagogy of Francisco Ferrer. He was a proponent of rationalist, secular education that emphasized reason, dignity, self-reliance, and scientific observation. The Ferrer movement’s philosophy had two distinct tendencies: non-didactic freedom from dogma and the more didactic fostering of counter-hegemonic beliefs. Towards non-didactic freedom from dogma, and fulfilled the child-centered tradition.” ref

Teach Real History: all our lives depend on it.
Damien sees lies about history as crimes against humanity. And we all must help humanity by addressing “any and all” who make harmful lies about history.

My favorite “Graham Hancock” Quote?
“In what archaeologists have studied, yes, we can say there is NO Evidence of an advanced civilization.” – (Time 1:27) Joe Rogan Experience #2136 – Graham Hancock & Flint Dibble

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


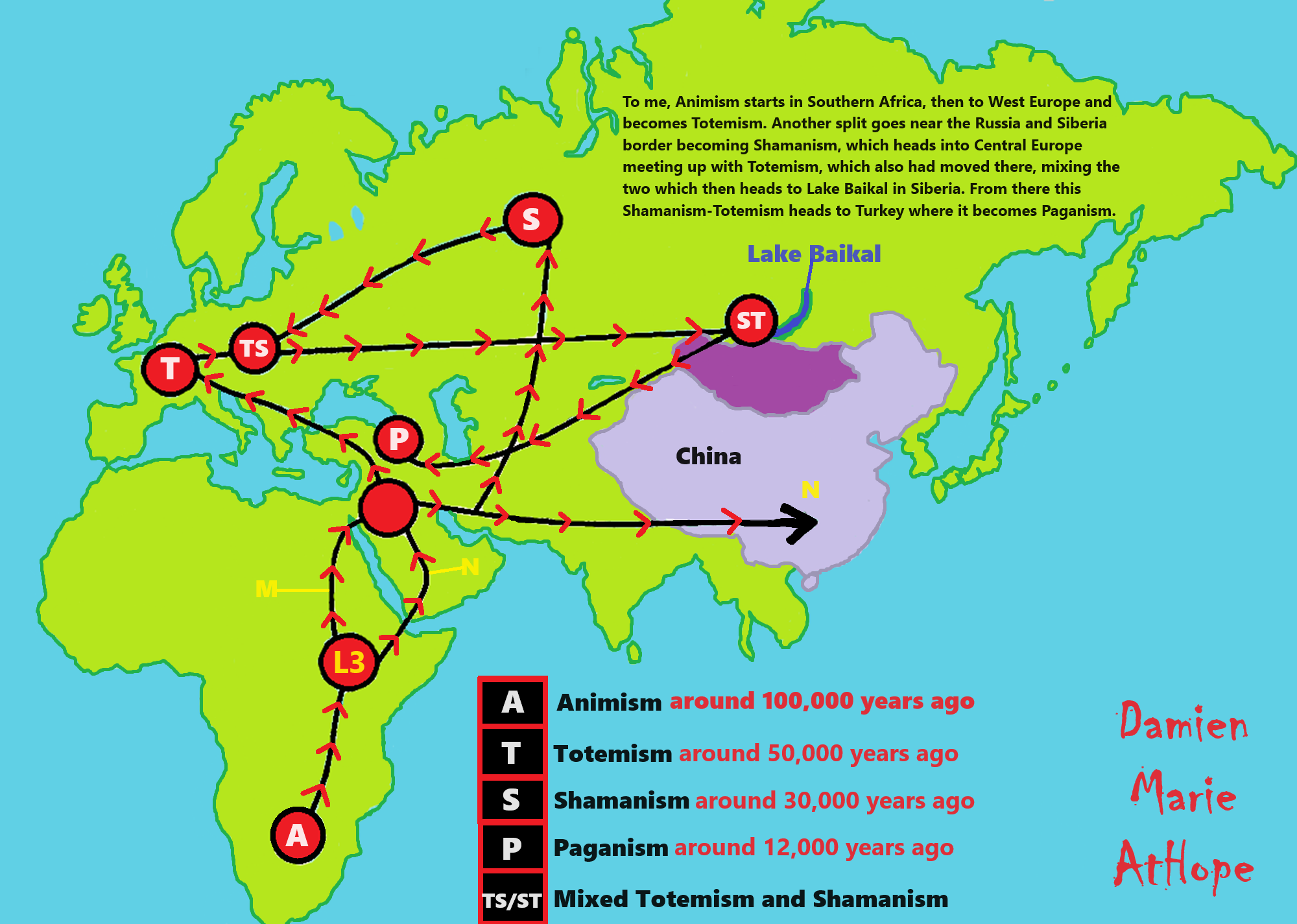
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.



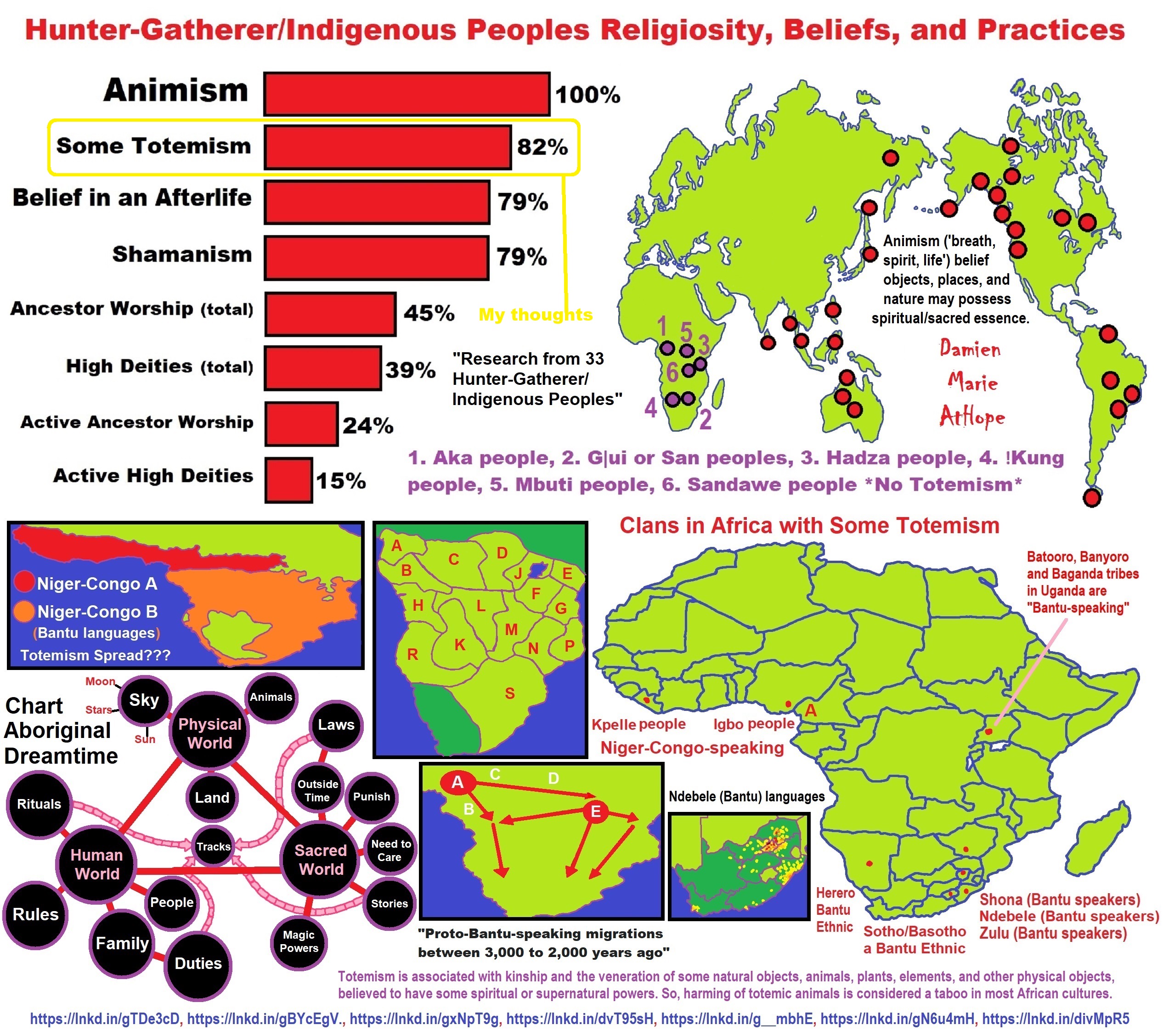
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
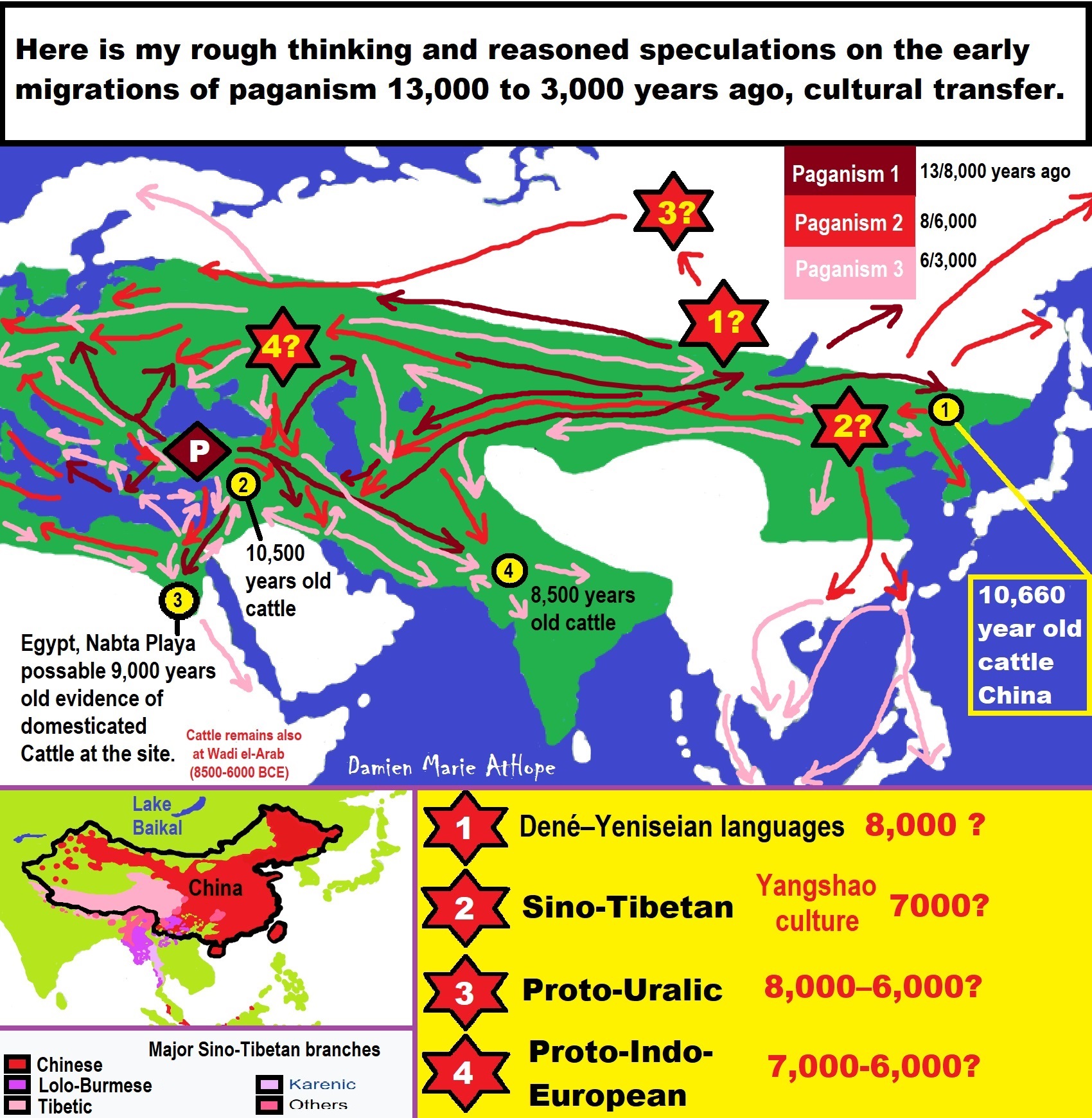
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.

Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com