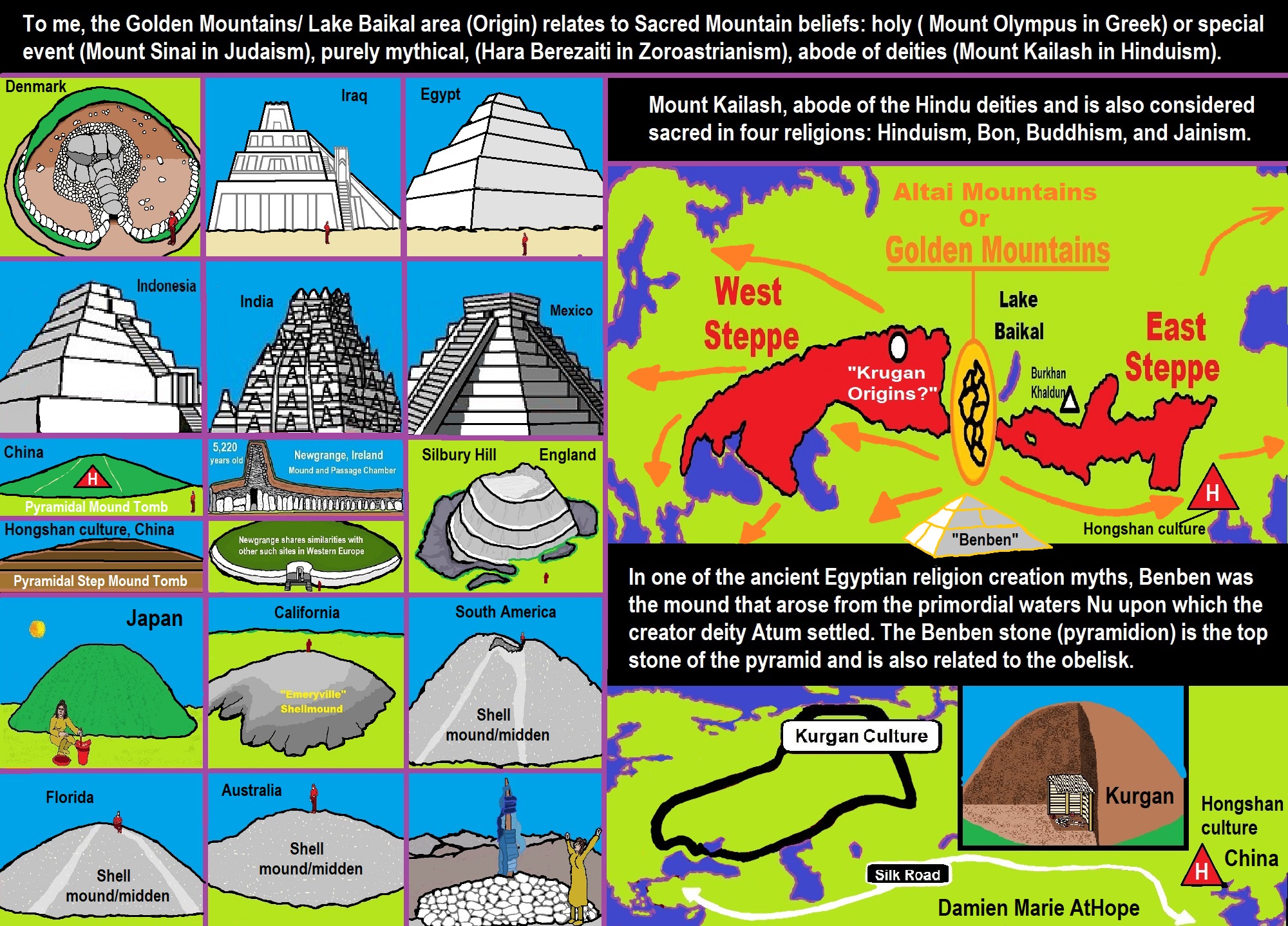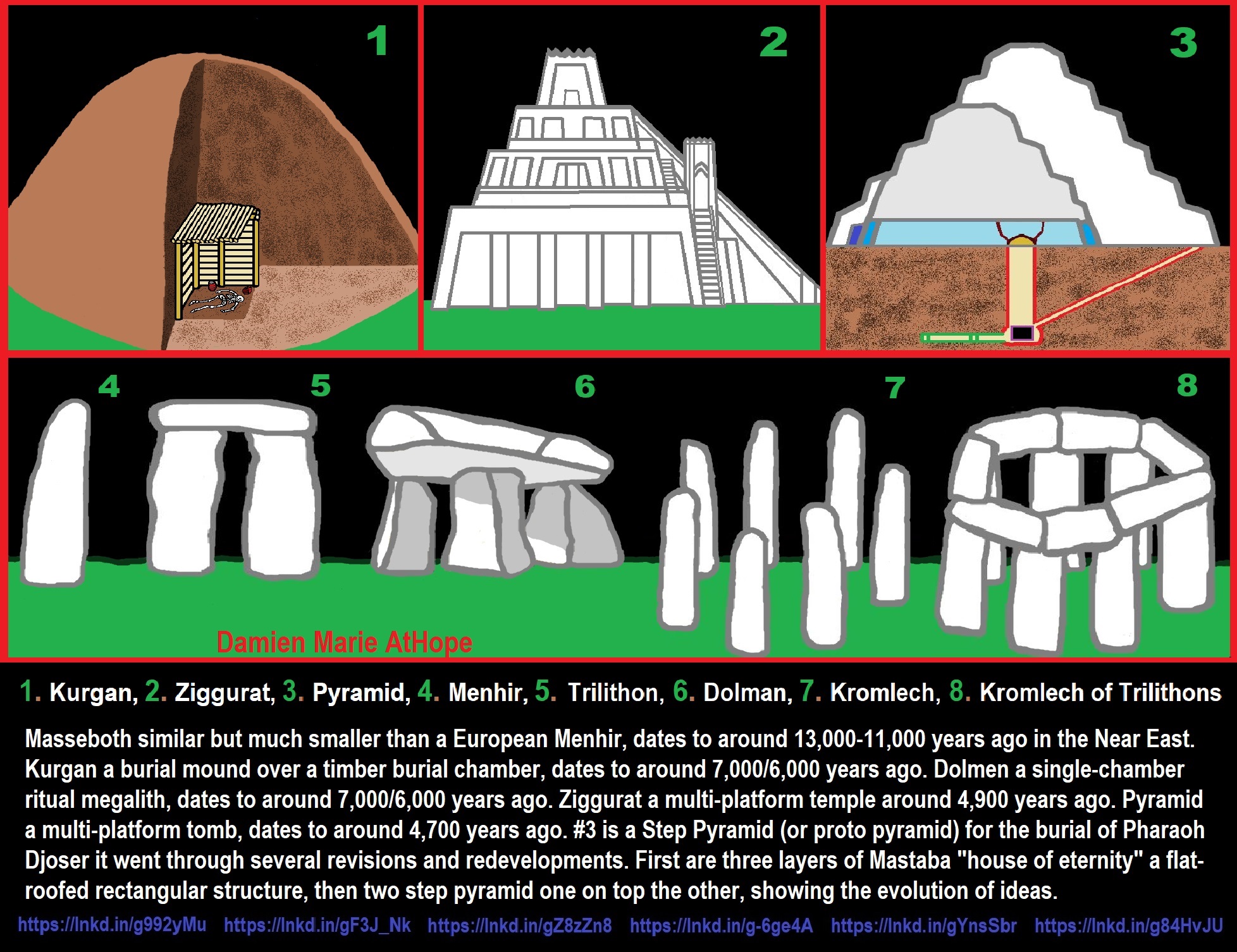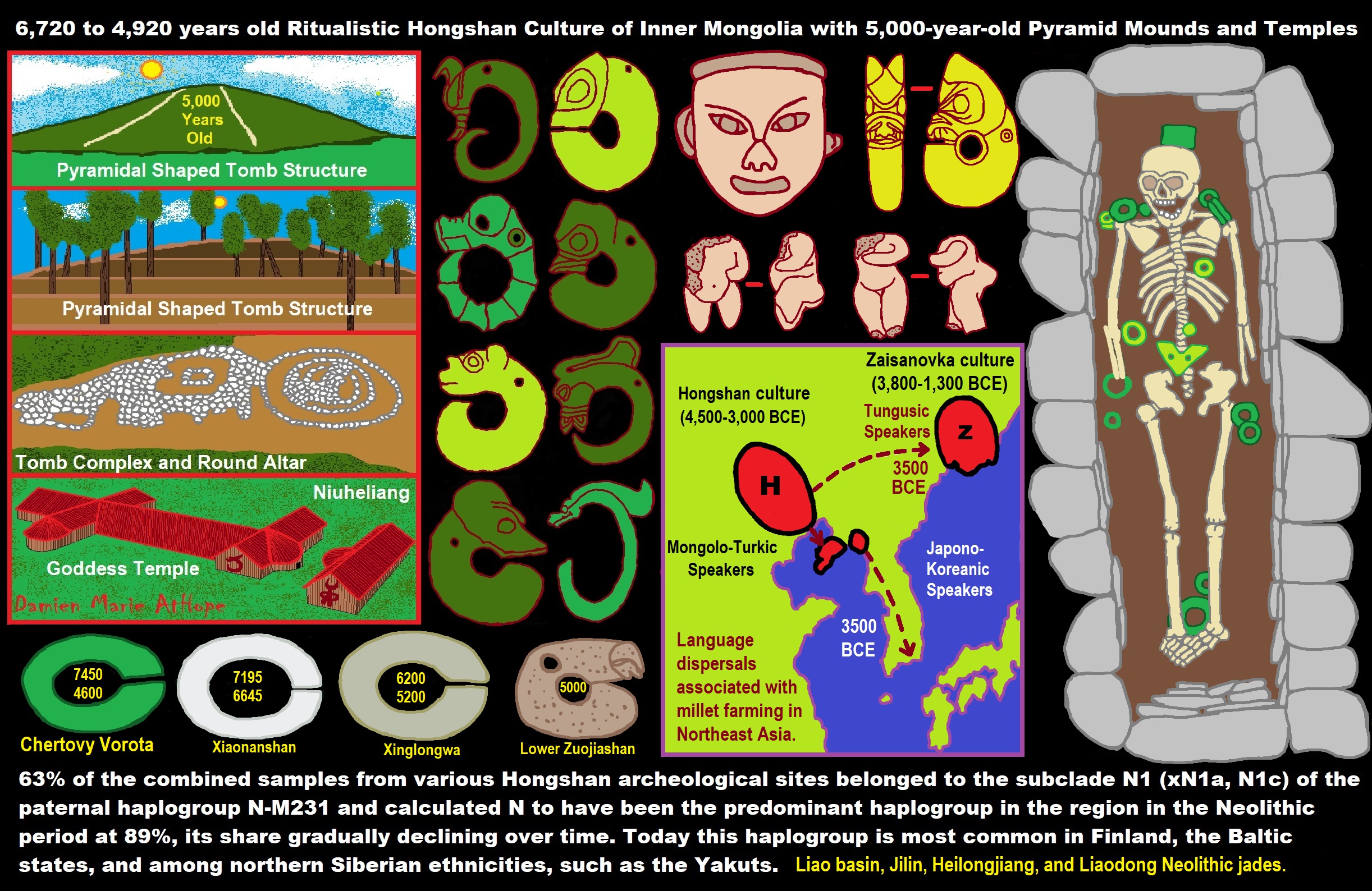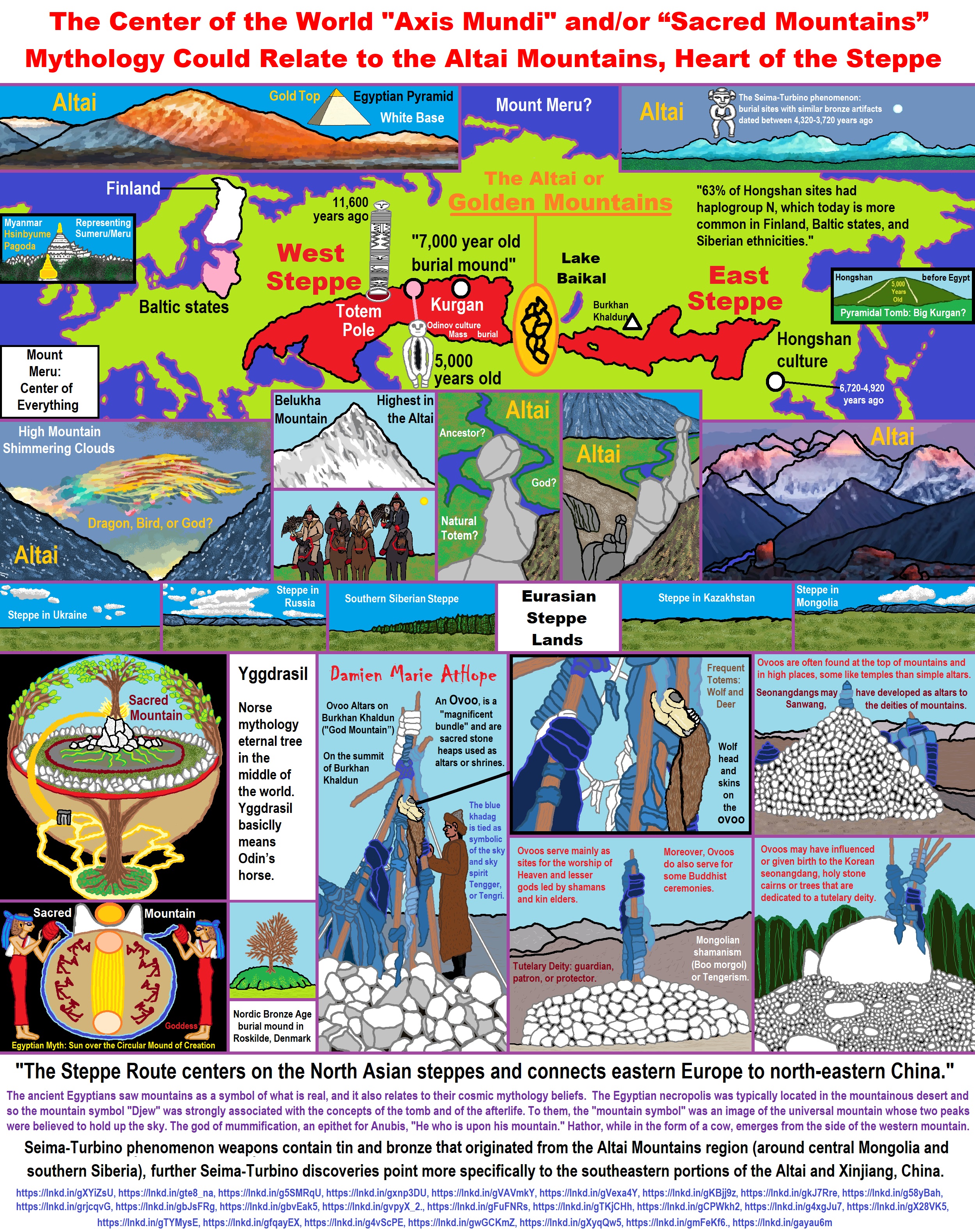
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
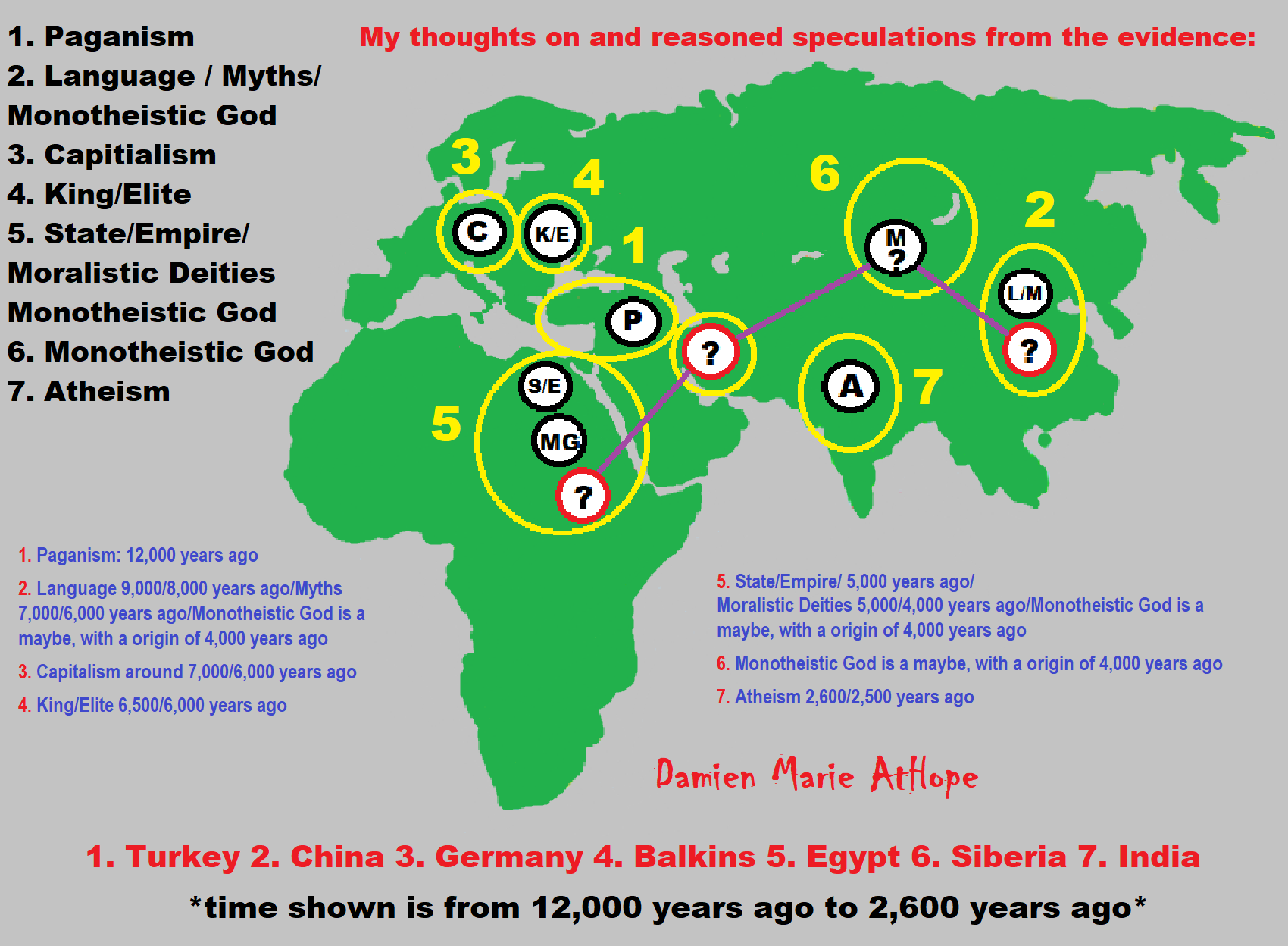
This art above explains my thinking from my life of investigation
I am an anarchist (Social anarchism, Left-wing anarchism, or Socialist anarchism) trying to explain prehistory as I see it after studying it on my own starting 2006. Anarchists are for truth and believe in teaching the plain truth; misinformation is against this, and we would and should fight misinformation and disinformation.
I see anarchism as a social justice issue not limited to some political issue or monetary persuasion. People own themselves, have self/human rights, and deserve freedoms. All humanity is owed respect for its dignity; we are all born equal in dignity and human rights, and no plot of dirt we currently reside on changes this.
I fully enjoy the value (axiology) of archaeology (empirical evidence from fact or artifacts at a site) is knowledge (epistemology) of the past, adding to our anthropology (evidence from cultures both the present and past) intellectual (rational) assumptions of the likely reality of actual events from time past.
I am an Axiological Atheist, Philosopher & Autodidact Pre-Historical Writer/Researcher, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Anarcho Humanist, LGBTQI, Race, & Class equality. I am not an academic, I am a revolutionary sharing education and reason to inspire more deep thinking. I do value and appreciate Academics, Archaeologists, Anthropologists, and Historians as they provide us with great knowledge, informing us about our shared humanity.
I am a servant leader, as I serve the people, not myself, not my ego, and not some desire for money, but rather a caring teacher’s heart to help all I can with all I am. From such thoughtfulness may we all see the need for humanism and secularism, respecting all as helpful servant leaders assisting others as often as we can to navigate truth and the beauty of reality.
‘Reality’ ie. real/external world things, facts/evidence such as that confirmed by science, or events taken as a whole documented understanding of what occurred/is likely to have occurred; the accurate state of affairs. “Reason” is not from a mind devoid of “unreason” but rather demonstrates the potential ability to overcome bad thinking. An honest mind, enjoys just correction. Nothing is a justified true belief without valid or reliable reason and evidence; just as everything believed must be open to question, leaving nothing above challenge.
I don’t believe in gods or ghosts, and nor souls either. I don’t believe in heavens or hells, nor any supernatural anything. I don’t believe in Aliens, Bigfoot, nor Atlantis. I strive to follow reason and be a rationalist. Reason is my only master and may we all master reason. Thinking can be random, but reason is organized and sound in its Thinking. Right thinking is reason, right reason is logic, and right logic can be used in math and other scientific methods. I don’t see religious terms Animism, Totemism, Shamanism, or Paganism as primitive but original or core elements that are different parts of world views and their supernatural/non-natural beliefs or thinking.
I am inspired by philosophy, enlightened by archaeology, and grounded by science that religion claims, on the whole, along with their magical gods, are but dogmatic propaganda, myths, and lies. To me, religions can be summed up as conspiracy theories about reality, a reality mind you is only natural and devoid of magic anything. And to me, when people talk as if Atlantis is anything real, I stop taking them seriously. Like asking about the reality of Superman or Batman just because they seem to involve metropolitan cities in their stores. Or if Mother Goose actually lived in a shoe? You got to be kidding.
We are made great in our many acts of kindness, because we rise by helping each other.
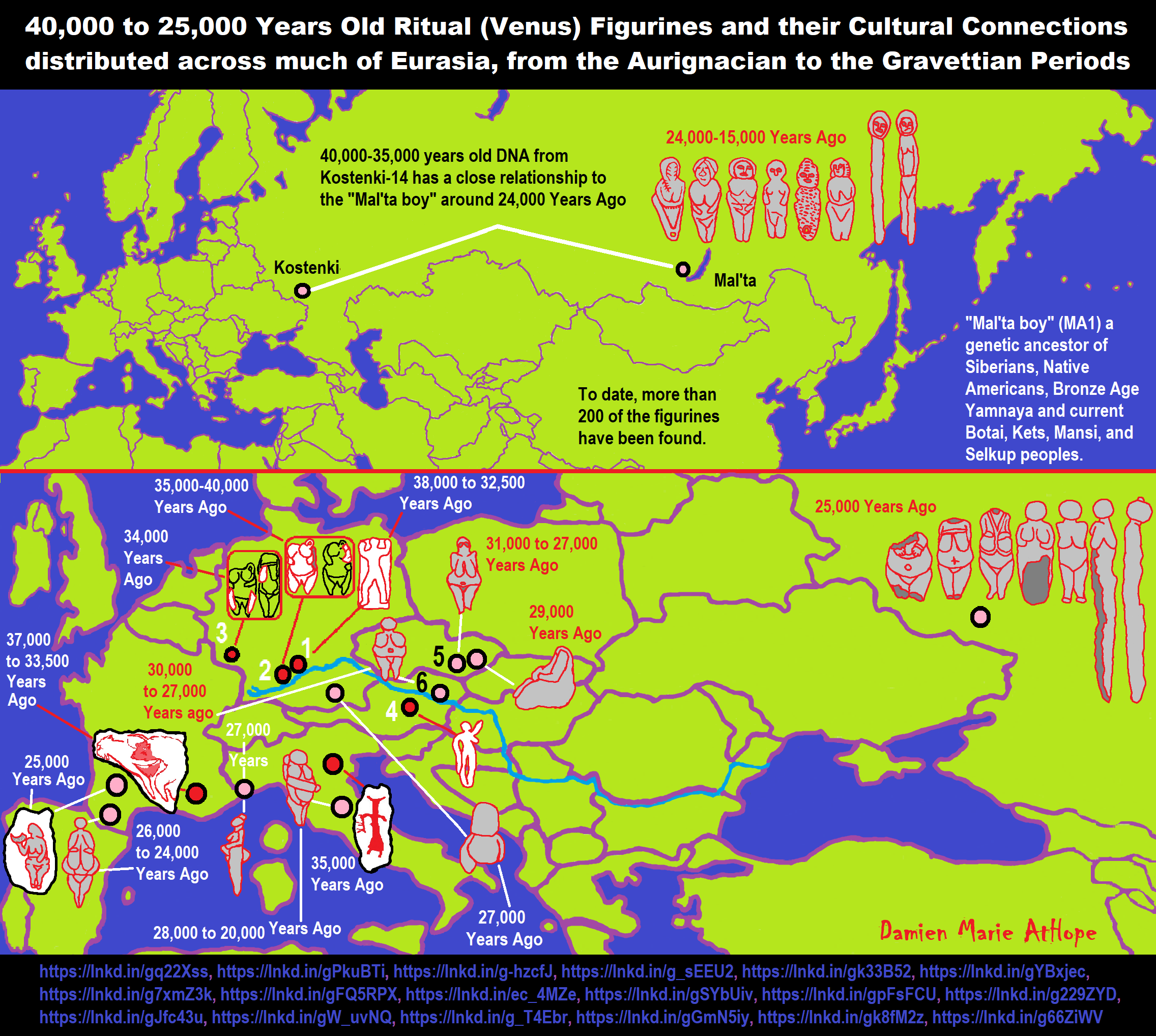
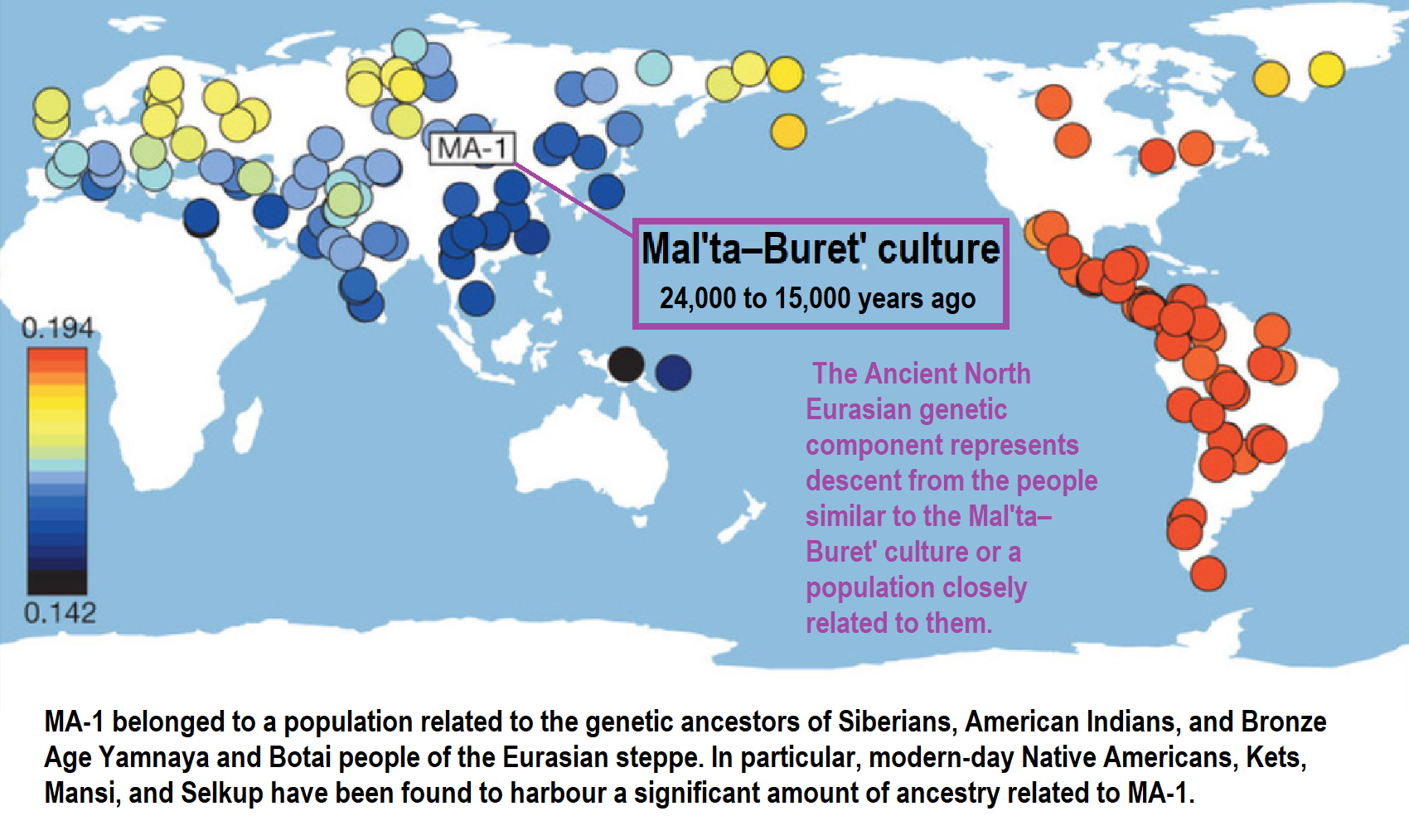
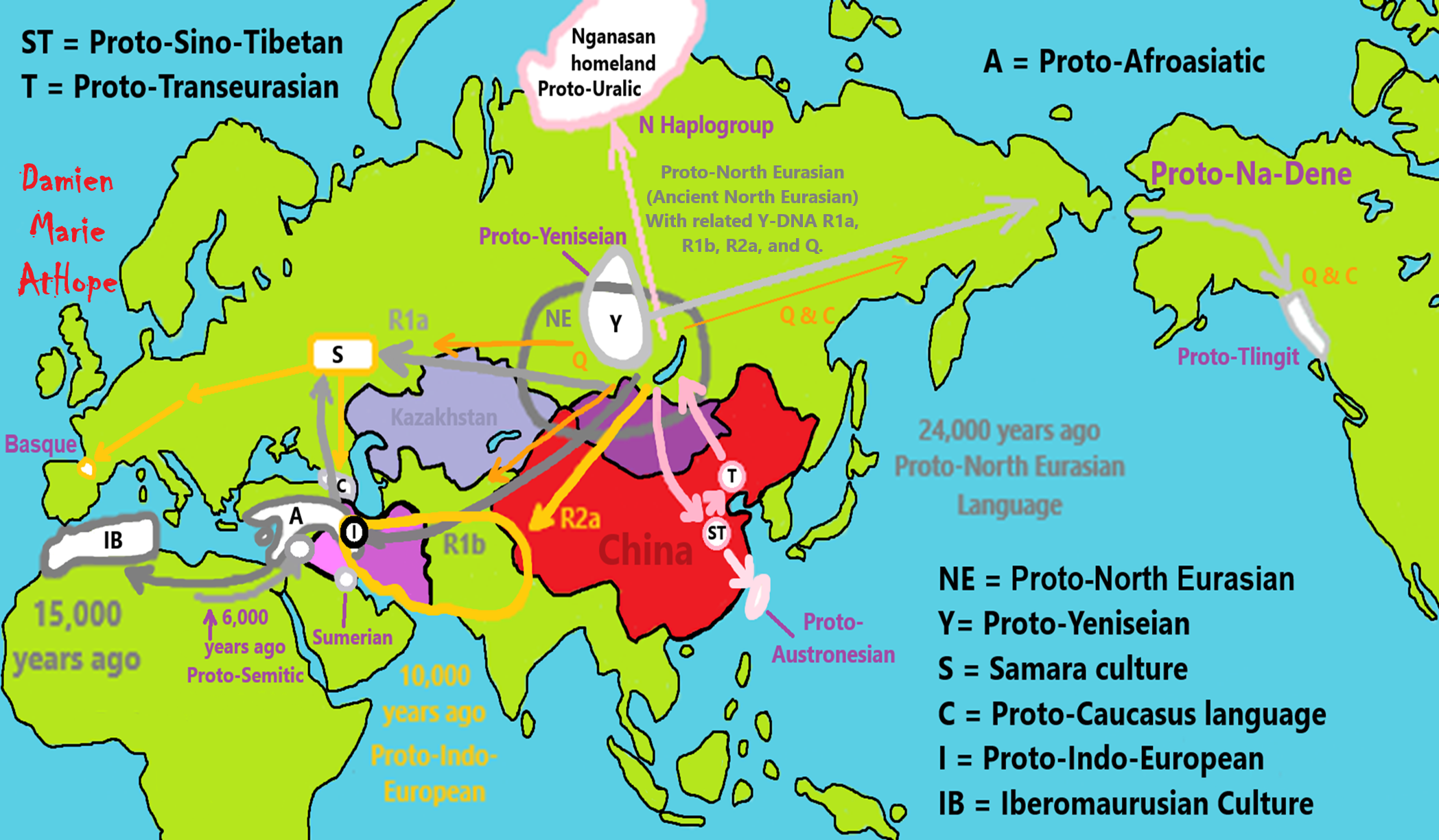
NE = Proto-North Eurasian/Ancient North Eurasian/Mal’ta–Buret’ culture/Mal’ta Boy “MA-1” 24,000 years old burial
A = Proto-Afroasiatic/Afroasiatic
S = Samara culture
ST = Proto-Sino-Tibetan/Sino-Tibetan
T = Proto-Transeurasian/Altaic
C = Proto-Northwest Caucasus language/Northwest Caucasian/Languages of the Caucasus
I = Proto-Indo-European/Indo-European
IB = Iberomaurusian Culture/Capsian culture
Natufian culture (15,000–11,500 years ago, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, the Sinai Peninsula, and the Negev desert)
Nganasan people/Nganasan language
Na-Dene languages/Dené–Yeniseian, Dené–Caucasian
Proto-Semitic/Semitic languages
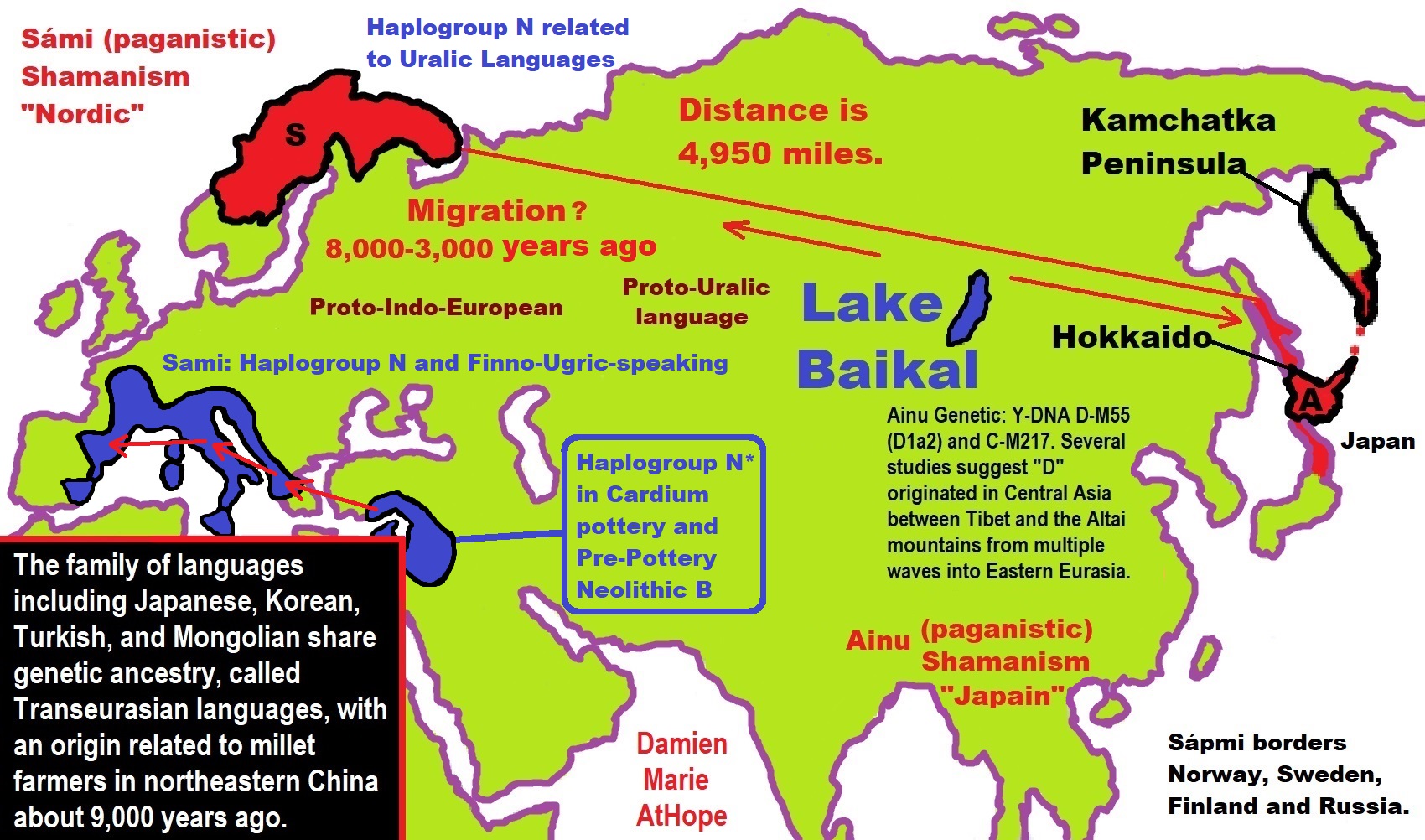
24,000 years ago, Proto-North Eurasian Language (Ancient North Eurasian) migrations?
My thoughts:
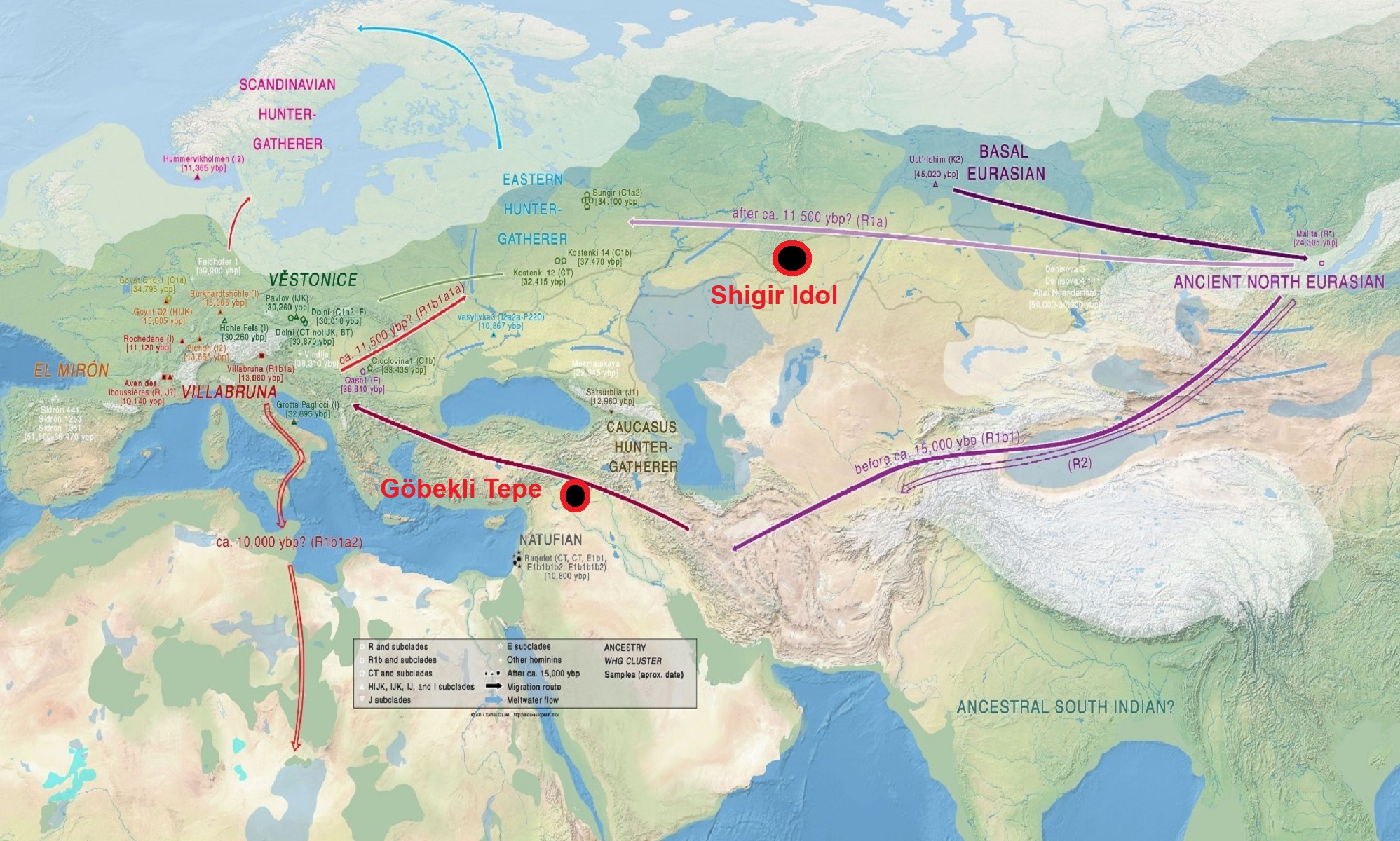
Proto-North Eurasian Language (Ancient North Eurasian) With related Y-DNA R1a, R1b, R2a, and Q Haplogroups.
R1b 22,0000-15,000 years ago in the Middle east creates Proto-Afroasiatic languages moving into Africa around 15,000-10,000 years ago connecting with the Iberomaurusian Culture/Taforalt near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
R2a 10,000 years ago in Iran brings/creates Proto-Indo-European language and also a possibility is R1a in Russia around 9,000 years ago may have had a version of Proto-Indo-European language.
Around 14,000-10,000 years ago??? Proto-North Eurasian Language goes to the Yellow River basin (eventually relating with the Yangshao culture) in China creates Proto-Sino-Tibetan language.
Proto-Sino-Tibetan language then moves to the West Liao River valley (eventually relating with the Hongshan culture) in China creating Proto-Transeurasian (Altaic) language around 9,000 years ago.
N Haplogroups 9,000 years ago with Proto-Transeurasian language possibly moves north to Lake Baikal. Then after living with Proto-North Eurasian Language 24,000-9,000 years ago?/Pre-Proto-Yeniseian language 9,000-7,000 years ago Q Haplogroups (eventually relating with the Ket language and the Ket people) until around 5,500 years ago, then N Haplogroups move north to the Taymyr Peninsula in North Siberia (Nganasan homeland) brings/creates the Proto-Uralic language.
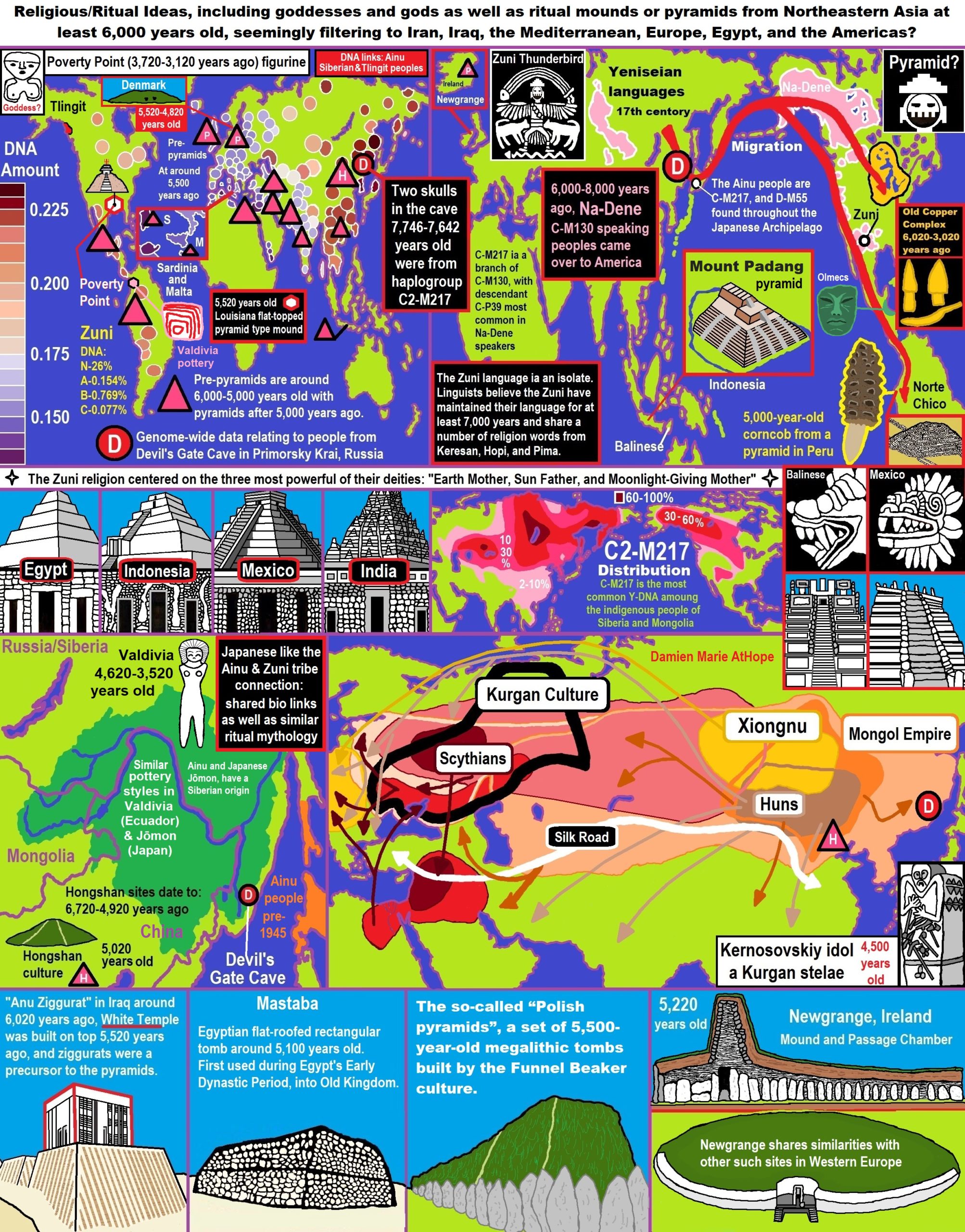
Q Haplogroups with Proto-Yeniseian language /Proto-Na-Dene language likely emerge 8,000/7,000 years ago or so and migrates to the Middle East (either following R2a to Iraq or R1a to Russia (Samara culture) then south to Iraq creates the Sumerian language. It may have also created the Proto-Caucasian languages along the way. And Q Haplogroups with Proto-Yeniseian language to a migration to North America that relates to Na-Dené (and maybe including Haida) languages, of which the first branch was Proto-Tlingit language 5,000 years ago, in the Pacific Northwest.
Sino-Tibetan language then moves more east in China to the Hemudu culture pre-Austronesian culture, next moved to Taiwan creating the Proto-Austronesian language around 6,000-5,500 years ago.
R1b comes to Russia from the Middle East around 7,500 years ago, bringing a version of Proto-Indo-European languages to the (Samara culture), then Q Y-DNA with Proto-Yeniseian language moves south from the (Samara culture) and may have been the language that created the Proto-Caucasian language. And R1b from the (Samara culture) becomes the 4,200 years or so R1b associated with the Basques and Basque language it was taken with R1b, but language similarities with the Proto-Caucasian language implies language ties to Proto-Yeniseian language.

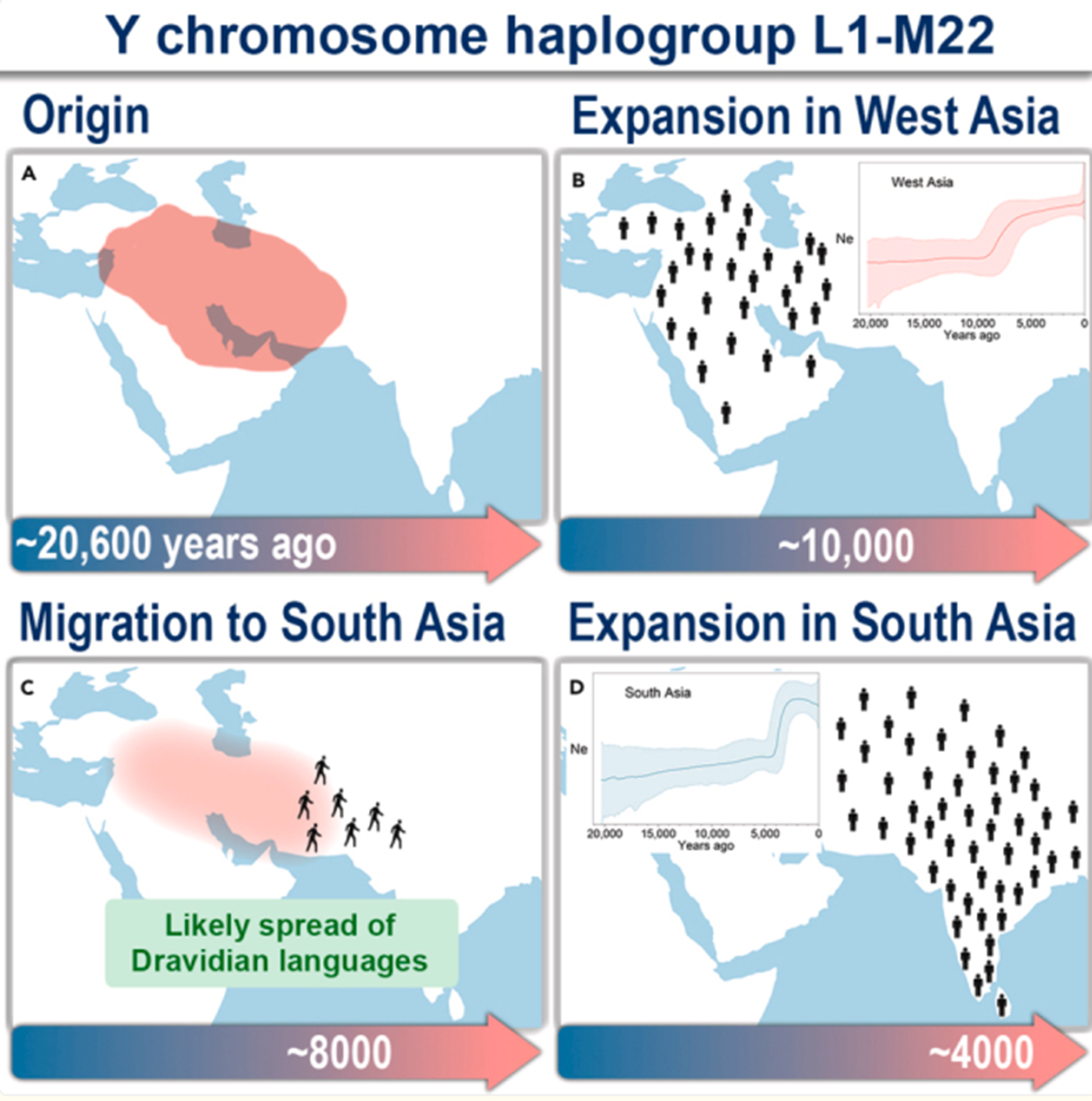
Human Y chromosome haplogroup L1-M22 traces Neolithic expansion in West Asia and supports the Elamite and Dravidian connection
“West and South Asian populations profoundly influenced Eurasian genetic and cultural diversity. We investigate the genetic history of the Y chromosome haplogroup L1-M22, which, while prevalent in these regions, lacks in-depth study. Robust Bayesian analyses of 165 high-coverage Y chromosomes favor a West Asian origin for L1-M22 ∼20,600 years ago. Moreover, this haplogroup parallels the genome-wide genetic ancestry of hunter-gatherers from the Iranian Plateau and the Caucasus. We characterized two L1-M22 harboring population groups during the Early Holocene. One expanded with the West Asian Neolithic transition. The other moved to South Asia ∼8,000-6,000 years ago but showed no expansion. This group likely participated in the spread of Dravidian languages. These South Asian L1-M22 lineages expanded ∼4,000-3,000 years ago, coinciding with the Steppe ancestry introduction. Our findings advance the current understanding of Eurasian historical dynamics, emphasizing L1-M22’s West Asian origin, associated population movements, and possible linguistic impacts.” ref
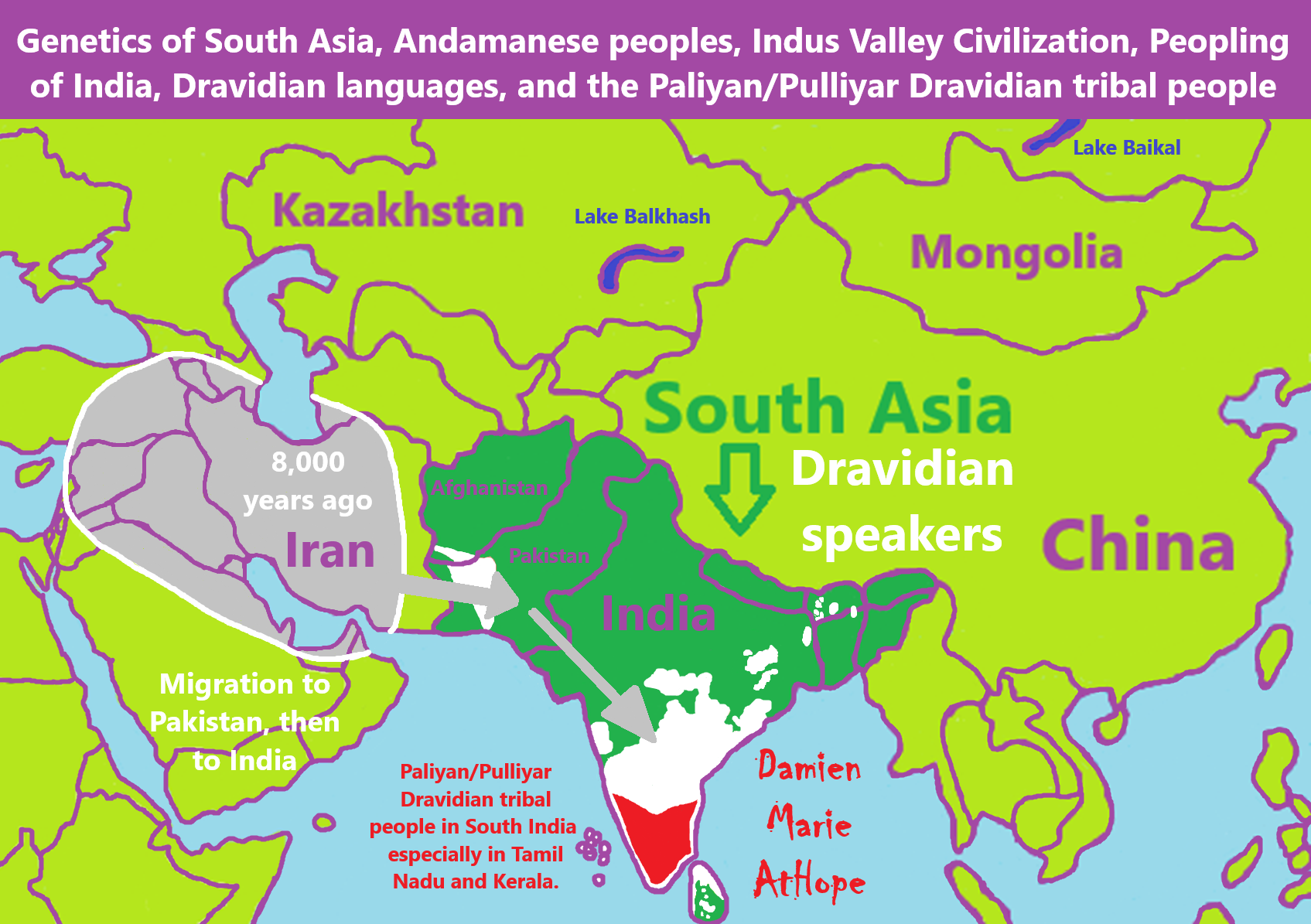
After looking at the info, I think Afroasiatic is likely the related origin of Dravidian languages, so an Afro-Dravidian Hypothesis. That still fits with my main Proto-North Eurasian Hypothesis, which I think links Afroasiatic. I think it was the likely language in Iran hunter-gatherer/proto-farmers R1b, L, and J, possibly even R1a, and thus, to me, would likely speak Afroasiatic or some version of it as they share a lot of cultural aspects with Turkey and the wider Fertal Cresent that spoke Afroasiatic. It is their cultural ideas and haplogroup L1-M22 that relate to Mehrgarh (7000 BCE to 2600 BCE) and Iran.
Here is a link, not mine, addressing it, but this is not how I came to think about this possibility of an Afro-Dravidian Hypothesis: Afroasiatic Origins and the Afro-Dravidian Hypothesis:
“The Afro-Dravidian hypothesis argues that the Dravidian language is a derivative of an African language from the Niger-Congo family of languages, and that much of the cultural and technological packet associated with Dravidian culture has African origins. Frenchman Bernard Sargent is one of its principle advocates. I’m not entirely convinced of this hypotheis, but there is enough data to back it up to warrant giving the idea serious consideration, so I don’t dismiss it out of hand either, as many do.” ref
“The linguistic evidence from within the Dravidian languages points to an origin of the Dravidian language of India around the time of the South Asian Neolithic ca. 2500 BCE. A few linguists have noted similarities between some Niger-Congo languages (particularly those on the Afro-Asiatic/Niger-Congo boundary area) and the proto-Dravidian language.
The crops used in early Dravidian agriculture were domesticated in and had their origins the African Sahel. There are no meaningful African mtDNA traces in Dravidian South Asia that can’t be attributed to events in the historic era, however, and the strongest outside Y-DNA signal, which coincides quite well with the locations of the proto-Dravidan society are rich in Y-DNA haplogroup T.” ref
“Given the fact that ancient peoples rich in Y-DNA haplogroup T were sailing the Red Sea and Indian Ocean from the Horn of Africa at the time, it makes sense that a male dominated group of people from the Horn of Africa might arrived on the east coast of India and bring new crops and technologies around 2500 BCE. Recent genetic profiles of tribal populations in India also support the inferrence that some of these populations may have genetic origins outside India in a time frame similar to that of the arrival of Indo-European and Austroasiatic food production and archeological cultures to India, rather than with the hunter-gatherers of India’s deep indigeneous past. So, the fact that some of the high frequency Y-DNA haplogroup T populations in Indian are tribal populations doesn’t necessarily contradict an Afro-Dravidian hypothesis.” ref
“The crops, technologies and potential linguistic links seem like a better fit to a Sahel agriculture, Niger-Congo language speaking people, however, than to a society that one might expect to be a Cushitic language speaking people then and there in what might have been the Kingdom of Punt or the Kingdom of Cush, which Y-DNA haplogroup T is currently common, and haplogroup T arguably looks like it has Egyptian or Mesopotamian origins, not Sahel African origins. Why would people with overwhelming Egyptian/Mesopotamian patrilines speak a Niger-Congo language or be familiar with Sahel agriculture? Was Cushitic limited to areas further north at the time, and were Niger-Congo languages (driven by the expansion of Sahel agriculture) a layer present before Afro-Asiatic languages were in the Horn of Africa? Did ethnic Egyptians precede the Cushitic language in the sea trade of the Horn of Africa?” ref
“The “substrate” genetics of East Africa after one removes markers that look like Eurasian back migrations and also removes markers strongly associated with one or another Afro-Asiatic linguistic family, in uniparental and autosomal genetics, are distinctly East African and do not suggest prior genetic unity with West African populations prior to a very remote date (ca. 30,000+ years). Another way to think about that fact is that East Africa has experienced at least two wave of Eurasian back migration. Sometime in the early Holocene (a period that bridges the Epipaleolithic and the Neolithic eras) associated with mtDNA haplogroups like M1 and U6. The other with the arrival of the Ethiosemitic languages. One plausible way to understand the spread of the Afro-Asiatic languages is to guess that it occured at the time of the early Holocene event.” ref
“But, East Africa has a distinct genetic identity that predates either of these events, and this identity is distinct from West Africa. West African sourced African genetics don’t appear in East Africa until around the time of Bantu expansion into East Africa, contradicting the plausible thought that West Africans could have had notable demic influences on East Africa starting when the West Africans developed Sahel agriculture. (As Jared Diamond explains in “Guns, Germs and Steel”, neither Sahel crops nor Fertile Crescent crops do well in the other’s climate due to their differing seasonal patterns, although Sahel crops can do well in the monsoon climate of Southern India, which has a seasonal pattern similar to the African Sahel.)” ref
“One possibility is that Horn of Africa people who could have brought the cultural package of Sahel agriculture to India may have themselves been recent recipients of that cultural package and experienced language shift in an early wave of Bantu, or pre-Bantu, expansion from West Africa, that was limited to a cultural/political elite and that the Niger-Congo language may have experienced similar linguistic trends to other languages on the Niger-Congo/Afro-Asiatic linguistic border like Swahili and some of the Niger-Congo languages spoken in the general vicinity of Senegal.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
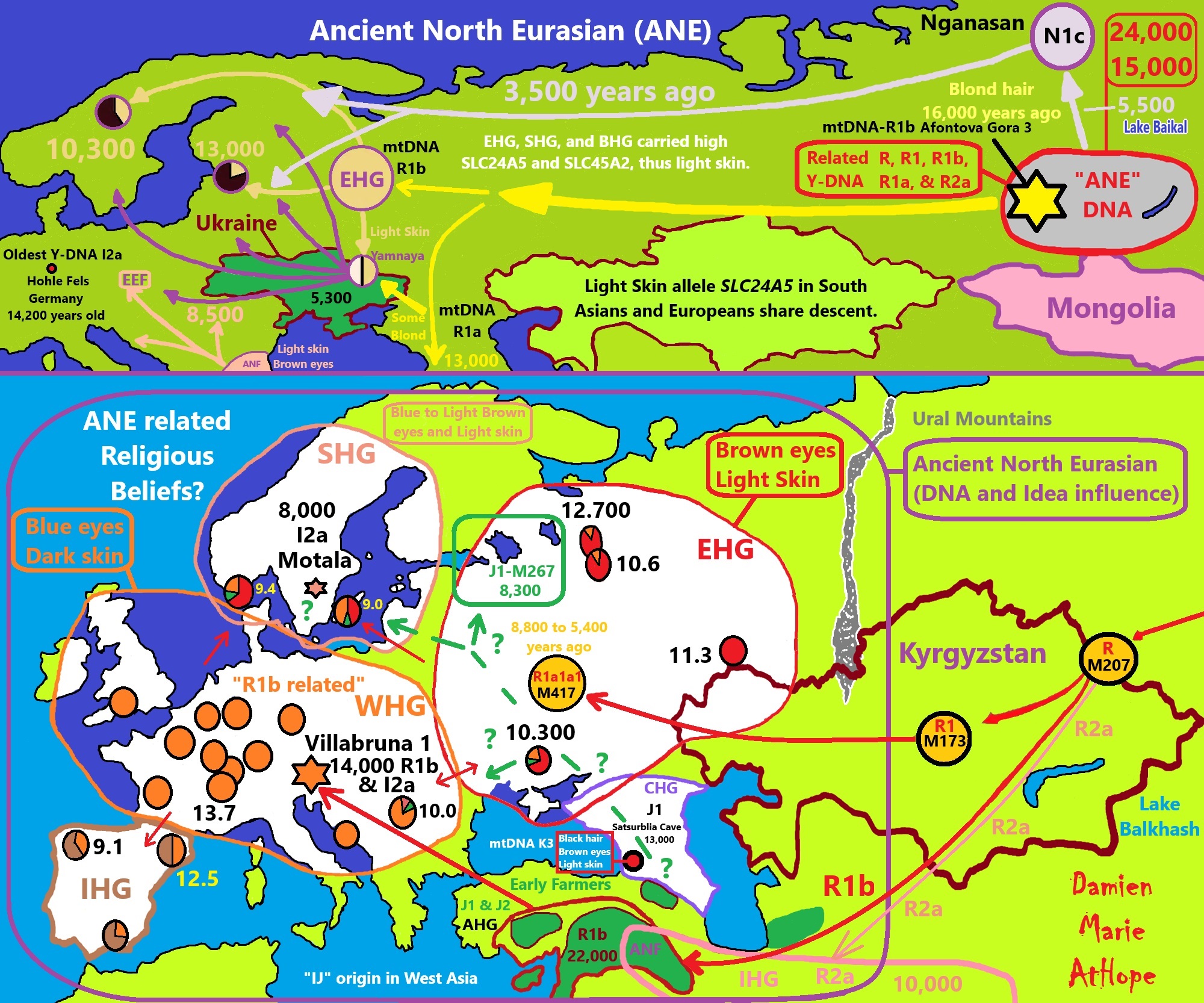
Genetic Relations to Ancient North Eurasians (ANE):
Eastern hunter-gatherer (EHG)
Caucasus hunter-gatherer (CHG)
Zagros/Iranian Hunter-Gatherer (IHG)
Iranian Neolithic Farmers (INF)
Anatolian hunter-gatherer (AHG)
Anatolian Neolithic Farmers (ANF)
Early European Farmers (EEF)
Yamnaya/Steppe Herders (WSH)
Villabruna 1 (burial)/Ripari Villabruna rock shelter in northern Italy (14,000 years old)
Satsurblia Cave (burial) in the Country of Georgia (13,000 years old)
Motala (burial) (8,000 years old)
Proto-Afroasiatic language
“Proto-Afroasiatic (PAA), also known as Proto-Hamito-Semitic, Proto-Semito-Hamitic, and Proto-Afrasian, is the reconstructed proto-language from which all modern Afroasiatic languages are descended. Though estimations vary widely, it is believed by scholars to have been spoken as a single language around 12,000 to 18,000 years ago (12 to 18 kya), that is, between 16,000 and 10,000 BC. Although no consensus exists as to the location of the Afroasiatic homeland, the putative homeland of Proto-Afroasiatic speakers, the majority of scholars agree that it was located within a region of Northeast Africa.” ref
“The reconstruction of Proto-Afroasiatic is problematic and has not progressed to the degree found in Indo-European linguistics. The immense amount of time over which the branches have been separated, coupled with the wide gap between the attestations of the original branches (3rd millennium BCE for Egyptian and Semitic, 19th and 20th centuries for many Chadic, Cushitic, and Omotic languages) mean that determining sound correspondences has not yet been possible. In addition to more traditional proposed consonant correspondences, there is also a divergent proposal that has become popular among Egyptologists; there is no agreement about PAA’s vowels, the existence of tone, or its syllable structure. At the same time, scholars disagree to whether and to what extent the classical Semitic languages are a conservative, faithful representation of PAA morphology. This is particularly important for the question of whether the lexical roots in the language were originally mostly biradical or triradical, that is, whether they originally had two or three consonants. It also plays into the question of the degree to which Proto-Afroasiatic had root-and-pattern morphology, as most fully displayed in the Semitic, Egyptian, and Cushitic branches.” ref
“There are nonetheless, some items of agreement and reconstructed vocabulary. Most scholars agree that Proto-Afroasiatic nouns had grammatical gender, at least two and possibly three grammatical numbers (singular, plural, and possibly dual), as well as a case system with at least two cases. Proto-Afroasiatic may have had marked nominative or ergative-absolutive alignment. A deverbal derivational prefix *mV- is also widely reconstructed. While there is disagreement about the forms of the PAA personal pronouns, there is agreement that there were independent and “bound” (unstressed, clitic) forms. There is also agreement that a widespread demonstrative pattern of n = masculine and plural, t= feminine goes back to PAA, as well as about the existence of an interrogative pronoun *mV, which may not have distinguished animacy. There is some agreement that the PAA verb had two or possibly three basic forms, though there is disagreement about what those forms were and what tenses, aspects, or moods they expressed. There is also widespread agreement that there were possibly two sets of conjugational affixes (prefixes and suffixes) used for different purposes. Additionally, the importance of verbal gemination and reduplication and the existence of three derivational affixes, especially of a causative -*s-, are commonly reconstructed. A numeral system cannot be reconstructed, although numerous PAA numerals and cognate sets from 1 to 9 have been proposed.” ref
“There is no consensus as to when Proto-Afroasiatic was spoken. The absolute latest date for when Proto-Afroasiatic could have been extant is c. 4000 BCE, after which Egyptian and the Semitic languages are firmly attested. However, in all likelihood these languages began to diverge well before this hard boundary. The estimations offered by scholars as to when Proto-Afroasiatic was spoken vary widely, ranging from 18,000 BCE to 8,000 BCE. An estimate at the youngest end of this range still makes Afroasiatic the oldest proven language family. Contrasting proposals of an early emergence, Tom Güldemann has argued that less time may have been required for the divergence than is usually assumed, as it is possible for a language to rapidly restructure due to areal contact, with the evolution of Chadic (and likely also Omotic) serving as pertinent examples.” ref
“At present, there is no commonly accepted reconstruction of Afroasiatic morphology, grammar, syntax, or phonology. Because of the great amount of time since Afroasiatic split into branches, there are limits to what scholars can reconstruct. Cognates tend to disappear from related languages over time. There are currently not many widely accepted Afroasiatic cognates, and it is difficult to derive sound correspondence rules from a small number of examples. The most convincing cognates in Afroasiatic often have the same or very similar consonants but very different vowels, a fact which has not yet been explained. Additionally, it is not always clear which words are cognates, as some proposed cognates may be chance resemblances. Moreover, at least some cognates are likely to have been altered irregularly due to analogical change, making them harder to recognize. As words change meaning over time, the question of which words might have originally meant the same thing is often difficult to answer. As a result, Robert Ratcliffe suggests that Proto-Afroasiatic may never be reconstructed in the same way that Proto-Indo-European has been.” ref
“The current state of reconstruction is also hindered by the fact that the Egyptian and Semitic branches of Afroasiatic are attested as early as 3000 BCE, while the languages of the Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, and Omotic branches are only attested much later, sometimes in the 20th century. The long history of scholarship of the Semitic languages compared to other branches is another obstacle in reconstructing Proto-Afroasiatic; typical features of Semitic have often been projected back to the proto-language, despite their cross-linguistic rarity and lack of correspondences in other branches. Like cognates, shared morphological features tend to disappear over time, as can be demonstrated within Afroasiatic by comparing Old Egyptian (2600–2000 BCE) with Coptic (after 200 CE). Yet it is also possible for forms closer to PAA to be preserved in languages recorded later, while languages recorded earlier may have forms that diverge more from PAA. In order to provide a more accurate reconstruction of Afroasiatic, it will be necessary to first reconstruct the proto-forms of the individual branches, a task which has proven difficult. As of 2023, there is only the beginning of a consensus on the reconstruction of Proto-Semitic, and no widely accepted reconstruction of any of the other branches’ proto-forms. Current attempts at reconstructing Afroasiatic often rely on comparing individual words or features in the daughter languages, which leads to results that are not convincing to many scholars.” ref
“The Afroasiatic languages (or Afro-Asiatic, sometimes Afrasian), also known as Hamito-Semitic or Semito-Hamitic, are a language family (or “phylum”) of about 400 languages spoken predominantly in West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and parts of the Sahara and Sahel. Over 500 million people are native speakers of an Afroasiatic language, constituting the fourth-largest language family after Indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, and Niger–Congo. Most linguists divide the family into six branches: Berber, Chadic, Cushitic, Egyptian, Semitic, and Omotic. The vast majority of Afroasiatic languages are considered indigenous to the African continent, including all those not belonging to the Semitic branch.” ref
“Arabic, if counted as a single language, is by far the most widely spoken within the family, with around 300 million native speakers concentrated primarily in the Middle East and North Africa. Other major Afroasiatic languages include the Chadic Hausa language with over 34 million native speakers, the Semitic Amharic language with 25 million, and the Cushitic Somali language with 15 million. Other Afroasiatic languages with millions of native speakers include the Semitic Tigrinya and Modern Hebrew, the Cushitic Sidaama, and the Omotic Wolaitta language, though most languages within the family are much smaller in size. There are many well-attested Afroasiatic languages from antiquity that have since died or gone extinct, including Egyptian and the Semitic languages Akkadian, Biblical Hebrew, Phoenician, Amorite, and Ugaritic. There is no consensus among historical linguists as to precisely where or when the common ancestor of all Afroasiatic languages, known as Proto-Afroasiatic, was originally spoken. However, most agree that the Afroasiatic homeland was located somewhere in northeastern Africa, with specific proposals including the Horn of Africa, Egypt, and the eastern Sahara. A significant minority of scholars argues for an origin in the Levant. The reconstructed timelines of when Proto-Afroasiatic was spoken vary extensively, with dates ranging from 18,000 to 8,000 BCE. Even the latest plausible dating makes Afroasiatic the oldest language family accepted by contemporary linguists.” ref
“Comparative study of Afroasiatic is hindered by the massive disparities in textual attestation between its branches: while the Semitic and Egyptian branches are attested in writing as early as the fourth millennium BC, Berber, Cushitic, and Omotic languages were often not recorded until the 19th or 20th centuries. While systematic sound laws have not yet been established to explain the relationships between the various branches of Afroasiatic, the languages share a number of common features. One of the most important for establishing membership in the branch is a common set of pronouns. Other widely shared features include a prefix m- which creates nouns from verbs, evidence for alternations between the vowel “a” and a high vowel in the forms of the verb, similar methods of marking gender and plurality, and some details of phonology such as the presence of pharyngeal fricatives. Other features found in multiple branches include a specialized verb conjugation using suffixes (Egyptian, Semitic, Berber), a specialized verb conjugation using prefixes (Semitic, Berber, Cushitic), verbal prefixes deriving middle (t-), causative (s-), and passive (m-) verb forms (Semitic, Berber, Egyptian, Cushitic), and a suffix used to derive adjectives (Egyptian, Semitic).” ref
“The Proto-Afroasiatic homeland is the hypothetical place where speakers of the Proto-Afroasiatic language lived in a single linguistic community, or complex of communities, before this original language dispersed geographically and divided into separate distinct languages. Afroasiatic languages are today mostly distributed in parts of Africa, and Western Asia. No consensus exists as to where proto-Afroasiatic originated. Scholars have proposed locations for the Afroasiatic homeland across Africa and western Asia. A complicating factor is the lack of agreement on the subgroupings of Afroasiatic (see Further subdivisions) – this makes associating archaeological evidence with the spread of Afroasiatic particularly difficult.” ref
“Nevertheless, there is a long-accepted link between the speakers of Proto-Southern Cushitic languages and the East African Savanna Pastoral Neolithic (3000 BCE), and archaeological evidence associates the Proto-Cushitic speakers with economic transformations in the Sahara dating c. 8,500 years ago, as well as the speakers of the Proto-Zenati variety of the Berber languages with an expansion across the Maghreb in the 5th century CE. More hypothetical links associate the proto-Afroasiatic-speakers with the Kebaran and the Mushabian culture, while others argue for a possible affiliation between proto-Afroasiatic and the Natufian culture.” ref
“The linguistic view on the location of the homeland of Afroasiatic languages is largely divided into proponents for a homeland within Africa, and proponents for a homeland in western Asia. To date, a homeland within Africa is favored by a majority of scholars, although a significant minority of scholars support a homeland in western Asia. Pagani and Crevecoeur (2019) argue that, given the still open debate on the origin of Afroasiatic, the consensus will probably settle on an intermediate “across-the-Sinai” solution. They also note that the very early interactions between African and Eurasian cultures, point “to a geographical shrinking of what can currently be defined as ‘strictly African’ in a long term perspective.” ref
Western Asian homeland theory
“Levant agriculturalists”
“Supporters of a western Asian origin for Afroasiatic are particularly common among those with a background in Semitic or Egyptological studies, and amongst archaeological proponents of the “farming/language dispersal hypothesis” according to which major language groups dispersed with early farming technology in the Neolithic. The leading linguistic proponent of this idea in recent times is Alexander Militarev, who argues that Proto-Afroasiatic was spoken by early agriculturalists in the Levant and subsequently spread to Africa. Militarev associates the speakers of Proto-Afroasiatic with the Levantine Post-Natufian Culture, arguing that the reconstructed lexicon of flora and fauna, as well as farming and pastoralist vocabulary indicates that Proto-AA must have been spoken in this area. Scholar Jared Diamond and archaeologist Peter Bellwood have taken up Militarev’s arguments as part of their general argument that the spread of linguistic macrofamilies (such as Afroasiatic, Bantu, and Austroasiatic) can be associated with the development of agriculture; they argue that there is clear archaeological support for farming spreading from the Levant into Africa via the Nile valley.” ref
“Militarev, who linked proto-Afroasiatic to the Levantine Natufian culture, that preceded the spread of farming technology, believes the language family to be about 10,000 years old. He wrote (Militarev 2002, p. 135) that the “Proto-Afrasian language, on the verge of a split into daughter languages”, meaning, in his scenario, into “Cushitic, Omotic, Egyptian, Semitic and Chadic–Berber“, “should be roughly dated to the ninth millennium BC”. Support for the migration of agricultural populations, according to linguists, are the word for dog (an Asian domesticate) reconstructed to Proto-Afroasiatic as well as words for bow and arrow, which, according to some archaeologists, spread rapidly across North Africa once they were introduced to North Africa from the Near East, viz. Ounan points. Lexicon linked to a pastoralist society (cattle-breeding) reconstructed for proto-Afroasiatic also supports a western Asian homeland, possibly indicating an earlier pastoralist migration.” ref
Autosomal DNA
“Scholars, such as Hodgson et al., present archaeogenetic evidence in favor for a place of dispersion within Africa, but argue that the speakers of Proto-Afroasiatic can ultimately be linked to a Paleolithic and pre-agricultural migration wave into Africa from Western Asia, and that the Semitic-branch represents a later back-migration to the Levant. According to an autosomal DNA research in 2014 on ancient and modern populations, the Afroasiatic languages likely spread across Africa and the Near East by an ancestral population(s) carrying a newly identified “non-African” (Western Eurasian) genetic component, which the researchers dub the “Ethio-Somali” component. This genetic component is most closely related to the “Maghrebi” component and is believed to have diverged from other “non-African” (Western Eurasian) ancestries at least 23,000 years ago. The “Ethio-Somali” genetic component is prevalent among modern Afroasiatic-speaking populations, and found at its highest levels among Cushitic peoples in the Horn of Africa.” ref
“On this basis, the researchers suggest that the original Ethio-Somali carrying population(s) probably arrived in the pre-agricultural period (12,000–23,000 years ago) from the Near East, having crossed over into northeast Africa via the Sinai Peninsula and then split into two, with one branch continuing west across North Africa and the other heading south into the Horn of Africa. They suggest that a descendant population migrated back to the Levant prior to 4000 BCE and developed the Semitic branch of Afroasiatic. Later migration from Arabia into the HOA beginning around 3 ka would explain the origin of the Ethio-Semitic languages at this time. A similar view has already been proposed earlier, suggesting that the ancestors of Afroasiatic speakers could have been a population originating in the Near East that migrated to Northeast Africa during the Late Palaeolithic with a subset later moving back to the Near East.” ref
“Subsequent archaeogenetic studies have corroborated the migrations of Western Eurasian ancestry during the Paleolithic into Africa, becoming the dominant component of Northern Africa since at least 15,000 BCE. The “Maghrebi” component, which gave rise to the Iberomaurusian culture, is described as autochthonous to Northern Africa, related to the Paleolithic Eurasian migration wave, and the characteristic ancestry components of modern Northern Africans along a West-to-East cline, with Northeastern Africans having an additionally higher frequency of a Neolithic Western Asian component associated with the Neolithic expansion. Genetic research on Afroasiatic-speaking populations revealed strong correlation between the distribution of Afroasiatic languages and the frequency of Northern African/Natufian/Arabian-like ancestry. In contrast, Omotic speakers display ancestry mostly distinct from other Afroasiatic-speakers, indicating language shift, or support for the exclusion of Omotic from the Afroasiatic group.” ref
“Genetic studies on a specimen of the Savanna Pastoral Neolithic excavated at the Luxmanda site in Tanzania, which has been associated with migrations of Cushitic-speaking peoples and the spread of pastoralism, found that the specimen carried a large proportion of ancestry related to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant (Natufian), similar to that borne by modern Afroasiatic-speaking populations inhabiting the Horn of Africa. It is suggested that a population related to the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant contributed significantly to historical Eastern African populations represented by the c. 5,000 year old Luxmanda specimen, while modern Cushitic-speaking populations have additional contributions from Dinka-related and “Neolithic Iranian-related” sources. This type of ancestry was later partially replaced by following migration events associated with the Bantu expansion, with Bantu-speaking Eastern Africans having only little ancestry associated with the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant.” ref
Y-chromosome evidence
“Keita (2008) examined a published Y-chromosome dataset on Afro-Asiatic populations and found that a key lineage E-M35/E-M78, sub-clade of haplogroup E, was shared between the populations in the locale of Egyptian and Libyan speakers and modern Cushitic speakers from the Horn. These lineages are present in Egyptians, Berbers, Cushitic speakers from the Horn of Africa, and Semitic speakers in the Near-East. He noted that variants are also found in the Aegean and Balkans, but the origin of the M35 subclade was in Egypt or Libya, and its clades were dominant in a core portion of Afro-Asiatic speaking populations which included Cushitic, Egyptian and Berber groups, in contrast, Semitic speakers showed a decline in frequency going west to east in the Levantine-Syria region. Keita identified high frequencies of M35 (>50%) among Omotic populations, but stated that this derived from a small, published sample of 12. Keita also wrote that the PN2 mutation was shared by M35 and M2 lineages and this paternal clade originated from East Africa.” ref
“He concluded that “the genetic data give population profiles that clearly indicate males of African origin, as opposed to being of Asian or European descent” but acknowledged that the biodiversity does not indicate any specific set of skin colors or facial features as populations were subject to microevolutionary pressures. Fregel summarized that the Y-chromosome diversity of North Africans was compatible with a demic expansion from the Middle East, because the age of common lineages in North Africa (E-M78 and J-304) were relatively recent. The North African pattern of Y-chromosome variation was mostly shaped during the Neolithic period. Ehret cited genetic evidence which had identified the Horn of Africa as a source of a genetic marker “M35/215” Y-chromosome lineage for a significant population component which moved north from that region into Egypt and the Levant. Ehret argued that this genetic distribution paralleled the spread of the Afrasian language family with the movement of people from the Horn of Africa into Egypt and added a new demic component to the existing population of Egypt 17,000 years ago.” ref
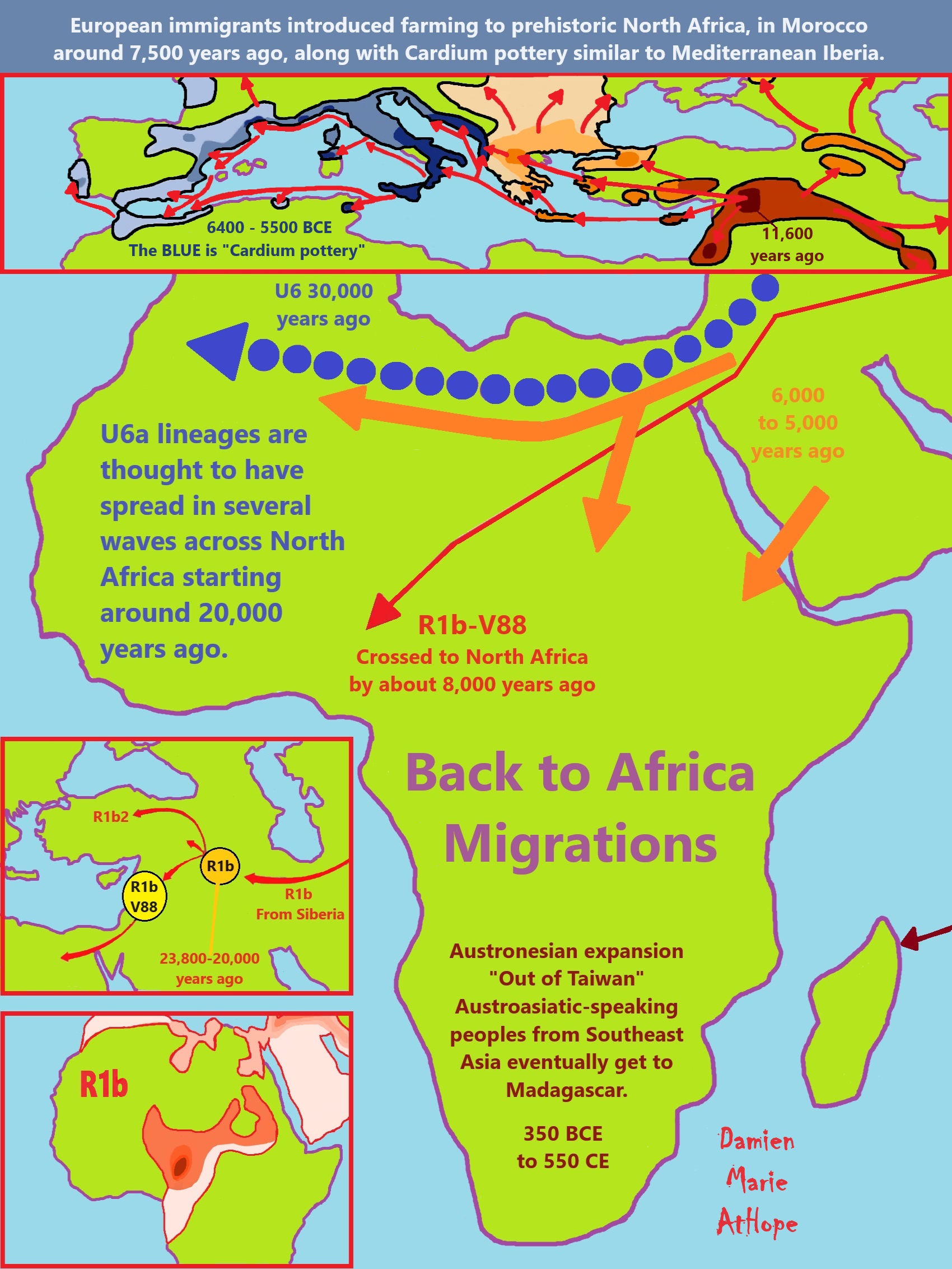
Human Y chromosome haplogroup R-V88: a paternal genetic record of early mid Holocene trans-Saharan connections and the spread of Chadic languages
“Abstract: Although human Y chromosomes belonging to haplogroup R1b are quite rare in Africa, being found mainly in Asia and Europe, a group of chromosomes within the paragroup R-P25* are found concentrated in the central-western part of the African continent, where they can be detected at frequencies as high as 95%. Phylogenetic evidence and coalescence time estimates suggest that R-P25* chromosomes (or their phylogenetic ancestor) may have been carried to Africa by an Asia-to-Africa back migration in prehistoric times. Here, we describe six new mutations that define the relationships among the African R-P25* Y chromosomes and between these African chromosomes and earlier reported R-P25 Eurasian sub-lineages. The incorporation of these new mutations into a phylogeny of the R1b haplogroup led to the identification of a new clade (R1b1a or R-V88) encompassing all the African R-P25* and about half of the few European/west Asian R-P25* chromosomes. A worldwide phylogeographic analysis of the R1b haplogroup provided strong support to the Asia-to-Africa back-migration hypothesis. The analysis of the distribution of the R-V88 haplogroup in >1800 males from 69 African populations revealed a striking genetic contiguity between the Chadic-speaking peoples from the central Sahel and several other Afroasiatic-speaking groups from North Africa. The R-V88 coalescence time was estimated at 9200–5600 kya, in the early mid Holocene. We suggest that R-V88 is a paternal genetic record of the proposed mid-Holocene migration of proto-Chadic Afroasiatic speakers through the Central Sahara into the Lake Chad Basin, and geomorphological evidence is consistent with this view.” ref
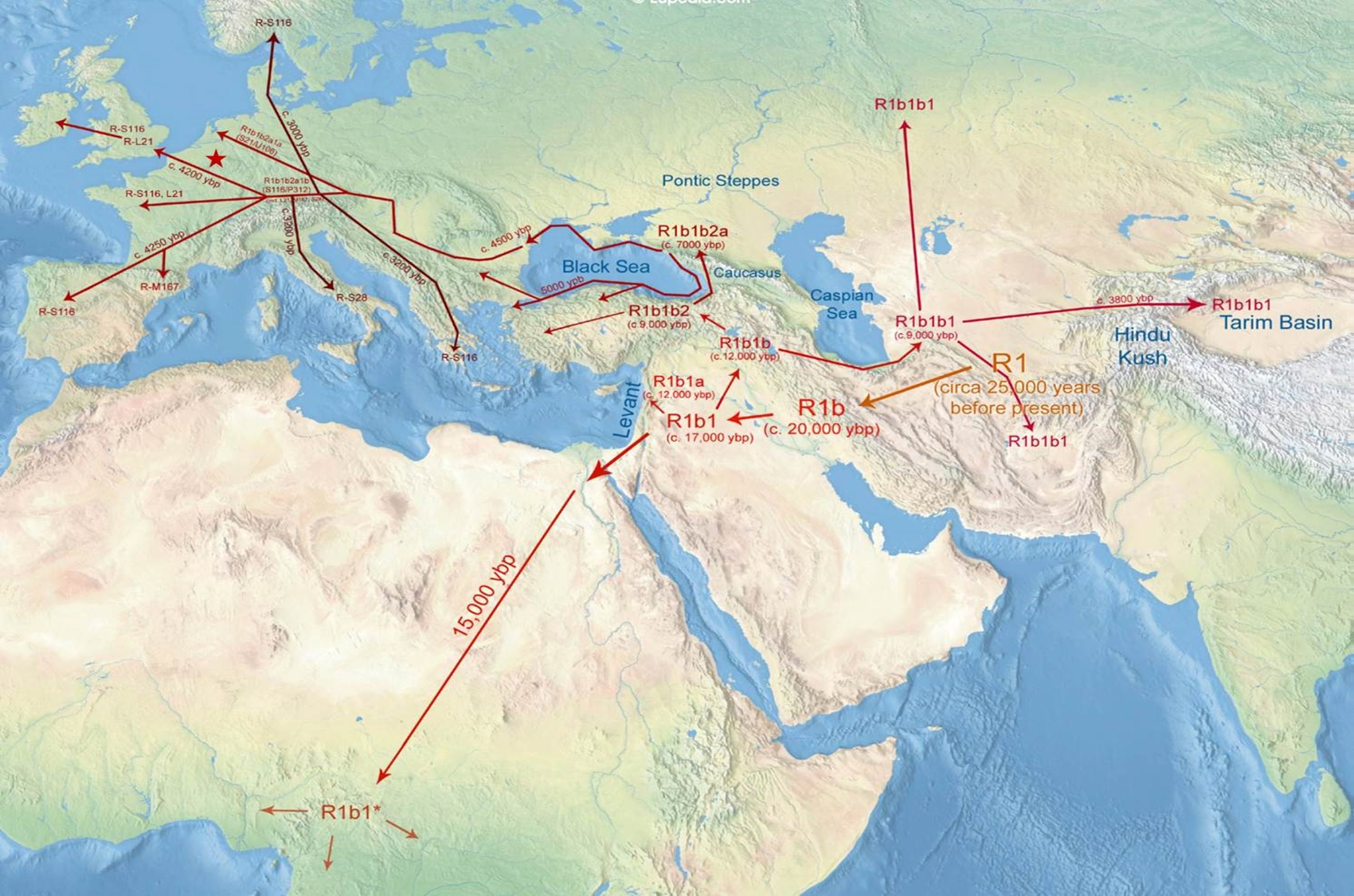
Haplogroup R1b
“The age of R1 was estimated by Tatiana Karafet et al. (2008) at between 12,500 and 25,700 years ago, and most probably occurred about 18,500 years ago. Since the earliest known example has been dated at circa 14,000 years ago, and belongs to R1b1 (R-L754), R1b must have arisen relatively soon after the emergence of R1.” ref
“Early human remains found to carry R1b include:
- Villabruna 1 (individual I9030), a Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG), found in an Epigravettian culture setting in the Cismon valley (modern Veneto, Italy), who lived circa 14000 years ago and belonged to R1b1a.
- Several males of the Iron Gates Mesolithic in the Balkans buried between 11200 and 8200 years ago carried R1b1a1a. These individuals were determined to be largely of WHG ancestry, with slight Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) admixture.
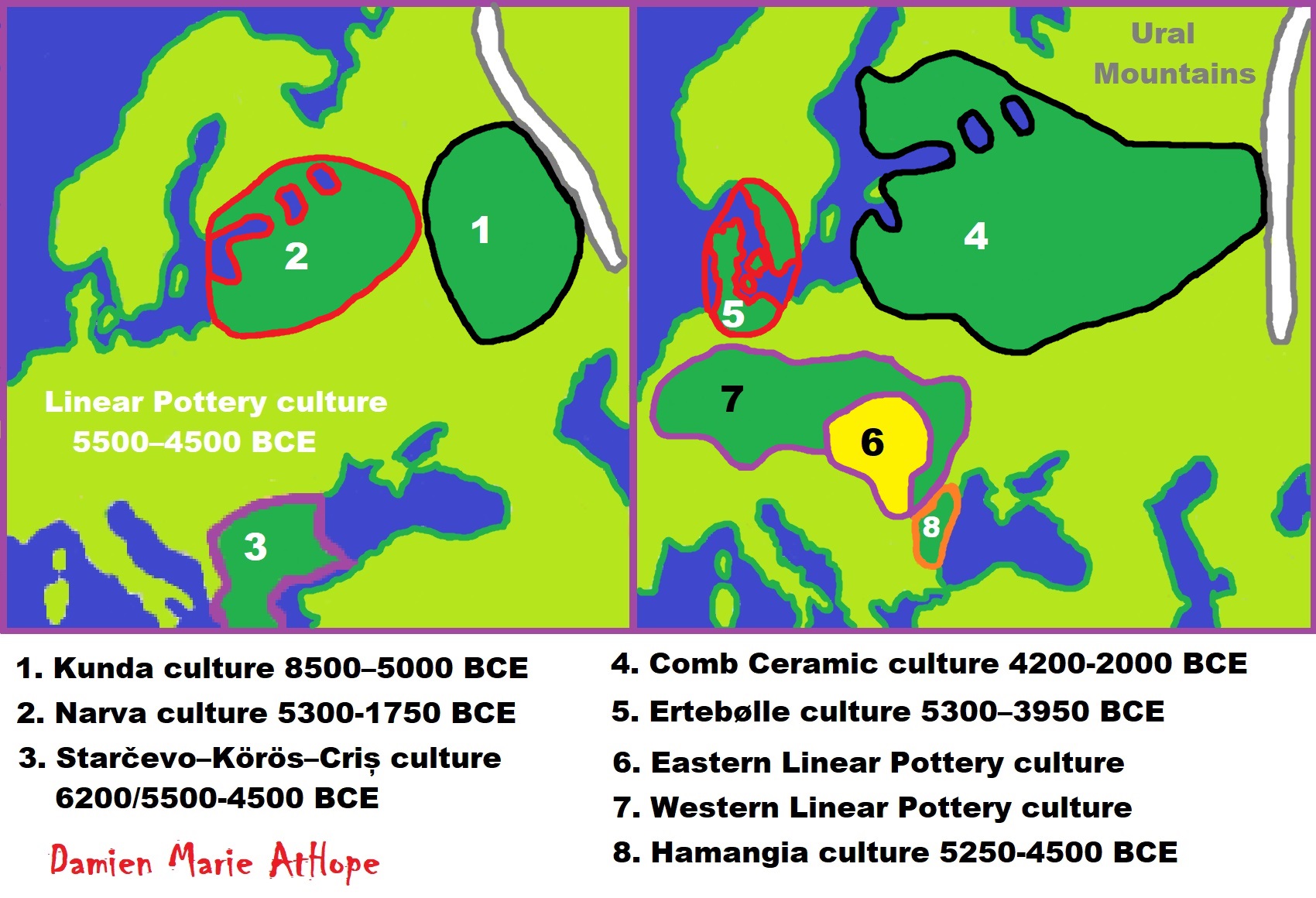
- Several males of the Mesolithic Kunda culture and Neolithic Narva culture buried in the Zvejnieki burial ground in modern-day Latvia c. 9500–6000 years ago carried R1b1b. These individuals were determined to be largely of WHG ancestry, with slight EHG admixture.
- Several Mesolithic and Neolithic males buried at Deriivka and Vasil’evka in modern-day Ukraine c. 9500-7000 years ago carried R1b1a. These individuals were largely of EHG ancestry, with significant WHG admixture.
- A WHG male buried at Ostrovul Corbuli, Romania c. 8700 years ago carried R1b1c.
- A male buried at Lepenski Vir, Serbia c. 8200-7900 years ago carried R1b1a.
- An EHG buried near Samara, Russia 7500 years ago carried R1b1a1a.
- An Eneolithic male buried at Khvalynsk, Russia c. 7200-6000 years ago carried R1b1a.
- A Neolithic male buried at Els Trocs, Spain c. 7178-7066 years ago, who may have belonged to the Epi-Cardial culture, was found to be a carrier of R1b1.
- A Late Chalcolithic male buried in Smyadovo, Bulgaria c. 6500 years ago carried R1b1a.
- An Early Copper Age male buried in Cannas di Sotto, Carbonia, Sardinia c. 6450 years ago carried R1b1b2.
- A male of the Baalberge group in Central Europe buried c. 5600 years ago carried R1b1a.
- A male of the Botai culture in Central Asia buried c. 5500 years ago carried R1b1a1 (R1b-M478).
- 7 males that were tested of the Yamnaya culture were all found to belong to the M269 subclade of haplogroup R1b.” ref
“R1b is a subclade within the “macro-haplogroup“ K (M9), the most common group of human male lines outside of Africa. K is believed to have originated in Asia (as is the case with an even earlier ancestral haplogroup, F (F-M89). Karafet T. et al. (2014) suggested that a “rapid diversification process of K-M526 likely occurred in Southeast Asia, with subsequent westward expansions of the ancestors of haplogroups R and Q“. However, the oldest example of R* has been found in an Ancient North Eurasian sample from Siberia (Mal’ta boy, 24,000 years ago), and its precursor P1 has been found in another Ancient North Eurasian sample from northern Siberia (Yana RHS) dating from c. 31,600 years ago.” ref
“Three genetic studies in 2015 gave support to the Kurgan hypothesis of Marija Gimbutas regarding the Proto-Indo-European homeland. According to those studies, haplogroups R1b-M269 and R1a, now the most common in Europe (R1a is also common in South Asia) would have expanded from the West Eurasian Steppe, along with the Indo-European languages; they also detected an autosomal component present in modern Europeans which was not present in Neolithic Europeans, which would have been introduced with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as Indo-European languages.” ref
Iberomaurusian
“The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is locally known as the Eastern Oranian. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), somewhere between c. 25,000 and 23,000 years ago. It would have lasted until the early Holocene c. 11,000 years ago. In 2005, the Mitochondrial DNA of 31 prehistoric skeletons dated from the site of Taforalt, Morocco in a cave called ‘Grotte des pigeons’ was analyzed by the Tunisian geneticist Rym Kefi (Pasteur Institute of Tunis) and her team. The remains at Taforalt were dated between 23,000 and 10,800 years ago. Later analysis of bones and charcoals using a high precision radiocarbon chronology showed that the Iberomaurusian industry appeared in TAF at least 22,093–21,420 years ago. In 2016 she updated the research and wrote a new article which also included 8 skeletons from the Algerian Iberomaurusian site called ‘Afalou’. The Afalou site is dated from 15,000 to 11,000 years ago. 23 individuals from the original 2005 Taforalt sample were determined in Kefi’s 2016 article to be of the maternal genetic lineage U6 and of Eurasian haplogroups H, U, R0 and at the Algerian Afalou site maternal groups were JT, J, T, H, R0a1 and U. This suggests genetic flow between North Africa and southern Mediterranean littoral since the Epipaleolithic.” ref
“In an article entitled ‘Pleistocene North African genomes link Near Eastern and sub-Saharan African human populations’, Marieke Van de Loosdrecht et al. (2018) did a full genome-wide analysis including Y-DNA from seven ancient individuals from the Taforalt site. The fossils were directly dated to between 15,100 and 13,900 calibrated years before present. All males at Taforalt belonged to haplogroup E1b1b1a1 (M-78). This haplogroup occurs most frequently in present-day North and East African populations. The closely related E1b1b1b (M-123) haplogroup has been reported for Epipaleolithic Natufians and Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levantines. Loosdrecht states: “Present-day North Africans share a majority of their ancestry with present-day Near Easterners, but not with sub-Saharan Africans”, although the predominant Y-DNA of the Maghreb is E-M81 (see Haplogroup E-Z827). Maternally, six individuals of the Taforalt remains bore the U6a haplogroup and one individual was of the M1b haplogroup, these Eurasian haplogroups proposed as markers for autochthonous Maghreb ancestry which might have been originally introduced into this region by a back-to-Africa migration from West Asia. A two-way admixture scenario using Natufian and modern sub-Saharan samples (including West Africans and the Tanzanian Hadza) as reference populations, inferred that the seven Taforalt individuals are best modeled genetically as 63.5% West-Eurasian-related and 36.5% sub-Saharan ancestry (with the latter having both West African-like and Hadza-like affinities), with no apparent gene flow from the Epigravettian culture of Paleolithic southern Europe.” ref
“However, the Sub-Saharan African DNA in Taforalt individuals was not found to have a good proxy in any present-day or ancient Holocene African groups. It was also found that if Iberomaurusians harbor sub-Saharan African-like ancestry, they would fail as a possible contributing source for Natufians or other Middle Eastern groups, except if the sub-Saharan African geneflow postdated Iberomaurusian geneflow into the Levant, or was a locally confined phenomenon. Jeong (2020) indicated that the Sub-Saharan African DNA of the Taforalt population has similarity with the remnant of a more basal African lineage (e.g. a basal Eurasian and/or basal West African lineage). Iosif Lazaridis et al. (2018), as summarized by Rosa Fregel (2021), contested the conclusion of Loosdrecht (2018) and argued instead that the Iberomaurusian population of Upper Paleolithic North Africa, represented by the Taforalt sample, “can be better modeled as an admixture between a Dzudzuana [West Eurasian] component and a sub-Saharan African component” (or an “Ancient North African” component, “that may represent an even earlier split than the Basal Eurasians“).” ref
“Iosif Lazaridis et al. (2018) also argued that an Iberomaurusian/Taforalt-like population contributed to the genetic composition of Natufians “and not the other way around”, and that this Iberomaurusian/Taforalt lineage also contributed around 13% ancestry to modern West Africans “rather than Taforalt having ancestry from an unknown Sub-Saharan African source”. Fregel (2021) summarized: “More evidence will be needed to determine the specific origin of the North African Upper Paleolithic populations.” Martiniano et al. (2022) later reassigned all the Taforalt samples to haplogroup E-M78 and none to E-L618, the predecessor to EV13. D’Atanasio et al. (2023) found that Iberomaurusian-like ancestry was characterizing for the unsampled “ancient Green Saharan” population about 12,000-5,000 years ago, and that modern-day Fula people derive around 30% of their ancestry from this ancient Saharan population, which was “modeled as a sister group of ancient Northern Africans, or alternatively, as an outgroup of all the “Eurasian-ancestry” enriched groups.” ref
“An estimation for Holocene-era Near Easterners (e.g., Mesolithic Caucasus hunter-gatherers, Mesolithic and Neolithic Iranians, and Natufians) suggests that they formed from a combination of Basal Eurasian ancestry, and Western Hunter-Gatherer-related (WHG) and or Ancient North Eurasians-related (ANE) ancestries respectively. The Mesolithic and Neolithic Iranian lineage is inferred to derived between 38–48% ancestry from Basal Eurasians respectively, with the remainder ancestry being made up by Ancient North Eurasian or Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) like ancestry, while Natufians derived a mean average of 50% Basal and 50% ‘unknown hunter-gatherer’ ancestry being closer to Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG). Alternatively, Mesolithic and Neolithic Iranians derive most of their ancestry from a deep West Eurasian source (WEC2; c. 72%) with c. 18% Basal Eurasian and c. 10% Ancient East Eurasian admixture. It has been found that the “models of genetic history of West Asian human populations who are modeled as a mixture of ‘basal Eurasians’ and West European hunter–gatherers” is in agreement with the genomic data on ‘East Mediterranean Dogs‘, who “are modeled as a mixture of a basal branch (splitting deeper than the divergence of the Asian and European dogs) and West European dogs.” ref
“The Ancient North African Iberomaurusian (Taforalt) individuals were found to have harbored ~65% West Eurasian-like ancestry and considered likely direct descendants of such “Basal Eurasian” population. However, they were shown to be genetically closer to Holocene-era Iranians and Levantine populations, which already harbored increased archaic (Neanderthal) admixture. Early European Farmers (EEFs), who had some Western European Hunter-Gatherer-related ancestry and originated in the Near East, also derive approximately 30% (to up to 44%) of their ancestry from this hypothetical Basal Eurasian lineage. An Upper Paleolithic specimen from Kotias Klde cave in the Caucasus (Caucasus_25,000BP) had around 24% Basal Eurasian and 76% Upper Paleolithic European ancestry.” ref
“Among modern populations, Basal-like ancestry peaks among Arabs (such as Qataris) at c. 45%, and among Iranian populations at c. 35%, and is also found in significant amounts among modern Northern Africans, in accordance with the high affinity towards the ‘Arabian branch’ of Eurasian diversity, which expanded into Northern and Northeastern Africa between 30 and 15 thousand years ago. Modern populations of the Levant derive between 35-38% ancestry from Basal Eurasians, modern Anatolians and populations from the Caucasus derive between 25-30% ancestry from Basal Eurasians, and modern Europeans derive around or less than 20% ancestry from Basal Eurasians. Modern Bedouins and Yemenis are considered to represent direct descendants of the Basal Eurasians, carrying the highest amount of indigenous ‘Arabian ancestry’, and being basal to all modern Eurasian populations without displaying higher ‘African-associated’ admixture, and thus “are among the best genetic representatives of the autochthonous population on the Arabian Peninsula.” ref
“Basal Eurasians may have originated in a region stretching from North Africa to the Middle East, before admixing with West-Eurasian populations. North Africa has been described as a strong candidate for the location of the emergence of Basal Eurasians by Loosdrecht et al. in 2018. Ferreira et al. in 2021 argued for a point of origin for Basal Eurasians into the Middle East, specifically in the Persian Gulf region on the Arab peninsula. As Basal Eurasians had low levels of Neanderthal ancestry, genetic and archaeological evidence for interactions between modern humans and Neanderthals may allow certain areas, such as the Levant, to be ruled out as possible sources for Basal Eurasians. In other areas, such as southern Southwest Asia, there is currently no evidence for an overlap between modern human and Neanderthal populations. Vallini et al. 2024 suggests a homeland for Basal Eurasians in the Arabian Peninsula, with a ‘Common Eurasian Hub’ in the Iranian Plateau, where they diverged into ‘Ancient West Eurasians’ and ‘Ancient East Eurasians‘.” ref
“A study by Lazaridis et al. in 2014 demonstrated that modern Europeans can be modeled as an admixture of three ancestral populations; Ancient North Eurasians (ANE), Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), and Early European Farmers (EEF). This same study also showed that EEFs harbor ancestry from a hypothetical non-African ‘ghost’ population, which the authors name ‘Basal Eurasians’. This group, who have not yet been sampled from ancient remains, are thought to have diverged from all non-African populations c. 60,000 to 100,000 years ago, before non-Africans admixed with Neanderthals (c. 50,000 to 60,000 years ago) and diversified from each other. A second study by Lazaridis et al. in 2016 found that populations with higher levels of Basal Eurasian ancestry have lower levels of Neanderthal ancestry, which suggests that Basal Eurasians had lower levels of Neanderthal ancestry compared with other non-Africans.” ref
“Another study by Ferreira et al. in 2021 suggested that Basal Eurasians diverged from other Eurasians between 50,000 and 60,000 years ago, and lived somewhere in the Arabian peninsula, specifically the Persian Gulf region, shortly before proper Eurasians admixed with a Neanderthal population in a region stretching from the Levant to northern Iran. Vallini et al. 2024 argues that the Basal Eurasian lineage diverged from other Eurasians soon after the Out-of-Africa migration, and subsequently became isolated, until it started to mix with other populations in the Middle East since around 25,000 years ago. These different Middle Eastern populations would later spread Basal Eurasian ancestry via the Neolithic Revolution to all of Western Eurasia. In modern populations, Neanderthal ancestry is around 10% to 20% lower in West Eurasians than East Eurasians, with intermediate levels found in South and Central Asian populations. Although a scenario involving multiple admixture events between modern humans and Neanderthals is an alternative possibility, the most likely explanation for this is that Neanderthal ancestry in West Eurasians and South and Central Asians was diluted by admixture with Basal Eurasian groups.” ref
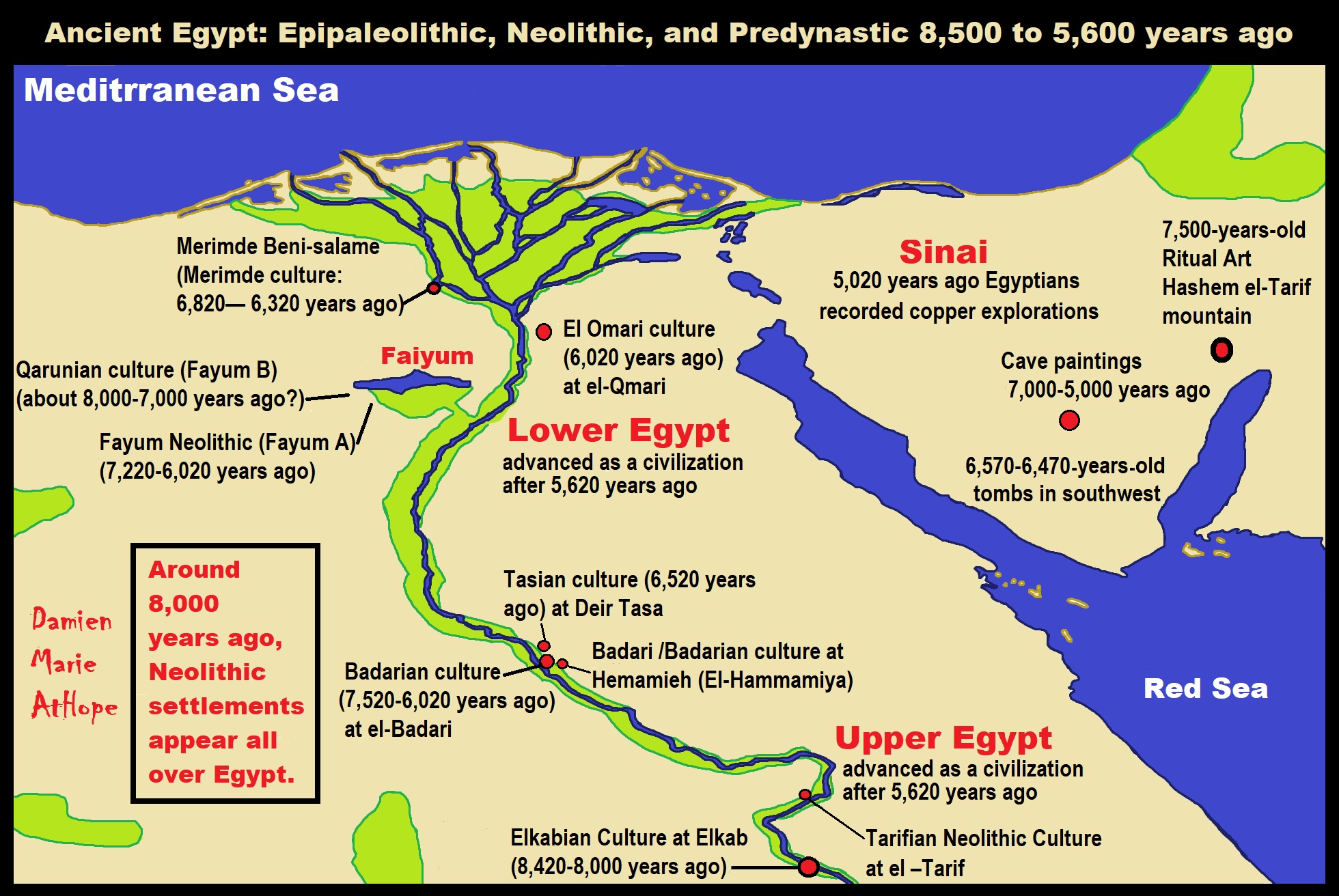
Natufian culture
“Natufian culture is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Neolithic prehistoric Levant in Western Asia, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction of agriculture. Natufian communities may be the ancestors of the builders of the first Neolithic settlements of the region, which may have been the earliest in the world. Some evidence suggests deliberate cultivation of cereals, specifically rye, by the Natufian culture at Tell Abu Hureyra, the site of earliest evidence of agriculture in the world. The world’s oldest known evidence of the production of bread-like foodstuff has been found at Shubayqa 1, a 14,400-year-old site in Jordan’s northeastern desert, 4,000 years before the emergence of agriculture in Southwest Asia. In addition, the oldest known evidence of possible beer-brewing, dating to approximately 13,000 years ago, was found in Raqefet Cave on Mount Carmel, although the beer-related residues may simply be a result of a spontaneous fermentation.” ref
“The Natufian developed in the same region as the earlier Kebaran culture. It is generally seen as a successor, which evolved out of elements within that preceding culture. There were also other industries in the region, such as the Mushabian culture of the Negev and the Sinai Peninsula, which are sometimes distinguished from the Kebaran culture or believed to have been involved in the evolution of the Natufian culture. More generally there has been discussion of the similarities of these cultures with those found in coastal North Africa. Graeme Barker notes there are: “similarities in the respective archaeological records of the Natufian culture of the Levant and of contemporary foragers in coastal North Africa across the late Pleistocene and early Holocene boundary.” According to Isabelle De Groote and Louise Humphrey, Natufians practiced the Iberomaurusian and Capsian custom of sometimes extracting their maxillary central incisors (upper front teeth).” ref
“Ofer Bar-Yosef has argued that there are signs of influences coming from North Africa to the Levant, citing the microburin technique and “microlithic forms such as arched backed bladelets and La Mouillah points.” But recent research has shown that the presence of arched backed bladelets, La Mouillah points, and the use of the microburin technique was already apparent in the Nebekian industry of the Eastern Levant. And Maher et al. state that, “Many technological nuances that have often been always highlighted as significant during the Natufian were already present during the Early and Middle EP [Epipalaeolithic] and do not, in most cases, represent a radical departure in knowledge, tradition, or behavior.” At the Natufian site of Ain Mallaha in Israel, dated to 12,000 BCE, the remains of an elderly human and a four-to-five-month-old puppy were found buried together. At another Natufian site at the cave of Hayonim, humans were found buried with two canids.” ref
“Authors such as Christopher Ehret have built upon the little evidence available to develop scenarios of intensive usage of plants having built up first in North Africa, as a precursor to the development of true farming in the Fertile Crescent, but such suggestions are considered highly speculative until more North African archaeological evidence can be gathered. In fact, Weiss et al. have shown that the earliest known intensive usage of plants was in the Levant 23,000 years ago at the Ohalo II site. Anthropologist C. Loring Brace (1993) cross-analysed the craniometric traits of Natufian specimens with those of various ancient and modern groups from the Near East, Africa and Europe. The Late Pleistocene Epipalaeolithic Natufian sample was described as problematic due to its small size (consisting of only three males and one female), as well as the lack of a comparative sample from the Natufians’ putative descendants in the Neolithic Near East.” ref
“Brace observed that the Natufian fossils lay between those of the Niger–Congo-speaking series included and the other samples (Near East, Europe), which he suggested may point to a Sub-Saharan influence in their constitution. Subsequent ancient DNA analysis of Natufian skeletal remains by Lazaridis et al. (2016) found that the specimens instead were a mix of 50% Basal Eurasian ancestral component (see Archaeogenetics) and 50% West-Eurasian Unknown Hunter Gatherer (UHG) population related to European Western Hunter-Gatherers. Natufians have also been described by anthropologists as a Proto-Mediterranean population. According to Bar-Yosef and Belfer-Cohen, “It seems that certain preadaptive traits, developed already by the Kebaran and Geometric Kebaran populations within the Mediterranean park forest, played an important role in the emergence of the new socioeconomic system known as the Natufian culture.” ref
“Natufian grave goods are typically made of shell, teeth (of red deer), bones, and stone. There are pendants, bracelets, necklaces, earrings, and belt-ornaments as well. In 2008, the 12,400–12,000 cal BCE grave of an apparently significant Natufian female was discovered in a ceremonial pit in the Hilazon Tachtit cave in northern Israel. Media reports referred to this person as a “shaman.” The burial contained the remains of at least three aurochs and 86 tortoises, all of which are thought to have been brought to the site during a funeral feast. The body was surrounded by tortoise shells, the pelvis of a leopard, forearm of a boar, a wingtip of a golden eagle, and skull of a beech marten. At Ain Mallaha (in Northern Israel), Anatolian obsidian and shellfish from the Nile valley have been found. The source of malachite beads is still unknown. Epipaleolithic Natufians carried parthenocarpic figs from Africa to the southeastern corner of the Fertile Crescent, c. 10,000 BCE.” ref
“There was a rich bone industry, including harpoons and fish hooks. Stone and bone were worked into pendants and other ornaments. There are a few human figurines made of limestone (El-Wad, Ain Mallaha, Ain Sakhri), but the favorite subject of representative art seems to have been animals. Ostrich-shell containers have been found in the Negev. In 2018, the world’s oldest brewery was found, with the residue of 13,000-year-old beer, in a prehistoric cave near Haifa in Israel when researchers were looking for clues into what plant foods the Natufian people were eating. This is 8,000 years earlier than experts previously thought beer was invented. A study published in 2019 shows an advanced knowledge of lime plaster production at a Natufian cemetery in Nahal Ein Gev II site in the Upper Jordan Valley dated to 12,000 years ago. Production of plaster of this quality was previously thought to have been achieved some 2,000 years later.” ref
“A pita-like bread has been found from 12,500 BCE attributed to Natufians. This bread is made of wild cereal seeds and papyrus cousin tubers, ground into flour. According to one theory, it was a sudden change in climate, the Younger Dryas event (c. 10,800 to 9500 BCE), which inspired the development of agriculture. The Younger Dryas was a 1,000-year-long interruption in the higher temperatures prevailing since the Last Glacial Maximum, which produced a sudden drought in the Levant. This would have endangered the wild cereals, which could no longer compete with dryland scrub, but upon which the population had become dependent to sustain a relatively large sedentary population. By artificially clearing scrub and planting seeds obtained from elsewhere, they began to practice agriculture. However, this theory of the origin of agriculture is controversial in the scientific community.” ref
“The population associated with the Natufian culture formed genetically by the merger of a West Eurasian-like population, sharing deep ancestry with Western Hunter-Gatherers of Europe, and Basal Eurasians of local Arabian origin.[citation needed] Vallini et al. (2024) modeled the amount of Basal Eurasian ancestry among Natufians at roughly 15%, with the remainder being associated with West Eurasian sources. The Natufian population also displays ancestral ties to Paleolithic Taforalt samples, the makers of the Epipaleolithic Iberomaurusian culture of the Maghreb, the Pre-Pottery Neolithic culture of the Levant, the Early Neolithic Ifri N’Amr Ou Moussa and the Late Neolithic Kelif el Boroud culture of North Africa, with samples associated with these early cultures all sharing a common genomic component dubbed the “Natufian component”, which diverged from other West Eurasian lineages ~26,000 years ago, and is most closely linked to the Arabian lineage. Possible bidirectional geneflow events between these groups has also been suggested, with particular evidence for affinity between the Natufians and Iberomaurusians.” ref
“Contact between Natufians and other Neolithic Levantines, Caucasus hunter-gatherers (CHG), Anatolian and Iranian farmers is believed to have decreased genetic variability among later populations in the Middle East. Migrations from the Near-East also occurred towards Africa, and the West Eurasian-like ancestry among populations in the Horn of Africa being best represented by the Levant Neolithic, and may be associated with the spread of Afroasiatic languages. Lazaridis et al. (2016) did not find a greater genetic affinity between Natufians and sub-Saharan Africans than that existing between sub-Saharan Africans and other ancient populations of Western Eurasia, and also stated that the ancestry of a primitive population from North Africa could not be tested because modern North Africans are largely descended from late migrant populations from Eurasia. However, Daniel Shriner (2018), using modern populations as a reference, found 28% autosomal African ancestry in Natufian samples, with 21.2% related to North Africa and 6.8% related to Omotic-speaking populations in southern Ethiopia, which reveals a plausible source for haplogroup E in Natufians; still according to Shriner, the Natufian samples had 61.2% ancestry related to Arabs and 10.8% ancestry related to West Asians.” ref
“As summarized by Rosa Fregel, a later preprint from Lazaridis et al. (2018) has contested Loosdrecht’s conclusion and argues for a minor sub-Saharan African component in Natufians, stating “that [the Iberomaurusians of] Taforalt can be better modeled as a mixture of a Dzudzuana component and a sub-Saharan African component” (or an ancient and now-extinct North African component that diverged prior to the Out-of-Africa migration) and “also argue that (…) the Taforalt people (…) contributed to the genetic composition of Natufians and not the other way around”, , which, according to Lazaridis et al., would be consistent with morphological and archaeological studies that indicate a dissemination of morphological characteristics and artifacts from North Africa to the Near East, as well as explaining the presence of Y-chromosome haplogroup E in Natufians and Levantine farmers. Fregel summarizes that “More evidence will be needed to determine the specific origin of the North African Upper Paleolithic populations.” ref
“In their 2017 paper, Ranajit Das, Paul Wexler, Mehdi Pirooznia and Eran Elhaik analyzed the Lazaridis et al. (2016) study concluding that the Natufians, together with one Neolithic Levantine sample, clustered in the proximity to modern Palestinians and Bedouins, and also “marginally overlapped” with Yemenite Jews. Ferreira et al. (2021) and Almarri et al. (2021) found that ancient Natufians cluster with modern Arabian groups, such as Saudi Arabians and Yemenis, which derive most of their ancestry from local Natufian-like hunter-gatherer peoples and have less Neolithic Anatolian ancestry than Levantines. Sirak et al. (2024) found that medieval Socotra (the Soqotri people), similar to modern Saudis, Yemenis and Bedouins, have a majority component that is “maximized in Late Pleistocene (Epipaleolithic) Natufian hunter–gatherers from the Levant.” ref
“Alexander Militarev, Vitaly Shevoroshkin and others have linked the Natufian culture to the proto-Afroasiatic language, which they in turn believe has a Levantine origin. Some scholars, for example Christopher Ehret, Roger Blench and others, contend that the Afroasiatic Urheimat is to be found in North Africa or Northeast Africa, probably in the area of Egypt, the Sahara, Horn of Africa or Sudan. Within this group, Ehret, who like Militarev believes Afroasiatic may already have been in existence in the Natufian period, would associate Natufians only with the Near Eastern Proto-Semitic branch of Afroasiatic.” ref
“E-Z827, also known as E1b1b1b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the parent lineage to the E-Z830 and E-V257 subclades, and defines their common phylogeny. The former is predominantly found in the Middle East; the latter is most frequently observed in North Africa, with its E-M81 subclade observed among the ancient Guanche natives of the Canary Islands. E-Z827 is also found at lower frequencies in Europe, and in isolated parts of Southeast Africa.” ref
“E-M35, also known as E1b1b1-M35, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M35 has two basal branches, E-V68 and E-Z827. E-V68 and E-Z827 are primarily distributed in North Africa and the Horn of Africa, and occur at lower frequencies in the Middle East, Europe, and Southern Africa. In June 2015, Trombetta et al. reported a previously unappreciated large difference in the age between haplogroup E-M215 (38,600 years ago; 95% CI 31.4–45,900 years ago) and its sub-haplogroup E-M35 (25,000 years ago; 95% CI 20,000–30,000 years ago) and estimated its origin to be in Horn of Africa, where the node separating the E-V38 and E-M215 branches occurs about 47,500 years ago (95% CI: 41,300–56,800 years ago). E-M35 was dated by Batini in 2015 to between 15,400 and 20,500 years ago.” ref
“All major sub-branches of E-M35 are thought to have originated in the same general area as the parent clade: in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, or nearby areas of the Near East. Some branches of E-M35 are assumed to have left Africa thousands of years ago, whereas others may have arrived from the Near East. For example, Underhill (2002) associates the spread of the haplogroup with the Neolithic Revolution, believing that the structure and regional pattern of E-M35 subclades potentially give “reagents with which to infer specific episodes of population histories associated with the Neolithic agricultural expansion”. Battaglia et al. (2008) also estimate that E-M78 (called E1b1b1a1 in that paper) has been in Europe longer than 10,000 years. Accordingly, human remains excavated in a Spanish funeral cave dating from approximately 7,000 years ago were shown to be in this haplogroup. Two more E-M78 have been found in the Neolithic Sopot and Lengyel cultures too.” ref
“Concerning E-M35 in Europe within this scheme, Underhill & Kivisild (2007) have remarked that E-M215 seems to represent a late-Pleistocene migration from North Africa to Europe over the Sinai Peninsula in Egypt. While this proposal remains uncontested, it has more recently been proposed by Trombetta et al. (2011) that there is also evidence for additional migration of E-M215 carrying men directly from North Africa to southwestern Europe, via a maritime route (see below.) According to Lazaridis et al. (2016), Natufian skeletal remains from the ancient Levant predominantly carried the Y-DNA haplogroup E1b1b. Of the five Natufian specimens analysed for paternal lineages, three belonged to the E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b), E1b1(xE1b1a1,E1b1b1b1) and E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b) subclades (60%).” ref
“Haplogroup E1b1b was also found at moderate frequencies among fossils from the ensuing Pre-Pottery Neolithic B culture, with the E1b1b1 and E1b1b1b2(xE1b1b1b2a,E1b1b1b2b) subclades observed in two of seven PPNB specimens (~29%). The scientists suggest that the Levantine early farmers may have spread southward into East Africa, bringing along Western Eurasian and Basal Eurasian ancestral components separate from that which would arrive later in North Africa. Additionally, haplogroup E1b1b1 has been found in an ancient Egyptian mummy excavated at the Abusir el-Meleq archaeological site in Middle Egypt, which dates from a period between the late New Kingdom and the Roman era.” ref
“Fossils at the Iberomaurusian site of Ifri n’Amr or Moussa in Morocco, which have been dated to around 5,000 BCE, also carried haplotypes related to the E1b1b1b1a (E-M81) subclade. These ancient individuals bore an autochthonous Maghrebi genomic component that peaks among modern North Africans, indicating that they were ancestral to populations in the area.[12] The E1b1b haplogroup has likewise been observed in ancient Guanche fossils excavated in Gran Canaria and Tenerife on the Canary Islands, which have been radiocarbon-dated to between the 7th and 11th centuries CE. The clade-bearing individuals that were analyzed for paternal DNA were inhumed at the Tenerife site, with all of these specimens found to belong to the E1b1b1b1a1 or E-M183 subclade (3/3; 100%).” ref
“Loosdrecht et al. (2018) analysed genome-wide data from seven ancient Iberomaurusian individuals from the Grotte des Pigeons near Taforalt in eastern Morocco. The fossils were directly dated to between 15,100 and 13,900 calibrated years before present. The scientists found that five male specimens with sufficient nuclear DNA preservation belonged to the E1b1b1a1 (M78) subclade, with one skeleton bearing the E1b1b1a1b1 parent lineage to E-V13, another male specimen belonged to E1b1b (M215*).” ref
“E-V257’s dominant sub-clade E-M81 is thought to have originated in the area of the northwest of Africa 7,000 years ago, but all Yfull members are M183 and have a TMRCA just 2700 years ago. E-M81 is the most common subclade of haplogroup E-L19/V257. It is concentrated in North Africa, and is dominated by its E-M183 subclade. E-M183 is believed to have originated in the Northwest of Africa, and has an estimated age of 2,284-2,984 years ago. The E-M183 sub haplogroup reaches a mean frequency of 42% in North Africa. It decreases in frequency from 100% in some populations to approximately 28.6% to the east of this range in Egypt. The E-M81 subclade is predominant among North African Berber-speaking populations. In Tunisia, it reached 100% frequency among a sample of Arabs from Zriba, 89.5% in Andalusians (Qalaat-al-Andalous), and 100% in Berbers from Chenini-Douiret, Jradou and Takrouna. It is generally found at frequencies around 45% in coastal cities of the Maghreb (Oran, Tunis, Algiers).” ref
“It is also prevalent among other Berber populations and reaches frequency of 72.4% in Marrakesh Berbers, 80% in Mozabite, and 71% in Middle Atlas Berbers (Moyen). It also reaches high levels (77.8%) among the Tuareg population inhabiting the Sahara in Burkina Faso, near Gor it reaches a much lower frequency of 11.1% in the vicinity of Tanut in the Republic of Niger. In this key area from Egypt to the Atlantic Ocean, report a pattern of decreasing STR haplotype variation (implying decreasing lineage age in those areas) from East to West (but reports West to East for M183), accompanied by a substantial increasing frequency. At the eastern extreme of this core range, M81 is found in 28.6% (10 out of 35 men) in El-Hayez in the Western desert in Egypt.” ref
“The pattern of distribution and variance to be consistent with the hypothesis of a post Paleolithic “demic diffusion” from the Middle East. The ancestral lineage of E-M81 in their hypothesis could have been linked with the spread of Neolithic food-producing technologies from the Fertile Crescent via the Nile, although pastoralism rather than agriculture. E-M81 and possibly proto-Afroasiatic language may have been carried either all the way from Asia, or they may represent a “local contribution to the North African Neolithic transition.” The E-M81 subclade has been found in ancient Guanche (Bimbapes) fossils excavated in Punta Azul, El Hierro, Canary Islands, which are dated to the 10th century (~44%). Also found in ifri n’ammar that makes the Northwest African origin the likely origin of where it expanded, and not the Middle East.” ref
Ifri N’Amr Ou Moussa
“Ifri n’Amr Ou Moussa is an archaeological site discovered in 2005, located in the rural commune of Aït Siberne, Khémisset Province, in Western Morocco. This site has revealed burials associated with both Moroccan Early Neolithic and Bell Beaker culture. Fregel et al. 2018 examined the remains of 7 individuals buried at Ifri N’Amr Ou Moussa (c. 5325-4786 BCE). The 2 samples of Y-DNA extracted belonged to the paternal haplogroup E-L19*, while the 5 samples of mtDNA extracted belonged to the maternal haplogroups M1b1*, U6a1b (two samples), U6a7b2 and U6a3. The paternal haplogroup E-L19* is very common in North Africa. The maternal haplogroups are associated with migrations from Eurasia into North Africa during the Upper Paleolithic. They were found to be closely related to the early Stone Age people buried at Taforalt, Morocco (c. 15000 BCE). Both the Taforalt and Ifri N’Amr ou Moussa people were found to also be related to people of the Natufian culture (c. 9000 BCE) and Pre-Pottery Neolithic (c. 6500 BCE) of the Levant, with whom they appeared to share a common origin.” ref
“This genetic continuity with the Taforalt suggested that the ancestors of the Ifri n’Amr ou Moussa people had adopted a Neolithic lifestyle without substantial migration, however a paper from 2023 dealing with ancient genomes in Morocco, found that a change from foraging to food production occurred 7,400 years ago, and farming practices were introduced by Neolithic European groups, being adopted by locals initially without demic diffusion. Among modern populations, the examined individuals were determined to be most closely related to the Mozabite people of Algeria. In contrast to the Ifri N’Amr individuals, the examined samples at the Late Neolithic site of Kelif el Boroud (~c. 4000 BCE or around 6,000 years ago), carried about 50% Early European Farmer (EEF) ancestry, suggesting substantial migration of Cardial Ware people from Iberia into North Africa during the Neolithic phases.” ref
“Both the studied groups buried at Ifri n’Amr ou Moussa and Kelif el Boroud carried a much lower amount of Sub-Saharan African admixture than modern North Africans, indicating that the trans-Saharan migrations occurred after Neolithic times (however, they also carried lower Sub-Saharan African admixture than the Stone Age people of Taforalt). Phenotypically, the Ifri n’Amr ou Moussa people were determined to have had dark skin and dark eye color. The ancient Guanches (c. 500 BCE – 1500 CE) of the Canary Islands were modeled as a mixture of ancestry from the Ifri N’Amr ou Moussa and Kelif el Boroud.” ref
Oldest DNA from Africa offers clues to mysterious ancient culture
North Africa was an ancient crossroads with a more sophisticated culture than expected
“About 15,000 years ago, in the oldest known cemetery in the world, people buried their dead in sitting positions with beads and animal horns, deep in a cave in what is now Morocco. These people were also found with small, sophisticated stone arrowheads and points, and 20th-century archaeologists assumed they were part of an advanced European culture that had migrated across the Mediterranean Sea to North Africa. But now, their ancient DNA—the oldest ever obtained from Africans—shows that these people had no European ancestry. Instead, they were related to both Middle Easterners and sub-Saharan Africans, suggesting that more people were migrating in and out of North Africa than previously believed.” ref
“The findings are really exciting,” says evolutionary geneticist Sarah Tishkoff of the University of Pennsylvania, who was not part of the work. One big surprise from the DNA, she says, is that it shows that “North Africa has been an important crossroads … for a lot longer than people thought.” The origins of the ancient Moroccans, known as the Iberomaurusians because 20th-century archaeologists thought they were connected to peoples of the Iberian Peninsula, have been a mystery ever since the Grotte des Pigeons cave was discovered near Oujda, Morocco, in 1908. Starting 22,000 or so years ago, these hunter-gatherers eschewed more primitive Middle Stone Age tools, such as larger blades used on spears, to produce microliths—small pointed bladelets that could be shot farther as projectile points or arrowheads. Similar tools show up earlier in Spain, France, and other parts of Europe, some associated with the famous Gravettian culture, known for its stone figurines of curvaceous women.” ref
“The idea in the 1960s was that the Iberomaurusians must have got the microblades from the Gravettian,” says co-author and archaeologist Louise Humphrey of the Natural History Museum in London. During the ice age 20,000 years ago, sea level would have been lower, and the Iberomaurusians were thought to have crossed the Mediterranean by boat at Gibraltar or Sicily. Humphrey and her Moroccan colleagues got a chance to test this view after they discovered 14 individuals associated with Iberomaurusian artifacts at the back of the Grotte des Pigeons cave in 2005. Paleogeneticists Marieke van de Loosdrecht and Johannes Krause of the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History (SHH) in Jena, Germany, with Matthias Meyer of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, used state-of-the-art methods to extract DNA from the ear bones of skeletons that had lain undisturbed since they were buried about 15,000 years ago.” ref
“That’s a major technical feat because ancient DNA degrades rapidly in warm climates; these samples are almost twice as old as any other DNA obtained from humans in Africa. DNA in hand, Van de Loosdrecht, and Choongwon Jeong, also of SHH, were able to analyze genetic material from the cell’s nucleus in five people and the maternally inherited mitochondrial DNA from seven people. However, they found no genetic tie to ancient Europeans. Instead, the ancient Iberomaurusians appear to be related to Middle Easterners and other Africans: They shared about two-thirds of their genetic ancestry with Natufians, hunter-gatherers who lived in the Middle East 14,500 to 11,000 years ago, and one-third with sub-Saharan Africans who were most closely related to today’s West Africans and the Hadza of Tanzania.” ref
“The Iberomaurusians lived before the Natufians, but they were not their direct ancestors: The Natufians lack DNA from Africa, Krause says. This suggests that both groups inherited their shared DNA from a larger population that lived in North Africa or the Middle East more than 15,000 years ago, the team reports today in Science. As for the sub-Saharan DNA in the Iberomaurusian genome, the Iberomaurusians may have gotten it from migrants from the south who were their contemporaries. Or they may have inherited the DNA from much more ancient ancestors who brought it from the south but settled in North Africa where some of the earliest members of our species, Homo sapiens, have been found at Jebel Irhoud in Morocco.” ref
“All this offers the first glimpse of the deep history of North Africans, who today have a large amount of European DNA. It suggests that there were more migrations between North Africa, the Middle East, and sub-Saharan Africa than previously believed. “Cleary, human populations were interacting much more with groups from other, more distant areas than was previously assumed,” Krause says. Further studies will search for the people who gave rise to both the Iberomaurusians and the Natufians. “It’s a thrill to look for the first time at ancient DNA from prehistoric peoples from North Africa, a place where repeated waves of migration have made reconstruction of the deep population history based on living populations almost impossible,” says population geneticist David Reich of Harvard University, who was not part of the team.” ref
Genomic insights into the origin of farming in the ancient Near East
“Researchers report genome-wide ancient DNA from 44 ancient Near Easterners ranging in time between ~12,000-1,400 BCE, from Natufian hunter-gatherers to Bronze Age farmers. We show that the earliest populations of the Near East derived around half their ancestry from a ‘Basal Eurasian’ lineage that had little if any Neanderthal admixture and that separated from other non-African lineages prior to their separation from each other. The first farmers of the southern Levant (Israel and Jordan) and Zagros Mountains (Iran) were strongly genetically differentiated, and each descended from local hunter-gatherers. By the time of the Bronze Age, these two populations and Anatolian-related farmers had mixed with each other and with the hunter-gatherers of Europe to drastically reduce genetic differentiation. The impact of the Near Eastern farmers extended beyond the Near East: farmers related to those of Anatolia spread westward into Europe; farmers related to those of the Levant spread southward into East Africa; farmers related to those from Iran spread northward into the Eurasian steppe; and people related to both the early farmers of Iran and to the pastoralists of the Eurasian steppe spread eastward into South Asia.” ref
“Between 10,000-9,000 BCE, humans began practicing agriculture in the Near East. In the ensuing five millennia, plants and animals domesticated in the Near East spread throughout West Eurasia (a vast region that also includes Europe) and beyond. The relative homogeneity of present-day West Eurasians in a world context suggests the possibility of extensive migration and admixture that homogenized geographically and genetically disparate sources of ancestry. The spread of the world’s first farmers from the Near East would have been a mechanism for such homogenization. To date, however, due to the poor preservation of DNA in warm climates, it has been impossible to study the population structure and history of the first farmers and to trace their contribution to later populations.” ref
“In order to overcome the obstacle of poor DNA preservation, we took advantage of two methodological developments. First, we sampled from the inner ear region of the petrous bone that can yield up to ~100 times more endogenous DNA than other skeletal elements. Second, we used in-solution hybridization to enrich extracted DNA for about 1.2 million single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) targets, making efficient sequencing practical by filtering out microbial and non-informative human DNA. We merged all sequences extracted from each individual, and randomly sampled a single sequence with minimum mapping and sequence quality to represent each SNP, restricting to individuals with at least 9,000 SNPs covered at least once (Methods). We obtained genome-wide data passing quality control for 45 individuals on whom we had a median coverage of 172,819 SNPs. We assembled radiocarbon dates for 26 individuals (22 new generated for this study).” ref
“The newly reported ancient individuals date to ~12,000-1,400 BCE and come from the southern Caucasus (Armenia), northwestern Anatolia (Turkey), Iran, and the southern Levant (Israel and Jordan). (One individual had a radiocarbon date that was not in agreement with the date of its archaeological context and was also a genetic outlier.) The samples include Epipaleolithic Natufian hunter-gatherers from Raqefet Cave in the Levant (12,000-9,800 BCE); a likely Mesolithic individual from Hotu Cave in the Alborz mountains of Iran (probable date of 9,100-8,600 BCE); Pre-Pottery Neolithic farmers from ‘Ain Ghazal and Motza in the southern Levant (8,300-6,700 BCE); and early farmers from Ganj Dareh in the Zagros mountains of western Iran (8,200-7,600 BCE).” ref
“The samples also include later Neolithic, Chalcolithic (~4,800-3,700 BCE), and Bronze Age (~3,350-1,400 BCE) individuals. We combined our data with previously published ancient data to form a dataset of 281 ancient individuals. We then further merged with 2,583 present-day people genotyped on the Affymetrix Human Origins array (238 new). We grouped the ancient individuals based on archaeological culture and chronology. We refined the grouping based on patterns evident in Principal Components Analysis (PCA), ADMIXTURE model-based clustering, and ‘outgroup’ f3-analysis. We used f4-statistics to identify outlier individuals and to cluster phylogenetically indistinguishable groups into ‘Analysis Labels’.” ref
Haplogroup R0
“Haplogroup R0 derives from the macro-haplogroup R. It is an ancestral clade to the R0a subclade and haplogroup HV, and is therefore antecedent to the haplogroups H and V. R0’s greater subclade variety in the Arabian Peninsula suggests that the clade originated in and spread from there. R0a is believed to have evolved in Ice Age oases in South Arabia around 22,000 years ago. The subclade would then have spread from there with the onset of the Late Glacial period circa 15,000 years ago. Haplogroup R0 has been found in around 55% of osteological remains belonging to the Eneolithic Trypillia culture.” ref
“The R0 clade has also been found among Iberomaurusian specimens at the Taforalt and Afalou prehistoric sites, which date from the Epipaleolithic. Among the Taforalt individuals, around 17% of the observed haplotypes belonged to various R0 subclades, including R0a1a (3/24; 13%) and R0a2c (1/24; 4%). Among the Afalou individuals, one R0a1a haplotype was detected (1/9; 11%). R0 has likewise been observed among mummies excavated at the Abusir el-Meleq archaeological site in Middle Egypt, which date from the Pre-Ptolemaic/late New Kingdom, Ptolemaic, and Roman periods. The 3rd century AD Catholic Church Saint, Fortunato of Serracapriola, was also found to carry the R0a’b subclade.” ref
“R0 today occurs commonly in the Arabian peninsula, with its highest frequency observed nearby among the Soqotri (40.7%). The Soqotri also have the greatest R0 subclade diversity. The clade is likewise found at high frequencies among the Kalash in South Asia (23%). Additionally, moderate frequencies of R0 occur in Northeast Africa, Anatolia, the Iranian Plateau, and Dalmatia. The haplogroup has been observed among Chad Arabs (19%), Sudanese Copts (13.8%), Tigrais (13.6%), Somalis (13.3%), Oromos (13.3%), Afar (12.5%), Amhara (11.5%), Gurage (10%), Reguibate Sahrawi (9.26%; 0.93% R0a and 8.33% R0a1a), Gaalien (9%), Beja (8.3%), Nubians (8%), Arakien (5.9%), Yemenis (5.1–27.7%), Iraqis (4.8%), Druze (4.3%), Palestinians (4%), Algerians (1.67%), and Saudis (0–25%).” ref
Ancient Paleo-Siberian
“In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Paleo-Siberian is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 15th-10th millennia before present, in northern and northeastern Siberia. The Ancient Paleo-Siberian population is thought to have arisen from an Ancient East Asian lineage, which diverged from other East Asian populations sometimes between 26,000 to 36,000 years ago, and merged with an Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) lineage sometimes between 20,000 to 25,000 years ago. The source for the East Asian component among Ancient Paleo-Siberians is to date best represented by Ancient Northern East Asian populations from the Amur region older than 13,000 years, such as AR19K and AR14K, and before the Devil’s Cave Ancient Northeast Asian specimens.” ref
“The Ancient Paleo-Siberians are mainly defined by two human archaeological specimens: the 14,000-year-old Ust-Kyakhta-3 (UKY) individual found near Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, and the 9-10,000-year-old Kolyma_M individual found in northeastern Siberia. Ancient Paleo-Siberians derive between 32–42% ancestry from the Ancient North Eurasians (ANE), deeply related to European hunter-gatherers, with the remainder ancestry (58–68%) being derived from an East Asian source. The Ancient Paleo-Siberians are closely related to the Ancient Beringians, and modern far-northeastern Siberia communities, such as the Koryaks, as well as to Native Americans. Ancestral Native Americans originated from a similar admixture event as Ancient Paleo-Siberians, carrying c. 56–64% East Asian-related ancestry and 36–44% ANE ancestry.” ref
“Technologically, Ancient Paleo-Siberians have been associated with microblade technologies and post-Last Glacial Maximum mammoth hunting. Ancient Paleo-Siberians, in conjunction with an Inner Northeast Asian (Yumin-like) lineage, gave rise to the Cisbaikal_LNBA ancestry, which may be associated with ancient Yeniseian speakers. Ancient Paleo-Siberians also formed the dominant ancestral source for Altai hunter-gatherers (7500 years ago), in conjunction with a Botai-like source, as well as for the subsequent Okunevo culture, in conjunction with additional Baikal hunter-gatherer and Afanasievo-like sources. They were later largely replaced by waves of Neo-Siberians and Neolithic Amur populations, which may be associated with the expansion of early Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic speakers, as well as possibly early Yukaghir and Uralic speakers (c. 7,000–11,000 years ago).” ref
Paleo-Siberian languages
“The Paleo-Siberian languages are several language isolates and small language families spoken in parts of Siberia. They are not known to have any genetic relationship to each other; their only common link is that they are held to have antedated the more dominant languages, particularly Tungusic and latterly Turkic languages, that have largely displaced them. Even more recently, Turkic (at least in Siberia) and especially Tungusic have been displaced in their turn by Russian.” ref
“Four small language families and isolates are usually considered to be Paleo-Siberian languages:
- The Chukotko-Kamchatkan family, sometimes known as Luoravetlan, includes Chukchi and its close relatives, Koryak, Alutor and Kerek. Itelmen, also known as Kamchadal, is also distantly related. Chukchi, Koryak and Alutor are spoken in easternmost Siberia by communities numbering in the thousands (Chukchi) or hundreds (Koryak and Alutor). Kerek is extinct, and Itelmen is now spoken by fewer than 5 people, mostly elderly, on the west coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula.
- Nivkh (Gilyak, Amuric) consists of two or three languages spoken in the lower Amur basin and on the northern half of Sakhalin island. It has a recent modern literature.
- The Yeniseian languages were a small family formerly spoken on the middle Yenisei River and its tributaries, but are now represented only by Ket, spoken in the Turukhansk district of Krasnoyarsk Krai by no more than 200 people.
- Yukaghir is spoken in two mutually unintelligible varieties in the lower Kolyma and Indigirka valleys. Other languages, including Chuvan, spoken further inland and further east, are now extinct. Yukaghir is held by some to be related to the Uralic languages.” ref
“On the basis of morphological, typological, and lexical evidence, Michael Fortescue suggests that Chukotko-Kamchatkan and Nivkh (Amuric) are related, forming a larger Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric language family. Fortescue does not consider Yeniseian and Yukaghir to be genetically related to Chukotko-Kamchatkan–Amuric.” ref
“The purpose of the existence of Paleo-Siberian itself lies in its practicability and remains a grouping of convenience for a variety of unclassifiable language isolates located in Northeast Eurasia. Some proposals for the relationship of languages located within the Paleo-Siberian group have been made by some scholars, including Edward Vajda, who suggests them to be related to the Na-Dené and Eskimo–Aleut families of Alaska and northern Canada. This would correlate with the widespread idea that North America’s aboriginal peoples migrated from present-day Siberia and other regions of Asia when the two continents were joined during the last ice age.” ref
“Ket, or more precisely the now largely extinct Yeniseian family, has been linked to the Na-Dené languages of North America. Dené–Yeniseian has been called “the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative-historical linguistics.” In the past, attempts to connect it to Sino-Tibetan, North Caucasian, and Burushaski have been made. Kim Bang-han proposed that placename glosses in the Samguk sagi reflect the original language of the Korean peninsula and a component in the formation of both Korean and Japanese. It is suggested that this language was related to Nivkh in some form.” ref
“Juha Janhunen suggests the possibility that similar consonant stop systems in Koreanic and Nivkh may be due to ancient contact. Martine Robbeets suggests that Proto-Korean had a Nivkh substrate influence. Further parallel developments in their sound inventory (Old to Middle Korean and Proto-Nivkh to Nivkh) as well as commonalities in the syntax between Koreanic and Nivkh specifically have been observed. The Ob-Ugric and Samoyedic languages predate the spread of Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic languages, but are part of the well established larger Uralic family, thus not Paleo-Siberian. Yukaghir has often been suggested as a more distant relative of Uralic as part of the Uralic-Yukaghir languages, as well as Eskimo-Aleut as part of the Uralo-Siberian languages. However, these hypotheses are controversial and not universally accepted.” ref
Yeniseian languages
“Proto-Yeniseian or Proto-Yeniseic is the unattested reconstructed proto-language from which all Yeniseian languages are thought to descend from. It is uncertain whether Proto-Yeniseian had a similar tone/pitch accent system as Ket. Many studies about Proto-Yeniseian phonology have been done; however, there are still many things unclear about Proto-Yeniseian. The probable location of the Yeniseian homeland is proposed on the basis of geographic names and genetic studies, which suggests a homeland in Southern Siberia.” ref
“The Yeniseian languages (/ˌjɛnɪˈseɪən/ YEN-ih-SAY-ən; sometimes known as Yeniseic, Yeniseyan, or Yenisei-Ostyak; occasionally spelled with –ss-) are a family of languages that are spoken by the Yeniseian people in the Yenisei River region of central Siberia. As part of the proposed Dené–Yeniseian language family, the Yeniseian languages have been argued to be part of “the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative–historical linguistics“. The only surviving language of the group today is Ket.” ref
“As noted by Tailleur and Werner, some of the earliest proposals of genetic relations of Yeniseian, by M.A. Castrén (1856), James Byrne (1892), and G.J. Ramstedt (1907), suggested that Yeniseian was a northern relative of the Sino–Tibetan languages. These ideas were followed much later by Kai Donner and Karl Bouda. A 2008 study found further evidence for a possible relation between Yeniseian and Sino–Tibetan, citing several possible cognates. Gao Jingyi (2014) identified twelve Sinitic and Yeniseian shared etymologies that belonged to the basic vocabulary, and argued that these Sino-Yeniseian etymologies could not be loans from either language into the other. From hydronymic and genetic data, it is suggested that the Yeniseian languages were spoken in a much greater area in ancient times, including parts of northern China and Mongolia. It has been further proposed that the recorded distribution of Yeniseian languages from the 17th century onward represents a relatively recent northward migration, and that the Yeniseian urheimat lies to the south of Lake Baikal.” ref
“The Yeniseians have been connected to the Xiongnu confederation, whose ruling elite may have spoken a southern Yeniseian language similar to the now extinct Pumpokol language. The Jie, who ruled the Later Zhao state of northern China, are likewise believed to have spoken a Pumpokolic language based on linguistic and ethnogeographic data. For those who argue the Xiongnu spoke a Yeniseian language, the Yeniseian languages are thought to have contributed many ubiquitous loanwords to Turkic and Mongolic vocabulary, such as Khan, Khagan, Tarqan, and the word for ‘god’ and ‘sky’, Tengri. This conclusion has primarily been drawn from the analysis of preserved Xiongnu texts in the form of Chinese characters.” ref
“The “Sino-Caucasian” hypothesis of Sergei Starostin posits that the Yeniseian languages form a clade with Sino-Tibetan, which he called Sino-Yeniseian. The Sino-Caucasian hypothesis has been expanded by others to “Dené–Caucasian” to include the Na-Dené languages of North America, Burushaski, Basque, and, occasionally, Etruscan. A narrower binary Dené–Yeniseian family has recently been well received. The validity of the rest of the family, however, is viewed as doubtful or rejected by nearly all historical linguists.” ref
“A link between the Na–Dené languages and Sino-Tibetan languages, known as Sino–Dené had also been proposed by Edward Sapir. Around 1920 Sapir became convinced that Na-Dené was more closely related to Sino-Tibetan than to other American families. Edward Vadja’s Dené–Yeniseian proposal renewed interest among linguists such as Geoffrey Caveney (2014) to look into support for the Sino–Dené hypothesis. Caveney considered a link between Sino-Tibetan, Na-Dené, and Yeniseian to be plausible but did not support the hypothesis that Sino-Tibetan and Na-Dené were related to the Caucasian languages (Sino–Caucasian and Dené–Caucasian).” ref
“A 2023 analysis by David Bradley using the standard techniques of comparative linguistics supports a distant genetic link between the Sino-Tibetan, Na-Dené, and Yeniseian language families. Bradley argues that any similarities Sino-Tibetan shares with other language families of the East Asia area such as Hmong-Mien, Altaic (which is a sprachbund), Austroasiatic, Kra–Dai, Austronesian came through contact; but as there has been no recent contact between the Sino-Tibetan, Na-Dené, and Yeniseian language families, any similarities these groups share must be residual.” ref
“The Glazkov culture, Glazkovo culture, or Glazkovskaya culture (2200-1200 BCE), was an archaeological culture in the Lake Baikal area during the Early Bronze Age. Glazkovs is a conditional name for the group of the ancient tribes inhabiting Siberia in the 2nd millennium BCE (Glazkov time) the headwaters of Angara river. Glazkov culture is named after a suburb of the city Irkutsk, where it was first found. Archeologists distinguish in the 2nd millennium BCE Southern Siberia two synchronous independent cultures: Glazkov in the east and the Andronovo culture in the west. All 4 tested Early Bronze Age individuals from the Ust-Ida burial site belonged to the Y-DNA haplogroup Q-YP4004 under Q1a2. Two earlier Late Neolithic burials from the same area yielded Y-haplogroups Q1a2 and N1c1.” ref
“In the Baikal territory lived a Glazkov group of related tribes, most likely the ancestors of modern Evenks, Evens or Yukagirs. Their culture was very close to the culture of the inhabitants of the upper Amur and Northern Manchuria, and of Mongolia to the Great Wall of China and Ordos Loop. It is possible, hence, that all this extensive area was populated by peoples culturally related with the hunter and fisher tribes of Neolith and Early Bronze… probably speaking related tribal languages”. Later the carriers of the southern part Glazkov culture tribes converged with some ancestors of the Huns, and intermixed with them. In the 18th century BCE the elements of the Andronovo culture seized the Minusinsk depression and almost encountered the Glazkovs on the Yenisei. Glazkovs and Andronovs played a secondary role in the 2nd millennium BCE Southern Siberia.” ref
“Glazkov burials brought new funeral traditions into the region: the deceased were oriented down the river, instead of previously common geographical direction orientations. The remains were placed in a crouched position, with intentionally broken artifacts, likely to protect the living from the danger presented by a deceased. To the end of the Glazkov time in the southern portion of the eastern Baikal area, there was an influx of people from Mongolia, who brought a distinctive tradition of stone kurgans with fences (chereksurs), which resulted in the formation of a Slab Grave culture that became the eastern wing of a huge nomadic world in Eurasia, which produced in the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE a bright civilization known as Scythian-Siberian World.” ref
“The genetic ancestry associated with the Glazkovo culture remains is known as “Baikal Early Bronze Age” (Baikal_EBA) ancestry, and falls into the Ancient Northern East Asian (ANEA) gene pool, with c. 11% (5-20%) admixture from Ancient North Eurasians (ANE). The Glazkovo remains display high genetic affinity with the “Cisbaikal_LNBA” ancestry, possibly associated with ancient Yeniseian speakers. Cisbaikal_LNBA ancestry is inferred to be rich in Ancient Paleo-Siberian ancestry, and also display affinity to Inner Northeast Asian (Yumin-like) groups. Modern Altaians display genetic affinity to the Glazkovo hunter-gatherer culture, and can be used as possible proxy for the East Eurasian component among Saka (Scytho-Siberian nomads).” ref
“The Xiongnu were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BCE to the late 1st century CE. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the “Five Barbarians“, they founded the dynastic states of Han-Zhao, Northern Liang and Helian Xia in northern China.” ref
Attempts to associate the Xiongnu with the nearby Sakas and Sarmatians were once controversial. However, archaeogenetics has confirmed their interaction with the Xiongnu, and also possibly their relation to the Huns. The identity of the ethnic core of Xiongnu has been a subject of varied hypotheses, because only a few words, mainly titles and personal names, were preserved in the Chinese sources. The name Xiongnu may be cognate with that of the Huns and/or the Huna, although this is disputed. Other linguistic links—all of them also controversial—proposed by scholars include Turkic, Iranian, Mongolic, Uralic, Yeniseian, or multi-ethnic.” ref
“The territories associated with the Xiongnu in central/east Mongolia were previously inhabited by the Slab Grave Culture (Ancient Northeast Asian origin), which persisted until the 3rd century BCE. Genetic research indicates that the Slab Grave people were the primary ancestors of the Xiongnu, and that the Xiongnu formed through substantial and complex admixture with West Eurasians. During the Western Zhou (1045-771 BCE), there were numerous conflicts with nomadic tribes from the north and the northwest, variously known as the Xianyun, Guifang, or various “Rong” tribes, such as the Xirong, Shanrong or Quanrong. These tribes are recorded as harassing Zhou territory, but at the time the Zhou were expanding northwards, encroaching on their traditional lands, especially into the Wei River valley. Archaeologically, the Zhou expanded to the north and the northwest at the expense of the Siwa culture. The Quanrong put an end to the Western Zhou in 771 BC, sacking the Zhou capital of Haojing and killing the last Western Zhou king You. Thereafter the task of dealing with the northern tribes was left to their vassal, the Qin state.” ref
“To the west, the Pazyryk culture (6th-3rd century BCE) immediately preceded the formation of the Xiongnus. A Scythian culture, it was identified by excavated artifacts and mummified humans, such as the Siberian Ice Princess, found in the Siberian permafrost, in the Altay Mountains, Kazakhstan and nearby Mongolia. To the south, the Ordos culture had developed in the Ordos Loop (modern Inner Mongolia, China) during the Bronze and early Iron Age from the 6th to 2nd centuries BCE, and is of unknown ethno-linguistic origin, and is thought to represent the easternmost extension of Indo-European-speakers. The Yuezhi were displaced by the Xiongnu expansion in the 2nd century BCE, and had to migrate to Central and Southern Asia.” ref
“The Xiongnu confederation was unusually long-lived for a steppe empire. The purpose of raiding the Central Plain was not simply for goods, but to force the Central Plain polity to pay regular tribute. The power of the Xiongnu ruler was based on his control of Han tribute which he used to reward his supporters. The Han and Xiongnu empires rose at the same time because the Xiongnu state depended on Han tribute. A major Xiongnu weakness was the custom of lateral succession. If a dead ruler’s son was not old enough to take command, power passed to the late ruler’s brother. This worked in the first generation but could lead to civil war in the second generation. The first time this happened, in 60 BCE, the weaker party adopted what Barfield calls the ‘inner frontier strategy.’ They moved south and submitted to the dominant Central Plain regime and then used the resources obtained from their overlord to defeat the Northern Xiongnu and re-establish the empire. The second time this happened, about 47 CE, the strategy failed. The southern ruler was unable to defeat the northern ruler and the Xiongnu remained divided.” ref
“The Xiongnu empire is widely thought to have been multiethnic. There are several theories on the ethnolinguistic identity of the Xiongnu, though there is no consensus among scholars as to what language was spoken by the Xiongnu elite. Lajos Ligeti was the first to suggest that the Xiongnu spoke a Yeniseian language. In the early 1960s Edwin Pulleyblank was the first to expand upon this idea with credible evidence. The Yeniseian theory proposes that the Jie, a western Xiongnu people, spoke a Yeniseian language. Hyun Jin Kim notes that the 7th AD Chinese conpendium, Jin Shu, contains a transliterated song of Jie origin, which appears to be Yeniseian. This song has led researchers Pulleyblank and Vovin to argue for a Yeniseian Jie dominant minority, that ruled over the other Xiongnu ethnicities, like Iranian and Turkic people. Kim has stated that the dominant Xiongnu language was likely Turkic or Yeniseian, but has cautioned that the Xiongnu were definitely a multi-ethnic society.” ref
“Pulleybank and D. N. Keightley asserted that the Xiongnu titles “were originally Siberian words but were later borrowed by the Turkic and Mongolic peoples”. Titles such as tarqan, tegin and kaghan were also inherited from the Xiongnu language and are possibly of Yeniseian origin. For example, the Xiongnu word for “heaven” is theorized to come from Proto-Yeniseian *tɨŋVr. Vocabulary from Xiongnu inscriptions sometimes appears to have Yeniseian cognates which were used by Vovin to support his theory that the Xiongnu has a large Yeniseian component, examples of proposed cognates include words such as Xiongnu kʷala ‘son’ and Ket qalek ‘younger son’, Xiongnu sakdak ‘boot’ and Ket sagdi ‘boot’, Xiongnu gʷawa “prince” and Ket gij “prince”, Xiongnu “attij” ‘wife’ and proto-Yeniseian “alrit”, Ket “alit” and Xiongnu dar “north” compared to Yugh tɨr “north.” ref
“Pulleyblank also argued that because Xiongnu words appear to have clusters with r and l, in the beginning of the word it is unlikely to be of Turkic origin, and instead believed that most vocabulary we have mostly resemble Yeniseian languages. Alexander Vovin also wrote, that some names of horses in the Xiongnu language appear to be Turkic words with Yeniseian prefixes. An analysis by Savelyev and Jeong (2020) has cast doubt on the Yeniseian theory. If assuming that the ancient Yeniseians were represented by modern Ket people, who are more genetically similar to Samoyedic speakers, the Xiongnu do not display a genetic affinity for Yeniseian peoples. A review by Wilson (2023) argues that the presence of Yeniseian-speakers among the multi-ethnic Xiongnu should not be rejected, and that “Yeniseian-speaking peoples must have played a more prominent (than heretofore recognized) role in the history of Eurasia during the first millennium of the Common Era.” ref
Sino-Tibetan languages
“Sino-Tibetan, also cited as Trans-Himalayan in a few sources, is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 billion native speakers of Sinitic languages. Other Sino-Tibetan languages with large numbers of speakers include Burmese (33 million) and the Tibetic languages (6 million). Other languages of the family are spoken in the Himalayas, the Southeast Asian Massif, and the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau. Most of these have small speech communities in remote mountain areas, and as such are poorly documented.” ref
“Several low-level subgroups have been securely reconstructed, but reconstruction of a proto-language for the family as a whole is still at an early stage, so the higher-level structure of Sino-Tibetan remains unclear. Although the family is traditionally presented as divided into Sinitic (i.e. Chinese languages) and Tibeto-Burman branches, a common origin of the non-Sinitic languages has never been demonstrated. The Kra–Dai and Hmong–Mien languages are generally included within Sino-Tibetan by Chinese linguists but have been excluded by the international community since the 1940s. Several links to other language families have been proposed, but none have broad acceptance.” ref
“Laurent Sagart proposes a “Sino-Austronesian” family with Sino-Tibetan and Austronesian (including Kra–Dai as a subbranch) as primary branches. Stanley Starosta has extended this proposal with a further branch called “Yangzian” joining Hmong–Mien and Austroasiatic. The proposal has been largely rejected by other linguists who argue that the similarities between Austronesian and Sino-Tibetan more likely arose from contact rather than being genetic.” ref
“Proto-Austronesian (commonly abbreviated as PAN or PAn) is a proto-language. It is the reconstructed ancestor of the Austronesian languages, one of the world’s major language families. Proto-Austronesian is assumed to have begun to diversify c. 4000 BCE – c. 3500 BCE in Taiwan. Lower-level reconstructions have also been made, and include Proto-Malayo-Polynesian, Proto-Oceanic, and Proto-Polynesian. Recently, linguists such as Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley have built large lexicons for Proto-Oceanic and Proto-Polynesian.” ref
Altaic (Transeurasian)
“”Transeurasian” renaming: In Robbeets and Johanson (2010), there was a proposal to replace the name “Altaic” with the name “Transeurasian”. While “Altaic” has sometimes included Japonic, Koreanic, and other languages or families, but only on the consideration of particular authors, “Transeurasian” was specifically intended to always include Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, Japonic, and Koreanic. Robbeets and Johanson gave as their reasoning for the new term: 1) to avoid confusion between the different uses of Altaic as to which group of languages is included, 2) to reduce the counterproductive polarization between “Pro-Altaists” and “Anti-Altaists”; 3) to broaden the applicability of the term because the suffix -ic implies affinity while -an leaves room for an areal hypothesis; and 4) to eliminate the reference to the Altai mountains as a potential homeland. In Robbeets and Savelyev, ed. (2020) there was a concerted effort to distinguish “Altaic” as a subgroup of “Transeurasian” consisting only of Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic, while retaining “Transeurasian” as “Altaic” plus Japonic and Koreanic.” ref
“The linguistic relatedness of the Transeurasian languages—also known as ‘Altaic’—is among the most disputed issues in linguistic prehistory. Transeurasian denotes a large group of geographically adjacent languages stretching across Europe and northern Asia, and includes five uncontroversial linguistic families: Japonic, Koreanic, Tungusic, Mongolic, and Turkic. The question of whether these five groups descend from a single common ancestor has been the topic of a long-standing debate between supporters of inheritance and borrowing. Recent assessments show that even if many common properties between these languages are indeed due to borrowing, there is nonetheless a core of reliable evidence for the classification of Transeurasian as a valid genealogical group. Accepting this classification, however, gives rise to new questions about the time depth, location, cultural identity, and dispersal routes of ancestral Transeurasian speech communities.” ref
“Here researchers challenge the traditional ‘pastoralist hypothesis’ that identifies the primary dispersals of the Transeurasian languages with nomadic expansions starting in the eastern steppe in the fourth millennium years ago, by proposing a ‘farming hypothesis’, which places those dispersals within the scope of the ‘farming/language dispersal hypothesis’. As these issues reach far beyond linguistics, we address them by integrating archaeology and genetics in a single approach termed ‘triangulation.’ Bayesian methods to infer a dated phylogeny of the Transeurasian languages. Our results indicate a time-depth of 9,181 years ago (5595–12793 95% highest probability density (95% HPD)) for the Proto-Transeurasian root of the family; 6,811 years ago (4404–10166 95% HPD) for Proto-Altaic, the unity of Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic languages; 4,491 years ago (2599–6373 95% HPD) for Mongolo-Tungusic; and 5,458 years ago (3335–8024 95% HPD) for Japano-Koreanic. These dates estimate the time-depth of the initial break-up of a given language family into more than one foundational subgroup.” ref
“Although Neolithic Northeast Asia was characterized by widespread plant cultivation25, cereal farming expanded from several centers of domestication, the most important of which for Transeurasian was the West Liao basin, where cultivation of broomcorn millet started 9000 years ago. Extracting data from the published literature, we scored 172 archaeological features for 255 Neolithic and Bronze Age sites and compiled an inventory of 269 directly carbon-14-dated early crop remains in northern China, the Primorye, Korea, and Japan.” ref
Uralo-Altaic (Transeurasian) hypothesis
“In 1844, the Finnish philologist Matthias Castrén proposed a broader grouping which later came to be called the Ural–Altaic family, which included Turkic, Mongolian, and Manchu-Tungus (=Tungusic) as an “Altaic” branch, and also the Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic languages as the “Uralic” branch (though Castrén himself used the terms “Tataric” and “Chudic”). The name “Altaic” referred to the Altai Mountains in East-Central Asia, which are approximately the center of the geographic range of the three main families. The name “Uralic” referred to the Ural Mountains. While the Ural-Altaic family hypothesis can still be found in some encyclopedias, atlases, and similar general references, since the 1960s it has been heavily criticized. Even linguists who accept the basic Altaic family, such as Sergei Starostin, completely discard the inclusion of the “Uralic” branch. The term continues to be used for the central Eurasian typological, grammatical and lexical convergence zone. Indeed, “Ural-Altaic” may be preferable to “Altaic” in this sense. For example, Juha Janhunen states that “speaking of ‘Altaic’ instead of ‘Ural-Altaic’ is a misconception, for there are no areal or typological features that are specific to ‘Altaic’ without Uralic.” ref
Uralic languages
“The Uralic languages, sometimes called the Uralian languages (/jʊəˈreɪliən/ yoor-AY-lee-ən), form a language family of 42 languages spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (which alone accounts for approximately 60% of speakers), Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still, smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; and the Samoyedic languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia.” ref
“The name Uralic derives from the family’s purported “original homeland” (Urheimat) hypothesized to have been somewhere in the vicinity of the Ural Mountains, and was first proposed by Julius Klaproth in Asia Polyglotta (1823). Finno-Ugric is sometimes used as a synonym for Uralic, though Finno-Ugric is widely understood to exclude the Samoyedic languages. Scholars who do not accept the traditional notion that Samoyedic split first from the rest of the Uralic family may treat the terms as synonymous. Uralic langagues are known for their often complex case systems and vowel harmony. Many relationships between Uralic and other language families have been suggested, but none of these is generally accepted by linguists at the present time: All of the following hypotheses are minority views at the present time in Uralic studies.” ref
“Uralo-Siberian is an expanded form of the Eskimo–Uralic hypothesis. It associates Uralic with Yukaghir, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskimo–Aleut. It was propounded by Michael Fortescue in 1998. Michael Fortescue (2017) presented new evidence in favor for a connection between Uralic and other Paleo-Siberian languages. Theories proposing a close relationship with the Altaic languages were formerly popular, based on similarities in vocabulary as well as in grammatical and phonological features, in particular the similarities in the Uralic and Altaic pronouns and the presence of agglutination in both sets of languages, as well as vowel harmony in some.” ref
“For example, the word for “language” is similar in Estonian (keel) and Mongolian (хэл (hel)). These theories are now generally rejected and most such similarities are attributed to language contact or coincidence. All Uralic languages are thought to have descended, through independent processes of language change, from Proto-Uralic. The internal structure of the Uralic family has been debated since the family was first proposed. Doubts about the validity of most or all of the proposed higher-order branchings (grouping the nine undisputed families) are becoming more common.” ref
“Proto-Uralic is the unattested reconstructed language ancestral to the modern Uralic language family. The reconstructed language is thought to have been originally spoken in a small area in about 7000–2000 BCE (estimates vary), and then expanded across northern Eurasia, gradually diverging into a dialect continuum and then a language family in the process. The location of the area or Urheimat is not known, and various strongly differing proposals have been advocated, but the vicinity of the Ural Mountains is generally accepted as the most likely.” ref
“In the early 21st century, these tree-like models have been challenged by the hypothesis of larger number of proto-languages giving an image of a linguistic “comb” rather than a tree. Thus, the second-order groups of the Uralic phylum would then be Sami, Finnic, Mordvinic, Mari, Permic, Hungarian, Mansi, Khanty, and Samoyedic, all on equal footing. This order is both the order of geographical positions as well as linguistic similarity, with neighboring languages being more similar than distant ones.” ref
Origin of the Basques
“The origin of the Basques and the Basque language is a controversial topic that has given rise to numerous hypotheses. Modern Basque, a descendant or close relative of Aquitanian and Proto-Basque, is the only pre-Indo-European language that is extant in western Europe. The Basques have therefore long been supposed to be a remnant of a pre-Indo-European population of Europe.” ref
“The main hypotheses about the origin of the Basques are:
- Native origin, the mainstream theory, according to which the Basque language would have developed over the millennia entirely between the north of the Iberian Peninsula and the current south of France, without the possibility of finding any kind of relationship between the Basque language and other modern languages in other regions.
- Basque-Iberism theorizes the existence of a kinship between the Basque and the Iberian language, and therefore between their speakers.
- Caucasian origin theorizes that the Basque language and the languages of the Caucasus may have a direct relation, explaining why they share some linguistic typologies absent in the Indo-European languages.” ref
“In 2008, the Finnish linguist Kalevi Wiik proposed that the current Basque language is the remainder of a group of “Basque languages” that were spoken in the Paleolithic throughout western Europe and that retreated with the progress of the Indo-European languages. Wiik states that his theory coincides with the homogeneous distribution of the Haplogroup R1b in Atlantic Europe. Ludomir R. Lozny states that “Wiik’s controversial ideas are rejected by the majority of the scholarly community, but they have attracted the enormous interest of a wider audience.” ref
“In May 2012, the National Geographic Society Genographic Project released a study that showed through detailed DNA analysis of samples from French and Spanish Basque regions that Basques share unique genetic patterns that distinguish them from the surrounding non-Basque populations. The results of the study clearly support the hypothesis of a partial genetic continuity of contemporary Basques with the preceding Paleolithic/Mesolithic settlers of their homeland. Paleogenetic investigations by the Complutense University of Madrid indicate that the Basque people have a genetic profile coincident with the rest of the European population and that goes back to Prehistoric times.” ref
“The haplotype of the mitochondrial DNA known as U5 entered in Europe during the Upper Paleolithic and developed varieties as the U8a, native of the Basque Country, which is considered to be Prehistoric, and as the J group, which is also frequent in the Basque population. The works of Alzualde A, Izagirre N, Alonso S, Alonso A, de la Rua C. about mitochondrial DNA of the Human remains found in the Prehistoric graveyard of Alaieta, in Alava, note that there are no differences between these remains and others found across Atlantic Europe. Studies based on the Y chromosome genetically relate the Basques with the Celtic Welsh, and Irish; Stephen Oppenheimer from the University of Oxford says that the current inhabitants of the British Isles have their origin in the Basque refuge during the last Ice age.” ref
“Oppenheimer reached this conclusion through the study of correspondences in the frequencies of genetic markers between various European regions. The haplogroup R1b, can be found most frequently in the Basque Country (91%), Wales (89%), and Ireland (81%). The age of the subclade which Basque carry, Haplogroup R1b-DF27, “is estimated at ~4,200 years ago, at the transition between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age, when the Y chromosome landscape of Western Europe was thoroughly remodeled. In spite of its high frequency in Basques, Y-STR internal diversity of R1b-DF27 is lower there, and results in more recent age estimates”, implying it was brought to the region from elsewhere.” ref
“In 2015, a new scientific study of Basque DNA was published which seems to indicate that Basques are descendants of Neolithic farmers who mixed with local hunters before becoming genetically isolated from the rest of Europe for millennia. Mattias Jakobsson from Uppsala University in Sweden analysed genetic material from eight Stone Age human skeletons found in El Portalón Cavern in Atapuerca, northern Spain. These individuals lived between 3,500 and 5,500 years ago, after the transition to farming in southwest Europe. The results show that these early Iberian farmers are the closest ancestors to present-day Basques.” ref
“The official findings were published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. “Our results show that the Basques trace their ancestry to early farming groups from Iberia, which contradicts previous views of them being a remnant population that trace their ancestry to Mesolithic hunter-gatherer groups,” says Prof. Jakobsson. However, the results also showed that Basques, along with many other Iberian groups, carry both Neolithic farmer ancestry as well as some local mesolithic hunter-gatherer ancestry; showing that “the incoming farmers admixed with local, Iberian hunter-gather groups, a process that continued for at least 2 millennia.” ref
“Rather, some 4500 years ago almost all Y-DNA heritage from Iberian admixture of Mesolithic hunter-gatherers and Neolithic farmers was replaced by the lineage of Indo-European herders from the steppe, and the Basque genetic distinctiveness is a result of centuries of low population size, genetic drift, and endogamy. In 2019, a study was published in Science in which a more fine-tuned and deep time-transect of Iberian ancient populations including the Basque were analyzed. From their abstract, it says: “and we reveal that present-day Basques are best described as a typical Iron Age population without the admixture events that later affected the rest of Iberia.” This indicates Basques were isolated from admixture with outside groups since at least 1000 BCE or 3000 years before the present. In Iberia, these later admixture (interbreeding) events were with central European (Celtic), eastern Mediterranean, and northern African populations, and genomic ancestry from them is found in all or most present-day Iberian populations, except for the Basque.” ref
“Some researchers have propounded the similarities between the Basque language and the Caucasian languages, especially the Georgian language. The comparison between the matrilineal and patrilineal DNA of the native peoples from the Basque Country and Georgia has allowed the discovery of significant differences. The hypothesis that related both populations is only based on the typological similarities, which is not an accepted marker of linguistic kinship. These superficial similarities in the linguistic typologies do not seem to accompany a genetic relation at a population level. The possible relation between Basque and the languages of the Caucasus is denied by authors such as Larry Trask, who stated that the comparisons were wrongly made, given the fact that the Basque language was compared with several Caucasian languages at the same time.” ref
“In human genetics, Haplogroup R-DF27 (R1b1a2a1a2a) is a Y-chromosome haplogroup which is a subdivision of haplogroup R-M269 (more specifically, its subclade R-) defined by the presence of the marker DF27 (also known as S250). Along with R-U152 and R-L21, the lineage is to a significant extent associated with Proto-Celtic, Celtic and later Celtiberian movements. It arose comparatively recently, after the beginning of the European Bronze Age, and is mostly prevalent in the population of the Pyrenees region. The regions where it has been mostly found are Basque Country, Navarre, Asturias, Galicia, Portugal, Aragon, Catalonia, Pyrénées-Atlantiques as well as some presence in Great Britain and Ireland, though it has been found in smaller quantities as far away as Germany and Poland. Specific subclades of DF27 have been associated with specific groups of people, for example R-M167 is associated with the Catalans and R-M153 is associated with the Basques.” ref
“According to a 2017 article published in Springer Nature entitled, Analysis of the R1b-DF27 haplogroup shows that a large fraction of Iberian Y-chromosome lineages originated recently in situ, DF27 was found in frequences of 40% in the general population of the Iberian Peninsula and in particular spikes at 70% among the Basques. Overall in France it accounts for between 6–20% of the population but has a high level in the Pyrenees area. It is estimated to have developed around 4,200 years ago in north-eastern Prehistoric Iberia as the Neolithic made way for the Atlantic Bronze Age. The DF27 subgroups correspond closely to the various pre-Roman kingdoms formed by the Celtiberians.” ref
“Haplogroup R-M269 is the sub-clade of human Y-chromosome haplogroup R1b that is defined by the SNP marker M269. According to ISOGG 2020 it is phylogenetically classified as R1b1a1b. It underwent intensive research and was previously classified as R1b1a2 (2003 to 2005), R1b1c (2005 to 2008), R1b1b2 (2008 to 2011) and R1b1a1a2 (2011 to 2020). R-M269 is of particular interest for the genetic history of Western Europe, being the most common European haplogroup. It increases in frequency on an east to west gradient (its prevalence in Poland estimated at 22.7%, compared to Wales at 92.3%). It is carried by approximately 110 million European men (2010 estimate). The age of the mutation M269 is estimated at 4,000 to 10,000 years ago.” ref
“R-M269 is of particular interest for the genetic history of Western Europe, being the most common European haplogroup. It increases in frequency on an east to west gradient (its prevalence in Poland estimated at 22.7%, compared to Wales at 92.3%). It is carried by approximately 110 million European men (2010 estimate). The age of the mutation M269 is estimated at 4,000 to 10,000 years ago. R-M269 had formerly been dated to the Upper Paleolithic, but by about 2010 it was thought to have formed near the beginning of the Neolithic Revolution, about 10,000 years ago. More recent archaeogenetics studies since 2015, however, strongly suggest an origin among Eneolithic hunter-gatherers from eastern Europe.” ref
“Balaresque et al. (2010) based on the pattern of Y-STR diversity argued for a single source in the Near East and introduction to Europe via Anatolia in the Neolithic Revolution. In this scenario, Mesolithic hunter-gatherers in Europe would have been nearly replaced by the incoming farmers. By contrast, Busby et al. (2012) could not confirm the results of Balaresque et al. (2010) and could not make credible estimates of the age of R-M269 based on Y-STR diversity. Furthermore, more recent studies have found that the Y-DNA of Early European Farmers is typically haplogroup G2a.” ref
“According to a 2015 study, a hunter-gatherer from Samara (dated 5640-5555 cal BCE) belonging to haplogroup R1b1(*) was ancestral for both haplogroups R-M269 and R-M478. According to the authors, the occurrence of basal forms of R1b in eastern European hunter-gatherers provides a “geographically plausible source” for haplogroup R-M269. Subclades of R-M269, such as R-Z2103, have been found to be prevalent in ancient DNA found in individuals associated with the Yamnaya culture and related populations, and the dispersal of this haplogroup is associated with the spread of so-called “steppe ancestry” and at least some of the Indo-European languages. According to Lazaridis et al. (2022), “the most likely hypothesis” is that the entire R-M269 clade originated “in the North Caucasus and steppe to the north.” ref
“The subclade R-P311 is substantially confined to Western Europe in modern populations. R-P311 is absent from Neolithic-era ancient DNA found in Western Europe, strongly suggesting that its current distribution is due to population movements within Europe taking place after the end of the Neolithic. The three major subclades of P311 are U106 (S21), L21 (M529, S145), and U152 (S28). These show a clear articulation within Western Europe, with centers in the Low Countries, the British Isles, and the Alps, respectively. These lineages are associated with the non-Iberian steppe-related groups of the Bell Beaker culture, and demonstrate the relationship between steppe-related ancestry and R1b-M269 subclades, which are “the major lineage associated with the arrival of Steppe ancestry in western Europe after 2500 BCE.” ref
Proto-Euphratean language
“Proto-Euphratean is a hypothetical unclassified language or languages which was considered by some Assyriologists (such as Samuel Noah Kramer) to be the substratum language of the people who introduced farming into Southern Iraq in the Early Ubaid period (5300–4700 BCE). Dyakonov and Ardzinba identified these hypothetical languages with the Samarran culture. Benno Landsberger and other Assyriologists argued that by examining the structure of Sumerian names of occupations, as well as toponyms and hydronyms, one can suggest that there was once an earlier group of people in the region who spoke an entirely different language, often referred to as Proto-Euphratean. Terms for “farmer”, “smith”, “carpenter”, and “date” (the fruit) do not appear to have a Sumerian or Semitic origin.” ref
“Igor Dyakonov and Vladislav Ardzinba proposed a different term, “banana languages”, based on a characteristic feature of multiple personal names attested in Sumerian texts, namely reduplication of syllables (as in the English word banana): Inanna, Zababa, Chuwawa/Humbaba, Bunene, Pazuzu, etc found in Sumerian, Akkadian, Assyrian and Babylonian texts. The same feature was attested in some other unclassified languages, including Minoan. The same feature is allegedly attested by several names of Hyksos rulers: although the Hyksos tribes were Semitic Canaanites, some of their names, like Bnon, Apophis, etc. were apparently non-Semitic in origin. Rubio challenged the substratum hypothesis, arguing that there is evidence of borrowing from more than one language. This theory is now predominant in the field (Piotr Michalowski, Gerd Steiner, etc.). A related proposal by Gordon Whittaker is that the language of the proto-literary texts from the Late Uruk period (c. 3350–3100 BCE) is an early Indo-European language that he terms “Euphratic”, although this does not have mainstream support.” ref
Sumerian language
“Sumerian was the language of ancient Sumer. It is one of the oldest attested languages, dating back to at least 2900 BCE. It is a local language isolate that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia, in the area that is modern-day Iraq. Akkadian, a Semitic language, gradually replaced Sumerian as the primary spoken language in the area c. 2000 BCE (the exact date is debated), but Sumerian continued to be used as a sacred, ceremonial, literary, and scientific language in Akkadian-speaking Mesopotamian states such as Assyria and Babylonia until the 1st century CE. Thereafter, it seems to have fallen into obscurity until the 19th century, when Assyriologists began deciphering the cuneiform inscriptions and excavated tablets that had been left by its speakers.” ref
“In spite of its extinction, Sumerian exerted a significant impact on the languages of the area. The cuneiform script, originally used for Sumerian, was widely adopted by numerous regional languages such as Akkadian, Elamite, Eblaite, Hittite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian; it similarly inspired the Old Persian alphabet which was used to write the eponymous language. The impact was perhaps the greatest on Akkadian, whose grammar and vocabulary were significantly influenced by Sumerian. The pictographic writing system used during the Proto-literate period (3200 – 3000 BCE), corresponding to the Uruk III and Uruk IV periods in archeology, was still so rudimentary that there remains some scholarly disagreement about whether the language written with it is Sumerian at all, although it has been argued that there are some, albeit still very rare, cases of phonetic indicators and spelling that show this to be the case. The texts from this period are mostly administrative; there are also a number of sign lists, which were apparently used for the training of scribes.” ref
“The next period, Archaic Sumerian (3000 – 2500 BCE), is the first stage of inscriptions that indicate grammatical elements, so the identification of the language is certain. It includes some administrative texts and sign lists from Ur (c. 2800 BCE). Texts from Shuruppak and Abu Salabikh from 2600 to 2500 BC (the so-called Fara period or Early Dynastic Period IIIa) are the first to span a greater variety of genres, including not only administrative texts and sign lists, but also incantations, legal and literary texts (including proverbs and early versions of the famous works The Instructions of Shuruppak and The Kesh temple hymn). However, the spelling of grammatical elements remains optional, making the interpretation and linguistic analysis of these texts difficult.” ref
“The Old Sumerian period (2500-2350 BCE) is the first one from which well-understood texts survive. It corresponds mostly to the last part of the Early Dynastic period (ED IIIb) and specifically to the First Dynasty of Lagash, from where the overwhelming majority of surviving texts come. The sources include important royal inscriptions with historical content as well as extensive administrative records. Sometimes included in the Old Sumerian stage is also the Old Akkadian period (c. 2350 – c. 2200 BCE), during which Mesopotamia, including Sumer, was united under the rule of the Akkadian Empire. At this time Akkadian functioned as the primary official language, but texts in Sumerian (primarily administrative) did continue to be produced as well.” ref
“The first phase of the Neo-Sumerian period corresponds to the time of Gutian rule in Mesopotamia; the most important sources come from the autonomous Second Dynasty of Lagash, especially from the rule of Gudea, which has produced extensive royal inscriptions. The second phase corresponds to the unification of Mesopotamia under the Third Dynasty of Ur, which oversaw a “renaissance” in the use of Sumerian throughout Mesopotamia, using it as its sole official written language. There is a wealth of texts greater than from any preceding time – besides the extremely detailed and meticulous administrative records, there are numerous royal inscriptions, legal documents, letters, and incantations.” ref
“In spite of the dominant position of written Sumerian during the Ur III dynasty, it is controversial to what extent it was actually spoken or had already gone extinct in most parts of its empire. Some facts have been interpreted as suggesting that many scribes and even the royal court actually used Akkadian as their main spoken and native language. On the other hand, evidence has been adduced to the effect that Sumerian continued to be spoken natively and even remained dominant as an everyday language in Southern Babylonia, including Nippur and the area to its south.” ref
“By the Old Babylonian period (c. 2000 – c. 1600 BCE), Akkadian had clearly supplanted Sumerian as a spoken language in nearly all of its original territory, whereas Sumerian continued its existence as a liturgical and classical language for religious, artistic and scholarly purposes. In addition, it has been argued that Sumerian persisted as a spoken language at least in a small part of Southern Mesopotamia (Nippur and its surroundings) at least until about 1900 BCE and possibly until as late as 1700 BCE. Nonetheless, it seems clear that by far, the majority of scribes writing in Sumerian at this point were not native speakers, and errors resulting from their Akkadian mother tongue become apparent. For this reason, this period as well as the remaining time during which Sumerian was written are sometimes referred to as the “Post-Sumerian” period. The written language of administration, law, and royal inscriptions continued to be Sumerian in the undoubtedly Semitic-speaking successor states of Ur III during the so-called Isin-Larsa period (c. 2000 – c. 1750 BCE). The Old Babylonian Empire, however, mostly used Akkadian in inscriptions, sometimes adding Sumerian versions.” ref
“The Old Babylonian period, especially its early part, has produced extremely numerous and varied Sumerian literary texts: myths, epics, hymns, prayers, wisdom literature, and letters. In fact, nearly all preserved Sumerian religious and wisdom literature and the overwhelming majority of surviving manuscripts of Sumerian literary texts in general can be dated to that time, and it is often seen as the “classical age” of Sumerian literature. Conversely, far more literary texts on tablets surviving from the Old Babylonian period are in Sumerian than in Akkadian, even though that time is viewed as the classical period of Babylonian culture and language. However, it has sometimes been suggested that many or most of these “Old Babylonian Sumerian” texts may be copies of works that were originally composed in the preceding Ur III period or earlier, and some copies or fragments of known compositions or literary genres have indeed been found in tablets of Neo-Sumerian and Old Sumerian provenance. In addition, some of the first bilingual Sumerian-Akkadian lexical lists are preserved from that time (although the lists were still usually monolingual, and Akkadian translations did not become common until the late Middle Babylonian period), and there are also grammatical texts – essentially bilingual paradigms listing Sumerian grammatical forms and their postulated Akkadian equivalents.” ref
“After the Old Babylonian period or, according to some, as early as 1700 BCE, the active use of Sumerian declined. Scribes did continue to produce texts in Sumerian at a more modest scale, but generally with interlinear Akkadian translations, and only part of the literature known in the Old Babylonian period continued to be copied after its end around 1600 BCE. During the Middle Babylonian period, approximately from 1600 to 1000 BCE, the Kassite rulers continued to use Sumerian in many of their inscriptions, but Akkadian seems to have taken the place of Sumerian as the primary language of texts used for the training of scribes and their Sumerian itself acquires an increasingly artificial and Akkadian-influenced form. In some cases, a text may not even have been meant to be read in Sumerian; instead, it may have functioned as a prestigious way of “encoding” Akkadian via Sumerograms (cf. Japanese kanbun). Nonetheless, the study of Sumerian and copying of Sumerian texts remained an integral part of scribal education and literary culture of Mesopotamia and surrounding societies influenced by it and it retained that role until the eclipse of the tradition of cuneiform literacy itself in the beginning of the Common Era. The most popular genres for Sumerian texts after the Old Babylonian period were incantations, liturgical texts, and proverbs; among longer texts, the classics Lugal-e and An-gim were most commonly copied.” ref
“Sumerian is widely accepted to be a local language isolate. Sumerian was at one time widely held to be an Indo-European language, but that view has been almost universally rejected. Since its decipherment in the early 20th century, scholars have tried to relate Sumerian to a wide variety of languages. Because Sumerian has prestige as the first attested written language, proposals for linguistic affinity sometimes have a nationalistic flavor. Attempts have been made to link Sumerian with a range of widely disparate groups such as the Austroasiatic languages, Dravidian languages, Uralic languages such as Hungarian and Finnish, Sino-Tibetan languages and Turkic languages (the last being promoted by Turkish nationalists as part of the Sun language theory). Additionally, long-range proposals have attempted to include Sumerian in broad macrofamilies. Such proposals enjoy virtually no support among modern linguists, Sumerologists, and Assyriologists and are typically seen as fringe theories.” ref
“It has also been suggested that the Sumerian language descended from a late prehistoric creole language (Høyrup 1992). However, no conclusive evidence, only some typological features, can be found to support Høyrup’s view. A more widespread hypothesis posits a Proto-Euphratean language that preceded Sumerian in Mesopotamia and exerted an areal influence on it, especially in the form of polysyllabic words that appear “un-Sumerian”—making them suspect of being loanwords—and are not traceable to any other known language. There is little speculation as to the affinities of this substratum language, or these languages, and it is thus best treated as unclassified. Other researchers disagree with the assumption of a single substratum language and argue that several languages are involved. A related proposal by Gordon Whittaker is that the language of the proto-literary texts from the Late Uruk period (c. 3350–3100 BCE) is really an early Indo-European language which he terms “Euphratic.” ref
“The Marsh Arabs are descendants of the ancient Sumerians and Akkadians and are groups of tribal people who make their home in this lush environment. This group of people developed a unique culture in antiquity centered on the natural resources of the marshes.” ref
“The Marsh Arabs (Arabic: عرب الأهوار ʻArab al-Ahwār “Arabs of the Marshlands”), also referred to as Ahwaris, the Maʻdān (Arabic: معدان “dweller in the plains”) or Shroog (Mesopotamian Arabic: شروگ “those from the east”)—the latter two often considered derogatory in the present day—are Arab inhabitants of the Mesopotamian marshlands in the modern-day south Iraq, as well as in the Hawizeh Marshes straddling the Iraq-Iran border. The origins of Marsh Arabs are still a matter of some dispute. British colonial ethnographers found it difficult to classify some of Ahwaris’ social customs and speculated that they might have originated in India. They may have descended from Zuṭṭ, who moved to the region of lower Iraq in the 8th and 9th centuries and followed similar customs and traditions.” ref
“Some scholars such as Ali al-Wardi have claimed they are descended from the Nabataeans of Iraq, the Aramaic-speaking people who inhabited Lower Mesopotamia in the Middle Ages, and some of their clans even follow their ancestry to Islamized Mandaeans. Other scholars have proposed historical and genetic links between the Marsh Arabs and the ancient Sumerians due to shared agricultural practices, methods of house-building, and location. There is, however, no written record of the marsh tribes until the ninth century and the Sumerians lost their distinct ethnic identity by around 1800 BCE, some 2700 years before. Links to Sumerian genetics can likely be traced back to the Arabization and assimilation of indigenous Mesopotamians.” ref
“A 2011 study showed that Marsh Arabs have a high concentration of Y-chromosomal Haplogroup J-M267 and mtDNA haplogroup J having the highest concentration, with haplogroups H, U and T following, the study included 143 Marsh Arab samples. According to this study, Marsh Arabs have the following haplogroups.
- Y-DNA haplogroups:
- E1b1b 6.3% (-M35* 2.1%, -M78* 0.7%, -M123* 1.4%, -M34 2.1%)
- G-M201 1.4%
- J1 81.1% (-M267* 7.0%, -P58 (Page08)* 72.7%, -M365 (shared with other J1 branches) 1.4%), J2-M172* 3.5%
- L-M76 0.7%
- Q-M242 2.8% (Q1a1b-M25 0.7%, Q1b-M378 2.1%)
- R-M207 4.2% (R1-L23 2.8%, R2-M124 1.4%)
- Mt-DNA haplogroups:
- West Eurasia (77.8%): R0 24.1% (R0* 0.7%, R0a 6.9%, HV 4.1%, H 12.4%), KU 15.9% (K 6.2%, U 9.7%), JT 22.7% (J 15.2%, T 7.6%), N 15.1% (I 0.7%, N1 8.2%, W 4.8%, X2 1.4%)
- North/East Africa (2.8%): M1 2.8%
- Sub-Saharan Africa (4.9%): L 4.9%
- East Asia (1.4%): B4c2 1.4%
- Southwest Asia (10.4%): M* 0.7%, M3 2.1%, R2 2.8%, U7 4.8%
- Others (2.8%): N* 0.7%, R* 2.1%” ref
“The term Maʻdān was used disparagingly by desert tribes to refer to those inhabiting the Iraqi river basins, as well as by those who farmed in the river basins to refer to the population of the marshes. Ahwaris speak South Mesopotamian Arabic and traditionally wore a variant of normal Arab dress: for males, a thawb (“long shirt”; in recent times, occasionally with a Western-style jacket over the top) and a keffiyeh (“headcloth”) worn twisted around the head in a turban, as few could afford an ʻiqāl. The society of the Marsh Arabs was divided into two main groups by occupation. One group bred and raised water buffaloes while others cultivated crops such as rice, barley, wheat, and pearl millet; they also kept some sheep and cattle. Rice cultivation was especially important; it was carried out in small plots cleared in April and sown in mid-May. Cultivation seasons were marked by the rising and setting of certain stars, such as the Pleiades and Sirius.” ref
“Some Ahwari branches were nomadic pastoralists, erecting temporary dwellings and moving buffaloes around the marshes according to the season. Some fishing, especially of species of barbel (notably the binni or bunni, Mesopotamichthys sharpeyi), was practiced using spears and datura poison, but large-scale fishing using nets was until recent times regarded as a dishonorable profession by Ahwaris and was mostly carried out by a separate low-status tribe known as the Berbera. By the early 1990s, however, up to 60% of the total amount of fish caught in Iraq’s inland waters came from the marshes. In the later twentieth century, a third main occupation entered Marsh Arab life; the weaving of reed mats on a commercial scale. Though they often earned far more than workers in agriculture, weavers were looked down upon by both Ahwaris and farmers alike: however, financial concerns meant that it gradually gained acceptance as a respectable profession.” ref
“As with most tribes of southern Iraq, the main authority was the tribal shaikh. To this day, the shaikh of a Marsh Arab group will collect a tribute from his tribe in order to maintain the mudhif, the tribal guesthouse, which acts as the political, social, judicial and religious centre of Marsh Arabic life. The mudhif is used as a place to settle disputes, to carry out diplomacy with other tribes and as a gathering point for religious and other celebrations. It is also the place where visitors are offered hospitality. Although the tribal shaykh was the principal figure, each Ahwari village (which may have contained members of several different tribes) would also follow the authority of the hereditary qalit “headman” of a tribe’s particular section. Blood feuds, which could only be settled by the qalit, were a feature of Marsh Arab life, in common with that of the Arab bedouin. Many of the Marsh Arabs’ codes of behaviour were similar to those of the desert tribes.” ref
“Most Marsh Arabs lived in arched reed houses considerably smaller than a mudhif. The typical dwelling was usually a little more than two meters wide, about six meters long, and a little less than three meters high, and was either constructed at the waterside or on an artificial island of reeds called a kibasha; a more permanent island of layered reeds and mud was called a dibin. Houses had entrances at both ends and a screen in the middle; one end was used as a dwelling and the other end (sometimes extended with a sitra, a long reed structure) was used to shelter animals in bad weather. A raba was a higher-status dwelling, distinguished by a north-facing entrance, which also served as a guesthouse where there was no mudhif. Traditional boats (the mashoof and tarada) were used as transport: Ahwaris would drive buffalo through the reedbeds during the season of low water to create channels, which would then be kept open by constant use, for the boats. The marsh environment meant that certain diseases, such as schistosomiasis and malaria, were endemic; Ahwari agriculture and homes were also vulnerable to periodic droughts and flooding.” ref
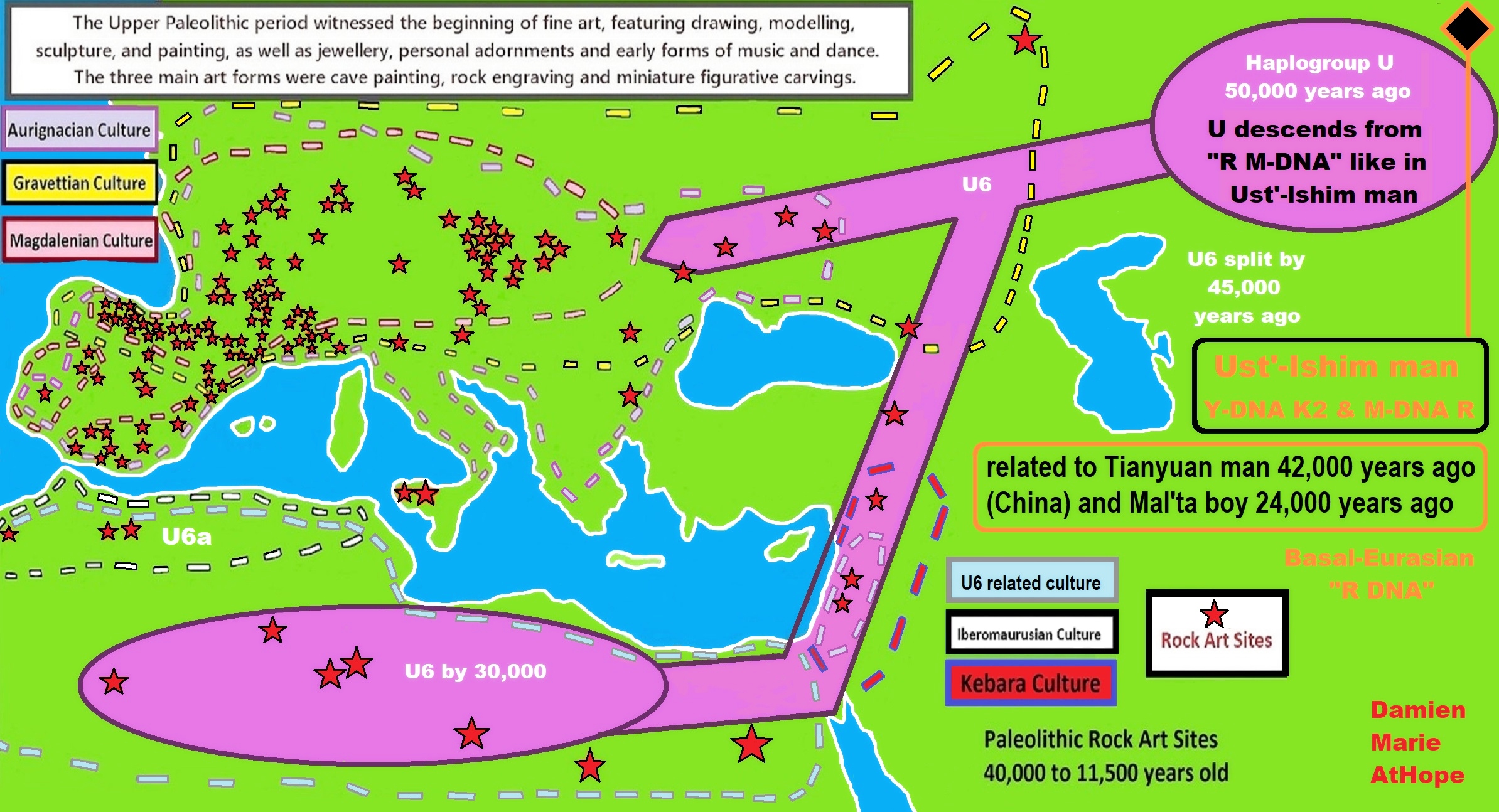
“Ust’-Ishim man is the term given to the 45,000-year-old remains of one of the early modern humans to inhabit western Siberia. He belonged to mitochondrial DNA haplogroup R*, differing from the root sequence of R by a single mutation. Ust’-Ishim man belongs to Y-DNA haplogroup K2. The two subclades of K2 are K2a and K2b. Haplogroup K is believed to have originated in the mid-Upper Paleolithic. It is the most common subclade of haplogroup U8b. The haplogroup U8b’s most common subclade is haplogroup K, and makes up a sizeable fraction of European and West Asian mtDNA lineages.” ref, ref, ref
“Both of these haplogroups and descendant subclades are now found among populations throughout Eurasia, Oceania, and The Americas, although no direct descendants of Ust Ishim man’s specific lineages are known from modern populations. Examination of the sequenced genome indicates that Ust’-Ishim man lived at a point in time (270,000 to 45,000 years ago) between the first wave of anatomically modern humans that migrated out of Africa and the divergence of that population into distinct populations, in terms of autosomal DNA in different parts of Eurasia. Consequently, Ust’-Ishim man is not more closely related to the first two major migrations of Homo Sapiens eastward from Africa into Asia: a group that migrated along the coast of South Asia, or a group that moved north-east through Central Asia. When compared to other ancient remains, Ust’-Ishim man is more closely related, in terms of autosomal DNA to Tianyuan man, found near Beijing and dating from 42,000 to 39,000 years ago; Mal’ta boy (or MA-1), a child who lived 24,000 years ago along the Bolshaya Belaya River near today’s Irkutsk in Siberia, or; La Braña man – a hunter-gatherer who lived in La Braña (modern Spain) about 8,000 years ago.” ref
“Ust’-Ishim was equally related to modern East Asians, Oceanians, and West Eurasian populations, such as the ancient Europeans. Modern Europeans are more closely related to other ancient remains. “The finding that the Ust’-Ishim individual is equally closely related to present-day Asians and to 8,000- to 24,000-year-old individuals from western Eurasia, but not to present-day Europeans, is compatible with the hypothesis that present-day Europeans derive some of their ancestry from a population that did not participate in the initial dispersals of modern humans into Europe and Asia.”In a 2016 study, modern Tibetans were identified as the modern population that has the most alleles in common with Ust’-Ishim man. According to a 2017 study, “Siberian and East Asian populations shared 38% of their ancestry” with Ust’-Ishim man. A 2021 study found that “the Ust’Ishim and Oase1 individuals showed no more affinity to western than to eastern Eurasian populations, suggesting that they did not contribute ancestry to later Eurasian populations, as previously shown.” ref
Paleolithic Y-chromosomal haplogroups by chronological period
- Proto-Aurignacian (47,000 to 43,000 years before present; eastern Europe): F
- Aurignacian Culture (43,000 to 28,000 ybp ; all ice-free Europe): CT, C1a, C1b, I
- Gravettian Culture (31,000 to 24,000 ybp ; all ice-free Europe): BT, CT, F, C1a2
- Epiravettian Culture (22,000 to 8,000 ybp ; Italy): R1b1a
- Magdalenian Culture 17,000 to 12,000 ybp ; Western Europe): IJK, I
- Epipaleolithic France (13,000 to 10,000 ybp): I
- Azilian Culture (12,000 to 9,000 ybp ; Western Europe): I2 ref
Paleolithic mitochondrial haplogroups by chronological period
- Proto-Aurignacian (47,000 to 43,000 years before present ; eastern Europe): N, R*
- Aurignacian Culture (43,000 to 28,000 ybp ; all ice-free Europe): M, U, U2, U6
- Gravettian Culture (31,000 to 24,000 ybp ; all ice-free Europe): M, U, U2’3’4’7’8’9, U2 (x5), U5 (x5), U8c (x2)
- Solutrean Culture (22,000 to 17,000 ybp ; France, Spain): U
- Epiravettian Culture (22,000 to 8,000 ybp ; Italy): U2’3’4’7’8’9, U5b2b (x2)
- Magdalenian Culture 17,000 to 12,000 ybp ; Western Europe): R0, R1b, U2’3’4’7’8’9, U5b (x2), U8a (x5)
- Epipaleolithic France (13,000 to 10,000 ybp): U5b1, U5b2a, U5b2b (x2)
- Epipaleolithic Germany (13,000 to 11,000 ybp): U5b1 (x2)
- Azilian Culture (12,000 to 9,000 ybp ; Western Europe): U5b1h ref
Mesolithic Y-chromosomal haplogroups by country
- Ireland: I2a1b, I2a2
- Britain: IJK, I2a2 (x2)
- France: I (x3), I2a1b2
- Luxembourg: I2a1b
- Germany: I2a2a
- Spain: C1a2
- Italy: I, I2a2
- Sweden: I2a1 (x2), I2a1a1a*, I2a1b (x2), I2c2
- Estonia: R1a-YP1272
- Latvia: I2a1 (x2), I2a1b, I2a2a1, I2a2a1b (x2), Q1a2, R1b1a1a-P297 (x7)
- Lithuania: I2a1b, I2a1a2a1a-L233
- Serbia: I, I2 (x2), I2a1, I2a2, I2a2a-M223, I2a2a-Z161 (x2), R, R1b1a-L794 (x8)
- Romania: R, R1, R1b
- Ukraine: IJ, I (x4), I2, I2a1, I2a2, I2a2a, I2a2a1b1-L702 (x2), R1a, R1b1a-L794
- Russia: J, R1a1* (x3), R1a1-YP1301, R1b1a, R1b1a1a-P297 ref
Mesolithic mitochondrial haplogroups by country
Note that the very late Mesolithic Pitted Ware culture (c. 3200–2300 BCE) in Sweden is listed separately as it is possible that intermarriages with Neolithic or Chalcolithic neighbors took place.
- Croatia: U5b2a5
- France: U5a2 (x2), U5b1, U5b1b
- Germany, Luxembourg: U2e, U4, U5a, U5a2c (x2), U5a2c3, U5b (x2), U5b1a, U5b1d1 (x2), U5b2a2, U5b2c1
- Greece: K1c (x2)
- Italy: U5b1
- Lithuania: U4, U5b (x3)
- Poland: U5a, U5b (x2), U5b1b
- Spain: U5b, U5b1, U5b2c1 (x2)
- Russia: C, C1g, C5d, D, H, U2e, U4 (x3), U4a, U4a1, U5a (x3), U5a1 (x2), U5a1d, T, Z1a (x2)
- Sweden: U2e1 (x2), U4b1, U5a1 (x3), U5a2, U5a2d (x2)
- Sweden (Pitted Ware): H, H1f, HV0 (x2), K1a, K1a1 (x3), T2b (x2), U, U4 (x8), U4a1, U4d (x3), U5a, U5a1a’g (x2), U5b (x2), U5b1, U5b2b1a ref
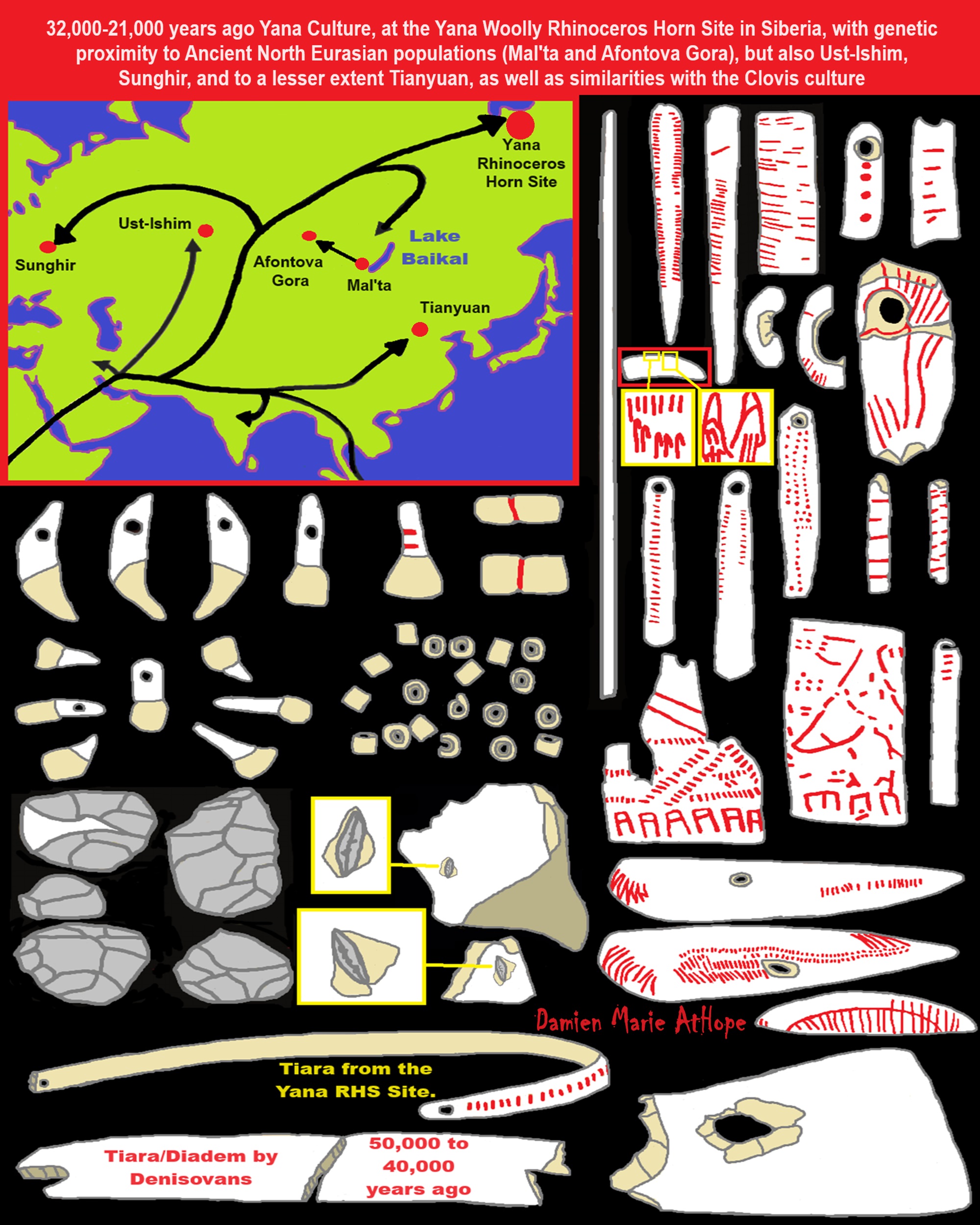
32,000-21,000 years ago, Yana Culture, at the Yana Woolly Rhinoceros Horn Site in Siberia, with genetic proximity to Ancient North Eurasian populations (Mal’ta, Afontova Gora), but also Ust-Ishim, Sunghir, and to a lesser extent Tianyuan, as well as similarities with the Clovis culture
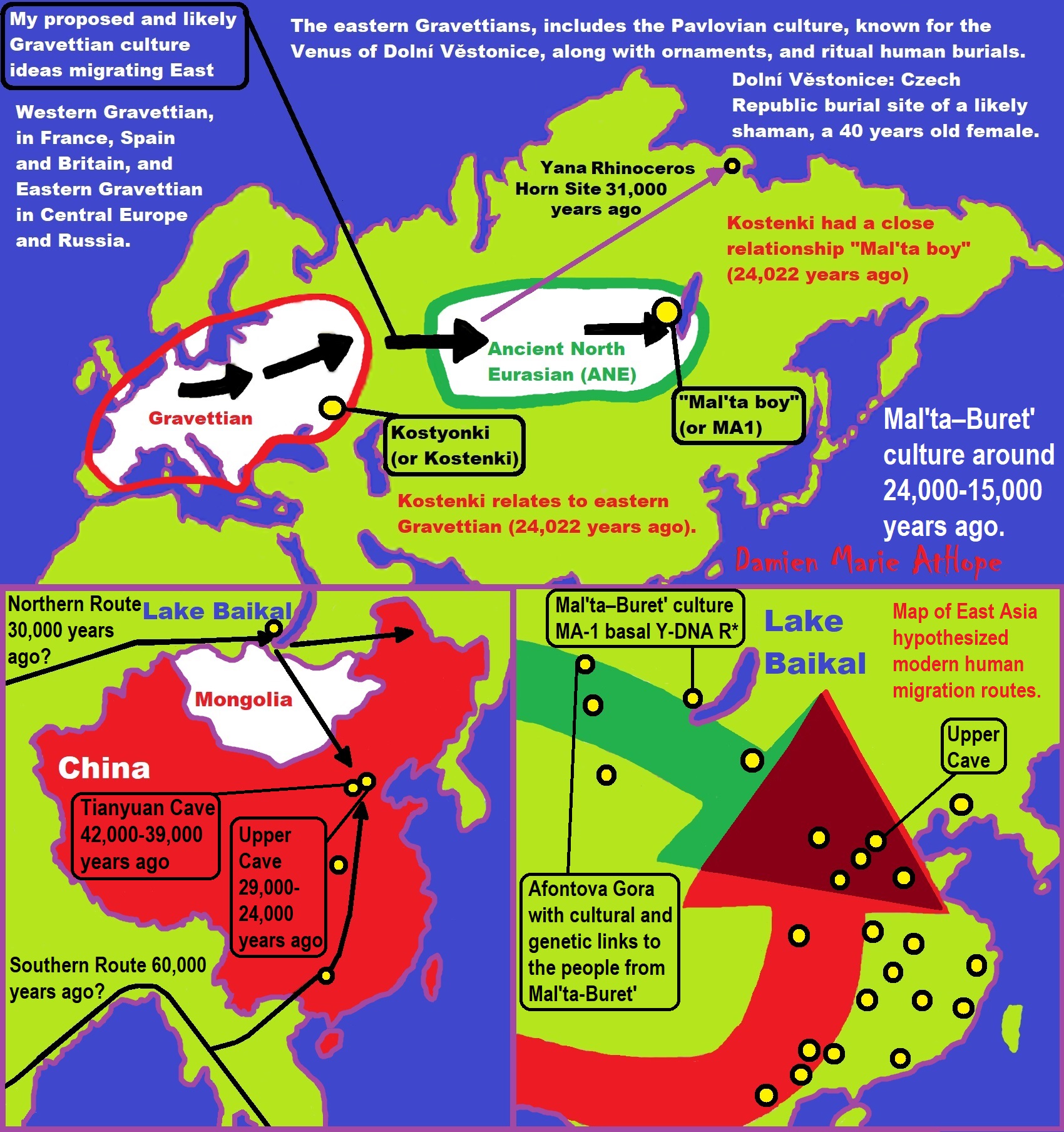
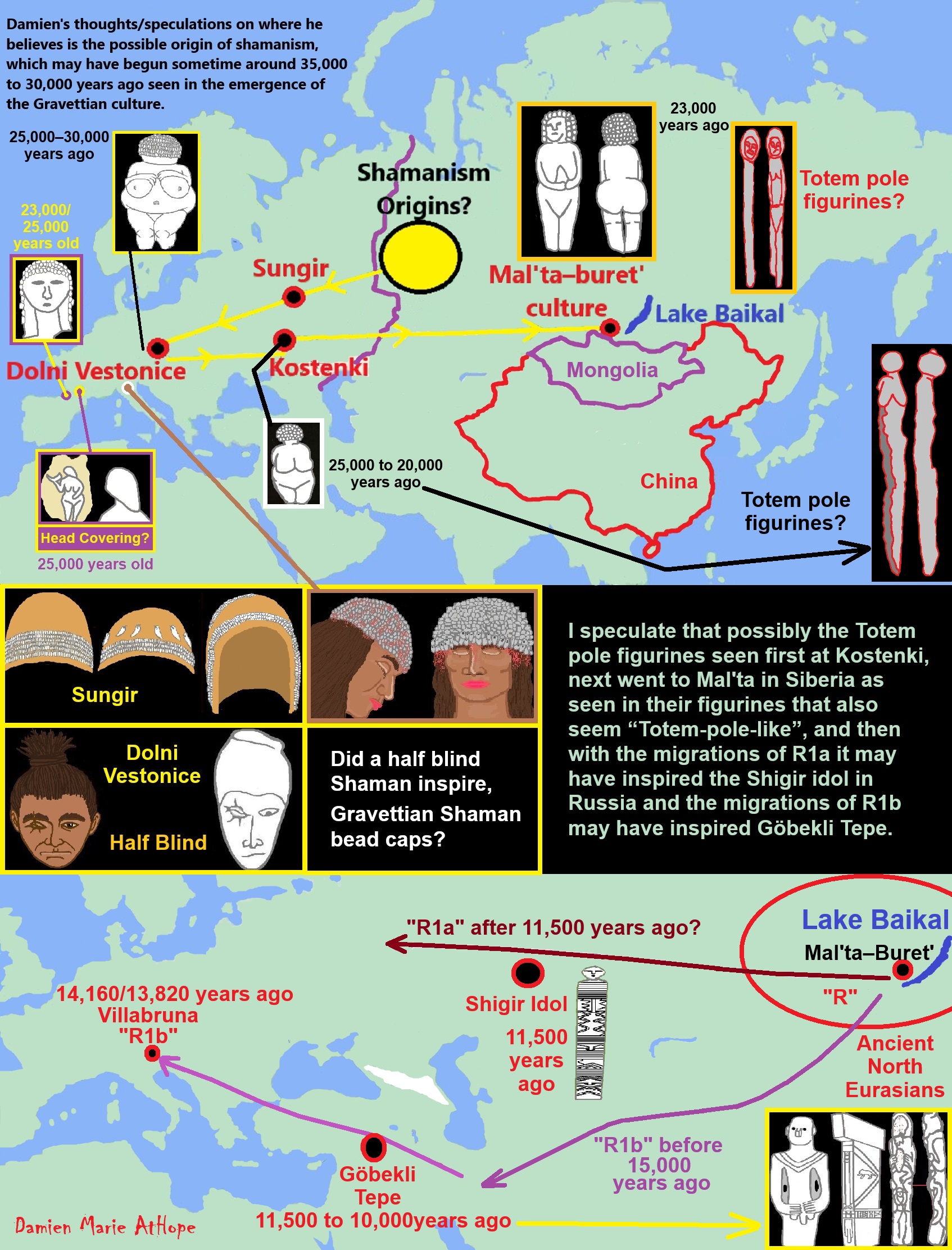
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Here are my thoughts/speculations on where I believe is the possible origin of shamanism, which may have begun sometime around 35,000 to 30,000 years ago seen in the emergence of the Gravettian culture, just to outline his thinking, on what thousands of years later led to evolved Asian shamanism, in general, and thus WU shamanism as well. In both Europe-related “shamanism-possible burials” and in Gravettian mitochondrial DNA is a seeming connection to Haplogroup U. And the first believed Shaman proposed burial belonged to Eastern Gravettians/Pavlovian culture at Dolní Věstonice in southern Moravia in the Czech Republic, which is the oldest permanent human settlement that has ever been found. It is at Dolní Věstonice where approximately 27,000-25,000 years ago a seeming female shaman was buried and also there was an ivory totem portrait figure, seemingly of her.
And my thoughts on how cultural/ritual aspects were influenced in the area of Göbekli Tepe. I think it relates to a few different cultures starting in the area before the Neolithic. Two different groups of Siberians first from northwest Siberia with U6 haplogroup 40,000 to 30,000 or so. Then R Haplogroup (mainly haplogroup R1b but also some possible R1a both related to the Ancient North Eurasians). This second group added its “R1b” DNA of around 50% to the two cultures Natufian and Trialetian. To me, it is likely both of these cultures helped create Göbekli Tepe. Then I think the female art or graffiti seen at Göbekli Tepe to me possibly relates to the Epigravettians that made it into Turkey and have similar art in North Italy. I speculate that possibly the Totem pole figurines seen first at Kostenki, next went to Mal’ta in Siberia as seen in their figurines that also seem “Totem-pole-like”, and then with the migrations of R1a it may have inspired the Shigir idol in Russia and the migrations of R1b may have inspired Göbekli Tepe.
“Migration from Siberia behind the formation of Göbeklitepe: Expert states. People who migrated from Siberia formed the Göbeklitepe, and those in Göbeklitepe migrated in five other ways to spread to the world, said experts about the 12,000-year-old Neolithic archaeological site in the southwestern province of Şanlıurfa.“ The upper paleolithic migrations between Siberia and the Near East is a process that has been confirmed by material culture documents,” he said.” ref
“Semih Güneri, a retired professor from Caucasia and Central Asia Archaeology Research Center of Dokuz Eylül University, and his colleague, Professor Ekaterine Lipnina, presented the Siberia-Göbeklitepe hypothesis they have developed in recent years at the congress held in Istanbul between June 11 and 13. There was a migration that started from Siberia 30,000 years ago and spread to all of Asia and then to Eastern and Northern Europe, Güneri said at the international congress.” ref
“The relationship of Göbeklitepe high culture with the carriers of Siberian microblade stone tool technology is no longer a secret,” he said while emphasizing that the most important branch of the migrations extended to the Near East. “The results of the genetic analyzes of Iraq’s Zagros region confirm the traces of the Siberian/North Asian indigenous people, who arrived at Zagros via the Central Asian mountainous corridor and met with the Göbeklitepe culture via Northern Iraq,” he added.” ref
“Emphasizing that the stone tool technology was transported approximately 7,000 kilometers from east to west, he said, “It is not clear whether this technology is transmitted directly to long distances by people speaking the Turkish language at the earliest, or it travels this long-distance through using way stations.” According to the archaeological documents, it is known that the Siberian people had reached the Zagros region, he said. “There seems to be a relationship between Siberian hunter-gatherers and native Zagros hunter-gatherers,” Güneri said, adding that the results of genetic studies show that Siberian people reached as far as the Zagros.” ref
“There were three waves of migration of Turkish tribes from the Southern Siberia to Europe,” said Osman Karatay, a professor from Ege University. He added that most of the groups in the third wave, which took place between 2600-2400 BCE, assimilated and entered the Germanic tribes and that there was a genetic kinship between their tribes and the Turks. The professor also pointed out that there are indications that there is a technology and tool transfer from Siberia to the Göbeklitepe region and that it is not known whether people came, and if any, whether they were Turkish.” ref
“Around 12,000 years ago, there would be no ‘Turks’ as we know it today. However, there may have been tribes that we could call our ‘common ancestors,’” he added. “Talking about 30,000 years ago, it is impossible to identify and classify nations in today’s terms,” said Murat Öztürk, associate professor from İnönü University. He also said that it is not possible to determine who came to where during the migrations that were accepted to have been made thousands of years ago from Siberia. On the other hand, Mehmet Özdoğan, an academic from Istanbul University, has an idea of where “the people of Göbeklitepe migrated to.” ref
“According to Özdoğan, “the people of Göbeklitepe turned into farmers, and they could not stand the pressure of the overwhelming clergy and started to migrate to five ways.” “Migrations take place primarily in groups. One of the five routes extends to the Caucasus, another from Iran to Central Asia, the Mediterranean coast to Spain, Thrace and [the northwestern province of] Kırklareli to Europe and England, and one route is to Istanbul via [Istanbul’s neighboring province of] Sakarya and stops,” Özdoğan said. In a very short time after the migration of farmers in Göbeklitepe, 300 settlements were established only around northern Greece, Bulgaria, and Thrace. “Those who remained in Göbeklitepe pulled the trigger of Mesopotamian civilization in the following periods, and those who migrated to Mesopotamia started irrigated agriculture before the Sumerians,” he said.” ref
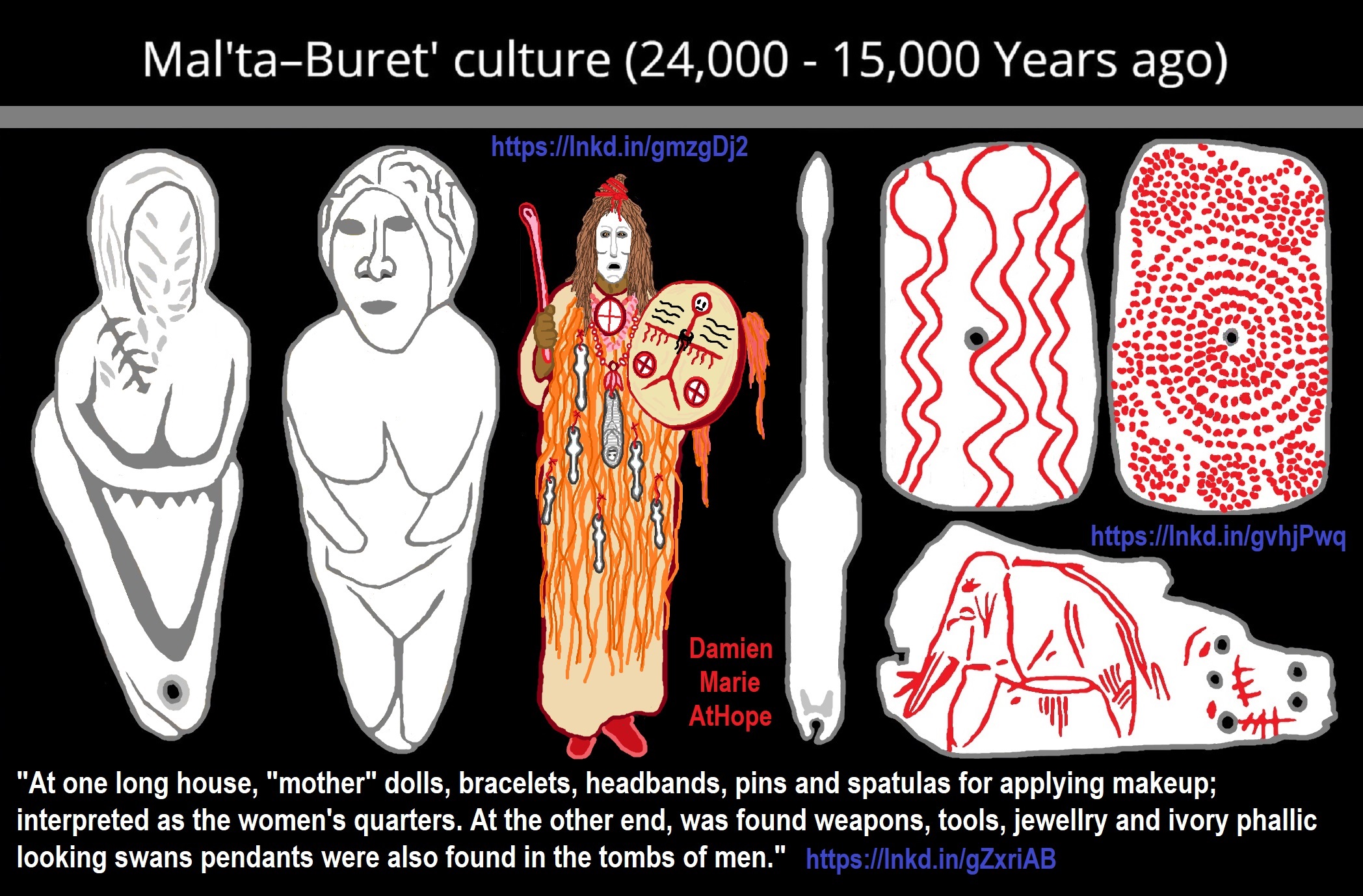
Mal’ta–Buret’ culture
“The Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (also Maltinsko-buretskaya culture) is an archaeological culture of the Upper Paleolithic (generally dated to 24,000-15,000 years ago). It is located roughly northwest of Lake Baikal, about 90km to the northwest of Irkutsk, on the banks of the upper Angara River. The type sites are named for the villages of Mal’ta (Мальта́), Usolsky District and Buret’ (Буре́ть), Bokhansky District (both in Irkutsk Oblast).” ref
“A boy whose remains were found near Mal’ta is usually known by the abbreviation MA-1 (or MA1) dated to 24,000 years ago. According to research published since 2013, MA-1 belonged to the population of Ancient North Eurasians, who were genetically “intermediate between modern western Eurasians and Native Americans, but distant from east Asians”, and partial genetic ancestors of Siberians, American Indians, and Bronze Age Yamnaya and Botai people of the Eurasian steppe. In particular, modern-day Native Americans, Kets, Mansi, and Selkup have been found to harbor a significant amount of ancestry related to MA-1. MA-1 is the only known example of basal Y-DNA R* (R-M207*) – that is, the only member of haplogroup R* that did not belong to haplogroups R1, R2, or secondary subclades of these. The mitochondrial DNA of MA-1 belonged to an unresolved subclade of haplogroup U.” ref
“Mal’ta consists of semi-subterranean houses that were built using large animal bones to assemble the walls, and reindeer antlers covered with animal skins to construct a roof that would protect the inhabitants from the harsh elements of the Siberian weather. These dwellings built from mammoth bones were similar to those found in Upper Paleolithic Western Eurasia, such as in the areas of France, Czechoslovakia, and Ukraine. Evidence seems to indicate that Mal’ta is the most ancient known site in eastern Siberia, with the nearby site of Buret’.” ref
“However, relative dating illustrates some irregularities. The use of flint flaking and the absence of pressure flaking used in the manufacture of tools, as well as the continued use of earlier forms of tools, seem to confirm the fact that the site belongs to the early Upper Paleolithic. Yet it lacks typical skreblos (large side scrapers) that are common in other Siberian Paleolithic sites. Additionally, other common characteristics such as pebble cores, wedge-shaped cores, burins, and composite tools have never been found. The lack of these features, combined with an art style found in only one other nearby site (the Venus of Buret’), make Mal’ta culture unique in Siberia.” ref
“There were two main types of art during the Upper Paleolithic: mural art, which was concentrated in Western Europe, and portable art. Portable art, typically some type of carving in ivory tusk or antler, spans the distance across Western Europe into Northern and Central Asia. Artistic remains of expertly carved bone, ivory, and antler objects depicting birds and human females are the most commonly found; these objects are, collectively, the primary source of Mal’ta’s acclaim.” ref
“In addition to the female statuettes there are bird sculptures depicting swans, geese, and ducks. Through ethnographic analogy comparing the ivory objects and burials at Mal’ta with objects used by 19th and 20th-century Siberian shamans, it has been suggested that they are evidence of a fully developed shamanism. Also, there are engraved representations on slabs of mammoth tusk. One is the figure of a mammoth, easily recognizable by the trunk, tusks, and thick legs. Wool also seems to be etched, by the placement of straight lines along the body. Another drawing depicts three snakes with their heads puffed up and turned to the side. It is believed that they were similar to cobras.” ref
“Perhaps the best example of Paleolithic portable art is something referred to as “Venus figurines“. The Mal’ta boy (dated 24,000 years ago) was buried with various artifacts and a Venus figurine. Until they were discovered in Mal’ta, “Venus figurines” were previously found only in Europe. Carved from the ivory tusk of a mammoth, these images were typically highly stylized, and often involved embellished and disproportionate characteristics (typically the breasts or buttocks). It is widely believed that these emphasized features were meant to be symbols of fertility. Around thirty female statuettes of varying shapes have been found in Mal’ta. The wide variety of forms, combined with the realism of the sculptures and the lack of repetitiveness in detail, are definite signs of developed, albeit early, art.” ref
“At first glance, what is obvious is that the Mal’ta Venus figurines are of two types: full-figured women with exaggerated forms, and women with a thin, delicate form. Some of the figures are nude, while others have etchings that seem to indicate fur or clothing. Conversely, unlike those found in Europe, some of the Venus figurines from Mal’ta were sculpted with faces. Most of the figurines were tapered at the bottom, and it is believed that this was done to enable them to be stuck into the ground or otherwise placed upright. Placed upright, they could have symbolized the spirits of the dead, akin to “spirit dolls” used nearly worldwide, including in Siberia, among contemporary people.” ref
“The Mal’ta figurines garner interest in the western world because they seem to be of the same basic form as European female figurines of roughly the same time period, suggestion some cultural and cultic connection. This similarity between Mal’ta and Upper Paleolithic Europe coincides with other suggested similarities between the two, such as in their tools and dwelling structures. A 2016 genomic study shows that the Mal’ta people have no genetic connections to the Dolní Věstonice people from the Gravettian culture. The researchers conclude that the similarity between the figurines may be either due to cultural diffusion or to a coincidence, but not to common ancestry between the populations.” ref
“Discussing this easternmost outpost of paleolithic culture, Joseph Campbell finishes by commenting on the symbolic forms of the artifacts found there:
We are clearly in apaleolithicprovince where theserpent,labyrinth, and rebirth themes already constitute a symbolic constellation, joined with the imagery of the sunbird andshamanflight, with the goddess in her classic role ofprotectress of the hearth, mother of man’s second birth, andlady of wild thingsand of the food supply.” ref
“The term Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) has been given in genetic literature to an ancestral component that represents descent from the people similar to the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture and the closely related population of Afontova Gora. A people similar to MA1 and Afontova Gora were important genetic contributors to Native Americans, Siberians, Europeans, Caucasians, Central Asians, with smaller contributions to Middle Easterners and some East Asians. Lazaridis et al. (2016) notes “a cline of ANE ancestry across the east-west extent of Eurasia.” The “ANE-cline”, as observed among Paleolithic Siberian populations and their direct descendants, developed from a sister lineage of Europeans with significant admixture from early East Asians. MA1 is also related to two older Upper Paleolithic Siberian individuals found at the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site called Ancient North Siberians (ANS).” ref
Afontova Gora
“Afontova Gora is a Late Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic Siberian complex of archaeological sites located on the left bank of the Yenisei River near the city of Krasnoyarsk, Russia. Afontova Gora has cultural and genetic links to the people from Mal’ta-Buret’. The complex was first excavated in 1884 by Ivan Savenkov. Afontova Gora is a complex, consisting of multiple stratigraphic layers, of five or more campsites. The campsites shows evidence of mammoth hunting and were likely the result of an eastward expansion of mammoth hunters. The human fossils discovered at Afontova Gora, a male and a girl dated to 17,000~15,000 years ago.” ref
“Afontova Gora I is situated on the western bank of the Enisei River and has yielded the remains from horse, mammoth, reindeer, steppe bison, and large canids. A canid tibia has been dated 16,900 years old and the skull has been taxonomically described as being that of a dog, but it is now lost. Its description falls outside of the range of Pleistocene or modern northern wolves. (The name Afontova Gora 1 refers to the remains of a canid.)” ref
“Afontova Gora II is the site human fossil remains were found, and remains of mammoth, Arctic fox, Arctic hare, reindeer, bison, and horse were discovered at the site. Afontova Gora II consists of 7 layers. Layer 3 from Afontova Gora II is the most significant: the layer produced the largest amount of cultural artifacts and is the layer where the human fossil remains were discovered. Over 20,000 artifacts were discovered at layer 3: this layer produced over 450 tools and over 250 osseous artifacts (bone, antler, ivory). The fossils of two distinct individuals were discovered in the initial excavations: the upper premolar of an 11-15-year-old child and the left radius, ulna, humerus, phalanx, and frontal bone of an adult.” ref
“The bodies of two individuals, known as Afontova Gora 2 (AG2). The human fossil remains of Afontova Gora 2 were dated to around 17,000 years ago. DNA from the humerus of Afontova Gora 2, despite significant contamination, DNA analysis confirmed that the individual was male. The individual showed close genetic affinities to Mal’ta 1 (Mal’ta boy). Afontova Gora 2 also showed a greater genetic affinity for the Karitiana people than for the Han Chinese. Around 1.9-2.7% of the genome was Neanderthal in origin. More human fossil remains were discovered at Afontova Gora II, The remains belonged to two different females: the atlas of an adult female and the mandible and five lower teeth of a teenage girl (Afontova Gora 3) estimated to be around 14–15 years old. Initially, the new findings were presumed to be roughly contemporaneous with Afontova Gora 2.” ref
“Afontova Gora III is a site that consists of 3 layers. Afontova Gora 3 (AG3) was discovered within the complex. Direct AMS dating revealed that Afontova Gora 3 is dated to around 16,090 cal BCE or around 18,090 years ago). Researchers analyzing the dental morphology of Afontova Gora 3 concluded that the teeth showed distinct characteristics with most similarities to another fossil (the Listvenka child) from the Altai-Sayan region and were neither western nor eastern. Afontova Gora 3 and Listvenka showed distinct dental characteristics that were also different from other Siberian fossils, including those from Mal’ta.” ref
“DNA was extracted from one of the teeth of Afontova Gora 3 and analyzed. Compared to Afontova Gora 2, researchers were able to obtain higher coverage genomes from Afontova Gora 3. DNA analysis confirmed that the individual was female. mtDNA analysis revealed that Afontova Gora 3 belonged to the mitochondrial Haplogroup R1b. Around 2.9-3.7% of the genome was Neanderthal in origin. Researchers determined that Afontova Gora 2, Afontova Gora 3, and Mal’ta 1 (Mal’ta boy) shared common descent and were clustered together in a Mal’ta cluster. Genetically, Afontova Gora 3 is not closer to Afontova Gora 2 when compared to Mal’ta 1. When compared to Mal’ta 1, the Afontova Gora 3 lineage apparently contributed more to modern humans and is genetically closer to Native Americans.” ref
“Phenotypic analysis shows that Afontova Gora 3 carries the derived rs12821256 allele associated with, and likely causal for, blond hair color, making Afontova Gora 3 the earliest individual known to carry this derived allele. The allele was found in three later members of the largely ANE-derived Eastern Hunter-Gatherers populations from Samara, Motala and Ukraine c. 10,000 years ago, suggesting that it originated in the Ancient North Eurasian population before spreading to western Eurasia. The hundreds of millions of copies of this mutated alelle (a single-nucleotide polymorphism) are at the root of the classic European blond hair mutation, as massive population migrations from the Eurasian steppe, by a people who had substantial Ancient North Eurasian ancestry, entered continental Europe.” ref
“A genetic study on the Tarim mummies found that they were primarily descended from a population represented by the Afontova Gora 3 specimen (AG3), genetically displaying “high affinity” with it. The genetic profile of the Afontova Gora 3 individual represented about 72% of the ancestry of the Tarim mummies, while the remaining 28% of their ancestry was derived from Baikal EBA (Early Bronze Age Baikal populations). The Tarim mummies are thus one of the rare Holocene populations who derive most of their ancestry from the Ancient North Eurasians (ANE, specifically the Mal’ta and Afontova Gora populations), despite their distance in time (around 14,000 years). More than any other ancient populations, they can be considered as “the best representatives” of the Ancient North Eurasians.” ref
“Afontova Gora V is the site where remains of hare, pika, cave lion, horse, reindeer, bison, and partridge were discovered at the site.” ref
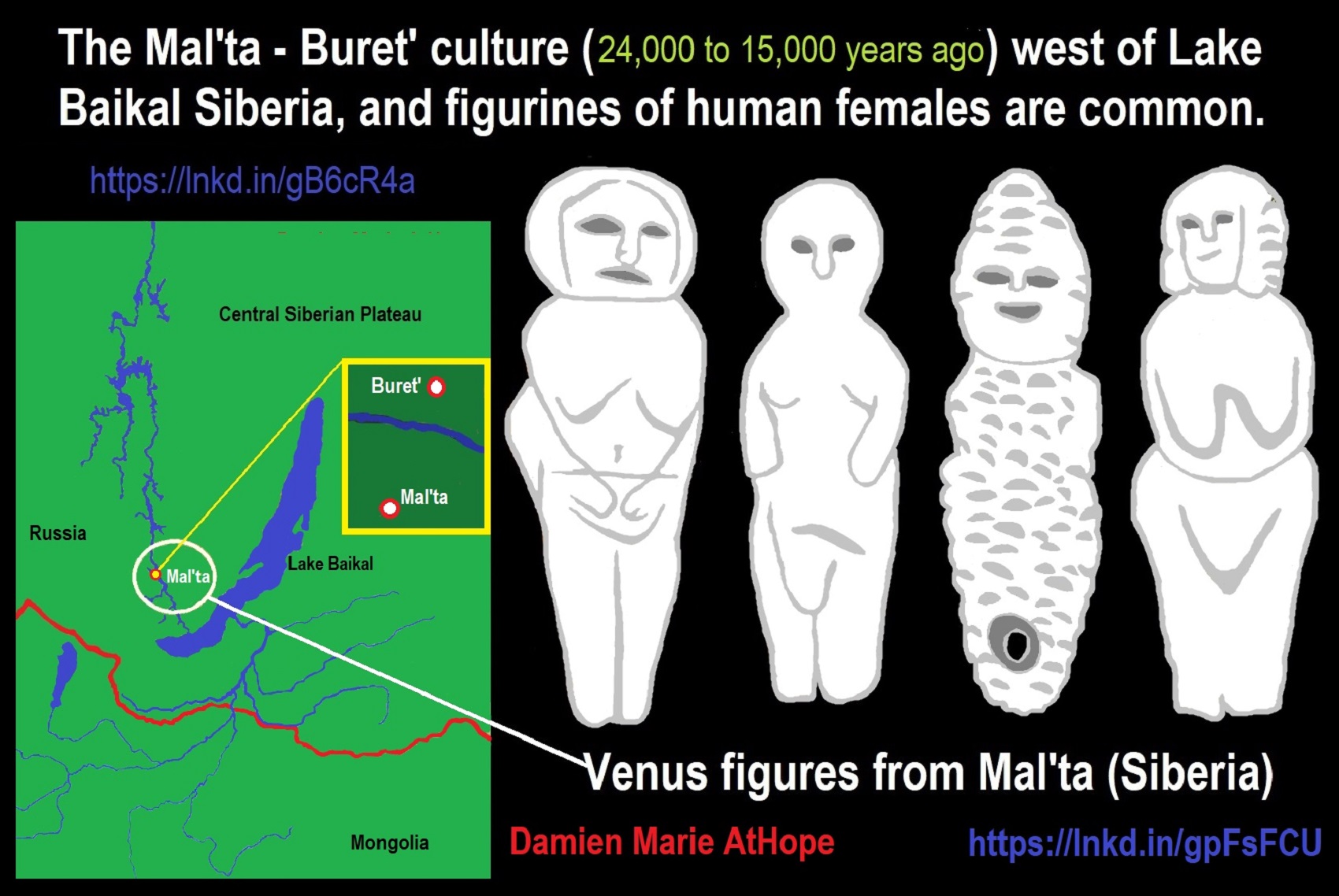
- Lake Baikal and Myths of Creation: Primordial waters, Supernatural Creatures of water, and the Mounds of creation
- Leda and the Swan: possibly relates back to 24,000–15,000 years old Mal’ta–Buret’ culture, Lake Baikal, Siberia?
- Shaman Rock, on Olkhon Island, Lake Baikal, Siberia, with a natural rock image that resembles a dragon. And is one of the “Nine Holy Sites of Asia.”
- Sacred Snakes or Dragons and Rivers, Lakes, and Seas?
Shamanism in Siberia
“A large minority of people in North Asia, particularly in Siberia, follow the religio-cultural practices of shamanism. Some researchers regard Siberia as the heartland of shamanism. The people of Siberia comprise a variety of ethnic groups, many of whom continue to observe shamanistic practices in modern times. Many classical ethnographers recorded the sources of the idea of “shamanism” among Siberian peoples. Siberian shamans’ spirit-journeys (reenacting their dreams wherein they had rescued the soul of the client) were conducted in, e.g., Oroch, Altai, and Nganasan healing séances.” ref
“Shamanism or samanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman or saman) interacting with the spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiritual energies into the physical world for the purpose of healing, divination, or to aid human beings in some other way. Beliefs and practices categorized as “shamanic” have attracted the interest of scholars from a variety of disciplines, including anthropologists, archeologists, historians, religious studies scholars, philosophers, and psychologists. Hundreds of books and academic papers on the subject have been produced, with a peer-reviewed academic journal being devoted to the study of shamanism.” ref
“The Modern English word shamanism derives from the Russian word šamán, which itself comes from the word samān from a Tungusic language – possibly from the southwestern dialect of the Evenki spoken by the Sym Evenki peoples, or from the Manchu language. The etymology of the word is sometimes connected to the Tungus root sā-, meaning “to know”. However, Finnish ethnolinguist Juha Janhunen questions this connection on linguistic grounds: “The possibility cannot be completely rejected, but neither should it be accepted without reservation since the assumed derivational relationship is phonologically irregular (note especially the vowel quantities).” ref
“Mircea Eliade noted that the Sanskrit word śramaṇa, designating a wandering monastic or holy figure, has spread to many Central Asian languages along with Buddhism and could be the ultimate origin of the word shaman. The term was adopted by Russians interacting with the indigenous peoples in Siberia. It is found in the memoirs of the exiled Russian churchman Avvakum. It was brought to Western Europe twenty years later by the Dutch traveler Nicolaes Witsen, who reported his stay and journeys among the Tungusic- and Samoyedic-speaking Indigenous peoples of Siberia in his book Noord en Oost Tataryen (1692). Adam Brand, a merchant from Lübeck, published in 1698 his account of a Russian embassy to China; a translation of his book, published the same year, introduced the word shaman to English speakers.” ref
“According to the Oxford English Dictionary, a shaman (/ˈʃɑːmən/ SHAH-men, /ˈʃæmən/ or /ˈʃeɪmən/) is someone who is regarded as having access to, and influence in, the world of benevolent and malevolent spirits, who typically enters into a trance state during a ritual, and practices divination and healing. The word “shaman” probably originates from the Tungusic Evenki language of North Asia. According to Juha Janhunen, “the word is attested in all of the Tungusic idioms” such as Negidal, Lamut, Udehe/Orochi, Nanai, Ilcha, Orok, Manchu and Ulcha, and “nothing seems to contradict the assumption that the meaning ‘shaman’ also derives from Proto-Tungusic” and may have roots that extend back in time at least two millennia. The term was introduced to the west after Russian forces conquered the shamanistic Khanate of Kazan in 1552.” ref
“The term “shamanism” was first applied by Western anthropologists as outside observers of the ancient religion of the Turks and Mongols, as well as those of the neighbouring Tungusic- and Samoyedic-speaking peoples. Upon observing more religious traditions around the world, some Western anthropologists began to also use the term in a very broad sense. The term was used to describe unrelated magicoreligious practices found within the ethnic religions of other parts of Asia, Africa, Australasia, and even completely unrelated parts of the Americas, as they believed these practices to be similar to one another. While the term has been incorrectly applied by cultural outsiders to many Indigenous spiritual practices, the words “shaman” and “shamanism” do not accurately describe the variety and complexity that is Indigenous spirituality. Each nation and tribe has its own way of life, and uses terms in their own languages.” ref
“There is no single agreed-upon definition for the word “shamanism” among anthropologists. Thomas Downson suggests three shared elements of shamanism: practitioners consistently alter consciousness, the community regards altering consciousness as an important ritual practice, and the knowledge about the practice is controlled. Anthropologist and archeologist Silvia Tomaskova argued that by the mid-1600s, many Europeans applied the Arabic term shaitan (meaning “devil”) to the non-Christian practices and beliefs of Indigenous peoples beyond the Ural Mountains. She suggests that shaman may have entered the various Tungus dialects as a corruption of this term, and then been told to Christian missionaries, explorers, soldiers, and colonial administrators with whom the people had increasing contact for centuries. A female shaman is sometimes called a shamanka, which is not an actual Tungus term but simply shaman plus the Russian suffix -ka (for feminine nouns).” ref
Shamanism Terminology in Siberian languages
- “‘shaman’: saman (Nedigal, Nanay, Ulcha, Orok), sama (Manchu). The variant /šaman/ (i.e., pronounced “shaman”) is Evenk (whence it was borrowed into Russian).
- ‘shaman’: alman, olman, wolmen (Yukagir)
- ‘shaman’: [qam] (Tatar, Shor, Oyrat), [xam] (Tuva, Tofalar)
- The Buryat word for shaman is бөө (böö) [bøː], from early Mongolian böge. Itself borrowed from Proto-Turkic *bögü (“sage, wizard”)
- ‘shaman’: ńajt (Khanty, Mansi), from Proto-Uralic *nojta (c.f. Sámi noaidi)
- ‘shamaness’: [iduɣan] (Mongol), [udaɣan] (Yakut), udagan (Buryat), udugan (Evenki, Lamut), odogan (Nedigal). Related forms found in various Siberian languages include utagan, ubakan, utygan, utügun, iduan, or duana. All these are related to the Mongolian name of Etügen, the hearth goddess, and Etügen Eke ‘Mother Earth’. Maria Czaplicka points out that Siberian languages use words for male shamans from diverse roots, but the words for female shaman are almost all from the same root. She connects this with the theory that women’s practice of shamanism was established earlier than men’s, that “shamans were originally female.” ref
“Shamanistic practice shows great diversity, even if restricted to Siberia. In some cultures, the music or song related to shamanistic practice may mimic natural sounds, sometimes with onomatopoeia. This holds true for the practices of the noaidi among Sami groups. Although the Sami people live outside of Siberia, many of their shamanistic beliefs and practice shared important features with those of some Siberian cultures. The joiks of the Sami were sung on shamanistic rites. Recently, joiks are sung in two different styles: one of these is sung only by young people; the traditional one may be the other, the “mumbling” style, which resembles magic spells. Several surprising characteristics of joiks can be explained by comparing the music ideals, as observed in joiks and contrasted to music ideals of other cultures. Some joiks intend to mimic natural sounds. This can be contrasted to bel canto, which intends to exploit human speech organs on the highest level to achieve an almost “superhuman” sound.” ref
“The intention to mimic natural sounds is present in some Siberian cultures as well: overtone singing, and also shamanic songs of some cultures can be examples.
- In a Soyot shamanic song, sounds of bird and wolf are imitated to represent helping spirits of the shaman.
- The seances of Nganasan shamans were accompanied by women imitating the sounds of the reindeer calf, (thought to provide fertility for those women). In 1931, A. Popov observed the Nganasan shaman Dyukhade Kosterkin imitating the sound of polar bear: the shaman was believed to have transformed into a polar bear.” ref
“Sound mimesis is not restricted to Siberian cultures and is not necessarily linked to shamanistic beliefs or practices. See, for example, Inuit throat singing, a game played by women, an example of Inuit music that employs overtone singing, and, in some cases, the imitation of natural sounds (mostly those of animals, e.g. geese). The imitation of animal sounds can also serve such practical reasons as luring game in hunt.” ref
“Uralic languages are proven to form a genealogical unit, a language family. Not all speakers of these languages live in Siberia or have shamanistic religions. The largest populations, the Hungarians and Finns, live outside Siberia and are mostly Christian. Sámi people had kept shamanic practices alive for a long time. They live in Europe, but practiced shamanism until the 18th century. Most others (e.g. Hungarian, Finnic, Mari) have only remnant elements of shamanism. The majority lives outside Siberia. Some of them used to live in Siberia, but have migrated to their present locations since then. The original location of the Proto-Uralic peoples (and its extent) is debated. Combined phytogeographical and linguistic considerations (distribution of various tree species and the presence of their names in various Uralic languages) suggest that this area was somewhere between the Kama and Vyatka rivers on the western side of the Ural Mountains.” ref
“Among several Samoyedic peoples shamanism was a living tradition also in modern times, especially at groups living in isolation until recent times (Nganasans). There were distinguished several types of shamans among Nenets, Enets, and Selkup people. (The Nganasan shaman used three different crowns, according to the situation: one for upper world, one for underneath word, one for occasion of childbirth.) Nenets people, Enets people, Nganasan people speak Northern Samoyedic languages. They live in North Siberia (Nenets live also in European parts), they provide classical examples. Selkups are the only ones who speak Southern Samoyedic languages nowadays. They live more to the south, shamanism was in decline also at the beginning of the 20th century, although folklore memories could be recorded even in the 1960s. Other Southern Samoyedic languages were spoken by some peoples living in the Sayan Mountains, but language shift has taken place, making all these languages extinct. There were several types of shamans distinguishing ones contacting upper world, ones contacting underneath world, ones contacting the dead.” ref
“The isolated location of Nganasan people enabled that shamanism was a living phenomenon among them even in the beginning of the 20th century, the last notable Nganasan shaman’s seances could be recorded on film in the 1970s. One of the occasions in which the shaman partook was the clean tent rite, held after the polar night, which included sacrifices. Some peoples of the Sayan Mountains spoke once Southern Samoyedic languages. Most of them underwent a language shift in the beginning and middle of the 19th century, borrowing the language of neighboring Turkic peoples. The Kamassian language survived longer: 14 old people spoke it yet in 1914. In the late 20th century, some old people had passive or uncertain knowledge of the language, but collecting reliable scientific data was no longer possible. Today Kamassian is regarded as extinct.” ref
“The shamanism of Samoyedic peoples in the Sayan Mountains survived longer (if we regard Karagas as a Samoyedic people, although such approaches have been refined: the problem of their origin may be more comple). Diószegi Vilmos could record not only folklore memories in the late 1950s, but he managed also to talk personally to (no longer practicing) shamans, record their personal memories, songs, some of their paraphernalia. Starting from the late 9th century onwards, the ancestors of the Hungarian people migrated from their Proto-Uralic homeland in Siberia to the Pannonian Basin, an area that includes present-day Hungary. Today, shamanism is no longer widely practiced by Hungarians, but elements of shamanism have been preserved in their folklore.” ref
“Comparative methods reveal that some motifs used in folktales, fragments of songs, and folk rhymes retain aspects of the ancient belief system. In an effort to prove that shamanistic remnants existed within Hungarian folklore ethnographer, Diószegi Vilmos, compared ethnographic records of Hungarian and neighboring peoples, and works about various shamanic traditions of some Siberian peoples. Mihály Hoppál continued Diószegi Vilmos’s work comparing shamanic beliefs of speakers of Uralic languages with those of several non-Uralic Siberian peoples. Although Ugrian folklore preserves many traces of shamanism, shamanism itself was a dying practice among the Khanty and Mansi people by the 1930s. Shamanism is still practiced by many indigenous peoples, but, among the modern Ugrians, shamanism is largely practiced by the Khanty.” ref
“Whether this shamanism is borrowed entirely from neighboring Turkic peoples, or whether it has some ethnic features, maybe remnants of Samoyedic origin, is unresolved. Comparative considerations suggest, that
- Karagas shamanism is affected by Abakan-Turkic and Buryat influence. Among the various Soyot cultures, the central Soyot groups, keeping cattle and horses, show Khalkha Mongol phenomena in their shamanism, the shamanism of Western Soyots, living on the steppe, is similar to that of Altai Turkic peoples. A shaman story narrates contacts between Soyots and Abakan Turkic peoples in a mythical form.
- Karagas and Eastern (reindeer-breeding, mountain-inhabiting) Soyots. have many similarities in their culture and shamanism. It was these two cultures who presented some ethnic features, phenomena lacking among neighboring Turkic peoples. E.g., the structure of their shamanic drum showed such peculiarity: it had two transoms. It was also these two cultures who showed some features, which could be possibly of Samoyedic origin: the shaman’s headdress, dress and boots has the effigies symbolizing human organs, mostly bones; in the case of headdress, representation of human face. Also the dress-initiating song of the Karagas shaman Kokuyev contained the expression “my shamanic dress with seven vertebrae”. Hoppál interprets the skeleton-like overlay of the Karagas shaman-dress as symbol of shamanic rebirth, similar remark applies for the skeleton-like iron ornamentation of the (not Samoyedic, but genealogically unclassified, Paleosiberian) Ket shamanic dress, although it may symbolize also the bones of the loon (the helper animal of the shaman). (The theory of Ket origin of the Karagas has already been mentioned above.) The skeleton-like overlay symbolized shamanic rebirth also among some other Siberian cultures.” ref
“The traditional culture of Ket people was researched by Matthias Castrén, Vasiliy Ivanovich Anuchin, Kai Donner, Hans Findeisen, Yevgeniya Alekseyevna Alekseyenko. Shamanism was a living practice in the 1930s yet, but by the 1960s almost no authentic shaman could be found. Ket shamanism shared features with those of Turkic and Mongolic peoples. Besides that, there were several types of shamans, differing in function (sacral rites, curing), power, and associated animal (deer, bear). Also among Kets (like at several other Siberian peoples, e.g. Karagas), there are examples of using skeleton symbolics, Hoppál interprets it as a symbol of shamanic rebirth, although it may symbolize also the bones of the loon (the helper animal of the shaman, joining air and underwater world, just like the shaman who traveled both to the sky and the underworld as well). The skeleton-like overlay represented shamanic rebirth also among some other Siberian cultures.” ref
“Turkic peoples spread over large territories, and are far from alike. In some cases, shamanism has been widely amalgamated with Islam, in others with Buddhism, but there are surviving traditions among the Siberian Tatars, Tuvans, and Tofalar. The Altai Turks may be related to neighboring Ugrian, Samoyed, Ket, or Mongols. There may be also ethnographic traces of such past of these nowadays Turkic-speaking peoples of the Altai. For example, some of them have phallic-erotic fertility rites, and that can be compared to similar rites of Ugriansɮ. Among the Tungusic peoples of Siberia, shamanism is also widespread. The Tale of the Nisan Shaman, a famous piece of folklore which describes the resurrection of a rich landowner’s son by a female shaman, is known among various Tungusic peoples including the Manchus, Evenks, and Nanai people.” ref
“Linguistically, Koryak and Chukchi are close congeners of Yup’il. Koryak shamanism is known. Yup’ik groups comprise a huge area stretching from Eastern Siberia through Alaska and Northern Canada (including Labrador Peninsula) to Greenland. Shamanistic practice and beliefs have been recorded at several parts of this vast area crosscutting continental borders. Like Yup’ik cultures themselves, shamanistic practices reveal diversity. Some mosaic-like examples from various cultures: the soul concepts of the various cultures were diverse as well, some groups believed that the young child had to be taken for by guardian names inherited from a recently deceased relative. Among some groups, this belief amounted to a kind of reincarnation. Also shamanism might include beliefs in soul dualism, where the free-soul of the shaman could fly to celestial or underneath realms, contacting mythological beings, negotiating with them in order to cease calamities or achieve success in hunt. If their wrath was believed to be caused by taboo breaches, the shaman asked for confessions by members of the community. In most cultures, shamanism could be refused by the candidate: calling could be felt by visions, but generally, becoming a shaman followed conscious considerations.” ref
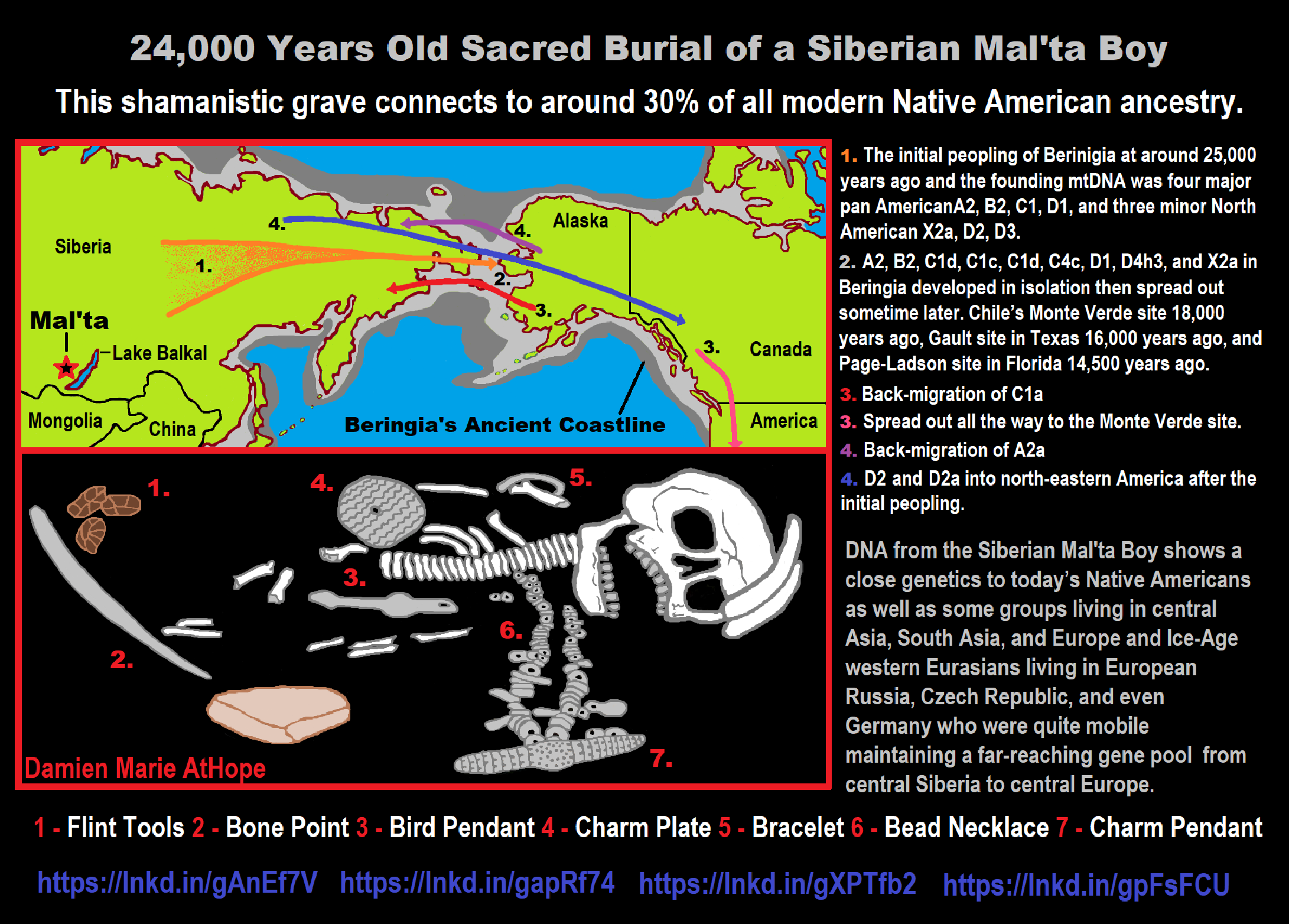
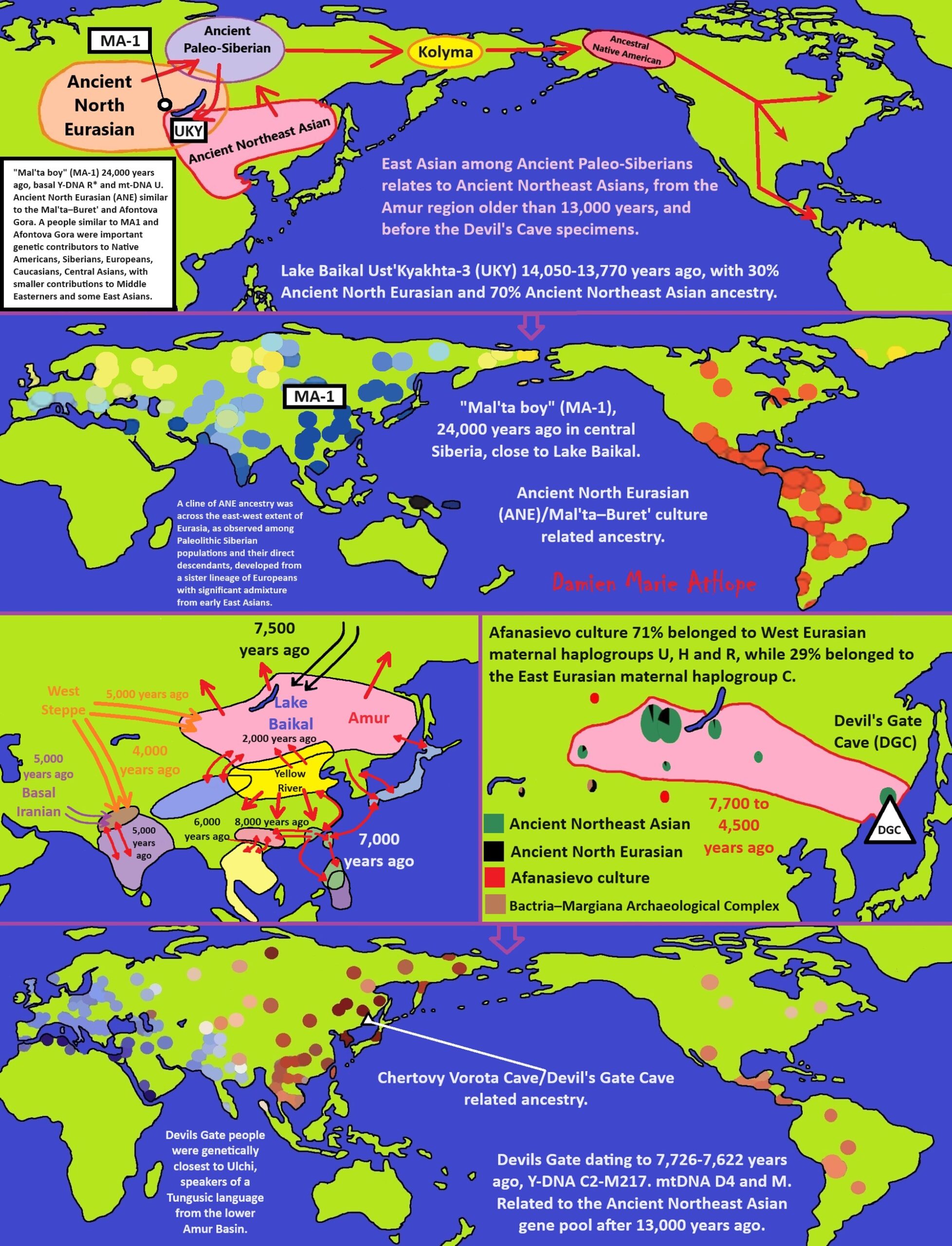
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“A 2016 study found that the global maximum of Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) ancestry occurs in modern-day Kets, Mansi, Native Americans, and Selkups. ANE ancestry has spread throughout Eurasia and the Americas in various migrations since the Upper Paleolithic, and more than half of the world’s population today derives between 5 and 42% of their genomes from the Ancient North Eurasians. Significant ANE ancestry can be found in Native Americans, as well as in regions of northern Europe, South Asia, Central Asia, and Siberia. It has been suggested that their mythology may have featured narratives shared by both Indo-European and some Native American cultures, such as the existence of a metaphysical world tree and a fable in which a dog guards the path to the afterlife.” ref
Ancient Northern East Asian/ later became Ancient Northeast Asian
Ancient Paleo-Siberian
Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (Mal’ta boy MA-1)
The Kolyma Shaitans: Legends and Reality (I only use just a small part)
“A unique “shaitan” burial was discovered on the bank of Omuk-Kuel Lake in the Middle-Kolyma ulus in Yakutia. According to the legends, buried in it are mummified remains of a shaman woman who died during a devastating smallpox epidemics in the 18th c. In an attempt to overcome the deadly disease, the shaman’s relatives used her remains as an emeget fetish. The author believes that these legends reflect the real events of those far-away years. The Arabic word “shaitan” came to the Russian language from Turkic languages. According to Islamic tradition, a shaitan is a genie, an evil spirit, a demon. During Russian colonization and Christianization of Siberia, all sacred things used by the aborigines as fetishes, patron spirits of the family, and the tribe, grew to be called “shaitans.” There are various facts, dating to the 18th and 19th cc., confirming that this word also referred to the mummified remains of outstanding shamans.” ref
“In the 1740s, a member of the Second Kamchatka Expedition Yakov Lindenau wrote, “Meat is scratched off the [shaman’s] bones and the bones are put together to form a skeleton, which is dressed in human’s clothes and worshipped as a deity. The Yukagirs place such dressed bones…in their yurts, their number can sometimes reach 10 or 15. If somebody commits even a minor sacrilege with respect to these bones, he stirs up rancor on the part of the Yukagirs… While traveling and hunting, the Yukagirs carry these bones in their sledges, and moreover, in their best sledges pulled by their best deer. When the Yukagirs are going to undertake something really important, they tell fortune using these skeletons: lift a skeleton up, and if it seems light, it means that their enterprise will have a favorable outcome. The Yukagirs call these skeletons stariks (old men), endow them with their best furs, and sit them on beds covered with deer hides, in a circle, as though they are alive.” (Lindenau, 1983, p. 155)” ref
“In the late 19th c., a famous explorer of aboriginal culture V. I. Jochelson noted the changes that occurred in the ritual in the last century and a half. So, the Yukagirs divided among themselves the shaman’s meat dried in the sun and then put it in separate tents. The dead bodies of killed dogs were left there as well. “After that,” V. I. Jochelson writes, “they would divide the shaman’s bones, dry them and wrap in clothes. The skull was an object of worshipping. It was put on top of a trunk (body) cut out of wood. A caftan and two hats – a winter and a summer one – were sewn for the idol. The caftan was all embroidered. On the skull, a special mask was put, with holes for the eyes and the mouth… The figure was placed in the front corner of the home. Before a meal, a piece of food was thrown into the fire and the idol was held above it. This feeding of the idol… was committed before each meal.” (V. I. Jochelson, 2005, pp. 236—237)” ref
“The idol was kept by the children of the dead shaman. One of them was inducted into the shamanism mysteries while his father was still alive. The idol was carried in a wooden box. Sometimes, in line with the air burial ritual, the box was erected on poles or trees, and the idol was taken out only before hunting or a long journey so that the outcome of the enterprise planned could be predicted. With time, the Yukagirs began using wooden idols as charms. V. I. Jochelson notes that by the late 19th c. the Yukagirs had developed a skeptical attitude towards idols and referred to them as “shaitans.” In this way, under the influence of Christianity, the worshipped ancestor’s spirit turned into its opposite – an evil spirit, a devil, a Satan.” ref
Ancestral Native American, Ancient Beringian
14,000-year-old Ust-Kyakhta-3 (UKY) individual found near Lake Baikal
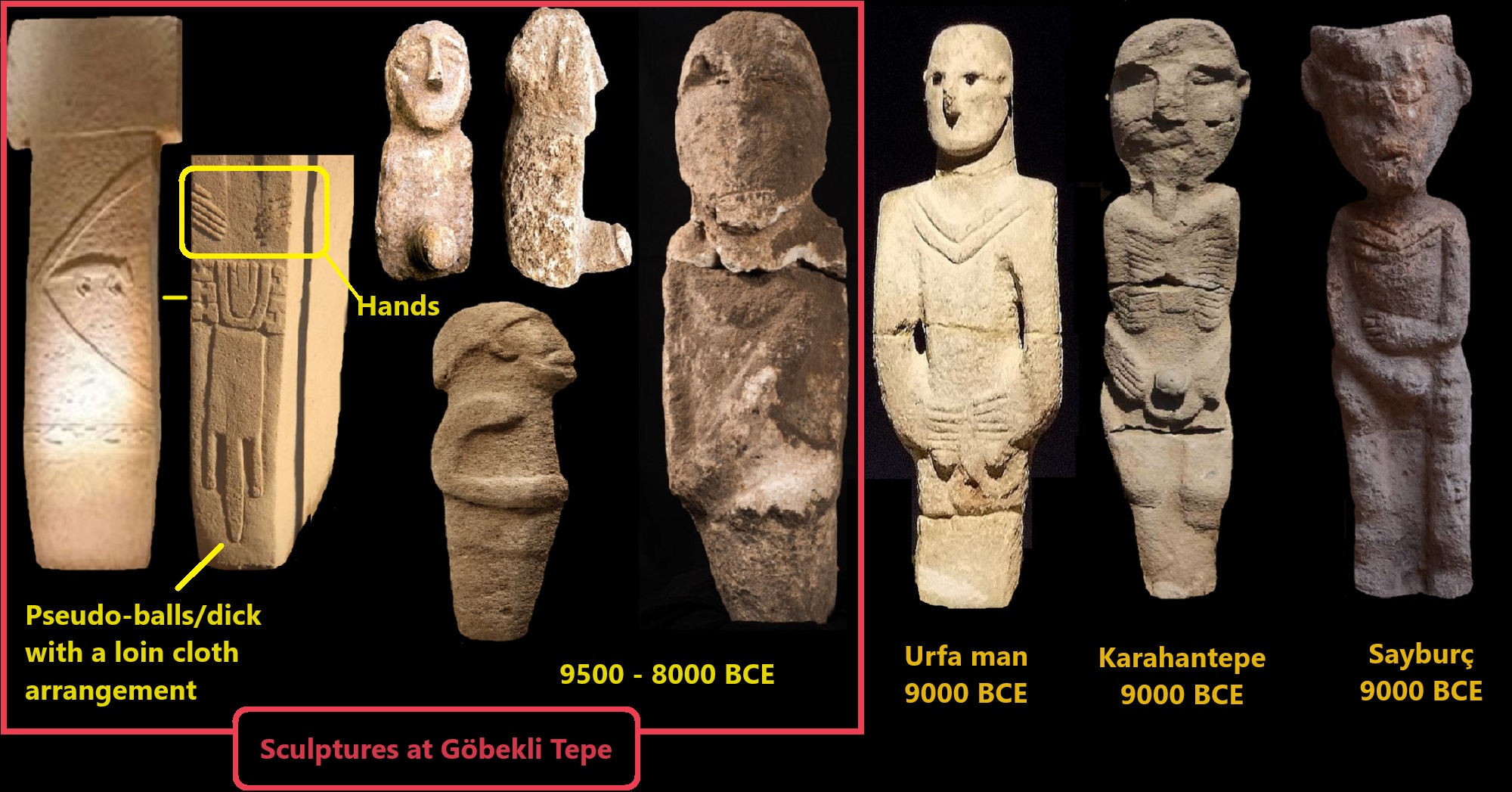

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Similarities were Similarities discovered at Göbeklitepe and Karahantepe, as well as others.
With Gobecli Tepe starts to me the male clan leader cult that later turns into the warrior cult and later kings and all this in the new hierarchies that emerged with agriculture and the ability to hoard wealth. “slavery became widespread only with agriculture 11,000 years ago.” ref
“Damien, based on your amazing research & artistic presentation do you think Göbekli Tepe is unique, special, in any way with human development?” – Questioner
My response, I think it was involved in the rise of agricultural religion (I label it paganism), this was at the very beginning and thus was more shamanism (with heavy totemism) related but they added deities to me likely totemistic animals around 13,000/12,000 years ago.
Progressed organized religion (at least 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
*Institutional religion “organized religion”, as a social institution with official dogma usually set in a hierarchical/bureaucratic structure that contains strict rules and practices dominating the believer’s life. And to me, paganism and Institutional religion are categorized into the following stages:
*The primal stage of organized religion was 13,000 to 10,000 years ago.
*The proto-stage of organized religion was around 10,000 to 7,000 years ago.
*The progressed stage of organized religion was around 7,000 to 5000 years ago.
The emergence of world religions arose after 4,000 years ago
After around 2,000 to 1,000 years ago monotheism and its male-centric religions became dominant
———————————————————————————————————————————————-
Paganism 12,000 years old: (Pre-Capitalism) the beginning of inequality and hierarchy of power:
“Social stratification is a system of ranking individuals and groups within societies. It refers to a society’s ranking of its people into socioeconomic tiers based on factors like wealth, income, race, education, and power. You may remember the word “stratification” from geology class. The distinct horizontal layers found in rock, called “strata,” are an illustrative way to visualize social structure. Society’s layers are made of people, and society’s resources are distributed unevenly throughout the layers. Social stratification has been a part of all societies dating from the agricultural revolution, which took place in various parts of the world between 7,000-10,000 BCE. Unlike relatively even strata in rock, though, there are not equal numbers of people in each layer of society. There are typically very few at the top and a great many at the bottom, with some variously populated layers in the middle.” ref
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and slaves:
“Something Weird Happened to Men 7,000 Years Ago, it fell to one man for every 17 women: fighting between patrilineal clans. Around 7,000 years ago – all the way back in the Neolithic – something really peculiar happened to human genetic diversity. Over the next 2,000 years, and seen across Africa, Europe, and Asia, the genetic diversity of the Y chromosome collapsed, becoming as though there was only one man for every 17 women. This points to a social, rather than an environmental, cause, and given the social restructures between 12,000 and 8,000 years ago as humans shifted to more agrarian cultures with patrilineal structures, this may have had something to do with it.” ref
“Slavery predates written records and has existed in many cultures. Slavery is rare among hunter-gatherer populations because it requires economic surpluses and a substantial population density. Thus, although it has existed among unusually resource-rich hunter-gatherers, such as the American Indian peoples of the salmon-rich rivers of the Pacific Northwest coast, slavery became widespread only with the invention of agriculture during the Neolithic Revolution about 11,000 years ago.” ref
When the First Farmers Arrived in Europe, Inequality Evolved
“Forests gave way to fields, pushing hunter-gatherers to the margins—geographically and socially. There is no clear genetic evidence of interbreeding along the central European route until the (Linear Pottery culture 5500–4500 BCE or 7,522-6,522 years ago) LBK farmers reached the Rhine. And yet the groups mixed in other ways—potentially right from the beginning. A tantalizing hint of such interactions came from Gamba’s discovery of a hunter-gatherer bone in a farming settlement at a place called Tiszaszőlős-Domaháza in Hungary. But there was nothing more to be said about that individual. Was he a member of that community? A hostage? Someone passing through?” ref
“With later evidence, the picture became clearer. At Bruchenbrücken, a site north of Frankfurt in Germany, farmers, and hunter-gatherers lived together roughly 7,300 years ago in what Gronenborn calls a “multicultural” settlement. It looks as if the hunters may have come there originally from farther west to trade with the farmers, who valued their predecessors’ toolmaking techniques—especially their finely chiseled stone arrowheads. Perhaps some hunter-gatherers settled, taking up the farming way of life. So fruitful were the exchanges at Bruchenbrücken and other sites, Gronenborn says, that they held up the westward advance of farming for a couple of centuries.” ref
“There may even have been rare exceptions to the rule that the two groups did not interbreed early on. The Austrian site of Brunn 2, in a wooded river valley not far from Vienna, dates from the earliest arrival of the LBK farmers in central Europe, around 7,600 years ago. Three burials at the site were roughly contemporaneous. Two were of individuals of pure farming ancestry, and the other was the first-generation offspring of a hunter and a farmer. All three lay curled up on their sides in the LBK way, but the “hunter” was buried with six arrowheads.” ref
My thoughts on how cultural/ritual was influenced in the area of Göbekli Tepe. I think it relates to a few different cultures starting in the area before the Neolithic. Two different groups of Siberians first from northwest Siberia with U6 haplogroup 40,000 to 30,000 or so. Then R Haplogroup (mainly haplogroup R1b but also some possible R1a both related to the Ancient North Eurasians). This second group added its “R1b” DNA of around 50% to the two cultures Natufian and Trialetian. To me, it is likely both of these cultures helped create Göbekli Tepe. Then I think the female art or graffiti seen at Göbekli Tepe to me possibly relates to the Epigravettians that made it into Turkey and have similar art in North Italy. I will also show you my art explaining this to help show my thoughts. I also have lots of links if interested to validate all this.

12,000-year-old Gobekli Tepe: “first human-made pagan temple”
Just think of the kind and amount of religious faith one would need to build such a site as this. Speaking of building, one of the most fascinating facts about this site is that they didn’t have the wheel nor metal tools. All they had were stone tools and little else.
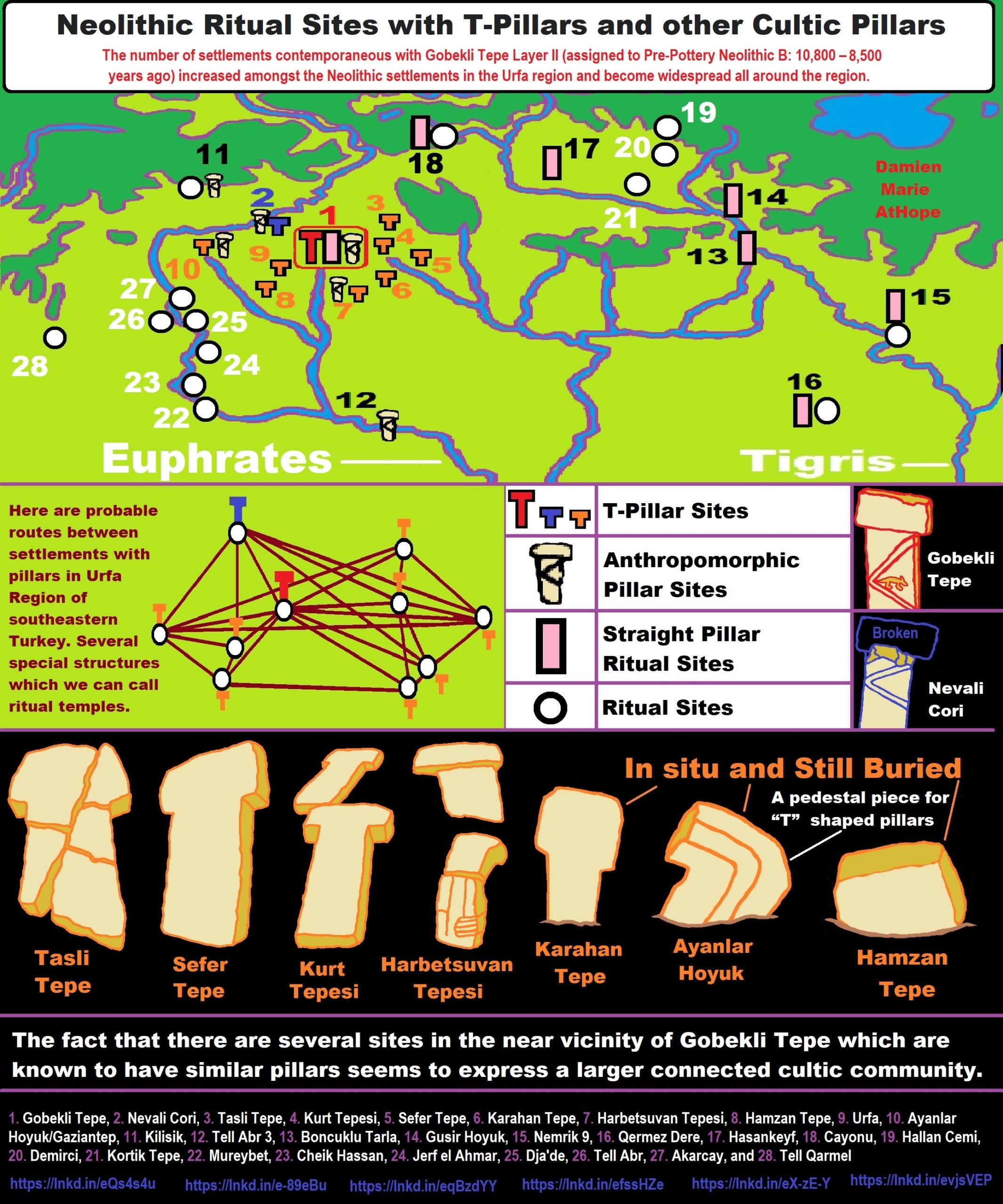
The number of settlements contemporaneous with Gobekli Tepe Layer II (assigned to Pre-Pottery Neolithic B: 10,800 – 8,500 years ago) increased amongst the Neolithic settlements in the Urfa region and become widespread all around the region.
- Gobekli Tepe, 2. Nevali Cori, 3. Tasli Tepe, 4. Kurt Tepesi, 5. Sefer Tepe, 6. Karahan Tepe, 7. Harbetsuvan Tepesi, 8. Hamzan Tepe, 9. Urfa, 10. Ayanlar Hoyuk/Gaziantep, 11. Kilisik, 12. Tell Abr 3, 13. Boncuklu Tarla, 14. Gusir Hoyuk, 15. Nemrik 9, 16. Qermez Dere, 17. Hasankeyf, 18. Cayonu, 19. Hallan Cemi, 20. Demirci, 21. Kortik Tepe, 22. Mureybet, 23. Cheik Hassan, 24. Jerf el Ahmar, 25. Dja’de, 26. Tell Abr, 27. Akarcay, and 28. Tell Qarmel
Göbekli Tepe is not alone, in fact, it is part of a religious/cultural connected ritual culture in the general region. There are several other similar sites with similar T-pillars to Göbekli Tepe or other types of stone pillar providing a seeming connected cult belief or religious culture of pillars seen in the PPNA-PPNB in the northern portion of the Near East.
“The locations of the sites that contain “T” shaped pillars are the main topic that needs more understanding to grasp the larger sociocultural-religious cultural complex in the same general region. Another matter under discussion is to comprehend the differences between the small-scale settlements that contain cult centers and “T” shaped pillars and the larger ones found at Gobekli Tepe layer III. The fact that settlements with “T” shaped pillars contain both the remains of circular domestic buildings and the pillars such as seen at Cayonu and Nevali Cori, which are also known to contain cult and domestic buildings. It is contemplated that such settlements are contemporary with Gobekli Tepe layer II and the cult building known from Nevali Cori based on the similarities and differences of the “T” shaped pillars. In the light of the finds unearthed from the settlements in Şanliurfa region that contain “T” shaped pillars, such settlements should be dated to the end of Late Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (LPPNA) and the Early Pre-Pottery Neolithic B (EPPNB).” ref
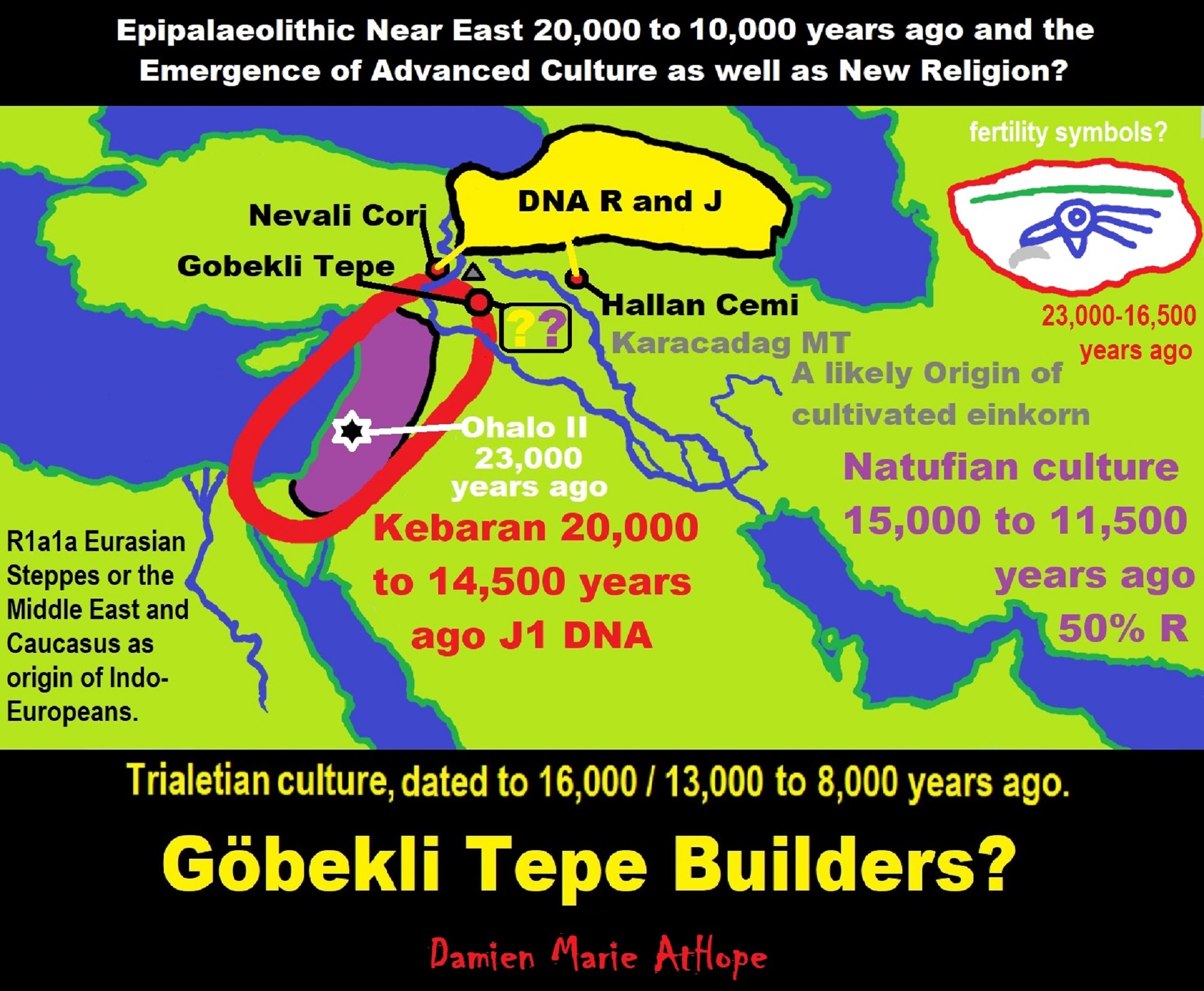
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Trialetian culture (16,000–8000 years ago) the Caucasus, Iran, and Turkey, likely involved in Göbekli Tepe. Migration 1?
Haplogroup R possible time of origin about 27,000 years in Central Asia, South Asia, or Siberia:
- Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (24,000-15,000 years ago)
- Afontova Gora culture (21,000-12,000 years ago)
- Trialetian culture (16,000–8000 years ago)
- Samara culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Khvalynsk culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Afanasievo culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Yamna/Yamnaya Culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Andronovo culture (4,000–2,900 years ago) ref
Trialetian sites
Caucasus and Transcaucasia:
- Edzani (Georgia)
- Chokh (Azerbaijan), layers E-C200
- Kotias Klde, layer B” ref
Eastern Anatolia:
- Hallan Çemi (from ca. 8.6-8.5k BC to 7.6-7.5k BCE)
- Nevali Çori shows some Trialetian admixture in a PPNB context” ref
Trialetian influences can also be found in:
- Cafer Höyük
- Boy Tepe” ref
Southeast of the Caspian Sea:
- Hotu (Iran)
- Ali Tepe (Iran) (from cal. 10,500 to 8,870 BCE)
- Belt Cave (Iran), layers 28-11 (the last remains date from ca. 6,000 BCE)
- Dam-Dam-Cheshme II (Turkmenistan), layers7,000-3,000 BCE)” ref


“Migration from Siberia behind the formation of Göbeklitepe: Expert states. People who migrated from Siberia formed the Göbeklitepe, and those in Göbeklitepe migrated in five other ways to spread to the world, said experts about the 12,000-year-old Neolithic archaeological site in the southwestern province of Şanlıurfa.“ The upper paleolithic migrations between Siberia and the Near East is a process that has been confirmed by material culture documents,” he said.” ref
“Semih Güneri, a retired professor from Caucasia and Central Asia Archaeology Research Center of Dokuz Eylül University, and his colleague, Professor Ekaterine Lipnina, presented the Siberia-Göbeklitepe hypothesis they have developed in recent years at the congress held in Istanbul between June 11 and 13. There was a migration that started from Siberia 30,000 years ago and spread to all of Asia and then to Eastern and Northern Europe, Güneri said at the international congress.” ref
“The relationship of Göbeklitepe high culture with the carriers of Siberian microblade stone tool technology is no longer a secret,” he said while emphasizing that the most important branch of the migrations extended to the Near East. “The results of the genetic analyzes of Iraq’s Zagros region confirm the traces of the Siberian/North Asian indigenous people, who arrived at Zagros via the Central Asian mountainous corridor and met with the Göbeklitepe culture via Northern Iraq,” he added.” ref
“Emphasizing that the stone tool technology was transported approximately 7,000 kilometers from east to west, he said, “It is not clear whether this technology is transmitted directly to long distances by people speaking the Turkish language at the earliest, or it travels this long-distance through using way stations.” According to the archaeological documents, it is known that the Siberian people had reached the Zagros region, he said. “There seems to be a relationship between Siberian hunter-gatherers and native Zagros hunter-gatherers,” Güneri said, adding that the results of genetic studies show that Siberian people reached as far as the Zagros.” ref
“There were three waves of migration of Turkish tribes from the Southern Siberia to Europe,” said Osman Karatay, a professor from Ege University. He added that most of the groups in the third wave, which took place between 2600-2400 BCE, assimilated and entered the Germanic tribes and that there was a genetic kinship between their tribes and the Turks. The professor also pointed out that there are indications that there is a technology and tool transfer from Siberia to the Göbeklitepe region and that it is not known whether people came, and if any, whether they were Turkish.” ref
“Around 12,000 years ago, there would be no ‘Turks’ as we know it today. However, there may have been tribes that we could call our ‘common ancestors,’” he added. “Talking about 30,000 years ago, it is impossible to identify and classify nations in today’s terms,” said Murat Öztürk, associate professor from İnönü University. He also said that it is not possible to determine who came to where during the migrations that were accepted to have been made thousands of years ago from Siberia. On the other hand, Mehmet Özdoğan, an academic from Istanbul University, has an idea of where “the people of Göbeklitepe migrated to.” ref
“According to Özdoğan, “the people of Göbeklitepe turned into farmers, and they could not stand the pressure of the overwhelming clergy and started to migrate to five ways.” “Migrations take place primarily in groups. One of the five routes extends to the Caucasus, another from Iran to Central Asia, the Mediterranean coast to Spain, Thrace and [the northwestern province of] Kırklareli to Europe and England, and one route is to Istanbul via [Istanbul’s neighboring province of] Sakarya and stops,” Özdoğan said. In a very short time after the migration of farmers in Göbeklitepe, 300 settlements were established only around northern Greece, Bulgaria, and Thrace. “Those who remained in Göbeklitepe pulled the trigger of Mesopotamian civilization in the following periods, and those who migrated to Mesopotamia started irrigated agriculture before the Sumerians,” he said.” ref
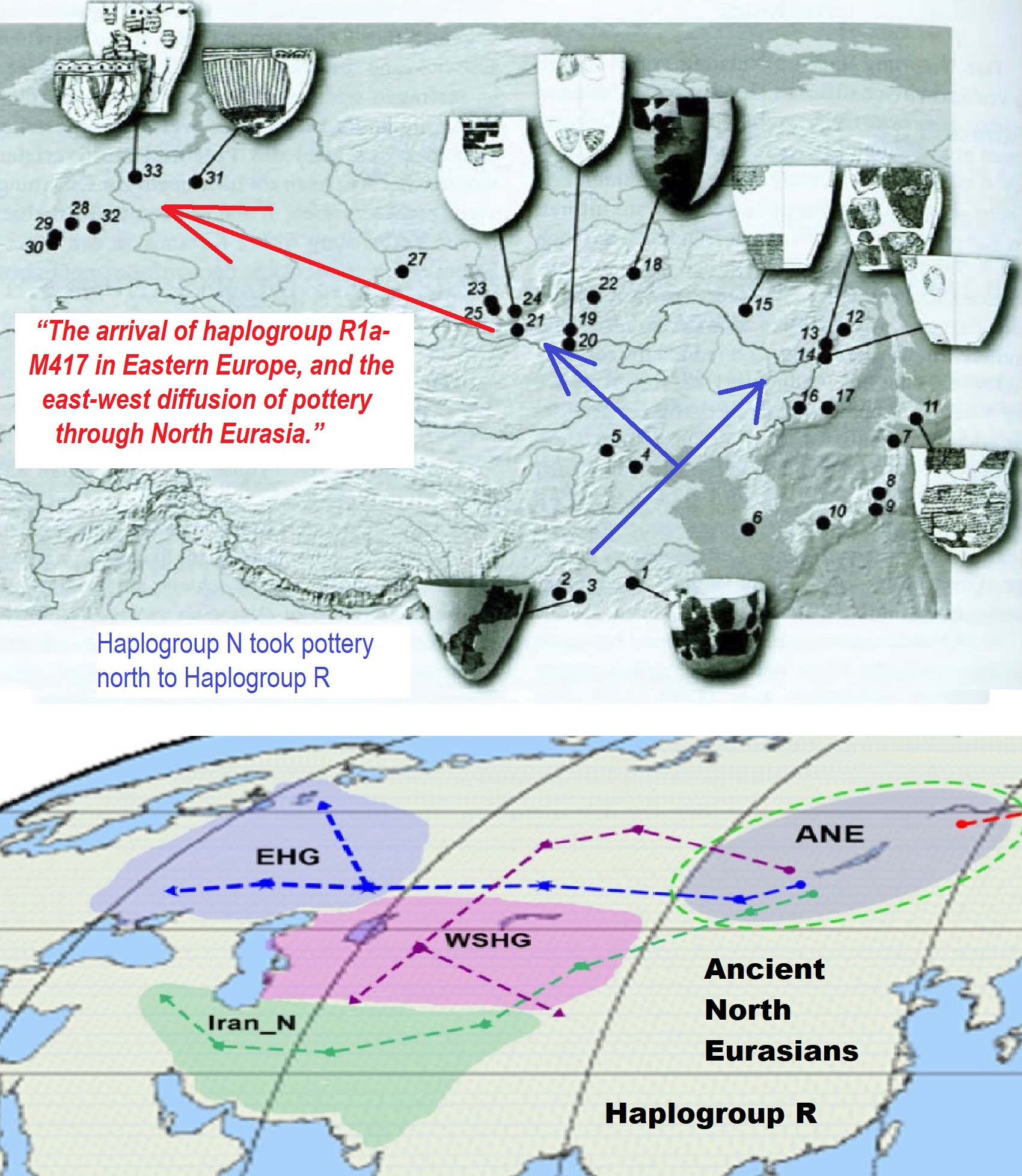
“The arrival of haplogroup R1a-M417 in Eastern Europe, and the east-west diffusion of pottery through North Eurasia.” ref
R-M417 (R1a1a1)
“R1a1a1 (R-M417) is the most widely found subclade, in two variations which are found respectively in Europe (R1a1a1b1 (R-Z282) ([R1a1a1a*] (R-Z282) and Central and South Asia (R1a1a1b2 (R-Z93) ([R1a1a2*] (R-Z93).” ref
R-Z282 (R1a1a1b1a) (Eastern Europe)
“This large subclade appears to encompass most of the R1a1a found in Europe.
- R1a1a1b1a [R1a1a1a*] (R-Z282*) occurs in northern Ukraine, Belarus, and Russia at a frequency of c. 20%.
- R1a1a1b1a3 [R1a1a1a1] (R-Z284) occurs in Northwest Europe and peaks at c. 20% in Norway.
- R1a1a1c (M64.2, M87, M204) is apparently rare: it was found in 1 of 117 males typed in southern Iran.” ref
R1a1a1b2 (R-Z93) (Asia)
“This large subclade appears to encompass most of the R1a1a found in Asia, being related to Indo-European migrations (including Scythians, Indo-Aryan migrations, and so on).
- R-Z93* or R1a1a1b2* (R1a1a2* in Underhill (2014)) is most common (>30%) in the South Siberian Altai region of Russia, cropping up in Kyrgyzstan (6%) and in all Iranian populations (1-8%).
- R-Z2125 occurs at highest frequencies in Kyrgyzstan and in Afghan Pashtuns (>40%). At a frequency of >10%, it is also observed in other Afghan ethnic groups and in some populations in the Caucasus and Iran.
- R-M434 is a subclade of Z2125. It was detected in 14 people (out of 3667 people tested), all in a restricted geographical range from Pakistan to Oman. This likely reflects a recent mutation event in Pakistan.
- R-M560 is very rare and was only observed in four samples: two Burushaski speakers (north Pakistan), one Hazara (Afghanistan), and one Iranian Azerbaijani.
- R-M780 occurs at high frequency in South Asia: India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, and the Himalayas. The group also occurs at >3% in some Iranian populations and is present at >30% in Roma from Croatia and Hungary.” ref
R-M458 (R1a1a1b1a1)
“R-M458 is a mainly Slavic SNP, characterized by its own mutation, and was first called cluster N. Underhill et al. (2009) found it to be present in modern European populations roughly between the Rhine catchment and the Ural Mountains and traced it to “a founder effect that … falls into the early Holocene period, 7.9±2.6 KYA.” M458 was found in one skeleton from a 14th-century grave field in Usedom, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. The paper by Underhill et al. (2009) also reports a surprisingly high frequency of M458 in some Northern Caucasian populations (for example 27.5% among Karachays and 23.5% among Balkars, 7.8% among Karanogays and 3.4% among Abazas).” ref
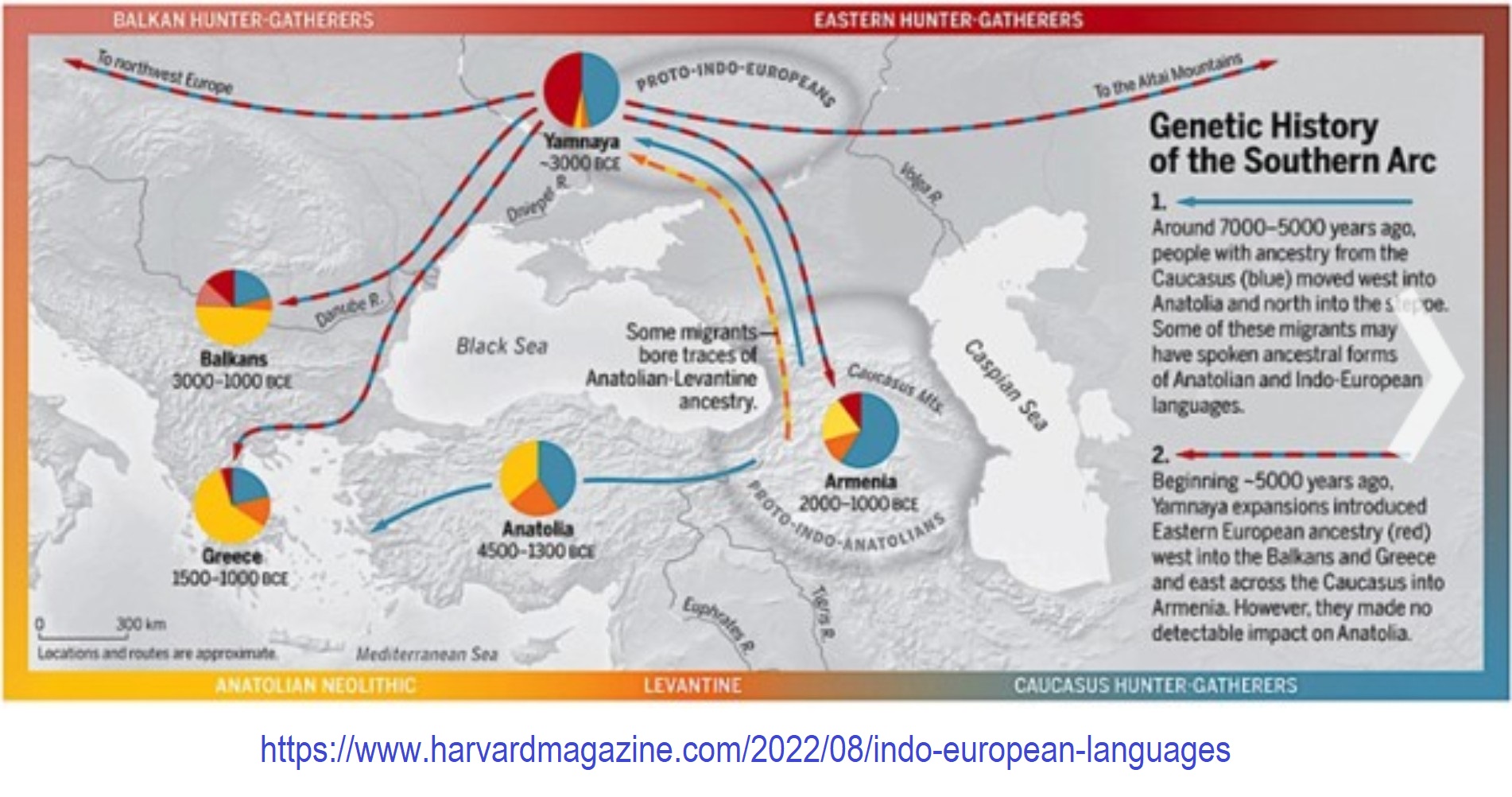
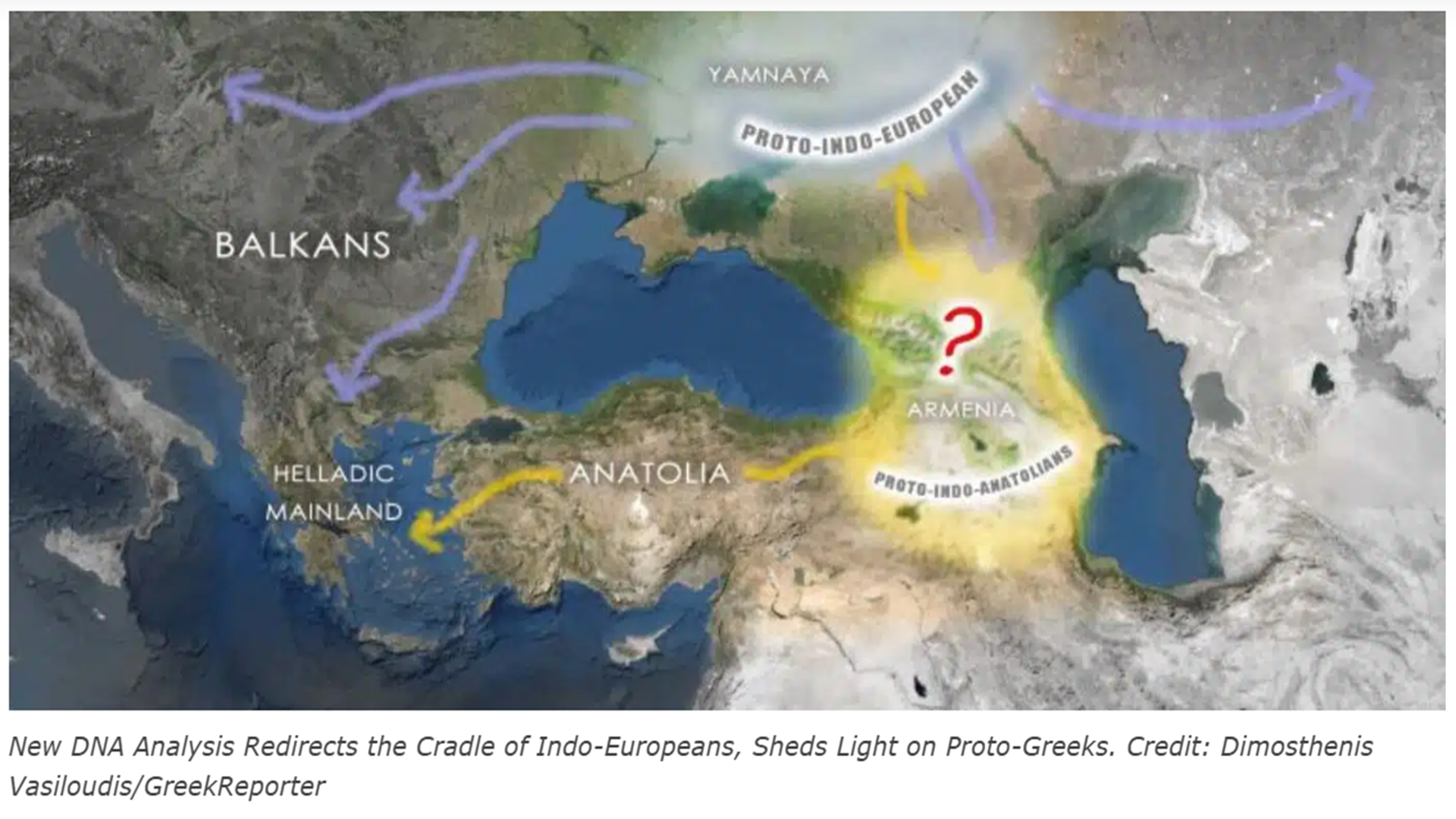
World’s oldest known fort was constructed by hunter-gatherers 8,000 years ago in Siberia
“The fact that this Stone Age fort was built by hunter-gatherers is transforming our understanding of ancient human societies. Hunter-gatherers built the oldest known fort in the world about 8,000 years ago in Siberia, a new study finds. Archaeologists have long associated fortresses with permanent agricultural settlements. However, this cluster of fortified structures reveals that prehistoric groups were constructing protective edifices much earlier than originally thought.” ref
“These hunter-gatherers “defy conventional stereotypes that depict such societies as basic and nomadic, unveiling their capacity to construct intricate structures,” study co-author Tanja Schreiber, an archaeologist at Free University of Berlin, told Live Science in an email. Located along the Amnya River in western Siberia, remains of the Amnya fort include roughly 20 pit-house depressions scattered across the site, which is divided into two sections: Amnya I and Amnya II. Radiocarbon dating confirmed that the settlement was first inhabited during the Mesolithic, or Middle Stone Age, according to the study. When constructed, each pit house would have been protected by earthen walls and wooden palisades — two construction elements that suggest “advanced agricultural and defensive capabilities” by the inhabitants, the archaeologists said in a statement.” ref
“One of the Amnya fort’s most astonishing aspects is the discovery that approximately 8,000 years ago, hunter-gatherers in the Siberian Taiga built intricate defense structures,” Schreiber said. “This challenges traditional assumptions that monumental constructions were solely the work of agricultural communities.” It’s unknown what triggered the need for these fortified structures in the first place, but the strategic location overlooking the river would have not only been an ideal lookout point for potential threats but also allowed hunter-gatherers to keep tabs on their fishing and hunting grounds, the researchers noted.” ref
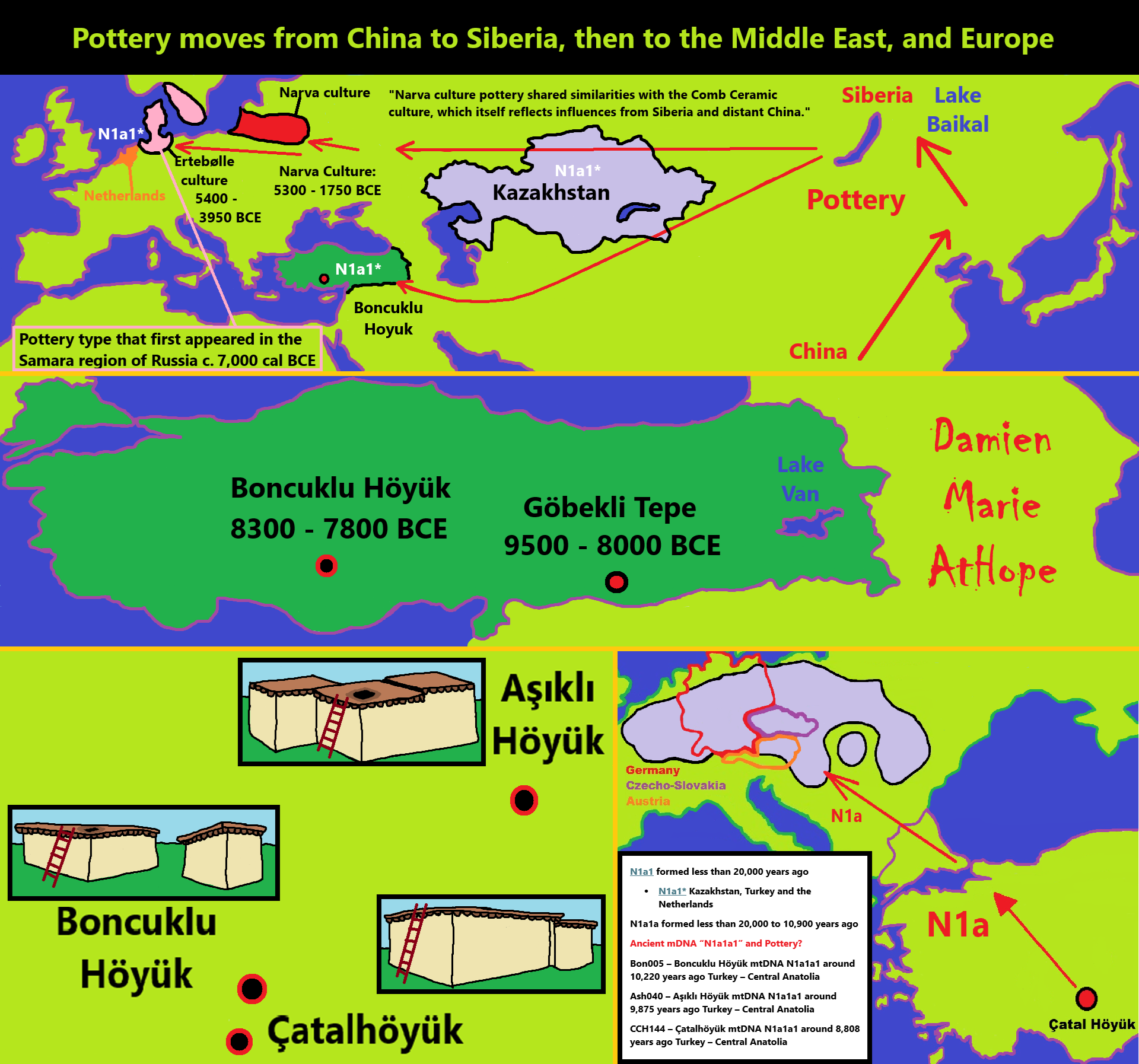
Pottery from at 10,000 at Boncuklu Höyük, to Aşıklı Höyük, to Çatalhöyük, then Europe by around 7,500 years ago.
Pottery moves from China to Siberia, then to the Middle East, and Europe
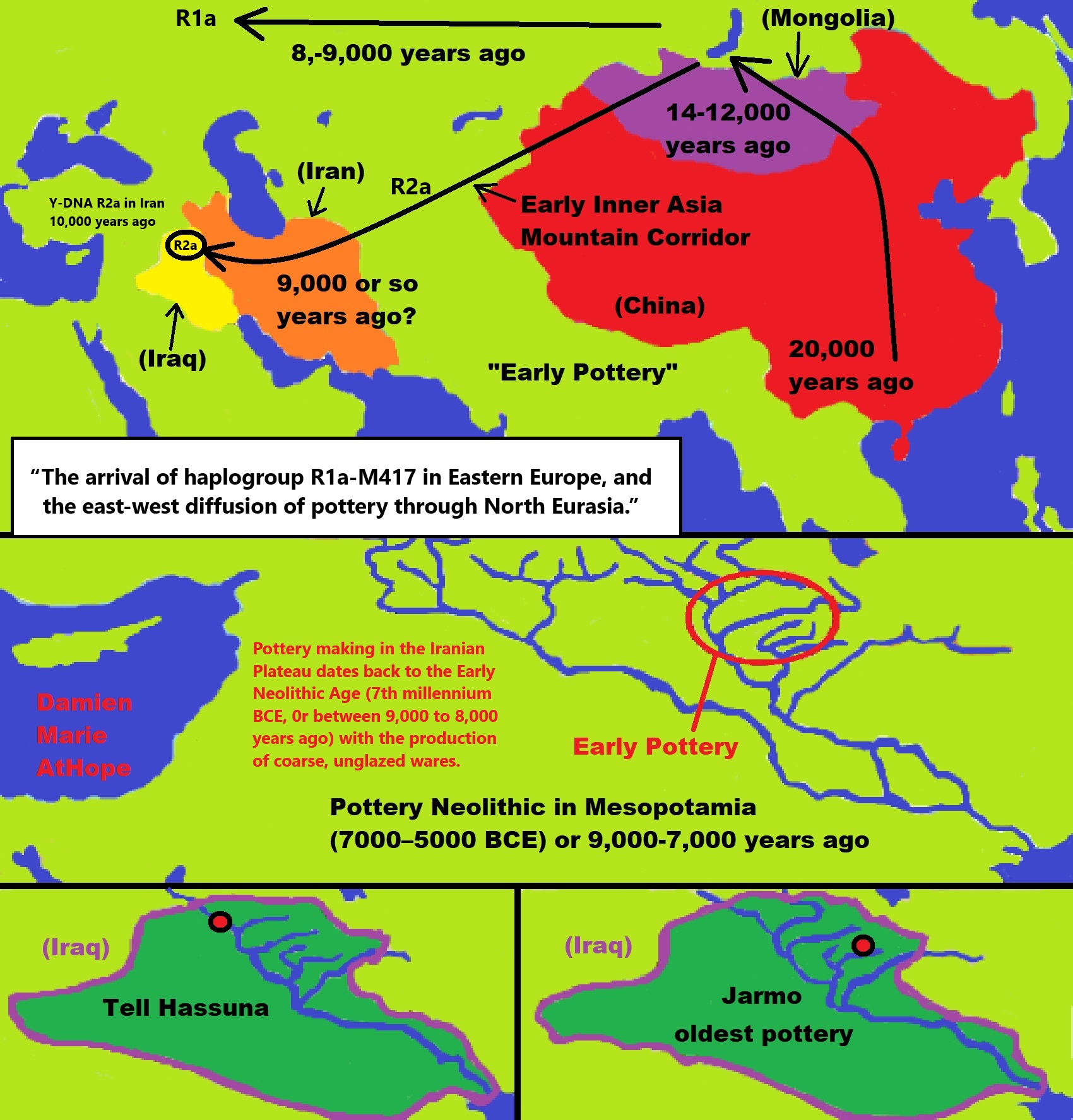
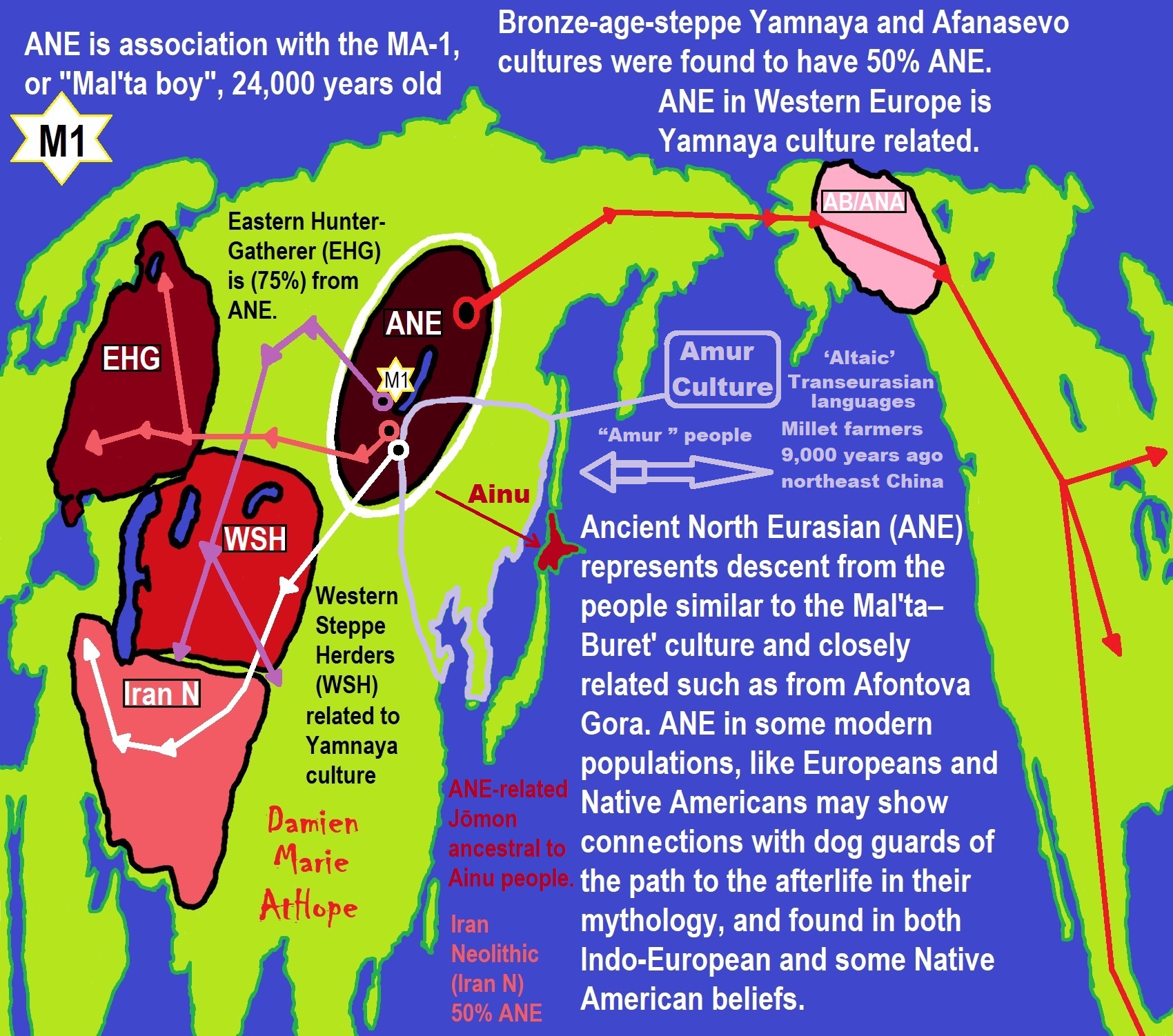
Ancient North Eurasian (ANE)
Ancient Beringian/Ancestral Native American (AB/ANA)
Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG)
Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG)
Western Steppe Herders (WSH)
Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG)
Early European Farmers (EEF)
Jōmon people (Ainu people OF Hokkaido Island)
Neolithic Iranian farmers (Iran_N) (Iran Neolithic)
Haplogroup R possible time of origin about 27,000 years in Central Asia, South Asia, or Siberia:
- Mal’ta–Buret’ culture (24,000-15,000 years ago)
- Afontova Gora culture (21,000-12,000 years ago)
- Trialetian culture (16,000–8000 years ago)
- Samara culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Khvalynsk culture (7,000-6,500 years ago)
- Afanasievo culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Yamna/Yamnaya Culture (5,300-4,500 years ago)
- Andronovo culture (4,000–2,900 years ago) ref
“The ANE lineage is defined by association with the MA-1, or “Mal’ta boy”, remains of 24,000 years ago in central Siberia Mal’ta-Buret’ culture 24,000-15,000 years ago. The Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) samples (Afontova Gora 3, Mal’ta 1, and Yana-RHS) show evidence for minor gene flow from an East Asian-related group (simplified by the Amis, Han, or Tianyuan) but no evidence for ANE-related geneflow into East Asians (Amis, Han, Tianyuan), except the Ainu, of North Japan.” ref
“The ANE lineage is defined by association with the MA-1, or “Mal’ta boy”, remains of 24,000 years ago in central Siberia Mal’ta-Buret’ culture 24,000-15,000 years ago “basal to modern-day Europeans”. Some Ancient North Eurasians also carried East Asian populations, such as Tianyuan Man.” ref
“Bronze-age-steppe Yamnaya and Afanasevo cultures were ANE at around 50% and Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) at around 75% ANE. Karelia culture: Y-DNA R1a-M417 8,400 years ago, Y-DNA J, 7,200 years ago, and Samara, of Y-haplogroup R1b-P297 7,600 years ago is closely related to ANE from Afontova Gora, 18,000 years ago around the time of blond hair first seen there.” ref
Ancient North Eurasian
“In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (often abbreviated as ANE) is the name given to an ancestral West Eurasian component that represents descent from the people similar to the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture and populations closely related to them, such as from Afontova Gora and the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site. Significant ANE ancestry are found in some modern populations, including Europeans and Native Americans.” ref
“The ANE lineage is defined by association with the MA-1, or “Mal’ta boy“, the remains of an individual who lived during the Last Glacial Maximum, 24,000 years ago in central Siberia, Ancient North Eurasians are described as a lineage “which is deeply related to Paleolithic/Mesolithic hunter-gatherers in Europe,” meaning that they diverged from Paleolithic Europeans a long time ago.” ref
“The ANE population has also been described as having been “basal to modern-day Europeans” but not especially related to East Asians, and is suggested to have perhaps originated in Europe or Western Asia or the Eurasian Steppe of Central Asia. However, some samples associated with Ancient North Eurasians also carried ancestry from an ancient East Asian population, such as Tianyuan Man. Sikora et al. (2019) found that the Yana RHS sample (31,600 BP) in Northern Siberia “can be modeled as early West Eurasian with an approximately 22% contribution from early East Asians.” ref
“Populations genetically similar to MA-1 were an important genetic contributor to Native Americans, Europeans, Central Asians, South Asians, and some East Asian groups, in order of significance. Lazaridis et al. (2016:10) note “a cline of ANE ancestry across the east-west extent of Eurasia.” The ancient Bronze-age-steppe Yamnaya and Afanasevo cultures were found to have a noteworthy ANE component at ~50%.” ref
“According to Moreno-Mayar et al. 2018 between 14% and 38% of Native American ancestry may originate from gene flow from the Mal’ta–Buret’ people (ANE). This difference is caused by the penetration of posterior Siberian migrations into the Americas, with the lowest percentages of ANE ancestry found in Eskimos and Alaskan Natives, as these groups are the result of migrations into the Americas roughly 5,000 years ago.” ref
“Estimates for ANE ancestry among first wave Native Americans show higher percentages, such as 42% for those belonging to the Andean region in South America. The other gene flow in Native Americans (the remainder of their ancestry) was of East Asian origin. Gene sequencing of another south-central Siberian people (Afontova Gora-2) dating to approximately 17,000 years ago, revealed similar autosomal genetic signatures to that of Mal’ta boy-1, suggesting that the region was continuously occupied by humans throughout the Last Glacial Maximum.” ref
“The earliest known individual with a genetic mutation associated with blonde hair in modern Europeans is an Ancient North Eurasian female dating to around 16000 BCE from the Afontova Gora 3 site in Siberia. It has been suggested that their mythology may have included a narrative, found in both Indo-European and some Native American fables, in which a dog guards the path to the afterlife.” ref
“Genomic studies also indicate that the ANE component was introduced to Western Europe by people related to the Yamnaya culture, long after the Paleolithic. It is reported in modern-day Europeans (7%–25%), but not of Europeans before the Bronze Age. Additional ANE ancestry is found in European populations through paleolithic interactions with Eastern Hunter-Gatherers, which resulted in populations such as Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers.” ref
“The Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) split from the ancestors of European peoples somewhere in the Middle East or South-central Asia, and used a northern dispersal route through Central Asia into Northern Asia and Siberia. Genetic analyses show that all ANE samples (Afontova Gora 3, Mal’ta 1, and Yana-RHS) show evidence for minor gene flow from an East Asian-related group (simplified by the Amis, Han, or Tianyuan). In contrast, no evidence for ANE-related geneflow into East Asians (Amis, Han, Tianyuan), except the Ainu, was found.” ref
“Genetic data suggests that the ANE formed during the Terminal Upper-Paleolithic (36+-1,5ka) period from a deeply European-related population, which was once widespread in Northern Eurasia, and from an early East Asian-related group, which migrated northwards into Central Asia and Siberia, merging with this deeply European-related population. These population dynamics and constant northwards geneflow of East Asian-related ancestry would later gave rise to the “Ancestral Native Americans” and Paleosiberians, which replaced the ANE as dominant population of Siberia.” ref
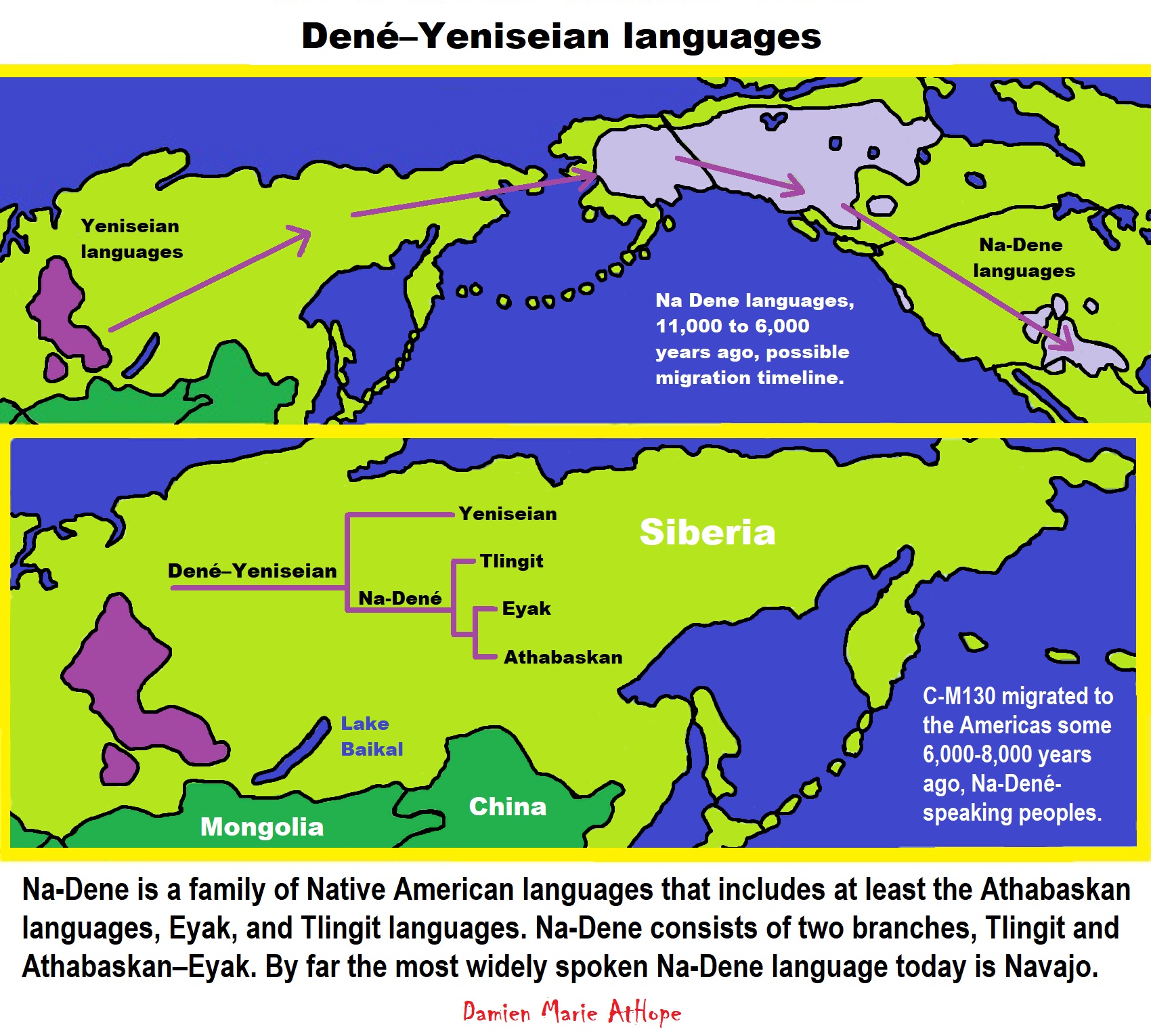
My art and when as well as who may have brought in the new elitism and compulsory authority to the Americas.
“For the Tlingit (branch of the Na-Dené language family), hereditary slavery was practiced extensively until it was outlawed by the United States. Wealth and economic power are important indicators of rank. Scientists suggest that the main ancestor of the Ainu and of the Tlingit can be traced back to Paleolithic groups in Southern Siberia.” ref
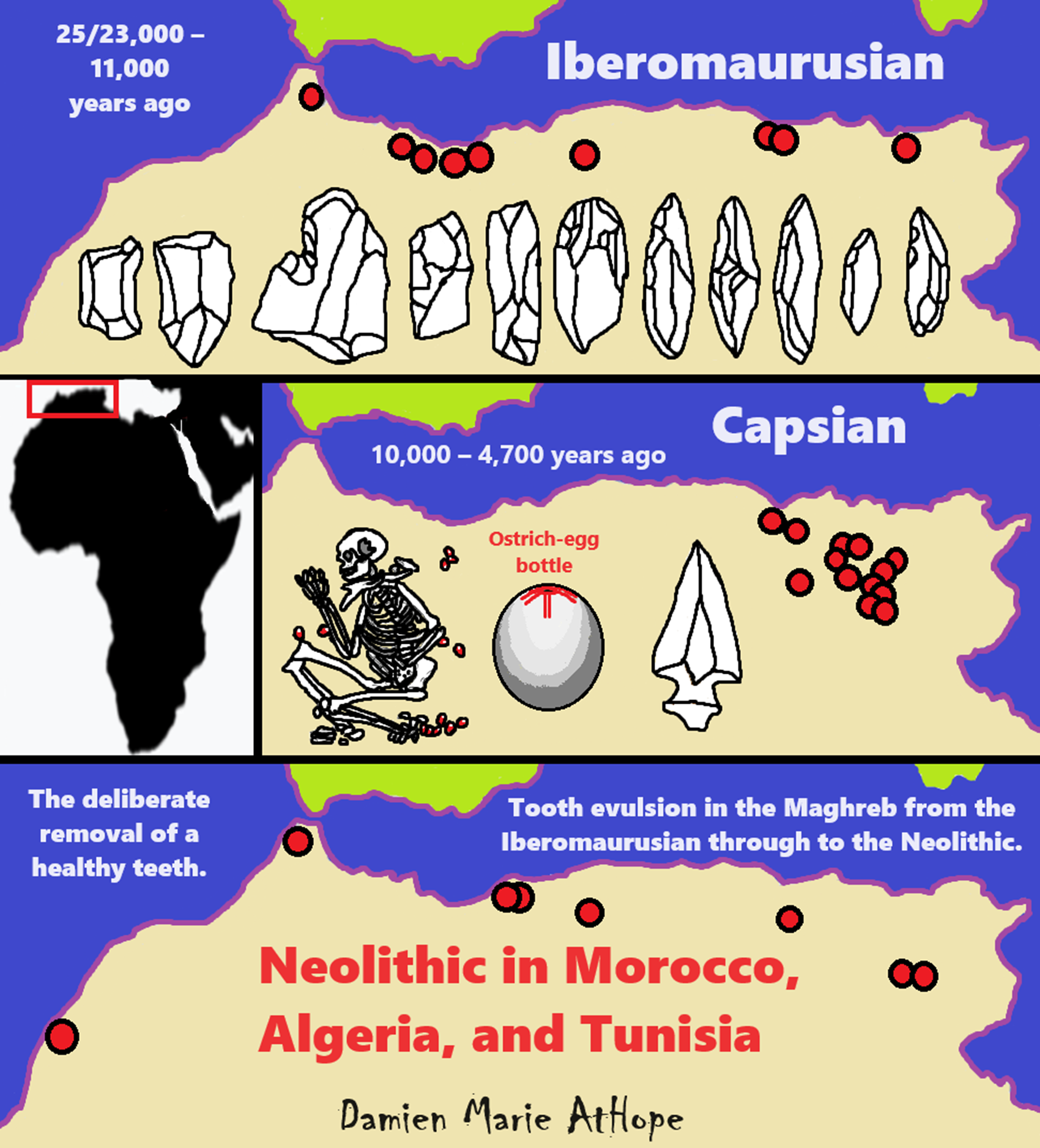
Iberomaurusian Culture
“The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is locally known as the Eastern Oranian. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), somewhere between c. 25,000 and 23,000 years ago. It would have lasted until the early Holocene c. 11,000 years ago. In Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya, but not in Morocco, the industry is succeeded by the Capsian industry, whose origins are unclear. The Capsian is believed either to have spread into North Africa from the Near East, or to have evolved from the Iberomaurusian. In Morocco and Western Algeria, the Iberomaurusian is succeeded by the Cardial culture after a long hiatus.” ref
“The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is locally known as the Eastern Oranian. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum, somewhere between 25,000 and 23,000 years ago. It would have lasted until the early Holocene c. 11,000 years ago. In Algeria, Tunisia, and Libya, but not in Morocco, the industry is succeeded by the Capsian industry, whose origins are unclear. The Capsian is believed either to have spread into North Africa from the Near East, or to have evolved from the Iberomaurusian. In Morocco and Western Algeria, the Iberomaurusian is succeeded by the Cardial culture after a long hiatus.” ref
“The Mitochondrial DNA of 31 prehistoric skeletons dated from the site of Taforalt, Morocco in a cave called ‘Grotte des pigeons’ was analyzed by the Tunisian geneticist Rym Kefi (Pasteur Institute of Tunis) and her team. The remains at Taforalt Iberomaurusian industry appeared at least 22,093–21,420 years ago and 8 skeletons from the Algerian Iberomaurusian site called ‘Afalou’ site dated from 15,000 to 11,000 years ago.” ref
“23 individuals from Taforalt sample were determined to be of the maternal genetic lineage U6 and of Eurasian haplogroups H, U, R0 and at the Algerian Afalou site maternal groups were JT, J, T, H, R0a1 and U. This suggests genetic flow between North Africa and southern Mediterranean littoral since the Epipaleolithic. In a article entitled ‘Pleistocene North African genomes link Near Eastern and sub-Saharan African human populations’, Marieke Van de Loosdrecht et al. (2018) did a full genome-wide analysis including Y-DNA from seven ancient individuals from the Taforalt site. The fossils were directly dated to between 15,100 and 13,900 calibrated years before present.” ref
“All males at Taforalt belonged to haplogroup E1b1b1a1 (M-78). This haplogroup occurs most frequently in present-day North and East African populations. The closely related E1b1b1b (M-123) haplogroup has been reported for Epipaleolithic Natufians and Pre-Pottery Neolithic Levantines. Loosdrecht states: “Present-day North Africans share a majority of their ancestry with present-day Near Easterners, but not with sub-Saharan Africans” although the predominant Y-DNA of the Maghreb is E-M81 (see Haplogroup E-Z827 ) Maternally, six individuals of the Taforalt remains bore the U6a haplogroup and one individual was of the M1b haplogroup, these haplogroups proposed as markers for autochthonous Maghreb ancestry. A two-way admixture scenario using Natufian and modern sub-Saharan samples (including West Africans and the Tanzanian Hadza) as reference populations inferred that the seven Taforalt individuals are best modeled genetically as of 63.5% West-Eurasian-related and 36.5% sub-Saharan ancestry (with the latter having both West African-like and Hadza-like affinities), with no apparent gene flow from the Epigravettian culture of Paleolithic southern Europe. ” ref
“The Sub-Saharan African DNA in Taforalt individuals has the closest affinity, most of all, to that of modern West Africans (e.g., Yoruba, or Mende). In addition to having similarity with the remnant of a more basal Sub-Saharan African lineage (e.g., a basal West African lineage shared between Yoruba and Mende peoples), the Sub-Saharan African DNA in the Taforalt individuals of the Iberomaurusian culture may be best represented by modern West Africans (e.g., Yoruba). Iosif Lazaridis et al. (2018), as summarized by Rosa Fregel (2021), contested the conclusion of Loosdrecht (2018) and argued instead that the Iberomaurusian population of Upper Paleolithic North Africa, represented by the Taforalt sample, can be better modeled as an admixture between a Dzudzuana-like [West-Eurasian] component and an “Ancient North African” component, “that may represent an even earlier split than the Basal Eurasians.” ref
“Losif Lazaridis et al. (2018) also argued that an Iberomaurusian/Taforalt-like population contributed to the genetic composition of Natufians “and not the other way around”, and that this Iberomaurusian/Taforalt lineage also contributed around 13% ancestry to modern West Africans “rather than Taforalt having ancestry from an unknown Sub-Saharan African source”. Fregel (2021) summarized: “More evidence will be needed to determine the specific origin of the North African Upper Paleolithic populations. Martiniano et al. (2022) later reassigned all the Taforalt samples to haplogroup E-M78 and none to E-L618, the predecessor to EV13. D’Atanasio et al. 2023 found that Iberomaurusian-like ancestry was characterizing for the “ancient Green Saharan” population about 12,000-5,000 years ago, and that modern-day Fula people derive around 30% of their ancestry from this ancient Saharan population, which was “modeled as a sister group of ancient Northern Africans, or alternatively, as an outgroup of all the “Eurasian-ancestry” enriched groups.” ref
“The practice of Tooth Evulsion was widespread in the Maghreb from the Iberomaurusian through to the Neolithic.” ref
Tooth Evulsion
“Tooth ablation (also known as tooth evulsion, dental evulsion and tooth extraction) is the deliberate removal of a person’s healthy teeth, and has been recorded in a variety of ancient and modern societies around the world. This type of dental modification is visually very striking and immediately obvious to other people from the same or different communities. There are numerous reasons for performing tooth ablation, including group identification, ornamentation, and rites of passage such as coming of age, marriage, and mourning. The social meaning of tooth evulsion is likely to remain unknown for ancient populations and may have changed over time within those groups. Dental evulsion can significantly affect the emergence, occlusion, and wear patterns of the remaining teeth.” ref
“There are various techniques used to perform dental evulsion; however, regardless of the technique, dental evulsion could not have been achieved without causing pain and a risk of infection. In Africa, extractive techniques were used. In Sudan, fish hooks and metal wires were used to remove deciduous tooth germs before an infant reached one month. In the Upper Nile, the entire tooth was removed by loosening the anterior teeth from their sockets with an iron spike. The Nuer people of South Sudan still practice an extractive technique whereby a fine blade is used to loosen the teeth alongside the root, which takes place without anesthetic, and the individual is not allowed to show emotion or pain. The evulsion of the lower teeth would have resulted in a highly visible change to the individual’s facial characteristics and would also have affected the pronunciation of language and other sounds.” ref
“Dental evulsion was at one time a common practice in Africa, especially in East and East Central Africa. In West Africa, the custom of extraction is rather uncommon, but it was found among the Ashanti who broke teeth out of their war prisoners, and a few tribes in Cameroon, Ghana, Togo, and Liberia. Dental evulsion also occurred in Angola and Namibia. In Kenya, Tanzania, and South Sudan, dental evulsion is mainly a Nilotic custom. In South Sudan, lower incisors (and sometimes also the canines), are extracted shortly after their eruption, as a rite of passage, for beauty, to allow the emission of specific linguistic sounds, and to facilitate oral sex. This is found among the Dinka, Nuer, and Maban tribes, especially in rural villages. The Luo people extract the six lower teeth as a form of initiation into adulthood. The Maasai people of Kenya extract the lower deciduous incisors of infants at six months, and the lower permanent incisors at six years; this is performed only for boys to facilitate feeding them in case they are ill with tetanus, and to exorcize the kidnapping of babies.” ref
Nile during the Last Glacial Maximum
“Geological cores in the eastern Mediterranean show that sediment input from the Nile during the LGM, while present, is highly reduced compared to previous periods. These data are consistent with a Nile that continued to flow during MIS 2, but possibly only seasonally or during major flood events. Element analyses of core sediments from the eastern Mediterranean confirm a negligible input from the White Nile, vs. an input from the Blue Nile and Atbara, and indicates an increase of Saharan dust input during the Last Glacial Maximum. A recent high-resolution multi-proxy study of a sediment core from the eastern Mediterranean documents the most severe period of aridity in the Nile Basin in the past 28,000 years, after the Last Glacial Maximum, during the second phase of HS 1, 16,000-14,500 years ago (HS 1b).” ref
“From 14,500 years ago, the Mediterranean sea level starts to rise again and several proxies, such as pollen data and lake levels, indicate wetter conditions over at least some areas of eastern Africa, in two phases 14,500 and 11,000 years ago. In particular, the abrupt return of precipitation over eastern Africa 14,500 years ago led to an overflow of Lake Victoria into Lake Albert, the Ugandan headwaters of the White Nile, which triggered high floods in the White Nile Valley as well as at the northern end of the Nile Valley. These data are mirrored by data from the Delta, indicating a marked increase in the sedimentary input of the Blue Nile and Atbara in Delta sediment cores, with evidence for high floods in the Delta ca. 15,000–10,000 years ago. However, millennial-scale episodes of aridity are noted, such as one ca. 13,000-12,000 years ago before a return to humid conditions 12,000 years ago. Maximum Nile flow is documented in the Delta at that time leading to the deposition of an organic-rich dark layer known as Sapropel 1 in the Delta ca. 9,500-7,000 years ago.” ref
“Under present environmental conditions, the Nile Valley acts as a ‘natural’ route between Africa and Eurasia, and is often considered as a corridor for dispersals out of and back into Africa in the past. This review aims to address the role played by the Nile Valley at the end of the Pleistocene (28,000-15,000 years ago) in the context of post-‘Out of Africa’ modern human dispersals. Genetic studies based on both modern and ancient DNA suggest pre-Holocene dispersals ‘back into Africa’ as well as genetic interactions between modern humans across Africa and the Levant. During the Last Glacial, the lowering, or even complete desiccation of major eastern African lakes, including Lake Victoria, reduced the White Nile to a highly seasonal river, depriving the main Nile from its most important tributary in the dry season. This had major consequences, the specifics of which are still debated, on the behavior of the main Nile and the landscape around the Nile Delta. Despite this shift to more arid conditions, there is abundant evidence for human occupation in the main Nile Valley.” ref
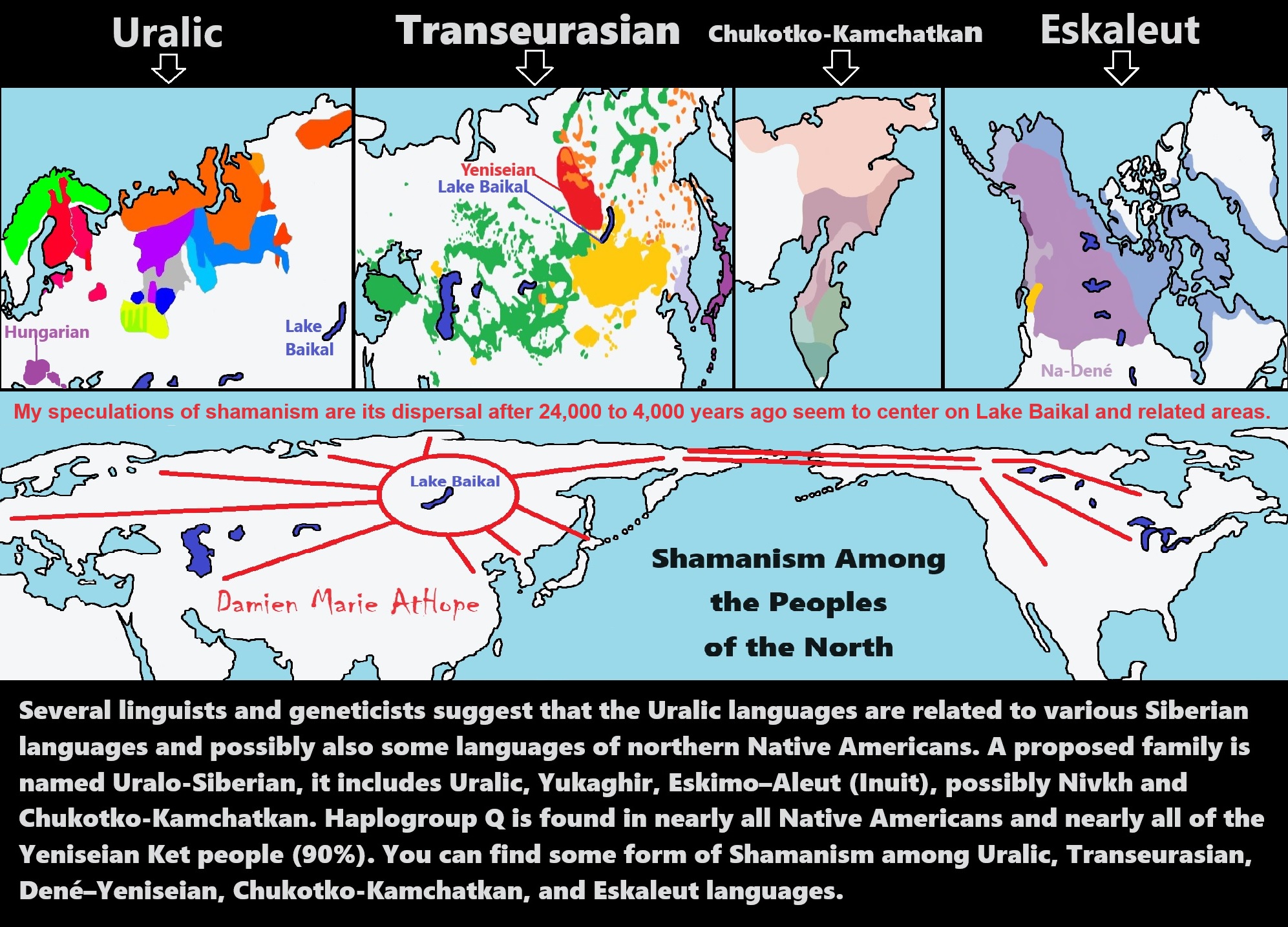
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“Several linguists and geneticists suggest that the Uralic languages are related to various Siberian languages and possibly also some languages of northern Native Americans. A proposed family is named Uralo-Siberian, it includes Uralic, Yukaghir, Eskimo–Aleut (Inuit), possibly Nivkh, and Chukotko-Kamchatkan. Haplogroup Q is found in nearly all Native Americans and nearly all of the Yeniseian Ket people (90%).” ref, ref
You can find some form of Shamanism, among Uralic, Transeurasian, Dené–Yeniseian, Chukotko-Kamchatkan, and Eskaleut languages.
My speculations of shamanism are its dispersals, after 24,000 to 4,000 years ago, seem to center on Lake Baikal and related areas. To me, the hotspot of Shamanism goes from west of Lake Baikal in the “Altai Mountains” also encompassing “Lake Baikal” and includes the “Amur Region/Watershed” east of Lake Baikal as the main location Shamanism seems to have radiated out from.
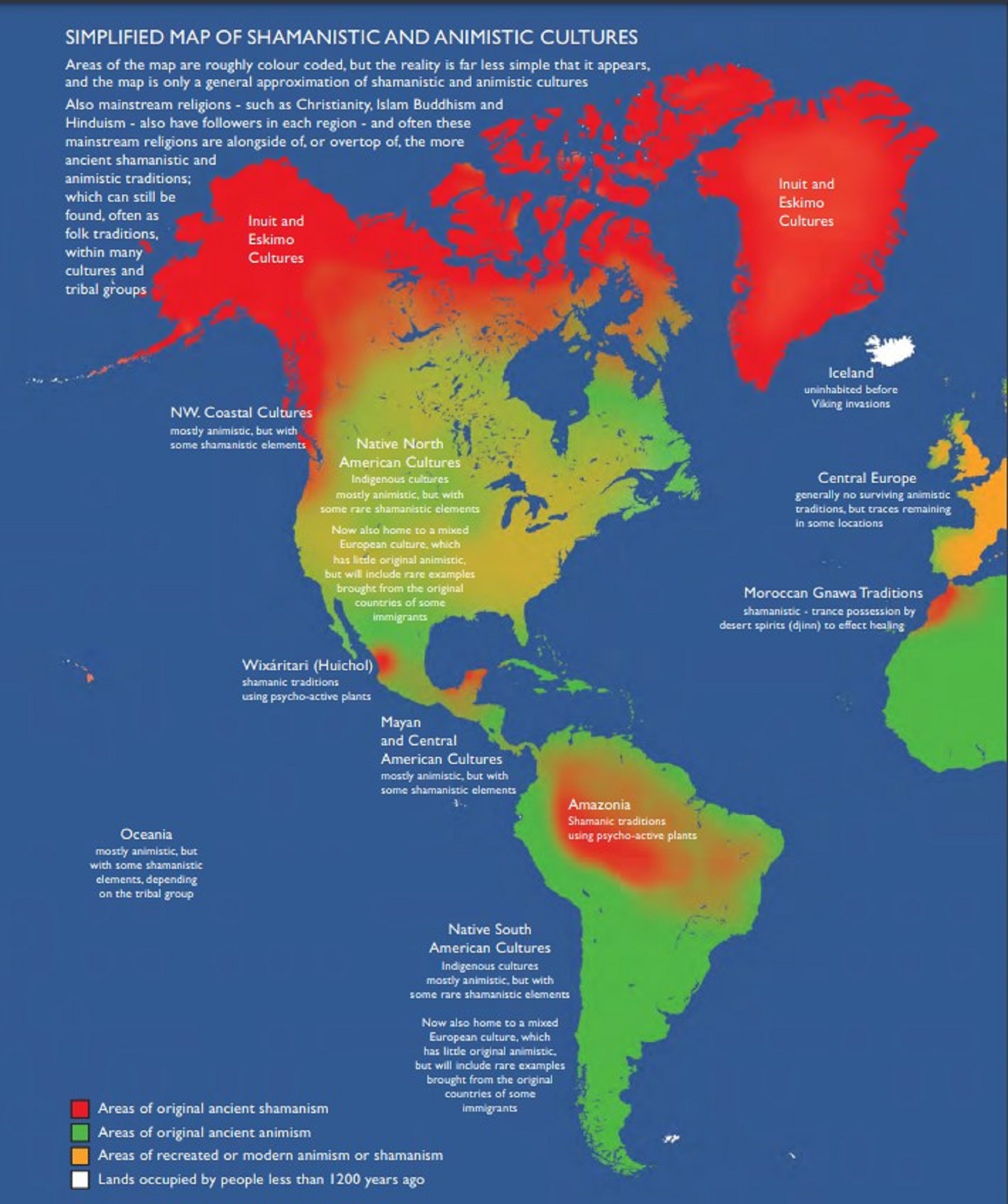
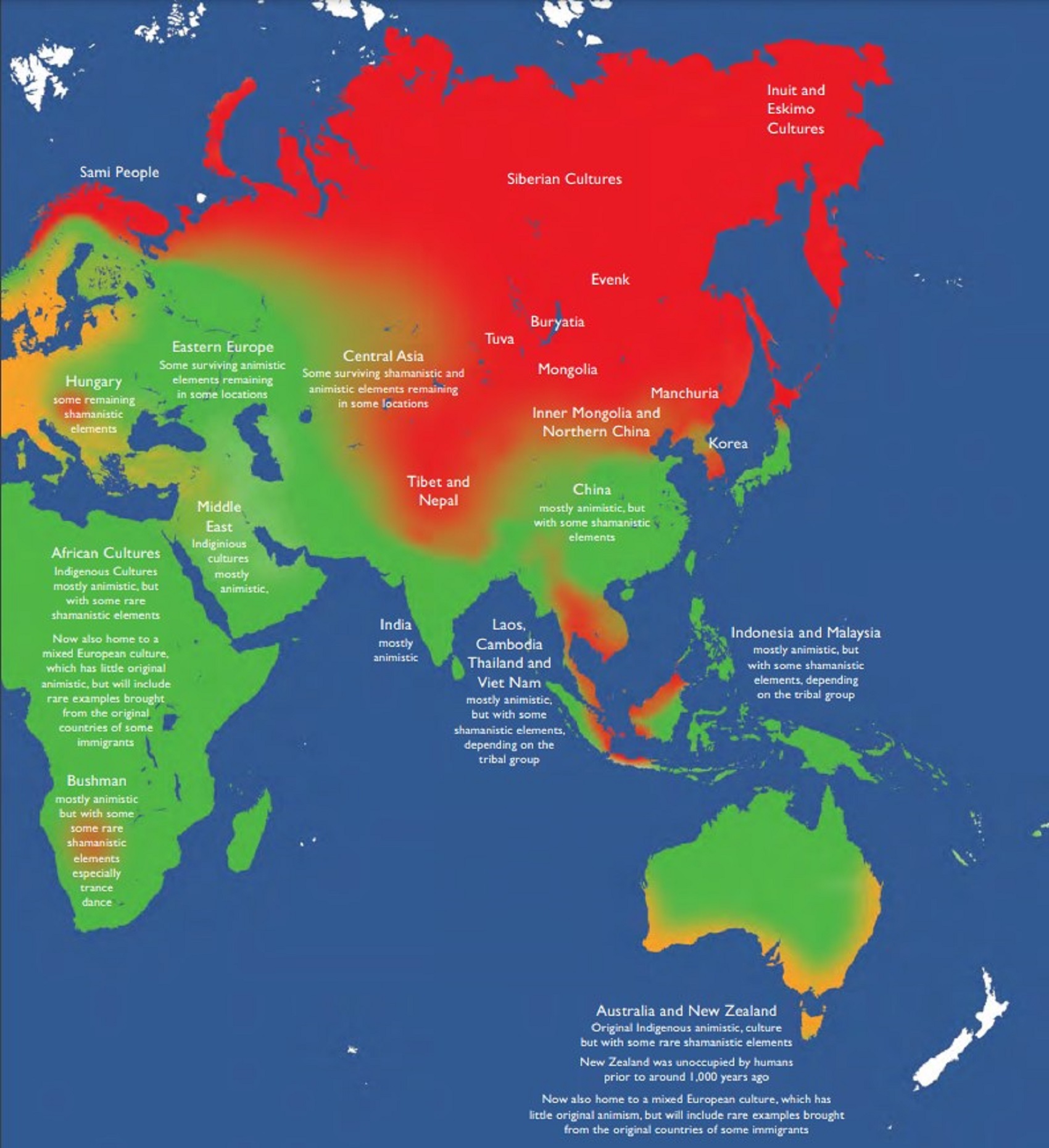
Shamanistic and Animistic Cultures map by “The Shamanism Magazine” (http://SacredHoop.org)
https://sacredhoop.org/Free-Guide-To-Shamanism/Sacred-Hoop-Free-Guide-To-Shamanism.pdf
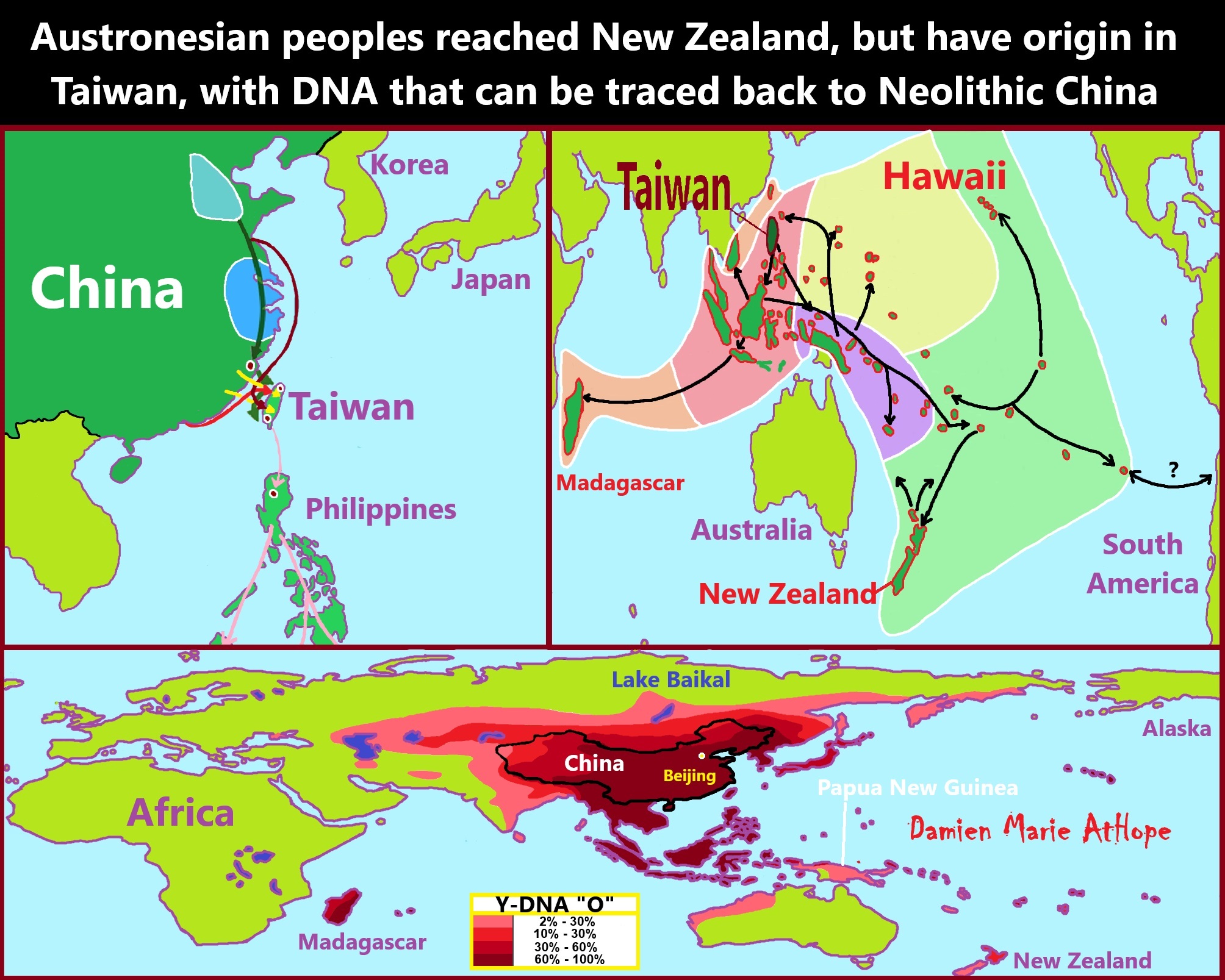
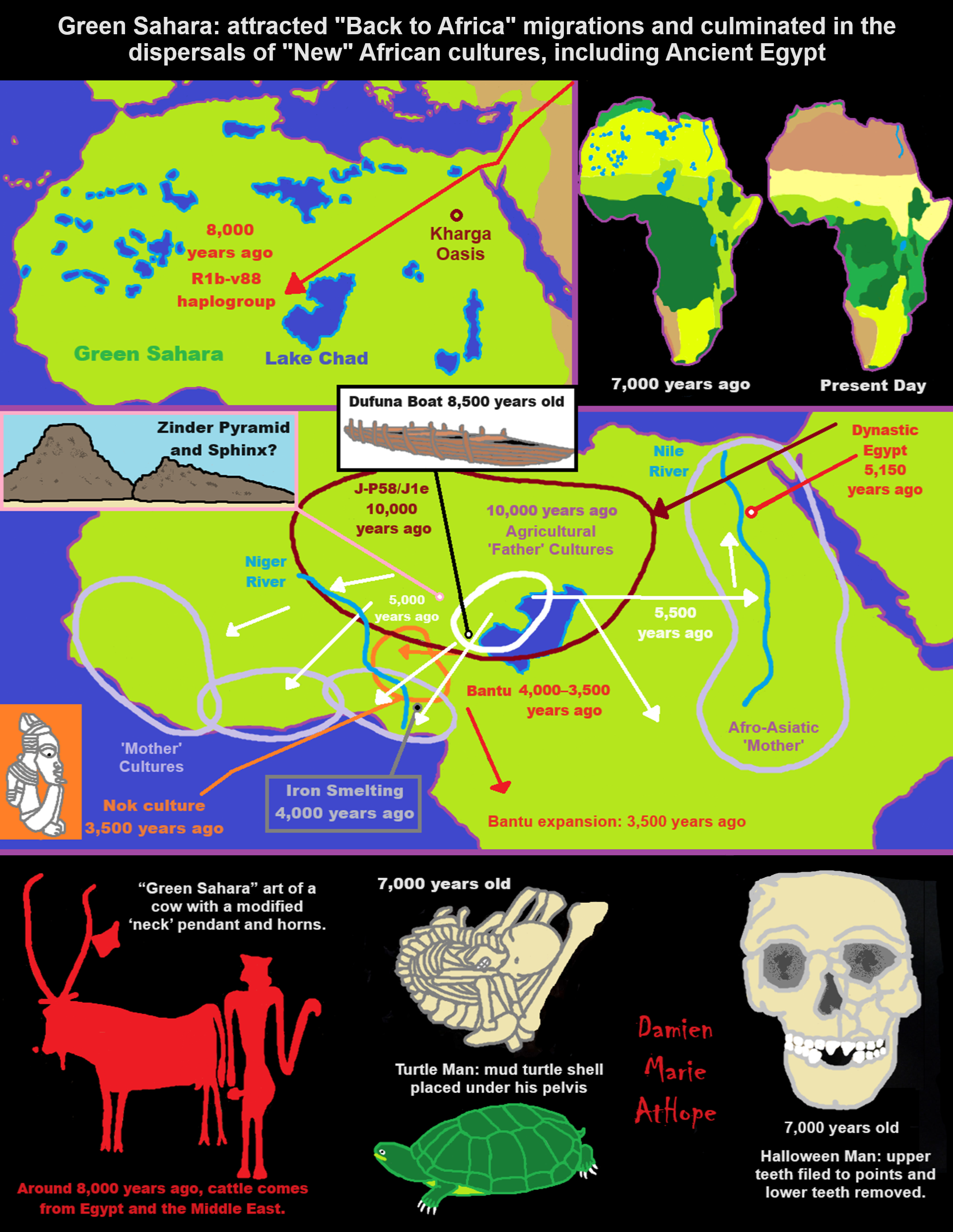
Nabta Playa
“Nabta Playa was once a large endorheic basin in the Nubian Desert, located approximately 800 kilometers south of modern-day Cairo or about 100 kilometers west of Abu Simbel in southern Egypt, 22.51° north, 30.73° east. Today the region is characterized by numerous archaeological sites. The Nabta Playa archaeological site, one of the earliest of the Egyptian Neolithic Period, is dated to circa 7500 BCE or around 9,500 years ago. Although today the western Egyptian desert is totally dry, this was not always the case. There is good evidence that there were several humid periods in the past (when up to 500 mm of rain would fall per year), the most recent one during the last interglacial and early last glaciation periods which stretched between 130,000 and 70,000 years ago. During this time, the area was a savanna and supported numerous animals such as extinct buffalo and large giraffes, varieties of antelope and gazelle. Beginning around the 10th millennium BC, this region of the Nubian Desert began to receive more rainfall, filling a lake. Early people may have been attracted to the region due to the source of water.” ref
“Archaeological findings indicate the presence of small seasonal camps in the region dating to the 9th–8th millennia BC. Fred Wendorf, the site’s discoverer, and ethno-linguist Christopher Ehret have suggested that the people who occupied this region at that time may have been early pastoralists, or like the Saami practiced semi-pastoralism. This is disputed by other sources as the cattle remains found at Nabta have been shown to be morphologically wild in several studies, and hunter-gatherers at the nearby Saharan site of Uan Afada in Libya were penning wild Barbary sheep, an animal that was never domesticated. According to Michael Brass (2018) early cattle remains from Nabta Playa were wild hunted aurochs, whilst domesticated cattle were introduced to northeast Africa in the late 7th millennium BC, originating from cattle domesticated in the Euphrates valley.” ref
“The Nabta Playa—Bir Kiseiba region of southern Egypt, and the initial rigorous debates. More recently, geneticists have entered the fray with determinations on the spread of haplotypes, and the timing thereof, that extend the scope and increase the complexity of the debate. Here, a new look at the botanical data and a re-analysis of the geology of Bir Kiseiba–Nabta Playa rejects the ecological foundations of the early African domestication model, while a detailed examination of the published osteological and radiometric data from the same area reveals a more nuanced picture than has been recognized to date. These results are placed into context by a wider review of the genetic and other archaeological evidence from the Western Desert of Northeast Africa, where no other cattle remains designated as domesticated have been found. It is concluded that (a) Bos remains from the early Holocene at Nabta Playa—Bir Kiseiba were those of hunted aurochs; (b) domesticated caprines were likely present in Northeast Africa before domesticated cattle; and (c) the domesticated cattle spreading across Northeast and northern Africa, including Nabta Playa—Bir Kiseiba, from the late seventh millennium BCE or early sixth millennium BCE onwards were descendants of Bos taurus domesticated in the Middle Euphrates area of the Middle East.” ref
“Most researchers thought the first domesticated cattle in Africa arrived from the Near East, perhaps as early as 7800 years ago. But in the 1980s, a few archaeologists began to argue that inhabitants of northeastern Africa had domesticated cattle independently some 10,000 years ago. A statistical analysis revealed three major genetic trends within current cattle populations across Africa. Two influences came from outside Africa. The genetic signature of zebu–a type of humped cattle domesticated some 8000 years ago in the area of Pakistan–was most prominent in cattle in the Horn of Africa. From this, the team concluded that zebu were introduced to that region primarily through sea trade. Cattle populations across northern Africa, in contrast, contained genetic influence from taurine cattle, which were domesticated at least 8000 years ago in the Fertile Crescent of Turkey and other countries. Another sizable component of the genetic variation featured neither of these influences, leading Hanotte’s team to suspect that it represents a unique domestication of native wild cattle in Africa. A few skeptics remain. “The article does not prove an earlier independent domestication event in Africa,” says Andrew Smith of the University of Cape Town, South Africa. For that, he wants to see archaeological evidence for African cattle domestication that might place it before the same achievement in Near East Asia. Fiona Marshall of Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, however, is more impressed. To her, the new finding reinforces the idea that people living in Africa during the last 10,000 or so years took an unusual path to food production: domesticating livestock before plants.” ref
“Larger settlements began to appear at Nabta Playa by the 7th millennium BC, relying on deep wells for sources of water. Small huts were constructed in straight rows. Sustenance included wild plants, such as legumes, millets, sorghum, tubers, and fruit. Around 6800 BCE or around 8,800 years ago they began to make pottery locally. In the late 7th millennium BCE goats and sheep, apparently imported from Western Asia, appear. Many large hearths also appear. Early pottery from the Nabta Playa-Bir Kiseiba area has characteristics unlike pottery from surrounding regions. This is followed by pottery with characteristics found only in the Western Desert. Later pottery from c. 5500 BCE (Al Jerar phase) has similarities with pottery from the Sudanese region. Pottery decorations included complex patterns of impressions applied with a comb in a rocking motion.” ref
“Northwest African Neolithic initiated by migrants from Iberia (Portugal and Spain) and the Levant (includes present-day Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, the Palestinian territories, and most of Turkey southwest of the middle Euphrates). During the Neolithic expansion, various megalithic cultures developed in the Iberian Peninsula. An open seas navigation culture from the east Mediterranean, called the Cardium culture, also extended its influence to the eastern coasts of the peninsula, possibly as early as the 5th millennium BCE. These people may have had some relation to the subsequent development of the Iberian civilization. This pottery style gives its name to the main culture of the Mediterranean Neolithic: Cardium pottery culture or Cardial culture, or impressed ware culture, which eventually extended from the Adriatic sea to the Atlantic coasts of Portugal and south to Morocco. Older Neolithic cultures existed already at this time in eastern Greece and Crete, apparently having arrived from Anatolia, but they appear distinct from the Cardial or impressed ware culture. The ceramic tradition in the central Balkans also remained distinct from that along the Adriatic coastline in both style and manufacturing techniques for almost 1,000 years from the 6th millennium BCE. Early Neolithic impressed pottery is found in the Levant, and certain parts of Anatolia, including Mezraa-Teleilat, and in North Africa at Tunus-Redeyef, Tunisia. Impressed pottery also appears in Egypt. Along the East Mediterranean coast impressed ware has been found in North Syria, Israel, and Lebanon. In northwestern Africa, lifestyle transitioned from foraging to food production around 7,400 years ago but what sparked that change remains unclear. Archaeological data support conflicting views: (1) that migrant European Neolithic farmers brought the new way of life to North Africa or (2) that local hunter-gatherers adopted technological innovations. The latter view is also supported by archaeogenetic data. Here we fill key chronological and archaeogenetic gaps for the Maghreb, from Epipalaeolithic to Middle Neolithic, by sequencing the genomes of nine individuals (to between 45.8- and 0.2-fold genome coverage). Notably, we trace 8,000 years of population continuity and isolation from the Upper Palaeolithic, via the Epipaleolithic, to some Maghrebi Neolithic farming groups. However, remains from the earliest Neolithic contexts showed mostly European Neolithic ancestry. We suggest that farming was introduced by European migrants and was then rapidly adopted by local groups. During the Middle Neolithic a new ancestry from the Levant appears in the Maghreb, coinciding with the arrival of pastoralism in the region, and all three ancestries blend together during the Late Neolithic. Our results show ancestry shifts in the Neolithization of northwestern Africa that probably mirrored a heterogeneous economic and cultural landscape, in a more multifaceted process than observed in other regions.” ref, ref, ref
“Joel D. Irish (2001), reported in “Holocene Settlement of the Egyptian Sahara”, based on osteological and dental data suggested a mainly sub-Saharan African affinity and origin at Nabta (with sub-Saharan tendencies most commonly detected), but also possible North African tendencies, concluding that, “Henneberg et al. suggest that the Nabta Playa people may have been most similar to Negroes from south of the Sahara. The present qualitative dental comparison tentatively supports this conclusion.”. Some researchers, including Christopher Ehret, have suggested a Nilo-Saharan linguistic affinity for the Nabta people.” ref
“By the 6th millennium BC or between 8,000 to 7,000 years ago, evidence of a prehistoric religion or cult appears. From 5500 BCE or around 7,500 years ago the Late Neolithic period began, with “a new group that had a complex social system expressed in a degree of organisation and control not previously seen.” These new people were responsible for sacrificial cattle burials in clay-lined and roofed chambers covered by rough stone tumuli. It has been suggested that the associated cattle cult indicated in Nabta Playa marks an early evolution of Ancient Egypt‘s Hathor cult. For example, Hathor was worshipped as a nighttime protector in desert regions (see Serabit el-Khadim). To directly quote professors Wendorf and Schild: “… there are many aspects of political and ceremonial life in prehistoric Egypt and the Old Kingdom that reflects a strong impact from Saharan cattle pastoralists …” Rough megalithic stone structures buried underground are also found in Nabta Playa, one of which included evidence of what Wendorf described as perhaps “the oldest known sculpture in Egypt.” ref
“In the 5th millennium BC or between 7,000 to 6,000 years agothese peoples fashioned what may be among the world’s earliest known archeoastronomical devices (roughly contemporary to the Goseck circle in Germany and the Mnajdra megalithic temple complex in Malta). These include alignments of stones that may have indicated the rising of certain stars and a “calendar circle” that indicates the approximate direction of summer solstice sunrise. “Calendar circle” may be a misnomer as the spaces between the pairs of stones in the gates are a bit too wide, and the distances between the gates are too short for accurate calendar measurements.” An inventory of Egyptian archaeoastronomical sites for the UNESCO World Heritage Convention evaluated Nabta Playa as having “hypothetical solar and stellar alignments.” ref
“Astrophysicist Thomas G. Brophy suggests the hypothesis that the southerly line of three stones inside the Calendar Circle represented the three stars of Orion’s Belt and the other three stones inside the calendar circle represented the shoulders and head stars of Orion as they appeared in the sky. These correspondences were for two dates – circa 4800 BC and at precessional opposition – representing how the sky “moves” long term. Brophy proposes that the circle was constructed and used circa the later date, and the dual date representation was a conceptual representation of the motion of the sky over a precession cycle. Near the Calendar Circle, which is made of smaller stones, there are alignments of large megalithic stones. The southerly lines of these megaliths, Brophy argues, aligned to the same stars as represented in the Calendar Circle, all at the same epoch, circa 6270 BCE. Brophy argues that the Calendar Circle correlation with Orion’s belt occurred between 6400 and 4900 BCE or around 8,400 to 6,900 years ago, matching radio-carbon dates of some campfires in the area.” ref
“A 2007 article by a team of University of Colorado archaeoastronomers and archaeologists (Malville, Schild, Wendorf and Brenmer, three of whom had been involved in the original discovery of the site and its astronomical alignment) responded to the work of Brophy and Rosen, in particular their claims for an alignment with Sirius in 6088 BC and other alignments which they dated to 6270 BC, saying that these dates “are about 1500 years earlier than our best estimates for the Terminal Neolithic and the construction of megalithic structures” at Nabta Playa.” ref
“The Sirius alignment in question was originally proposed by Wendorf and Malville, for one of the most prominent alignments of megaliths labelled the “C-line”, which they said aligned to the rising of Sirius circa 4820 BCE or around 6,820 years ago. Brophy and Rosen stated in 2005 that megalith orientations and star positions reported by Wendorf and Malville were in error, noting that “Given these corrected data, we see that Sirius actually aligned with the C-line circa 6000 BCE. We estimate that 6088 BCE or around 8,088 years ago Sirius had a declination of -36.51 degrees, for a rising azimuth exactly on the C-line average”. However, according to Malville, Schild et al. (2007) the dates proposed by Brophy are inconsistent with the archaeological evidence, and “inference in archaeoastronomy must always be guided and informed by archaeology, especially when substantial field work has been performed in the region”. They also concluded that, on closer inspection, the C-line of megaliths “consists of stones resting on the sides and tops of dunes and may not represent an original set of aligned stele.” ref
“More complex structures followed during a megalith period the researchers dated to between about 4500 to 3600 BCE or around 6,500 to 5,600 years ago. Using their original measurements, complemented by satellite imagery and GPS measurements by Brophy and Rosen, they confirmed possible alignments with Sirius, Arcturus, Alpha Centauri, and the Belt of Orion. They suggest that there are three pieces of evidence suggesting astronomical observations by the herdsmen using the site, which may have functioned as a necropolis. “The repetitive orientation of megaliths, stele, human burials and cattle burials reveals a very early symbolic connection to the north.” Secondly, there is the orientation of the cromlech mentioned above. The third piece of evidence is the fifth millennium alignments of stele to bright stars. They conclude their report by writing that “The symbolism embedded in the archaeological record of Nabta Playa in the Fifth Millennium BCE is very basic, focussed on issues of major practical importance to the nomads: cattle, water, death, earth, sun and stars.” ref

“The Cave of Swimmers is a cave with ancient rock art in the mountainous Gilf Kebir plateau of the Libyan Desert section of the Sahara. It is located in the New Valley Governorate of southwest Egypt, near the border with Libya. It contains Neolithic pictographs (rock painting images) and is named due to the depictions of people with their limbs bent as if they were swimming. The drawings include those of giraffe and hippopotamus. They are estimated to have been created as early as 10,000 years ago with the beginning of the African Humid Period, when the Sahara was significantly greener and wetter than it is today. The cause of the climate change 10,000 years ago was due to changes in summer solar insolation and vegetation and dust feedbacks. Due to similar artwork being found in nearby caves, such as the Cave of Beasts, and the continuous line that the figures create extending across a majority of the cave’s interior has led researchers to believe that the cave art may display developing concepts that were later adapted to the configuration of the Nile valley.” ref
“The African humid period (AHP; also known by other names) is a climate period in Africa during the late Pleistocene and Holocene geologic epochs, when northern Africa was wetter than today. The covering of much of the Sahara desert by grasses, trees and lakes was caused by changes in the Earth’s axial tilt; changes in vegetation and dust in the Sahara which strengthened the African monsoon; and increased greenhouse gases. During the preceding Last Glacial Maximum, the Sahara contained extensive dune fields and was mostly uninhabited. It was much larger than today, and its lakes and rivers such as Lake Victoria and the White Nile were either dry or at low levels. The humid period began about 14,600–14,500 years ago at the end of Heinrich event 1, simultaneously to the Bølling–Allerød warming. Rivers and lakes such as Lake Chad formed or expanded, glaciers grew on Mount Kilimanjaro and the Sahara retreated. Two major dry fluctuations occurred; during the Younger Dryas and the short 8.2 kiloyear event. The African humid period ended 6,000–5,000 years ago during the Piora Oscillation cold period. While some evidence points to an end 5,500 years ago, in the Sahel, Arabia, and East Africa, the end of the period appears to have taken place in several steps, such as the 4.2-kiloyear event.” ref
“The African humid period took place in the late Pleistocene and early-middle Holocene, and saw increased precipitation in Northern and Western Africa due to a northward migration of the tropical rainbelt. The AHP is the most profound climate change of the low latitudes during the last 100,000 years and stands out within the otherwise relatively climatically stable Holocene. It is part of the so-called Holocene climatic optimum and coincides with a global warm phase, the Holocene Thermal Maximum. Liu et al. 2017 subdivided the humid period into an “AHP I” which lasted until 8,000 years ago, and an “AHP II” from 8,000 years onward, with the former being wetter than the latter. The AHP led to a widespread settlement of the Sahara and the Arabian Deserts, and had a profound effect on African cultures, such as the birth of the Ancient Egyptian civilization. People in the Sahara lived as hunter-gatherers and domesticated cattle, goats and sheep. They left archaeological sites and artifacts such as one of the oldest ships in the world, and rock paintings such as those in the Cave of Swimmers and in the Acacus Mountains. Earlier humid periods in Africa were postulated after the discovery of these rock paintings in now-inhospitable parts of the Sahara. When the period ended, humans gradually abandoned the desert in favour of regions with more secure water supplies, such as the Nile Valley and Mesopotamia, where they gave rise to early complex societies.” ref
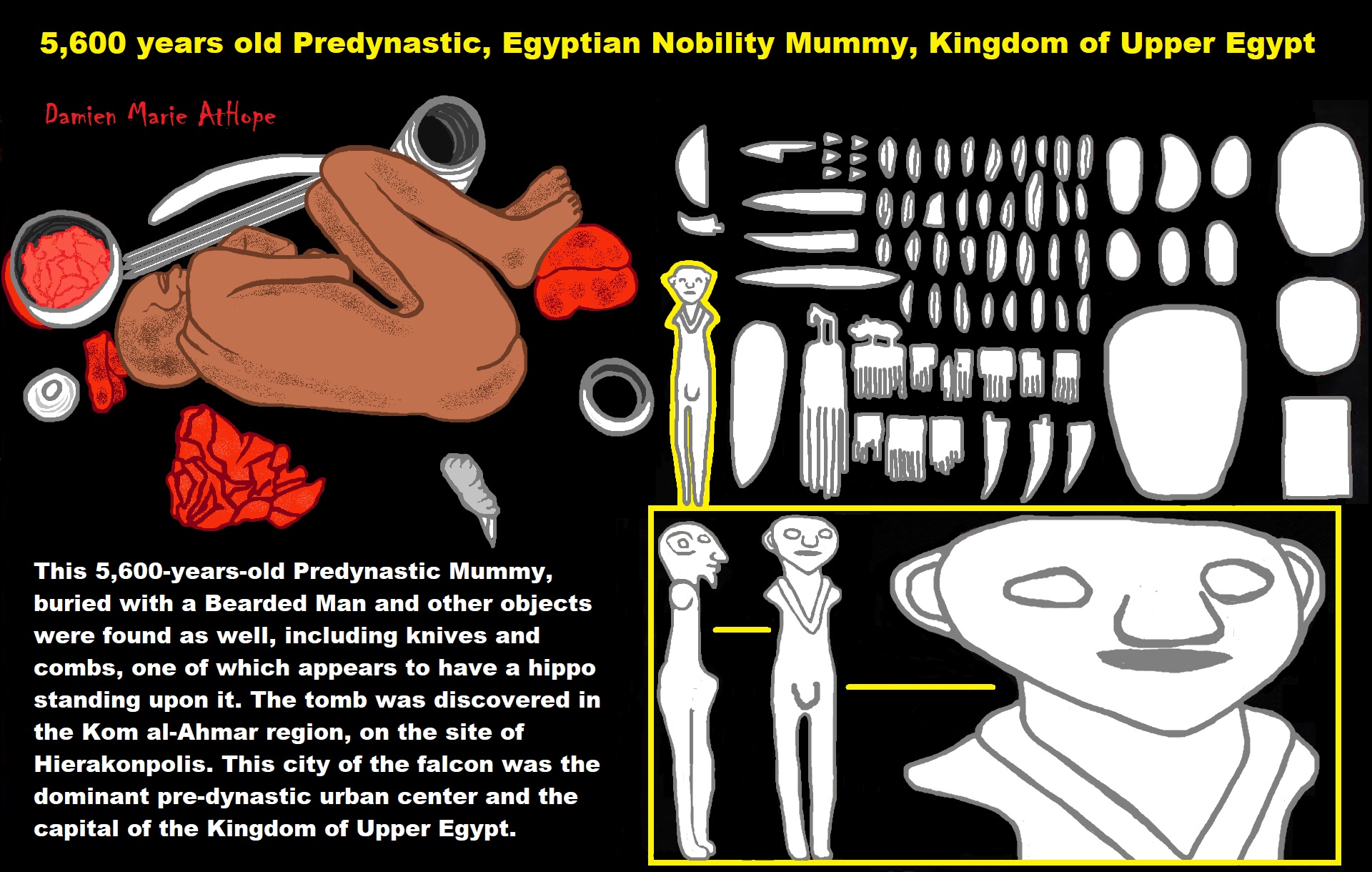

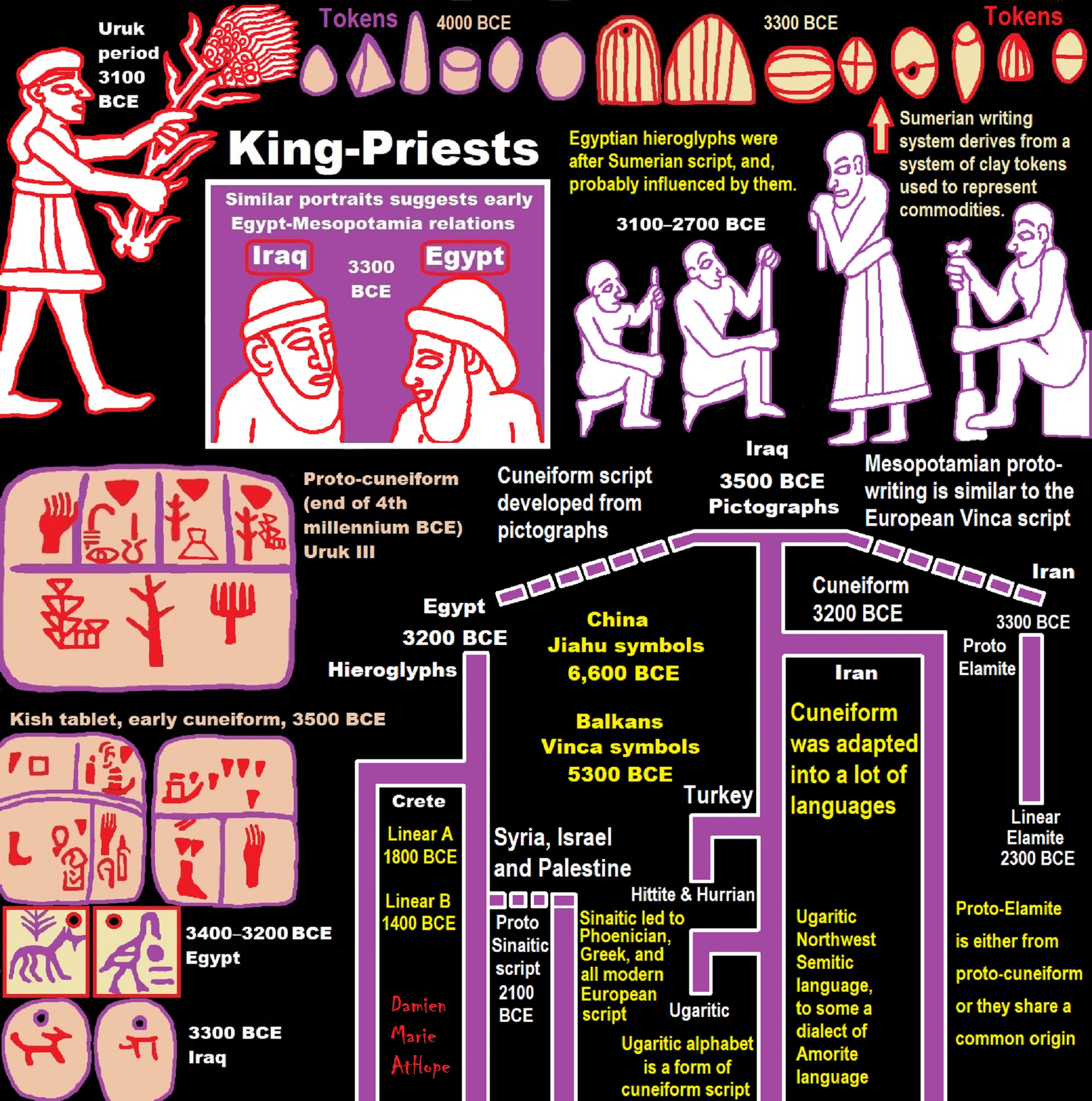
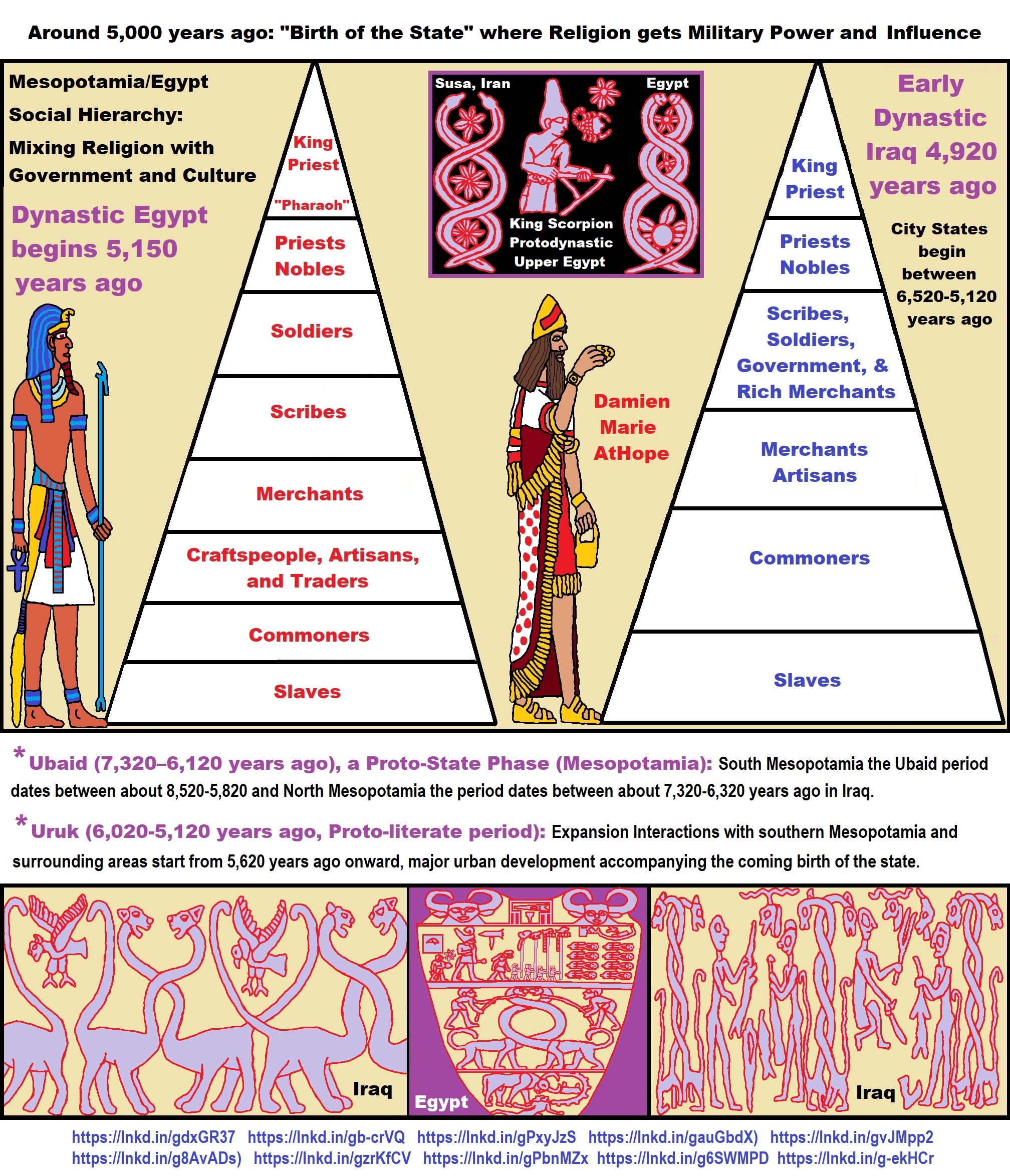



ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
12 Powerful Women that Held the Position of Rulers/Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt
Here are the names and possible dates for these women who may have been rulers. 1. Queen Meryt-Neith ruled 5,020 years ago. 2. Queen Nimaathap (Third Dynasty, 4,706–4,633 years ago). 3. Queen Khentkaus (Fourth Dynasty, 4,633–4,514 years ago). 4. Queen Ankhesenpepi II (Sixth Dynasty, 4,385–4,201 years ago). 5. Princess Neithhikret (Died 4,201 years ago). 6. Princess-Queen Sobeknefru (Died 3,822 years ago). 7. Queen Ashotep (3,580–3,550 years ago). 8. Princess-Queen Ahmose-Nefertari (3,582–3,515 years ago). 9. Queen Hatshepsut (3,527–3,478 years ago). 10. Queen Nefertiti (3,390–3,350 years ago). 11. Queen Tausret (Died 3,209 years ago). 12. Queen Cleopatra I (2,224–2,196 years ago).
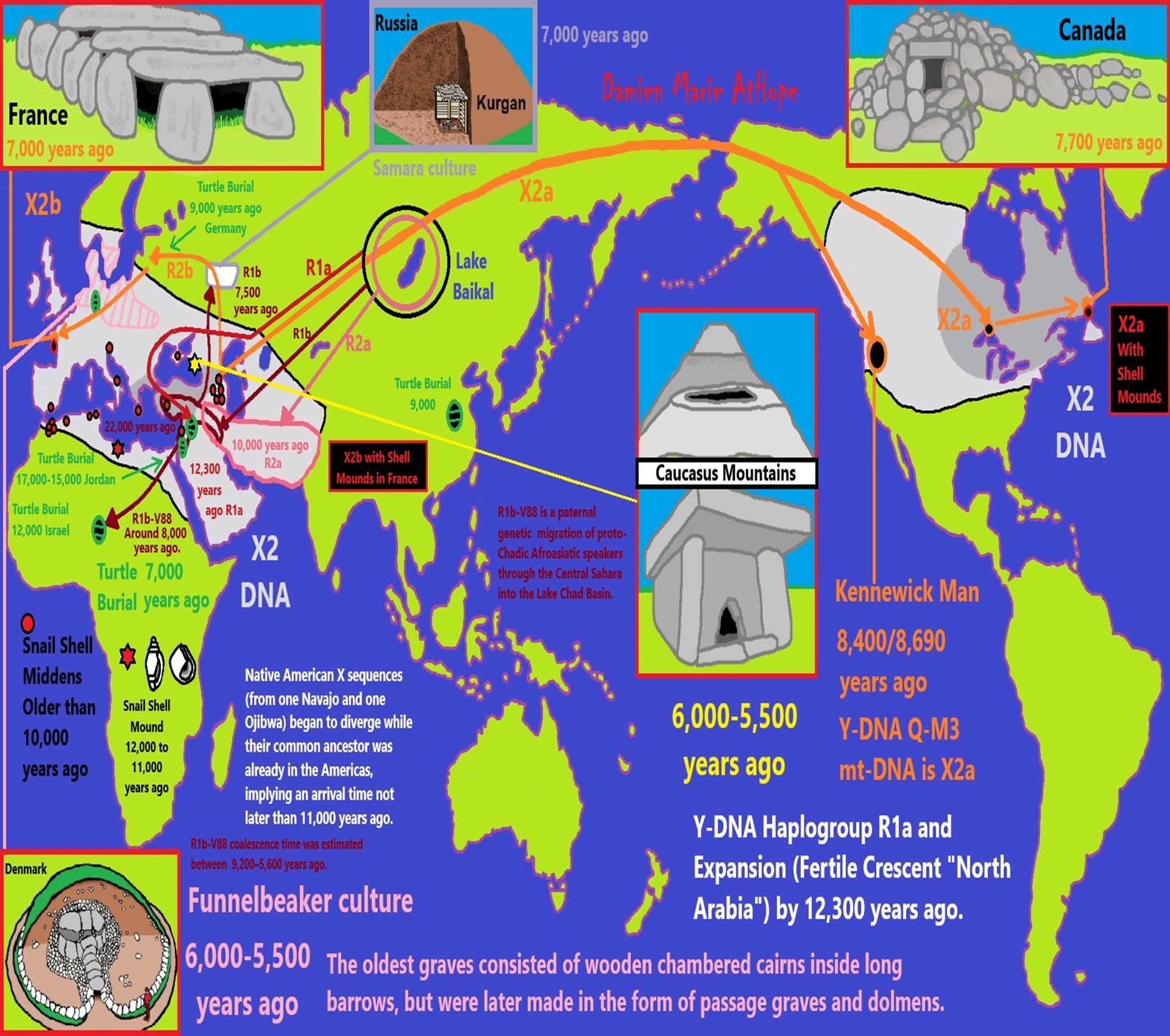
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Earth diver mythology or something similar??? Could be. In a way, snails are a kind of mound shape, thus similar to turtle shells, both may represent a mound of creation in the earth-diver myth. In Peru, there were snail shells, and snail shells are also used in the earth diver.
My thoughts on Dolmen origins and migrations, as well as Snail Shell Middens or Snail Burials/Turtle Shell Burials, and links from “Y-DNA R (R1a, R1b, and R2a)” migrations, maybe R2a leading to Proto-Indo-European, transferring it to R1b, taking it to the steppe 7,500 years ago.
Religion is a cultural product. So, it has been part of the human experience, similar to languages, from before we left Africa, spreading humanity across the world.
Dolmens, to me, like other types of mounds, may have cosmic ocean, primordial waters, or celestial river mythological motifs connected, such as Mound of Creation emerging out of the water, World Turtle, or Earth Diver type of mythological thinking.
Dolmen migrations at first seem related with MtDNA X2, going to Canada with X2a making a 7,700-year-old Dolmen as well as shell mounds and to France with X2b making a 7,000-year-old Dolmen as well as shell mounds.
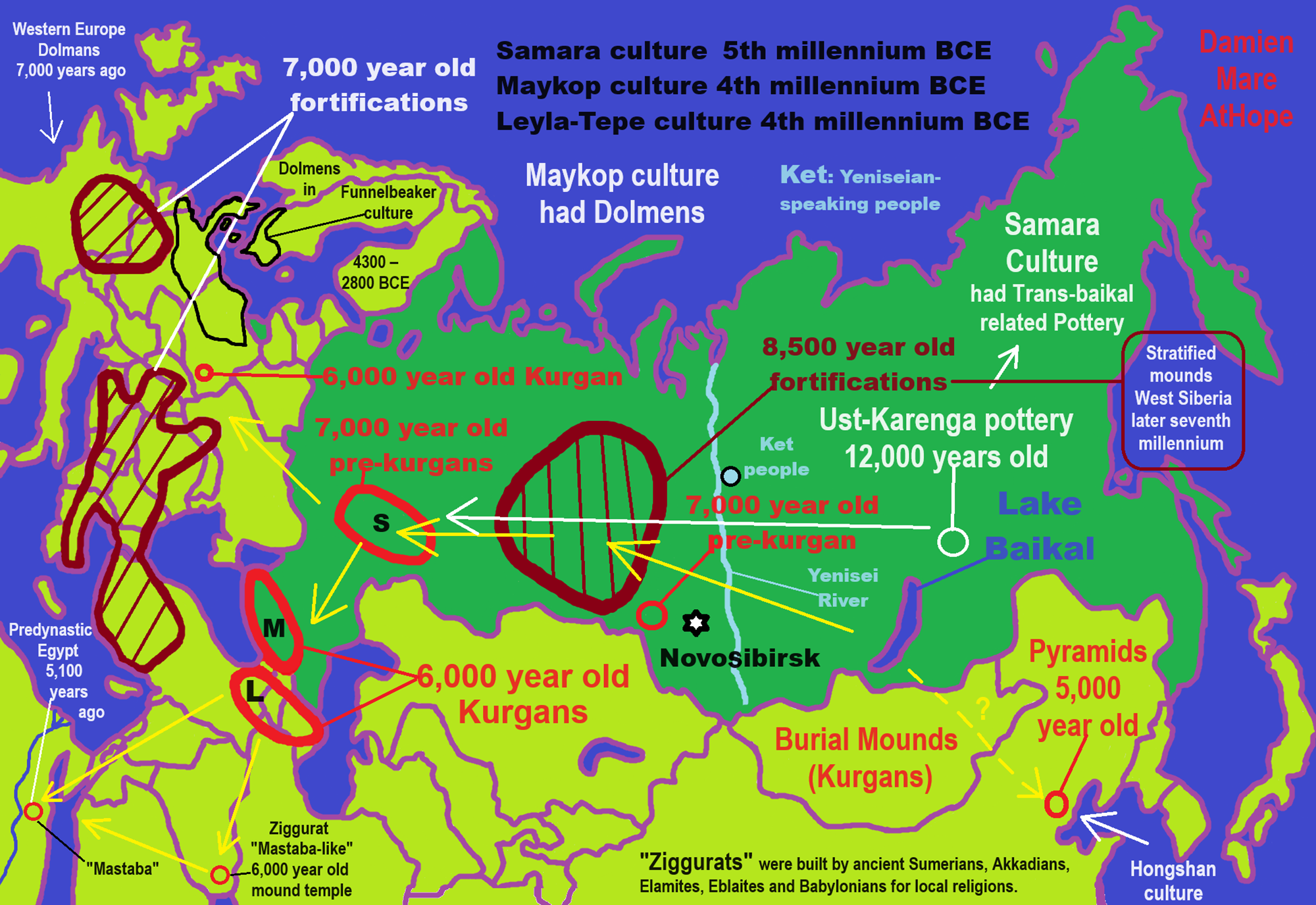
My Speculations are in Comparative Mythologies?
For instance, the mytheme of an ancient belief that is seemingly shared though changed and adapted, a fundamental generic unit of narrative structure seems to be shared a common relation with mountains/ancestors/gods or sacred animals with Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids.
Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep Mythology connections?
Haplogroup “R” Y-DNA Migrations
To me, there are at least three main migrations of Haplogroup “R” Y-DNA from Siberia to the Middle East areas. First was R1b Y-DNA at 22,000 years ago; next was R1a Y-DNA at 12,300 years ago in Arabia; and last was R2a Y-DNA at 10,000 years ago in Iran Neolithic.
1. R1b in the Middle East areas 22,000 years ago
2. R1a in Arabia 12,300 years ago
3. R2a in Iran 10,000 years ago
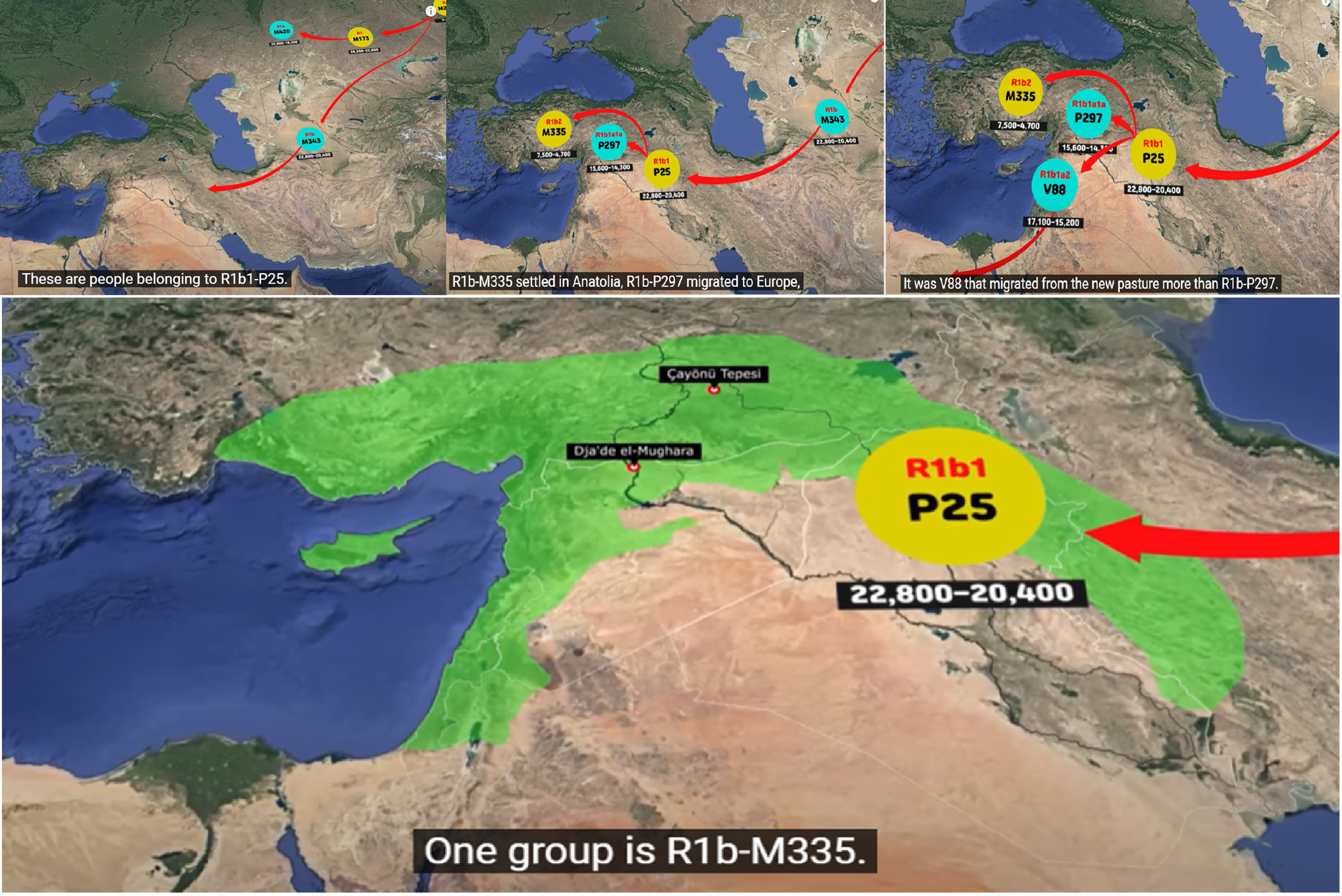
“Rb1-V88 around 8,000 years ago. R1b-V88 coalescence time was estimated between 9,200–5,600 years ago. Researchers suggest R1b-V88 is a paternal genetic record of the proposed mid-Holocene migration of proto-Chadic Afroasiatic speakers through the Central Sahara into the Lake Chad Basin, and geomorphological evidence is consistent with this view.” ref
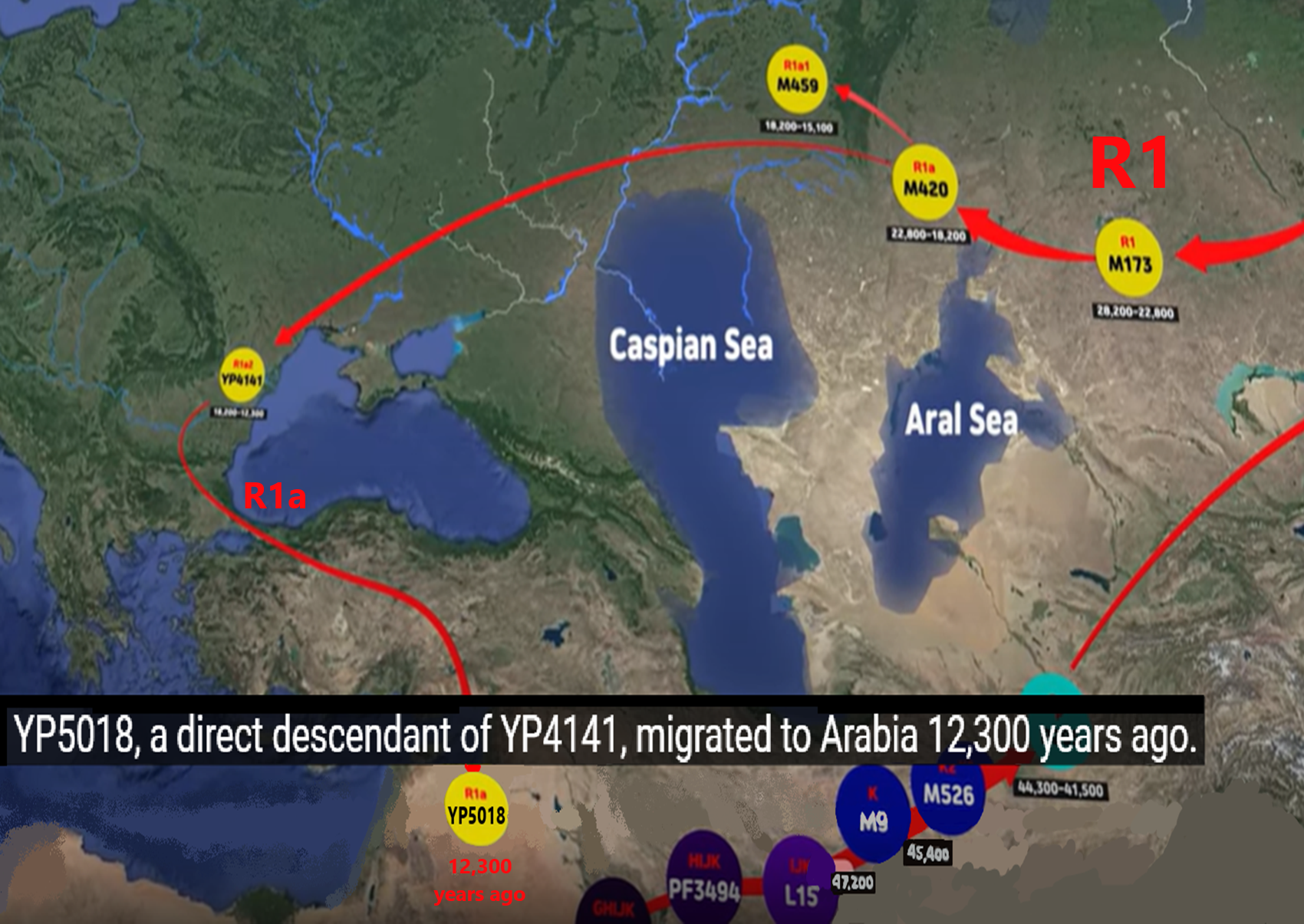
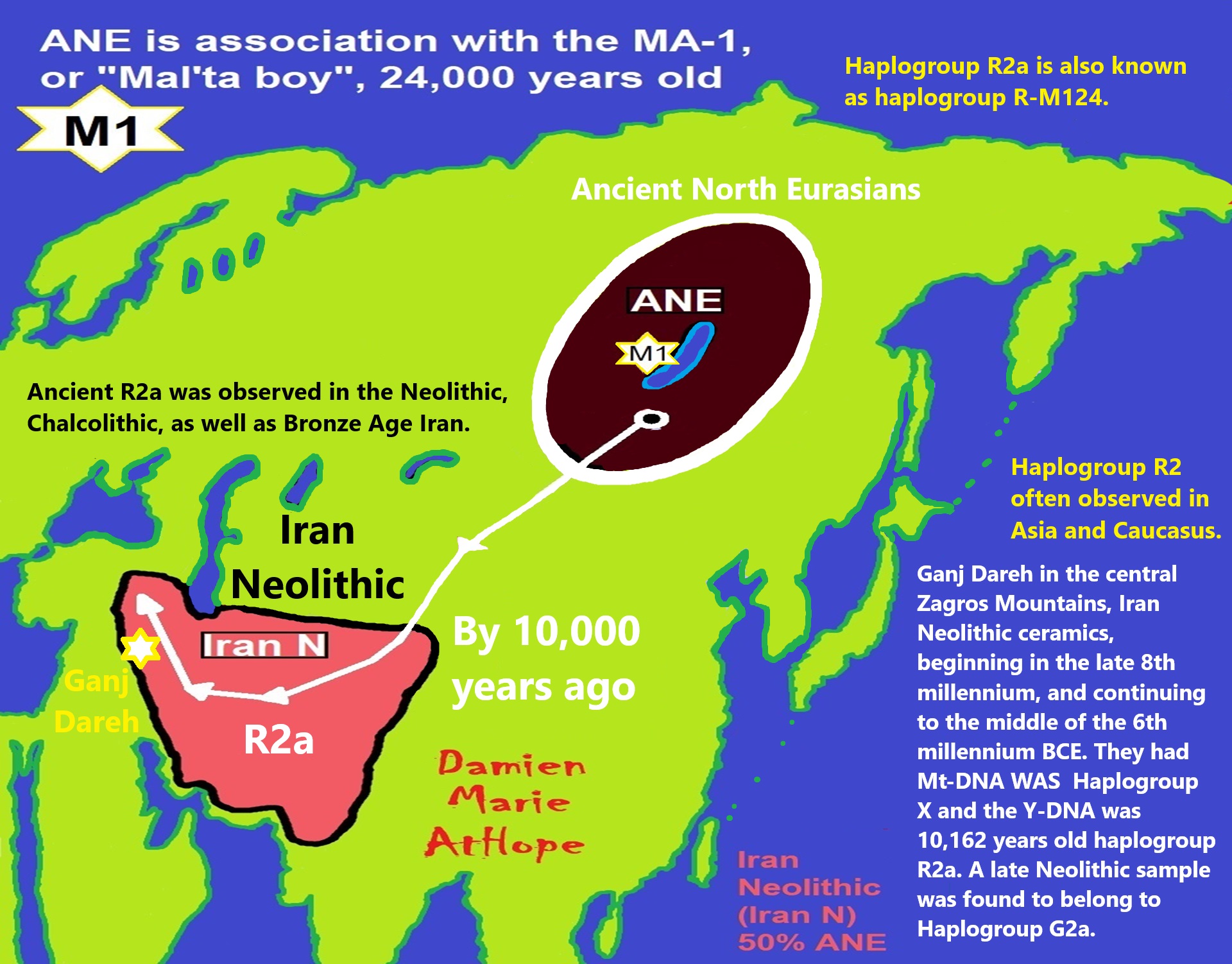
“Haplogroup R2a (R-M124) is characterized by SNPs M124, F820/Page4, L381, P249, and is mainly found in South Asia, with lower frequencies in Central Asia. R-M124 is also found in multiple Jewish populations: Iraqi Jews, Persian Jews, Mountain Jews, and Ashkenazi Jews. Most research has tested only for the presence of R-M479 (R2) and R-M124 (R2a) – or SNPs downstream from M124 like P249, P267, L266, PAGES00004, and L381 SNPs). Because the other primary branch, R2b (R-FGC21706) was discovered later than R2a, it has often not been tested for. Hence most results are best described as R2(xR2a). n addition, relatively little research has been done within South Asia, which is known to have the greatest concentration of R2. (Hence the figures cited in the table right may not be indicative of true frequencies, i.e. Pakistan is the only South Asian country that has been included.) In 2013, R2(xR2a) was found in 5 out of 19 males from the Burusho minority of North Pakistan. Haplogroup R2, or R-M479, has been concentrated geographically in South Asia and Central Asia since prehistory. It appears to reach its highest levels among the Burusho people in North Pakistan.” ref
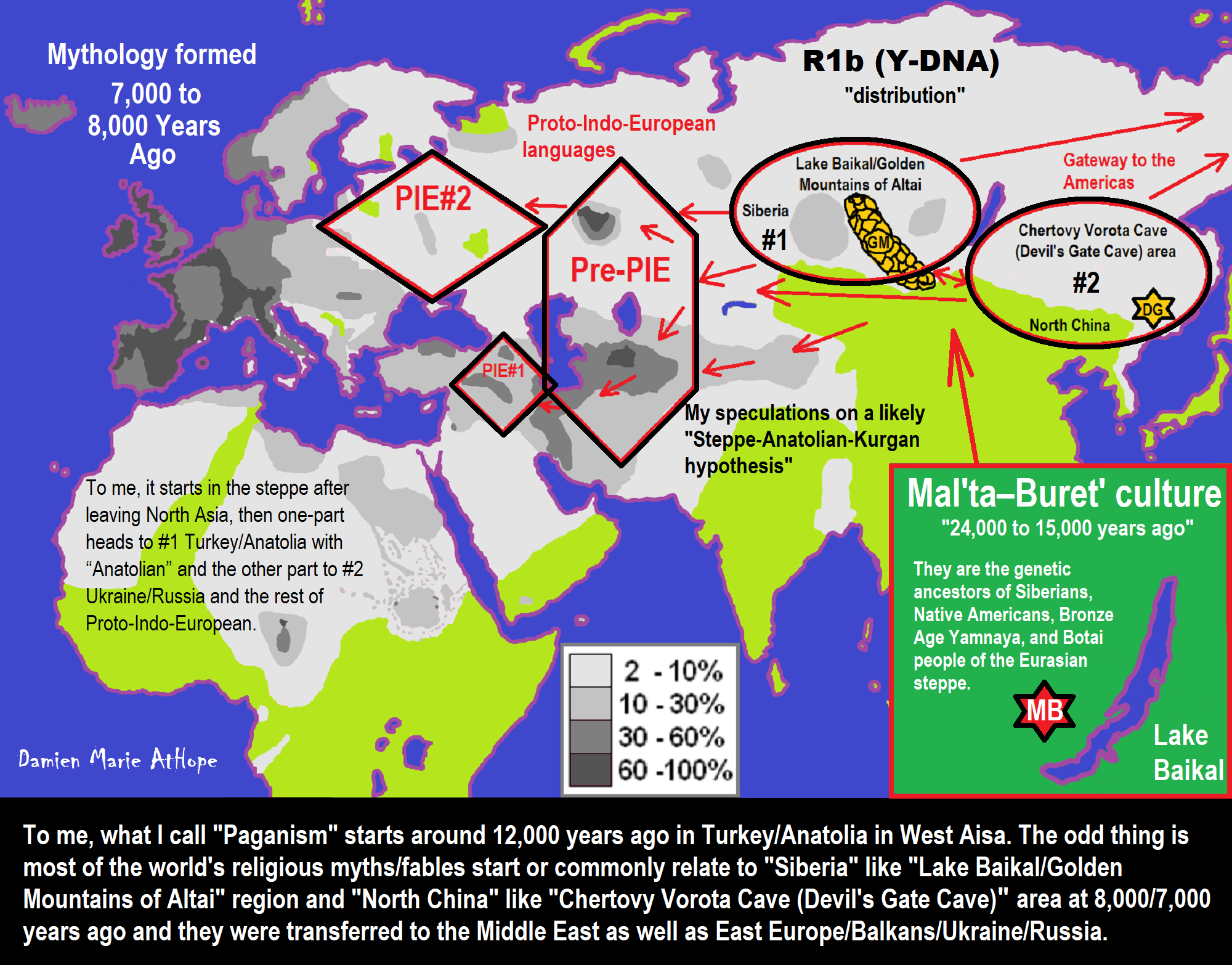
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
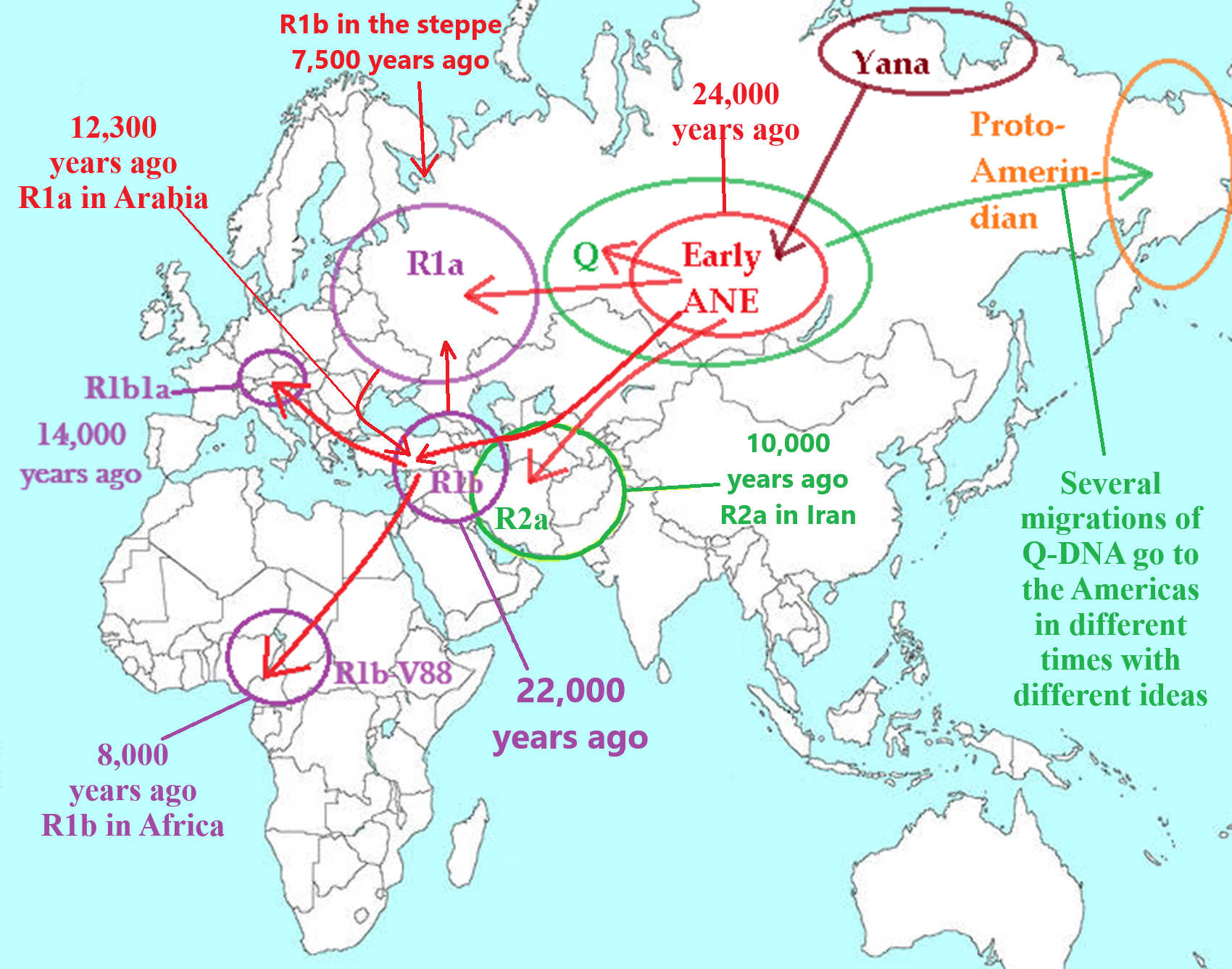
Haplogroup migrations related to the Ancient North Eurasians: I added stuff to this map to help explain.
People reached Lake Baikal Siberia around 25,000 years ago. They (to Damien) were likely Animistic Shamanists who were also heavily totemistic as well. Being animistic thinkers they likely viewed amazing things in nature as a part of or related to something supernatural/spiritual (not just natural as explained by science): spirit-filled, a sprit-being relates to or with it, it is a sprit-being, it is a supernatural/spiritual creature, or it is a great spirit/tutelary deity/goddess-god. From there comes mythology and faith in things not seen but are believed to somehow relate or interact with this “real world” we know exists.
Both areas of Lake Baikal, one on the west side with Ancient North Eurasian culture and one on the east side with Ancient Northern East Asian culture (later to become: Ancient Northeast Asian culture) areas are the connected areas that (to Damien) are the origin ancestry religion area for many mythologies and religious ideas of the world by means of a few main migrations and many smaller ones leading to a distribution of religious ideas that even though are vast in distance are commonly related to and centering on Lake Baikal and its surrounding areas like the Amur region and Altai Mountains region.
To an Animistic Thinker: “Things are not just as they seem, they may have a spirit, or spirit energy relates to them”
To a Totemistic Thinker: “Things are not just as they seem, they may have a spirit, or spirit energy relates to them; they may have religio-cultural importance.”
“Ancient North Eurasian population had Haplogroups R, P, U, and Q DNA types: defined by maternal West-Eurasian ancestry components (such as mtDNA haplogroup U) and paternal East-Eurasian ancestry components (such as yDNA haplogroup P1 (R*/Q*).” ref
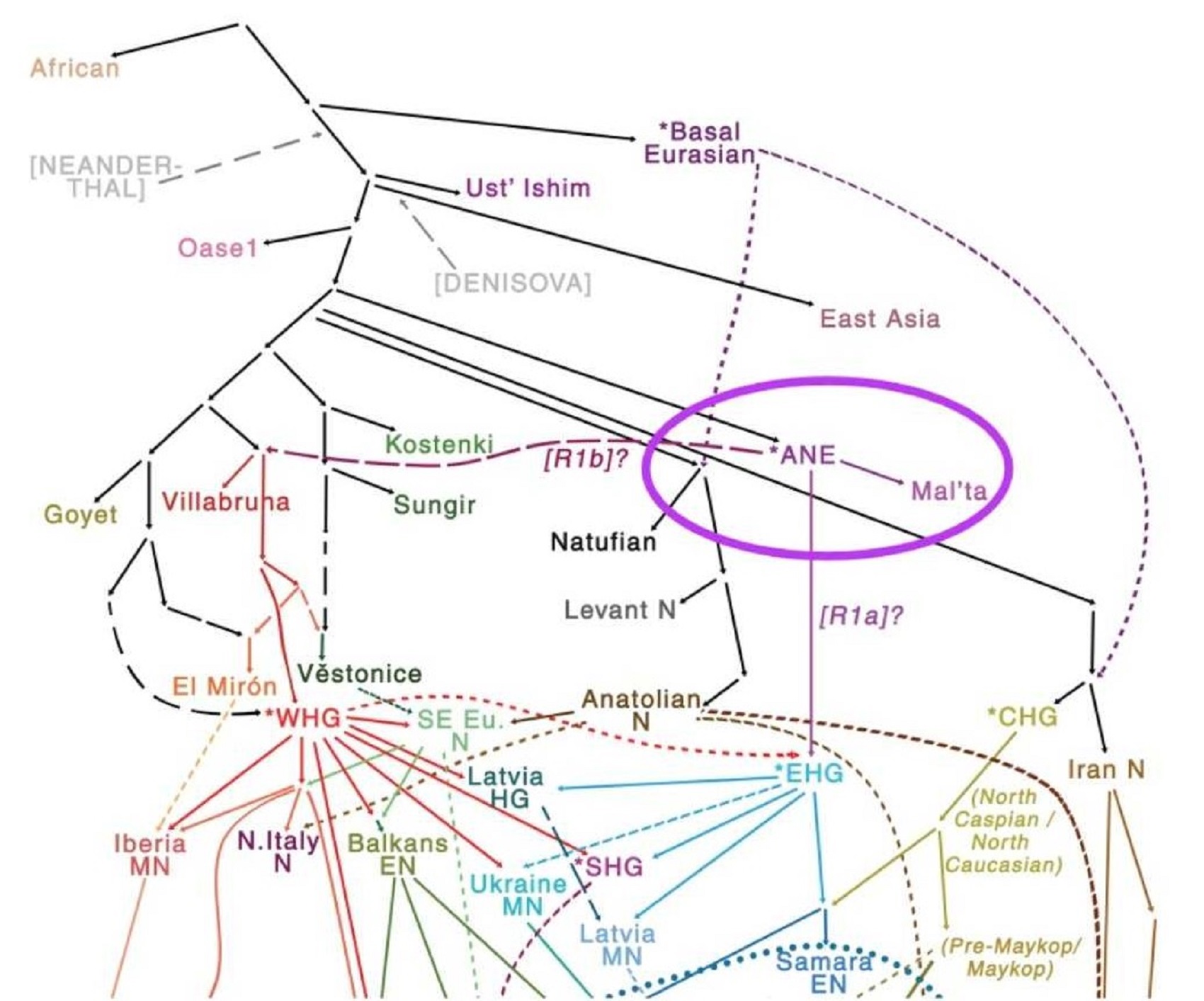
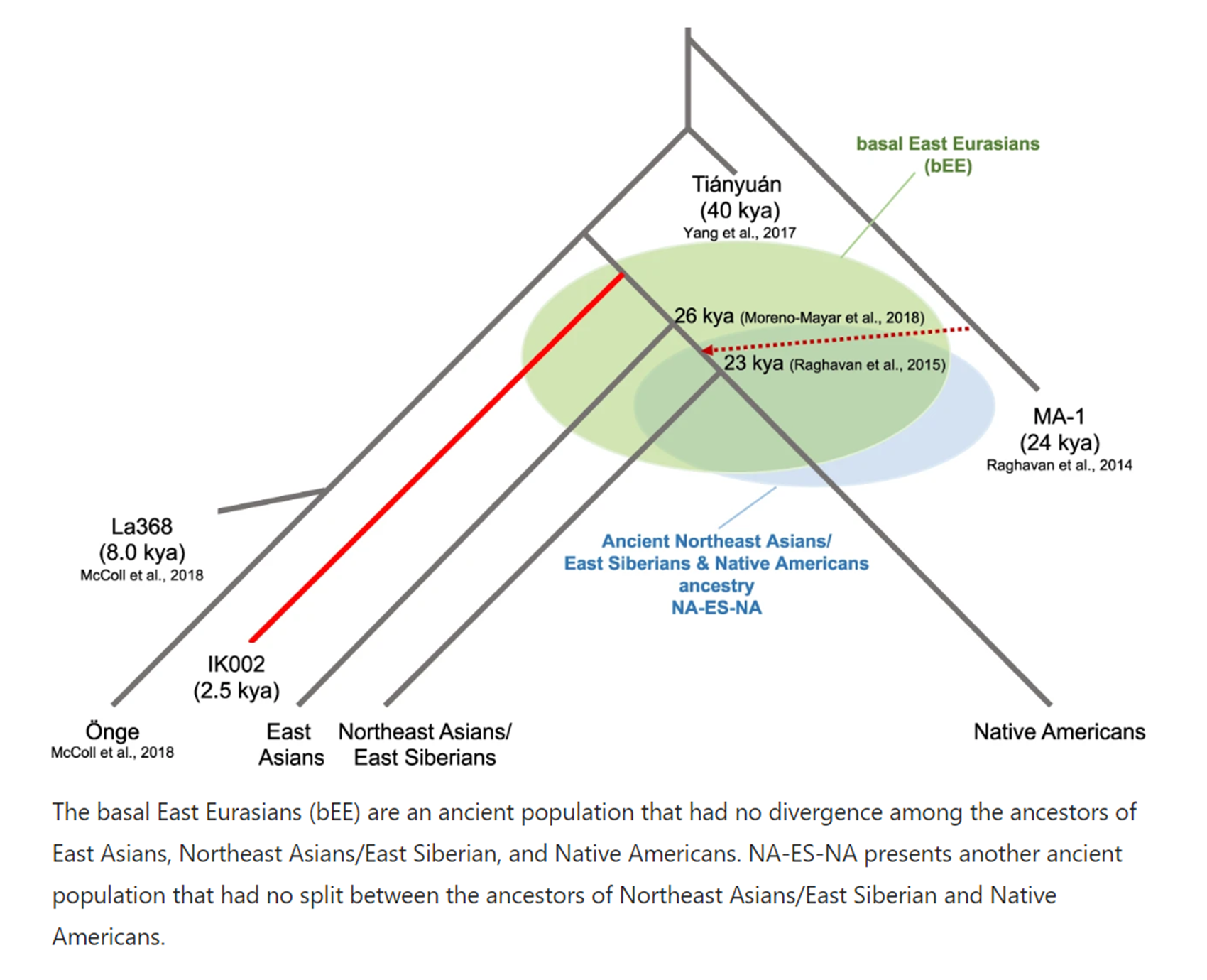
“The basal East Eurasians (bEE) are an ancient population that had no divergence among the ancestors of East Asians, Northeast Asians/East Siberian, and Native Americans. NA-ES-NA presents another ancient population that had no split between the ancestors of Northeast Asians/East Siberian and Native Americans.” ref
“Schematic of peopling history in Southeast and East Asians, Northeast Asian/East Siberians and Native Americans.” ref
Q Haplogroup
“Q-M242 is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among Native Americans and several peoples of Central Asia and Northern Siberia. Q-M242 is believed to have arisen around the Altai Mountains area (or South Central Siberia), approximately 17,000 to 31,700 years ago (approximately 24,500 years ago). Several branches of haplogroup Q-M242 have been predominant pre-Columbian male lineages in indigenous peoples of the Americas. Most of them are descendants of the major founding groups who migrated from Asia into the Americas by crossing the Bering Strait. These small groups of founders must have included men from the Q-M346, Q-L54, Q-Z780, and Q-M3 lineages.” ref
“In North America, two other Q-lineages also have been found. These are Q-P89.1 (under Q-MEH2) and Q-NWT01. They may have not been from the Beringia Crossings but instead come from later immigrants who traveled along the shoreline of Far East Asia and then the Americas using boats. It is unclear whether the current frequency of Q-M242 lineages represents their frequency at the time of immigration or is the result of the shifts in a small founder population over time. Regardless, Q-M242 came to dominate the paternal lineages in the Americas.” ref
“In the indigenous people of North America, Q-M242 is found in Na-Dené speakers at an average rate of 68%. The highest frequency is 92.3% in Navajo, followed by 78.1% in Apache, 87% in SC Apache, and about 80% in North American Eskimo (Inuit, Yupik)–Aleut populations. (Q-M3 occupies 46% among Q in North America). On the other hand, a 4000-year-old Saqqaq individual belonging to Q1a-MEH2* has been found in Greenland. Surprisingly, he turned out to be genetically more closely related to Far East Siberians such as Koryaks and Chukchi people rather than Native Americans. Today, the frequency of Q runs at 53.7% (122/227: 70 Q-NWT01, 52 Q-M3) in Greenland, showing the highest in east Sermersooq at 82% and the lowest in Qeqqata at 30%.” ref
“Haplogroup Q-M242 has been found in approximately 94% of Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and South America. The frequencies of Q among the whole male population of each country reach as follows:
- 61% in Bolivia.
- 51% in Guatemala,
- 40.1% (159/397) to 50% in Peru
- 37.6% in Ecuador,
- 37.3% (181/485) in Mexico (30.8% (203/659) among the specifically Mestizo segment)
- 31.2% (50/160) in El Salvador,
- 15.3% (37/242) to 21.8% (89/408) in Panama,
- 16.1% in Colombia,
- 15.2% (25/165) in Nicaragua,
- 9.7% (20/206) in Chile,
- 5.3% (13/246 in 8 provinces in northeastern, central, southern regions) to 23.4% (181/775 in 8 provinces in central-west, central, northwest regions) in Argentina,
- 5% in Costa Rica,
- 3.95% in Brazil, and so on.” ref
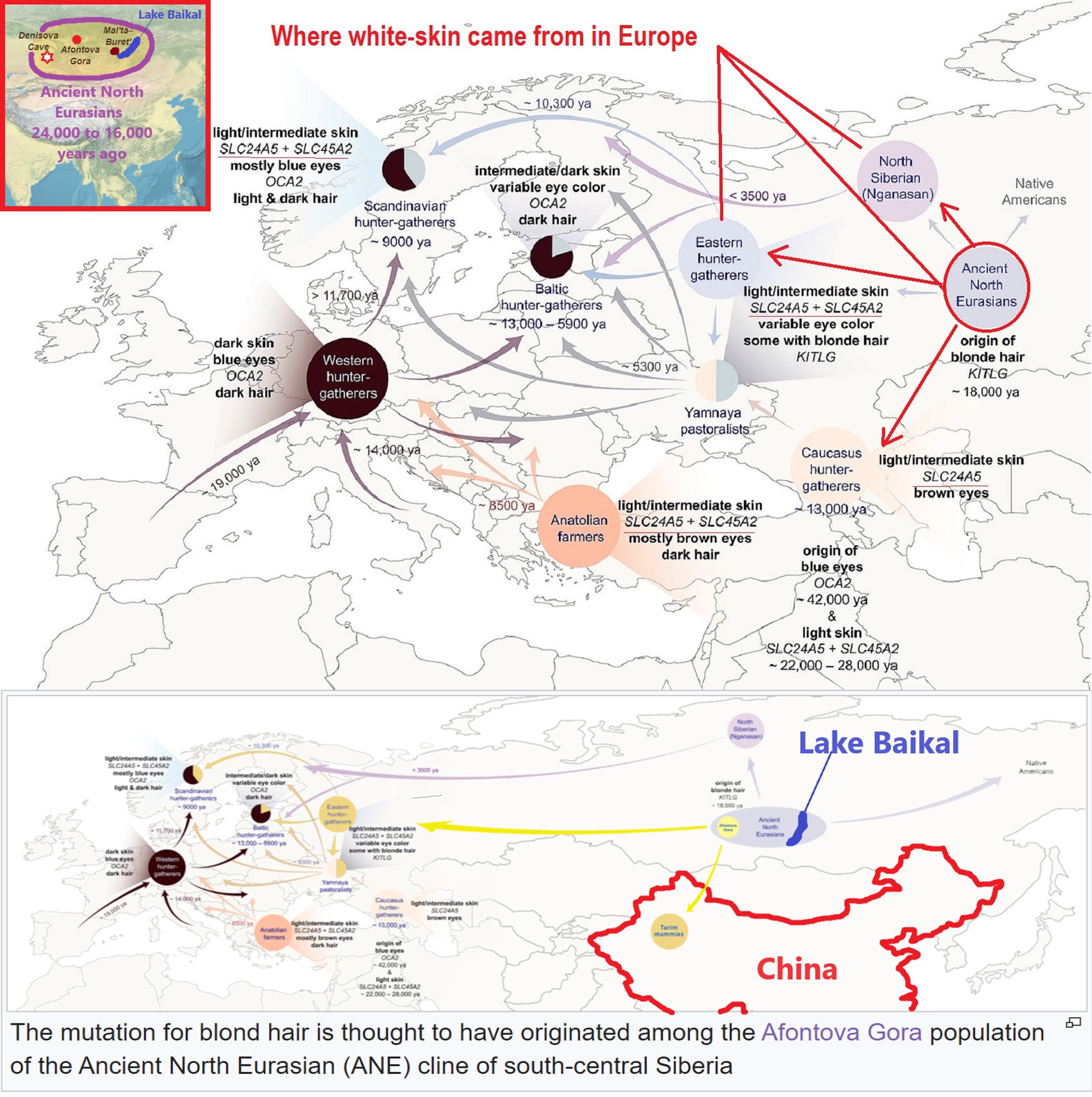
“Lighter skin and blond hair evolved in the Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) population. The SLC24A5 gene’s derived threonine or Ala111Thr allele (rs1426654) has been shown to be a major factor in the light skin tone of Europeans. Possibly originating as long as 19,000 years ago, it has been the subject of selection in the ancestors of Europeans as recently as within the last 5,000 years, and is fixed in modern European populations.” ref, ref
DNA-researcher: It’s not ‘woke’ to portray prehistoric Europeans with dark skin.
“It’s evolution. Ancient DNA analyses suggest that prehistoric Europeans looked different from modern Europeans today, but some people find that hard to accept. There was an artistic picture of an almost 6,000-year-old, girl who was walking along Lolland’s south coast and spits a piece of birch tar into the reeds. It didn’t taste great, but it helped to soothe her toothache. Fast forward 6,000 years, Danish archaeologists working on the Fehmarnbelt project stumble across the piece and recognize it for what it is: an almost 6,000-year-old piece of chewing gum. This ancient piece of gum is now on display at the Museum Lolland-Falster in southern Denmark among an amazing collection of Stone Age artifacts uncovered during the excavations. If you have not been, it is well worth a visit. In 2019, my research team at the University of Copenhagen managed something quite remarkable: We succeeded in extracting DNA from the gum and used it to reconstruct the girl’s entire genome — the first time anyone had sequenced an ancient human genome from anything other than skeletal remains. As the gum had been found on Lolland, we affectionately nicknamed her ‘Lola’.” ref
Stone-age girl in social media ‘shitstorm’
“The story of Lola and her chewing gum made headlines around the world when we published the genome in 2019 and then, suddenly, in the summer of 2023, Lola was back in the news, caught up in a media ‘shitstorm’. The ‘shitstorm’ first gathered pace on X, the platform formerly known as Twitter, and escalated to the point where the museum had to defend itself on national TV. Even the Danish newspaper ‘Ekstrabladet’ felt they had to comment and gave their opinion in a passionate editorial. So, what happened? These things are difficult to reconstruct, but evidently some people who had seen the image of Lola thought that she looked “way too dark” and accused us—and the museum—of ‘blackwashing’ the past. I suppose this episode says more about our own biases than anything else, and I would like to take this opportunity to explain why we portrayed Lola the way we did and what this tells us about the evolution of skin color in this part of the world.” ref
What we know about Lola
“First a disclaimer, we do not know exactly how old Lola was when she spat that chewing gum into the water. But based on her genome and other DNA trapped in the gum, we learned a lot of other things about her and her world. For example, we learned that she was a hunter-gatherer who lived off wild resources like fish, nuts, and wild game. At the time, small farming communities started to appear in other parts of Europe, but from what we can tell Lola and her kin still lived — as her ancestors had done for thousands of years before her — as hunter-gatherers. We also learned that she likely had dark skin, dark hair, and blue eyes. But how do we know that?” ref
The genetics of human skin pigmentation
“Skin color is a highly heritable and polygenic trait, meaning that it is influenced by multiple genes and their interactions with one another. One of the most well-known genes associated with skin pigmentation is the melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R), but there are dozens more that have been reported to be involved in the pigmentation process. Most of these genes influence skin color by regulating the production of melanin, a dark pigment that protects from the deleterious effects of UV radiation. Basically, the more melanin you have in your skin, the darker it will be, and the more sun your skin can tolerate before you get sunburn. Eye and hair color are determined in a similar way, but the mechanisms that control the production of melanin in the eyes and hair are quite complex and independent processes. That is why it is possible to end up with different combinations of traits, such as the dark hair and blue eyes that are often seen in Europeans today, or the light hair and brown eyes that are common for Solomon Islanders, for example.” ref
How do we know what Lola looked like?
“Because the genes involved in pigmentation have been well studied, it is possible to predict the skin, eye, and hair color of an individual based on their genotype with a certain probability, something that is routinely done in forensic investigations. In practice, this works by checking which variants of a gene are present and what phenotype they are associated with. The more genes we can include in this analysis, the more confident we can be that our prediction is correct. In Lola’s case, we studied 41 gene variants across her genome that have been associated with skin, hair, and eye color in humans, and concluded that she likely had this unusual (at least for today) combination of dark skin, dark hair, and blue eyes.” ref
A common look in prehistoric Europe
“It is difficult to know exactly what people looked like 10,000 years ago. But based on ancient DNA studies, it appears that Lola’s ‘look’ was much more common in prehistoric Europe than it is today. Thanks to advances in ancient DNA sequencing, we now have the genomes of dozens of Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic (i.e. the period between around 50,000 and 5,000 years before present in Europe) individuals from Western Europe. And interestingly they all seem to lack the skin-lightening variants that are so common in Europeans today, indicating that they had dark skin. This is true for ‘Cheddar Man’ who lived around 10,000 years ago in southern England, as well as dozens of other Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic hunter-gatherer individuals from France, northern Italy, Spain, the Baltic, and other parts of Europe. Like skin color, eye color is also a fairly complex trait, involving the interaction of many different genes. Therefore, eye color is fairly difficult to predict, but it looks like Upper Palaeolithic and Mesolithic hunter-gatherers from Western Europe often had blue eyes, just like Lola. Overall, it looks like Lola’s phenotype—the combination of dark skin, dark hair, and blue eyes—was much more common in prehistoric Europe than it is today.” ref
How Europeans got their lighter skin
“So, why did people in prehistoric Europe look so different from northern Europeans today? The answer to this question lies in a complex interplay between our genes, our changing diets, population movements, and the environment. It has been theorized for some time that lighter skin emerged as an adaptive trait to light poor environments as it allows you to absorb sunlight more effectively, which is essential for the production of vitamin D. However, it was unclear when this happened. Early studies suggested that we first may have evolved lighter skin as our ancestors moved out of Africa and into Europe c. 50,000 years ago, but we now believe that this happened much later in European prehistory. In fact, there is evidence that lighter skin only evolved within the last 5,000 years or so, as a result of genetic admixture from Neolithic farming populations (who carried the skin-lightening variant) and strong selection favoring lighter skin.” ref
Our changing diet also played a part
“In addition, it looks like our changing diets also played a part. During most of European prehistory people relied on wild resources like nuts, game, and fish that are all rich in vitamin D, which is essential to our health. That changed dramatically during the Neolithic when people started to rely on a farmer’s diet that was rich in carbohydrates, but poor in vitamin D. Interestingly, this is exactly the period when we see lighter skin tones evolve in Western Europe and we think that the lack of vitamin D in the diet may have increased the selection pressures favouring lighter skin. All in all, there is solid evidence to suggest that lighter skin tones only evolved in Europe within the last 5,000 years or so, and that people who lived in Europe before then typically had darker skin. It is not that surprising, then, that Lola had darker skin. It simply reflects the fact that she lived at a time when Europeans had not yet evolved their lighter skin.” ref
People reached Lake Baikal Siberia around 25,000 years ago. They (to Damien) were likely Animistic Shamanists who were also heavily totemistic as well. Being animistic thinkers they likely viewed amazing things in nature as a part of or related to something supernatural/spiritual (not just natural as explained by science): spirit-filled, a sprit-being relates to or with it, it is a sprit-being, it is a supernatural/spiritual creature, or it is a great spirit/tutelary deity/goddess-god. From there comes mythology and faith in things not seen but are believed to somehow relate or interact with this “real world” we know exists.
Both areas of Lake Baikal, one on the west side with Ancient North Eurasian culture and one on the east side with Ancient Northern East Asian culture (later to become: Ancient Northeast Asian culture) areas are the connected areas that (to Damien) are the origin ancestry religion area for many mythologies and religious ideas of the world by means of a few main migrations and many smaller ones leading to a distribution of religious ideas that even though are vast in distance are commonly related to and centering on Lake Baikal and its surrounding areas like the Amur region and Altai Mountains region.
“Lakes are often mysterious bodies of water, especially if they are very deep or surrounded by mountains. No wonder legends and mysteries thrive about them, including monsters that supposedly lurk in their bottomless depths.” ref
People may have first seen the Shaman Rock with the natural brown rock formation resembling a dragon between 30,000 to 25,000 years ago.
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
- Medicine Wheel
- Serpent Mound
- Mesa Verde
- Chaco Canyon
- Casas Grandes/Paquime
- Ciudad Perdida “lost city”; Teyuna
- Ingapirca “Inca”
- Chavín de Huántar “pre-Inca”
- Sacred City of Caral-Supe *Caral culture developed between 3000 – 1800 BCE*
- Machu Picchu
- Nazca Lines
- Sacsayhuamán
- Tiwanaku/Tiahuanaco
- Atacama Giant/Lines
- Pucará de Tilcara “pre-Inca”
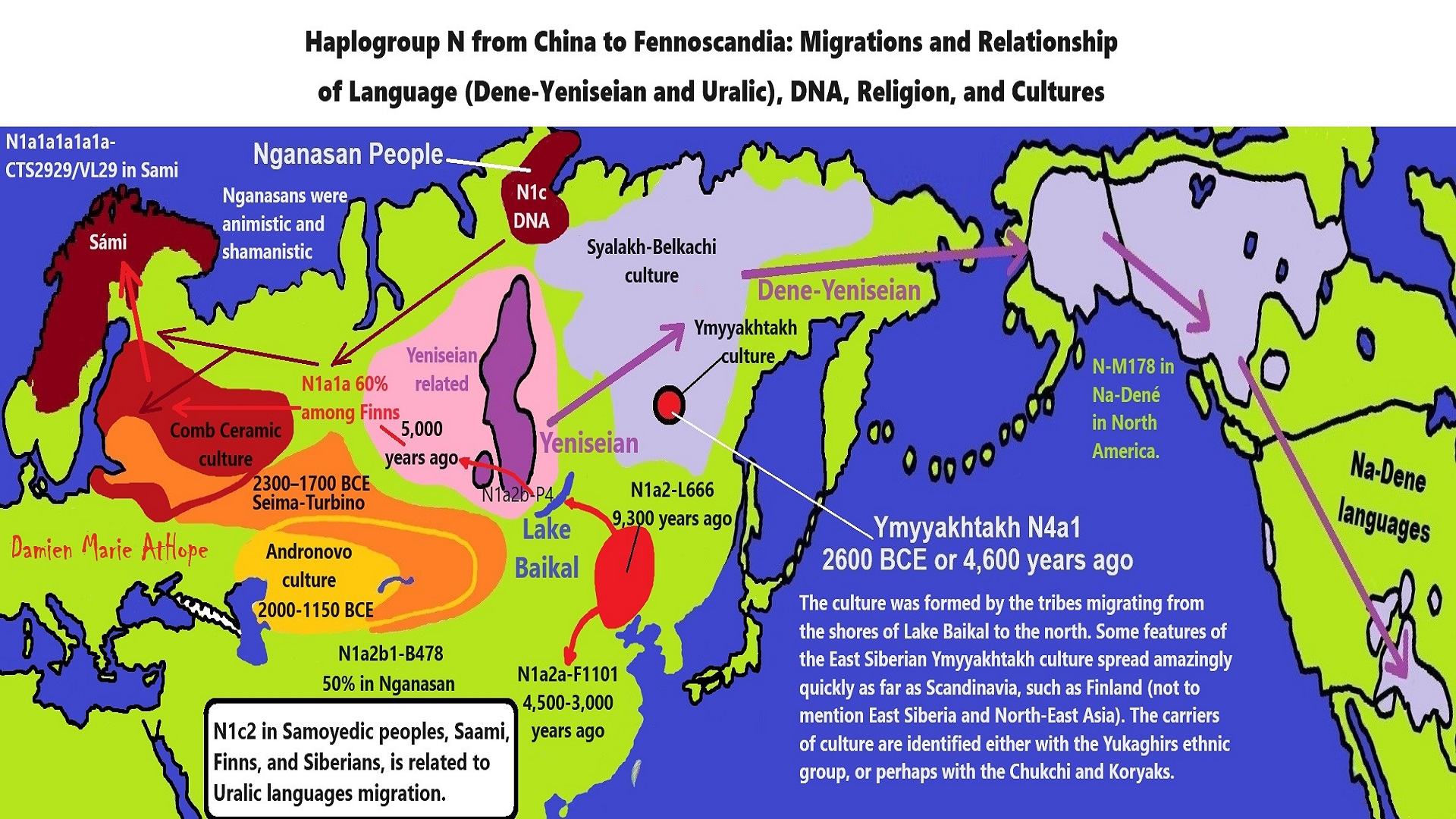
Postglacial genomes from foragers across Northern Eurasia reveal prehistoric
mobility associated with the spread of the Uralic and Yeniseian languages
Abstract
“The North Eurasian forest and forest-steppe zones have sustained millennia of sociocultural connections among northern peoples. We present genome-wide ancient DNA data for 181 individuals from this region spanning the Mesolithic, Neolithic, and Bronze Age. We find that Early to Mid-Holocene hunter-gatherer populations from across the southern forest and forest-steppes of Northern Eurasia can be characterized by a continuous gradient of ancestry that remained stable for millennia, ranging from fully West Eurasian in the Baltic region to fully East Asian in the Transbaikal region. In contrast, cotemporaneous groups in far Northeast Siberia were genetically distinct, retaining high levels of continuity from a population that was the primary source of ancestry for Native Americans. By the mid-Holocene, admixture between this early Northeastern Siberian population and groups from Inland East Asia and the Amur River Basin produced two distinctive populations in eastern Siberia that played an important role in the genetic formation of later people. Ancestry from the first population, Cis-Baikal Late Neolithic-Bronze Age (Cisbaikal_LNBA), is found substantially only among Yeniseian-speaking groups and those known to have admixed with them. Ancestry from the second, Yakutian Late Neolithic-Bronze Age (Yakutia_LNBA), is strongly associated with present-day Uralic speakers. We show how Yakutia_LNBA ancestry spread from an east Siberian origin ~4.5kya, along with subclades of Y-chromosome haplogroup N occurring at high frequencies among present-day Uralic speakers, into Western and Central Siberia in communities associated with Seima-Turbino metallurgy: a suite of advanced bronze casting techniques that spread explosively across an enormous region of Northern Eurasia ~4.0kya. However, the ancestry of the 16 Seima-Turbino-period individuals–the first reported from sites with this metallurgy–was otherwise extraordinarily diverse, with partial descent from Indo-Iranian-speaking pastoralists and multiple hunter-gatherer populations from widely separated regions of Eurasia. Our results provide support for theories suggesting that early Uralic speakers at the beginning of their westward dispersal where involved in the expansion of Seima-Turbino metallurgical traditions, and suggests that both cultural transmission and migration were important in the spread of Seima-Turbino material culture.” ref
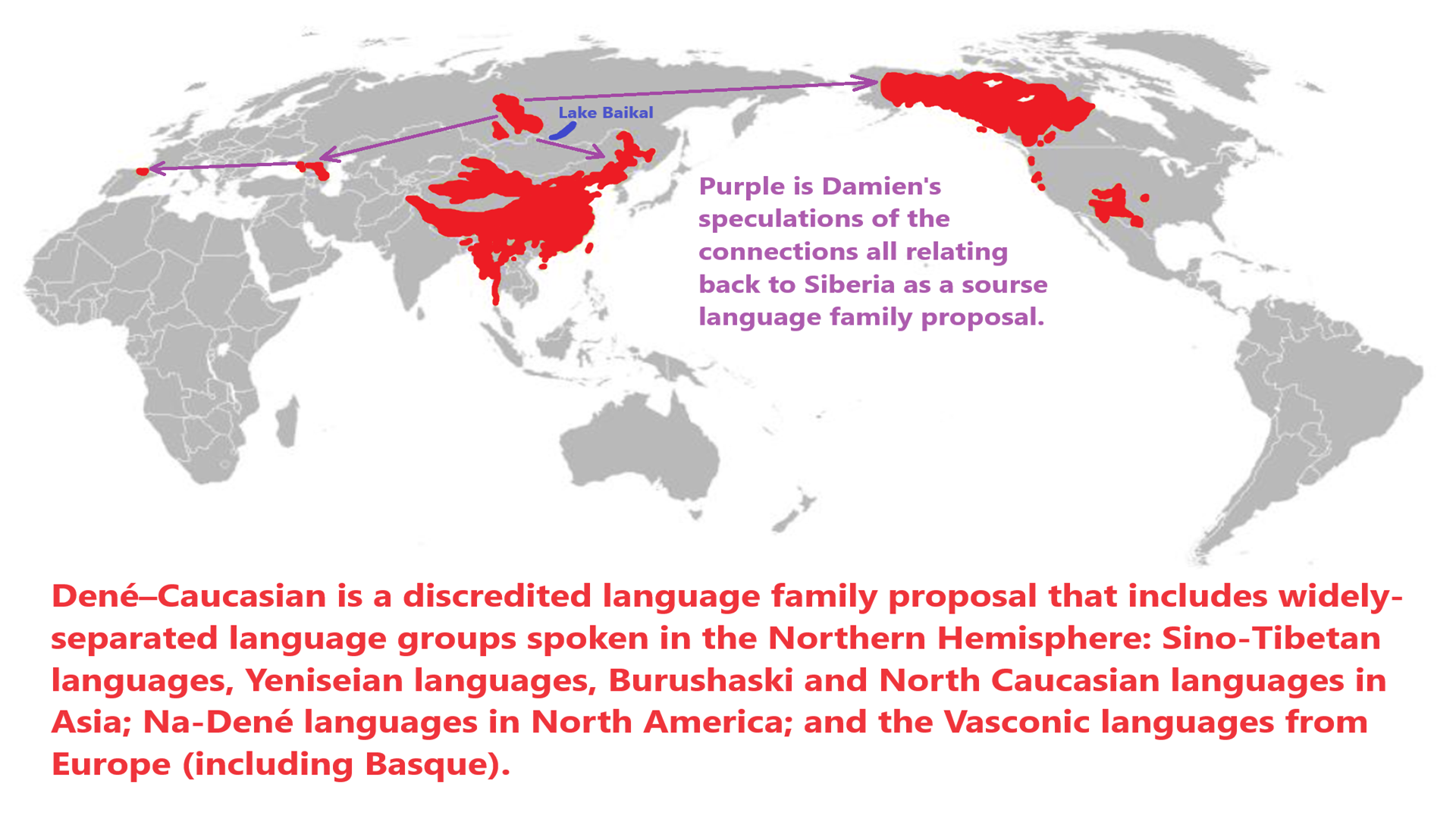
“Dené–Caucasian is a discredited language family proposal that includes widely-separated language groups spoken in the Northern Hemisphere: Sino-Tibetan languages, Yeniseian languages, Burushaski and North Caucasian languages in Asia; Na-Dené languages in North America; and the Vasconic languages from Europe (including Basque). A narrower connection specifically between North American Na-Dené and Siberian Yeniseian (the Dené–Yeniseian languages hypothesis) was proposed by Edward Vajda in 2008, and has met with some acceptance within the community of professional linguists. The validity of the rest of the family, however, is viewed as doubtful or rejected by nearly all historical linguists.” ref
“The Dené–Caucasian family tree and approximate divergence dates (estimated by modified glottochronology) proposed by S. A. Starostin and his colleagues from the Tower of Babel project:
- Dené–Caucasian languages [8,700 BCE or around 10,700 years ago]
- Na-Dené languages (Athabascan–Eyak–Tlingit)
- Sino-Vasconic languages [7,900 BCE or around 9,900 years ago]
- Vasconic (see below)
- Sino-Caucasian languages [6,200 BCE or around 8,200 years ago]
- Burushaski
- Caucaso-Sino-Yeniseian [5,900 BCE or around 7,900 years ago]
- North Caucasian languages
- Sino-Yeniseian [5,100 BCE or around 7,100 years ago]
“John D. Bengtson groups Basque, Caucasian and Burushaski together in a Macro-Caucasian (earlier Vasco-Caucasian) family (see the section on Macro-Caucasian below). According to him, it is as yet premature to propose other nodes or subgroupings, but he notes that Sumerian seems to share the same number of isoglosses with the (geographically) western branches as with the eastern ones:
- Dené–Caucasian
- The Macro-Caucasian family
- Basque
- North Caucasian
- Burushaski
- Sumerian
- Sino-Tibetan
- Yeniseian
- Na-Dené” ref
- The Macro-Caucasian family
“It has been conjectured that the North-West Caucasian languages may be genetically related to the Indo-European family, at a time depth of perhaps 12,000 years before the present. This hypothesized proto-language is called Proto-Pontic, but is not widely accepted. There does at least appear to have been extensive contact between the two proto-languages, and the resemblances may be due to this influence. A few linguists have proposed even broader relationships, of which the Dene–Caucasian hypothesis is perhaps the most popular. Dene–Caucasian links the North Caucasian (including Northwest Caucasian), Basque, Burushaski, Yeniseian, Sino-Tibetan, and Na–Dene families. However, this is an even more tentative hypothesis than Nostratic, which attempts to relate Kartvelian, Indo-European, Uralic, and Altaic, etc., and which is widely considered to be undemonstrated.” ref
“Nostratic is a hypothetical language macrofamily including many of the language families of northern Eurasia. Though a historically important proposal, in a contemporary context it is typically considered a fringe theory. Although the exact composition varies based on proponent, it typically comprises Kartvelian, Indo-European and Uralic languages; some languages from the similarly controversial Altaic family; the Afroasiatic languages; as well as the Dravidian languages (sometimes also Elamo-Dravidian).” ref
“Iran Neolithic (Iran_N) individuals dated ~8,500 years ago carried 50% Ancient North Eurasian-derived admixture and 50% Dzudzuana-related admixture, marking them as different from other Near-Eastern and Anatolian Neolithics who didn’t have Ancient North Eurasian admixture. Iran Neolithics were later replaced by Iran Chalcolithics, who were a mixture of Iran Neolithic and Near Eastern Levant Neolithic.” ref
I speculate that possibly this “Iran Neolithic” difference is a later migration relating to Ancient North Eurasian admixture, with the source languages from Siberia (pre-proto-indo-europeain, like some kind of pre/proto-Yeniseian, or Dené–Yeniseian languages/or Dené–Caucasian) that then merged into proto-indo-European languages seen just west of Iran in the Caucasus and East Turkey areas. Also, I speculate that the idea of pottery was likewise brought by these peoples and they, to me could have influenced the creation of the earliest pottery in Tell Hassuna and Jarmo (Iraq).
“Proto-Yeniseian or Proto-Yeniseic is the unattested reconstructed proto-language from which all Yeniseian languages are thought to descend from. It is uncertain whether Proto-Yeniseian had a similar tone/pitch accent system as Ket people, who practiced Shamanism and connected to Tengrism. Many studies about Proto-Yeniseian phonology have been done, however there are still many things unclear about Proto-Yeniseian. The probable location of the Yeniseian homeland is proposed on the basis of geographic names and genetic studies, which suggests a homeland in Southern Siberia.” ref
“Tengri (Old Turkic: 𐰚𐰇𐰚:𐱅𐰭𐰼𐰃, romanized: Kök Teŋri/Teŋiri, lit. ’Blue Heaven’; Old Uyghur: tängri; Middle Turkic: تآنغرِ; Ottoman Turkish: تڭری; Kyrgyz: Теңир; Kazakh: Тәңір; Turkish: Tanrı; Azerbaijani: Tanrı; Bulgarian: Тангра; Proto-Turkic *teŋri / *taŋrɨ; Mongolian script: ᠲᠩᠷᠢ, T’ngri; Mongolian: Тэнгэр, Tenger; Uyghur: تەڭرى tengri ) is the all-encompassing God of Heaven in the traditional Turkic, Yeniseian, Mongolic, and various other nomadic Altaic religious beliefs. Tengri is not considered a deity in the usual sense, but a personification of the universe. However, some qualities associated with Tengri as the judge and source of life, and being eternal and supreme, led European and Muslim writers to identify Tengri as a deity of Turkic and Mongolic peoples. According to Mongolian belief, Tengri’s will (jayayan) may break its own usual laws and intervene by sending a chosen person to earth. It is also one of the terms used for the primary chief deity of the early Turkic and Mongolic peoples. Worship surrounding Tengri is called Tengrism. The core beings in Tengrism are the Sky Father (Tenger Etseg) and the Earth Mother (Umay Ana). It involves ancestor worship, as Tengri was thought to have been the ancestral progenitor of mankind in Turkic regions and Mongolia, shamanism, animism, and totemism.” ref
“Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a religion originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri, who is not considered a deity in the usual sense but a personification of the universe. According to some scholars, adherents of Tengrism view the purpose of life to be in harmony with the universe. It was the prevailing religion of the Göktürks, Xianbei, Bulgars, Xiongnu, Yeniseian, and Mongolic peoples and Huns, as well as the state religion of several medieval states: the First Turkic Khaganate, the Western Turkic Khaganate, the Eastern Turkic Khaganate, Old Great Bulgaria, the First Bulgarian Empire, Volga Bulgaria, Khazaria, and the Mongol Empire. In the Irk Bitig, a ninth century manuscript on divination, Tengri is mentioned as Türük Tängrisi (God of Turks). According to many academics, Tengrism was, and to some extent still is, a predominantly polytheistic religion based on the shamanistic concept of animism, and was first influenced by monotheism during the imperial period, especially by the 12th–13th centuries. Abdulkadir Inan argues that Yakut and Altai shamanism are not entirely equal to the ancient Turkic religion.” ref
“The term also describes several contemporary Turkic and Mongolic native religious movements and teachings. All modern adherents of “political” Tengrism are monotheists. Tengrism has been advocated for in intellectual circles of the Turkic nations of Central Asia (Kyrgyzstan with Kazakhstan) and Russia (Tatarstan, Bashkortostan) since the dissolution of the Soviet Union during the 1990s. Still practiced, it is undergoing an organized revival in Buryatia, Sakha (Yakutia), Khakassia, Tuva and other Turkic nations in Siberia. Altaian Burkhanism and Chuvash Vattisen Yaly are contemporary movements similar to Tengrism. The term tengri (compare with Kami) can refer to the sky deity Tenger Etseg – also Gök Tengri; Sky father, Blue sky – or to other deities. While Tengrism includes the worship of personified gods (tngri) such as Ülgen and Kaira,Tengri is considered an “abstract phenomenon”. In Mongolian folk religion, Genghis Khan is considered one of the embodiments, if not the main embodiment, of Tengri’s will. The forms of the name Tengri (Old Turkic: Täŋri) among the ancient and modern Turkic and Mongolic are Tengeri, Tangara, Tangri, Tanri, Tangre, Tegri, Tingir, Tenkri, Tangra, Teri, Ter, and Ture. The name Tengri (“the Sky”) is derived from Old Turkic: Tenk (“daybreak”) or Tan (“dawn”). Meanwhile, Stefan Georg proposed that the Turkic Tengri ultimately originates as a loanword from Proto-Yeniseian *tɨŋgɨr- “high”. Mongolia is sometimes poetically called the “Land of Eternal Blue Sky” (Mönkh Khökh Tengeriin Oron) by its inhabitants. According to some scholars, the name of the important deity Dangun (also Tangol) (God of the Mountains) of the Korean folk religion is related to the Siberian Tengri (“Heaven”), while the bear is a symbol of the Big Dipper (Ursa Major).” ref
“Tiān (天) is one of the oldest Chinese terms for heaven and a key concept in Chinese mythology, philosophy, and religion. During the Shang dynasty (17th―11th century BCE), the Chinese referred to their highest god as Shàngdì (上帝, “Lord Above”) or Dì (帝, “Lord”). During the following Zhou dynasty, Tiān became synonymous with this figure. Before the 20th century, worship of Tiān was an orthodox state religion of China. In Chinese culture, heaven tends to be “synonymous with order”, “containing the blueprints for creation”, “the mandate by which earthly rulers govern, and the standards by which to measure beauty, goodness, and truth.” Zhou dynasty nobles made the worship of heaven a major part of their political philosophy and viewed it as “many gods” who embodied order and kingship, as well as the mandate of heaven. For the etymology of tiān, Schuessler links it with the Mongolian word tengri “sky, heaven, heavenly deity” or the Tibeto-Burman words taleŋ (Adi) and tǎ-lyaŋ (Lepcha), both meaning “sky”. He also suggests a likely connection between Chinese tiān 天, diān 巔 “summit, mountaintop”, and diān 顛 “summit, top of the head, forehead”, which have cognates such as Zemeic Naga tiŋ “sky”. However, other reconstructions of 天’s OC pronunciation *qʰl’iːn or *l̥ˤi[n] reconstructed a voiceless lateral onset, either a cluster or a single consonant, respectively. Baxter & Sagart pointed to attested dialectal differences in Eastern Han Chinese, the use of 天 as a phonetic component in phono-semantic compound Chinese characters, and the choice of 天 to transcribe foreign syllables, all of which prompted them to conclude that, around 200 CE, 天’s onset had two pronunciations: coronal *tʰ & dorsal *x, both of which likely originated from an earlier voiceless lateral *l̥ˤ.” ref
“In Taoism and Confucianism, Tiān (the celestial aspect of the cosmos, often translated as “Heaven“) is mentioned in relationship to its complementary aspect of Dì (地, often translated as “Earth“). They are thought to maintain the two poles of the Three Realms (三界) of reality, with the middle realm occupied by Humanity (人, rén), and the lower world occupied by demons (魔, mó) and “ghosts”, the damned, (鬼, guǐ). Tiān was variously thought as a “supreme power reigning over lesser gods and human beings” that brought “order and calm…or catastrophe and punishment”, a god, destiny, an “impersonal” natural force that controlled various events, a holy world or afterlife containing other worlds or afterlives, or one or more of these. “Confucianism has a religious side with a deep reverence for Heaven and Earth (Di), whose powers regulate the flow of nature and influence human events.” Yin and yang are also thought to be integral to this relationship and permeate both, as well as humans and man-made constructs. This “cosmos” and its “principles” is something that “[t]he ways of man should conform to, or else” frustration will result. Many Confucianists, both historically and in current times, use the I Ching to divine events through the changes of Tiān and other “natural forces”. Historical and current Confucianists were/are often environmentalists out of their respect for Heaven and the other aspects of nature and the “Principle” that comes from their unity and, more generally, harmony as a whole, which is “the basis for a sincere mind.” The Emperor of China as Tianzi was formerly vital to Confucianism. Mount Tai is seen as a sacred place in Confucianism and was traditionally the most revered place where Chinese emperors offered sacrifices to heaven and earth. Some tiān in Chinese folk religion were thought to be many different or a hierarchy of multiple, sphere-like realms that contained morally ambiguous creatures and spirits such as huli jing and fire-breathing dragons. ” ref
“Paleo-Siberian languages, languages spoken in Asian Russia (Siberia) that belong to four genetically unrelated groups—Yeniseian, Luorawetlan, Yukaghir, and Nivkh.” ref
Proto-Indo-European mythology
“Proto-Indo-European mythology is the body of myths and deities associated with the Proto-Indo-Europeans, speakers of the hypothesized Proto-Indo-European language. Although the mythological motifs are not directly attested – since Proto-Indo-European speakers lived in preliterate societies – scholars of comparative mythology have reconstructed details from inherited similarities found among Indo-European languages, based on the assumption that parts of the Proto-Indo-Europeans’ original belief systems survived in the daughter traditions. The Proto-Indo-European pantheon includes a number of securely reconstructed deities, since they are both cognates – linguistic siblings from a common origin – and associated with similar attributes and body of myths: such as *Dyḗws Ph₂tḗr, the daylight-sky god; his consort *Dʰéǵʰōm, the earth mother; his daughter *H₂éwsōs, the dawn goddess; his sons the Divine Twins; and *Seh₂ul and *Meh₁not, a solar goddess and moon god, respectively. Some deities, like the weather god *Perkʷunos or the herding-god *Péh₂usōn, are only attested in a limited number of traditions – Western (i.e. European) and Graeco-Aryan, respectively – and could therefore represent late additions that did not spread throughout the various Indo-European dialects.” ref
“Some myths are also securely dated to Proto-Indo-European times, since they feature both linguistic and thematic evidence of an inherited motif: a story portraying a mythical figure associated with thunder and slaying a multi-headed serpent to release torrents of water that had previously been pent up; a creation myth involving two brothers, one of whom sacrifices the other in order to create the world; and probably the belief that the Otherworld was guarded by a watchdog and could only be reached by crossing a river. Various schools of thought exist regarding possible interpretations of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European mythology. The main mythologies used in comparative reconstruction are Indo-Iranian, Baltic, Roman, and Norse, often supported with evidence from the Celtic, Greek, Slavic, Hittite, Armenian, Illyrian, and Albanian traditions as well.” ref
“Early agricultural communities such as Chogha Golan in 10,000 BCE or around 12,000 years ago, along with settlements such as Chogha Bonut (the earliest village in Elam) in 8000 BCE or around 10,000 years ago, began to flourish in and around the Zagros Mountains region in western Iran. Around about the same time, the earliest-known clay vessels and modeled human and animal terracotta figurines were produced at Ganj Dareh, also in western Iran. There are also 10,000-year-old human and animal figurines from Tepe Sarab in Kermanshah Province among many other ancient artifacts.” ref
I also speculate that there may be a connection with this to the earliest pottery in Turkey from Boncuklu Höyük as well.
“12 fired clay samples and an unfired marl sample from the late 9th and early 8th-millennium BCE site of Boncuklu Höyük (8300–7800 cal BCE or around 10,300 to 9,800 years ago) in the Konya Plain, Turkey. The clay vessels from Boncuklu Höyük, an early Neolithic site in central Anatolia, are much earlier than the accepted date for the introduction of pottery in Anatolia, c. 7000 cal BCE or around 9,000 years ago.” ref
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family:
| Subdivisions |
|---|
“Western Iran was inhabited by a population genetically most similar to hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus, but distinct from the Neolithic Anatolian people who later brought food production into Europe. While some degree of cultural diffusion between Anatolia, Western Iran, and other neighboring regions is possible, the genetic dissimilarity between early Anatolian farmers and the inhabitants of Ganj Dareh supports a model in which Neolithic societies in these areas were distinct. The genome of an early Neolithic female from Ganj Dareh, GD13a, from the Central Zagros (Western Iran), dated to 10000-9700 cal years ago, a region located at the eastern edge of the Near East. Ganj Dareh is well known for providing the earliest evidence of herd management of goats beginning at 9,900 years ago. The mitochondrion of GD13a (91.74X) was assigned to haplogroup X, most likely to the subhaplogroup X2, which has been associated with an early expansion from the Near East and has been found in early Neolithic samples from Anatolia, Hungary, and Germany. GD13a did not cluster with any other early Neolithic individual from Eurasia in any of the analyses. Also genetically close to GD13a were ancient samples from Steppe populations (Yamanya & Afanasievo) that were part of one or more Bronze age migrations into Europe, as well as early Bronze age cultures in that continent (Corded Ware), in line with previous relationships observed for the Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers.” ref
“Subclade X2 appears to have undergone extensive population expansion and dispersal around or soon after the Last Glacial Maximum, roughly 20,000 years ago. It is more strongly represented in the Near East, the Caucasus, and southern Europe, and somewhat less strongly present in the rest of Europe. The highest concentrations are found in the Ojibwe (25%), Sioux (15%), Nuu-Chah-Nulth (12%), Georgia (8%), Orkney (7%), and amongst the Druze Assyrian community in Israel (27%). Subclades of X2 are not present in South Americans Amerindian populations. The oldest known human associated with X2 is Kennewick Man, whose c. 9000-year old remains were discovered in Washington State. The lineage of haplogroup X in the Americas is not derived from a European subclade, but rather represents an independent subclade, labeled X2a. The X2a subclade has not been found in Eurasia, and has most likely arisen within the early Paleo-Indian population, at roughly 13,000 years ago. A basal variant of X2a was found in the Kennewick Man fossil (ca. 9,000 years ago). No presence of mt-DNA ancestral to X2a has been found in Europe or the Near East. New World lineages X2a and X2g are not derived from the Old World lineages X2b, X2c, X2d, X2e, and X2f, indicating an early origin of the New World lineages “likely at the very beginning of their expansion and spread from the Near East.” ref
“Although it occurs only at a frequency of about 3% for the total current indigenous population of the Americas, it is a bigger haplogroup in northern North America, where among the Algonquian peoples it comprises up to 25% of mtDNA types. It is also present in lesser percentages to the west and south of this area—among the Sioux (15%), the Nuu-chah-nulth (11%–13%), the Navajo (7%), and the Yakama (5%). In Latin America, Haplotype X6 was present in the Tarahumara 1.8% (1/53) and Huichol 20% (3/15) X6 and X7 was also found in 12% in Yanomani people. Unlike the four main Native American mtDNA haplogroups (A, B, C, D), X is not strongly associated with East Asia. The main occurrence of X in Asia discovered so far is in the Altai people in Siberia. One theory of how the X Haplogroup ended up in North America is that the people carrying it migrated from central Asia along with haplogroups A, B, C, and D, from an ancestor from the Altai Region of Central Asia. Two sequences of haplogroup X2 were sampled further east of Altai among the Evenks of Central Siberia. These two sequences belong to X2* and X2b. It is uncertain if they represent a remnant of the migration of X2 through Siberia or a more recent input.” ref
“Haplogroup X has been found in various other bone specimens that were analysed for ancient DNA, including specimens associated with the Alföld Linear Pottery (X2b-T226C, Garadna-Elkerülő út site 2, 1/1 or 100%), Linearbandkeramik (X2d1, Halberstadt-Sonntagsfeld, 1/22 or ~5%), and Iberia Chalcolithic (X2b, La Chabola de la Hechicera, 1/3 or 33%; X2b, El Sotillo, 1/3 or 33%; X2b, El Mirador Cave, 1/12 or ~8%) cultures. Abel-beth-maachah 2201 was a man who lived between 1014 and 836 BCE during the Levant Iron Age and was found in the region now known as Abel Beth Maacah, Metula, Israel. He was associated with the Galilean cultural group. His direct maternal line belonged to mtDNA haplogroup X2b. Haplogroup X has been found in ancient Assyria and ancient Egyptian mummies excavated at the Abusir el-Meleq archaeological site in Middle Egypt, which date from the late New Kingdom and Roman periods. Fossils excavated at the Late Neolithic site of Kelif el Boroud in Morocco, which have been dated to around 5,000 years old, have also been found to carry the X2 subclade.” ref
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

“The Pyramid of Capitalist System is a common name of a 1911 American cartoon caricature critical of capitalism, based on older similar pictures. In 1900, the Belgian Labour Party used a picture called “Pyramide à renverser” (lit. ’a pyramid that has to be overthrown’) during its electoral campaign. The basic message of the image is a critique of the capitalist system, depicting a hierarchy of power and wealth. It illustrates a working class supporting all others, and if it would withdraw their support from the system it could topple the existing social order.” ref
“Anti-capitalism is a political ideology and movement encompassing a variety of attitudes and ideas that oppose capitalism. In this sense, anti-capitalists are those who wish to replace capitalism with another type of economic system, such as socialism or communism. Socialism advocates public or direct worker ownership and administration of the means of production and allocation of resources, and a society characterized by equal access to resources for all individuals, with an egalitarian method of compensation. Karl Marx saw capitalism as a historical stage, once progressive but which would eventually stagnate due to internal contradictions and would eventually be followed by socialism. Marx claimed that capitalism was nothing more than a necessary stepping stone for the progression of man, which would then face a political revolution before embracing the classless society.” ref
“In addition to individualist anarchist Benjamin Tucker‘s “big four” monopolies (land, money, tariffs, and patents), Kevin Carson argues that the state has also transferred wealth to the wealthy by subsidizing organizational centralization, in the form of transportation and communication subsidies. He believes that Tucker overlooked this issue due to Tucker’s focus on individual market transactions, whereas Carson also focuses on organizational issues. Carson holds that “capitalism, arising as a new class society directly from the old class society of the Middle Ages, was founded on an act of robbery as massive as the earlier feudal conquest of the land. It has been sustained to the present by continual state intervention to protect its system of privilege without which its survival is unimaginable.” ref
“Within anarchism there emerged a critique of wage slavery, which refers to a situation perceived as quasi-voluntary slavery, where a person’s livelihood depends on wages, especially when the dependence is total and immediate. It is a negatively connoted term used to draw an analogy between slavery and wage labor by focusing on similarities between owning and renting a person. The term wage slavery has been used to criticize economic exploitation and social stratification, with the former seen primarily as unequal bargaining power between labor and capital (particularly when workers are paid comparatively low wages, e.g. in sweatshops), and the latter as a lack of workers’ self-management, fulfilling job choices and leisure in an economy. Libertarian socialists believe if freedom is valued, then society must work towards a system in which individuals have the power to decide economic issues along with political issues. Libertarian socialists seek to replace unjustified authority with direct democracy, voluntary federation, and popular autonomy in all aspects of life, including physical communities and economic enterprises.” ref

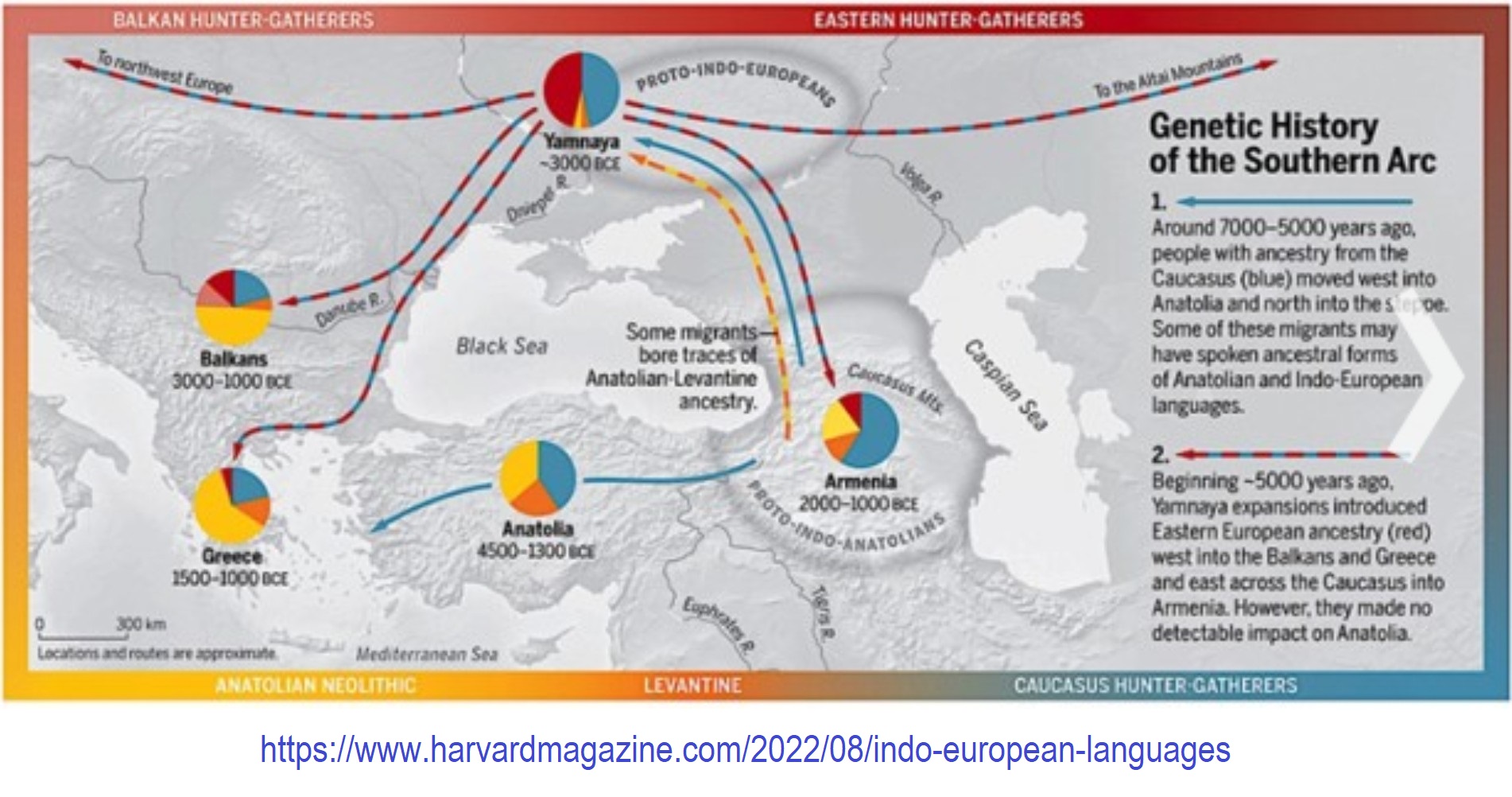
Indo-European dialects dispersed across Eurasia in successive waves over the course of 8,000 years.
Word origins and ancient DNA reveal the evolutionary path traveled by the languages spoken by half the world.
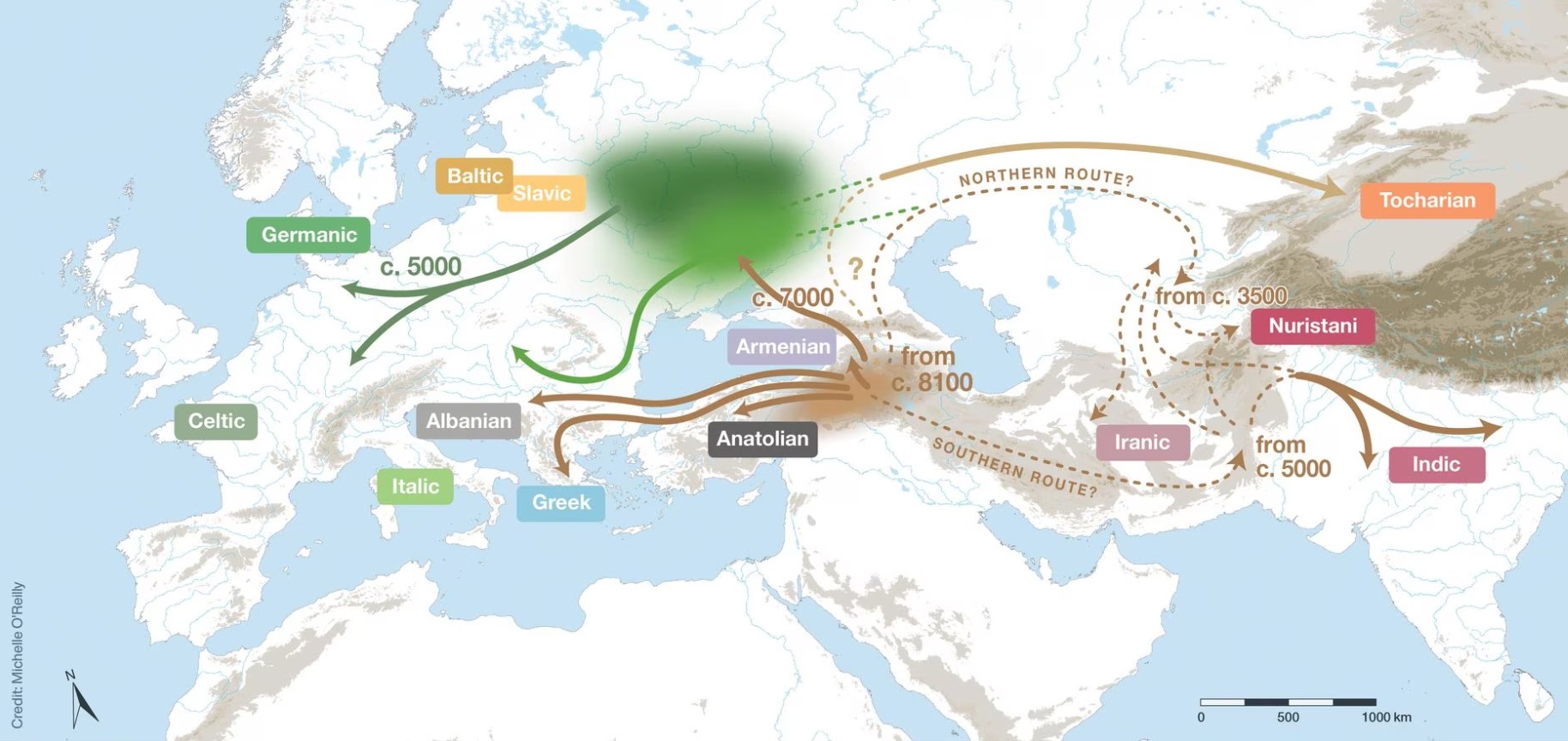
“Approximately 7,000 years ago, the Indo-European linguistic lineage had already split into numerous distinct branches, according to the study published in Science. “This would rule out the steppe hypothesis,” said Heggarty. Around 8,120 years ago, the Proto-Indo-European language likely experienced its initial diversification event, give or take a few centuries. Recent studies of ancient DNA suggest that farmers from the Caucasus region — between the Black Sea and Caspian Sea — migrated towards Anatolia, which supports the Anatolian theory. Hittite, an extinct language spoken by the Anatolian civilization, is another significant branch of the Indo-European family. For decades, a large group of linguists argued that Hittite was the common ancestor of the other Indo-European languages, with some even considering it to be the direct heir of Proto-Indo-European.” ref
“Ancient DNA, on the other hand, has provided compelling evidence in support of the steppe hypothesis. Since 2015, it has become clear that individuals originating from the Pontic steppe, situated to the south and northeast of present-day Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan, migrated to Central Europe approximately 6,000 to 4,500 years ago. Their genetic legacy is evident in both modern Europeans and the indigenous populations of that era. Notably, studies conducted in 2018 and 2019 revealed how these migrant eastern populations replaced a significant proportion of males on the Iberian Peninsula. Furthermore, they brought with them Italic, Germanic, and Celtic languages. It is important to note that when they departed from their original homeland, they likely spoke a common or closely related language descended from Proto-Indo-European. However, as their very slow journey progressed (the Celts took centuries to reach present-day Ireland) and they settled in new territories, language diversification began to emerge.” ref
“The Albanians, Greek-speaking Mycenaeans, and Hittites do not have a dominant genetic signal from the steppe.” ref
Paul Heggarty, researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Germany.
“Heggarty’s team made a significant contribution by shedding light on this question. By combining phylogenetic analysis of cognates with insights from ancient DNA, they found potentially two distinct origins. Expansion initially originated from the southern Caucasus region, resulting in the separation of five major language families approximately 7,000 years ago. “The Albanians, Greek-speaking Mycenaeans, and Hittites do not have a dominant genetic signal from the steppe,” said Heggarty. Several millennia later, another wave emerged, led by nomadic steppe herders from the north. This wave not only influenced the development of western branches of the language tree, but it also possibly played a role in the evolution of Slavic and Baltic languages. It even extended its influence to the Indian subcontinent, while giving rise to the now-extinct Tocharian languages in what is present-day Tibet.” ref
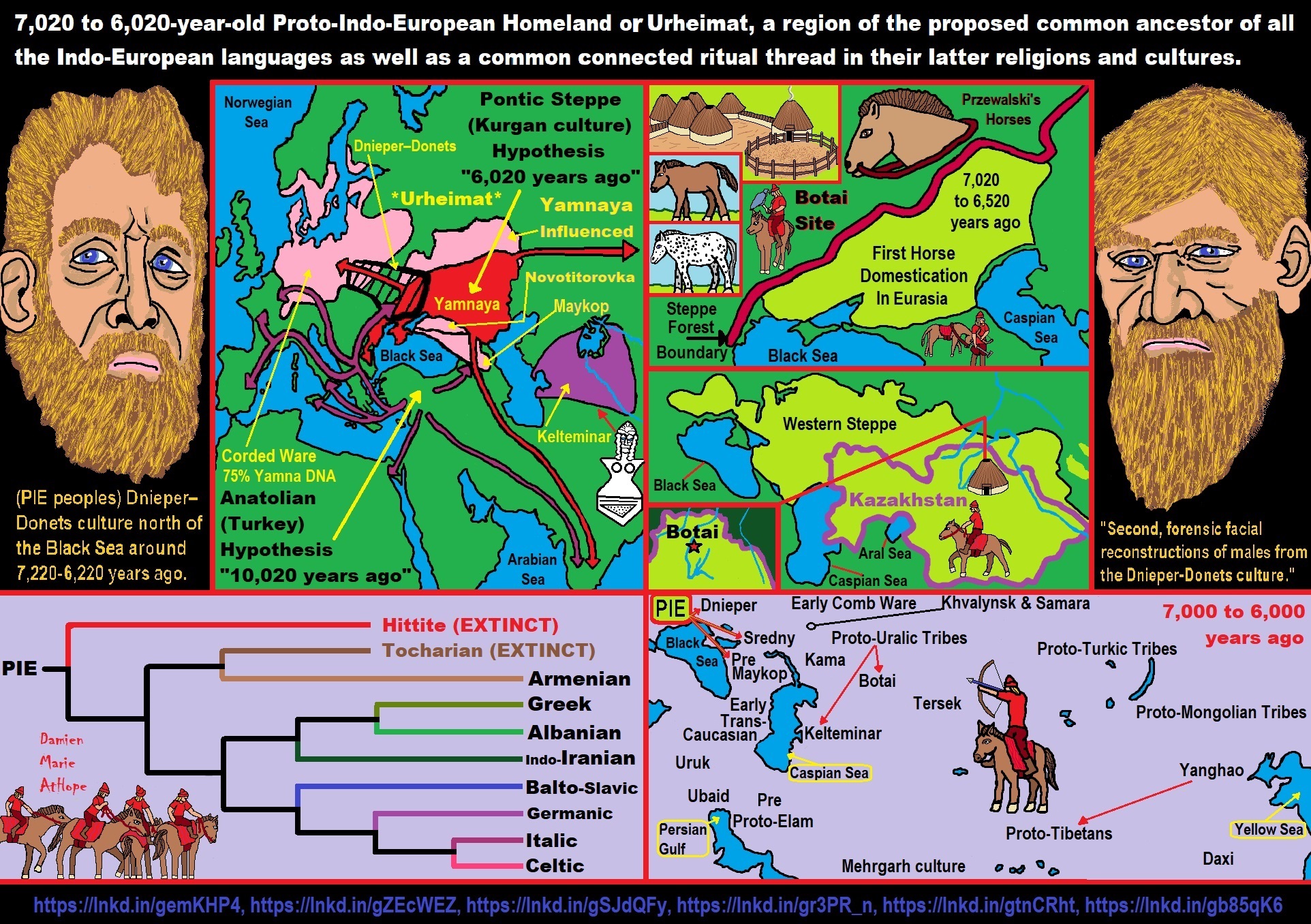
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Proto-Indo-Europeans: Western Steppe Herders
“The Proto-Indo-Europeans are a hypothetical prehistoric population of Eurasia who spoke Proto-Indo-European (PIE), the ancestor of the Indo-European languages according to linguistic reconstruction. Knowledge of them comes chiefly from that linguistic reconstruction, along with material evidence from archaeology and archaeogenetics. The Proto-Indo-Europeans likely lived during the late Neolithic, or roughly the 4th millennium BCE. Mainstream scholarship places them in the Pontic–Caspian steppe zone in Eastern Europe (present-day Ukraine and southern Russia).” ref
“Some archaeologists would extend the time depth of PIE to the middle Neolithic (5500 to 4500 BCE or 7,522-6,522 years ago) or even the early Neolithic (7500 to 5500 BCE or 9,522-7,522 years ago), and suggest alternative location hypotheses. By the early second millennium BCE, descendants of the Proto-Indo-Europeans had reached far and wide across Eurasia, including Anatolia (Hittites), the Aegean (the linguistic ancestors of Mycenaean Greece), the north of Europe (Corded Ware culture), the edges of Central Asia (Yamnaya culture), and southern Siberia (Afanasievo culture).” ref
“While ‘Proto-Indo-Europeans’ is used in scholarship to designate the group of speakers associated with the reconstructed proto-language and culture, the term ‘Indo-Europeans’ may refer to any historical people that speak an Indo-European language. In the words of philologist Martin L. West, “If there was an Indo-European language, it follows that there was a people who spoke it: not a people in the sense of a nation, for they may never have formed a political unity, and not a people in any racial sense, for they may have been as genetically mixed as any modern population defined by language.” ref
“Using linguistic reconstruction from old Indo-European languages such as Latin and Sanskrit, hypothetical features of the Proto-Indo-European language are deduced. Assuming that these linguistic features reflect the culture and environment of the Proto-Indo-Europeans, the following cultural and environmental traits are widely proposed:
- pastoralism, including domesticated cattle, horses, and dogs
- agriculture and cereal cultivation, including technology commonly ascribed to late-Neolithic farming communities, e.g., the plow
- transportation by or across water
- the solid wheel, used for wagons, but not yet chariots with spoked wheels
- worship of a sky god, *Dyḗus Ph2tḗr (lit. “sky father”; > Vedic Sanskrit Dyáuṣ Pitṛ́, Ancient Greek Ζεύς (πατήρ) / Zeus (dyeus)), vocative *dyeu ph2ter (> Latin Iūpiter, Illyrian Deipaturos)
- oral heroic poetry or song lyrics that used stock phrases such as imperishable fame (*ḱléwos ń̥dʰgʷʰitom) and the wheel of the sun (*sh₂uens kʷekʷlos).
- a patrilineal kinship-system based on relationships between men” ref
“A 2016 phylogenetic analysis of Indo-European folktales found that one tale, The Smith and the Devil, could be confidently reconstructed to the Proto-Indo-European period. This story, found in contemporary Indo-European folktales from Scandinavia to India, describes a blacksmith who offers his soul to a malevolent being (commonly a devil in modern versions of the tale) in exchange for the ability to weld any kind of materials together. The blacksmith then uses his new ability to stick the devil to an immovable object (often a tree), thus avoiding his end of the bargain. According to the authors, the reconstruction of this folktale to PIE implies that the Proto-Indo-Europeans had metallurgy, which in turn “suggests a plausible context for the cultural evolution of a tale about a cunning smith who attains a superhuman level of mastery over his craft.” ref
“Researchers have made many attempts to identify particular prehistoric cultures with the Proto-Indo-European-speaking peoples, but all such theories remain speculative. The scholars of the 19th century who first tackled the question of the Indo-Europeans’ original homeland (also called Urheimat, from German), had essentially only linguistic evidence. They attempted a rough localization by reconstructing the names of plants and animals (importantly the beech and the salmon) as well as the culture and technology (a Bronze Age culture centered on animal husbandry and having domesticated the horse).” ref
“The scholarly opinions became basically divided between a European hypothesis, positing migration from Europe to Asia, and an Asian hypothesis, holding that the migration took place in the opposite direction. In the early 20th century, the question became associated with the expansion of a supposed “Aryan race“, a now-discredited theory promoted during the expansion of European empires and the rise of “scientific racism“. The question remains contentious within some flavors of ethnic nationalism (see also Indigenous Aryans).” ref
“A series of major advances occurred in the 1970s due to the convergence of several factors. First, the radiocarbon dating method (invented in 1949) had become sufficiently inexpensive to be applied on a mass scale. Through dendrochronology (tree-ring dating), pre-historians could calibrate radiocarbon dates to a much higher degree of accuracy. And finally, before the 1970s, parts of Eastern Europe and Central Asia had been off-limits to Western scholars, while non-Western archaeologists did not have access to publications in Western peer-reviewed journals.” ref
“The pioneering work of Marija Gimbutas, assisted by Colin Renfrew, at least partly addressed this problem by organizing expeditions and arranging for more academic collaboration between Western and non-Western scholars. The Kurgan hypothesis, as of 2017 the most widely held theory, depends on linguistic and archaeological evidence, but is not universally accepted. It suggests PIE origin in the Pontic–Caspian steppe during the Chalcolithic. A minority of scholars prefer the Anatolian hypothesis, suggesting an origin in Anatolia during the Neolithic. Other theories (Armenian hypothesis, Out of India theory, Paleolithic Continuity Theory, Balkan hypothesis) have only marginal scholarly support.” ref
“In regard to terminology, in the 19th and early 20th centuries, the term Aryan was used to refer to the Proto-Indo-Europeans and their descendants. However, Aryan more properly applies to the Indo-Iranians, the Indo-European branch that settled parts of the Middle East and South Asia, as only Indic and Iranian languages explicitly affirm the term as a self-designation referring to the entirety of their people, whereas the same Proto-Indo-European root (*aryo-) is the basis for Greek and Germanic word forms which seem only to denote the ruling elite of Proto-Indo-European (PIE) society.” ref
“In fact, the most accessible evidence available confirms only the existence of a common, but vague, socio-cultural designation of “nobility” associated with PIE society, such that Greek socio-cultural lexicon and Germanic proper names derived from this root remain insufficient to determine whether the concept was limited to the designation of an exclusive, socio-political elite, or whether it could possibly have been applied in the most inclusive sense to an inherent and ancestral “noble” quality which allegedly characterized all ethnic members of PIE society. Only the latter could have served as a true and universal self-designation for the Proto-Indo-European people.” ref
“By the early twentieth century, this term had come to be widely used in a racist context referring to a hypothesized white, blonde, and blue-eyed “master race” (Herrenrasse), culminating with the pogroms of the Nazis in Europe. Subsequently, the term Aryan as a general term for Indo-Europeans has been largely abandoned by scholars (though the term Indo-Aryan is still used to refer to the branch that settled in Southern Asia).” ref
Proto-Indo-European Urheimat hypotheses and Indo-European migrations
“According to some archaeologists, PIE speakers cannot be assumed to have been a single, identifiable people or tribe, but were a group of loosely related populations ancestral to the later, still partially prehistoric, Bronze Age Indo-Europeans. This view is held especially by those archaeologists who posit an original homeland of vast extent and immense time depth. However, this view is not shared by linguists, as proto-languages, like all languages before modern transport and communication, occupied small geographical areas over a limited time span, and were spoken by a set of close-knit communities—a tribe in the broad sense. Researchers have put forward a great variety of proposed locations for the first speakers of Proto-Indo-European. Few of these hypotheses have survived scrutiny by academic specialists in Indo-European studies sufficiently well to be included in modern academic debate.” ref
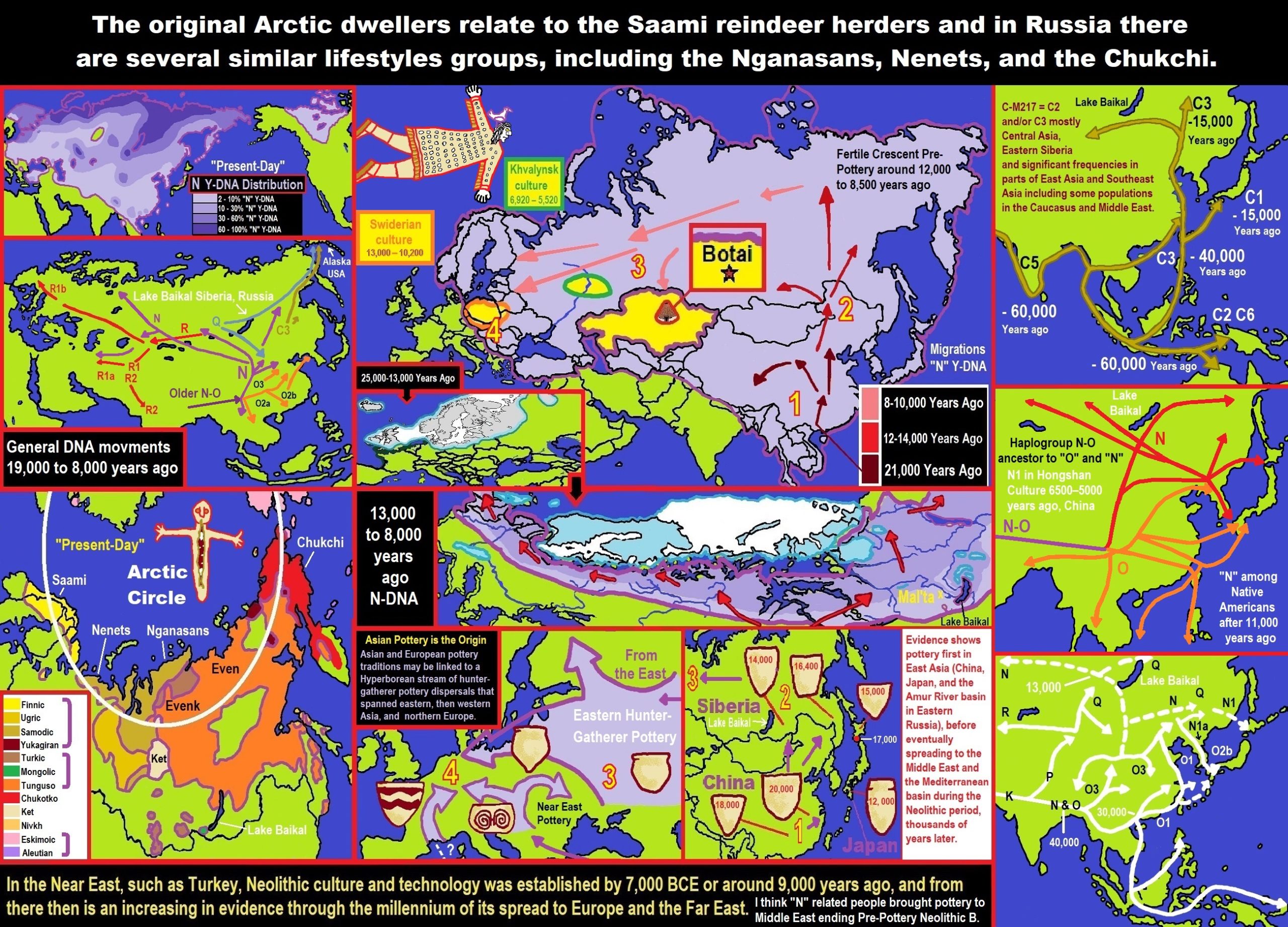
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“The shaman is, above all, a connecting figure, bridging several worlds for his people, traveling between this world, the underworld, and the heavens. He transforms himself into an animal and talks with ghosts, the dead, the deities, and the ancestors. He dies and revives. He brings back knowledge from the shadow realm, thus linking his people to the spirits and places which were once mythically accessible to all.–anthropologist Barbara Meyerhoff” ref
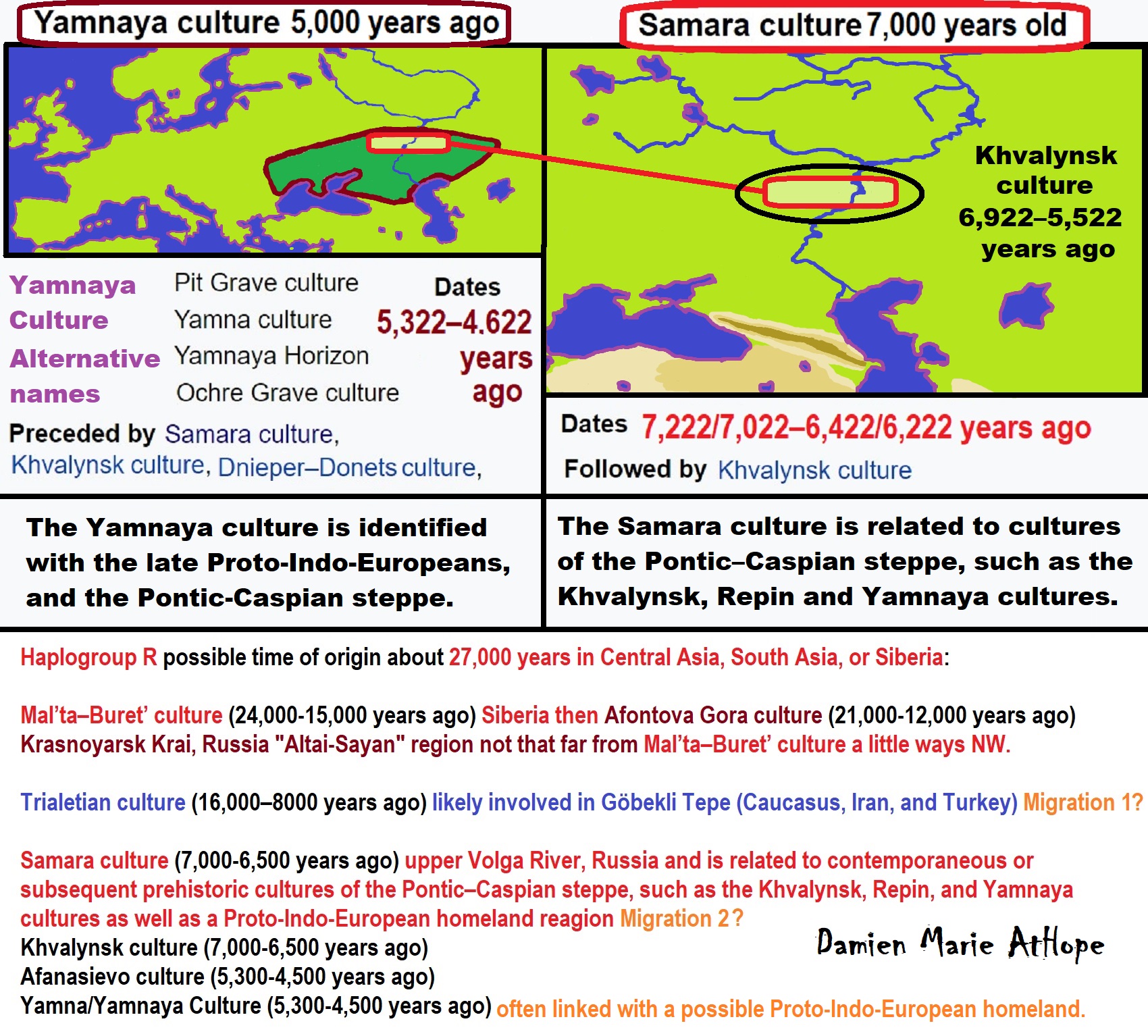
“The Samara culture was an Eneolithic (Copper Age) culture that flourished around the turn of the 5th millennium BCE, at the Samara Bend of the Volga River (modern Russia). The Samara culture is regarded as related to contemporaneous or subsequent prehistoric cultures of the Pontic–Caspian steppe, such as the Khvalynsk, Repin, and Yamna (or Yamnaya) cultures.” ref
“Genetic analyses of a male buried at Lebyazhinka, radiocarbon dated to 5640-5555 BCE, found that he belonged to a population often referred to as “Samara hunter-gatherers”, a group closely associated with Eastern Hunter-Gatherers. The male sample carried Y-haplogroup R1b1a1a and mitochondrial haplogroup U5a1d.” ref
“Pottery consists mainly of egg-shaped beakers with pronounced rims. They were not able to stand on a flat surface, suggesting that some method of supporting or carrying must have been in use, perhaps basketry or slings, for which the rims would have been a useful point of support. The carrier slung the pots over the shoulder or onto an animal. The decoration consists of circumferential motifs: lines, bands, zig-zags, or wavy lines, incised, stabbed, or impressed with a comb. These patterns are best understood when seen from the top. They appear then to be a solar motif, with the mouth of the pot as the sun. Later developments of this theme show that in fact the sun is being represented.” ref
“The culture is characterized by the remains of animal sacrifice, which occur over most of the sites. There is no indisputable evidence of riding, but there were horse burials, the earliest in the Old World. Typically the head and hooves of cattle, sheep, and horses are placed in shallow bowls over the human grave, smothered with ochre. Some have seen the beginning of the horse sacrifice in these remains, but this interpretation has not been more definitely substantiated. We know that the Indo-Europeans sacrificed both animals and people, like many other cultures.” ref
“The graves found are shallow pits for single individuals, but two or three individuals might be placed there. Some of the graves are covered with a stone cairn or a low earthen mound, the very first predecessor of the kurgan. The later, fully developed kurgan was a hill on which the deceased chief might ascend to the sky god, but whether these early mounds had that significance is doubtful.” ref
“Grave offerings included ornaments depicting horses. The graves also had an overburden of horse remains; it cannot yet be determined decisively if these horses were domesticated and ridden or not, but they were certainly used as a meat-animal. Most controversial are bone plaques of horses or double oxen heads, which were pierced. The graves yield well-made daggers of flint and bone, placed at the arm or head of the deceased, one in the grave of a small boy. Weapons in the graves of children are common later. Other weapons are bone spearheads and flint arrowheads. Other carved bone figurines and pendants were found in the graves.” ref
“The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture, also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–Caspian steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE or around 5,300 to 4,600 years ago. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaeological excavations near the Donets River in 1901–1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: Я́мная (romanization: yamnaya) is a Russian adjective that means ‘related to pits (yama)’, as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers.” ref
“The Yamnaya economy was based upon animal husbandry, fishing, and foraging, and the manufacture of ceramics, tools, and weapons. The people of the Yamnaya culture lived primarily as nomads, with a chiefdom system and wheeled carts and wagons that allowed them to manage large herds. They are also closely connected to Final Neolithic cultures, which later spread throughout Europe and Central Asia, especially the Corded Ware people and the Bell Beaker culture, as well as the peoples of the Sintashta, Andronovo, and Srubnaya cultures.” ref
“Back migration from Corded Ware also contributed to Sintashta and Andronovo. In these groups, several aspects of the Yamnaya culture are present. Yamnaya material culture was very similar to the Afanasevo culture of South Siberia, and the populations of both cultures are genetically indistinguishable. This suggests that the Afanasevo culture may have originated from the migration of Yamnaya groups to the Altai region or, alternatively, that both cultures developed from an earlier shared cultural source.” ref
“Genetic studies have suggested that the people of the Yamnaya culture can be modelled as a genetic admixture between a population related to Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG) and people related to hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus (CHG) in roughly equal proportions, an ancestral component which is often named “Steppe ancestry”, with additional admixture from Anatolian, Levantine, or Early European farmers. Genetic studies also indicate that populations associated with the Corded Ware, Bell Beaker, Sintashta, and Andronovo cultures derived large parts of their ancestry from the Yamnaya or a closely related population.” ref
“The origin of the Yamnaya culture continues to be debated, with proposals for its origins pointing to both the Khvalynsk and Sredny Stog cultures. The Khvalynsk culture (4700–3800 BCE) (middle Volga) and the Don-based Repin culture (c. 3950–3300 BCE) in the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe, and the closely related Sredny Stog culture (c. 4500–3500 BCE) in the western Pontic-Caspian steppe, preceded the Yamnaya culture (3300–2500 BCE). The Yamnaya culture was succeeded in its western range by the Catacomb culture (2800–2200 BCE); in the east, by the Poltavka culture (2700–2100 BCE) at the middle Volga. These two cultures were followed by the Srubnaya culture (18th–12th century BCE).” ref
“Further efforts to pinpoint the location came from Anthony (2007), who suggested that the Yamnaya culture (3300–2600 BCE) originated in the Don–Volga area at c. 3400 BCE, preceded by the middle Volga-based Khvalynsk culture and the Don-based Repin culture (c. 3950–3300 BCE), arguing that late pottery from these two cultures can barely be distinguished from early Yamnaya pottery. Earlier continuity from eneolithic but largely hunter-gatherer Samara culture and influences from the more agricultural Dnieper–Donets II are apparent.” ref
“He argues that the early Yamnaya horizon spread quickly across the Pontic–Caspian steppes between c. 3400 and 3200 BCE:
The spread of the Yamnaya horizon was the material expression of the spread of late Proto-Indo-European across the Pontic–Caspian steppes.
[…] The Yamnaya horizon is the visible archaeological expression of a social adjustment to high mobility – the invention of the political infrastructure to manage larger herds from mobile homes based in the steppes.” ref
“Alternatively, Parpola (2015) relates both the Corded ware culture and the Yamnaya culture to the late Trypillia (Tripolye) culture. He hypothesizes that “the Tripolye culture was taken over by PIE speakers by c. 4000 BCE,” and that in its final phase the Trypillian culture expanded to the steppes, morphing into various regional cultures which fused with the late Sredny Stog (Serednii Stih) pastoralist cultures, which, he suggests, gave rise to the Yamnaya culture. Dmytro Telegin viewed Sredny Stog and Yamna as one cultural continuum and considered Sredny Stog to be the genetic foundation of the Yamna.” ref
“The Yamnaya culture was nomadic or semi-nomadic, with some agriculture practiced near rivers, and a few fortified sites, the largest of which is Mikhaylivka. Characteristic for the culture are the burials in pit graves under kurgans (tumuli), often accompanied by animal offerings. Some graves contain large anthropomorphic stelae, with carved human heads, arms, hands, belts, and weapons. The dead bodies were placed in a supine position with bent knees and covered in ochre. Some kurgans contained “stratified sequences of graves.” ref
“Kurgan burials may have been rare, and were perhaps reserved for special adults, who were predominantly, but not necessarily, male. Status and gender are marked by grave goods and position, and in some areas, elite individuals are buried with complete wooden wagons. Grave goods are more common in eastern Yamnaya burials, which are also characterized by a higher proportion of male burials and more male-centred rituals than western areas.” ref
“The Yamnaya culture had and used two-wheeled carts and four-wheeled wagons, which are thought to have been oxen-drawn at this time, and there is evidence that they rode horses. For instance, several Yamnaya skeletons exhibit specific characteristics in their bone morphology that may have been caused by long-term horseriding. Metallurgists and other craftsmen are given a special status in Yamnaya society, and metal objects are sometimes found in large quantities in elite graves.” ref
“New metalworking technologies and weapon designs are used. Stable isotope ratios of Yamna individuals from the Dnipro Valley suggest the Yamnaya diet was terrestrial protein based with insignificant contribution from freshwater or aquatic resources. Anthony speculates that the Yamnaya ate meat, milk, yogurt, cheese, and soups made from seeds and wild vegetables, and probably consumed mead.” ref
“Mallory and Adams suggest that Yamnaya society may have had a tripartite structure of three differentiated social classes, although the evidence available does not demonstrate the existence of specific classes such as priests, warriors, and farmers.” ref
“According to Jones et al. (2015) and Haak et al. (2015), autosomal tests indicate that the Yamnaya people were the result of a genetic admixture between two different hunter-gatherer populations: distinctive “Eastern Hunter-Gatherers” (EHG), from Eastern Europe, with high affinity to the Mal’ta–Buret’ culture or other, closely related people from Siberia and a population of “Caucasus hunter-gatherers” (CHG) who probably arrived from the Caucasus or Iran. Each of those two populations contributed about half the Yamnaya DNA. This admixture is referred to in archaeogenetics as Western Steppe Herder (WSH) ancestry.” ref
“Admixture between EHGs and CHGs is believed to have occurred on the eastern Pontic-Caspian steppe starting around 5,000 BCE, while admixture with Early European Farmers (EEF) happened in the southern parts of the Pontic-Caspian steppe sometime later. More recent genetic studies have found that the Yamnaya were a mixture of EHGs, CHGs, and to a lesser degree Anatolian farmers and Levantine farmers, but not EEFs from Europe due to lack of WHG DNA in the Yamnaya. This occurred in two distinct admixture events from West Asia into the Pontic-Caspian steppe.” ref
“Haplogroup R1b, specifically the Z2103 subclade of R1b-L23, is the most common Y-DNA haplogroup found among the Yamnaya specimens. This haplogroup is rare in Western Europe and mainly exists in Southeastern Europe today. Additionally, a minority are found to belong to haplogroup I2. They are found to belong to a wider variety of West Eurasian mtDNA haplogroups, including U, T, and haplogroups associated with Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers and Early European Farmers. A small but significant number of Yamnaya kurgan specimens from Northern Ukraine carried the East Asian mtDNA haplogroup C4.” ref
“In 2014, a study discovered a new mtDNA subclade C1f from the remains of 3 people found in north-western Russia and dated to 7,500 years ago. The subclades C1b, C1c, C1d, and C4c are found in the first people of the Americas. C1a is found only in Asia.” ref
“C4 – Upper Palaeolithic (14050 – 13770 years ago) Ust-Kyakhta (Buryatia), Late Neolithic-Bronze Age Irkutsk Oblast, Late Neolithic-Iron Age Yakutia, Tubalar (Ederbes), Todzhin (Toora-Hem, Iiy, Adir-Kezhig), Yukaghir (Andrushkino), Yukaghir/Chuvan (Markovo), Russian, Myanmar
-
- C4a’b’c – Irkutsk Oblast (6815 years ago), India (Jenu Kuruba)
- C4a – China (Guangdong, Han from Beijing)
- C4a1 – Mongol from Chifeng and Hulunbuir, Tashkurgan (Kyrgyz, Sarikoli, Wakhi), Czech Republic, Denmark
- C4a1a – Korea, China, Uyghur, Buryat (South Siberia), Denmark, Sweden, France, Scotland, Canada
- C4a1a1
- C-T195C! – Ireland, Scotland, England, USA, Hungary (Szeged region), Poland, Belarus, Russia (Russian, Buryat), Turkey, Pakistan (Hazara), India (Jammu and Kashmir), China (Bargut and Mongol in Inner Mongolia, etc.), Korea
- C4a1a2 – China
- C4a1a2a – China (Han from Ili, Han from Henan, etc.)
- C4a1a2b
- C4a1a2b1 – China
- C4a1a2b2 – Uyghur
- C4a1a3 – Bronze Age Irkutsk Oblast (Ust’-Belaya, Khaptsagai, Silinskij, Chastaja Padi), Russian (Kemerovo Oblast), Koryak, Yukaghir, Yakut, Evenk (Nyukzha, Chumikan, Nelkan/Dzhigda), Even (Sakkyryyr, Sebjan, Tompo, Markovo, Kamchatka), Udinsk Buryat (Kushun), Todzhin (Toora-Hem, Adir-Kezhig), Altai Kizhi, Iran (Qashqai), Sweden
- C4a1a3a – Yakut, Buryat (Buryat Republic, Irkutsk Oblast), Bargut, Nentsi
- C4a1a3a1 – Yakut, Nganasan (Vadei of Taimyr Peninsula)
- C4a1a3a1a – Evenk (Taimyr, Stony Tunguska)
- C4a1a3a1b – Tofalar
- C4a1a3a1 – Yakut, Nganasan (Vadei of Taimyr Peninsula)
- C4a1a3b – Bargut, Uyghur
- C4a1a3b1 – Chelkan, Tubalar
- C4a1a3c – Evenk (Taimyr Peninsula, Stony Tunguska)
- C4a1a3d – Yakut
- C4a1a3a – Yakut, Buryat (Buryat Republic, Irkutsk Oblast), Bargut, Nentsi
- C4a1a4 – Buryat, Kazakhstan
- C4a1a4a – Evenk (Okhotsk region), Shor
- C4a1a2 – China
- C4a1a5 – Teleut, Ladakh
- C4a1a6
- C4a1a6a – Russia (Bashkortostan, Khamnigan), Kyrgyzstan (Kyrgyz), Inner Mongolia (Bargut, Buryat)
- C4a1a6b – Buryat (South Siberia, Inner Mongolia), Uyghur
- C4a1a7 – Denmark
- C4a1b – China, Thailand (Palaung)
- C4a1c – Russia (Bashkortostan, Adygei), Iran (Azerbaijanian), China (Xibo, Mongol from Tianjin)
- C4a1a – Korea, China, Uyghur, Buryat (South Siberia), Denmark, Sweden, France, Scotland, Canada
- C4a2
- C4a2a – Yakut, Evenk (Chumikan)
- C4a2a1 – Bronze Age (2275 – 2040 cal BCE or around 4,275 to 4,040 years ago) Irkutsk Oblast (specimen irk076 from burial 3 at the Shamanka 2 site, South Baikal), Shor, Chelkan, Teleut, Altai Kizhi, Yakut, Kazakh, Ket, Evenk (Stony Tunguska, Taimyr), Buryat (Irkutsk Oblast, Inner Mongolia), China, Korea
- C4a2a1a – Yukaghir, Yakut, Evenk (Nyukzha, Iyengra, Nelkan/Dzhigda), Even (Tompo)
- C4a2a1b – Evenk (Nyukzha), Yakut
- C4a2a1b1 – Evenk (Nyukzha)
- C4a2a1c – China (Zhejiang, Uyghurs), Buryat, Todzhin (Iiy), Karanogay (Dagestan)
- C4a2a1c1 – Tofalar (Alygdzher, Nerkha, V. Gutara), Khamnigan
- C4a2a1c2 – Uyghurs
- C4a2a1d – Uyghurs
- C4a2a1d1 – Udinsk Buryat (Kushun), Tofalar (V. Gutara), Evenk (Central Siberia)
- C4a2a1d2 – Evenk (Nelkan/Dzhigda), Evenk/Nivkh (Val)
- C4a2a1e – Bargut (Inner Mongolia), Buryat (Irkutsk Oblast)
- C4a2a1f – Buryat (South Siberia, Irkutsk Oblast)
- C4a2a1g – Ket
- C4a2a1 – Bronze Age (2275 – 2040 cal BCE or around 4,275 to 4,040 years ago) Irkutsk Oblast (specimen irk076 from burial 3 at the Shamanka 2 site, South Baikal), Shor, Chelkan, Teleut, Altai Kizhi, Yakut, Kazakh, Ket, Evenk (Stony Tunguska, Taimyr), Buryat (Irkutsk Oblast, Inner Mongolia), China, Korea
- C4a2b – Tibet, Korea
- C4a2b1 – Wancho
- C4a2b2 – China (Han from Beijing)
- C4a2b2a – Tibet (Sherpa)
- C4a2c – Bargut (Inner Mongolia)
- C4a2c1 – India (Jenu Kuruba)
- C4a2c2 – Lepcha
- C4a2c2a – Ladakh
- C4a2a – Yakut, Evenk (Chumikan)
- C4a1 – Mongol from Chifeng and Hulunbuir, Tashkurgan (Kyrgyz, Sarikoli, Wakhi), Czech Republic, Denmark
- C4b – Mongol from Jilin and Hulunbuir, Yukaghir, Altai Kizhi, Ukraine, Slovakia
- C4c – Ijka
- C4c1 – Sioux (Carson County of South Dakota), Shuswap, Canada, USA, France, Spain
- C4c1a – Cherokee (Flint District of Oklahoma)
- C4c1b – Chippewa (Trempealeau in Wisconsin), Ottawa or Chippewa (Sault Saint Marie, Chippewa County, Michigan), Canada
- C4c2 – Métis (Red River, Manitoba), USA
- C4c1 – Sioux (Carson County of South Dakota), Shuswap, Canada, USA, France, Spain
- C4a – China (Guangdong, Han from Beijing)
- C4-T152C! – Russia (Bashkortostan), England
- C4-T152C!-A12780G – Uyghur
- C4d – Turkey, Tibet (Chamdo, Nyingchi, Shannan, Lhoba), Thailand (Khon Mueang from Chiang Mai Province), Han from Beijing, Mongol from Tongliao
- C4-T152C!-T4742C – Altai Republic (ancient DNA), Uyghur
- C4-T152C!-T4742C-T16093C – Kyrgyz (Kyrgyzstan), Tibet (Nyingchi)
- C4-T152C!-T4742C-T8602C – Sarikoli (Tashkurgan), Burusho (Pakistan)
- C4-T152C!-T4742C-T8602C-G11176A – Pamiri (Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan)
- C4e – Teleut, Shor” ref
- C4-T152C!-A12780G – Uyghur
- C4a’b’c – Irkutsk Oblast (6815 years ago), India (Jenu Kuruba)
“People of the Yamnaya culture are believed to have had mostly brown eye colour, light to intermediate skin, and brown hair colour, with some variation.” ref
“Some Yamnaya individuals are believed to have carried a mutation to the KITLG gene associated with blond hair, as several individuals with Steppe ancestry are later found to carry this mutation. The Ancient North Eurasian Afontova Gora group, who contributed significant ancestry to Western Steppe Herders, are believed to be the source of this mutation. A study in 2015 found that Yamnaya had the highest ever calculated genetic selection for height of any of the ancient populations tested. It has been hypothesized that an allele associated with lactase persistence (conferring lactose tolerance into adulthood) was brought to Europe from the steppe by Yamnaya-related migrations.” ref
“A 2022 study by Lazaridis et al. found that the typical phenotype among the Yamnaya population was brown eyes, brown hair, and intermediate skin colour. None of their Yamnaya samples were predicted to have either blue eyes or blond hair, in contrast with later Steppe groups in Russia and Central Asia, as well as the Bell Beaker culture in Europe, who did carry these phenotypes in high proportions.” ref
“The geneticist David Reich has argued that the genetic data supports the likelihood that the people of the Yamnaya culture were a “single, genetically coherent group” who were responsible for spreading many Indo-European languages. Reich’s group recently suggested that the source of Anatolian and Indo-European subfamilies of the Proto-Indo-European (PIE) language may have been in west Asia and the Yamna were responsible for the dissemination of the latter. Reich also argues that the genetic evidence shows that Yamnaya society was an oligarchy dominated by a small number of elite males.” ref
“The genetic evidence for the extent of the role of the Yamnaya culture in the spread of Indo-European languages has been questioned by Russian archaeologist Leo Klejn and Balanovsky et al., who note a lack of male haplogroup continuity between the people of the Yamnaya culture and the contemporary populations of Europe. Klejn has also suggested that the autosomal evidence does not support a Yamnaya migration, arguing that Western Steppe Herder ancestry in both contemporary and Bronze Age samples is lowest around the Danube in Hungary, near the western limits of the Yamnaya culture, and highest in Northern Europe, which Klejn argues is the opposite of what would be expected if the geneticists’ hypothesis is correct.” ref
Yamnaya culture and the Proto-Indo-Europeans (PIE) Language
“Marija Gimbutas identified the Yamnaya culture with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans (PIE) in her Kurgan hypothesis. In the view of David Anthony, the Pontic-Caspian steppe is the strongest candidate for the Urheimat (original homeland) of the Proto-Indo-European language, citing evidence from linguistics and genetics which suggests that the Yamnaya culture may be the homeland of the Indo-European languages, with the possible exception of the Anatolian languages. On the other hand, Colin Renfrew has argued for a Near Eastern origin of the earliest Indo-European speakers.” ref
“According to David W. Anthony, the genetic evidence suggests that the leading clans of the Yamnaya were of EHG (Eastern European hunter-gatherer) and WHG (Western European hunter-gatherer) paternal origin and implies that the Indo-European languages were the result of “a dominant language spoken by EHGs that absorbed Caucasus-like elements in phonology, morphology, and lexicon.” It has also been suggested that the PIE language evolved through trade interactions in the circum-Pontic area in the 4th millennium BCE, mediated by the Yamna predecessors in the North Pontic steppe.” ref
“Guus Kroonen et al. 2022 found that the “basal Indo-European stage”, also known as Indo-Anatolian or Pre-Proto-Indo-European language, largely but not totally, lacked agricultural-related vocabulary, and only the later “core Indo-European languages” saw an increase in agriculture-associated words. According to them, this fits a homeland of early core Indo-European within the westernmost Yamnaya horizon, around and west of the Dnieper, while its basal stage, Indo-Anatolian, may have originated in the Sredny Stog culture, as opposed to the eastern Yamnaya horizon.” ref
“The Corded Ware culture may have acted as major source for the spread of later Indo-European languages, including Indo-Iranian, while Tocharian languages may have been mediated via the Catacomb culture. They also argue that this new data contradicts a possible earlier origin of Pre-Proto-Indo-European among agricultural societies South of the Caucasus, rather “this may support a scenario of linguistic continuity of local non-mobile herders in the Lower Dnieper region and their genetic persistence after their integration into the successive and expansive Yamnaya horizon”. Furthermore the authors mention that this scenario can explain the difference in paternal haplogroup frequency between the Yamnaya and Corded Ware cultures, while both sharing similar autosomal DNA ancestry.” ref
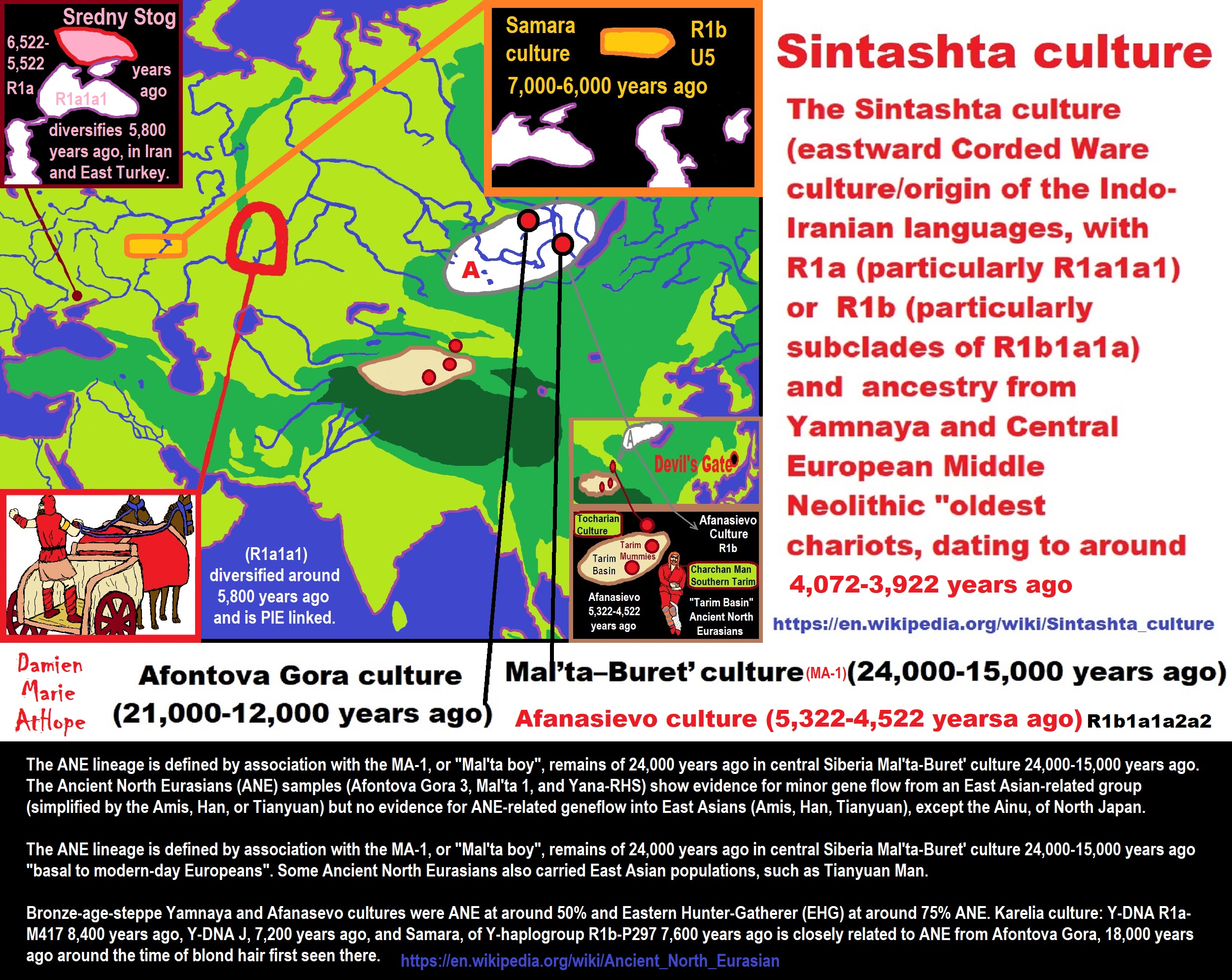
Sintashta culture
“The Sintashta culture is a Middle Bronze Age archaeological culture of the Southern Urals, dated to the period c. 2200–1900 BCE. It is the first phase of the Sintashta–Petrovka complex, c. 2200–1750 BCE or around 4,200 to 3,750 years ago. The culture is named after the Sintashta archaeological site, in Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia, and spreads through Orenburg Oblast, Bashkortostan, and Northern Kazakhstan. The Sintashta culture is thought to represent an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture.” ref
“Sintashta settlements are estimated to have a population of between 200 and 700 individuals with economies that “heavily exploited domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats alongside horses with occasional hunting of wild fauna”. Anthony (2007) assumes that probably the people of the Sintashta culture spoke “Common-Indo-Iranian”. This identification is based primarily on similarities between sections of the Rig Veda, a religious text which includes ancient Indo-Iranian hymns recorded in Vedic Sanskrit, and the funerary rituals of the Sintashta culture as revealed by archaeology.” ref
“Some cultural similarities with Sintashta have also been found to be common with the Nordic Bronze Age of Scandinavia. There is linguistic evidence of interaction between Finno-Ugric and Indo-Iranian languages, showing influences from the Indo-Iranians into the Finno-Ugric culture. From the Sintashta culture the Indo-Iranian followed the migrations of the Indo-Iranians to Anatolia, the Iranian plateau and the Indian subcontintinent. From the 9th century BCE onward, Iranian languages also migrated westward with the Scythians back to the Pontic steppe where the proto-Indo-Europeans came from.” ref
“It is widely regarded as the origin of the Indo-Iranian languages (Indo-Iranic languages), whose speakers originally referred to themselves as the Arya. The earliest known chariots have been found in Sintashta burials, and the culture is considered a strong candidate for the origin of the technology, which spread throughout the Old World and played an important role in ancient warfare. Sintashta settlements are also remarkable for the intensity of copper mining and bronze metallurgy carried out there, which is unusual for a steppe culture. Among the main features of the Sintashta culture are high levels of militarism and extensive fortified settlements, of which 23 are known.” ref
“Because of the difficulty of identifying the remains of Sintashta sites beneath those of later settlements, the culture was only distinguished in the 1990s from the Andronovo culture. It was then recognised as a distinct entity, forming part of the “Andronovo horizon”. Koryakova (1998) concluded from their archaeological findings that the Sintashta culture originated from the interaction of the two precursors Poltavka culture and Abashevo culture. Allentoft et al. (2015) concluded from their genetic results that the Sintashta culture should have emerged from an eastward migration of peoples from the Corded Ware culture. In addition, Narasimshan et al. (2019) cautiously cite that “morphological data has been interpreted as suggesting that both Fedorovka and Alakul’ skeletons are similar to Sintashta groups, which in turn may reflect admixture of Neolithic forest HGs and steppe pastoralists, descendants of the Catacomb and Poltavka cultures.” ref
“Sintashta emerged during a period of climatic change that saw the already arid Kazakh steppe region become even colder and drier. The marshy lowlands around the Ural and upper Tobol rivers, previously favored as winter refuges, became increasingly important for survival. Under these pressures both Poltavka and Abashevo herders settled permanently in river valley strongholds, eschewing more defensible hill-top locations. Its immediate predecessor in the Ural-Tobol steppe was the Poltavka culture, an offshoot of the cattle-herding Yamnaya horizon that moved east into the region between 2800 and 2600 BCE. Several Sintashta towns were built over older Poltavka settlements or close to Poltavka cemeteries, and Poltavka motifs are common on Sintashta pottery.” ref
“Sintashta material culture also shows the influence of the late Abashevo culture, derived from the Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture, a collection of Corded Ware settlements in the forest steppe zone north of the Sintashta region that were also predominantly pastoralist. Radiocarbon dating indicates that the Sintashta culture dates to between c. 2200 and 1750 BCE, roughly contemporary with the associated Abashevo and Petrovka cultures. Some authors date the Petrovka culture slightly later, from c. 1900 BCE.” ref
“In Cis-Urals, burial sites Berezovaya and Tanabergen II showed Sintashta culture established there c. 2290–1750 BCE (68.2% probability), and the earliest values of this culture, in Trans-Urals, at the burial sites Sintashta II and Kamenny Ambar-5 (Kurgan 2) are c. 2200–2000 BCE. Chariots appear in southern Trans-Urals region in middle and late phases of the culture, c. 2050-1750 BC. Blöcher et al. (2023) consider Sintashta-Petrovka period came to an end in Trans-Urals c. 1900–1800 BCE.” ref
Genetics
“Allentoft et al. 2015 analyzed the remains of four individuals ascribed to the Sintastha culture. One male carried Y-haplogroup R1a and mt-J1c1b1a, while the other carried Y-R1a1a1b and mt-J2b1a2a. The two females carried U2e1e and U2e1h respectively. The study found a close autosomal genetic relationship between peoples of Corded Ware culture and Sintashta culture, which “suggests similar genetic sources of the two,” and may imply that “the Sintashta derives directly from an eastward migration of Corded Ware peoples.” ref
“Sintashta individuals and Corded Ware individuals both had a relatively higher ancestry proportion derived from the Central Europe, and both differed markedly in such ancestry from the population of the Yamnaya Culture and most individuals of the Poltavka Culture that preceded Sintashta in the same geographic region. Individuals from the Bell Beaker culture, the Unetice culture, and contemporary Scandinavian cultures were also found to be closely genetically related to Corded Ware. A particularly high lactose tolerance was found among Corded Ware and the closely related Nordic Bronze Age. In addition, the study found samples from the Sintashta culture to be closely genetically related to the succeeding Andronovo culture.” ref
“Narasimhan et al. 2019 analyzed the remains of several individuals associated with the Sintashta culture. mtDNA was extracted from two females buried at the Petrovka settlement. They were found to be carrying subclades of U2 and U5. The remains of fifty individuals from the fortified Sintastha settlement of Kamennyi Ambar was analyzed. This was the largest sample of ancient DNA ever sampled from a single site. The Y-DNA from thirty males was extracted. Eighteen carried R1a and various subclades of it (particularly subclades of R1a1a1), five carried subclades of R1b (particularly subclades of R1b1a1a), two carried Q1a and a subclade of it, one carried I2a1a1a, and four carried unspecified R1 clades. The majority of mtDNA samples belonged to various subclades of U, while W, J, T, H and K also occurred. A Sintashta male buried at Samara was found to be carrying R1b1a1a2 and J1c1b1a.” ref
“The authors of the study found the majority of Sintashta people (ca. 80%) to be closely genetically related to the people of the Corded Ware culture, the Srubnaya culture, the Potapovka culture, and the Andronovo culture. These were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the Yamnaya culture and peoples of the Central European Middle Neolithic, like the Globular Amphora culture. The remaining sampled Sintashta individuals belonged to various ancestral types different from the majority population, with affinities to earlier populations such as Eneolithic samples collected at Khvalynsk and hunter-gatherers from Tyumen Oblast in western Siberia. This indicates that the Sintashta settlement of Kamennyi Ambar was a cosmopolitan site that united a genetically heterogenous population in a single social group. Estimates based on DATES (Distribution of Ancestry Tracts of Evolutionary Signals) suggest that genetic characteristics typical of the Sintashta culture formed by c. 3200 BCE.” ref
Warfare
“The preceding Abashevo culture was already marked by endemic intertribal warfare; intensified by ecological stress and competition for resources in the Sintashta period. This drove the construction of fortifications on an unprecedented scale and innovations in military technique such as the invention of the war chariot. Increased competition between tribal groups may also explain the extravagant sacrifices seen in Sintashta burials, as rivals sought to outdo one another in acts of conspicuous consumption analogous to the North American potlatch tradition.” ref
“Sintashta artefact types such as spearheads, trilobed arrowheads, chisels, and large shaft-hole axes were taken east. Many Sintashta graves are furnished with weapons, although the composite bow associated later with chariotry does not appear. Higher-status grave goods include chariots, as well as axes, mace-heads, spearheads, and cheek-pieces. Sintashta sites have produced finds of horn and bone, interpreted as furniture (grips, arrow rests, bow ends, string loops) of bows; there is no indication that the bending parts of these bows included anything other than wood. Arrowheads are also found, made of stone or bone rather than metal. These arrows are short, 50–70 cm long, and the bows themselves may have been correspondingly short.” ref
“Sintashta culture, and the chariot, are also strongly associated with the ancestors of modern domestic horses, the DOM2 population. DOM2 horses originated from the Western Eurasia steppes, especially the lower Volga-Don, but not in Anatolia, during the late fourth and early third millennia BCE. Their genes may show selection for easier domestication and stronger backs.” ref
“The Sintashta economy came to revolve around copper metallurgy. Copper ores from nearby mines (such as Vorovskaya Yama) were taken to Sintashta settlements to be processed into copper and arsenical bronze. This occurred on an industrial scale: all the excavated buildings at the Sintashta sites of Sintashta, Arkaim and Ust’e contained the remains of smelting ovens and slag. Around 10% of graves, mostly adult male, contained artifacts related to bronze metallurgy (molds, ceramic nozzles, ore and slag remains, metal bars and drops). However, these metal-production related grave goods rarely co-occur with higher-status grave goods. This likely means that those who engaged in metal production were not at the top of the social-hierarchy, even though being buried at a cemetery evidences some sort of higher status.” ref
“Much of Sintashta metal was destined for export to the cities of the Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) in Central Asia. The metal trade between Sintashta and the BMAC for the first time connected the steppe region to the ancient urban civilisations of the Near East: the empires and city-states of modern Iran and Mesopotamia provided a large market for metals. These trade routes later became the vehicle through which horses, chariots and ultimately Indo-Iranian-speaking people entered the Near East from the steppe.” ref

Genetic history of Europe, Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia, and Genetic history of the Middle East
PIE Speakers and Haplogroups R1b as well as R1a
“According to three autosomal DNA studies, haplogroups R1b and R1a, now the most common in Europe (R1a is also very common in South Asia) would have expanded from the Pontic steppes, along with the Indo-European languages; they also detected an autosomal component present in modern Europeans which was not present in Neolithic Europeans, which would have been introduced with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as Indo-European languages. Studies that analyzed ancient human remains in Ireland and Portugal suggest that R1b was introduced in these places along with autosomal DNA from the Pontic steppes.” ref
“The subclade R1a1a (R-M17 or R-M198) is most commonly associated with Indo-European speakers. Data so far collected indicate that there are two widely separated areas of high frequency, one in Eastern Europe, around Poland and the Russian core, and the other in South Asia, around Indo-Gangetic Plain. The historical and prehistoric possible reasons for this are the subject of on-going discussion and attention amongst population geneticists and genetic genealogists, and are considered to be of potential interest to linguists and archaeologists also. Ornella Semino et al. propose a postglacial (Holocene) spread of the R1a1 haplogroup from north of the Black Sea during the time of the Late Glacial Maximum, which was subsequently magnified by the expansion of the Kurgan culture into Europe and eastward.” ref
“A large, 2014 study by Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eurasia, concluded there was compelling evidence, that R1a-M420 originated in the vicinity of Iran. The mutations that characterize haplogroup R1a occurred ~10,000 years ago. Its defining mutation (M17) occurred about 10,000 to 14,000 years ago. Pamjav et al. (2012) believe that R1a originated and initially diversified either within the Eurasian Steppes or the Middle East and Caucasus region.” ref
Yamnaya culture
“All Yamnaya individuals sampled by Haak et al. (2015) belonged to the Y-haplogroup R1b. According to Jones et al. (2015) and Haak et al. (2015), autosomal tests indicate that the Yamnaya-people were the result of admixture between “Eastern Hunter-Gatherers” from eastern Europe (EHG) and “Caucasus hunter-gatherers” (CHG). Each of those two populations contributed about half the Yamnaya DNA. According to co-author Dr. Andrea Manica of the University of Cambridge:
The question of where the Yamnaya come from has been something of a mystery up to now […] we can now answer that, as we’ve found that their genetic make-up is a mix of Eastern European hunter-gatherers and a population from this pocket of Caucasus hunter-gatherers who weathered much of the last Ice Age in apparent isolation.” ref
“Based on these findings and by equating the people of the Yamnaya culture with the Proto-Indo-Europeans, David W. Anthony (2019) suggests that the Proto-Indo-European language formed mainly from a base of languages spoken by Eastern European hunter-gathers with influences from languages of northern Caucasus hunter-gatherers, in addition to a possible later influence from the language of the Maikop culture to the south (which is hypothesized to have belonged to the North Caucasian family) in the later neolithic or Bronze Age involving little genetic impact.” ref
Eastern European hunter-gatherers
“According to Haak et al. (2015), “Eastern European hunter-gatherers” who inhabited Russia were a distinctive population of hunter-gatherers with high affinity to a ~24,000-year-old Siberian from the Mal’ta-Buret’ culture, or other, closely related Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) people from Siberia and to the Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG). Remains of the “Eastern European hunter-gatherers” have been found in Mesolithic or early Neolithic sites in Karelia and Samara Oblast, Russia, and put under analysis. Three such hunter-gathering individuals of the male sex have had their DNA results published. Each was found to belong to a different Y-DNA haplogroup: R1a, R1b, and J. R1b is also the most common Y-DNA haplogroup found among both the Yamnaya and modern-day Western Europeans. R1a is more common in Eastern Europeans and in the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent.” ref
Near East population
“The Near East population were most likely hunter-gatherers from the Caucasus (CHG) c.q. Iran Chalcolithic related people with a major CHG-component. Jones et al. (2015) analyzed genomes from males from western Georgia, in the Caucasus, from the Late Upper Palaeolithic (13,300 years old) and the Mesolithic (9,700 years old). These two males carried Y-DNA haplogroup: J* and J2a. The researchers found that these Caucasus hunters were probably the source of the farmer-like DNA in the Yamnaya, as the Caucasians were distantly related to the Middle Eastern people who introduced farming in Europe.” ref
“Their genomes showed that a continued mixture of the Caucasians with Middle Eastern took place up to 25,000 years ago, when the coldest period in the last Ice Age started. According to Lazaridis et al. (2016), “a population related to the people of the Iran Chalcolithic contributed ~43% of the ancestry of early Bronze Age populations of the steppe.” According to Lazaridis et al. (2016), these Iranian Chalcolithic people were a mixture of “the Neolithic people of western Iran, the Levant, and Caucasus Hunter-Gatherers.” Lazaridis et al. (2016) also note that farming spread at two places in the Near East, namely the Levant and Iran, from where it spread, Iranian people spreading to the steppe and south Asia.” ref
Northern and Central Europe
“Haak et al. (2015) studied DNA from 94 skeletons from Europe and Russia aged between 3,000 and 8,000 years old. They concluded that about 4,500 years ago there was a major influx into Europe of Yamnaya culture people originating from the Pontic–Caspian steppe north of the Black Sea and that the DNA of copper-age Europeans matched that of the Yamnaya. The four Corded Ware people could trace an astonishing three-quarters of their ancestry to the Yamnaya, according to the paper. That suggests a massive migration of Yamnaya people from their steppe homeland into Eastern Europe about 4500 years ago when the Corded Ware culture began, perhaps carrying an early form of Indo-European language.” ref
Bronze age Greece
“A 2017 archaeogenetics study of Mycenaean and Minoan remains published in the journal Nature concluded that the Mycenaean Greeks were genetically closely related with the Minoans but unlike the Minoans also had a 13-18% genetic contribution from Bronze Age steppe populations.” ref
Haplogroup R1a
“Haplogroup R1a, or haplogroup R-M420, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup that is distributed in a large region in Eurasia, extending from Scandinavia and Central Europe to southern Siberia and South Asia. While R1a originated ca. 22,000 to 25,000 years ago, its subclade M417 (R1a1a1) diversified ca. 5,800 years ago. The place of origin of the subclade plays a role in the debate about the origins of Proto-Indo-Europeans.” ref
“The split of R1a (M420) is computed to ca. 22,000 or 25,000 years ago, which is the time of the last glacial maximum. A 2014 study by Peter A. Underhill et al., using 16,244 individuals from over 126 populations from across Eurasia, concluded that there was “a compelling case for the Middle East, possibly near present-day Iran, as the geographic origin of hg R1a.” The ancient DNA record has shown the first R1a during the Mesolithic in Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (from Eastern Europe), and the earliest case of R* among Upper Paleolithic Ancient North Eurasians, from which the Eastern Hunter-Gatherers predominantly derive their ancestry. No early samples of R1a have so far been found in Iran.” ref
“According to Underhill et al. (2014), the downstream R1a-M417 subclade diversified into Z282 and Z93 circa 5,800 years ago “in the vicinity of Iran and Eastern Turkey.” Even though R1a occurs as a Y-chromosome haplogroup among various languages such as Slavic and Indo-Iranian, the question of the origins of R1a1a is relevant to the ongoing debate concerning the urheimat of the Proto-Indo-European people, and may also be relevant to the origins of the Indus Valley Civilization. R1a shows a strong correlation with Indo-European languages of Southern and Western Asia, Central and Eastern Europe and to some extent Scandinavia being most prevalent in Eastern Europe, West Asia, and South Asia. In Europe, Z282 is prevalent, particularly while in Asia Z93 dominates. The connection between Y-DNA R-M17 and the spread of Indo-European languages was first noted by T. Zerjal and colleagues in 1999.” ref
Proposed steppe dispersal of R1a1a: Indo-European migrations and Indo-Aryan migrations and R1a
“Semino et al. (2000) proposed Ukrainian origins, and a postglacial spread of the R1a1 gene during the Late Glacial Maximum, subsequently magnified by the expansion of the Kurgan culture into Europe and eastward. Spencer Wells proposes Central Asian origins, suggesting that the distribution and age of R1a1 points to an ancient migration corresponding to the spread by the Kurgan people in their expansion from the Eurasian steppe. According to Pamjav et al. (2012), R1a1a diversified in the Eurasian Steppes or the Middle East and Caucasus region:
Inner and Central Asia is an overlap zone for the R1a1-Z280 and R1a1-Z93 lineages [which] implies that an early differentiation zone of R1a1-M198 conceivably occurred somewhere within the Eurasian Steppes or the Middle East and Caucasus region as they lie between South Asia and Central- and Eastern Europe.” ref
“Three genetic studies in 2015 gave support to the Kurgan theory of Gimbutas regarding the Indo-European Urheimat. According to those studies, haplogroups R1b and R1a, now the most common in Europe (R1a is also common in South Asia) would have expanded from the Pontic–Caspian steppes, along with the Indo-European languages; they also detected an autosomal component present in modern Europeans which was not present in Neolithic Europeans, which would have been introduced with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as Indo-European languages.” ref
Source of R1a1a1 in Corded Ware culture
“David Anthony considers the Yamnaya culture to be the Indo-European Urheimat. According to Haak et al. (2015), a massive migration from the Yamnaya culture northwards took place ca. 2,500 BCE or 4,622 years ago, accounting for 75% of the genetic ancestry of the Corded Ware culture, noting that R1a and R1b may have “spread into Europe from the East after 3,000 BCE” or 5,022 years ago. Yet, all their seven Yamnaya samples belonged to the R1b-M269 subclade, but no R1a1a has been found in their Yamnaya samples. This raises the question of where the R1a1a in the Corded Ware culture came from, if it was not from the Yamnaya culture.” ref
“Semenov & Bulat (2016) do argue for such an origin of R1a1a in the Corded Ware culture, noting that several publications point to the presence of R1a1 in the Comb Ware culture. Haak et al. (2015) found that part of the Yamnaya ancestry derived from the Middle East and that neolithic techniques probably arrived at the Yamnaya culture from the Balkans. The Rössen culture (4,600–4,300 BCE or 6,622-6,322 years ago), which was situated on Germany and predates the Corded Ware culture, an old subclade of R1a, namely L664, can still be found.” ref
Transcaucasia & West Asian origins and possible influence on Indus Valley Civilization
Kura–Araxes culture, Uruk period, and Origins of the Indus Valley Civilisation
“Part of the South Asian genetic ancestry derives from west Eurasian populations, and some researchers have implied that Z93 may have come to India via Iran and expanded there during the Indus Valley Civilization. However, according to Narasimhan et al. (2018), steppe pastoralists are a likely source for R1a in India.” ref
“Mascarenhas et al. (2015) proposed that the roots of Z93 lie in West Asia, and proposed that “Z93 and L342.2 expanded in a southeasterly direction from Transcaucasia into South Asia,” noting that such an expansion is compatible with “the archeological records of eastward expansion of West Asian populations in the 4th millennium BCE culminating in the so-called Kura-Araxes migrations in the post-Uruk IV period.” Yet, Lazaridis noted that sample I1635 of Lazaridis et al. (2016), their Armenian Kura-Araxes sample, carried Y-haplogroup R1b1-M415(xM269) (also called R1b1a1b-CTS3187).” ref
“According to Underhill et al. (2014) the diversification of Z93 and the “early urbanization within the Indus Valley […] occurred at [5,600 years ago] and the geographic distribution of R1a-M780 may reflect this.” Poznik et al. (2016) note that ‘striking expansions’ occurred within R1a-Z93 at ~4,500–4,000 years ago, which “predates by a few centuries the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilisation.” ref
Proposed South Asian origins
“Kivisild et al. (2003) have proposed either South or West Asia, while Mirabal et al. (2009) see support for both South and Central Asia. Sharma et al.(2009) showcased the existence of R1a in India beyond 18,000 years to possibly 44,000 years in origin. South Asian populations have the highest STR diversity within R1a1a, and subsequent older TMRCA datings, and R1a1a is present among both higher (Brahmin) castes and lower castes, although the frequency is higher among Brahmin castes. From these findings some researchers have concluded that R1a1a originated in South Asia, excluding a substantial genetic influx from Indo-European migrants.” ref
“However, this diversity, and the subsequent older TMRCA-datings, can also be explained by the historically high population numbers, which increases the likelihood of diversification and microsatellite variation. According to Sengupta et al. (2006), “[R1a1 and R2] could have actually arrived in southern India from a southwestern Asian source region multiple times.” Silva et al. (2017) noted that R1a in South Asia most “likely spread from a single Central Asian source pool, there do seem to be at least three and probably more R1a founder clades within the Subcontinent, consistent with multiple waves of arrival.” According to Martin P. Richards, co-author of Silva et al. (2017), “[the prevalence of R1a in India was] very powerful evidence for a substantial Bronze Age migration from central Asia that most likely brought Indo-European speakers to India.” ref
R-M458 (R1a1a1b1a1) 7,900 years old?
“R-M458 is a mainly Slavic SNP, characterized by its own mutation, and was first called cluster N. Underhill et al. (2009) found it to be present in modern European populations roughly between the Rhine catchment and the Ural Mountains and traced it to “a founder effect that […] falls into the early Holocene period, 7,900±2.6 KYA.” M458 was found in one skeleton from a 14th-century grave field in Usedom, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. The paper by Underhill et al. (2009) also reports a surprisingly high frequency of M458 in some Northern Caucasian populations (for example 27.5% among Karachays and 23.5% among Balkars, 7.8% among Karanogays and 3.4% among Abazas).” ref
R-L260 (R1a1a1b1a1a)
“R1a1a1b1a1a (R-L260), commonly referred to as West Slavic or Polish, is a subclade of the larger parent group R-M458, and was first identified as an STR cluster by Pawlowski et al. 2002. In 2010 it was verified to be a haplogroup identified by its own mutation (SNP). It apparently accounts for about 8% of Polish men, making it the most common subclade in Poland. Outside of Poland it is less common. In addition to Poland, it is mainly found in the Czech Republic and Slovakia, and is considered “clearly West Slavic.” The founding ancestor of R-L260 is estimated to have lived between 2000 and 3000 years ago, i.e. during the Iron Age, with significant population expansion less than 1,500 years ago.” ref
“In Mesolithic Europe, R1a is characteristic of Eastern Hunter-Gatherers (EHGs). A male EHG of the Veretye culture buried at Peschanitsa near Lake Lacha in Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia ca. 10,700 BCE or 12,722 years ago was found to be a carrier of the paternal haplogroup R1a5-YP1301 and the maternal haplogroup U4a. A Mesolithic male from Karelia ca. 8,800 to 7950 BCE or 10,822-9,972 years ago has been found to be carrying haplogroup R1a. A Mesolithic male buried at Deriivka ca. 7000 to 6700 BCE or 9,022-8,722 years ago carried the paternal haplogroup R1a and the maternal U5a2a. Another male from Karelia from ca. 5,500 to 5,000 BCE or 7,522-7,022 years ago, who was considered an EHG, carried haplogroup R1a. A male from the Comb Ceramic culture in Kudruküla ca. 5,900 to 3,800 BCE 7,922-5,822 years ago has been determined to be a carrier of R1a and the maternal U2e1.” ref
“According to archaeologist David Anthony, the paternal R1a-Z93 was found at Alexandria, Ukraine ca. 4000 BCE or 6,022 years ago, Sredny Stog culture, “the earliest known sample to show the genetic adaptation to lactase persistence (I3910-T).” R1a has been found in the Corded Ware culture, in which it is predominant. Examined males of the Bronze Age Fatyanovo culture belong entirely to R1a, specifically subclade R1a-Z93. Haplogroup R1a has later been found in ancient fossils associated with the Urnfield culture; as well as the burial of the remains of the Sintashta, Andronovo, the Pazyryk, Tagar, Tashtyk, and Srubnaya cultures, the inhabitants of ancient Tanais, in the Tarim mummies, and the aristocracy Xiongnu. The skeletal remains of a father and his two sons, from an archaeological site discovered in 2005 near Eulau (in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany) and dated to about 2600 BCE or 4,622 years ago, tested positive for the Y-SNP marker SRY10831.2. The Ysearch number for the Eulau remains is 2C46S. The ancestral clade was thus present in Europe at least 4600 years ago, in association with one site of the widespread Corded Ware culture.” ref
R1a and Europe
“In Europe, the R1a1 sub-clade is found at highest levels among peoples of Central and Eastern European descent, with results ranging from 35-65% among Czechs, Hungarians, Poles, Slovaks, western Ukrainians (particularly Rusyns), Belarusians, Moldovans, and Russians. In the Baltics, R1a1a frequencies decrease from Lithuania (45%) to Estonia (around 30%). There is a significant presence in peoples of Scandinavian descent, with the highest levels in Norway and Iceland, where between 20 and 30% of men are in R1a1a. Vikings and Normans may have also carried the R1a1a lineage further out; accounting for at least part of the small presence in the British Isles, the Canary Islands, and Sicily. In East Germany, where Haplogroup R1a1a reaches a peak frequency in Rostock at a percentage of 31.3%, it averages between 20 and 30%.” ref
“In Southern Europe, R1a1a is not common, but significant levels have been found in pockets, such as in the Pas Valley in Northern Spain, areas of Venice, and Calabria in Italy. The Balkans shows wide variation between areas with significant levels of R1a1a, for example, 36–39% in Slovenia, 27%-34% in Croatia, and over 30% in Greek Macedonia, but less than 10% in Albania, Kosovo, and parts of Greece south of Olympus gorge. R1a is virtually composed only of the Z284 subclade in Scandinavia. In Slovenia, the main subclade is Z282 (Z280 and M458), although the Z284 subclade was found in one sample of a Slovenian. There is a negligible representation of Z93 in each region other than Turkey.” ref
“West Slavs and Hungarians are characterized by a high frequency of the subclade M458 and a low Z92, a subclade of Z280. Hundreds of Slovenian samples and Czechs lack the Z92 subclade of Z280, while Poles, Slovaks, Croats and Hungarians only show a very low frequency of Z92. The Balts, East Slavs, Serbs, Macedonians, Bulgarians, and Romanians demonstrate a ratio Z280>M458 and a high, up to a prevailing share of Z92. Balts and East Slavs have the same subclades and similar frequencies in a more detailed phylogeny of the subclades. The Russian geneticist Oleg Balanovsky speculated that there is a predominance of the assimilated pre-Slavic substrate in the genetics of East and West Slavic populations, according to him the common genetic structure that contrasts East Slavs and Balts from other populations may suggest the explanation that the pre-Slavic substrate of the East Slavs consisted most significantly of Baltic-speakers, which at one point predated the Slavs in the cultures of the Eurasian steppe according to archaeological and toponymic references.” ref
R1a and Central Asia
“Zerjal et al. (2002) found R1a1a in 64% of a sample of the Tajiks of Tajikistan and 63% of a sample of the Kyrgyz of Kyrgyzstan. Haber et al. (2012) found R1a1a-M17(xM458) in 26.0% (53/204) of a set of samples from Afghanistan, including 60% (3/5) of a sample of Nuristanis, 51.0% (25/49) of a sample of Pashtuns, 30.4% (17/56) of a sample of Tajiks, 17.6% (3/17) of a sample of Uzbeks, 6.7% (4/60) of a sample of Hazaras, and in the only sampled Turkmen individual.” ref
“Di Cristofaro et al. (2013) found R1a1a-M198/M17 in 56.3% (49/87) of a pair of samples of Pashtuns from Afghanistan (including 20/34 or 58.8% of a sample of Pashtuns from Baghlan and 29/53 or 54.7% of a sample of Pashtuns from Kunduz), 29.1% (37/127) of a pool of samples of Uzbeks from Afghanistan (including 28/94 or 29.8% of a sample of Uzbeks from Jawzjan, 8/28 or 28.6% of a sample of Uzbeks from Sar-e Pol, and 1/5 or 20% of a sample of Uzbeks from Balkh), 27.5% (39/142) of a pool of samples of Tajiks from Afghanistan (including 22/54 or 40.7% of a sample of Tajiks from Balkh, 9/35 or 25.7% of a sample of Tajiks from Takhar, 4/16 or 25.0% of a sample of Tajiks from Samangan, and 4/37 or 10.8% of a sample of Tajiks from Badakhshan), 16.2% (12/74) of a sample of Turkmens from Jawzjan, and 9.1% (7/77) of a pair of samples of Hazara from Afghanistan (including 7/69 or 10.1% of a sample of Hazara from Bamiyan and 0/8 or 0% of a sample of Hazara from Balkh).” ref
“Malyarchuk et al. (2013) found R1a1-SRY10831.2 in 30.0% (12/40) of a sample of Tajiks from Tajikistan. Ashirbekov et al. (2017) found R1a-M198 in 6.03% (78/1294) of a set of samples of Kazakhs from Kazakhstan. R1a-M198 was observed with greater than average frequency in the study’s samples of the following Kazakh tribes: 13/41 = 31.7% of a sample of Suan, 8/29 = 27.6% of a sample of Oshaqty, 6/30 = 20.0% of a sample of Qozha, 4/29 = 13.8% of a sample of Qypshaq, 1/8 = 12.5% of a sample of Tore, 9/86 = 10.5% of a sample of Jetyru, 4/50 = 8.0% of a sample of Argyn, 1/13 = 7.7% of a sample of Shanyshqyly, 8/122 = 6.6% of a sample of Alimuly, 3/46 = 6.5% of a sample of Alban. R1a-M198 also was observed in 5/42 = 11.9% of a sample of Kazakhs of unreported tribal affiliation.” ref
R1a and South Asia
“In South Asia, R1a1a has often been observed in a number of demographic groups. In India, high frequencies of this haplogroup are observed in West Bengal Brahmins (72%) to the east, Gujarat Lohanas (60%) to the west, Khatris (67%) in the north, and Iyengar Brahmins (31%) in the south. It has also been found in several South Indian Dravidian-speaking Adivasis including the Chenchu (26%) and the Valmikis of Andhra Pradesh, Kota (22.58%), and the Kallar of Tamil Nadu suggesting that R1a1a is widespread in Tribal Southern Indians. Besides these, studies show high percentages in regionally diverse groups such as Manipuris (50%) to the extreme North-East and among Punjabis (47%) to the extreme North West. In Pakistan, it is found at 71% among the Mohanna tribe in Sindh province to the south and 46% among the Baltis of Gilgit-Baltistan to the north. Among the Sinhalese of Sri Lanka, 23% were found to be R1a1a (R-SRY1532) positive. Hindus of Chitwan District in the Terai region Nepal show it at 69%.” ref
R1a and East Asia
“The frequency of R1a1a is comparatively low among some Turkic-speaking groups like Yakuts, yet levels are higher (19 to 28%) in certain Turkic or Mongolic-speaking groups of Northwestern China, such as the Bonan, Dongxiang, Salar, and Uyghurs. A Chinese paper published in 2018 found R1a-Z94 in 38.5% (15 / 39) of a sample of Keriyalik Uyghurs from Darya Boyi / Darya Boye Village, Yutian County, Xinjiang (于田县达里雅布依乡), R1a-Z93 in 28.9% (22/76) of a sample of Dolan Uyghurs from Horiqol township, Awat County, Xinjiang (阿瓦提县乌鲁却勒镇), and R1a-Z93 in 6.3% (4/64) of a sample of Loplik Uyghurs from Karquga / Qarchugha Village, Yuli County, Xinjiang (尉犁县喀尔曲尕乡). R1a(xZ93) was observed only in one of 76 Dolan Uyghurs. Note that Darya Boyi Village is located in a remote oasis formed by the Keriya River in the Taklamakan Desert. A 2011 Y-dna study found Y-dna R1a1 in 10% of a sample of southern Hui people from Yunnan, 1.6% of a sample of Tibetan people from Xizang (Tibet Autonomous Region), 1.6% of a sample of Xibe people from Xinjiang, 3.2% of a sample of northern Hui from Ningxia, 9.4% of a sample of Hazak (Kazakhs) from Xinjiang, and rates of 24.0%, 22.2%, 35.2%, 29.2% in 4 different samples of Uyghurs from Xinjiang, 9.1% in a sample of Mongols from Inner Mongolia, 10% of a sample of Northern Han Chinese from Gansu and 8.9% of a sample of Northern Han from western Henan. A different subclade of R1 was also found in 1.5% of a sample of northern Hui from Ningxia.” ref
“In the same study, there were no cases of R1a detected at all in 6 samples of Han Chinese in Yunnan, 1 sample of Han in Guangxi, 5 samples of Han in Guizhou, 2 samples of Han in Guangdong, 2 samples of Han in Fujian, 2 samples of Han in Zhejiang, 1 sample of Han in Shanghai, 1 samples of Han in Jiangxi, 2 samples of Han in Hunan, 1 sample of Han in Hubei, 2 samples of Han in Sichuan, 1 sample of Han in Chongqing, 3 samples of Han in Shandong, 5 samples of Han in Gansu, 3 samples of Han in Jilin and 2 samples of Han in Heilongjiang. T-M70, R-M207 (a subclade of R1a), Q-M242, L-M20, J-P209, I-M170, H-M69, G-M201, C5-M356 and E-SRY4064 collectively make up only 6.79% of the total male population of East Asia (from samples in North Korea and China). The vast majority of East Asia is N-M231, C-M130 except for C5-M356, D-M174, and O-M175 which is 92.87% of the population and are all East Eurasian male haplogroups. R-M207 (a subclade of R1a) came into East Asia via the north from the Central South Asia region (CSA) during paleolithic times in the post-glacial period, especially R1a1a. R1a1a in East Asia is an extremely ancient subclade from the Central Asia-South Asia region and is older than the Western Eurasian (European_ and Central Asian-South Asian (CSA) R1a1*-M17, rivaling the R1a1*-M17 of IWest India in age from testing on variations in STR. The Europe and West Asian R1a1*-M17 split into 7 subbranches only after R1a1 came to North-East Asia, indicating R1a1 in East Asia is an extremely ancient one dating back 15,370 years ago juding from variation in STR (predating the more recent Aryan and Indo-European expansions).” ref
“In a 2014 paper, R1a1a has been detected in 1.8% (2/110) of Chinese samples. These two samples (R-M17, R-M198, R-M434, R-M458 for both) belonged to Han individuals from Fujian and Shanxi provinces. 40% of Salars, 45.2% of Tajiks of Xinjiang, 54.3% of Dongxiang, 60.6% of Tatars, and 68.9% of Kyrgyz in Xinjiang in northwestern China tested in one sample had R1a1-M17. Bao’an (Bonan) had the most haplogroup diversity of 0.8946±0.0305 while the other ethnic minorities in northwestern China had a high haplogroup diversity like Central Asians, of 0.7602±0.0546. In Eastern Siberia, R1a1a is found among certain indigenous ethnic groups including Kamchatkans and Chukotkans, and peaking in Itel’man at 22%.” ref
R1a and West Asia
“R1a1a has been found in various forms, in most parts of Western Asia, in widely varying concentrations, from almost no presence in areas such as Jordan, to much higher levels in parts of Kuwait and Iran. The Shimar (Shammar) Bedouin tribe in Kuwait show the highest frequency in the Middle East at 43%. Wells 2001, noted that in the western part of the country, Iranians show low R1a1a levels, while males of eastern parts of Iran carried up to 35% R1a1a. Nasidze et al. 2004 found R1a1a in approximately 20% of Iranian males from the cities of Tehran and Isfahan. Regueiro 2006 in a study of Iran, noted much higher frequencies in the south than the north.” ref
“A newer study has found 20.3% R-M17* among Kurdish samples which were taken in the Kurdistan Province in western Iran, 19% among Azerbaijanis in West Azerbaijan, 9.7% among Mazandaranis in North Iran in the province of Mazandaran, 9.4% among Gilaks in province of Gilan, 12.8% among Persian and 17.6% among Zoroastrians in Yazd, 18.2% among Persians in Isfahan, 20.3% among Persians in Khorasan, 16.7% Afro-Iranians, 18.4% Qeshmi “Gheshmi”, 21.4% among Persian Bandari people in Hormozgan and 25% among the Baloch people in Sistan and Baluchestan Province.” ref
“Di Cristofaro et al. (2013) found haplogroup R1a in 9.68% (18/186) of a set of samples from Iran, though with a large variance ranging from 0% (0/18) in a sample of Iranians from Tehran to 25% (5/20) in a sample of Iranians from Khorasan and 27% (3/11) in a sample of Iranians of unknown provenance. All Iranian R1a individuals carried the M198 and M17 mutations except one individual in a sample of Iranians from Gilan (n=27), who was reported to belong to R1a-SRY1532.2(xM198, M17).” ref
“Malyarchuk et al. (2013) found R1a1-SRY10831.2 in 20.8% (16/77) of a sample of Persians collected in the provinces of Khorasan and Kerman in eastern Iran, but they did not find any member of this haplogroup in a sample of 25 Kurds collected in the province of Kermanshah in western Iran. Further to the north of these Western Asian regions, on the other hand, R1a1a levels start to increase in the Caucasus, once again in an uneven way. Several populations studied have shown no sign of R1a1a, while the highest levels so far discovered in the region appears to belong to speakers of the Karachay-Balkar language among whom about one-quarter of men tested so far are in haplogroup R1a1a.” ref
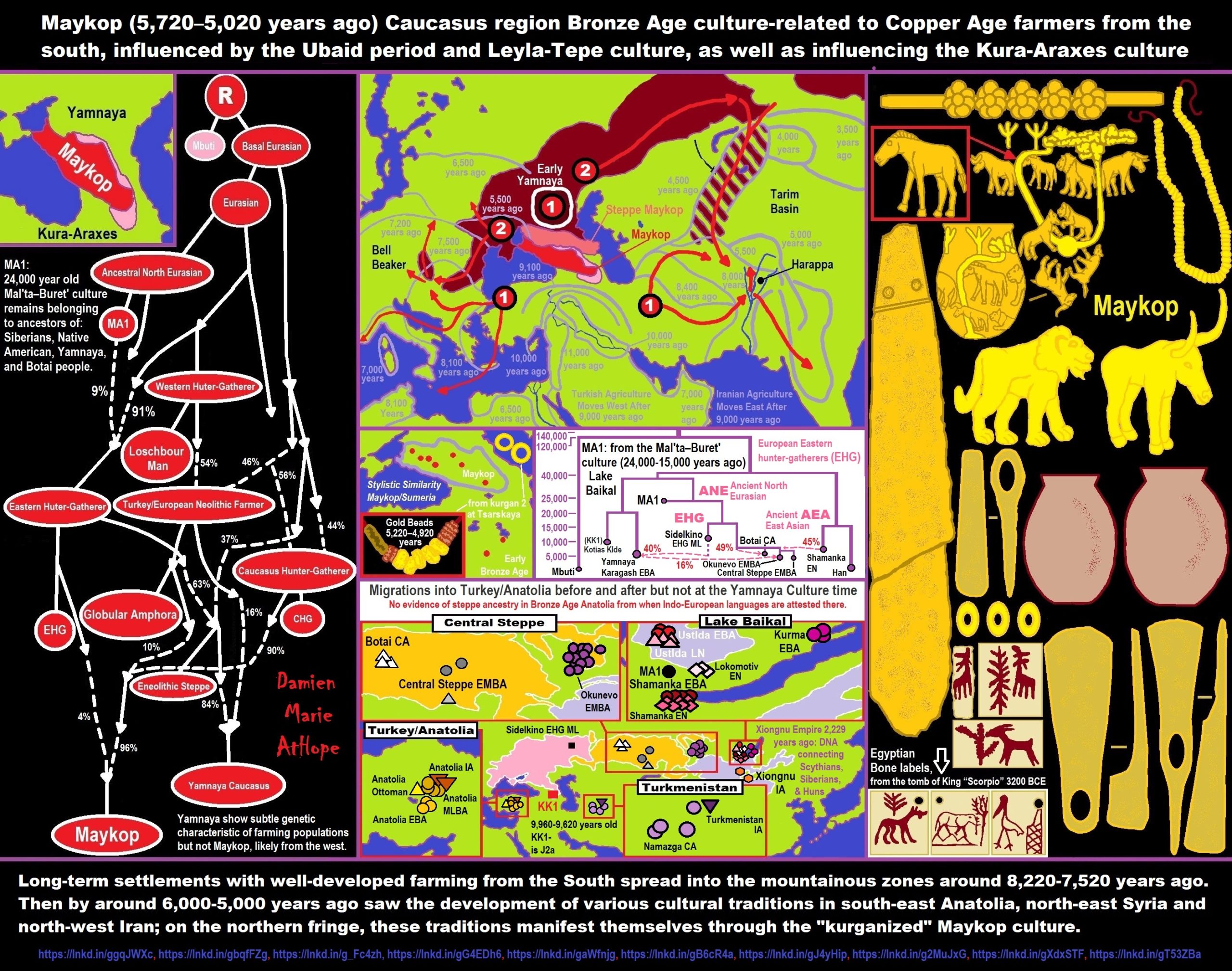
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
The Maykop culture, the R1b link to the Steppe?
“The Maykop culture (3700-2500 BCE) in the north-west Caucasus was culturally speaking a sort of southern extension of the Yamna horizon. Although not generally considered part of the Pontic-Caspian steppe culture due to its geography, the North Caucasus had close links with the steppes, as attested by numerous ceramics, gold, copper, and bronze weapons and jewelry in the contemporaneous cultures of Mikhaylovka, Sredny Stog, and Kemi Oba. The link between the northern Black Sea coast and the North Caucasus is older than the Maykop period. Its predecessor, the Svobodnoe culture (4400-3700 BCE), already had links to the Suvorovo-Novodanilovka and early Sredny Stog cultures. The even older Nalchik settlement (5000-4500 BCE) in the North Caucasus displayed a similar culture as Khvalynsk in the Caspian Steppe and Volga region. This may be the period when R1b started interacting and blending with the R1a population of the steppes.” ref
“The Yamna and Maykop people both used kurgan burials, placing their deads in a supine position with raised knees and oriented in a north-east/south-west axis. Graves were sprinkled with red ochre on the floor, and sacrificed domestic animal buried alongside humans. They also had in common horses, wagons, a heavily cattle-based economy with a minority of sheep kept for their wool, use of copper/bronze battle-axes (both hammer-axes and sleeved axes), and tanged daggers. In fact, the oldest wagons and bronze artefacts are found in the North Caucasus, and appear to have spread from there to the steppes.” ref
“Maykop was an advanced Bronze Age culture, actually one of the very first to develop metalworking, and therefore metal weapons. The world’s oldest sword was found at a late Maykop grave in Klady kurgan 31. Its style is reminiscent of the long Celtic swords, though less elaborated. Horse bones and depictions of horses already appear in early Maykop graves, suggesting that the Maykop culture might have been founded by steppe people or by people who had close link with them. However, the presence of cultural elements radically different from the steppe culture in some sites could mean that Maykop had a hybrid population. Without DNA testing it is impossible to say if these two populations were an Anatolian R1b group and a G2a Caucasian group, or whether R1a people had settled there too. The two or three ethnicities might even have cohabited side by side in different settlements. The one typical Caucasian Y-DNA lineage that does follow the pattern of Indo-European migrations is G2a-L13, which is found throughout Europe, Central Asia, and South Asia. In the Balkans, the Danube basin, and Central Europe its frequency is somewhat proportional to the percentage of R1b.” ref
“Maykop people are the ones credited for the introduction of primitive wheeled vehicles (wagons) from Mesopotamia to the Steppe. This would revolutionize the way of life in the steppe, and would later lead to the development of (horse-drawn) war chariots around 2000 BCE. Cavalry and chariots played an vital role in the subsequent Indo-European migrations, allowing them to move quickly and defeat easily anybody they encountered. Combined with advanced bronze weapons and their sea-based culture, the western branch (R1b) of the Indo-Europeans from the Black Sea shores are excellent candidates for being the mysterious Sea Peoples, who raided the eastern shores of the Mediterranean during the second millennium BCE.” ref
“The rise of the IE-speaking Hittites in Central Anatolia happened a few centuries after the disappearance of the Maykop and Yamna cultures. Considering that most Indo-European forms of R1b found in Anatolia today belong to the R1b-Z2103 subclade, it makes little doubt that the Hittites came to Anatolia via the Balkans, after Yamna/Maykop people invaded Southeast Europe. The Maykop and Yamna cultures were succeeded by the Srubna culture (1600-1200 BCE), possibly representing an advance of R1a-Z282 people from the northern steppes towards the Black Sea shores, filling the vacuum left by the R1b tribes who migrated to Southeast Europe and Anatolia.” ref
The Siberian & Central Asian branch corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“When R1b crossed the Caucasus in the Late Neolithic, it split into two main groups. The western one (L51) would settle the eastern and northern of the Black Sea. The eastern one (Z2103) migrated to the Don-Volga region, where horses were domesticated circa 4600 BCE. R1b probably mixed with indigenous R1a people and founded the Repin culture (3700-3300 BCE) a bit before the Yamna culture came into existence in the western Pontic Steppe. R1b would then have migrated with horses along the Great Eurasian Steppe until the Altai mountains in East-Central Asia, where they established the Afanasevo culture (c. 3600-2400 BCE). Afanasevo people might be the precursors of the Tocharian branch of Indo-European languages. In 2014, Clément Hollard of Strasbourg University tested three Y-DNA samples from the Afanasevo culture and all three turned out to belong to haplogroup R1b, including two to R1b-M269.” ref
“The R1b people who stayed in the Volga-Ural region were probably the initiators of the Poltavka culture (2700-2100 BCE), then became integrated into the R1a-dominant Sintashta-Petrovka culture (2100-1750 BCE) linked to the Indo-Aryan conquest of Central and South Asia (=> see R1a for more details). Nowadays in Russia R1b is found at higher frequencies among ethnic minorities of the Volga-Ural region (Udmurts, Komi, Mordvins, Tatars) than among Slavic Russians. R1b is also present in many Central Asian populations, the highest percentages being observed among the Uyghurs (20%) of Xinjiang in north-west China, the Yaghnobi people of Tajikistan (32%), and the Bashkirs (47%, or 62.5% in the Abzelilovsky district) of Bashkortostan in Russia (border of Kazakhstan). R1b-M73, found primarily in North Asia (Altai, Mongolia), Central Asia, and the North Caucasus is thought to have spread during the Neolithic from the Middle East to Central and North Asia, and therefore can be considered to be pre-Indo-European.” ref
The European & Middle Eastern branch corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The Indo-Europeans’s bronze weapons and the extra mobility provided by horses would have given them a tremendous advantage over the autochthonous inhabitants of Europe, namely the native haplogroup C1a2, F, and I (descendants of Cro-Magnon) and the early Neolithic herders and farmers (G2a, H2, E1b1b, and T1a). This allowed R1a and R1b to replace most of the native male lineages (=> see How did R1b come to replace most of the older lineages in Western Europe?), although female lineages seem to have been less affected.” ref
“A comparison with the Indo-Iranian invasion of South Asia shows that 40% of the male linages of northern India are R1a, but less than 10% of the female lineages could be of Indo-European origin. The impact of the Indo-Europeans was more severe in Europe because European society 4,000 years ago was less developed in terms of agriculture, technology (no bronze weapons), and population density than that of the Indus Valley civilization. This is particularly true of the native Western European cultures where farming arrived much later than in the Balkans or Central Europe. Greece, the Balkans and the Carpathians were the most advanced of European societies at the time and were the least affected in terms of haplogroup replacement. neolithic lineages survived better in regions that were more difficult to reach or less hospitable to horse breeders, like the Alps, the Dinaric Alps, the Apennines, and Sardinia.” ref
The Conquest of “Old Europe” and Central Europe (4200-2500 BCE) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The first forays of Steppe people into the Balkans happened between 4200 BCE and 3900 BCE, when cattle herders equipped with horse-drawn wagons crossed the Dniester and Danube and apparently destroyed the towns of the Gumelnița, Varna, and Karanovo VI cultures in Eastern Romania and Bulgaria. A climatic change resulting in colder winters during this exact period probably pushed steppe herders to seek milder pastures for their stock, while failed crops would have led to famine and internal disturbance within the Danubian and Balkanic communities. The ensuing Cernavodă culture (Copper Age, 4000-3200 BCE), Coțofeni/Usatovo culture (Copper to Bronze Age, 3500-2500 BCE), Ezero culture (Bronze Age, 3300-2700 BCE), in modern Romania, seems to have had a mixed population of steppe immigrants and people from the old tell settlements. These Steppe immigrants were likely a mixture of both R1a and R1b lineages, with a probably higher percentage of R1a than later Yamna-era invasions.” ref
“The Steppe invaders would have forced many Danubian farmers to migrate to the Cucuteni-Trypillian towns in the eastern Carpathians, causing a population boom and a north-eastward expansion until the Dnieper valley, bringing Y-haplogroups G2a, I2a1 (probably the dominant lineage of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture), E1b1b, J2a, and T1a in what is now central Ukraine. This precocious Indo-European advance westward was fairly limited, due to the absence of Bronze weapons and organized army at the time, and was indeed only possible thanks to climatic catastrophes which reduced the defenses of the towns of Old Europe. The Carphatian, Danubian, and Balkanic cultures were too densely populated and technologically advanced to allow for a massive migration.” ref
“In comparison, the forest-steppe R1a people successfully penetrated into the heart of Europe with little hindrance, due to the absence of developed agrarian societies around Poland and the Baltic. The Corded Ware culture (3200-1800 BCE) was a natural northern and western expansion of the Yamna culture, reaching as far west as Germany and as far north as Sweden and Norway. DNA analysis from the Corded Ware confirmed the presence of R1a and R1b in Poland c. 2700 BCE and R1a central Germany around 2600 BCE. The Corded Ware tribes expanded from the northern fringe of the Yamna culture where R1a lineages were prevalent over R1b ones.” ref
“The expansion of R1b people into Old Europe was slower, but proved inevitable. In 2800 BCE, by the time the Corded Ware had already reached Scandinavia, the Bronze Age R1b cultures had barely moved into the Pannonian Steppe. They established major settlements in the Great Hungarian Plain, the most similar habitat to their ancestral Pontic Steppes. Around 2500 BCE, the western branch of Indo-European R1b were poised for their next major expansion into modern Germany and Western Europe. By that time, the R1b immigrants had blended to a great extent with the indigenous Mesolithic and Neolithic populations of the Danubian basin, where they had now lived for 1,700 years.” ref
“The strongly patriarchal Indo-European elite remained almost exclusively R1b on the paternal side, but absorbed a high proportion of non-Indo-European maternal lineages. Hybridized, the new Proto-Indo-European R1b people would have lost most of their remaining Proto-Europoid or Mongolid features inherited from their Caspian origins (which were still clearly visible in numerous individuals from the Yamna period). Their light hair, eye and skin pigmentation, once interbred with the darker inhabitants of Old Europe, became more like that of modern Southern Europeans. The R1a people of the Corded Ware culture would come across far less populous societies in Northern Europe, mostly descended from the lighter Mesolithic population, and therefore retained more of their original pigmentation (although facial traits evolved considerably in Scandinavia, where the I1 inhabitants were strongly dolicocephalic and long-faced, as opposed to the brachycephalic and broad-faced Steppe people).” ref
The Conquest of Western Europe (2500-1200 BCE) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The R1b conquest of Europe happened in two phases. For nearly two millennia, starting from circa 4200 BCE, Steppe people limited their conquest to the rich Chalcolithic civilizations of the Carpathians and the Balkans. These societies possessed the world’s largest towns, notably the tell settlements of the Cucuteni-Tripolye culture. Nothing incited the R1b conquerors to move further into Western Europe at such an early stage, because most of the land north and west of the Alps was still sparsely populated woodland. The Neolithic did not reach the British Isles and Scandinavia before circa 4000 BCE. Even northern France and most of the Alpine region had been farming or herding for less than a millennium and were still quite primitive compared to Southeast Europe and the Middle East.” ref
“North-west Europe remained a tribal society of hunter-gatherers practicing only limited agriculture for centuries after the conquest of the Balkans by the Indo-Europeans. Why would our R1b “conquistadors” leave the comfort of the wealthy and populous Danubian civilizations for the harsh living conditions that lie beyond? Bronze Age people coveted tin, copper, and gold, of which the Balkans had plenty, but that no one had yet discovered in Western Europe.” ref
“R1b-L51 is thought to have arrived in Central Europe (Hungary, Austria, Bohemia) around 2500 BCE, approximately two millennia after the shift to the Neolithic lifestyle in these regions. Agrarian towns had started to develop. Gold and copper had begun to be mined. The prospects of a conquest were now far more appealing.” ref
“The archeological and genetic evidence (distribution of R1b subclades) point at several consecutive waves towards eastern and central Germany between 2800 BCE and 2300 BCE. The Unetice culture was probably the first culture in which R1b-L11 lineages played a major role. It is interesting to note that the Unetice period happen to correspond to the end of the Maykop (2500 BCE) and Kemi Oba (2200 BCE) cultures on the northern shores of the Black Sea, and their replacement by cultures descended from the northern steppes. It can therefore be envisaged that the (mostly) R1b population from the northern half of the Black Sea migrated westward due to pressure from other Indo-European people (R1a) from the north, for example that of the burgeoning Proto-Indo-Iranian branch, linked to the contemporary Poltavka and Abashevo cultures.” ref
“It is doubtful that the Bell Beaker culture (2900-1800 BCE) in Western Europe was already Indo-European because its attributes are in perfect continuity with the native Megalithic cultures. The Beaker phenomenon started during the Late Neolithic and Early Chalcolithic in Portugal and propagated to the north-east towards Germany. During the same period Bronze Age Steppe cultures spread from Germany in the opposite direction towards Iberia, France and Britain, progressively bringing R1b lineages into the Bell Beaker territory. It is more likely that the beakers and horses found across Western Europe during that period were the result of trade with neighboring Indo-European cultures, including the first wave of R1b into Central Europe. It is equally possible that the Beaker people were R1b merchants or explorers who traveled across Western Europe and brought back tales of riches poorly defended by Stone Age people waiting to be to be conquered. This would have prompted a full-scale Indo-European (R1b) invasion from about 2500 BCE in Germany, reaching the Atlantic (north of the Pyrenees at least) around 2200 BCE.” ref
“Ancient DNA tests conducted by Lee et al. (2012), Haak et al. (2015) and Allentoft et al. (2015) have all confirmed the presence of R1b-L51 (and deeper subclades such as P312 and U152) in Germany from the Bell Beaker period onwards, but none in earlier cultures. German Bell Beaker R1b samples only had about 50% of Yamna autosomal DNA and often possessed Neolithic non-Steppe mtDNA, which confirms that R1b invaders took local wives as they advanced westward. Another study by Olalde et al. (2017) confirmed that Iberian Bell Beakers were genetically distinct from the previously tested German samples. None of the Spanish or Portuguese individuals associated with Bell Beaker pottery possessed any Steppe admixture, and none belonged to the Indo-European haplogroup R1b-L23 or its subclades. Instead, they belonged to typical Megalithic lineages like G2a, I2a1, I2a2, and the Neolithic R1b-V88. The paper also confirmed a high frequency of R1b-L51 lineages in central Europe during the Beall Beaker period.” ref
In Britain, Megalithic individuals belonged exclusively to Y-haplogroup I2 (mostly I2a2 and I2a1b-L161), but were entirely replaced by R1b-L51 (mosly L21 clade) in the Early Bronze Age. This means that the Bell Beaker culture was not associated with one particular ethnic group. Beaker pottery originated in Megalithic Iberia, but then spread to France and central Europe and was used by invading R1b-L51 Steppe people, who brought it with them to the British Isles, while wiping out most of the indigenous Megalithic population. There was therefore no ‘Bell Beaker people’, but just various populations trading and using Beaker pots during that period.” ref
“DNA samples from the Unetice culture (2300-1600 BCE) in Germany, which emerged less than two centuries after the appearance of the first R1b-L51 individuals in the late Bell Beaker Germany, had a slightly higher percentage of Yamna ancestry (60~65%) and of Yamna-related mtDNA lineages, which indicates a migration of both Steppe men and women. That would explain why archeological artifacts from the Unetice culture are clearly Yamna-related (i.e. Indo-European), as they abruptly introduced new technologies and a radically different lifestyle, while the Bell Beaker culture was in direct continuity with previous Neolithic or Chalcolithic cultures. R1b men may simply have conquered the Bell Beaker people and overthrown the local rulers without obliterating the old culture due to their limited numbers. Taking the analogy of the Germanic migrations in the Late Antiquity, the R1b invasion of the Bell Beaker period was more alike to that of the Goths, Burgunds, and Vandals, who all migrated in small numbers, created new kingdoms within the Roman empire, but adopted Latin language and Roman culture. In contrast, the Corded Ware and Unetice culture involved large-scale migrations of Steppe people, who imposed their Indo-European language and culture and conquered people, just like the Anglo-Saxons or the Bavarians did in the 5th century.” ref
“The cultures that succeeded to Unetice in Central Europe, chronologically the Tumulus culture (1600-1200 BCE), Urnfield culture (1300-1200 BCE) and Hallstatt culture (1200-750 BCE) cultures remained typically Indo-European. The Hallstatt culture, centered around the Alps, is considered the first classical Celtic culture in Europe. It quickly expanded to France, Britain, Iberia, northern Italy, and the Danube valley, probably spreading for the first time Celtic languages, although not bronze technology nor R1b lineages, which had both already spread over much of western Europe during the Bell Beaker period. => See also Metal-mining and stockbreeding explain R1b dominance in Atlantic fringe” ref
Did the Indo-Europeans corresponding to haplogroup R1b really invade Western Europe?
“Proponents of the Paleolithic or Neolithic continuity model argue that bronze technology and horses could have been imported by Western Europeans from their Eastern European neighbors, and that no actual Indo-European invasion need be involved. It is harder to see how Italic, Celtic and Germanic languages were adopted by Western and Northern Europeans without at least a small scale invasion. It has been suggested that Indo-European (IE) languages simply disseminated through contact, just like technologies, or because it was the language of a small elite and therefore its adoption conferred a certain perceived prestige. However, people don’t just change language like that because it sounds nicer or more prestigious. Even nowadays, with textbooks, dictionaries, compulsory language courses at school, private language schools for adults, and multilingual TV programs, the majority of the people cannot become fluent in a completely foreign language, belonging to a different language family. The linguistic gap between pre-IE vernaculars and IE languages was about as big as between modern English and Chinese. English, Greek, Russian, and Hindi are all related IE languages and therefore easier to learn for IE speakers than non-IE languages like Chinese, Arabic, or Hungarian. From a linguistic point of view, only a wide-scale migration of IE speakers could explain the thorough adoption of IE languages in Western Europe – leaving only Basque as a remnant of the Neolithic languages.” ref
“One important archeological argument in favor of the replacement of Neolithic cultures by Indo-European culture in the Bronze Age comes from pottery styles. The sudden appearance of bronze technology in Western Europe coincides with ceramics suddenly becoming more simple and less decorated, just like in the Pontic Steppe. Until then, pottery had constantly evolved towards greater complexity and details for over 3,000 years. People do not just decide like that to revert to a more primitive style. Perhaps one isolated tribe might experiment with something simpler at one point, but what are the chances that distant cultures from Iberia, Gaul, Italy, and Britain all decide to undertake such an improbable shift around the same time? The best explanation is that this new style was imposed by foreign invaders. In this case, it is not mere speculation; there is ample evidence that this simpler pottery is characteristic of the steppes associated with the emergence of Proto-Indo-European speakers.” ref
“Besides pottery, archaeology provides ample evidence that the early Bronze Age in Central and Western Europe coincides with a radical shift in food production. Agriculture experiences an abrupt reduction in exchange for an increased emphasis on domesticates. This is also a period when horses become more common and cow milk is being consumed regularly. The overall change mimics the Steppic way of life almost perfectly. Even after the introduction of agriculture around 5200 BCE, the Bug-Dniester culture and later Steppe cultures were characterized by an economy dominated by herding, with only limited farming. This pattern expands into Europe exactly at the same time as bronze working.” ref
“Religious beliefs and arts undergo a complete reversal in Bronze Age Europe. Neolithic societies in the Near East and Europe had always worshipped female figurines as a form of fertility cult. The Steppe cultures, on the contrary, did not manufacture female figurines. As bronze technology spreads from the Danube valley to Western Europe, symbols of fertility and fecundity progressively disappear and are replaced by cultures of domesticated animals.” ref
“Another clue that Indo-European Steppe people came in great number to Central and Western Europe is to be found in burial practices. Neolithic Europeans either cremated their dead (e.g. Cucuteni-Tripolye culture) or buried them in collective graves (this was the case of Megalithic cultures). In the Steppe, each person was buried individually, and high-ranking graves were placed in a funeral chamber and topped by a circular mound. The body was typically accompanied by weapons (maces, axes, daggers), horse bones, and a dismantled wagon (or later chariot). These characteristic burial mounds are known as kurgans in the Pontic Steppe.” ref
“Men were given more sumptuous tombs than women, even among children, and differences in hierarchy are obvious between burials. The Indo-Europeans had a strongly hierarchical and patrilinear society, as opposed to the more egalitarian and matrilinear cultures of Old Europe. The proliferation of ststus-conscious male-dominant kurgans (or tumulus) in Central Europe during the Bronze Age is a clear sign that the ruling elite had now become Indo-European. The practice also spread to central Asia and southern Siberia, two regions where R1a and R1b lineages are found nowadays, just like in Central Europe.” ref
“The ceremony of burial is one of the most emotionally charged and personal aspect of a culture. It is highly doubtful that people would change their ancestral practice “just to do like the neighbors”. In fact, different funerary practices have co-existed side by side during the European Neolithic and Chalcolithic. The ascendancy of yet another constituent of the Pontic Steppe culture in the rest of Europe, and in this case one that does not change easily through contact with neighbors, adds up to the likelihood of a strong Indo-European migration. The adoption of some elements of a foreign culture tends to happen when one civilization overawes the adjacent cultures by its superiority.” ref
“This process is called ‘acculturation’. However, there is nothing that indicates that the Steppe culture was so culturally superior as to motivate a whole continent, even Atlantic cultures over 2000 km away from the Pontic Steppe, to abandon so many fundamental symbols of their own ancestral culture, and even their own language. In fact, Old Europe was far more refined in its pottery and jewelry than the rough Steppe people. The Indo-European superiority was cultural but military, thanks to horses, bronze weapons, and an ethic code valuing individual heroic feats in war (these ethic values are known from the old IE texts, like the Rig Veda, Avesta, or the Mycenaean and Hittite literature).” ref
“After linguistics and archaeology, the third category of evidence comes from genetics itself. It had first been hypothesized that R1b was native to Western Europe, because this is where it was most prevalent. It has since been proven that R1b haplotypes displayed higher microsatellite diversity in Anatolia and in the Caucasus than in Europe. European subclades are also more recent than Middle Eastern or Central Asian ones. The main European subclade, R-P312/S116, only dates back to approximately 3500 to 3000 BCE. It does not mean that the oldest common ancestor of this lineage arrived in Western Europe during this period, but that the first person who carried the mutation R-P312/S116 lived at least 5,000 years ago, assumably somewhere in the lower Danube valley or around the Black Sea. In any case, this timeframe is far too recent for a Paleolithic origin or a Neolithic arrival of R1b. The discovery of what was thought to be “European lineages” in Central Asia, Pakistan, and India hit the final nail on the coffin of a Paleolithic origin of R1b in Western Europe, and confirmed the Indo-European link.” ref
“All the elements concur in favor of a large scale migration of Indo-European speakers (possibly riding on horses) to Western Europe between 2500 to 2100 BCE, contributing to the replacement of the Neolithic or Chalcolithic lifestyle by an inherently new Bronze Age culture, with simpler pottery, less farming, more herding, new rituals (single graves) and new values (patrilinear society, warrior heroes) that did not evolve from local predecessors.” ref
The Atlantic Celtic branch (L21) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The Proto-Italo-Celto-Germanic R1b people had reached in what is now Germany by 2500 BCE. By 2300 BCE they had arrived in large numbers and founded the Unetice culture. Judging from the propagation of bronze working to Western Europe, those first Indo-Europeans reached France and the Low Countries by 2200 BCE, Britain by 2100 BCE and Ireland by 2000 BCE, and Iberia by 1800 BCE. This first wave of R1b presumably carried R1b-L21 lineages in great number (perhaps because of a founder effect), as these are found everywhere in western, northern, and Central Europe. Cassidy et al. (2015) confirmed the presence of R1b-L21 (DF13 and DF21 subclades) in Ireland around 2000 BCE. Those genomes closely resembled those of the Unetice culture autosomally, but differed greatly from the earlier Neolithic Irish samples. This confirms that a direct migration of R1b-L21 from Central Europe was responsible for the introduction of the Bronze Age to Ireland.” ref
“The early split of L21 from the main Proto-Celtic branch around Germany would explain why the Q-Celtic languages (Goidelic and Hispano-Celtic) diverged so much from the P-Celtic branch (La Tène, Gaulish, Brythonic), which appears to have expanded from the later Urnfield and Hallstat cultures. Some L21 lineages from the Netherlands and northern Germany later entered Scandinavia (from 1700 BCE) with the dominant subclade of the region, R1b-S21/U106 (see below). The stronger presence of L21 in Norway and Iceland can be attributed to the Norwegian Vikings, who had colonized parts of Scotland and Ireland and taken slaves among the native Celtic populations, whom they brought to their new colony of Iceland and back to Norway. Nowadays about 20% of all Icelandic male lineages are R1b-L21 of Scottish or Irish origin.” ref
“In France, R1b-L21 is mainly present in historical Brittany (including Mayenne and Vendée) and in Lower Normandy. This region was repopulated by massive immigration of insular Britons in the 5th century due to pressure from the invading Anglo-Saxons. However, it is possible that L21 was present in Armorica since the Bronze age or the Iron age given that the tribes of the Armorican Confederation of ancient Gaul already had a distinct identity from the other Gauls and had maintained close ties with the British Isles at least since the Atlantic Bronze Age.” ref
The Gallic & Iberian branch (DF27/S250) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The first Proto-Celtic R1b lineages to reach France and the Iberian peninsula from Central Europe were probably L21 and DF27. Whereas L21 might have taken a northern route through Belgium and northern France on its way to the British Isles, DF27 seems to have spread all over France but heading in greater number toward the south.” ref
“The Bronze Age did not appear in Iberia until 1800 BCE, and was mostly confined to the cultures of El Argar and Los Millares in south-east Spain, with sporadic sites showing up in Castile by 1700 BCE and in Extremadura and southern Portugal by 1500 BCE. These Early Bronze Age sites typically did not have more than some bronze daggers or axes and cannot be considered proper Bronze Age societies, but rather Copper Age societies with occasional bronze artifacts (perhaps imported). These cultures might have been founded by small groups of R1b adventurers looking for easy conquests in parts of Europe that did not yet have bronze weapons. They would have become a small ruling elite, would have had children with local women, and within a few generations their Indo-European language would have been lost, absorbed by the indigenous languages (=> see How did the Basques become R1b?).” ref
“Martiniano et al. (2017) sequenced the genomes of various skeletons from West Iberia dating from the Middle and Late Neolithic, Chalcolithic and Middle Bronze Age (since the Early Bronze Age did not reach that region). They found that Neolithic and Chalcolithic individuals belonged to Y-haplogroups I*, I2a1, and G2a. In contrast, all three Bronze Age Portuguese men tested belonged to R1b (one M269 and two P312), although they carried Neolithic Iberian maternal lineages (H1, U5b3, X2b) and lacked any discernible Steppe admixture. This is concordant with a scenario of Indo-European R1b men entering Iberia from 1800 BCE as a small group of adventurers and taking local wives, thus diluting their DNA at each generation, until hardly any Steppe admixture was left after a few centuries, by the time they reached Portugal. Nowadays, Spaniards and Portuguese do possess about 25% of Steppe admixture, which means that other more important Indo-European migrations took place later on, during the Late Bronze Age and the Iron Age.” ref
“Iberia did not become a fully-fledged Bronze Age society until the 13th century BCE, when the Urnfield culture (1300-1200 BCE) expanded from Germany to Catalonia via southern France, then the ensuing Hallstatt culture (1200-750 BCE) spread throughout most of the peninsula (especially the western half). This period belongs to the wider Atlantic Bronze Age (1300-700 BCE), when Iberia was connected to the rest of Western Europe through a complex trade network.” ref
“It is hard to say when exactly DF27 entered Iberia. Considering its overwhelming presence in the peninsula and in south-west France, it is likely that DF27 arrived early, during the 1800 to 1300 BCE period, and perhaps even earlier, if R1b adventurers penetrated the Bell Beaker culture, as they appear to have done all over Western Europe from 2300 BCE to 1800 BCE. The Atlantic Bronze Age could correspond to the period when DF27 radiated more evenly around Iberia and ended up, following Atlantic trade routes, all the way to the British Isles, the Netherlands, and Scandinavia.” ref
The Italo-Celtic branch (S28/U152/PF6570) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“Furtwängler et al. (2020) analyzed 96 ancient genomes from Switzerland, Southern Germany, and the Alsace region in France, covering the Middle/Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age. They confirmed that R1b arrived in the region during the transitory Bell Beaker period (2800-1800 BCE). The vast majority of Bell Beaker R1b samples belonged to the U152 > L2 clade (11 out of 14; the other being P312 or L51).” ref
“Starting circa 1300 BCE, a new Bronze Age culture flourished around the Alps thanks to the abundance of metal in the region, and laid the foundation for the classical Celtic culture. It was actually the succession of three closely linked culture: the Urnfield culture, which would evolve into the Hallstatt culture (from 1200 BCE) and eventually into the La Tène culture (from 450 BCE). After the Unetice expansion to Western Europe between 2300 and 1800 BCE, the Urnfield/Hallstatt/La Tène period represents the second major R1b expansion that took place from Central Europe, pushing west to the Atlantic, north to Scandinavia, east to the Danubian valley, and eventually as far away as Greece, Anatolia, Ukraine and Russia, perhaps even until the Tarim basin in north-west China (=> see Tarim mummies.” ref
“R1b-U152 would have entered Italy in successive waves from the northern side of the Alps, starting in 1700 BCE with the establishment of the Terramare culture in the Po Valley. From 1200 BCE, a larger group of Hallstatt-derived tribes founded the Villanova culture (see below). This is probably the migration that brought the Italic-speaking tribes to Italy, who would have belonged mainly the Z56 clade of R1b-U152. During the Iron Age, the expansion of the La Tène culture from Switzerland is associated with the diffusion of the Z36 branch, which would generate the Belgae around modern Belgium and in the Rhineland, the Gauls in France, and the Cisalpine Celts in Italy.” ref
“Antonio et al. (2019) analysed the genomes of Iron Age Latins dating between 900 and 200 BCE, and the samples tested belonged primarily to haplogroup R1b-U152 (including the clades L2, Z56 and Z193), as well as one R1b-Z2103 and one R1b-Z2118. One common linguistic trait between Italic and Gaulish/Brythonic Celtic languages linked to the Hallstatt expansion is that they shifted the original IE *kw sound into *p.” ref
They are known to linguists as the P-Celtic branch (as opposed to Q-Celtic). It is thought that this change occurred due to the inability to pronounce the *kw sound by the pre-Indo-European population of Central Europe, Gaul, and Italy, who were speakers of Afro-Asiatic dialects that had evolved from Near-Eastern languages inherited from the Neolithic. The Etruscans, although later incomers from the eastern Mediterranean, also fit in this category. It has recently been acknowledged that Celtic languages borrowed part of their grammar from Afro-Asiatic languages.” ref
“This shift could have happened when the Proto-Italo-Celtic speakers moved from the steppes to the Danube basin and mixed with the population of Near-Eastern farmers belonging to haplogroups E1b1b, G2a, J, and T. However, such an early shift would not explain why Q-Celtic and Germanic languages did not undergo the same linguistic mutation. It is therefore more plausible that the shift happened after the Proto-Italo-Celts and Proto-Germanics had first expanded across all western and northern Europe. The S28/U152 connection to P-Celtic (and Italic) suggests that the shift took place around the Alps after 1800 BCE, but before the invasion of Italy by the Italic tribes circa 1200 BCE.” ref
“The expansion of the Urnfield/Hallstatt culture to Italy is evident in the form of the Villanovan culture (c. 1100-700 BCE), which shared striking resemblances with the Urnfield/Hallstatt sites of Bavaria and Upper Austria. The Villanova culture marks a clean break with the previous Terramare culture. Although both cultures practiced cremation, whereas Terramare people placed cremated remains in communal ossuaries like their Neolithic ancestors from the Near East, Villanovans used distinctive Urnfield-style double-cone shaped funerary urns, and elite graves containing jewelry, bronze armor and horse harness fittings were separated from ordinary graves, showing for the first time the development of a highly hierarchical society, so characteristic of Indo-European cultures.” ref
“Quintessential Indo-European decorations, such as swastikas, also make their appearance. Originally a Bronze-age culture, the Villanova culture introduced iron working to the Italian peninsula around the same time as it appeared in the Hallstatt culture, further reinforcing the link between the two cultures. In all likelihood, the propagation of the Villanova culture represents the Italic colonization of the Italian peninsula. The highest proportion of R1b-U152 is found precisely where the Villanovans were the more strongly established, around modern Tuscany and Emilia-Romagna. The Villanova culture was succeeded by the Etruscan civilisation, which displayed both signs of continuity with Villanova and new hybrid elements of West Asian origins, probably brought by Anatolian settlers (who would have belonged to a blend of haplogroups G2a, J2, and R1b-Z2103).” ref
The Germanic branch (S21/U106/M405) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The principal Proto-Germanic branch of the Indo-European family tree is R1b-S21 (a.k.a. U106 or M405). This haplogroup is found at high concentrations in the Netherlands and north-west Germany. It is likely that R1b-S21 lineages expanded in this region through a founder effect during the Unetice period, then penetrated into Scandinavia around 1700 BCE (probably alongside R1a-L664), thus creating a new culture, that of the Nordic Bronze Age (1700-500 BCE). R1b-S21 would then have blended for more than a millennium with preexisting Scandinavian populations, represented by haplogroups I1, I2-L801, R1a-Z284. When the Germanic Iron Age started c. 500 BCE, the Scandinavian population had developed a truly Germanic culture and language, but was divided in many tribes with varying levels of each haplogroup. R1b-S21 became the dominant haplogroup among the West Germanic tribes, but remained in the minority against I1 and R1a in East Germanic and Nordic tribes, including those originating from Sweden such as the Goths, the Vandals, and Lombards.” ref
“The presence of R1b-S21 in other parts of Europe can be attributed almost exclusively to the Germanic migrations that took place between the 3rd and the 10th century. The Frisians and Anglo-Saxons disseminated this haplogroup to England and the Scottish Lowlands, the Franks to Belgium and France, the Burgundians to eastern France, the Suebi to Galicia, and northern Portugal, and the Lombards to Austria and Italy. The Goths help propagate S21 around Eastern Europe, but apparently their Germanic lineages were progressively diluted by blending with Slavic and Balkanic populations, and their impact in Italy, France, and Spain was very minor. Later the Danish and Norwegian Vikings have also contributed to the diffusion of R1b-S21 (alongside I1, I2b1, and R1a) around much of Western Europe, but mainly in Iceland, in the British Isles, in Normandy, and in the southern Italy.” ref
“From the Late Middle Ages until the early 20th century, the Germans expanded across much of modern Poland, pushing as far as Latvia to the north-east and Romania to the south-east. During the same period the Austrians built an empire comprising what is now the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Serbia, and parts of Romania, western Ukraine, and southern Poland. Many centuries of German and Austrian influence in central and Eastern Europe resulted in a small percentage of Germanic lineages being found among modern populations. In Romania 4% of the population still consider themselves German. The low percentage of R1b-S21 in Finland, Estonia, and Latvia can be attributed to the Swedish or Danish rule from the late Middle Ages to the late 19th century.” ref
“O’Sullivan et al. (2018) tested the genomes of Merovingian nobles from an early Medieval Alemannic graveyard in Baden-Württemberg. Apart from one individual belonging to haplogroup G2a2b1, all men were members of R1b, and all samples that yielded deep clade results fell under the R1b-U106 > Z381 > Z301 > L48 > Z9 > Z325 clade. The lineage of the Kings of France was inferred from the Y-DNA of several descendant branches (see famous members below) and also belongs to R1b-U106 > Z381. Their earliest-known male-line ancestor was from Robert II, Count of Hesbaye, a Frankish nobleman from present-day Belgium. The House of Wettin (see famous members below), one of the oldest dynasties in Europe, which ruled over many states at various times in history, was yet another well-known noble Germanic lineage part of R1b-U106 > Z381.” ref
How did R1b come to replace most of the older lineages in Western Europe?
“Until recently it was believed that R1b originated in Western Europe due to its strong presence in the region today. The theory was that R1b represented the Paleolithic Europeans (Cro-Magnon) that had sought refuge in the Franco-Cantabrian region at the peak of the last Ice Age, then recolonised Central and Northern Europe once the ice sheet receded. The phylogeny of R1b proved that this scenario was not possible, because older R1b clades were consistently found in Central Asia and the Middle East, and the youngest in Western and Northern Europe. There was a clear gradient from East to West tracing the migration of R1b people (see map above). This age of the main migration from the shores of the Black Sea to Central Europe also happened to match the timeframe of the Indo-European invasion of Europe, which coincides with the introduction of the Bronze-Age culture in Western Europe, and the proliferation of Italo-Celtic and Germanic languages.” ref
“Historians and archeologists have long argued whether the Indo-European migration was a massive invasion, or rather a cultural diffusion of language and technology spread only by a small number of incomers. The answer could well be “neither”. Proponents of the diffusion theory would have us think that R1b is native to Western Europe, and R1a alone represents the Indo-Europeans. The problem is that haplogroup R did arise in Central Asia, and R2 is still restricted to Central and South Asia, while R1a and the older subclades of R1b are also found in Central Asia. The age of R1b subclades in Europe coincides with the Bronze-Age. R1b must consequently have replaced most of the native Y-DNA lineages in Europe from the Bronze-Age onwards.” ref
“However, a massive migration and nearly complete annihilation of the Paleolithic population can hardly be envisaged. Western Europeans do look quite different in Ireland, Holland, Aquitaine, or Portugal, despite being all regions where R1b is dominant. Autosomal DNA studies have confirmed that the Western European population is far from homogeneous. A lot of maternal lineages (mtDNA) also appear to be of Paleolithic origin (e.g. H1, H3, U5, or V) based on ancient DNA tests. What a lot of people forget is that there is also no need of a large-scale exodus for patrilineal lineages to be replaced fairly quickly. Here is why.” ref
- “Polygamy. Unlike women, men are not limited in the number of children they can procreate. Men with power typically have more children. This was all the truer in primitive societies, where polygamy was often the norm for chieftains and kings.
- Status & Power. Equipped with Bronze weapons and horses, the Indo-Europeans would have easily subjugated the Neolithic farmers and with even greater ease Europe’s last hunter-gatherers. If they did not exterminate the indigenous men, the newcomers would have become the new ruling class, with a multitude of local kings, chieftains, and noblemen (Bronze-Age Celts and Germans lived in small village communities with a chief, each part of a small tribe headed by a king) with higher reproductive opportunities than average.
- Gender imbalance. Invading armies normally have far more men than women. Men must therefore find women in the conquered population. Wars are waged by men, and the losers suffer heavier casualties, leaving more women available to the winners.
- Aggressive warfare. The Indo-Europeans were a warlike people with a strong heroic code emphasizing courage and military prowess. Their superior technology (metal weapons, wheeled vehicles drawn by horses) and attitude to life would have allowed them to slaughter any population that did not have organized armies with metal weapons (i.e. anybody except the Middle-Eastern civilizations).
- Genetic predisposition to conceive boys. The main role of the Y-chromosome in man’s body is to create sperm. Haplogroups are determined based on mutations differentiating Y-chromosomes. Each mutation is liable to affect sperm production and sperm motility. Preliminary research has already established a link between certain haplogroups and increased or reduced sperm motility. The higher the motility, the higher the chances of conceiving a boy. It is absolutely possible that R1b could confer a bias toward more male offspring. Even a slightly higher percentage of male births would significantly contribute to the replacement of other lineages with the accumulation effect building up over a few millennia. Not all R1b subclades might have this boy bias. The bias only exist in relation to other haplogroups found in a same population. It is very possible that the fairly recent R1b subclades of Western Europe had a significant advantage compared to the older haplogroups in that region, notably haplogroup I2 and E-V13. Read more” ref
“Replacement of patrilineal lineages following this model quickly becomes exponential. Imagine 100 Indo-European men conquering a tribe of 1000 indigenous Europeans (a ratio of 1:10). War casualties have resulted in a higher proportion of women in the conquered population. Let’s say that the surviving population is composed of 700 women and 300 men. Let’s suppose that the victorious Indo-European men end up having twice as many children reaching adulthood as the men of the vanquished tribe. There is a number of reason for that. The winners would take more wives, or take concubines, or even rape women of the vanquished tribe. Their higher status would guarantee them greater wealth and therefore better nutrition for their offspring, increasing the chances of reaching adulthood and procreating themselves.” ref
“An offspring ratio of 2 to 1 for men is actually a conservative estimate, as it is totally conceivable that Bronze-Age sensibilities would have resulted in killing most of the men on the losing side, and raping their women (as attested by the Old Testament). Even so, it would only take a few generations for the winning Y-DNA lineages to become the majority. For instance, if the first generation of Indo-Europeans had two surviving sons per man, against only one per indigenous man, the number of Indo-European paternal lineages would pass to 200 individuals at the second generation, 400 at the third, 800 at the fourth, and 1600 at the fifth, and so on. During that time indigenous lineages would only stagnate at 300 individuals for each generation.” ref
“Based on such a scenario, the R1b lineages would have quickly overwhelmed the local lineages. Even if the Indo-European conquerors had only slightly more children than the local men, R1b lineages would become dominant within a few centuries. Celtic culture lasted for over 1000 years in Continental Europe before the Roman conquest putting an end to the privileges of the chieftains and nobility. This is more than enough time for R1b lineages to reach 50 to 80% of the population.” ref
“The present-day R1b frequency forms a gradient from the Atlantic fringe of Europe (highest percentage) to Central and Eastern Europe (lowest), the rises again in the Anatolian homeland. This is almost certainly because agriculture was better established in Eastern, then Central Europe, with higher densities of population, leaving R1b invaders more outnumbered than in the West. Besides, other Indo-Europeans of the Corded Ware culture (R1a) had already advanced from modern Russia and Ukraine as far west as Germany and Scandinavia. It would be difficult for R1b people to rival with their R1a cousins who shared similar technology and culture. The Pre-Celto-Germanic R1b would therefore have been forced to settled further west, first around the Alps, then overtaking the then sparsely populated Western Europe.” ref
The Balkanic and Asian branch (Z2103) corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“Haak et al. (2015) tested six Y-DNA samples from the eastern reaches of Yamna culture, in the Volga-Ural region, and all of them turned out to belong to haplogroup R1b. Four of them were positive for the Z2103 mutation. IN all likelihood, R1b-Z2103 was a major lineage of the Poltavka culture, which succeeded to the Yamna culture between the Volga River and the Ural mountains. It eventually merged with the Abashevo culture (presumably belonging chiefly to R1a-Z93) to form the Sintashta culture. Through a founder effect or through political domination, R1a-Z93 lineages would have outnumbered R1b-Z2103 after the expansion to Central and South Asia, although important pockets of Z2103 survived, notably in Bashkorostan, Turkmenistan, and Uyghurstan (Chinese Turkestan).” ref
“R1b-Z2103 would have become an Indo-Iranian lineage like R1a-Z93. This is true of two Z2103 subclades in particular: L277.1 and L584. The former is found in Russia to Central Asia then to India and the Middle East, just like the R1a-L657 subclade of Z93. It can be associated with the Andronovo culture and Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex, as well as the Indo-Aryan migrations. R1b-L584 is found especially in Iran, northern Iraq, the South Caucasus, and Turkey, and correlates more with the Iranian branch of Indo-Europeans, which includes Persians, Kurds, and Scythians.” ref
Anatolian branch corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“The Hittites (c. 2000-1178 BCE) were the first Indo-Europeans to defy (and defeat) the mighty Mesopotamian and Egyptian empires. There are two hypotheses regarding the origins of the Hittites. The first is that they came from the eastern Balkans and invaded Anatolia by crossing the Bosphorus. That would mean that they belonged either to the L23* or the Z2103 subclade. The other plausible scenario is that they were an offshoot of the late Maykop culture, and that they crossed the Caucasus to conquer the Hattian kingdom (perhaps after being displaced from the North Caucasus by the R1a people of the Catacomb culture). In that case, the Hittites might have belonged to the R1b-Z2103 or the R1b-PF7562 subclade. The first hypothesis has the advantage of having a single nucleus, the Balkans, as the post-Yamna expansion of all Indo-European R1b. The Maykop hypothesis, on the other hand, would explain why the Anatolian branch of IE languages (Hittite, Luwian, Lydian, Palaic) is so archaic compared to other Indo-European languages, which would have originated in Yamna rather than Maykop.” ref
“There is substantial archaeological and linguistic evidence that Troy was an Indo-European city associated with the Steppe culture and haplogroup R1b. The Trojans were Luwian speakers related to the Hittites (hence Indo-European), with attested cultural ties to the culture of the Pontic-Caspian Steppe. The first city of Troy dates back to 3000 BCE, right in the middle of the Maykop period. Troy might have been founded by Maykop people as a colony securing the trade routes between the Black Sea and the Aegean. The founding of Troy happens to coincide exactly with the time the first galleys were made. Considering the early foundation of Troy, the most likely of the two Indo-European paternal haplogroups would be R1b-M269 or L23.” ref
“The Phrygians and the Proto-Armenians are two other Indo-European tribes stemming from the Balkans. Both appear to have migrated to Anatolia around 1200 BCE, during the ‘great upheavals’ of the Eastern Mediterranean (see below). The Phrygians (or Bryges) founded a kingdom (1200-700 BCE) in west central Anatolia, taking over most of the crumbling Hittite Empire. The Armenians crossed all Anatolia until Lake Van and settled in the Armenian Highlands. Nowadays 30% of Armenian belong to haplogroup R1b, the vast majority to the L584 subclade of Z2103 (=> see The Indo-European migrations to Armenia).” ref
“Most of the R1b found in Greece today is of the Balkanic Z2103 variety. There is also a minority of Proto-Celtic S116/P312 and of Italic/Alpine Celtic S28/U152. Z2103 could have descended from Albania or Macedonia during the Dorian invasion (see below), thought to have happened in the 12th century BCE. Their language appears to have been close enough to Mycenaean Greek to be mutually intelligible and easy for locals to adopt. The Mycenaeans might have brought some R1b (probably also Z2103) to Greece, but their origins can be traced back through archaeology to the Catacomb culture and the Seima-Turbino phenomenon of the northern forest-steppe, which would make them primarily an R1a tribe.” ref
“Greek and Anatolian S116 and some S28 lineages could be attributed to the La Tène Celtic invasions of the 3rd century BCE. The Romans also certainly brought S28 lineages (=> see Genetics of the Italian people), and probably also the Venetians later on, notably on the islands. Older clades of R1b, such as P25 and V88, are only a small minority and would have come along E1b1b, G2a, and J2 from the Middle East.” ref
The great upheavals circa 1200 BCE corresponding to haplogroup R1b
“1200 BCE was a turning point in European and Near-Eastern history. In Central Europe, the Urnfield culture evolved into the Hallstatt culture, traditionally associated with the classical Celtic civilization, which was to have a crucial influence on the development of ancient Rome. In the Pontic Steppe, the Srubna culture make way to the Cimmerians, a nomadic people speaking an Iranian or Thracian language. The Iron-age Colchian culture (1200-600 BCE) starts in the North Caucasus region. Its further expansion to the south of the Caucasus corresponds to the first historical mentions of the Proto-Armenian branch of Indo-European languages (circa 1200 BCE). In the central Levant the Phoenicians start establishing themselves as significant maritime powers and building their commercial empire around the southern Mediterranean.” ref
“But the most important event of the period was incontestably the destruction of the Near-Eastern civilizations, possibly by the Sea Peoples. The great catastrophe that ravaged the whole Eastern Mediterranean from Greece to Egypt circa 1200 BCE is a subject that remains controversial. The identity of the Sea Peoples has been the object of numerous speculations. What is certain is that all the palace-based societies in the Near-East were abruptly brought to an end by tremendous acts of destruction, pillage, and razing of cities. The most common explanation is that the region was invaded by technologically advanced warriors from the north. They could have been either Indo-Europeans descended from the Steppe via the Balkans, or Caucasian people (G2a, J1, J2a, T1a) linked with the expansion of the earlier Kura-Araxes culture to eastern Anatolia and the Levant.” ref
“The Hittite capital Hattusa was destroyed in 1200 BCE, and by 1160 BCE the empire had collapsed, probably under the pressure of the Phrygians and the Armenians coming from the Balkans. The Mycenaean cities were ravaged and abandoned throughout the 12th century BCE, leading to the eventual collapse of Mycenaean civilization by 1100 BCE. The kingdom of Ugarit in Syria was annihilated and its capital never resettled. Other cities in the Levant, Cyprus, and Crete were burned and left abandoned for many generations. The Egyptians had to repel assaults from the Philistines from the East and the Libyans from the West – two tribes of supposed Indo-European origin. The Lybians were accompanied by mercenaries from northern lands (the Ekwesh, Teresh, Lukka, Sherden, and Shekelesh), whose origin is uncertain, but has been placed in Anatolia, Greece, and/or southern Italy.” ref
“The devastation of Greece followed the legendary Trojan War (1194-1187 BCE). It has been postulated that the Dorians, an Indo-European people from the Balkans (probably coming from modern Bulgaria or Macedonia), invaded a weakened Mycenaean Greece after the Trojan War, and finally settled in Greece as one of the three major ethnic groups. The Dorian regions of classical Greece, where Doric dialects were spoken, were essentially the southern and eastern Peloponnese, Crete, and Rhodes, which is also the part of Greece with the highest percentage of R1b-Z2103.” ref
“Another hypothesis is that the migration of the Illyrians from north-east Europe to the Balkans displaced previous Indo-European tribes, namely the Dorians to Greece, the Phrygians to north-western Anatolia, and the Libu to Libya (after a failed attempt to conquer the Nile Delta in Egypt). The Philistines, perhaps displaced from Anatolia, finally settled in Palestine around 1200 BCE, unable to enter Egypt.” ref
Other migrations of R1b
“Other migrations occurred from Europe to the Near East and Central Asia during the Antiquity and Middle Ages. R1b-S28 (U152) was found in Romania, Turkey, northern Bashkortostan (a staggering 71.5% of the local population according to Myres et al.), and at the border of Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan. Some of it was surely brought by the La Tène Celts, known to have advanced along the Danube, and created the Galatian kingdom in central Anatolia. The rest could just as well be Roman, given that R1b-S28 is the dominant form of R1b in the Italian peninsula.” ref
“Some have hypothesized that some “lost” Roman legions went as far as Central Asia or China and never came back, marrying local women and leaving their genetic marker in isolated pockets in Asia. A more prosaic version is that Roman merchants ended up in China via the Silk Road, which existed since the 2nd century BCE. A small percentage of Western European R1b subclades were also found among Christian communities in Lebanon. They are most likely descendants of the crusaders.” ref
The lactase persistence allele and R1b cattle pastoralists
“Lactose (milk sugar) is an essential component of breast milk consumed by infants. Its digestion is made possible by an enzyme, called lactase, which breaks down lactose in simple sugars that can be absorbed through the intestinal walls and into the bloodstream. In most mammals (humans included), the production of the lactase enzyme is dramatically reduced soon after weaning. As a result, older children and adults become lactose intolerant. That is true of a big part of the world population. Some people possess a genetic mutation that allows the production of lactase through adulthood. This is called lactase persistence (LP). Lactase persistence is particularly common among Northwest Europeans, descended from the ancient Celtic and Germanic people, and in parts of Africa where cattle herding has been practiced for thousands of years. The highest incidence for the lactase persistence alleles, known to geneticists as -13,910*T (rs4988235) and -22018*A (rs182549), are found among Scandinavian, Dutch, British, Irish, and Basque people. Sub-Saharan populations with lactase persistence have different mutations, such as -14010*C, -13915*G, and -13907*G.” ref
“R1b men are thought to be the first people on earth to successfully domesticate cattle and to develop a lifestyle based on cattle husbandry and herding during the Pre-Pottery Neolithic (see Neolithic section). Looking for pasture for their cows, R1b tribes migrated from the Near East to the savannah of North Africa (which has since underwent desertification and become the Sahara) and to the Pontic Steppe in southern Russia and Ukraine. For several millennia no other human population was so dependent on cattle for their survival as these R1b tribes.” ref
“It is known that most Neolithic herding societies consumed at least some animal milk and even made cheese from it (since cheese contains less lactose and is easier to digest for people who are lactose intolerant). In most of Europe, the Middle East, and South Asia, people essentially herded goats and sheep, better suited to mountainous environment of the Mediterranean basin, Anatolia, and Iran. Goats and sheep could also be kept easily inside villages by sedentary cereal cultivators, while cows needed vast pastures for grazing, which were particularly scarce in the Middle East. Domesticated cattle were sometimes found in small number among other Neolithic populations, but the ones that relied almost entirely on them were the R1b tribes of the Pontic Steppe and North Africa. To this very day, semi-nomadic pastoralists in the Sahel, such as the Fulani and the Hausa, who are descended from Neolithic R1b-V88 migrants from the Near East, still maintain primarily herds of cattle. It is among these cattle herders that selective pressure for lactase persistence would have been the strongest.” ref
“There has been speculations among geneticists and evolutionary biologists regarding the origin of the lactase persistence allele in Europeans. Over 100 ancient DNA samples have been tested from Mesolithic, Neolithic, and Bronze Age Europe and Syria, and the -13910*T allele has been found only in Late Neolithic/Chalcolithic and Bronze Age individuals. The origin of the mutation does not really matter, since it could have been present at low frequencies in the human gene pool for tens of thousands of years before it underwent postive selective pressure among cattle-herding societies. What is certain is that individuals from Bronze Age cultures associated with the arrival of Indo-European speakers from the Pontic Steppe already possessed relatively high percentages of the LP allele. For example, the LP allele was found at a frequency of 27% (see Schilz 2006) among the 13 individuals from the Lichtenstein Cave in Germany, who belonged to the Urnfield culture, and were a mix of Y-haplogroups R1b, R1a, and I2a2b.” ref
“Nowadays, the LP allele is roughly proportional to the percentage of R1b, and to a lower extent R1a, found in a population. In the British Isles, the Low Countries and south-west Scandinavia, where LP is the highest in the world, the combined percentage of R1a and R1b exceeds 70% of the population. In Iberia, the highest percentage of LP is observed among the Basques, who have the highest percentage of R1b. In Italy, LP is most common in the north, like R1b. The lowest incidence of LP in Europe are found in South Italy, Greece, and the Balkans, the regions that have the least R1b lineages.” ref
“Tishkoff et al. (2017) confirmed that the Hausa and the Fulani, two Sahel tribes with high incidence of R1b-V88, possessed the same LP allele as Europeans, but that East African pastoralist populations with a high prevalence of the lactase persistence trait possess a completely different mutation, which arose independently. This finding is the strongest evidence so far that the -13,910*T allele originated with the first R1b cattle herders in the Near East, who are the ancestors of both the Indo-Europeans and of African R1b-V88 tribes.” ref
R1 populations spread genes for light skin, blond hair, and red hair
“There is now strong evidence that both R1a and R1b people contributed to the diffusion of the A111T mutation of the SLC24A5, which explains approximately 35% of skin tone difference between Europeans and Africans, and most variations within South Asia. The distribution pattern of the A111T allele (rs1426654) of matches almost perfectly the spread of Indo-European R1a and R1b lineages around Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia, and South Asia. The mutation was probably passed on in the Early neolithic to other Near Eastern populations, which explains why Neolithic farmers in Europe already carried the A111T allele (e.g. Keller 2012 p.4, Lazaridis 2014 suppl. 7), although at lower frequency than modern Europeans and southern Central Asians.” ref
“The light skin allele is also found at a range of 15 to 30% in various ethnic groups in northern sub-Saharan Africa, mostly in the Sahel and savannah zones inhabited by tribes of R1b-V88 cattle herders like the Fulani and the Hausa. This would presuppose that the A111T allele was already present among all R1b people before the Pre-Pottery Neolithic split between V88 and P297. R1a populations have an equally high incidence of this allele as R1b populations. On the other hand, the A111T mutation was absent from the 24,000-year-old R* sample from Siberia, and is absent from most modern R2 populations in Southeast India and Southeast Asia.” ref
“Consequently, it can be safely assumed that the mutation arose among the R1* lineage during the late Upper Paleolithic, probably some time between 20,000 and 13,000 years ago. Fair hair was another physical trait associated with the Indo-Europeans. In contrast, the genes for blue eyes were already present among Mesolithic Europeans belonging to Y-haplogroup I. The genes for blond hair are more strongly correlated with the distribution of haplogroup R1a, but those for red hair have not been found in Europe before the Bronze Age, and appear to have been spread primarily by R1b people (=> see The origins of red hair).” ref
What were the original mtDNA lineages of Neolithic R1b tribes in the Near East?
“R1b tribes are thought to have domesticated cattle in that region 10,500 years ago, yet only moved across the Caucasus some time between 7,500 and 6,500 years ago. For three or four millennia, semi-nomadic R1b herders were bound to have intermingled with some of the Near Eastern or Caucasian neighbors. One way of determining what mt-haplogroups R1b tribes carried at the very beginning of the Neolithic, is to compare the above haplogroups with those of African ethnic groups known to possess elevated percentages of R1b-V88. The best studied group are the Fulani, whose mtDNA includes three European-looking haplogroups H, J1b1a, U5, and V making up about 15% of their total maternal lineages.” ref
“These haplogroups have been identified in all four Central African countries sampled, confirming a strong correlation with haplogroup R1b. However, their H, V, and U5 could have come from the Berbers of Northwest Africa. The Berbers also carry R1b-V88, but it’s possible that some of it came from different Neolithic migrations, including a re-expansion from Iberia, as Berbers carry H1, H3, V1a1a, V5, and U5b1b1, lineages that are all found in the Iberian peninsula. U5b1b1 descends from Mesolithic West Europeans, but at present, it is not yet clear how the other haplogroups reached Iberia or Northwest Africa. One hypothesis is that they came from the Near East during the Neolithic, perhaps with R1b-V88 tribes.” ref
“African R1b-V88 and Eurasian haplogroup R1b-P297 split roughly 10,000 years ago, almost certainly in Eastern Europe, where they carried mostly mt-haplogroup U5. Toward the end of the last glaciation, some R1b men would have migrated from Eastern Europe to the region of modern Kurdistan accompanied by women belonging to mtDNA U5. Soon after they arrived J1b1a (and maybe V) would have been the first indigenous Near Eastern lineages assimilated by R1b tribes. R1b-V88 might have assimilated H1 and H3 women in the Levant before moving to North Africa, but that remains highly hypothetical.” ref
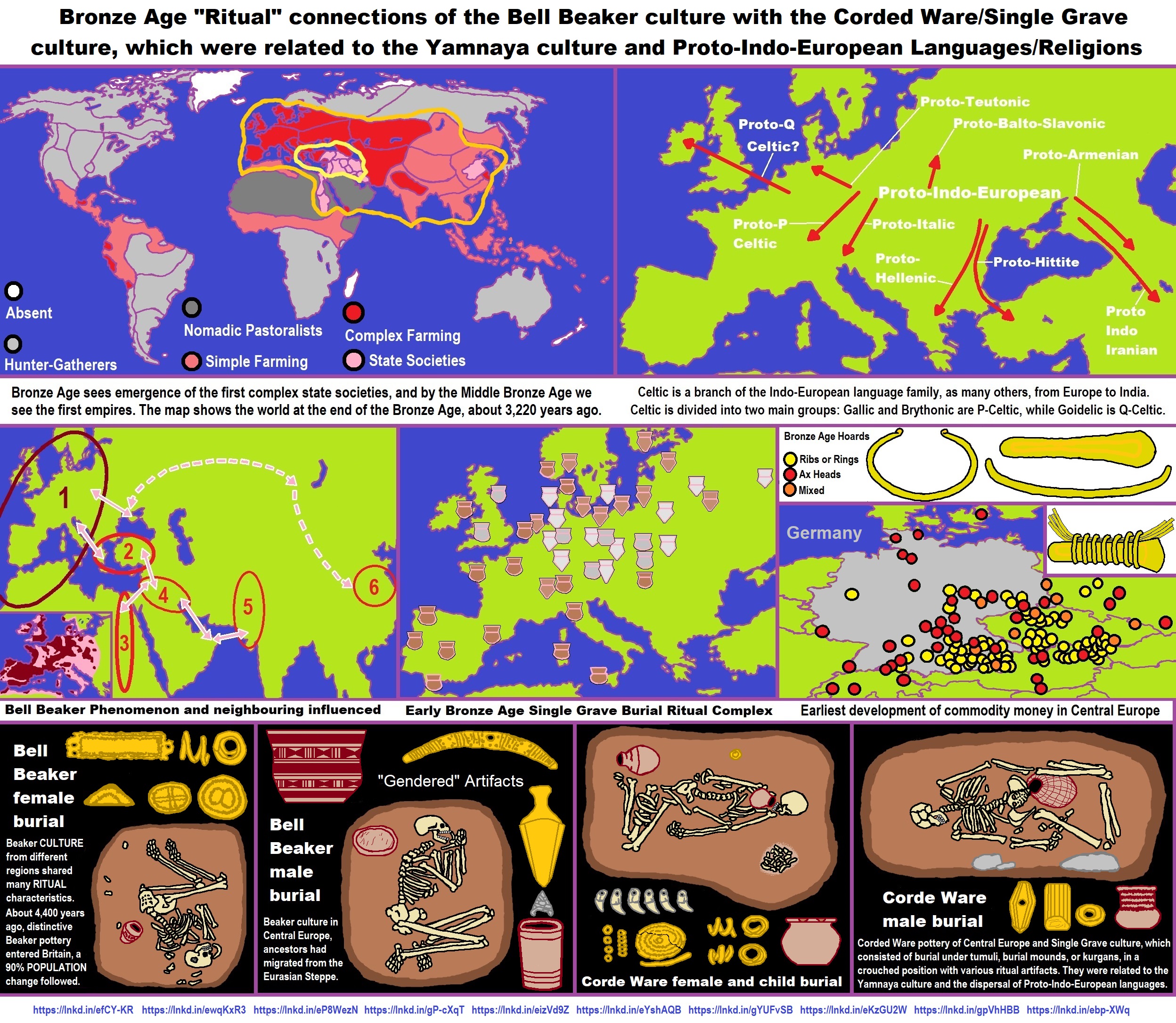
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Proto-Indo-European society
“Proto-Indo-European society is the reconstructed culture of Proto-Indo-Europeans, the ancient speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language, ancestor of all modern Indo-European languages. Archaeologist David W. Anthony and linguist Donald Ringe distinguish three different cultural stages in the evolution of the Proto-Indo-European language:
- Early (4500–4000 BCE), the common ancestor of all attested Indo-European languages, before the Anatolian split (Cernavodă culture; 4000 BCE); associated with the early Khvalynsk culture,
- Classic, or “post-Anatolian” (4000–3500 BCE), the last common ancestor of the non-Anatolian languages, including Tocharian; associated with the late Khvalynsk and Repin cultures,
- Late (3500–2500 BCE), in its dialectal period due to the spread of the Yamnaya horizon over a large area.” ref
Early Khvalynsk (4900–3900) and Proto-Indo-European society
“Domesticated cattle were introduced around 4700 BCE from the Danube valley to the Volga–Ural steppes where the Early Khvalynsk culture (4900–3900 BCE) had emerged, associated by Anthony with the Early Proto-Indo-European language. Cattle and sheep were more important in ritual sacrifices than in diet, suggesting that a new set of cults and rituals had spread eastward across the Pontic-Caspian steppes, with domesticated animals at the root of the Proto-Indo-European conception of the universe. Anthony attributes the first and progressive domestication of horses, from taming to actually working with the animal, to this period. Between 4500–4200 BCE, copper, exotic ornamental shells, and polished stone maces were exchanged across the Pontic–Caspian steppes from Varna, in the eastern Balkans, to Khvalynsk, near the Volga river. Around 4500, a minority of richly decorated single graves, partly enriched by imported copper items, began to appear in the steppes, contrasting with the remaining outfitted graves.” ref
“The Anatolian distinctive sub-family may have emerged from a first wave of Indo-European migration into southeastern Europe around 4200–4000 BCE, coinciding with the Suvorovo–to–Cernavoda I migration, in the context of a progression of the Khvalynsk culture westwards towards the Danube area, from which had also emerged the Novodanilovka (4400–3800) and Late Sredny Stog (4000–3500 BCE) cultures.” ref
Late Khvalynsk/Repin (3900–3300) and Proto-Indo-European society
“Steppe economies underwent a revolutionary change between 4200 to 3300 BCE, in a shift from a partial reliance on herding, when domesticated animals were probably used principally as a ritual currency for public sacrifices, to a later regular dietary dependence on cattle, and either sheep or goat meat and dairy products. The Late Khvalynsk and Repin cultures (3900–3300 BCE), associated with the classic (post-Anatolian) Proto-Indo-European language, showed the first traces of cereal cultivation after 4000 BCE, in the context of a slow and partial diffusion of farming from the western parts of the steppes to the east. Around 3700–3300 BCE, a second migration wave of proto-Tocharian speakers towards South Siberia led to the emergence of the Afanasievo culture (3300–2500 BCE).” ref
“The spoke-less wheeled wagon was introduced to the Pontic-Caspian steppe around 3500 BCE from the neighboring North Caucasian Maykop culture (3700–3000 BCE), with which Proto-Indo-Europeans traded wool and horses. Interactions with the hierarchical Maykop culture, itself influenced by the Mesopotamian Uruk culture, had notable social effects on the Proto-Indo-European way of life. Meanwhile, the Khvalynsk-influenced cultures that had emerged in the Danube-Donets region after the first migration gave way to the Cernavodă (4000–3200 BCE), Usatovo (3500–2500 BCE), Mikhaylovka (3600–3000 BCE) and Kemi Oba (3700—2200 BCE) cultures, from west to east respectively.” ref
Yamnaya period (3300–2600) and Proto-Indo-European society
“The Yamnaya horizon, associated with the Late Proto-Indo-European language (following both the Anatolian and Tocharian splits), originated in the Don–Volga region before spreading westwards after 3300 BCE, establishing a cultural horizon founded on kurgan funerals that stretched over a vast steppe area between the Dnieper and Volga rivers. It was initially a herding-based society, with limited crop cultivation in the eastern part of the steppes, while the Dnieper–Donets region was more influenced by the agricultural Tripolye culture. Paleolinguistics likewise postulates Proto-Indo-European speakers as a semi-nomadic and pastoral population with subsidiary agriculture.” ref
“Bronze was introduced to the Pontic-Caspian steppes during this period. Following the Yamnaya expansion, long-distance trade in metals and other valuables, such as salt in the hinterlands, probably brought prestige and power to Proto-Indo-European societies. However, the native tradition of pottery making was weakly developed. The Yamnaya funeral sacrifice of wagons, carts, sheep, cattle, and horses was likely related to a cult of ancestors requiring specific rituals and prayers, a connection between language and cult that introduced the Late Proto-Indo-European language to new speakers. Yamnaya chiefdoms had institutionalized differences in prestige and power, and their society was organized along patron-client reciprocity, a mutual exchange of gifts and favors between their patrons, the gods, and human clients. The average life expectancy was fairly high, with many individuals living to 50–60 years old. The language itself appeared as a dialect continuum during this period, meaning that neighboring dialects differed only slightly between each other, whereas distant language varieties were probably no longer mutually intelligible due to accumulated divergences over space and time.” ref
“As the steppe became dryer and colder between 3500–3000 BCE, herds needed to be moved more frequently in order to feed them sufficiently. Yamnaya distinctive identity was thus founded on mobile pastoralism, permitted by two earlier innovations: the introduction of the wheeled wagon and the domestication of the horse. Yamnaya herders likely watched over their cattle and raided on horseback, while they drove wagons for the bulk transport of water or food. Light-framework dwellings could be easily assembled and disassembled to be transported on pack animals.” ref
“Another climate change that occurred after around 3000 BCE led to a more favorable environment allowing for grassland productivity. Yamnaya new pastoral economy then experienced a third wave of rapid demographic expansion, that time towards Central and Northern Europe. Migrations of Usatovo people towards southeastern Poland, crossing through the Old European Tripolye culture from around 3300 BCE, followed by Yamnya migrations towards the Pannonian Basin between 3100–2800 BCE, are interpreted by some scholars as movements of pre-Italic, pre-Celtic and pre-Germanic speakers.” ref
“The Proto-Indo-European language probably ceased to be spoken after 2500 BCE as its various dialects had already evolved into non-mutually intelligible languages that began to spread across most of western Eurasia during the third wave of Indo-European migrations (3300–1500 BCE). Indo-Iranian languages were introduced to Central Asia, present-day Iran, and South Asia after 2000 BCE.” ref
Class Structure and Proto-Indo-European society
“It is generally agreed that Proto-Indo-European society was hierarchical, with some form of social ranking and various degrees of social status. It is unlikely however that they had a rigidly stratified structure, or castes such as are found in historical India. There was a general distinction between free persons and slaves, typically prisoners of war or debtors unable to repay a debt. The free part of society was composed of an elite class of priests, kings, and warriors, along with the commoners, with each tribe following a chief (*wiḱpots) sponsoring feasts and ceremonies, and immortalized in praise poetry.” ref
“The presence of kurgan graves prominently decorated with dress, body ornaments, and weaponry, along with well-attested roots for concepts such as “wealth” (*h₂ép-), “to be in need” (*h₁eg-) or “servant” (*h₂entbʰi-kʷolos, “one who moves about on both sides”; and *h₂upo-sth₂-i/o-, “one standing below”), indicate that a hierarchy of wealth and poverty was recognized. Some graves, larger than the average and necessitating a considerable number of people to be built, likewise suggest a higher status given to some individuals. These prestigious funerals were not necessarily reserved to the wealthiest person. Smiths in particular were given sumptuous graves, possibly due to the association of smithery with magic during the early Bronze Age. In general, such graves were mostly occupied by males in the eastern Don-Volga steppes, while they were more egalitarian in the western Dnieper-Donets region.” ref
Kinship and Proto-Indo-European society
“Linguistics has allowed for the reliable reconstruction of a large number of words relating to kinship relations. These all agree in exhibiting a patriarchal, patrilocal and patrilineal social fabric. Patrilocality is confirmed by lexical evidence, including the word *h₂u̯edh-, ‘to lead (away)’, being the word that denotes a male wedding a female. Rights, possessions, and responsibilities were consequently reckoned to the father, and wives were to reside after marriage near the husband’s family, after the payment of a bride-price.” ref
“The household (*domos) was generally ruled by the senior male of the family, the *dems-potis (‘master of the household’), and could also consist of his children, grandchildren, and perhaps unrelated slaves or servants. His wife probably also played a complementary role: some evidence suggest that she would have kept her position as the mistress (*pot-n-ih₂) of the household in the event her husband dies, while the eldest son would have become the new master. The Proto-Indo-European expansionist kinship system was likely supported by both marital exogamy (the inclusion of foreign women through marriage) and the exchange of foster children with other families and clans, as suggested by genetic evidence and later attestations from Indo-European-speaking groups.” ref
“Once established, the family lasted as long as the male stock of its founder endured, and clan or tribal founders were often portrayed as mythical beings stemming from a legendary past in Indo-European traditions. In this form of kinship organization, the individual’s genetic distance from the clan’s founding ancestor determined his social status. But if he was of exceptional prowess or virtue, the same individual could in his turn gain social prestige among the community and eventually found his own descent-group.” ref
“In the reconstructed lexicon linking the individual to the clan, *h₂erós means a ‘member of one’s own group’, ‘one who belongs to the community’ (in contrast to an outsider). It gave way to the Indo-Iranian *árya (an endonym), and probably to the Celtic *aryos (‘noble, freeman’), the Hittite arā- (‘peer, companion’), and the Germanic *arjaz (‘noble, distinguished’). It is unlikely however that the term had an ethnic connotation, and we do not know if Proto-Indo-European speakers had a term to designate themselves as a group. Another word, *h₁leudhos, means ‘people’, ‘freemen’ in a more general way.” ref
Patron-client and Proto-Indo-European society
“Proto-Indo-European had several words for ‘leader’: *tagós was a general term derived from *tā̆g- (‘set in place, arrange’); *h₃rḗǵs meant a ruler who also had religious functions, with the Roman rex sacrorum (‘king of the sacred’) as a heritage of the priestly function of the king; *w(n̩)nákts designated a ‘lord’ and possessed a feminine equivalent, *wnáktih₂ (a ‘queen’); while the *wiḱpots (or *wiḱ-potis) was the chief of the settlement (*weiḱs), the seat of a tribe, clan or family.” ref
“Public feasts sponsored by such patrons were a way for them to promote and secure a political hierarchy built on the unequal mobilization of labor and resources, by displaying their generosity towards the rest of the community. Rivals competed publicly through the size and complexity of their feasts, and alliances were confirmed by gift-giving and promises made during those public gatherings. The host of the feast was called the *ghosti-potis, the ‘lord of the guests’, who honored the immortal gods and his mortal guests with gifts of food, drink, and poetry.” ref
Guest-Host and Proto-Indo-European society
“Vertical social inequalities were partly balanced by horizontal mutual obligations of hospitality between guests and hosts. According to Anthony, the domestication of horses and the introduction of the wagon in the Pontic-Caspian steppe between 4500 to 3500 BCE led to an increase in mobility across the Yamnaya horizon, and eventually to the emergence of a guest-host political structure. As various herding clans began to move across the steppes, especially during harsh seasons, it became necessary to regulate local migrations on the territories of tribes that had likely restricted these obligations to their kins or co-residents (*h₂erós) until then. In Proto-Indo-European, the term *ghós-ti-, whose original meaning must have been “table companion”, could either mean a host or a guest. The connotation of an obligatory reciprocity between both guests and hosts has persisted in descendant cognates, such as Latin hospēs (“foreigner, guest; host”), Old English ġiest (“stranger, guest”), or Old Church Slavonic gostĭ (“guest”) and gospodĭ (“master”).” ref
“Guests and hosts were indeed involved in a mutual and reciprocal relationship bound by oaths and sacrifices. The giving and receiving of favors was accompanied by a set of ritual actions that indebted the guest to show hospitality to his host at any time in the future. The obligation could even be heritable: Homer’s warriors, Glaukos and Diomedes, stopped fighting and presented gifts to each other when they learned that their grandfathers had shared a guest-host relationship. Violations of the guest-host obligations were considered immoral, illegal, and unholy: in Irish law, refusing hospitality was deemed a crime as serious as murder. The killing of a guest was also greeted with a singular revulsion, as was the abuse of hospitality.” ref
Legal System and Proto-Indo-European society
“Because of the archaic nature of traditional legal phraseology—which preserves old forms and meaning for words—and the necessity for legal sentences to be uttered precisely the same way each time to remain binding, it is possible to securely reconstruct some elements of the Proto-Indo-European legal system. For instance, the word *serk– (‘to make a circle, complete’) designated a type of compensation where the father (or master) had to either pay for the damages caused by his son (or slave), or surrender the perpetrator to the offended party. It is attested by a common legal and linguistic origin in both Roman and Hittite laws. Another root denoting a compensation, *kwey-, had the meanings of ‘blood-price‘, ‘vengeance’ or ‘guilt’ in daughter languages, suggesting that it was specifically applied to the restitution for theft or violence.” ref
“Law was apparently designed to preserve the ‘order’ (*h₂értus) of the universe, with the underlying idea that the cosmic harmony should be maintained, be it in the physical universe or the social world. There was however probably no public enforcement of justice, nor were there formal courts as we know them today. Contractual obligations were protected by private individuals acting as sureties: they pledged to be responsible for payments of debts incurred by someone else if the latter defaulted. In case of litigation, one could either take matter into their own hands, for instance by barring someone from accessing their property to compel payment, or bring the case before judges (perhaps kings) that included witnesses. The word for ‘oath’, *óitos, derives from the verb *h₁ei- (‘to go’), after the practice of walking between slaughtered animals as part of taking an oath.” ref
“The root *h₂értus (from *h₂er-, ‘to fit’) is associated with the concept of a cosmic order, that is which is ‘fitting, right, ordered’. It is one of most securely reconstructed Proto-Indo-European words, with cognates attested in most sub-families: Latin artus (‘joint’); Middle High German art (‘innate feature, nature, fashion’); Greek artús (ἀρτύς, ‘arrangement’), possibly arete (ἀρετή, ‘excellence’); Armenian ard (արդ, ‘ornament, shape’); Avestan arəta- (‘order’) and ṛtá (‘truth’); Sanskrit ṛtú- (ऋतु, ‘right time, order, rule’); Hittite āra (????????????, ‘right, proper’); Tocharian A ārt- (‘to praise, be pleased with’).” ref
Trifunctional Hypothesis and Proto-Indo-European society
“The trifunctional hypothesis, proposed by Georges Dumézil, postulates a tripartite ideology reflected in a threefold division between a clerical class (encompassing both the religious and social functions of the priests and rulers), a warrior class (connected with the concepts of violence and braveness), and a class of farmers or husbandmen (associated with fertility and craftsmanship), on the basis that many historically-known groups speaking Indo-European languages show such a division. Dumézil initially contended that it derived from an actual division in Indo-European societies, but later toned down his approach by representing the system as functions or general organizing principles. Dumézil’s theory has been influential and some scholars continue to operate under its framework, although it has also been criticized as aprioristic and too inclusive, and thus impossible to be proved or disproved.” ref
Rituals and Proto-Indo-European society
Proto-Indo-Europeans practiced a polytheistic religion centered on sacrificial rites of cattle and horses, probably administered by a class of priests or shamans. Animals were slaughtered (*gʷʰn̥tós) and dedicated to the gods (*déiwos) in the hope of winning their favor. The king as the high priest would have been the central figure in establishing good relations with the other world. The Khvalynsk culture, associated with early Proto-Indo-European, had already shown archeological evidence for the sacrifice of domesticated animals. Proto-Indo-Europeans also had a sacred tradition of horse sacrifice for the renewal of kinship involving the ritual mating of a queen or king with a horse, which was then sacrificed and cut up for distribution to the other participants in the ritual.” ref
“Although we know little about the role of magic in Proto-Indo-European society, there is no doubt that it existed as a social phenomenon, as several branches attest the use of similarly worded charms and curses, such as ones against worms. Furthermore, incantations and spells were frequently regarded as one of the three categories of medicine, along with the use of surgical instruments and herbs or drugs. Since the earliest evidence for the burning of the plant was found in Romanian kurgans dated 3,500 BCE, some scholars suggest that cannabis was first used as a psychoactive drug by Proto-Indo-Europeans during ritual ceremonies, a custom they eventually spread throughout western Eurasia during their migrations. Descendant cognates of the root *kanna- (“cannabis”) have been proposed in Sanskrit śaná, Greek kánnabis (κάνναβις), Germanic *hanipa (German Hanf, English hemp), Russian konopljá, Albanian kanëp, Armenian kanap and Old Prussian knapios. Other linguists suggest that the common linguistic inheritance does not date back to the Indo-European period and contend that the word cannabis likely spread later across Eurasia as a Wanderwort (‘wandering word’), ultimately borrowed into Ancient Greek and Sanskrit from a non-Indo-European language.” ref
Poetry and Proto-Indo-European society
“Poetry and songs were central to Proto-Indo-European society. The poet-singer was the society’s highest-paid professional, possibly a member of a hereditary profession that ran in certain families, the art passing from father to son as the poet had to acquire all the technical aspects of the art and to master an extensive body of traditional subject matter. He performed against handsome rewards—such as gifts of horses, cattle, wagons, and women—and was held in high esteem. In some cases, the poet-singer had a stable relationship with a particular noble prince or family. In other cases, he traveled about with his dependants, attaching himself to one court after another.” ref
“A transmitter of inherited cultural knowledge, the poet sang as a recall of the old heroic times, entrusted with telling the praises of heroes, kings, and gods. Composing sacred hymns ensured the gods would in turn bestow favorable fate to the community, and for kings that their memory would live on many generations. A lexeme for a special song, the *erkw (“praise of the gift”) has been identified in early Proto-Indo-European. Such praise poems proclaimed the generosity of the gods (or a patron) and enumerated their gifts, expanding the patron’s fame, the path to immortality otherwise only attainable for mortals through conspicuous acts of war or piety.” ref
“The concept of fame (*ḱléwos) was central to Proto-Indo-European poetry and culture. Many poetic dictions built on this term can be reconstituted, including *ḱléwos wéru (“wide fame”), *ḱléwos meǵh₂ (“great fame”), *ḱléuesh₂ h₂nróm (“the famous deeds of men, heroes”), or *dus-ḱlewes (“having bad repute”). Indo-European poetic tradition was probably oral-formulaic: stock formulas, such as the imperishable fame (*ḱléwos ń̥dʰgʷʰitom), the swift horses (*h₁ōḱéwes h₁éḱwōs), the eternal life (*h₂iu-gʷih₃), the metaphor of the wheel of the sun (*sh₂uens kʷekʷlos), or the epithet man-killer (*hₐnr̥-gʷhen), attached to Hektor and Rudra alike, were transmitted among poet-singers to fill out traditional verse-lines in epic song lyrics. The task of the Indo-European poet was to preserve over the generations the famous deeds of heroes. He would compose and retell poems based on old and sometimes obscure formulations, reconnecting the motifs with his own skills and improvisations. Poetry was therefore associated with the acts of weaving words (*wékʷos webh-) and crafting speech (*wékʷos teḱs-).” ref
Warfare: Kóryos and Proto-Indo-European society
“Although Proto-Indo-Europeans have been often cast as warlike conquerors, their reconstructed arsenal is not particularly extensive. There is no doubt that they possessed archery, as several words with the meaning of “spear” (*gʷéru ; *ḱúh₁los), “pointed stick” (*h₂eiḱsmo), or “throwing spear” (*ǵʰai-só-s) are attested. The term *wēben meant a “cutting weapon”, probably a knife, and *h₂/₃n̩sis a “large offensive knife”, likely similar to bronze daggers found across Eurasia around 3300–3000 BCE. Proto-Indo-Europeans certainly did not know swords, which appeared later around 2000–1500 BCE. The ax was known as *h₄edʰés, while the word *spelo/eh₂ designated a wooden or leather shield. The term *leh₂wós meant “military unit” or “military action”, while *teutéh₂- might have referred to the “adult male with possession” who would mobilize during warfare, perhaps originally a Proto-Indo-European term meaning “the people under arms.” ref
“A number of scholars propose that Proto-Indo-European rituals included the requirement that young unmarried men initiate into manhood by joining a warrior-band named *kóryos. They were led by a senior male and lived off the country by hunting and engaging in raiding and pillaging foreign communities. Kóryos members served in such brotherhoods (Männerbunden) for a number of years before returning home to adopt more respectable identities as mature men. During their initiation period, the young males wore the skin and bore the names of wild animals, especially wolves (*wl̩kʷo) and dogs (*ḱwōn), in order to assume their nature and escape the rules and taboos of their host society.” ref
“Most kurgan stelae found in Pontic-Caspian steppe feature a man wearing with a belt and weapons carved on the stone. In later Indo-European traditions, notably the (half-)naked warrior figures of Germanic and Celtic art, *kóryos raiders wore a belt that bound them to their leader and the gods, and little else. The tradition of kurgan stelae featuring warriors with a belt is also common in Scythian cultures. A continuity of an “animal-shaped raid culture” has been also postulated based on various elements attested in later Indo-European-speaking cultures, such as the Germanic Berserkers, the Italic Ver Sacrum, and the Spartan Crypteia, as well as in the mythical Celtic fianna and Vedic Maruts, and in the legend of the werewolf (“man-wolf”), found in Greek, Germanic, Baltic and Slavic traditions alike.” ref
“In a mostly patriarchal economy based on bride competition, the escalation of the bride-price in periods of climate change could have resulted in an increase in cattle raiding by unmarried men. Scholars also suggest that, alongside the attractiveness of the patron-client and the guest-host relationships, the *kóryos could have played a key role in diffusing Indo-European languages across most of Eurasia.” ref
Personal names and Proto-Indo-European society
“The use of two-word compound words for personal names, typically but not always ascribing some noble or heroic feat to their bearer, is so common in Indo-European languages that it is certainly an inherited feature. These names often belonged in early dialects to the class of compound words that in the Sanskrit tradition are called bahuvrihi. As in Vedic bahuvrihi (literally “much-rice”, meaning “one who has much rice”), those compounds are formed as active structures indicating possession and do not require a verbal root. From the Proto-Indo-European personal name *Ḱléwos-wésu (lit. “good-fame”, meaning “possessing good fame”) derive the Liburnian Vescleves, the Greek Eukleḗs (Εὐκλεής), the Old Persian Huçavah, the Avestan Haosravah-, and the Sanskrit Suśráva.” ref
“A second type of compound consists of a noun followed by a verbal root or stem, describing an individual performing an action. Compounds more similar to synthetics are found in the Sanskrit Trasá-dasyus (“one who causes enemies to tremble”), the Greek Archelaus (Ἀρχέλαος, “one who rules people”), and the Old Persian Xšayāršan (“one who rules men”).” ref
“Many Indo-European personal names are associated with the horse (*h₁éḱwos) in particular, which expressed both the wealth and nobility of their bearer, including the Avestan Hwaspa (“owning good horses”), the Greek Hippónikos (“winning by his horses”), or the Gaulish Epomeduos (“master of horses”). Since domestic animals also served to sacrifice, there were often used as exocentric structures in compound names (the bearers are not ‘horses’ themselves but ‘users of horses’ in some way), in contrast to endocentric personal names rather associated with wild animals like the wolf, for instance in the German Adolf (“a noble wolf”) or the Serbian Dobrovuk (“a good wolf”).” ref
Economy and Proto-Indo-European society
“Proto-Indo-Europeans possessed a Neolithic mixed economy based on livestock and subsidiary agriculture, with a wide range of economic regimes and various degrees of mobility that could be expected across the large Pontic-Caspian steppe. Tribes were typically more influenced by farming in the western Dnieper–Donets region, where cereal cultivation was practiced, while the eastern Don–Volga steppes were inhabited by semi-nomadic and pastoral populations mostly relying on herding. Proto-Indo-European distinguished between unmovable and movable wealth (*péḱu, the “livestock”). As for the rest of society, the economy was founded on reciprocity. A gift always entailed a counter-gift, and each party was bound to the other in a mutual relationship cemented by trust.” ref
Trade and Proto-Indo-European society
“The early Khvalynsk culture, located in the Volga–Ural steppes and associated with early Proto-Indo-European, had trade relationship with Old European cultures. Domesticated cattle, sheep, and goats, as well as copper, were introduced eastward from the Danube valley around 4700–4500 BCE. Copper objects show an artistic influence from Old Europe, and the appearance of sacrificed animals suggests that a new set of rituals emerged following the introduction of herding from the west. The Old European Tripolye culture continued to influence the western part of the steppes, in the Dnieper–Donets region, where the Yamnaya culture was more agricultural and less male-centered.” ref
“Proto-Indo-European speakers also had indirect contacts with Uruk around 3700–3500 through the North Caucasian Maikop culture, a trade route that introduced the wheeled wagon into the Caspian-Pontic steppes. Wheel-made pottery imported from Mesopotamia were found in the Northern Caucasus, and Maikop chieftain was buried wearing Mesopotamian symbols of power—the lion paired with the bull. The late Khvalynsk and Repin cultures probably traded wool and domesticated horses in exchange, as suggested by the widespread appearance of horses in archeological sites across Transcaucasia after 3300 BCE. Socio-cultural interactions with Northwest Caucasians have been proposed, on the ground that the Proto-Indo-European language shows a number of lexical parallels with Proto-Northwest Caucasian. Proto-Indo-European also exhibits lexical loans to or from other Caucasian languages, particularly Proto-Kartvelian.” ref
“Proto-Indo-European probably also had trade relationships with Proto-Uralic speakers around the Ural Mountains. Words for “sell” and “wash” were borrowed in Proto-Uralic, and words for “price” and “draw, lead” were introduced in the Proto-Finno-Ugric language. James P. Mallory suggested that the expansion of the Uralic languages across the northern forest zone might have been stimulated by organizational changes within Uralic forager societies, resulting partly from interaction with more complex, hierarchical Proto-Indo-European and (later) Indo-Iranian pastoral societies at the steppe/forest-steppe ecological border.” ref
Technology and Proto-Indo-European society
“From the reconstructable lexicon, it is clear that Proto-Indo-Europeans were familiar with wheeled vehicles—certainly horse-drawn wagons (*weǵʰnos)—as they knew the wheel (*kʷekʷlóm), the axle (*h₂eḱs-), the shaft (*h₂/₃éih₁os), and the yoke (*yugóm). Although wheels were most likely not invented by Proto-Indo-Europeans, the word *kʷekʷlóm is a native derivation of the root *kʷel– (“to turn”) rather than a borrowing, suggesting short contacts with the people who introduced the concept to them.” ref
“The technology used was a solid wheel made of three planks joined together with their outer edges trimmed to a circle. The swift chariot with spoked wheels, which made the mode of transport much more rapid and lighter, appeared later within the Sintashta culture (2100–1800 BCE), associated with the Indo-Iranians. As the word for “boat” (*néh₂us) is widely attested across the language groups, the means of transport (likely a dugout canoe) was certainly known by Proto-Indo-Europeans.” ref
“The vocabulary associated with metallurgy is very restricted and at best we can attest the existence of copper/bronze, gold, and silver. The basic word for “metal” (*h₂ey-es) is generally presumed to mean “copper” or a copper-tin alloy of “bronze”. “Gold” is reliably reconstructed as *h₂eusom, and *h₂erǵ-n̩t-om designated a “white metal” or “silver”. Proto-Indo-Europeans were also familiar with the sickle (*sr̩po/eh₂), the awl (*h₁óleh₂) for working leather or drilling wood, and used a primitive plough (*h₂érh₃ye/o) made of a curved and forked branch.” ref
“The term for “oven” or “cooking vessel” (*h₂/₃ukʷ) has been reconstructed based on four branches, as for “baking” (*bʰōg-) and “boiling” (*yes-). They certainly drank beer (*h₂elut) and mead (*médʰu), and the word for “wine” (*wóinom) has been proposed, although this remains a debated issue. Proto-Indo-Europeans produced textile, as attested by the reconstructed roots for wool (*wĺh₂neh₂), flax (*linom), sewing (*syuh₁-), spinning (*(s)pen-), weaving (*h₂/₃webʰ-) and plaiting (*pleḱ-), as well as needle (*skʷēis) and thread (*pe/oth₂mo). They were also familiar with combs (*kes) and ointments with salve (*h₃engʷ-).” ref
Animals and Proto-Indo-European society
“Animals (mammals in particular) are fairly abundant in the reconstructed lexicon. We can ascribe about seventy-five names to various animal species, but it hardly recovers all the animals to have been distinguished in the proto-language. While *kʷetwor-pod designated a four-footed animal (tetrapod), *gʷyéh₃wyom seems to have been the general term for animals, derived from the root *gʷyeh₃-, “to live”. Proto-Indo-European speakers also made a distinction between wild animals (*ǵʰwḗr) and the livestock (*péḱu).” ref
Domesticated Animals and Proto-Indo-European society
“The reconstructed lexicon suggests a Neolithic economy with extensive references to domesticated animals. They were familiar with cows (*gʷṓus), sheep (*h₃ówis), goats (*díks, or *h₂eiĝs), and pigs (*sūs ; also *pórḱos, “piglet”). They knew dogs (*ḱwōn), milk (*ǵl̩ákt; also *h₂melǵ-, “to milk”) and dairy foods, wool (*wĺh₂neh₂) and woolen textiles, agriculture, wagons, and honey (*mélit). The domestication of the horse (*h₁éḱwos), thought to be an extinct Tarpan species, probably originated with these peoples, and scholars invoke this innovation as a factor contributing to their increased mobility and rapid expansion.” ref
“The dog was perceived as a symbol of death and depicted as the guardian of the Otherworld in Indo-European cultures (Greek Cerberus, Indic Śarvarā, Norse Garmr). The mytheme possibly stems from an older Ancient North Eurasian belief, as evidenced by similar motifs in Native American and Siberian mythology, in which case it might be one of the oldest mythemes recoverable through comparative mythology. In various Indo-European traditions, the worst throw at the game of dice was named the “dog”, and the best throw was known as the “dog-killer”. Canine teeth of dogs were frequently worn as pendants in Yamnaya graves in the western Pontic steppes, particularly in the Ingul valley.” ref
Wild Animals and Proto-Indo-European society
“Linguistic evidence suggests that Proto-Indo-European speakers were also in contact with various wild animals, such as red foxes (*wl(o)p), wolves (*wl̩kʷo), bears (*h₂ŕ̩tḱos), red deers (*h₁elh₁ēn), elks (moose) (*h₁ólḱis), eagles (*h₃or), otters (*udrós), snakes (*h₁ógʷʰis), mice (*mūs ; from *mus-, “to steal”), or trouts (*lóḱs). Some of them were featured in mythological and folkloric motifs. Goats draw the chariots of the Norse and Indic gods Thor and Pushan, and they are associated with the Baltic god Perkūnas and the Greek god Pan. The words for both the wolf and the bear underwent taboo deformation in a number of branches, suggesting that they were feared as symbols of death in Proto-Indo-European culture.” ref
“In Indo-European culture, the term “wolf” is generally applied to brigands and outlaws who live in the wild. Ritual and mythological concepts connected with wolves, in some cases similar with Native American beliefs, may represent a common Ancient North Eurasian heritage: mai-coh meant both “wolf” and “witch” among Navajos, and shunk manita tanka a “doglike powerful spirit” among Sioux, while the Proto-Indo-European root *ṷeid (“knowledge, clairvoyance”) designated the wolf in both Hittite (ṷetna) and Old Norse (witnir), and a “werewolf” in Slavic languages (Serb vjedo-gonja, Slovenian vedanec, Ukrainian viščun).” ref
Beliefs: Proto-Indo-European mythology
“The reconstructed cosmology of the proto-Indo-Europeans shows that the ritual sacrifice of cattle, cows in particular, was at the root of their beliefs, as the primordial condition of the world order. The myth of *Trito, the first warrior, involves the liberation of cattle stolen by a three-headed serpent named *Ngwhi. After recovering the wealth of the people, Trito eventually offered the cattle to the priest in order to ensure the continuity of the cycle of giving between gods and humans. The creation myth could have rationalized raiding as the recovery of cattle that the gods had intended for the people who sacrificed properly. Many Indo-European cultures preserved the tradition of cattle raiding, which they often associated with epic myths. Georges Dumézil suggested that the religious function was represented by a duality, one reflecting the magico-religious nature of the priesthood, while the other is involved in religious sanction to human society (especially contracts), a theory supported by common features in Iranian, Roman, Scandinavian and Celtic traditions. The study of astronomy was not much developed among Proto-Indo-Europeans, and they probably had established names for only a few individual stars and star-groups (e.g. Sirius, Ursa Major).” ref
“The basic word for “god” in proto-Indo-European is *deiwós (“celestial”), itself a derivative of *dei– (“to shine, be bright”). On the other hand, the word for “earth” (*dʰéǵʰōm) is at root of both “earthly” and “human”, as it is notably attested in the Latin cognates humus and homo. This suggests a hierarchical conception of the status of mankind regarding the gods, confirmed by the use of the term “mortal” (*mr̩tós) as a synonym of “human” as opposed to the never-dying gods in Indo-European traditions. The idea is expressed in the Homeric phrase “of the immortal gods and of men who walk on earth”.” ref
Proto-Indo-European beliefs were influenced by a resistant animistic substratum, and the few names that can be reconstructed based upon both linguistic (cognates) and thematic (reflexes) evidence are the cosmic and elemental deities: the ‘Daylight-Sky’ (*Dyḗus), his partner ‘Earth’ (*Dʰéǵʰōm), his daughter the ‘Dawn’ (*H₂éwsōs), and his Twin Sons, the ‘Sun’ (*Séh₂ul) and the Sun-Maiden, and deities of winds, waters, fire, rivers and springs. The Proto-Indo-European creation myth tells of a primordial sacrifice performed by the first man *Manu (“Man”) on his twin brother *Yemo (“Twin”), from whom emerged the cosmological elements. Other deities, such as the weather-god *Perkʷunos and the guardian of roads and herds, *Péh₂usōn, are probably late innovations since they are attested in a restricted number of traditions, Western (European) and Graeco-Aryan, respectively.” ref
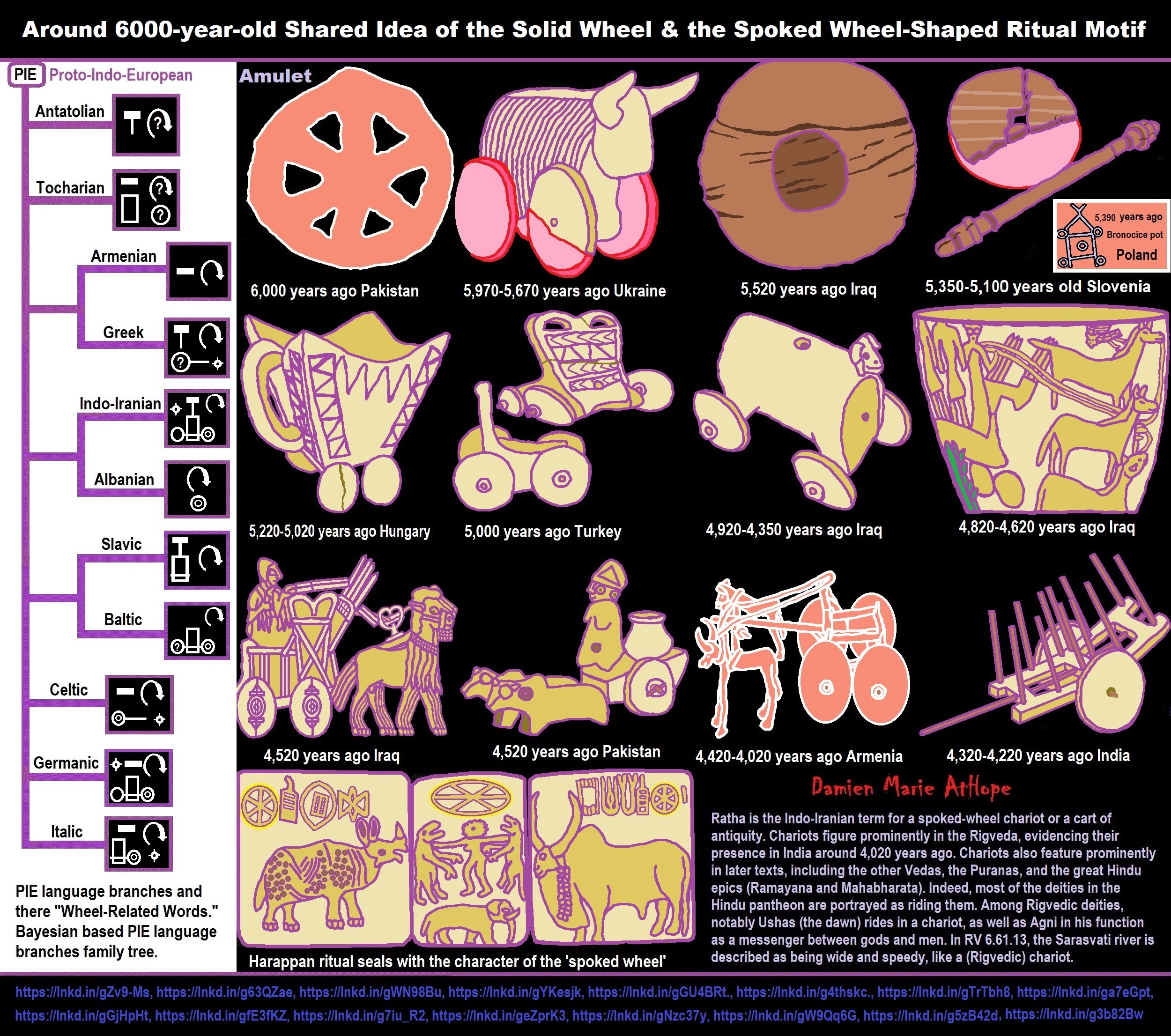
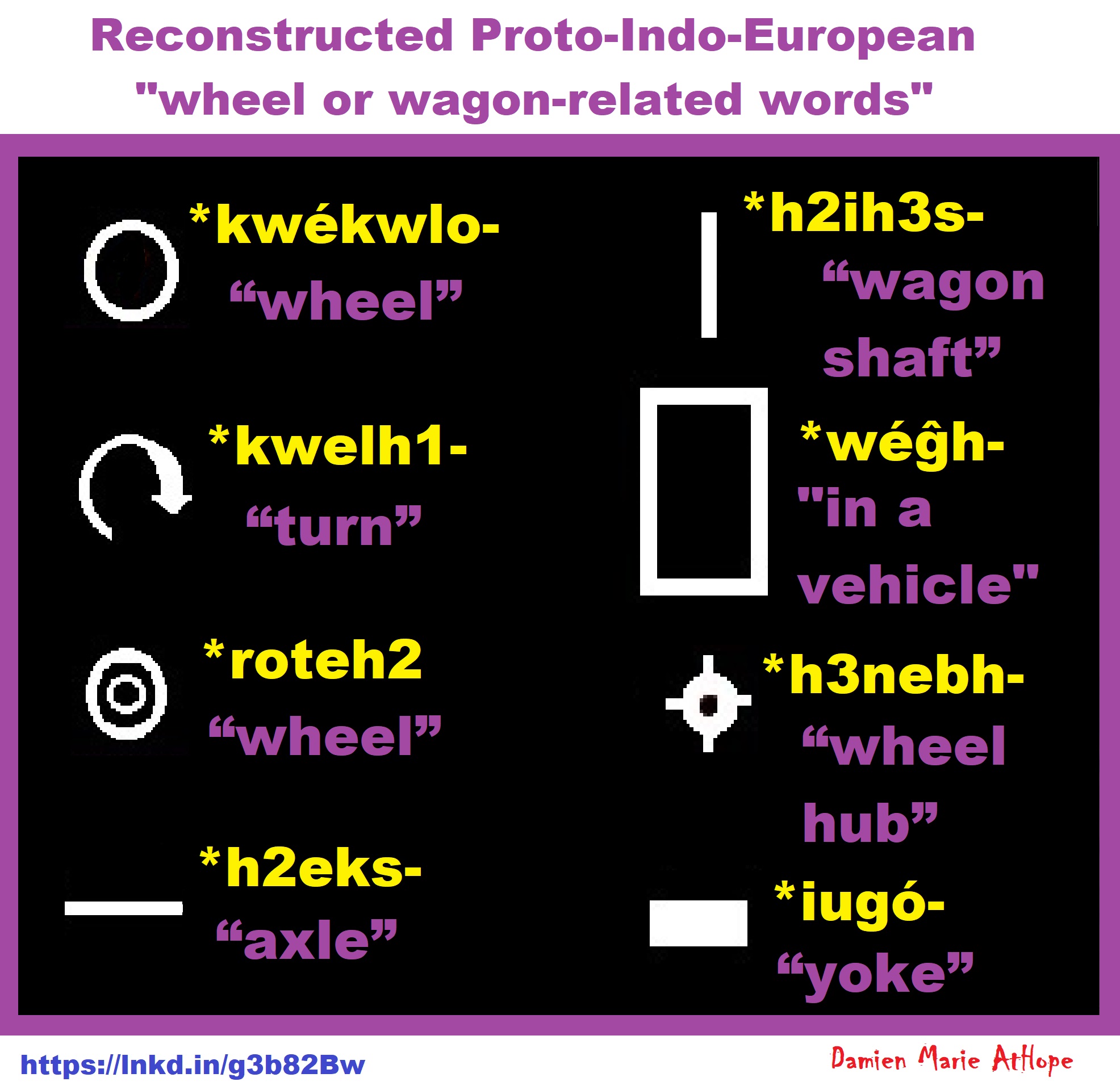
The “wheel” related word list
“Most linguists argue that the PIEs (Proto-Indo-Europeans) did have words for wheel. The candidates put forward for wheel or wagon-related words are nine reconstructed PIE word forms. These are:
- *hurki , argued to mean “wheel”
- *roteh2, argued to mean “wheel”
- *kwékwlo-, argued to mean “wheel”
- *kwelh1-, argued to mean “turn” perhaps in the sense of a turning wheel.
- *h2eks-, argued to mean “axle”
- *h2ih3s-, argued to mean “thill” or “wagon shaft”
- *wéĝh-, argued to mean “convey in a vehicle”
- *h3nebh-, argued to mean “nave” or “wheel hub”
- *iugó-, argued to mean “yoke” ref
Proto-Indo-European language
“Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result.” ref
“PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 to 2500 BCE during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Europe. The linguistic reconstruction of PIE has provided insight into the pastoral culture and patriarchal religion of its speakers.” ref
“As speakers of Proto-Indo-European became isolated from each other through the Indo-European migrations, the regional dialects of Proto-Indo-European spoken by the various groups diverged, as each dialect underwent shifts in pronunciation (the Indo-European sound laws), morphology, and vocabulary. Over many centuries, these dialects transformed into the known ancient Indo-European languages. From there, further linguistic divergence led to the evolution of their current descendants, the modern Indo-European languages. Today, the descendant languages of PIE with the most native speakers are Spanish, English, Portuguese, Hindustani (Hindi and Urdu), Bengali, Russian, Punjabi, German, Persian, French, Marathi, Italian, and Gujarati.” ref
“PIE is believed to have had an elaborate system of morphology that included inflectional suffixes (analogous to English child, child’s, children, children’s) as well as ablaut (vowel alterations, as preserved in English sing, sang, sung, song) and accent. PIE nominals and pronouns had a complex system of declension, and verbs similarly had a complex system of conjugation. The PIE phonology, particles, numerals, and copula are also well-reconstructed. Asterisks are used as a conventional mark of reconstructed words, such as *wódr̥, *ḱwṓ, or *tréyes; these forms are the reconstructed ancestors of the modern English words water, hound, and three, respectively.” ref
“Commonly proposed subgroups of Indo-European languages include Italo-Celtic, Graeco-Aryan, Graeco-Armenian, Graeco-Phrygian, Daco-Thracian, and Thraco-Illyrian. There are numerous lexical similarities between the Proto-Indo-European and Proto-Kartvelian languages due to early language contact, though some morphological similarities—notably the Indo-European ablaut, which is remarkably similar to the root ablaut system reconstructible for Proto-Kartvelian—may suggest a higher-level phylogenetic relationship.” ref
“The Lusitanian language was a marginally attested language spoken in areas near the border between present-day Portugal and Spain. The Venetic and Liburnian languages known from the North Adriatic region are sometimes classified as Italic. Albanian and Greek are the only surviving Indo-European descendants of a Paleo-Balkan language area, named for their occurrence in or in the vicinity of the Balkan peninsula. Most of the other languages of this area—including Illyrian, Thracian, and Dacian—do not appear to be members of any other subfamilies of PIE, but are so poorly attested that proper classification of them is not possible. Forming an exception, Phrygian is sufficiently well-attested to allow proposals of a particularly close affiliation with Greek, and a Graeco-Phrygian branch of Indo-European is becoming increasingly accepted.” ref
List of Indo-European languages
“The Indo-European languages include some 449 (SIL estimate, 2018 edition) language families spoken by about or more than 3.5 billion people (roughly half of the world population). Most of the major languages belonging to language branches and groups of Europe, and western and southern Asia, belong to the Indo-European language family. Therefore, Indo-European is the biggest language family in the world by number of mother-tongue speakers (but not by number of languages in which it is the 3rd or 5th biggest). Eight of the top ten biggest languages, by number of native speakers, are Indo-European. One of these languages, English, is the de facto World Lingua Franca with an estimate of over one billion second-language speakers.” ref
“Each subfamily or linguistic branch in this list contains many subgroups and individual languages. Indo-European language family has 10 known branches or subfamilies, of which eight are living and two are extinct. The relation of Indo-European branches, how they are related to one another and branched from the ancestral proto-language is a matter of further research and not yet well known. There are some individual Indo-European languages that are unclassified within the language family, they are not yet classified in a branch and could be members of their own branch. The 449 Indo-European languages identified in the SIL estimate, 2018 edition, are mostly living languages, however, if all the known extinct Indo-European languages are added, they number more than 800 or close to one thousand. This list includes all known Indo-European languages, living and extinct.” ref
“A distinction between a language and a dialect is not clear-cut and simple because there is, in many cases, several dialect continuums, transitional dialects, and languages and also because there is no consensual standard to what amount of vocabulary, grammar, pronunciation, and prosody differences there is a language or there is a dialect. (Mutual intelligibility can be a standard but there are closely related languages that are also mutual intelligible to some degree, even if it is an asymmetric intelligibility.) Because of this, in this list, several dialect groups and some individual dialects of languages are shown (in italics), especially if a language is or was spoken by a large number of people and over a big land area, but also if it has or had divergent dialects. The contact between different peoples and languages, especially as a result of European colonization, also gave origin to the many pidgins, creoles, and mixed languages that are mainly based in Indo-European languages (many of which are spoken in island groups and coastal regions).” ref
The ancestral population and language, Proto-Indo-Europeans that spoke Proto-Indo-European, estimated to have lived about 4500 BCE (around 6500 years ago), at some time in the past, starting about 4000 BCE (around 6000 years ago) expanded through migration and cultural influence. This started a complex process of population blend or population replacement, acculturation, and language change of peoples in many regions of western and southern Eurasia. This process gave origin to many languages and branches of this language family. At the end of the second millennium BCE Indo-European speakers were many millions and lived in a vast geographical area in most of western and southern Eurasia (including western Central Asia). In the following two millennia, the number of speakers of Indo-European languages increased even further.” ref
“By geographical area, Indo-European languages remained spoken in big land areas, although most of western Central Asia and Asia Minor was lost to another language family (mainly Turkic) due to Turkic expansion, conquests, and settlement (after the middle of the first millennium AD and the beginning and middle of the second millennium CE respectively) and also to Mongol invasions and conquests (that changed Central Asia ethnolinguistic composition). Another land area lost to non-Indo-European languages was today’s Hungary due to Magyar/Hungarian (Uralic language speakers) conquest and settlement. However, in the second half of the second millennium CE, Indo-European languages expanded their territories to North Asia (Siberia), through Russian expansion, and North America, South America, Australia, and New Zealand as the result of the age of European discoveries and European conquests through the expansions of the Portuguese, Spanish, French, English and the Dutch. (These peoples had the biggest continental or maritime empires in the world and their countries were major powers.)” ref
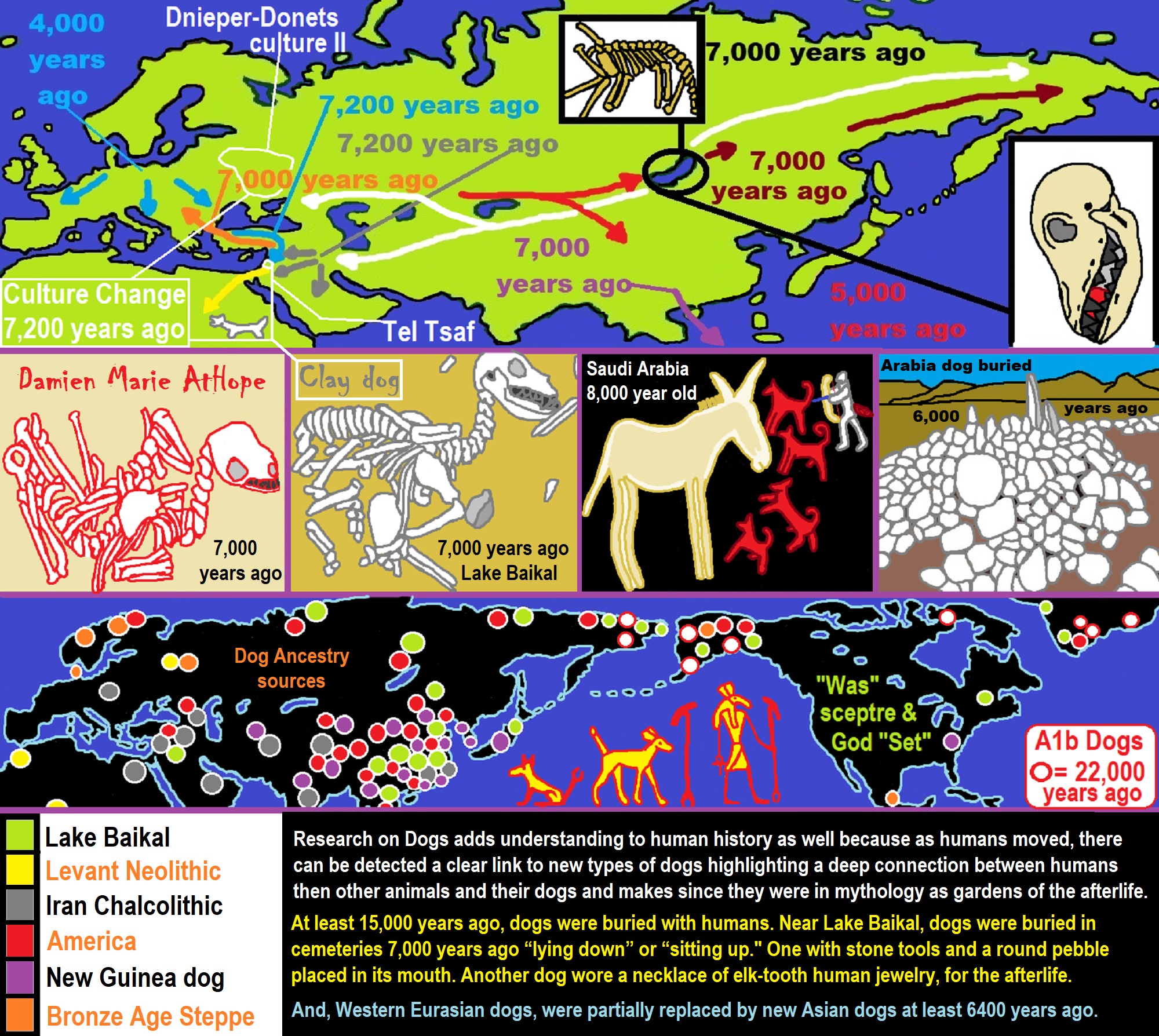

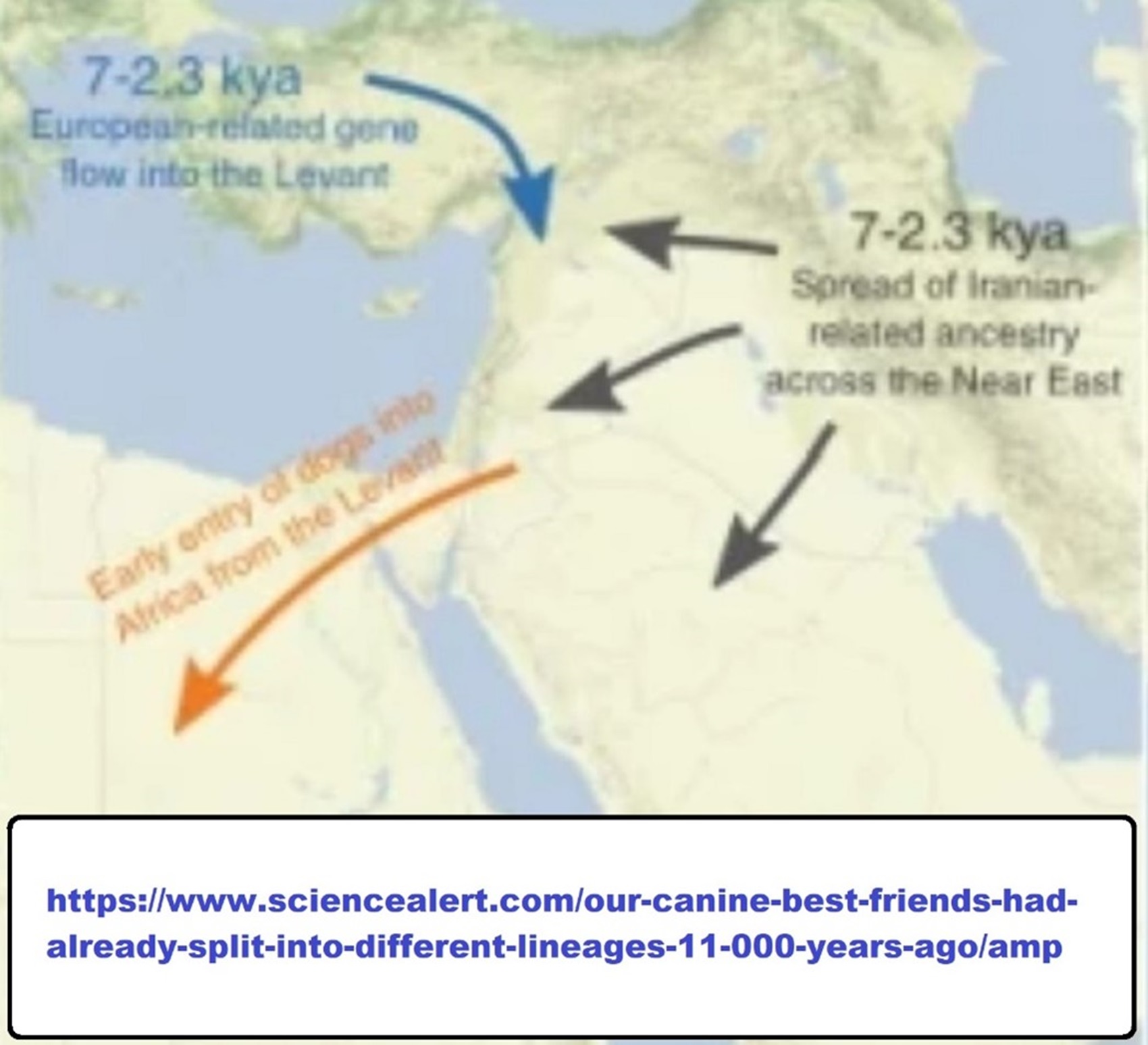
7,000-year-old Leopard (Or Dog?) Temples of Uvda basin in southern Israel
“7,000-year-old Leopard Temple of Uvda, in the Uvda basin in the desert of southern Israel. Uvda (Hebrew: עובדה) is the name of a region in the southern Negev desert, directly north of Eilat. The name derives from the Hebrew word uvda (meaning fact). The Uvda Valley is known for the 7000-year-old Leopard Temple archaeological site. They also began to worship something, perhaps the sun, perhaps their own ancestors, and intriguingly, perhaps the local scourge, the wild leopard.” ref, ref
“Uvda Valley Site 6, “stone drawings” of 15 leopards and one oryx, next to an open-air sanctuary, a vertical view (small stones indicate reconstruction).” ref
“Jebel Ḥashem al-Taref, eastern Sinai, three examples of “stone drawings” built next to pairs of open-air sanctuaries: (a) Excavated; (b,c) Unexcavated, dark stones—vertically set, light stones—fallen. Radiometric dates available to date from open sanctuaries are of the 6th and 5th millennia BCE. Nevertheless, Pre-Pottery Neolithic B flint items were also found in some of them (8th–7th millennia BCE), while other finds indicate continuation through the third millennium BCE, even the early second (Middle Bronze Age).” ref
“All open sanctuaries were built next to ancient roads (Figure 21c and Figure 27), while clusters of sanctuaries were built next to road junctions, for example, a cluster of 33 open sanctuaries near Jebel Ḥashem al-Taref in Sinai, 35 km west of Eilat; 4 pairs of sanctuaries at Ramat Saharonim; and 28 sanctuaries near Har Tzuriʻaz, in the southern Negev. Some sanctuaries were built in burial sites, also located next to ancient roads and road junctions.” ref
“This is also the female’s position in the drawing of a couple from Kuntilat ʻAjrud (Figure 17), slightly behind the male, presented as standing on a higher-like level, and her right leg is hidden behind the male’s left leg. Many open sanctuaries are circular, (Figure 21, Figure 28, and Figure 33). Most of them are 6–18 m in diameter, but tiny circular sanctuaries are also known, ca. 3 m in diameter (Figure 33), as well as large circular cult enclosures up to 70 m in diameter (Figure 33b). Stone alignments are attached to most of the circular sanctuaries, mainly in the form of “ladders,” which are chains of square cells made of a single line of stones or of small flagstones set vertically into the ground (Figure 34 and Figure 36). Their length ranges from a few meters to 78 m, and they present one of the combination of lines and circles.” ref
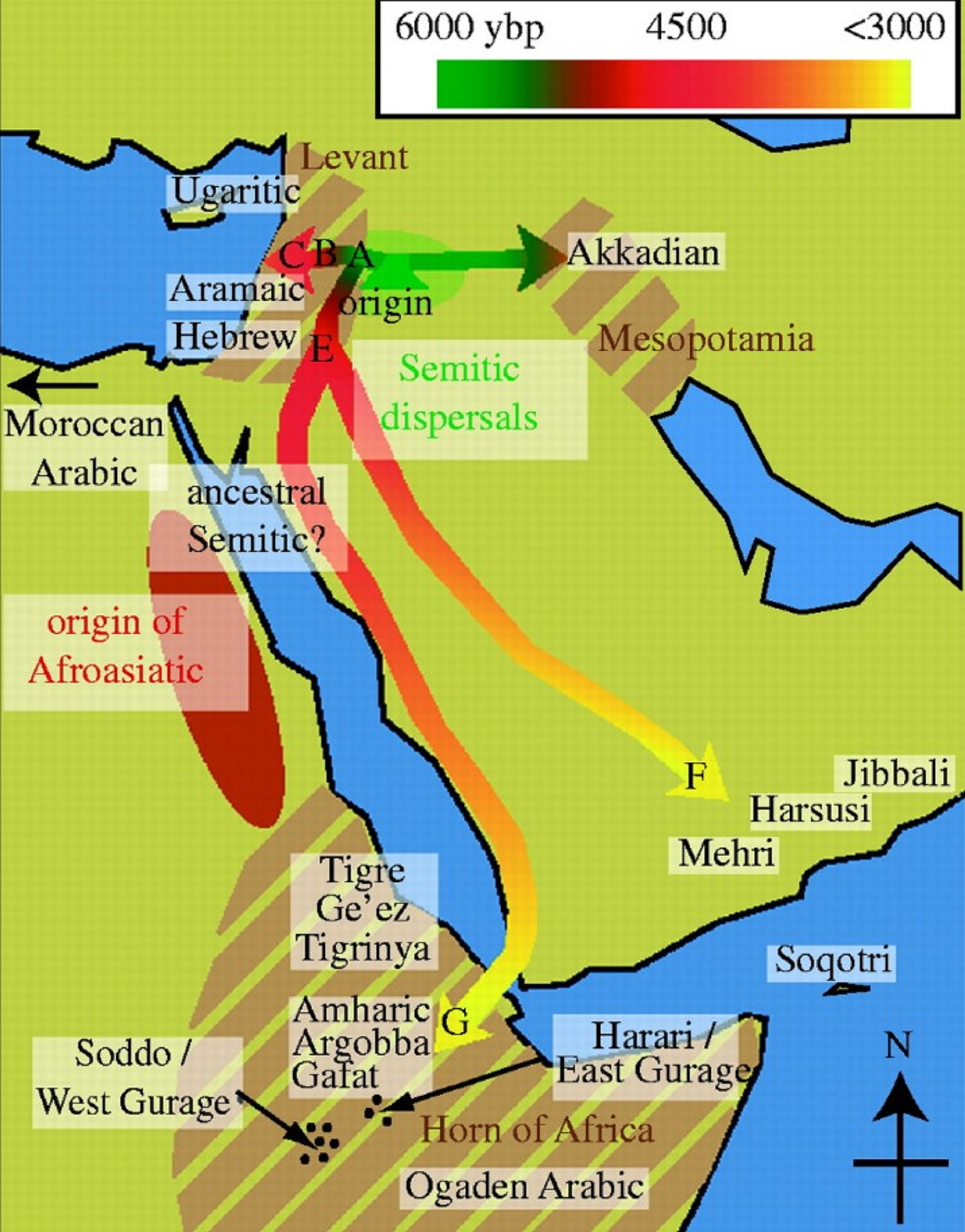
Proto-Semitic dates to ca. 4500–3500 BCE or around 6,500 to 5,500 years ago.
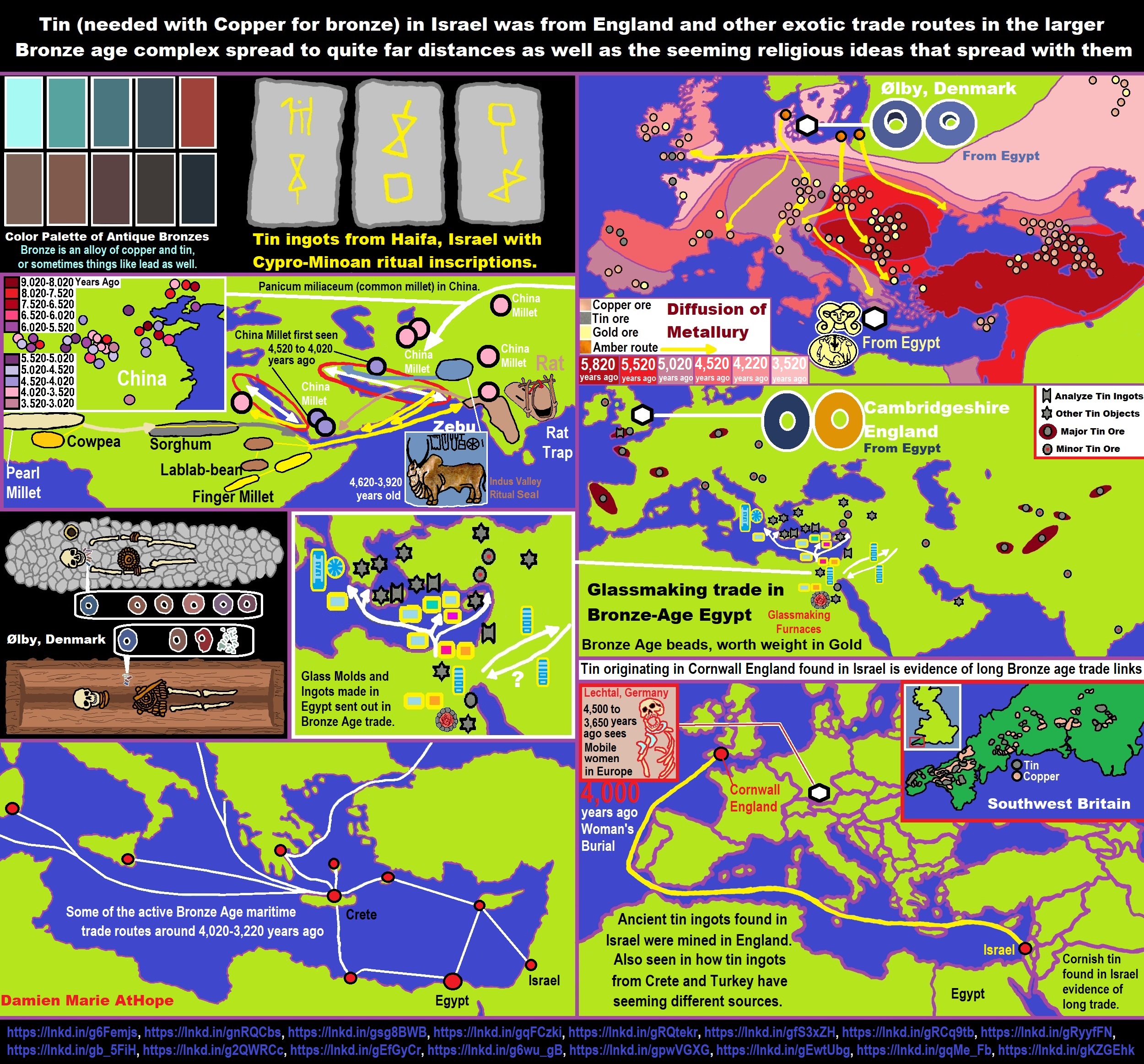
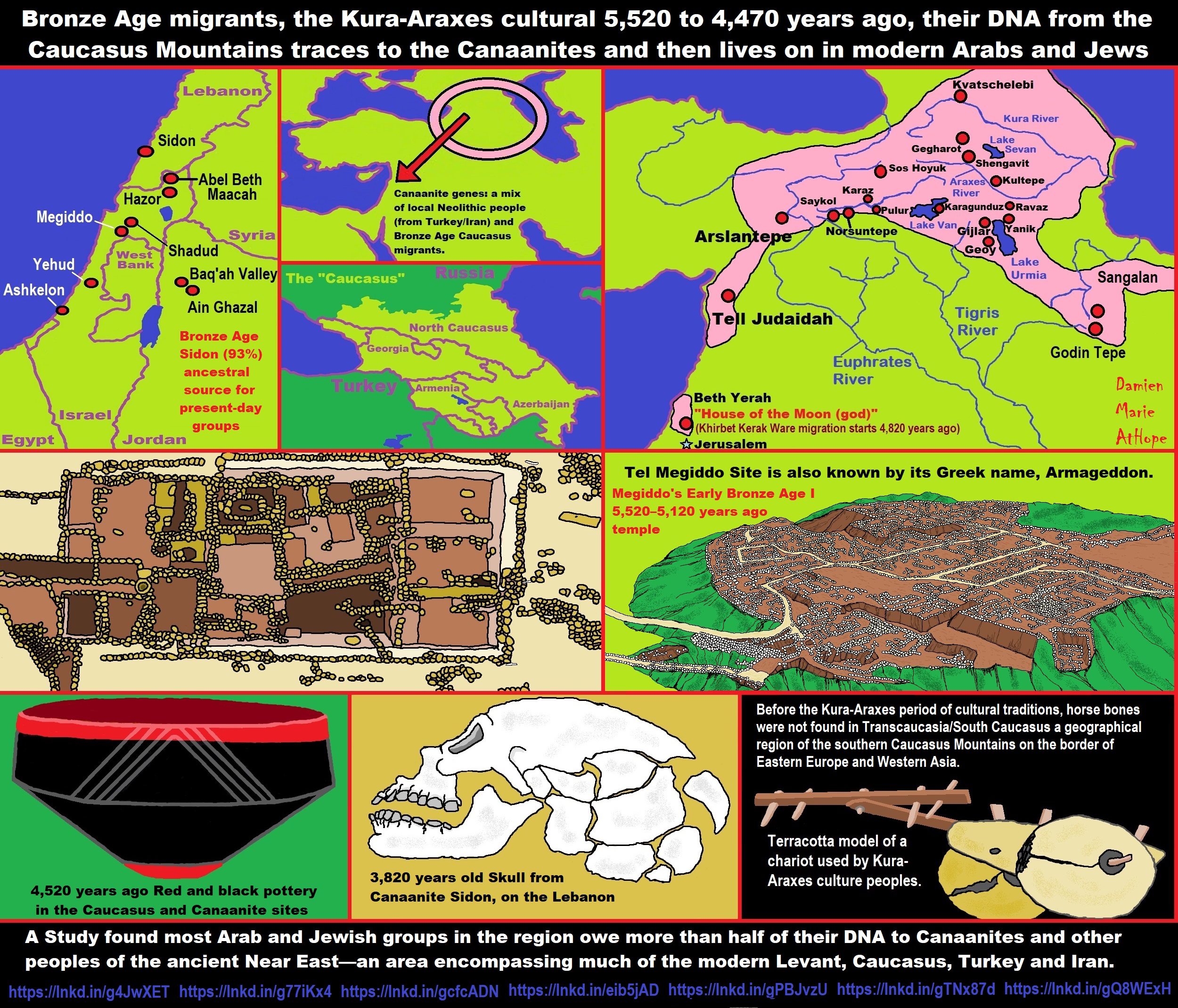

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
By day the LORD went ahead of them in a pillar of cloud to guide them on their way and by night in a pillar of fire to give them light, so that they could travel by day or night.
- By day the “Bible God” was in a cloud pillar.
- By night the “Bible God” was in a fire pillar.
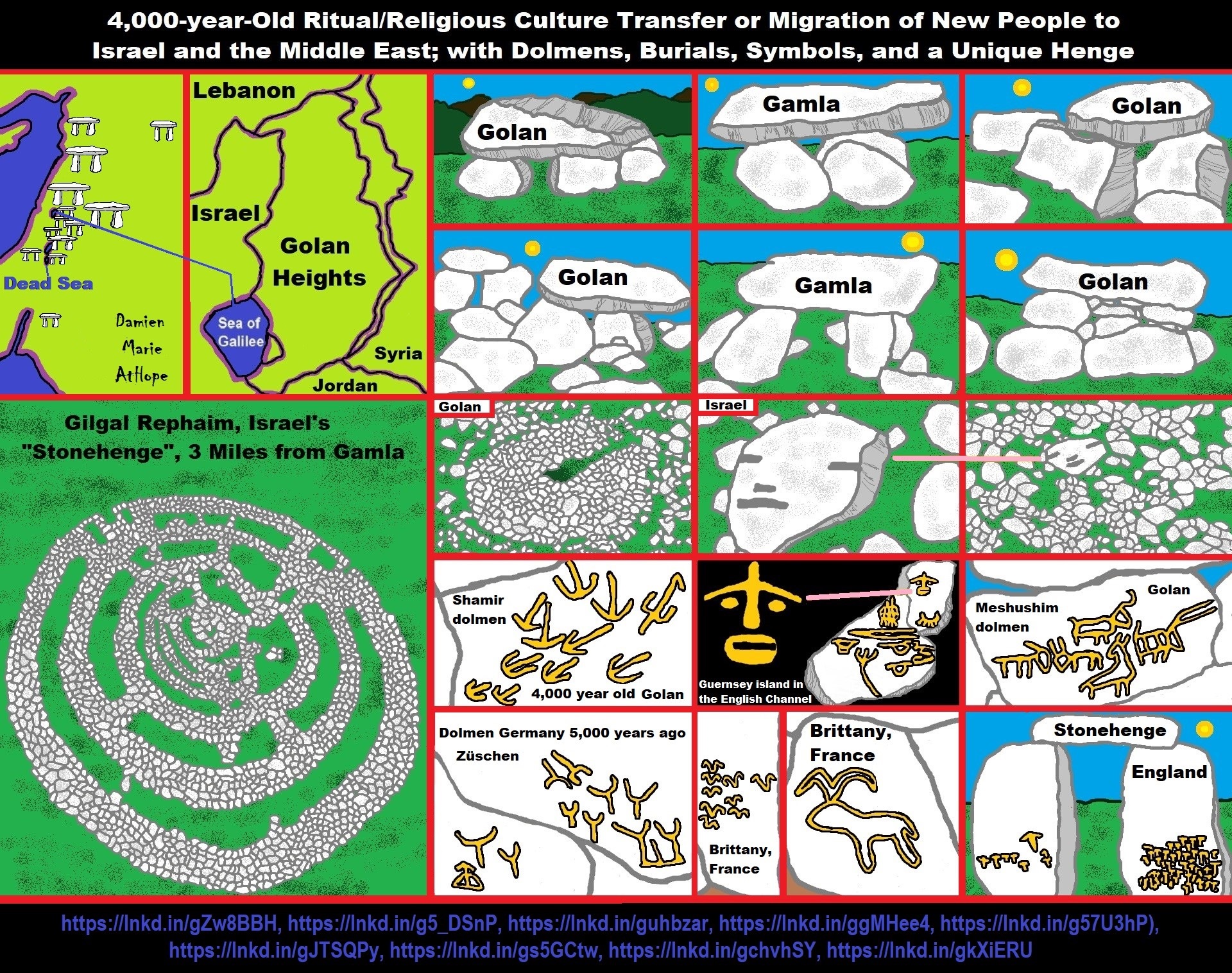
“The First Nations of Saskatchewan are: Nêhiyawak (Plains Cree), Nahkawininiwak (Saulteaux), Nakota (Assiniboine), Dakota and Lakota (Sioux), and Denesuline (Dene/Chipewyan).” ref
“Native Americans in Florida are: Ais, Apalachee, Calusa, Creek, Miccosukee, Seminole, Timucua, and Yemassee.” ref
Colonization and Colonialism of Florida, its Indigenous Peoples, and a little on Masculinity (VIDEO)

My favorite “Graham Hancock” Quote?
“In what archaeologists have studied, yes, we can say there is NO Evidence of an advanced civilization.” – (Time 1:27) Joe Rogan Experience #2136 – Graham Hancock & Flint Dibble
Help the Valentine fight against pseudoarchaeology!!!
In a world of “Hancocks” supporting evidence lacking claims, be a “John Hoopes” supporting what evidence explains.
#SupportEvidenceNotWishfullThinking
Graham Hancock: @Graham__Hancock
John Hoopes: @KUHoopes

People don’t commonly teach religious history, even that of their own claimed religion. No, rather they teach a limited “pro their religion” history of their religion from a religious perspective favorable to the religion of choice.
Do you truly think “Religious Belief” is only a matter of some personal choice?
Do you not see how coercive one’s world of choice is limited to the obvious hereditary belief, in most religious choices available to the child of religious parents or caregivers? Religion is more commonly like a family, culture, society, etc. available belief that limits the belief choices of the child and that is when “Religious Belief” is not only a matter of some personal choice and when it becomes hereditary faith, not because of the quality of its alleged facts or proposed truths but because everyone else important to the child believes similarly so they do as well simply mimicking authority beliefs handed to them. Because children are raised in religion rather than being presented all possible choices but rather one limited dogmatic brand of “Religious Belief” where children only have a choice of following the belief as instructed, and then personally claim the faith hereditary belief seen in the confirming to the belief they have held themselves all their lives. This is obvious in statements asked and answered by children claiming a faith they barely understand but they do understand that their family believes “this or that” faith, so they feel obligated to believe it too. While I do agree that “Religious Belief” should only be a matter of some personal choice, it rarely is… End Hereditary Religion!

Animism: Respecting the Living World by Graham Harvey
“How have human cultures engaged with and thought about animals, plants, rocks, clouds, and other elements in their natural surroundings? Do animals and other natural objects have a spirit or soul? What is their relationship to humans? In this new study, Graham Harvey explores current and past animistic beliefs and practices of Native Americans, Maori, Aboriginal Australians, and eco-pagans. He considers the varieties of animism found in these cultures as well as their shared desire to live respectfully within larger natural communities. Drawing on his extensive casework, Harvey also considers the linguistic, performative, ecological, and activist implications of these different animisms.” ref

We are like believing machines we vacuum up ideas, like Velcro sticks to almost everything. We accumulate beliefs that we allow to negatively influence our lives, often without realizing it. Our willingness must be to alter skewed beliefs that impend our balance or reason, which allows us to achieve new positive thinking and accurate outcomes.

My thoughts on Religion Evolution with external links for more info:
- (Pre-Animism Africa mainly, but also Europe, and Asia at least 300,000 years ago), (Pre-Animism – Oxford Dictionaries)
- (Animism Africa around 100,000 years ago), (Animism – Britannica.com)
- (Totemism Europe around 50,000 years ago), (Totemism – Anthropology)
- (Shamanism Siberia around 30,000 years ago), (Shamanism – Britannica.com)
- (Paganism Turkey around 12,000 years ago), (Paganism – BBC Religion)
- (Progressed Organized Religion “Institutional Religion” Egypt around 5,000 years ago), (Ancient Egyptian Religion – Britannica.com)
- (CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS after 4,000 years ago) (Origin of Major Religions – Sacred Texts)
- (Early Atheistic Doubting at least by 2,600 years ago) (History of Atheism – Wikipedia)
“Religion is an Evolved Product” and Yes, Religion is Like Fear Given Wings…
Atheists talk about gods and religions for the same reason doctors talk about cancer, they are looking for a cure, or a firefighter talks about fires because they burn people and they care to stop them. We atheists too often feel a need to help the victims of mental slavery, held in the bondage that is the false beliefs of gods and the conspiracy theories of reality found in religions.
Understanding Religion Evolution:
- Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago)
- Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago)
- Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago)
- Shamanism (Siberia: 30,000 years ago)
- Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago)
- Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago), (Egypt, the First Dynasty 5,150 years ago)
- CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago)
- Early Atheistic Doubting (at least by 2,600 years ago)
“An Archaeological/Anthropological Understanding of Religion Evolution”
It seems ancient peoples had to survived amazing threats in a “dangerous universe (by superstition perceived as good and evil),” and human “immorality or imperfection of the soul” which was thought to affect the still living, leading to ancestor worship. This ancestor worship presumably led to the belief in supernatural beings, and then some of these were turned into the belief in gods. This feeble myth called gods were just a human conceived “made from nothing into something over and over, changing, again and again, taking on more as they evolve, all the while they are thought to be special,” but it is just supernatural animistic spirit-belief perceived as sacred.
Quick Evolution of Religion?
Pre-Animism (at least 300,000 years ago) pre-religion is a beginning that evolves into later Animism. So, Religion as we think of it, to me, all starts in a general way with Animism (Africa: 100,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in supernatural powers/spirits), then this is physically expressed in or with Totemism (Europe: 50,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in mythical relationship with powers/spirits through a totem item), which then enlists a full-time specific person to do this worship and believed interacting Shamanism (Siberia/Russia: 30,000 years ago) (theoretical belief in access and influence with spirits through ritual), and then there is the further employment of myths and gods added to all the above giving you Paganism (Turkey: 12,000 years ago) (often a lot more nature-based than most current top world religions, thus hinting to their close link to more ancient religious thinking it stems from). My hypothesis is expressed with an explanation of the building of a theatrical house (modern religions development). Progressed organized religion (Egypt: 5,000 years ago) with CURRENT “World” RELIGIONS (after 4,000 years ago).
Historically, in large city-state societies (such as Egypt or Iraq) starting around 5,000 years ago culminated to make religion something kind of new, a sociocultural-governmental-religious monarchy, where all or at least many of the people of such large city-state societies seem familiar with and committed to the existence of “religion” as the integrated life identity package of control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine, but this juggernaut integrated religion identity package of Dogmatic-Propaganda certainly did not exist or if developed to an extent it was highly limited in most smaller prehistoric societies as they seem to lack most of the strong control dynamics with a fixed closed magical doctrine (magical beliefs could be at times be added or removed). Many people just want to see developed religious dynamics everywhere even if it is not. Instead, all that is found is largely fragments until the domestication of religion.
Religions, as we think of them today, are a new fad, even if they go back to around 6,000 years in the timeline of human existence, this amounts to almost nothing when seen in the long slow evolution of religion at least around 70,000 years ago with one of the oldest ritual worship. Stone Snake of South Africa: “first human worship” 70,000 years ago. This message of how religion and gods among them are clearly a man-made thing that was developed slowly as it was invented and then implemented peace by peace discrediting them all. Which seems to be a simple point some are just not grasping how devastating to any claims of truth when we can see the lie clearly in the archeological sites.
I wish people fought as hard for the actual values as they fight for the group/clan names political or otherwise they think support values. Every amount spent on war is theft to children in need of food or the homeless kept from shelter.
Here are several of my blog posts on history:
- To Find Truth You Must First Look
- (Magdalenian/Iberomaurusian) Connections to the First Paganists of the early Neolithic Near East Dating from around 17,000 to 12,000 Years Ago
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- Possible Clan Leader/Special “MALE” Ancestor Totem Poles At Least 13,500 years ago?
- Jewish People with DNA at least 13,200 years old, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- Baltic Reindeer Hunters: Swiderian, Lyngby, Ahrensburgian, and Krasnosillya cultures 12,020 to 11,020 years ago are evidence of powerful migratory waves during the last 13,000 years and a genetic link to Saami and the Finno-Ugric peoples.
- The Rise of Inequality: patriarchy and state hierarchy inequality
- Fertile Crescent 12,500 – 9,500 Years Ago: fertility and death cult belief system?
- 12,400 – 11,700 Years Ago – Kortik Tepe (Turkey) Pre/early-Agriculture Cultic Ritualism
- Ritualistic Bird Symbolism at Gobekli Tepe and its “Ancestor Cult”
- Male-Homosexual (female-like) / Trans-woman (female) Seated Figurine from Gobekli Tepe
- Could a 12,000-year-old Bull Geoglyph at Göbekli Tepe relate to older Bull and Female Art 25,000 years ago and Later Goddess and the Bull cults like Catal Huyuk?
- Sedentism and the Creation of goddesses around 12,000 years ago as well as male gods after 7,000 years ago.
- Alcohol, where Agriculture and Religion Become one? Such as Gobekli Tepe’s Ritualistic use of Grain as Food and Ritual Drink
- Neolithic Ritual Sites with T-Pillars and other Cultic Pillars
- Paganism: Goddesses around 12,000 years ago then Male Gods after 7,000 years ago
- First Patriarchy: Split of Women’s Status around 12,000 years ago & First Hierarchy: fall of Women’s Status around 5,000 years ago.
- Natufians: an Ancient People at the Origins of Agriculture and Sedentary Life
- J DNA and the Spread of Agricultural Religion (paganism)
- Paganism: an approximately 12,000-year-old belief system
- Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism)
- Shaman burial in Israel 12,000 years ago and the Shamanism Phenomena
- Need to Mythicized: gods and goddesses
- 12,000 – 7,000 Years Ago – Paleo-Indian Culture (The Americas)
- 12,000 – 2,000 Years Ago – Indigenous-Scandinavians (Nordic)
- Norse did not wear helmets with horns?
- Pre-Pottery Neolithic Skull Cult around 11,500 to 8,400 Years Ago?
- 10,400 – 10,100 Years Ago, in Turkey the Nevail Cori Religious Settlement
- 9,000-6,500 Years Old Submerged Pre-Pottery/Pottery Neolithic Ritual Settlements off Israel’s Coast
- Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city” around 9,500 to 7,700 years ago (Turkey)
- Cultic Hunting at Catal Huyuk “first religious designed city”
- Special Items and Art as well as Special Elite Burials at Catal Huyuk
- New Rituals and Violence with the appearance of Pottery and People?
- Haplogroup N and its related Uralic Languages and Cultures
- Ainu people, Sámi people, Native Americans, the Ancient North Eurasians, and Paganistic-Shamanism with Totemism
- Ideas, Technology and People from Turkey, Europe, to China and Back again 9,000 to 5,000 years ago?
- First Pottery of Europe and the Related Cultures
- 9,000 years old Neolithic Artifacts Judean Desert and Hills Israel
- 9,000-7,000 years-old Sex and Death Rituals: Cult Sites in Israel, Jordan, and the Sinai
- 9,000-8500 year old Horned Female shaman Bad Dürrenberg Germany
- Neolithic Jewelry and the Spread of Farming in Europe Emerging out of West Turkey
- 8,600-year-old Tortoise Shells in Neolithic graves in central China have Early Writing and Shamanism
- Swing of the Mace: the rise of Elite, Forced Authority, and Inequality begin to Emerge 8,500 years ago?
- Migrations and Changing Europeans Beginning around 8,000 Years Ago
- My “Steppe-Anatolian-Kurgan hypothesis” 8,000/7,000 years ago
- Around 8,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Mistress of Animals, “Ritual” Motif
- Pre-Columbian Red-Paint (red ochre) Maritime Archaic Culture 8,000-3,000 years ago
- 7,522-6,522 years ago Linear Pottery culture which I think relates to Arcane Capitalism’s origins
- Arcane Capitalism: Primitive socialism, Primitive capital, Private ownership, Means of production, Market capitalism, Class discrimination, and Petite bourgeoisie (smaller capitalists)
- 7,500-4,750 years old Ritualistic Cucuteni-Trypillian culture of Moldova, Romania, and Ukraine
- Roots of a changing early society 7,200-6,700 years ago Jordan and Israel
- Agriculture religion (Paganism) with farming reached Britain between about 7,000 to 6,500 or so years ago and seemingly expressed in things like Western Europe’s Long Barrows
- My Thoughts on Possible Migrations of “R” DNA and Proto-Indo-European?
- “Millet” Spreading from China 7,022 years ago to Europe and related Language may have Spread with it leading to Proto-Indo-European
- Proto-Indo-European (PIE), ancestor of Indo-European languages: DNA, Society, Language, and Mythology
- The Dnieper–Donets culture and Asian varieties of Millet from China to the Black Sea region of Europe by 7,022 years ago
- Kurgan 6,000 years ago/dolmens 7,000 years ago: funeral, ritual, and other?
- 7,020 to 6,020-year-old Proto-Indo-European Homeland of Urheimat or proposed home of their Language and Religion
- Ancient Megaliths: Kurgan, Ziggurat, Pyramid, Menhir, Trilithon, Dolman, Kromlech, and Kromlech of Trilithons
- The Mytheme of Ancient North Eurasian Sacred-Dog belief and similar motifs are found in Indo-European, Native American, and Siberian comparative mythology
- Elite Power Accumulation: Ancient Trade, Tokens, Writing, Wealth, Merchants, and Priest-Kings
- Sacred Mounds, Mountains, Kurgans, and Pyramids may hold deep connections?
- Between 7,000-5,000 Years ago, rise of unequal hierarchy elite, leading to a “birth of the State” or worship of power, strong new sexism, oppression of non-elites, and the fall of Women’s equal status
- Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite & their slaves
- Hell and Underworld mythologies starting maybe as far back as 7,000 to 5,000 years ago with the Proto-Indo-Europeans?
- The First Expression of the Male God around 7,000 years ago?
- White (light complexion skin) Bigotry and Sexism started 7,000 years ago?
- Around 7,000-year-old Shared Idea of the Divine Bird (Tutelary and/or Trickster spirit/deity), “Ritual” Motif
- Nekhbet an Ancient Egyptian Vulture Goddess and Tutelary Deity
- 6,720 to 4,920 years old Ritualistic Hongshan Culture of Inner Mongolia with 5,000-year-old Pyramid Mounds and Temples
- First proto-king in the Balkans, Varna culture around 6,500 years ago?
- 6,500–5,800 years ago in Israel Late Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Period in the Southern Levant Seems to Express Northern Levant Migrations, Cultural and Religious Transfer
- KING OF BEASTS: Master of Animals “Ritual” Motif, around 6,000 years old or older…
- Around 6000-year-old Shared Idea of the Solid Wheel & the Spoked Wheel-Shaped Ritual Motif
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan; a Proto-Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna or Star of Venus?
- Religious/Ritual Ideas, including goddesses and gods as well as ritual mounds or pyramids from Northeastern Asia at least 6,000 years old, seemingly filtering to Iran, Iraq, the Mediterranean, Europe, Egypt, and the Americas?
- Maykop (5,720–5,020 years ago) Caucasus region Bronze Age culture-related to Copper Age farmers from the south, influenced by the Ubaid period and Leyla-Tepe culture, as well as influencing the Kura-Araxes culture
- 5-600-year-old Tomb, Mummy, and First Bearded Male Figurine in a Grave
- Kura-Araxes Cultural 5,520 to 4,470 years old DNA traces to the Canaanites, Arabs, and Jews
- Minoan/Cretan (Keftiu) Civilization and Religion around 5,520 to 3,120 years ago
- Evolution Of Science at least by 5,500 years ago
- 5,500 Years old birth of the State, the rise of Hierarchy, and the fall of Women’s status
- “Jiroft culture” 5,100 – 4,200 years ago and the History of Iran
- Stonehenge: Paganistic Burial and Astrological Ritual Complex, England (5,100-3,600 years ago)
- Around 5,000-year-old Shared Idea of the “Tree of Life” Ritual Motif
- Complex rituals for elite, seen from China to Egypt, at least by 5,000 years ago
- Around 5,000 years ago: “Birth of the State” where Religion gets Military Power and Influence
- The Center of the World “Axis Mundi” and/or “Sacred Mountains” Mythology Could Relate to the Altai Mountains, Heart of the Steppe
- Progressed organized religion starts, an approximately 5,000-year-old belief system
- China’s Civilization between 5,000-3,000 years ago, was a time of war and class struggle, violent transition from free clans to a Slave or Elite society
- Origin of Logics is Naturalistic Observation at least by around 5,000 years ago.
- Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State)
- Ziggurats (multi-platform temples: 4,900 years old) to Pyramids (multi-platform tombs: 4,700 years old)
- Did a 4,520–4,420-year-old Volcano In Turkey Inspire the Bible God?
- Finland’s Horned Shaman and Pre-Horned-God at least 4,500 years ago?
- 4,000-year-Old Dolmens in Israel: A Connected Dolmen Religious Phenomenon?
- Creation myths: From chaos, Ex nihilo, Earth-diver, Emergence, World egg, and World parent
- Bronze Age “Ritual” connections of the Bell Beaker culture with the Corded Ware/Single Grave culture, which were related to the Yamnaya culture and Proto-Indo-European Languages/Religions
- Low Gods (Earth/ Tutelary deity), High Gods (Sky/Supreme deity), and Moralistic Gods (Deity enforcement/divine order)
- The exchange of people, ideas, and material-culture including, to me, the new god (Sky Father) and goddess (Earth Mother) religion between the Cucuteni-Trypillians and others which is then spread far and wide
- Koryaks: Indigenous People of the Russian Far East and Big Raven myths also found in Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and other Indigenous People of North America
- 42 Principles Of Maat (Egyptian Goddess of the justice) around 4,400 years ago, 2000 Years Before Ten Commandments
- “Happy Easter” Well Happy Eostre/Ishter
- 4,320-3,820 years old “Shimao” (North China) site with Totemistic-Shamanistic Paganism and a Stepped Pyramid
- 4,250 to 3,400 Year old Stonehenge from Russia: Arkaim?
- 4,100-year-old beaker with medicinal & flowering plants in a grave of a woman in Scotland
- Early European Farmer ancestry, Kelif el Boroud people with the Cardial Ware culture, and the Bell Beaker culture Paganists too, spread into North Africa, then to the Canary Islands off West Africa
- Flood Accounts: Gilgamesh epic (4,100 years ago) Noah in Genesis (2,600 years ago)
- Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)
- When was the beginning: TIMELINE OF CURRENT RELIGIONS, which start around 4,000 years ago.
- Early Religions Thought to Express Proto-Monotheistic Systems around 4,000 years ago
- Kultepe? An archaeological site with a 4,000 years old women’s rights document.
- Single God Religions (Monotheism) = “Man-o-theism” started around 4,000 years ago with the Great Sky Spirit/God Tiān (天)?
- Confucianism’s Tiān (Shangdi god 4,000 years old): Supernaturalism, Pantheism or Theism?
- Yes, Your Male God is Ridiculous
- Mythology, a Lunar Deity is a Goddess or God of the Moon
- Sacred Land, Hills, and Mountains: Sami Mythology (Paganistic Shamanism)
- Horse Worship/Sacrifice: mythical union of Ruling Elite/Kingship and the Horse
- The Amorite/Amurru people’s God Amurru “Lord of the Steppe”, relates to the Origins of the Bible God?
- Bronze Age Exotic Trade Routes Spread Quite Far as well as Spread Religious Ideas with Them
- Sami and the Northern Indigenous Peoples Landscape, Language, and its Connection to Religion
- Prototype of Ancient Analemmatic Sundials around 3,900-3,150 years ago and a Possible Solar Connection to gods?
- Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
- The Weakening of Ancient Trade and the Strengthening of Religions around 3000 years ago?
- Are you aware that there are religions that worship women gods, explain now religion tears women down?
- Animistic, Totemistic, and Paganistic Superstition Origins of bible god and the bible’s Religion.
- Myths and Folklore: “Trickster gods and goddesses”
- Jews, Judaism, and the Origins of Some of its Ideas
- An Old Branch of Religion Still Giving Fruit: Sacred Trees
- Dating the BIBLE: naming names and telling times (written less than 3,000 years ago, provable to 2,200 years ago)
- Did a Volcano Inspire the bible god?
- Dené–Yeniseian language, Old Copper Complex, and Pre-Columbian Mound Builders?
- No “dinosaurs and humans didn’t exist together just because some think they are in the bible itself”
- Sacred Shit and Sacred Animals?
- Everyone Killed in the Bible Flood? “Nephilim” (giants)?
- Hey, Damien dude, I have a question for you regarding “the bible” Exodus.
- Archaeology Disproves the Bible
- Bible Battle, Just More, Bible Babble
- The Jericho Conquest lie?
- Canaanites and Israelites?
- Accurate Account on how did Christianity Began?
- Let’s talk about Christianity.
- So the 10 commandments isn’t anything to go by either right?
- Misinformed christian
- Debunking Jesus?
- Paulism vs Jesus
- Ok, you seem confused so let’s talk about Buddhism.
- Unacknowledged Buddhism: Gods, Savior, Demons, Rebirth, Heavens, Hells, and Terrorism
- His Foolishness The Dalai Lama
- Yin and Yang is sexist with an ORIGIN around 2,300 years ago?
- I Believe Archaeology, not Myths & Why Not, as the Religious Myths Already Violate Reason!
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Aquatic Ape Theory/Hypothesis? As Always, Just Pseudoscience.
- Ancient Aliens Conspiracy Theorists are Pseudohistorians
- The Pseudohistoric and Pseudoscientific claims about “Bakoni Ruins” of South Africa
- Why do people think Religion is much more than supernaturalism and superstitionism?
- Religion is an Evolved Product
- Was the Value of Ancient Women Different?
- 1000 to 1100 CE, human sacrifice Cahokia Mounds a pre-Columbian Native American site
- Feminist atheists as far back as the 1800s?
- Promoting Religion as Real is Mentally Harmful to a Flourishing Humanity
- Screw All Religions and Their Toxic lies, they are all fraud
- Forget Religions’ Unfounded Myths, I Have Substantiated “Archaeology Facts.”
- Religion Dispersal throughout the World
- I Hate Religion Just as I Hate all Pseudoscience
- Exposing Scientology, Eckankar, Wicca and Other Nonsense?
- Main deity or religious belief systems
- Quit Trying to Invent Your God From the Scraps of Science.
- Archaeological, Scientific, & Philosophic evidence shows the god myth is man-made nonsense.
- Ancient Alien Conspiracy Theorists: Misunderstanding, Rhetoric, Misinformation, Fabrications, and Lies
- Misinformation, Distortion, and Pseudoscience in Talking with a Christian Creationist
- Judging the Lack of Goodness in Gods, Even the Norse God Odin
- Challenging the Belief in God-like Aliens and Gods in General
- A Challenge to Christian use of Torture Devices?
- Yes, Hinduism is a Religion
- Trump is One of the Most Reactionary Forces of Far-right Christian Extremism
- Was the Bull Head a Symbol of God? Yes!
- Primate Death Rituals
- Christian – “God and Christianity are objectively true”
- Australopithecus afarensis Death Ritual?
- You Claim Global Warming is a Hoax?
- Doubter of Science and Defamer of Atheists?
- I think that sounds like the Bible?
- History of the Antifa (“anti-fascist”) Movements
- Indianapolis Anti-Blasphemy Laws #Free Soheil Rally
- Damien, you repeat the golden rule in so many forms then you say religion is dogmatic?
- Science is a Trustable Methodology whereas Faith is not Trustable at all!
- Was I ever a believer, before I was an atheist?
- Atheists rise in reason
- Mistrust of science?
- Open to Talking About the Definition of ‘God’? But first, we address Faith.
- ‘United Monarchy’ full of splendor and power – Saul, David, and Solomon? Most likely not.
- Is there EXODUS ARCHAEOLOGY? The short answer is “no.”
- Lacking Proof of Bigfoots, Unicorns, and Gods is Just a Lack of Research?
- Religion and Politics: Faith Beliefs vs. Rational Thinking
- Hammer of Truth that lying pig RELIGION: challenged by an archaeologist
- “The Hammer of Truth” -ontology question- What do You Mean by That?
- Navigation of a bad argument: Ad Hominem vs. Attack
- Why is it Often Claimed that Gods have a Gender?
- Why are basically all monotheistic religions ones that have a male god?
- Shifting through the Claims in support of Faith
- Dear Mr. AtHope, The 20th Century is an Indictment of Secularism and a Failed Atheist Century
- An Understanding of the Worldwide Statistics and Dynamics of Terrorist Incidents and Suicide Attacks
- Intoxication and Evolution? Addressing and Assessing the “Stoned Ape” or “Drunken Monkey” Theories as Catalysts in Human Evolution
- Sacred Menstrual cloth? Inanna’s knot, Isis knot, and maybe Ma’at’s feather?
- Damien, why don’t the Hebrews accept the bible stories?
- Dealing with a Troll and Arguing Over Word Meaning
- Knowledge without Belief? Justified beliefs or disbeliefs worthy of Knowledge?
- Afrocentrism and African Religions
- Crecganford @crecganford offers history & stories of the people, places, gods, & culture
- Empiricism-Denier?
I am not an academic. I am a revolutionary that teaches in public, in places like social media, and in the streets. I am not a leader by some title given but from my commanding leadership style of simply to start teaching everywhere to everyone, all manner of positive education.


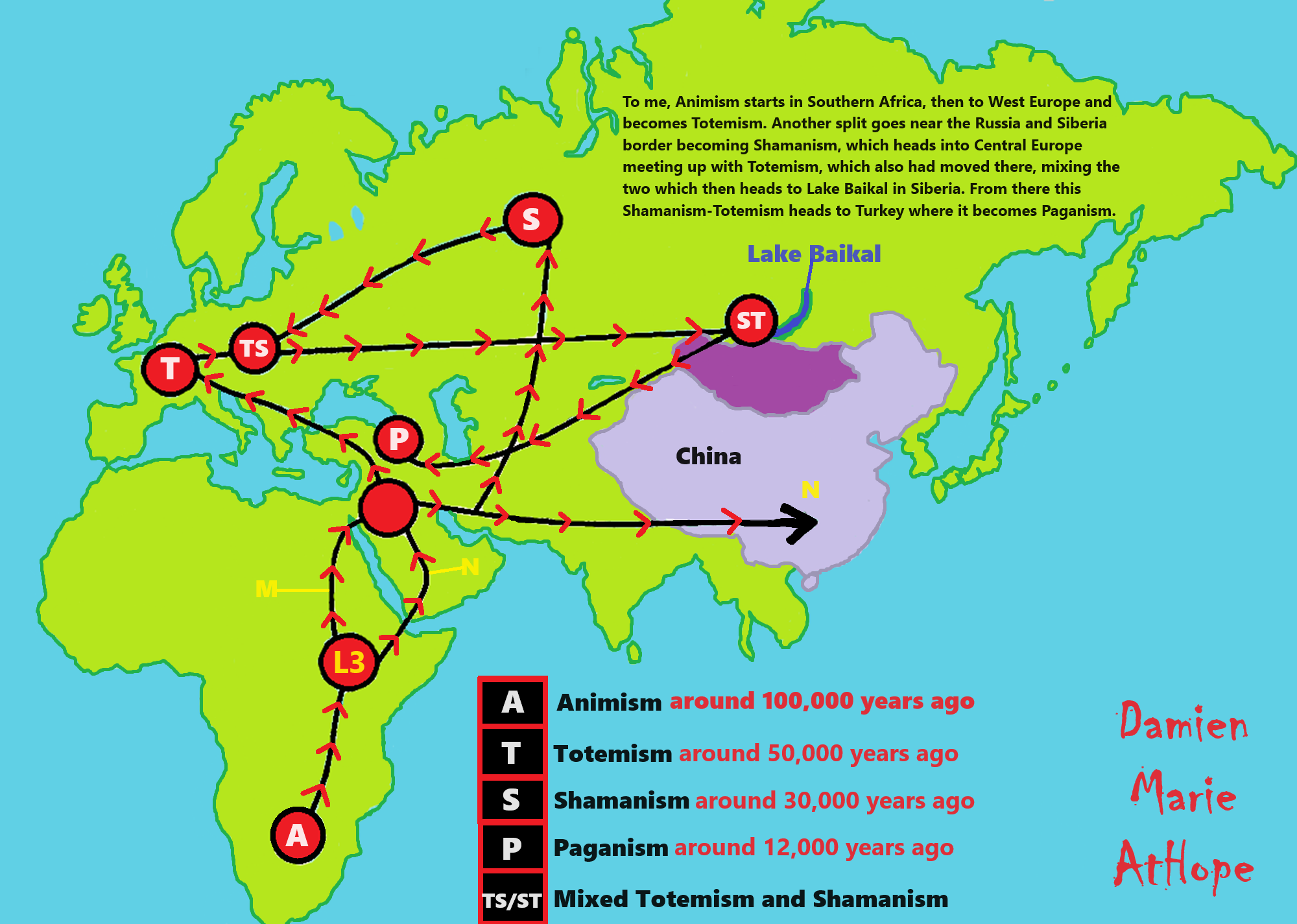
To me, Animism starts in Southern Africa, then to West Europe, and becomes Totemism. Another split goes near the Russia and Siberia border becoming Shamanism, which heads into Central Europe meeting up with Totemism, which also had moved there, mixing the two which then heads to Lake Baikal in Siberia. From there this Shamanism-Totemism heads to Turkey where it becomes Paganism.
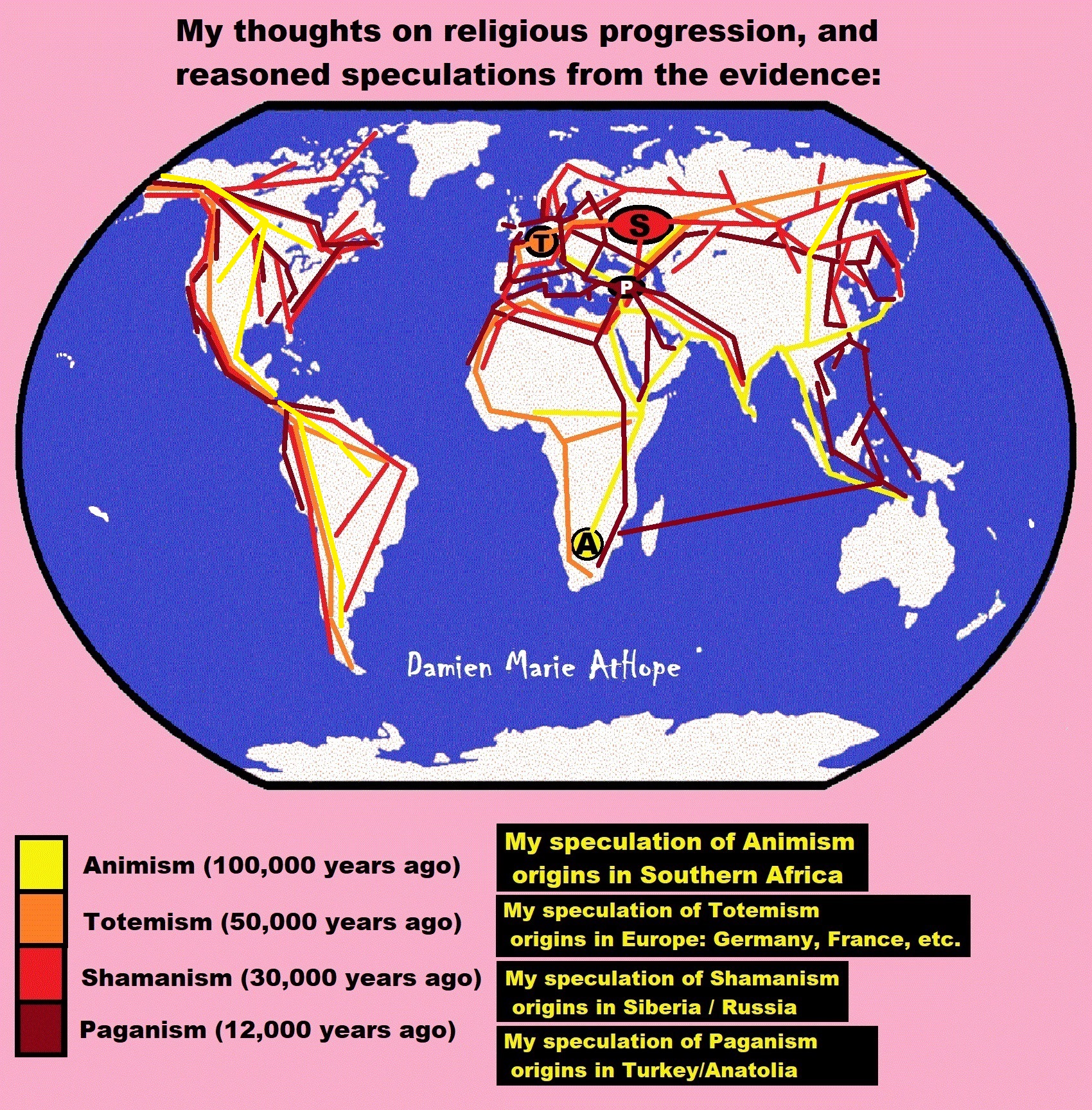



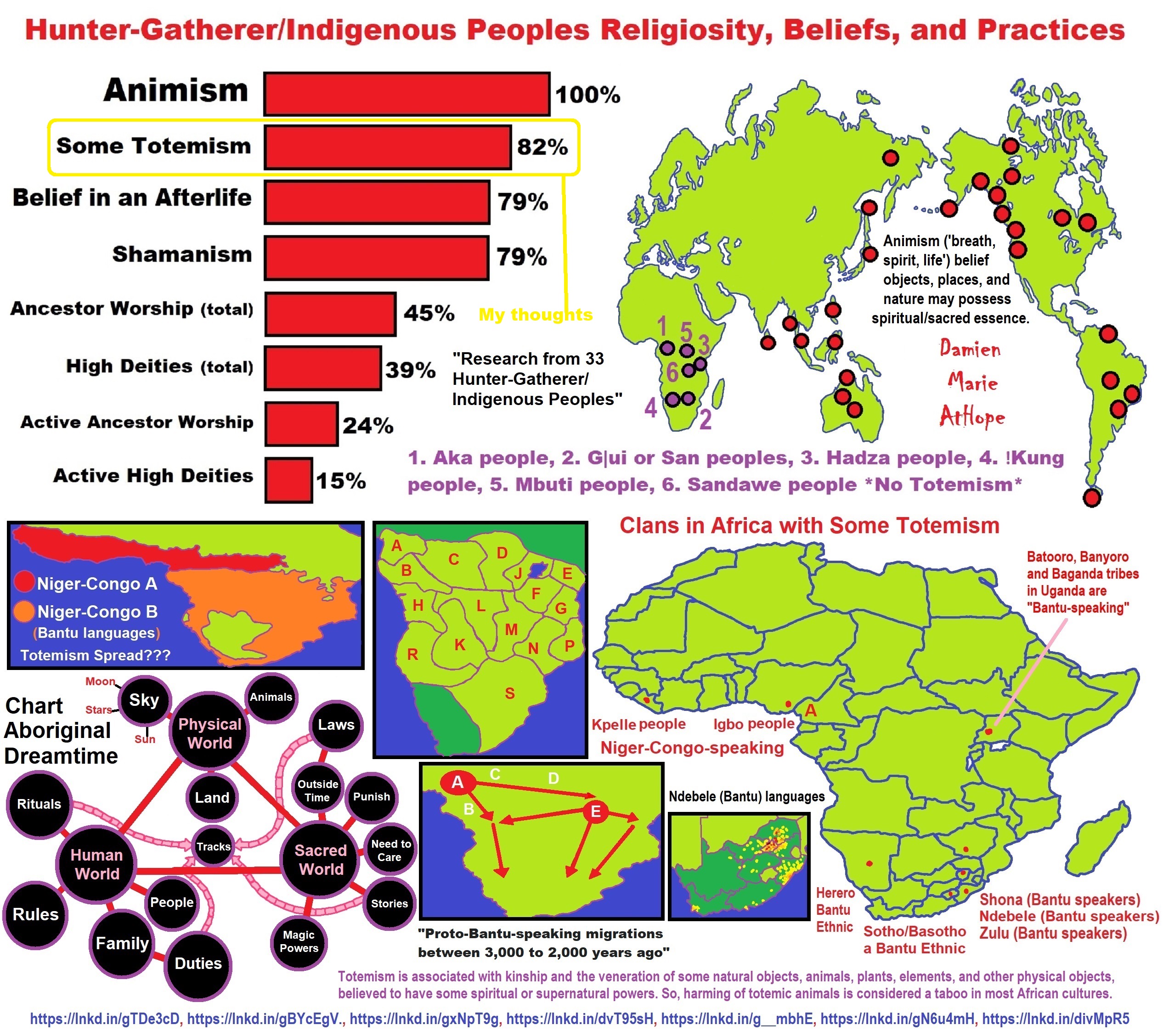
Not all “Religions” or “Religious Persuasions” have a god(s) but
All can be said to believe in some imaginary beings or imaginary things like spirits, afterlives, etc.
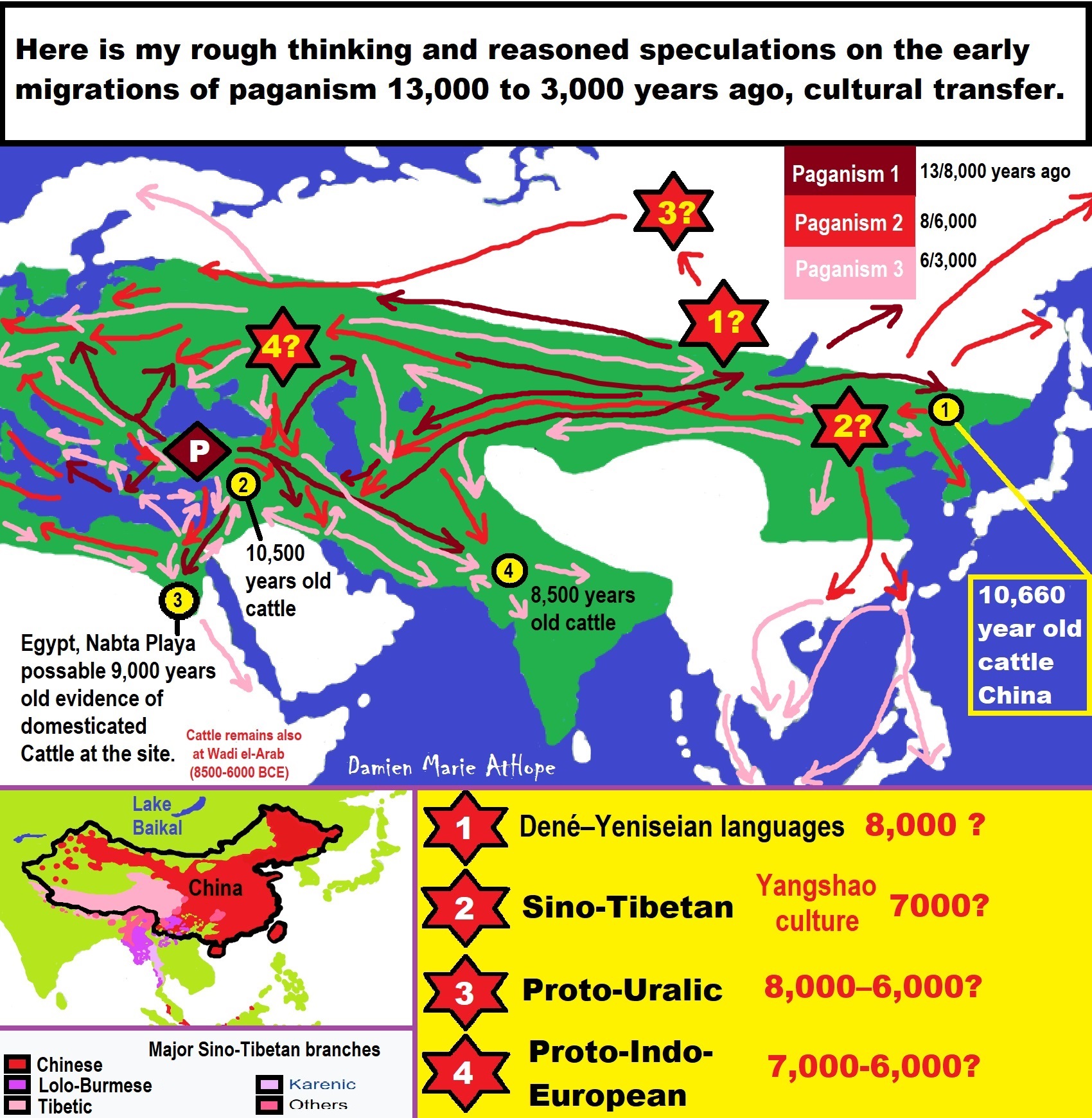
Paganism 12,000-4,000 years old
12,000-7,000 years old: related to (Pre-Capitalism)
7,000-5,000 years old: related to (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
5,000 years old: related to (Kings and the Rise of the State)
4,000 years old: related to (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism)

ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Low Gods “Earth” or Tutelary deity and High Gods “Sky” or Supreme deity
“An Earth goddess is a deification of the Earth. Earth goddesses are often associated with the “chthonic” deities of the underworld. Ki and Ninhursag are Mesopotamian earth goddesses. In Greek mythology, the Earth is personified as Gaia, corresponding to Roman Terra, Indic Prithvi/Bhūmi, etc. traced to an “Earth Mother” complementary to the “Sky Father” in Proto-Indo-European religion. Egyptian mythology exceptionally has a sky goddess and an Earth god.” ref
“A mother goddess is a goddess who represents or is a personification of nature, motherhood, fertility, creation, destruction or who embodies the bounty of the Earth. When equated with the Earth or the natural world, such goddesses are sometimes referred to as Mother Earth or as the Earth Mother. In some religious traditions or movements, Heavenly Mother (also referred to as Mother in Heaven or Sky Mother) is the wife or feminine counterpart of the Sky father or God the Father.” ref
“Any masculine sky god is often also king of the gods, taking the position of patriarch within a pantheon. Such king gods are collectively categorized as “sky father” deities, with a polarity between sky and earth often being expressed by pairing a “sky father” god with an “earth mother” goddess (pairings of a sky mother with an earth father are less frequent). A main sky goddess is often the queen of the gods and may be an air/sky goddess in her own right, though she usually has other functions as well with “sky” not being her main. In antiquity, several sky goddesses in ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Near East were called Queen of Heaven. Neopagans often apply it with impunity to sky goddesses from other regions who were never associated with the term historically. The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.” ref
“In comparative mythology, sky father is a term for a recurring concept in polytheistic religions of a sky god who is addressed as a “father”, often the father of a pantheon and is often either a reigning or former King of the Gods. The concept of “sky father” may also be taken to include Sun gods with similar characteristics, such as Ra. The concept is complementary to an “earth mother“. “Sky Father” is a direct translation of the Vedic Dyaus Pita, etymologically descended from the same Proto-Indo-European deity name as the Greek Zeûs Pater and Roman Jupiter and Germanic Týr, Tir or Tiwaz, all of which are reflexes of the same Proto-Indo-European deity’s name, *Dyēus Ph₂tḗr. While there are numerous parallels adduced from outside of Indo-European mythology, there are exceptions (e.g. In Egyptian mythology, Nut is the sky mother and Geb is the earth father).” ref
Tutelary deity
“A tutelary (also tutelar) is a deity or spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of “tutelary” expresses the concept of safety and thus of guardianship. In late Greek and Roman religion, one type of tutelary deity, the genius, functions as the personal deity or daimon of an individual from birth to death. Another form of personal tutelary spirit is the familiar spirit of European folklore.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Korean shamanism, jangseung and sotdae were placed at the edge of villages to frighten off demons. They were also worshiped as deities. Seonangshin is the patron deity of the village in Korean tradition and was believed to embody the Seonangdang. In Philippine animism, Diwata or Lambana are deities or spirits that inhabit sacred places like mountains and mounds and serve as guardians. Such as: Maria Makiling is the deity who guards Mt. Makiling and Maria Cacao and Maria Sinukuan. In Shinto, the spirits, or kami, which give life to human bodies come from nature and return to it after death. Ancestors are therefore themselves tutelaries to be worshiped. And similarly, Native American beliefs such as Tonás, tutelary animal spirit among the Zapotec and Totems, familial or clan spirits among the Ojibwe, can be animals.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Austronesian beliefs such as: Atua (gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori or the Hawaiians), Hanitu (Bunun of Taiwan‘s term for spirit), Hyang (Kawi, Sundanese, Javanese, and Balinese Supreme Being, in ancient Java and Bali mythology and this spiritual entity, can be either divine or ancestral), Kaitiaki (New Zealand Māori term used for the concept of guardianship, for the sky, the sea, and the land), Kawas (mythology) (divided into 6 groups: gods, ancestors, souls of the living, spirits of living things, spirits of lifeless objects, and ghosts), Tiki (Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne and represents deified ancestors found in most Polynesian cultures). ” ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
Mesopotamian Tutelary Deities can be seen as ones related to City-States
“Historical city-states included Sumerian cities such as Uruk and Ur; Ancient Egyptian city-states, such as Thebes and Memphis; the Phoenician cities (such as Tyre and Sidon); the five Philistine city-states; the Berber city-states of the Garamantes; the city-states of ancient Greece (the poleis such as Athens, Sparta, Thebes, and Corinth); the Roman Republic (which grew from a city-state into a vast empire); the Italian city-states from the Middle Ages to the early modern period, such as Florence, Siena, Ferrara, Milan (which as they grew in power began to dominate neighboring cities) and Genoa and Venice, which became powerful thalassocracies; the Mayan and other cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica (including cities such as Chichen Itza, Tikal, Copán and Monte Albán); the central Asian cities along the Silk Road; the city-states of the Swahili coast; Ragusa; states of the medieval Russian lands such as Novgorod and Pskov; and many others.” ref
“The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BCE; also known as Protoliterate period) of Mesopotamia, named after the Sumerian city of Uruk, this period saw the emergence of urban life in Mesopotamia and the Sumerian civilization. City-States like Uruk and others had a patron tutelary City Deity along with a Priest-King.” ref
“Chinese folk religion, both past, and present, includes myriad tutelary deities. Exceptional individuals, highly cultivated sages, and prominent ancestors can be deified and honored after death. Lord Guan is the patron of military personnel and police, while Mazu is the patron of fishermen and sailors. Such as Tu Di Gong (Earth Deity) is the tutelary deity of a locality, and each individual locality has its own Earth Deity and Cheng Huang Gong (City God) is the guardian deity of an individual city, worshipped by local officials and locals since imperial times.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) in Hinduism, personal tutelary deities are known as ishta-devata, while family tutelary deities are known as Kuladevata. Gramadevata are guardian deities of villages. Devas can also be seen as tutelary. Shiva is the patron of yogis and renunciants. City goddesses include: Mumbadevi (Mumbai), Sachchika (Osian); Kuladevis include: Ambika (Porwad), and Mahalakshmi. In NorthEast India Meitei mythology and religion (Sanamahism) of Manipur, there are various types of tutelary deities, among which Lam Lais are the most predominant ones. Tibetan Buddhism has Yidam as a tutelary deity. Dakini is the patron of those who seek knowledge.” ref
“A tutelary (also tutelar) The Greeks also thought deities guarded specific places: for instance, Athena was the patron goddess of the city of Athens. Socrates spoke of hearing the voice of his personal spirit or daimonion:
You have often heard me speak of an oracle or sign which comes to me … . This sign I have had ever since I was a child. The sign is a voice which comes to me and always forbids me to do something which I am going to do, but never commands me to do anything, and this is what stands in the way of my being a politician.” ref
“Tutelary deities who guard and preserve a place or a person are fundamental to ancient Roman religion. The tutelary deity of a man was his Genius, that of a woman her Juno. In the Imperial era, the Genius of the Emperor was a focus of Imperial cult. An emperor might also adopt a major deity as his personal patron or tutelary, as Augustus did Apollo. Precedents for claiming the personal protection of a deity were established in the Republican era, when for instance the Roman dictator Sulla advertised the goddess Victory as his tutelary by holding public games (ludi) in her honor.” ref
“Each town or city had one or more tutelary deities, whose protection was considered particularly vital in time of war and siege. Rome itself was protected by a goddess whose name was to be kept ritually secret on pain of death (for a supposed case, see Quintus Valerius Soranus). The Capitoline Triad of Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva were also tutelaries of Rome. The Italic towns had their own tutelary deities. Juno often had this function, as at the Latin town of Lanuvium and the Etruscan city of Veii, and was often housed in an especially grand temple on the arx (citadel) or other prominent or central location. The tutelary deity of Praeneste was Fortuna, whose oracle was renowned.” ref
“The Roman ritual of evocatio was premised on the belief that a town could be made vulnerable to military defeat if the power of its tutelary deity were diverted outside the city, perhaps by the offer of superior cult at Rome. The depiction of some goddesses such as the Magna Mater (Great Mother, or Cybele) as “tower-crowned” represents their capacity to preserve the city. A town in the provinces might adopt a deity from within the Roman religious sphere to serve as its guardian, or syncretize its own tutelary with such; for instance, a community within the civitas of the Remi in Gaul adopted Apollo as its tutelary, and at the capital of the Remi (present-day Rheims), the tutelary was Mars Camulus.” ref
Household deity (a kind of or related to a Tutelary deity)
“A household deity is a deity or spirit that protects the home, looking after the entire household or certain key members. It has been a common belief in paganism as well as in folklore across many parts of the world. Household deities fit into two types; firstly, a specific deity – typically a goddess – often referred to as a hearth goddess or domestic goddess who is associated with the home and hearth, such as the ancient Greek Hestia.” ref
“The second type of household deities are those that are not one singular deity, but a type, or species of animistic deity, who usually have lesser powers than major deities. This type was common in the religions of antiquity, such as the Lares of ancient Roman religion, the Gashin of Korean shamanism, and Cofgodas of Anglo-Saxon paganism. These survived Christianisation as fairy-like creatures existing in folklore, such as the Anglo-Scottish Brownie and Slavic Domovoy.” ref
“Household deities were usually worshipped not in temples but in the home, where they would be represented by small idols (such as the teraphim of the Bible, often translated as “household gods” in Genesis 31:19 for example), amulets, paintings, or reliefs. They could also be found on domestic objects, such as cosmetic articles in the case of Tawaret. The more prosperous houses might have a small shrine to the household god(s); the lararium served this purpose in the case of the Romans. The gods would be treated as members of the family and invited to join in meals, or be given offerings of food and drink.” ref
“In many religions, both ancient and modern, a god would preside over the home. Certain species, or types, of household deities, existed. An example of this was the Roman Lares. Many European cultures retained house spirits into the modern period. Some examples of these include:
- Brownie (Scotland and England) or Hob (England) / Kobold (Germany) / Goblin / Hobgoblin
- Domovoy (Slavic)
- Nisse (Norwegian or Danish) / Tomte (Swedish) / Tonttu (Finnish)
- Húsvættir (Norse)” ref
“Although the cosmic status of household deities was not as lofty as that of the Twelve Olympians or the Aesir, they were also jealous of their dignity and also had to be appeased with shrines and offerings, however humble. Because of their immediacy they had arguably more influence on the day-to-day affairs of men than the remote gods did. Vestiges of their worship persisted long after Christianity and other major religions extirpated nearly every trace of the major pagan pantheons. Elements of the practice can be seen even today, with Christian accretions, where statues to various saints (such as St. Francis) protect gardens and grottos. Even the gargoyles found on older churches, could be viewed as guardians partitioning a sacred space.” ref
“For centuries, Christianity fought a mop-up war against these lingering minor pagan deities, but they proved tenacious. For example, Martin Luther‘s Tischreden have numerous – quite serious – references to dealing with kobolds. Eventually, rationalism and the Industrial Revolution threatened to erase most of these minor deities, until the advent of romantic nationalism rehabilitated them and embellished them into objects of literary curiosity in the 19th century. Since the 20th century this literature has been mined for characters for role-playing games, video games, and other fantasy personae, not infrequently invested with invented traits and hierarchies somewhat different from their mythological and folkloric roots.” ref
“In contradistinction to both Herbert Spencer and Edward Burnett Tylor, who defended theories of animistic origins of ancestor worship, Émile Durkheim saw its origin in totemism. In reality, this distinction is somewhat academic, since totemism may be regarded as a particularized manifestation of animism, and something of a synthesis of the two positions was attempted by Sigmund Freud. In Freud’s Totem and Taboo, both totem and taboo are outward expressions or manifestations of the same psychological tendency, a concept which is complementary to, or which rather reconciles, the apparent conflict. Freud preferred to emphasize the psychoanalytic implications of the reification of metaphysical forces, but with particular emphasis on its familial nature. This emphasis underscores, rather than weakens, the ancestral component.” ref
“William Edward Hearn, a noted classicist, and jurist, traced the origin of domestic deities from the earliest stages as an expression of animism, a belief system thought to have existed also in the neolithic, and the forerunner of Indo-European religion. In his analysis of the Indo-European household, in Chapter II “The House Spirit”, Section 1, he states:
The belief which guided the conduct of our forefathers was … the spirit rule of dead ancestors.” ref
“In Section 2 he proceeds to elaborate:
It is thus certain that the worship of deceased ancestors is a vera causa, and not a mere hypothesis. …
In the other European nations, the Slavs, the Teutons, and the Kelts, the House Spirit appears with no less distinctness. … [T]he existence of that worship does not admit of doubt. … The House Spirits had a multitude of other names which it is needless here to enumerate, but all of which are more or less expressive of their friendly relations with man. … In [England] … [h]e is the Brownie. … In Scotland this same Brownie is well known. He is usually described as attached to particular families, with whom he has been known to reside for centuries, threshing the corn, cleaning the house, and performing similar household tasks. His favorite gratification was milk and honey.” ref
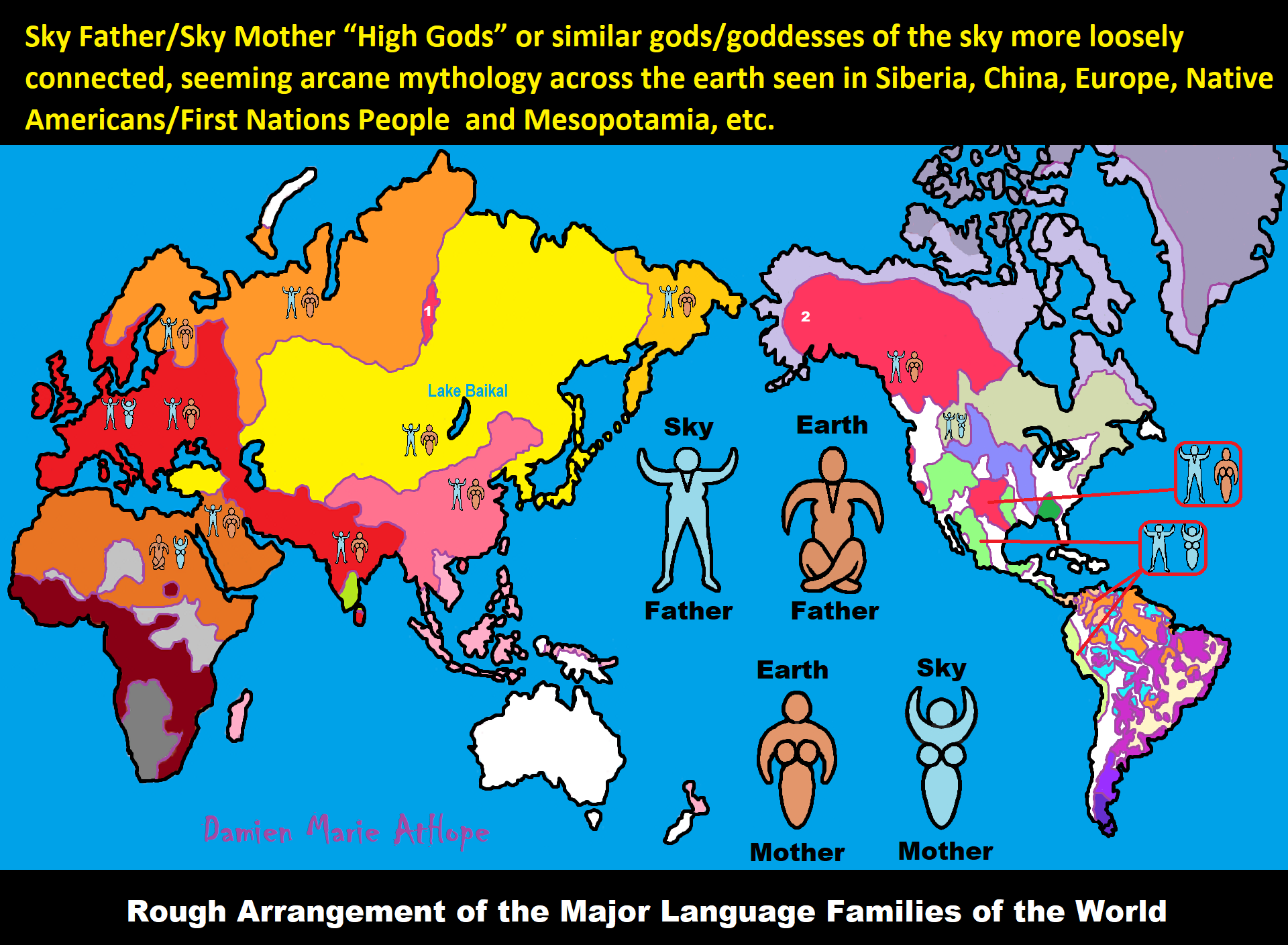
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref
“These ideas are my speculations from the evidence.”
I am still researching the “god‘s origins” all over the world. So you know, it is very complicated but I am smart and willing to look, DEEP, if necessary, which going very deep does seem to be needed here, when trying to actually understand the evolution of gods and goddesses. I am sure of a few things and less sure of others, but even in stuff I am not fully grasping I still am slowly figuring it out, to explain it to others. But as I research more I am understanding things a little better, though I am still working on understanding it all or something close and thus always figuring out more.
Sky Father/Sky God?
“Egyptian: (Nut) Sky Mother and (Geb) Earth Father” (Egypt is different but similar)
Turkic/Mongolic: (Tengri/Tenger Etseg) Sky Father and (Eje/Gazar Eej) Earth Mother *Transeurasian*
Hawaiian: (Wākea) Sky Father and (Papahānaumoku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
New Zealand/ Māori: (Ranginui) Sky Father and (Papatūānuku) Earth Mother *Austronesian*
Proto-Indo-European: (Dyḗus/Dyḗus ph₂tḗr) Sky Father and (Dʰéǵʰōm/Pleth₂wih₁) Earth Mother
Indo-Aryan: (Dyaus Pita) Sky Father and (Prithvi Mata) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Italic: (Jupiter) Sky Father and (Juno) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Etruscan: (Tinia) Sky Father and (Uni) Sky Mother *Tyrsenian/Italy Pre–Indo-European*
Hellenic/Greek: (Zeus) Sky Father and (Hera) Sky Mother who started as an “Earth Goddess” *Indo-European*
Nordic: (Dagr) Sky Father and (Nótt) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Slavic: (Perun) Sky Father and (Mokosh) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Illyrian: (Deipaturos) Sky Father and (Messapic Damatura’s “earth-mother” maybe) Earth Mother *Indo-European*
Albanian: (Zojz) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Baltic: (Perkūnas) Sky Father and (Saulė) Sky Mother *Indo-European*
Germanic: (Týr) Sky Father and (?) *Indo-European*
Colombian-Muisca: (Bochica) Sky Father and (Huythaca) Sky Mother *Chibchan*
Aztec: (Quetzalcoatl) Sky Father and (Xochiquetzal) Sky Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Incan: (Viracocha) Sky Father and (Mama Runtucaya) Sky Mother *Quechuan*
China: (Tian/Shangdi) Sky Father and (Dì) Earth Mother *Sino-Tibetan*
Sumerian, Assyrian and Babylonian: (An/Anu) Sky Father and (Ki) Earth Mother
Finnish: (Ukko) Sky Father and (Akka) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Sami: (Horagalles) Sky Father and (Ravdna) Earth Mother *Finno-Ugric*
Puebloan-Zuni: (Ápoyan Ta’chu) Sky Father and (Áwitelin Tsíta) Earth Mother
Puebloan-Hopi: (Tawa) Sky Father and (Kokyangwuti/Spider Woman/Grandmother) Earth Mother *Uto-Aztecan*
Puebloan-Navajo: (Tsohanoai) Sky Father and (Estsanatlehi) Earth Mother *Na-Dene*
ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref, ref

Hinduism around 3,700 to 3,500 years old. ref
Judaism around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (The first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew” dated to around 3,000 years ago Khirbet Qeiyafa is the site of an ancient fortress city overlooking the Elah Valley. And many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed around 2,500) ref, ref
Judaism is around 3,450 or 3,250 years old. (“Paleo-Hebrew” 3,000 years ago and Torah 2,500 years ago)
“Judaism is an Abrahamic, its roots as an organized religion in the Middle East during the Bronze Age. Some scholars argue that modern Judaism evolved from Yahwism, the religion of ancient Israel and Judah, by the late 6th century BCE, and is thus considered to be one of the oldest monotheistic religions.” ref
“Yahwism is the name given by modern scholars to the religion of ancient Israel, essentially polytheistic, with a plethora of gods and goddesses. Heading the pantheon was Yahweh, the national god of the Israelite kingdoms of Israel and Judah, with his consort, the goddess Asherah; below them were second-tier gods and goddesses such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, all of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees, and a third and fourth tier of minor divine beings, including the mal’ak, the messengers of the higher gods, who in later times became the angels of Judaism, Christianity and Islam. Yahweh, however, was not the ‘original’ god of Israel “Isra-El”; it is El, the head of the Canaanite pantheon, whose name forms the basis of the name “Israel”, and none of the Old Testament patriarchs, the tribes of Israel, the Judges, or the earliest monarchs, have a Yahwistic theophoric name (i.e., one incorporating the name of Yahweh).” ref
“El is a Northwest Semitic word meaning “god” or “deity“, or referring (as a proper name) to any one of multiple major ancient Near Eastern deities. A rarer form, ‘ila, represents the predicate form in Old Akkadian and in Amorite. The word is derived from the Proto-Semitic *ʔil-, meaning “god”. Specific deities known as ‘El or ‘Il include the supreme god of the ancient Canaanite religion and the supreme god of East Semitic speakers in Mesopotamia’s Early Dynastic Period. ʼĒl is listed at the head of many pantheons. In some Canaanite and Ugaritic sources, ʼĒl played a role as father of the gods, of creation, or both. For example, in the Ugaritic texts, ʾil mlk is understood to mean “ʼĒl the King” but ʾil hd as “the god Hadad“. The Semitic root ʾlh (Arabic ʾilāh, Aramaic ʾAlāh, ʾElāh, Hebrew ʾelōah) may be ʾl with a parasitic h, and ʾl may be an abbreviated form of ʾlh. In Ugaritic the plural form meaning “gods” is ʾilhm, equivalent to Hebrew ʾelōhîm “powers”. In the Hebrew texts this word is interpreted as being semantically singular for “god” by biblical commentators. However the documentary hypothesis for the Old Testament (corresponds to the Jewish Torah) developed originally in the 1870s, identifies these that different authors – the Jahwist, Elohist, Deuteronomist, and the Priestly source – were responsible for editing stories from a polytheistic religion into those of a monotheistic religion. Inconsistencies that arise between monotheism and polytheism in the texts are reflective of this hypothesis.” ref
Jainism around 2,599 – 2,527 years old. ref
Confucianism around 2,600 – 2,551 years old. ref
Buddhism around 2,563/2,480 – 2,483/2,400 years old. ref
Christianity around 2,o00 years old. ref
Shinto around 1,305 years old. ref
Islam around 1407–1385 years old. ref

Knowledge to Ponder:
Stars/Astrology:
- Possibly, around 30,000 years ago (in simpler form) to 6,000 years ago, Stars/Astrology are connected to Ancestors, Spirit Animals, and Deities.
- The star also seems to be a possible proto-star for Star of Ishtar, Star of Inanna, or Star of Venus.
- Around 7,000 to 6,000 years ago, Star Constellations/Astrology have connections to the “Kurgan phenomenon” of below-ground “mound” stone/wood burial structures and “Dolmen phenomenon” of above-ground stone burial structures.
- Around 6,500–5,800 years ago, The Northern Levant migrations into Jordon and Israel in the Southern Levant brought new cultural and religious transfer from Turkey and Iran.
- “The Ghassulian Star,” a mysterious 6,000-year-old mural from Jordan may have connections to the European paganstic kurgan/dolmens phenomenon.
“Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindus, Chinese, and the Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, from where it spread to Ancient Greece, Rome, the Islamicate world and eventually Central and Western Europe. Contemporary Western astrology is often associated with systems of horoscopes that purport to explain aspects of a person’s personality and predict significant events in their lives based on the positions of celestial objects; the majority of professional astrologers rely on such systems.” ref
Around 5,500 years ago, Science evolves, The first evidence of science was 5,500 years ago and was demonstrated by a body of empirical, theoretical, and practical knowledge about the natural world. ref
Around 5,000 years ago, Origin of Logics is a Naturalistic Observation (principles of valid reasoning, inference, & demonstration) ref
Around 4,150 to 4,000 years ago: The earliest surviving versions of the Sumerian Epic of Gilgamesh, which was originally titled “He who Saw the Deep” (Sha naqba īmuru) or “Surpassing All Other Kings” (Shūtur eli sharrī) were written. ref
Hinduism:
- 3,700 years ago or so, the oldest of the Hindu Vedas (scriptures), the Rig Veda was composed.
- 3,500 years ago or so, the Vedic Age began in India after the collapse of the Indus Valley Civilization.
Judaism:
- around 3,000 years ago, the first writing in the bible was “Paleo-Hebrew”
- around 2,500 years ago, many believe the religious Jewish texts were completed
Myths: The bible inspired religion is not just one religion or one myth but a grouping of several religions and myths
- Around 3,450 or 3,250 years ago, according to legend, is the traditionally accepted period in which the Israelite lawgiver, Moses, provided the Ten Commandments.
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, a collection of ancient religious writings by the Israelites based primarily upon the Hebrew Bible, Tanakh, or Old Testament is the first part of Christianity’s bible.
- Around 2,400 years ago, the most accepted hypothesis is that the canon was formed in stages, first the Pentateuch (Torah).
- Around 2,140 to 2,116 years ago, the Prophets was written during the Hasmonean dynasty, and finally the remaining books.
- Christians traditionally divide the Old Testament into four sections:
- The first five books or Pentateuch (Torah).
- The proposed history books telling the history of the Israelites from their conquest of Canaan to their defeat and exile in Babylon.
- The poetic and proposed “Wisdom books” dealing, in various forms, with questions of good and evil in the world.
- The books of the biblical prophets, warning of the consequences of turning away from God:
- Henotheism:
- Exodus 20:23 “You shall not make other gods besides Me (not saying there are no other gods just not to worship them); gods of silver or gods of gold, you shall not make for yourselves.”
- Polytheism:
- Judges 10:6 “Then the sons of Israel again did evil in the sight of the LORD, served the Baals and the Ashtaroth, the gods of Aram, the gods of Sidon, the gods of Moab, the gods of the sons of Ammon, and the gods of the Philistines; thus they forsook the LORD and did not serve Him.”
- 1 Corinthians 8:5 “For even if there are so-called gods whether in heaven or on earth, as indeed there are many gods and many lords.”
- Monotheism:
- Isaiah 43:10 “You are my witnesses,” declares the LORD, “and my servant whom I have chosen, so that you may know and believe me and understand that I am he. Before me no god was formed, nor will there be one after me.
Around 2,570 to 2,270 Years Ago, there is a confirmation of atheistic doubting as well as atheistic thinking, mainly by Greek philosophers. However, doubting gods is likely as old as the invention of gods and should destroy the thinking that belief in god(s) is the “default belief”. The Greek word is apistos (a “not” and pistos “faithful,”), thus not faithful or faithless because one is unpersuaded and unconvinced by a god(s) claim. Short Definition: unbelieving, unbeliever, or unbelief.

Expressions of Atheistic Thinking:
- Around 2,600 years ago, Ajita Kesakambali, ancient Indian philosopher, who is the first known proponent of Indian materialism. ref
- Around 2,535 to 2,475 years ago, Heraclitus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher, a native of the Greek city Ephesus, Ionia, on the coast of Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor or modern Turkey. ref
- Around 2,500 to 2,400 years ago, according to The Story of Civilization book series certain African pygmy tribes have no identifiable gods, spirits, or religious beliefs or rituals, and even what burials accrue are without ceremony. ref
- Around 2,490 to 2,430 years ago, Empedocles, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a citizen of Agrigentum, a Greek city in Sicily. ref
- Around 2,460 to 2,370 years ago, Democritus, Greek pre-Socratic philosopher considered to be the “father of modern science” possibly had some disbelief amounting to atheism. ref
- Around 2,399 years ago or so, Socrates, a famous Greek philosopher was tried for sinfulness by teaching doubt of state gods. ref
- Around 2,341 to 2,270 years ago, Epicurus, a Greek philosopher known for composing atheistic critics and famously stated, “Is God willing to prevent evil, but not able? Then he is not omnipotent. Is he able, but not willing? Then he is malevolent. Is he both able and willing? Then whence cometh evil? Is he neither able nor willing? Then why call him god?” ref
This last expression by Epicurus, seems to be an expression of Axiological Atheism. To understand and utilize value or actually possess “Value Conscious/Consciousness” to both give a strong moral “axiological” argument (the problem of evil) as well as use it to fortify humanism and positive ethical persuasion of human helping and care responsibilities. Because value-blindness gives rise to sociopathic/psychopathic evil.

“Theists, there has to be a god, as something can not come from nothing.”
Well, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something. This does not tell us what the something that may have been involved with something coming from nothing. A supposed first cause, thus something (unknown) happened and then there was something is not an open invitation to claim it as known, neither is it justified to call or label such an unknown as anything, especially an unsubstantiated magical thinking belief born of mythology and religious storytelling.


While hallucinogens are associated with shamanism, it is alcohol that is associated with paganism.
The Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries Shows in the prehistory series:
Show two: Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show tree: Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show four: Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show five: Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”
Show six: Emergence of hierarchy, sexism, slavery, and the new male god dominance: Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves!
Prehistory: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” the division of labor, power, rights, and recourses: VIDEO
Pre-animism 300,000 years old and animism 100,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Totemism 50,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Shamanism 30,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism”: VIDEO
Paganism 12,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Pre-Capitalism): VIDEO
Paganism 7,000-5,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Capitalism) (World War 0) Elite and their slaves: VIEDO
Paganism 5,000 years old: progressed organized religion and the state: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (Kings and the Rise of the State): VIEDO
Paganism 4,000 years old: related to “Anarchism and Socialism” (First Moralistic gods, then the Origin time of Monotheism): VIEDO
I do not hate simply because I challenge and expose myths or lies any more than others being thought of as loving simply because of the protection and hiding from challenge their favored myths or lies.
The truth is best championed in the sunlight of challenge.
An archaeologist once said to me “Damien religion and culture are very different”
My response, So are you saying that was always that way, such as would you say Native Americans’ cultures are separate from their religions? And do you think it always was the way you believe?
I had said that religion was a cultural product. That is still how I see it and there are other archaeologists that think close to me as well. Gods too are the myths of cultures that did not understand science or the world around them, seeing magic/supernatural everywhere.
I personally think there is a goddess and not enough evidence to support a male god at Çatalhöyük but if there was both a male and female god and goddess then I know the kind of gods they were like Proto-Indo-European mythology.
This series idea was addressed in, Anarchist Teaching as Free Public Education or Free Education in the Public: VIDEO
Our 12 video series: Organized Oppression: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of power (9,000-4,000 years ago), is adapted from: The Complete and Concise History of the Sumerians and Early Bronze Age Mesopotamia (7000-2000 BC): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szFjxmY7jQA by “History with Cy“
Show #1: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Samarra, Halaf, Ubaid)
Show #2: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #3: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Uruk and the First Cities)
Show #4: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (First Kings)
Show #5: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Early Dynastic Period)
Show #6: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power
Show #7: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Sargon and Akkadian Rule)
Show #9: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Gudea of Lagash and Utu-hegal)
Show #12: Mesopotamian State Force and the Politics of Power (Aftermath and Legacy of Sumer)

The “Atheist-Humanist-Leftist Revolutionaries”
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ Atheist Leftist @Skepticallefty & I (Damien Marie AtHope) @AthopeMarie (my YouTube & related blog) are working jointly in atheist, antitheist, antireligionist, antifascist, anarchist, socialist, and humanist endeavors in our videos together, generally, every other Saturday.
Why Does Power Bring Responsibility?
Think, how often is it the powerless that start wars, oppress others, or commit genocide? So, I guess the question is to us all, to ask, how can power not carry responsibility in a humanity concept? I know I see the deep ethical responsibility that if there is power their must be a humanistic responsibility of ethical and empathic stewardship of that power. Will I be brave enough to be kind? Will I possess enough courage to be compassionate? Will my valor reach its height of empathy? I as everyone, earns our justified respect by our actions, that are good, ethical, just, protecting, and kind. Do I have enough self-respect to put my love for humanity’s flushing, over being brought down by some of its bad actors? May we all be the ones doing good actions in the world, to help human flourishing.
I create the world I want to live in, striving for flourishing. Which is not a place but a positive potential involvement and promotion; a life of humanist goal precision. To master oneself, also means mastering positive prosocial behaviors needed for human flourishing. I may have lost a god myth as an atheist, but I am happy to tell you, my friend, it is exactly because of that, leaving the mental terrorizer, god belief, that I truly regained my connected ethical as well as kind humanity.
Cory and I will talk about prehistory and theism, addressing the relevance to atheism, anarchism, and socialism.
At the same time as the rise of the male god, 7,000 years ago, there was also the very time there was the rise of violence, war, and clans to kingdoms, then empires, then states. It is all connected back to 7,000 years ago, and it moved across the world.
Cory Johnston: https://damienmarieathope.com/2021/04/cory-johnston-mind-of-a-skeptical-leftist/?v=32aec8db952d
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist (YouTube)
Cory Johnston: Mind of a Skeptical Leftist @Skepticallefty
The Mind of a Skeptical Leftist By Cory Johnston: “Promoting critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics by covering current events and talking to a variety of people. Cory Johnston has been thoughtfully talking to people and attempting to promote critical thinking, social justice, and left-wing politics.” http://anchor.fm/skepticalleft
Cory needs our support. We rise by helping each other.
Cory Johnston ☭ Ⓐ @Skepticallefty Evidence-based atheist leftist (he/him) Producer, host, and co-host of 4 podcasts @skeptarchy @skpoliticspod and @AthopeMarie
Damien Marie AtHope (“At Hope”) Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist. Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Poet, Philosopher, Advocate, Activist, Psychology, and Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Historian.
Damien is interested in: Freedom, Liberty, Justice, Equality, Ethics, Humanism, Science, Atheism, Antiteism, Antireligionism, Ignosticism, Left-Libertarianism, Anarchism, Socialism, Mutualism, Axiology, Metaphysics, LGBTQI, Philosophy, Advocacy, Activism, Mental Health, Psychology, Archaeology, Social Work, Sexual Rights, Marriage Rights, Woman’s Rights, Gender Rights, Child Rights, Secular Rights, Race Equality, Ageism/Disability Equality, Etc. And a far-leftist, “Anarcho-Humanist.”
I am not a good fit in the atheist movement that is mostly pro-capitalist, I am anti-capitalist. Mostly pro-skeptic, I am a rationalist not valuing skepticism. Mostly pro-agnostic, I am anti-agnostic. Mostly limited to anti-Abrahamic religions, I am an anti-religionist.
To me, the “male god” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 7,000 years ago, whereas the now favored monotheism “male god” is more like 4,000 years ago or so. To me, the “female goddess” seems to have either emerged or become prominent around 11,000-10,000 years ago or so, losing the majority of its once prominence around 2,000 years ago due largely to the now favored monotheism “male god” that grow in prominence after 4,000 years ago or so.
My Thought on the Evolution of Gods?
Animal protector deities from old totems/spirit animal beliefs come first to me, 13,000/12,000 years ago, then women as deities 11,000/10,000 years ago, then male gods around 7,000/8,000 years ago. Moralistic gods around 5,000/4,000 years ago, and monotheistic gods around 4,000/3,000 years ago.
To me, animal gods were likely first related to totemism animals around 13,000 to 12,000 years ago or older. Female as goddesses was next to me, 11,000 to 10,000 years ago or so with the emergence of agriculture. Then male gods come about 8,000 to 7,000 years ago with clan wars. Many monotheism-themed religions started in henotheism, emerging out of polytheism/paganism.


Damien Marie AtHope (Said as “At” “Hope”)/(Autodidact Polymath but not good at math):
Axiological Atheist, Anti-theist, Anti-religionist, Secular Humanist, Rationalist, Writer, Artist, Jeweler, Poet, “autodidact” Philosopher, schooled in Psychology, and “autodidact” Armchair Archaeology/Anthropology/Pre-Historian (Knowledgeable in the range of: 1 million to 5,000/4,000 years ago). I am an anarchist socialist politically. Reasons for or Types of Atheism
My Website, My Blog, & Short-writing or Quotes, My YouTube, Twitter: @AthopeMarie, and My Email: damien.marie.athope@gmail.com